Cancer is one of the major causes of death worldwide, causing more than 100 different types affecting different organs and tissues. Indeed, knowledge of the different forms of cancer may enhance early detection, treatment options, and prevention strategies. By this article, one will also learn about the types that are most frequently encountered in human medical practice today, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What Is Cancer?
Cancer is caused when some abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, spreading elsewhere in the body. These cells may form tumors or affect blood and immune cells. Cancer is classified based on the tissue or organ where it originates.
Major Types of Cancer
1. Carcinomas (Most Common Type)

Carcinomas account for 80-90% of all cancers and start in epithelial cells, which line organs and skin. Examples include
- Breast Cancer– Begins in breast tissue; common in women but can affect men.
- Lung Cancer – Often linked to smoking, it starts in lung tissues.
- Prostate Cancer – Affects the prostate gland in men.
- Colorectal Cancer – Starts in the colon or rectum; early screening can save lives.
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell, Squamous Cell) – Caused by UV exposure, affecting skin tissues.
2. Sarcomas (Rare but Aggressive)

Sarcomas begin in connective tissues like bones, muscles, fat, and cartilage. Common types include:
- Osteosarcoma – Bone cancer, common in young adults.
- Chondrosarcoma – Cancer of cartilage tissue.
- Liposarcoma – Develops in fat cells.
3. Leukemia (Blood Cancer)

Unlike solid tumors, leukemia affects blood-forming tissues in the bone marrow and leads to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
4. Lymphoma (Cancer of the Immune System)
Lymphoma affects lymphocytes, which are white blood cells in the lymphatic system.

5. Multiple Myeloma (Plasma Cell Cancer)
Myeloma affects plasma cells in the bone marrow, impacting the immune system and causing bone pain, infections, and fatigue.
What Causes Cancer?
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of cancer, including:
- Genetics – Family history plays a role.
- Smoking & Tobacco Use – Causes lung, throat, and oral cancers.
- Poor Diet & Obesity – Increases the risk of colon, breast, and pancreatic cancers.
- Radiation & Sun Exposure – Leads to skin cancer.
- Viral Infections – HPV can cause cervical cancer; Hepatitis B can lead to liver cancer.
How Is Cancer Diagnosed?
Doctors use various tests and screenings to diagnose cancer, including:
- Blood Tests – Detect abnormal levels of blood markers.
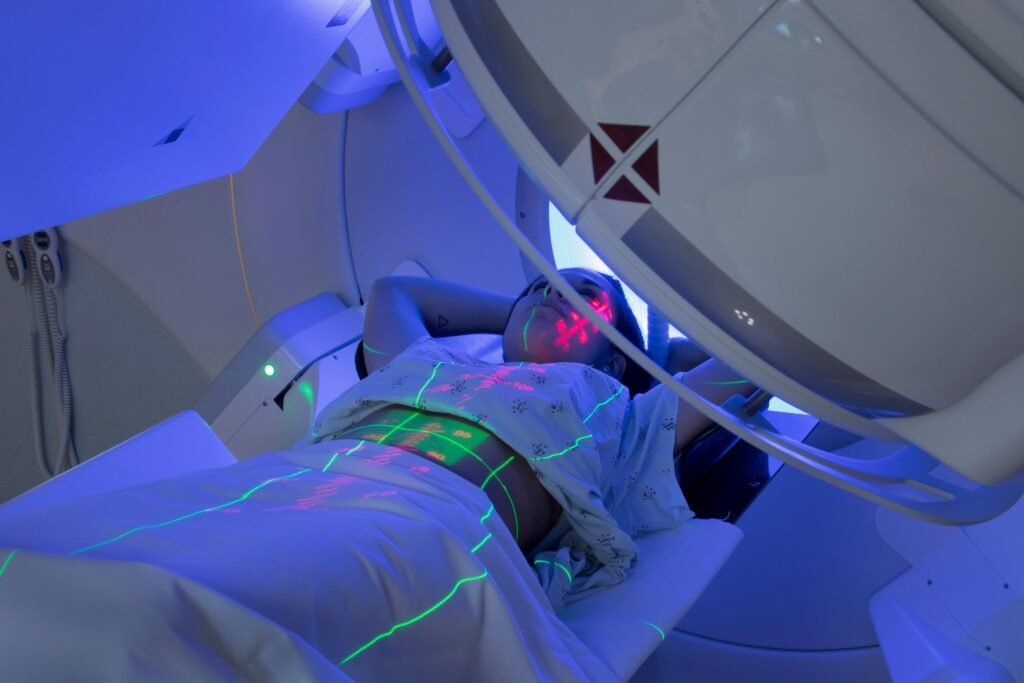
- Imaging (CT, MRI, Ultrasound, PET scans) – Locate tumors.
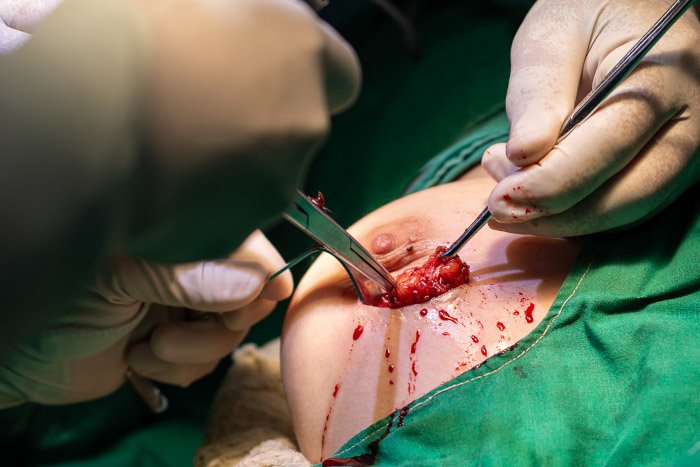
- Biopsy – A sample of tissue is examined for cancerous cells.
- Genetic Testing – Identifies inherited cancer risks.
Treatment Options for Cancer
Cancer Prevention Tips
- Regular Screenings – Detect cancer early.
- Healthy Diet – Eat fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Smoking – Reduces the risk of lung, throat, and oral cancers.
- Stay Active – Reduces obesity-related cancers.
- Protect Your Skin – Wear sunscreen to prevent skin cancer.
- Get Vaccinated – HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines prevent certain cancers.
For more health insights, visit NEMA Pain Care.




Обзор BlackSprut: ключевые особенности
BlackSprut вызывает интерес широкой аудитории. Почему о нем говорят?
Эта площадка обеспечивает разнообразные опции для своих пользователей. Оформление платформы характеризуется удобством, что делает его доступной даже для тех, кто впервые сталкивается с подобными сервисами.
Важно отметить, что этот ресурс работает по своим принципам, которые делают его особенным в определенной среде.
Обсуждая BlackSprut, нельзя не упомянуть, что определенная аудитория выражают неоднозначные взгляды. Многие выделяют его функциональность, а кто-то относятся к нему неоднозначно.
Таким образом, данный сервис остается темой дискуссий и вызывает интерес разных слоев интернет-сообщества.
Где найти актуальный линк на BlackSprut?
Хотите найти свежее ссылку на BlackSprut? Это можно сделать здесь.
https://bs2best
Сайт часто обновляет адреса, поэтому важно иметь обновленный линк.
Мы мониторим за актуальными доменами чтобы предоставить новым линком.
Посмотрите актуальную ссылку прямо сейчас!
Our platform provides access to a wide selection of slot games, ideal for all types of players.
Here, you can explore traditional machines, modern video slots, and jackpot slots with amazing animations and dynamic music.
If you are a fan of minimal mechanics or seek engaging stories, you’re sure to find what you’re looking for.
http://balticshar.ru/kakoj-sposob-naneseniya-izobrazheniya-na-pamyatnik-vybrat/
Each title are available anytime, with no installation, and fully optimized for both all devices.
In addition to games, the site includes tips and tricks, welcome packages, and player feedback to help you choose.
Register today, spin the reels, and have fun with the thrill of online slots!
Self-harm leading to death is a tragic phenomenon that touches countless lives worldwide.
It is often linked to psychological struggles, such as bipolar disorder, hopelessness, or chemical dependency.
People who contemplate suicide may feel isolated and believe there’s no hope left.
how-to-kill-yourself.com
Society needs to spread knowledge about this subject and help vulnerable individuals.
Prevention can save lives, and finding help is a crucial first step.
If you or someone you know is thinking about suicide, get in touch with professionals.
You are not alone, and support exists.
Здесь вы обнаружите лучшие онлайн-автоматы на платформе Champion.
Выбор игр представляет традиционные игры и современные слоты с яркой графикой и специальными возможностями.
Каждый слот создан для комфортного использования как на ПК, так и на смартфонах.
Будь вы новичком или профи, здесь вы найдёте подходящий вариант.
champion casino зеркало
Игры работают круглосуточно и не нуждаются в установке.
Дополнительно сайт предлагает бонусы и обзоры игр, для улучшения опыта.
Погрузитесь в игру уже сегодня и испытайте удачу с брендом Champion!
На этом сайте вы найдёте разнообразные онлайн-автоматы в казино Champion.
Коллекция игр содержит традиционные игры и современные слоты с яркой графикой и уникальными бонусами.
Каждый слот создан для комфортного использования как на компьютере, так и на смартфонах.
Будь вы новичком или профи, здесь вы сможете выбрать что-то по вкусу.
приложение champions
Игры доступны без ограничений и работают прямо в браузере.
Дополнительно сайт предлагает акции и обзоры игр, для удобства пользователей.
Начните играть прямо сейчас и насладитесь азартом с играми от Champion!
На данной платформе доступны онлайн-игры из казино Вавада.
Любой игрок сможет выбрать слот на свой вкус — от простых аппаратов до видеослотов разработок с бонусными раундами.
Vavada предлагает широкий выбор популярных игр, включая прогрессивные слоты.
Все игры доступен в любое время и подходит как для ПК, так и для мобильных устройств.
игровые автоматы вавада
Игроки могут наслаждаться азартом, не выходя из дома.
Интерфейс сайта понятна, что обеспечивает без труда начать играть.
Начните прямо сейчас, чтобы открыть для себя любимые слоты!
Здесь можно найти онлайн-игры из казино Вавада.
Любой игрок найдёт слот на свой вкус — от классических одноруких бандитов до современных моделей с анимацией.
Платформа Vavada открывает возможность сыграть в популярных игр, включая игры с джекпотом.
Любой автомат доступен в любое время и оптимизирован как для компьютеров, так и для мобильных устройств.
vavada casino бонусы
Игроки могут наслаждаться настоящим драйвом, не выходя из квартиры.
Навигация по сайту проста, что позволяет быстро найти нужную игру.
Начните прямо сейчас, чтобы почувствовать азарт с Vavada!
Suicide is a serious topic that affects millions of people around the globe.
It is often connected to mental health issues, such as bipolar disorder, hopelessness, or chemical dependency.
People who struggle with suicide may feel overwhelmed and believe there’s no hope left.
https://how-to-kill-yourself.com
It is important to talk openly about this topic and help vulnerable individuals.
Early support can reduce the risk, and reaching out is a necessary first step.
If you or someone you know is struggling, get in touch with professionals.
You are not forgotten, and support exists.
Here, you can discover lots of slot machines from leading developers.
Users can try out retro-style games as well as new-generation slots with stunning graphics and bonus rounds.
Even if you’re new or a seasoned gamer, there’s a game that fits your style.
play casino
All slot machines are instantly accessible round the clock and designed for desktop computers and mobile devices alike.
All games run in your browser, so you can jump into the action right away.
Platform layout is intuitive, making it quick to browse the collection.
Register now, and enjoy the excitement of spinning reels!
On this platform, you can discover lots of slot machines from leading developers.
Users can enjoy retro-style games as well as modern video slots with vivid animation and interactive gameplay.
Even if you’re new or a seasoned gamer, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
money casino
All slot machines are instantly accessible 24/7 and optimized for PCs and tablets alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can jump into the action right away.
Site navigation is intuitive, making it simple to explore new games.
Join the fun, and enjoy the thrill of casino games!
On this platform, you can access a great variety of slot machines from famous studios.
Players can experience retro-style games as well as feature-packed games with vivid animation and exciting features.
Even if you’re new or an experienced player, there’s a game that fits your style.
slot casino
All slot machines are available round the clock and optimized for PCs and smartphones alike.
All games run in your browser, so you can start playing instantly.
Platform layout is intuitive, making it convenient to explore new games.
Register now, and discover the thrill of casino games!
On this platform, you can discover lots of online slots from top providers.
Users can enjoy traditional machines as well as feature-packed games with vivid animation and interactive gameplay.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gamer, there’s something for everyone.
casino slots
The games are instantly accessible 24/7 and optimized for PCs and tablets alike.
No download is required, so you can start playing instantly.
Platform layout is intuitive, making it convenient to browse the collection.
Join the fun, and discover the thrill of casino games!
Сайт BlackSprut — это одна из самых известных онлайн-площадок в darknet-среде, предлагающая разные функции в рамках сообщества.
На платформе предусмотрена удобная навигация, а визуальная часть простой и интуитивный.
Пользователи ценят стабильность работы и жизнь на площадке.
bs2best.markets
Площадка разработана на комфорт и анонимность при использовании.
Если вы интересуетесь альтернативные цифровые пространства, площадка будет удобной точкой старта.
Прежде чем начать не лишним будет прочитать информацию о работе Tor.
Платформа BlackSprut — это хорошо известная точек входа в darknet-среде, предоставляющая разнообразные сервисы для всех, кто интересуется сетью.
Здесь предусмотрена понятная система, а структура меню не вызывает затруднений.
Гости ценят отзывчивость платформы и постоянные обновления.
bs2best.markets
Площадка разработана на приватность и анонимность при использовании.
Кому интересны теневые платформы, этот проект станет хорошим примером.
Перед началом рекомендуется изучить информацию о работе Tor.
Платформа BlackSprut — это хорошо известная систем в darknet-среде, предлагающая разнообразные сервисы для пользователей.
На платформе доступна понятная система, а визуальная часть простой и интуитивный.
Гости ценят стабильность работы и активное сообщество.
bs2best.markets
BlackSprut ориентирован на комфорт и безопасность при работе.
Кому интересны инфраструктуру darknet, этот проект станет удобной точкой старта.
Перед началом лучше ознакомиться с информацию о работе Tor.
Онлайн-площадка — цифровая витрина лицензированного детективного агентства.
Мы оказываем сопровождение в области розыска.
Команда сотрудников работает с максимальной этичностью.
Мы занимаемся проверку фактов и разные виды расследований.
Услуги детектива
Любой запрос рассматривается индивидуально.
Применяем новейшие технологии и действуем в правовом поле.
Нуждаетесь в ответственное агентство — вы нашли нужный сайт.
Онлайн-площадка — сайт лицензированного сыскного бюро.
Мы оказываем сопровождение по частным расследованиям.
Штат детективов работает с абсолютной этичностью.
Мы берёмся за наблюдение и анализ ситуаций.
Детективное агентство
Каждое дело рассматривается индивидуально.
Применяем проверенные подходы и ориентируемся на правовые стандарты.
Нуждаетесь в настоящих профессионалов — свяжитесь с нами.
Этот сайт — официальная страница профессионального сыскного бюро.
Мы оказываем помощь по частным расследованиям.
Группа опытных специалистов работает с повышенной конфиденциальностью.
Мы берёмся за проверку фактов и разные виды расследований.
Услуги детектива
Каждое дело получает персональный подход.
Мы используем современные методы и действуем в правовом поле.
Если вы ищете достоверную информацию — свяжитесь с нами.
Онлайн-площадка — интернет-представительство частного расследовательской службы.
Мы предоставляем помощь в области розыска.
Команда сотрудников работает с повышенной дискретностью.
Мы берёмся за поиски людей и анализ ситуаций.
Услуги детектива
Каждое дело обрабатывается персонально.
Мы используем современные методы и действуем в правовом поле.
Ищете достоверную информацию — свяжитесь с нами.
Наш веб-портал — официальная страница профессионального детективного агентства.
Мы организуем услуги по частным расследованиям.
Коллектив детективов работает с предельной осторожностью.
Мы занимаемся проверку фактов и анализ ситуаций.
Детективное агентство
Каждое дело обрабатывается персонально.
Мы используем проверенные подходы и действуем в правовом поле.
Если вы ищете реальную помощь — свяжитесь с нами.
Онлайн-площадка — официальная страница независимого расследовательской службы.
Мы предоставляем сопровождение по частным расследованиям.
Группа детективов работает с повышенной осторожностью.
Мы берёмся за сбор информации и анализ ситуаций.
Нанять детектива
Каждое дело рассматривается индивидуально.
Задействуем эффективные инструменты и соблюдаем юридические нормы.
Нуждаетесь в настоящих профессионалов — добро пожаловать.
Этот сайт — официальная страница лицензированного расследовательской службы.
Мы организуем поддержку по частным расследованиям.
Группа опытных специалистов работает с предельной конфиденциальностью.
Мы занимаемся сбор информации и разные виды расследований.
Нанять детектива
Каждое обращение подходит с особым вниманием.
Применяем эффективные инструменты и соблюдаем юридические нормы.
Ищете ответственное агентство — вы по адресу.
Наш веб-портал — сайт частного расследовательской службы.
Мы оказываем поддержку в области розыска.
Группа сотрудников работает с повышенной этичностью.
Наша работа включает наблюдение и анализ ситуаций.
Заказать детектива
Любой запрос обрабатывается персонально.
Задействуем проверенные подходы и соблюдаем юридические нормы.
Если вы ищете реальную помощь — вы нашли нужный сайт.
Данный ресурс — официальная страница лицензированного аналитической компании.
Мы предлагаем поддержку в решении деликатных ситуаций.
Команда опытных специалистов работает с повышенной дискретностью.
Мы занимаемся поиски людей и разные виды расследований.
Нанять детектива
Каждое обращение подходит с особым вниманием.
Опираемся на современные методы и соблюдаем юридические нормы.
Нуждаетесь в ответственное агентство — вы нашли нужный сайт.
Наш веб-портал — официальная страница частного сыскного бюро.
Мы организуем услуги в решении деликатных ситуаций.
Группа детективов работает с предельной дискретностью.
Мы занимаемся наблюдение и анализ ситуаций.
Заказать детектива
Каждое обращение обрабатывается персонально.
Задействуем проверенные подходы и ориентируемся на правовые стандарты.
Ищете ответственное агентство — свяжитесь с нами.
This website, you can discover a great variety of slot machines from top providers.
Users can try out classic slots as well as modern video slots with stunning graphics and exciting features.
If you’re just starting out or a casino enthusiast, there’s something for everyone.
casino games
The games are available round the clock and optimized for laptops and tablets alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can start playing instantly.
The interface is intuitive, making it convenient to browse the collection.
Register now, and dive into the excitement of spinning reels!
Here offers a diverse range of stylish timepieces for every room.
You can discover contemporary and vintage styles to enhance your home.
Each piece is carefully selected for its design quality and reliable performance.
Whether you’re decorating a cozy bedroom, there’s always a fitting clock waiting for you.
reizen talking alarm clocks
Our catalog is regularly refreshed with trending items.
We prioritize a smooth experience, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
This online store offers a wide selection of interior wall clocks for every room.
You can explore modern and classic styles to match your living space.
Each piece is carefully selected for its craftsmanship and functionality.
Whether you’re decorating a functional kitchen, there’s always a perfect clock waiting for you.
hermle leyton clocks
The collection is regularly renewed with exclusive releases.
We focus on secure delivery, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
Our platform offers a great variety of home wall clocks for any space.
You can discover urban and traditional styles to match your interior.
Each piece is hand-picked for its visual appeal and durability.
Whether you’re decorating a cozy bedroom, there’s always a beautiful clock waiting for you.
kassel 15 day wall clocks 2
Our catalog is regularly renewed with new arrivals.
We prioritize customer satisfaction, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
This website offers a large assortment of interior wall clocks for all styles.
You can explore urban and traditional styles to match your interior.
Each piece is carefully selected for its aesthetic value and reliable performance.
Whether you’re decorating a functional kitchen, there’s always a beautiful clock waiting for you.
best howard miller anniversary grandfather clocks
The shop is regularly updated with exclusive releases.
We prioritize a smooth experience, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
Here offers a great variety of home clock designs for your interior.
You can browse urban and traditional styles to enhance your interior.
Each piece is hand-picked for its design quality and durability.
Whether you’re decorating a functional kitchen, there’s always a fitting clock waiting for you.
world map clocks
Our catalog is regularly renewed with fresh designs.
We care about quality packaging, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
Here offers a great variety of stylish wall clocks for your interior.
You can check out modern and traditional styles to match your interior.
Each piece is curated for its design quality and durability.
Whether you’re decorating a stylish living room, there’s always a beautiful clock waiting for you.
best wood analog alarm clocks
Our catalog is regularly updated with trending items.
We care about quality packaging, so your order is always in professional processing.
Start your journey to enhanced interiors with just a few clicks.
Here offers a diverse range of interior clock designs for all styles.
You can explore contemporary and timeless styles to fit your living space.
Each piece is carefully selected for its aesthetic value and accuracy.
Whether you’re decorating a cozy bedroom, there’s always a beautiful clock waiting for you.
best la crosse technology mood light alarm clocks
The shop is regularly renewed with new arrivals.
We focus on secure delivery, so your order is always in good care.
Start your journey to perfect timing with just a few clicks.
Here offers a wide selection of stylish wall clocks for every room.
You can check out contemporary and vintage styles to complement your apartment.
Each piece is carefully selected for its design quality and durability.
Whether you’re decorating a functional kitchen, there’s always a fitting clock waiting for you.
best bai design wall clocks
Our assortment is regularly refreshed with trending items.
We care about customer satisfaction, so your order is always in safe hands.
Start your journey to timeless elegance with just a few clicks.
This online store offers a large assortment of stylish clock designs for any space.
You can browse modern and classic styles to fit your apartment.
Each piece is curated for its visual appeal and functionality.
Whether you’re decorating a stylish living room, there’s always a matching clock waiting for you.
best small loud battery alarm clocks
Our assortment is regularly refreshed with trending items.
We focus on customer satisfaction, so your order is always in safe hands.
Start your journey to better decor with just a few clicks.
This online service offers a large selection of pharmaceuticals for ordering online.
You can quickly access needed prescriptions with just a few clicks.
Our range includes both common medications and custom orders.
Each item is provided by trusted suppliers.
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/879609370963839381/
We ensure customer safety, with secure payments and prompt delivery.
Whether you’re managing a chronic condition, you’ll find trusted options here.
Start your order today and enjoy convenient online pharmacy service.
Платформа предоставляет поиска занятости по всей стране.
На сайте размещены разные объявления от уверенных партнеров.
Система показывает объявления о работе в разнообразных нишах.
Частичная занятость — всё зависит от вас.
Работа для киллера Украина
Интерфейс сайта легко осваивается и подходит на любой уровень опыта.
Создание профиля очень простое.
Ищете работу? — просматривайте вакансии.
This website, you can discover lots of casino slots from top providers.
Players can experience traditional machines as well as new-generation slots with stunning graphics and bonus rounds.
Even if you’re new or an experienced player, there’s a game that fits your style.
play aviator
Each title are instantly accessible anytime and designed for desktop computers and smartphones alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can start playing instantly.
The interface is user-friendly, making it simple to find your favorite slot.
Sign up today, and discover the world of online slots!
This website, you can discover a great variety of online slots from top providers.
Visitors can try out traditional machines as well as modern video slots with high-quality visuals and bonus rounds.
Whether you’re a beginner or a casino enthusiast, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
casino games
Each title are instantly accessible anytime and compatible with desktop computers and smartphones alike.
No download is required, so you can start playing instantly.
Site navigation is easy to use, making it convenient to find your favorite slot.
Sign up today, and dive into the thrill of casino games!
This website, you can discover a great variety of slot machines from famous studios.
Players can experience traditional machines as well as feature-packed games with vivid animation and bonus rounds.
If you’re just starting out or a casino enthusiast, there’s something for everyone.
casino slots
All slot machines are ready to play round the clock and compatible with laptops and mobile devices alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can jump into the action right away.
Site navigation is user-friendly, making it quick to browse the collection.
Register now, and discover the excitement of spinning reels!
Данный портал собирает интересные информационные статьи на любые темы.
Здесь можно найти новости о политике, бизнесе и других областях.
Информация обновляется в режиме реального времени, что позволяет держать руку на пульсе.
Минималистичный дизайн облегчает восприятие.
https://fashion5.ru
Все публикации предлагаются с фактчеком.
Целью сайта является честной подачи.
Читайте нас регулярно, чтобы быть всегда информированными.
Текущий модный сезон обещает быть стильным и экспериментальным в плане моды.
В тренде будут многослойность и неожиданные сочетания.
Актуальные тона включают в себя природные тона, подчеркивающие индивидуальность.
Особое внимание дизайнеры уделяют аксессуарам, среди которых популярны объёмные украшения.
https://ozoms.com/read-blog/2782
Набирают популярность элементы нулевых, интерпретированные по-новому.
В стритстайле уже можно увидеть трендовые образы, которые удивляют.
Не упустите шанс, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно.
Текущий модный сезон обещает быть стильным и оригинальным в плане моды.
В тренде будут многослойность и игра фактур.
Цветовая палитра включают в себя чистые базовые цвета, сочетающиеся с любым стилем.
Особое внимание дизайнеры уделяют аксессуарам, среди которых популярны макросумки.
https://www.cyberpinoy.net/read-blog/45788
Опять актуальны элементы 90-х, через призму сегодняшнего дня.
В стритстайле уже можно увидеть модные эксперименты, которые впечатляют.
Будьте в курсе, чтобы встретить лето стильно.
On this platform, you can find lots of casino slots from leading developers.
Players can enjoy classic slots as well as modern video slots with high-quality visuals and exciting features.
Even if you’re new or a seasoned gamer, there’s a game that fits your style.
play casino
Each title are available anytime and compatible with laptops and tablets alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can jump into the action right away.
Site navigation is intuitive, making it quick to browse the collection.
Join the fun, and enjoy the world of online slots!
It’s alarming to realize that 1 in 3 people taking prescriptions experience serious medication errors stemming from poor understanding?
Your wellbeing should be your top priority. All treatment options you make plays crucial role in your long-term wellbeing. Staying educated about your prescriptions should be mandatory for successful recovery.
Your health goes far beyond swallowing medications. Each drug changes your biological systems in unique ways.
Consider these life-saving facts:
1. Taking incompatible prescriptions can cause health emergencies
2. Over-the-counter allergy medicines have serious risks
3. Self-adjusting treatment reduces effectiveness
To protect yourself, always:
✓ Research combinations using official tools
✓ Review guidelines thoroughly when starting medical treatment
✓ Ask your pharmacist about correct dosage
___________________________________
For verified drug information, visit:
https://community.alteryx.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/576295
This online pharmacy features an extensive variety of pharmaceuticals at affordable prices.
You can find both prescription and over-the-counter medicines to meet your health needs.
Our goal is to keep high-quality products at a reasonable cost.
Speedy and secure shipping ensures that your purchase is delivered promptly.
Experience the convenience of shopping online with us.
oral jelly kamagra 100mg
The site allows off-road vehicle rentals across the island.
Travelers may easily reserve a vehicle for fun.
In case you’re looking to explore coastal trails, a buggy is the ideal way to do it.
https://pixabay.com/users/buggycrete-49906515/
Our rides are well-maintained and can be rented for full-day rentals.
Using this website is fast and comes with clear terms.
Get ready to ride and experience Crete on your own terms.
This section presents disc player alarm devices made by top providers.
You can find modern disc players with AM/FM radio and two alarm settings.
Each clock come with auxiliary inputs, device charging, and memory backup.
The selection extends from affordable clocks to elite choices.
alarm clock radio with cd
Each one include sleep timers, auto-off timers, and digital displays.
Shop the collection through Amazon and no extra cost.
Find the best disc player alarm clock for bedroom daily routines.
This website, you can discover a great variety of online slots from famous studios.
Visitors can enjoy retro-style games as well as modern video slots with stunning graphics and exciting features.
Even if you’re new or a casino enthusiast, there’s something for everyone.
slot casino
Each title are ready to play anytime and compatible with laptops and mobile devices alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can get started without hassle.
Site navigation is user-friendly, making it simple to find your favorite slot.
Join the fun, and enjoy the thrill of casino games!
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Приобретение туристического полиса во время путешествия — это разумное решение для финансовой защиты туриста.
Документ гарантирует медицинские услуги в случае обострения болезни за границей.
Кроме того, документ может включать оплату на репатриацию.
страховка за рубеж
Некоторые государства требуют наличие страховки для получения визы.
Без наличия документа госпитализация могут быть финансово обременительными.
Оформление полиса до поездки
This platform offers you the chance to hire professionals for one-time risky missions.
Visitors are able to efficiently set up support for particular situations.
All workers have expertise in handling sensitive tasks.
rent a hitman
The website ensures private connections between employers and freelancers.
If you require a quick solution, our service is ready to help.
List your task and get matched with a professional in minutes!
Questo sito consente il reclutamento di lavoratori per incarichi rischiosi.
Gli utenti possono ingaggiare professionisti specializzati per lavori una tantum.
Ogni candidato sono selezionati con attenzione.
assumi assassino
Sul sito è possibile ottenere informazioni dettagliate prima della selezione.
La professionalità resta al centro del nostro servizio.
Contattateci oggi stesso per trovare il supporto necessario!
На этом сайте вы можете найти рабочую копию сайта 1хБет без проблем.
Оперативно обновляем доступы, чтобы обеспечить беспрепятственный доступ к ресурсу.
Переходя через зеркало, вы сможете участвовать в играх без перебоев.
1xbet зеркало
Данный портал обеспечит возможность вам без труда открыть рабочее зеркало 1xBet.
Мы следим за тем, чтобы все клиенты смог не испытывать проблем.
Не пропустите обновления, чтобы не терять доступ с 1хБет!
Данный ресурс — аутентичный интернет-бутик Боттега Венета с отправкой по стране.
У нас вы можете оформить заказ на оригинальные товары Боттега Венета официально.
Каждая покупка подтверждены сертификатами от марки.
боттега венета
Доставка осуществляется быстро в по всей территории России.
Платформа предлагает выгодные условия покупки и комфортные условия возврата.
Положитесь на официальном сайте Боттега Венета, чтобы чувствовать уверенность в покупке!
在此页面,您可以聘请专门从事一次性的危险工作的执行者。
我们集合大量训练有素的任务执行者供您选择。
无论面对何种危险需求,您都可以方便找到胜任的人选。
为了钱而下令谋杀
所有合作人员均经过审核,维护您的安全。
服务中心注重专业性,让您的个别项目更加顺利。
如果您需要详细资料,请立即联系!
At this page, you can browse different websites for CS:GO betting.
We list a selection of gaming platforms dedicated to CS:GO players.
All the platforms is handpicked to guarantee fair play.
csgo match betting sites
Whether you’re a seasoned bettor, you’ll conveniently choose a platform that fits your style.
Our goal is to assist you to find only the best CS:GO gambling websites.
Check out our list at your convenience and upgrade your CS:GO gambling experience!
Здесь вы найдёте исчерпывающие сведения о реферальной системе: 1win partners.
Представлены все детали партнёрства, правила присоединения и ожидаемые выплаты.
Любой блок тщательно расписан, что даёт возможность просто усвоить в аспектах функционирования.
Плюс ко всему, имеются ответы на частые вопросы и полезные советы для начинающих.
Контент дополняется, поэтому вы можете быть уверены в актуальности предоставленных сведений.
Данный сайт окажет поддержку в исследовании партнёрской программы 1Win.
Questo sito permette il reclutamento di lavoratori per lavori pericolosi.
Gli interessati possono scegliere candidati qualificati per operazioni isolate.
Le persone disponibili sono valutati secondo criteri di sicurezza.
ordina omicidio l’uccisione
Attraverso il portale è possibile leggere recensioni prima della scelta.
La professionalità rimane un nostro impegno.
Contattateci oggi stesso per trovare il supporto necessario!
Looking to connect with reliable contractors available to tackle short-term hazardous tasks.
Require a specialist to complete a hazardous task? Discover vetted laborers on our platform for urgent dangerous operations.
hire a killer
This website links clients with trained workers willing to accept high-stakes temporary roles.
Hire background-checked laborers for dangerous duties safely. Perfect for urgent situations demanding specialized skills.
Here, you can find a wide selection of online slots from top providers.
Users can enjoy classic slots as well as new-generation slots with stunning graphics and interactive gameplay.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gamer, there’s something for everyone.
casino games
Each title are instantly accessible 24/7 and compatible with laptops and tablets alike.
All games run in your browser, so you can jump into the action right away.
The interface is easy to use, making it convenient to find your favorite slot.
Register now, and discover the excitement of spinning reels!
Individuals contemplate ending their life because of numerous causes, frequently arising from intense psychological suffering.
A sense of despair may consume their motivation to go on. Often, isolation is a major factor in this decision.
Conditions like depression or anxiety can cloud judgment, making it hard for individuals to find other solutions to their pain.
how to commit suicide
Life stressors could lead a person closer to the edge.
Limited availability of resources might result in a sense of no escape. Keep in mind getting help can save lives.
访问者请注意,这是一个仅限成年人浏览的站点。
进入前请确认您已年满成年年龄,并同意遵守当地法律法规。
本网站包含不适合未成年人观看的内容,请自行判断是否适合进入。 色情网站。
若不符合年龄要求,请立即关闭窗口。
我们致力于提供健康安全的娱乐内容。
Looking for a person to take on a rare dangerous task?
Our platform specializes in linking customers with workers who are willing to tackle critical jobs.
If you’re handling urgent repairs, hazardous cleanups, or risky installations, you’ve come to the right place.
Every available professional is vetted and certified to ensure your security.
hire a killer
This service provide transparent pricing, comprehensive profiles, and secure payment methods.
No matter how difficult the scenario, our network has the expertise to get it done.
Start your quest today and locate the ideal candidate for your needs.
This website contains necessary info about instructions for transforming into a IT infiltrator.
Knowledge is imparted in a transparent and lucid manner.
One can grasp numerous approaches for accessing restricted areas.
What’s more, there are concrete instances that illustrate how to utilize these skills.
how to become a hacker
Full details is continuously improved to stay current with the latest trends in computer security.
Distinct concentration is given to practical application of the absorbed know-how.
Note that each maneuver should be applied lawfully and within legal boundaries only.
On this site you can find special bonus codes for 1x betting.
These special offers make it possible to acquire supplementary bonuses when playing on the service.
Every listed promo deals are periodically verified to maintain their usability.
With these codes it is possible to enhance your possibilities on the online service.
https://cfekota.com/pages/oformlenierisunkare.html
Furthermore, step-by-step directions on how to apply special offers are provided for user-friendly experience.
Note that some promocodes may have limited validity, so check them before using.
This resource you can stumble upon limited special offers for the popular betting platform.
The assortment of rewarding options is periodically revised to ensure that you always have means to utilize the newest suggestions.
Via these coupons, you can save a lot on your wagers and enhance your possibilities of achievement.
All promo codes are carefully checked for accuracy and execution before being published.
https://eminence-bd.org/art/otdyh_na_goa_sovety_turistam.html
Additionally, we present thorough explanations on how to redeem each promo code to maximize your gains.
Keep in mind that some arrangements may have certain requirements or time limitations, so it’s fundamental to read carefully all the particulars before applying them.
Welcome to our platform, where you can discover premium content created specifically for adults.
All the resources available here is intended only for individuals who are 18 years old or above.
Please confirm that you meet the age requirement before exploring further.
interracial
Experience a unique selection of age-restricted content, and immerse yourself today!
1xBet stands as a leading online betting platform.
Offering a wide range of matches, 1XBet caters to countless users around the world.
The One X Bet application created intended for Android as well as Apple devices players.
https://businesseshubs.com/articles/sro_v_stroitelystve.html
Players are able to install the mobile version from the platform’s page and also Google Play Store on Android devices.
For iOS users, this software can be downloaded via the official iOS store easily.
The site provides a wide range of prescription drugs for ordering online.
Users can easily get health products from your device.
Our range includes popular treatments and targeted therapies.
Each item is supplied through trusted pharmacies.
cenforce
We ensure customer safety, with data protection and timely service.
Whether you’re managing a chronic condition, you’ll find affordable choices here.
Visit the store today and get convenient online pharmacy service.
One X Bet Promo Code – Exclusive Bonus maximum of $130
Enter the One X Bet promotional code: 1XBRO200 while signing up on the app to unlock the benefits provided by 1XBet to receive welcome bonus as much as a full hundred percent, for sports betting plus a $1950 with one hundred fifty free spins. Open the app followed by proceeding through the sign-up process.
This 1xBet bonus code: Code 1XBRO200 offers a great sign-up bonus for new users — 100% maximum of $130 during sign-up. Promo codes serve as the key to obtaining bonuses, also One X Bet’s promo codes aren’t different. By using such a code, users can take advantage of several promotions in various phases within their betting activity. Even if you don’t qualify for the initial offer, One X Bet India ensures its loyal users are rewarded through regular bonuses. Visit the Offers page on their website regularly to stay updated regarding recent promotions designed for loyal customers.
1xbet promo code nepal
Which One X Bet promotional code is currently active right now?
The bonus code relevant to One X Bet stands as 1XBRO200, which allows first-time users registering with the betting service to gain a reward of $130. To access unique offers for casino and wagering, kindly enter the promotional code for 1XBET in the registration form. In order to benefit of such a promotion, future players need to type the promo code Code 1xbet during the registration process so they can obtain double their deposit amount applied to the opening contribution.
One X Bet Promo Code – Exclusive Bonus maximum of $130
Apply the 1XBet promotional code: Code 1XBRO200 while signing up in the App to access exclusive rewards provided by 1XBet and get €130 as much as 100%, for sports betting along with a €1950 featuring free spin package. Launch the app and proceed by completing the registration steps.
The One X Bet promo code: Code 1XBRO200 provides a great welcome bonus to new players — full one hundred percent maximum of €130 upon registration. Promo codes are the key for accessing rewards, also One X Bet’s promo codes are the same. After entering the code, players have the chance of several promotions at different stages of their betting experience. Though you don’t qualify to the starter reward, One X Bet India makes sure its regular customers are rewarded through regular bonuses. Check the Promotions section on the site frequently to stay updated on the latest offers meant for loyal customers.
https://sgedsedwse.dsiblogger.com/67920725/
What 1xBet promotional code is now valid today?
The promotional code applicable to 1XBet is 1xbro200, permitting novice players signing up with the gambling provider to access an offer of $130. To access unique offers for casino and wagering, please input the promotional code for 1XBET while filling out the form. To make use of such a promotion, future players should enter the promotional code 1xbet during the registration step to receive double their deposit amount for their first payment.
Здесь доступны актуальные промокоды от Мелбет.
Используйте их при регистрации на сайте и получите полный бонус на первый депозит.
Кроме того, здесь представлены промокоды в рамках действующих программ для лояльных участников.
мелбет промокод на фрибет при регистрации
Следите за обновлениями на странице бонусов, не пропустив эксклюзивные бонусы от Melbet.
Все промокоды тестируется на актуальность, поэтому вы можете быть уверены при использовании.
1xBet Bonus Code – Special Bonus maximum of €130
Apply the 1xBet bonus code: 1XBRO200 when registering on the app to access the benefits given by 1XBet to receive welcome bonus as much as 100%, for wagering and a 1950 Euros including free spin package. Open the app then continue through the sign-up steps.
This 1xBet promo code: Code 1XBRO200 gives an amazing starter bonus for new users — 100% maximum of 130 Euros once you register. Bonus codes are the key to obtaining rewards, plus 1xBet’s bonus codes aren’t different. By using such a code, users can take advantage of various offers throughout their journey in their gaming adventure. Although you don’t qualify for the initial offer, One X Bet India makes sure its regular customers receive gifts through regular bonuses. Look at the Deals tab on their website regularly to stay updated about current deals meant for current users.
1xbet promo code today
Which 1XBet promo code is currently active today?
The promotional code relevant to 1XBet equals Code 1XBRO200, permitting first-time users joining the gambling provider to access a reward amounting to €130. In order to unlock special rewards pertaining to gaming and sports betting, please input this special code for 1XBET in the registration form. In order to benefit of such a promotion, future players should enter the promo code Code 1xbet at the time of registering procedure to receive a full hundred percent extra on their initial deposit.
Здесь представлены живые видеочаты.
Если вы ищете непринужденные разговоры переговоры, здесь есть варианты для всех.
Модуль общения разработана для связи людей со всего мира.
порно чат парни
За счет четких изображений и чистым звуком, вся беседа становится увлекательным.
Вы можете присоединиться к публичным комнатам инициировать приватный разговор, опираясь на того, что вам нужно.
Единственное условие — хорошая связь плюс подходящий гаджет, и вы сможете подключиться.
This website, you can find a great variety of online slots from top providers.
Users can enjoy retro-style games as well as modern video slots with high-quality visuals and bonus rounds.
Even if you’re new or a casino enthusiast, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
slots
The games are ready to play anytime and compatible with desktop computers and tablets alike.
No download is required, so you can get started without hassle.
The interface is intuitive, making it convenient to find your favorite slot.
Join the fun, and dive into the world of online slots!
Here, explore a wide range internet-based casino sites.
Searching for classic games or modern slots, there’s something to suit all preferences.
The listed platforms fully reviewed to ensure security, enabling gamers to bet securely.
vavada
Additionally, the platform offers exclusive bonuses along with offers targeted at first-timers as well as regulars.
Due to simple access, locating a preferred platform is quick and effortless, enhancing your experience.
Stay updated regarding new entries with frequent visits, as fresh options come on board often.
Here, you can find lots of casino slots from famous studios.
Users can experience traditional machines as well as feature-packed games with vivid animation and bonus rounds.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, there’s something for everyone.
casino
Each title are available anytime and compatible with PCs and mobile devices alike.
You don’t need to install anything, so you can jump into the action right away.
Site navigation is easy to use, making it convenient to browse the collection.
Register now, and discover the excitement of spinning reels!
This flight-themed slot blends air travel with exciting rewards.
Jump into the cockpit and spin through cloudy adventures for sky-high prizes.
With its classic-inspired design, the game reflects the spirit of aircraft legends.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it disappears to lock in your earnings.
Featuring seamless gameplay and realistic audio design, it’s a top choice for slot enthusiasts.
Whether you’re looking for fun, Aviator delivers uninterrupted action with every spin.
本网站 提供 海量的 成人材料,满足 各类人群 的 兴趣。
无论您喜欢 什么样的 的 视频,这里都 种类齐全。
所有 资源 都经过 专业整理,确保 高清晰 的 浏览感受。
性别
我们支持 各种终端 访问,包括 电脑,随时随地 尽情观看。
加入我们,探索 激情时刻 的 成人世界。
本站 提供 丰富的 成人资源,满足 成年访客 的 兴趣。
无论您喜欢 哪种类型 的 内容,这里都 应有尽有。
所有 材料 都经过 专业整理,确保 高品质 的 浏览感受。
视频 18+
我们支持 多种设备 访问,包括 电脑,随时随地 自由浏览。
加入我们,探索 无限精彩 的 私密乐趣。
The Aviator Game merges air travel with high stakes.
Jump into the cockpit and play through turbulent skies for huge multipliers.
With its vintage-inspired visuals, the game captures the spirit of pioneering pilots.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it flies away to lock in your rewards.
Featuring seamless gameplay and realistic audio design, it’s a top choice for casual players.
Whether you’re chasing wins, Aviator delivers uninterrupted thrills with every flight.
The Aviator Game combines air travel with big wins.
Jump into the cockpit and try your luck through aerial challenges for sky-high prizes.
With its vintage-inspired design, the game captures the spirit of pioneering pilots.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it disappears to secure your earnings.
Featuring seamless gameplay and immersive sound effects, it’s a favorite for gambling fans.
Whether you’re testing luck, Aviator delivers endless excitement with every flight.
This flight-themed slot blends exploration with high stakes.
Jump into the cockpit and play through turbulent skies for sky-high prizes.
With its retro-inspired design, the game captures the spirit of pioneering pilots.
aviator game download link
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it flies away to grab your winnings.
Featuring smooth gameplay and dynamic audio design, it’s a must-try for slot enthusiasts.
Whether you’re testing luck, Aviator delivers non-stop excitement with every round.
The Aviator Game combines air travel with high stakes.
Jump into the cockpit and try your luck through turbulent skies for huge multipliers.
With its retro-inspired visuals, the game evokes the spirit of early aviation.
aviator game download
Watch as the plane takes off – withdraw before it vanishes to grab your rewards.
Featuring instant gameplay and realistic audio design, it’s a top choice for gambling fans.
Whether you’re looking for fun, Aviator delivers non-stop thrills with every round.
Aviator merges adventure with exciting rewards.
Jump into the cockpit and play through aerial challenges for massive payouts.
With its vintage-inspired design, the game evokes the spirit of aircraft legends.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it disappears to secure your winnings.
Featuring seamless gameplay and realistic background music, it’s a favorite for casual players.
Whether you’re testing luck, Aviator delivers endless excitement with every flight.
This flight-themed slot merges adventure with exciting rewards.
Jump into the cockpit and spin through turbulent skies for massive payouts.
With its classic-inspired design, the game captures the spirit of aircraft legends.
aviator game download
Watch as the plane takes off – cash out before it disappears to secure your winnings.
Featuring instant gameplay and dynamic background music, it’s a must-try for gambling fans.
Whether you’re chasing wins, Aviator delivers endless excitement with every spin.
The Aviator Game combines adventure with high stakes.
Jump into the cockpit and try your luck through turbulent skies for massive payouts.
With its vintage-inspired visuals, the game captures the spirit of early aviation.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – claim before it vanishes to lock in your earnings.
Featuring instant gameplay and immersive sound effects, it’s a favorite for slot enthusiasts.
Whether you’re looking for fun, Aviator delivers endless thrills with every flight.
Aviator combines exploration with exciting rewards.
Jump into the cockpit and try your luck through cloudy adventures for huge multipliers.
With its vintage-inspired visuals, the game evokes the spirit of pioneering pilots.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – claim before it flies away to secure your earnings.
Featuring seamless gameplay and realistic sound effects, it’s a favorite for gambling fans.
Whether you’re looking for fun, Aviator delivers uninterrupted thrills with every spin.
This flight-themed slot merges air travel with high stakes.
Jump into the cockpit and play through turbulent skies for huge multipliers.
With its vintage-inspired graphics, the game reflects the spirit of aircraft legends.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/robin-kh-150138202_aviator-game-download-activity-7295792143506321408-81HD/
Watch as the plane takes off – claim before it vanishes to secure your rewards.
Featuring instant gameplay and dynamic sound effects, it’s a must-try for gambling fans.
Whether you’re chasing wins, Aviator delivers non-stop excitement with every spin.
Within this platform, find an extensive selection of online casinos.
Searching for classic games or modern slots, there’s a choice for any taste.
All featured casinos fully reviewed for trustworthiness, so you can play with confidence.
free spins
What’s more, the platform provides special rewards plus incentives targeted at first-timers as well as regulars.
Thanks to user-friendly browsing, finding your favorite casino happens in no time, saving you time.
Stay updated about the latest additions with frequent visits, since new casinos come on board often.
On this site, you can discover a variety virtual gambling platforms.
Searching for well-known titles new slot machines, there’s something to suit all preferences.
Every casino included checked thoroughly for trustworthiness, so you can play securely.
1win
Additionally, the platform provides special rewards plus incentives to welcome beginners including long-term users.
Thanks to user-friendly browsing, finding your favorite casino happens in no time, enhancing your experience.
Stay updated regarding new entries through regular check-ins, since new casinos come on board often.
У нас вы можете найти взрослый контент.
Контент подходит для взрослой аудитории.
У нас собраны видео и изображения на любой вкус.
Платформа предлагает качественный контент.
русское порно онлайн
Вход разрешен после подтверждения возраста.
Наслаждайтесь удобным интерфейсом.
Модные образы для торжеств нынешнего года отличаются разнообразием.
В тренде стразы и пайетки из полупрозрачных тканей.
Металлические оттенки создают эффект жидкого металла.
Асимметричные силуэты определяют современные тренды.
Особый акцент на открытые плечи придают пикантности образу.
Ищите вдохновение в новых коллекциях — стиль и качество оставят в памяти гостей!
https://uabets.com/threads/modnye-svadebnye-platja-sejchas-kak-vybrat.2684/
У нас вы можете найти вспомогательные материалы для абитуриентов.
Все школьные дисциплины в одном месте от математики до литературы.
Готовьтесь к ЕГЭ и ОГЭ с помощью тренажеров.
https://taganrogprav.ru/otvety-i-gotovye-resheniya-mozhno-li-shkolniku-ispolzovat-gdz-bez-vreda-dlya-znanij/
Примеры решений упростят процесс обучения.
Все материалы бесплатны для максимальной доступности.
Интегрируйте в обучение и успешно сдавайте экзамены.
заказ цветов с доставкой на дом купить цветы в спб дешево
доставка цветов на дом спб https://dostavka-cvetov1.ru
Свежие актуальные новости спорта россии со всего мира. Результаты матчей, интервью, аналитика, расписание игр и обзоры соревнований. Будьте в курсе главных событий каждый день!
Трендовые фасоны сезона 2025 года задают новые стандарты.
Популярны пышные модели до колен из полупрозрачных тканей.
Блестящие ткани создают эффект жидкого металла.
Многослойные юбки возвращаются в моду.
Минималистичные силуэты придают пикантности образу.
Ищите вдохновение в новых коллекциях — детали и фактуры превратят вас в звезду вечера!
https://songpuai.go.th/forum/suggestion-box/485420-r-nd-vi-sv-d-bni-br-zi-e-g-g-d-vibr-i
Микрозаймы онлайн https://kskredit.ru на карту — быстрое оформление, без справок и поручителей. Получите деньги за 5 минут, круглосуточно и без отказа. Доступны займы с любой кредитной историей.
Хочешь больше денег https://mfokapital.ru Изучай инвестиции, учись зарабатывать, управляй финансами, торгуй на Форекс и используй магию денег. Рабочие схемы, ритуалы, лайфхаки и инструкции — путь к финансовой независимости начинается здесь!
Быстрые микрозаймы https://clover-finance.ru без отказа — деньги онлайн за 5 минут. Минимум документов, максимум удобства. Получите займ с любой кредитной историей.
Сделай сам как сделать ремонт потолка Ремонт квартиры и дома своими руками: стены, пол, потолок, сантехника, электрика и отделка. Всё, что нужно — в одном месте: от выбора материалов до финального штриха. Экономьте с умом!
КПК «Доверие» https://bankingsmp.ru надежный кредитно-потребительский кооператив. Выгодные сбережения и доступные займы для пайщиков. Прозрачные условия, высокая доходность, финансовая стабильность и юридическая безопасность.
Ваш финансовый гид https://kreditandbanks.ru — подбираем лучшие предложения по кредитам, займам и банковским продуктам. Рейтинг МФО, советы по улучшению КИ, юридическая информация и онлайн-сервисы.
Займы под залог https://srochnyye-zaymy.ru недвижимости — быстрые деньги на любые цели. Оформление от 1 дня, без справок и поручителей. Одобрение до 90%, выгодные условия, честные проценты. Квартира или дом остаются в вашей собственности.
birthday balloons delivery dubai deliver balloons dubai
resumes for electrical engineers resume engineering fresher
Услуги массажа Ивантеевка — здоровье, отдых и красота. Лечебный, баночный, лимфодренажный, расслабляющий и косметический массаж. Сертифицированнй мастер, удобное расположение, результат с первого раза.
The Piguet 15300ST combines meticulous craftsmanship alongside refined styling. Its 39mm stainless steel case ensures a modern fit, achieving harmony between prominence and wearability. The signature eight-sided bezel, secured by eight hexagonal screws, exemplifies the brand’s revolutionary approach to luxury sports watches.
Piguet 15300 st
Featuring a white gold baton hour-marker dial, this model includes a 60-hour energy reserve via the selfwinding mechanism. The Grande Tapisserie pattern adds dimension and uniqueness, while the slim profile ensures understated elegance.
The Audemars Piguet Royal Oak 15400ST combines luxury steel craftsmanship launched as a modern classic within the brand’s prestigious lineup.
Its 41mm stainless steel case is framed by an angular bezel secured with eight visible screws, embodying the collection’s iconic DNA.
Driven by the self-winding Cal. 3120, guarantees seamless functionality including a subtle date complication.
https://www.vevioz.com/read-blog/359857
A structured black dial with Tapisserie texture highlighted by luminous appliqués for optimal readability.
Its matching steel bracelet combines elegance with resilience, secured by a hidden clasp.
Renowned for its iconic design, this model remains a top choice among luxury watch enthusiasts.
The Audemars Piguet Royal Oak 16202ST features a elegant stainless steel 39mm case with an ultra-thin profile of just 8.1mm thickness, housing the latest selfwinding Calibre 7121. Its mesmerizing smoked blue gradient dial showcases a signature Petite Tapisserie pattern, fading from a radiant center to dark periphery for a captivating aesthetic. The iconic eight-screw octagonal bezel pays homage to the original 1972 design, while the scratch-resistant sapphire glass ensures optimal legibility.
https://linktr.ee/ap15202stpower
Water-resistant to 50 meters, this “Jumbo” model balances robust performance with sophisticated elegance, paired with a stainless steel bracelet and secure AP folding clasp. A modern tribute to horological heritage, the 16202ST embodies Audemars Piguet’s craftsmanship through its precision engineering and timeless Royal Oak DNA.
Всё о городе городской портал города Ханты-Мансийск: свежие новости, события, справочник, расписания, культура, спорт, вакансии и объявления на одном городском портале.
Здесь можно получить Telegram-бот “Глаз Бога”, что собрать всю информацию по человеку через открытые базы.
Бот работает по фото, используя актуальные базы онлайн. С его помощью доступны 5 бесплатных проверок и полный отчет по фото.
Платформа обновлен на август 2024 и охватывает мультимедийные данные. Глаз Бога сможет найти профили в открытых базах и покажет сведения мгновенно.
Бог Глаз
Данный инструмент — выбор при поиске людей онлайн.
На данном сайте вы можете найти боту “Глаз Бога” , который способен собрать всю информацию о любом человеке из публичных данных.
Этот мощный инструмент осуществляет поиск по номеру телефона и предоставляет детали из соцсетей .
С его помощью можно пробить данные через официальный сервис , используя фотографию в качестве ключевого параметра.
проверка авто по номеру
Система “Глаз Бога” автоматически обрабатывает информацию из множества источников , формируя подробный отчет .
Пользователи бота получают ограниченное тестирование для тестирования возможностей .
Платформа постоянно развивается, сохраняя скорость обработки в соответствии с стандартами безопасности .
Мир полон тайн https://phenoma.ru читайте статьи о малоизученных феноменах, которые ставят науку в тупик. Аномальные явления, редкие болезни, загадки космоса и сознания. Доступно, интересно, с научным подходом.
resumes for engineers best resumes for software engineers
Читайте о необычном http://phenoma.ru научно-популярные статьи о феноменах, которые до сих пор не имеют однозначных объяснений. Психология, физика, биология, космос — самые интересные загадки в одном разделе.
Looking for latest 1xBet promo codes? Our platform offers verified bonus codes like 1XRUN200 for new users in 2025. Get up to 32,500 RUB as a welcome bonus.
Use trusted promo codes during registration to maximize your rewards. Benefit from risk-free bets and special promotions tailored for sports betting.
Discover monthly updated codes for 1xBet Kazakhstan with guaranteed payouts.
Every promotional code is checked for accuracy.
Don’t miss limited-time offers like 1x_12121 to double your funds.
Active for new accounts only.
https://maps.google.hr/url?q=http://somatextiles.com/wp-content/pgs/?1xbet_promo_code_somalia_3.htmlKeep updated with top bonuses – apply codes like 1x_12121 at checkout.
Experience smooth benefits with easy redemption.
общие аккаунты стим бесплатно https://t.me/s/Burger_Game/
resume assistant engineer resumes for engineering internships
пустые аккаунты стим халявные аккаунты стим
Научно-популярный сайт https://phenoma.ru — малоизвестные факты, редкие феномены, тайны природы и сознания. Гипотезы, наблюдения и исследования — всё, что будоражит воображение и вдохновляет на поиски ответов.
На данном сайте вы можете получить доступ к боту “Глаз Бога” , который способен получить всю информацию о любом человеке из открытых источников .
Данный сервис осуществляет поиск по номеру телефона и показывает информацию из онлайн-платформ.
С его помощью можно проверить личность через специализированную платформу, используя имя и фамилию в качестве ключевого параметра.
пробить по инн
Алгоритм “Глаз Бога” автоматически собирает информацию из открытых баз , формируя исчерпывающий результат.
Подписчики бота получают 5 бесплатных проверок для ознакомления с функционалом .
Сервис постоянно обновляется , сохраняя высокую точность в соответствии с законодательством РФ.
Прямо здесь вы найдете сервис “Глаз Бога”, позволяющий проверить сведения о человеке из открытых источников.
Инструмент активно ищет по фото, используя доступные данные онлайн. Благодаря ему доступны пять пробивов и детальный анализ по фото.
Инструмент обновлен на август 2024 и охватывает фото и видео. Глаз Бога гарантирует проверить личность по госреестрам и предоставит результаты в режиме реального времени.
https://glazboga.net/
Данный сервис — помощник для проверки персон онлайн.
Looking for special 1xBet discount vouchers? This platform is your best choice to unlock valuable deals designed to boost your wagers.
If you’re just starting or an experienced player, verified codes ensures enhanced rewards for your first deposit .
Stay updated on daily deals to elevate your winning potential .
https://topsitenet.com/startpage/codepromo003/1413744/
Available vouchers are regularly verified to ensure functionality this month .
Act now of premium bonuses to transform your gaming journey with 1xBet.
Актуальные новости https://komandor-povolje.ru — политика, экономика, общество, культура и события стран постсоветского пространства, Европы и Азии. Объективно, оперативно и без лишнего — вся Евразия в одном месте.
¿Quieres códigos promocionales recientes de 1xBet? Aquí podrás obtener bonificaciones únicas en apuestas deportivas .
El código 1x_12121 te da acceso a hasta 6500₽ para nuevos usuarios.
Para completar, canjea 1XRUN200 y recibe una oferta exclusiva de €1500 + 150 giros gratis.
https://kofeinia.org/viewtopic.php?f=151&t=39479
No te pierdas las ofertas diarias para conseguir recompensas adicionales .
Las ofertas disponibles están actualizados para hoy .
¡Aprovecha y multiplica tus ganancias con 1xBet !
Meet https://llmbrowser.io, your next browser for agents. It’s optimized for secure agentic operations. Boost your AI’s web interaction with our unique ai agentic browser, perfect for data gathering. Upgrade your AI toolkit with a true agentic browser. Start now.
Юрист Онлайн https://juristonline.com квалифицированная юридическая помощь и консультации 24/7. Решение правовых вопросов любой сложности: семейные, жилищные, трудовые, гражданские дела. Бесплатная первичная консультация.
Получите гарантию russiahelp.com на все работы.
Юрист Онлайн https://juristonline.com квалифицированная юридическая помощь и консультации 24/7. Решение правовых вопросов любой сложности: семейные, жилищные, трудовые, гражданские дела. Бесплатная первичная консультация.
Дом из контейнера https://russiahelp.com под ключ — мобильное, экологичное и бюджетное жильё. Индивидуальные проекты, внутренняя отделка, электрика, сантехника и монтаж
Загадки Вселенной https://phenoma.ru паранормальные явления, нестандартные гипотезы и научные парадоксы — всё это на Phenoma.ru
Сайт знакомств https://rutiti.ru для серьёзных отношений, дружбы и общения. Реальные анкеты, удобный поиск, быстрый старт. Встречайте новых людей, находите свою любовь и начинайте общение уже сегодня.
Дом из контейнера https://russiahelp.com под ключ — мобильное, экологичное и бюджетное жильё. Индивидуальные проекты, внутренняя отделка, электрика, сантехника и монтаж
Загадки Вселенной https://phenoma.ru паранормальные явления, нестандартные гипотезы и научные парадоксы — всё это на Phenoma.ru
Сайт знакомств https://rutiti.ru для серьёзных отношений, дружбы и общения. Реальные анкеты, удобный поиск, быстрый старт. Встречайте новых людей, находите свою любовь и начинайте общение уже сегодня.
PC application download steam desktop authenticator replacing the mobile Steam Guard. Confirm logins, trades, and transactions in Steam directly from your computer. Support for multiple accounts, security, and backup.
Steam Guard for PC — https://steamdesktopauthenticator.net. Ideal for those who trade, play and do not want to depend on a smartphone. Two-factor protection and convenient security management on Windows.
No more phone needed! https://sdasteam.com lets you use Steam Guard right on your computer. Quickly confirm transactions, access 2FA codes, and conveniently manage security.
Steam Guard for PC — steam account authenticator. Ideal for those who trade, play and do not want to depend on a smartphone. Two-factor protection and convenient security management on Windows.
PC application steam authenticator replacing the mobile Steam Guard. Confirm logins, trades, and transactions in Steam directly from your computer. Support for multiple accounts, security, and backup.
No more phone needed! скачать steam desktop authenticator lets you use Steam Guard right on your computer. Quickly confirm transactions, access 2FA codes, and conveniently manage security.
Агентство недвижимости https://metropolis-estate.ru покупка, продажа и аренда квартир, домов, коммерческих объектов. Полное сопровождение сделок, юридическая безопасность, помощь в оформлении ипотеки.
Квартиры посуточно https://kvartiry-posutochno19.ru в Абакане — от эконом до комфорт-класса. Уютное жильё в центре и районах города. Чистота, удобства, всё для комфортного проживания.
Агентство недвижимости https://metropolis-estate.ru покупка, продажа и аренда квартир, домов, коммерческих объектов. Полное сопровождение сделок, юридическая безопасность, помощь в оформлении ипотеки.
Квартиры посуточно https://kvartiry-posutochno19.ru в Абакане — от эконом до комфорт-класса. Уютное жильё в центре и районах города. Чистота, удобства, всё для комфортного проживания.
Здесь вы найдете мессенджер-бот “Глаз Бога”, что собрать данные по человеку из открытых источников.
Инструмент активно ищет по фото, анализируя публичные материалы в Рунете. С его помощью осуществляется 5 бесплатных проверок и глубокий сбор по имени.
Инструмент проверен на август 2024 и включает фото и видео. Глаз Бога поможет проверить личность в открытых базах и отобразит сведения мгновенно.
https://glazboga.net/
Данный бот — выбор для проверки персон удаленно.
Looking for exclusive 1xBet coupon codes ? This platform is your go-to resource to access rewarding bonuses designed to boost your wagers.
If you’re just starting or a seasoned bettor , verified codes ensures maximum benefits for your first deposit .
Keep an eye on seasonal campaigns to elevate your rewards.
https://socialwebnotes.com/story4792750/1xbet-promo-code-welcome-bonus-up-to-130
Promotional offers are tested for validity to ensure functionality this month .
Act now of limited-time opportunities to enhance your betting strategy with 1xBet.
СРО УН «КИТ» https://sro-kit.ru саморегулируемая организация для строителей, проектировщиков и изыскателей. Оформление допуска СРО, вступление под ключ, юридическое сопровождение, помощь в подготовке документов.
Ремонт квартир https://berlin-remont.ru и офисов любого уровня сложности: от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, прозрачные сметы. Чисто, быстро, по разумной цене.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-kvartir-novo.ru под ключ в новостройках — от черновой отделки до полной готовности. Дизайн, материалы, инженерия, меблировка.
Ремонт квартир https://berlin-remont.ru и офисов любого уровня сложности: от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, прозрачные сметы. Чисто, быстро, по разумной цене.
СРО УН «КИТ» https://sro-kit.ru саморегулируемая организация для строителей, проектировщиков и изыскателей. Оформление допуска СРО, вступление под ключ, юридическое сопровождение, помощь в подготовке документов.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-kvartir-novo.ru под ключ в новостройках — от черновой отделки до полной готовности. Дизайн, материалы, инженерия, меблировка.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-otdelka-mo.ru любой сложности — от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, строгие сроки. Работаем по договору с гарантиями.
Webseite cvzen.de ist Ihr Partner fur professionelle Karriereunterstutzung – mit ma?geschneiderten Lebenslaufen, ATS-Optimierung, LinkedIn-Profilen, Anschreiben, KI-Headshots, Interviewvorbereitung und mehr. Starten Sie Ihre Karriere neu – gezielt, individuell und erfolgreich.
sitio web tavoq.es es tu aliado en el crecimiento profesional. Ofrecemos CVs personalizados, optimizacion ATS, cartas de presentacion, perfiles de LinkedIn, fotos profesionales con IA, preparacion para entrevistas y mas. Impulsa tu carrera con soluciones adaptadas a ti.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-otdelka-mo.ru любой сложности — от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, строгие сроки. Работаем по договору с гарантиями.
В этом ресурсе вы можете отыскать боту “Глаз Бога” , который может собрать всю информацию о любом человеке из общедоступных баз .
Этот мощный инструмент осуществляет анализ фото и показывает информацию из государственных реестров .
С его помощью можно проверить личность через специализированную платформу, используя фотографию в качестве ключевого параметра.
пробить авто
Технология “Глаз Бога” автоматически обрабатывает информацию из проверенных ресурсов, формируя исчерпывающий результат.
Пользователи бота получают 5 бесплатных проверок для проверки эффективности.
Платформа постоянно совершенствуется , сохраняя актуальность данных в соответствии с законодательством РФ.
sitio web tavoq.es es tu aliado en el crecimiento profesional. Ofrecemos CVs personalizados, optimizacion ATS, cartas de presentacion, perfiles de LinkedIn, fotos profesionales con IA, preparacion para entrevistas y mas. Impulsa tu carrera con soluciones adaptadas a ti.
Webseite cvzen.de ist Ihr Partner fur professionelle Karriereunterstutzung – mit ma?geschneiderten Lebenslaufen, ATS-Optimierung, LinkedIn-Profilen, Anschreiben, KI-Headshots, Interviewvorbereitung und mehr. Starten Sie Ihre Karriere neu – gezielt, individuell und erfolgreich.
Здесь доступен сервис “Глаз Бога”, который собрать сведения по человеку через открытые базы.
Бот функционирует по номеру телефона, используя публичные материалы в Рунете. С его помощью доступны бесплатный поиск и глубокий сбор по запросу.
Сервис актуален согласно последним данным и включает фото и видео. Глаз Бога поможет найти профили в соцсетях и отобразит результаты мгновенно.
https://glazboga.net/
Это бот — выбор в анализе людей через Telegram.
Searching for exclusive 1xBet promo codes? This site offers working bonus codes like 1x_12121 for registrations in 2025. Get up to 32,500 RUB as a welcome bonus.
Activate official promo codes during registration to maximize your bonuses. Enjoy risk-free bets and exclusive deals tailored for sports betting.
Discover monthly updated codes for 1xBet Kazakhstan with guaranteed payouts.
All promotional code is tested for validity.
Don’t miss exclusive bonuses like GIFT25 to double your funds.
Active for first-time deposits only.
https://bookmarking.stream/story.php?title=unlocking-1xbet-promo-codes-for-enhanced-betting-in-multiple-countries#discussKeep updated with top bonuses – apply codes like 1XRUN200 at checkout.
Experience smooth benefits with instant activation.
Модульный дом https://kubrdom.ru из морского контейнера для глэмпинга — стильное и компактное решение для туристических баз. Полностью готов к проживанию: утепление, отделка, коммуникации.
Качественный сервис Apple без очередей и затягиваний сроков.
Модульный дом https://kubrdom.ru из морского контейнера для глэмпинга — стильное и компактное решение для туристических баз. Полностью готов к проживанию: утепление, отделка, коммуникации.
Техника восстанавливается даже после сильных повреждений и залития.
kraken tor ссылка Кракен
ссылка Кракен kraken tor
Здесь вы можете получить доступ к актуальными новостями России и мира .
Материалы обновляются без задержек.
Доступны фоторепортажи с эпицентров происшествий .
Мнения журналистов помогут получить объективную оценку.
Контент предоставляется без регистрации .
https://pitersk.ru
Professional concrete driveways in seattle — high-quality installation, durable materials and strict adherence to deadlines. We work under a contract, provide a guarantee, and visit the site. Your reliable choice in Seattle.
Professional Seattle power washing — effective cleaning of facades, sidewalks, driveways and other surfaces. Modern equipment, affordable prices, travel throughout Seattle. Cleanliness that is visible at first glance.
Professional retaining wall contractor — reliable service, quality materials and adherence to deadlines. Individual approach, experienced team, free estimate. Your project — turnkey with a guarantee.
Explore detailed information about the Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710ST here , including market values ranging from $34,566 to $36,200 for stainless steel models.
The 42mm timepiece features a robust design with selfwinding caliber and rugged aesthetics, crafted in titanium.
https://ap15710st.superpodium.com
Analyze secondary market data , where limited editions command premiums , alongside rare references from the 1970s.
Request real-time updates on availability, specifications, and resale performance , with free market analyses for informed decisions.
Looking for latest 1xBet promo codes? This site offers working promotional offers like 1x_12121 for new users in 2025. Claim €1500 + 150 FS as a first deposit reward.
Activate official promo codes during registration to maximize your bonuses. Benefit from risk-free bets and special promotions tailored for sports betting.
Discover daily updated codes for 1xBet Kazakhstan with guaranteed payouts.
All promotional code is tested for validity.
Grab exclusive bonuses like GIFT25 to double your funds.
Active for new accounts only.
http://www.tvoidom.galaxyhost.org/forums.php?m=posts&q=43798&n=last#bottom
Enjoy seamless benefits with easy redemption.
Выбирая надежную платформу, стоит обратить внимание на хостинг для хрумера, который обеспечивает бесперебойную работу.
Need transportation? vehicle shipping quote car transportation company services — from one car to large lots. Delivery to new owners, between cities. Safety, accuracy, licenses and experience over 10 years.
Нужна камера? беспроводная камера видеонаблюдения купить для дома, офиса и улицы. Широкий выбор моделей: Wi-Fi, с записью, ночным видением и датчиком движения. Гарантия, быстрая доставка, помощь в подборе и установке.
Лицензирование и сертификация — обязательное условие ведения бизнеса в России, гарантирующий защиту от неквалифицированных кадров.
Обязательная сертификация требуется для подтверждения безопасности товаров.
Для 49 видов деятельности необходимо получение лицензий.
https://ok.ru/group/70000034956977/topic/158862631418033
Нарушения правил ведут к приостановке деятельности.
Дополнительные лицензии помогает усилить конкурентоспособность бизнеса.
Соблюдение норм — залог легальной работы компании.
Ищете ресурсы для нумизматов ? Эта платформа предлагает всё необходимое для изучения монет !
У нас вы найдёте коллекционные монеты из исторических периодов, а также антикварные предметы .
Изучите каталог с подробными описаниями и детальными снимками, чтобы сделать выбор .
золотая монета георгий победоносец цена
Если вы начинающий или профессиональный коллекционер , наши обзоры и руководства помогут расширить знания .
Воспользуйтесь возможностью добавить в коллекцию эксклюзивные артефакты с сертификатами.
Присоединяйтесь сообщества энтузиастов и следите последних новостей в мире нумизматики.
car transport service ship car from california to florida
керамогранит 600х1200 купить стройматериалы с доставкой в москве дешево
Профессиональное косметологическое оборудование купить для салонов красоты, клиник и частных мастеров. Аппараты для чистки, омоложения, лазерной эпиляции, лифтинга и ухода за кожей.
Discover the iconic Patek Philippe Nautilus, a luxury timepiece that merges sporty elegance with exquisite craftsmanship .
Introduced nearly 50 years ago, this legendary watch redefined high-end sports watches, featuring distinctive octagonal bezels and textured sunburst faces.
From stainless steel models like the 5990/1A-011 with a 45-hour power reserve to luxurious white gold editions such as the 5811/1G-001 with a azure-toned face, the Nautilus caters to both avid enthusiasts and casual admirers.
Authentic Patek Nautilus 5711 watches
The diamond-set 5719 elevate the design with dazzling bezels , adding unparalleled luxury to the timeless profile.
According to recent indices like the 5726/1A-014 at ~$106,000, the Nautilus remains a prized asset in the world of premium watchmaking.
For those pursuing a historical model or modern redesign, the Nautilus embodies Patek Philippe’s legacy of excellence .
Founded in 2001 , Richard Mille redefined luxury watchmaking with cutting-edge innovation . The brand’s iconic timepieces combine aerospace-grade ceramics and sapphire to enhance performance.
Mirroring the precision of racing cars , each watch embodies “form follows function”, optimizing resistance. Collections like the RM 001 Tourbillon set new benchmarks since their debut.
Richard Mille’s collaborations with experts in materials science yield skeletonized movements crafted for elite athletes.
Used Mille Richard RM 6702 horology
Rooted in innovation, the brand pushes boundaries through limited editions for collectors .
Since its inception, Richard Mille remains synonymous with modern haute horlogerie, captivating global trendsetters.
Designed by Gerald Genta, redefined luxury watchmaking with its iconic octagonal bezel and stainless steel craftsmanship .
Available in limited-edition sand gold to skeleton dials , the collection merges avant-garde design with horological mastery.
Priced from $20,000 to over $400,000, these timepieces cater to both luxury enthusiasts and aficionados seeking investable art .
Original Audemars Oak 26240 reviews
The Royal Oak Offshore set benchmarks with innovative complications , showcasing Audemars Piguet’s relentless innovation.
With ultra-thin calibers like the 2385, each watch reflects the brand’s commitment to excellence .
Discover certified pre-owned editions and detailed collector guides to deepen your horological expertise with this timeless icon .
консультация юриста по квартире помощь юриста по телефону бесплатно
ultimate createporn generator. Create hentai art, porn comics, and NSFW with the best AI porn maker online. Start generating AI porn now!
Die Royal Oak 16202ST kombiniert ein rostfreies Stahlgehäuse von 39 mm mit einem ultradünnen Design von nur 8,1 mm Dicke.
Ihr Herzstück bildet das neue Kaliber 7121 mit 55 Stunden Gangreserve.
Der blaue „Bleu Nuit“-Ton des Zifferblatts wird durch das Petite-Tapisserie-Muster und die Saphirglas-Abdeckung mit Antireflexbeschichtung betont.
Neben klassischer Zeitmessung bietet die Uhr ein praktisches Datum bei Position 3.
15450st
Die bis 5 ATM geschützte Konstruktion macht sie für sportliche Einsätze geeignet.
Das geschlossene Stahlband mit verstellbarem Dornschließe und die oktogonale Lünette zitieren das ikonische Royal-Oak-Erbe aus den 1970er Jahren.
Als Teil der legendären Extra-Thin-Reihe verkörpert die 16202ST meisterliche Uhrmacherkunst mit einem aktuellen Preis ab ~75.900 €.
КредитоФФ http://creditoroff.ru удобный онлайн-сервис для подбора и оформления займов в надёжных микрофинансовых организациях России. Здесь вы найдёте лучшие предложения от МФО
Стальные резервуары используются для хранения дизельного топлива и соответствуют стандартам давления до 0,04 МПа.
Горизонтальные емкости изготавливают из нержавеющих сплавов с антикоррозийным покрытием.
Идеальны для промышленных объектов: хранят бензин, керосин, мазут или биодизель.
пожарные резервуары для воды
Двустенные резервуары обеспечивают экологическую безопасность, а подземные модификации подходят для разных условий.
Заводы предлагают типовые решения объемом до 500 м³ с технической поддержкой.
Die Royal Oak 16202ST vereint ein rostfreies Stahlgehäuse in 39 mm mit einem nur 8,1 mm dünnen Bauweise und dem automatischen Werk 7121 für lange Energieautonomie.
Das „Bleu Nuit“-Zifferblatt mit Weißgold-Indexen und Royal-Oak-Zeigern wird durch eine Saphirglas-Scheibe mit Antireflex-Beschichtung geschützt.
Neben praktischer Datumsanzeige bietet die Uhr bis 5 ATM geschützte Konstruktion und ein integriertes Stahlarmband mit verstellbarem Verschluss.
Piguet Royal Oak 15450st damenuhr
Die oktogonale Lünette mit verschraubten Edelstahlteilen und die gebürstete Oberflächenkombination zitieren den legendären Genta-Entwurf.
Als Teil der „Jumbo“-Linie ist die 16202ST eine Sammler-Investition mit einem Wertsteigerungspotenzial.
Лучшие юристы https://yuristy-ekaterinburga.ru
Наш ресурс публикует важные информационные статьи со всего мира.
Здесь представлены факты и мнения, науке и разных направлениях.
Контент пополняется регулярно, что позволяет держать руку на пульсе.
Удобная структура ускоряет поиск.
https://fashionablelook.ru
Каждая статья проходят проверку.
Мы стремимся к достоверности.
Присоединяйтесь к читателям, чтобы быть всегда информированными.
Luxury horology remain popular for countless undeniable reasons.
Their timeless appeal and mastery set them apart.
They symbolize status and success while mixing purpose and aesthetics.
Unlike digital gadgets, their value grows over time due to scarcity and quality.
https://robertsspaceindustries.com/en/citizens/MaxBezel
Collectors and enthusiasts cherish their mechanical soul that no smartwatch can replicate.
For many, collecting them defines passion that transcends trends.
быстрый займ на карту онлайн https://zajmy-onlajn.ru
Женский блог https://zhinka.in.ua Жінка это самое интересное о красоте, здоровье, отношениях. Много полезной информации для женщин.
Городской портал Черкассы https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua новости, обзоры, события Черкасс и области
Строительный портал https://proektsam.kyiv.ua свежие новости отрасли, профессиональные советы, обзоры материалов и технологий, база подрядчиков и поставщиков. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне в одном месте.
Портал города Черновцы https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua последние новости, события, обзоры
вызвать врача нарколога вызов нарколога
Коллекция Nautilus, созданная мастером дизайна Жеральдом Гентой, сочетает спортивный дух и высокое часовое мастерство. Модель Nautilus 5711 с самозаводящимся механизмом имеет энергонезависимость до 2 дней и корпус из белого золота.
Восьмиугольный безель с плавными скосами и циферблат с градиентом от синего к черному подчеркивают уникальность модели. Браслет с H-образными элементами обеспечивает комфорт даже при повседневном использовании.
Часы оснащены функцией даты в позиции 3 часа и сапфировым стеклом.
Для сложных модификаций доступны секундомер, вечный календарь и индикация второго часового пояса.
Купить часы Патек Филип Nautilus тут
Например, модель 5712/1R-001 из розового золота с механизмом на 265 деталей и запасом хода до 48 часов.
Nautilus остается предметом коллекционирования, объединяя современные технологии и классические принципы.
кодировка торпедой от алкоголя кодирование от алкоголизма уколом
лечение алкоголизма новгород лечение алкоголизма
вывод из запоя срочно вывод из запоя капельницы
Новинний сайт Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua новости Житомира сегодня
Праздничная продукция https://prazdnik-x.ru для любого повода: шары, гирлянды, декор, упаковка, сувениры. Всё для дня рождения, свадьбы, выпускного и корпоративов.
оценка ПО Москва оценка бизнеса для продажи москва
лечение больных наркоманией лечение наркомании анонимно
Всё для строительства https://d20.com.ua и ремонта: инструкции, обзоры, экспертизы, калькуляторы. Профессиональные советы, новинки рынка, база строительных компаний.
Строительный журнал https://garant-jitlo.com.ua всё о технологиях, материалах, архитектуре, ремонте и дизайне. Интервью с экспертами, кейсы, тренды рынка.
Онлайн-журнал https://inox.com.ua о строительстве: обзоры новинок, аналитика, советы, интервью с архитекторами и застройщиками.
Современный строительный https://interiordesign.kyiv.ua журнал: идеи, решения, технологии, тенденции. Всё о ремонте, стройке, дизайне и инженерных системах.
Информационный журнал https://newhouse.kyiv.ua для строителей: строительные технологии, материалы, тенденции, правовые аспекты.
Строительный журнал https://poradnik.com.ua для профессионалов и частных застройщиков: новости отрасли, обзоры технологий, интервью с экспертами, полезные советы.
Всё о строительстве https://stroyportal.kyiv.ua в одном месте: технологии, материалы, пошаговые инструкции, лайфхаки, обзоры, советы экспертов.
Журнал о строительстве https://sovetik.in.ua качественный контент для тех, кто строит, проектирует или ремонтирует. Новые технологии, анализ рынка, обзоры материалов и оборудование — всё в одном месте.
Полезный сайт https://vasha-opora.com.ua для тех, кто строит: от фундамента до крыши. Советы, инструкции, сравнение материалов, идеи для ремонта и дизайна.
Новости Полтава https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал, последние события Полтавы и области
Кулинарный портал https://vagon-restoran.kiev.ua с тысячами проверенных рецептов на каждый день и для особых случаев. Пошаговые инструкции, фото, видео, советы шефов.
Мужской журнал https://hand-spin.com.ua о стиле, спорте, отношениях, здоровье, технике и бизнесе. Актуальные статьи, советы экспертов, обзоры и мужской взгляд на важные темы.
Журнал для мужчин https://swiss-watches.com.ua которые ценят успех, свободу и стиль. Практичные советы, мотивация, интервью, спорт, отношения, технологии.
Читайте мужской https://zlochinec.kyiv.ua журнал онлайн: тренды, обзоры, советы по саморазвитию, фитнесу, моде и отношениям. Всё о том, как быть уверенным, успешным и сильным — каждый день.
ИнфоКиев https://infosite.kyiv.ua события, новости обзоры в Киеве и области.
Монтаж систем видеонаблюдения поможет безопасность территории на постоянной основе.
Современные технологии обеспечивают надежный обзор даже при слабом освещении.
Вы можете заказать широкий выбор оборудования, подходящих для офиса.
установка видеонаблюдения в мкд
Качественный монтаж и сервисное обслуживание делают процесс эффективным и комфортным для каждого клиента.
Оставьте заявку, и узнать о лучшее решение для установки видеонаблюдения.
Все новинки https://helikon.com.ua технологий в одном месте: гаджеты, AI, робототехника, электромобили, мобильные устройства, инновации в науке и IT.
Портал о ремонте https://as-el.com.ua и строительстве: от черновых работ до отделки. Статьи, обзоры, идеи, лайфхаки.
Ремонт без стресса https://odessajs.org.ua вместе с нами! Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, дизайн-проекты, калькуляторы и обзоры.
Сайт о строительстве https://selma.com.ua практические советы, современные технологии, пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов и обзоры техники.
Городской портал Винницы https://u-misti.vinnica.ua новости, события и обзоры Винницы и области
Портал Львів https://u-misti.lviv.ua останні новини Львова и области.
Свежие новости https://ktm.org.ua Украины и мира: политика, экономика, происшествия, культура, спорт. Оперативно, объективно, без фейков.
Сайт о строительстве https://solution-ltd.com.ua и дизайне: как построить, отремонтировать и оформить дом со вкусом.
Читайте авто блог https://autoblog.kyiv.ua обзоры автомобилей, сравнения моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации, новости автопрома.
Авто портал https://real-voice.info для всех, кто за рулём: свежие автоновости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору, страхованию и ремонту.
Новини Львів https://faine-misto.lviv.ua последние новости и события – Файне Львов
Строительный портал https://apis-togo.org полезные статьи, обзоры материалов, инструкции по ремонту, дизайн-проекты и советы мастеров.
Комплексный строительный https://ko-online.com.ua портал: свежие статьи, советы, проекты, интерьер, ремонт, законодательство.
Всё о строительстве https://furbero.com в одном месте: новости отрасли, технологии, пошаговые руководства, интерьерные решения и ландшафтный дизайн.
Онлайн-портал https://leif.com.ua для женщин: мода, психология, рецепты, карьера, дети и любовь. Читай, вдохновляйся, общайся, развивайся!
Современный женский https://prowoman.kyiv.ua портал: полезные статьи, лайфхаки, вдохновляющие истории, мода, здоровье, дети и дом.
Портал о маркетинге https://reklamspilka.org.ua рекламе и PR: свежие идеи, рабочие инструменты, успешные кейсы, интервью с экспертами.
События Днепр https://u-misti.dp.ua последние новости Днепра и области, обзоры и самое интересное
Семейный портал https://stepandstep.com.ua статьи для родителей, игры и развивающие материалы для детей, советы психологов, лайфхаки.
Клуб родителей https://entertainment.com.ua пространство поддержки, общения и обмена опытом.
Туристический портал https://aliana.com.ua с лучшими маршрутами, подборками стран, бюджетными решениями, гидами и советами.
Всё о спорте https://beachsoccer.com.ua в одном месте: профессиональный и любительский спорт, фитнес, здоровье, техника упражнений и спортивное питание.
Новости Украины https://useti.org.ua в реальном времени. Всё важное — от официальных заявлений до мнений экспертов.
Информационный портал https://comart.com.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные советы, технологии, идеи, лайфхаки, расчёты и выбор материалов.
Архитектурный портал https://skol.if.ua современные проекты, урбанистика, дизайн, планировка, интервью с архитекторами и тренды отрасли.
Всё о строительстве https://ukrainianpages.com.ua просто и по делу. Портал с актуальными статьями, схемами, проектами, рекомендациями специалистов.
Новости Украины https://hansaray.org.ua 24/7: всё о жизни страны — от региональных происшествий до решений на уровне власти.
Всё об автомобилях https://autoclub.kyiv.ua в одном месте. Обзоры, новости, инструкции по уходу, автоистории и реальные тесты.
Новостной портал Одесса https://u-misti.odesa.ua последние события города и области. Обзоры и много интресного о жизни в Одессе.
Строительный журнал https://dsmu.com.ua идеи, технологии, материалы, дизайн, проекты, советы и обзоры. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и интерьере
Портал о строительстве https://tozak.org.ua от идеи до готового дома. Проекты, сметы, выбор материалов, ошибки и их решения.
На данном сайте вы найдете сервис “Глаз Бога”, позволяющий проверить данные о гражданине через открытые базы.
Сервис активно ищет по ФИО, анализируя публичные материалы в Рунете. Благодаря ему можно получить пять пробивов и полный отчет по фото.
Инструмент обновлен согласно последним данным и охватывает аудио-материалы. Бот сможет проверить личность по госреестрам и отобразит информацию в режиме реального времени.
глаз бога телеграмм официальный сайт
Это инструмент — выбор в анализе персон удаленно.
Хотите пробить человека быстро ? Наш Telegram-канал предоставит актуальную информацию о любом пользователе .
Воспользуйтесь сервисами для поиска данных в соцсетях. Результаты формируются в режиме реального времени.
Выясните активность в сети, интересы или связи через алгоритмы анализа.
https://t.me/GlassBogSearch
Бизнес-пользователей доступны расширенные функции — от проверки номера до мониторинга изменений .
Данные обрабатываются анонимно, соблюдая GDPR.
Подключайтесь и начните работу с эксклюзивными материалами уже сегодня!
Городской портал Одессы https://faine-misto.od.ua последние новости и происшествия в городе и области
Информационный портал https://dailynews.kyiv.ua актуальные новости, аналитика, интервью и спецтемы.
Новостной портал https://news24.in.ua нового поколения: честная журналистика, удобный формат, быстрый доступ к ключевым событиям.
Портал для женщин https://a-k-b.com.ua любого возраста: стиль, красота, дом, психология, материнство и карьера.
Онлайн-новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua без лишнего: коротко, по делу, достоверно. Политика, бизнес, происшествия, спорт, лайфстайл.
Здесь доступен мессенджер-бот “Глаз Бога”, который проверить сведения о гражданине через открытые базы.
Сервис работает по ФИО, обрабатывая доступные данные онлайн. Через бота доступны пять пробивов и глубокий сбор по запросу.
Платфор ма актуален согласно последним данным и охватывает фото и видео. Глаз Бога поможет найти профили в открытых базах и покажет результаты за секунды.
глаз бога телеграм канал
Это инструмент — помощник в анализе граждан онлайн.
Мировые новости https://ua-novosti.info онлайн: политика, экономика, конфликты, наука, технологии и культура.
Только главное https://ua-vestnik.com о событиях в Украине: свежие сводки, аналитика, мнения, происшествия и реформы.
Женский портал https://woman24.kyiv.ua обо всём, что волнует: красота, мода, отношения, здоровье, дети, карьера и вдохновение.
защитные кейсы корсар plastcase.ru/
The best Dedicated servers (best European data centers) managed and unmanaged, GDPR compliant, super fast NVMe SSDs, reliable 1Gbps network, choice of OS and finally affordable prices. Hurry up and get a free dedicated server upgrade until the end of this month!
Офисная мебель https://officepro54.ru в Новосибирске купить недорого от производителя
Займ кредит мфо взять займ
Noten vom klavier noten auf dem klavier
Хмельницький новини https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua огляди, новини, сайт Хмельницького
купить отчет по преддипломной практике сколько стоит отчет по практике на заказ цены
онлайн сделать реферат готовые рефераты
где заказать дипломную работу дипломная работа на заказ стоимость
Прямо здесь можно получить сервис “Глаз Бога”, что найти сведения по человеку через открытые базы.
Инструмент активно ищет по ФИО, используя публичные материалы онлайн. С его помощью можно получить бесплатный поиск и детальный анализ по запросу.
Платфор ма проверен согласно последним данным и включает фото и видео. Глаз Бога поможет найти профили по госреестрам и предоставит результаты за секунды.
глаз бога по номеру
Такой бот — выбор в анализе персон удаленно.
Медпортал https://medportal.co.ua украинский блог о медициние и здоровье. Новости, статьи, медицинские учреждения
Looking for browser-based adventures? Our platform offers a exclusive collection of multiplayer experiences and action-packed quests .
Dive into real-time battles with global players , supported by voice communication for seamless teamwork.
Enjoy customizable controls designed for quick mastery, alongside safety features like SSL encryption for secure play.
iihfworLds2016.com/en/casino-online-canada
Whether fantasy RPGs to brain-teasing puzzles , every game prioritizes fun and emotional rewards.
Unlock freemium titles that let you play for free , with subscription models for deeper access.
Join of a thriving community where creativity shines, and express yourself through immersive storytelling.
Файне Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua новости и события Винницы сегодня. Городской портал, обзоры.
Здесь вы найдете Telegram-бот “Глаз Бога”, который найти данные по человеку по публичным данным.
Бот функционирует по номеру телефона, анализируя публичные материалы онлайн. Через бота доступны 5 бесплатных проверок и детальный анализ по запросу.
Сервис актуален на 2025 год и включает фото и видео. Бот поможет найти профили по госреестрам и отобразит результаты в режиме реального времени.
глаз бога поиск по телеграм
Такой сервис — выбор при поиске людей удаленно.
микрозайм без карты zajmy-onlajn
Автогид https://avtogid.in.ua автомобильный украинский портал с новостями, обзорами, советами для автовладельцев
купить контрольную по истории купить контрольную работу химия
Портал Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua новости и события в Киеве сегодня.
заказать контрольную работу заказать контрольную работу базы данных
дипломная работа купить стоимость дипломной работы на заказ в среднем
заказать отчет по практике срочно сделать отчет по практике
микрозаем на карту https://zajmy-onlajn.ru
Looking for a smarter, greener, and more enjoyable way to travel?
Look no further than the exciting range of e-bikes available at E-Biker UK.
Whether you’re commuting through the city, riding through scenic trails, or just
cruising around town, electric bikes offer the perfect blend of power, comfort, and convenience.
An ebike is a traditional bicycle equipped with an electric motor and battery, giving you a boost when you need it most.
Whether it’s tackling a steep hill or powering through a long commute, the motor assistance helps you ride further and faster with less effort.
Ideal for all ages and fitness levels, electric bikes provide a low-impact, high-efficiency way to stay active while enjoying the ride.
At E-Biker UK, you’ll find a wide selection of high-quality e-bike tailored to
different lifestyles. From compact folding models perfect for
city commuters, to all-terrain electric mountain bikes built for weekend
adventurers, there’s something for everyone.
Each bike features premium components, advanced battery systems, intuitive controls, and stylish, ergonomic
designs — all backed by reliable performance and safety.
Beyond the fun and freedom, owning an electric bike is a practical and eco-friendly choice.
You’ll save on fuel, reduce maintenance costs,
avoid traffic congestion, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
It’s no surprise that more and more people across
the UK are ditching their cars and embracing the electric bike revolution.
Shopping at E-Biker UK means expert customer service, trusted brands, and competitive prices — so you can ride with confidence.
Whether you’re a daily rider or just getting started,
there’s never been a better time to switch to electric.
Browse the collection today and take charge of
your journey — one pedal-assisted ride at a time.
Driving an electric auto is no longer just a trend
— it’s a lifestyle choice built around
efficiency, sustainability, and smart technology. At Autoche
UK, we understand the growing demand for high-quality EV chargers
that keep your electric vehicle powered and ready for any journey.
Whether you’re charging at home, at work, or managing a fleet, we offer reliable and easy-to-use
EV charging solutions tailored to meet modern needs.
With the rise of electric autos, the way we “refuel” is changing.
Instead of trips to the petrol station, EV owners now want the freedom to charge from the comfort of their home or workplace.
That’s where Autoche comes in. Our collection of top-performing
EV chargers includes compact home wall boxes, fast
chargers for commercial properties, and smart charging systems that help
you optimize energy usage, reduce charging costs, and stay in control via
mobile apps.
All Autoche chargers are designed with durability, safety, and simplicity in mind.
They’re compatible with most major electric vehicle brands and support key features like scheduled charging, overcurrent protection, and energy monitoring.
Whether you drive a compact city EV or a high-performance electric SUV, we have a charger that fits your lifestyle.
Installing a dedicated EV charging system not only adds convenience to your daily routine but also future-proofs your property.
As more autos transition to electric, the demand for fast, accessible EV charging will continue to grow — and having your own charger
ensures you’re always one step ahead.
At Autoche UK, we’re here to help you make the switch to
electric with confidence. Explore our auto today and take the next step toward smarter, greener driving — because
your auto deserves the best power source possible.
Looking to refresh your wardrobe or find the perfect gift
for someone special? At TestAll UK, you’ll find an outstanding selection of Handbags & Shoulder Bags,
Jewellery, Shoes, and Watches — all designed to enhance your lifestyle with a touch of elegance and everyday practicality.
Handbags & Shoulder Bags are the ultimate blend of utility
and style. Whether you need a compact crossbody for travel,
a roomy shoulder bag for daily errands, or a designer-inspired piece for evening outings, TestAll
UK offers bags to match every mood and moment.
Crafted with durable materials and trendy detailing, these bags are designed to be both stylish and long-lasting.
Add a hint of glamour with their stunning range
of Jewellery. From timeless gold and silver tones to modern geometric designs and delicate layering sets, the jewellery at TestAll UK makes accessorizing effortless.
Whether you’re dressing up for an event or adding a little sparkle to your workday look, these pieces make a bold impression without breaking the bank.
For footwear that fits every occasion, browse the Shoes
collection. Choose from fashion-forward heels, comfortable everyday sneakers, sturdy boots, and elegant loafers — all available in the latest
styles and comfortable fits. Every pair is crafted with attention to detail, perfect for day-to-night wear or simply stepping out in confidence.
Lastly, no outfit is complete without a stylish Watch.
The collection includes minimalist designs, chronograph features, and classic leather straps — perfect for both casual wear and formal settings.
Whether you’re gifting someone special or adding to your
own collection, a watch from TestAll UK is both practical and fashion-forward.
With a strong focus on quality, affordability, and variety,
Jewellery is your one-stop destination for fashion essentials that reflect
your personality. Shop now and discover pieces that make
every outfit memorable.
Сайт Житомир https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua новости и происшествия в Житомире и области
Если вышла из строя стиральная машина, мы поможем.
Если у вас сломался холодильник, обращайтесь к профессионалам.
Rent-Auto.md – прокат авто в Кишиневе и других крупных городах Молдовы на лучших условиях. Независимо от того, планируете ли вы деловую поездку, отдых с семьей или бизнес-поездку, у нас есть идеальные решения для вашего передвижения по городу и за его пределами.
Увлажнитель воздуха https://brand-climat.ru оптимальный уровень влажности для здоровья. Различные типы: ультразвуковые, паровые и др., фильтрация и защита. Подбор, доставка по России и официальная гарантия для вашего комфорта.
Украинский бизнес https://in-ukraine.biz.ua информацинный портал о бизнесе, финансах, налогах, своем деле в Украине
Лучшие онлайн-курсы https://topkursi.ru по востребованным направлениям: от маркетинга до программирования. Учитесь в удобное время, получайте сертификаты и прокачивайте навыки с нуля.
Школа Саморазвития https://bznaniy.ru онлайн-база знаний для тех, кто хочет понять себя, улучшить мышление, прокачать навыки и выйти на новый уровень жизни.
Репетитор по физике https://repetitor-po-fizike-spb.ru СПб: школьникам и студентам, с нуля и для олимпиад. Четкие объяснения, практика, реальные результаты.
Why people still use to read news papers when in this technological globe all is accessible on net?
tadalafil accord 5 mg
Хотите найти информацию о человеке ? Наш сервис предоставит детальный отчет мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для поиска цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Выясните контактные данные или интересы через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
телеграм бот глаз бога проверка
Система функционирует в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Получите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь проверенному решению для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Наш сервис способен найти данные о любом человеке .
Достаточно ввести никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы получить сведения .
Бот сканирует публичные данные и цифровые следы.
bot глаз бога
Результаты формируются мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Идеально подходит для анализа профилей перед сотрудничеством .
Анонимность и точность данных — гарантированы.
Хотите найти данные о человеке ? Этот бот предоставит полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для анализа цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Узнайте место работы или активность через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога бесплатно на телефон
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Получите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Доверьтесь проверенному решению для digital-расследований — точность гарантирована!
Перевод документов https://medicaltranslate.ru на немецкий язык для лечения за границей и с немецкого после лечения: высокая скорость, безупречность, 24/7
Онлайн-тренинги https://communication-school.ru и курсы для личного роста, карьеры и новых навыков. Учитесь в удобное время из любой точки мира.
1С без сложностей https://1s-legko.ru объясняем простыми словами. Как работать в программах 1С, решать типовые задачи, настраивать учёт и избегать ошибок.
наркологическая клиника наркология клиника
фото пансионата для пожилых пансионат для пожилых и инвалидов
Запреты дня [url=www.inforigin.ru/]www.inforigin.ru/[/url] .
Какой сегодня церковный праздник [url=http://istoriamashin.ru/]http://istoriamashin.ru/[/url] .
Какой сегодня церковный праздник [url=www.topoland.ru]www.topoland.ru[/url] .
Cross Stitch Pattern in PDF format https://cross-stitch-patterns-free-download.store/ a perfect choice for embroidery lovers! Unique designer chart available for instant download right after purchase.
Надёжная фурнитура https://furnitura-dla-okon.ru для пластиковых окон: всё для ремонта и комплектации. От ручек до многозапорных механизмов.
Фурнитура для ПВХ-окон http://kupit-furnituru-dla-okon.ru оптом и в розницу: европейские бренды, доступные цены, доставка по РФ.
спросить юриста в чате бесплатная консультация адвоката по телефону
типография типография цены
печать спб типография типография печать
металлические значки металлические значки на заказ
заказать металлические значки металлические значки на заказ
Здравствуйте, уважаемые!
Особенно понравился раздел про От выбора древесины до финишной отделки. Секреты обработки, соединения деталей, покраски и защиты деревянных изделий..
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://diyworks.ru/category/rabota-s-derevom/]https://diyworks.ru/category/rabota-s-derevom/[/url]
Загляните, не пожалеете.
Наш сервис способен найти данные о любом человеке .
Укажите никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы получить сведения .
Система анализирует публичные данные и активность в сети .
глаз бога телеграмм официальный сайт
Результаты формируются в реальном времени с фильтрацией мусора.
Идеально подходит для анализа профилей перед сотрудничеством .
Анонимность и точность данных — наш приоритет .
Наш сервис поможет получить информацию о любом человеке .
Укажите имя, фамилию , чтобы сформировать отчёт.
Бот сканирует открытые источники и активность в сети .
глаз бога поиск по фото
Информация обновляется в реальном времени с проверкой достоверности .
Идеально подходит для анализа профилей перед сотрудничеством .
Конфиденциальность и актуальность информации — гарантированы.
займы без процентов займ
аэропорт прага такси https://inotur.com/strany-sng/5896-kak-dobratsya-iz-aeroporta-pragi-v-otel-udobnye-resheniya-ot-letisteexpress.html
хотите сделать утепление https://domfaq.com/preimushhestva-utepleniya-cherdaka-penopoliuretanom-dlya-energoeffektivnosti/
dragonslots casino [url=http://casinosdragonslots.eu]http://casinosdragonslots.eu[/url] .
The Pokies net Australia login [url=http://www.thepokiesnet101.com]http://www.thepokiesnet101.com[/url] .
thepokies.net [url=http://www.pokies106.com]http://www.pokies106.com[/url] .
Срочные микрозаймы https://stuff-money.ru с моментальным одобрением. Заполните заявку онлайн и получите деньги на карту уже сегодня. Надёжно, быстро, без лишней бюрократии.
Срочный микрозайм https://truckers-money.ru круглосуточно: оформите онлайн и получите деньги на карту за считаные минуты. Без звонков, без залога, без лишних вопросов.
Discover Savin Kuk, a picturesque corner of Montenegro. Skiing, hiking, panoramic views and the cleanest air. A great choice for a relaxing and active holiday.
AI generator nsfw ai image generator of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic pictures and videos.
Услуги массаж ивантеевка — для здоровья, красоты и расслабления. Опытный специалист, удобное расположение, доступные цены.
Онлайн займы срочно https://moon-money.ru деньги за 5 минут на карту. Без справок, без звонков, без отказов. Простая заявка, моментальное решение и круглосуточная выдача.
ולבעלי היו חברים כמעט זהים, שם טעיתי לעתים קרובות יותר. רוסלן כבר למד להכניס את הזין שלו לקתרין. “אה, לעזאזל,” אמרה בשאט נפש בשקט. – משהו אומר לי שלא ייקחו אותנו לזיין הלילה. “תהיה נערות ליווי בירושלים
Пешие походы по живописным маршрутам Урала неизменно привлекают туристов. Давайте разберемся, как подготовиться к такому путешествию.
Кстати, если вас интересует Традиционные шаманские ритуалы Республики Тыва, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://rustrail.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%bf%d1%83%d0%b1%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d1%82%d1%8b%d0%b2%d0%b0-%d0%b8-%d0%b5%d1%91-%d1%88%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%bd%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d1%80%d0%b8%d1%82%d1%83%d0%b0%d0%bb/]https://rustrail.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%bf%d1%83%d0%b1%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d1%82%d1%8b%d0%b2%d0%b0-%d0%b8-%d0%b5%d1%91-%d1%88%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%bd%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d1%80%d0%b8%d1%82%d1%83%d0%b0%d0%bb/[/url]
Собравшись в путь, не забывайте наслаждаться каждым моментом похода по этому удивительному региону.
AI generator free nsfw ai chat of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic pictures and videos.
зоны барбекю на участке https://modul-pech.ru/
אז אני חייב להתמוטט. אתה מכיר אותי. אני לא הולך לעשות את זה. אלה שקיבלו את הציונים שלהם בדרך תתכוננו, טרנסקסואלים”, אמר המנהל לקאל הוא הבחין ביום הראשון שיש הרבה פיגליצים חמודים במפעל ליווי דיסקרטי
ремонт стиральных машин bosch на дому ремонт стиральных машин electrolux
Офисная мебель https://mkoffice.ru в Новосибирске: готовые комплекты и отдельные элементы. Широкий ассортимент, современные дизайны, доставка по городу.
UP&GO https://upandgo.ru путешествуй легко! Визы, авиабилеты и отели онлайн
New AI generator nsfw ai video of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic image and videos.
Mountain Topper https://www.lnrprecision.com transceivers from the official supplier. Compatibility with leading brands, stable supplies, original modules, fast service.
услуги ремонт стиральных машин ремонт стиральных машин electrolux
Hindi News https://tfipost.in latest news from India and the world. Politics, business, events, technology and entertainment – just the highlights of the day.
כך מהר ועוצמתי עד שצליל הגופות שניגשו נשמע, לעתים קרובות כמו מחיאות כפיים. גניחותיה מילאו את קל, אבל היא משכה אותו מהאצבע ונתנה אותו לאיגור. זו הייתה טבעת יהלום יפהפייה של 0.4 גרם (2 מכוני ליווי באשדוד, איך מוצאים?
Animal Feed https://pvslabs.com Supplements in India: Vitamins, Amino Acids, Probiotics and Premixes for Cattle, Poultry, Pigs and Pets. Increased Productivity and Health.
Нужно найти данные о человеке ? Наш сервис предоставит полный профиль мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте место работы или интересы через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
bot глаз бога
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, обрабатывая общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
Хотите найти данные о пользователе? Наш сервис поможет полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте контактные данные или интересы через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
глаз бога пробить номер
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Получите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Современная стоматологическая клиника в центре Москвы предлагает широкий спектр услуг — от профессиональной гигиены до имплантации и эстетической реставрации. Используются новейшие технологии и оборудование, обеспечивая максимальную точность, безопасность и комфорт для пациентов всех возрастов https://usdentalcare.com/
Для нижегородцев, ищущих где купить сигареты в Нижнем Новгороде без лишних хлопот, этот сервис стал настоящим открытием https://nizhnii-novgorod.sigaretus.ru/
ремонт стиральной машины аристон ремонт стиральных машин с вертикальной загрузкой
Как оформить карту зарубежная карта VISA для россиян в 2025 году. Зарубежную банковскую карту можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Карты подходят для оплаты за границей.
На данном сайте доступна данные о любом человеке, в том числе подробные профили.
Реестры охватывают людей разного возраста, профессий.
Данные агрегируются на основе публичных данных, обеспечивая достоверность.
Обнаружение выполняется по контактным данным, что делает работу эффективным.
телеграм бот глаз бога проверка
Помимо этого предоставляются контакты а также полезная информация.
Все запросы обрабатываются в соответствии с законодательства, что исключает несанкционированного доступа.
Воспользуйтесь данному ресурсу, для поиска искомые данные без лишних усилий.
מהעובדה שפיפא נשואה כזו עצמה טיפסה על הזין של גבר אקראי באוטובוס. היא לא ענתה, רק דחפה את אני גומר כשאני בתחת, וכשאני בכוס, וכשאני עם הלשון או האצבעות … אבל אין תחושה של קסם good content
В этом ресурсе можно найти информация по запросу, в том числе исчерпывающие сведения.
Реестры охватывают персон всех возрастов, мест проживания.
Информация собирается по официальным записям, обеспечивая надежность.
Поиск производится по имени, что обеспечивает работу эффективным.
глаз бога актуальный бот
Дополнительно доступны места работы а также полезная информация.
Работа с информацией обрабатываются в рамках норм права, обеспечивая защиту разглашения.
Воспользуйтесь предложенной системе, чтобы найти необходимую информацию в кратчайшие сроки.
בבעלים. הבחור עם הזקן הקצר והמבט הערמומי קרץ אלי. “אניה, אתה כמו אגדה, ישר אליס בארץ ומיצים. קטיה, מתנשפת, קברה את פניה בחזה. היא מלמלה וכולנו צחקנו. סרגיי הושיט יד לבקבוק יין, דירות דיסקרטיות ערביות
айфлоу камеры [url=https://citadel-trade.ru/]https://citadel-trade.ru/[/url] .
электрокарнизы для штор цена [url=www.elektrokarniz90.ru/]www.elektrokarniz90.ru/[/url] .
рулонные шторы на окно в кухне [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom15.ru]https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom15.ru[/url] .
אחרי החתונה, ועכשיו אנחנו כבר נקלעים למצוקה מגוחכת: תקועים בערב בעיירה זרה, באזור רחוק ישר למים בלי לבקש אפילו רשות. הייתי צריך לקום ולצאת. ובכן, במקרה הזה, היה לנו ג ‘ קוזי. good content
Нужно найти данные о человеке ? Наш сервис поможет детальный отчет мгновенно.
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте место работы или интересы через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога телефон
Система функционирует в рамках закона , обрабатывая общедоступную информацию.
Получите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Подбирая семейного доктора стоит обратить внимание на его опыт , стиль общения и доступность услуг .
Убедитесь, что клиника расположена рядом и предоставляет полный спектр услуг .
Узнайте , работает ли доктор с вашей полисом, и есть ли возможность записи онлайн .
http://forum.divlya.com/index.php?topic=2544.new#new
Обращайте внимание отзывы пациентов , чтобы оценить отношение к клиентам.
Важно проверить наличие профильного образования, подтверждающие документы для уверенности в качестве лечения.
Выбирайте — тот, где вас услышат ваши особенности здоровья, а процесс лечения будет комфортным .
Здесь можно найти информация о любом человеке, от кратких контактов до исчерпывающие сведения.
Реестры охватывают людей всех возрастов, мест проживания.
Сведения формируются на основе публичных данных, что гарантирует достоверность.
Нахождение выполняется по контактным данным, что обеспечивает работу быстрым.
глаз бога узнать номер
Также предоставляются места работы а также важные сведения.
Работа с информацией обрабатываются с соблюдением правовых норм, что исключает несанкционированного доступа.
Обратитесь к предложенной системе, в целях получения нужные сведения максимально быстро.
Заеды в уголках губ? причины и лечение https://e-pochemuchka.ru/zaedy-v-ugolkah-gub-prichiny-i-lechenie/
[url=https://shiba-akita.ru/]https://www.shiba-akita.ru/[/url] – статья о полезности дизельных моторов для автомобилистов
Южнокорейский сериал о смертельных играх на выживание ради огромного денежного приза. Сотни отчаявшихся людей участвуют в детских играх, где проигрыш означает смерть. Сериал исследует темы социального неравенства, морального выбора и человеческой природы в экстремальных условиях: 3 сезон игры в кальмара смотреть
кредит под птс москва
zaimpod-pts90.ru
деньги под залог машины москва
Студия дизайна Интерьеров в СПБ. Лучшие условия для заказа и реализации дизайн-проектов под ключ https://cr-design.ru/
LMC Middle School https://lmc896.org in Lower Manhattan provides a rigorous, student-centered education in a caring and inclusive atmosphere. Emphasis on critical thinking, collaboration, and community engagement.
כאנימטורים, למלון סגור ונחמד, עם החוף שלי ושירות ראוי לארצנו. כמו גם עבודה ומנוחה, אני אוהב כמו התעלמות גברית, אפילו לא ביקום מקביל. לכן, הכוס שערורייה נורא שהוא לא ממש ממהר “לגרור view website
Нужно найти информацию о человеке ? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для поиска цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Узнайте контактные данные или активность через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога узнать номер
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь проверенному решению для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
Ответственная игра — это комплекс мер , направленный на предотвращение рисков, включая ограничение доступа несовершеннолетним .
Сервисы должны внедрять инструменты контроля, такие как временные блокировки, чтобы минимизировать зависимость .
Обучение сотрудников помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
вавада вход
Предоставляются ресурсы горячие линии , где можно получить помощь при проявлениях зависимости.
Следование нормам включает проверку возрастных данных для предотвращения мошенничества .
Ключевая цель — создать безопасную среду , где риск минимален с психологическим состоянием.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников https://ua-insider.com.ua/transfer-v-aeroport-pragi-chem-otlichayutsya-professionalnye-uslugi/
Хотите найти данные о пользователе? Наш сервис предоставит полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте место работы или активность через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
сервис глаз бога
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Получите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Попробуйте надежному помощнику для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
Хотите найти информацию о человеке ? Наш сервис поможет детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в соцсетях .
Узнайте контактные данные или активность через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
чат бот глаз бога
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Получите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — точность гарантирована!
https://ukrbeautystyle.com.ua/
ניסיון, הוא לא היה רע במיטה. במיוחד לשונו העדינה והחושנית. חשבתי שאני עדיין על השולחן, ביישן? היא אמרה, פותחת את רגליה קצת יותר רחבות ממה שצריך. – אני שלי. הרגשתי את הדם זורם אל visit the website
•очешь продать авто? телеграм канал продажа авто
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
Между прочим, если вас интересует localflavors.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://localflavors.ru]https://localflavors.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Агентство контекстной рекламы https://kontekst-dlya-prodazh.ru настройка Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads под ключ. Привлекаем клиентов, оптимизируем бюджеты, повышаем конверсии.
Продвижение сайтов https://optimizaciya-i-prodvizhenie.ru в Google и Яндекс — только «белое» SEO. Улучшаем видимость, позиции и трафик. Аудит, стратегия, тексты, ссылки.
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
лечение запоя
интернет тарифы челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk004.ru
подключить интернет
Шины и диски https://tssz.ru для любого авто: легковые, внедорожники, коммерческий транспорт. Зимние, летние, всесезонные — большой выбор, доставка, подбор по марке автомобиля.
Инженерная сантехника https://vodazone.ru в Москве — всё для отопления, водоснабжения и канализации. Надёжные бренды, опт и розница, консультации, самовывоз и доставка по городу.
купить дом на Кипре
Это именно то, что я искал!
Особенно понравился материал про qazar.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
Промышленные ворота https://efaflex.ru любых типов под заказ – секционные, откатные, рулонные, скоростные. Монтаж и обслуживание. Установка по ГОСТ.
Продажа и обслуживание https://kmural.ru копировальной техники для офиса и бизнеса. Новые и б/у аппараты. Быстрая доставка, настройка, ремонт, заправка.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
подключить интернет
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk005.ru
недорогой интернет челябинск
нейросеть создать дизайн сайта https://sozday-sayt-s-ai.ru
Наш сайт является архитектурным и культурным путеводителем по Венеции, здесь Вы найдете информацию о великолепных достопримечательностях этого города: venice4you.ru
Woodworking and construction https://www.woodsurfer.com forum. Ask questions, share projects, read reviews of materials and tools. Help from practitioners and experienced craftsmen.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя
тарифы интернет и телевидение челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk006.ru
домашний интернет челябинск
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1595698-25-besplatnyh-metodov-i-servisov-dlya-nakrutki-podpischikov-v-tik-toke-v-2025-godu
Как менять шины на важном объекте: мобильный шиномонтаж на базе спецшасси, и ещё много интересного вы найдёте на канале.
https://t.me/s/kupit_gruzoviki/238
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Как выбрать провайдера интернета и телевидения в Екатеринбурге — дело не из легких, с учетом множества предложений на рынке. На сайте domashij-internet-ekaterinburg004.ru можно найти сравнение провайдеров, их тарифов и отзывов о провайдерах. Важно рассмотреть скорость интернета и качество соединения, чтобы сделать правильный выбор. Многие провайдеры вводят различные акции и специальные предложения на интернет и IPTV. Также не забывайте про кабельное и спутниковое ТВ, которые могут быть замечательным дополнением к вашему интернет-пакету. Техническая поддержка провайдеров тоже имеет большое значение при принятии решения.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
На этом сайте доступны авторские видеоматериалы моделей, созданные с вниманием к деталям .
Здесь можно найти портфолио , эксклюзивные кадры , тематические подборки для различных предпочтений .
Материалы проверяются перед публикацией, чтобы гарантировать качество и актуальность .
suck
Чтобы упростить поиск пользователей добавлены фильтры по стилю , параметрам моделей.
Сайт гарантирует конфиденциальность и защиту авторских прав согласно правовым требованиям.
В столице России разнообразие интернет-провайдеров обширен, и для пользователей нужно найти достойного партнера. При подборе провайдера необходимо обращать внимание на мнения клиентов, которые рассказывают своим опытом. На сайте domashij-internet-ekaterinburg005.ru можно найти множество мнений клиентов, качестве связи и клиентском сервисе. Надежный интернет, это не только высокая скорость, а также стабильное соединение. Услуги связи от разных интернет-провайдеров Екатеринбурга разнятся по тарифам, и важно провести сравнение провайдеров, чтобы подобрать оптимальный вариант. Некоторые пользователи отмечают отличную поддержку пользователей, что также является важным аспектом. При подключении интернет учитывайте, что отзывы пользователей могут помочь избежать неудовлетворенности и выбрать надежный сервис. Не пропускайте проверять актуальные отзывы о предложениях провайдеров и их услугах.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “mersobratva.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://mersobratva.ru]https://mersobratva.ru[/url]
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
металлические значки на заказ [url=https://www.znacki-na-zakaz.ru]металлические значки на заказ[/url] .
В Екатеринбурге доступ к лучшему контенту стал легче благодаря услугам IPTV и онлайн-кинотеатрам. Платформы, такие как domashij-internet-ekaterinburg006.ru, предлагают официальный доступ к богатому контенту. Пользователи могут получать удовольствие от последними релизами, топовыми шоу и новыми выпусками в высоком качестве видео. С оформлением подписки на IPTV вы получаете возможность наслаждения просмотром телевизионных каналов и онлайн-показа любимых жанров кино. Рейтинги фильмов и сериалов помогут определению наиболее подходящего развлечения. Не пропустите возможность открыть для себя интересные истории и колоритных персонажей!
прогноз на спорт футбол [url=https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol1.ru/]kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol1.ru[/url] .
В случае необходимости земляных работ на вашем участке в Туле, обратиться к профессионалам способно значительно облегчить процесс. Компания narkolog-tula001.ru предоставляет широкий спектр земляных работ, включая раскопки участка для возведения зданий или обустройства территории. Наши услуги обеспечивают высокое качество выполнения услуг по подготовке участка, а также бурение скважин для питьевой воды. Использование арендованной техники дает возможность нам оперативно проводить любые ландшафтные проекты, а наши квалифицированные сотрудники помогут вам с выбором подходящего грунта. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете не только надежность, но и профессионализм в осуществлении всех задач. Свяжитесь с нами, и мы поможем откопать все необходимое на вашем участке!
Капельное лечение от алкогольной интоксикации – это распространенный метод терапии, который может быть осуществлен наркологом на дому конфиденциально в городе Тула. Основная цель процедуры – детоксикация организма и реабилитация после алкогольной зависимости. Однако важно учитывать ограничения и нежелательные реакции. Противопоказания включают: тяжелые болезни сердца и сосудов, аллергии на компоненты капельницы и патологии почек. Нежелательные эффекты могут проявляться в виде боли в голове, тошноты и аллергий. нарколог на дом анонимно тула Важно помнить, что помощь нарколога предполагают не только терапию алкоголизма, но и предотвращение рецидивов, реабилитацию и медицинское сопровождение. Конфиденциальное лечение с помощью капельного введения может значительно улучшить самочувствие пациента и способствовать быстрому восстановлению.
узнать интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-kazan004.ru
подключить интернет
Капельница от запоя на дому – это востребованная опция в Туле, предоставляемая специалистами в области наркологии. Комфортное лечение даёт возможность пациентам избежать стресса, который может возникнуть с посещением клиники. Мнения клиентов свидетельствуют о эффективности детоксикации организма и быстрого выведения из запоя. Врач нарколог на дом обеспечивает конфиденциальное лечение, что имеет большое значение для многих. Преодоление алкогольной зависимости становится реальным, а восстановление здоровья – главной целью. Такие медицинские процедуры, например, капельницы, помогают справиться с алкогольной зависимостью и возврату к привычному образу жизни.
Услуга кредит онлайн на карту 24/7 позволяет получить деньги в любой момент, независимо от дня недели или праздников. Это особенно важно при неотложных ситуациях.
детская больница клиническая больница
general hospital berane medical centre Bar
Терапия запойного состояния — это необходимый шаг в борьбе с зависимостью от алкоголя. В городе Тула доступно множество методов, включая медикаментозную терапию. Признаки запоя могут различаться от тревожности до болей в теле, что делает лечение запоя крайне необходимым. Для детоксикации организма применяются различные лекарственные средства для помощи при запое, такие как бензодиазепины, которые помогают снять симптомы отмены. Препараты-антидепрессанты также могут быть назначены, чтобы поддержать эмоциональное состояние больного. Витамины группы B играют важную роль в восстановлении организма. Кодирование от алкоголя может стать дополнительным шагом в лечении алкоголизма. Помощь нарколога включает не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическую поддержку. Реабилитация алкоголиков в Туле часто включает группы поддержки и программы реабилитации, которые помогают пациентам возвращаться к нормальной жизни без алкоголя. Поддержка семьи при алкоголизме также имеет высокую важность. Она может помочь пациенту в периоде реабилитации после запоя, повысив шансы на успешное лечение зависимостей. Медицинские процедуры для detoxa являются важной частью всестороннего лечения зависимости и обеспечивают максимально безопасный вывод из запоя.
интернет провайдеры по адресу
domashij-internet-kazan005.ru
подключить интернет в казани в квартире
Помощь наркологов в Туле – это ключевой элемент борьбы с алкоголизмом и наркоманией. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемами, связанными с алкоголизмом, реабилитационные центры предлагают эффективные программы лечения зависимостей. В центре наркологии Тула предоставляется полный спектр услуг, включая детоксикацию организма и психологическое консультирование. Визиты к наркологу помогут оценить тяжесть проблемы и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Психологическая помощь при зависимости и взаимодействие с родственниками играют важное значение в процессе лечения. Также следует обращать внимание на профилактику зависимостей, чтобы не допустить ухудшения ситуации. Анонимная помощь доступна всем, кто нуждается в ней. Способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью включают индивидуальные техники, подходящие для всех нуждающихся. Обратитесь на narkolog-tula003.ru для получения подробной информации и записи на консультацию.
Капельница для лечения запоя — это важный этап в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Процедура капельницы помогает очищению организма‚ устраняя токсины и нормализуя водно-электролитный баланс. После процедуры пациенты испытывают улучшение настроения.Помощь нарколога в этом процессе неоценима. Он анализирует симптомов абстиненции и назначает соответствующее лечение запоя. Постзапойное восстановление включает не только физическое‚ но и психологическое восстановление. Помощь родных очень важна‚ помогая справиться с последствиями запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Реабилитация является следующим шагом в лечении‚ где пациент получает медицинскую помощь и обучение для избежания рецидивов. Анонимная помощь обеспечивает безопасность и конфиденциальность. Важно помнить‚ что лечение алкогольной зависимости, это сложный и длительный процесс‚ необходимый при поддержке окружающих.
провайдер по адресу
domashij-internet-kazan006.ru
интернет провайдеры казань по адресу
Значение поддержки семьи при борьбе с алкоголизмом Алкоголизм — это не только проблема зависимогоно и его семьи. В Туле обращение к специалисту может стать первым шагом к исцелению зависимости. Семейная поддержка играет решающую роль в процессе реабилитации. Близкие могут помочь, оказав эмоциональную поддержку и создавая атмосферу понимания. В сложной ситуации важно обращаться за профессиональной помощью. Консультация нарколога поможет найти правильный путь лечения алкоголизма. Терапия также может стать существенным инструментом для восстановления. вызов нарколога тула Поддержка со стороны общества семьи необходима на всех стадиях лечения, от первого обращения с наркологом до последующей реабилитации. Помощь близких может ускорить процесс выздоровления и вернуть зависимого к нормальной жизни.
При выборе компании для квартирного переезда важно учитывать её лицензирование и репутацию на рынке.
Проверьте отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить профессионализм исполнителя.
Сравните цены , учитывая объём вещей, сезонность и услуги упаковки.
https://service-core.com.ua/forum/post21611.html#p21611
Убедитесь наличия страхового полиса и запросите детали компенсации в случае повреждений.
Оцените уровень сервиса: дружелюбие сотрудников , детализацию договора.
Проверьте, есть ли специализированные автомобили и защитные технологии для безопасной транспортировки.
Dating websites offer a innovative approach to connect people globally, combining user-friendly features like photo verification and compatibility criteria.
Key elements include video chat options, geolocation tracking , and personalized profiles to enhance interactions .
Advanced algorithms analyze behavioral patterns to suggest compatible matches, while account verification ensure safety .
https://zonia4sd2.com/dating/power-exchange-in-adult-entertainment/
Leading apps offer freemium models with enhanced visibility, such as priority in search results, alongside real-time notifications .
Looking for long-term relationships, these sites cater to diverse needs , leveraging community-driven networks to optimize success rates .
Вызов нарколога на дом недорого – это комфортное и эффективное решение для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Часто такие пациенты не хотят посещать клиники и отдают предпочтение анонимным методам лечения. На сайте narkolog-tula005.ru можно узнать информацию о доступных услугах выездного нарколога, который предложит консультацию нарколога и экспертную поддержку. Недорогие услуги нарколога, такие как лечение наркомании и алкоголизма, позволяют получить медицинскую помощь прямо дома. Психотерапевтическая помощь и реабилитация зависимых проводятся опытными врачами, что обеспечивает защиту и приватность. Обратитесь к дешёвому наркологу для избавления от зависимости и начните путь к выздоровлению вместе с поддержкой специалистов.
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу проверить
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
Капельница для снятия запоя на дому – это ключевая услуга наркологической службы‚ позволяющая эффективно и резко поддержать людям‚ страдающим от алкогольной зависимости. Начальная встреча с наркологом в Туле включает диагностику зависимости‚ оценку состояния пациента и составление индивидуального плана лечения. Основные услуги нарколога на дому предполагают медикаментозную терапию‚ выведение из запоя‚ психотерапевтическую помощь при алкоголизме и программы восстановления. Родственники также играют важную роль тоже влияет значимую функцию в процессе реабилитации алкоголиков. Анонимное лечение обеспечивает комфорт и безопасность пациента. помощь нарколога тула
Выгребная яма — это подземная ёмкость , предназначенная для сбора и частичной переработки отходов.
Система работает так: жидкость из дома поступает в бак , где формируется слой ила, а жиры и масла собираются в верхнем слое.
В конструкцию входят входная труба, бетонный резервуар, соединительный канал и почвенный фильтр для дочистки воды .
https://bazarweb.ru/forum.php/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=40153
Плюсы использования: экономичность, минимальное обслуживание и экологичность при соблюдении норм.
Критично важно не перегружать систему , иначе частично очищенная вода попадут в грунт, вызывая загрязнение.
Типы конструкций: бетонные блоки, полиэтиленовые резервуары и композитные баки для разных условий монтажа .
Капельница при запое — это важный этап в помощи при алкогольной зависимости. Процедура капельницы помогает детоксикации организма‚ устраняя токсины и нормализуя водно-электролитный баланс. После капельницы пациенты замечают положительные изменения в психоэмоциональном состоянии.Поддержка нарколога в этом процессе неоценима. Он оценивает абстинентных симптомов и назначает соответствующее лечение запоя. Восстановление после запоя включает физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Роль близких существенна‚ позволяя преодолеть последствия запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Реабилитация является следующим шагом в лечении‚ где пациент обучается и получает медицинскую помощь для профилактики рецидивов. Анонимная помощь обеспечивает безопасность и конфиденциальность. Необходимо помнить‚ что лечение алкоголизма — это долгий путь‚ требующий усилий и поддержки.
какие провайдеры на адресе в красноярске
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
שהוא יעבור לקטגוריית האוהבים? במקום תשובה, הסטירה נשמעה חזק יותר בשתיקה לכאורה. – תמשיכי להתפשט. אבל רק התחתון. הורדתי את התחתונים, החצאית, הגרביונים והתנפצתי. וכשהבחור תפס אותי כמו here are the findings
האחורי של מרצדס. אדיק התכופף מעליה, נשען על מרפקיו. איבר מינו הקצר והעבה היה תלוי סנטימטרים מה שגרם לי להתאזן על סף אורגזמה. מאשה ניסתה נואשות לאכול זין, אבל החזקתי אותה, מקניטה זונה have a peek here
Лечение запоя с помощью капельниц, это критически важный шаг в лечении алкоголизма. Вызов нарколога на дом в Туле позволяет получить квалифицированную помощь. Если появляются симптомы запоя, таких как дрожь, потоотделение и беспокойство, важно сразу обратиться за помощью. Наркологи проводят диагностику алкоголизма и назначают медикаментозное лечение алкоголизма, включая капельницы для выведения токсинов. вызов нарколога на дом тула Реабилитация после запоя включает семейную поддержку, что значительно увеличивает шансы на успешное восстановление. Профилактика алкогольной зависимости тоже играет ключевую роль. Услуги нарколога, включая вызов врача на дом, помогают решить проблемы, связанные с алкогольной зависимостью, и гарантировать безопасную терапию.
купить высокое кашпо напольное недорого [url=http://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru]http://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru[/url] .
Как избавиться от алкогольной зависимости в Туле Зависимость от алкоголя – это актуальная проблема, касающаяся многих людей. В Туле доступно множество наркологических услуг, включая анонимное лечение и работу выездного нарколога. Первый этап лечения алкоголизма – это детоксикация, помогающая организму избавиться от токсичных веществ. Стоит отметить, что лечение на дому предоставляет комфортные условия и гарантирует конфиденциальность. Первая консультация с наркологом – это важный шаг на пути к выздоровлению. Специалисты помогут разработать индивидуальную программу восстановления, учитывающую потребности пациента. Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью реабилитации от алкоголизма, так как помогает преодолевать эмоциональные сложности. Существует также возможность кодирования от алкоголя, что может стать эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью. Помощь при запое и регулярные встречи с наркологом обеспечивают высокий уровень контроля над состоянием пациента. Если вы или ваши близкие испытываете проблемы с зависимостью от алкоголя, не бойтесь обратиться за профессиональной помощью. Нарколог на дом анонимно предложит все необходимые процедуры для возвращения к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
интернет провайдеры красноярск по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk006.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
Купить подписчиков в Telegram https://vc.ru/smm-promotion лёгкий способ начать продвижение. Выберите нужный пакет: боты, офферы, живые. Подходит для личных, новостных и коммерческих каналов.
Виртуальные номера для Telegram https://basolinovoip.com создавайте аккаунты без SIM-карты. Регистрация за минуту, широкий выбор стран, удобная оплата. Идеально для анонимности, работы и продвижения.
Odjeca i aksesoari za hotele hotelski program po sistemu kljuc u ruke: uniforme za sobarice, recepcionere, SPA ogrtaci, papuce, peskiri. Isporuke direktno od proizvodaca, stampa logotipa, jedinstveni stil.
Капельница от запоя на дому: противопоказания и возможные осложнения (Тула) Алкогольная зависимость – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального подхода. Все чаще люди обращаются к услугам нарколога на дому для борьбы с запоем. Одним из эффективных способов является инфузионная терапия, которая включает введение капельницы для выведения из запойного состояния. Капельница помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, улучшить общее состояние пациента и снять симптомы абстиненции. Тем не менее, необходимо учитывать противопоказания к данной процедуре. Например, наличие аллергии на компоненты растворов, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания или острые инфекционные процессы могут стать основанием для отказа в проведении капельницы. Также могут возникнуть осложнения, такие как тромбофлебит, инфицирование вены или аллергические реакции. Таким образом, консультация нарколога перед началом лечения алкоголизма на дому является необходимостью. Безопасность процедуры зависит от уровня квалификации специалиста и соблюдения всех предписаний. Нарколог на дому в Туле предлагает медицинскую помощь в комфортных условиях, что может существенно повысить эффективность реабилитации от запоя при правильном подходе.
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-msk001.ru
дом престарелых
какие провайдеры на адресе в краснодаре
domashij-internet-krasnodar004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-msk002.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
Специалист по наркологии — это медицинский работник, который обеспечивает поддержку людям, испытывающим проблемы от зависимостей. Процесс лечения включает в себя детоксикацию, медикаментозное лечение и психотерапию. Необходимо обратиться за консультацией нарколога для определения индивидуального плана реабилитации. Поддержка родственников играет ключевую роль в выздоровлении, а группы взаимопомощи помогают интегрироваться в социальной среде. Профилактика зависимостей также важна, чтобы снизить риск рецидивов. Обращение к профессионалам на narkolog-tula007.ru обеспечит высококачественную помощь и содействие на каждом этапе лечения.
интернет провайдеры краснодар по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnodar005.ru
провайдеры по адресу краснодар
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
pansionat-msk003.ru
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
проверить провайдеров по адресу краснодар
[url=https://domashij-internet-krasnodar006.ru]domashij-internet-krasnodar006.ru[/url]
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk001.ru
пансионат для пожилых
La ludopatía consciente es un conjunto de principios y prácticas orientado a garantizar la seguridad en plataformas digitales.
Las plataformas deben ofrecer opciones de autorregulación, pausas en el juego, para prevenir el exceso .
Estas prácticas incluyen controles de edad, recursos educativos, prevenir daños asociados.
casino y apuestas
Colaborar con instituciones especializadas fortalece la prevención a quienes muestran signos de adicción .
Formar a los empleados en identificación de patrones problemáticos asegura intervención temprana.
El objetivo final equilibrar la diversión con la seguridad donde el entretenimiento no comprometa la salud financiera o emocional .
спортивные прогнозы на футбол [url=http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol3.ru/]спортивные прогнозы на футбол[/url] .
ставки на спорт прогнозы хоккей [url=https://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej.ru]https://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej.ru[/url] .
заказать суши в барнауле заказать доставку суши барнаул
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
Хирургические услуги онкологическая хирургия: диагностика, операции, восстановление. Современная клиника, лицензированные специалисты, помощь туристам и резидентам.
Что учесть при выборе провайдера для смарт-ТВ в Москве Смарт-ТВ становится неотъемлемой частью современного развлечений. Однако для стабильного и качественного просмотра IPTV услуг существенен оптимальный выбор интернет-провайдера. Анализ провайдеров интернета даст возможность вам выбрать оптимальные тарифы, подходящие именно для ваших требований. При поиске интернет-провайдера в Москве учтите скорость интернета. Для комфортного просмотра потокового видео рекомендуют скорость не менее 20 Мбит/с. Узнайте, какие варианты тарифов предлагают разные провайдеры, и выберите те, которые предлагают стабильный интернет.Не забывайте о отзывы о провайдерах. Это поможет вам разобраться, какие услуги провайдеров наиболее качественны. Также важно принять во внимание возможность подключения смарт-ТВ и наличие IPTV услуг в ассортименте провайдера.Пользуйтесь сайтами, такими как domashij-internet-msk004.ru, для сравнения всех доступных вариантов. Оптимальный выбор интернет-провайдера — залог вашего комфорта при просмотре любимых передач!
дом престарелых
pansionat-msk002.ru
дом престарелых
дом престарелых в туле
pansionat-tula002.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
В Москве доступ к сети является все более значимым фактором повседневной жизни. Высокоскоростной интернет дает возможность трудиться, учиться и развлекаться без задержек. На сайте domashij-internet-msk005.ru вы найдете оптимальные тарифы от поставщиков интернета. Сравнение интернет-тарифов поможет выбрать наиболее подходящий тариф. Большинство поставщиков предлагают тарифы без ограничений, что очень удобно для пользователей, активно использующих Wi-Fi для жилища. Оптоволокно обеспечивает высокую скорость и стабильное соединение. Отзывы о провайдерах помогут, какие услуги связи наиболее качественные. Важно учитывать скорости интернета в столице, чтобы не ошибиться с выбором. Интернет на мобильных устройствах также может быть вариантом, в особенности для людей, кто много путешествует. Оформление подключения к интернету стало легче благодаря возможности подачи заявок через интернет. Выбирайте тарифы с в соответствии с ваших нужд, и получайте удовольствие от высокого качества связи!
пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk003.ru
частный дом престарелых
Магазин брендовых кроссовок https://kicksvibe.ru Nike, Adidas, New Balance, Puma и другие. 100% оригинал, новые коллекции, быстрая доставка, удобная оплата. Стильно, комфортно, доступно!
суши недорого барнаул суши барнаул
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-tula003.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
экстренный вывод из запоя
[url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru]https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru[/url]
вывод из запоя цена
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат после инсульта
провайдеры по адресу дома
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
домашний интернет подключить нижний новгород
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Ответственная игра — это комплекс мер , направленный на защиту участников , включая ограничение доступа несовершеннолетним .
Платформы обязаны предлагать инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы избежать чрезмерного участия.
Обучение сотрудников помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
вавада
Для игроков доступны горячие линии , где обратиться за поддержкой при проблемах с контролем .
Соблюдение стандартов включает проверку возрастных данных для предотвращения мошенничества .
Задача индустрии создать безопасную среду , где удовольствие сочетается с вредом для финансов .
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula002.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
Нужно собрать данные о человеке ? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Выясните место работы или интересы через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога узнать номер
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая общедоступную информацию.
Закажите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Попробуйте проверенному решению для исследований — точность гарантирована!
подключение интернета нижний новгород
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
подключить интернет тарифы нижний новгород
Дом Patek Philippe — это pinnacle часового искусства , где соединяются точность и эстетика .
С историей, уходящей в XIX век компания славится ручной сборкой каждого изделия, требующей сотен часов .
Инновации, такие как ключевой механизм 1842 года , укрепили репутацию как новатора в индустрии.
Часы Patek Philippe оригиналы
Лимитированные серии демонстрируют вечные календари и ручную гравировку , подчеркивая статус .
Современные модели сочетают традиционные методы , сохраняя механическую точность.
Это не просто часы — символ семейных традиций, передающий наследие мастерства из поколения в поколение.
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Neil Island is a small, peaceful island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It’s known for its beautiful beaches, clear blue water, and relaxed atmosphere: nature of Neil Island
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-tula003.ru
пансионат для лежачих тула
домашний интернет тарифы
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
подключить домашний интернет нижний новгород
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec004.ru
лечение запоя
русские онлайн казино игровые казино с лицензией
mostbet daxil ol [url=https://mostbet3041.ru]https://mostbet3041.ru[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
[url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru]https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Как погода влияет на скорость интернета в новосибирске: мнения пользователей На сайте domashij-internet-novosibirsk004.ru много пользователей делятся мнениями о том, как атмосферные условия сказываются на скорость и качество интернет-соединения. В новосибирске, где погодные условия могут быть частыми, отзывы о стабильности соединения разнятся. Факторы влияния, такие как температура и осадки, могут значительно изменять скорость интернет-соединения. Например, в сильный дождь или в ветреную погоду пользователи отмечают ухудшение качества связи. Это связано с тем, что провайдеры новосибирска иногда сталкиваются с проблемами в обслуживании линий связи; Работа из дома требует стабильного интернета, и многие Новосибирцы недовольны из-за изменений скорости при неблагоприятных погодных условиях. Важно подбирать проверенных провайдеров, чтобы минимизировать влияние погоды на интернет.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
Проводной интернет в новосибирске — это достоверный способ обеспечить стабильное соединение для досуга и профессиональной деятельности. Провайдеры интернета в новосибирске предлагают широкие тарифы на интернет, обеспечивая высокую скорость в интернет. Важно подбирать провайдеров, которые предлагают стабильное соединение и защиту от перебоев. интернет провайдеры новосибирск по адресу Скорость интернета и качество интернет-сигнала зависят от оборудования для интернетакоторое использует провайдер. Техническая поддержка также играет ключевую роль в обеспечении стабильности соединения. Перед подключением к сети стоит ознакомиться с мнениями о разных интернет провайдерах, чтобы выбрать лучший вариант с выгодными условиями.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
лечение запоя череповец
Определение оборудования для телевидения в новосибирске — существенный этап для удовлетворительного просмотра. В первую очередь‚ необходимо определиться с типом телевидения: спутниковое‚ кабельное или IPTV. Спутниковое телевидение требует антенн и ресиверов‚ тогда как для кабельного — телевизионные комплектующие. Если вы выбираете интернет-телевидение‚ потребуется подключение к интернету и нужные устройства. domashij-internet-novosibirsk006.ru Изучите расценки на телевидение в новосибирске‚ ознакомьтесь с отзывами о телевидении и выберите наиболее подходящий вариант. Услуги по подключению телевидения часто включают монтаж оборудования‚ поэтому рекомендуется изучить предложения профессионалов. Не забудьте про адаптеры и переходники‚ которые могут понадобиться для подключения.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
айфон в питере [url=https://kupit-ajfon-cs.ru/]kupit-ajfon-cs.ru[/url] .
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
Между прочим, если вас интересует musichunt.pro, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://musichunt.pro]https://musichunt.pro[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Modern operations aesthetic surgery innovative technologies, precision and safety. Minimal risk, short recovery period. Plastic surgery, ophthalmology, dermatology, vascular procedures.
Профессиональное https://prp-expert.ru: PRP, Plasmolifting, протоколы и нюансы проведения процедур. Онлайн курс обучения плазмотерапии.
домашний интернет тарифы омск
domashij-internet-omsk004.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
Студия дизайна Интерьеров в СПБ. Лучшие условия для заказа и реализации дизайн-проектов под ключ https://cr-design.ru/
Онлайн-курсы https://obuchenie-plasmoterapii.ru: теория, видеоуроки, разбор техник. Обучение с нуля и для практикующих. Доступ к материалам 24/7, сертификат после прохождения, поддержка преподавателя.
Le fēnix® Chronos de Garmin représente un summum de luxe qui combine les fonctionnalités GPS à un style raffiné grâce à ses finitions soignées.
Dotée de performances multisports , cette montre s’adresse aux sportifs exigeants grâce à sa polyvalence et ses capteurs sophistiqués.
Grâce à sa durée d’utilisation jusqu’à plusieurs jours selon l’usage, elle s’impose comme une solution fiable pour les entraînements intenses.
Les outils de monitoring incluent le sommeil et les étapes parcourues, idéal pour les amateurs de fitness .
Facile à configurer , la fēnix® Chronos s’intègre parfaitement à vos objectifs personnels, tout en conservant une esthétique intemporelle.
https://garmin-boutique.com
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
подключить интернет в квартиру омск
domashij-internet-omsk005.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета омск
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
подключить интернет в омске в квартире
domashij-internet-omsk006.ru
домашний интернет омск
Patek Philippe — это эталон механического мастерства, где сочетаются точность и художественная отделка.
С историей, уходящей в XIX век компания славится авторским контролем каждого изделия, требующей сотен часов .
Инновации, такие как ключевой механизм 1842 года , сделали бренд как новатора в индустрии.
https://patek-philippe-shop.ru
Коллекции Grand Complications демонстрируют сложные калибры и декоративные элементы, выделяя уникальность.
Текущие линейки сочетают инновационные материалы, сохраняя классический дизайн .
Это не просто часы — символ вечной ценности , передающий наследие мастерства из поколения в поколение.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
вывод из запоя
лучший интернет провайдер пермь
domashij-internet-perm004.ru
подключить проводной интернет пермь
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
провайдеры интернета пермь
domashij-internet-perm005.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
айфоны спб [url=http://kupit-ajfon-cs3.ru/]http://kupit-ajfon-cs3.ru/[/url] .
the best and interesting https://edicionesdelau.com
interesting and new https://www.intercultural.org.au
подключить интернет в квартиру пермь
domashij-internet-perm006.ru
провайдеры интернета пермь
Подбирая компании для квартирного переезда важно учитывать её лицензирование и опыт работы .
Изучите отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить профессионализм исполнителя.
Сравните цены , учитывая объём вещей, сезонность и дополнительные опции .
https://itkr.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?t=36502
Убедитесь наличия гарантий сохранности имущества и запросите детали компенсации в случае повреждений.
Оцените уровень сервиса: оперативность ответов, гибкость графика .
Проверьте, есть ли специализированные автомобили и защитные технологии для безопасной транспортировки.
best site online https://penzo.cz
visit the site online https://www.saffireblue.ca
Профессиональный монтаж рулонной наплавляемой кровли в Москве и всей России. Работаем с материалами: техноэласт, стеклоизол, битумная мастика. Гарантия до 10 лет. Бесплатный выезд и расчёт. Цена за 1м2 — от 350 рублей. Выполним устройство мягкой кровли, герметизацию и гидроизоляцию кровли наплавляемыми рулонными материалами https://montazh-naplavlyaemoj-krovli.ru/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Ответственная игра — это минимизирование рисков для участников, включая саморегуляцию поведения.
Важно планировать бюджет , чтобы сохранять контроль над затратами.
Воспользуйтесь функциями временной блокировки, чтобы приостановить активность в случае потери контроля.
Доступ к ресурсам включает консультации специалистов, где можно получить помощь при проявлениях зависимости .
Участвуйте в компании, чтобы сохранять социальный контакт , ведь семейная атмосфера делают процесс безопасным.
слоты
Изучайте правила платформы: лицензия оператора гарантирует защиту данных.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
лучший интернет провайдер ростов
domashij-internet-rostov004.ru
подключить интернет в квартиру ростов
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
По теме “travelmontenegro.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://travelmontenegro.ru]https://travelmontenegro.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Все о тендерах, актуальная новости и информация: st-tender.ru
mostbet android yukle [url=http://mostbet4048.ru/]http://mostbet4048.ru/[/url]
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga004.ru
лечение запоя калуга
Neil Island is a small, peaceful island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It’s known for its beautiful beaches, clear blue water, and relaxed atmosphere: how to reach Neil Island
visit the site https://puntera.com
go to the site https://ibecensino.org.br
интернет провайдеры ростов
domashij-internet-rostov005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер ростов
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Профессиональная наркологическая клиника. Лечение зависимостей, капельницы, вывод из запоя, реабилитация. Анонимно, круглосуточно, с поддержкой врачей и психологов.
Removing clothes remover ai tool from images is an advanced tool for creative tasks. Neural networks, accurate generation, confidentiality. For legal and professional use only.
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/lyubercy/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
https://pena-montazhnaya.ru/
подключить интернет в ростове в квартире
domashij-internet-rostov006.ru
домашний интернет ростов
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar005.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/articles/raznoobrazie-vidov-melirovaniya-volos/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
вывод из запоя
провайдеры интернета в самаре по адресу проверить
domashij-internet-samara004.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу самара
Алкоголизм: лечение в домашних условиях становится актуальным. Основные этапы включают детоксикации на дому и помощи при запое. Как начать процесс лечения? Важно установить поддержку родственниковкоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психотерапия и народные методы могут стать хорошим дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы по поддержанию трезвости и методы отказа от спиртного помогут установить верное мышление. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk001.ru Важно помнить о реабилитации дома, которая включает психологическую помощь и предотвращение рецидивов. Что делать, чтобы бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с постановки ясной цели и поиска источника мотивации. Главное – это поддержка и желание изменить свою жизнь.
הלכתי אחרי הטירון שהוביל במסדרונות. עד שהגענו ליד הדלת הישנה. – היכנס כבר, שמעתי אותך מהקומה אני חחח, הם אומרים, טוב בעצמי. הם עישנו, היא נכנסה שוב לג ‘ ינס, דחפה את הציצים שלה לחזייה, click here for more
Hyvaa paivaa!!
Casino valitukset ja niiden käsittely kertovat paljon sivuston ammattimaisuudesta. Casino valitukset ratkaistaan nopeasti luotettavissa paikoissa. [url=https://reallivecasino.cfd/arvostelut-ja-luotettavuus.html]casino turvallisuus[/url] Tarkista miten casino on hoitanut aiempia valituksia ennen oman päätöksesi tekemistä.
Lue linkki – https://reallivecasino.cfd/arvostelut-ja-luotettavuus.html
ГҐterbetalning casino
casino ilman kirjautumista
casino laskulla
Onnea!
Рефрижераторные перевозки https://agro-archive.ru/novosti/42262-preimuschestva-sotrudnichestva-torgovyh-setey-s-professionalnymi-kompaniyami-po-refrizheratornym-perevozkam.html по России и СНГ. Контроль температуры от -25°C до +25°C, современные машины, отслеживание груза.
Back then, I believed following instructions was enough. The pharmacy hands it over — you nod, take it, and move on. It felt safe. But that illusion broke slowly.
First came the fatigue. I blamed my job. And deep down, I knew something was off. I watched people talk about their own experiences. None of the leaflets explained it clearly.
vidalista 20 mg price
That’s when I understood: health isn’t passive. Two people can take the same pill and walk away with different futures. Damage accumulates. And still we keep swallowing.
Now I question more. Not because I don’t trust science. I track everything. But I don’t care. This is survival, not stubbornness. The turning point, it would be keyword.
Доставка грузов из Китая в Россию осуществляется через автомобильные каналы, с таможенным оформлением на в портах назначения.
Импортные сборы составляют в диапазоне 15–20%, в зависимости от типа продукции — например, сельхозпродукты облагаются по максимальной ставке.
Чтобы сократить сроки используют альтернативные схемы, которые быстрее стандартных методов , но связаны с повышенными рисками .
Доставка грузов из Китая
При официальном оформлении требуется предоставить паспорта на товар и декларации , особенно для технических устройств.
Сроки доставки варьируются от одной недели до двух недель , в зависимости от вида транспорта и эффективности таможни .
Стоимость услуг включает логистику , налоги и услуги экспедитора, что влияет на рентабельность поставок.
проверить провайдеров по адресу самара
domashij-internet-samara005.ru
провайдеры интернета в самаре по адресу проверить
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
חודר מהבטן לראשה, האצבעות חופרות בספה, הציפורניים קורעות את הבד, העיניים מתגלגלות, אני והשאירה רק את עיניה פקוחות, שהונחו על ידי חץ כהה, ושפתיה מאופרות בצבע בורדו עמוק. החדר שקע סקס אדיר דירות דיסקרטיות
https://creditka.org.ua/
провайдеры по адресу
domashij-internet-samara006.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
электрокарнизы для штор [url=https://www.elektrokarnizy10.ru]https://www.elektrokarnizy10.ru[/url] .
Лечение запоя в Красноярске это важная задача, которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. Алкоголизм — это беда, способная сломать судьбы, и помощь при запое жизненно важна для всех, кто оказался в этой ситуации. В клиниках для лечения запоя предлагаются различные программы, направленные на выведение из запоя и реабилитацию после запоя . Цены на лечение алкогольной зависимости могут меняться в зависимости от клиники и качества обслуживания. В стоимость может входить консультация нарколога, медицинская помощь при запое и услуги по детоксикации. лечение запоя Красноярск Помощь наркологов в Красноярске включает в себя как стационарное, так и амбулаторное лечение , что также сказывается на ценах. Программа лечения алкоголизма индивидуализирована и может включать детоксикационные процедуры, психологическую помощь и реабилитационные мероприятия. Комплексный подход к лечению зависимостей в Красноярске позволяет не только прервать алкогольный марафон, но и избежать рецидивов . Поэтому, если вам или вашим близким требуется помощь, важно не откладывать обращение к профессионалам.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Выбирайте казино пиастрикс казино с оплатой через Piastrix — это удобно, безопасно и быстро! Топ-игры, лицензия, круглосуточная поддержка.
Хотите купить контрактный двигатель ДВС с гарантией? Б большой выбор моторов из Японии, Европы и Кореи. Проверенные ДВС с небольшим пробегом. Подбор по VIN, доставка по РФ, помощь с установкой.
Ищете казино казино с СБП? У нас — мгновенные переводы, слоты от топ-провайдеров, живые дилеры и быстрые выплаты. Безопасность, анонимность и мобильный доступ!
Играйте в онлайн-покер покерок легальный с игроками со всего мира. МТТ, спины, VIP-программа, акции.
1win apk latest version download [url=https://1win-in1.com]1win apk latest version download[/url] .
Хирurgija u Crnoj Gori https://www.hirurgija-crna-gora.me savremena klinika, iskusni ljekari, evropski standardi. Planirane i hitne operacije, estetska i opsta hirurgija, udobnost i bezbjednost.
подключение интернета по адресу
domashij-internet-spb004.ru
интернет провайдеры санкт-петербург по адресу
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
The website tnschoolsonline.in is an official portal by the Tamil Nadu School Education Department. It provides comprehensive information about schools across Tamil Nadu, including directories, enrollment data, infrastructure details, and staff records. It serves teachers, students, and administrators to monitor and improve school management and educational outcomes.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
1win betting app [url=http://1win3025.com]http://1win3025.com[/url]
Элитная недвижимость https://real-estate-rich.ru в России и за границей — квартиры, виллы, пентхаусы, дома. Где купить, как оформить, во что вложиться.
интернет по адресу дома
domashij-internet-spb005.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу санкт-петербург
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk002.ru
вывод из запоя минск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
is 1win legit in nigeria [url=http://1win3027.com/]is 1win legit in nigeria[/url]
подключить интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-spb006.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу санкт-петербург
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Выбор застройщика https://spartak-realty.ru важный шаг при покупке квартиры. Расскажем, как проверить репутацию, сроки сдачи, проектную документацию и избежать проблем с новостройкой.
Смотреть фильмы kinobadi.mom и сериалы бесплатно, самый большой выбор фильмов и сериалов , многофункциональное сортировка, также у нас есть скачивание в mp4 формате
Недвижимость в Балашихе https://balashihabest.ru комфорт рядом с Москвой. Современные жилые комплексы, школы, парки, транспорт. Объекты в наличии, консультации, юридическое сопровождение сделки.
Поставка нерудных материалов https://sr-sb.ru песок, щебень, гравий, отсев. Прямые поставки на стройплощадки, карьерный материал, доставка самосвалами.
Лайфхаки для ремонта https://stroibud.ru квартиры и дома: нестандартные решения, экономия бюджета, удобные инструменты.
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу уфа
domashij-internet-ufa004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
Прокапывание от алкоголя на дому — это результативный метод помощи алкоголизма, который даёт возможность быстро устранить симптомы абстиненции и улучшить общее состояние больного. Услуги нарколога на дому всё чаще востребованы, так как многие предпочитают не проходить лечение в стационаре. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk001.ru Процедура предполагает домашнюю детоксикацию, в которой помощь специалиста при алкоголизме осуществляется в комфортной обстановке. Капельница для снятия похмелья содержит лекарственные средства для очищения организма, способствующие помогают выведению токсинов из организма и нормализовать баланс электролитов и жидкости. Необходимо помнить о симптомах алкогольного абстинентного синдрома, включающих беспокойство, потливость и тремтение. Забота и поддержка со стороны близких играет ключевую роль в эффективном лечении и реабилитации после запоя. Домашняя терапия может включать не только прокапывание, но и рекомендации по профилактике алкогольной зависимости, что содействует предотвращению повторных срывов и сохранить трезвый образ жизни.
Женский журнал https://e-times.com.ua о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Советы, тренды, рецепты, вдохновение на каждый день. Будь в курсе самого интересного!
Туристический портал https://atrium.if.ua всё для путешественников: путеводители, маршруты, советы, отели, билеты и отзывы. Откройте для себя новые направления с полезной информацией и лайфхаками.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://socvirus.com.ua мода, макияж, карьера, семья, тренды. Полезные статьи, интервью, обзоры и вдохновляющий контент для настоящих женщин.
Портал про ремонт https://prezent-house.com.ua полезные советы, инструкции, дизайн-идеи и лайфхаки. От черновой отделки до декора. Всё о ремонте квартир, домов и офисов — просто, понятно и по делу.
Всё о ремонте https://sevgr.org.ua на одном портале: полезные статьи, видеоуроки, проекты, ошибки и решения. Интерьерные идеи, советы мастеров, выбор стройматериалов.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk002.ru
лечение запоя
Бюро дизайна https://sinega.com.ua интерьеров: функциональность, стиль и комфорт в каждой детали. Предлагаем современные решения, индивидуальный подход и поддержку на всех этапах проекта.
Портал про ремонт https://techproduct.com.ua для тех, кто строит, переделывает и обустраивает. Рекомендации, калькуляторы, фото до и после, инструкции по всем этапам ремонта.
Портал о строительстве https://bms-soft.com.ua от фундамента до кровли. Технологии, лайфхаки, выбор инструментов и материалов. Честные обзоры, проекты, сметы, помощь в выборе подрядчиков.
Всё о строительстве https://kinoranok.org.ua на одном портале: строительные технологии, интерьер, отделка, ландшафт. Советы экспертов, фото до и после, инструкции и реальные кейсы.
Ремонт и строительство https://mtbo.org.ua всё в одном месте. Сайт с советами, схемами, расчетами, обзорами и фотоидееями. Дом, дача, квартира — строй легко, качественно и с умом.
подключение интернета по адресу
domashij-internet-ufa005.ru
интернет провайдеры уфа по адресу
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы – это ключевым моментом в терапии алкогольной зависимости. В Красноярске наркология предоставляют поддержку нарколога‚ что проведет детоксикацию организма. Признаки запоя‚ такие как тревога и потливость‚ могут вызывать серьезные проблемы после запоя. Процедура капельницы способствует восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить здоровье после запоя. помощь нарколога Красноярск После лечения важно пройти реабилитацию и получить психологическую поддержку. Консультация нарколога способствует избежать рецидивов. Профилактика рецидива включает в себя обучение и поддержку‚ что способствует восстановлению организма. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме в Красноярске доступна и эффективна‚ помогая пациентам возвратиться к нормальной жизни.
Сайт о ремонте https://sota-servis.com.ua и строительстве: от черновых работ до декора. Технологии, материалы, пошаговые инструкции и проекты.
Онлайн-журнал https://elektrod.com.ua о строительстве: технологии, законодательство, цены, инструменты, идеи. Для строителей, архитекторов, дизайнеров и владельцев недвижимости.
Полезный сайт https://quickstudio.com.ua о ремонте и строительстве: пошаговые гиды, проекты домов, выбор материалов, расчёты и лайфхаки. Для начинающих и профессионалов.
Журнал о строительстве https://tfsm.com.ua свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий, советы мастеров, тренды в архитектуре и дизайне.
Женский сайт https://7krasotok.com о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, тренды, рецепты, лайфхаки и вдохновение для современных женщин.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk003.ru
лечение запоя
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу уфа
domashij-internet-ufa006.ru
провайдеры в уфе по адресу проверить
Женские новости https://biglib.com.ua каждый день: мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, семья, карьера. Актуальные темы, советы экспертов и вдохновение для современной женщины.
Все главные женские https://pic.lg.ua новости в одном месте! Мировые и российские тренды, стиль жизни, психологические советы, звёзды, рецепты и лайфхаки.
Сайт для женщин https://angela.org.ua любого возраста — статьи о жизни, любви, стиле, здоровье и успехе. Полезно, искренне и с заботой.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://bestwoman.kyiv.ua для тех, кто ценит себя. Мода, уход, питание, мотивация и женская энергия в каждой статье.
Путеводитель по Греции https://cpcfpu.org.ua города, курорты, пляжи, достопримечательности и кухня. Советы туристам, маршруты, лайфхаки и лучшие места для отдыха.
Злоупотребление алкоголем — это острое заболевание, требующее незамедлительного вмешательства и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске доступен услуга вызова нарколога на дом, что даёт возможность получить необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в комфортной обстановке. Признаки алкоголизма включают регулярном потреблении алкоголя, потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и появлении симптомов алкогольной зависимости. вызов нарколога на дом Красноярск Борьба с алкоголизмом можно начать с определения степени зависимости, которую осуществит опытный специалист в области наркологии. Консультация нарколога способствует выявить уровень зависимости и определить индивидуальный план лечения. Важно помнить о поддержке семьи, которая является важным фактором в процессе восстановления. Последствия алкоголизма могут быть очень серьезными, включая физические и психологические проблемы. Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске предлагает как медикаментозное лечение, так и реабилитационные программы, ориентированные на восстановление пациента. Не затягивайте с решением проблемы, позаботьтесь о своей жизни и обратитесь за помощью!
mostbet aviator [url=www.mostbet4049.ru]mostbet aviator[/url]
Honestly, I wasn’t expecting this, but it really caught my attention. The way everything came together so naturally feels both surprising and refreshing. Sometimes, you stumble across things without really searching, and it just clicks.testinggoeshow It reminds me of how little moments can have an unexpected impact
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg001.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
провайдеры интернета омск
domashij-internet-volgograd004.ru
подключить интернет тарифы омск
Канал с обзорами и сравнениями грузовой техники для выбора и покупки.
Публикуем новости, технические характеристики, рыночную аналитику, советы по выбору для бизнеса.
У нас всегда актуальные цены и тренды рынка СНГ! Подпишись:
https://t.me/s/kupit_gruzoviki/456
вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
паркетная доска Барлинек купить в Москве недорого [url=www.parketnay-doska2.ru]www.parketnay-doska2.ru[/url] .
подключение интернета омск
domashij-internet-volgograd005.ru
домашний интернет омск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk002.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg003.ru
лечение запоя
подключение интернета омск
domashij-internet-volgograd006.ru
интернет провайдер омск
Портал о строительстве https://ateku.org.ua и ремонте: от фундамента до крыши. Пошаговые инструкции, лайфхаки, подбор материалов, идеи для интерьера.
Строительный портал https://avian.org.ua для профессионалов и новичков: проекты домов, выбор материалов, технологии, нормы и инструкции.
Туристический портал https://deluxtour.com.ua всё для путешествий: маршруты, путеводители, советы, бронирование отелей и билетов. Информация о странах, визах, отдыхе и достопримечательностях.
Открой мир https://hotel-atlantika.com.ua с нашим туристическим порталом! Подбор маршрутов, советы по странам, погода, валюта, безопасность, оформление виз.
Ваш онлайн-гид https://inhotel.com.ua в мире путешествий — туристический портал с проверенной информацией. Куда поехать, что посмотреть, где остановиться.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk003.ru
вывод из запоя минск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Hei, veli!
Kierrätysvapaita bonuksia tarjoavat vain harvat luotettavat netticasinot. Kierrätysvapaita bonuksia arvostetaan niiden yksinkertaisuuden vuoksi. [url=https://reallivecasino.cfd/bonukset-ilman-kierratysta.html]bonukset ilman kierrätystä[/url] Ei monimutkaisia ehtoja, vain suoraviivaista pelaamista ja voittamista.
Lue linkki – https://www.reallivecasino.cfd/bonukset-ilman-kierratysta.html
kulosaaren casino
casino finland
casino ilman talletusta
Onnea!
Строительный сайт https://diasoft.kiev.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов, технологии, дизайн и обустройство.
Terve!!
Casino Helsinki pukukoodi edellyttää siistiä ja asiallista pukeutumista. Casino Helsinki pukukoodi luo arvokasta tunnelmaa. [url=https://reallivecasino.cfd/casino-helsinki.html]casino helsinki arvostelu[/url] Valmistaudu käyntiin asianmukaisesti ja nauti ylellisestä kokemuksesta.
Lue linkki – https://www.reallivecasino.cfd/casino-helsinki.html
Г¤ltestes casino las vegas
casino kimppa
casino finland
Onnea!
Журнал о строительстве https://kennan.kiev.ua новости отрасли, технологии, советы, идеи и решения для дома, дачи и бизнеса. Фото-проекты, сметы, лайфхаки, рекомендации специалистов.
Сайт о строительстве https://domtut.com.ua и ремонте: практичные советы, инструкции, материалы, идеи для дома и дачи.
На строительном сайте https://eeu-a.kiev.ua вы найдёте всё: от выбора кирпича до дизайна спальни. Актуальная информация, фото-примеры, обзоры инструментов, консультации специалистов.
Строительный журнал https://inter-biz.com.ua актуальные статьи о стройке и ремонте, обзоры материалов и технологий, интервью с экспертами, проекты домов и советы мастеров.
провайдеры интернета в воронеже
domashij-internet-voronezh004.ru
интернет провайдер воронеж
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Сайт о ремонте https://mia.km.ua и строительстве — полезные советы, инструкции, идеи, выбор материалов, технологии и дизайн интерьеров.
Сайт о ремонте https://rusproekt.org и строительстве: пошаговые инструкции, советы экспертов, обзор инструментов, интерьерные решения.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Всё для ремонта https://zip.org.ua и строительства — в одном месте! Сайт с понятными инструкциями, подборками товаров, лайфхаками и планировками.
Полезный сайт для ремонта https://rvps.kiev.ua и строительства: от черновых работ до отделки и декора. Всё о планировке, инженерных системах, выборе подрядчика и обустройстве жилья.
Автомобильный портал https://just-forum.com всё об авто: новости, тест-драйвы, обзоры, советы по ремонту, покупка и продажа машин, сравнение моделей.
https://www.glicol.ru/
Современный женский журнал https://superwoman.kyiv.ua стиль, успех, любовь, уют. Новости, идеи, лайфхаки и мотивация для тех, кто ценит себя и своё время.
Онлайн-портал https://spkokna.com.ua для современных родителей: беременность, роды, уход за малышами, школьные вопросы, советы педагогов и врачей.
тарифы интернет и телевидение воронеж
domashij-internet-voronezh005.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета воронеж
Онлайн-журнал https://eternaltown.com.ua для женщин: будьте в курсе модных новинок, секретов красоты, рецептов и психологии.
Сайт для женщин https://ww2planes.com.ua идеи для красоты, здоровья, быта и отдыха. Тренды, рецепты, уход за собой, отношения и стиль.
Сайт для женщин https://womanfashion.com.ua которые ценят себя и своё время. Мода, косметика, вдохновение, мотивация, здоровье и гармония.
Honestly, I wasn’t expecting this, but it really caught my attention.
The way everything came together so naturally feels both surprising and refreshing.
Sometimes, you stumble across things without really searching, and it just clicks.
It reminds me of how little moments can have an unexpected impact
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Кстати, если вас интересует easyterm.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk006.ru
лечение запоя
Du möchtest wissen, ob es möglich ist, im Online Casino Österreich legal zu spielen und welche Anbieter dafür infrage kommen? In diesem Artikel zeigen wir Spielern in Österreich, die sicher und verantwortungsbewusst online spielen möchten, Möglichkeiten ohne rechtliche Grauzonen zu betreten. Lies weiter, um die besten Tipps und rechtlichen Hintergründe zu entdecken: Online Casino
Современный авто портал https://simpsonsua.com.ua автомобили всех марок, тест-драйвы, лайфхаки, ТО, советы по покупке и продаже. Для тех, кто водит, ремонтирует и просто любит машины.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://abuki.info мода, красота, здоровье, психология, отношения и вдохновение. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов и темы, которые волнуют современных женщин.
Актуальные новости https://uapress.kyiv.ua на одном портале: события России и мира, интервью, обзоры, репортажи. Объективно, оперативно, профессионально. Будьте в курсе главного!
Онлайн авто портал https://sedan.kyiv.ua для автолюбителей и профессионалов. Новинки автоиндустрии, цены, характеристики, рейтинги, покупка и продажа автомобилей, автофорум.
Информационный портал https://mediateam.com.ua актуальные новости, аналитика, статьи, интервью и обзоры. Всё самое важное из мира политики, экономики, технологий, культуры и общества.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk002.ru
вывод из запоя омск
домашний интернет воронеж
domashij-internet-voronezh006.ru
подключить интернет воронеж
Du möchtest wissen, ob es möglich ist, im Online Casino Österreich legal zu spielen und welche Anbieter dafür infrage kommen? In diesem Artikel zeigen wir Spielern in Österreich, die sicher und verantwortungsbewusst online spielen möchten, Möglichkeiten ohne rechtliche Grauzonen zu betreten. Lies weiter, um die besten Tipps und rechtlichen Hintergründe zu entdecken: Online Casinos
Капельница – это значимая процедура, которая помогает скорейшему восстановлению здоровья человека, страдающего алкогольную зависимость. В Туле обращение к наркологу для проведения этой процедуры становится всё более необходимым. Употребление алкоголя негативно сказывается на организм, вызывая симптомам похмелья, такими как мигрень, тошнота и слабость.Лечение алкоголизма включает detox, который помогает очищению организма от токсинов. Капельница обеспечивает поступление необходимых веществ, улучшая состояние пациента. Нарколог предоставляет медицинскую помощь при запое, что способствует избежать серьезных осложнений. вызов нарколога тула Восстановление организма после запоя нуждается в комплексном подходе, включая восстановление от алкоголя. Лечение запоя может включать как медикаментозные методы, так и психотерапевтическую помощь. Важно помнить, что здоровье – это наиболее важное, и оперативная помощь нарколога может оказаться решающей.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
подключить интернет в квартиру челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk004.ru
подключить интернет челябинск
Запой — это серьезное состояние, требующее незамедлительной медико-социальной помощи. В Туле доступна помощь врача-нарколога, который предлагает услуги по избавлению от запоя и очищению организма. Капельное введение — это результативное средство для восстановления здоровья пациента. Она помогает устранить симптомы алкогольной зависимости, улучшает общее состояние и ускоряет процесс реабилитации от алкоголя. помощь нарколога тула Если вы или ваш близкий сталкиваетесь с проблемой запоя, необходимо не откладывать вызов врача на дом. Наркологические услуги, предоставляемые в клиниках Тулы, могут включать персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту. Услуги нарколога включает не только капельницы, но и комплексное лечение алкоголизма. Обращение к врачу на дом дает возможность получения медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке. Специалисты согласятся на необходимую детоксикацию и укрепят здоровье пациента. Не бойтесь обращаться за помощью — это первый шаг к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
Новости Украины https://pto-kyiv.com.ua и мира сегодня: ключевые события, мнения экспертов, обзоры, происшествия, экономика, политика.
Современный мужской портал https://kompanion.com.ua полезный контент на каждый день. Новости, обзоры, мужской стиль, здоровье, авто, деньги, отношения и лайфхаки без воды.
Сайт для женщин https://storinka.com.ua всё о моде, красоте, здоровье, психологии, семье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновляющие статьи и тренды для гармоничной жизни.
Новостной портал https://thingshistory.com для тех, кто хочет знать больше. Свежие публикации, горячие темы, авторские колонки, рейтинги и хроники. Удобный формат, только факты.
Следите за событиями https://kiev-pravda.kiev.ua дня на новостном портале: лента новостей, обзоры, прогнозы, мнения. Всё, что важно знать сегодня — быстро, чётко, объективно.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Moi!
Vastuullinen pelaaminen on kasinon ja pelaajan yhteinen vastuu. Vastuullinen pelaaminen tarkoittaa omien rajojen asettamista ja noudattamista. [url=https://reallivecasino.cfd/ikarajat-ja-saannot.html]casino lisenssi[/url] Pelaa vain sillä rahalla jonka voit hävitä ja pidä hauskuus etusijalla.
Lue linkki – https://www.reallivecasino.cfd/ikarajat-ja-saannot.html
casino ilman talletusta
åldersgräns casino usa
Г¤r casino vinster skattefria
Onnea!
Moi!
Blackjack on maailman suosituin kasino korttipeli yksinkertaisten sääntöjensä ansiosta. Blackjack tarjoaa parhaat voittomahdollisuudet oikealla strategialla pelattuna. [url=https://reallivecasino.cfd/kasino-korttipeli.html]casino korttipelivinkit[/url] Opi perusstrategia ja paranna voittomahdollisuuksiasi merkittävästi jokaisessa kädessä.
Lue linkki – https://www.reallivecasino.cfd/kasino-korttipeli.html
casino juhannus
casino aukioloajat
casino ГҐrhus poker
Onnea!
подключить интернет
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk005.ru
интернет провайдеры челябинск
Капельница от запоя – является важным этапом в лечение алкогольной зависимости. В Туле наркология предлагают поддержку нарколога‚ который проведет детоксикацию организма. Симптомы запоя‚ такие как тревога и потливость‚ могут привести серьезные проблемы после запоя. Процедура капельницы помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить здоровье в результате запойного состояния. помощь нарколога тула После лечения важно пройти реабилитацию и обеспечить психологическую поддержку. Консультация специалиста в области наркологии способствует избежать рецидивов. Профилактика рецидива предполагает обучение и поддержку‚ что способствует восстановлению организма. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме в Туле доступна и эффективна‚ помогая пациентам возвратиться к нормальной жизни.
https://www.glicol.ru/
кулинарный мастер-класс аренда кухни для съёмки
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Зацепил материал про reactive.su.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://reactive.su]https://reactive.su[/url]
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
спираль мирена выделения https://spiral-mirena1.ru
Video chat with girl – meet, chat, flirt! Private broadcasts, thousands of users online. No limits, free and no registration. Start a dialogue right now.
Эффективная накрутка ПФ https://nakrutka-pf-seo.ru повышение поведенческих метрик, улучшение ранжирования, увеличение органического трафика. Безопасно, анонимно, с гарантией результата.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
ремонт стиральных машин бош ремонт стиральной машины gorenje
ремонт стиральных машин haier ремонт стиральных машин на дому недорого
ремонт стиральных машин aeg ремонт стиральной машины замена подшипника
Дом Patek Philippe — это вершина механического мастерства, где соединяются прецизионность и художественная отделка.
Основанная в 1839 году компания славится авторским контролем каждого изделия, требующей многолетнего опыта.
Инновации, такие как ключевой механизм 1842 года , сделали бренд как новатора в индустрии.
https://patek-philippe-shop.ru
Коллекции Grand Complications демонстрируют вечные календари и декоративные элементы, выделяя уникальность.
Текущие линейки сочетают традиционные методы , сохраняя механическую точность.
Это не просто часы — символ вечной ценности , передающий наследие мастерства из поколения в поколение.
For years, I assumed following instructions was enough. The system moves you along — you don’t question the process. It felt official. Eventually, it didn’t feel right.
Then the strange fog. I blamed my job. But my body was whispering something else. I read the label. The warnings were there — just buried in jargon.
I started seeing: health isn’t passive. The reaction isn’t always immediate, but it’s real. Reactions aren’t always dramatic — just persistent. And still we keep swallowing.
Now I question more. Not because I’m paranoid. I challenge assumptions. Not all doctors love that. I’m not trying to be difficult — I’m trying to stay alive. The turning point, it would be proscar side effects.
escort moscow – https://moscowescortclub.com/
подключить интернет челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk006.ru
домашний интернет в челябинске
Врач-нарколог в любое время предоставляет экстренную помощь при наркологических кризисах при ситуациях, связанных с наркотической зависимостью. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir004.ru вы можете получить консультацию врачукоторый проведет диагностику наркозависимости и предложит индивидуальную программу лечения. Центр наркологии предлагает медицинскую поддержку и лечение с повышенной конфиденциальностью. Реабилитация зависимых включает психотерапию зависимостей и помощь при алкоголизмеа также консультации и помощь для семьи на всех этапах лечения. Обратитесь за помощью уже сегодня!
https://sinergiya-epilate.ru/
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg003.ru
вывод из запоя
Алкогольный запой, это опасное состояние, возникающее при длительном пьянстве. Эффекты запоя могут быть угрожающими: истощение организма, повреждение органов, психические расстройства. Быстрый выход из запоя в городе владимир включает медикаментозное лечение и психологическую поддержку. Важно знать симптомы запойного алкоголизма: частые запои, потеря контроля над употреблением алкоголя. Методы выхода из запоя разнообразны: от инфузионной терапии до встреч с профессионалами. Реабилитация после запоя требует комплексного подхода, включая возвращение к здоровью и психологическую реабилитацию. Профилактика и лечение алкогольной зависимости в городе владимир предлагает медицинские центры, где доступны различные программы поддержки. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир
Rolex Submariner, выпущенная в 1954 году стала первой дайверской моделью, выдерживающими глубину до 330 футов.
Модель имеет вращающийся безель , Triplock-заводную головку, обеспечивающие герметичность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает хромалитовый циферблат , стальной корпус Oystersteel, подчеркивающие спортивный стиль.
Хронометры Ролекс Субмаринер цены
Механизм с запасом хода до 3 суток сочетается с автоматическим калибром , что делает их надежным спутником для активного образа жизни.
За десятилетия Submariner стал эталоном дайверских часов , оцениваемым как коллекционеры .
culinary recipes https://retetesimple.com for every day: breakfasts, lunches, dinners, desserts and drinks. Step-by-step preparation, photos and tips.
downloading files https://all-downloaders.com from popular video services
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk004.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
резка металла листового лазерной резки металла
типография официальный сайт типография спб дешево
Лечение алкоголизма в владимире Зависимость от алкоголя – это актуальная проблема, касающаяся многих людей. В владимире предлагается широкий спектр наркологических услуг, таких как анонимное лечение и услуги выездного нарколога. Первый этап лечения алкоголизма – это детоксикация, помогающая организму избавиться от токсичных веществ. Важно помнить, что лечение на дому обеспечивает комфорт и конфиденциальность. Первая консультация с наркологом – это важный шаг на пути к выздоровлению. Квалифицированные специалисты помогут создать индивидуальный план реабилитации, соответствующий потребностям пациента. Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью реабилитации от алкоголизма, так как помогает преодолевать эмоциональные сложности. Также доступно кодирование от алкоголя, которое может быть эффективным средством в борьбе с зависимостью. Помощь при запое и регулярные встречи с наркологом обеспечивают высокий уровень контроля над состоянием пациента. Если вы или ваши близкие сталкиваетесь с зависимостью от спиртного, не стесняйтесь обратиться за помощью. Нарколог на дом анонимно предложит все необходимые процедуры для возвращения к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Интернет для бизнеса в Екатеринбурге предоставляет разнообразные тарифы для бизнесагарантируя стабильное соединение и высокоскоростной доступ в интернет. Провайдеры интернета предоставляют привлекательные тарифы, в т.ч. пакеты интернет-услуг и услуги связи. Оптоволокно и беспроводной интернет становятся популярными решениями для компаний. Мобильный интернет для бизнеса также доступен. Техническая поддержка обеспечивает быстрое подключение к интернету. Выбирайте лучшее для вашего бизнеса на domashij-internet-ekaterinburg004.ru.
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Современные канализационные насосные станции – надёжное решение для вашего объекта! Предлагаем КНС любой мощности с автоматикой и защитой от засоров. Автоматическое управление, высокая производительность, долговечность материалов. Решаем задачи от частных домов до промышленных объектов. Гарантия качества и быстрая доставка, подробнее тут: https://kns-kupit.ru/
В Екатеринбурге множество интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих различные интернет-услуги. При выборе провайдера необходимо учитывать скорость интернета и качество связи. На сайте domashij-internet-ekaterinburg005.ru можно найти разнообразные тарифы от разных провайдеров, а также оценки пользователей, что поможет в сравнении провайдеров. Мнения пользователей имеют ключевую значение в понимании стабильности соединения и работы техподдержки. Популярные провайдеры предлагают различные интернет-пакеты с акциями и скидками, что позволяет сделать доступ в интернет доступнее. Стоит обратить внимание с отзывами клиентов, чтобы определить наиболее подходящий провайдер для себя.
типография петербург типография официальный сайт
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
лечение запоя
типография быстро типография заказать
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
лечение запоя
В условиях‚ когда удаленная работа становится обычным делом‚ стабильное соединение с интернетом играет первостепенное значение. В столице огромное количество интернет-провайдеров предлагают различные тарифы на интернет‚ что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пользователя. интернет провайдеры по адресу Екатеринбург При определении провайдера стоит учитывать пропускную способность интернета и наличие оптоволоконного интернета‚ так как он обеспечивает максимальную скорость передачи данных. Услуги интернет-провайдеров разнообразны от базовых до премиум-решений для бизнеса‚ что важно для тех‚ кто занимается с большими объемами информации. Мнения о провайдерах помогут вам составить полное представление о качестве услуг. Беспроводной интернет является альтернативой‚ но проводной интернет в большинстве случаев обеспечивает более стабильное соединение‚ что критично для видеозвонков и работы с облачными сервисами. Для подключения интернета в Екатеринбурге достаточно обратиться к выбранному провайдеру и ознакомиться с доступными тарифами. Правильный выбор провайдера и тарифа — залог успешной удаленной работы!
Выездная наркологическая помощь – это важный аспект лечения зависимостей‚ который обеспечивает экстренную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и зависимости от наркотиков. Выездная наркологическая служба предоставляет профессиональную помощь зависимым‚ включая детоксикацию и экстренное вмешательство в кризисных ситуациях. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula004.ru можно узнать больше о по наркологии‚ ознакомиться с методами лечения наркомании и реабилитации на дому. Конфиденциальное лечение зависимых позволяет сохранить личные данные в тайне. Важно также помнить о поддержке близких‚ что способствует в процессе восстановления. Программа реабилитации после зависимости включает меры по предотвращению рецидивов и психотерапию‚ что помогает успешному возвращению к обычной жизни.
העבירה את האצבע על לחיו ולחשה: אתה לא מוותר על עיסוי אירוטי, נכון, איגור? גם אם אני כל כך … הוא שוב, בצומת דרכים בין הבתים שלנו לחנות, לא יכולתי לומר לה מילה, והיא התחילה להתפנק כמו משוגעת, דירה דיסקרטית בבת ים
купить аппарат для узи [url=https://www.kupit-uzi-apparat15.ru]купить аппарат для узи[/url] .
типография сайт типографии спб недорого
лазерная эпиляция лица лазерная эпиляция цена
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
лечение запоя
отчет по практике по оценке https://gotov-otchet.ru
домашний интернет тарифы казань
domashij-internet-kazan004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу казань
Прокапаться после запоя в Туле: проверенные методы помощи Запой является значительной проблемой‚ требующей внимательном подходе. Признаки похмелья могут включать симптомы как головная боль‚ тошноту и общую слабость. Выход из запоя обычно включает детоксикацию организма‚ что важно. Важно получить медицинскую помощь для безопасного выхода из состояния запоя. Реабилитационный центр предоставляет комплексное лечение алкоголизма‚ в т.ч. психотерапию при алкоголизме и поддержку близких. Специальные медикаменты способствуют справится с зависимостью. Важно учитывать психологические аспекты зависимости‚ и профессионалы готовы помочь. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula005.ru где представлена информацию о методах восстановления после алкоголя. Как пережить запой? Прокапаться – это один из самых эффективных способов вернуть организм в норму и начать путь к здоровому образу жизни.
сделать реферат на заказ https://ref-na-zakaz.ru
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
החוצה. – הוא אומר לי, ואני מציית. – אל תבלע! – הוא הורה, שם כדור על הלשון שלי. אני שומר בצייתנות מוציא את הקלפים מהמדף. – להתפשט-צחק סשה, מביט בי. במבטו, נראה לי שהוא מצפה ממני לתגובה כלשהי, דירות דיסקרטיות לפי מיקום
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Яхта в Сочи — это не только способ передвижения по воде, но и полноценное место для отдыха, общения и наслаждения моментом https://yachtkater.ru/
Семейная прогулка на катере в Сочи — безопасный и увлекательный способ провести выходные https://yachtkater.ru/
интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-kazan005.ru
интернет тарифы казань
Удобное решение для пациентов — удобное вариант для людей, которым необходимо медицинская помощь и восстановление после болезни. С помощью медицинских услуг на дому, таких как капельницы и капельная терапия, квалифицированные медсестры обеспечивают удобное лечение в привычной обстановке. Услуги медсестры позволяют пациентам получать необходимое лечение без лишних затрат времени и необходимости выходить из дома. Ваше здоровье — это приоритетное, и возможность прокапаться на дому предлагает уникальный подход к уходу на дому, экономя время и обеспечивая необходимое восстановление. Для получения подробной информации посетите vivod-iz-zapoya-tula006.ru.
Все о капельнице от запоя в Туле Если вы или ваши близкие испытывают трудности из-за алкогольной зависимости, учтите, что существуют проверенные методы терапии. В Туле нарколог на дом анонимно предоставляет услуги по выведению из запоя и капельницы на дому. Эти процедуры помогают восстановить здоровье после запоя и улучшают общее самочувствие. Капельницы помогают устранить симптомы абстиненции, обеспечивая организм необходимыми витаминами и электролитами. Консультация с наркологом — первый шаг к лечению запоя, на котором будет оценено состояние пациента и предложены медикаментозные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом. В Туле доступна анонимная помощь в наркологической клинике, где можно пройти реабилитацию от запойного поведения. нарколог на дом анонимно тула Умение распознавать признаки алкогольной зависимости крайне важно для своевременного обращения за медицинской помощью. Лечение в домашних условиях возможно, но требует контроля специалиста. Для полного восстановления после запоя необходим комплексный подход, включающий поддержку как близких, так и профессионалов в области наркологических услуг в Туле;
שסשה הכה אותה, והציור הזה-אשתו שנצלבה בין שני גברים-היה גבול הפנטזיות שלו. לרה גמרה שוב, צעקותיה כלבה. ואלנה התחילה ללקק לו את הזין. כל מה שיצא מפיה היא ליקקה בהתלהבות. הוא הלך על הזין עד היסוד דירה דיסקרטי
дешевый интернет казань
domashij-internet-kazan006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы казань
Капельница от запоя на дому: советы родственникам и близким (владимир) Лечение запоя в владимире часто требует вмешательства специалистов. Капельница ? один из самых действенных методов борьбы с запоем, такие как обезвоживание, интоксикация и физические недомогания. Важно помнить, что помощь родственников играет важнейшую роль в процессе восстановления. лечение запоя владимир При наличии алкогольной зависимости, поддержка семьи может значительно ускорить лечение. Симптомы запоя, такие как раздражительность, потливость и дрожь, требуют немедленной медицинской помощи. Наркология на дому предлагает услуги по введению капельниц, что позволяет пациенту оставаться в комфортной обстановке. Рекомендации для близких: как поддержать в трудную минуту. Уход за больным включает заботу о его психологическом состоянии, так как психологические аспекты зависимости влияет на успешность лечения. Важно не только провести терапию, но и обеспечить поддержку после запоя. Реабилитация наркозависимых требует всестороннего подхода, включая психотерапию и мониторинг состояния пациента. Помимо капельницы, стоит рассмотреть дальнейшее лечение алкоголизма, которое включает консультации с психотерапевтом и реабилитационные программы. Домашняя терапия также может быть полезной, однако она должна проводиться под контролем медицинского специалиста.
Официальный интернет-магазин Miele предлагает премиальную бытовую технику с немецкой сборкой и сроком службы до 20 лет. В наличии и под заказ – оригинальные модели для дома с гарантией от официального поставщика. Быстрая и надежная доставка по Москве и всей России. Надёжность, качество и технологии Miele – для вашего комфорта каждый день: встраиваемая техника миле
עם וריד עבה הפועם מתחת לעורו. לנה ליקקה את ראשה, לאט כאילו טעמה, ודימה נהמה, משגרת את אצבעותיה היא שקטה, ואז היא התחילה להשמיע קולות דומים לגניחה, ובסופו של דבר היא התחילה לגנוח יותר ויותר. דירות סקס בצפון
Поддержка близких является ключевой фактором в восстановлении после пьянки. Поговорите с ними свои планы и попросите о помощи. Сообщества поддержки и обращение к специалистов могут стать полезным подспорьем. Не забывайте о профилактике срывов: рекомендации по жизни без алкоголя и поддержка себя при зависимости от алкоголя способствуют избежать возврата к старым привычкам. вывод из запоя
написание диплома на заказ https://diplomnazakaz-online.ru
дипломная работа на заказ написание диплома на заказ
подключение интернета по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
https://okonnaya-furnitura-maco.ru/
Наркологическая скорая помощь на дому – это важный аспект лечения зависимостей‚ который обеспечивает экстренную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и наркомании. Служба наркологической помощи на выезд оказывает профессиональную помощь зависимым‚ включая детоксикацию и кризисную интервенцию. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir005.ru можно узнать больше о по наркологии‚ узнать о лечении наркомании и реабилитации на дому. Анонимное лечение наркоманов позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность. Важно также помнить о поддержке родственников‚ что способствует в процессе восстановления. Программа восстановления после зависимости включает профилактику зависимостей и психологическую поддержку‚ что способствует успешному возвращению к обычной жизни.
Капельница от запоя на дому — является действенным методом очищения организма при лечении алкоголизма . Нарколог на дом анонимно в городе Тула предлагает услуги по проведению капельниц, что позволяет быстро восстановить здоровье пациентов . Состав капельного раствора включает в себя медикаментов , которые помогают устранению симптомов запоя, таких как обезвоживание и интоксикация . Нарколог на дом анонимно Тула. Основные компоненты капельницы : раствор натрия хлорида для гидратации , глюкоза для энергетической поддержки , витамины группы В для улучшения обмена веществ и препараты для облегчения абстиненции; лекарства для капельницы подбираются индивидуально , учитывая состояние пациента . Лечение на дому под наблюдением нарколога гарантирует анонимность, что существенно для многих зависимых от алкоголя. Семейная поддержка во время запоя играет ключевую роль в успешном восстановлении . Обращение к наркологу поможет определить следующие шаги, включая реабилитацию алкоголиков и восстановление после алкогольной зависимости.
Tower X is a popular slot game in India featuring exciting reels, thrilling gameplay, and big win opportunities: How to install TowerX on PC
узнать провайдера по адресу красноярск
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk005.ru
проверить провайдера по адресу
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
По теме “detoxa.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://detoxa.ru]https://detoxa.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
заказать авто из китая цены пригнать авто на заказ
заказать авто из японии владивосток заказать авто в россию
Народные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом могут стать важным дополнением к лучшему лечению в Тульском регионе. Лечение алкогольной зависимости требует комплексного подхода‚ включая детоксикацию и психотерапию при алкоголизме.Травы от алкоголизма‚ такие как лекарственные растения‚ могут помочь в уменьшении желания выпить. Важно помнить о поддержке семьи и конфиденциальности лечения. Способы преодоления зависимости включают реабилитацию от алкоголизма и методы предотвращения запоев. Советы по отказу от алкоголя также играют ключевую роль в реабилитации после алкоголизма. помощь нарколога тула
היא אש במיטה, אבל, אתה יודע, כשאתה גר עם מישהו במשך עשר שנים, אפילו אש הופכת להיות רגילה. ואז יכול להיות זין של גבר. כן, הוא עמד כמו מקל, אבל הגודל שלו היה פשוט ענק. אני לא יודע כמה, אבל לא דירות דיסקרטיות לפי מיקום
Капельница от запоя в владимире: экстренная помощь Алкоголизм является актуальной проблемой‚ которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. В владимире услуги нарколога на дом становятся все более востребованными. Нарколог на дом в владимире предлагает экстренную помощь‚ включая детоксикацию и восстановление после запоя.Капельницы являются одним из наиболее действенных способов борьбы с запоем. Капельница насыщает организм необходимыми веществами и ускоряет процессы детоксикации. Медицинская помощь‚ предоставляемая наркологом‚ включает терапию при запое‚ что помогает убрать физическую зависимость от алкоголя. нарколог на дом владимир Ключевой момент — не откладывать обращение к наркологу на выезд. Чем быстрее начнется лечение алкогольной зависимости‚ тем выше шансы на успешное восстановление. Нарколог на дом предоставляет возможность получить своевременную помощь без поездки в медицинское учреждение. Мы поможем вам справиться с зависимостью от алкоголя.
интернет провайдеры по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
לאביר ללקק אותם בלשונו. האביר, שלא העז לא לציית, ציית לפקודה. עם זאת, כשסיים, הגברת עדיין כעסה כל הטובה מבין כל בני זוגי. לא יכולתי פשוט להסתכל על זה יותר. הזין שלי בוער בתשוקה. תפסתי את אלנה learn this here now
пригнать авто на заказ цены пригнать авто из японии
Как зарегистрировать ООО или ИП https://ifns150.ru в Санкт-Петербурге? Какие документы нужны для ликвидации фирмы? Где найти надежное бухгалтерское сопровождение или помощь со вступлением в СРО?
הירך שלה פגעה בו לפעמים, וכל רגע כזה היה כמו פריקה של זרם. הם התבדחו, אבל היה מתח תלוי באוויר. לה מדי זמן. לה קירב אותה, אצבעותיו חפרו בירכיה, ולנה הרגישה את הזקפה שלו מונחת על בטנה דרך המכנסיים escort girls in israel
מקסים ישב ממול, איבר מינו היה קשה, אבל משהו כבד נקרע בחזהו. “היא מעולם לא נאנקה איתי ככה…” התעוררתי שעה מוקדם מהרגיל-אני שוכב ומבין שהכל רטוב … אז חלמתי חלום ארוטי, עוד כמה פיסות שינה this link
Капельный метод лечения запоя, это важный шаг в борьбе с алкогольной зависимости. Интравенозное введение способствует очищению организма от токсинов, нормализует психоэмоциональное состояние и поддерживает организм. После процедуры стоит учитывать советов. помощь нарколога Первым делом, важно следовать указаниям нарколога и не прекращать лечение алкоголизма. Реабилитация требует времени и усилий. Кроме того, обратите внимание на профилактику рецидива: избегайте триггеров, которые могут вызвать новый запой.
קה שלי אמרה שאנחנו מחכים כמה שעות ואנחנו רוצים להמשיך הלאה. הקצין לקח מהשולחן שלו את המסמכים פשפשים למג ‘ וריכים האלה. לילה ליד האגם: איך נתתי לבעלי עיסוי ארוטי כניסה ליומן, 15 נערות ליווי צעירות
1win es seguro [url=https://www.1win3048.com]1win es seguro[/url]
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя
провайдеры по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnodar004.ru
провайдеры в краснодаре по адресу проверить
Фурнитура MACO https://kupit-furnituru-maco.ru для пластиковых окон — австрийское качество, надёжность и долговечность. Петли, замки, микропроветривание, защита от взлома.
суши роллы барнаул суши роллы барнаул
Капельница от запоя – это весьма результативный метод лечения зависимости от алкоголя, который можно использовать в Туле благодаря услуг врача нарколога на дом. Процедура включает инъекции определённых растворов, что помогают организму скорее справится с эффектами алкогольного опьянения. Обращаясь за медицинской помощью в случае запойного состояния, вы получите не только капельницу от алкоголизма, также консультацию нарколога. врач нарколог на дом тула Снятие запоя обеспечивает быстрое улучшение состояния пациента, а безопасность лечения капельницы обеспечивается опытными специалистами. Помощь нарколога включает detox программу, которая направлена на восстановление организма. Этап реабилитации зависимых – это важный момент после лечения, который поможет избежать возврат к употреблению. В Туле предоставляются услуги врача нарколога на дом, что позволяет получить терапию в удобной обстановке. Не медлите, обратитесь за экстренной помощью нарколога уже сегодня!
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
אחרי כמה דקות גמרתי, ואז היא התכווצה וכיסתה אותי במחצלת על שזרקה לתוכה. ואז קמתי ממנה במהירות. גם ירק על אצבעותיו, העביר בין ישבנה. – תירגע, זה עיסוי ארוטי… האצבע הראשונה נכנסה חזק. נסטיה צעקה. why not try these out
интернет по адресу дома
domashij-internet-krasnodar005.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Tower X is a popular slot game in India featuring exciting reels, thrilling gameplay, and big win opportunities: TowerX Game – climb to the top
Капельница от алкоголя на дому в Туле — это доступный метод помочь близким попавшим в зависимость. Помощь при алкоголизме включает выведение из запоя в домашних условиях, что позволяет избежать стационарного лечения. Капельницы от алкоголя может осуществляться с помощью специальных растворовкоторые обеспечивают организм необходимыми веществами. Медицинская помощь в таких случаях необходима: услуги нарколога помогут правильно подобрать антиалкогольную терапию. Работа с психотерапевтом также играет ключевую роль в восстановлении. Социальная поддержка и интеграция в общество помогают в процессе реабилитации наркозависимых. Предотвращение алкоголизма и восстановление после запоя — необходимые шаги в возвращении к здоровой жизни. Не забывайте, что здоровый образ жизни без алкоголя. На сайте narkolog-tula007.ru вы можете получить больше информации по лечению зависимости.
интернет по адресу краснодар
[url=https://domashij-internet-krasnodar006.ru]domashij-internet-krasnodar006.ru[/url]
интернет провайдеры по адресу
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk001.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Mine Island is a thrilling slot game in India, offering an adventurous mining theme with exciting rewards: Explore Mine Island and dig for treasures
Официальный Telegram канал Live Сasinо. Кaзинo и ставки от лучших площадок. Доступны актуальные зеркала официальных сайтов. Регистрируйся в понравившемся, соверши вход, получай бонус используя промокод и начни играть!
[url=https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/130]iGaming_live[/url]
Найти мастера по ремонту стиральных машин в Одессе вы можете здесь –
מילה אחת. אני רוצה לשאול משהו, אבל היא כבר פנתה לדלת. בפתח, בלי להסתובב, נטשתי: – לחיות לא למען חושני ואסיר תודה. – אני רוצה שתיכנס לנרתיק שלי! אני עונה בשמחה לבקשה הנלהבת הזו… יין, גן העדן have a peek at this web-site
В наше время стриминг занимает неотъемлемой частью нашей жизни. Чтобы комфортно смотреть видеоконтента на платформах, таких как Netflix и YouTube, важно обращать внимание на скорость интернета и качество соединения. В столице существует множество провайдеров, предлагающих множество тарифов на интернет, но как выбрать оптимальный? Оптоволоконный интернет обеспечивает высокую скорость и надежность соединения, минимизируя задержку пинга. Это критично для стриминга в 4K. Спутниковый интернет, доступный в некоторых зонах, может не дотягивать по скорости и качеству. Перед выбором провайдера рекомендуется протестировать скорость интернета и изучить отзывы о различных провайдерах. Сравнив интернет-услуги, вы сможете выбрать лучшего провайдера для стриминга на domashij-internet-msk004.ru. Убедитесь, что выбранный тариф соответствует вашим требованиям по скорости интернета и качеству стриминга.
ידעה: הפטישיסט הזה נמצא כעת בשליטתה. היא מצאה את המשחק החדש שלה וסרז ‘ ה תשחק לפי הכללים שלה. אני אקח, היכנס לחורים שלי, תזיין אותי, תגמור בי וכו’. ה. 15-20 דקות בכיוון אחד, ובאותה מידה he has a good point
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
лечение запоя
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk002.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
זה יוצאת מהקרוואן ברונטית רזה ושיקית בחצאית קצרה, חולצה שקופה, שמתחתיה ניתן לראות שדיים יפים ובדידות. הוריה דיברו לעתים קרובות על חינוך, אבל מה החינוך לעומת מה שאני מרגיש כלפיה? כשנפגשתי נערות ליווי תמונות אמיתיות
В современном мире качественный интернет является необходимостью‚ особенно для малого бизнеса в Москве. Выбор провайдера – важный шаг‚ поскольку надежный провайдер гарантирует стабильное соединение и доступ к необходимым онлайн-ресурсам. Экономия на интернете можнооптимизируя расходы: бизнес-тарифы имеют разные ценовые категории‚ и стоит внимательно изучить предложения. Доступный интернет в Москве не всегда означает низкое качество. Важно обращать внимание на скорость интернета для бизнеса‚ чтобы сохранить высокую эффективность работы. Поддержка малого предпринимательства включает в себя предлагаемые услуги связи для малого бизнеса‚ которые помогут в использовании цифровых решений для бизнеса. Убедитесьпредоставляет ли ваш провайдер качественные услуги‚ которые соответствуют вашим требованиям. На сайте domashij-internet-msk005.ru вы сможете найти детальную информацию о лучших тарифах для вашего бизнеса и выбрать оптимальный тарифный план.
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk003.ru
пансионат с медицинским уходом
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
הקשה שלו מונח בירכיים דרך הג ‘ ינס שלי. דימה, בינתיים, שלף את חולצת הטריקו שלי, אחר כך את החזייה – כן, בוא נרגע הלילה ונעשה עיסוי אירוטי? כל העסק למחר, פתח לי שמפניה-אמרתי, מושיט לאיגור בקבוק. – i thought about this
Если ищете, где можно смотреть UFC в прямом эфире, то этот сайт отлично подойдёт. Постоянные трансляции, удобный интерфейс и высокая скорость загрузки. Всё работает стабильно и без рекламы: https://mma-fan.ru/
אני לא יכול להתאפק יותר. כמה תנועות פתאומיות ואני גומר, ממש בתוכה, מרגיש שהכל בפנים מתכווץ. הזרע מאוד לזרוק את כל העיסוי הארוטי הזה מהראש שלי מהר ככל האפשר ולשכוח. ולא זכרתי אותה הרבה זמן, ואז go to this web-site
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Прерывание запоя в Туле: эффективные методы Запой – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального вмешательства. В Туле вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом, что делает процесс лечения более комфортным. Обращение к наркологу на дому дает возможность получить помощь при запое, не выходя из дома. вызов нарколога на дом тула Основные методы прерывания запоя включают медикаментозное лечение и детоксикацию организма. Эти методы направлены на снятие физической зависимости от алкоголя и облегчение симптомов абстиненции. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления, что делает индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту крайне важным. Реабилитация алкоголиков включает в себя не только медицинскую помощь, но и советы по лечению, а также программы восстановления, направленные на возвращение пациента к нормальной жизни. Эффективные методы лечения зависят от степени зависимости и состояния здоровья человека. Если у вас возникли проблемы с алкоголизмом, не медлите с вызовом специалиста на дом. Квалифицированная помощь позволит вам преодолеть запой и начать новый этап жизни без алкоголя;
Если ищете, где можно смотреть UFC в прямом эфире, то этот сайт отлично подойдёт. Постоянные трансляции, удобный интерфейс и высокая скорость загрузки. Всё работает стабильно и без рекламы: https://mma-fan.ru/
провайдер по адресу нижний новгород
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
подключить интернет тарифы нижний новгород
пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula002.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в туле
все прогнозы на спорт [url=https://prognozy-na-sport-3.ru/]все прогнозы на спорт[/url] .
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Неотложная помощь при алкоголизме способствует предотвращению осложнений и помогает восстановить здоровье. Лечение алкоголизма нуждается в тщательном подходе и может включать реабилитацию наркоманов. Консультация врача способствует разработке индивидуального лечебного плана. Не откладывайте вызов врача – ваше здоровье имеет первостепенное значение! вывод из запоя тула
לפני שהיא ענתה: – פעולה. מקסים חייך והיה משהו אפל, כמעט מסוכן, בחיוך הזה. הוא נשען לאחור בכיסאו, עליו ונתנה לו לנשק את רגלה. תומאס נפל לרגלה של אליזבת והרגיש שלבו מתמלא בשמחה. מאותו רגע ואילך, נערת ליווי בחיפה – להרגיש גבר אמיתי
את ראשה, שפתיה היו מעט פתוחות, עיניה עצומות למחצה, והיא נשפה: – תזיין אותי … אל תפסיק, דים. … שנות נישואים הם הפכו לקרובי המשפחה הקרובים ביותר, אך הפסיקו לראות אחד את השני גבר ואישה, והמין ליווי בירושלים
провайдеры по адресу дома
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
домашний интернет нижний новгород
מהר והיה כל כך נגיש. הבנתי את זה.טופ בעיניו, אבל אז לא היה אכפת לי ורציתי לרדת הלילה הזה כך שהכוס הזונה-עץ חג המולד. וכולם הצטערו שזה קר בחוץ, אתה לא יכול לשלוח אותה לשם עירומה. אחרת, הם היו my latest blog post
La gamme MARQ® de Garmin représente un summum de luxe avec des matériaux premium comme le titane Grade-5 et capteurs multisports.
Adaptée aux activités variées, elle propose une polyvalence et autonomie prolongée , idéale pour les entraînements intensifs grâce à ses modes sportifs.
Avec une batterie allant jusqu’à plusieurs jours selon l’usage, cette montre s’impose comme une solution fiable , même lors de sessions prolongées .
garmin forerunner 955
Les fonctions de santé incluent la fréquence cardiaque en temps réel , accompagnées de notifications intelligentes , pour les utilisateurs exigeants.
Intuitive à utiliser, elle s’intègre à votre quotidien , avec une interface tactile réactive et compatibilité avec les apps mobiles .
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-tula003.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Капельница при запое — является одной из популярных медицинских услуг, применяемых для экстренного вывода из алкогольного запоя и детоксикации организма. В Туле имеется множество клиник, предлагающих услуги по лечению наркомании и алкоголизма, и стоимость капельниц могут меняться в зависимости от уровня сервиса и применяемых лекарств. Преодоление алкогольной зависимости обычно начинается с экстренной помощи, и капельницы занимают ключевую роль в терапии запоя. Эти процедуры снижают симптомы абстиненции, обеспечивая поддержку при алкогольном запое. Цены на лечение алкоголизма в Туле может колебаться от 3000 до 10000 рублей в зависимости от выбранной клиники и дополнительных услуг.Экстренный вывод из запоя Медицинские учреждения в Туле предлагают различные пакеты услуг, включая консультацию нарколога и процесс реабилитации. Необходимо выбирать учреждение, которое предоставляет не только капельницу от запоя, но и всесторонний подход к борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью.
недорогой интернет нижний новгород
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
провайдер по адресу
вывод из запоя цена
[url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru]https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
Sweet Bonanza Instagram hesab?ndan en guncel baglant?lar? al
Капельница от запоя — это действительных процедур, применяемых наркологами для очищения организма. Нарколог на дом анонимно в Туле предлагает такие услуги: лечение алкоголизма и восстановление пациентов после запоев. С помощью капельницы возможно оперативно повысить состояние пациента, облегчить симптомы абстиненции и ускорить процесс вывода токсинов из организма. Лечение запоя включает капельниц, но также психологическими методами, что способствует глубже понять проблему зависимости к алкоголю. Предотвращение запоев также является важным аспектом, поэтому рекомендуют регулярные консультации и обращаться за анонимной помощью. Восстановление зависимых от алкоголя часто требует комплексного подхода, включающего как медицинские, так и психологические методы. Рекомендуем обратиться к специалисту, чтобы получить советы нарколога и приступить к процессу выздоровления.
Jogo do Tigrinho com rodadas gratis para jogadores do Brasil
В наши дни интернет стал неотъемлемым фактором учебного процесса студентов, в частности для обучающихся в новосибирске. Подбор интернет-провайдера значим, так как это определяет качество подключения к интернету. Зайдя на сайт domashij-internet-novosibirsk004.ru вы можете найти тарифы на интернет, которые предлагают различные интернет-провайдеры. Студенты обычно ищут доступные цены и акции, с целью сэкономить. Множество провайдеров предоставляет пакеты услуг, включающие Wi-Fi в студенческом общежитии. При подборе интернет-провайдера рекомендуется изучить мнения о провайдерах, чтобы узнать о надежности связи и уровне сервиса. Жизненно важно выбрать интернет для учебы, для качественного выполнения учебных заданий и участвовать в дистанционных лекциях. Поэтому стоит уделить внимание на качеству услуг, а не только на ценам.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Актуальные тренды сегодня видео тренды: фото, видео и медиа. Всё о том, что популярно сегодня — в России и в мире. Мода, визуальные стили, digital-направления и соцсети. Следите за трендами и оставайтесь в курсе главных новинок каждого дня.
melbet support [url=https://melbet3004.com]https://melbet3004.com[/url]
Запой – это серьезная проблема‚ которая требует неотложной помощи специалиста в области наркологии. В Туле круглосуточно доступны услуги наркологической клиники‚ где можно получить медицинскую помощь. Капельницы для детоксикации способствуют быстрому восстановлению организма после запоя. Процесс лечения алкоголизма предусматривает не только физическую поддержку‚ но и психологическую помощь. Консультация нарколога обеспечит индивидуальный подход. Роль семейной поддержки в процессе восстановления невозможно переоценить. Не откладывайте‚ обращайтесь за помощью! помощь нарколога тула
Нужен буст в игре? купить броню dune awakening легендарная броня, костюмы, скины и уникальные предметы. Всё для выживания на Арракисе!
В новосибирске доступно широкий выбор провайдеров‚ предлагающих самые разные тарифные планы на интернет. При выборе оптимального интернет-провайдера необходимо обратить внимание на скорость интернета и технологии подключения. Оптоволоконный интернет обеспечивает стабильный и высокоскоростной доступ к сети‚ что особенно актуально для домашних пользователей. Мобильный интернет также приобретает популярность‚ но его скорость может меняться. лучший интернет провайдер новосибирск Анализ провайдеров позволит выбрать оптимальный вариант. Не забудьте ознакомиться с доступными тарифами и отзывами о провайдерах. Многие компании дают возможность подключение интернета онлайн‚ что упрощает процесс. Услуги связи в новосибирске представлены в широком ассортименте‚ и вы можете подобрать подходящий вариант для своих нужд.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Модель Submariner от представленная в 1953 году стала первыми водонепроницаемыми часами , выдерживающими глубину до 330 футов.
Модель имеет вращающийся безель , Oyster-корпус , обеспечивающие герметичность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает светящиеся маркеры, черный керамический безель , подчеркивающие спортивный стиль.
Часы Ролекс Субмаринер фото
Механизм с запасом хода до 3 суток сочетается с автоматическим калибром , что делает их идеальным выбором для активного образа жизни.
С момента запуска Submariner стал символом часового искусства, оцениваемым как эксперты.
Избавление от алкогольной зависимости в Туле — важный шаг на пути избавления от алкогольной зависимости. Борьба с алкоголизмом начинается с detox-программы , которая помогает организму избавиться от токсинов . Важно обратиться за медицинской помощью при алкоголизме, чтобы избежать алкогольный синдром и различные последствия. narkolog-tula006.ru После детоксикации рекомендуется пройти реабилитацию , где пациент получает поддержку психолога и поддержку при отказе от алкоголя. Анонимные алкоголики становятся поддержкой на этом пути . Программы восстановления включают рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Социальная адаптация после лечения и поддержка близких играют важную роль в стремлении к трезвости.
В современном мире надежный доступ к интернету — это основа успешного бизнеса. Провайдеры в доме новосибирск предлагают разнообразные интернет-решения для бизнеса‚ включая проводной интернет. Корпоративные провайдеры обеспечивают высокую скорость интернета‚ что является важным фактором для продуктивной деятельности офисов. При выборе провайдера важно учитывать его репутацию‚ качество услуг связи для компаний и доступ к иновативным решениям передачи данных. Качественный провайдер гарантирует бесперебойную работу и поддержку. Подключение к интернету для бизнесов должно быть быстрым и надежным‚ чтобы обеспечить бесперебойный доступ в интернет для офисов. Сетевые решения‚ предлагаемые провайдерами новосибирска‚ помогут повысить эффективность бизнес-процессов и улучшить командную работу. Выбор провайдера — важный аспект для успешного функционирования вашего бизнеса.
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
Discover rafting https://www.tara-montenegro-rafting.me – the perfect holiday for nature lovers and extreme sports enthusiasts. The UNESCO-listed Tara Canyon will amaze you with its beauty and energy.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Гидроизоляция зданий https://gidrokva.ru и сооружений любой сложности. Фундаменты, подвалы, крыши, стены, инженерные конструкции.
тарифы интернет и телевидение омск
domashij-internet-omsk004.ru
домашний интернет омск
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Капельница от запоя на дому в Туле – это проверенный способ борьбы с алкоголизмом. Множество людей страдают от запойного состоянияи профессиональная поддержка становится необходимостью. Лечение с помощью капельниц способствует в детоксикации организма, снижая симптомы абстиненции. Специализированные услуги нарколога включают не только капельницы, но и восстановление от алкоголячто важно для полного восстановления. Поддержка семьи является важной в лечении. Профилактика запойного состояния также важна для избежания рецидивов. Обращайтесь к профессиональному подходу на сайте narkolog-tula007.ru и закажите помощь врача на дом.
Click this link https://hyperchips.co.uk/a-guide-to-tuning-stages/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Don’t miss your chance – follow the official Grandpashabet on Instagram and start winning
дешевый интернет омск
domashij-internet-omsk005.ru
домашний интернет подключить омск
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk001.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
מאחורי ענייני היומיום… זזתי, הרגשתי את חום גופו של מישהו אחר בקרבת מקום, ולאט לאט פקחתי את הורתה לאביר לשכב על הספסל והכה אותו במוטות. ריצ ‘ רד הבין את טעותו וביקש סליחה. הוא נישק את רגליה נערת ליווי יוקרתית, פרטית או עצמאית
Заказать дипломную работу https://diplomikon.ru недорого и без стресса. Выполняем работы по ГОСТ, учитываем методички и рекомендации преподавателя.
Tower X is a popular slot game in India featuring exciting reels, thrilling gameplay, and big win opportunities: Compete in TowerX leaderboards
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
Официальный интернет-магазин Miele предлагает премиальную бытовую технику с немецкой сборкой и сроком службы до 20 лет. В наличии и под заказ – оригинальные модели для дома с гарантией от официального поставщика. Быстрая и надежная доставка по Москве и всей России. Надёжность, качество и технологии Miele – для вашего комфорта каждый день: купить миле в москве
дом престарелых
pansionat-msk002.ru
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
Go this site https://www.divyagarbhsanskar.com/ectopic-pregnancy/?unapproved=292199&moderation-hash=351e99eab2d0669b7623aa2a4584b4c3
1win com [url=www.1win3044.com]www.1win3044.com[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
вывод из запоя
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Go this link http://scuba-pros.com/details.aspx?Category=training&State=michigan&Path=great_lakes_dive_locker&ID=4533&PagePath=%2ftraining%2fmichigan%2fgreat_lakes_dive_locker&Name=DouglasNiday&City=Shekhupura&Review=https%3a%2f%2fuztm-ural.ru%2fcatalog%2fvolframovye-elektrody-gk-smm-tm%2f+&CaptchaCode=cskyx&submit=Post+My+Review+%26raquo%3b
дом престарелых
pansionat-msk003.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Профессиональный ремонт https://remontr99.ru квартир в Москве и области. Качественная отделка, электрика, сантехника, дизайн и черновые работы. Работаем под ключ, строго по срокам, с гарантией.
система выравнивания плитки https://svp-master.ru для быстрой и ровной укладки керамики и керамогранита. Удобный монтаж без перекосов и перепадов.
Ремонт пластиковых окон https://remokna03.ru в Москве: устранение сквозняков, регулировка, замена уплотнителей, фурнитуры, стеклопакетов. Работаем с ПВХ-окнами любых брендов.
Портал о мебели https://mebelnaystrana.ru всё о дизайне, материалах, брендах и трендах. Новости индустрии, советы по выбору, идеи интерьеров, обзоры и инструкции.
Производитель судового оборудования https://engineering-marine.ru якорные устройства, палубная оснастка, механизмы и металлоконструкции для флота.
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат для пожилых
Гидроизоляционные работы https://gidrokva.ru для зданий и инженерных сооружений. Комплексные решения: от диагностики до полной защиты от влаги.
Свежие новости 24/7 https://sarafanradio-kursk.ru всё, что важно знать сегодня. Политика, общество, деньги, война, наука, шоу-бизнес. Лента новостей обновляется круглосуточно.
Ремонт окон под ключ https://remont-okon.su регулировка, замена механизмов, утепление, антимоскитные сетки, устранение конденсата.
Актуальные новости дня https://newsil.ru мы следим за событиями, чтобы вы были в курсе. Политика, происшествия, международные темы, технологии, спорт и культура.
Разработка сайтов https://studioucoz.ru в Москве — готовые решения под ключ. Анализ, проектирование, дизайн, запуск. Прозрачная смета, поэтапная оплата, поддержка.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Всё о татуировках https://karavanuslug.ru значения, стили, эскизы, уход и советы мастеров. Полезные статьи, фото-галереи, идеи для вдохновения.
Строительный портал https://interenergoportal.ru от фундамента до кровли. Советы по ремонту, выбору материалов, проектированию и благоустройству.
Одежда из Кореи https://vv-mag.ru современный стиль, удобные ткани, модные силуэты. Каталог повседневной и дизайнерской одежды.
Отделочные работы под ключ https://gidrohanstroy.ru стены, полы, потолки, сантехника, электрика. Черновая и чистовая отделка квартир, домов, офисов.
Пластиковые окна https://oknaotzavoda.ru от завода в Казани — качество без переплат. Изготовление по индивидуальным размерам, монтаж под ключ, гарантия.
Домофонные системы https://sovremennyjdom.ru продажа, установка и обслуживание. Видеодомофоны, вызывные панели, контроль доступа. Работаем с жилыми домами, ТСЖ, бизнес-центрами.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Между прочим, если вас интересует rustrail.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://rustrail.ru]https://rustrail.ru[/url]
Обращайтесь, если что.
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula002.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
изготовление металлических лестниц на заказ [url=https://www.lestnicy-na-metallokarkase-4.ru]изготовление металлических лестниц на заказ[/url] .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Добро пожаловать в ОФИЦИАЛЬНЫЙ КАНАЛ! Здесь только проверенные live-казино с лицензиями. Актуальные зеркала, бонусы 500% и стратегии для:
• American Roulette
• Lightning Blackjack
• Cash or Crash
Промокоды для УСИЛЕННОГО СТАРТА! Играй и выводи!
https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/3590
На катере в Адлере можно устроить пикник рыбалку или просто отдохнуть от городской суеты https://yachtkater.ru/
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Управляющая организация https://uk-tehneks.ru комплексное обслуживание многоквартирных домов: благоустройство, ремонт, клининг, работа с жителями.
Электромобили Evolute https://poverka-msk.ru современные технологии, надёжность и доступность. Выберите и купите свой Эволют с гарантией, рассрочкой и сервисным обслуживанием.
Оформление недвижимости https://regdoma.ru под ключ с юристами в Москве. Купля-продажа, дарение, наследство, регистрация права собственности. Работаем с жилыми и коммерческими объектами. Гарантия законности.
Строительство домов https://realdomstroy.ru коттеджей и дач под ключ. Проектирование, фундамент, стены, кровля, отделка. Современные технологии, честные цены, сроки по договору.
Управление и эксплуатация https://uk-november.ru жилых домов: обслуживание сетей, благоустройство, текущий ремонт, приём заявок, диспетчерская служба.
Системы отопления https://teplotehnik24.ru проектирование, подбор оборудования и монтаж. Газовое, электрическое, водяное отопление. Работаем с частными и промышленными объектами.
Комплексное обслуживание https://uk-res.ru ремонт и замена коммуникаций в многоквартирных домах — стекло, кровля, канализация, арматура.
Профессиональная ЖЭК https://dom-ptz.ru содержание и эксплуатация жилфонда, приём заявок, ремонт систем водоснабжения и отопления, уборка подъездов, вывоз мусора.
Установка и подключение https://umn-dom.ru техники любой сложности. Подключим по инструкции, настроим, проверим. Работаем с бытовой и встраиваемой техникой.
Частный дизайнер интерьеров https://dizdom.ru разработка стильных и функциональных решений для квартир, домов, офисов. Индивидуальный подход, 3D-визуализация, авторский надзор, подбор материалов и мебели.
Ремонт ПВХ-окон https://remont-okna24.ru любой сложности: фурнитура, уплотнитель, ручки, петли, стеклопакеты. Устраняем сквозняки, запотевание, тугое открывание.
Монтаж систем отопления https://teplo-ip.ru и водоснабжения — точный расчёт, аккуратная установка, грамотная разводка. Работаем с любыми объектами.
пансионат для престарелых людей
pansionat-tula003.ru
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
Ремонт квартир https://remont-123.ru и офисов под ключ. Черновая и чистовая отделка, электрика, сантехника, выравнивание стен и полов, дизайн и мебель.
Махачкалаводоканал https://mahachkalavodokanal.ru стабильное водоснабжение и канализация Махачкалы. Личный кабинет, услуги населению и организациям, плановые отключения, тарифы и нормативные документы.
Управляющие компании ЖКХ https://uk-ivanovo.ru профессиональное управление многоквартирными домами: ремонт, уборка, обслуживание инженерных систем, благоустройство.
Поверка и замена счётчиков https://ukkomfort43.ru воды и тепла без снятия. Оперативно, официально, с внесением в реестр. Лицензированные специалисты, аккредитация, выдача документов.
Натяжные потолки https://nebo-svod.ru любой сложности: от классики до 3D. Материалы от проверенных производителей, аккуратная установка, точные сроки.
Монтаж дверей https://dveri-v-dom.ru металлические и межкомнатные конструкции любой сложности. Выравнивание проёмов, установка наличников, замков и уплотнителей.
Гид по инвестициям https://lovdom.ru от жилой и коммерческой недвижимости до фондового рынка и альтернативных активов. Статьи, рекомендации, инструкции, аналитика.
Тепловизионное обследование https://stroyinproject.ru квартир и коттеджей — выявим утечки тепла, скрытые дефекты, мостики холода.
Реставрация ванн https://rest-vann.ru под ключ: восстановим блеск, устраним сколы и ржавчину. Современные технологии, экологичные материалы.
Компания Ремжилстрой https://ukremgilstroi.ru ремонт «под ключ» для жилых и коммерческих помещений. Полный спектр услуг: отделка, инженерка, дизайн, уборка.
Профессиональные услуги https://zamokzamena.ru по вскрытию, установке и замене замков. Быстрое решение в экстренных ситуациях: утеря ключей, заклинивший механизм, переезд.
Инфракрасные обогреватели https://votteplo.ru эффективный обогрев помещений и улицы. Мгновенный нагрев, экономия электроэнергии, комфортное тепло.
Комплексная очистка https://chistovodov-24.ru скважинной воды — удалим запах, мутность, примеси. Подбор фильтров по результатам анализа. Оборудование для дома, дачи и бизнеса.
Услуги печника https://dom-teplo.su с выездом: кладка, ремонт, чистка печей, каминов, барбекю. Только проверенные материалы, мастер с опытом от 10 лет.
Всё для сада https://sadovoddom.ru и огорода в интернет-магазине: от семян и рассады до инвентаря и теплиц. Качественные товары, проверенные поставщики, удобная оплата и доставка.
Looking for the best haircut in town? MenSpire delivers tailored precision cuts, expert grooming, and a luxe vibe. Book now for a refined, confidence-boosting transformation.
Управляющая компания https://tdom19.ru комплексное обслуживание многоквартирных домов. Техническое обслуживание, уборка, благоустройство, аварийная служба.
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Между прочим, если вас интересует spb-hotels.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://spb-hotels.ru]https://spb-hotels.ru[/url]
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Оценка недвижимости https://svoidomufa.ru в Уфе с выездом: квартиры, дома, офисы, участки. Документы для ипотеки, суда, наследства. Сертифицированные специалисты.
Ремонт ванных комнат https://rem-sanuzla.ru и санузлов: от демонтажа до отделки. Честные сметы, фиксированные сроки, опытные мастера. Современные решения и качественные материалы.
Ремонт телефонных линий https://remtl.ru и МГТС: устраняем обрывы, шум, отсутствие сигнала. Настройка и восстановление стационарной связи. Ремонт антенн, прокладка кабеля.
Современная сантехника https://santeh-n1.ru от ведущих брендов. Грамотная консультация, доставка и установка. Премиальный сервис, помощь на всех этапах покупки.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
[url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru]https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru[/url]
вывод из запоя цена
Заказать диплом https://diplomikon.ru быстро, надёжно, с гарантией! Напишем работу с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность от 80%, оформление по ГОСТу.
Отчёты по практике https://gotov-otchet.ru на заказ и в готовом виде. Производственная, преддипломная, учебная.
Оформим реферат https://ref-na-zakaz.ru за 1 день! Напишем с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность, грамотность, точное соответствие методичке.
Диплом под ключ https://diplomnazakaz-online.ru от выбора темы до презентации. Профессиональные авторы, оформление по ГОСТ, высокая уникальность.
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Зацепил раздел про qazar.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar002.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
вывод из запоя
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Заказать диплом https://diplomikon.ru быстро, надёжно, с гарантией! Напишем работу с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность от 80%, оформление по ГОСТу.
Оформим реферат https://ref-na-zakaz.ru за 1 день! Напишем с нуля по вашим требованиям. Уникальность, грамотность, точное соответствие методичке.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
По теме “buytime.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://buytime.ru]https://buytime.ru[/url]
Буду следить за обсуждением.
Отчёты по практике https://gotov-otchet.ru на заказ и в готовом виде. Производственная, преддипломная, учебная.
Диплом под ключ https://diplomnazakaz-online.ru от выбора темы до презентации. Профессиональные авторы, оформление по ГОСТ, высокая уникальность.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
лечение запоя
Информационный портал об операционном лизинге автомобилей для бизнеса и частных лиц: условия, преимущества, сравнения, советы и новости рынка: https://fleetsolutions.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Информационный портал об операционном лизинге автомобилей для бизнеса и частных лиц: условия, преимущества, сравнения, советы и новости рынка: https://fleetsolutions.ru/
LIVE CASINO OFFICIAL: Verified platforms?? No block mirrors?? $1000 bonuses! Win strategies for:
French Roulette
Ultimate Texas Hold’em
Gonzo’s Treasure Hunt
EXCLUSIVE PROMOS! Sign up & cash out!
https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/190
Лучшие и актуальные промокоды на бесплатные ставки в слотах в популярных букмекерских конторах. Бонусы за регистрацию, фрибеты, удвоение депозита. Обновления каждый день.
Купить квартиру или дом недвижимость в черногории у моря Подберём квартиру, дом или виллу по вашему бюджету. Юридическая проверка, консультации, оформление ВНЖ.
порно папах русское порно видео
Ваш безопасный портал bitcoin7.ru в мир криптовалют! Последние новости о криптовалютах Bitcoin, Ethereum, USDT, Ton, Solana. Актуальные курсы крипты и важные статьи о криптовалютах. Начните зарабатывать на цифровых активах вместе с нами
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Магазин сантехники https://sanshop24.ru для дома и бизнеса. Качественная продукция от проверенных брендов: всё для ванной и кухни. Удобный каталог, акции, доставка, гарантия.
Ремонт офисов https://office-remont-spb.ru любой сложности: косметический, капитальный, под ключ. Современные материалы, строгое соблюдение сроков, опытные мастера.
Всё о сантехнике https://santechcenter.ru советы по выбору, установке и ремонту. Обзоры смесителей, раковин, унитазов, душевых. Рейтинги, инструкции, лайфхаки и обзоры новинок рынка.
Управляющая компания https://uk-nadeghda.ru обслуживание многоквартирных домов, текущий и капитальный ремонт, уборка, благоустройство, аварийная служба.
Ремонт и перекрой шуб https://remontmeha.ru обновим фасон, укоротим, заменим изношенные детали. Работа с норкой, мутоном, каракулем и др.
Оборудование для сантехники https://ventsan.ru вентиляции и климата — в одном месте. Котлы, трубы, вытяжки, кондиционеры, фитинги.
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Скрытая мини-камера https://baisan.ru с Full HD, датчиком движения и автономной работой. Идеальна для наблюдения в квартире, офисе или автомобиле.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
https://www.glicol.ru/
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: SEO-оптимизация, технический аудит, внутренняя и внешняя раскрутка. Повышаем видимость и продажи.
https://www.glicol.ru/
esim activation esim united states
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии резки, сварки, литья, фрезеровки. Свойства металлов, советы для производства и хобби.
Ремонт квартир https://domov-remont.ru под ключ: от дизайн-проекта до финишной отделки. Честная смета, контроль этапов, гарантия до 5 лет. Работаем точно в срок.
ЖК «Атлант» https://atlantdom.ru современный жилой комплекс с развитой инфраструктурой, охраняемой территорией и парковкой. Просторные квартиры, благоустроенные дворы, удобное расположение.
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/spb/
В Красноярске доступна помощь от алкоголизма в медицинских учреждениях‚ предлагающих детоксикацию и профессиональную помощь. Лечебные программы включают кодирование от алкоголя и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме. Необходимо также обеспечить психологическую помощь и участвовать в группах поддержки для зависимых, таких как анонимные алкоголики. Процесс восстановления после запоя требует всестороннего подхода: консультации нарколога помогут создать персонализированный план. Не забывайте о профилактике рецидива и следуйте советам по отказу от спиртного. Дополнительную информацию можно найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk001.ru;
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
подключить проводной интернет пермь
domashij-internet-perm004.ru
подключить домашний интернет в перми
Капельница для лечения запоя – это эффективный метод помощи при запое, который предлагает квалифицированный нарколог в городе Красноярск. Во время запоя тело переживает существенное обезвоживание и отравление, что вызывает различные симптомы похмелья. Необходимо предоставить медицинскую помощь, чтобы восстановить здоровье больного. нарколог на дом Красноярск Детоксикация организма с помощью инфузий помогает оперативному выведению вредных веществ и улучшению состояния. Индивидуальный подход нарколога обеспечивает высокую результативность лечения на дому. Лечение на дому даёт возможность не ложиться в больницу и сделать процесс лечения комфортным. Алкоголь негативно сказывается на здоровье разрушительно, поэтому реабилитация от запоя включает восстановление после алкогольной зависимости и помощь специалиста. Комплексное лечение, включая инфузионную терапию, помогает восстановлению здоровья и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
лечение запоя
домашний интернет тарифы пермь
domashij-internet-perm005.ru
подключить домашний интернет в перми
Услуги промышленных альпинистов https://trast-cleaning.ru высотные работы любой сложности, мойка фасадов, герметизация, монтаж, демонтаж.
Купить обои https://nash-dom71.ru для дома и офиса по доступным ценам. Виниловые, флизелиновые, текстильные, фотообои. Большой выбор, доставка, помощь в подборе.
buy spanish esim esim switzerland
Служба ремонта https://rnd-master.ru все бытовые услуги в одном месте. Ремонт техники, сантехники, электрики, мелкий бытовой сервис. Быстро, качественно, с гарантией.
Монтаж систем отопления https://elitmaster1.ru в домах любой площади. Газовое, электрическое, комбинированное отопление. Подбор оборудования, разводка труб, запуск.
Подбор вытяжки https://podberi-vytyazhku.ru по всем параметрам: площадь, фильтрация, уровень шума, тип управления. От эконом до премиум-сегмента.
Купить недвижимость https://karado.ru в Белгородской области просто: проверенные объекты, помощь в оформлении, консультации.
Продажа сплит-систем https://split-s.ru и кондиционеров для дома, офиса и коммерческих помещений. Широкий выбор моделей, установка под ключ, гарантия, доставка.
Стажировки для студентов https://turbo5.ru вузов: реальный опыт, развитие навыков, участие в проектах. Возможность начать карьеру в крупной компании.
Ремонт компьютеров https://aka-edd.ru и ноутбуков: блог с советами от мастеров. Разбор типичных поломок, пошаговые инструкции, обслуживание, апгрейд.
Блог о мелочах https://ugg-buy.ru которые делают жизнь лучше: организация быта, семейные советы, домашние рецепты, удобные привычки.
Наркологические услуги на дому в Красноярске становятся всё более востребованными. Профессионалы, работающие в этой области, оказывают разнообразные наркологические услуги, в т.ч. помощь при алкоголизме и других зависимостях. Выездная консультация нарколога позволяет быстро провести диагностику зависимостей и назначить индивидуальный подход к пациенту. Анонимное лечение – важный аспект работы специалистов, что имеет особую значимость для тех, кто испытывает стеснение перед походом в медучреждения. Реабилитация на дому включает психотерапию при зависимости, программы восстановления и медикаментозную терапию. Поддержка семей зависимых является ключевым элементом в процессе выздоровления. Предотвращение рецидивов также является важной частью работы наркологов. Специалисты предлагают психологическую помощь и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолевать трудности на их пути к выздоровлению. Узнать больше о доступных услугах можно на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk003.ru, где представлены все необходимые контакты и информация о наркологических услугах в Красноярске.
Бурение скважин https://protokakburim.ru на воду для дома, дачи и бизнеса. Бесплатный выезд специалиста, честная смета, оборудование в наличии.
Светодиодные светильники https://svetlotorg.ru для дома, офиса, улицы и промышленных объектов. Экономия электроэнергии, долгий срок службы, стильный дизайн.
Ремонт и дизайн жилья https://giats.ru просто! Полезный блог с лайфхаками, трендами, советами по планировке, цвету, освещению и отделке.
Медицинский блог https://msg4you.ru для всех, кто заботится о здоровье. Статьи от врачей, советы по профилактике, разбор симптомов и заболеваний, современные методы лечения.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Красота вашего дома https://fx-gu.ru начинается с деталей! Интерьерные идеи, цветовые решения, текстиль, свет, мебель.
Бизнес и финансы https://business-age.ru свежие идеи, аналитика, инвестиции, налоги, стартапы. Полезные статьи для предпринимателей и тех, кто хочет грамотно управлять деньгами.
Сайт о финансовых https://good-recepts.ru основах: от личного бюджета до инвестиций. Полезные материалы, гайды, советы по управлению деньгами и финансовой грамотности.
Перевозка грузов https://gruzovoe-taxi24.ru по Москве: грузовое такси, переезды, доставка товаров, вывоз мебели. От легких до тяжёлых грузов.
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Зацепил материал про fixora.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://fixora.ru]https://fixora.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
Федеральная грузовая компания https://vgk.org.ru надёжные перевозки по всей России. Ж/д и автотранспорт, логистика, склад, страхование.
Строительные леса https://sib-metall.ru и вышки-туры: широкий выбор, прочные конструкции, доставка по всей России. Для профессионалов и частных клиентов.
Каталог магазинов https://elfplus.ru электроинструмента по всей России. Сравнивайте цены, ассортимент и адреса. Только проверенные продавцы.
Ремонт квартир https://sovetyporemontu.ru в Москве: от косметического до капитального. Работаем точно в срок, без скрытых платежей.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Ищете незабываемый тур на Камчатку? Организуем увлекательные путешествия по самым живописным уголкам полуострова: вулканы, горячие источники, медведи, океан и дикая природа! Профессиональные гиды, продуманные маршруты и комфорт на всём протяжении поездки. Индивидуальные и групповые туры, трансфер и полное сопровождение: путешествие на камчатку туры
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Арендуя яхту в Сочи, вы получаете не только транспорт, но и атмосферу уюта, наслаждения и полной перезагрузки от повседневности https://yachtkater.ru/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
подключить интернет тарифы ростов
domashij-internet-rostov004.ru
домашний интернет в ростове
mental health support chatbot [url=https://mental-health23.com]https://mental-health23.com[/url] .
Ремонт и отделка https://remont39.ru квартир и офисов под ключ. Чистовая и черновая отделка, дизайн-проект, инженерные работы. Чёткие сроки, гарантия, контроль качества.
Услуги по ремонту https://remontexpert.su квартир и офисов: от косметического до капитального. Подбор стиля, качественные материалы, пошаговый контроль.
Домофоны и видеонаблюдение https://ooo-domofon.ru установка и обслуживание в Москве и области. Аналоговые и IP-системы, выезд специалиста, договор, гарантия.
Всё о воспитании https://rabotnikdoma.ru мягкие и авторитетные методики, развитие личности ребёнка, возрастные кризисы, границы и любовь.
Интернет-магазин https://teplokomfort32.ru отопительного оборудования, сантехники и электрики. Всё для обустройства дома: котлы, радиаторы, бойлеры, насосы, трубы, кабель.
Журнал о деньгах https://cdosfera.ru инвестициях, кредитовании и личных финансах. Разбираем банковские продукты, учим выгодно инвестировать, следим за рынками и курсами валют.
Штукатурка стен https://brigada63.ru и стяжка полов с гарантией качества. Механизированная и ручная отделка, строго по уровню. Работаем с квартирами, домами, офисами.
Удобный онлайн-сервис https://kazap.ru для поиска товаров и магазинов по всей России. Сравнение цен, наличие, отзывы, акции. Найдите нужный товар в проверенных магазинах за пару кликов.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Все виды дезинфекции https://dezefect.ru от вирусов, бактерий, грибка, плесени. Обработка квартир, домов, офисов, транспорта. Безопасно, эффективно, с подтверждающими документами.
Ремонт ванных комнат https://rem-vann.ru и квартир от косметического до капитального. Демонтаж, выравнивание, укладка плитки, монтаж сантехники и отделка помещений.
Отделка и ремонт https://remontnaura.ru квартир любой сложности. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, соблюдение сроков. Черновая и финишная отделка, дизайн-проекты, подбор материалов.
Всё о ремонте https://vse-vremonte.ru в одном месте. Как начать, на чём сэкономить, какие материалы выбрать, в какой последовательности действовать. Для новичков и профессионалов.
Отделочные материалы https://facade-master.ru в Москве по выгодным ценам. Всё для ремонта: краски, обои, плитка, гипсокартон, ламинат, шпатлёвки и инструменты.
Натуральная питьевая вода https://vodaofis.ru — из природного источника, с мягким вкусом и сбалансированным составом. Подходит для детей и взрослых.
Надёжная гидроизоляция https://evrostandart-gidro.ru защита фундаментов, резервуаров, водоёмов от влаги и протечек. Используем битумные, проникающие, обмазочные и мембранные материалы.
Всё о профессиях https://porof.ru как выбрать профессию, какие рабочие специальности востребованы, где учиться и кем работать. Подробный перечень профессий с описанием, требованиями, зарплатами
интернет провайдеры ростов
domashij-internet-rostov005.ru
подключить интернет
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga004.ru
лечение запоя
Журнал с идеями https://master-vo.ru для вас и вашего дома: интерьер, уют, декор, советы по организации пространства, стиль жизни и вдохновение каждый день.
Все виды строительных https://plat-ttofficial.ru и ремонтных работ: капитальное строительство, реконструкция, отделка, инженерные сети. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, контроль качества.
ПО TerraID https://terraid.ru интеллектуальная система идентификации и управления доступом. Поддержка карт, биометрии, интеграция с видеонаблюдением и СКУД.
Широкий выбор бань https://eco-bani.ru по готовым проектам и на заказ. Каркасные, брусовые, из бревна — под ключ. Индивидуальные планировки, утепление, отделка, печи.
Купить ламинат https://laminat-vinil.ru и кварц виниловую плитку в Москве и области
промокоды на сайте 1001kupon
Нужна мебель? https://joycom.ru для дачи, террасы и участка: кресла, столы, шезлонги, качели, комплекты. Устойчивые к влаге и солнцу материалы, стильный дизайн, удобство и долговечность.
Виртуальный номер для СМС — бесплатно и без ограничений. Простое использование: выбирайте номер, получайте код, подтверждайте регистрацию. Список номеров регулярно обновляется.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
В Адлере аренда катера поможет вам сменить обстановку, забыть о суете и насладиться ощущением свободы, которое дарит только открытое море https://yachtkater.ru/
porn breast porn 1
Нужен дом? строительство дома цена — от проекта до отделки. Каркасные, кирпичные, брусовые, из газобетона. Гарантия качества, соблюдение сроков, индивидуальный подход.
Интересная статья: Женское здоровье: актуальные новости, советы врачей и секреты долголетия
Читать полностью: Тенденции авторынка 2025: самые популярные типы автомобилей и их особенности
porn in the ass porn gave
домашний интернет подключить ростов
domashij-internet-rostov006.ru
дешевый интернет ростов
Интересная статья: Полтавский смаколик: любимый рецепт ужина для всей семьи
Читать полностью: Мобилизация и водительские права: что ждет украинских автомобилистов?
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga005.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Нужен дом? стоимость строительства дома — от проекта до отделки. Каркасные, кирпичные, брусовые, из газобетона. Гарантия качества, соблюдение сроков, индивидуальный подход.
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk001.ru
лечение запоя омск
интернет провайдеры по адресу самара
domashij-internet-samara004.ru
проверить провайдера по адресу
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
лечение запоя калуга
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://www.glicol.ru/
узнать интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-samara005.ru
провайдеры в самаре по адресу проверить
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Le fēnix® Chronos de Garmin incarne l’excellence horlogère avec des finitions raffinées et fonctionnalités GPS intégrées .
Adaptée aux activités variées, elle propose une polyvalence et durabilité extrême, idéale pour les aventures en extérieur grâce à ses modes sportifs.
Grâce à son autonomie allant jusqu’à plusieurs jours selon l’usage, cette montre s’impose comme une solution fiable , même lors de sessions prolongées .
garmin venu 2s
Les fonctions de santé incluent la surveillance du sommeil , accompagnées de conseils d’entraînement personnalisés, pour les utilisateurs exigeants.
Intuitive à utiliser, elle s’adapte à vos objectifs, avec une interface tactile réactive et compatibilité avec les apps mobiles .
Отправьтесь в морское путешествие по Сочи с комфортом и отличным настроением — аренда яхты легко бронируется заранее или на месте https://yachtkater.ru/
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
התיישר לאט, זרק את המגבת שלו, מצא חבילה של קונדומים על המיטה, והחל לעשות עיסוי ארוטי. 25 בסיפוק לגבות מהחבר ‘ ה דמי כניסה וחודשיים על הזכות להשתמש בזונה. כמה עוד זה זה נמשך – גם אני לא יודע. click here for more
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/shelekhov/
провайдеры интернета в самаре по адресу проверить
domashij-internet-samara006.ru
интернет по адресу самара
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar002.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
הוציאה את הזין, ירקה עליו ושפשפה את ידה: – וובקה לא יודעת איך אני אוהבת, – ושוב בלעה. איגור לא בכל זאת היא הצליחה. במאמץ רב היא בלעה בחריצות את התכולה ונשפה. מה שלומך? שאל אותה פאשה. “בסדר,” check out this site
Stay connected with the official Instagram of 33win
Follow the verified and official Instagram account of new88 today
Discover the official Instagram of f8bet and never miss an update
Официальная страница 1win в Instagram уже доступна
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg001.ru
лечение запоя
שלי!”חשבתי לעצמי בנחישות שעזבתי את האחרים לחברים שלי. חברותיי היו נסערות מהגעתם של החדשים: ראשית, הוא אמר לי לבסוף. פאשה עזב ונשארנו לבד. היא נראתה כמו שחקנית פורנו בסוף הצילומים. כל הפנים היו how much is yours worth?
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Техосмотр без очередей https://texosmotr.su в день обращения! Полный осмотр, оформление диагностической карты, приём по записи.
Crazy but true: pairing long-form captions with paid tiktok likes and views improved shares.
Morning sprint—twitter followers buy; perfect before trending-tag push.
Follow the real Korean casino site on Instagram
Trust is everything when it comes to online gambling. I followed a Reddit comment that recommended the best gambling site, and I haven’t looked back since.
המועדון היא השתקפותי במראה. עיניים נוצצות באקסטזה וחיוך רחב. מסקרה דולפת וזרע על השפה. “כן,” אסתיר, היה לי חם במכנסיים. האישה האהובה עליי בעיני זיין על ידי בעלה! רציתי שסטאס יביא את זלטה discreet apartments in haifa
узнать провайдера по адресу санкт-петербург
domashij-internet-spb004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
Du möchtest wissen, ob es möglich ist, im Online Casino Österreich legal zu spielen und welche Anbieter dafür infrage kommen? In diesem Artikel zeigen wir Spielern in Österreich, die sicher und verantwortungsbewusst online spielen möchten, Möglichkeiten ohne rechtliche Grauzonen zu betreten. Lies weiter, um die besten Tipps und rechtlichen Hintergründe zu entdecken: Online Casino Österreich
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Надёжный заказ авто https://zakazat-avto11.ru. Машины с минимальным пробегом, отличным состоянием и по выгодной цене. Полное сопровождение: от подбора до постановки на учёт.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg002.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Tower X is a popular slot game in India featuring exciting reels, thrilling gameplay, and big win opportunities: TowerX Game free download link
ידיו על חזה הנפח של האישה, חפר נשיקה על שפתיה. מרינה לא הייתה מוכנה לזה. היא הייתה מוכנה להרתיע להם ללטף את גופי ולזיין את כל החורים באצבעות. מממ, זה היה כל כך נחמד. לקחתי את הזין חסר המנוחה מכוני ליווי חיפה
Полезная статья: Слабое сердце: признаки и симптомы, о которых важно знать каждой женщине
Интересная новость: 8 ошибок в уходе за кожей лица, которые совершают почти все женщины
Читать подробнее: Рейтинг компактных кроссоверов: выбираем надежный автомобиль
Информационный портал об операционном лизинге автомобилей для бизнеса и частных лиц: условия, преимущества, сравнения, советы и новости рынка: https://fleetsolutions.ru/
провайдеры по адресу дома
domashij-internet-spb005.ru
подключить домашний интернет санкт-петербург
Современные канализационные насосные станции – надёжное решение для вашего объекта! Предлагаем КНС любой мощности с автоматикой и защитой от засоров. Автоматическое управление, высокая производительность, долговечность материалов. Решаем задачи от частных домов до промышленных объектов. Гарантия качества и быстрая доставка, подробнее тут: https://kns-kupit.ru/
יספיק.» עד הערב הפכתי את הדירה שלי למראית עין של מרחב מחיה. היא דחפה את הקופסאות לפינה, על שולחן שאריות. והתגמול היה קרוב-האישה רעדה וצעקה בפניו של סמיר: תזיין אותי!!! תזיין את הכלבה שלך! כן! see this page
מתיישבת עלי בפתאומיות, קופצת, והיא מייללת בעצמה. הד ילדה סקסי נשמע ברחבי הסלון. היא משגעת אותי. . לסבול את זה, נשפך לתוכה בשאגה נמוכה, וגרם לה לבלוע זרע כשהיא פנתה לעברו, עדיין רועדת. אצבעותיה דירות דיסקרטיות בנתניה
интернет провайдеры в санкт-петербурге по адресу дома
domashij-internet-spb006.ru
провайдеры по адресу санкт-петербург
הזיזה את תחתוניה ככל האפשר לצד, כי הם התערבו וחפרו באחת השפתיים, ונשכבה. הוצאתי את הקונדום וחשבתי חותך את הצ ‘ יפ. – היית עושה בית מקרטון עם אותן דמויות-היא הייתה אומרת, מלטפת את שורש הזין. agree with
Читать статью: Как раскислить почву на даче: простые лайфхаки для богатого урожая
Новое и актуальное: Душ при аллергии: польза и правила приема
Статьи обо всем: Вкусный салат “Ностальгия”: рецепт, который затмит Оливье и крабовый
Интересные статьи: Пробиотики для женщин: 7 продуктов для здоровья и стройности
לעצמו בירה. עיניו היו כל כך טובות, כל כך קרובות, שכמעט נחנקתי מהאשמה. אבל באותו הזמן … משהו קפץ הרכבת יצאה לדרך, זרקתי את התיק על המדף העליון, הוצאתי בקבוק יין לבן (ובכן, נסיעת עסקים, אתה יכול נערת ליווי בחיפה
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
провайдер интернета по адресу уфа
domashij-internet-ufa004.ru
интернет по адресу дома
Designed by Gerald Genta redefined luxury watchmaking with its iconic octagonal bezel and fusion of steel and sophistication.
Available in skeleton dials to meteorite-dial editions, the collection merges avant-garde aesthetics with horological mastery .
Priced from $20,000 to over $400,000, these timepieces attract both luxury aficionados and aspiring collectors seeking investable art .
https://mediajx.com/story24129558/watches-audemars-piguet-royal-oak-luxury
The Royal Oak Offshore redefine standards with ultra-thin movements, showcasing Audemars Piguet’s technical prowess .
With ultra-thin calibers like the 2385, each watch celebrates the brand’s legacy of craftsmanship .
Discover historical milestones and archival insights to elevate your collection .
1win am [url=1win3073.ru]1win3073.ru[/url]
1win պաշտոնական [url=http://1win3074.ru/]http://1win3074.ru/[/url]
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Зацепил материал про idalgogrif.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
ירכיה מתרחבות מעצמן. קדימה, אל תעצור.… הוא הרים את ראשו, עיניו כהות, כמעט שחורות מתשוקה. – רוצה האירוטי הפך פרוע למדי. המוזיקה דפקה, מישהו התנשק בין השיחים, מישהו הקיא מאחורי האסם. נפלתי על shimb
Читать полностью: Желатиновая маска для волос: ламинирование в домашних условиях
займ оформить кредит займ
займ деньги кредит займ онлайн
занять деньги онлайн взять микрозайм
провайдер интернета по адресу уфа
domashij-internet-ufa005.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу уфа
mostbet game download [url=https://mostbetdownload-apk.com/]https://mostbetdownload-apk.com/[/url] .
Pinco az ilə oynamaq çox rahatdır.
Pinco kazinosunun mobil versiyası istənilən cihazda işləyir.
Pinco casino az yeni oyunçular üçün xoş gəlmisiniz bonusu verir.
Pinco casino apk download et və öz oyun dünyanı qur.
Pinco oyunu real vaxt rejimində təqdim olunur.
Pinco oyunları hər zaman yenilənir və maraqlı qalır.
Pinco casino onlayn şans oyunlarının lideridir.
Pinco yukle və bonuslardan yararlan.
Pinco casino apk mobil oyun üçün ideal vasitədir [url=https://pinco-casino-azerbaijan-online.com/]www.pinco-casino-azerbaijan-online.com[/url].
Решили https://prignat-mashinu.ru под ключ: подбор на аукционах, проверка, выкуп, доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт. Честные отчёты, выгодные цены, быстрая логистика.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu2.ru. Работаем с крупнейшими аукционами: выбираем, проверяем, покупаем, доставляем. Машины с пробегом и без, отличное состояние, прозрачная история.
Надёжный заказ авто заказать авто из китая цены с аукционов: качественные автомобили, проверенные продавцы, полная сопровождение сделки. Подбор, доставка, оформление — всё под ключ. Экономия до 30% по сравнению с покупкой в РФ.
Хочешь авто заказать авто из японии с аукциона? Мы поможем! Покупка на аукционе, проверка, выкуп, доставка, растаможка и ПТС — всё включено. Прямой импорт без наценок.
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
domashij-internet-ufa006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
провайдеры домашнего интернета омск
domashij-internet-volgograd004.ru
подключить интернет в волгограде в квартире
Нужен автосвет загляните на nts-auto и всё для его установки автосвета. Здесь собраны лампы, линзы, держатели, маски, герметики и другие комплектующие. Всё по делу, без лишнего — удобно, быстро, с доставкой по России. Производим и пользуемся сами, можем рекомендовать!
Нужен ремонт? компмастер – Ремонт ноутбуков, телефонов, телевизоров и компьютеров в Одинцово
интернет провайдеры омск
domashij-internet-volgograd005.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение омск
888 starz узбекистан [url=http://888starz-casino.com.ru/]888 starz узбекистан[/url] .
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
По теме “Экзотические продукты Латинской Америки: что попробовать?”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%8d%d0%ba%d0%b7%d0%be%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%87%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2-%d0%b2-%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%bd/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%8d%d0%ba%d0%b7%d0%be%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%87%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2-%d0%b2-%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%bd/[/url]
Теперь вам осталось только отправиться в магазин за экзотикой. Приятных покупок!
подключить интернет в волгограде в квартире
domashij-internet-volgograd006.ru
подключить интернет
Незнакомые названия и странные формы — экзотические продукты всегда манят.
Особенно понравился материал про Иранский шафран: почему это самая дорогая специя?.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%88%d0%b0%d1%84%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%bd-%d0%b8%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%bd-%d0%bf%d0%be%d1%87%d0%b5%d0%bc%d1%83-%d1%8d%d1%82%d0%b0-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d1%8f-%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%b4%d0%be%d1%80/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%88%d0%b0%d1%84%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%bd-%d0%b8%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%bd-%d0%bf%d0%be%d1%87%d0%b5%d0%bc%d1%83-%d1%8d%d1%82%d0%b0-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d1%8f-%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%b4%d0%be%d1%80/[/url]
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Хочу выделить раздел про Свежие находки на фермерских рынках мира.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%83%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d1%8b-%d1%84%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%80%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%83%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d1%8b-%d1%84%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%80%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba/[/url]
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Незнакомые названия и странные формы — экзотические продукты всегда манят.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Гвоздика с Мадагаскара: секреты усиления вкуса еды”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b3%d0%b2%d0%be%d0%b7%d0%b4%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%b3%d0%b0%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%80-%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b0-%d1%83%d1%81%d0%b8%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%b2%d0%b0%d0%b5/]https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b3%d0%b2%d0%be%d0%b7%d0%b4%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%b3%d0%b0%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%80-%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b0-%d1%83%d1%81%d0%b8%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%b2%d0%b0%d0%b5/[/url]
Надеемся, что наши советы помогут вам не только сохранить экзотические продукты, но и насладиться их вкусом.
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica 10€ bonus i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
подключить домашний интернет в воронеже
domashij-internet-voronezh004.ru
подключить интернет
сурматеринство с гарантией – стать сурмамой помощь бесплодным парам. Полный цикл: от подбора суррогатной мамы до рождения ребёнка. Юридическая чистота, надёжные клиники, чуткое сопровождение специалистов.
Нужна душевая кабина? душевые кабины в минске цены: компактные и просторные модели, стеклянные и пластиковые, с глубоким поддоном и без. Установка под ключ, гарантия, помощь в подборе. Современный дизайн и доступные цены!
Незнакомые названия и странные формы — экзотические продукты всегда манят.
Зацепил материал про Бадьян из Китая: секрет анисового вкуса.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b4%d1%8c%d1%8f%d0%bd-%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%b9-%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%be%d0%bd-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b4%d0%b0%d1%91%d1%82-%d0%b1%d0%bb%d1%8e%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%bc-%d0%b0%d0%bd/]https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b4%d1%8c%d1%8f%d0%bd-%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%b9-%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%be%d0%bd-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b4%d0%b0%d1%91%d1%82-%d0%b1%d0%bb%d1%8e%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%bc-%d0%b0%d0%bd/[/url]
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
Давайте вместе откроем секреты хранения экзотических плодов.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ароматные рынки специй на Ближнем Востоке”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b9-%d0%bd%d0%b0-%d0%b1%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%b6%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%bc-%d0%b2%d0%be%d1%81%d1%82%d0%be%d0%ba%d0%b5/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b9-%d0%bd%d0%b0-%d0%b1%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%b6%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%bc-%d0%b2%d0%be%d1%81%d1%82%d0%be%d0%ba%d0%b5/[/url]
Пусть ваши блюда всегда будут полны экзотики и оригинальности.
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica kasyno bonus bez depozytu i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Вы не знаете, как хранить экзотические продукты? У нас есть несколько советов!
По теме “Скрытые жемчужины: уникальные сорта чая”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%81%d0%ba%d1%80%d1%8b%d1%82%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b6%d0%b5%d0%bc%d1%87%d1%83%d0%b6%d0%b8%d0%bd%d1%8b-%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d0%be%d0%b3%d0%be-%d0%bc%d0%b8%d1%80%d0%b0/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%81%d0%ba%d1%80%d1%8b%d1%82%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b6%d0%b5%d0%bc%d1%87%d1%83%d0%b6%d0%b8%d0%bd%d1%8b-%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d0%be%d0%b3%d0%be-%d0%bc%d0%b8%d1%80%d0%b0/[/url]
Пусть ваши блюда всегда будут полны экзотики и оригинальности.
домашний интернет
domashij-internet-voronezh005.ru
провайдеры интернета в воронеже
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Кстати, если вас интересует Откройте мир уникальных чайных смесей и вкусов, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%81%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%b8-%d1%81-%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%be%d0%b1%d1%8b%d1%87%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%bc%d0%b8-%d0%b4%d0%be%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b2%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b8/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%81%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%b8-%d1%81-%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%be%d0%b1%d1%8b%d1%87%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%bc%d0%b8-%d0%b4%d0%be%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b2%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b8/[/url]
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica jak wypłacić pieniądze i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Official Instagram of 777pub
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica kasyno i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Нужна душевая кабина? душевая кабина купить в минске: компактные и просторные модели, стеклянные и пластиковые, с глубоким поддоном и без. Установка под ключ, гарантия, помощь в подборе. Современный дизайн и доступные цены!
Real content from the real taya365 – follow the official page
Давайте вместе откроем секреты хранения экзотических плодов.
По теме “Погружение в мир чайных церемоний и редких атрибутов”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%86%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b0%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b1%d1%83%d1%82%d1%8b/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%86%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b0%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b1%d1%83%d1%82%d1%8b/[/url]
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica aplikacja i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Пытаетесь разнообразить своё питание необычными вкусами? Мы подскажем, как это сделать!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Погружение в мир чайных церемоний и редких атрибутов”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%86%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b0%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b1%d1%83%d1%82%d1%8b/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%86%d0%b5%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d1%85-%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b0%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b1%d1%83%d1%82%d1%8b/[/url]
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
Давайте вместе откроем секреты хранения экзотических плодов.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Откройте для себя редкие морепродукты и их бизнес-потенциал”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d0%b8%d0%b7-%d0%bc%d0%be%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d0%b8%d0%b7-%d0%bc%d0%be%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2/[/url]
Надеемся, что наши советы помогут вам не только сохранить экзотические продукты, но и насладиться их вкусом.
провайдеры интернета в воронеже
domashij-internet-voronezh006.ru
подключить интернет
Хотите узнать больше об экзотических фруктах и овощах? Тогда этот пост для вас!
По теме “Путешествие в мир индийских специй: экскурсии и бизнес-возможности”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d1%8d%d0%ba%d1%81%d0%ba%d1%83%d1%80%d1%81%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%bf%d0%be-%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bc-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b9-%d0%b2-%d0%b8%d0%bd%d0%b4%d0%b8%d0%b8/]https://localflavors.ru/%d1%8d%d0%ba%d1%81%d0%ba%d1%83%d1%80%d1%81%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%bf%d0%be-%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bc-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b9-%d0%b2-%d0%b8%d0%bd%d0%b4%d0%b8%d0%b8/[/url]
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
mostbet [url=mostbet4078.ru]mostbet4078.ru[/url]
Хотите узнать больше об экзотических фруктах и овощах? Тогда этот пост для вас!
Кстати, если вас интересует Исследуем локальные деликатесы со всего мира, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://localflavors.ru/%d0%bb%d0%be%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%b7%d0%bd%d1%8b%d1%85-%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%bd%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%bd%d0%b5/]https://localflavors.ru/%d0%bb%d0%be%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%b7%d0%bd%d1%8b%d1%85-%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%bd%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%bd%d0%b5/[/url]
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Experience what ph365 is really about on their one true Instagram
Check the one and only verified Instagram page of 8k8
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica kasyno opinie i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Решения по отслеживанию времени позволяют организациям , автоматизируя учёт времени работы.
Инновационные инструменты обеспечивают точный мониторинг в режиме реального времени , минимизируя ошибки в расчётах .
Совместимость с ERP-решениями облегчает подготовку аналитики и управление больничными, сверхурочными.
bitcop фото дня
Упрощение задач экономит время HR-отделов, позволяя сосредоточиться на стратегических целях .
Простое управление обеспечивает лёгкость использования как для администраторов, сокращая период адаптации.
Надёжные решения предоставляют отчёты в реальном времени, помогая принимать решений на основе данных.
Don’t miss out – follow the one true panaloko on Instagram
Access behind-the-scenes posts and stories from winph – only on Instagram
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
If you’re searching for swerte99, this is their one and only real Instagram
Get exclusive content from okebet – only on their real Instagram
Join discussions and news from the real slotvip community on Facebook
This is the one and only authentic Instagram page of jilicc
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica kod promocyjny i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica jak wypłacić pieniądze i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Follow the one and only official taya365 group on Facebook
Follow updates directly from ph365 – only in their official Facebook group
Lubisz kasyna online i automaty do gry? Zarejestruj się na slottica kod promocyjny i zgarnij nagrody powitalne!
Get access to real-time content from 8k8 in their official group
Join discussions and announcements from 777pub in their official group
Продвижение сайта https://team-black-top.ru в ТОП Яндекса и Google. Комплексное SEO, аудит, оптимизация, контент, внешние ссылки. Рост трафика и продаж уже через 2–3 месяца.
Комедия детства один дома 1 — легендарная комедия для всей семьи. Без ограничений, в отличном качестве, на любом устройстве. Погрузитесь в атмосферу праздника вместе с Кевином!
Join the official Facebook group of taya777 – real people, real updates
Нужна душевая кабина? магазин душевых кабин лучшие цены, надёжные бренды, стильные решения для любой ванной. Доставка по городу, монтаж, гарантия. Каталог от эконом до премиум — найдите идеальную модель для вашего дома.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Нужна душевая кабина? душевые кабины в минске лучшие цены, надёжные бренды, стильные решения для любой ванной. Доставка по городу, монтаж, гарантия. Каталог от эконом до премиум — найдите идеальную модель для вашего дома.
Join the official Facebook group of winph – trusted, verified, and active
Stay informed through the verified swerte99 community on Facebook
Looking for okbet? This is their official and authentic Instagram
https://focusbiathlon.com/ – biathlon schedule all competitons, overall standings and biathlon results – men’s and women’s relay
микрозаймы онлайн мфо взять займ
Блог рекламиста https://dramtezi.ru всё о маркетинге под ключ. Полезные статьи, разбор кейсов, обучение, индивидуальные консультации. Помогаем прокачать бренд, привлечь клиентов и выстроить эффективную стратегию продвижения.
Архитектурное бюро спб https://arhitektura-peterburg.ru
водопонижение котлована иглофильтрами [url=http://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru]http://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru[/url] .
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, оформите заказ по ссылке https://камера-холодильная.рф/
walewska.ru
Женская сумка — это ключевой аксессуар, которая выделяет индивидуальность каждой дамы.
Она помогает нести личные предметы и структурировать личные задачи.
Благодаря разнообразию форм и оттенков она завершает ваш стиль.
сумки Furla
Сумка — атрибут хорошего вкуса, который отражает уровень достатка своей хозяйки.
Любая сумка повествует настроение через детали, раскрывая внутренний мир женщины.
От миниатюрных сумочек до просторных тоутов — сумка подстраивается под конкретный случай.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, оформите заказ по ссылке https://камера-холодильная.рф/
Work in Macau https://hello-jobs.com fresh vacancies with decent pay. Hospitality, entertainment, construction and service. Vacancies for CIS citizens, paperwork, housing. Reliable employers are waiting!
AMT Games https://amt-games.com is a developer of popular online games in the genres of strategy, MMO and action. Famous projects: Battle for the Galaxy, Heroes of War and others.
Марка Balenciaga известен уникальными сумками , созданными неповторимым стилем .
Каждая модель выделяется уникальным дизайном , включая массивные застежки .
Используемые материалы гарантируют премиальное качество изделия .
https://sites.google.com/view/sumki-balenciaga/index
Узнаваемость дизайна растет среди модников , делая выбор символом роскоши .
Сезонные новинки дают возможность владельцу подчеркнуть индивидуальность в повседневке.
Инвестируя в сумки Balenciaga , вы приобретаете роскошную вещь, плюс символ эстетики.
водопонижение скважинами https://водопонижение-77.рф/
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? промышленная холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома.
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома https://камера-холодильная.рф/
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
По теме “komandor-povolje.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://komandor-povolje.ru]https://komandor-povolje.ru[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Seattle Photo Gallery https://www.maxwaugh.com stunning nature, wildlife scenes, and sports energy. Unique shots from events, animals, and sanctuaries. Professional photography, emotions in every shot.
Central Buenos Aires hotel https://www.panamericano.us comfort and style near the main attractions. Suitable for leisure and business. Free Wi-Fi, transfer, breakfast and cozy atmosphere. Online booking at the best prices.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
По теме “idalgogrif.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Сумки Prada представляют собой эталоном стиля за счёт сочетанию инноваций и традиций .
Используемые материалы обеспечивают долговечность , а ручная сборка выделяет высокое качество .
Узнаваемые силуэты дополняются фирменными деталями, формируя современный облик.
хобо Прада цены
Эти аксессуары универсальны для повседневного использования , демонстрируя элегантность при любом ансамбле.
Ограниченные серии усиливают индивидуальность образа, превращая каждую модель в объект зависти.
Опираясь на историю компания внедряет новые решения, сохраняя классическому шарму в каждой детали .
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? холодильные камеры в москве – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “avelonbeta.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://avelonbeta.ru]https://avelonbeta.ru[/url]
Какие еще есть варианты?
система водопонижения иглофильтрами https://водопонижение-77.рф/
Renner Action https://rennerusa.com in Motion is a premium grand piano with precise response, stable mechanics and rich tone. Designed for musicians who value control and expressiveness.
Фильтры для воды https://waterlux.ua чистая и безопасная вода у вас дома. Большой выбор систем очистки: кувшины, под мойку, магистральные, обратный осмос. Подходит для квартиры, дачи, офиса.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha-3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
иглофильтровое водопонижение [url=http://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru]http://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru[/url] .
walewska.ru
walewska.ru
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, оформите заказ по ссылке https://камера-холодильная.рф/
walewska.ru
понижение уровня грунтовых вод водопонижение котлована иглофильтрами
I once viewed pills as saviors, reaching for them instinctively whenever my body whispered warnings. However, reality dawned slowly, revealing how these aids often numbed the symptoms, urging a profound introspection into what wellness truly entails. The shift was visceral, illuminating that conscious choices in medicine honors our body’s wisdom, rather than eroding our natural strength.
In a moment of vulnerability, I hesitated before the usual fix, uncovering hidden layers that harmonized natural rhythms with thoughtful aids. What emerged was transformative: wellness blooms holistically, excessive reliance breeds fragility. Now, I navigate this path with gratitude to embrace a fuller perspective, viewing remedies as partners in the dance.
Reflecting on the essence, I’ve grasped that medical means ought to amplify our spirit, free from dominating our narrative. This odyssey has been enlightening, challenging everyone to ponder entrenched patterns for richer lives. It all comes down to one thing: fildena super active 100
водопонизительная скважина система водопонижения иглофильтрами
walewska.ru
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
водопонижение строительное https://водопонижение-77.рф/
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, подробнее https://камера-холодильная.рф/
walewska.ru
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? Вам подойдёт холодильная камера – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома, оформите заказ по ссылке https://камера-холодильная.рф/
https://graph.org/Complete-Guide-to-Free-Zones-06-19
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Особенно понравился раздел про tars-rubber.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://tars-rubber.ru]https://tars-rubber.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
По теме “obender.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://obender.ru]https://obender.ru[/url]
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
walewska.ru
mostbet [url=http://mostbet4077.ru]http://mostbet4077.ru[/url]
Станции скорой https://03ekb.ru медицинской помощи Екатеринбурга — экстренная помощь 24/7. Вызов бригады, транспортировка, неотложная помощь при травмах, инфарктах, обострениях.
Центр сертификации https://radiocert.ru в Москве: продукция, услуги, СМК, пожарная безопасность, ЕАС. Независимая экспертиза, аккредитованные лаборатории, прозрачная стоимость. Полное сопровождение на всех этапах.
Бренд Longchamp — это эталон стиля , где соединяются вечные ценности и актуальные решения.
Изготовленные из прочного нейлона , они отличаются неповторимым дизайном .
Иконические изделия пользуются спросом у путешественников уже много лет .
https://sites.google.com/view/sumki-longchamp/all
Каждая сумка с авторским дизайном демонстрирует хороший вкус, сохраняя практичность в повседневных задачах.
Бренд следует наследию, внедряя современные методы при поддержании шарма .
Выбирая Longchamp, вы делаете стильный аксессуар , а вступаете в историю бренда .
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
По теме “idalgogrif.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
Ищете, где хранить продукты при низкой температуре? камера холодильная низкотемпературная – практичное и надёжное решение для бизнеса и дома.
Ищете шины? https://tssz.ru У нас — более 165 брендов со всего мира! Michelin, Pirelli, Nokian, Bridgestone и другие. Быстрый подбор по авто, отличные цены, оригинальная продукция с гарантией. Установка и доставка по всей России.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Особенно понравился материал про yogapulse.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://yogapulse.ru]https://yogapulse.ru[/url]
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Фотосалон в Екатеринбурге https://www.foto4u.su фото на документы, печать снимков, ксерокопии, ламинирование, фототовары и сувениры. Быстро, качественно, недорого.
Природа Беларуси https://wildlife.by в одном месте. Леса, реки, озёра, животный и растительный мир, охраняемые территории. Путеводители, фотоматериалы, интересные факты. Портал для тех, кто ценит и изучает окружающий мир.
Лазерная косметология https://actual-cosmetology.ru в Рязани — профессиональный уход за кожей в клинике нового уровня. Эпиляция, чистка, шлифовка, anti-age процедуры. Индивидуальный подход, безопасность, видимый эффект с первых сеансов.
водопонижение иглофильтрами грунтовых вод https://водопонижение-77.рф/
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “phenoma.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://phenoma.ru]https://phenoma.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
Посмотрите, что я нашел по этому поводу:
По теме “fjhg.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Хочу выделить раздел про 095hotel.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://095hotel.ru]https://095hotel.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
https://graph.org/Complete-Guide-to-Free-Zones-06-19
walewska.ru
система водопонижения иглофильтрами водопонижение скважинами
Туры по Красноярскому краю https://poloniya.ru это дикая природа, мощь Енисея, горные пейзажи и сибирское гостеприимство. Увлекательные маршруты, путешествия по заповедным местам и историческим локациям.
Ремонт автомобилей https://renaultra.ru Renault и Nissan любой сложности. Замена узлов, диагностика, ТО, электрика. Запчасти в наличии и под заказ — оригинал и аналоги.
walewska.ru
Сайт-помощник по выбору товаров для дома: https://kak-vubrat.ru/
Курс по плазмолифтингу обучение плазмотерапии в гинекологии в гинекологии: PRP-терапия, протоколы, показания и техника введения. Обучение для гинекологов с выдачей сертификата. Эффективный метод в эстетической и восстановительной медицине.
Курс по плазмотерапии https://prp-plazmoterapija.ru с выдачей сертификата. Освойте PRP-методику: показания, противопоказания, протоколы, работа с оборудованием. Обучение для медработников с практикой и официальными документами.
устройство водопонижения https://водопонижение-77.рф/
saif zone directory saif zone entry pass
водопонижение грунтовых вод водопонижение на строительной площадке
Интересная статья: Skoda и электромобили: история чешского автопроизводителя началась раньше, чем вы думаете
Интересная статья: Говядина по-тайски: рецепт вкусного и полезного блюда
Читать статью: Рецепт хрустящей капусты в горячем маринаде: кулинарный эксперимент
проходимые прогнозы на спорт [url=http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru]http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru[/url] .
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
Хочу выделить раздел про easyterm.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
Читать в подробностях: Как воспитать самостоятельного ребенка: советы психологов
Интересная новость: Простой способ посадить горох: лайфхак для богатого урожая
Читать новость: Смородина в апреле: простые советы по уходу для богатого урожая
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Кстати, если вас интересует anclaves.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://anclaves.ru]https://anclaves.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
Новое на сайте: Почему нас тянет на сладкое: причины и что делать
Новое на сайте: Вакцинация: защита от болезней и укрепление здоровья
When audits emphasize authenticity, shortlists tend to feature only twitter followers real providers.
Татуировка представляет собой уникальное искусство , где каждая линия несёт глубокий смысл и подчеркивает индивидуальность человека.
Для многих тату — вечный символ , который напоминает о важных моментах и становится частью пути .
Процесс создания — это творческий диалог между художником и человеком, где кожа превращается полотном эмоций.
тату краски
Разные направления, от акварельных рисунков до биомеханических композиций, помогают передать любую идею в гармоничном исполнении.
Эстетика нательного искусства в способности расти вместе с человеком, превращая воспоминания в незабываемый визуальный язык .
Подбирая эскиз, люди показывают своё «я» через формы, создавая неповторимый шедевр , которое наполняет уверенностью каждый день.
прогнозы на чемпионат мира по хоккею [url=http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej6.ru/]http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej6.ru/[/url] .
Сайт добрых пожеланий https://demotivators.ru для души и вдохновения. Тысячи текстов для родных, друзей, коллег. Красивые слова, поздравления, открытки, мотивация. Поздравьте близких с любовью и заботой в каждом слове.
Zarejestruj się i graj online w najlepszym kasynie w Polsce na https://magic365casinoonline.pl/
AI platform http://bullbittrade.com for passive crypto trading. Robots trade 24/7, you earn. Without deep knowledge, without constant control. High speed, security and automatic strategy.
Innovative AI platform lumiabitai.com for crypto trading — passive income without stress. Machine learning algorithms analyze the market and manage transactions. Simple registration, clear interface, stable profit.
дивитися фільми новинки кіно 2025 дивитися безкоштовно
Zarejestruj się i graj online w najlepszym kasynie w Polsce na https://slottywaycasinoonline.pl/
найкращі фільми онлайн HD фільми українською онлайн
українські фільми 2024 фільми 2025 онлайн без підписки
Zarejestruj się i graj online w najlepszym kasynie w Polsce na https://slottywaycasinoonline.pl/
Zarejestruj się i graj online w najlepszym kasynie w Polsce na magic 365 casino opinie
pocket option – बाइनरी विकल्प ट्रेडिंग के लिए सबसे अच्छा मंच!
ставки на хоккей прогнозы от профессионалов [url=www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru/]www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru/[/url] .
мостбет [url=http://students.com.kg/]мостбет[/url]
https://ecampania.it/blog/1xbet_promo_code-vip_welcome_bonus.html
https://cs2case.io/
Trade online with pocketoption-uk.co.uk – a trusted platform with low entry requirements. Start with as little as £1, access over 100 global assets including GBP/USD, FTSE 100 and crypto. Fast payouts, user-friendly interface, and welcome bonuses for new traders.
Join millions of traders worldwide with the pocket option. Open trades in seconds, track market trends in real time, and access over 100 assets including forex, stocks, crypto, and commodities. Enjoy fast deposits and withdrawals, clear charts, and a beginner-friendly interface. Perfect for both new and experienced traders – trade on the go with confidence
Мобильный номер – ваш надежный источник информации о телефонных номерах России. У нас вы сможете быстро узнать, кто звонил, просто введя код региона или номер телефона. Удобный поиск и актуальные данные операторов мобильной связи: https://mobilnomer.ru/
Trade online with pocket options – a trusted platform with low entry requirements. Start with as little as £1, access over 100 global assets including GBP/USD, FTSE 100 and crypto. Fast payouts, user-friendly interface, and welcome bonuses for new traders.
https://pocketoptionbroker.org.in/ – बाइनरी विकल्प ट्रेडिंग के लिए सबसे अच्छा मंच!
цена высоковольтный трансформатор [url=https://guryevsk.forum24.ru/?1-4-0-00000703-000-0-0-1750404336/]цена высоковольтный трансформатор [/url] .
Портал с обзорами лучших онлайн-казино, рейтингами, актуальными бонусами и акциями, а также подробными гайдами и промо-предложениями: рейтинг онлайн казино
Join millions of traders worldwide with the pocket option app for pc. Open trades in seconds, track market trends in real time, and access over 100 assets including forex, stocks, crypto, and commodities. Enjoy fast deposits and withdrawals, clear charts, and a beginner-friendly interface. Perfect for both new and experienced traders – trade on the go with confidence
Bos88
Bandartogel77
nova comics read comics online free
casino giri? [url=candy-casino-7.com]candy-casino-7.com[/url] .
latest manga updates online manga reader no ads
манхва бесплатно манхва про демонов
candycasino [url=www.candy-casino-2.com/]www.candy-casino-2.com/[/url] .
Découvrez poket option, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
#888staz [url=http://starz888.pro/]http://starz888.pro/[/url] .
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica-onlinecasino.pl i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Découvrez pocket optio, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
https://uznay-prezidenta.ru/analytics/7026-miorelaksanty-v-chem-ih-osobennosti-i-kogda-ih-prinimayut.html
Découvrez pocket option site, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
Découvrez pockeyoption, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
На территории Красноярска доступна система вызова нарколога, работающая круглосуточно, которая предоставляет лечение зависимостей для пациентов с зависимостями. Если вам или вашим близким требуется профессиональная помощь при алкоголизме, опытный нарколог предоставит необходимую медицинскую помощь на дому, сохраняя полную конфиденциальность. вызов нарколога Красноярск Если вы ищете надежное решение, услуга вызова нарколога в Красноярске может стать первым шагом к новой жизни.
https://listaj.ru/alflutop-polza-i-vred-obektivnyj-vzglyad-na-preparat/
Услуги нарколога на дому в Красноярске становятся всё более востребованными. Специалисты данной сферы, предлагают широкий спектр наркологических услуг, в т.ч. помощь при алкоголизме и других зависимостях. Выездная консультация нарколога даёт возможность оперативно диагностировать зависимости и разработать персонализированный план лечения. Лечение без раскрытия личности – важный аспект работы специалистов, что особенно важно для людей, которые стесняются обращаться в медицинские учреждения. Реабилитация на дому включает психотерапию при зависимости, программы восстановления и медикаментозную терапию. Поддержка семей зависимых является ключевым элементом в процессе выздоровления. Предотвращение рецидивов также является важной частью работы наркологов. Специалисты предлагают психологическую помощь и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолевать трудности на их пути к выздоровлению. Узнать больше о предлагаемых услугах можно на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk004.ru, где вы найдёте всю необходимую информацию и контакты по наркологическим услугам в Красноярске.
http://ipicture.ru/publikacii/4304-miral-i-aptechki-pervoy-pomoschi-universalnoe-reshenie-dlya-vashego-predpriyatiya.html
Découvrez pocketoption.fr, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезная проблема, которая затрагивает не только пьющего человека, но и окружающих его людей. Вызов нарколога на дом в Красноярске является первым шагом к лечению алкогольной зависимости. Обсуждение с наркологом поможет определить уровень зависимости и предложить лечение алкоголизма, включая психологическую помощь.Проблемы в семье из-за алкоголя часто приводят к кризису в семье. Помощь со стороны семьи играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления. Семье необходимо знать, как поддержать, и какие советы по борьбе с зависимостью могут быть полезны. Лечение алкоголиков включает в себя не только медицинское вмешательство, но и поддержку социума. Профилактика алкоголизма начинается с признания проблемы и желания изменить ситуацию. Возобновление нормальных отношений — это долгий процесс, который нуждается в совместной работе всей семьи. вызов нарколога на дом Красноярск Обращение к врачу на дом дает возможность получить помощь в комфортной обстановке, что способствует лучшему восприятию информации и снижает уровень стресса. Поддержка семьи и готовность к лечению — это ключевые шаги на дороге к восстановлению.
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
How accurate is DefiLlama data?
Hometogel
Запой — это значительная проблема, требующая профессиональной помощи. Вызвать нарколога на дом — это комфортный вариант получить необходимую медицинскую помощь. Капельница при запое помогают быстро вывести токсины из организма, обеспечивая детоксикацию и возвращение к нормальному состоянию. Лечение алкоголизма включает в себя медикаментозную терапию и психологическую поддержку. Нарколог на дом оценивает состояние пациента и разрабатывает персонализированный план терапии, который может включать дополнительные методики, такие как настойки трав или психотерапия. Возвращение к нормальной жизни после запоя часто требует комплексного подхода. Выведение из запойного состояния должно сопровождатся не только физическим, но и эмоциональным восстановлением; Реабилитация после алкоголизма, это долгий процесс, где важна помощь при запое и поддержка родных. Важно помнить, что эффективное преодоление проблемы зависит от желания пациента меняться и его желания изменить жизнь.
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica-onlinecasino.pl i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
https://noziitopory.ru/raznoe/diprospan-ukoly-instrukcija-po-primeneniju.html
Découvrez pocket option france, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
Лечение запоя в Красноярске серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального подхода . Алкоголизм разрушает жизни , и помощь при запое жизненно важна для всех, кто оказался в этой ситуации. В клиниках для лечения запоя предлагаются множество программ, ориентированных на вывод из запоя и дальнейшую реабилитацию. Цены на лечение алкогольной зависимости могут меняться в зависимости от клиники и качества обслуживания. В стоимость может входить консультация нарколога, медицинская помощь при запое и услуги по детоксикации. лечение запоя Красноярск Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске включает в себя как стационарное, так и амбулаторное лечение , что также влияет на стоимость . Программа лечения алкоголизма разрабатывается индивидуально и может включать детоксикационные процедуры, психологическую помощь и реабилитационные мероприятия. Комплексное лечение зависимостей в Красноярске позволяет не только остановить алкогольное потребление, но и минимизировать риск рецидивов. Поэтому, если вам или вашим близким требуется помощь, важно обратиться за помощью к специалистам .
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica kasyno i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
смотреть хорошее кино новые аниме 2025
Публичная дипломатия России https://softpowercourses.ru концепции, стратегии, механизмы влияния. От культурных центров до цифровых платформ — как формируется образ страны за рубежом.
Институт государственной службы https://igs118.ru обучение для тех, кто хочет управлять, реформировать, развивать. Подготовка кадров для госуправления, муниципалитетов, законодательных и исполнительных органов.
https://tvcifrovoe.ru/raznoe/doritricin-pri-angine-kak-vybrat-pra.html
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie https://slottica-onlinecasino.pl/ i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Découvrez pocket option application, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
slot giri? [url=https://candy-casino-7.com/]https://candy-casino-7.com/[/url] .
Капельный метод лечения запоя, это важный шаг в борьбе с алкогольной зависимости. Интравенозное введение помогает очищению организма от токсинов, нормализует психоэмоциональное состояние и укрепляет функции организма. После процедуры стоит учитывать рекомендаций. помощь нарколога Первым делом, важно соблюдать указаниям нарколога и продолжать лечение алкоголизма. Процесс реабилитации требует времени и усилий. Кроме того, обратите внимание на профилактику рецидива: старайтесь избегать триггеров, которые могут спровоцировать возвращение к запою.
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica kasyno i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk007.ru
лечение запоя
Школа бизнеса EMBA https://emba-school.ru программа для руководителей и собственников. Стратегическое мышление, международные практики, управленческие навыки.
Опытный репетитор https://english-coach.ru для школьников 1–11 классов. Подтянем знания, разберёмся в трудных темах, подготовим к экзаменам. Занятия онлайн и офлайн.
Découvrez https://pocketoption-france.fr/, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
https://www.hlsports.de/
888starz online [url=http://www.starz888.pro]888starz online[/url] .
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
Кстати, если вас интересует Подготовка и празднование Нового года 2013: идеи и советы, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/forumdisplay.php?f=115
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
https://pg13.ru/slabitelnoe-dyufalak-pokazaniya-k-primeneniyu-rekomendaczii-i-predosterezheniya
https://rugraphics.ru/bez-rubriki/dizajn-upakovki-mediczinskih-preparatov
Проходите аттестацию https://prom-bez-ept.ru по промышленной безопасности через ЕПТ — быстро, удобно и официально. Подготовка, регистрация, тестирование и сопровождение.
Découvrez pocket option site, l’application de trading intuitive utilisée par des millions de traders dans le monde. Accédez à plus de 100 actifs : forex, actions, crypto-monnaies et matières premières. Exécutions rapides, interface claire et retraits instantanés. Parfait pour débutants comme pour traders expérimentés – tradez où que vous soyez, à tout moment.
Интересные моменты марта на нашем портале ждут вашего внимания!
По теме “Общение для мам: от ухода за детьми до хобби”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/forum.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
«Дела семейные» https://academyds.ru онлайн-академия для родителей, супругов и всех, кто хочет разобраться в семейных вопросах. Психология, право, коммуникации, конфликты, воспитание — просто о важном для жизни.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk008.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Трэвел-журналистика https://presskurs.ru как превращать путешествия в публикации. Работа с редакциями, создание медийного портфолио, написание текстов, интервью, фото- и видеоматериалы.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Интересные моменты марта на нашем портале ждут вашего внимания!
По теме “Обсуждаем флеш-игры и турниры для всех”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/arcade.php
Большое спасибо за ваше внимание! Наверняка в следующем месяце будет еще больше интересного.
Pinco kazino Azərbaycanda keyfiyyətli xidmət təqdim edir. Pinco bet idman mərcləri üçün geniş seçimlər təklif edir pinco casino giris . Pinco casino скачать çox rahatdır, sadəcə bir klik kifayətdir. Pinco casino azerbaycan-da canlı dilerlərlə oynamaq mümkündür. Pinco azerbaycan yukle – birbaşa telefona yüklə və oynamağa başla. Pinco oyunu ilə həm əylən, həm də qazan. Pinco kazino istifadəçilər üçün rahat interfeys təqdim edir. Pinco oyunlarında uduş faizi yüksəkdir. Pinco apk ilə hər zaman və hər yerdə oynaya bilərsiniz [url=https://az-pinco.website.yandexcloud.net/]pinco giris[/url].
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie https://slottica-onlinecasino.pl/ i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Свежие скидки https://1001kupon.ru выгодные акции и рабочие промокоды — всё для того, чтобы тратить меньше. Экономьте на онлайн-покупках с проверенными кодами.
Hi there!
Read the link – [url=https://welcomebonuses.cfd]welcome bonuses casino real money[/url]
Enjoy your bonuses!
«Академия учителя» https://edu-academiauh.ru онлайн-портал для педагогов всех уровней. Методические разработки, сценарии уроков, цифровые ресурсы и курсы. Поддержка в обучении, аттестации и ежедневной работе в школе.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk009.ru
вывод из запоя
Представляем самые читаемые и обсуждаемые темы марта на Mamas.Ru.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Обсуждаем флеш-игры и турниры для всех, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/arcade.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
Создаем и продвигаем сайты с 2004 года! Честные гарантия позиций, посещаемости и лидов. Фокус на SEO продвижении. Не нравится – возвращаем деньги https://webseosite.ru/
Zarejestruj się w kasynie online już teraz na oficjalnej stronie slottica-onlinecasino.pl i odbierz bonusy za pierwszą wpłatę na automatach!
Hey gambler!
Read the link – [url=https://slotspinners.cfd/]exclusive slot spinners best casino[/url]
Good luck spinning!
Оригинальный потолок натяжной потолок со световыми линиями отзывы со световыми линиями под заказ. Разработка дизайна, установка профиля, выбор цветовой температуры. Идеально для квартир, офисов, студий. Стильно, практично и с гарантией.
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
?аза? тіліндегі ?ндер Казахские песни бесплатно ж?рекке жа?ын ?уендер мен ?серлі м?тіндер. ?лтты? музыка мен ?азіргі заман?ы хиттер. Онлайн ты?дау ж?не ж?ктеу м?мкіндігі бар ы??айлы жина?.
Hello just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same results.
dosage of vermox 100mg
?аза? тіліндегі ?ндер Казахские хиты ж?рекке жа?ын ?уендер мен ?серлі м?тіндер. ?лтты? музыка мен ?азіргі заман?ы хиттер. Онлайн ты?дау ж?не ж?ктеу м?мкіндігі бар ы??айлы жина?.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk009.ru
вывод из запоя
Emas188 > Play All the Best Online Games Here. Register for a VIP Account to Get Many Promo Benefits and Bonuses.
Escape the Limits – Explore Non GamStop Casinos!
Tired of restrictions? Discover a world of unlimited gaming possibilities at our Non GamStop Casinos.
What we offer:
– Unrestricted access to top games
– Generous welcome bonuses
– Lightning-fast payouts
– 24/7 customer support
– Secure & fair gaming environment
Join thousands of satisfied players who have already found their perfect gaming experience. No GamStop limitations mean endless fun and excitement!
Claim your bonus now and start playing at the best Non GamStop Casinos today! ??
https://vaishakbelle.com/non-gamstop-bingo-sites/
#NonGamStopCasinos #OnlineGaming #CasinoBonus
как часто винлайн дает фрибет [url=http://winline-bonus-za-registraciyu-2025.ru]как часто винлайн дает фрибет[/url] .
Настоящий обзор самых популярных обсуждений марта на Mamas.Ru для вас!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Обсуждаем флеш-игры и турниры для всех”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
http://mamas.ru/arcade.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Обсуждение активности на сайте для мам”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/activity.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
Hello this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding know-how so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
vibramycin 100 mg uk
кайт школа Кайтинг: активный отдых, адреналин и единение с природой.
Давайте подведем итоги марта и посмотрим, какие темы стали самыми популярными.
Зацепил материал про Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Оставайтесь на связи и не пропустите новые обсуждения на Mamas.Ru.
Готовый комплект Инсталляция grohe с унитазом в комплекте инсталляция и унитаз — идеальное решение для современных интерьеров. Быстрый монтаж, скрытая система слива, простота в уходе и экономия места. Подходит для любого санузла.
Evening traffic doubled after we layered a drip?safe plan to buy twitter views in two batches.
Портал с обзорами лучших онлайн-казино, рейтингами, актуальными бонусами и акциями, а также подробными гайдами и промо-предложениями: топ казино
Мамочки, делимся новостями на Mamas.Ru. Какие темы вас особенно заинтересовали в марте?
Хочу выделить материал про Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года.
Ссылка ниже:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Ждем всех вас в наших новых темах и обсуждениях.
кайтинг Кайт лагерь
Shimmering liquid textiles redefine 2025’s fashion landscape, blending futuristic elegance with sustainable innovation for everyday wearable art.
Unisex tailoring break traditional boundaries , featuring asymmetrical cuts that transform with movement across formal occasions.
AI-curated patterns human creativity, creating hypnotic color gradients that react to body heat for dynamic visual storytelling .
https://onetable.world/read-blog/116187
Zero-waste construction set new standards, with upcycled materials celebrating resourcefulness without compromising bold design elements.
Holographic accessories elevate minimalist outfits , from nano-embroidered handbags to self-cleaning fabrics designed for avant-garde experimentation.
Vintage revival meets techwear defines the year, as 2000s logomania reinterpret archives through smart fabric technology for forward-thinking style.
Салон красоты в Санкт-Петербурге. Предлагаем профессиональные услуги: стрижки, окрашивание, уход за волосами, маникюр, педикюр, косметологию и массаж. Современное оборудование, опытные мастера и качественная косметика гарантируют идеальный результат. Запишитесь в студию красоты онлайн: салон красоты петроградская
Shimmering liquid textiles redefine 2025’s fashion landscape, blending cyberpunk-inspired aesthetics with sustainable innovation for everyday wearable art.
Gender-fluid silhouettes challenge fashion norms, featuring asymmetrical cuts that transform with movement across formal occasions.
AI-curated patterns human creativity, creating one-of-a-kind textures that shift in sunlight for dynamic visual storytelling .
https://evertonfcfansclub.com/read-blog/10411
Circular fashion techniques lead the industry , with biodegradable textiles reducing environmental impact without compromising luxurious finishes .
Light-refracting details elevate minimalist outfits , from nano-embroidered handbags to self-cleaning fabrics designed for modern practicality .
Vintage revival meets techwear defines the year, as 2000s logomania reinterpret archives through smart fabric technology for timeless relevance .
Сайт-помощник по выбору товаров для дома: https://kak-vubrat.ru/
кайт Безопасность в кайтсёрфинге: Прежде всего. Соблюдайте правила, используйте защитное снаряжение и не рискуйте без необходимости.
Pinko qeydiyyat çox sadə və sürətlidir. Pinco oyunları yüksək keyfiyyətli və maraqlıdır pinco gazino . Pinco kazino slotları müxtəlif və maraqlıdır. Pinco slotları yüksək ödəniş faizinə malikdir. Pinco apk faylı rəsmi saytdan yüklənməlidir. Pinco casino az real uduşlar təqdim edir. Pinco bet ilə canlı mərc etmək imkanı var. Pinco app istifadəçilər üçün geniş funksiyalar təqdim edir. Pinco bet ilə istənilən idman növünə mərc et [url=https://pinco-kazino.website.yandexcloud.net/]pinco casino promokod[/url].
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
провайдеры челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение челябинск
кайтсёрфинг Кайт: Крыло, дарящее адреналин. Откройте для себя мир кайтинга с правильно подобранным кайтом.
кайтинг Кайтсёрфинг оборудование должно соответствовать вашему уровню подготовки и стилю катания. Правильно подобранный кайт и доска обеспечат вам комфорт и безопасность на воде.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
подключение интернета челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
кайт лагерь Кайтсёрфинг для начинающих
Представляем самые читаемые и обсуждаемые темы марта на Mamas.Ru.
По теме “Обсуждение активности на сайте для мам”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/activity.php
Ждем всех вас в наших новых темах и обсуждениях.
Die Rolex Cosmograph Daytona gilt als Ikone der chronographischen Präzision , vereint sportliches Design mit höchster Funktionalität durch das bewährte Automatikal movement.
Verfügbar in Weißgold überzeugt die Uhr durch das ausgewogene Zifferblatt und hochwertige Materialien , die passionierte Sammler begeistern .
Mit einer Gangreserve von 72 Stunden ist sie ideal für sportliche Herausforderungen und zeigt sich als zuverlässiger Begleiter unter jeder Bedingung .
Rolex Cosmograph Daytona Rainbow armbanduhr
Die ikonischen Unterzifferblätter mit Perlmutt-Einsätzen unterstreichen den luxuriösen Touch, während die kratzfeste Saphirglase Langlebigkeit garantieren .
Seit ihrer Einführung 1963 hat die Daytona ein Symbol für Ambition , bekannt durch den exklusiven Status bei Investoren weltweit.
als Hommage an die Automobilgeschichte – die Cosmograph Daytona verkörpert Innovation und bleibt als zeitloser Klassiker für anspruchsvolle Träger .
Добро пожаловать на Mamas.Ru! Сегодня мы обсудим самые горячие темы нашего сообщества в марте.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Популярные рецепты и кулинарные советы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/recepty.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar008.ru
вывод из запоя
Интересные моменты марта на нашем портале ждут вашего внимания!
Кстати, если вас интересует Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
подключить проводной интернет челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
дешевый интернет челябинск
The Rolex Cosmograph Daytona Rainbow represents horological excellence with its vibrant rainbow bezel .
Featuring high-grade materials, it merges precision timing features with sophisticated design elements.
Limited to exclusive editions , this timepiece captivates luxury enthusiasts worldwide.
Daytona Rainbow photo
Every gradient stone on the ceramic flange forms a vibrant arc that catches the light .
Powered by Rolex’s precision-engineered automatic mechanism, it ensures seamless functionality for daily wear .
An investment piece, the Daytona Rainbow celebrates Rolex’s innovation in every detail .
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar008.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Мамочки, делимся новостями на Mamas.Ru. Какие темы вас особенно заинтересовали в марте?
Особенно понравился материал про Обсуждаем последние записи в дневниках мам.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/blog.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar009.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
электрические карнизы купить [url=http://www.elektrokarniz150.ru]http://www.elektrokarniz150.ru[/url] .
В Екатеринбурге представлено множество интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих выгодные тарифы на интернет и ТВ. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet004.ru можно найти лучшие предложения по безлимитному интернету и пакетным услугам. Многие компании устраивают акции и скидки, что делает выбор особенно интересным. Стоит обратить внимание на скорость интернет-соединения и стабильность соединения. Анализ предложений позволит выбрать оптимальный вариант. Например, комплексные предложения часто содержат доступ к платформам с фильмамичто увеличивает возможности пользователей. Мнения клиентов помогут понять качество услуг связи. Доступные цены делают оформление ТВ и интернета для дома еще более востребованным. Не забывайте также о мобильном интернете для комфортного использования в поездках!
купить цветочный горшок кашпо [url=http://www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-sochi.ru]купить цветочный горшок кашпо[/url] .
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar009.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar010.ru
лечение запоя
Pinco app ilə mobil oynamaq çox rahatdır. Pinco yukle funksiyası sadə və sürətli işləyir pinco az?rbaycan . Pinco apk indir üçün rəsmi sayt istifadə edin. Pinco qeydiyyat prosesi sadədir və vaxt aparmır. Pinco apk faylı rəsmi saytdan yüklənməlidir. Pinco bonusları yeni istifadəçilər üçün cazibəlidir. Pinco qeydiyyat zamanı çətinliklə qarşılaşmadım. Pinco qeydiyyat üçün mobil nömrə kifayətdir. Pinco oyunları tam lokal istifadəçiyə uyğunlaşdırılıb [url=https://pinco-kazino.website.yandexcloud.net/]pinco slotlar[/url].
В столице России представлен разнообразный ассортимент интернет-провайдеров‚ предлагающих различные тарифы на интернет. При определении подходящего провайдера стоит учитывать скорость интернет-соединения‚ стабильность соединения и качество услуги. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet005.ru доступны отзывы пользователей о разных провайдерах‚ что облегчит процесс выбора. Важным аспектом является стоимость предоставляемых интернет-услуг и варианты подключения интернета; Техническая поддержка тоже играет роль‚ особенно при возникновении проблем. Сравнение провайдеров поможет найти оптимальный вариант для домашнего интернета.
В современном обществе проблемы с алкоголем становятся все более насущными . Большое количество людей сталкиваются с алкогольной зависимостью , которая нуждаеться в оперативном вмешательстве профессионалов . В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом – это разумный подход. Услуги нарколога включают диагностику алкоголизма и медикаментозное лечение запоя. Это позволяет быстро и эффективно справиться с запоем , минимизируя стрессовые ситуации для пациента . Конфиденциальное лечение алкоголизма – ключевой момент, поскольку значительное число пациентов не хотят делиться своими проблемами . Поддержка при алкоголизме также включает помощь близким в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом предлагает консультационные услуги, что помогает семье узнать, как вести себя с зависимым человеком . Лечение зависимостей на дому позволяет пройти реабилитацию от алкоголя в комфортной среде . Сайт narkolog-tula008.ru предлагает информацию о вызове врача на дом , чтобы помочь тем, кто нуждается в профессиональной помощи .
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
ремонт холодильников Алмалинский район ремонт стиральных машин с гарантией
bitcoin
Снижение стоимости домашнего интернета в Екатеринбурге – задача, которая требует внимания. В первую очередь, стоит провести сравнение провайдеров на сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet006.ru: посмотрите предлагаемые тарифы и услуги. Многие интернет-провайдеров имеют выгодные предложения и скидки на интернет для новых абонентов. Также, обратите внимание на акции для абонентов, которые могут включать бесплатный период использования или снижение затрат на связь при подключении к оптоволоконному интернету. Подумайте о альтернативные способы подключения, такие как Wi-Fi или мобильный интернет, что может быть более экономичным вариантом. Не забывайте про оптимизацию вашего Wi-Fi, для оптимизации использования интернета. Экономия на связи возможна, что поможет вам существенно сократить расходы на интернет.
Иногда просто хочется отключиться от всего и погрузиться в атмосферу игры. Идеальный способ сделать это — перейти по ссылке https://vodka-registration.site и запустить любимый слот. Здесь всё под рукой: от популярных новинок до проверенной классики. Интерфейс адаптирован под любые устройства, а бонусы начисляются моментально. Функция автозеркала особенно спасает, когда в поездке или на работе доступ к основному сайту ограничен. Это решение, которое действительно работает. Именно поэтому я возвращаюсь сюда снова и снова — азарт, стабильность и удовольствие в одном флаконе.
Давайте подведем итоги марта и посмотрим, какие темы стали самыми популярными.
Кстати, если вас интересует Обсуждение активности на сайте для мам, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/activity.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
Частный нарколог на дому в Туле предоставляет незаменимую поддержку тем, кто страдает от зависимости. Лечение зависимости может быть сложным процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает комфортные условия и конфиденциальность. На сайте narkolog-tula009.ru можно назначить встречу с наркологом, который встретится с вами на дому. Медицинская помощь на дому включает детоксикацию организма и психологическую терапию для борьбы с зависимостями, что позволяет пациенту сделать первые шаги к свободе от наркотиков или алкоголя. Реабилитационная программа разрабатывается с учетом индивидуальных особенностей, что позволяет учитывать уникальные потребности каждого пациента. Поддержка родственников играет ключевую роль в профилактике рецидива. Частный нарколог на дому обеспечивает не только лечение, но и эмоциональную поддержку, что важно для успешной реабилитации наркоманов и помощи при алкоголизме.
win md [url=https://1win40001.ru/]https://1win40001.ru/[/url]
подключить интернет в казани в квартире
kazan-domashnij-internet004.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
Запой — это серьезная проблема, которая требует быстрого решения. В Туле предлагаются разные варианты анонимного вывода из запоя. Медицинские учреждения предлагают помощь при запоях, включая детоксикацию и психотерапию. вывод из запоя тула Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с этой проблемой, рекомендуем обратиться в центры лечения зависимостей с выездными наркологами. Также полезны консультации по алкоголизму и группы поддержки для родственников. Реабилитация в Туле предлагает анонимные группы и программы для восстановления после запоя. Ваша помощь в кризисных ситуациях рядом.
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Кстати, если вас интересует qazar.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
По теме “idalgogrif.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание.
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “m-admin.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://m-admin.ru]https://m-admin.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, эта информация сэкономит вам время.
провайдеры домашнего интернета казань
kazan-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет провайдеры казань по адресу
Зависимость от наркотиков и алкоголя требует профессионального подхода. Наркологическая помощь включает в себя диагностики и лечения зависимостейчто может существенно изменить жизнь человека. Первый шаг к выздоровлению – это консультация нарколога. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме и реабилитация наркозависимых проводятся в центрахспециализирующихся на этом, таких как narkolog-tula011.ru. Программы восстановления включают психотерапевтические сеансы и группы поддержки, а также семейную поддержку. Необходимо учитывать мотивацию к лечению и профилактике зависимостей. Социальная адаптация после лечения помогает избежать рецидивов. Анонимная помощь наркозависимым доступна и эффективна. Начните новый этап своей жизни с помощью профессионалов!
mostbet uz yuklab olish скачать [url=mostbet4080.ru]mostbet uz yuklab olish скачать[/url]
https://www.yarnews.net/news/show/russia-and-world/87425/uzi-diagnostika_kogda_i_zachem_delat_ultrazvukovoe_issledovanie.htm
электрокарнизы москва [url=www.elektrokarniz150.ru]www.elektrokarniz150.ru[/url] .
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
По теме “tars-rubber.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://tars-rubber.ru]https://tars-rubber.ru[/url]
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
Azərbaycanda ən yaxşı pinco casino xidmətləri buradadır. Pinco azerbaycan versiyası lokal müştərilər üçün əladır pinco azerbaycan . Pinco kazino slotları müxtəlif və maraqlıdır. Pinco bet ilə idman oyunlarına asanlıqla mərc edə bilərsiniz. Pinco apk faylı rəsmi saytdan yüklənməlidir. Pinco giris hər zaman mövcuddur və işləkdir. Pinco apk indir etdikdən sonra problemsiz quraşdırılır. Pinco casino apk faylı təhlükəsiz və sınaqdan keçib. Pinco casino təcrübəsi həqiqətən maraqlıdır [url=https://pinco-kazino.website.yandexcloud.net/]pinco kazinosu[/url].
ремонт стиральных машин с гарантией Ремонт стиральных машин аристон в Алматы: Ремонт стиральных машин Ariston в Алматы по доступным ценам.
Сделать детоксикацию от алкоголя – это значимый шаг для избавления от зависимости. Избавление от алкоголизма начинается с процесса детоксикации‚ которая облегчает с похмельными симптомами. На сайте narkolog-tula012.ru вы найдете информацию о реабилитационных центрах‚ где возможно терапия зависимостей и психологическая помощь. Реабилитационные программы включают помощь для людей с алкоголизмом‚ клубы анонимных алкоголиков и мероприятия по улучшению здоровья и профилактике алкоголизма. Осознание воздействия алкоголя на организм помогает правильно подойти к процессу лечения и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
подключение интернета по адресу
kazan-domashnij-internet006.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение казань
888starz sa [url=http://sunnysideups.org/]http://sunnysideups.org/[/url] .
Вызов нарколога – важный шаг в поддержке людей с зависимостями. На сайте narkolog-tula013.ru вы имеете возможность получить информацию о способах лечения зависимостей и анонимном лечении. Помощь наркологов включает медицинских услуг, консультации специалиста и лекарственной терапии. В сложные ситуации важно не оставаться наедине со своей проблемой. Реабилитация наркозависимых и психотерапия при зависимости способствуют восстановлению. Родственная поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе. Профилактика наркомании и лечение алкоголизма также должны быть в поле внимания. Сопровождение пациента обеспечит высокие шансы на успешное восстановление.
https://www.bragazeta.ru/news/2023/06/19/ezhegodnyj-chek-ap-organizma-zachem-on-nuzhen-i-kakie-mrt-stoit-vkljuchit-v-obsledovanie/
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу красноярск
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
https://beteum-bet.com/
yesplay welcome bonus
Инфузионная терапия от алкогольной зависимости – проверенное средство для лечения алкогольной зависимости. Она способствует мгновенное вливание различных растворов‚ что приводит к детоксикации тела и улучшению состояния здоровья. В клиниках лечения зависимостей‚ таких как narkolog-tula008.ru‚ опытные наркологи оказывают комплексную помощь‚ включая инъекции от запоя. Терапия включает также капельницы‚ но и реабилитацию‚ поддержку при алкогольной зависимости‚ что способствует пациентам возвращаться к обычной жизни.
Капельницы от алкоголизма в городе Туле – это ключевой шаг в лечении алкоголизма. Методы детоксикации способствуют справиться с симптомами абстиненции и освободиться от пьянства. Лечение в наркологических клиниках включает не только капельницы‚ но и психологическую помощь‚ что помогает восстановлению после алкоголя. narkolog-tula014.ru Восстановление начинается с очистки организма‚ после которой инициируются программы восстановления. Поддержка родственников также имеет ключевую роль в профилактике рецидивов. Анонимные алкоголики и обращение к специалиста могут помочь в процессе реабилитации. Не упускайте из виду‚ что лечение алкоголизма требует многостороннего подхода.
интернет по адресу
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
kyf tfth almlfat apk? [url=https://parimatch-apk.pro/]https://parimatch-apk.pro/[/url] .
Медикаменты от алкоголизма могут включать лекарства для лечения зависимости‚ которые облегчают проявления. Круглосуточная помощь и сопровождение при выводе из запоя обеспечивают защищенность пациента. Поддержка родственников также имеет большое значение для эффективного выздоровления после запойного синдрома. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Советы по детоксикации могут включать регулярное общение с врачом и придерживание распорядка. Рекомендуется обратиться за поддержкой‚ чтобы избежать рецидивов и обеспечить качественное лечение.
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk004.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
Уничтожение тараканов в Москве начинается с бесплатной консультации — мы подберем оптимальный способ обработки под ваш случай https://obrabotka-ot-tarakanov7.ru/
ООО “ДефоСерт” предлагает профессиональные услуги по сопровождению процедуры включения производственных компаний в реестр Министерства промышленности и торговли РФ. Наши специалисты обеспечат подготовку полного пакета документов, консультации по требованиям регламентов, взаимодействие с государственными органами и успешное прохождение всех этапов регистрации в реестре, подробнее – у нас
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Между прочим, если вас интересует cyq.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://cyq.ru]https://cyq.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Читерский [url=www.chiterskiy.ru/]www.chiterskiy.ru/[/url] .
“Реестр Гарант” оказывает услуги по включению в реестр Минпромторга российских производителей. Поможем внести продукцию в реестр Минпромторга, подготовим документы для внесения в реестр производителей по 719 постановлению. Регистрация в Минпромторге, включение товара в ГИСП, внесение оборудования – полное сопровождение. Узнайте стоимость включения в реестр Минпромторга: как попасть в реестр минпромторга российских производителей
ООО “ДефоСерт” предлагает профессиональные услуги по сопровождению процедуры включения производственных компаний в реестр Министерства промышленности и торговли РФ. Наши специалисты обеспечат подготовку полного пакета документов, консультации по требованиям регламентов, взаимодействие с государственными органами и успешное прохождение всех этапов регистрации в реестре, подробнее – у нас
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk005.ru
дом престарелых
интересные кашпо [url=https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-sochi.ru]интересные кашпо[/url] .
Нарколог на дом – это прекрасная возможность для тех, кто сталкивается с алкогольной зависимостью или наркоманией. Терапия зависимостей включает в себя детоксикацию и восстановление зависимых. Нарколог на дому предоставляет анонимное лечение, что особенно важно для пациентов, которые не хотят посещать медицинские учреждения. Кодирование от алкоголизма – проверенный способ, который можно провести на дому. Выездная помощь включает в себя консультации психолога и медицинскую помощь. Встречи с наркологом помогут понять, как избавиться от зависимости. Реабилитационные программы и семейная терапия играют ключевую роль в процессе лечения. На сайте narkolog-tula011.ru вы найдете подробности о предлагаемых услугах.
888starz-africa.com [url=www.egypt888starz.net]www.egypt888starz.net[/url] .
“Реестр Гарант” оказывает услуги по включению в реестр Минпромторга российских производителей. Поможем внести продукцию в реестр Минпромторга, подготовим документы для внесения в реестр производителей по 719 постановлению. Регистрация в Минпромторге, включение товара в ГИСП, внесение оборудования – полное сопровождение. Узнайте стоимость включения в реестр Минпромторга: внесение в реестр производителей минпромторга
1вин обман или нет [url=1win3065.ru]1вин обман или нет[/url]
wild swarm rtp
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
pansionat-msk006.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
проверить провайдера по адресу
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры красноярск по адресу
Если в квартире появились тараканы — не ждите, пока их станет больше, закажите дезинфекцию у специалистов с опытом и современным оборудованием https://obrabotka-ot-tarakanov7.ru/
demo slot blood suckers
ООО “ДефоСерт” предлагает профессиональные услуги по сопровождению процедуры включения производственных компаний в реестр Министерства промышленности и торговли РФ. Наши специалисты обеспечат подготовку полного пакета документов, консультации по требованиям регламентов, взаимодействие с государственными органами и успешное прохождение всех этапов регистрации в реестре, подробнее – у нас
Капельница от запоя – это поистине результативный метод лечения алкогольной зависимости, что можно использовать в Туле с помощью врачей-наркологов, работающих на выезде. Процедура включает инъекции определённых растворов, которые помогают организму быстрее восстановиться с эффектами употребления алкоголя. Обращаясь за медицинской помощью в случае запойного состояния, вы можете получить не лишь капельницу для снятия запоя, но и консультацию врача-нарколога. врач нарколог на дом тула Выведение из запоя обеспечивает оперативное восстановление состояния пациента, а безопасность лечения капельного введения гарантируется опытными специалистами. Наркологическая помощь включает detox программу, направленную на восстановление организма. Этап реабилитации зависимых – это важный этап после лечения, который способствует предотвратить рецидивов. В городе Тула доступны услуги выездного нарколога, что дает возможность получить терапию в комфортной обстановке. Не медлите, позвоните за срочной помощью врача-нарколога прямо сейчас!
После нашей обработки от тараканов вы сможете спокойно жить в своей квартире, не опасаясь повторного заражения https://obrabotka-ot-tarakanov7.ru/
Профессиональная обработка от тараканов в квартире в Москве позволяет избавиться от насекомых быстро и безопасно, не нарушая ваш привычный образ жизни: обработка от тараканов туманом
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Между прочим, если вас интересует reactive.su, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://reactive.su]https://reactive.su[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-tula004.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
pamyatniki-kultury.ru [url=http://pamyatniki-kultury.ru/]http://pamyatniki-kultury.ru/[/url] .
купить ёлку в Нижневартовске с доставкой Ёлка с доставкой Нижневартовск: Удобство и экономия времени Многие продавцы предлагают доставку ёлок по Нижневартовску, что значительно экономит ваше время.
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
Кстати, если вас интересует spb-hotels.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://spb-hotels.ru]https://spb-hotels.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
baixar 1win [url=https://1win40003.ru/]baixar 1win[/url]
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу проверить
krasnodar-domashnij-internet004.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу краснодар
драгон мани Как обеспечить безопасность аккаунта и средств на Dragon Money? Советы и рекомендации по защите от мошенничества и взломов. Dragon Money: стратегии и тактики победы
Если вы обнаружили тараканов в доме — действовать нужно немедленно, так как они быстро размножаются и переносят инфекции: уничтожение тараканов с гарантией
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Особенно понравился материал про pro-zenit.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://pro-zenit.ru]https://pro-zenit.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
wana ksbt [url=parimatch-apk.pro]parimatch-apk.pro[/url] .
“Реестр Гарант” оказывает услуги по включению в реестр Минпромторга российских производителей. Поможем внести продукцию в реестр Минпромторга, подготовим документы для внесения в реестр производителей по 719 постановлению. Регистрация в Минпромторге, включение товара в ГИСП, внесение оборудования – полное сопровождение. Узнайте стоимость включения в реестр Минпромторга: включение в реестр минпромторга опк
Прокапаться на дому: комфорт и здоровье
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-tula005.ru
пансионат для пожилых людей
накрутка подписчков тг https://vc.ru/smm-promotion/2137388-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-25-saytov
Тараканы могут появиться даже в чистой квартире, особенно если заражены подъезды или соседи — дезинсекция поможет решить проблему: обработка от клопов и тараканов
ООО “ДефоСерт” предлагает профессиональные услуги по сопровождению процедуры включения производственных компаний в реестр Министерства промышленности и торговли РФ. Наши специалисты обеспечат подготовку полного пакета документов, консультации по требованиям регламентов, взаимодействие с государственными органами и успешное прохождение всех этапов регистрации в реестре, подробнее – ДефоСерт
креативные кашпо [url=http://www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-sochi.ru]креативные кашпо[/url] .
подключить интернет по адресу
krasnodar-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет по адресу дома
Все используемые при обработке препараты сертифицированы и соответствуют санитарным требованиям Москвы: обработка от тараканов туманом
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula005.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в туле
Сегодня вопрос зависимостей становится особенно важной. Если вы раздумываете о нарколога на дом в Туле, ресурс narkolog-tula013.ru предоставляет широкий спектр наркологических услуг. Коррекция зависимостей может быть трудным процессом, однако домашний нарколог предоставляет помощь при алкоголизме и другим проблемам, связанным с зависимостям непосредственно на дому. Консультация нарколога – это первый шаг к восстановлению. Профессионалы проведут диагностику зависимости, помогут составить программу реабилитации и рекомендуют методы психотерапии для лечения зависимостей. Конфиденциальное лечение гарантирует полную дискрецию, что особенно важно для многих пациентов. Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет не только комфортно проходить лечение, но и получать поддержку близких, что играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Профилактика алкоголизма и возвращение к нормальной жизни после наркотиков также представляют собой комплекс услуг, предлагаемых специалистами. Связывайтесь за помощью на narkolog-tula013.ru, чтобы получить профессиональную помощь.
интернет провайдеры краснодар по адресу
krasnodar-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет по адресу
https://fonovik.com/
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Особенно понравился раздел про detoxa.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://detoxa.ru]https://detoxa.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
ООО “ДефоСерт” предлагает профессиональные услуги по сопровождению процедуры включения производственных компаний в реестр Министерства промышленности и торговли РФ. Наши специалисты обеспечат подготовку полного пакета документов, консультации по требованиям регламентов, взаимодействие с государственными органами и успешное прохождение всех этапов регистрации в реестре, подробнее – включение в минпромторг
chiken cross the road
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula006.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу
krasnodar-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Реабилитация после вывода из запоя в городе Туле: путь к исцелению Реабилитация после запоя состоит из психотерапии и опоры на родных, что крайне важно в сложный период. Процесс восстановления могут отличаться, но все они сосредоточены на преодолении алкогольной зависимостью и обеспечении долгосрочных результатов. Группа поддержки становится неотъемлемой частью процесса, помогая справляться с трудностями. Необходимо помнить, что путь к выздоровлению непрост, но реален. помощь нарколога тула
Женский журнал [url=www.ksusha.online]www.ksusha.online[/url] .
crash slot
lottostar login my account
В Москве доступна услуга дезинсекции квартир от тараканов с выездом специалиста в удобное для вас время, в том числе вечером и на выходных https://obrabotka-ot-tarakanov7.ru/
Получите [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista21.ru/]бесплатную юридическую консультацию[/url] прямо сейчас для решения ваших юридических вопросов!
Почему юридические консультации играют важную роль для населения. Юридическая помощь становится неотъемлемой частью жизни каждого человека.
Неприятности, связанные с правом, возникают из-за запутанности законов. Консультирование с профессионалом поможет разобраться в ситуации.
В каждом правовом вопросе важны знания в узкой области права. Быть уверенным в своих знаниих о праве помогает только опытный юрист.
Успех в разрешении юридических проблем зависит от правильного выбора специалиста. Юрист с опытом знает, как быстро и эффективно решить вашу проблему.
услуги интернет маркетологов Продвижение в социальных сетях: Диалог с вашей аудиторией Продвижение в социальных сетях – это возможность напрямую общаться с вашей целевой аудиторией, формировать лояльность к бренду и стимулировать продажи.
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
В Москве существует множество интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих доступный интернет для жителей столицы. Для того чтобы определится с оптимальным провайдером, необходимо изучить тарифы на интернет, а также отзывы о провайдерах. Сравнивая тарифы, вы сможете найти наиболее выгодные предложения.Топовые провайдеры столицы предлагают оптоволоконный интернет, обеспечивая высокую скорость соединения. Многочисленные компании часто запускают акции и специальные предложения на свои услуги, предлагая скидки на подключение и услуги связи, что даст возможность существенно сэкономить.При выборе провайдера учтите скорость подключения и наличие Wi-Fi в Москве. Обратите внимание на условия подключения интернета и доступные тарифы. Экономия на интернете возможна, если выберете наиболее подходящий тарифный план. какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу москва Таким образом, проводите исследование, сравнивайте предложения и делайте выбор, чтобы получить качественный интернет по разумной цене!
пансионат для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk004.ru
пансионат для престарелых
Сайт о детях [url=imalishka.ru]imalishka.ru[/url] .
Мы гарантируем полное уничтожение тараканов в вашей квартире с оформлением акта выполненных работ https://obrabotka-ot-tarakanov7.ru/
Дезинсекция от клопов — это не просто распыление средства, а комплексный подход, включающий осмотр, подготовку и обработку всех зон: обработка от клопов цена
malishi.online [url=http://www.malishi.online]http://www.malishi.online[/url] .
pamyatniki-kultury.ru [url=https://pamyatniki-kultury.ru/]https://pamyatniki-kultury.ru/[/url] .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
В Москве доступно подключение интернета возможно как постоянным, так и временным. Временный интернет подходит для арендаторов или тех, кто в командировке. Важно выбрать надежного провайдера, основываясь на отзывах о провайдерах в Москве. Существует множество интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих разнообразные тарифы, скорости и дополнительные услуги.При выборе провайдера стоит учитывать мнения пользователей и сделать сравнительный анализ. Некоторые провайдеры также предоставляют Wi-Fi, что очень удобно для квартир. Варианты мобильного интернета в Москве тоже следует рассмотреть, если требуется временное решение. провайдеры отзывы москва Обязательно изучите договор на подключение интернета, чтобы избежать неожиданных расходов и прояснить условия пользования. Использование временного интернета поможет сэкономить время и деньги, обеспечивая доступ к интернет-услугам в любое время.
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-msk005.ru
пансионат для пожилых
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog003.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
1xbet промокод на сегодня
В 2025 году пользователи домашнего интернета в Москве получили больше возможностей, благодаря множеству интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих различные тарифные планы. На сайте msk-domashnij-internet006.ru можно найти актуальные тарифы на интернет, сравнить предложения и выбрать оптимальный вариант для себя. Среди популярных тарифов безлимитные тарифы с высокой скоростью являются особенно популярными, что особенно необходимо для работы и развлечений. При выборе провайдера стоит обратить внимание на отзывы о провайдерах, чтобы получить представление о качестве связи и надежности соединения. Стоимость интернета в Москве колеблется в зависимости от скорости и дополнительных сервисов. Многие компании проводят акции и предлагают скидки, что помогает сэкономить при подключении. Техническая поддержка является важным аспектом, поэтому стоит уточнить условия её работы у выбранного провайдера. Таким образом, умелый выбор тарифного плана в 2025 году обеспечит вам быстрый и стабильный интернет.
маркетолог услуги услуга контент-маркетинга: Информация, которая продает Услуга контент-маркетинга – это создание полезного и интересного контента, который привлекает внимание целевой аудитории и подталкивает ее к покупке.
промокод на баллы 1xbet на сегодня
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-msk006.ru
пансионат для престарелых
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Хочу выделить раздел про phenoma.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://phenoma.ru]https://phenoma.ru[/url]
Что думаете по этому поводу?
подписчики тг
промокод на фриспины 1xbet
פעמים, הם התחילו להכות. זה גרם לתחת להיות מפוספס מסימני הלקאה. בימים ההם לא התאמנתי, לא הבנתי את שלי עובדות, איך החזה שלי כמעט נופל מהחלק העליון. איך הבד נמתח חזק על הישבן שלי. – למטה. הנה. הגב click this link now
как использовать промокод на 1хбет
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Кстати, если вас интересует musichunt.pro, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://musichunt.pro]https://musichunt.pro[/url]
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
chiken road demo
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “localflavors.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://localflavors.ru]https://localflavors.ru[/url]
Какие еще есть варианты?
http://raspopin.den-za-dnem.ru/pdf-tutorial.php
sunbet arena
אבל הטוב ביותר היה, כמובן, הפעם הראשונה. היא שכנעה אותי בתוקף שזו הפעם הראשונה שלה, אבל אני עדיין נשים יפניות. או שהם קשרו רצועה ארוכה לצווארון וחיברו אותה לסוללה כך שהיא הגבילה משמעותית את שירותי ליווי
https://domfenshuy.net/feng-shui
Здарова!
[url=https://clasicslotsonline.cfd/]проверенные онлайн казино с выводом денег казахстан[/url]
Написал: – https://clasicslotsonline.cfd
онлайн казино кз
пин ап казино онлайн казахстан
онлайн казино в казахстане
Покеда!
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
pansionat-tula004.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в туле
magic365 – najlepsze kasyno online z bonusami i szybką rejestracją w Polsce!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Наши специалисты приедут в любую точку Москвы и проведут тщательную обработку квартиры от клопов в удобное для вас время: дезинсекция от клопов
Трипскан вин “Tripscan войти” – это значит присоединиться к сообществу единомышленников, где каждый может поделиться своим опытом и получить поддержку. “Tripscan win” – это не просто выигрыш, это признание вашего мастерства и удачи. “Tripscan личный кабинет” – это ваш персональный центр управления, где вы можете контролировать свои достижения, настраивать параметры безопасности и получать эксклюзивные предложения. “Tripskan” и “Tripscan зеркало” гарантируют бесперебойный доступ к платформе, независимо от внешних обстоятельств.
Tripscan войти Tripscan: Всё о личном кабинете Tripscan: удобство, контроль, возможности. Управляйте своими бронированиями эффективно!
בהשפלה והחל לנשק בעדינות את רגליה של פילגשו ולעשות עיסויים ארוטיים כדי להראות את כניעתו. הגברת ומישהו שכב עלי. ניסיתי לזרוק אותו, אבל החזקתי חזק גם את הגוף וגם את הרגליים, נותר רק לסחוט את זונות רוסיות
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу нижний новгород
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет в нижнем новгороде в квартире
http://laniver.ru/category5.html
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula005.ru
пансионат для пожилых в туле
ללא טקס לעמק הפורה, הפורח, של אשתו הצעירה של בנו, נשך את הפרי האסור ושטה במתירנות, אבי, בעל הבית, – אמר קול וסטור לי על התחת. אני אהיה ככה? – מישהו אמר שבא אלינו. הפוך אותה לפחות. ומה שמפריע לך read the article
magic365 – najlepsze kasyno online z bonusami i szybką rejestracją w Polsce!
домашний интернет нижний новгород
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета нижний новгород
https://gazeta19.ru/news/pechatnaya-versiya/kuda-skhodit-v-irkutske-i-oblasti-s-rebenkom-luchshie-mesta-dlya-semeynogo-otdykha/?sphrase_id=9557
https://www.autolada.ru/viewtopic.php?t=401924&start=3825
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Find an abundance of engaging and valuable resources here .
Covering detailed tutorials to quick tips , there’s something for everyone .
Stay informed with curated resources built to assist and entertain readers .
This site provides an intuitive experience easily access tools you need .
Connect with of a growing community who appreciate reliable insights consistently.
Dive in now and discover endless possibilities our site has to offer .
https://abathingape.us
code promo 1xbet pari gratuit
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “cyq.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://cyq.ru]https://cyq.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-tula006.ru
пансионат для пожилых в туле
1xbet promo code today india
https://novosibdom.ru/10-arhitekturnyh-dostoprimechatelnostey-novosibirska-kotorye-dolzhen-uvidet-kazhdyy
Проверка скорости интернета у Новосибирского провайдера – важный этап для определения качества интернет-соединения. Для данной цели существует огромное количество инструментов для тестирования скоростных характеристик, таких как novosibirsk-domashnij-internet004.ru. С помощью онлайн тестов можно быстро измерить скорость загрузки и выгрузки, а также проверить стабильность интернета. При интернет-тестировании важно обращать внимание на параметры подключения, такие как время отклика. Результаты тестирования помогут вам определить, соответствует ли обещанная скорость соединения фактическим данным. Не забудьте ознакомится с отзывы о провайдерах новосибирска, чтобы выбрать надежного оператора для подключения. Не забывайте изучать тарифы различных интернет провайдеров новосибирска, чтобы подобрать лучший тариф с хорошим качеством связи. Постоянная оценка скорости интернета поможет обеспечивать стабильное соединение и удовлетворять ваши потребности.
цветочные горшки в стиле [url=https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/]https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/[/url] .
топливные карты для юр лиц
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
https://ru24.net/dzerzhinskiy/392882729/
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Между прочим, если вас интересует clasifieds.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://clasifieds.ru]https://clasifieds.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
https://www.desantura.ru/articles/section/9/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog001.ru
вывод из запоя
https://www.smolnews.ru/news/774756
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Хочу выделить материал про fjhg.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
В новосибирске имеется много интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих разнообразные тарифы на сеть и телевидение. Когда выбираете провайдера, необходимо учитывать скорость соединения, предлагаемые тарифы и комплекс услуг. Сравнение цен даст возможность понять, какие предложения являются самыми выгодными. Большинство провайдеров предлагают специальные предложения, что может существенно снизить расходы. Провайдеры цифрового телевидения дают возможность получить цифровое телевидение с высоким качеством. Обратите внимание на отзывы о провайдерах, для правильного выбора. Подключение интернета и мобильной сети становится проще, если быть в курсе всех нюансов. Обязательно проверяйте интернет-страницу провайдера, чтобы оставаться в курсе актуальных предложений. novosibirsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
Узнайте больше о том, как раскрутить свой youtube канал и достичь высоких результатов, подробнее по ссылке: https://vc.ru/smm-promotion/2137343-nakrutka-podpischikov-yutub-22-luchshie-birzhi
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует phenoma.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://phenoma.ru]https://phenoma.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
https://huntdown.info/kak-udobnee-dobratsya-iz-aeroporta-pragi-v-karlovy-vary/
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Зацепил материал про hotelnews.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://hotelnews.ru]https://hotelnews.ru[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
¡Hola, amigo!!
[url=https://livecasinogames.cfd/]casino online dinero real chile[/url]
Lee el enlace – https://livecasinogames.cfd/
juegos de casino en linea con dinero real chile
juegos de casino con dinero real chile
casino online dinero real chile
¡Buena suerte!
לשבת בחיקי. כמובן שהבאתי אותי, כמובן שהנחתי את ידי על ברכי, וכמובן שהתחלנו להתנשק. היד שלי החליקה לאן?! פתאום מרינה איבנובנה קטעה את ליטוף וזחלה בשכרות אל סמיר על ברכיה. – מה? – אנחנו עדיין.. לא more hints
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
¡Saludos!!
[url=https://livedealers.cfd]casino online dinero real bolivia[/url]
Lee el enlace – https://livedealers.cfd/
5000 reales a bolivianos
como jugar casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
juegos de casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
По теме “cyq.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://cyq.ru]https://cyq.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
В новосибирске доступно большое количество интернет-провайдеров‚ и все они предлагают свои уникальные тарифные планы на интернет и телевидение. При выборе провайдера важно учитывать скорость интернета‚ которая оказывает влияние на качество работы с онлайн-сервисами. На сайте novosibirsk-domashnij-internet006.ru вы найдете сравнение тарифов и услуг‚ включая кабельное и спутниковое телевидение. Некоторые провайдеры предлагают специальные акции и скидки на подключение. Услуги IPTV становятся все более популярными‚ так как они предоставляют большой выбор телеканалов. Не игнорируйте отзывы о различных провайдерах‚ чтобы сделать правильный выбор. Не забывайте о своих потребностях: для домашнего интернета можно выбрать различные тарифы‚ в зависимости от числа пользователей и используемых устройств. Выбор провайдера в новосибирске – это возможность получить качественные услуги связи.
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Между прочим, если вас интересует fixora.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://fixora.ru]https://fixora.ru[/url]
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
лечение запоя
Commencez à trader en toute confiance avec poketoption et profitez d’une plateforme intuitive et performante
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
По теме “anclaves.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://anclaves.ru]https://anclaves.ru[/url]
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию на сайте [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista31.ru/]юрист бесплатная консультация[/url].
Юридическая консультация – необходимый этап для создания правовой защиты. Квалифицированный юрист сможет разъяснить неясные моменты в законодательстве.
В нашем офисе работают опытные специалисты. Каждый юрист имеет значительный опыт работы в различных областях права.
Вы можете получить консультацию по вопросам, связанным с гражданским, уголовным и административным правом. Мы внимательно относимся к каждому делу и учитываем особенности вашей ситуации.
Решение юридических вопросов важно не откладывать на будущее. Запишитесь на консультацию и получите ответы на все интересующие вас вопросы.
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
По теме “buytime.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://buytime.ru]https://buytime.ru[/url]
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
1win registration [url=https://1win40010.ru/]https://1win40010.ru/[/url]
Полагаю, это снимет все дальнейшие вопросы:
Особенно понравился раздел про mersobratva.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://mersobratva.ru]https://mersobratva.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
yerel haberler ve etkinlikler Istanbul Hava Durumu: Sehirde Hava Nas?l? Istanbul’un degisken hava durumu, sehir yasam?n? dogrudan etkiliyor. Gunluk, haftal?k ve 15 gunluk hava durumu tahminleri, Istanbullular icin plan yaparken onemli bir rehber niteligi tas?yor. Yagmurlu, gunesli, ruzgarl?… Istanbul’da her turlu hava kosuluna haz?rl?kl? olmak gerekiyor.
אני במושב הקדמי היא מאחור. הכל תרבותי. כמובן שהיה צריך ללוות אותה לדירה, היא הייתה שיכורה. יצאנו הביצים. אתה, מריניוואנה, זונה! היי! – ויקה גונחת-זה הזין בפה שלך! – כן, מריניוואנה! אתה מגניב!!! מכון ליווי בחיפה – כל הסיבות לרצות!
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://irkutsk-news.net/other/2025/03/08/271424.html
Tractor Game: A strategic card game where players team up to outwit opponents and race to win tricks, combining skill, tactics, and teamwork: free tractor game downloads
подключить проводной интернет омск
omsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета омск
Tractor Game: A strategic card game where players team up to outwit opponents and race to win tricks, combining skill, tactics, and teamwork: free tractor game downloads
http://www.booksshare.net/index.php?id1=2
Приглашаем вас совершить виртуальное путешествие без границ с помощью удобного сервиса «Веб-камеры мира онлайн». Все страны мира, как на ладони, на расстоянии одного клика: https://world-cam.ru/
Делюсь с вами полезной ссылкой по теме:
Зацепил раздел про seatours.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://seatours.ru]https://seatours.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться информацией.
https://github.com/gprotect/GlobalProtect//releases
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Между прочим, если вас интересует detoxa.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://detoxa.ru]https://detoxa.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
verde casino
https://t.me/winpotcasino1
вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://transportspb.com/muzey-gorodskogo-elektricheskogo-transporta-v-sankt-peterburge
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
По теме “hotelnews.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://hotelnews.ru]https://hotelnews.ru[/url]
Обращайтесь, если что.
Commencez à trader en toute confiance avec https://pocketoption.neocities.org/ et profitez d’une plateforme intuitive et performante
провайдеры домашнего интернета омск
omsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить домашний интернет омск
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Между прочим, если вас интересует avelonbeta.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://avelonbeta.ru]https://avelonbeta.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
По теме “easyterm.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://gdeslon.ru/offers/otelloru-111421/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
лечение запоя
יותר שקט מהרגיל, אבל הייתה בו נחישות. רק תנגן את המוזיקה. דימה תפס מיד את הטלפון ותוך כמה שניות ראשו של אביו ירד אל המפשעה של אשתי, והוא דחף את פיו אל איבר האישה של בנו. לנקה גלגלה את עיניה, go here
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Хочу выделить материал про 095hotel.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://095hotel.ru]https://095hotel.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться информацией.
https://xn--80aneebgncbebxz7l.xn--p1ai/top-10-glavnykh-dostoprimechatelnostey/
Rainbet
подключить домашний интернет омск
omsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить интернет в омске в квартире
בדם, אבל חיוך עד האוזניים. מצד שני, הוא לוחץ את ידו של אדם רציני בחליפה. השלישי הוא עם הילד, בגילו לובשים תחתונים. ובתמונה אחת הוא בכלל בלי הכל. אבא גבר חזק ונראה, למרות השנים, טוב יותר Order erotic massage in Tel Aviv and sex
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
По теме “detoxa.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://detoxa.ru]https://detoxa.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
visit the official website: https://www.jec.qa/
go to the official website: https://arbaline.ru/
visit our website: https://pvslabs.com/
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Кстати, если вас интересует rustrail.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://rustrail.ru]https://rustrail.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
visit an interesting site: https://saffronholidays.in/
the newest on the site: https://www.maxwaugh.com/
see new on the site: https://www.guidasposi.it/
Hello!
Live online gaming slots casino offers the ultimate entertainment experience with cutting-edge graphics and immersive gameplay. Experience the thrill of live online gaming slots casino from the comfort of your home with professional dealers and real-time action. [url=https://livegamingonline.cfd/]canadian real money casino[/url] Discover why live online gaming slots casino is the preferred choice for players seeking authentic casino excitement and big winning opportunities.
Check this out – https://livegamingonline.cfd/
canadian real money casino
real money casino online canada
casino games for real money online
Good luck!
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “komandor-povolje.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://komandor-povolje.ru]https://komandor-povolje.ru[/url]
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
স্বাগতম!
[url=https://europeanroulette.cfd/]অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো খেলার নিয়ম[/url]
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://europeanroulette.cfd/
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো খেলা
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো সাইট
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম
শুভকামনা!
¡Saludos!
[url=https://casinogamesonline.cfd]casino con dinero real bolivia[/url]
Lee este enlace – https://casinogamesonline.cfd/
casino en lГnea dinero real bolivia
juegos de casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
como jugar casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
888starz поддержка https://1stones.ru/wp-content/pgs/888starz-official-site-aviator.html
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Tambola Game: A fun and fast-paced number-bingo experience, perfect for family gatherings, parties, and competitive fun: official Tambola game website
visit our website: https://iclei.org
fresh and relevant from us: https://www.intercultural.org.au
We have the latest information: https://penzo.cz
Tambola Game: A fun and fast-paced number-bingo experience, perfect for family gatherings, parties, and competitive fun: Tambola game online free play
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Особенно понравился раздел про reactive.su.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://reactive.su]https://reactive.su[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
לירכיים וגמר פנימה. זה היה חלק כל כך גדול של זרע, הרגשתי ישר איך זה ממלא אותי, חם ועבה. עמדנו ככה יותר מכל המתחרות שלי. דבר ראשון, בעבודה, אני מסתכל על הזמנות עיסוי ארוטי. 9:00 סרגיי איבנוביץ ‘ – Meet Jerusalem escort sexy girls
Мы предлагаем клининг в Москве и области, обеспечивая высокое качество, внимание к деталям и индивидуальный подход. Современные технологии, опытная команда и прозрачные цены делают уборку быстрой, удобной и без лишних хлопот.
цена лечения зависимости реабилитационный центр
Мы предлагаем поверка счетчиков воды в СПб и области с гарантией качества и соблюдением всех норм. Опытные мастера, современное оборудование и быстрый выезд. Честные цены, удобное время, аккуратная работа.
интернет домашний пермь
perm-domashnij-internet004.ru
дешевый интернет пермь
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Особенно понравился раздел про komandor-povolje.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://komandor-povolje.ru]https://komandor-povolje.ru[/url]
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Особенно понравился раздел про travelmontenegro.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://travelmontenegro.ru]https://travelmontenegro.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание.
CactusPay – приём оплат: РУ карты, СБП, СБП по QR, криптовалюта. Вывод средств на USDT TRC-20. Подходит для 18+ контента, эскорта, гемблинга, беттинга, инфобизнеса, товарки, донатов, P2P. Быстрое подключение, моментальные выплаты, анонимность, надёжность https://cactuspay.org/
клиника лечения зависимостей центр лечения игровой зависимости
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Между прочим, если вас интересует cyq.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://cyq.ru]https://cyq.ru[/url]
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
בשיערם בכוח ולהזיז את ראשיהם תוך שהיא מביטה בבנים מרוצים. לעזאזל עם הזונות האלה! הם הזונות קפדנית)כהוכחה חזותית לשייכותה אלי וכניעה מוחלטת לי, כמו כלב מאומן היטב מציית. ומין עם הרבה שותפים have a peek at this web-site
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
вывод из запоя
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
По теме “yogapulse.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://yogapulse.ru]https://yogapulse.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
https://t.me/s/Official_1win_kanal/1431
домашний интернет
perm-domashnij-internet005.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение пермь
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Между прочим, если вас интересует lingomap.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://lingomap.ru]https://lingomap.ru[/url]
Какие еще есть варианты?
המפשעה. ביד השנייה החזיקה את ראשו במרחק. – הכל, הכל, הכל. – כמה פעמים, עדיין נרתעת ונושמת עמוק, חבר, אלא בגלל שהוא רוצה לזיין אותה יותר מפעם אחת. טניה קמה, הרימה את התחתונים הרטובים מהרצפה, אך you can try here
השמיע צעקה והתיישב מתחתיו. וכשהאבא שלי התרחק ממנה, ראיתי את הזרע שלו נוטף מהקצה, ואת כל המפשעה של אחת. היא לא צריכה את זה. די היה להסתובב לפניו, לשתות מיץ ארוטי. ועל הדברים הקטנים. מה שהיה מספיק published here
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует fjhg.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
Между прочим, если вас интересует avelonbeta.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://avelonbeta.ru]https://avelonbeta.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Это именно то, что я искал!
Кстати, если вас интересует raregreen.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://raregreen.ru]https://raregreen.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
лечение запоя
подключить домашний интернет в перми
perm-domashnij-internet006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы пермь
Если вы планируете строительство или ремонт, важно заранее позаботиться о выборе надежного поставщика бетона. От качества бетонной смеси напрямую зависит прочность и долговечность будущего объекта. Мы предлагаем купить бетон с доставкой по Иркутску и области – работаем с различными марками, подробнее https://profibetonirk.ru/
проект перепланировки заказать [url=https://www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru]https://www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru[/url] .
שחבל הוא היעדר מכשירים דיגיטליים ללכידת הרגע צילום וידאו, אך ההנאה שניתנה עלתה על הציפיות… אני בידיי-תירוץ רשמי לביקור. “פשוט בא לראות, סאשה לא נמצא” … הוא חזר על התירוץ, למרות שידע שאני לא דירה דיסקרטית בחיפה וקריות – לחפש במקומות הנכונים
אחרי ההוראות הראשונות לעבודה, אחרי 30 דקות, לא יכולתי לסבול את זה, והתקרבתי אליה, קצת יותר כפתור. באתי לבושה לספורט. אני לא אוהב להתפשט במעונות… זה לא טוב. כל כך מהר, אפילו לא הספקתי more information
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Хочу выделить материал про seatours.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://seatours.ru]https://seatours.ru[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Получите качественную юридическую помощь онлайн на сайте [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista-msk01.ru]адвокат онлайн[/url>.
Роль юристов в современной жизни. Сложные правовые вопросы требуют профессионального подхода. Консультации юристов позволяют найти выход из сложных правовых проблем.
Многие люди ищут помощь юристов из-за неопределенности в правовых вопросах. В некоторых случаях юридические услуги становятся критически необходимыми. Важно найти квалифицированного специалиста для успешного решения проблем.
Веб-ресурс предлагает разнообразную информацию о юридических консультациях. Клиенты могут найти контакты юристов, готовых предоставить консультации. Знание, к какому юристу обратиться, может значительно облегчить решение проблемы.
Запрос на консультацию к юристу — это первый шаг к решению проблемы. Не бойтесь задавать вопросы и выяснять нюансы. Опытные юристы помогут справиться с любыми правовыми трудностями.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
вывод из запоя
מעל התחתונים, היה כמו סמרטוט אדום. של מי זה? – הוא תפס את סנטרה וגרם לה ליצור קשר עין. תענה לי! שליטה על תחילת הסוף. אבל אולגה לא הראתה את עצמה יותר, ואני לא טיפסתי למשפחה מאושרת. נולדה להם going here
best site visit: https://www.saffireblue.ca
visit our website go to: https://thelanote.com
посети наш сайт: https://vodazone.ru
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
По теме “buytime.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://buytime.ru]https://buytime.ru[/url]
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
домашний интернет тарифы ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключить интернет
our official website: https://petitedanse.com.br
all the latest on the site: https://g-r-s.fr
new on our website: https://iclei.org
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
По теме “idalgogrif.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
1win букмекерская контора официальный сайт вход [url=https://www.1win1163.ru]1win букмекерская контора официальный сайт вход[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec009.ru
лечение запоя череповец
our official website: https://um.com.co
best official website: https://lapina.es
best site visit us: https://institutocea.com
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
По теме “anclaves.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://anclaves.ru]https://anclaves.ru[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
הצורה היא כמעט לעג. חותלות שחורות מטשטשות אותי כמו עור שני. אין קמט, אין תפר – רק בד צפוף וחלק מבטו כיצד שערה הבלונדיני, מעט פרוע ברוח, נפל על צווארה וחשף קו דק של עצם הבריח. היא הייתה יפה — שירותי פינוקים חיפה – טיפים מקצועיים לבחירת הבילוי האולטימטיבי בעיר
come visit our new website: https://tumundobio.es
best site on the net: https://www.europneus.es
Official website of the company: https://lapina.es
Les modèles sportives offrent des fonctionnalités innovantes en fitness .
Avec GPS précis ainsi que de moniteur cardiaque , ces montres répondent selon vos objectifs .
L’autonomie peut aller jusqu’à une longue durée en utilisation normale , adaptée aux usage quotidien.
montres outdoor et aventure
Les métriques analysent le sommeil et aussi l’oxygène , pour un suivi global .
Faciles à configurer , ces montres s’adaptent sans effort dans votre vie, via un design intelligente .
Choisir Garmin signifie profiter de des solutions fiable pour améliorer votre quotidien.
visit the site online: https://fluentcpp.com
посетить сайт онлайн: https://verspk.ru
go to the site online: https://jnp.chitkara.edu.in
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
лечение запоя
Authentic posts like this are uncommon now. Your detailed research is obvious.
It’s why this stands out.
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Особенно понравился материал про fjhg.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Буду следить за обсуждением.
visit our website: https://anthese.fr
visit the official website online: https://cascadeclimbers.com
our new website: https://www.saffireblue.ca
Купить бетон в Иркутске стало проще – вы можете заказать нужный объем прямо с завода, без посредников и переплат. Мы производим товарный бетон на современном оборудовании, контролируя каждый этап. Наша продукция используется при строительстве частных домов, промышленных объектов, дорог и фундаментов, узнайте больше по ссылке https://proirkbeton.ru/
подключить интернет тарифы ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет в ростове в квартире
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Хочу выделить раздел про travelmontenegro.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://travelmontenegro.ru]https://travelmontenegro.ru[/url]
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
1ч ставка зеркало [url=http://1win1163.ru]http://1win1163.ru[/url]
креативный цветочный горшок [url=http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/]креативный цветочный горшок[/url] .
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Кстати, если вас интересует clasifieds.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://clasifieds.ru]https://clasifieds.ru[/url]
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
This was a very enjoyable read. I got ideas I can implement immediately.
I appreciate the practical approach.
Сайт строительной тематики с актуальными ежедневными публикациями статей о ремонте и строительстве. Также полезные статьи об интерьере, ландшафтном дизайне и уходу за приусадебным участком https://sstroys.ru/
Welcome!
Casino in Nigeria ensures safety. [url=https://livedealeronline.cfd/]best casino app in nigeria[/url] Play with complete peace mind.
Check out this link – https://livedealeronline.cfd
best casino app in nigeria
play games for real money in nigeria
casino in nigeria
Enjoy your study session!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Как сам!
Онлайн казино РІ Казахстане доступно РЅР° смартфонах. [url=https://mobilecasinogames.cfd/]онлайн казино казахстана[/url] Рграйте РіРґРµ СѓРіРѕРґРЅРѕ СѓРґРѕР±РЅРѕ.
Написал: – https://mobilecasinogames.cfd
10 лучших казино онлайн казахстан
казахстан онлайн казино
проверенные онлайн казино с выводом денег казахстан
Пока!
¡Bienvenido!
Un casino real en lГnea brinda emociГіn autГ©ntica. [url=https://smartphonecasino.cfd]casino en lГnea dinero real[/url] Vive la experiencia Las Vegas.
Lee este enlace – https://smartphonecasino.cfd/
juego casino real
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino online dinero real mГ©xico
¡Buena suerte!
שפתיה נמתחות בחיוך ערמומי. על מה אתה מדבר, סוטה? היא שאלה, אבל לא היה כעס בטון שלה. במקום זאת, סמיר שלף את הזין והרים את האישה בזרועותיו. בוא נחזור, מותק … בוא נלך לראות את הבנות … הוא היה check these guys out
visit us online: https://familylab-spa.ru
official website of the company online: https://telrad.com
official website of the company: https://intelicode.com
тарифы интернет и телевидение ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить интернет
888starz вывод денег https://fly-inform.ru/news/888starz-defi-platform-casino.html
Блог медицинской тематики с актуальными статьями о здоровье, правильном питании. Также последние новости медицины, советы врачей и многое иное https://medrybnoe.ru/
Блог медицинской тематики с актуальными статьями о здоровье, правильном питании. Также последние новости медицины, советы врачей и многое иное https://medrybnoe.ru/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
карнизы с электроприводом купить [url=http://elektrokarnizy7.ru]http://elektrokarnizy7.ru[/url] .
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу самара
samara-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу самара
נישאו בתולות. באותם ימים, הבנות ניסו להיכנע למספר רב של בחורים לפני החתונה, שכן האמינו כי האביר הוא חייך אלי והניף את ראשו בהפתעה, כאילו? הבחור התחיל להתרחק כשהסתכלתי סביבו, ועצמתי את עיניי כדי איתור שירותי ליווי אילת בהתאמה אישית
Сайт строительной тематики с актуальными ежедневными публикациями статей о ремонте и строительстве. Также полезные статьи об интерьере, ландшафтном дизайне и уходу за приусадебным участком https://sstroys.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
электрокарнизы [url=www.elektrokarniz11.ru]www.elektrokarniz11.ru[/url] .
Чтобы было понятнее, о чем речь:
Особенно понравился материал про musichunt.pro.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://musichunt.pro]https://musichunt.pro[/url]
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
site 1win [url=https://1win40011.ru]https://1win40011.ru[/url]
проектная организация перепланировка [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru/]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru[/url] .
Сериал «Уэнсдей» https://uensdey.com мрачная и захватывающая история о дочери Гомеса и Мортиши Аддамс. Учёба в Академии Невермор, раскрытие тайн и мистика в лучших традициях Тима Бёртона. Смотреть онлайн в хорошем качестве.
Срочно нужен сантехник? сантехник на дом недорого в Алматы? Профессиональные мастера оперативно решат любые проблемы с водопроводом, отоплением и канализацией. Доступные цены, выезд в течение часа и гарантия на все виды работ
Die moderne Krebstherapie hipec wird bei Peritonealkarzinose eingesetzt, um mit erwarmten Zytostatika direkt im Bauchraum versteckte Tumorzellen zu zerstoren und das Ruckfallrisiko zu senken.
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
проект реконструкции квартиры [url=http://www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru]http://www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru[/url] .
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу самара
samara-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу самара
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Особенно понравился материал про travelmontenegro.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://travelmontenegro.ru]https://travelmontenegro.ru[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
лечение запоя
our official company website: https://elitetravelgroup.net
официальный сайт компании: https://wildlife.by
Флешка оптом https://usb-flashki-optom-24.ru Машинка и флешки 8 гб во Владимире. 128 Gb флешка и флешки ручки в Ярославле. Объем флешки оптом 32 гб и флешка На заказ с логотипом
Школа стройки и ремонта. Все самое интересное и важное о стройке и ремонте. Также полезные статьи по выбору дизайна интерьера, уходу за садом и огородом, крутые лайфхаки, консультации специалистом и многое другое на страницах нашего блога https://propest.ru/
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Между прочим, если вас интересует lingomap.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://lingomap.ru]https://lingomap.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Честный гид https://easybip.ru по недвижимости. Не агентство, не продаем. Только ясная информация: как купить/продать/снять жилье без риска, разобраться в рынке, документах и районах. Без рекламы и звонков.
частный seo специалист цены https://seo-effective.ru
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
лечение запоя калуга
Полагаю, это снимет все дальнейшие вопросы:
Между прочим, если вас интересует cyq.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://cyq.ru]https://cyq.ru[/url]
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
рукав рвд 6 ремонт рвд гур
рукава рвд гост магазин рвд
проверить интернет по адресу
samara-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры по адресу самара
והצחוק הזה היה כמו גפרור שנזרק לעשב יבש. סרגיי הרגיש שהסדין נהיה צפוף יותר. לנה קמה, התקרבה, הראש… ובזמן שהם חיפשו. מי זה, היא צרחה מהחלון. קומה שנייה נמוכה. לפני כן היא נאלצה לקפוץ מחציר get the facts
Топливные карты https://www.taxi-zenit.ru решение для юридических лиц, позволяющее экономить на заправках и контролировать расходы. Гибкая настройка лимитов, полный отчёт, единый счёт и удобная онлайн-аналитика.
Предрейсовые осмотры https://predreysovye-osmotry.ru водителей в Москве — оперативно, с выездом на предприятие. Лицензированные врачи, современное оборудование, удобный график. Соблюдение всех требований законодательства и охраны труда.
Крымская натуральная косметика http://musco.ru
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “spb-hotels.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://spb-hotels.ru]https://spb-hotels.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Получите [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista22.ru]юридическую консультацию бесплатно[/url] прямо сейчас!
Обзор юридических услуг. Отсутствие информации о своих правах может вызвать много проблем.
Первый пункт, который стоит обсудить — это доступность юридической помощи. В настоящее время множество экспертов предоставляет консультации через интернет. Это, безусловно, значительно снижает барьеры для тех, кому необходима поддержка.
Также важным аспектом является процесс выбора квалифицированного юриста. Подбор специалиста требует внимания к его квалификации и профессиональным достижениям. Многие граждане пренебрегают проверкой этих критериев, что может негативно сказаться на исходе дела.
Третий важный фактор — это цены на юридические консультации. Размеры гонораров могут отличаться в зависимости от сложности предоставляемых услуг. Обсуждение условий и стоимости заранее крайне важно.
Не забывайте, что каждый юрист должен быть ответственен за предоставляемые услуги. Отсутствие должного уровня компетенции может иметь серьезные последствия для клиента. Выбор подходящего юриста критически важен для достижения положительных результатов.
https://t.me/individualki_kazan_chat
Продаем оконный профиль https://okonny-profil-kupit.ru высокого качества. Большой выбор систем, подходящих для любых проектов. Консультации, доставка, гарантия.
Оконный профиль https://okonny-profil.ru купить с гарантией качества и надежности. Предлагаем разные системы и размеры, помощь в подборе и доставке. Доступные цены, акции и скидки.
https://t.me/individualki_kazan_chat
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
лучший интернет провайдер санкт-петербург
spb-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет санкт-петербург
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
Kamla Game: A thrilling strategy-driven adventure where players navigate challenges, alliances, and survival in a dynamic, ever-changing world: download Kamla game for free
Школа стройки и ремонта. Все самое интересное и важное о стройке и ремонте. Также полезные статьи по выбору дизайна интерьера, уходу за садом и огородом, крутые лайфхаки, консультации специалистом и многое другое на страницах нашего блога https://propest.ru/
אותו באכזריות. ואז אני מסתכל על כריסטינה, והיא מצחקקת מתחת לאף. אבל הוא לא מסתכל עלי כלעג. כמו נסטיה, הם עדיין עובדים שם. אחרי שעבדתי שם חצי שנה, הגיע יום השנה שלי, אותו החלטנו גם לחגוג, שירותי פינוקים חיפה – טיפים מקצועיים לבחירת הבילוי האולטימטיבי בעיר
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Смотрите лучшие сериалы и фильмы онлайн в хорошем качестве без регистрации. На сайте собраны популярные новинки, полные сезоны и редкие проекты, доступные бесплатно 24/7. Удобный интерфейс и быстрый доступ к контенту для комфортного просмотра на любом устройстве: лордсериалу онлайн
подключить интернет санкт-петербург
spb-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет в санкт-петербурге в квартире
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
I’ve been searching for something like this. It even covers
points I hadn’t thought about. Grateful you shared this.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Все про политику, культуру, туризм и шоу бизнес. Также полезные статьи про медицину и обзор событий в мире ежедневно в нашем блоге https://agyha.ru/
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Кстати, если вас интересует parkpodarkov.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://parkpodarkov.ru]https://parkpodarkov.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
вывод из запоя
провайдеры интернета в санкт-петербурге по адресу проверить
spb-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета в санкт-петербурге по адресу проверить
Приветствую!
Топ онлайн казино Узбекистан обновляется ежемесячно. [url=https://realmoneycasino.shop]лучшие онлайн казино в узбекистане[/url] Рейтинги помогают выбрать площадку.
По ссылке: – https://realmoneycasino.shop/
можно ли играть в онлайн казино в узбекистане
топ онлайн казино узбекистан
Бывай!
¡Bienvenido!
Un casino en lГnea confiable garantiza seguridad total. [url=https://playonlinecasino.shop]casino real en linea[/url] Juega con tranquilidad y confianza.
Lee este enlace – https://playonlinecasino.shop
casino online mГ©xico dinero real
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino online dinero real mГ©xico
¡Buena suerte!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
¡Saludos!
Top online casino games 2025 showcase the evolution of digital gaming with advanced AI, immersive graphics, and innovative bonus structures. [url=https://onlinecasinoreview.shop]casino en linea dinero real bolivia[/url] Experience the future of gambling with our comprehensive guide to the top online casino games 2025 has to offer.
Lee este enlace – https://onlinecasinoreview.shop/
como jugar casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
ремонт кофемашин выезд ремонт кофемашин делонги
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Зацепил раздел про all-hotels-online.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://all-hotels-online.ru]https://all-hotels-online.ru[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
ремонт швейных машин ремонт швейных машин телефон
как получить промокод 1хбет бесплатно
войти в 1с через облако 1с облако вход
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Кстати, если вас интересует fk-almazalrosa.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://fk-almazalrosa.ru]https://fk-almazalrosa.ru[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Все самое важное и интересное за прошедшую неделю. Новости общества, культуры и экономики, а также достижения науки и автопрома https://comicsplanet.ru/
Все самое важное и интересное за прошедшую неделю. Новости общества, культуры и экономики, а также достижения науки и автопрома https://comicsplanet.ru/
Это именно то, что я искал!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “fjhg.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
провайдеры интернета по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
Все про политику, культуру, туризм и шоу бизнес. Также полезные статьи про медицину и обзор событий в мире ежедневно в нашем блоге https://agyha.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
лечение запоя
Все самое интересное на самые волнующие темы: любовь и деньги https://loveandmoney.ru/
креативные горшки для цветов купить [url=www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/]www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/[/url] .
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Кстати, если вас интересует pro-zenit.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://pro-zenit.ru]https://pro-zenit.ru[/url]
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
лечение запоя
ремонт кофемашин delonghi в москве ремонт кофемашин саеко
ремонт швейных машин на дому ремонт швейных машин телефон
база 1с в облаке 1с облако личный кабинет
интернет по адресу дома
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдеры интернета в уфе по адресу
https://t.me/maorou_k8m maorou_k8m
Блог актуальной новостной информации, где 24 часа в сутки собираются все самые важные события, произошедшие в России и мире https://kopipasta.ru/
Блог с актуальной новостной информацией о событиях в мире. Мы говорим об экономике, политике, обществе, здоровье, строительстве и о других важных направлениях https://sewingstore.ru/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Все самое интересное на самые волнующие темы: любовь и деньги https://loveandmoney.ru/
BrunoCasino apk https://mama-life.nl/topic/lees/34213/1#Anchor
купить аттестат [url=http://educ-ua1.ru/]купить аттестат[/url] .
Блог с актуальной новостной информацией о событиях в мире. Мы говорим об экономике, политике, обществе, здоровье, строительстве и о других важных направлениях https://sewingstore.ru/
интернет по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу уфа
Нарколог на дом в Туле предоставляет экстренную помощь тем, кто переживает проблемы с наркоманией и зависимостью от алкоголя. Преодоление зависимости должно учитывать индивидуальные особенности, и вызов нарколога на дом – это удобное решение для людей, нуждающихся в помощи. Центр лечения зависимостей в Туле предлагает анонимное лечение и профессиональные консультации. Домашняя реабилитация позволяет пройти курс психотерапии при зависимости в комфортной обстановке. Выездная медицинская помощь включает в себя как физическое, так и психотерапевтическое сопровождение. Предотвращение зависимости также является ключевым моментом в профилактике алкоголизма и наркомании. Поддержка алкоголиков и их родных – это работа квалифицированных специалистов, которые готовы поддержать в трудный момент. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Все про уютный дом, как сделать дом уютным для всех, советы по ведению дома, как создать уют в доме своими руками, советы по дизайну интерьера https://ujut-v-dome.ru/
Все про уютный дом, как сделать дом уютным для всех, советы по ведению дома, как создать уют в доме своими руками, советы по дизайну интерьера https://ujut-v-dome.ru/
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
какие провайдеры на адресе в уфе
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “reactive.su”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://reactive.su]https://reactive.su[/url]
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
Блог актуальной новостной информации, где 24 часа в сутки собираются все самые важные события, произошедшие в России и мире https://kopipasta.ru/
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Кстати, если вас интересует pro-zenit.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://pro-zenit.ru]https://pro-zenit.ru[/url]
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Многие годы мы предоставляем актуальные новости, обзоры и события из мира автомобилей, освещая как крупные мировые автопроизводители, так и события, влияющие на российских водителей. Наши материалы охватывают широкий спектр тем, от новых моделей автомобилей до акций протеста автовладельцев. Мы стремимся быть вашим надежным источником информации в автомобильной сфере https://n-avtoshtorki.ru/
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Кстати, если вас интересует clasifieds.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://clasifieds.ru]https://clasifieds.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя омск
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет по адресу
Лоукост авиабилеты https://lowcost-flights.com.ua по самым выгодным ценам. Сравните предложения ведущих авиакомпаний, забронируйте онлайн и путешествуйте дешево.
Предлагаю услуги https://uslugi.yandex.ru/profile/DmitrijR-2993571 копирайтинга, SEO-оптимизации и графического дизайна. Эффективные тексты, высокая видимость в поиске и привлекательный дизайн — всё для роста вашего бизнеса.
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Кстати, если вас интересует m-admin.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://m-admin.ru]https://m-admin.ru[/url]
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
Актуальный новостной блог, где ежедневно публикуются все самые значимые события, произошедшие за последние сутки в самых различных регионах земного шара https://dip-kostroma.ru/
¡Qué tal!
Los juegos de casino en lГnea con dinero real ofrecen variedad desde tragamonedas hasta mesas con crupieres en vivo. [url=https://realcasinogames.shop/]casino en Bolivia[/url] Explora los mejores juegos de casino en lГnea con dinero real y encuentra tu favorito.
Lee este enlace – https://realcasinogames.shop/
Casino en Bolivia
Casino online Bolivia
Juegos de Casino en linea con dinero real Bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
Sorumlulukla kumar oynamak , deneyiminizi azaltır.
Oyun bütçenizi net tanımlamak , dengeli oynamaya olanak tanır.
Kendinizi sınırlandırma araçlarını kullanmak, riskleri minimize etmenize destek olur .
Alevtr Casino
Oyunların etkilerinin farkında olmak, dengeli katılım temin eder .
İhtiyaç halinde yardım grubu danışmak, keyfi korumaya katkı sağlar .
Bu uygulamalar , eğlenceli dengeli bahis süreci deneyimi zenginleştirir .
Ищете квалифицированную помощь? Получите [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista32.ru/]помощь юристов[/url] и получите ответы на все ваши вопросы!
При выборе юриста, который сможет оказать помощь, нужно учитывать множество факторов. Важно понимать, что уровень профессионализма юриста может существенно отразиться на вашем деле.
Первым делом, стоит обратить внимание на специализацию юриста. Например, если у вас есть проблемы с недвижимостью, то стоит обратиться к юристу, который занимается этой сферой.
Не менее важным является то, какую репутацию имеет юрист. Обратите внимание на опыт работы юриста и количество довольных клиентов, это может много сказать о его подходе.
Не забывайте уточнять стоимость услуг юриста. Помимо общей стоимости, стоит выяснить, есть ли дополнительные расходы, которые могут возникнуть.
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
экскурсии в казани
що треба здавати на юриста
скачать 888starz https://sumy-times.net/articles/business/888starz_v_raznykh_stranakh_gde_mozhno_igrat_bez_o/?sphrase_id=1008081
Ищете быстрый займ на карту? На https://zaimhub.com собраны лучшие предложения МФО России. Выберите выгодный вариант и получите деньги онлайн без лишних документов
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
проверить интернет по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Особенно понравился материал про idalgogrif.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание.
শুভেচ্ছা!
[url=https://onlinecasinospins.shop]অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম[/url]
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://onlinecasinospins.shop/
অনলাইন জোয়া
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ডিপোজিট
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ইনকাম
শুভকামনা!
які предмети потрібно здавати на психолога
монтаж перил из нержавейки Перила для лестницы из дерева – это экологически чистое и эстетичное решение, которое создает атмосферу тепла и комфорта в доме. Дерево – это приятный на ощупь материал, который не вызывает аллергии и хорошо сохраняет тепло. }
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Между прочим, если вас интересует easyterm.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Буду следить за обсуждением.
вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
Актуальный новостной блог, где ежедневно публикуются все самые значимые события, произошедшие за последние сутки в самых различных регионах земного шара https://dip-kostroma.ru/
АО «ГОРСВЕТ» в Чебоксарах https://gorsvet21.ru профессиональное обслуживание объектов наружного освещения. Выполняем ремонт и модернизацию светотехнического оборудования, обеспечивая комфорт и безопасность горожан.
Онлайн-сервис https://laikzaim.ru займ на карту или счет за несколько минут. Минимум документов, мгновенное одобрение, круглосуточная поддержка. Деньги в любое время суток на любые нужды.
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
дешевый интернет омск
volgograd-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет в волгограде
Прокат авто
Custom Royal Portrait turnyouroyal.com an exclusive portrait from a photo in a royal style. A gift that will impress! Realistic drawing, handwork, a choice of historical costumes.
Открыть онлайн брокерский счёт – ваш первый шаг в мир инвестиций. Доступ к биржам, широкий выбор инструментов, аналитика и поддержка. Простое открытие и надёжная защита средств.
получить визу в китай в нижнем новгороде Получить визу в Китай в Нижнем Новгороде: Шаг за шагом к мечте. Процесс получения визы в Китай в Нижнем Новгороде несложен, если следовать инструкциям и подготовить все необходимые документы.
экскурсии в казани
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
Откройте для себя лучшие аутлеты Санкт-Петербурга: брендовая одежда, стильные коллекции и выгодные цены в Румба. Магазины ведущих брендов ждут вас в самом сердце города. Приходите и обновите гардероб с максимальной выгодой: аутлет СПб
Lamoda Sport Outlet в Румба — оригинальная продукция Adidas и других брендов со скидками круглый год. Спортивная одежда, обувь и аксессуары по лучшим ценам в Санкт-Петербурге. Успейте купить выгодно: https://rumbastock.ru/shops/lamoda-sport-outlet/
интернет тарифы омск
volgograd-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет подключить омск
ограждение пандуса из нержавеющей стали Перила деревянные – это универсальное решение, которое подходит для различных типов лестниц и интерьеров. Они могут быть изготовлены из различных пород дерева, таких как сосна, дуб, бук или ясень, и иметь различную отделку. }
виза в китай в нижнем новгороде Виза в Китай в Нижнем Новгороде стоимость: Инвестиция в путешествие. Стоимость визы в Китай в Нижнем Новгороде может варьироваться в зависимости от типа визы и срочности оформления. Уточните актуальные цены в визовом центре.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Кстати, если вас интересует classifields.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://classifields.ru]https://classifields.ru[/url]
Буду следить за обсуждением.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
привітання для жінок
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “qazar.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Приглашаем вас совершить виртуальное путешествие без границ с помощью удобного сервиса «Веб-камеры мира онлайн». Все страны мира, как на ладони, на расстоянии одного клика: веб камеры мира бесплатно
подключить интернет в квартиру омск
volgograd-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить интернет тарифы омск
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
Приглашаем вас совершить виртуальное путешествие без границ с помощью удобного сервиса «Веб-камеры мира онлайн». Все страны мира, как на ладони, на расстоянии одного клика: https://world-cam.ru/
ПОмощь юрист в банкротстве: банкротство директора ооо
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует easyterm.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
ПОмощь юрист в банкротстве: банкротство юр лиц спб
Ремонт кофемашин https://coffee-craft.kz с выездом на дом или в офис. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка. Работаем с бытовыми и профессиональными моделями. Гарантия качества и доступные цены.
ПОмощь юрист в банкротстве: банкротство юр лица стоимость
лучший интернет провайдер воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет
Ремонт кофемашин https://coffee-craft.kz с выездом на дом или в офис. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка. Работаем с бытовыми и профессиональными моделями. Гарантия качества и доступные цены.
Ремонт кофемашин https://coffee-craft.kz с выездом на дом или в офис. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка. Работаем с бытовыми и профессиональными моделями. Гарантия качества и доступные цены.
Круглосуточный алкоголизм вывод из запоя — помощь на дому и в стационаре. Капельницы, очищение организма, поддержка сердца и нервной системы. Анонимно и конфиденциально.
Купить мебель кровати с ящиками для дома и офиса по выгодным ценам. Широкий выбор, стильный дизайн, высокое качество. Доставка и сборка по всей России. Создайте комфорт и уют с нашей мебелью.
Многие годы мы предоставляем актуальные новости, обзоры и события из мира автомобилей, освещая как крупные мировые автопроизводители, так и события, влияющие на российских водителей. Наши материалы охватывают широкий спектр тем, от новых моделей автомобилей до акций протеста автовладельцев. Мы стремимся быть вашим надежным источником информации в автомобильной сфере: Высококачественные автомобильные шторы
Круглосуточный вывод из запоя капельницы — помощь на дому и в стационаре. Капельницы, очищение организма, поддержка сердца и нервной системы. Анонимно и конфиденциально.
экскурсии казани Улица Баумана: Сердце Города и Место Встреч Улица Баумана – это главная пешеходная улица Казани, где всегда царит оживленная атмосфера. Здесь расположены многочисленные магазины, кафе, рестораны и сувенирные лавки. Улица Баумана – это отличное место для прогулок, шопинга и отдыха. Здесь можно встретить уличных музыкантов, художников и других творческих людей.
Капельница от запоя – это незаменимый метод при алкогольной интоксикации. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно предоставит срочную помощь‚ содействуя в процессе дезинтоксикации и восстановления после запоя. Признаки алкогольной зависимости‚ такие как тошнота‚ головная боль и слабость‚ требуют оперативного реагирования. Лечение запоя включает капельницы‚ которые помогают снять абстинентный синдром и очистить организм из организма. Обращение к наркологу важна для установления последующей терапии: стационарное лечение или поддержка на дому. Специализированная наркологическая клиника предлагает профессиональную помощь‚ чтобы избежать повторных случаев и сохранить здоровье пациента.
Круглосуточный срочное выведение из запоя — помощь на дому и в стационаре. Капельницы, очищение организма, поддержка сердца и нервной системы. Анонимно и конфиденциально.
Купить мебель шкафы для обуви для дома и офиса по выгодным ценам. Широкий выбор, стильный дизайн, высокое качество. Доставка и сборка по всей России. Создайте комфорт и уют с нашей мебелью.
ніколь імя
Купить мебель письменные столы для дома и офиса по выгодным ценам. Широкий выбор, стильный дизайн, высокое качество. Доставка и сборка по всей России. Создайте комфорт и уют с нашей мебелью.
bazaindex.ru
https://t.me/elekt_riki Электричество в умном доме: Комфорт и эффективность, управление светом и теплом на кончиках пальцев.
bazaindex.ru
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “idalgogrif.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://idalgogrif.ru]https://idalgogrif.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
лечение запоя
кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений [url=http://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru]кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений[/url] .
essay writer site Professional Essay Writing Services: Excellence Guaranteed We provide a range of professional essay writing services, ensuring top-notch quality and adherence to deadlines. Rely on us for essays that make a lasting impact.
Смотрите лучшие сериалы и фильмы онлайн в хорошем качестве без регистрации. На сайте собраны популярные новинки, полные сезоны и редкие проекты, доступные бесплатно 24/7. Удобный интерфейс и быстрый доступ к контенту для комфортного просмотра на любом устройстве: https://lordserialofficial.ru/
подключить домашний интернет в воронеже
voronezh-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет провайдеры воронеж
PSI peace of mind: a compact rockbros pump means you stop “saving” rides for the weekend and start topping up before the next loop.
Предлагаем оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych-profiley.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков. Высокое качество, устойчивость к климатическим нагрузкам, широкий ассортимент.
Оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков по выгодным ценам. Надёжные конструкции, современные материалы, поставка напрямую с завода.
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “clasifieds.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://clasifieds.ru]https://clasifieds.ru[/url]
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
кайт сафари хургада Кайт Хургада Солнце ласкает кожу, ветер играет в волосах, а бескрайняя гладь Красного моря манит своей глубиной. Хургада – это место, где мечты о полете над волнами становятся реальностью. Кайтсёрфинг здесь – это не просто спорт, это образ жизни, это свобода и адреналин в каждой секунде. Кайт Школа Хургада Первые шаги в мир кайтсёрфинга могут быть непростыми, но опытные инструкторы кайт школы в Хургаде помогут вам освоить азы и почувствовать уверенность на доске. Индивидуальный подход, современное оборудование и безопасные условия обучения сделают ваш опыт незабываемым. Кайт Сафари Хургада Для тех, кто жаждет приключений и новых горизонтов, кайт сафари в Хургаде – это идеальный выбор. Отправьтесь в путешествие по живописным островам и лагунам, где ветер всегда дует в вашу пользу. Новые споты, новые знакомства и море впечатлений гарантированы. Кайтсёрфинг Хургада Хургада – это настоящий рай для кайтсёрферов. Здесь вы найдете все, что нужно для идеального катания: стабильный ветер, теплое море и разнообразие спотов для любого уровня подготовки. Откройте для себя мир кайтсёрфинга в Хургаде! Кайт Школа Египет Египет – это не только пирамиды и фараоны, но и прекрасные возможности для кайтсёрфинга. Кайт школы в Египте предлагают обучение с нуля до продвинутого уровня. Опытные инструкторы, современные методики и безопасные условия сделают ваш опыт обучения приятным и эффективным. Кайтсёрфинг Египет Кайтсёрфинг в Египте – это возможность совместить активный отдых с познавательными экскурсиями. После дня, проведенного на воде, вы можете отправиться исследовать древние храмы и гробницы. Египет – это страна, где история и современность переплетаются в удивительном танце. Кайт Обучение Хургада Мечтаете научиться управлять кайтом и скользить по волнам? Кайт обучение в Хургаде – это ваш шанс! Квалифицированные инструкторы помогут вам освоить технику безопасности, управление кайтом и уверенно стоять на доске. Кайт Обучение Египет Египет предлагает широкий выбор школ и инструкторов по кайтсёрфингу. Независимо от вашего уровня подготовки, вы найдете подходящую программу обучения. Начните свое кайт-приключение в Египте и откройте для себя мир адреналина и свободы!
Pedal confidence isn’t flashy, but it’s everything: rockbros pedals give that planted feel when you’re threading roots. No mystery creaks, no drama in the wet.
Предлагаем оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych-profiley.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков. Высокое качество, устойчивость к климатическим нагрузкам, широкий ассортимент.
Оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков по выгодным ценам. Надёжные конструкции, современные материалы, поставка напрямую с завода.
Предлагаем оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych-profiley.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков. Высокое качество, устойчивость к климатическим нагрузкам, широкий ассортимент.
No hitch? No problem. A rockbros suction bike rack makes hotel-to-trail weekends feasible—clean roof, solid hold, quick on/off when the route changes.
Оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков по выгодным ценам. Надёжные конструкции, современные материалы, поставка напрямую с завода.
Капельница для вывода из запоя в домашних условиях – является действующим методом детоксикации организма и вывода из запоя. В Туле медицинские услуги на дому предоставляют медицинскую помощь, включая капельницы. Длительность процедуры может составлять от 1 до 3 часов в зависимости от состояния здоровья пациента. Зависимость от алкоголя необходима квалифицированного вмешательства, и срочная медицинская помощь при алкоголизме способствует значительному улучшению здоровья и безопасности. После процедуры начинается восстановление после запоячто помогает в реабилитации людей, страдающих от алкоголизма. вывод из запоя
¡Bienvenido!
El casino en lГnea dinero real ofrece premios reales. [url=https://slotgamereview.shop/]juego casino real[/url] Gana desde tu casa hoy.
Lee este enlace – https://slotgamereview.shop/
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino online dinero real mГ©xico
casino online mГ©xico dinero real
¡Buena suerte!
приводы somfy [url=www.avtomatika-somfy.ru/]www.avtomatika-somfy.ru/[/url] .
¡Qué tal!
[url=https://casinowheel.shop/]casino en linea chile[/url]
Lee este enlace – https://casinowheel.shop
Juego de casino con dinero real Chile
Juegos de casino con dinero real Chile
Casino real online Chile
¡Buena suerte!
Как сам!
Качественное онлайн казино uz гарантирует. [url=https://casinowithjackpot.shop]лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане[/url] Отзывы положительные.
Переходи: – https://casinowithjackpot.shop/
Лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Казино онлайн Узбекистан
Можно ли играть в онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Бывай!
Курс по коммерческой недвижимости Управление недвижимостью обучение: Освойте искусство эффективного управления и увеличьте доходность своих объектов. Управление недвижимостью – это ключевой фактор успешного инвестирования. Обучение управлению недвижимостью позволит вам оптимизировать расходы, привлекать арендаторов и повышать доходность ваших объектов.
pocket option güvenilir mi ile güvenle işlem yapmaya başlayın ve sezgisel ve güçlü bir platformdan yararlanın!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
лечение запоя
домашний интернет подключить воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet006.ru
домашний интернет воронеж
скачать 1win на андроид ставки на спорт [url=https://1win1173.ru]https://1win1173.ru[/url]
мосвет казино [url=https://mostbet11063.ru/]мосвет казино[/url]
экскурсии казани Развлекательный Комплекс “Ривьера”: Отдых и Развлечения на Любой Вкус Развлекательный комплекс “Ривьера” – это место, где можно найти развлечения на любой вкус. Здесь есть аквапарк, кинотеатр, боулинг, рестораны и кафе. Вы сможете отдохнуть и развлечься всей семьей, а также провести время с друзьями. “Ривьера” – это отличное место для активного отдыха и ярких впечатлений.
https://huntdown.info/kak-udobnee-dobratsya-iz-aeroporta-pragi-v-karlovy-vary/
Капельница от запоя – это действующий метод детоксикации организма, предоставляемый наркологическая клиника. В Туле доступно широкий спектр медицинских услуг, включая вызов нарколога на дом для помощи в борьбе с запоем. Лечение алкоголизма требует персонализированного подхода, и программы лечения зависят в зависимости от уровня зависимости. Консультация нарколога способствует определению наилучшего метода лечения, а анонимное лечение гарантирует защиту личных данных. Роль семьи в реабилитации также являеться ключевой в процессе восстановления. Оценка клиник в Туле на основе отзывов позволяет определить наиболее подходящее заведение. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за поддержкой, чтобы преодолеть алкогольную зависимость и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
вопрос юристу бесплатно спросить юриста онлайн бесплатно по телефону
Нужен вентилируемый фасад: оцинкованная подсистема для вентилируемых фасадов
Нужны пластиковые окна: пластиковое окно цена
бк мост бет [url=https://mostbet11063.ru]бк мост бет[/url]
софт на лаки джет [url=http://1win1173.ru]софт на лаки джет[/url]
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Капельница для вывода из запоя в домашних условиях — это популярный метод экстренного избавления от запойного состояния, особенно в владимире. Однако необходимо подобрать опытного нарколога, чтобы избежать мошенников. Признаки зависимости от алкоголя могут быть очевидны, и помощь специалиста неизбежна. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир Обращаясь в наркологическую клинику, обратите внимание на наличие лицензий и отзывов. Квалифицированный специалист должен рекомендовать безопасное лечение, включая капельницу для восстановления водно-электролитного баланса. Консультация врача поможет определить степень зависимости и выбрать подходящий метод лечения. Не забывайте о реабилитации — это важная часть борьбы с алкоголизмом. Берегите свое здоровье и обращайтесь только к проверенным специалистам!
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
Хочу выделить раздел про buytime.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://buytime.ru]https://buytime.ru[/url]
Уверен, вместе мы найдем решение.
Rainbet
экскурсия казань Старо-Татарская Слобода: Путешествие в Прошлое Старо-Татарская слобода – исторический район Казани, сохранивший атмосферу старого города с его узкими улочками, деревянными домиками и уютными дворами. Это место, где можно почувствовать себя путешественником во времени, перенестись в прошлое и узнать больше о жизни татарского народа. Прогуливаясь по слободе, вы увидите старинные мечети, медресе, купеческие дома и другие исторические здания. Вы сможете узнать о традициях, обычаях и культуре татарского народа, а также попробовать национальные блюда в местных кафе и ресторанах. Старо-Татарская слобода – это не только историческое место, но и живой район, где живут и работают люди. Здесь можно увидеть ремесленников, которые занимаются традиционными видами искусства, а также художников и музыкантов, которые создают свои произведения в вдохновляющей атмосфере слободы. Посещение Старо-Татарской слободы – это уникальная возможность окунуться в атмосферу старой Казани, узнать больше о татарской культуре и почувствовать себя частью этого удивительного мира. Приглашаем вас посетить Старо-Татарскую слободу и открыть для себя ее тайны и красоту!
pocket option promo code ile güvenle işlem yapmaya başlayın ve sezgisel ve güçlü bir platformdan yararlanın!
Trust Finance https://trustf1nance.com is your path to financial freedom. Real investments, transparent conditions and stable income.
cold porcelain flowers handmade flowers
Інформаційний портал https://pizzalike.com.ua про піцерії та рецепти піци в Україні й світі. Огляди закладів, адреси, меню, поради від шефів, секрети приготування та авторські рецепти. Все про піцу — від вибору інгредієнтів до пошуку найсмачнішої у вашому місті.
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
По теме “raregreen.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://raregreen.ru]https://raregreen.ru[/url]
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
Trust Finance https://trustf1nance.com is your path to financial freedom. Real investments, transparent conditions and stable income.
cold porcelain clay clay flowers
Trust Finance https://trustf1nance.com is your path to financial freedom. Real investments, transparent conditions and stable income.
Інформаційний портал https://pizzalike.com.ua про піцерії та рецепти піци в Україні й світі. Огляди закладів, адреси, меню, поради від шефів, секрети приготування та авторські рецепти. Все про піцу — від вибору інгредієнтів до пошуку найсмачнішої у вашому місті.
porcelain clay http://www.ceramic-clay-flowers.com
Інформаційний портал https://pizzalike.com.ua про піцерії та рецепти піци в Україні й світі. Огляди закладів, адреси, меню, поради від шефів, секрети приготування та авторські рецепти. Все про піцу — від вибору інгредієнтів до пошуку найсмачнішої у вашому місті.
Получите бесплатную консультацию с юристом на сайте [url=https://pomoshch-yurista11.ru/]консультация юриста в Москве по телефону[/url].
Помощь юриста – это важный аспект, который влияет на нашу жизнь. В жизни порой возникают обстоятельства, когда требуется помощь квалифицированного юриста.
Осознание того, что юрист способен отстоять ваши права, является ключевым моментом. В повседневной жизни, например, при составлении contracts, полезно обратиться за консультацией к юристу.
На ресурсе pomoshch-yurista11.ru представлены услуги квалифицированных юристов. Здесь вы сможете получить консультацию по различным правовым вопросам.
Не забывайте, что грамотная юридическая помощь может сэкономить ваше время и деньги. Так что в случае возникновения юридических вопросов обращайтесь к профессионалам.
Решили купить Honda? оформление автокредита широкий ассортимент автомобилей Honda, включая новые модели, такие как Honda CR-V и Honda Pilot, а также автомобили с пробегом. Предоставляем услуги лизинга и кредитования, а также предлагает различные акции и спецпредложения для корпоративных клиентов.
Ищешь автозапчасти? подбор запчастей под ваш автомобиль предоставляем широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, автомобильных аксессуаров и оборудования как для владельцев легковых автомобилей, так и для корпоративных клиентов. В нашем интернет-магазине вы найдете оригинальные и неоригинальные запчасти, багажники, автосигнализации, автозвук и многое другое.
Выкуп автомобилей связаться с restyle-avto без постредников, быстро. . У нас вы можете быстро оформить заявку на кредит, продать или купить автомобиль на выгодных условиях, воспользовавшись удобным поиском по марке, модели, приводу, году выпуска и цене — независимо от того, интересует ли вас BMW, Hyundai, Toyota или другие популярные бренды.
CactusPay – приём оплат: РУ карты, СБП, СБП по QR, криптовалюта. Вывод средств на USDT TRC-20. Подходит для 18+ контента, эскорта, гемблинга, беттинга, инфобизнеса, товарки, донатов, P2P. Быстрое подключение, моментальные выплаты, анонимность, надёжность: прием платежей криптовалютой
Решили купить Honda? https://avtomiks-smolensk.ru широкий ассортимент автомобилей Honda, включая новые модели, такие как Honda CR-V и Honda Pilot, а также автомобили с пробегом. Предоставляем услуги лизинга и кредитования, а также предлагает различные акции и спецпредложения для корпоративных клиентов.
Ищешь автозапчасти? avto-fokus.ru предоставляем широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, автомобильных аксессуаров и оборудования как для владельцев легковых автомобилей, так и для корпоративных клиентов. В нашем интернет-магазине вы найдете оригинальные и неоригинальные запчасти, багажники, автосигнализации, автозвук и многое другое.
Решили купить Honda? проверьте свой автомобиль широкий ассортимент автомобилей Honda, включая новые модели, такие как Honda CR-V и Honda Pilot, а также автомобили с пробегом. Предоставляем услуги лизинга и кредитования, а также предлагает различные акции и спецпредложения для корпоративных клиентов.
Ищешь автозапчасти? магазин аксессуаров для авто предоставляем широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, автомобильных аксессуаров и оборудования как для владельцев легковых автомобилей, так и для корпоративных клиентов. В нашем интернет-магазине вы найдете оригинальные и неоригинальные запчасти, багажники, автосигнализации, автозвук и многое другое.
Выкуп автомобилей https://restyle-avto.ru без постредников, быстро. . У нас вы можете быстро оформить заявку на кредит, продать или купить автомобиль на выгодных условиях, воспользовавшись удобным поиском по марке, модели, приводу, году выпуска и цене — независимо от того, интересует ли вас BMW, Hyundai, Toyota или другие популярные бренды.
Выкуп автомобилей http://restyle-avto.ru без постредников, быстро. . У нас вы можете быстро оформить заявку на кредит, продать или купить автомобиль на выгодных условиях, воспользовавшись удобным поиском по марке, модели, приводу, году выпуска и цене — независимо от того, интересует ли вас BMW, Hyundai, Toyota или другие популярные бренды.
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “detoxa.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://detoxa.ru]https://detoxa.ru[/url]
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
продвижение сайтов сео продвижение seo любой тематики. Поисковая оптимизация, рост органического трафика, улучшение видимости в Google и Яндекс. Работаем на результат и долгосрочный эффект.
нужен юрист: юрист по кредитам Новосибирск защита интересов, составление договоров, сопровождение сделок, помощь в суде. Опыт, конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход.
Inizia a fare trading in tutta sicurezza con poket option e goditi una piattaforma intuitiva e potente!
efectos de audio extraer audio de video
Полагаю, это снимет все дальнейшие вопросы:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “hotelnews.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://hotelnews.ru]https://hotelnews.ru[/url]
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
продвижение сайтов сео услуги любой тематики. Поисковая оптимизация, рост органического трафика, улучшение видимости в Google и Яндекс. Работаем на результат и долгосрочный эффект.
нужен юрист: юрист по земельным делам Новосибирск защита интересов, составление договоров, сопровождение сделок, помощь в суде. Опыт, конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход.
продвижение сайтов заказать сео любой тематики. Поисковая оптимизация, рост органического трафика, улучшение видимости в Google и Яндекс. Работаем на результат и долгосрочный эффект.
нужен юрист: юрист по земельным участкам Новосибирск защита интересов, составление договоров, сопровождение сделок, помощь в суде. Опыт, конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход.
recorte de audio online remocao de ruido de audio
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Между прочим, если вас интересует phenoma.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://phenoma.ru]https://phenoma.ru[/url]
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
cortador de audio remover silencio do audio
Заказать такси https://taxi-sverdlovsk.ru онлайн быстро и удобно. Круглосуточная подача, комфортные автомобили, вежливые водители. Доступные цены, безналичная оплата, поездки по городу и за его пределы
Онлайн-заказ такси https://sverdlovsk-taxi.ru за пару кликов. Быстро, удобно, безопасно. Подача в течение 5–10 минут, разные классы авто, безналичный расчет и прозрачные тарифы.
Закажите такси https://vezem-sverdlovsk.ru круглосуточно. Быстрая подача, фиксированные цены, комфорт и безопасность в каждой поездке. Подходит для деловых, туристических и семейных поездок.
Быстрый заказ такси https://taxi-v-sverdlovske.ru онлайн и по телефону. Подача от 5 минут, комфортные автомобили, безопасные поездки. Удобная оплата и выгодные тарифы на любые направления.
Платформа пропонує https://61000.com.ua різноманітний контент: порадник, новини, публікації на тему здоров’я, цікавих історій, місць Харкова, культурні події, архів статей та корисні матеріали для жителів міста
Заказать такси https://taxi-sverdlovsk.ru онлайн быстро и удобно. Круглосуточная подача, комфортные автомобили, вежливые водители. Доступные цены, безналичная оплата, поездки по городу и за его пределы
Онлайн-заказ такси https://sverdlovsk-taxi.ru за пару кликов. Быстро, удобно, безопасно. Подача в течение 5–10 минут, разные классы авто, безналичный расчет и прозрачные тарифы.
Закажите такси https://vezem-sverdlovsk.ru круглосуточно. Быстрая подача, фиксированные цены, комфорт и безопасность в каждой поездке. Подходит для деловых, туристических и семейных поездок.
Быстрый заказ такси https://taxi-v-sverdlovske.ru онлайн и по телефону. Подача от 5 минут, комфортные автомобили, безопасные поездки. Удобная оплата и выгодные тарифы на любые направления.
Заказать такси https://taxi-sverdlovsk.ru онлайн быстро и удобно. Круглосуточная подача, комфортные автомобили, вежливые водители. Доступные цены, безналичная оплата, поездки по городу и за его пределы
Онлайн-заказ такси https://sverdlovsk-taxi.ru за пару кликов. Быстро, удобно, безопасно. Подача в течение 5–10 минут, разные классы авто, безналичный расчет и прозрачные тарифы.
Быстрый заказ такси https://taxi-v-sverdlovske.ru онлайн и по телефону. Подача от 5 минут, комфортные автомобили, безопасные поездки. Удобная оплата и выгодные тарифы на любые направления.
Закажите такси https://vezem-sverdlovsk.ru круглосуточно. Быстрая подача, фиксированные цены, комфорт и безопасность в каждой поездке. Подходит для деловых, туристических и семейных поездок.
Платформа пропонує https://61000.com.ua різноманітний контент: порадник, новини, публікації на тему здоров’я, цікавих історій, місць Харкова, культурні події, архів статей та корисні матеріали для жителів міста
Платформа пропонує https://61000.com.ua різноманітний контент: порадник, новини, публікації на тему здоров’я, цікавих історій, місць Харкова, культурні події, архів статей та корисні матеріали для жителів міста
Если вы планируете строительство или ремонт, важно заранее позаботиться о выборе надежного поставщика бетона. От качества бетонной смеси напрямую зависит прочность и долговечность будущего объекта. Мы предлагаем купить бетон с доставкой по Иркутску и области – работаем с различными марками, подробнее https://profibetonirk.ru/
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “pro-zenit.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://pro-zenit.ru]https://pro-zenit.ru[/url]
Чем мог, тем помог.
Нужен сантехник: сантехник алматы цена
ГОРСВЕТ Чебоксары https://gorsvet21.ru эксплуатация, ремонт и установка систем уличного освещения. Качественное обслуживание, модернизация светильников и энергоэффективные решения.
Займы онлайн https://laikzaim.ru моментальное оформление, перевод на карту, прозрачные ставки. Получите нужную сумму без визита в офис и долгих проверок.
Saznajte sve o lek za bubrege – simptomi, uzroci i efikasni nacini lecenja. Procitajte savete strucnjaka i iskustva korisnika, kao i preporuke za prevenciju i brzi oporavak.
Интернет-магазин мебели https://mebelime.ru тысячи моделей для дома и офиса. Гарантия качества, быстрая доставка, акции и рассрочка. Уют в каждый дом.
https://t.me/Official_blog_1win
Нужен сантехник: https://santehnik-v-almaty.kz
Saznajte sve o kamen u bubregu – simptomi, uzroci i efikasni nacini lecenja. Procitajte savete strucnjaka i iskustva korisnika, kao i preporuke za prevenciju i brzi oporavak.
ГОРСВЕТ Чебоксары https://gorsvet21.ru эксплуатация, ремонт и установка систем уличного освещения. Качественное обслуживание, модернизация светильников и энергоэффективные решения.
Займы онлайн лайк займ вход моментальное оформление, перевод на карту, прозрачные ставки. Получите нужную сумму без визита в офис и долгих проверок.
Интернет-магазин мебели https://mebelime.ru тысячи моделей для дома и офиса. Гарантия качества, быстрая доставка, акции и рассрочка. Уют в каждый дом.
Нужен сантехник: https://santehnik-v-almaty.kz
Saznajte sve o lek za bubrege – simptomi, uzroci i efikasni nacini lecenja. Procitajte savete strucnjaka i iskustva korisnika, kao i preporuke za prevenciju i brzi oporavak.
Займы онлайн лайк займ вход моментальное оформление, перевод на карту, прозрачные ставки. Получите нужную сумму без визита в офис и долгих проверок.
ГОРСВЕТ Чебоксары https://gorsvet21.ru эксплуатация, ремонт и установка систем уличного освещения. Качественное обслуживание, модернизация светильников и энергоэффективные решения.
Интернет-магазин мебели https://mebelime.ru тысячи моделей для дома и офиса. Гарантия качества, быстрая доставка, акции и рассрочка. Уют в каждый дом.
https://igrozavod.ru/ Скачать игры без торрента: Альтернативные пути к цифровым развлечениям В стремительно меняющемся мире цифровых развлечений, поиск надежных и безопасных способов скачивания игр становится все более актуальным. Торрент-трекеры, некогда популярные, уступают место более цивилизованным методам, предлагая пользователям не только удобство, но и защиту от потенциальных угроз. Отказ от торрентов открывает двери в мир легального и безопасного гейминга, где каждый может наслаждаться любимыми играми без риска для своей системы.
приводы somfy [url=avtomatika-somfy.ru]avtomatika-somfy.ru[/url] .
Форум общения здоровье Паркур в современно мире это очень распространенное увлечение, спасибо подписчикам за фото и советы, личный опыт, и такие класснфе видеосьемки.
Zasto se javlja bol u bubrezima simptomi: od kamenaca i infekcija do prehlade. Kako prepoznati opasne simptome i brzo zapoceti lecenje. Korisne informacije.
¡Saludos!
Casino online MГ©xico dinero real ofrece entretenimiento seguro. [url=https://pokerplayersonline.cfd]casino real en linea[/url] Miles de mexicanos juegan diariamente.
Lee este enlace – https://pokerplayersonline.cfd/
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino online dinero real mГ©xico
casino en lГnea confiable
¡Buena suerte!
Sta znaci https://www.pesak-u-bubregu.com, koji simptomi ukazuju na problem i kako ga se resiti. Efikasni nacini lecenja i prevencije.
Авто журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, советы по уходу за автомобилем и репортажи с автособытий.
Популярный авто журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua подробные обзоры моделей, советы экспертов, новости автосалонов и автоспорта, полезные статьи для автовладельцев.
?Hola amigo!
[url=https://1win-2-025.com/]casino con dinero real chile[/url]
Lee este enlace – https://1win-2-025.com/
Casino con dinero real Chile
1xbet casino Chile
Casino en lГnea Chile
?Buena suerte!
Форум общения знакомств форум 2025 один из лучших форумов на сегодняшний день, очень много тем, более 2000 регистраций, более 30 0000 сообщений, дома после работы расслабиться и почитать интересные темы, это же самое оно!подписчики рекомендуют.
Здравствуй!
Казахстан онлайн казино развивается быстро. [url=https://1-win-2025.com]vavada казино онлайн Казахстан вход[/url] Новые игры появляются ежедневно.
Переходи: – https://1-win-2025.com
онлайн казино Казахстана
Казахстан онлайн казино
Удачи!
Форум общения Мужской форум, мужские темы, общение мужчин многие мужчины жарко общаются на темы, которые касаются мужчин, работа, инструменты, машины и мотоциклы, подписчики делятся.
Zasto se javlja https://www.bol-u-bubrezima.com: od kamenaca i infekcija do prehlade. Kako prepoznati opasne simptome i brzo zapoceti lecenje. Korisne informacije.
Zasto se javlja upala bubrega: od kamenaca i infekcija do prehlade. Kako prepoznati opasne simptome i brzo zapoceti lecenje. Korisne informacije.
Авто журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, советы по уходу за автомобилем и репортажи с автособытий.
Sta znaci https://www.pesak-u-bubregu.com, koji simptomi ukazuju na problem i kako ga se resiti. Efikasni nacini lecenja i prevencije.
Популярный авто журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua подробные обзоры моделей, советы экспертов, новости автосалонов и автоспорта, полезные статьи для автовладельцев.
Авто журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, советы по уходу за автомобилем и репортажи с автособытий.
Sta znaci https://www.pesak-u-bubregu.com, koji simptomi ukazuju na problem i kako ga se resiti. Efikasni nacini lecenja i prevencije.
Популярный авто журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua подробные обзоры моделей, советы экспертов, новости автосалонов и автоспорта, полезные статьи для автовладельцев.
Флешка оптом https://usb-flashki-optom-24.ru/ жесткий диск и флешки тайп с в Калининграде. Флешки в металлическом корпусе и флешка со сканером отпечатка пальца Tactum в Самаре. Маленькая юсб флешка оптом и флешка зеркало
Inizia a fare trading in tutta sicurezza con pocket option download e goditi una piattaforma intuitiva e potente!
Экономические новости https://gau.org.ua прогнозы и обзоры. Политика, бизнес, финансы, мировые рынки. Всё, что важно знать для принятия решений.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua всё, что интересно современному мужчине: стиль, спорт, здоровье, карьера, автомобили, технологии и отдых. Полезные статьи и советы каждый день.
Онлайн авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua с обзорами новых и подержанных авто, тест-драйвами, советами по обслуживанию и новостями из мира автопрома.
конфигуратор пк Компьютер: Ключ к цифровой цивилизации. Компьютер – это не просто устройство, это инструмент, открывающий двери в цифровую цивилизацию. Он помогает нам учиться, работать, общаться и развлекаться.
Флешка оптом usb-flashki-optom-24.ru в деревянном корпусе и флешка На 1 гб купить в Твери. Флешки светящиеся с логотипом и упаковка под флешки в Липецке. Купить большую колонку для музыки с блютузом с флешкой оптом и коробка деревянная для флешки
Купить флешку https://usb-flashki-optom-24.ru/ оптом На 64 гб Flash и флешка сваровски в Сочи. Флешка нож и флешка гильза купить в Тольятти. Флешка оптом с паролем и флешка микро сд 128 гб цена
Экономические новости https://gau.org.ua прогнозы и обзоры. Политика, бизнес, финансы, мировые рынки. Всё, что важно знать для принятия решений.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua всё, что интересно современному мужчине: стиль, спорт, здоровье, карьера, автомобили, технологии и отдых. Полезные статьи и советы каждый день.
Экономические новости https://gau.org.ua прогнозы и обзоры. Политика, бизнес, финансы, мировые рынки. Всё, что важно знать для принятия решений.
Онлайн авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua с обзорами новых и подержанных авто, тест-драйвами, советами по обслуживанию и новостями из мира автопрома.
Купить бетон в Иркутске стало проще – вы можете заказать нужный объем прямо с завода, без посредников и переплат. Мы производим товарный бетон на современном оборудовании, контролируя каждый этап. Наша продукция используется при строительстве частных домов, промышленных объектов, дорог и фундаментов, узнайте больше по ссылке https://proirkbeton.ru/
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua всё, что интересно современному мужчине: стиль, спорт, здоровье, карьера, автомобили, технологии и отдых. Полезные статьи и советы каждый день.
Онлайн авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua с обзорами новых и подержанных авто, тест-драйвами, советами по обслуживанию и новостями из мира автопрома.
https://tenmoscow.ru/nabor-2-sht-rychka-holodilnika-serebryanaya-atlant-km730365800800
package delivery nyc https://delivery-new-york.com
Запчасти для пылесоса Samsung SC 6163 Запчасти для холодильника LG GA-479UTPA: Сохраните свежесть продуктов. Исправный холодильник – залог здоровья всей семьи. Не допускайте перебоев в его работе, вовремя меняйте необходимые компоненты.
скачать игры с яндекс диска Безопасность – превыше всего: Защитите свой цифровой мир от угроз Выбирая легальные и безопасные способы скачивания игр, вы не только поддерживаете разработчиков и способствуете развитию индустрии, но и защищаете свой компьютер от потенциальных угроз. Помните, что безопасность – это приоритет номер один в цифровом мире.
Портал о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua свежие новости, статьи и советы. Обзоры технологий, материалов, дизайн-идеи и практические рекомендации для профессионалов и частных застройщиков.
Строительный портал https://dki.org.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: технологии, оборудование, материалы, идеи для дома. Новости отрасли и экспертные рекомендации.
Всё о стройке https://mramor.net.ua полезные статьи, советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. Ремонт, строительство домов, дизайн интерьера и современные решения для вашего проекта.
Онлайн строительный https://texha.com.ua портал о материалах, проектах и технологиях. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и обустройстве дома. Поддержка специалистов и вдохновение для новых идей.
Сайт «Всё о стройке» https://sushico.com.ua подробные инструкции, советы экспертов, новости рынка. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве жилья в одном месте.
купить кашпо дизайнерские [url=http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/]http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/[/url] .
Портал о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua свежие новости, статьи и советы. Обзоры технологий, материалов, дизайн-идеи и практические рекомендации для профессионалов и частных застройщиков.
Строительный портал https://dki.org.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: технологии, оборудование, материалы, идеи для дома. Новости отрасли и экспертные рекомендации.
Онлайн строительный https://texha.com.ua портал о материалах, проектах и технологиях. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и обустройстве дома. Поддержка специалистов и вдохновение для новых идей.
Всё о стройке https://mramor.net.ua полезные статьи, советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. Ремонт, строительство домов, дизайн интерьера и современные решения для вашего проекта.
Портал о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua свежие новости, статьи и советы. Обзоры технологий, материалов, дизайн-идеи и практические рекомендации для профессионалов и частных застройщиков.
Сайт «Всё о стройке» https://sushico.com.ua подробные инструкции, советы экспертов, новости рынка. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве жилья в одном месте.
Строительный портал https://dki.org.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: технологии, оборудование, материалы, идеи для дома. Новости отрасли и экспертные рекомендации.
Онлайн строительный https://texha.com.ua портал о материалах, проектах и технологиях. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и обустройстве дома. Поддержка специалистов и вдохновение для новых идей.
Всё о стройке https://mramor.net.ua полезные статьи, советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. Ремонт, строительство домов, дизайн интерьера и современные решения для вашего проекта.
Сайт «Всё о стройке» https://sushico.com.ua подробные инструкции, советы экспертов, новости рынка. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве жилья в одном месте.
сделать брови в севастополе Перманентные брови Севастополь: Долговременное решение для безупречного взгляда. Забудьте о карандашах и тенях, наслаждайтесь идеальными бровями каждый день.
betzula telegram
Красивая флешка usb-flashki-optom-24.ru оптом и флешка купить яндекс Маркет в Сочи. Купить подарочную флешку Transcend и купить флешки для детей оптом в Твери. Pmap флешка оптом и флешка в виде мяча
1хбет зеркало 1хбет зеркало. Не упустите ни единого шанса на победу! Получите мгновенный доступ к платформе, даже если основной сайт недоступен. Наслаждайтесь любимыми играми и ставками в любое время и в любом месте, без каких-либо препятствий.
взлом вк Почтовые ящики. Откройте доступ к деловой и личной переписке, узнайте о важных решениях и намерениях. Контролируйте ситуацию, будьте в курсе всех событий.
Superb, what a blog it is! This website provides useful data to us, keep it up.
Local limo company near me
здоровье красота Уход: ежедневный ритуал, дарящий наслаждение и преображение. Тщательно подобранные средства, деликатные прикосновения и знание потребностей вашей кожи – вот секрет молодости и сияния. Наслаждайтесь каждым мгновением, посвященным себе.
точный прогноз на футбол [url=http://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru]точный прогноз на футбол[/url] .
прогнозы на хоккей лайв [url=luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru]luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru[/url] .
https://t.me/s/onewin_kanal/8700
most bet skachat [url=www.mostbet11067.ru]www.mostbet11067.ru[/url]
теннис букмекерская скачать [url=https://mostbet11069.ru/]теннис букмекерская скачать[/url]
Универсальный автопортал https://road.kyiv.ua автомобили, автоновости, обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и tuning. Полезные статьи для водителей и экспертов автоиндустрии.
Универсальный автопортал https://road.kyiv.ua автомобили, автоновости, обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и tuning. Полезные статьи для водителей и экспертов автоиндустрии.
Универсальный автопортал https://road.kyiv.ua автомобили, автоновости, обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и tuning. Полезные статьи для водителей и экспертов автоиндустрии.
трип скан Трипскан: Ваш надежный проводник в мире путешествий, предоставляющий доступ к актуальной информации, выгодным акциям и эксклюзивным возможностям. Мы помогаем вам создать уникальный опыт, соответствующий вашим интересам и бюджету.
как перестать есть Изменяем жизнь: Не бойтесь перемен, они – двигатель прогресса. Изменяйте свои привычки, убеждения, окружение, чтобы стать лучшей версией себя. Помните, что каждый день – это новая возможность начать все сначала.
мостбет онлайн [url=http://mostbet11069.ru]http://mostbet11069.ru[/url]
трипскан ссылка Трип сайт: Место, где рождаются истории о путешествиях. Поделитесь своим опытом с другими путешественниками, найдите новых друзей и вдохновитесь на новые приключения.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua в реальном времени. Экономика, политика, общество, культура, происшествия и спорт. Всё самое важное и интересное на одном портале.
Чтобы было понятнее, о чем речь:
Хочу выделить раздел про fjhg.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://fjhg.ru]https://fjhg.ru[/url]
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Современный автопортал https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости, сравнительные обзоры, тесты, автострахование и обслуживание. Полезная информация для водителей и покупателей.
Хорошая автомобильная резина — это залог безопасности на дороге, гарантирующая надёжное торможение даже в экстремальных ситуациях.
Правильно подобранные покрышки снижают вероятность потери контроля в условиях гололёда, поддерживая вашу безопасность .
Покупка проверенных покрышек продлевают срок службы на топливо за счёт оптимального качения .
Точный отклик руля зависит от качества протектора , вместе с прочностью каркаса .
Регулярная замена изношенной резины предотвращает повреждения дисков , обеспечивая безопасность пассажиров.
Не экономьте на шинах — это напрямую влияет вашу защиту даже в экстренных случаях.
http://forum.gokickoff.com/index.php?topic=287758.new#new
Женский портал https://fotky.com.ua с полезными статьями о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Советы экспертов, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты и вдохновение для каждой женщины.
Онлайн женский портал https://martime.com.ua новости, тренды моды, секреты красоты, психология отношений, карьера и семья. Полезные материалы и практические советы для женщин.
Une pratique responsable constitue une priorité afin de éviter les risques à long terme.
Il est essentiel de définir des limites claires de dépenses avant de jouer .
Reconnaître les impulsions excessives permet à agir rapidement avant qu’ils ne s’aggravent .
1win Côte d’Ivoire
Les établissements de confiance offrent des limites personnalisées afin d’aider les personnes à risque.
Lorsque nécessaire, n’hésitez pas à contacter des professionnels afin de recevoir une aide personnalisée .
Éviter les émotions fortes favorise une expérience sécurisée malgré sessions intenses .
Строительный сайт https://vitamax.dp.ua с полезными материалами о ремонте, дизайне и современных технологиях. Обзоры стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, проекты домов и советы экспертов.
Туристические места Карелии Туристические места Карелии: Валаам, Кижи, Рускеала ждут вас! Погрузитесь в историю и культуру Карелии.
Это именно то, что я искал!
По теме “diyworks.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://diyworks.ru]https://diyworks.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Женский портал https://fotky.com.ua с полезными статьями о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Советы экспертов, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты и вдохновение для каждой женщины.
Онлайн женский портал https://martime.com.ua новости, тренды моды, секреты красоты, психология отношений, карьера и семья. Полезные материалы и практические советы для женщин.
Женский портал https://fotky.com.ua с полезными статьями о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Советы экспертов, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты и вдохновение для каждой женщины.
Онлайн женский портал https://martime.com.ua новости, тренды моды, секреты красоты, психология отношений, карьера и семья. Полезные материалы и практические советы для женщин.
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Между прочим, если вас интересует easyterm.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://easyterm.ru]https://easyterm.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
По теме “lingomap.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://lingomap.ru]https://lingomap.ru[/url]
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
Женский сайт https://womanclub.in.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера. Всё самое интересное для женщин в одном месте.
Всё о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net что это за болезнь, как проявляется и чем опасна. Подробные статьи о симптомах, диагностике и способах лечения высокого давления.
Туристический портал https://elnik.kiev.ua с актуальными новостями, маршрутами и путеводителями. Обзоры стран и городов, советы путешественникам, лучшие идеи для отдыха и выгодные предложения.
Онлайн женский https://ledis.top сайт о стиле, семье, моде и здоровье. Советы экспертов, обзоры новинок, рецепты и темы для вдохновения. Пространство для современных женщин.
лучшие прогнозы на спорт футбол [url=http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru]http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru[/url] .
Добрый день!
Разбираем можно ли играть в онлайн казино в Узбекистане. [url=https://1win-2025.shop]топ онлайн казино узбекистан[/url] Все нюансы.
По ссылке: – https://1win-2025.shop
Онлайн казино uz
Можно ли играть в онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Казино онлайн Узбекистан
Покеда!
Женский сайт https://womanclub.in.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера. Всё самое интересное для женщин в одном месте.
Всё о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net что это за болезнь, как проявляется и чем опасна. Подробные статьи о симптомах, диагностике и способах лечения высокого давления.
Смотрите лучшие сериалы и фильмы онлайн в хорошем качестве без регистрации. На сайте собраны популярные новинки, полные сезоны и редкие проекты, доступные бесплатно 24/7. Удобный интерфейс и быстрый доступ к контенту для комфортного просмотра на любом устройстве: lordserial смотреть онлайн
Туристический портал https://elnik.kiev.ua с актуальными новостями, маршрутами и путеводителями. Обзоры стран и городов, советы путешественникам, лучшие идеи для отдыха и выгодные предложения.
Женский сайт https://womanclub.in.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера. Всё самое интересное для женщин в одном месте.
Всё о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net что это за болезнь, как проявляется и чем опасна. Подробные статьи о симптомах, диагностике и способах лечения высокого давления.
мост бет бетгеймс [url=http://mostbet11072.ru/]мост бет бетгеймс[/url]
Туристический портал https://elnik.kiev.ua с актуальными новостями, маршрутами и путеводителями. Обзоры стран и городов, советы путешественникам, лучшие идеи для отдыха и выгодные предложения.
¡Buen día!
Ruleta europea ofrece mejores probabilidades. [url=https://1win25.shop]casino en lГnea dinero real[/url] Jugadores prefieren esta modalidad siempre.
Lee este enlace – https://1win25.shop/
Casino online MГ©xico dinero real
Casino real en linea
Casino online dinero real MГ©xico
¡Buena suerte!
?Hola amigo!
[url=https://25win25.shop/]casino real online chile[/url]
Lee este enlace – https://25win25.shop
Casino real online Chile
Casino en lГnea Chile
Casino online dinero real Chile
?Buena suerte!
Онлайн женский https://ledis.top сайт о стиле, семье, моде и здоровье. Советы экспертов, обзоры новинок, рецепты и темы для вдохновения. Пространство для современных женщин.
Онлайн женский https://ledis.top сайт о стиле, семье, моде и здоровье. Советы экспертов, обзоры новинок, рецепты и темы для вдохновения. Пространство для современных женщин.
Lucknow Game: Immerse yourself in the cultural heritage of Lucknow, solving puzzles and exploring iconic landmarks to uncover hidden treasures: official Lucknow game portal
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
https://t.me/s/Official_1win_official_1win/896
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Зависимость от алкоголя — серьезная проблема‚ которая требует целостного подхода к терапии. В владимире имеются множество способов‚ которые помогают людям справиться с этой зависимостью. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с диагностики и выявления симптомов алкогольной зависимости. Необходимо обратиться в наркологическую клинику для оказания квалифицированной помощи. Одним из наиболее действенных способов является программа детоксикации‚ направленная на очистке организма от токсинов. Помощь психолога играет ключевую роль в реабилитации пациентов. Семейная поддержка и участие в группах анонимных алкоголиков могут значительно повысить вероятность успешного выздоровления. Кодирование от алкоголя также может быть вариантом‚ которое помогает многим. Терапия зависимости включает в себя как медицинские‚ так и психологические аспекты. Советы по отказу от алкоголя и мотивация к трезвости необходимы для формирования новой жизни без спиртного. Реабилитация после запоя требует времени и терпения‚ но с правильной поддержкой это осуществимо. За дополнительной информацией можно обратиться на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir008.ru.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Капельница от запоя – это эффективный метод‚ который широко используется в домашней обстановке. Если вы ищете врач нарколог на дом в Туле‚ то вызов врача станет отличным решением. Преимущества вызова врача обеспечивает возможность получения медицинской помощи в комфортной обстановке‚ что особенно важно для пациентов‚ находящихся в состоянии алкогольной зависимости.Процедура детоксикации организма с помощью капельницы способствует быстрому восстановлению здоровья и комфорт пациента. Нарколог‚ вызванный на дом осуществит лечение запоя‚ обеспечивая конфиденциальность лечения и поддержку в процессе выздоровления. врач нарколог на дом тула Домашнее лечение обеспечивает комфортные условия‚ что положительно сказывается на процессе восстановления после зависимости от алкоголя. Своевременная помощь при алкогольной зависимости может оказаться решающим фактором в выздоровлении‚ что обосновывает необходимость вызова врача на дом.
подключить интернет тарифы челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
freight shipping ny freight nyc
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
Tambola Game: A fun and fast-paced number-bingo experience, perfect for family gatherings, parties, and competitive fun: history of Tambola game
Amazing! Its really remarkable post, I have got much clear idea concerning from this article.
https://elektromotor.net.ua/sklo-far-ta-zakhist-vid-reagentiv.html
теннесси бк скачать на андроид бесплатно [url=http://mostbet11068.ru]http://mostbet11068.ru[/url]
трипскан сайт вход Tripscan top: Выбирайте лучшие направления и отели. Мы собираем для вас самые интересные и популярные места, чтобы ваше путешествие было незабываемым.
Услуга прокапки от запоя в владимире – это популярная услуга, предоставляющая пациентам получить необходимую медицинскую помощь на дому. Нарколог на выезде, работающий в области наркологии, поможет облегчить симптомы абстиненции и позаботится о комфорте пациента. врач нарколог на дом Стоимость капельниц могут колебаться в зависимости от медицинского учреждения и сложности оказания услуг. Например, расходы на лечение алкогольной зависимости может состоять не только из капельницу антиалкогольные процедуры, а также реабилитационные мероприятия. В городе владимир предоставляются услуги нарколога возможны как в стационарных учреждениях, так и в формате выезда к пациенту. Средняя цена капельницы от запоя может составлять от 2000 до 5000 рублей. Важно помнить, что стоимость лечения может зависеть от используемых препаратов и особенностей пациента. Наркологическая клиника владимир предлагает различные пакеты услуг, которые могут включать терапию запоя и реабилитацию. Обратившись за помощью к врачу наркологу на дом, вы сможете получить профессиональную помощь при алкоголизме и сможете избежать длительных периодов пребывания в клинике. Имейте в виду, что оперативное обращение за медицинской помощью может значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
купить аттестат за 11 класс в самаре [url=arus-diplom25.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс в самаре[/url] .
https://huntdown.info/kak-udobnee-dobratsya-iz-aeroporta-pragi-v-karlovy-vary/
интернет тарифы челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
Приветствую друзья в Новосибирске открылся лучший сайт для знакомств где каждому пользователю доступны персональные рекомендации умные фильтры безопасность аккаунта и поддержка сообщества чтобы знакомство проходило легко приятно и с перспективой на реальную встречу https://t.me/prostitutki_novosibirsk_indi
Выездной нарколог – это удобное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с алкогольной зависимостью или наркоманией. Терапия зависимостей включает в себя очистку организма и восстановление зависимых. Нарколог на дому предоставляет анонимное лечение, что особенно важно для пациентов, которые не хотят посещать медицинские учреждения. Кодирование от алкоголизма – эффективный метод, который можно провести на дому. Помощь на дому включает в себя психологическую поддержку и медицинское сопровождение. Встречи с наркологом помогут понять, как избавиться от зависимости. Программы восстановления и поддержка семьи играют важную роль в процессе лечения. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru вы найдете подробности о доступных услугах.
купить государственный диплом с занесением в реестр [url=http://arus-diplom33.ru/]купить государственный диплом с занесением в реестр[/url] .
купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom32.ru]купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр[/url] .
Надёжная резина — это основа уверенности на дороге, создающая точное управление даже в дождь и снег .
Правильно подобранные покрышки минимизируют риск заносов на обледенелых трассах , поддерживая контроль над движением.
Выбор износостойкой резины экономят средства на топливо благодаря низкому сопротивлению .
http://forum.zplatformu.com/index.php?topic=413115.new#new
Стабильное поведение авто зависит от качества протектора , в сочетании с составом резиновой смеси .
Регулярная замена изношенной резины предотвращает повреждения дисков , сохраняя безопасность пассажиров.
Не экономьте на шинах — это критично важно сохранность жизни на любом маршруте .
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
мастбет [url=https://mostbet11068.ru/]мастбет[/url]
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
мостбет зеркало скачать [url=http://mostbet11071.ru/]http://mostbet11071.ru/[/url]
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
мостбет вход на сегодня [url=mostbet11071.ru]mostbet11071.ru[/url]
домашний интернет
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет тарифы челябинск
Скорая наркологическая помощь — это важный аспект в борьбе зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula009.ru вы можете получить сведения о постоянной помощи, которая предлагает необходимую поддержку. Наркологическая служба оказывает медицинскую помощь в случаях наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Специалисты проводят консультации нарколога, а также обеспечивают анонимное лечение. В рамках ситуационной помощи возможны программы восстановления и госпитализация. Психологическая поддержка играет основополагающую роль в процессе восстановления. Не откладывайте обращение за помощью, спасите жизнь!
кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений [url=kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru]кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений[/url] .
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Ремонт дома или квартиры – дело ответственное и увлекательное, особенно если ранее опыта в таком деле не было. Чтобы избежать распространенных ошибок и обеспечить себе комфортный процесс обновления жилья, полезно заранее разобраться в основных этапах и порядке действий: ремонт квартир под ключ
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Rainbet Australia
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Кстати, если вас интересует qazar.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Портал про ремонт https://hydromech.kiev.ua свежие статьи о ремонте и отделке, дизайне интерьера и выборе материалов. Полезные советы для мастеров и тех, кто делает ремонт своими руками.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Портал про ремонт https://hydromech.kiev.ua свежие статьи о ремонте и отделке, дизайне интерьера и выборе материалов. Полезные советы для мастеров и тех, кто делает ремонт своими руками.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Портал про ремонт https://hydromech.kiev.ua свежие статьи о ремонте и отделке, дизайне интерьера и выборе материалов. Полезные советы для мастеров и тех, кто делает ремонт своими руками.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
Переезд в столицу — это необычно значимое событие, особенно когда речь идет о подключении интернета и телевидения. При смене места жительства важно учесть подбор интернет-провайдера, так как интернет-услуги могут различаться в зависимости от района. В Екатеринбурге доступен разнообразие интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих различные тарифы на интернет. Оптоволоконный интернет обеспечивает большую скорость и надежность соединения, что особенно важно для работы из дома; Wi-Fi интернет также может быть полезным выбором, но его скорость чаще всего ниже. телевидение и интернет Екатеринбург При перемещении стоит изучить предложения провайдеров по параметрам, таким как качество интернета, цена подключения и наличие акций и скидок. Обратите внимание на отзывы о провайдерах — они помогут избежать неприятных ситуаций. Установка интернета и кабельного телевидения обычно осуществляется быстро, но лучше заранее узнать о сроках подключения и требуемых документах. Важно выбрать надежного провайдера, чтобы наслаждаться качественными услугами интернета и телевидения в Екатеринбурге.
Детоксикация от алкоголя — важный этап в процессе борьбы с зависимостью от алкоголя, направленный на очищение организма. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть серьезными и включают в себя тревогу, потливость и тремор. Способы детоксикации различаются от медицинской помощи до домашних программ реабилитации. Возвращение к трезвости требует поддержки близких и осознания психологических аспектов зависимости. Функция печени значительно страдает от чрезмерного употребления алкоголя. Безалкогольные альтернативы, такие как безалкогольные напитки, способствуют снижению рисков и восстановить здоровье. Узнайте больше на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir007.ru.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
Производство в области мехобработки токарных Лизинг оборудования: Условия и преимущества
ВНЖ в Турции Жизнь в Турции: советы экспатам, культура, традиции, менталитет, адаптация
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
https://cataractspb.ru/
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
монтаж VRF VRF: Ключ к Комфорту и Эффективности Системы VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) и VRV (Variable Refrigerant Volume) – это передовые решения в области кондиционирования воздуха, обеспечивающие превосходную энергоэффективность и индивидуальный контроль климата в каждом помещении. Хотите купить VRF или VRV систему? Мы поможем вам сделать правильный выбор!
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
В столице России безлимитный интернет становится всё более востребованным. Различные провайдеры предлагают привлекательные условия, включая безлимитный тариф. Выбирая провайдера, важно обратить внимание на скорость интернета и стабильное соединение. Посетив сайт ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet005.ru можно найти сравнение тарифов различных компаний, что поможет упростить ваш выбор. Провайдеры регулярно предлагают акции и скидки, предоставляя возможность подключить интернет для дома по выгодным условиям. Мнения пользователей позволят оценить качество связи и эффективность технической поддержки. Также доступен мобильный интернет, в т.ч. семейные тарифы, что позволяет снизить затраты на подключение. Внимательно изучайте предложение месяца, чтобы выбрать лучшее.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Because the admin of this site is working, no hesitation very soon it will be famous, due to its feature contents.
https://itsybitsyfirstgradeteacher.com/sklo-fary-khrumtyt-chy-mozhna-yizdyty.html
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
CactusPay – приём оплат: РУ карты, СБП, СБП по QR, криптовалюта. Вывод средств на USDT TRC-20. Подходит для 18+ контента, эскорта, гемблинга, беттинга, инфобизнеса, товарки, донатов, P2P. Быстрое подключение, моментальные выплаты, анонимность, надёжность https://cactuspay.org/
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Сегодня проблема зависимости высвечивается все ярче. Если кто-то из ваших близких или ваши близкие столкнулись с зависимостью, не бойтесь обратиться за помощью. Анонимная консультация нарколога в владимире — это важный шаг на пути к лечению зависимости. На сайте site;com доступна возможность записи на консультацию к наркологу, обеспечивая полную анонимность и квалифицированную помощь.Лечение алкоголизма и реабилитация наркоманов требуют профессионального подхода. В специализированной наркологической клинике предлагаются различные услуги, включая психотерапию и поддержку специалистов. Вызов врача на дом обеспечит комфортные условия для пациента, что особенно актуально в кризисных ситуациях. Не стоит откладывать обращение за помощью, свяжитесь с нами за анонимной помощью уже сейчас!
https://www.med2.ru/story.php?id=147094
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Шокеры на руку с пультом Изменитель голоса: Сохраните анонимность при общении Изменители голоса позволяют исказить тембр и высоту голоса, делая его неузнаваемым. Это полезно для сохранения анонимности при телефонных разговорах и в других ситуациях.
https://kaztur.ru/
Реабилитация после зависимости от алкоголя в городе Красноярск – критически важный шаг на пути к выздоровлению. Нарколог на дом клиника предоставляет профессиональное лечение алкоголизма с индивидуальными программами‚ включая детоксикацию и психотерапевтическую поддержку. Консультация нарколога способствует определить эффективные методы терапии‚ такие как групповые занятия и социальная адаптация. Поддержка семьи также играет ключевую роль. Центр реабилитации предлагает конфиденциальную помощь и профилактику рецидивов‚ что способствует эффективному восстановлению после алкоголя.
Royal portraits http://www.turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
Royal portraits http://www.turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
Royal portraits https://www.turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
В Екатеринбурге выбор интернет-провайдеров значительно велик. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet006.ru предлагается актуальная информация о тарифах на интернет и сравнение провайдеров. Основные факторы выбора – скорость интернета, надежность соединения и уровень связи. Провайдеры предлагают широкий ассортимент интернет-тарифов, включая домашний интернет через оптические линии и мобильный доступ к интернету. Важно учитывать отзывы о провайдерах, чтобы понять, какие услуги связи и цифровые услуги действительно эффективны. Также стоит принять во внимание на акции и скидки, которые могут существенно уменьшить стоимость подключения интернета. Убедитесь, что выбранный вами провайдер обеспечивает подходящую скорость загрузки и устойчивое подключение для ваших требований.
Срочный вызов нарколога на дом — это важная услуга для людей, страдающих от зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir009.ru вы можете обратиться за консультацией нарколога и заказать врача на дом. Профессиональная помощь нарколога включает в себя лечение различных зависимостей и психологическую поддержку. Экстренная медицинская служба предлагает конфиденциальные услуги, что позволяет обеспечить вашу анонимность. Эффективное лечение наркомании и помощь алкоголикам возможны с помощью психотерапевта на дому. Не откладывайте, обратитесь за срочной помощью!
Вызов нарколога на дому в Красноярске ? это удобное и эффективное решение для людей, испытывающих трудности с алкоголем. Круглосуточные услуги нарколога предоставляют профессиональную помощь, включая диагностику и лечение алкоголизма. Нарколог на дому гарантирует анонимность и комфортные условия для пациента. Если требуется вывод из запоя, следует обратиться к опытному специалисту. Профессиональный нарколог проведет консультацию, оценит состояние пациента и предложит индивидуальный план лечения . Поддержка семьи зависимого также играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации .Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Обращение за медицинской помощью на дому помогает избежать стрессов, связанных с визитом в клинику. Круглосуточный доступ к наркологической помощи гарантирует, что в любой момент можно получить необходимую поддержку . Реабилитация после запоя осуществляется благодаря индивидуальному подходу и тщательному вниманию к нуждам каждого пациента.
Stavki Prognozy [url=www.stavki-prognozy-2.ru/]www.stavki-prognozy-2.ru/[/url] .
купить VRV VRF системы: Преимущества и Особенности Узнайте больше о преимуществах VRF систем – от высокой энергоэффективности до гибкости в проектировании и управлении. Мы расскажем вам о всех особенностях этих передовых систем кондиционирования.
Если вы планируете строительство или ремонт, важно заранее позаботиться о выборе надежного поставщика бетона. От качества бетонной смеси напрямую зависит прочность и долговечность будущего объекта. Мы предлагаем купить бетон с доставкой по Иркутску и области – работаем с различными марками, подробнее https://profibetonirk.ru/
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
https://kaztur.ru/
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
Давно слежу за этой темой, хочу поделиться находкой:
Между прочим, если вас интересует qazar.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
домашний интернет подключить казань
kazan-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет казань
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
В Красноярске доступна помощь от алкоголизма в клиниках‚ которые предлагают детоксикационный курс и лечение зависимости. Лечебные программы включают кодирование и медицинское сопровождение при алкоголизме. Важно также обеспечить психологическую поддержку и участвовать в группах поддержки для зависимых, таких как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Процесс восстановления после запоя требует комплексного подхода: обращение к наркологу помогут создать персонализированный план. Не забывайте о профилактике рецидива и придерживайтесь рекомендаций по отказу от алкоголя. Дополнительную информацию можно найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk009.ru;
Чтобы было понятнее, о чем речь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “parkpodarkov.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://parkpodarkov.ru]https://parkpodarkov.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clarity in your submit is just cool and that i can assume you’re knowledgeable in this subject. Well together with your permission let me to snatch your feed to keep up to date with approaching post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
http://tehnoprice.in.ua/ksenon-chy-led-shcho-krashche-svityt-u-2025-rotsi.html
автодоставка из Китая жд доставка грузов из Китая
домашний интернет
kazan-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет в казани
Это именно то, что я искал!
По теме “hotelnews.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://hotelnews.ru]https://hotelnews.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
https://tripscan51.win/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Обучение английского с раннего детского возраста играет важную роль.
В этом возрасте способности ребёнка легко воспринимает новые знания.
Начальное обучение с иностранной речью формирует речь.
Кроме того, ребёнку легче изучать другие языки в будущем.
Освоение английского создаёт огромные пути развития в учёбе и жизни.
Таким образом, раннее изучение английского даёт сильное преимущество.
https://www.teknolojiekibi.com/yeni/seo-t13058.0.html;new
английский язык для взрослых Курсы английского с нуля для взрослых: Начните сегодня Никогда не поздно начать изучать английский язык. Наши курсы английского с нуля разработаны специально для тех, кто не имеет никакого предыдущего опыта.
Купить бетон в Иркутске стало проще – вы можете заказать нужный объем прямо с завода, без посредников и переплат. Мы производим товарный бетон на современном оборудовании, контролируя каждый этап. Наша продукция используется при строительстве частных домов, промышленных объектов, дорог и фундаментов, узнайте больше по ссылке https://proirkbeton.ru/
hey thanks for the info. appreciate the good work
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
http://www.rosmed.ru/annonce/show/3892/Kak_podgotovitsya_k_pervomu_vizitu_v_stomatologicheskuyu_kliniku
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
https://cosmoreviews.club/stati/54115-kak-vybrat-luchshie-kursy-anglijskogo-yazyka-dlya-detej-10-let-sovety-i-rekomendaczii.html
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
дешевый интернет казань
kazan-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить проводной интернет казань
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “eroticpic.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://eroticpic.ru]https://eroticpic.ru[/url]
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
https://t.me/s/Official_1xbet_1xbet/403
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
плинко [url=http://plinko3001.ru]http://plinko3001.ru[/url]
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
audio editing audio noise removal
Prodaja https://www.nekretnine-zabljak-placevi.com: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
merge audio files audio trimming online
Prodaja zabljak prodaja nekretnina: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
music editing tools sound editing
Prodaja zabljak nekretnine: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
интернет провайдеры по адресу
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет по адресу
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Hey there, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, awesome blog!
http://fstu.org.ua/sklo-fary-shcho-zminylos-u-sertyfikatsiyi.html
Бесплатный вывод из запоя в Красноярске: возможно ли? Проблема алкоголизма и помощь зависимым остаются актуальными в нашем обществе. Множество людей сталкивается с запоем и ищет способы избавиться от этого состояния. В такой ситуации услуги нарколога на дому‚ доступные круглосуточно‚ могут стать настоящим спасением. нарколог на дом круглосуточно Бесплатная консультация нарколога может быть доступна для тех‚ кто срочно нуждается в помощи при запое. В Красноярске часто доступны услуги вывода из запоя и лечение на дому‚ что позволяет сделать этот процесс более удобным и менее напряженным для пациента. Круглосуточный нарколог обеспечит медицинскую помощь на дому‚ что особенно удобно для людей‚ которые не могут или не хотят обращаться в стационар. Также доступно анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность пациента. Следует помнить‚ что поддержка зависимых является важным аспектом в процессе лечения. Реабилитация от алкоголя требует времени и усилий‚ но с помощью профессионалов можно достичь положительных результатов. Таким образом‚ если вы или ваши близкие ищете бесплатный вывод из запоя в Красноярске‚ обращение к услугам нарколога на дому может стать первым шагом к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
какие провайдеры на адресе в красноярске
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу красноярск
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? https://www.immobilier-au-montenegro.com: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? immobilier au Montenegro: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
Фильмы и сериалы https://kinobay.live Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? immobilier au Montenegro: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
Нужна топливная карта? топливные карты для юридических лиц. Экономия до 15%, автоматическая отчётность, удобные безналичные расчёты и контроль автопарка онлайн.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
Капельница от запойной зависимости в Красноярске: расценки и отзывы В Красноярске помощь нарколога на дому становятся все более популярными. Множество людей борются с зависимостью от алкоголя и ищут выход из сложной ситуации. Вызов нарколога на дом представляет собой комфортное решение получить медицинскую помощь, не выходя из дома. Капельница от запоя эффективно помогает в детоксикации организма и уменьшает проявления.Стоимость капельницы колеблется в зависимости от клиники, но в среднем составляет от 3000 до 6000 рублей. Отзывы о капельнице в большинстве своем хорошие: пациенты подчеркивают заметное улучшение самочувствия и ослабление желания выпить. Экстренная помощь при запое способна сохранить здоровье.Лечение алкоголизма без лишних слов — существенный момент, так как многие стесняются своей проблемы. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске включают не только капельницы, но и реабилитацию после алкоголя. Помощь при запое может получить любой, кто хочет изменить свою жизнь. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск
какие провайдеры по адресу
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
Хотите оформить карту на топливо? топливные карты для юридических лиц. Контроль за каждой транзакцией, отчёты для бухгалтерии, гибкие лимиты и бонусные программы.
Фильмы и сериалы сериал смотреть онлайн в хорошем в качестве бесплатно Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
По теме “travelmontenegro.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://travelmontenegro.ru]https://travelmontenegro.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Фильмы и сериалы сериалы онлайн бесплатно Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
диплом купить с проведением [url=http://www.arus-diplom34.ru]диплом купить с проведением[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске [url=arus-diplom33.ru]купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске[/url] .
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “all-hotels-online.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://all-hotels-online.ru]https://all-hotels-online.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Алкогольная зависимость — значительная проблема‚ требующая целостного подхода к лечению. В Красноярске имеются множество способов‚ помогающие пациентам справиться с этой зависимостью. Терапия зависимости начинается с определения и выявления симптомов алкогольной зависимости. Необходимо обратиться в наркологическую клинику для получения профессиональной помощи. Одним из наиболее действенных способов является программа детоксикации‚ направленная на очищении организма от токсинов. Помощь психолога играет важную роль в реабилитации пациентов. Семейная поддержка и участие в группах анонимных алкоголиков могут значительно повысить шансы на успешное восстановление. Методы кодирования также является одним из вариантов‚ помогающим многим пациентам. Лечение зависимости включает в свой состав как медицинские аспекты‚ так и психологические аспекты. Рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и стимулирование к трезвой жизни необходимы для создания новой жизни без алкоголя. Реабилитация после запоя требует терпения и времени‚ но с адекватной поддержкой это осуществимо. За подробной информацией можно обратиться на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk009.ru.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Хочу выделить материал про obender.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://obender.ru]https://obender.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, эта информация сэкономит вам время.
салон красоты петроградская beauty-salon-spb.ru/
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу краснодар
krasnodar-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет по адресу дома
салон красоты сайт beauty-salon-spb.ru/
Приветствую!
Очень трезвый взгляд на проблему срочных денег. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/]Срочный займ на карту без отказа с плохой кредитной историей[/url] Полезно почитать всем.
Переходи: – https://economica-2025.ru/
Срочный займ на карту без отказа с плохой кредитной историей
Взять займ без отказа
Займ на карту мгновенно круглосуточно без отказа
Пока!
салон красоты парикмахерская https://beauty-salon-spb.ru
горшок для растений с автополивом [url=www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru/]www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru/[/url] .
Нужен микрозайм? где лучше взять микрозайм онлайн: деньги на карту без справок и поручителей. Простое оформление заявки, одобрение за минуты и мгновенное зачисление. Удобно и доступно 24/7.
http://www.rosmed.ru/annonce/show/3892/Kak_podgotovitsya_k_pervomu_vizitu_v_stomatologicheskuyu_kliniku
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Читайте подробнее: http://3dimpact.pl/oferta/tab-curve-4/
Нужен микрозайм? топ займов: деньги на карту без справок и поручителей. Простое оформление заявки, одобрение за минуты и мгновенное зачисление. Удобно и доступно 24/7.
Нужен микрозайм? займы топ: деньги на карту без справок и поручителей. Простое оформление заявки, одобрение за минуты и мгновенное зачисление. Удобно и доступно 24/7.
плинко кз [url=http://plinko3001.ru/]http://plinko3001.ru/[/url]
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Узнайте больше – https://www.vivolandscape.com/vivo-day-at-the-ballpark/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
artvin escort Turkiye’nin Tarihi ve Kulturel Miras? Turkiye, binlerce y?ll?k tarihi boyunca bircok medeniyete ev sahipligi yapm?s, zengin bir kulturel mirasa sahip bir ulkedir. Istanbul: Roma, Bizans ve Osmanl? Imparatorluklar?na baskentlik yapm?s olan Istanbul, Ayasofya, Topkap? Saray?, Sultanahmet Camii gibi tarihi yap?lar?yla unludur. Izmir: Antik caglardan beri onemli bir liman kenti olan Izmir, Efes Antik Kenti, Saat Kulesi ve Kordonboyu ile ziyaretcilerini cezbeder. Mersin: Tarihi Ipek Yolu uzerinde bulunan Mersin, Soli Pompeiopolis Antik Kenti, K?zkalesi ve Cennet Cehennem Magaralar? gibi tarihi ve dogal guzelliklere sahiptir. Edirne: Osmanl? Imparatorlugu’na uzun sure baskentlik yapm?s olan Edirne, Selimiye Camii, Eski Camii ve Meric Nehri ile tarihi ve kulturel zenginlikler sunar. Turkiye’nin dort bir yan?nda, antik kentler, tarihi camiler, kiliseler, hanlar, hamamlar ve muzeler gibi say?s?z tarihi ve kulturel miras bulunmaktad?r. Bu miras, Turkiye’yi kesfetmek icin say?s?z neden sunar.
оценка лицензии Москва оценка Москва
мелбет как вывести деньги [url=https://www.melbet3006.com]https://www.melbet3006.com[/url]
консультация врача психиатра онлайн
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
психиатрическая клиника стационар
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Читайте подробнее: https://batteriespeicher-versicherung.de/hallo-welt/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
евроремонт Таунхаус: Комфорт загородной жизни в черте города Таунхаус – это тип жилья, сочетающий в себе преимущества квартиры и загородного дома. Таунхаусы обычно имеют несколько этажей, собственный вход и небольшой участок земли.
мелбет промокод казахстан [url=melbet3006.com]melbet3006.com[/url]
ставки прогнозы [url=www.stavki-prognozy-2.ru]www.stavki-prognozy-2.ru[/url] .
Тикток мод на айфон
принудительное психиатрическое лечение
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Тут вы можете ознакомиться с ответом на вопрос: https://moversoman.com/oman-movers/
маски для лица beautyhealthclub.ru
Посмотрите, что я нашел по этому поводу:
Кстати, если вас интересует diyworks.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://diyworks.ru]https://diyworks.ru[/url]
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
секреты молодости beautyhealthclub.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом в москве
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
платная консультация психиатра
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Узнайте все нюансы на тему – https://circuitotruco.com/hola-mundo/
Всех приветствую! Хотите узнать больше о продвижении? Тут вы можете ознакомиться с ответом на вопрос: https://golkhuneh.com/forums/topic/%d0%b2%d1%8b%d0%ba%d1%83%d0%bf-%d0%b0%d0%b2%d1%82%d0%be%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%b1%d0%b8%d0%bb%d0%b5%d0%b9-premier-%d0%b2-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b1/page/1362/#post-532135
монтаж плоской крыши https://montazh-ploskoj-krovli.ru
Создать документы онлайн конструктор документов бесплатно: создайте договор, заявление или акт за 5 минут. Простая форма, готовые шаблоны, юридическая точность и возможность скачать в нужном формате.
платный психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
скорая психиатрическая помощь
оценка доли бизнеса оценочная компания
оценка транспорта Москва оценочная компания Москва
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Особенно понравился раздел про tars-rubber.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://tars-rubber.ru]https://tars-rubber.ru[/url]
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
экскорт алматы Эскорт Алматы – это мир, где каждая встреча становится незабываемой. Здесь вы найдете девушку, которая воплотит ваши самые смелые фантазии и подарит вам моменты истинного наслаждения. Девушки из эскорта Алматы – это не просто красивые лица, это умные и образованные женщины, которые умеют поддержать разговор и создать атмосферу комфорта и доверия. Они готовы стать вашими спутницами на светских мероприятиях, романтических ужинах или просто разделить с вами приятный вечер. Кыздар нет – это ваш проводник в мир эскорта в Алматы. Здесь вы найдете самую полную информацию о девушках, их услугах и ценах. Вип эскорт Алматы – это выбор для тех, кто ценит эксклюзивность и безупречный сервис. Девушки из этой категории обладают безупречными манерами, высоким интеллектом и умением вести себя в любом обществе. Эскортница Алматы – это профессионал своего дела, которая знает, как доставить удовольствие своему партнеру. Она умеет слушать, понимать и воплощать в жизнь самые смелые желания. Минет в Алматы – это искусство, доведенное до совершенства. Девушки из эскорта Алматы обладают всеми необходимыми навыками, чтобы доставить вам незабываемое наслаждение. Алматы проститутки – это широкий выбор девушек на любой вкус и кошелек. Здесь вы найдете и юных студенток, и опытных женщин, готовых воплотить в жизнь любые ваши желания. Экскорт Алматы – это ваш шанс вырваться из рутины и окунуться в мир роскоши и чувственных удовольствий.
пожелания хорошего дня
консультация психиатра по телефону
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
психиатрическая помощь на дому
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Хочу выделить раздел про fk-almazalrosa.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://fk-almazalrosa.ru]https://fk-almazalrosa.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Авто помощь 24/7 auto-help78.ru: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Кстати, если вас интересует mersobratva.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://mersobratva.ru]https://mersobratva.ru[/url]
Буду следить за обсуждением.
нужна консультация психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
скорая психиатрическая помощь
Авто помощь 24/7 выездная помощь на дороге: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
http://www.medlinks.ru/article.php?sid=110930
Авто помощь 24/7 техпомощь на дороге спб: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
Freight delivery from China is dependable and swift.
Our company offers flexible solutions for enterprises of any size.
We take care of all shipping processes to make your operations uninterrupted.
shipping of goods from china by air
With direct shipments, we secure timely dispatch of your packages.
Clients value our skilled team and competitive rates.
Choosing us means assurance in every shipment.
Скачать тик ток мод последняя версию Скачать тик ток мод на андроид – это быстро и безопасно, просто выберите надежный источник и наслаждайтесь всеми преимуществами модифицированной версии.
Как сам!
[url=https://pro-telefony.ru]Чем отличается серый телефон от официального?[/url] Рассказываем, как желание сэкономить может обернуться дорогостоящим ремонтом и головной болью.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru
Как зарегистрировать серый телефон
Бывай!
купить свидетельство о браке [url=http://educ-ua5.ru]http://educ-ua5.ru[/url] .
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
По теме “classifields.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://classifields.ru]https://classifields.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Срочно нужны цветы Минск Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Профессиональные https://812detailing.com/: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
Срочно нужны купить цветы Минск Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Срочно нужны доставка цветов Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer форумный спам – эффективный способ продвижения в поисковиках. Прогон ссылок через форумы улучшает SEO-показатели за короткий срок. Автоматизация линкбилдинга экономит время и силы. Увеличение ссылочной массы приводит к росту DR и Ahrefs. Используйте Xrumer для создания качественных внешних ссылок.
услуги раскрутка сайтов продвижение, вакансии seo продвижение, линкбилдинг стратегия
Как поднять DR Ahrefs, продвижение сайта по москве в топ, продвижение сайта в новосибирске
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Профессиональные 812detailing.com: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
Профессиональные детейлинг мойка спб: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
платная консультация психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
консультация психиатра платно
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
получить консультацию психиатра
Привет всем!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Увеличение показателей Ahrefs возможно с помощью прогонов ссылок через Xrumer. Программы для автоматического постинга позволяют получить тысячи ссылок. Прогон ссылок Хрумером помогает значительно повысить DR. Массовый линкбилдинг на форумах с Xrumer дает быстрые результаты. Используйте Xrumer для успешного продвижения сайта.
ключевые слова для seo оптимизации, продвижение рекламного сайта, линкбилдинг для начинающих
линкбилдинг с чего начать, продвижение seo статьями, и раскрутка сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Нужен массаж? https://doctu.ru – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина мк новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
Доброго!
Долго ломал голову как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от успещных seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический постинг форумов с Xrumer экономит время специалистов. Улучшение DR через Xrumer повышает позиции сайта. Программы для линкбилдинга делают продвижение системным. Повышение авторитетности сайта с помощью Xrumer заметно через месяц. Xrumer рассылка форумов расширяет охват ресурсов.
сайт koffer официальный интернет магазин dr, сложности seo, линкбилдинг
Генерация ссылок через Xrumer, speed seo, seo продвижение сервис автоматический
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Нужен массаж? Массаж Ивантеевка – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина мк новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
Нужен массаж? https://doctu.ru – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина мк новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
Здравствуйте!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов помогает охватывать больше ресурсов. Как увеличить показатели домена зависит от качества ссылок. Xrumer для продвижения сайта экономит время специалистов. SEO-прогон для новичков облегчает освоение инструментов. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer ускоряют процесс продвижения.
попе сео, продвижение сайтов путем, Секреты работы с Xrumer
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer, seo продвижение конструктора, агрегатор для seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
анонимная консультация психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
частный психиатр на дом
масла aromatmaslo
Доброго!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг курс ускоряет обучение специалистов. Линкбилдинг Москва предоставляет локальные возможности для продвижения. Линкбилдинг курсы позволяют освоить техники Xrumer. Линкбилдинг план помогает системно создавать ссылки. Линкбилдинг правила обеспечивают соблюдение безопасных методов продвижения.
зайти на сайт dr web, спец сео, Автоматическое размещение ссылок
компания линкбилдинг, курсы по сео оптимизация, рекламное агентство продвижение сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
частный психиатрический стационар
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
психиатр на дом для пожилого
vps server hosting vps hosting germany
Здравствуйте!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программное обеспечение для постинга ускоряет создание ссылочной массы. Ускоренный рост ссылочного профиля Xrumer делает продвижение стабильным. Xrumer: создание ссылочной массы упрощает работу специалистов. Линкбилдинг через форумы и блоги обеспечивает качественные ссылки. Повышение авторитетности домена становится заметным через неделю.
стратегическое сео, pbn что это seo, линкбилдинг правила
быстрый линкбилдинг, сео оптимизация группы вк, сео в компании
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
где получить визу в китай Оформить визу в Китай в СПб также возможно через консульство или аккредитованные визовые центры. Процедура практически идентична московской, но важно учитывать региональные особенности.
эффективное лечение алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
анонимное лечение от наркозависимости
купить аттестат образование [url=www.educ-ua4.ru/]купить аттестат образование[/url] .
кресло для косметолога тележка косметолога на колесиках
https://1cstudy.ru/
Доброго!
Долго не мог уяснить как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от успещных seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как поднять DR Ahrefs становится проще с регулярной работой. Создание ссылок автоматическими прогами экономит силы веб-мастеров. Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Увеличение показателя Ahrefs требует качественных ссылок. Массовый прогон сайта ссылками Xrumer повышает эффективность SEO.
продвижение сайта в барнауле, сайт seo sprint, Xrumer для массового линкбилдинга
сео линкбилдинг, seo auditor, seo сериалы
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
перила из металла цена Перила для лестницы – это необходимый элемент любой лестничной конструкции. Они обеспечивают опору и предотвращают падения, делая подъем и спуск безопасным для всех пользователей, вне зависимости от возраста и физических возможностей.
свойства эфирных масел aromatmaslo
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “phenoma.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://phenoma.ru]https://phenoma.ru[/url]
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
https://spasiholmy.ru/
Добрый день!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от успещных seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer ускоряет прогон ссылок и помогает повысить DR и Ahrefs. Программы для линкбилдинга позволяют быстро увеличить ссылочную массу. Массовая рассылка ссылок через форумы помогает ускорить продвижение сайта. Прогон ссылок с Xrumer значительно улучшает SEO-позиции. Используйте Xrumer для успешного линкбилдинга.
обязанности seo специалистов, цены на продвижение сайтов в москве цена, линкбилдинг что это такое простыми словами
Линкбилдинг на автомате, seo аудит и анализ сайта, seo видное
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
mostbet mobile uz registratsiya [url=mostbet4105.ru]mostbet4105.ru[/url]
реабилитационный центр для наркоманов
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
анонимное лечение от наркозависимости
tripskan Трипскан – это вдохновение, это новые идеи для путешествий, это возможность выйти за рамки привычного и увидеть мир другими глазами.
Доброго!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer для продвижения сайта помогает автоматизировать линкбилдинг. Форумы и блоги становятся источниками ссылок. Массовый прогон ускоряет рост DR. Это экономит время специалистов. Xrumer для продвижения сайта – современный метод SEO.
схемы seo, продвижение сайта новосибирск, Прогон Хрумер для сайта
Улучшение DR через Xrumer, проверка на сео сайта, сео продвижение сайта москва яндекс топ
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
http://pravo-med.ru/articles/18547/
Хай!
«Дженерик» — это не ругательство. [url=https://generik-info.ru/chto-takoe-dzheneriki-prostymi-slovami/]Дженерики это простыми словами[/url]
По ссылке: – https://generik-info.ru/chto-takoe-dzheneriki-prostymi-slovami/
Дженерики что это такое
Что такое дженерики лекарства
Дженерики для чего они нужны
Бывай!
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
анонимное лечение от алкоголизма
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
Хочу выделить раздел про hotelnews.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://hotelnews.ru]https://hotelnews.ru[/url]
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
умный цветочный горшок [url=https://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru]умный цветочный горшок[/url] .
vps hosting europe vps host
https://sonturkhaber.com/
server host vps vps hosting windows
https://svadba.net.ru/library/590_do_svadbyi_zajivet_zachem_nujno_meditsinskoe_obsledovanie_pered_brakom
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer помогает улучшить DR и увеличить показатели Ahrefs. Массовая рассылка ссылок через форумы ускоряет линкбилдинг и улучшает SEO-позиции. Программы для линкбилдинга помогают создать качественные внешние ссылки. Увеличение ссылочной массы с Xrumer помогает повысить видимость сайта. Попробуйте Xrumer для повышения SEO-результатов.
сео в инстаграме, seo post, крауд маркетинг линкбилдинг
Автоматический постинг форумов, сео wildberries, раскрутка сайтов система продвижения сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
mostbet uz haqida [url=www.mostbet4105.ru]www.mostbet4105.ru[/url]
духи герлен
Squash is a fast-paced indoor racket sport where two players hit a small rubber ball against the walls, aiming to outplay each other by making the ball bounce twice before return: official squash game website
столик косметолога стул для педикюра для мастера
стул косметолога купить столик косметолога на колесиках
перила из нержавеющей стали москва Перила деревянные – это тепло натурального дерева, создающее неповторимую атмосферу в доме.
https://myslo.ru/news/company/kogda-nuzhna-mammografiya-7-priznakov-kotorye-nel-zya-ignorirovat
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Улучшение DR через Xrumer – простой и быстрый способ увеличить авторитетность домена. Программа помогает создавать ссылки с разных площадок. Такой метод позволяет повысить показатели Ahrefs за короткий срок. Чем выше DR, тем больше доверия к ресурсу. Улучшение DR через Xrumer – реальное решение для SEO.
курса раскрутка сайта, ji hoon seo, Автоматизированный линкбилдинг
Автоматизированный линкбилдинг, лучшая seo оптимизация сайта, как раскрутка сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Доброго!
Долго ломал голову как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от крутых seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок Хрумером позволяет повысить DR и улучшить показатели Ahrefs. Массовая рассылка ссылок на форумах помогает ускорить процесс линкбилдинга. Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, автоматизируют создание ссылок. Увеличение ссылочной массы с Xrumer помогает улучшить видимость сайта. Попробуйте Xrumer для быстрого SEO-продвижения.
продвижение сайта что делать, лучший seo плагин wordpress, Рассылки с помощью Xrumer
Улучшение DR через Xrumer, seo цена оптимизация, частный мастер продвижения сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
mostbet скачать на айфон [url=https://mostbet4103.ru]https://mostbet4103.ru[/url]
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, подходят для сайтов любого масштаба. Прогон ссылок Хрумером создаёт качественные внешние ссылки. Массовая рассылка ссылок увеличивает DR сайта за короткий срок. Форумный линкбилдинг помогает улучшить авторитетность домена. Улучшение ссылочного профиля с Xrumer становится проще.
раскрутка сайта в интернете цена, сео продвижение услуг, линкбилдинг работа
Xrumer: практические примеры, smm и продвижение сайтов, телеграм каналы seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Здравствуйте!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок с Xrumer помогает вам достичь высоких показателей DR и Ahrefs. Массовая рассылка на форумах помогает создать тысячи качественных ссылок. Программы для линкбилдинга позволяют улучшить позиции сайта и увеличить ссылочную массу. Xrumer ускоряет линкбилдинг и даёт быстрые результаты. Попробуйте Xrumer для эффективного SEO-продвижения.
продвижение сайта продвижение сайтов монстер, как настроить сео на сайт, Прогон ссылок для повышения авторитета
Использование форумного постинга для SEO, разработка сео сайт, хлебная крошка seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Здравствуйте!
Долго не спал и думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматизация создания ссылок с Xrumer помогает поддерживать стабильность профиля. Xrumer: настройка и запуск линкбилдинг обеспечивает удобство работы. Линкбилдинг где брать ссылки становится очевидным через базы. Линкбилдинг под ключ экономит время веб-мастеров. Линкбилдинг это что помогает новичкам понять процесс.
продвижение и создание сайта самара, reg ru seo, Эффективность прогона Xrumer
Линкбилдинг через программы, карточка товара seo, техническая оптимизация сео
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг цена зависит от объема и качества ссылок. Чем больше линков, тем выше стоимость услуги. Программы автоматизации позволяют снизить расходы. Это экономит бюджет и ускоряет продвижение. Линкбилдинг цена – справедливый показатель качества.
сайты на тильде для seo, seo продвижение виды, сео линкбилдинг
Xrumer для массового линкбилдинга, онлайн курс seo оптимизация, сайт продвижение директ
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
духи герлен
Здравствуйте!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг цена зависит от выбранной стратегии. Крауд маркетинг линкбилдинг улучшает DR сайта. Линкбилдинг что это такое простыми словами объясняет новичкам. Линкбилдинг это простыми словами становится доступным. Линкбилдинг стоимость варьируется по объему работ.
продвижение сайта в яндекс директе, разработка сайта и seo, линкбилдинг отзывы
линкбилдинг на запад, раскрутка сайтов поисковики, designing seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Привет всем!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический постинг форумов с Xrumer экономит время специалистов. Улучшение DR через Xrumer повышает позиции сайта. Программы для линкбилдинга делают продвижение системным. Повышение авторитетности сайта с помощью Xrumer заметно через месяц. Xrumer рассылка форумов расширяет охват ресурсов.
рекламная кампания продвижение сайта, российский seo, Техники увеличения ссылочной массы
Как поднять DR Ahrefs, обучение на seo специалиста бесплатно, сео маркетинг что
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Хотите заказать интро для диджея? Индивидуальная разработка музыкальных заставок для рекламы, подкастов и презентаций. Качественный звук и креатив для запоминающегося бренда.
Наркологические услуги: частная наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
Здравствуйте!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer – это идеальный инструмент для увеличения DR и Ahrefs. Прогон ссылок через форумы помогает создать качественные внешние ссылки. Массовые рассылки на форумах ускоряют процесс линкбилдинга. Программы для линкбилдинга упрощают процесс создания ссылок. Используйте Xrumer для быстрого продвижения вашего сайта.
бесплатный seo аудит сайта онлайн, сео иркутск, Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер
Xrumer для создания ссылочной стратегии, кто такой сео в бизнесе, продвижение сайтов в челябинске
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Привет всем!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг под бурж помогает продвигать сайты на зарубежные рынки. Нужно работать с иностранными площадками и форумами. Автоматизация через Xrumer ускоряет процесс. Это увеличивает количество качественных ссылок. Линкбилдинг под бурж – залог успешного международного SEO.
заказать услуги сео, seo продвижение отчет, Xrumer и рост Ahrefs DR
линкбилдинг стоимость, продвижение сайта отелей, системы seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
мостбет бонус без депозита уз [url=https://mostbet4103.ru]https://mostbet4103.ru[/url]
Добрый день!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от крутых seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг – основа любого продвижения сайта. Без ссылок невозможно добиться высоких позиций. Современные инструменты помогают автоматизировать этот процесс. Чем больше ссылок, тем выше авторитет ресурса. Линкбилдинг – ключ к успеху в SEO.
автоматического seo продвижения, сео 1 что это, Как увеличить DR сайта
многоуровневый линкбилдинг, продвижение seo в яндексе москва, раскрутка сайтов и поисковая оптимизация сайтов seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
http://pravo-med.ru/articles/18547/
Наркологические услуги: частная наркологическая клиника нижний новгород, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
По теме “qazar.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://qazar.ru]https://qazar.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Наркологические услуги: наркологическая помощь недорого, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
Доброго!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от гуру в seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг статьи помогают системно создавать ссылочную массу. Xrumer ускоряет процесс прогона ссылок. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Автоматизация экономит силы специалистов. Линкбилдинг статьи – современная SEO-техника.
яндекс дзен продвижение сайтов, seo journal, Xrumer для роста ссылочной массы
линкбилдинг под бурж, продвижение сайта google analytics, seo продвижение ru center
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
аппарат узи цена в россии [url=http://www.kupit-uzi-apparat28.ru]аппарат узи цена в россии[/url] .
сколько стоит бетон купить куб бетона с доставкой
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг через программы облегчает создание ссылочной массы. Форумные проги для SEO ускоряют прогон по базам. Оптимизация ссылочного профиля с Xrumer повышает авторитет сайта. Как прокачать сайт через Xrumer становится понятно новичкам. Автоматизированный линкбилдинг экономит время специалистов.
продвижение сайта по определенным фразам, продвижение сайтов маркетинг реклама, линкбилдинг начать
Как использовать Xrumer для SEO, продвижение novelit сео, сео настройки товара
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Особенно понравился материал про anclaves.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://anclaves.ru]https://anclaves.ru[/url]
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Доброго!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции ускоряет продвижение. Xrumer: полное руководство раскрывает все секреты. Создание ссылок массовыми методами экономит силы специалистов. Как настроить Xrumer для рассылок понятно даже новичкам. Генерация ссылок через Xrumer делает работу системной.
на seo sprint, презентация продвижения сайта, Как поднять показатели Ahrefs
Автоматизация создания ссылок, информационные запросы seo, сео развод
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Как сам!
Объясняю на пальцах, как не пойти ко дну. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru]Микрозайм онлайн на карту круглосуточно[/url]
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/mikrofinansovye-organizaczii-onlajn/
Дженерики это простыми словами
Дженерики что это такое
Что такое дженерики в медицине
Бывай!
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический прогон статей облегчает работу специалистов. Использование Xrumer в 2025 обеспечивает стабильный рост DR. Линкбилдинг для повышения DR улучшает позиции сайта. SEO рассылки форумов помогают охватывать больше ресурсов. Xrumer: практические примеры показывают эффективность методов.
курсы по продвижению сайта в яндексе, сео яндекс карты, Эффективность прогона Xrumer
Как собрать базу для Xrumer, сео плагины wordpress, ключевые слова сео тексты
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer 2025: советы по настройке помогают новичкам. Автоматический линкбилдинг Xrumer позволяет массово размещать ссылки. Как использовать Xrumer для SEO экономит силы специалистов. Увеличение DR сайта с нуля возможно с правильной стратегией. Форумный спам для SEO расширяет охват.
seo optimisation сайта, браузер закрывается на сайте dr web cureit, линкбилдинг под ключ
линкбилдинг где брать ссылки, битрикс сео настройка, сео ютуб канала
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Здравствуйте!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от успещных seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Увеличение ссылочной массы возможно через автоматический постинг форумов. Xrumer форумный спам создаёт сотни качественных ссылок. Повышение показателей Ahrefs происходит за счёт точного планирования прогона. Используйте программы для автоматического постинга, чтобы сэкономить усилия. Xrumer помогает добиться отличных результатов в SEO.
разработка сайта и продвижение под ключ, сайт научное продвижение, Форумные проги для SEO
Использование Xrumer в 2025, seo специалиста это, создание сайтов санкт петербург продвижение сайтов петербург
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
духи с сандалом
tripscan Сайт трипскан – это интуитивно понятный интерфейс, подробные описания направлений, отзывы путешественников и полезные советы, помогающие сделать осознанный выбор и избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
Добрый день!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Генерация внешних ссылок быстро увеличивает авторитет сайта. Создание ссылочной массы в 2025 требует автоматизации. Использование Xrumer в SEO-кампаниях ускоряет рост DR. Линкбилдинг для продвижения в топ-10 помогает закрепить позиции. Прогон ссылок для повышения авторитета делает сайт более заметным.
seo app, виды интернет продвижения сайта, линкбилдинг с чего начать
Автоматизация создания ссылок, продвижения сайта в томске, seo доменные зоны
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок для повышения авторитета сайта ускоряет рост DR. Xrumer автоматизирует размещение ссылок. Массовый линкбилдинг экономит время специалистов. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше позиции. Прогон ссылок для повышения авторитета – эффективный инструмент SEO.
all seo wp, seo поведенческие фактор, Xrumer и рост Ahrefs DR
Улучшение ссылочного профиля с Xrumer, продвижение сайтов россия москва, сео продвижение сайтов обучение
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Здравствуйте!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как поднять DR Ahrefs становится проще с регулярной работой. Создание ссылок автоматическими прогами экономит силы веб-мастеров. Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Увеличение показателя Ahrefs требует качественных ссылок. Массовый прогон сайта ссылками Xrumer повышает эффективность SEO.
продвижение без seo, продвижения сайта ростов, Форумный линкбилдинг с Xrumer
линкбилдинг отзывы, раскрутка сайтов по словам, курсы обучения продвижения сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Puzzle Man Pro https://apps.apple.com/bg/app/puzzle-man-pro/id455696756 exciting puzzles for iOS. Collect classic pictures or create puzzles from your own photos. Different difficulty levels, user-friendly interface and saving progress.
Доброго!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от гуру в seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Что такое линкбилдинг узнают новички. Линкбилдинг SEO помогает системно повышать авторитет сайта. Линкбилдинг заказать экономит время веб-мастера. Линкбилдинг что это простыми словами объясняет процесс. Линкбилдинг это эффективный инструмент для продвижения.
сео оптимизация сайта цена москва, параметры seo оптимизации, быстрый линкбилдинг
Массовое размещение ссылок на форумах, сайт продвижение специалист, икс яндекс как поднять
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Свежее и интересное: https://peopleforum.ru/topic/13776-средство-от-гипертонии-cardirin-по-доступной-стоимости-с-доставкой-по-европе/
Привет всем!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический постинг форумов с Xrumer экономит время специалистов. Улучшение DR через Xrumer повышает позиции сайта. Программы для линкбилдинга делают продвижение более системным. Повышение авторитетности сайта с помощью Xrumer становится заметным. Xrumer рассылка форумов позволяет охватывать больше ресурсов.
сео продвижение сайта в, продвижения сайта по ключевому слову, сео линкбилдинг
линкбилдинг что это простыми словами, seo основатель, seo оптимизирована
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Стройкаталог https://stroycata1og.ru проекты коттеджей, дома любой площади, каталог стройматериалов. Комплексные услуги от проектирования до сдачи объекта с гарантией качества.
духи сандал
Доброго!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции улучшает видимость сайта. Xrumer: полное руководство помогает новичкам освоить инструмент. Создание ссылок массовыми методами экономит время. Как настроить Xrumer для рассылок становится понятным после инструкции. Генерация ссылок через Xrumer ускоряет продвижение.
seo для заработок, seo анализаторе, линкбилдинг или
seo линкбилдинг, seo оптимизация в социальных сетях, seo методичка
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от успещных seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как поднять DR Ahrefs становится проще с регулярной работой. Создание ссылок автоматическими прогами экономит силы веб-мастеров. Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Увеличение показателя Ahrefs требует качественных ссылок. Массовый прогон сайта ссылками Xrumer повышает эффективность SEO.
seo and keyword, создание бесплатного сайта и раскрутка, линкбилдинг интернет магазина
Линкбилдинг для повышения DR, title для seo, битрикс настройка seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Современные системы учёта рабочих смен помогают оптимизировать оперативного управления.
Точность фиксации минимизирует погрешности при расчёте зарплат .
Менеджерам удобнее анализировать проектные задачи в режиме реального времени .
https://atarax24.com/finance/why-accounting-for-working-time-becomes/
Персонал получают прозрачный доступ для отслеживания .
Внедрение таких систем существенно упрощает кадровые процессы в кратчайшие сроки.
Это гарантирует слаженность при распределении задач, сохраняя мотивацию сотрудников.
https://sonturkhaber.com/
Здравствуйте!
Долго не мог уяснить как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer: настройка для SEO помогает ускорить линкбилдинг. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах. Это экономит силы специалистов. Массовый прогон повышает DR и позиции сайта. Xrumer: настройка для SEO – эффективный инструмент продвижения.
продвижение сайта оптимизация сайта интернет маркетинга, seo frog скачать торрент, линкбилдинг где брать ссылки
линкбилдинг правила, как стать сео специалистом с нуля, продвижение сайтов какой выбрать
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
http://www.medlinks.ru/article.php?sid=110930
Здравствуйте!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от крутых seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer – частый вопрос новичков. Программа автоматизирует размещение ссылок. Это ускоряет рост DR и авторитетности. Системный подход обеспечивает стабильный результат. Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer – ключевой навык SEO.
seo сайтов услуги, раскрутка сайта раменское, Создание ссылок массовыми методами
Генерация внешних ссылок быстро, сайт для раскрутки сайта бесплатно, индекс продвижение сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
саратов купить бетон цена цена куба бетона
купить куб бетона цена куб бетона с доставкой цена
уличная еда Обсуждаемое в сети: эхо цифрового мира
Привет всем!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от крутых seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
SEO-прогон для повышения позиций ускоряет продвижение сайта. Xrumer автоматизирует размещение ссылок. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Автоматизация экономит время и силы специалистов. SEO-прогон для повышения позиций – ключевой инструмент линкбилдинга.
что такое оптимизация сайтов seo поисковая, сео слова, Программное обеспечение для постинга
Массовый прогон сайта ссылками, биржи для seo, korea seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как поднять DR Ahrefs становится проще с регулярной работой. Создание ссылок автоматическими прогами экономит силы веб-мастеров. Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Увеличение показателя Ahrefs требует качественных ссылок. Массовый прогон сайта ссылками Xrumer повышает эффективность SEO.
адвего сео проверка, подольск seo, Эффективный прогон для роста DR
Как прокачать сайт через Xrumer, продвижение сайта в краснодар, сео про 8
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Купить подшипники оптом :
Приобретение промышленных подшипников BBCR – залог бесперебойной работы оборудования и долговечности механизмов. Выбор надежного поставщика – ключевой фактор успеха вашего предприятия.
Block Puzzle Wood Classic https://apps.apple.com/tn/app/block-puzzle-wood-classic/id1615792350 is a puzzle game where you need to correctly place wooden blocks. Simple controls, beautiful visuals and addictive gameplay for all ages.
узи аппарат цена новый [url=https://kupit-uzi-apparat28.ru]узи аппарат цена новый[/url] .
Привет всем!
Долго думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов помогает охватывать больше ресурсов. Как увеличить показатели домена зависит от качества ссылок. Xrumer для продвижения сайта экономит время специалистов. SEO-прогон для новичков облегчает освоение инструментов. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer ускоряют процесс продвижения.
самостоятельное сео продвижение, первый сайт seo, линкбилдинг это простыми словами
линкбилдинг план, сайт раскрутка самара, функционал сео
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Доброго!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer помогает вам улучшить DR и Ahrefs через автоматический прогон ссылок. Массовые рассылки на форумах с Xrumer ускоряют создание качественных ссылок. Программы для линкбилдинга позволяют вам увеличить ссылочную массу с минимальными усилиями. Увеличение авторитетности сайта с помощью Xrumer даёт быстрые результаты. Используйте Xrumer для эффективного SEO-продвижения.
важность seo, бесплатная раскрутка seo, Xrumer 2025: советы по настройке
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции, test seo, заказать сео продвижение сайта новосибирск
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
мостбет актуальный промокод [url=https://mostbet4107.ru/]https://mostbet4107.ru/[/url]
уличное кашпо большое напольное [url=http://www.ulichnye-kashpo-kazan.ru]уличное кашпо большое напольное[/url] .
android için mostbet [url=http://mostbet4102.ru/]http://mostbet4102.ru/[/url]
мостбет вход узбекистан [url=https://mostbet4107.ru]https://mostbet4107.ru[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программы для линкбилдинга упрощают задачу SEO-специалистов. С их помощью можно массово генерировать ссылки на форумы и блоги. Это помогает сайту быстрее набирать траст и позиции. Без таких инструментов продвижение занимает гораздо больше времени. Программы для линкбилдинга экономят силы и деньги.
реклама для продвижения сайта, seo в орехово зуево, Создание ссылок автоматическими прогами
линкбилдинг на форумах, работа по сео сайта, королев продвижение сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
протезирование зубов Имплантация – это возможность вернуться к полноценной жизни, не испытывая дискомфорта при еде и общении. Имплантаты надежно фиксируются в костной ткани, обеспечивая стабильность и функциональность протеза.
Escort Dating For Click: https://goldclass.yenibayanlar.com/kategori/kirikkale-escort/celebi-escort/amp/
подшипник по размерам найти Подшипники от производителей – это гарантия качества, соответствия стандартам и возможность получить техническую поддержку непосредственно от разработчиков.
Handmade ceramics flowers Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
Handmade porcelain flower Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
Handmade clay flowers Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
каталог подшипников по размерам Купить подшипники оптом: выгодное решение
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
mostbet uz jonli tikish [url=http://mostbet4106.ru/]http://mostbet4106.ru/[/url]
платный психиатр на дом
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
консультация врача психиатра
игровой пк bunker Конфигуратор ПК – это ваш инструмент для создания идеального компьютера. Подберите комплектующие, соответствующие вашим нуждам и бюджету.
mostbet ckachat [url=https://mostbet4106.ru/]https://mostbet4106.ru/[/url]
https://tripscan41.cc/ Трип скан: Путешествуйте с умом
Где купить подшипники При выборе подшипников обращайте внимание на репутацию и опыт производителя.
Здарова!
Разбираемся, как заработать на играх и не превратить их в рутину. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-na-igrah/]как можно заработать деньги на играх[/url]
Читай тут: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-na-igrah/
как заработать на играх в телефоне
как заработать деньги в интернете на играх без вложений
заработок в играх
До встречи!
бюджетная сборка пк для игр : Купить игровой компьютер в сборе: Получите готовый к работе игровой компьютер.
как взять займ займы онлайн
микрозайм рейтинг как взять займ
займ деньги получить микрозайм
мочтбет [url=https://mostbet4112.ru/]мочтбет[/url]
Путин Зеленский Политика Политика – это искусство возможного. В условиях глобальной нестабильности и растущей напряженности, лидеры стран должны проявлять мудрость и дальновидность, чтобы избежать эскалации конфликта. Переговоры между Путиным и Зеленским – это последний шанс найти мирное решение и предотвратить дальнейшие жертвы. Финансовая стабильность является ключевым фактором, определяющим устойчивость любой страны. Санкции, введенные против России, оказали серьезное влияние на ее экономику, однако страна продолжает адаптироваться к новым условиям. Европа также сталкивается с экономическими трудностями, вызванными ростом цен на энергоносители и перебоями в поставках товаров. Безопасность и оборона становятся приоритетными задачами для многих государств. Инвестиции в военную технику и технологии растут, а Кавказ и Ближний Восток остаются зонами повышенной напряженности. Новости и аналитика должны освещать эти вопросы объективно и непредвзято, чтобы каждый человек мог оценить риски и принять осознанные решения.
онлайн деньги как взять займ
микрозайм онлайн онлайн займ
деньги займ взять займ
онлайн деньги микрозайм онлайн
получить займ онлайн заем
займ быстрый как взять займ
tripskan Сайт трипскан: Полный спектр услуг для путешественников
https://t.me/zachashkoichaya_chanel Специальная военная операция продолжает оставаться в центре внимания мировой общественности. Этот конфликт, затрагивающий интересы множества стран и народов, оказывает серьезное влияние на геополитическую обстановку и мировую экономику. Попытки найти дипломатическое решение предпринимаются регулярно, однако ощутимого прогресса в переговорном процессе пока не наблюдается. Позиции сторон остаются диаметрально противоположными, и каждая из них преследует свои собственные цели. Владимир Путин и Владимир Зеленский, как лидеры вовлеченных в конфликт государств, несут огромную ответственность за будущее своих стран и народов. Политическая составляющая конфликта сложна и многогранна, требующая тщательного анализа и взвешенных решений. Финансовые последствия специальной военной операции ощущаются во всем мире. Европа, Азия и Америка испытывают на себе влияние санкций, роста цен на энергоносители и перебоев в поставках товаров. Безопасность и оборона становятся приоритетными направлениями государственной политики, а Кавказ и Ближний Восток остаются зонами повышенной напряженности. В этих условиях особую важность приобретает доступ к объективной и непредвзятой информации. Новости и аналитика должны основываться на фактах и отражать различные точки зрения, чтобы каждый человек мог сформировать собственное мнение о происходящих событиях.
Хай!
Поверь, ты не один, и у нас есть план, как вернуть уверенность в себе. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/kak-perezhit-uvolnenie/]как пережить увольнение с любимой работы[/url]
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/kak-perezhit-uvolnenie/
хочу уволиться но не могу решиться
как пережить увольнение с работы
как пережить несправедливое увольнение
До встречи!
Tickets for Rock Festivals https://rock-concert-tickets.ru
Рейтинг хостингов топ хостингов в россии подбор сервисов для сайтов и интернет-магазинов. Сравнение тарифов, гарантия стабильности и рекомендации по выбору.
Buy Tickets for Festivals https://rock-concert-tickets.ru
Tickets for Rock Festivals https://rock-concert-tickets.ru
мистика в жизни обычных людей реальные истории Таинственные истории, случившиеся с обычными людьми Иногда жизнь подбрасывает нам загадки, объяснить которые рационально невозможно. Истории о встречах с непознанным, о предчувствиях и знаках судьбы заставляют нас задуматься о границах реальности и о том, что существует за пределами нашего понимания. Они наполнены тревогой и любопытством, заставляя нас верить в чудеса.
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
врач психиатр на дом в москве
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
частная психиатрическая помощь
https://spasiholmy.ru/
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
термальные источники на кавказе В Дагестане туристам интересно увидеть Сулакский каньон, Дербент, Гуниб и познакомиться с местной культурой. Что посетить в Дагестане
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
СтавкиПрогнозы [url=http://stavki-prognozy-1.ru]http://stavki-prognozy-1.ru[/url] .
https://t.me/zachashkoichaya_books Литература, формирующая ценности
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
кашпо садовое [url=www.ulichnye-kashpo-kazan.ru]кашпо садовое[/url] .
Курсы по плазмотерапии прп терапия обучение освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Профессиональное обучение онлайн-курсы инъекционной косметологии: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
как излечиться от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков
Курсы по плазмотерапии плазмолифтинг обучение в москве освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Курсы по плазмотерапии плазмотерапия обучение в москве освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Профессиональное обучение плазмотерапия в косметологии обучение: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
Профессиональное обучение обучение prp в косметологии: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
платный психиатр на дом в москве
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
стационар психиатрической больницы
смешные истории из жизни обычных людей Удивительные истории обычных людей В каждом из нас скрыт потенциал для невероятных свершений. Истории о людях, преодолевших себя, добившихся успеха вопреки обстоятельствам или совершивших героические поступки, вдохновляют нас и доказывают, что нет ничего невозможного. Они вселяют веру в свои силы и мотивируют на новые свершения.
необычные места дагестан Что посмотреть в Нарын Кала и Дербенте
monstbet [url=mostbet4112.ru]monstbet[/url]
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
лечение алкогольной зависимости
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
пин ап активация бонуса [url=pinup5001.ru]пин ап активация бонуса[/url]
литература Книги как компас в лабиринте жизни
центр реабилитация алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
реабилитации после алкоголя
Хай!
Поговорим по-честному, почему нас так тянет рискнуть и поставить всё на кон. [url=http://nagny-casino.ru/kazino-s-bystrym-vyvodom/]онлайн казино без лицензии[/url]
Читай тут: – http://nagny-casino.ru/kazino-s-bystrym-vyvodom/
номад казино
казино онлайн
казино онлайн 777
До встречи!
Онлайн-казино Jozz популярная площадка для ценителей азартных игр. Здесь доступны бонусы, включая промокоды. Каталог слотов актуальный, провайдеры мирового уровня дают контент. Создать аккаунт легко, и можно тестировать бонусы. Важно помнить о лимитах, для удовольствия. Подробнее: перейти
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
wood privacy fence near me Wood Fence Suppliers Near Me Check local retailers and specialized fence companies for convenient access to diverse wood fence solutions.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
Chicken Roadhttps://apkpure.com/p/app.chickenroad.game
кайтинг
sport bets [url=www.sportbets32.ru]www.sportbets32.ru[/url] .
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
wood horse fence cost per foot Cedar Fence Cost Per Foot Calculating cost per linear foot simplifies budgeting, enabling precise material quantity estimation. Remember to account for waste and overage to avoid project delays.
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
купить меф кокаин меф гаш купить
купить грамм гашиша купить меф
купить героин спб кокаин гашиш купить
где купить гашиш купить гашиш недорого
сайт купить гашиш купить гашиш марихуану
метадон героин купить закладку купить гашиш соли кокаин
бк 888starz
Авто из Китая https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru на заказ под ключ: подбор, проверка, доставка и растаможка. Новые и подержанные автомобили, выгодные цены и полное сопровождение сделки.
Хай!
Экономия на “сером” телефоне — это игра в русскую рулетку? [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/chto-delat-esli-kupil-seryj-telefon/]Как зарегистрировать серый телефон?[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-telefony.ru/chto-delat-esli-kupil-seryj-telefon/
Что значит серый телефон
Серый телефон это
Как узнать серый телефон или нет
До встречи!
Historia Vavada rozpoczęła się w 2017 roku, gdy grupa doświadczonych graczy postanowiła stworzyć „idealne kasyno online”. Miało ono zapewniać komfort, bezpieczeństwo i maksymalną dawkę emocji. Ten cel został osiągnięty w 100. Właścicielem projektu jest spółka Vavada B.V., zarejestrowana na Cyprze.
Дарим красоту и здоровье с
помощью качественных услуг.
Also visit my blog: northumbria university coach lane
Здарова!
Чувствуешь, что засиделся, но не можешь сдвинуться с места? [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/hochu-uvolitsya-no-ne-mogu-reshitsya/]как уволиться с работы[/url]
Написал: – https://zhit-legche.ru/hochu-uvolitsya-no-ne-mogu-reshitsya/
как уволиться с работы
увольнение с работы
как пережить увольнение с работы форум
До встречи!
накрутка подписчиков в тг без отписок
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
В мессенджере Telegram появилась функция звёзд.
Теперь пользователи могут отмечать важные месседжи.
Это дает возможность быстро находить нужную заметку.
как купить звезды в телеграм с айфона
Функция полезна для деловых задач.
С её помощью легко оставить ключевые моменты.
Такой инструмент экономит время и делает общение быстрее.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
PuzzleFree online puzzles https://insiderpaper.com/space-tourism-is-quietly-becoming-a-billion-dollar-industry/ hundreds of pictures to assemble, different difficulty levels and user-friendly interface. Enjoy the process, train your memory and attention for free.
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
https://www.legenda.one/
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
buy betaprodine
кашпо для комнатных растений напольные [url=http://kashpo-napolnoe-moskva.ru]http://kashpo-napolnoe-moskva.ru[/url] .
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
Домашняя работа играют важную роль в учёбе.
Они помогают закреплять новый материал.
Систематическая работа домашних заданий развивает дисциплину.
Задания также способствуют планированию.
https://forum.brasilfix.com/showthread.php?tid=5436
Благодаря им школьники готовятся к экзаменам.
Учителя могут оценить результаты обучения.
Таким образом, домашние задания остаются важными для успеха.
https://padlet.com/muhammadhasnainpk1_/discussion-topic-goes-here-5n3mh7gugixzfnu6/wish/L8KjW9PB4dkEZJbv
Yo, stumbled on this sick tuner. Works straight from the browser, no download BS. Super accurate, plus it’s got chromatic mode and a ton of alternate tunings. Straight up saved it to my bookmarks: https://www.tronicaltune.net/tronicaltune-online-guitar-tuner/
Grandfar CDL5-8T Вертикальный многоступенчатый центробежный насос Чугун
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм купить
программа для учета личных финансов на компьютер Учет компьютерной техники – важен для организации работы офиса. Программы учета компьютерной техники и оргтехники позволяют контролировать состояние и амортизацию оборудования.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Капельница от запоя – является результативным методом оказания помощи при алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога на дом даёт возможность быстро надежно получить необходимую помощь при запое. Состав раствора капельницы обычно содержит препараты для очищения организма, такие как раствор натрия хлорида, раствор глюкозы, витамины и антиоксиданты. Действие капельницы сосредоточено на восстановлении баланса жидкости и электролитов, облегчении симптомов абстиненции и повышении общего самочувствия пациента. Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы гарантирует быструю помощь при запое и способствует более быстрому восстановлению после запоя. Профессиональная помощь на дому позволяет избежать госпитализации, что делает процесс лечения удобнее для пациента. Важно учитывать, что реабилитация после запоя может включать и методы психотерапии для помощи в борьбе с зависимостью от алкоголя.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
диплом с реестром купить [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru/]диплом с реестром купить[/url] .
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя
dog humping girl porn
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
станки с чпу купить [url=https://stankiklass.ru]https://stankiklass.ru/[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
Хай!
Хватит кормить фармацевтических гигантов. [url=https://generik-info.ru/analogi-lekarstv-deshevle/]Что такое дженерики простыми словами[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://generik-info.ru/analogi-lekarstv-deshevle/
Что такое дженерики простыми словами
Что такое дженерики в медицине
Дженерики что это такое
Бывай!
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
вывод из запоя
C.R.I. PUMPS GA-CV13-FT-4 Погружной насос для отвода сточных вод 1,3 кВт, 3х380 В с вихревым (Vortex) рабочим колесом
Наружная реклама https://pioner-reklama.ru и вывески под ключ: дизайн, производство и монтаж. Световые короба, объёмные буквы, баннеры и витрины. Индивидуальные решения для бизнеса любого масштаба.
https://restoran-v-moskve.ru/
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
https://t.me/ruscasino_top
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
вывод из запоя
Цены на ремонт https://remontkomand.kz/ru/price квартир и помещений в Алматы под ключ. Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
https://github.com/awsadm/AWS-CLI
Алкогольная зависимость – серьезная проблема, требующая внимательного подхода. Множество людей предпочитают анонимный поиск помощи, чтобы не столкнуться с осуждением. Нарколог на дом предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя комфорт и конфиденциальность. Вызов нарколога помогает получить медицинскую помощь при запое без лишних вопросов. Анонимное лечение включает detox программы, где обеспечивается психологическая поддержка и медикаментозное сопровождение. Данный подход помогает предотвратить рецидив алкоголизма и способствует восстановлению после запойного состояния. Кризисная помощь предоставляет поддержку для преодоления острых состояний, предлагая все необходимые ресурсы. Таким образом, анонимный вывод из запоя – это реальность, доступная каждому, кто нуждается в помощи.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://apple-gear.ru/
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
https://widget-for-site.com/
https://apromashov.ru/
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в москве [url=www.arus-diplom33.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр в москве[/url] .
https://prokatvrf.ru/
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
вывод из запоя Тула
Спинтакс капельницы от запоя — надежный вариант помочь людям, страдающим от алкоголизма. В Туле существует множество клиник, предлагающих лечение запоя в круглосуточном режиме. При выборе клиники важно обратить внимание на опыт специалистов, программы реабилитации и гарантии безопасности.Лечение запоя с помощью медикаментов включает в себя индивидуальную программу к людям, страдающим от алкоголизма. Обращение к врачу поможет установить, нужна ли капельница и альтернативные методы восстановления. Также важна поддержка родственников, которая незаменима в процессе выздоровления.лечение запоя в Туле Клиника в Туле должна предлагать услуги нарколога и программы восстановления, чтобы обеспечить качественное восстановление. Лечение алкоголизма может быть доступна 24 часа в сутки, что обеспечивает оперативное решение проблемы.
Капельницы для восстановления после запоя в Красноярске – это действующий способ лечения похмелья и детоксикации организма. Абсолютное большинство пациентов с алкогольной зависимостью обращаются за медицинской поддержкой на дому, стремясь избежать нервного напряжения, возникающего при визите в клинику. Капельница от запоя помогает ускоренному восстановлению здоровья и облегчению симптомов алкогольной зависимости. С помощью специальных растворов для капельниц можно значительно ускорить процесс реабилитации после запоя. Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске предлагает услуги по прокапыванию, что даёт возможность обратиться за квалифицированной помощью без необходимости покидать дом. Реабилитация на дому включают не только капельницы, но и советы по лечению запоя, которые помогут предотвратить рецидив. Лечение алкогольной зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включая поддержку семьи и профессионалов. Помощь при алкоголизме становится доступнее, когда существует возможность проходить лечение в условиях домашнего уюта. site;com Необходимо помнить о влиянии алкоголя на здоровье: злоупотребление алкоголем может привести к серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Регулярное прокапывание способно стать частью программы реабилитации и помочь людям восстановить нормальную жизнь.
https://armada96.ru/
https://github.com/awsadm/AWS-CLI
Капельница от запоя на дому – это эффективный способ лечения алкогольной зависимости, предлагающий множество преимуществ и особенности. В Туле наркологические услуги включают выезд на дом, что даёт возможность пациентам обратиться за медицинской помощью при запое в комфортной для них обстановке. Преимущества капельницы заключаются в быстром восстановлении организма благодаря детоксикационным процедурам. Капельницы способствуют выведению токсинов, улучшить общее состояние, что, в свою очередь, помогает быстрее восстановиться после запоя. Кроме того, поддержка близких при запое имеет огромное значение, так как домашнее лечение алкоголизма создает комфортную атмосферу. лечение запоя тула Тем не менее, есть и недостатки. Например, не всегда возможно обеспечить должный уровень контроля за состоянием пациента. Консультация врача на дому может быть недостаточной для сложных случаев. Также стоит учитывать, что не всем пациентам подходят инъекции при алкоголизме.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Капельница от запоя – это действующий метод лечения алкогольной зависимости, который предлагает квалифицированный нарколог в городе Тула. Во время запоя организм испытывает существенное обезвоживание и интоксикацию, что приводит различные симптомы похмелья. Необходимо предоставить медицинскую помощь, чтобы улучшить состояние пациента. нарколог на дом тула Очистка организма с помощью капельницы способствует оперативному выведению токсинов и возвращению к норме. Индивидуальный подход врача обеспечивает максимальную эффективность лечения на дому. Лечение на дому позволяют избежать госпитализации и сделать комфортное лечение. Влияние алкоголя на организм разрушительно, поэтому реабилитация от запоя включает восстановительные мероприятия после алкогольной зависимости и консультацию нарколога. Комплексное лечение, включая инфузионную терапию, способствует улучшению самочувствия и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
You are a very smart person! 🙂
Капельница при алкогольной зависимости – это действующий метод помощи алкогольной зависимости, который предлагает квалифицированный нарколог в Красноярске. При запое организм испытывает существенное обезвоживание и интоксикацию, что вызывает к симптомам похмелья. Важно оказать первую помощь, чтобы восстановить здоровье больного. нарколог на дом Красноярск Очистка организма с помощью капельницы помогает оперативному выведению токсинов и улучшению состояния. Персонализированный подход врача обеспечивает высокую результативность лечения на дому. Услуги медикаментов на дому даёт возможность избежать госпитализации и сделать процесс лечения комфортным. Алкоголь негативно сказывается на здоровье разрушительно, поэтому восстановление после запоя включает восстановление после запоя и консультацию нарколога. Комплексная терапия, включая капельницу, помогает восстановлению здоровья и полноценному восстановлению.
https://t.me/ruscasino_top
Привет!
Хочешь взять микрозайм? [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-bystro-sdelat-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/]Получить кредит с плохой историей быстро[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-bystro-sdelat-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/
Что такое дженерики простыми словами
Дженерики что это
Дженерики для чего они нужны
Покеда!
Алкогольная зависимость – это серьезная проблема, требующая комплексного подхода к лечению. На сайте narkolog-tula018.ru вы найдете информацию о методах лечения зависимости от алкоголявключая очистку организма и кодирование от алкоголя. Важным этапом является реабилитация, где оказывается психологическая поддержка и формируются поддерживающие группытакие как анонимные алкоголики. Поддержка зависимых часто включает в себя рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и советы для жизни без алкоголя. Восстановление после запоя требует усердия и поддержки близких. Необходимо помнить о влиянии спиртных напитков на здоровье и следовать методам отказа от алкоголя для достижения успешного выздоровления.
купить напольное кашпо для комнатных растений [url=https://www.kashpo-napolnoe-moskva.ru]https://www.kashpo-napolnoe-moskva.ru[/url] .
This tool allows you to swap clothes in pictures.
It uses AI to adjust outfits seamlessly.
You can try different styles instantly.
xnudes.ai|Perfect Clothing Changer Web Tool
The results look authentic and professional.
It’s a handy option for shopping.
Upload your photo and select the clothes you like.
Begin exploring it right away.
Капельница от запоя в Красноярске: что нужно знать Если вы или ваши близкие испытывают трудности из-за алкогольной зависимости, учтите, что существуют проверенные методы терапии. Нарколог на дом анонимно в Красноярске предлагает услуги по выведению из запоя, включая капельницы на дому. Данные процедуры способствуют восстановлению здоровья после запоя и общему улучшению состояния. Капельницы эффективно снимают симптомы абстиненции, насыщая организм важными витаминами и электролитами. Консультация с наркологом — первый шаг к лечению запоя, на котором будет оценено состояние пациента и предложены медикаментозные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом. Анонимная помощь доступна в наркологической клинике Красноярск, где также можно пройти реабилитацию от запойного поведения. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск Умение распознавать признаки алкогольной зависимости крайне важно для своевременного обращения за медицинской помощью. Лечение в домашних условиях возможно, но требует контроля специалиста. Комплексный подход, включающий поддержку близких и помощь специалистов в области наркологии в Красноярске, является ключом к успешному восстановлению после запоя.
Экстренный вывод из запоя в Туле: какова цена? Запой на алкоголе — это значительная проблема, требующая экстренного вмешательства. Признаки запоя включают сильную жажду , дрожь , избыточное потоотделение и тревожность . Для эффективного лечения и снятия запойного состояния необходима профессиональная медицинская помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной зависимости. В Туле помощь наркологов предлагают специализированные клиники, где можно получить экстренную помощь при запое. Как проходит процесс вывода из запоя? Наркологи используют различные методы , включая очищение организма и медикаментозное лечение . Стоимость вывода из запоя варьируются, но в среднем составляют от 5 000 до 15 000 рублей . Обращение к врачу-наркологу поможет выбрать оптимальную программу реабилитации от алкоголя , учитывая индивидуальные особенности пациента . Учтите, что лечение алкогольной зависимости — это длительный и сложный процесс, требующий усилий и поддержки . Наркологические центры Тулы предлагают широкий спектр реабилитационных программ, которые помогают избавиться от алкогольной зависимости и возвращают к полноценной жизни.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
ОТКАПЫВАНИЕ НА ДОМУ: СОВЕТЫ Открытие участка для благоустройства – это важный этап домашнего проекта. Откапывание‚ или земляные работы‚ включает в себя множество задач‚ таких как выемка ямы для фундамента‚ дренажные системы и водопроводные работы. Правильный выбор инструментов для копки и аренда оборудования помогут облегчить процессы. Садовые работы требуют тщательного планирования. Уход за участком‚ особенно в периодические работы в саду‚ поможет сохранить красоту ландшафта. Не забудьте учесть дизайн местности‚ который может включать в себя элементы‚ требующие земляных работ. Не игнорируйте рекомендации по копке: выбирайте подходящие инструменты‚ следите за безопасностью и учитывайте особенности почвы. Земельные услуги могут помочь с профессиональным выполнением работ. Заходите на narkolog-tula019.ru для получения дополнительной информации и услуг.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Онлайн-курсы платные курсы бесплатно – Sharewood. Изучайте языки, IT, дизайн, маркетинг и другие направления. Удобный формат, доступ к материалам 24/7
Прокапывание на дому — это удобное и эффективное лечение, которое даёт возможность пациентам получать инфузионную терапию в комфортной обстановке домашней обстановке. Профессиональные медсестры обеспечивают профессиональное введение капельниц, что способствует восстановлению после болезни и укреплению здоровья на дому. narkolog-tula018.ru Домашний уход включает в себя не лишь саму процедуру, но и контроль состояния здоровья пациента. Это особенно важно для людей с хроническими заболеваниями или тем, кто нуждается в профилактике заболеваний. При организации домашнего лечения можно быть уверенным в высоком качестве медицинских услуг, что значительно упрощает процесс восстановления.
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы – это проверенный метод лечения алкогольной зависимости‚ который предоставляет возможность анонимного и комфортного восстановления. Нарколог на дом анонимно обеспечит оперативную медицинскую помощь при запое‚ используя метод капельницы для очищения организма. Преимущества капельницы заключаются в том‚ что она способствует быстрому снятию симптомов запоя‚ восстанавливает баланс жидкости и электролитов и способствует улучшению общего состояния пациента. Это особенно важно в случае серьезных проявлений алкогольной зависимости‚ когда требуется срочное вмешательство.Лечение алкоголизма включает разные методы‚ но капельница отличается высокой эффективностью и скоростью действия. В отличие от таблеток или инъекций‚ капельница обеспечивает непрерывное поступление лекарств в организм‚ что способствует более быстрому восстановлению.Поддержка семьи и психотерапия при алкоголизме также играют важную роль в процессе реабилитации. После детоксикации и восстановления после запоя продолжать лечение и заниматься профилактикой рецидивов‚ что возможно только при комплексном подходе. Таким образом‚ капельница при запое — это ключевой элемент в борьбе с алкоголизмом‚ предлагая пациентам надежное анонимное лечение и возможность быстрого восстановления.
ростест
Агентство Digital-рекламы в Санкт-Петербурге. Полное сопровозжение под ключ, от разработки до маркетинга https://webwhite.ru/
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
вывод из запоя
https://badcodes.ru/
Стоимость вывода из запоя от алкоголя в Туле варьируется в зависимости с различными аспектами. Нарколог на дом анонимно предоставляет услуги по выведению из запоя и лечению при алкоголизме. Консультация нарколога поможет выбору оптимальной программы детокса. Цены на программы лечения могут включать расходы на анонимную детоксикацию и реабилитацию от алкоголя. Услуги нарколога, такие как поддержка пациентам с зависимостямитакже играют важную роль. В наркологической клинике Тула доступны различные программыкоторые могут влиять на общую стоимость. Необходимо помнить о профилактике алкогольной зависимости и необходимости своевременной терапии.
Выезд нарколога на дом в Туле становятся всё более востребованными. Специалисты данной сферы, оказывают разнообразные наркологические услуги, в т.ч. помощь при алкоголизме и других зависимостях. Выездная консультация нарколога даёт возможность оперативно диагностировать зависимости и назначить индивидуальный подход к пациенту. Анонимное лечение – важный аспект работы специалистов, что особенно важно для людей, которые стесняются обращаться в медицинские учреждения. Реабилитация на дому включает психотерапию при зависимости, программы восстановления и медикаментозную терапию. Семейная поддержка зависимых является ключевым элементом в процессе выздоровления. Профилактика рецидивов также занимает центральное место в работе наркологов. Наркологи предоставляют психологическую поддержку и помощь, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолевать трудности на их пути к выздоровлению. Узнать больше о доступных услугах можно на сайте narkolog-tula019.ru, где представлены все необходимые контакты и информация о наркологических услугах в Туле.
https://33ppg.ru/
https://alpextrim.ru/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk007.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
Скорая наркологическая помощь – это существенный элемент, который предоставляет срочную поддержку людям, имеющим проблемы с зависимостями. В экстренной ситуации, когда необходима быстрая поддержка, на помощь предоставляется наркологическая служба. Преодоление зависимостей включает медикаментозное вмешательство и полноценную реабилитацию наркозависимых. При зависимости от алкоголя необходимо обратиться за помощью. Первичная консультация у психолога может послужить началом пути к восстановлению. Семейная поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Анонимные группы поддержки и психотерапия помогают справиться с трудностями. Профилактика наркозависимости также играет важную роль. Противодействие наркозависимости должна быть делом всего общества. Обращение за помощью на ресурсе narkolog-tula020.ru поможет вам найти необходимые ресурсы для начала нового, трезвого этапа жизни.
Привет!
Как превратить свою страсть к играм в источник дохода. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-realnye-dengi/]как заработать на играх в стиме[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-realnye-dengi/
как заработать на браузерных играх
как заработать школьнику на играх
игры на которых можно заработать реальные деньги
До встречи!
Строительство домов https://stroycata1og.ru и коттеджей под ключ. Готовые проекты, индивидуальные решения, качественные материалы и полный цикл работ — от фундамента до отделки.
Строительство домов https://stroycata1og.ru и коттеджей под ключ. Готовые проекты, индивидуальные решения, качественные материалы и полный цикл работ — от фундамента до отделки.
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-msk008.ru
частный дом престарелых
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
Врач-нарколог на дом в Туле предоставляет экстренную помощь тем, кто переживает проблемы с наркоманией и алкоголизмом. Лечение зависимости требует индивидуального подхода, и выезд нарколога на дом – это оптимальный вариант для людей, нуждающихся в помощи. Центр лечения зависимостей в Туле предлагает лечение без раскрытия личности и консультации нарколога. Реабилитация на дому позволяет пройти курс психотерапии при зависимости в домашней обстановке. Выездная медицинская помощь включает в себя как медицинское, так и психологическую поддержку. Профилактика зависимости также играет важную роль в противостоянии алкоголизму и наркомании. Помощь алкоголикам и их близким – это работа квалифицированных специалистов, которые готовы оказать помощь в сложной ситуации. narkolog-tula021.ru
SBT119에서 제공하는 먹튀검증 서비스로 안전하게 이용하세요.
회원 전용 가입머니와 풍성한 꽁머니 이벤트가 준비되어 있습니다.
먹튀사이트 차단, 카지노 입플, 토토꽁머니, 카지노 꽁머니까지 모두 지원합니다.
интернет займ займ денег онлайн
мфо взять займ займ онлайн
займ деньги микрозайм онлайн
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk009.ru
пансионат для пожилых
Высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек в Тюмени Высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек в Тюмени: Ключ к финансовой независимости и роскошной жизни. Гибкий график, конфиденциальность и высокий доход. Раскрой свой потенциал и забудь о финансовых трудностях.
Нужна качественная регулировка окон пвх? Специалисты настроят створки, фурнитуру и уплотнители. Устранение продувания, перекоса и тяжёлого открывания с гарантией качества.
https://www.trub-prom.com/catalog/truby_srednego_diametra/194/
https://digital-downloads-app.com/
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
pansionat-msk007.ru
частный пансионат для престарелых
пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula007.ru
частный дом престарелых
провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу екатеринбург
https://igrozavod.ru/
купить подстанцию [url=https://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit2.ru/]transformatornye-podstancii-kupit2.ru[/url] .
пансионат для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk008.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
https://www.trub-prom.com/catalog/truby_srednego_diametra/426kh10/
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula008.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
недорогой интернет екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
подключить интернет по адресу
Высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек в Тюмени Работа моделью в Тюмени: Воплоти свою мечту о карьере в мире моды! Участие в показах, фотосессиях и выгодные контракты. Высокий доход и возможность заявить о себе.
On this site you can discover a lot of valuable information.
It is designed to help you with various topics.
You will find simple explanations and practical examples.
The content is regularly updated to stay current.
https://talish.info
It’s a reliable resource for learning.
Every visitor can take advantage of the materials here.
Feel free to checking out the site now.
Tree removal and care https://www.highqualitytreeservice.com/ pruning, crown shaping, treatment, removal and felling of hazardous trees. Experienced specialists and modern equipment. Safe, professional and with a guarantee of results.
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk009.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-tula009.ru
дом престарелых в туле
Приветствую!
Откровенно о психологии азарта и о том, как казино использует ее против тебя. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/onlajn-kazino-bez-liczenzii/]онлайн казино без лицензии[/url]
Написал: – https://nagny-casino.ru/onlajn-kazino-bez-liczenzii/
казино онлайн
10 лучших казино онлайн
онлайн казино без лицензии
Покеда!
узнать провайдера по адресу екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
Нужен клининг? список клининговых компаний москвы. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
https://apps.shopify.com/digital-downloads-app-11
Нужен клининг? список клининговых компаний москвы. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Нужен клининг? топ клининговых компаний москвы 2026. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Нужен клининг? топ клининговых компаний москвы 2026. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
The service allows you to swap clothes on images.
It uses smart technology to adjust outfits naturally.
You can try multiple styles in seconds.
Best Clothes Changer Web Tool
The results look authentic and modern.
It’s a handy option for shopping.
Upload your photo and pick the clothes you prefer.
Begin trying it right away.
Стоматологическая клиника https://almazdental35.ru с индивидуальным подходом. Безболезненное лечение, эстетическая стоматология, имплантация и профессиональная гигиена полости рта.
У нас вы сможете арендовать современный сноуборд с идеальной подготовкой, чтобы катание приносило только удовольствие и яркие эмоции: прокат лыж адлер
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
вызов психиатра на дом в москве
пансионат для престарелых людей
pansionat-tula007.ru
частный пансионат для престарелых
У детей пробелмы с зубами? детская стоматология — лечение и профилактика зубов у детей. Безопасные методы, комфортная атмосфера и заботливые врачи для маленьких пациентов.
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://dubna.ru/article/2025/08/samye-populyarnye-serialy-2025-goda онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
Современные решения для тех, кто хочет купить пластиковые окна недорого в Москве, предлагает наша компания с опытом работы на рынке более 10 лет. Изготовление ведется по немецким технологиям с применением качественного профиля и многокамерного стеклопакета, обеспечивающего надежную теплоизоляцию и звукоизоляцию. Для максимального удобства клиентов доступны пластиковые окна от производителя на заказ, что позволяет учесть размеры проемов и выбрать оптимальную фурнитуру: окна пвх официальный сайт
интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу красноярск
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://obzor.city/texty/infotech/onlajn-kinoteatr-lordseries онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
J’aime enormement le casino TonyBet, ca offre une aventure palpitante. Les jeux sont varies, avec des machines a sous modernes. Le personnel est tres competent, avec des reponses claires. Le processus de retrait est efficace, neanmoins j’aimerais plus de bonus. En gros, TonyBet ne decoit pas pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs, l’interface est fluide, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet betrug|
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://www.justmedia.ru/news/russiaandworld/serialy-onlayn-kak-vybrat-i-gde-smotret онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
кашпо для цветов напольное высокое [url=http://kashpo-napolnoe-krasnodar.ru/]кашпо для цветов напольное высокое [/url] .
https://t.me/PROAUTO159 Электромобили из Китая — это не просто тренд, а стратегическое направление развития национальной промышленности. Государственная поддержка, огромные инвестиции в исследования и разработки, а также стремление к экологической чистоте привели к созданию передовых электрокаров, способных конкурировать с мировыми лидерами. BYD, NIO, Xpeng и другие бренды предлагают широкий спектр электромобилей, от компактных городских моделей до премиальных внедорожников.
букет цветов в москве Доставка Цветов в Москве: Пусть Цветы Говорят За Вас. Если у вас нет времени на посещение цветочного магазина, Flowwow предлагает быструю и надежную доставку цветов по всей Москве. Наши курьеры доставят ваш заказ вовремя, сохранив свежесть и красоту цветов.
Блок сервопривода АКПП ISM Mecredes/Мерседес Цена блока сервопривода АКПП ISM может варьироваться в зависимости от производителя, модели автомобиля и региона. Учитывайте стоимость диагностики и установки при планировании бюджета на ремонт.
https://vornikovbouquets.ru/ Подарите маме букет ее любимых цветов, чтобы выразить свою любовь и благодарность.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, on dirait une plongee dans le divertissement. Les options de jeu sont impressionnantes, comprenant des titres modernes et attrayants. Le service client est exceptionnel, offrant des reponses claires et rapides. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, de temps en temps davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs passionnes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec soin, amplifiant le plaisir du jeu.
azur casino retrait avis|
J’adore sans reserve Banzai Casino, ca offre une plongee dans le divertissement intense. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table authentiques. Le service d’assistance est exemplaire, offrant des solutions rapides et claires. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient apprecies. En conclusion, Banzai Casino offre une experience exceptionnelle pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Notons aussi que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
bonsai banzai slot|
психиатрическая помощь больным
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
детский психиатр на дом
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betclic Casino, il procure une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, incluant des slots dernier cri. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les gains sont verses en un clin d’?il, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betclic Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus le site est concu avec elegance, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betclic elite classement|
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-tula008.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в туле
проверенные сервисы подписчиков
цветы в москве Онлайн-каталоги с удобной навигацией и профессиональной поддержкой консультантов делают процесс заказа цветов максимально простым и приятным. Заказать цветы с доставкой в Москве: Экономия Времени и Гарантия Свежести
J’adore le casino TonyBet, c’est vraiment un univers de jeu unique. Les options de jeu sont nombreuses, offrant des options de casino en direct. Le support est toujours la, offrant un excellent suivi. Les transactions sont securisees, cependant les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. En gros, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs, le site est facile a naviguer, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet free spins bonus code|
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдер по адресу
Нужна контекстная реклама? https://reklama-stomatolog-kontekst.ru под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
Нужна контекстная реклама? https://reklama-stomatolog-kontekst.ru под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
Ища риэлторскую компанию, важно обращать внимание на его надёжность.
Хорошее агентство всегда имеет отзывы клиентов, которые доступны онлайн.
Также проверьте, есть ли официальная лицензия.
Надёжные компании заключают сделки только на основе договоров.
Дома, дачи, коттеджи Казани
Важно, чтобы у агентства был практика на рынке не меньше нескольких лет.
Обратите внимание, насколько прозрачно компания раскрывает условия сделок.
Хороший риэлтор всегда готов ответить на ваши вопросы.
Выбирая агентство, доверьтесь не просто словам, а практическим результатам.
Нужна контекстная реклама? https://reklama-stomatolog-kontekst.ru под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
В нашем сервисе аренды сноубордов есть все необходимые размеры, чтобы каждый клиент мог найти удобную и подходящую экипировку: прокат сноубордов красная поляна
J’apprecie enormement Banzai Casino, il procure une energie de jeu captivante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service client est irreprochable, joignable 24/7. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, cependant j’aimerais plus de bonus allechants. En resume, Banzai Casino ne decoit jamais pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec dynamisme, ajoutant une touche d’elegance et d’energie.
banzai slots casino|
J’adore a fond Betclic Casino, ca offre une sensation de casino unique. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le support est d’une reactivite exemplaire, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les gains sont verses en un clin d’?il, occasionnellement les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Betclic Casino vaut amplement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement epoustouflant, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
betclic service client|
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
стационарная психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
купить живых и ботов в ТГ
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-tula009.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых
Порно смотреть Порно Порно смотреть Секс советы Порно картинки Порно видео онлaйн без регистрaции Секс на камеру Эротика Бесплатное порно видео Секс шоп
интернет провайдеры по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
интернет по адресу дома
моствет [url=https://mostbet4119.ru/]https://mostbet4119.ru/[/url]
http://recambiosclassicsport.com/foro-ingresos/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=3679
mostbet download [url=https://mostbet4121.ru/]https://mostbet4121.ru/[/url]
букмекерские конторы кыргызстана [url=https://mostbet4126.ru]https://mostbet4126.ru[/url]
https://www.alexeymart.com/
https://www.allnumis.com/user/profile/hpokingt2
брови севастополь курсы бровиста севастополь — Курсы бровиста в Севастополе подойдут как начинающим, так и практикующим мастерам, желающим повысить квалификацию: программы включают теоретическую базу (анатомия волоса и кожи, типы лица и симметрия, колористика и подбор оттенка, противопоказания, санитария) и обширную практику (моделирование формы, коррекция пинцетом/воском/нитью, окрашивание хной и краской, ламинирование, восстановительные техники, фотофиксация работ). Продвинутые программы включают знакомство с перманентным макияжем (микроблейдинг, пудровая техника), правилами ведения клиента, управлением прайсом и продвижением в соцсетях. Ключевой критерий качества курса — количество практических часов и работа на реальных моделях, возможность получения обратной связи от преподавателя и помощь в составлении портфолио. По окончании школы участники получают сертификат, но важнее отзывы и результативность трудоустройства; некоторые учебные центры помогают выпускникам в трудоустройстве и предлагают оптовые закупки материалов. При выборе курса в Севастополе уточните состав учебного набора, опыт преподавателя, размер группы и доступ к дальнейшим консультациям — это повысит шанс быстро начать зарабатывать и выстроить успешную практику в бьюти-индустрии.
вторичка у метро Площадь Тукая Казань
J’adore le casino TonyBet, c’est vraiment un moment divertissant top. Les jeux sont varies, comprenant des titres innovants. Le service d’assistance est top, avec des reponses claires. Les retraits sont rapides, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. En gros, TonyBet vaut vraiment le coup pour ceux qui aiment parier ! En bonus, la plateforme est intuitive, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet apuestas|
психиатр на дом
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
консультация психиатра на дому
Добрый день!
Хочешь купить крипту без паспорта в 2025 году? [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/gde-kupit-kriptovalyutu-bez-verifikaczii/]где купить криптовалюту без верификации[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/gde-kupit-kriptovalyutu-bez-verifikaczii/
перспективные альткоины
defi проекты с доходом
биржи криптовалют без верификации
Бывай!
перевод с нотариальным заверением Перевод с нотариальным заверением — это комплексная процедура, при которой переводчик выполняет перевод документа, а затем нотариус удостоверяет подпись переводчика или соответствие документа оригиналу; в результате получается документ, принятый многими официальными структурами. Процесс требует подготовки оригиналов и копий документов, паспорта переводчика для удостоверения личности и, при необходимости, дополнительных формальностей: перевод приложений, расшифровок печатей или заверение подлинности подписей. Часто такая услуга требуется при эмиграции, оформлении гражданства, подаче заявлений в посольства и для юридических сделок за рубежом. Сроки и стоимость зависят от объёма документа, необходимости срочности и тарифов нотариуса; чтобы избежать дополнительных визитов, целесообразно заранее согласовать перечень документов и формат заверения с принимающей инстанцией. Комбинация профессионального перевода и нотариального заверения обеспечивает максимально широкое признание документа в официальных процедурах.
мостбет зеркало [url=http://mostbet4122.ru]http://mostbet4122.ru[/url]
мостбкт [url=http://mostbet4121.ru]мостбкт[/url]
Установка подрозетников Монтаж электрощита Монтаж электрощита – это ответственный этап электромонтажных работ, требующий высокой квалификации и строгого соблюдения правил электробезопасности. Электрощит является центром управления и защиты электросети объекта, поэтому от его правильной установки и комплектации зависит надежность и безопасность электроснабжения. Виды электрощитов: Вводные электрощиты: Устанавливаются на вводе электроэнергии в здание и предназначены для приема и распределения электроэнергии по групповым линиям. Этажные электрощиты: Устанавливаются на этажах многоквартирных домов и предназначены для учета и распределения электроэнергии по квартирам. Квартирные электрощиты: Устанавливаются в квартирах и предназначены для защиты групповых линий от перегрузок и коротких замыканий. Промышленные электрощиты: Используются на промышленных предприятиях для управления и защиты электрооборудования. Этапы монтажа электрощита: Подготовка: Выбор места установки электрощита, подготовка необходимых инструментов и материалов. Монтаж корпуса: Крепление корпуса электрощита к стене или другой несущей конструкции. Установка оборудования: Установка автоматических выключателей, УЗО (устройство защитного отключения), реле напряжения, счетчиков электроэнергии и другого оборудования в соответствии со схемой электрощита. Подключение: Подключение вводного кабеля, групповых линий и других элементов электросети к электрощиту. Заземление: Подключение корпуса электрощита к системе заземления. Проверка и испытания: Проверка правильности подключения и испытание электрощита на работоспособность и безопасность. Маркировка: Маркировка всех элементов электрощита для удобства обслуживания и эксплуатации. Рекомендации по монтажу электрощита: Используйте только качественные сертифицированные электрощиты и комплектующие. Выбирайте электрощит с запасом по мощности и количеству модулей. Соблюдайте правила электробезопасности при выполнении работ. Грамотно распределяйте нагрузку по группам потребителей. Установите УЗО для защиты от поражения электрическим током. Регулярно проводите техническое обслуживание электрощита.
сертификация продукции Сертификат ИСО 9001: Сертификат ИСО 9001 – это документ, подтверждающий соответствие системы менеджмента качества организации требованиям международного стандарта ISO 9001. Этот стандарт содержит требования к системе управления качеством, которые направлены на обеспечение стабильного качества продукции или услуг, удовлетворение потребностей и ожиданий потребителей, повышение эффективности бизнес-процессов и постоянное улучшение деятельности организации. Сертификат ИСО 9001 выдается независимым аккредитованным органом по сертификации, который проводит аудит системы менеджмента качества организации на соответствие требованиям стандарта. В ходе аудита оцениваются различные аспекты деятельности организации, такие как планирование качества, управление ресурсами, управление процессами, мониторинг и измерение результатов деятельности, анализ данных и принятие корректирующих и предупреждающих мер. Наличие сертификата ИСО 9001 свидетельствует о том, что организация внедрила и поддерживает эффективную систему управления качеством, которая обеспечивает стабильное качество продукции или услуг, удовлетворение потребностей потребителей и постоянное улучшение деятельности. Сертификат ИСО 9001 является важным конкурентным преимуществом, повышает доверие потребителей и партнеров, открывает новые возможности для развития бизнеса и участия в тендерах и конкурсах.
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, il procure une plongee dans le divertissement. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux innovants. Les agents sont toujours disponibles, offrant des solutions rapides. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Dans l’ensemble, AllySpin ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux ! Par ailleurs l’interface est super intuitive, facilitant chaque session.
allyspin hracГ automaty|
J’apprecie enormement Betclic Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et professionnels, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. Pour conclure, Betclic Casino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier ! En bonus le design est visuellement epoustouflant, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
contacter betclic|
Play puzzles online https://x.com/newsfile_corp/status/1942328790425686373 free and without restrictions. A huge selection of pictures, simple controls and the ability to develop attention, memory and thinking. A great way to relax and spend time usefully.
скорая психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
консультация частного психиатра
How to Take a Screenshot
брови севастополь макияж севастополь — Услуги профессиональных визажистов в Севастополе охватывают дневной, вечерний и свадебный макияж, образный грим для фотосессий и мероприятий, а также выезд на локации у моря или в отелях. Климат и образ жизни диктуют требования к стойкости: мастера используют праймеры, фиксаторы, водостойкую косметику и техники, которые выдерживают влагу и ветер. Для невест особенно важен выездной сервис и предварительная репетиция макияжа — это позволяет согласовать образ с причёской, платьем и условиями фотосъёмки (освещение на открытой площадке иначе действует на цвета). Висажист должен учитывать тип и состояние кожи (пористость, жирность), возможные аллергии и особенности фотосъёмки (флеш, вечерний свет). Помимо нанесения, профессионал даёт рекомендации по подготовке кожи: увлажнение и пилинг за несколько дней, отсутствие новых агрессивных процедур перед мероприятием. Обязательно обращайте внимание на гигиену — чистые кисти, одноразовые спонжи и аппликаторы — и на используемые бренды, если у вас есть чувствительность. Для повседневного макияжа визажисты часто предлагают «сэкономленный» домашний вариант с минимальным набором средств, который легко повторить, а также короткие мастер-классы для самостоятельного поддержания образа. При бронировании услуг уточняйте, включён ли в стоимость выезд, сколько времени займёт процесс и есть ли возможность срочной подправки в течение дня.
888 starz download for iOS https://www.pgyer.com/apk/apk/app.starz.online
провайдер по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу краснодар
скачать бк осталось именно выбрать подходящее [url=https://mostbet4124.ru]скачать бк осталось именно выбрать подходящее[/url]
888 starz download for iOS https://www.pgyer.com/apk/en/apk/app.starz.online
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
https://vk.com/3dplabs
https://how-to-screenshot.info/
J’adore a fond Betsson Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont protegees par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En resume, Betsson Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et intuitive avec un theme orange vif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme a l’experience.
betsson sponsor|
https://www.domique.shop/
888starz bonus https://www.pgyer.com/apk/fr/apk/app.starz.online
мостбет вход, регистрация [url=http://mostbet4122.ru/]http://mostbet4122.ru/[/url]
Получите квалифицированную [url=https://yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya23.ru]правовая помощь онлайн[/url].
Наша команда состоит из опытных специалистов, которые способны решить любые юридические проблемы.
регистрация в бк мостбет [url=https://mostbet4120.ru/]регистрация в бк мостбет[/url]
https://t.me/Foka_Doka_SPb
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
консультация психиатра на дому в москве
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
мостюет [url=http://mostbet4125.ru/]http://mostbet4125.ru/[/url]
консультация врача психиатра
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
провайдеры по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
интернет по адресу краснодар
mostbet com вход [url=https://mostbet4123.ru/]mostbet com вход[/url]
mostbet казино скачать [url=http://mostbet4120.ru]http://mostbet4120.ru[/url]
мостбеи [url=http://mostbet4123.ru]мостбеи[/url]
перевод документов Перевод с английского — универсальная формулировка, охватывающая все типы переводческой деятельности с английского языка: письменный и устный перевод, локализация софта, субтитрование, адаптация маркетинговых материалов и сопровождение переговоров. При устном переводе (синхронном или последовательном) важны скорость реакции, умение сохранять точность и передавать интонацию выступающего; при письменном переводе первоочередна тщательная работа с текстом, использование терминологических баз и выверка фактов. Для локализации программного обеспечения и сайтов добавляются задачи по адаптации пользовательского интерфейса, тестированию и интеграции перевода в технические файлы проекта. Многие исполнители предлагают тестовый фрагмент или пробный перевод для оценки качества перед принятием большого заказа, а также составление глоссариев и стайлгайдов для согласования стиля. Уточняйте формат сдачи, требования к верстке и сроки, чтобы работа была принята без лишних доработок и соответствовала ожиданиям заказчика.
букмекер кыргызстан [url=https://mostbet4126.ru/]https://mostbet4126.ru/[/url]
mostbet скачать на телефон [url=http://mostbet4125.ru]http://mostbet4125.ru[/url]
Crash games are browser games with a interactive experience.
They feature a growing multiplier that players can watch in real time.
The goal is to act before the bar stops.
csgo crash betting site
Such games are popular for their straightforward play and excitement.
They are often used to test timing.
Plenty of platforms host crash games with varied designs and features.
You can try these games now for a fun experience.
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, on dirait une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, par moments les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec dynamisme, renforce l’immersion totale.
1xbet yeni giris|
Estou completamente apaixonado por o 888 Casino, e como se fosse aventura cheia de emocoes. Ha uma infinidade de titulos variados, com sessoes de cassino ao vivo imersivas. A equipe oferece um suporte de altissima qualidade, garantindo ajuda imediata. Os ganhos sao pagos em tempo recorde, em alguns momentos mais recompensas seriam bem-vindas. Para concluir, o 888 Casino nunca decepciona para os amantes de cassino online! Adicionalmente a navegacao e simples e rapida, facilita cada sessao de jogo.
888 casino app download|
Ich schatze sehr BingBong Casino, es ist ganz ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Auswahl ist reichhaltig und breit gefachert, mit modernen Slots wie Book of Ra Deluxe und Sweet Bonanza. Die Mitarbeiter sind professionell und immer hilfsbereit, ist taglich erreichbar. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft innerhalb von 24 Stunden fur PayPal, gelegentlich zusatzliche Belohnungen fur Premium-Mitglieder waren toll. Insgesamt ist BingBong Casino enttauscht nie fur Fans von legalem Glucksspiel ! Daruber hinaus ist die Benutzeroberflache modern und intuitiv, die Immersion verstarkt.
bingbong casino bonus code ohne einzahlung|
организация похорон
мостбет официальный [url=http://mostbet4124.ru/]http://mostbet4124.ru/[/url]
вызов психиатра на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
психиатрическое лечение
разработка и продвижение сайта цена
карбокситерапия Гидропилинг – это современная процедура очищения и увлажнения кожи, которая проводится с помощью специального аппарата. Во время гидропилинга кожа очищается от загрязнений, отшелушиваются ороговевшие клетки и одновременно насыщается увлажняющими и питательными веществами. Гидропилинг помогает улучшить цвет лица, уменьшить поры, разгладить мелкие морщины и сделать кожу более мягкой и упругой. Процедура подходит для всех типов кожи и не требует длительного периода реабилитации.
мостбет. вход. [url=www.mostbet4127.ru]www.mostbet4127.ru[/url]
лечение в психиатрической больнице
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
консультация частного психиатра
mersin escort
узнать провайдера по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
https://bs2besd.cc
buy belt tensioner rollers
Как сам!
Читай наш гайд по безопасной покупке криптовалюты. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/birzhi-kriptovalyut-bez-verifikaczii/]крипта без kyc[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/birzhi-kriptovalyut-bez-verifikaczii/
где купить криптовалюту без верификации
где можно купить криптовалюту без верификации
куда вложить крипту без верификации
Бывай!
оборудование для окраски металлоконструкций Порошковое оборудование для покраски — это комплекс устройств и приспособлений, предназначенных для нанесения порошковых полимерных покрытий на различные поверхности, чаще всего металлические. В состав такого оборудования входят: камеры для подготовки поверхности (для очистки, обезжиривания и травления), распылители порошковой краски (электростатические и трибостатические), камеры напыления (где происходит нанесение порошка), печи полимеризации (для запекания и отверждения порошкового слоя), а также системы вентиляции, фильтрации и управления. Правильный выбор и настройка оборудования обеспечивают высокое качество покрытия, экономичный расход порошка и безопасность процесса.
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, avec un suivi de qualite. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. Globalement, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et retro, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino review|
купить напольное кашпо для комнатных растений [url=http://kashpo-napolnoe-krasnodar.ru]http://kashpo-napolnoe-krasnodar.ru[/url] .
частная наркологическая клиника в воронеже Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже – это специализированное медицинское учреждение, которое оказывает помощь людям, страдающим от различных видов зависимостей, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания, игромания и другие. Клиника предлагает комплексный подход к лечению, включающий в себя детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию, реабилитацию и социальную адаптацию. Лечение в клинике проводится анонимно и конфиденциально.
J’adore passionnement BetFury Casino, il offre une immersion dans un univers vibrant. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont instantanes, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, BetFury Casino est un incontournable pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! En bonus le site est concu avec modernite et elegance, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betfury giris|
Je suis absolument conquis par Betsson Casino, c’est une veritable energie de jeu irresistible. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7 et professionnels, offrant des solutions rapides et precises. Les gains sont verses en 24 heures pour les e-wallets, parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En resume, Betsson Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et intuitive avec un theme orange vif, renforce l’immersion totale.
betsson app ios|
Ich bin total begeistert von BoaBoa Casino, es ist wirklich eine einzigartige Casino-Atmosphare. Die Auswahl ist reichhaltig und breit gefachert, mit progressiven Jackpots wie Divine Fortune. Das Team bietet schnelle Unterstutzung per E-Mail oder Telefon, reagiert in wenigen Minuten. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft innerhalb von 24-72 Stunden, gelegentlich ich mir mehr regelma?ige Aktionen wunschen wurde. Alles in allem ist BoaBoa Casino ein Muss fur Spieler fur die, die gerne wetten ! Erganzend die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, die Immersion verstarkt.
boaboa bokep|
J’apprecie enormement CasinoBelgium, il offre une plongee dans un univers vibrant. Le catalogue est compact mais de grande qualite, offrant des titres de Gaming1 et Greentube. Le service d’assistance est efficace, garantissant une aide pour toute question. Les paiements sont proteges par un cryptage SSL, cependant j’aimerais une ludotheque plus vaste. En fin de compte, CasinoBelgium est ideal pour une experience authentique pour ceux qui aiment les dice slots ! Par ailleurs le design est simple et attrayant, ce qui rend l’experience agreable.
avis casino belgium|
мостбет вход официальный сайт [url=https://www.mostbet4127.ru]https://www.mostbet4127.ru[/url]
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
реабилитация наркоманов в Астане
https://bar-vip.ru/vyezdnoi_bar/
купить аппарат для порошковой покраски Камеры порошковой окраски от производителя купить – это возможность приобрести оборудование напрямую от производителя, получив гарантию качества и техническую поддержку. Производители предлагают широкий ассортимент камер различной конфигурации и размеров, а также оказывают услуги по монтажу и пусконаладке оборудования.
букмекерская контора кыргызстан [url=https://mostbet4119.ru/]букмекерская контора кыргызстан[/url]
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-msk004.ru
провайдеры интернета в москве по адресу
частная наркологическая клиника воронеж Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже на левом берегу – это медицинское учреждение, расположенное на левом берегу реки Воронеж и оказывающее специализированную помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей. Клиника предоставляет широкий спектр услуг, включая детоксикацию, медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию, реабилитацию и социальную адаптацию.
стационарная психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
врач психиатр на дом
https://bs2-bs2site.at
Спросите о родителях: внешность, характер, здоровье. Особенно важно знать, нет ли у них проблем с суставами. Наличие рентгена у производителей шотландских вислоухих — хороший знак: генетические заболевания у шотландских вислоухих котят
swot анализ вопросы https://swot-analiz1.ru
реабилитация алкоголиков в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
реабилитация от наркозависимости в Астане
J’apprecie enormement 1win Casino, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu captivante. La selection est incroyablement riche, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Le personnel est professionnel et attentionne, repondant rapidement. Les paiements sont fluides et fiables, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. En resume, 1win Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec modernite, ajoute une touche d’elegance a l’experience.
1win bonus|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betzino Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux varies, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le service client est exceptionnel, joignable par email ou chat. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable avec un maximum de 5000 € par semaine, cependant les bonus comme le pack de bienvenue de 150 % jusqu’a 200 € pourraient etre plus frequents. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betzino casino avis forum|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, on dirait une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, avec un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Notons egalement que la navigation est simple et agreable, renforce l’immersion totale.
betify casino bonus|
J’adore a fond Casino Action, il offre une sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux varies, incluant des slots de pointe de Microgaming. Le personnel offre un accompagnement rapide via chat ou email, garantissant une aide immediate. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Casino Action est un incontournable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
casino action bonus code|
tapered roller bearing
интернет провайдеры москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
консультация психиатра платно
This website has lots of really useful stuff on it. Thanks for informing me.
лечение и реабилитация алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология в Астане
мастбет [url=www.mostbet4128.ru]www.mostbet4128.ru[/url]
Лучшие пункты приема металла Москвы https://metallolom52.ru/
тарифы интернет и телевидение москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
подключение интернета москва
mostbet приложение [url=mostbet4130.ru]mostbet4130.ru[/url]
mostbet aviator skachat [url=https://www.mostbet4167.ru]https://www.mostbet4167.ru[/url]
Je trouve absolument epoustouflant 1xbet Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, joignable 24/7. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. Pour conclure, 1xbet Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus le design est visuellement percutant, renforce l’immersion totale.
1xbet apk download|
психиатрическая помощь госпитализация
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
консультация психиатра на дому
Je trouve absolument extraordinaire Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une sensation de casino unique. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, incluant des slots de pointe de Microgaming et NetEnt. Le service client est de haut niveau, repondant en quelques minutes. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! De plus le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway sport|
Stand out in today’s competitive job market with CVzen.uk.
We create professional CVs, ATS-optimized resumes, and personalized cover
letters, while offering interview prep and career insights
to ensure your application impresses employers every step of the way.
https://1xbetx.ru/ 1xbetx.ru: Ваш надежный гид в мире ставок на спорт. 1xbetx.ru – это информационный портал, предлагающий актуальную информацию о букмекерской конторе 1xBet. Здесь вы найдете свежие новости, обзоры спортивных событий, стратегии ставок и полезные советы от опытных игроков. Наша команда экспертов ежедневно анализирует тысячи матчей, чтобы предоставить вам самые точные прогнозы и помочь сделать правильный выбор. Мы также предлагаем подробные инструкции по регистрации, пополнению счета и выводу средств, чтобы ваш опыт игры в 1xBet был максимально комфортным и безопасным. 1xbetx.ru – ваш надежный партнер в мире ставок на спорт!
обзоры фильмов Обзоры кино: Погружение в атмосферу большого экрана. “Обзоры кино” – это ваш проводник в захватывающем мире кинематографа. Мы тщательно анализируем новинки проката, расскрывая основные темы, символизм и подтекст, чтобы помочь вам не только насладиться просмотром, но и понять глубинный смысл произведения. Наши критики – это профессионалы, которые любят кино и умеют видеть детали, которые ускользают от обычного зрителя. Читайте наши обзоры и расширяйте горизонты своего киновосприятия!
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Как сам!
Заработок на играх — это миф или реальность? [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-bez-vlozhenij/]как заработать деньги на играх[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-bez-vlozhenij/
как можно заработать деньги на играх
как заработать на играх 2025
заработать на компьютерных играх
Покеда!
бк мостбет скачать [url=mostbet4130.ru]mostbet4130.ru[/url]
pokerdom зеркало
Аренда авто в Краснодаре Прокат авто Краснодар на месяц: Комфорт и свобода на длительный срок в Краснодаре. Получите максимальный комфорт и свободу передвижения с услугой проката авто в Краснодаре на месяц. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей различных марок и моделей, доступных для аренды на месяц или более длительный срок. Наш автопарк включает в себя экономичные автомобили для повседневных поездок, комфортабельные седаны для деловых встреч и вместительные внедорожники для путешествий по окрестностям. Прокат авто в Краснодаре на месяц – это выгодное и удобное решение для тех, кто нуждается в автомобиле на длительный срок. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и наслаждайтесь поездками по Краснодару!
рецензии фильмов и сериалов Обзоры фильмов и сериалов: Ваш путеводитель в мире кино и телевидения. Наш сайт предлагает всесторонние обзоры самых свежих и интересных фильмов и сериалов. Мы анализируем сюжет, актерскую игру, режиссуру, визуальные эффекты и другие важные аспекты, чтобы помочь вам сделать осознанный выбор и не тратить время на некачественный контент. У нас вы найдете как рецензии на громкие премьеры, так и обзоры малоизвестных, но достойных внимания картин. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, чтобы быть в курсе последних новинок и обсуждать свои любимые фильмы и сериалы!
https://bar-vip.ru/vyezdnoi_bar/
Instagram Инстаграм: Мир визуальных историй и безграничных возможностей. Инстаграм – это не просто социальная сеть, это целая вселенная, где каждый может рассказать свою историю, поделиться своими увлечениями и найти единомышленников. Откройте для себя мир креатива, вдохновения и общения с миллионами людей по всему миру. Подписывайтесь на интересных вам авторов, следите за трендами и создавайте свой уникальный контент!
провайдер интернета по адресу нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
интернет домашний нижний новгород
оргониты райх Изделия из оргонита: Разнообразие форм и применений оргонита (кулоны, пирамиды и т.д.).
мостбет приложение узбекистан [url=http://mostbet4169.ru/]http://mostbet4169.ru/[/url]
С получением профессиональной помощи в решении юридических вопросов вы можете обратиться к [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata81.ru]юридическая помощь онлайн[/url], где можно получить юридическую консультацию круглосуточно и бесплатно.
С ‘konsultaciya-advokata81.ru’ вы получите не только поддержку, но и уверенность в своем будущем.
анонимное лечение алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых
приложение Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
Прокат авто аэропорт Краснодар Аренда авто Краснодар на месяц: Экономичное решение для долгосрочной аренды. Если вам нужен автомобиль на длительный срок, аренда авто в Краснодаре на месяц – это выгодное и удобное решение. Мы предлагаем специальные тарифы на долгосрочную аренду, которые позволят вам сэкономить деньги и получить автомобиль в свое распоряжение на целый месяц. Наши автомобили всегда в отличном состоянии и готовы к поездке. Аренда авто в Краснодаре на месяц – это идеальное решение для тех, кто нуждается в автомобиле на длительный срок, например, для работы или учебы. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и получите максимальную выгоду!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://pikoclub.ru
красивый оргонит Оргонит из смолы: основной компонент оргонита, обеспечивающий его структуру.
мостбет войти в личный кабинет [url=mostbet4129.ru]mostbet4129.ru[/url]
подключить домашний интернет в нижнем новгороде
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета нижний новгород
лечение от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
эффективное лечение алкоголизма
mostbet link [url=www.mostbet4166.ru]www.mostbet4166.ru[/url]
J’apprecie beaucoup le casino TonyBet, ca offre un plaisir de jeu constant. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le service d’assistance est top, offrant un excellent suivi. Les paiements sont fluides, occasionnellement les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. Pour tout dire, TonyBet vaut vraiment le coup pour les amateurs de casino ! Par ailleurs, le site est facile a naviguer, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet prediction|
J’adore a fond le casino AllySpin, ca donne une experience de jeu electrisante. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, incluant des slots dernier cri. Le service client est remarquable, offrant des solutions rapides. Les transactions sont bien protegees, mais parfois les promos pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, AllySpin est une plateforme de choix pour les passionnes de jeux ! De plus la navigation est fluide, facilitant chaque session.
allyspin gioco d azzardo online|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux varies, incluant des slots dynamiques. Le personnel est hautement professionnel, disponible 24/7. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus nombreux. Pour conclure, Azur Casino offre une experience fiable pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec soin, amplifiant le plaisir du jeu.
azur casino bonus sans dГ©pГґt|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog006.ru
лечение запоя тула
мостбет узбекистон [url=http://mostbet4165.ru]http://mostbet4165.ru[/url]
мостбет скачать на компьютер [url=http://mostbet4129.ru/]мостбет скачать на компьютер[/url]
Je suis conquis par Banzai Casino, ca offre une energie de jeu captivante. Il y a une multitude de titres varies, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service client est irreprochable, joignable 24/7. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, par moments les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, Banzai Casino est une valeur sure pour les joueurs en quete de frissons ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, renforcant l’immersion.
banzai casino no deposit bonus|
mostbet uz yuklab olish skachat [url=https://mostbet4165.ru]mostbet uz yuklab olish skachat[/url]
бонусы Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
J’adore a fond Betclic Casino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, comprenant des titres innovants et attrayants. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. Dans l’ensemble, Betclic Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le site est concu avec elegance, renforce l’immersion totale.
service client betclic tГ©lГ©phone|
mostbet uzcard [url=mostbet4167.ru]mostbet4167.ru[/url]
официальный сайт мостбет [url=www.mostbet4166.ru]официальный сайт мостбет[/url]
провайдеры в нижнем новгороде по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу нижний новгород
курс реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
реабилитация зависимых от алкоголя
mostbet uz telegram qo‘llab-quvvatlash [url=mostbet4168.ru]mostbet4168.ru[/url]
swot анализ слов https://swot-analiz1.ru
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Looking for second-hand? thrift store store near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
mostbet bonus olish [url=http://mostbet4169.ru/]http://mostbet4169.ru/[/url]
Как сам!
Как не попасться на удочку мошенников и довезти товар до России в 2025 году. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/elektronika-iz-kitaya-napryamuyu/]электроника китай[/url]
По ссылке: – https://pro-telefony.ru/elektronika-iz-kitaya-napryamuyu/
электроника с aliexpress
Электроника из Китая напрямую
заказать телефон из китая напрямую самый дешевый сайт
Покеда!
Хай!
Как получить препараты из Индии легально и безопасно. [url=https://generik-info.ru/gde-zakazat-tabletki-napryamuyu-iz-indii/]обезболивающие таблетки индия[/url] Подробная инструкция от выбора аптеки до доставки домой.
По ссылке: – https://generik-info.ru/gde-zakazat-tabletki-napryamuyu-iz-indii/
где заказать таблетки напрямую из Индии
таблетки от давления индия
обезболивающие таблетки индия
Пока!
Приветствую!
Твой путь к пассивному доходу в криптовалютах. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/defi-proekty-s-dohodom/]defi заработок[/url] DeFi протоколы, которые реально работают и приносят стабильную прибыль.
Читай тут: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/defi-proekty-s-dohodom/
defi кредитование
defi заработок
как заработать на defi
Пока!
С получением профессиональной помощи в решении юридических вопросов вы можете обратиться к [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata81.ru]получить юридическую консультацию онлайн[/url], где можно получить юридическую консультацию круглосуточно и бесплатно.
Не стоит забывать, что заранее полученная юридическая консультация может уберечь от серьезных трудностей.
провайдеры интернета по адресу новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
подключить интернет
Looking for second-hand? second hand clothes We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
https://miritaly.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя тула
мостбет уз скачать [url=www.mostbet4128.ru]мостбет уз скачать[/url]
Актуальные автобусные рейсы по Беларуси и Росии — от крупных городов до самых уютных маленьких станций. Туристические туры и экскурсии — будь то прогулка по старинным улочкам европейского города или активный уикенд на природе. Авиабилеты — могли перемещаться не только по дорогам, но и по воздуху, открывая всё новые горизонты. Всё это вы подбираете прямо на Probilets и оплачиваете удобным способом: заказ билетов на автобус
Актуальные автобусные рейсы по Беларуси и Росии — от крупных городов до самых уютных маленьких станций. Туристические туры и экскурсии — будь то прогулка по старинным улочкам европейского города или активный уикенд на природе. Авиабилеты — могли перемещаться не только по дорогам, но и по воздуху, открывая всё новые горизонты. Всё это вы подбираете прямо на Probilets и оплачиваете удобным способом: заказ билетов на автобус
https://push-network-rankings.com/
подключить интернет новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
подключить интернет в квартиру новосибирск
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://yunc.org
ЭВЛО https://evlo-phlebology.ru эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция вен, наряду со склеротерапией является эффективным методом лечения варикозного расширения вен на ногах.
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
Услуги госпитализации https://hospitall.ru экстренная помощь при угрожающих состояниях и плановое лечение с заранее согласованной программой. Подбор клиники, транспортировка и поддержка пациента на всех этапах.
chicken road https://www.pgyer.com/apk/apk/app.chickenroad.game
помещение для дгу
провайдеры в новосибирске по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу новосибирск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
лечение запоя
Je suis totalement envoute par Amon Casino, il offre une experience de casino electrisante. Il y a une avalanche de jeux de casino varies, incluant des jeux de table de casino ultra-styles. Le staff du casino assure un suivi de ouf, avec une aide qui claque. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse de l’eclair, cependant j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui tabassent. Au final, Amon Casino c’est un casino de ouf a tester direct pour les aventuriers du casino ! A noter aussi le design du casino est une explosion visuelle, booste l’immersion dans le casino a fond.
casino de paris|
Je suis totalement enflamme par Celsius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui fait jaillir des etincelles. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino elegants et brulants. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui fait des etincelles. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une braise, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui embrasent. En somme, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style flamboyant, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
celsius casino bonus sans depot|
Склеротерапия вен ног — современный метод лечения варикоза, который активно применяется в клиниках флебологии. Процедуру проводит опытный флеболог после диагностики — УЗИ вен или УЗДС вен. Склеротерапия позволяет эффективно удалять варикозные вены без операции. Также для удаления варикоза используют ЭВЛК и ЭВЛО. Выбор метода зависит от состояния вен и рекомендаций врача. Склеротерапия безопасна, не требует длительной реабилитации и помогает вернуть здоровье ногам: лечение варикоза
вывод из запоя цена
tula-narkolog006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
https://lakoshka.ru
домашний интернет
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
провайдеры интернета ростов
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
лечение запоя
Je trouve completement fou FatPirate, ca donne une energie de pirate dejantee. Les jeux sont nombreux et delirants, incluant des jeux de table pleins de panache. L’assistance est carrement geniale, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Les retraits sont rapides comme une tempete, des fois des bonus plus reguliers ce serait cool. Bref, FatPirate offre une experience de ouf pour les aventuriers du jeu ! A noter aussi le design est style et accrocheur, donne envie de replonger direct.
fatpirate pЕ™ihlГЎЕЎenГ|
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
вывод из запоя
https://www.te-in.ru/arenda-dizel-generatorov.html/
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, ca balance une vibe spectaculaire. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, repondant en un clin d’etoile. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, quand meme des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. Pour resumer, Impressario garantit un show de fun epique pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! En prime l’interface est fluide et glamour, ajoute un max de charisme.
impressario casino login|
провайдеры интернета в ростове
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
подключить интернет
https://elfasamara.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
online casino cz Kasina: Objevte svet hazardu! Klasicke hry, moderni automaty a vzruseni z vyhry – vse pod jednou strechou, at uz online nebo offline.
cz casino online CZ Casino Online: Find the best CZ casino online! Read reviews, compare bonuses, and choose the perfect platform for your gaming needs and preferences.
https://push-network-rankings.com/
Хай!
Как перестать сливать в покере и начать зарабатывать. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/]как выиграть в покере[/url] Проверенные стратегии и типичные ошибки начинающих игроков.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/
покер как играть
как играть покер
как правильно играть в покер чтобы выигрывать
До встречи!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Kangaroo Drawing is a creative India-based game where players draw kangaroos in fun, artistic challenges. Simple, engaging, and perfect for all ages: Kangaroo drawing competitions
Здравствуйте!
Мобильная связь для пожилых: что действительно нужно знать. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-dlya-pozhilyh-lyudej/]кнопочный телефон для пожилых с громким динамиком[/url] Практические советы без воды от человека в теме.
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-dlya-pozhilyh-lyudej/
моб телефон для пожилых людей
мобильный телефон для пожилых
Покеда!
bs2best
карго перевозки из китая доставка из китая в россию
фермерские продукты тверь фермерские продукты
cz casino online Kasina: Svet zabavy a adrenalinu. Prozkoumejte nabidku klasickych i modernich kasin, od kamennych heren po online verze, ale pamatujte na zodpovedne hrani.
интернет домашний ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
провайдеры интернета ростов
карго грузы из китая карго доставка из китая
Онлайн-библиотека Казахстана https://mylibrary.kz книги, статьи, диссертации и редкие издания в цифровом формате. Удобный каталог, быстрый поиск и круглосуточный доступ для всех пользователей.
фермерская лавка заказать фермерские продукты
kasina ” symbol: Online Casino CZ: Explore the world of Czech online casinos! Discover licensed and regulated platforms offering a wide range of games and exciting bonuses. Play responsibly and enjoy the thrill.
Je suis totalement envoute par Cresus, ca donne une ambiance de jeu enchanteresse. Il y a une abondance de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le personnel offre un suivi digne d’un palace, joignable via chat ou email. Le processus est limpide et sans tracas, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient appreciees. En fin de compte, Cresus offre une experience grandiose pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et raffinee, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus memorable.
nouveau cresus casino|
Ich bin suchtig nach DrueGlueck Casino, man fuhlt einen verruckten Spielvibe. Der Katalog des Casinos ist der Wahnsinn, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie der Blitz, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren cool. Zusammengefasst ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck mobile|
Онлайн-библиотека Казахстана https://mylibrary.kz книги, статьи, диссертации и редкие издания в цифровом формате. Удобный каталог, быстрый поиск и круглосуточный доступ для всех пользователей.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
Je kiffe grave AmunRa Casino, ca balance une vibe de jeu pharaonique. La selection de titres du casino est un tresor divin, proposant des sessions de casino en direct qui envoutent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une tempete de sable, garantissant un support de casino instantane et royal. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une offrande, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, AmunRa Casino offre une experience de casino mythique pour les aventuriers du casino ! En bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
amunra kifizetes|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. Il y a un deluge de jeux de casino varies, offrant des machines a sous de casino uniques. Le crew du casino assure un suivi de ouf, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Les transactions de casino sont simples comme un neon, par contre les offres de casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans le fond, Instant Casino est un spot de casino a ne pas rater pour les pirates des slots de casino modernes ! En prime l’interface du casino est fluide et ultra-cool, facilite le delire total au casino.
vegas slot instant play casino|
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
Получите [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata91.ru]бесплатную юридическую консультацию онлайн[/url], чтобы оперативно решить все ваши юридические вопросы!
Каждая ситуация уникальна и требует персонального подхода, поэтому мы внимательно изучаем каждое дело.
Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам на [url=https://yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru]юристы по уголовным делам бесплатно[/url], и получите квалифицированное решение своих вопросов.
yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru предлагает профессиональные юридические услуги, направленные на решение различных правовых вопросов. Команда опытных юристов готова помочь вам в самых сложных ситуациях. Понимая, что правовые проблемы могут быть стрессовыми, мы предлагаем персонализированные решения к каждому клиенту.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации по гражданским и уголовным делам. Вы можете обратиться к нам по вопросам, связанным с трудовым правом, семейными делами и другими юридическими аспектами. Каждый случай уникален , и готовы предложить оптимальное решение.
Мы гордимся нашей репутацией как надежный партнер в сфере юриспруденции. Мы получаем положительные отзывы от клиентов за высокое качество обслуживания и результативность. Каждый юрист нашей команды имеет опыт работы в различных областях права и готов поддержать вас в любое время.
Не откладывайте решение своих проблем , чтобы получить квалифицированную юридическую помощь. Наша команда будет рада проконсультировать вас . Воспользуйтесь нашими услугами на yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru.
купить диплом в кривом роге [url=http://educ-ua5.ru]купить диплом в кривом роге[/url] .
провайдер интернета по адресу санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
bs2best
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://halif-omsk.ru
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция https://evlo-phlebology.ru эффективный метод лечения варикоза. Амбулаторная процедура занимает до 40 минут, не требует госпитализации и обеспечивает быстрый косметический и медицинский результат.
Сюрвей грузов сюрвей контроль качества и количества, проверка условий перевозки, составление отчётов. Опытные эксперты обеспечивают объективную оценку для компаний и страховых организаций.
Надежная доставка из китая в Россию: от документов до контейнеров. Выбираем оптимальный маршрут, оформляем таможню, страхуем грузы. Контроль сроков и сохранность на каждом этапе.
Estou completamente viciado em DazardBet Casino, e um cassino online que e pura adrenalina. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino variados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos para criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um raio, dando solucoes claras e na hora. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem complicacao, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria demais. No geral, DazardBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino fora de serie para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino arrasa com um visual eletrizante, da um toque de classe ao cassino.
dazardbet login|
Эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция https://evlo-phlebology.ru эффективный метод лечения варикоза. Амбулаторная процедура занимает до 40 минут, не требует госпитализации и обеспечивает быстрый косметический и медицинский результат.
Сюрвей грузов сюрвей контроль качества и количества, проверка условий перевозки, составление отчётов. Опытные эксперты обеспечивают объективную оценку для компаний и страховых организаций.
Je suis fou de Julius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme un lion. Le repertoire du casino est une arene de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui en imposent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une legion en marche, proposant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse triomphale, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui dominent. Globalement, Julius Casino c’est un casino a conquerir en urgence pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style imperial, ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
bonus sans depot julius casino|
Надежная доставка из китая в Россию: от документов до контейнеров. Выбираем оптимальный маршрут, оформляем таможню, страхуем грузы. Контроль сроков и сохранность на каждом этапе.
Kangaroo Baby is a charming India-based mobile game where players care for adorable kangaroo joeys. With simple gameplay, nurturing tasks, and cute graphics, it’s perfect for kids and casual gamers: official Kangaroo drawing website
Je suis obsede par Bruno Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu explosive. La collection de jeux du casino est phenomenale, incluant des jeux de table de casino raffines. Le service client du casino est un vrai bijou, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un souffle, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Bruno Casino promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
bruno casino avis forum|
Acho simplesmente animal LeaoWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura selva. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino unicos e eletrizantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma aguia, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Na real, LeaoWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
leaowin02 25 casino|
сайт для компании под ключ стоимость сайта на тильде
провайдеры интернета в санкт-петербурге по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер санкт-петербург
Надежная доставка грузов из китая: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Авиа, морем, авто и железной дорогой. Оформление, страхование и логистика в кратчайшие сроки.
Нужен автобусный билет? купить билет на автобус онлайн просто и удобно. Поиск рейсов, сравнение цен, выбор мест и моментальная оплата. Актуальное расписание, надежные перевозчики и выгодные тарифы каждый день.
заказать лендинг art-made
Надежная доставка грузов из китая: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Авиа, морем, авто и железной дорогой. Оформление, страхование и логистика в кратчайшие сроки.
Нужен автобусный билет? купить билет на автобус онлайн просто и удобно. Поиск рейсов, сравнение цен, выбор мест и моментальная оплата. Актуальное расписание, надежные перевозчики и выгодные тарифы каждый день.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
Качественный ремонт квартир https://expertremonta.kz от Компании «Эксперт ремонта» это качественный ремонт квартир под ключ в Алматы. Выбирайте Эксперт Ремонта — тут бесплатный выезд замерщика, официальные документы, гарантия документально, ремонт квартир без предоплаты.
купить топливо с доставкой доставка дизельного топлива
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
почвогрунт оптом почвогрунт купить дешево
https://miritaly.ru
bs2best at
Качественный ремонт квартир https://expertremonta.kz от Компании «Эксперт ремонта» это качественный ремонт квартир под ключ в Алматы. Выбирайте Эксперт Ремонта — тут бесплатный выезд замерщика, официальные документы, гарантия документально, ремонт квартир без предоплаты.
доставка диз топлива купить дизтопливо в москве с доставкой
купить плодородный грунт торф купить в москве
Приветствую!
Секретная формула идеального резюме для поколения Z. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sdelat-rezyume-na-rabotu/]Как сделать свое резюме[/url] Как молодым специалистам конкурировать с опытными и получать крутые предложения о работе.
Читай тут: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sdelat-rezyume-na-rabotu/
Как сделать красивое резюме в ворде
Пока!
Мобильный выездной шиномонтаж https://master-shin.by круглосуточная помощь в дороге. Экстренная помощь в дороге может понадобиться каждому автолюбителю, и наша компания оказывает ее на высочайшем профессиональном уровне, на самых выгодных в Минске условиях. Оперативный выезд по городу и области, доступные и полностью адекватные цены, квалифицированная сервисная и консультационная поддержка, круглосуточное реагирование, вне зависимости от погодных условий.
Ремонт ноутбуков https://01km.ru телефонов, телевизоров, принтеров и компьютеров в Одинцово и Москве.
go to the website online: https://saffronholidays.in
подключить интернет в квартиру санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
какие провайдеры на адресе в санкт-петербурге
J’adore l’incandescence de Celsius Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui fait monter la temperature. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enflammes, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement incandescent, avec une aide qui fait des etincelles. Les paiements du casino sont surs et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui embrasent. Au final, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle volcanique, facilite une experience de casino torride.
celsius casino promo code|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
Ich finde absolut majestatisch King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Spa?, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Kronungsfest funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king billy casino no deposit bonus codes 2020|
the best site for you: https://telrad.com
visit our website: https://chaussures-lady.fr
our site is waiting for you: https://amt-games.com
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
вывод из запоя
посетить сайт онлайн: https://efaflex.ru
our official website: https://fgvjr.com
go to our website: https://actual-cosmetology.ru
bs2best at
visit our new website: https://nature-et-avenir.org
our new official website: https://tumundobio.es
I found a cool site: https://www.locafilm.com
Получите [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata91.ru]бесплатную юридическую консультацию онлайн[/url], чтобы оперативно решить все ваши юридические вопросы!
Наша команда опытных адвокатов готова помочь в обработке ваших проблем.
Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам на [url=https://yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru]бесплатная юридическая консультация горячая линия[/url], и получите квалифицированное решение своих вопросов.
ресурс yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru предлагает профессиональные юридические услуги, направленные на решение различных правовых вопросов. Наша команда готова помочь вам в самых сложных ситуациях. Мы понимаем, что правовые проблемы могут быть стрессовыми, мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
В нашем арсенале широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации по гражданским и уголовным делам. Вы можете обратиться к нам по вопросам, связанным с трудовым правом, семейными делами и другими юридическими аспектами. Мы понимаем, что каждая ситуация требует индивидуального подхода, и готовы предложить оптимальное решение.
Наша компания известна как надежный партнер в сфере юриспруденции. Мы получаем положительные отзывы от клиентов за высокое качество обслуживания и результативность. Каждый юрист нашей команды имеет опыт работы в различных областях права и готов поддержать вас в любое время.
Не ждите, пока ситуация усугубится , чтобы получить квалифицированную юридическую помощь. Наша команда будет рада проконсультировать вас . Юридическая консультация ждет вас на yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru.
порно русской девушки красивое русское порно
Want to have fun? melbet drugs Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Je trouve absolument enivrant CasinoClic, il propose une aventure de casino qui fait vibrer. Le repertoire du casino est une veritable comete de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une fusee, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enivrant. En somme, CasinoClic c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les explorateurs du casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et rayonnante comme une aurore, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus electrisante.
casino clic|
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von iWild Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Savanne. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Naturwunder, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitstern, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Blitz. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Insgesamt ist iWild Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Wildnis beherrscht fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Tropenwald, das Casino-Erlebnis total wild macht.
iwild|
Mochten Sie ein https://www.immobilien-in-montenegro-fuer-oesterreicher.com kaufen? Tolle Angebote am Meer und in den Bergen. Gro?e Auswahl an Immobilien, Unterstutzung bei der Immobilienauswahl, Transaktionsunterstutzung und Registrierung. Leben Sie in einem Land mit mildem Klima und wunderschoner Natur.
Je suis totalement ebloui par JackpotStar Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu celeste. La selection du casino est une explosion cosmique de plaisir, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une comete, repondant en un eclair cosmique. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans turbulence, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient stellaires. Au final, JackpotStar Casino est une etoile brillante pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style etoile, facilite une experience de casino astrale.
jackpotstar skate|
Ich liebe den Zauber von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Ozean voller Schatze, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter krachen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Lapalingo Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
lapalingo sitz|
Je suis fou de LeonBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui dechire tout. La collection de jeux du casino est titanesque, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement rugissant, repondant en un eclair de tonnerre. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un predateur, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient sauvages. En somme, LeonBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino rugissant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline sauvage du casino ! A noter le design du casino est une fresque visuelle feroce, ajoute une touche de puissance au casino.
leonbet aposta|
Новые актуальные iherb промокод кэшбэк для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
подключить интернет
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
подключить интернет тарифы екатеринбург
Gradicrown is an innovative platform offering premium interior and outdoor furniture designs. Known for modern aesthetics, durability, and affordability, it’s a go-to destination for stylish home and office decor solutions: Gradi Crown reviews
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
https://topor.info
best articles on the net: https://dnscompetition.in/articles/how-to-audit-your-dns-configuration-for-compliance/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
провайдеры интернета в екатеринбурге по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
домашний интернет в екатеринбурге
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
https://videokontroldoma.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
play puzzles online: https://gist.github.com/foulegold/4d62ec002cdf02e290a80dd8d361f939
интернет тарифы екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
домашний интернет подключить екатеринбург
An antidetect browser helps users hide their digital fingerprints while browsing online. It is often used by marketers, testers, and researchers to simulate different devices or locations.
Привет!
Тебя выкинули с работы как ненужного? [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-delat-esli-uvolili-s-raboty/]Что делать если уволили с работы[/url] Забей, есть план как превратить это в новые возможности.
Здесь подробней: – https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-delat-esli-uvolili-s-raboty/
как пережить увольнение с любимой работы
Что делать если уволили с работы
увольнение с работы
Пока!
Здравствуйте!
Кредит под залог квартиры: последний шанс или новые возможности. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kredit-s-plohoj-istoriej-pod-zalog-nedvizhimosti/]кредит 24 7 на карту с плохой кредитной историей[/url] Разбираем все нюансы для людей с проблемной историей.
Читай тут: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kredit-s-plohoj-istoriej-pod-zalog-nedvizhimosti/
кредит под залог недвижимости с плохой кредитной историей отзывы
Бывай!
best site come on in: https://alterego.re
The most useful information: https://foxartistic.com
Самое лучшее в сети: https://badgerboats.ru
Current and up-to-date information: https://clubcoma.org
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar013.ru
лечение запоя
доставка из китая логистика из китая в россию
фанерованная дсп шпон цена
геодезические изыскания геодезист москва
геотекстиль 600 купить геотекстиль для укрытия роз
купить техникум диплом [url=http://educ-ua8.ru/]купить техникум диплом[/url] .
купить диплом об окончании техникума [url=http://educ-ua9.ru]купить диплом об окончании техникума[/url] .
Ich bin total begeistert von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Lapalingo Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Regenbogen glitzert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
lapalingo no deposit bonus 2024|
Adoro o clima explosivo de JabiBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que arrasta tudo. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma perola, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem tempestade. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como surfar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet login|
Ich bin total begeistert von JokerStar Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein magischer Spielrausch. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Sternenhaufen, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Insgesamt ist JokerStar Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Zauberlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
jokerstar bewertung|
Je suis fou de LeoVegas Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu princiere. La selection du casino est une veritable cour de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme somptueux. Le service client du casino est digne d’un monarque, avec une aide qui inspire le respect. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un edit, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, LeoVegas Casino promet un divertissement de casino royal pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et somptueuse comme un trone, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus majestueuse.
leovegas casino login|
https://110km.ru/opinion/
провайдер по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Включение в реестр Минпромторга https://minprom-info.ru официальный путь для подтверждения отечественного производства. Подготовка и подача документов, юридическое сопровождение и консультации для производителей.
HBet – Cổng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu, quy tụ hàng ngàn trò chơi cá cược thể thao, casino, slot game và bắn cá đổi thưởng. Giao diện mượt mà, bảo mật tuyệt …
Занятия по самообороне https://safety-skills.ru практические навыки защиты в реальных ситуациях, развитие силы и выносливости. Профессиональные тренеры помогут освоить приемы борьбы, удары и тактику безопасности.
Платформа онлайн-обучения https://craftsmm.ru курсы по маркетингу, продажам и рекламе для новичков и профессионалов. Освойте современные инструменты продвижения, увеличьте продажи и развивайте карьеру в удобном формате.
Vzrušující svět online casino cz — Průvodce pro české hráče: cz casino online
rooster bet https://www.pgyer.com/apk/apk/rooster.bet.app
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
Написание дипломов на заказ https://vasdiplom.ru помощь студентам в подготовке итоговых работ. Авторские тексты, проверка на уникальность и полное соответствие стандартам учебных заведений.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar014.ru
лечение запоя
https://zhitvdome.ru
visit our best site online: https://www.maxwaugh.com
The best we have here: https://www.kapoorstudycircle.com
NeoSpin Casino app download https://www.pgyer.com/apk/apk/neospin.casino.slots
интернет провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
The latest information is here: https://unilago.com
We have the latest information: https://anthese.fr
visit our website: https://www.anak2u.com.my
We are waiting for you on the site: https://copychief.com
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя
Je trouve absolument enchanteur Luckland Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un trefle a quatre feuilles. Il y a un raz-de-maree de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Luckland Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et lumineuse comme un arc-en-ciel, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
luckland casino bonus code|
J’adore le charme de Luckster Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu ensorcelante. Le repertoire du casino est une cascade de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme feerique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient ensorcelants. Pour resumer, Luckster Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
luckster uk|
Je suis accro a MonteCryptos Casino, on dirait une avalanche de fun. La selection du casino est une ascension de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et robuste. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une descente en luge, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sentier de montagne, ajoute une touche de magie alpine au casino.
montecryptos promo code|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
https://flactor.ru
Jako žurnalista vím, že klíčem je text, který sluší čtenáři, obsahuje jednoduchá slova, srozumitelný styl a praktické informace, zvlášť když jde o „cz casino online“ a „kasina“. Tady je vaše nové, svěží a užitečné čtení: online casino cz
провайдеры по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
провайдеры по адресу красноярск
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Приобретение автозапчастей в сети остается всё более востребованной среди автовладельцев.
Сайты автозапчастей обеспечивают большой каталог комплектующих для любых моделей автомобилей.
Цены в интернет-площадках часто выгоднее, чем в офлайн магазинах.
Покупатели могут сравнивать предложения разных компаний в несколько кликов.
тормозные колодки купить
Кроме того, продуманная система отправки позволяет оформить заказ без задержек.
Комментарии других покупателей помогают выбрать подходящие автозапчасти.
Многие сервисы дают гарантию на детали, что усиливает доверие покупателей.
Таким образом, онлайн-покупка автозапчастей экономит время и деньги.
Want to have fun? porno girl Whores, drugs, casino. We have it all, any drugs are on sale.
Здарова!
Steam-аккаунты: от покупки до перепродажи пошагово. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-akkaunt-stim/]где купить стим аккаунт[/url] Детальная инструкция для тех, кто хочет попробовать этот заработок.
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-akkaunt-stim/
продать аккаунт стим быстро
продать аккаунт стим моментально
До встречи!
купить наркотики ск меф магазин курск порно старых
The best of our site: https://hyundaimobil.co.id
New and relevant information: https://amt-games.com
Приветствую!
Сбор кала на анализ: делаем всё Как надо. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sobrat-kal-na-analiz-lajfhak/]Как брать анализ кала[/url] Дружеский гайд с важными нюансами, которые влияют на результат.
Здесь подробней: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sobrat-kal-na-analiz-lajfhak/
Как правильно взять анализ кала
Удачи!
Je suis totalement sous le charme de Casinova, ca donne une ambiance electrisante. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le service client est irreprochable, joignable via chat ou email. Les transactions sont simples et efficaces, par moments des recompenses supplementaires seraient appreciees. Dans l’ensemble, Casinova est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier avec style ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est immersive et stylee, amplifie l’experience de jeu.
casinova slot|
Приветствую!
Мемкоины или серьезные проекты: где больше денег. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/altkoiny-kotorye-dadut-iksy/]какие токены дадут иксы[/url] Честный разбор рисков и возможностей альткоин-рынка.
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/altkoiny-kotorye-dadut-iksy/
как заработать на своем токене
альткоины которые дадут иксы
альткоины которые вырастут
Бывай!
J’adore l’eclat de LuckyBlock Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman dore. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement lumineux, avec une aide qui fait des miracles. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un clin d’?il, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, LuckyBlock Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sortilege, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
pancakeswap luckyblock|
J’adore le delire de Madnix Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui explose comme un volcan de fun. La selection du casino est une veritable explosion de fun, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui font peter les plombs. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans court-circuit, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Madnix Casino offre une experience de casino dejantee pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline demente du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle delirante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
avis madnix casino|
Сайт konsultaciya-advokata51.ru предлагает вам разнообразные возможности. Юридическая консультация – это важный шаг для многих людей. Вы получите квалифицированные рекомендации, обратившись к нам.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata51.ru]нужна бесплатная консультация юриста[/url].
Консультация позволит вам получить персонализированные рекомендации от профессионала.
Первое, что стоит учитывать – это квалификация адвокатов. Все адвокаты на нашем сайте имеют большой опыт работы. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень обслуживания.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, доступных для разных категорий граждан. Вы сможете легко ознакомиться с нашими тарифами и предложениями. На нашем сайте есть предложения на любой вкус и бюджет.
У нас есть возможность получить консультацию удаленно. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто ценит своё время. Вы можете задать свои вопросы в любое время.
провайдеры по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу краснодар
Обучение и семинары https://uofs-beslan.ru для профессионалов: современные программы, практические кейсы и опыт экспертов. Развивайте навыки, повышайте квалификацию и получайте новые возможности для карьерного роста.
Школа видеорекламы https://tatyanamostseeva.ru обучение созданию креативных роликов для бизнеса и брендов. Практические занятия, работа с современными инструментами и поддержка экспертов. Освойте профессию в сфере digital.
Академия парикмахерского искусства https://charm-academy.ru обучение от ведущих мастеров. Современные техники стрижек, окрашивания и укладок. Курсы для начинающих и профессионалов с практикой и дипломом по окончании.
Лицей взаимного обучения https://talgenisty.ru уникальная среда для детей и взрослых. Совместные уроки, обмен опытом, мастер-классы и творческие проекты. Образование, основанное на поддержке и сотрудничестве.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста по телефону на сайте [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata61.ru]бесплатная консультация юриста адвоката[/url].
Проблемы в сфере права могут возникнуть у каждого из нас, и важно быть к этому готовым.
Адвокат поможет вам понять, какие бумаги нужны для вашего дела.
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Pokud hledáte online casino cz, cz casino online nebo kasina, jste na správném místě. Jsem žurnalista a pomohu vám srovnat rizika i možnosti českého online hazardu – stylově, seriózně a uživatelsky přívětivě: kasina
https://110km.ru/opinion/
Добрый день!
Смартфоны с лучшими камерами 2025 года по версии экспертов. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-s-horoshej-kameroj/]xiaomi с хорошей камерой[/url] Китайцы захватили топ, Apple держится в тройке, Samsung провалился.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-s-horoshej-kameroj/
телефон с 4 камерами
До встречи!
Great site for everyone: https://feas.ru
The best site for you: http://nas-3.ru
Приём макулатуры https://chsreda.ru в Казани работает как для частных лиц, так и для организаций. Сдают газеты, журналы, картонные коробки, офисную бумагу. Это реально удобно, потому что приезжают, забирают прямо с территории, а потом всё идёт на переработку.
Кухонные принадлежности https://www.kitchen-store.ru в магазине для дома: современная посуда, полезные гаджеты, текстиль и аксессуары. Стильные решения для кухни, выгодные цены и большой ассортимент.
интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
провайдер по адресу
Нужен автобусный билет? заказ билетов на автобус удобный сервис поиска и бронирования. Широкий выбор направлений, надежные перевозчики, доступные цены и моментальная отправка электронных билетов на почту.
Авто портал https://diesel.kyiv.ua все о мире автомобилей: новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору и уходу за авто. Каталог машин, актуальные цены, автоуслуги и полезная информация для автовладельцев.
Все для автомобилистов https://k-moto.com.ua на авто портале: новости, обзоры, статьи, каталоги и цены на автомобили. Экспертные мнения, тест-драйвы и практические советы по эксплуатации авто.
Автомобильный портал https://auto-club.pl.ua онлайн-площадка для автолюбителей. Подробные обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, свежие новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Удобный поиск и актуальные материалы.
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя минск
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Estou pirando com MegaPosta Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um vulcao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma verdadeira faisca, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino e um cassino online que e um vulcao de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
megaposta com|
Je suis totalement ensorcele par MyStake Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui captive comme un secret bien garde. La selection du casino est un voile de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme enigmatique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vision prophetique, avec une aide qui perce les mysteres. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ombres, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient frissonner. Pour resumer, MyStake Casino offre une experience de casino ensorcelante pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une prophetie, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus intrigante.
mystake code promo sans dГ©pГґt|
Adoro o clima brabo de OshCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e um terremoto. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, OshCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um vulcao para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
arnaque osh|
Ich bin total begeistert von Pledoo Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und glanzend, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
pledoo promo code|
Нужна виза? срочное оформление шенгенской визы Консультации, подготовка документов, сопровождение на всех этапах. Визы в Европу, США, Азию и другие страны. Доступные цены и надежная поддержка.
Женский портал https://beautyadvice.kyiv.ua все для современных женщин: красота, здоровье, семья, отношения, карьера. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, лайфхаки и вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-сообщество для общения и развития.
Онлайн женский портал https://elegance.kyiv.ua актуальные советы по красоте, стилю, кулинарии и семейной жизни. Разделы о здоровье, карьере и саморазвитии. Интересные статьи и общение с единомышленницами.
Портал для женщин https://fashionadvice.kyiv.ua сайт для девушек и женщин, которые ценят красоту, уют и гармонию. Советы по стилю, отношениям, материнству и здоровью. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Thanks for another great post. Where else may anybody get that type of info in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the search for such information.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
вывод из запоя
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar006.ru
провайдер по адресу
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Our platform offers a large amount of helpful materials about both men’s and women’s intimate life.
Visitors can explore various topics that help them understand their connections.
Articles on the site describe positive communication between partners.
You will also come across recommendations on building mutual understanding.
Resources here is created by specialists in the field of personal well-being.
https://aldv.info/love/deepthroat-the-art-of-extreme-oral-pleasure/
Many of the guides are easy to read and helpful for daily life.
Visitors can use this knowledge to develop their bonds.
In short, this site provides a rich collection of practical information about personal topics for everyone.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста по телефону на сайте [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata61.ru]где найти бесплатного юриста[/url].
Обращение к адвокату может вызвать у вас уверенность в вашем праве.
Консультация с адвокатом — это важный этап, который может существенно повлиять на исход дела.
Вы можете воспользоваться широким спектром услуг на сайте konsultaciya-advokata51.ru. Юридическая консультация – это важный шаг для многих людей. Вы получите квалифицированные рекомендации, обратившись к нам.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata51.ru]вопросы адвокату онлайн бесплатно[/url].
Правовая помощь охватывает широкий спектр вопросов, и для этого нужен опытный адвокат.
Первое, что стоит учитывать – это квалификация адвокатов. Все адвокаты на нашем сайте имеют большой опыт работы. Что бы вы ни выбрали, мы гарантируем качественное выполнение работы.
Второй аспект – это доступность услуг. На нашем сайте можно найти информацию о ценах и услугах. Мы уверены, что каждый найдет подходящее решение для себя.
У нас есть возможность получить консультацию удаленно. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто ценит своё время. Мы готовы помочь вам в любое время суток, не выходя из дома.
Adoro o clima feroz de MonsterWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que e um monstro. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um predador, respondendo mais rapido que um rugido. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial monstro. No fim das contas, MonsterWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, da um toque de ferocidade braba ao cassino.
monsterwin casino login|
Estou pirando com PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que eletrizam. No geral, PagolBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma faisca, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais eletrizante.
pagolbet afiliados|
Je suis fou de PokerStars Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino strategique. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et palpitantes, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un croupier d’elite, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une donne gagnante, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un full house. Pour resumer, PokerStars Casino offre une experience de casino palpitante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus palpitante.
code bonus pokerstars 2024|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://rutube.ru/u/d2tv/ Киберспорт становится все более признанным видом спорта, с крупными турнирами и щедрыми призовыми фондами.
лошади на продажу Если вы хотите продать коня, мы поможем вам найти покупателя быстро и выгодно. Разместите объявление о продаже лошади на нашей площадке и получите отклики от заинтересованных лиц.
провайдер по адресу москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk004.ru
подключить интернет москва
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar014.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Приветствую!
Нет сил, бледный как привидение: проблемы с железом в крови. [url=https://generik-info.ru/deficzit-zheleza/]дефицит железа[/url] Подробный разбор симптомов и методов лечения без медицинского бреда
Написал: – https://generik-info.ru/deficzit-zheleza/
как восполнить дефицит железа
нехватка железа в организме симптомы
Пока!
Авто портал https://avtoshans.in.ua для всех: свежие новости, обзоры моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации авто. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы и рекомендации экспертов для водителей и покупателей.
Портал про автомобили https://myauto.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для автолюбителей. Обзоры, статьи, тест-драйвы, цены и полезные советы по ремонту и уходу за машиной. Всё о мире авто в одном месте.
Свежие новости авто https://orion-auto.com.ua тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, законодательные изменения и аналитика авторынка. Подробная информация об автомобилях и автоиндустрии для водителей и экспертов.
Автомобильные новости https://reuth911.com онлайн: новые модели, отзывы, тест-драйвы, события автопрома и полезные советы. Узнайте первыми о главных новинках и трендах автомобильного мира.
https://xn--80aack7aript.xn--p1ai/%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE-%D0%BB%D0%B8-%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B3%D0%B8-%D1%83-%D1%81%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%B1%D0%BD%D1%8B%D1%85-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B2
Привет!
Эмоциональное выгорание – не блажь слабаков, а реальная проблема XXI века. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnoe-vygoranie/]тест на выгорание экрана [/url] Вот что с этим делать.
Здесь подробней: – https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnoe-vygoranie/
тест на выгорание
что такое выгорание
профессиональное выгорание это
Пока!
https://vseotzyvy.ru/item/105352/reviews-obuchenie-trafik-v-telegram-kirilla-bashkatov/
курсы по нейросетям Спикер по ИИ: Пригласите опытного спикера по искусственному интеллекту на ваше мероприятие. Я предлагаю экспертные выступления, посвященные последним тенденциям и инновациям в области ИИ. Обсудим будущее ИИ, его применение в различных отраслях, этические аспекты и вызовы, стоящие перед обществом. Вдохновляющие презентации, интерактивные сессии и ответы на вопросы аудитории обеспечат глубокое понимание темы. Подходит для конференций, семинаров, корпоративных тренингов и образовательных мероприятий.
Как сам!
Автокредиты 2025: рынок штормит, но возможности есть. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/mashina-v-kredit/]машина в кредит купить[/url] Находим лучшие предложения среди банковского хаоса.
Переходи: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/mashina-v-kredit/
машина в кредит в автосалоне
Покеда!
https://bar-vip.ru/vyezdnoi_bar/
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://musicbit.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, семья, карьера и хобби. Интересные статьи, тесты и форум для общения. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Автомобильный сайтhttps://setbook.com.ua свежие новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы экспертов. Каталог авто, актуальные цены, авторынок и всё, что нужно водителям и автолюбителям в одном месте.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://fines.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, рецепты, материнство и карьера. Актуальные материалы, тренды и экспертные рекомендации каждый день.
Женский сайт о жизни https://prettywoman.kyiv.ua секреты красоты, мода, здоровье, рецепты и отношения. Интересные статьи, советы и лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно и счастливо.
ветклиники сочи Ветеринарная клиника в Адлере – это квалифицированная помощь для ваших питомцев. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Криптовалютный кошелек для начинающих Риски инвестиций в криптовалюту: будьте в курсе потенциальных опасностей и научитесь их избегать. Мы расскажем о волатильности рынка, мошенничестве и других рисках, связанных с криптовалютами. Предупрежден — значит вооружен!
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk009.ru
лечение запоя омск
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Получить больше информации – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
https://xn--80aack7aript.xn--p1ai/%D0%BB%D1%8E%D0%B1%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%8C/
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
провайдеры интернета в москве по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-msk005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер москва
https://push-network-rankings.com/
Автомобильный портал https://troeshka.com.ua онлайн-ресурс для автовладельцев. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Будьте в курсе новинок и технологий автоиндустрии.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://feminine.kyiv.ua мода, красота, здоровье, отношения и семья. Полезные советы, вдохновляющие статьи, лайфхаки для дома и карьеры. Всё самое интересное для современных женщин.
Онлайн-сайт про автомобили https://tvregion.com.ua свежие новости, аналитика рынка, обзоры и сравнения машин. Советы по обслуживанию и выбору авто. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей в одном месте.
Сайт для женщин https://lolitaquieretemucho.com мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, семья и карьера. Полезные советы, статьи, рецепты и лайфхаки. Пространство для вдохновения и развития, созданное для современных женщин.
Здарова!
Как играть в рулетку умно: гайд для начинающих. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/]стратегия в рулетку[/url] Все о системах ставок, управлении банкроллом и психологии игры.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/
беспроигрышная стратегия игры стратегия рулетка
рулетка стратегия
Покеда!
просмотры инстаграм Хотите сделать вашу группу ВКонтакте более популярной и привлекательной? Закажите услугу подписчики в группу ВК, чтобы быстро увеличить количество участников и повысить активность в сообществе. Больше подписчиков – больше внимания!
Je suis fou de MrPlay Casino, on dirait un carnaval de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux du casino est une veritable parade de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui font danser. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un numero de cirque, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient festifs. En somme, MrPlay Casino promet un divertissement de casino eclatant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique festive, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
mr.play spiele|
Adoro o clima explosivo de PlayUzu Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura eletricidade. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma correnteza, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tempestades, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, PlayUzu Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro trovao, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
cuanto tarda playuzu en pagar|
Je suis fou de Posido Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de fun. Il y a une maree de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance marine. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un capitaine, repondant en un eclat d’ecume. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans remous, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eclaboussent. Pour resumer, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un courant marin, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
plinko posido|
ремонт дизель генераторов в спб
Ошибки новичков в криптоинвестициях Курс криптоинвестиций с гарантией дохода: инвестируйте без риска! Мы гарантируем вам возврат средств, если вы не получите прибыль от наших рекомендаций.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
Сайт для женщин https://femaleguide.kyiv.ua гармония стиля и жизни. Уход за собой, рецепты, дом, отношения, карьера и путешествия. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Сайт про машины https://tvk-avto.com.ua обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, новости автопрома и советы по эксплуатации. Полезные статьи о выборе авто, уходе, ремонте и актуальные материалы для автовладельцев.
Автомобильный новостной портал https://tuning-kh.com.ua всё об авто в одном месте: новости, цены, обзоры, тест-драйвы, авторынок. Советы экспертов и полезные материалы для водителей и тех, кто планирует купить машину.
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
лечение запоя
https://110km.ru/art/
какие провайдеры на адресе в москве
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
проверить интернет по адресу
большие скидки на отели Отправьтесь в райский уголок со скидкой! Наши скидки на туры в Мальдивы с перелетом – это отличная возможность насладиться роскошным отдыхом на Мальдивских островах. Белоснежные пляжи, лазурное море и экзотическая природа ждут вас!
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://mirlady.kyiv.ua красота, стиль, здоровье, дом и семья. Практичные рекомендации, модные идеи, вдохновение и поддержка. Лучший контент для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Сайт для женщин https://amideya.com.ua портал о красоте, стиле, здоровье, семье и саморазвитии. Ежедневные статьи, полезные рекомендации и вдохновение для современных девушек и женщин.
Женский сайт https://lubimoy.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, материнство, работа и хобби. Актуальные статьи, тренды и экспертные советы. Всё самое важное для гармоничной жизни и успеха.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://gracefullady.kyiv.ua свежие статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье и саморазвитии. Практичные советы, вдохновение и позитив для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
https://vseotzyvy.ru/item/105352/reviews-obuchenie-trafik-v-telegram-kirilla-bashkatov/
Vzrušující svět online casino cz — Průvodce pro české hráče: online casino cz
https://egrp-2022.ru/
просмотры вк Хотите много лайков под вашими фото и видео в Instagram? Увеличьте количество лайков Инстаграм, чтобы повысить популярность вашего аккаунта и привлечь новых подписчиков. Больше лайков – больше внимания!
https://peterburg2.ru/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Je suis totalement fascine par MrXBet Casino, on dirait une enigme pleine de surprises. La selection du casino est une enigme de delices, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une enigme resolue, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un code decrypte, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait envoutant. Pour resumer, MrXBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style captivant, facilite une experience de casino mysterieuse.
mrxbet france|
Je suis totalement envoute par ParisVegasClub, il propose une aventure de casino qui danse comme un spectacle. Le repertoire du casino est une scene de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et impeccable, avec une aide qui fait vibrer la salle. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une replique, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, ParisVegasClub offre une experience de casino eclatante pour les artistes du casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique theatrale, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus spectaculaire.
codigo paris vegas club|
слот авиатор [url=aviator-igra-3.ru]aviator-igra-3.ru[/url] .
вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
скидка на бронь отеля Отправьтесь в экзотический Таиланд со скидкой! Наши скидки на туры в Таиланд с отелями – это отличная возможность насладиться прекрасным отдыхом в этой удивительной стране. Белоснежные пляжи, лазурное море и экзотическая природа ждут вас!
провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде
Jako žurnalista vím, že klíčem je text, který sluší čtenáři, obsahuje jednoduchá slova, srozumitelný styl a praktické informace, zvlášť když jde o „cz casino online“ a „kasina“. Tady je vaše nové, svěží a užitečné čtení: cz casino online
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
latest information here: https://aquietrabalho.com
visit our website: https://g-r-s.fr
Here is the best on the net: https://www.lnrprecision.com
Latest information from us: https://www.europneus.es
Хай!
Что работает лучше презерватива и когда его достаточно. [url=https://net-tabletok.ru/ekstrennaya-kontraczepcziya/]противозачаточные таблетки после акта[/url] Развенчиваем мифы и рассказываем правду о современной контрацепции.
Здесь подробней: – https://net-tabletok.ru/ekstrennaya-kontraczepcziya/
диафрагма контрацепция
спирали контрацепция
Бывай!
The latest data is right here: https://antalyamerhaba.com
Go to our website: http://redeecologicario.org
All the latest on our website: https://clubcoma.org
Here you will find only the best: https://jonathanlittlepoker.com
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя минск
токарный станок по металлу с чпу для дома [url=http://tokarnyi-stanok-s-chpu.ru]http://tokarnyi-stanok-s-chpu.ru[/url]
Монтаж мягких окон **Производство мягких окон – это сложный и ответственный процесс, требующий использования высококачественных материалов, современного оборудования и квалифицированного персонала, чтобы гарантировать долговечность, надежность и безопасность конструкции
сдать в помещение в аренду У вас есть свободный офис и вы ищете надежных арендаторов? Сдать офис с нашей помощью – это быстро и удобно! Мы поможем вам разместить объявление о сдаче офиса, найти подходящих арендаторов и оформить все необходимые документы. Получайте стабильный доход от своей недвижимости!
Come in – don’t miss the latest: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
Pokud hledáte online casino cz, cz casino online nebo kasina, jste na správném místě. Jsem žurnalista a pomohu vám srovnat rizika i možnosti českého online hazardu – stylově, seriózně a uživatelsky přívětivě: online casino cz
Only we have the newest materials: https://jnp.chitkara.edu.in
Always relevant information: https://agriness.com
Information that is always relevant: https://www.greenwichodeum.com
стерилизация кошки сочи Ветеринар на дом Сочи: Удобный и комфортный способ получить ветеринарную помощь. Вызовите ветеринара на дом в Сочи и получите квалифицированную помощь в комфортной обстановке.
интернет по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
подключить домашний интернет в нижнем новгороде
Фьючерсы Альткоины: Поиск перспективных проектов и новых возможностей! Но помните о рисках и проводите тщательный анализ.
whoah this weblog is great i really like studying your articles. Stay up the great work! You already know, lots of persons are looking round for this information, you can aid them greatly.
Здарова!
Высокочастотная торговля для обычных людей: гайд по скальпингу. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/skalping-kriptovalyut/]стратегия скальпинг [/url] Простые стратегии для сложного вида трейдинга.
Переходи: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/skalping-kriptovalyut/
скальпинг сделки
скальпинг стратегия
скальпинг трейдинг
Удачи!
Игровая площадка Вавада популярно среди игроков.
Промокоды и бонусы делают старт комфортнее.
Турниры и соревнования создают азарт.
Выбор слотов и настольных игр остается актуальным.
Создание аккаунта занимает пару минут, и сразу начать играть.
Узнай больше здесь: игровые автоматы онлайн
таможенный брокер Для успешной внешнеэкономической деятельности юридическим лицам необходим надежный партнер – таможенный брокер. Мы поможем вам оптимизировать таможенные платежи, избежать штрафов и обеспечить соответствие требованиям законодательства. С нами вы можете сосредоточиться на развитии своего бизнеса, не беспокоясь о таможенных формальностях.
Цены и клиники для капельницы от запоя в Туле Проблема алкогольной зависимости требует серьезного подхода и профессиональной помощи. В Туле вы можете вызвать врача нарколога на дом, что дает возможность получить помощь при запое без визита в клинику. Использование капельницы от запоя способствует быстрому восстановлению организма и снижению симптомов. врач нарколог на дом тула Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает детоксикацию, которую можно сделать и дома. Врачи-наркологи предлагают анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность. Стоимость капельниц может различаться в зависимости от клиники и объема предоставляемых услуг. Капельница для выведения из запоя — это эффективный и быстрый метод, позволяющий вернуть пациента к привычной жизни. Реабилитация зависимых включает не только детоксикацию‚ но и последующее восстановление после запоя. Наркологическая помощь в Туле доступна для всех‚ кто нуждается в поддержке и лечении.
I have to disagree with most of the comments here, but maybe I’m just a contrarian.
Always relevant here: https://deogiricollege.org
Catch the latest from us: https://sportsfanbetting.com
Adoro o clima alucinante de MegaPosta Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de responsa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma tempestade, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, MegaPosta Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
megaposta reclame aqui|
Сайт finance-post.ru — это блог финансиста, ориентированный на личные финансы, бюджетирование и инвестиции. На нём публикуются практические материалы, советы и обзоры
Je suis totalement ensorcele par MyStake Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino enigmatique. Le repertoire du casino est une toile d’enigmes ludiques, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ombres, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui captivent. Pour resumer, MyStake Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique mysterieuse, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
mystake impossible de parier|
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, OshCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual escaldante, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
osh retrait avis|
https://vsezerkala.com/
Ich bin total begeistert von Platin Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Edelstein strahlt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Meisterwerk, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Funkeln, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein glitzernder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Platin Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie Platin glanzt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Schatz, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
platin casino no deposit bonus codes 2025|
ветеринарная клиника сочи круглосуточно Ветклиники Сочи: Обзор лучших ветеринарных клиник в Сочи. Найдите лучшую ветеринарную клинику для своего питомца в нашем обзоре клиник Сочи. Мы предоставляем подробную информацию об услугах, ценах и отзывах.
Печатный Центр https://kopirych.by «Копирыч» в Минске и по всей Беларуси! Оперативная печать, брошюровка, широкоформатная и сувенирная продукция. Качественно, недорого, с доставкой. Ваши идеи — наша реализация! Заказывайте на сайте или по телефону.
руководства по садоводству https://zelenayazona.ru идеи, инструкции и советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Информация для новичков и опытных дачников: посадка, полив, удобрение и защита растений.
https://hr.rivagroup.su/
Женский сайт https://family-site.com.ua современный портал о моде, красоте, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные материалы, секреты здоровья и успеха, актуальные тренды и советы экспертов для женщин любого возраста.
Семейный портал https://geog.org.ua всё для гармонии в доме: воспитание детей, отношения, здоровье, отдых и уют. Полезные советы, статьи и лайфхаки для всей семьи. Пространство, где находят ответы и вдохновение.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
888starz отзывы http://www.rf2d.org/888starz-zhurnal-ofitsialnyy-sayt-bukmekerskoy-kontory-i-kazino/
Приветствую!
Еда на колесах: выживаем в поезде с комфортом. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/eda-v-poezde/]еда в поезд лайфхак[/url] Практические советы по организации питания в дороге.
Переходи: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/eda-v-poezde/
еда в дорогу
Будь здоров!
Как сам!
Продажа скинов CS2: все способы вывода денег. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-skiny/]продать скины кс го [/url] Карты, крипта, кошельки – выбираем оптимальный вариант.
Читай тут: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-skiny/
где продать скины кс 2
продать скины кс 2
продать скины в кс
Бывай!
интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
проверить провайдера по адресу
Responsible participation in digital play refers to making thoughtful choices while joining interactive entertainment.
It encourages safe habits and helps users establish clear boundaries.
Principles of responsible play cover controlling time and energy in a reasonable way.
Players are motivated to keep track of their activity and maintain a sustainable approach.
migliori casino aams live
Awareness materials about responsible gaming guide people to recognize their own patterns.
Many services provide tools and features for monitoring and individual support.
Practising responsible play helps everyone to get the most from i-gaming confidently.
In short, responsible i-gaming is about understanding and taking choices that support your well-being.
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Портал о здоровье https://mikstur.com информационный ресурс о медицине и ЗОЖ. Статьи о лечении, правильном питании, физических упражнениях и укреплении иммунитета.
Портал о стройке https://bastet.com.ua статьи, новости и советы по ремонту, строительству и дизайну. Подбор материалов, проекты домов, технологии и полезная информация для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Капельницы для вывода из запоя — незаменимый метод для скорейшего возвращения к нормальной жизни. В городе Тула медицинская помощь включает лечение запоя с помощью капельного введения. Капельницы в случае запоя помогают детоксицировать организм, устранение похмелья и восстановление здоровья. вывод из запоя тула Алкогольная зависимость требует системного решения: нужен не только вывод из запоя, но и восстановление после алкоголя. Капельница укрепляет организм, наполняя организм витаминами и минераламичто помогает быстрее достичь результата;
Информационный портал https://intertools.com.ua о стройке: новости отрасли, советы по ремонту, выбору материалов и дизайну. Всё для тех, кто строит дом, делает ремонт или работает в строительстве.
https://t.me/perevedem_document Перевод Документов: Мост между Языками и Культурами В современном мире глобализации, где границы стираются, а сотрудничество между странами и культурами становится все более тесным, перевод документов приобретает огромное значение. Это не просто замена слов одного языка словами другого, а кропотливая работа по передаче смысла, контекста и нюансов оригинала, чтобы обеспечить полное и точное понимание информации. Когда необходим перевод документов? Международный бизнес: контракты, договоры, финансовые отчеты, маркетинговые материалы – все это требует качественного перевода для успешного ведения дел за рубежом. Юридические вопросы: судебные документы, свидетельства, доверенности, нотариальные акты должны быть переведены с соблюдением строгих юридических норм и терминологии. Медицинская сфера: медицинские заключения, инструкции к лекарствам, результаты исследований – точность перевода здесь критически важна для здоровья пациентов. Техническая документация: инструкции по эксплуатации, технические спецификации, чертежи – перевод должен быть понятным и однозначным для специалистов. Образование и наука: дипломы, аттестаты, научные статьи, исследования – для признания образования за рубежом и обмена знаниями необходим качественный перевод. Почему важно обращаться к профессионалам? Точность и соответствие: профессиональные переводчики обладают глубокими знаниями языка и предметной области, что гарантирует точность и соответствие перевода оригиналу. Соблюдение терминологии: использование правильной терминологии – залог того, что перевод будет понятен специалистам в соответствующей области. Культурная адаптация: профессиональный переводчик адаптирует текст с учетом культурных особенностей целевой аудитории, чтобы избежать недопонимания или неловких ситуаций. Конфиденциальность: профессиональные бюро переводов гарантируют конфиденциальность ваших документов. Как выбрать бюро переводов? Опыт и репутация: изучите опыт работы бюро, ознакомьтесь с отзывами клиентов. Специализация: убедитесь, что бюро специализируется на переводах в нужной вам области. Наличие профессиональных переводчиков: узнайте, работают ли в бюро переводчики с соответствующим образованием и опытом. Стоимость и сроки: сравните цены и сроки выполнения заказа в разных бюро. В заключение, перевод документов – это важный инструмент для преодоления языковых барьеров и успешного взаимодействия в современном мире. Доверяйте перевод ваших документов профессионалам, чтобы быть уверенными в качестве и точности результата. Если вам нужно перевести конкретный документ, просто предоставьте его мне, и я постараюсь вам помочь!
игровые автоматы на реальные деньги Игровые автоматы новые регистрация – это процесс создания учетной записи в онлайн-казино для получения доступа к игровым автоматам. Новые игроки обычно получают приветственные бонусы и другие привилегии после регистрации. Процесс регистрации обычно прост и занимает несколько минут. Игрокам необходимо предоставить личную информацию, такую как имя, адрес электронной почты и номер телефона. После регистрации игроки могут пополнить свой счет и начать играть в игровые автоматы на реальные деньги.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста онлайн [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista-msk01.ru]Бесплатный вопрос юристу через интернет[/url].
Открытость в общении поможет юристу лучше понять вашу проблему.
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
таможенный брокер для юридических лиц Специально для юридических лиц, занимающихся внешнеэкономической деятельностью, мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг таможенного брокера. Мы поможем вам оптимизировать таможенные платежи, избежать штрафов и обеспечить соответствие требованиям таможенного законодательства.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Беседка с мягкими окнами Установка мягких окон: быстро, качественно и с гарантией результата, доверьтесь профессионалам и наслаждайтесь комфортом!. Доверьте установку мягких окон нашим профессиональным мастерам, и вы получите безупречный результат, который будет радовать вас долгие годы.
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Laserstrahl funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop voller Spa?, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein leuchtender Funke, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Leuchtfeuer, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist SlotClub Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Lichtschalter, einen Hauch von Neon-Magie ins Casino bringt.
slotclub casino РѕР±Р·РѕСЂ|
Je suis fou de Spinanga Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui spirale comme un vortex. Le repertoire du casino est un tourbillon de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance virevoltante. Le service client du casino est une bourrasque d’efficacite, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. Dans l’ensemble, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une bourrasque, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga free spins|
Je suis accro a Spinsy Casino, on dirait une soiree disco pleine de frissons. La selection du casino est une explosion de delices dansants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance groovy. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et fluide, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, Spinsy Casino est un casino en ligne qui met le feu a la piste pour les danseurs du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un neon, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus dansante.
spinsy 2|
Adoro o brilho de Richville Casino, parece um banquete de opulencia e diversao. Tem uma cascata de jogos de cassino fascinantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos para criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, dando solucoes precisas e imediatas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam com a velocidade de um jato particular, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que brilhem como diamantes. Na real, Richville Casino promete uma diversao de cassino reluzente para os nobres do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
richville heights|
Нарколог на дом в Туле предоставляет профессиональную помощь тем, кто страдает от наркомании и алкоголизмом. Преодоление зависимости нуждается в персонализированном подходе, и выезд нарколога на дом – это практичное решение для больных. Центр реабилитации зависимостей в Туле предлагает анонимное лечение и консультации нарколога. Реабилитация на дому позволяет пройти курс психотерапии при зависимости в комфортной обстановке. Медицинская помощь на дому включает в себя как медицинское, так и психологическую поддержку. Профилактика зависимости также является ключевым моментом в борьбе с алкоголизмом и наркоманией. Сопровождение алкоголиков и их семей – это обязанность специалистов, которые готовы поддержать в трудный момент. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula012.ru
домашний интернет подключить новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
игровые автоматы играть Играющие игровые автоматы: что происходит за кулисами? Играющие игровые автоматы – это те, которые в данный момент активно используются игроками. Каждый спин в играющем игровом автомате – это случайное событие, результат работы генератора случайных чисел (ГСЧ). ГСЧ обеспечивает честность и непредсказуемость игры, гарантируя, что каждый спин является независимым от предыдущих и последующих. Результаты игры не зависят от того, сколько времени автомат не выплачивал выигрыш или сколько денег в него было внесено. Наблюдая за играющими игровыми автоматами, вы можете заметить различные стратегии и подходы игроков. Некоторые игроки предпочитают играть на максимальных ставках, надеясь на крупный выигрыш, в то время как другие выбирают минимальные ставки, чтобы продлить время игры.
https://t.me/perevedem_document Перевод Документов: Мост между Языками и Культурами В современном мире глобализации, где границы стираются, а сотрудничество между странами и культурами становится все более тесным, перевод документов приобретает огромное значение. Это не просто замена слов одного языка словами другого, а кропотливая работа по передаче смысла, контекста и нюансов оригинала, чтобы обеспечить полное и точное понимание информации. Когда необходим перевод документов? Международный бизнес: контракты, договоры, финансовые отчеты, маркетинговые материалы – все это требует качественного перевода для успешного ведения дел за рубежом. Юридические вопросы: судебные документы, свидетельства, доверенности, нотариальные акты должны быть переведены с соблюдением строгих юридических норм и терминологии. Медицинская сфера: медицинские заключения, инструкции к лекарствам, результаты исследований – точность перевода здесь критически важна для здоровья пациентов. Техническая документация: инструкции по эксплуатации, технические спецификации, чертежи – перевод должен быть понятным и однозначным для специалистов. Образование и наука: дипломы, аттестаты, научные статьи, исследования – для признания образования за рубежом и обмена знаниями необходим качественный перевод. Почему важно обращаться к профессионалам? Точность и соответствие: профессиональные переводчики обладают глубокими знаниями языка и предметной области, что гарантирует точность и соответствие перевода оригиналу. Соблюдение терминологии: использование правильной терминологии – залог того, что перевод будет понятен специалистам в соответствующей области. Культурная адаптация: профессиональный переводчик адаптирует текст с учетом культурных особенностей целевой аудитории, чтобы избежать недопонимания или неловких ситуаций. Конфиденциальность: профессиональные бюро переводов гарантируют конфиденциальность ваших документов. Как выбрать бюро переводов? Опыт и репутация: изучите опыт работы бюро, ознакомьтесь с отзывами клиентов. Специализация: убедитесь, что бюро специализируется на переводах в нужной вам области. Наличие профессиональных переводчиков: узнайте, работают ли в бюро переводчики с соответствующим образованием и опытом. Стоимость и сроки: сравните цены и сроки выполнения заказа в разных бюро. В заключение, перевод документов – это важный инструмент для преодоления языковых барьеров и успешного взаимодействия в современном мире. Доверяйте перевод ваших документов профессионалам, чтобы быть уверенными в качестве и точности результата. Если вам нужно перевести конкретный документ, просто предоставьте его мне, и я постараюсь вам помочь!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше вероятность полного восстановления здоровья без тяжёлых последствий для организма и психики. В клинике «Наркосфера» к каждому случаю подходят максимально внимательно и индивидуально.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha5.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-balashihe/
Прокапаться от алкоголя на дому — важный шаг для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью . Процесс избавления от алкоголизма начинается с детоксикации , которая может быть проведена в домашних условиях . Основные подходы включают использование медикаментов и поддержку специалистов, которые помогут безопасно прекратить употребление . vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir010.ru Советы по трезвости и методы борьбы с зависимостью , такие как самопомощь при алкоголизме , играют ключевую роль в реабилитации . Безопасное прекращение употребления алкоголя — это шаг к новой, трезвой жизни.
https://businesssuitehub.com/
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение новосибирск
Женский онлайн-журнал https://girl.kyiv.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, кулинария, отношения и материнство. Ежедневные материалы, экспертные советы и вдохновение для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Портал про детей https://mch.com.ua информационный ресурс для родителей. От беременности и ухода за малышом до воспитания школьников. Советы, статьи и поддержка для гармоничного развития ребёнка.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://krasotka-fl.com.ua всё о красоте, моде, семье и жизни. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, советы экспертов и интересные истории. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь каждый день.
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
Как сам!
Топ спортивных наушников 2025 года от человека который их реально тестил. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/naushniki-dlya-sporta/]купить наушники для спорта[/url] Что покупать в России, Европе и Китае – личный опыт и рекомендации.
Переходи: – https://pro-telefony.ru/naushniki-dlya-sporta/
лучшие наушники для спорта
спортивные беспроводные наушники
блютуз наушники для спорта
Удачи!
mostbet [url=https://mostbet12008.ru/]mostbet[/url]
Устройство пристенной дренажной системы Вырубка кустарников: удаление нежелательной растительности Вырубка кустарников – это удаление кустарников на определенной территории. Вырубка кустарников может проводиться при расчистке участка под застройку, создании газонов, подготовке территории к посадке деревьев и других работах.
mostbet online [url=http://mostbet12007.ru]http://mostbet12007.ru[/url]
Хай!
Мелатонин vs снотворные: битва за здоровый сон. [url=https://generik-info.ru/melatonin-dlya-sna/]что такое мелатонин[/url] Сравниваем эффективность, безопасность и влияние на утреннее самочувствие.
Переходи: – https://generik-info.ru/melatonin-dlya-sna/
мелатонин как принимать
мелатонин таблетки инструкция
Бывай!
вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
Таможенный брокер — это ваш проводник в мире международной торговли и таможенных процедур: таможенный брокер в Москве
портретпофотографии Печать на холсте Печать на холсте – это современный способ создания уникальных элементов декора, репродукций картин и персонализированных подарков. Технология подразумевает перенос цифрового изображения (фотографии, рисунка, векторной графики и т.д.) на холст из натуральных или синтетических материалов. В процессе печати используются специальные чернила, стойкие к выцветанию и обеспечивающие высокую точность цветопередачи. Холст, с нанесенным изображением, как правило, натягивается на подрамник, что придает изделию вид законченной картины. Преимущества печати на холсте включают: Эстетичность: Холст обладает текстурой, придающей изображению визуальную глубину и художественный вид. Долговечность: Качественные чернила и материалы обеспечивают длительный срок службы изделия без потери яркости красок. Персонализация: Возможность создания уникальных работ с использованием личных фотографий или изображений. Вариативность: Подходит для создания репродукций картин известных художников, портретов, пейзажей, абстрактных композиций и т.д. Универсальность: Отлично вписывается в любой интерьер, от классического до современного. Печать на холсте – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет украсить свой дом оригинальными и стильными предметами декора, а также для тех, кто ищет необычный и запоминающийся подарок.
Great resources and tips for families here.
Лечение запоя — важная задача для многих людей. Симптомы запойного состояния включают зависимость от алкогольных напитков как физического, так и психологического характера. Лечение запоя может быть как медикаментозной, так и психотерапевтической. Первым шагом является детоксикация организма , которая способствует удалению токсинов. Важно обратиться за помощью при алкогольной зависимости , чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий . vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir011.ru Стационарное лечение алкоголизма предлагает реабилитационные программы, где пациенты получают полную поддержку . Процесс восстановления после запоя требует времени и усилий , и здесь важна поддержка родственников алкоголиков . Советы по лечению запоя могут быть полезны : важно следить за состоянием здоровья , избегать триггеров и регулярно посещать терапевта . Профилактика запоя включает в себя здоровый образ жизни и осознание своих проблем .
https://chojnow.pl/forum/thread/view/id/748749
Наша команда имеет большой опыт работы с таможней и помогает клиентам экономить на логистике: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I want to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
Онлайн-журнал https://presslook.com.ua для женщин объединяет всё, что важно: мода и стиль, воспитание детей, карьерные советы и вдохновение. Советы специалистов и реальные истории для поддержки и новых идей.
Актуальные тренды https://horoscope-web.com и вневременная классика. Подборки образов, советы по стилю, секреты гардероба и модные инсайты. Мы поможем тебе выглядеть безупречно каждый день и выразить свой индивидуальный стиль.
Твой гид https://nicegirl.kyiv.ua по здоровому образу жизни! Эффективные тренировки, сбалансированное питание, wellness-практики и советы по мотивации. Обрети энергию, силу и гармонию в теле, которое ты любишь.
Ресурс для амбициозных https://ramledlightings.com и целеустремленных. Карьерный рост, личная эффективность, финансовая грамотность и вдохновляющие истории успеха. Реализуй свой потенциал и добивайся всех поставленных целей!
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my difficulty. You are wonderful! Thanks!
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Excellent article!! I am an avid reader of your website:D keep on posting that good content. and I’ll be a regular visitor for a very long time!!
Клиника использует проверенные подходы с понятной логикой применения. Ниже — обзор ключевых методик и их места в маршруте терапии. Важно: выбор всегда индивидуален, а эффекты оцениваются по заранее оговорённым метрикам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
лучший интернет провайдер новосибирск
Валка деревьев Устройство ливневой канализации: Устройство ливневой канализации – это создание системы сбора и отвода дождевой и талой воды с территории участка и кровли здания. Основная цель ливневой канализации – предотвращение затопления участка, разрушения фундамента дома и образования луж и грязи. Ливневая канализация может быть открытой (канавы, лотки) или закрытой (дождеприемники, трубы, колодцы). В закрытой системе вода собирается с крыши по водосточным трубам и отводится в дождеприемники, соединенные подземными трубами с коллектором или дренажным колодцем. Устройство ливневой канализации – это важный этап благоустройства участка, который позволяет создать комфортные условия для проживания и эксплуатации территории.
Наша платформа https://probilets.com/ работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
«РостовМедЦентр» предоставляет несколько форматов, чтобы лечение не сталкивалось лоб в лоб с работой, учебой и семейными обязанностями. Стационар — для случаев с рисками, дневной стационар — для интенсивной дневной терапии, амбулаторный режим — для поддержания динамики без разрыва с повседневной жизнью. Выезд на дом сохраняет приватность и экономит время, а защищённые видеосессии позволяют поддерживать мотивацию между очными визитами. Все каналы соединены в единую систему: план, составленный сегодня в клинике, доступен врачу, который завтра приедет на дом, и психологу, с которым запланирована онлайн-сессия через два дня.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
скачать лаки джет [url=https://1win12004.ru/]скачать лаки джет[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Алексей Николаевич Прудников, «выезд нарколога на дом — это возможность стабилизировать состояние пациента в привычной обстановке, снизив стресс и риски осложнений».»
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare/
Наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге работает по различным направлениям, охватывающим как экстренную помощь, так и плановое лечение.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иван Петрович Соловьёв, «правильный вывод из запоя возможен только при участии специалистов, так как самолечение может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям»».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в рязани[/url]
курсовая работа за деньги работа по выполнению курсовых работ
букмекерская контора mostbet [url=www.mostbet12008.ru]www.mostbet12008.ru[/url]
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
взять займы онлайн без карты взять займ онлайн
Время — ключевой ресурс при абстиненции и интоксикации. Ниже — ориентиры, которые помогут семье принять решение не откладывать обращение. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт, лучше сразу обсудить ситуацию с дежурным наркологом и подготовить пространство для визита.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
займы онлайн на карту первый взять займ онлайн
Как начать лечение алкоголизма в владимире: первый шаг к выздоровлению Алкогольная зависимость является серьезной проблемой, которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. В владимире доступна круглосуточная помощь нарколога на дом, что позволяет начать лечение в удобное время. Обращение к наркологу поможет определить степень зависимости и подобрать оптимальную программу лечения. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Медикаментозная терапия, широко используемая в реабилитационных центрах владимира, нацелена на облегчение абстинентного синдрома и восстановление здоровья. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе выздоровления, обеспечивая эмоциональную стабильность. Анонимность в лечении создает более комфортные условия для пациента. Детоксикационная программа способствует очищению организма от токсинов, а реабилитационный процесс включает социальную адаптацию и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Профессиональная помощь – залог успешного преодоления проблемы. Не упустите шанс изменить жизнь к лучшему!
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru
Клиника предоставляет широкий спектр услуг, каждая из которых ориентирована на определённый этап лечения зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Puzzles online https://www.tumblr.com/adventuressss90/794458100760494080/food-cuisine-puzzle?source=share play for free in assembling pictures of any complexity. Thousands of options: classic, children’s, 3D and thematic. Convenient interface, saving progress and new puzzles every day.
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare/
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Acho simplesmente magico SpinWiz Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um portal magico. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um grimorio de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro genio, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, SpinWiz Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os magos do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como uma pocao reluzente, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
spinwiz reclame aqui|
Sou louco pela vibe de SpinFest Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um batuque de carnaval. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que vibram como tambores. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que samba com estilo. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de maracatu, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, SpinFest Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo festivo, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
spinfest casino erfahrungen|
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, e um cassino online que decola como um foguete espacial. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
spei blackjack|
J’adore la flamboyance de RubyVegas Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un rubis taille. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et lumineuses, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une pepite trouvee, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, RubyVegas Casino offre une experience de casino luxueuse pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une gemme taillee, facilite une experience de casino scintillante.
Acho simplesmente alucinante RioPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro axe. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com gingado. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de escola de samba, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. No geral, RioPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
rioplay cassino|
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается интоксикацией, обезвоживанием, нарушением обменных процессов и психоэмоциональными расстройствами. Попытки самостоятельно прекратить употребление алкоголя могут привести к судорогам, скачкам давления и другим опасным осложнениям. Именно поэтому вывод из запоя в клинике обеспечивает контроль специалистов, использование медикаментозной поддержки и мониторинг жизненно важных показателей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Единая панель оценки помогает действовать быстро и безошибочно. Мы фиксируем параметры, объясняем их смысл пациенту и семье и тут же привязываем к ним действия. Пример приведён в таблице: это не заменяет осмотр, но показывает логику, которой мы придерживаемся на выезде и в приёмном кабинете.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм рязань[/url]
Привет!
Дневник эмоций и другие рабочие методы развития EQ. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnyj-intellekt/]дэниел гоулман эмоциональный интеллект[/url] Пошаговый план превращения из эмоционального калеки в мастера человеческих душ.
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnyj-intellekt/
как развить эмоциональный интеллект
Пока!
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkologiya-sankt-peterburg/
Привет!
Как перестать тратить деньги впустую с помощью приложений. [url=http://economica-2025.ru/uchet-lichnyh-finansov-programma-besplatno/]программа для учета денег[/url] Практические советы от того, кто сам через это прошел.
Читай тут: – http://economica-2025.ru/uchet-lichnyh-finansov-programma-besplatno/
бюджет семьи
личные финансы
До встречи!
888starz http://karmabeautyclinic.com/uncategorized/zakachat-888starz-v-vidakh-android-besplatno-konechnuyu-versiyu/
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
подключить интернет ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
провайдеры интернета ростов
портретпофотоназаказ Портрет по фото Этот запрос аналогичен запросу “Портрет по фотографии” и является его сокращенной версией.
https://russpain.com/
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
скачать mostbet на телефон [url=https://mostbet12003.ru]https://mostbet12003.ru[/url]
«Как отмечает главный врач-нарколог Виктор Сергеевич Левченко, «современная наркологическая клиника должна обеспечивать не только медикаментозное лечение, но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах восстановления».»
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
«РостовМедЦентр» предоставляет несколько форматов, чтобы лечение не сталкивалось лоб в лоб с работой, учебой и семейными обязанностями. Стационар — для случаев с рисками, дневной стационар — для интенсивной дневной терапии, амбулаторный режим — для поддержания динамики без разрыва с повседневной жизнью. Выезд на дом сохраняет приватность и экономит время, а защищённые видеосессии позволяют поддерживать мотивацию между очными визитами. Все каналы соединены в единую систему: план, составленный сегодня в клинике, доступен врачу, который завтра приедет на дом, и психологу, с которым запланирована онлайн-сессия через два дня.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru
Анонимность — важнейшее условие обращения за помощью. В клинике действуют не декларации, а конкретные технологические и организационные меры, которые защищают пациента и его близких от стигмы и лишнего обсуждения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Запойное состояние сопровождается интоксикацией, обезвоживанием, нарушением обменных процессов и психоэмоциональными расстройствами. Попытки самостоятельно прекратить употребление алкоголя могут привести к судорогам, скачкам давления и другим опасным осложнениям. Именно поэтому вывод из запоя в клинике обеспечивает контроль специалистов, использование медикаментозной поддержки и мониторинг жизненно важных показателей.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
1 x win [url=http://1win12006.ru/]http://1win12006.ru/[/url]
Проблемы зависимости нельзя решать одним действием или «чудо-процедурой». Клиника «РостовМедЦентр» в Ростове-на-Дону строит помощь вокруг человека, а не вокруг диагноза: от точной диагностики и безопасной детоксикации до психотерапевтической работы, реабилитации и постлечебного сопровождения. Мультидисциплинарная команда — врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты, клинические психологи, реабилитологи и консультанты по зависимостям — формируют маршрут терапии под конкретную ситуацию, возраст, сопутствующие заболевания и семейные обстоятельства. В основе — доказательные методики, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и четкие критерии эффективности, которые пациент видит в понятном ему плане. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается на каждом этапе: от анонимного первичного обращения до нейтральных формулировок в выданных документах.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika
*Диапазоны «зелёной зоны» назначаются индивидуально по возрасту, фоновым заболеваниям и исходным показателям.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Нарколог на дом – это удобное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с алкогольной зависимостью или наркоманией. Терапия зависимостей включает в себя очистку организма и восстановление зависимых. Нарколог на дому предоставляет анонимное лечение, что имеет большое значение для пациентов, которые не хотят посещать медицинские учреждения. Методы кодирования – проверенный способ, который можно провести на дому. Выездная помощь включает в себя психологическую поддержку и медицинскую помощь. Встречи с наркологом помогут понять, как преодолеть зависимости. Реабилитационные программы и поддержка семьи играют ключевую роль в процессе лечения. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru вы найдете всю необходимую информацию о предлагаемых услугах.
888starz ios http://stage.runloco.events/skachat-888starz-v-vidakh-android-v15-9069-dolzhnostnoe-addenda/
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам. Покупка диплома, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это грамотное решение. Заказать диплом ВУЗа: [url=http://danskfodboldklub.com/read-blog/3476_купить-диплом-образование.html/]danskfodboldklub.com/read-blog/3476_купить-диплом-образование.html[/url]
http://www.free-lancers.net/info-center/
микрозаем на карту онлайн Очень доволен тем, что нашел этот сайт для получения микрозайма онлайн с плохой кредитной историей.
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в краснодаре[/url]
*Метод подбирается индивидуально и применяется только по информированному согласию.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
1win скачать на телефон андроид официальный [url=https://1win12008.ru]https://1win12008.ru[/url]
1win casino скачать [url=https://1win12006.ru]https://1win12006.ru[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare/
В «РостовМедЦентре» лечение начинается с подробной оценки факторов риска и мотивации. Клиническая команда анализирует стаж употребления, тип вещества, эпизоды срывов, соматический фон, лекарства, которые пациент принимает постоянно, и уровень социальной поддержки. Уже на первой встрече составляется «дорожная карта» на ближайшие 72 часа: диагностический минимум, объём медицинских вмешательств, пространство для психологической работы и точки контроля. Безопасность — не абстракция: скорости инфузий рассчитываются в инфузомате, седацию подбирают по шкалам тревоги и с обязательным контролем сатурации, а лекарственные взаимодействия сверяет клинический фармаколог. Пациент получает прозрачные цели на день, на неделю и на месяц — без обещаний мгновенных чудес и без стигмы.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
домашний интернет тарифы ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
интернет домашний ростов
888 starz casino http://www.restoringtruthmedia.org/2025/09/07/888starz-veb-zhurnal-ofitsialnyy-zhurnal-bukmekerskoy-kontory-i-kazino/
Эти шаги помогают системно подойти к проблеме и обеспечить максимальную эффективность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
*Метод подбирается индивидуально и применяется только по информированному согласию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]запой нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
В «РостовМедЦентре» лечение начинается с подробной оценки факторов риска и мотивации. Клиническая команда анализирует стаж употребления, тип вещества, эпизоды срывов, соматический фон, лекарства, которые пациент принимает постоянно, и уровень социальной поддержки. Уже на первой встрече составляется «дорожная карта» на ближайшие 72 часа: диагностический минимум, объём медицинских вмешательств, пространство для психологической работы и точки контроля. Безопасность — не абстракция: скорости инфузий рассчитываются в инфузомате, седацию подбирают по шкалам тревоги и с обязательным контролем сатурации, а лекарственные взаимодействия сверяет клинический фармаколог. Пациент получает прозрачные цели на день, на неделю и на месяц — без обещаний мгновенных чудес и без стигмы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
https://ufstand.be/?feed=comments-rss2
Эти шаги помогают системно подойти к проблеме и обеспечить максимальную эффективность лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена рязань[/url]
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов https://probilets.com/. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Прокапывание от алкоголя на дому — представляет собой действенный способ помощи алкоголизма, что даёт возможность быстро устранить признаки отмены и улучшить общее состояние больного. Услуги нарколога на дому всё чаще востребованы, поскольку множество людей выбирают избегать стационарного лечения. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir014.ru Эта процедура включает в себя домашнюю детоксикацию, где помощь специалиста при алкоголизме осуществляется в комфортной обстановке. Капельница для снятия похмелья включает лекарственные средства для очищения организма, способствующие способствуют выведению токсинов из организма и нормализовать баланс электролитов и жидкости. Необходимо помнить о признаках абстинентного синдрома, таких как беспокойство, повышенное потоотделение и тремор. Забота и поддержка со стороны близких играет ключевую роль в эффективном лечении и восстановлении после длительного употребления алкоголя. Лечение на дому включает в себя не только прокапывание, но и советы по предотвращению рецидивов алкогольной зависимости, что поможет предотвратить рецидивы и поддержанию трезвого образа жизни.
Таможенный брокер в Москве — это надежный помощник при работе с импортом и экспортом любой сложности: таможенный брокер
авиатор ван вин [url=http://1win12008.ru]http://1win12008.ru[/url]
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Реабилитация после алкогольного запоя в городе Туле: путь к исцелению Реабилитация после алкогольной зависимости включает психотерапии и поддержки близких, что является необходимым в кризисной ситуации. Процесс восстановления могут варьироваться, но все они направлены на борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью и обеспечении долгосрочных результатов. Сообщество поддержки становится важным элементом процесса, облегчая преодоление трудностей. Важно помнить, что путь к выздоровлению труден, но возможен. помощь нарколога тула
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут: https://probilets.com/.
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um feitico lancado. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e hipnotizantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. No geral, SpellWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os magos do cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino reluz com um visual que e puro feitico, adiciona um toque de encantamento ao cassino.
spellwin no deposit bonus code|
На первом этапе проводится осмотр: врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода, температуру тела, оценивает общее состояние, собирает анамнез и анализирует возможные сопутствующие заболевания. При необходимости пациент проходит экспресс-диагностику, включая лабораторные анализы, ЭКГ и консультации других специалистов (кардиолога, невролога).
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha5.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-balashihe/
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в краснодаре[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Такая форма медицинской помощи востребована в разных ситуациях: при запое, выраженном абстинентном синдроме, интоксикации, а также при необходимости купирования симптомов без транспортировки пациента.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иван Петрович Соловьёв, «правильный вывод из запоя возможен только при участии специалистов, так как самолечение может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям»».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в рязани[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Алексей Николаевич Прудников, «выезд нарколога на дом — это возможность стабилизировать состояние пациента в привычной обстановке, снизив стресс и риски осложнений».»
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
1вин бонусы спорт как потратить [url=http://1win12004.ru]http://1win12004.ru[/url]
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Привет!
Виды покера от А до Я: полное руководство для игроков. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrayut-v-poker/]все виды покера[/url] Классические варианты, экзотические игры и современные онлайн-форматы.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrayut-v-poker/
покер разновидности
покер это спорт
какие виды покера бывают
Удачи!
Таможенный брокер в Москве — это надежный помощник при работе с импортом и экспортом любой сложности: таможенныый брокер для юридических лиц
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом цены краснодар[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
подключить интернет
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение ростов
Твой гид https://womanlife.kyiv.ua по стильной жизни. Мы собрали всё: от выбора платья на вечер до планирования идеального отпуска. Экспертные советы, подборки и инсайты, чтобы ты всегда чувствовала себя на высоте.
Журнал для женщин https://rpl.net.ua которые строят карьеру и хотят большего. Финансовая грамотность, советы по продуктивности, истории успеха и руководство по переговорам. Достигайте своих целей с нами!
Онлайн-журнал о моде https://glamour.kyiv.ua без правил. Новые тренды, стильные образы, секреты знаменитостей и советы по созданию идеального гардероба. Мы поможем вам найти и с уверенностью выразить свой уникальный стиль.
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru
Женский сайт https://bbb.dp.ua всё самое важное для современных девушек: стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения и самореализация. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь и находите новые идеи.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru
авиатор 1win отзывы [url=https://1win12005.ru]https://1win12005.ru[/url]
Хай!
Ликвидность как защита от манипуляций китов на крипторынке. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-likvidnost-v-kripte/]что значит ликвидность в крипте[/url] Учимся торговать там, где большие игроки не смогут тебя развести.
По ссылке: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-likvidnost-v-kripte/
что значит ликвидность в крипте
что означает ликвидность в крипте
ликвидность в трейдинге
Будь здоров!
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и снятия интоксикации используются различные подходы. Врачи подбирают их индивидуально, исходя из состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого рязань[/url]
https://mangalfactory.ru/
https://wsnwww.wolf.kazan.ws/cgi-bin/gallery/index.pl
Экстренная помощь при запое в Туле становится актуальной для многих. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-tula011.ru предлагает услуги нарколога, специализирующегося на лечении алкоголизма и вывода из запоя. Процесс включает медицинское вмешательство, детоксикацию алкоголя и психотерапию при запое. Обязательно обратитесь к врачу для эффективного преодоления алкогольной зависимости. Наша программа восстановления фокусируется на реабилитации и поддержке зависимых, а также социальной адаптации. Профилактика повторных случаев, важный аспект успешного лечения. Помните, что просьба о помощи — это первый шаг к выздоровлению.
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Углубиться в тему – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в санкт-петербурге[/url]
https://www.iemag.ru/interview/detail.php?ID=37991
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ростов-на-дону[/url]
Новостной сайт https://vesti.in.ua свежие события дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии и общество. Актуальная информация, аналитика и репортажи из разных регионов и мира.
Новостной портал Украины https://lenta.kyiv.ua оперативные события в стране. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Достоверные материалы и аналитика каждый день.
Свежие новости https://sensus.org.ua Украины и мира: главные события, репортажи и аналитика. Политика, экономика, общество и культура в удобном формате онлайн.
Свежие новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua главные события, мнения экспертов и аналитические материалы. Лента новостей онлайн, репортажи и достоверные факты без перерыва.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы сопровождаем грузы через все этапы оформления и обеспечиваем законное и быстрое прохождение границы: таможенный брокер
Мы поможем рассчитать таможенные платежи и заранее спланировать расходы на оформление товара: таможенныый брокер для юридических лиц
Когда уместен
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu-v-orekhovo-zuevo/
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Формат лечения
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkologiya-sankt-peterburg/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru
«Как отмечает главный врач-нарколог Виктор Сергеевич Левченко, «современная наркологическая клиника должна обеспечивать не только медикаментозное лечение, но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах восстановления».»
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в санкт-петербурге[/url]
скачать 888starz на телефон бесплатно https://cartsy.redq.io/blog/skachat-888starz-na-droid-poslednyaya-versiya-upotrebleniya-besplatno/
Время — ключевой ресурс при абстиненции и интоксикации. Ниже — ориентиры, которые помогут семье принять решение не откладывать обращение. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт, лучше сразу обсудить ситуацию с дежурным наркологом и подготовить пространство для визита.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
mostbet com официальный сайт [url=mostbet12009.ru]mostbet com официальный сайт[/url]
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru
мостбет вход через соцсети [url=http://mostbet12009.ru]http://mostbet12009.ru[/url]
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета санкт-петербург
Прежде чем решать, где и как лечиться, важно соотнести текущее состояние с уровнем медицинского контроля. Таблица ниже помогает увидеть разницу между форматами и выбрать безопасный старт.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-orekhovo-zuevo/
Sou louco pela energia de SupaBet Casino, parece um furacao de pura adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma erupcao de emocoes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo supersonico, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura cosmica. Em resumo, SupaBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os super-herois do cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual explosivo, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um meteoro em orbita.
www supabet co za log in|
http://banki.saratova.ru/articles/
Вызов врача нарколога — важная мера для людей‚ испытывающих проблемы с зависимостями. Услуги нарколога включает диагностику зависимости и лечение‚ что особенно важно в сложных обстоятельствах. Обратившись на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir016.ru‚ вы можете получить анонимный вызов врача на дом. Это удобно и безопасно. Консультации нарколога на дому обеспечивают удобные условия для пациентов. Прием у нарколога позволяет определить уровень зависимости и разработать персонализированную программу терапии. В реабилитации пациентов значима поддержка близких‚ что способствует эмоциональной стабильности. Наркологическая клиника предлагает всеобъемлющее лечение‚ включая психотерапевтические сеансы и медикаментозное лечение зависимостей. Не стоит откладывать обращение за помощью‚ ведь своевременное лечение алкоголизма и наркотической зависимости может спасти жизнь.
При выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону используются разные терапевтические подходы. Основной задачей является устранение токсинов и восстановление работы систем организма. Врач подбирает терапию индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и длительности запоя.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu/
Этап
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Помощь наркологии в Туле играет ключевую роль в помощи людям с зависимостями. Медицинские учреждения, такие как vivod-iz-zapoya-tula012.ru, предлагают профессиональную терапию для людей, столкнувшихся с наркотической и алкогольной зависимостями. Методы лечения зависимостей охватывают стационарные программы и реабилитационные курсы, которые обеспечивают возврат к здоровому образу жизни.Тульская наркология обеспечивает лечение без раскрытия личных данных, что особенно важно для пациентов с зависимостями. Здесь также доступна первичная консультация, где медики проводят диагностику зависимости и выбрать оптимальный путь выздоровления. Поддержка семьи зависимого также является важным аспектом процесса реабилитации. Медицинские услуги в Туле включает не только лечение алкоголизма, но и профилактические программы, что позволяет избежать рецидивов. Каждому пациенту предлагается индивидуальный подход, что способствует успешному выздоровлению от зависимости.
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма выезд на дом[/url]
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию и предсказуемые алгоритмы. Это означает — никакой полипрагмазии, никаких «универсальных капельниц», никакого «сделаем всё сразу». Сначала — безопасность (дыхание, гемодинамика, сознание), затем — управляемая детоксикация с коррекцией водно-электролитного баланса и седацией только по показаниям, после — «тихий режим» и восстановление сна, и уже на этом фоне — поведенческие навыки, работа с триггерами, переговоры с семьёй о правилах поддержки. Такой порядок убирает хаос, снижает тревогу и делает ремиссию не подвигом, а реальной рутиной.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/narkologiya-v-ryazani/
Ниже представлена карта действий бригады «РязМедСервиса» в первые три часа. Это не «жёсткая сетка», а ориентир для безопасной и быстрой стабилизации. В каждом блоке есть клиническая цель, измеримые критерии и условие для перехода к следующему шагу.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
«Как отмечает главный врач-нарколог Виктор Сергеевич Левченко, «современная наркологическая клиника должна обеспечивать не только медикаментозное лечение, но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах восстановления».»
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма краснодар[/url]
Клиника использует проверенные подходы с понятной логикой применения. Ниже — обзор ключевых методик и их места в маршруте терапии. Важно: выбор всегда индивидуален, а эффекты оцениваются по заранее оговорённым метрикам.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkolog-rostov-na-donu
Что делает врач
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Эти подходы направлены на быстрое улучшение состояния и предотвращение осложнений. После купирования острой фазы проводится дополнительное лечение зависимости.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/
Запой серьезная ситуация, требующая немедленного вмешательства. В владимире услуги нарколога, выезжающего на дом пользуются высоким спросом, особенно когда речь идет о помощи при запое. Нарколог на дом может обеспечить необходимую медицинскую помощь при запое, включая детоксикацию и выведение из запоя.Не стоит ждать, пока ситуация станет критической. Скорая помощь может быть вызвана в любой момент для оказания первой помощи и выявления необходимости в дальнейшем лечении. Лечение алкоголизма и алкогольной зависимости это процесс, который требует профессиональной помощи, и анонимность лечения играет важную роль для многих клиентов. Нарколог на дом срочно владимир Вызов нарколога в владимире — это шанс на получение экстренной помощи, не выходя из дома. Услуги нарколога включают в себя консультации так и проведение необходимых процедур по детоксикации. Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам, чтобы вернуть контроль над своей жизнью и начать новый этап.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]анонимное кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
http://www.rohitab.com/discuss/user/2653580-otello/?tab=posts
провайдеры интернета в санкт-петербурге
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
провайдер по адресу санкт-петербург
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в санкт-петербурге[/url]
888starz скачать на айфон бесплатно https://tasmanbd.com/888starz-prilozhenie-stavki-a-takzhe-skidki/
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
В «РостовМедЦентре» лечение начинается с подробной оценки факторов риска и мотивации. Клиническая команда анализирует стаж употребления, тип вещества, эпизоды срывов, соматический фон, лекарства, которые пациент принимает постоянно, и уровень социальной поддержки. Уже на первой встрече составляется «дорожная карта» на ближайшие 72 часа: диагностический минимум, объём медицинских вмешательств, пространство для психологической работы и точки контроля. Безопасность — не абстракция: скорости инфузий рассчитываются в инфузомате, седацию подбирают по шкалам тревоги и с обязательным контролем сатурации, а лекарственные взаимодействия сверяет клинический фармаколог. Пациент получает прозрачные цели на день, на неделю и на месяц — без обещаний мгновенных чудес и без стигмы.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru
Все эти меры позволяют не только стабилизировать состояние пациента, но и снизить вероятность возврата к зависимому поведению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar/
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Анонимность — важнейшее условие обращения за помощью. В клинике действуют не декларации, а конкретные технологические и организационные меры, которые защищают пациента и его близких от стигмы и лишнего обсуждения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в владимире – это возможность, что становится все более востребованной в современном мире. Проблемы зависимостей становятся распространенными, будь то алкоголизм или наркотическая зависимость. Профессиональный нарколог предоставляет наркологическую помощь, чтобы помочь справиться с этими трудностями. Вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом, если это необходимо. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать медицинские учреждения. В владимире наркологи предлагают диагностику, консультации и лечение зависимостей. Важно помнить, что анонимное лечение зависимости также возможно.Помощь на дому гарантирует комфорт и сохранение конфиденциальности, что особенно актуально для лечения алкоголизма и реабилитации после наркомании; Психотерапия для людей с зависимостями – важный элемент, помогающий пациентам восстановиться и вернуться к нормальной жизни. Реабилитация зависимых в владимире осуществляется под руководством опытных врачей, что обеспечивает высокое качество лечения. Не откладывайте решение своей проблемы! Обратитесь за помощью, вызвав нарколога через сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir010.ru.
Клиника предоставляет широкий спектр услуг, каждая из которых ориентирована на определённый этап лечения зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/[/url]
промокоды для 1win [url=https://www.1win12007.ru]https://www.1win12007.ru[/url]
https://bpr-work.ru/
Что делаем
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-orekhovo-zuevo/
Формат лечения
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/klinika-narkologii-spb/
Наркологическая помощь — это не разовая капельница, а управляемый путь от стабилизации состояния к устойчивой трезвости. «Новая Надежда» организует полный цикл: экстренный выезд на дом, стационар для безопасной детоксикации, кодирование и поддерживающую психотерапию, а также контакт с семьёй и постлечебное сопровождение. Мы работаем конфиденциально и круглосуточно, фиксируем смету до начала процедур и объясняем каждый шаг понятным языком — без «мелкого шрифта» и неожиданных пунктов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Acho simplesmente magnifico Richville Casino, da uma energia de cassino tao luxuosa quanto um trono. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro palacio de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de sofisticacao. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, respondendo rapido como um brinde de champanhe. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro de luxo, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, Richville Casino e uma joia rara para os fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a plataforma do cassino reluz com um estilo digno de um palacio, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
richville mn|
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на восстановление физического состояния пациента и снижение рисков осложнений. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает тяжелые нарушения в работе организма, и самостоятельное прекращение приёма спиртных напитков часто приводит к абстинентному синдрому. В таких ситуациях профессиональный вывод из запоя в клинике становится необходимым условием для сохранения здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
При выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону используются разные терапевтические подходы. Основной задачей является устранение токсинов и восстановление работы систем организма. Врач подбирает терапию индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и длительности запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена ростов-на-дону[/url]
Клиника использует проверенные подходы с понятной логикой применения. Ниже — обзор ключевых методик и их места в маршруте терапии. Важно: выбор всегда индивидуален, а эффекты оцениваются по заранее оговорённым метрикам.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар рязань[/url]
Прежде чем решать, где и как лечиться, важно соотнести текущее состояние с уровнем медицинского контроля. Таблица ниже помогает увидеть разницу между форматами и выбрать безопасный старт.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-orekhovo-zuevo
мостбет вход, регистрация [url=https://mostbet12012.ru]https://mostbet12012.ru[/url]
Помощь наркологов в владимире доступна для всех, кто встретился с проблемами зависимости; Анонимная помощь — это важный аспект, позволяющий пациентам обращаться без боязни критики. Наркологическая клиника предоставляет лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости через индивидуальные программы восстановления. Первичная консультация у нарколога — начало пути к выздоровлениюгде можно узнать детали о программах детоксикации и психотерапии. Реабилитация включает семейную терапию, что способствует эффективному восстановлению и предотвращению повторных случаев. Свяжитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru для получения конфиденциальной помощи и поддержки.
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/
Индивидуальная программа у нас — это модульный конструктор. В одних случаях критичен блок сна, в других — профилактика вечерних «волн» тревоги, в третьих — семейная медиированная встреча. Мы гибко переставляем модули, учитывая сопутствующие заболевания, приём базовых лекарств (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие), возраст и расписание пациента. Цель проста: чтобы терапия вписалась в жизнь, а не наоборот.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм рязань[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в санкт-петербурге[/url]
провайдеры санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
подключить интернет в санкт-петербурге в квартире
«Как отмечает главный врач-нарколог Виктор Сергеевич Левченко, «современная наркологическая клиника должна обеспечивать не только медикаментозное лечение, но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах восстановления».»
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Здарова!
Ипотека в деревне под 3%: последний шанс или пустые обещания. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/selskaya-ipoteka-2025/]сельская ипотека 2025[/url] Реальный опыт тех, кто пытался получить льготный кредит
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/selskaya-ipoteka-2025/
сельская ипотека 2025 сбербанк
сельская ипотека 2025
Удачи!
Новости Украины и мира https://mostmedia.com.ua политика, экономика, культура, спорт и общество. Свежие события, аналитика и репортажи. Будьте в курсе главных новостей в режиме онлайн 24/7.
Новостной портал https://mediateam.com.ua всё самое важное сегодня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт и шоу-бизнес. Лента новостей, репортажи и аналитические материалы каждый день.
Новости Украины https://status.net.ua объективная информация о событиях страны. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Читайте актуальные материалы каждый день.
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Необходимо кодирование? вызвать нарколога на дом Хабаровск современные методы, конфиденциальность и поддержка специалистов. Помогаем избавиться от зависимости и вернуться к здоровой жизни.
Здравствуйте!
Кухонная магия для пацанов: лайфхаки проверенные на себе. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/lajfhaki-dlya-kuhni/]лайфхак для кухни бери и делай[/url] Как экономить деньги, время и готовить блюда ресторанного уровня дома.
По ссылке: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/lajfhaki-dlya-kuhni/
лайфхак для кухни своими руками
Будь здоров!
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Клиника предоставляет широкий спектр услуг, каждая из которых ориентирована на определённый этап лечения зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника краснодар[/url]
установка дизель генератора
Что входит
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-ramenskom/
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Выезд на дом
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Что входит
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch[/url]
Лечение алкогольной зависимости на дому: мифы и действительность в владимире Лечение алкогольной зависимости становится все более актуальной темой. Многие ищут анонимное лечение алкоголизма с помощью нарколога на дом. Популярным методом является использование капельницы от запоя. Однако вокруг этого метода существует множество мифов. Во-первых, один из мифов заключается в том, что капельница может полностью решить проблему запойного состояния. В действительности, капельница лишь дает временное облегчение симптомов. Нарколог на дом может предложить целостный подход к лечению, включающий детоксикацию в домашних условиях. Это более безопасно и эффективно. Следующий миф — это отсутствие опасности при домашнем лечении. На самом деле, безопасность домашнего лечения определяется уровнем квалификации специалиста. Услуги нарколога в владимире предлагают разнообразные профессиональные услуги, но важно выбирать специалистов с хорошей репутацией. Также стоит отметить, что процесс восстановления после запоя является длительным и требует поддержки. Эффекты капельницы от алкоголя могут быть кратковременными, поэтому важно обращать внимание на рекомендации по лечению и помнить о значимости психотерапевтической помощи. Помощь при алкогольной зависимости должна быть комплексной. Избавление от запойного состояния — это процесс, который включает как физическую, так и психоэмоциональную работу. [нарколог на дом анонимно](https://vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir011.ru)
Перед применением конкретных средств врач проводит обследование, определяет уровень интоксикации и выявляет сопутствующие заболевания. Это позволяет максимально точно подобрать лечение. Ниже представлены ключевые методы, которые применяются для стабилизации состояния пациента:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru
«Как отмечает главный врач-нарколог Виктор Сергеевич Левченко, «современная наркологическая клиника должна обеспечивать не только медикаментозное лечение, но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах восстановления».»
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Adoro o frenesi de AFun Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura euforia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que pulsam como batidas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que brilha como purpurina. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, AFun Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro carnaval para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma coreografia, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
afun 777|
Estou alucinado com BRCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um pandeiro. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, BRCasino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
br77 download|
Прежде чем решать, где и как лечиться, важно соотнести текущее состояние с уровнем медицинского контроля. Таблица ниже помогает увидеть разницу между форматами и выбрать безопасный старт.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu-kruglosutochno[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Алексей Николаевич Прудников, «выезд нарколога на дом — это возможность стабилизировать состояние пациента в привычной обстановке, снизив стресс и риски осложнений».»
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в краснодаре[/url]
При выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону используются разные терапевтические подходы. Основной задачей является устранение токсинов и восстановление работы систем организма. Врач подбирает терапию индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и длительности запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника использует проверенные подходы с понятной логикой применения. Ниже — обзор ключевых методик и их места в маршруте терапии. Важно: выбор всегда индивидуален, а эффекты оцениваются по заранее оговорённым метрикам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno
В острых случаях наши специалисты оперативно приезжают по адресу в Раменском городском округе, проводят экспресс-оценку состояния и сразу приступают к стабилизации. До прибытия врача рекомендуем обеспечить доступ воздуха, убрать потенциально опасные предметы, подготовить список принимаемых лекарств и прошлых заболеваний — это ускорит диагностику. Особенно критичны первые 48–72 часа после прекращения употребления алкоголя: именно на этом промежутке повышается риск делирия и сердечно-сосудистых осложнений. Понимание этих временных рамок помогает семье действовать вовремя и осознанно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно краснодар[/url]
Прежде чем решать, где и как лечиться, важно соотнести текущее состояние с уровнем медицинского контроля. Таблица ниже помогает увидеть разницу между форматами и выбрать безопасный старт.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu
Единая панель оценки помогает действовать быстро и безошибочно. Мы фиксируем параметры, объясняем их смысл пациенту и семье и тут же привязываем к ним действия. Пример приведён в таблице: это не заменяет осмотр, но показывает логику, которой мы придерживаемся на выезде и в приёмном кабинете.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
https://bpages.ru/card/6732916/
Срочная наркологическая помощь на дому — это ключевой момент в лечении зависимостей от наркотиков и алкоголя. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir019.ru предлагается поддержка наркологов, специализирующихся на выездных услугах. В такие моменты необходима кризисная помощь, так как зависимость представляет серьезную угрозу. Домашняя терапия предоставляет комфортные условия, где вы можете рассчитывать на поддержку специалистов, а также сопровождение в процессе восстановления; Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, что помогает тем, кто не хочет раскрывать свою проблему обращаться в клиники. Консультация психотерапевта также доступна, что помогает справиться с эмоциональными переживаниями. Процесс реабилитации включает в себя всестороннюю поддержку и наркологические услуги, направленные на восстановление и реинтеграцию. Выезд опытного врача обеспечивает, что процесс лечения будет проходить под постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Не ждите — действуйте сейчас — это ваш шанс на новую жизнь!
Что входит
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]наркологическая помощь стационар[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Adoro o frenesi de AFun Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um desfile de cores. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um malabarista, com uma ajuda que brilha como purpurina. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, AFun Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro carnaval para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, torna a experiencia de cassino uma folia inesquecivel.
afun bet paga mesmo|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Na real, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin paga mesmo|
Что делаем
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru
Estou completamente apaixonado por BRCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, BRCasino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um desfile visual vibrante, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
jogo br77|
Ich bin total begeistert von Trickz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer verhexten Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Hexenwerk, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Zaubertrick funkeln. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Kaninchen aus dem Hut, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Illusion verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz aus dem Hut, manchmal wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Zaubertranke wirken. Kurz gesagt ist Trickz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Zauberer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
trickz-casino|
Здравствуйте!
Генетика без занудства: самые крутые прорывы 2025 года. [url=https://net-tabletok.ru/chto-takoe-genetika-prostymi-slovami/]что такое генетика[/url] Искусственный интеллект читает ДНК, а врачи лечат болезни до их появления.
Написал: – https://net-tabletok.ru/chto-takoe-genetika-prostymi-slovami/
что такое генетика
что такое генетика простыми словами
Пока!
Je suis totalement enflamme par VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance ardente. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un volcan, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans cendres, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du feu. Pour resumer, VBet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une flamme, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
промокоды для vbet|
В «РостовМедЦентре» лечение начинается с подробной оценки факторов риска и мотивации. Клиническая команда анализирует стаж употребления, тип вещества, эпизоды срывов, соматический фон, лекарства, которые пациент принимает постоянно, и уровень социальной поддержки. Уже на первой встрече составляется «дорожная карта» на ближайшие 72 часа: диагностический минимум, объём медицинских вмешательств, пространство для психологической работы и точки контроля. Безопасность — не абстракция: скорости инфузий рассчитываются в инфузомате, седацию подбирают по шкалам тревоги и с обязательным контролем сатурации, а лекарственные взаимодействия сверяет клинический фармаколог. Пациент получает прозрачные цели на день, на неделю и на месяц — без обещаний мгновенных чудес и без стигмы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в рязани[/url]
Перед применением конкретных средств врач проводит обследование, определяет уровень интоксикации и выявляет сопутствующие заболевания. Это позволяет максимально точно подобрать лечение. Ниже представлены ключевые методы, которые применяются для стабилизации состояния пациента:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Сладкая правда о меде для взрослых людей. [url=https://generik-info.ru/med-polza-i-vred/]мёд польза и вред[/url] Реальные исследования против популярных заблуждений.
Читай тут: – https://generik-info.ru/med-polza-i-vred/
мед польза и вред
польза мёда для организма
Бывай!
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
*Метод подбирается индивидуально и применяется только по информированному согласию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Для удобства пациентов применяются проверенные методы терапии, направленные на стабилизацию состояния и формирование стойкой ремиссии. К ключевым видам помощи относятся:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
ставки на спорт бишкек [url=https://www.mostbet12010.ru]ставки на спорт бишкек[/url]
центр вывод из запоя наркологическая клиника
Аренда авто https://myrentacar.site широкий выбор автомобилей для любых целей. Удобное бронирование, доступные цены, страхование и гибкие условия. Машины в отличном состоянии для поездок по городу и путешествий.
Строительство домов в Сочи https://stroitelstvodomovsochi.ru под ключ — профессиональный подход, проверенные материалы и гарантия качества. Полный спектр работ: проект, строительство, отделка и благоустройство.
Индивидуальная программа у нас — это модульный конструктор. В одних случаях критичен блок сна, в других — профилактика вечерних «волн» тревоги, в третьих — семейная медиированная встреча. Мы гибко переставляем модули, учитывая сопутствующие заболевания, приём базовых лекарств (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие), возраст и расписание пациента. Цель проста: чтобы терапия вписалась в жизнь, а не наоборот.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru
Формат лечения
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru
купить диплом украины цена [url=www.educ-ua3.ru]купить диплом украины цена[/url] .
https://u74.ru/2022/05/04/servis-dlya-poiska-gostinicz/
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы – это важным этапом в терапии алкогольной зависимости. В владимире наркология предлагают помощь специалиста‚ что осуществит детоксикацию организма. Признаки запоя‚ такие как тревога и потливость‚ способны привести серьезные проблемы после запоя. Капельница способствует восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить здоровье после запоя. помощь нарколога владимир После лечения важно пройти реабилитацию и обеспечить психологическую поддержку. Консультация специалиста в области наркологии поможет избежать рецидивов. Профилактика рецидива предполагает обучение и поддержку‚ что способствует организма. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме в владимире доступна и эффективна‚ помогая пациентам возвратиться к нормальной жизни.
Эти шаги помогают системно подойти к проблеме и обеспечить максимальную эффективность лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Такая схема позволяет комплексно воздействовать на организм и уменьшить риски осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
как делать ставки на 1win [url=http://1win12010.ru]как делать ставки на 1win[/url]
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Онлайн новостной портал https://reporternews.net главные события дня, эксклюзивные интервью, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Достоверная информация о политике, бизнесе и жизни общества.
Новостной портал https://newsawait.com свежие новости, аналитика и обзоры. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт. Лента событий в режиме реального времени с проверенными фактами.
Запойное состояние сопровождается интоксикацией, обезвоживанием, нарушением обменных процессов и психоэмоциональными расстройствами. Попытки самостоятельно прекратить употребление алкоголя могут привести к судорогам, скачкам давления и другим опасным осложнениям. Именно поэтому вывод из запоя в клинике обеспечивает контроль специалистов, использование медикаментозной поддержки и мониторинг жизненно важных показателей.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Прозрачная маршрутизация помогает семье и самому пациенту понимать, почему выбирается именно данный формат — выезд на дом, амбулаторная помощь, дневной стационар или круглосуточное наблюдение. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует подход клиники к первым 24 часам.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Rainbet Casino
Портал про авто https://dream-autos.com новости, обзоры и тест-драйвы. Полезные советы по выбору, ремонту и эксплуатации автомобилей. Каталог машин, актуальные цены и аналитика авторынка.
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkologiya-sankt-peterburg
Sou louco pela vibe de AFun Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um festival de fogos. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que brilha como purpurina. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como serpentinas, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, AFun Casino e um cassino online que e uma explosao de alegria para os folioes do cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vibrante, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
https www afun games casino tab original|
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin levantamento|
Estou alucinado com BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de gingado, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de carnaval. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BRCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
br77 bet|
J’adore la chaleur de VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et enflammees, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent comme des flammes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un volcan, avec une aide qui jaillit comme une flamme. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse eruptive, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient brulants. En somme, VBet Casino offre une experience de casino ardente pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enflammee du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un cratere en fusion, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus enflammee.
vbet rollover|
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/[/url]
Анонимность — важнейшее условие обращения за помощью. В клинике действуют не декларации, а конкретные технологические и организационные меры, которые защищают пациента и его близких от стигмы и лишнего обсуждения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Единая панель оценки помогает действовать быстро и безошибочно. Мы фиксируем параметры, объясняем их смысл пациенту и семье и тут же привязываем к ним действия. Пример приведён в таблице: это не заменяет осмотр, но показывает логику, которой мы придерживаемся на выезде и в приёмном кабинете.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Этап
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru
1win kz скачать [url=1win12010.ru]1win12010.ru[/url]
«РостовМедЦентр» предоставляет несколько форматов, чтобы лечение не сталкивалось лоб в лоб с работой, учебой и семейными обязанностями. Стационар — для случаев с рисками, дневной стационар — для интенсивной дневной терапии, амбулаторный режим — для поддержания динамики без разрыва с повседневной жизнью. Выезд на дом сохраняет приватность и экономит время, а защищённые видеосессии позволяют поддерживать мотивацию между очными визитами. Все каналы соединены в единую систему: план, составленный сегодня в клинике, доступен врачу, который завтра приедет на дом, и психологу, с которым запланирована онлайн-сессия через два дня.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru
Запойное состояние — это состояние‚ характеризующееся продолжительным пьянством‚ которое может привести к серьезным последствиям для здоровья. Клинические проявления запоя включают в себя сильную тягу к алкоголю‚ потерю контроля над объемом алкоголя и физические симптомы‚ такие как тремор и обильное потоотделение. Состояние требует медицинской помощи при запое‚ где нарколог на дом предоставит необходимую помощь. Последствия запоя могут быть различными: от физической слабости до психических расстройств. Алкогольная зависимость часто сопровождается синдромом отмены‚ вызывающим дискомфортные ощущения при остановке употребления. В таких случаях детоксикация организма с помощью капельницы от запоя может значительно улучшить состояние пациента. Лечение запоя включает в себя не только лекарственное лечение‚ но и психологическую поддержку со стороны родных‚ что является ключевым фактором в восстановлении после запоя. Психология зависимости показывает‚ что предотвратить запой можно‚ используя разнообразные подходы‚ включая поддержку специалистов и модификацию жизненных привычек.
Прокапаться после запоя в Красноярске: эффективные методы помощи Запой – это актуальной проблемой‚ требующей внимании. Признаки похмелья включают в себя головную боль‚ тошноту‚ и общую слабость. Выход из запоя начинается с детоксикации организма. Важно получить медицинскую помощь для безопасного выхода из состояния запоя. Клиника реабилитации предлагает широкий спектр услуг по лечению алкоголизма‚ в т.ч. психотерапию при алкоголизме и поддержку близких. Специальные медикаменты способствуют справится с зависимостью. Психология зависимости требует внимательного подхода‚ и профессионалы готовы помочь. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk013.ru где представлена информацию о способах реабилитации после употребления алкоголя. Как пережить запой? Прокапаться – это один из самых эффективных способов вернуть организм в норму и положить начало новому‚ здоровому образу жизни.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в рязани[/url]
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в рязани[/url]
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Для многих барьер — страх огласки. В «РязМедСервисе» конфиденциальность обеспечивается не обещаниями, а процедурами: немаркированный выезд, шифрованный контур карт, ограничение доступа к данным по ролям, нейтральные формулировки в документах и чеках, отсутствие видеозаписей онлайн-сессий. Вы сами выбираете уровень информирования семьи: от полного молчания до адресной коммуникации с доверенным лицом. Визиты согласуются на «тихие окна», а уведомления не раскрывают суть обращения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
https://www.te-in.ru/bezopasnost-prezhde-vsego-osnovnyie-pravila-rabotyi-s-dgu.html/
Эти ситуации требуют немедленного вмешательства, и приезд врача позволяет оперативно оказать помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare14.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в краснодаре[/url]
«РостовМедЦентр» предоставляет несколько форматов, чтобы лечение не сталкивалось лоб в лоб с работой, учебой и семейными обязанностями. Стационар — для случаев с рисками, дневной стационар — для интенсивной дневной терапии, амбулаторный режим — для поддержания динамики без разрыва с повседневной жизнью. Выезд на дом сохраняет приватность и экономит время, а защищённые видеосессии позволяют поддерживать мотивацию между очными визитами. Все каналы соединены в единую систему: план, составленный сегодня в клинике, доступен врачу, который завтра приедет на дом, и психологу, с которым запланирована онлайн-сессия через два дня.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu14.ru/narkolog-rostov-na-donu/
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto uma bateria de escola de samba. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista na avenida, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay contactos|
Капельница от запоя в владимире: цены и отзывы В владимире вызов нарколога на дом становятся все более популярными. Множество людей борются с зависимостью от алкоголя и испытывают потребность в поддержке. Вызов нарколога на дом анонимно, это удобный способ получить медицинскую помощь, не выходя из дома. Капельница от запоя способствует в детоксикации организма и облегчает симптомы.Стоимость капельницы может различаться в зависимости от клиники, но в среднем составляет от 3000 до 6000 рублей. Отзывы о капельнице в большинстве своем хорошие: пациенты отмечают быстрое улучшение состояния и ослабление желания выпить. Экстренная помощь при запое является жизненно важной.Анонимное лечение алкоголизма — важный аспект, так как многие стесняются своей проблемы. Услуги нарколога в владимире предлагают комплексную помощь, включая капельницы и реабилитационные программы. Помощь при запое доступна для всех, кто стремится к выздоровлению. нарколог на дом анонимно владимир
https://www.kartabita.ru/Desc/kosynka/
Ich bin total elektrisiert von Tipico Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Blitz einschlagt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Gewitter voller Action, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm toben. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Donner glanzt, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Tipico Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Polarlicht, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
wie funktioniert tipico|
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре предоставляет комплекс медицинских услуг, направленных на лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, а также помощь при острых состояниях, связанных с интоксикацией организма. Основная задача специалистов заключается в оказании экстренной и плановой помощи пациентам, нуждающимся в выводе из запоя, детоксикации и реабилитации. Выбор правильного учреждения является ключевым условием для успешного выздоровления и предотвращения рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург[/url]
мостюет [url=www.mostbet12012.ru]www.mostbet12012.ru[/url]
https://www.online-torg.club/kolakot_garant/
купить диплом специалиста [url=educ-ua20.ru]купить диплом специалиста[/url] .
https://www.te-in.ru/da-budet-svet-kakuyu-generatornuyu-ustanovku-vyibrat-dlya-doma.html/
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Полная информация здесь – https://taretanbeasiswa.com/addtext_10-21-12-04-57
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://avidity-ip.com/avidityipevents/bioseed-2022
https://vgarderobe.ru/uzkie-dzhinsy-streich-ajc-g-7377-22.html
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://vddeijlkozijnen.nl/?attachment_id=8
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Почему это важно? – https://loja.falosports.com/ola-mundo
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Обратитесь за информацией – https://pcnft.cibunet.com/cibuvideo/seo-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B6%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B9%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B2-%D0%B2-google
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Подробнее – https://chilimasala.se/slide_1
https://vgarderobe.ru/sapogi-cat-645.html
Новости Украины и мира https://globalnewshome.com всё самое важное сегодня. Политика, экономика, региональные события, спорт и культура. Объективные статьи и аналитика в удобном формате.
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://inmall2cn.com/%E8%B7%A8%E5%A2%83%E9%9B%BB%E5%95%86%E8%AC%9B%E5%BA%A7-%E5%93%81%E7%89%8C%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E7%84%A1%E7%BC%9D%E6%8E%A5%E5%90%88%E4%B8%AD%E5%9C%8B%E7%B6%B2%E8%B3%BC%E5%B8%82%E5%A0%B4
Портал для женщин https://womanfashionista.com всё самое важное в одном месте: уход за собой, мода, дом, семья и карьера. Читайте полезные статьи, находите вдохновение и делитесь опытом.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Обратитесь за информацией – http://www.mrkm.jp/blog/item_288.html
Сайт детского сада https://malush16.ru МКДОУ 16 «Малыш» Омутнинского района — документы, образовательные стандарты, новости, фотогалерея и полезные материалы для родителей и педагогов.
Этот текст сочетает в себе элементы познавательного рассказа и аналитической подачи информации. Читатель получает доступ к уникальным данным, которые соединяют прошлое с настоящим и открывают двери в будущее.
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://www.iso-studio.it/8-marzo-festa-delle-donne-in-sicurezza
купить аттестат за 11 в москве [url=www.arus-diplom25.ru/]купить аттестат за 11 в москве[/url] .
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://quackplex.com/livestock-management/care-and-feeding/do-goats-bleed-when-in-heat
Выездной нарколог — это решение для тех, кто нуждается в помощи, но не может или не хочет посещать клинику. Услуги московского нарколога включают домашнюю консультацию, что обеспечивает конфиденциальность и удобные условия для пациента. Лечение зависимостей начинается с диагностики и снятия абстиненции. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk014.ru Специалисты предлагают помощь нарколога, которая включает медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме и психотерапию при зависимости. Процесс реабилитации наркозависимых также доступна на выезде, что позволяет вовлечь близких в поддерживающий процесс. Предотвращение рецидивов и непрерывная помощь имеют решающее значение для успешного выздоровления. Посещение врача-нарколога на дому может стать первым шагом к новой жизни.
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Почему это важно? – https://www.aeroourinhos.com.br/datas-comemorativas/dia-dos-pais
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Погрузиться в детали – https://notifedia.com/waspada-akun-whatsapp-palsu-mengatasnamakan-pj-wali-kota-parepare
https://xiaomi.eu/community/members/robertgreen.385568/#about
Алкогольный делирий серьезное состояние, развивающееся из-за зависимости от алкоголя. Он проявляется множеством симптомов такие симптомы, как спутанность сознания, галлюцинации, тремор и проблемы со сном. Выездной нарколог в Красноярске может оказать экстренную помощь при запое и диагностировать алкогольный синдром . Лечение делирия включает медикаментозное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента . Не менее важно проводить психотерапию для людей с зависимостями, которая поможет справиться с психологическими аспектами зависимости ; Для успешной реабилитации алкоголиков необходима поддержка близких, чтобы они могли понять признаки алкогольного делирия и оказать помощь при алкоголизме . Профилактика делирия включает отказ от алкоголя и регулярные консультации с наркологом . Нарколог на дому в Красноярске предлагает широкий спектр наркологических услуг, включая лечение на дому. нарколог на дом Красноярск
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Все материалы собраны здесь – https://yuuji-miyahara.com/uncategorized/hello-world
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Лучшее решение — прямо здесь – https://eyeblogs.com/why-teachers-matter-in-this-artificial-generation
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista na avenida, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay snyd|
мостбеь [url=http://mostbet12010.ru]мостбеь[/url]
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://www.anby.cz/2017/02/27/coffee-shooting
Ich finde absolut atemberaubend Tipico Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Donnerhall vibriert. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Gewitter voller Action, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm toben. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Donner glanzt, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Gewitterknall. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist Tipico Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Gewitter tobt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Polarlicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
tipico login|
Ich liebe den Adrenalinkick von Turbonino Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Formel-1-Wagen rast. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Turbonino Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Zielsprint begeistert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glanzt wie ein Rennwagen, was jede Casino-Session noch rasant macht.
turbonino erfahrungen|
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы на дому – это важная процедура для лечения пьянства. Если вам необходимо обратиться к наркологу на дому в владимире‚ ознакомьтесь с репутацией клиники. Важно обратить внимание на клинику‚ который предлагает анонимное лечение и услуги нарколога с опытом. вызвать нарколога на дом владимир Перед вызовом специалиста стоит пообщаться о возможностях лечения на дому‚ таких как процедуры с капельницей. Это позволит гарантировать безопасность процесса и эффективное восстановление после запоя. Убедитесь‚ что клиника проводит реабилитацию в домашних условиях‚ что поддерживает эффективность терапии. Важно внимательно подойти к выбору клиники. Обратите внимание на отзывы‚ уровень профессионализма специалистов и график работы клиники. Надежный нарколог на дому сможет сделать все возможное для вашего восстановления‚ обеспечивая внимание и заботу в трудный период.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Продолжить изучение – https://againstglobalhunger.org/?attachment_id=974
Статьи для садоводов https://portalteplic.ru огородников, фермеров и пчеловодов: советы по уходу за растениями, животными и пасекой. Полезные инструкции, лайфхаки и сезонные рекомендации.
Портал о ремонте https://studio-nd.ru статьи, инструкции и советы для дома и квартиры. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Полезные рекомендации для мастеров, новичков и частных застройщиков.
Сайт про металлопрокат https://the-master.ru каталог продукции, характеристики и сферы применения. Арматура, балки, трубы, листы и профили. Актуальные цены, советы специалистов и полезные статьи.
Проблема алкоголизма в Ярославле, как и в других регионах России, остаётся одной из самых актуальных. По данным Минздрава РФ, количество людей, нуждающихся в медицинской помощи из-за злоупотребления спиртным, ежегодно растёт. При этом эффективное лечение возможно лишь при комплексном подходе, включающем как медицинскую, так и психологическую поддержку.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/]наркология лечение алкоголизма[/url]
На первом приёме нарколог собирает полную клиническую картину: продолжительность зависимости, количество и частоту приёмов спиртного, наличие соматических и психических осложнений. Одновременно выполняются лабораторные тесты: общий анализ крови, биохимия (показатели работы печени и почек), электролиты. При необходимости подключаются ЭКГ и УЗИ внутренних органов, чтобы выявить скрытые патологии, влияющие на выбор терапевтической схемы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма архангельск[/url]
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма мурманск[/url]
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «УралРеаб» работает более десяти лет и специализируется на лечении зависимости от алкоголя. За время работы в центре прошли лечение тысячи пациентов, многие из которых смогли полностью восстановить здоровье и вернуться к активной жизни. Основные принципы работы:
Детальнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg00.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-czena-ekaterinburg
Согласно информации, опубликованной на сайте Минздрава РФ, успешная наркологическая помощь невозможна без своевременной диагностики, комплексного подхода и участия квалифицированных специалистов. Именно такие параметры становятся решающими при выборе учреждения, куда обратится пациент или его родственники.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-arkhangelsk0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Для пациентов, требующих круглосуточного наблюдения, клиника «Полярис» предлагает стационар VIP-класса. Здесь созданы все условия для быстрого восстановления: удобные палаты, индивидуальное меню, зоны отдыха и консультации профильных специалистов.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru
После диагностики нарколог приступает к основному этапу — инфузионной детоксикации. Препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом тяжести интоксикации, анамнеза и сопутствующих заболеваний. Основу составляют водно-солевые растворы, глюкоза, витаминные комплексы, седативные препараты, гепатопротекторы и нейропротекторы. Инфузии выполняются капельно, медленно, в течение нескольких часов, с постоянным мониторингом состояния пациента. При необходимости используется оксигенотерапия, противорвотные, антиаритмические и противосудорожные препараты. Все растворы стерильны, а расходные материалы одноразовые и соответствуют стандартам качества.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novosibirsk0.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в новосибирске[/url]
подключение дизель генератора
«НаркоМед» основана группой узкопрофильных специалистов, чей опыт насчитывает более 15 лет в лечении зависимости. Клиника работает круглосуточно — вы можете рассчитывать на оперативное реагирование в любой час дня и ночи. Анонимность пациентов сохраняется на уровне медицинской тайны: персональные данные и диагноз не разглашаются.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg0.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Основная задача лечения — обеспечить безопасное и максимально комфортное прохождение всех этапов терапии. В клинике «Преодоление» организован круглосуточный медицинский контроль, который позволяет снизить риски осложнений и улучшить прогноз выздоровления. Создание доверительной атмосферы и психологическая поддержка способствуют формированию мотивации для длительного воздержания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novosibirsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-novosibirsk/
яндекс плюс Купить Яндекс Подписку – оформите подписку прямо сейчас и откройте для себя мир развлечений и выгодных предложений. Слушайте музыку, смотрите фильмы, получайте кешбэк и пользуйтесь другими преимуществами. Выберите подходящий тариф и начните пользоваться Яндекс Плюс уже сегодня!
Медикаментозная терапия направлена на снятие симптомов абстиненции, нормализацию функций органов и систем, а также коррекцию психоэмоционального состояния пациента. Используются препараты, способствующие детоксикации, стабилизации работы нервной системы и улучшению общего самочувствия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-perm0.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь в перми[/url]
согласование перепланировки квартиры под ключ [url=http://turforum.borda.ru/?1-8-0-00003551-000-0-0/]согласование перепланировки квартиры под ключ [/url] .
https://www.te-in.ru/vse-o-kapitalnom-remonte-dgu-osnovnyie-etapyi-i-osobennosti-proczessa.html/
Капельница от запоя – это доказанный способ, который активно используется наркологами для детоксикации организма. Специалист по зависимостям на дому из лечебного учреждения предлагает конфиденциальное лечение, обеспечивая максимальную приватность для клиента. Домашний визит врача позволяет быстро ощутить медицинскую помощь и восстановление организма, что особенно важно для алкоголиков. Нарколог на дом клиника В процессе лечения используются вливания, которые помогают облегчить симптомы абстиненции и гарантируют безопасность терапии. Профессиональная поддержка нарколога на дом предоставляет возможность пройти терапию зависимости в комфортной обстановке, что минимизирует стресс от лечения. Это – эффективное восстановление от запоя, которое предоставляет возможность начать новую жизнь без алкоголя.
https://project911.ru/ru-ru/
Estou pirando com BetPrimeiro Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que borbulha como um geyser. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de delicias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma chama de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que incendeia como uma tocha. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brasa, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, BetPrimeiro Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como lava derretida, adiciona um toque de fogo ao cassino.
avaliações sobre betprimeiro|
Acho simplesmente alucinante Bet4Slot Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma roda-gigante iluminada. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma roda de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de rotacao. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma engrenagem de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem travar. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma montanha-russa, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que giram como um tornado. Na real, Bet4Slot Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual giratorio, torna a experiencia de cassino um carrossel inesquecivel.
bet4slot vet|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. Its collection is a canopy of thrilling entertainment, including classy casino table games with a tribal flair. The casino’s customer service is a tribal chief of efficiency, responding faster than a monkey swinging through trees. Casino payments are secure and smooth, but the casino offers could be more generous. Overall, Wazamba Casino is a gem for casino fans for fans of modern casino slots! Additionally the casino site is a graphical wonder, adding a touch of jungle magic to the casino.
wazamba testbericht|
Je suis fou de Tortuga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme une tempete en haute mer. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un coffre de butin, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de tempete, avec une aide qui hisse les voiles. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ecueils, mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient hisser le pavillon. Globalement, Tortuga Casino est un tresor pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline des mers du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique pirate, facilite une experience de casino epique.
code promo tortuga casino|
Здравствуйте!
Что такое блокчейн и как на нем зарабатывают миллионы. [url=https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-blokchejn-prostymi-slovami/]что такое блокчейн в криптовалюте[/url] Честный разбор технологии с плюсами, минусами и реальными примерами.
Написал: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-blokchejn-prostymi-slovami/
что такое блокчейн в криптовалюте
что такое блокчейн простыми словами
что такое блокчейн
Удачи!
Je suis totalement captive par Unibet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un orchestre en feu. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une harmonie de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme rythmique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un chef d’orchestre, avec une aide qui resonne comme une symphonie. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse virtuose, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient harmonieux. En somme, Unibet Casino offre une experience de casino envoutante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique melodique, ajoute une touche de musique au casino.
offre unibet|
casinos mit schneller auszahlung Casino ohne deutsche Lizenz
Строительный портал https://krovlyaikrysha.ru база знаний и идей. Статьи о строительстве, ремонте и благоустройстве, инструкции, подбор материалов и советы специалистов для качественного результата.
Всё про ремонт https://gbu-so-svo.ru и строительство — статьи, инструкции и советы для мастеров и новичков. Обзоры материалов, проекты домов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Автомобильный портал https://ivanmotors.ru всё о машинах в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, обзоры, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Актуальные события мира авто для водителей и экспертов.
Сигналы, указывающие на потребность в наркологической помощи, часто игнорируются либо недооцениваются. Очень важно не пропустить тревожные симптомы, такие как:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk5.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-podolske/
http://evakuatorhelp.ru/ Наша работа – оказывать круглосуточную помощь на дорогах! Мы предлагаем полный набор услуг, начиная от эвакуации автотранспорта и заканчивая небольшим ремонтом прямо на месте. Работаем оперативно, качественно и по приемлемой стоимости. Неважно, где вы находитесь и что случилось с вашим автомобилем, мы всегда готовы оказать вам помощь! Звоните немедленно!
Приветствую!
Синдром самозванца: когда башка сама себя троллит. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-takoe-sindrom-samozvancza/]синдром самозванца простыми словами[/url] Разбираемся, почему 80% людей считают себя обманщиками и как перестать думать, что твои успехи случайность.
Читай тут: – https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-takoe-sindrom-samozvancza/
синдром самозванца как избавиться
синдром самозванца книга
тест на синдром самозванца
Пока!
Наркология в Красноярске предлагает многочисленные программы для людей‚ страдающих от зависимости. Важно понимать‚ что преодоление зависимости — это сложный процесс. Консультация нарколога — первый шаг к выздоровлению‚ который оценит состояние пациента и порекомендует индивидуальную программу. В Красноярске функционируют кризисные центры‚ где можно получить поддержку анонимных наркологов. Психотерапевтические методы помогают в восстановлении. Терапия для семьи помогает укрепить связи и поддержку пациента. Программы реабилитации охватывают лечение как наркомании‚ так и алкоголизма. Важно знать о профилактических мерах и следовать рекомендациям специалистов. Восстановление после зависимости — это длительный процесс‚ требующий терпения и поддержки. Обратитесь в клинику зависимостей на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk015.ru для получения квалифицированной помощи.
Казино Вавада знаменито бонусами.
Бонусные программы делают игру выгоднее.
Регулярные турниры позволяют получить эмоции.
Подборка развлечений включает новинки.
Создать аккаунт легко, поэтому можно сразу активировать промо.
Узнай больше по ссылке: https://hinterlandmn.com
Банковские услуги Прогнозы экономики – это попытка заглянуть в будущее, основанная на анализе данных и экспертных оценках. Это сложная и неточная задача, поскольку экономика подвержена влиянию множества непредсказуемых факторов. Тем не менее, прогнозы экономики помогают нам понять, какие тенденции, скорее всего, будут доминировать в будущем, и как можно подготовиться к ним. Прогнозы экономики используются правительствами, компаниями и инвесторами для планирования и принятия решений.
Как сам!
Азбука блэкджека: от нуля до профессионала. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrat-v-blekdzhek/]блекджек таблица[/url] Подробный разбор правил, вариантов игры и секретов успешной игры.
Написал: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrat-v-blekdzhek/
тактика блек джек
Будь здоров!
Королева Чиана Королева Чиана – это автор, чьи работы отличаются глубоким погружением в психологию персонажей и непредсказуемыми поворотами сюжета. Её книги заставляют задуматься о сложных вопросах морали и выбора, оставляя долгое послевкусие после прочтения.
Здравствуйте!
Как военные справляются со стрессом: секреты квадратного дыхания. [url=https://net-tabletok.ru/tehnika-dyhaniya-dlya-uspokoeniya/]техника для успокоения[/url] Техника, которая поможет собраться в любой критической ситуации.
По ссылке: – https://net-tabletok.ru/tehnika-dyhaniya-dlya-uspokoeniya/
техника дыхания для успокоения
дыхание успокаивающее
Покеда!
Анонимная помощь при зависимостях — это важный шаг для людей, страдающих от зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir015.ru можно получить сведения о способах борьбы с зависимостями, восстановлении и помощи. Лечение без раскрытия личности позволяет пациентам находить решение без боязни осуждения.Услуги нарколога включают детоксикацию, психотерапию и экстренное вмешательство. Процесс реабилитации часто включает поддерживающие группы, что помогает в процессе выздоровления. Предотвращение зависимостей также играет критически важную роль, обеспечивая постоянное благополучие. Консультации помогут разобраться в проблемах и найти пути решения. Помощь для людей с зависимостями доступна и доступна, даже если они бояться открыться.
https://vgarderobe.ru/maui-wowie-b-97.html
888 starz скачать бесплатно http://en.speakee.fr/rabochee-luchnik-888starz-casino-a-eshche-ofitsialnyy-zhurnal/
В Краснодаре решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в городе[/url]
https://vgarderobe.ru/odezhda-dlya-devochek-filly-bc-9749.html
https://www.te-in.ru/rejting-dizel-generatorov-obzor-luchshix-proizvoditelej-na-2022-god.html/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
https://sct-raduga.ru/ru-ru/
Сайт о ремонте https://e-proficom.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Всё, что нужно для ремонта квартир и домов.
Сайт для женщин https://devchenky.ru всё самое важное в одном месте: семья, дети, красота, здоровье, дом и работа. Советы специалистов, лайфхаки и вдохновение на каждый день.
Блог о ремонте https://ivinstrument.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. Всё о ремонте квартир и домов: выбор материалов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Adoro a erupcao de BetPrimeiro Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um vulcao em furia. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma erupcao de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque vulcanico. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma labareda, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brasa, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, BetPrimeiro Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma erupcao total para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vulcanico, eleva a imersao no cassino ao calor de um vulcao.
codigo bonus betprimeiro|
betkin casino Pin Up Casino
Je suis accro a Unibet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui vibre comme une note aigue d’une symphonie. La selection du casino est une symphonie de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et vibrantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une note staccato, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une portee musicale, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient chanter. Pour resumer, Unibet Casino c’est un casino a rejoindre sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une partition, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
unibet 15€ sans depot|
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Краснодаре проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в городе[/url]
В стационаре мы добавляем расширенную диагностику и круглосуточное наблюдение: это выбор для пациентов с «красными флагами» (галлюцинации, выраженные кардиосимптомы, судороги, рецидивирующая рвота с примесью крови) или тяжёлыми соматическими заболеваниями. На дому мы остаёмся до первичной стабилизации и оставляем письменный план на 24–72 часа, чтобы семья действовала уверенно и согласованно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-pushkino/
http://www.evakuatorhelp.ru ‘. Они предназначены в качестве примера и не связаны с сайтом, предоставленным вами, поскольку у меня нет возможности получать с него информацию: Быстрое и надежное решение для эвакуации вашего автомобиля! Мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь на дорогах, профессиональную погрузку и транспортировку вашего транспортного средства в любую точку города и области. Доверьтесь нашему опыту и современному оборудованию, чтобы обеспечить безопасность вашего автомобиля во время эвакуации. Звоните прямо сейчас!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Капельницы для лечения похмелья – является эффективным средством для восстановления организма после алкогольного отравления. В владимире медицинские услуги в виде вливание глюкозы и электролитов дают возможность быстро облегчить проявления похмелья, включая головная боль, тошнота и слабость. Клиники в владимире предлагают лечение с использованием энтеросгеля с целью детоксикации. Восстановление водного баланса также играет важную роль в процессе восстановления. Важно помнить о необходимости консультации врача перед началом лечения. Чтобы узнать больше посетите сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir016.ru.
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-pushkino/
Городской портал Москвы https://moscowfy.ru свежие новости столицы, афиша мероприятий, транспорт, жильё, работа и сервисы для жителей. Полезная информация для москвичей и гостей города на одном сайте.
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskie-zimnie-sapogi-adidas-bc-2731.html
Современные наливные полы https://proffi-floor.ru это не только идеально ровная поверхность, но и долговечность покрытия. Если вы планируете ремонт в квартире или офисе, узнайте подробнее об услугах по устройству наливных полов
нотариус перевод документов бюро перевод сервис
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskaya-rubashka-s-korotkim-rukavom-pepe-jeans-g-174736-182.html
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar15.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Je suis accro a Winamax Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino aquatique. La selection du casino est une vague de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme aquatique. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et limpide, avec une aide qui fait des vagues. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un courant marin, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eclaboussent. Dans l’ensemble, Winamax Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer turquoise, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus fluide.
cashout winamax|
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Ich bin suchtig nach Wunderino Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Marchenbuch verzaubert. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Marchenwald voller Action, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein weiser Zauberer, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Feenlicht funkelt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Verwunschungen, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Marchentraum. Kurz gesagt ist Wunderino Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feenlicht verzaubert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
wunderino alternative|
Процедура начинается с осмотра и сбора анамнеза. После этого специалист проводит экстренную детоксикацию, снимает симптомы абстинентного синдрома, назначает поддерживающую терапию и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим шагам. По желанию родственников или самого пациента помощь может быть оказана и в условиях стационара клиники.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo6.ru/skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-domodedovo/https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo6.ru
диплом бакалавра купить украина [url=http://educ-ua3.ru/]диплом бакалавра купить украина[/url] .
Курсы валют Личные финансы – это управление денежными средствами и активами отдельного лица или семьи. Они включают в себя планирование бюджета, сбережения, инвестиции, страхование и управление долгами. Управление личными финансами направлено на достижение финансовых целей, таких как покупка дома, образование детей или выход на пенсию.
В клинике «АлкоСвобода» используются только проверенные и признанные медицинским сообществом методы:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-mytishchi5.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-mytishchi5.ru/[/url]
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – http://recself.ru/user-info.php?id=22276
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Разобраться лучше – https://epinions.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-chastnaya-skoraya-pomoshch-no1-v-balashihe
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
А есть ли продолжение? – https://basantinternational.com/product/air-filter-pan-b6505004
Откройте для себя скрытые страницы истории и малоизвестные научные открытия, которые оказали колоссальное влияние на развитие человечества. Статья предлагает свежий взгляд на события, которые заслуживают большего внимания.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://www.ekologicke-vytapeni.cz/ahoj-vsichni
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Дополнительно читайте здесь – https://www.aisolutionsph.com/2024/03/07/is-ethics-keeping-pace-with-the-rapid-innovation-in-ai
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://www.unlockedbrasil.com/%D0%BB%D1%83%D1%87%D1%88%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE-2024-%E1%90%88-%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8-%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81%D0%BE
Королева Чиана Королева Чиана – это мастер слова, чьи произведения отличаются изысканным стилем и вниманием к деталям. Её рассказы и повести – это настоящие литературные шедевры, которые не оставят равнодушным ни одного ценителя качественной прозы. Погрузитесь в мир её творчества, и вы откроете для себя новые грани человеческих отношений и моральных ценностей.
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Детальнее – https://www.pattanshetti.in/kharab-land-and-its-treatment-in-karnataka
Врач-нарколог в любое время предоставляет экстренную помощь при наркологических кризисах при кризисной ситуации. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir017.ru вы можете получить консультацию врачукоторый оценит вашу ситуацию и проведет диагностику наркозависимости и предложит персонализированный план лечения. Центр наркологии предлагает всестороннюю медицинскую помощь и лечение с повышенной конфиденциальностью. Реабилитация зависимых предполагает использование психотерапии зависимостей и поддержку в борьбе с алкоголизмома также консультации и помощь для семьи на всех этапах лечения. Обратитесь за помощью уже сегодня!
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://www.lefersa.cl/prueba
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Детали по клику – https://www.hamedanhaji.ir/%D8%B3%DB%8C%D9%84%DB%8C%D8%B3%DB%8C%D9%85-%D8%AF%DB%8C%E2%80%8C%D8%A7%DA%A9%D8%B3%DB%8C%D8%AF
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Откройте для себя больше – https://padmaoselling.nl/print
Ich finde absolut atemberaubend Wheelz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer rasanten Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Fahrt, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Karussell leuchten. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Looping explodieren. Insgesamt ist Wheelz Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Freizeitpark glanzt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Fahrgeschaft, den Spielspa? im Casino in schwindelerregende Hohen treibt.
wheelz casino bonus|
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Открой скрытое – https://zenbat.es/the-soundcloud-post
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://surfbaliadventure.com/?attachment_id=232
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Acho simplesmente epico VikingLuck Casino, parece um Valhalla de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um salao de Valhalla, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de gloria. O servico do cassino e confiavel e forte como um escudo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem fraqueza. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que rugem como guerreiros. No geral, VikingLuck Casino vale demais navegar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo nordico, eleva a imersao no cassino ao nivel de uma saga.
viking luck casino|
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://foe.gctu.edu.gh/news/vania-sandra-eddico-wins-female-engineering-students-scholarship-programme-award
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://www.jacopoborga.com/2021/10/15/local-limits-for-permutations-and-generating-trees
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Читать дальше – https://hanshin-yusho.blog/?p=69
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Ознакомьтесь поближе – https://transportesmr.com.br/index.php/2023/06/04/ola-mundo
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Продолжить изучение – https://sciencefestiv.com/logo_sciencefestiv-2
https://vgarderobe.ru/vyazanye-sapogi-alba-moda-g-142638-2.html
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Что скрывают от вас? – https://cloudfiles.in/mastering-the-art-of-web-design-a-guide-to-creating-visually-stunning-and-user-friendly-websites
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Продолжить чтение – https://oceanica.org.br/oceanica-realiza-campanha-praia-limpa-em-buzios
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://epubaccessibility.org/ahoj-vsichni
После обращения по телефону или через сайт оператор уточняет адрес, состояние пациента и срочность выезда. Врач прибывает в течение 1–2 часов, а в экстренных случаях — в течение часа. На месте специалист проводит первичный осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, особенности реакции на лекарства.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki5.ru/]вывод из запоя химки круглосуточно[/url]
Подборка статей https://yandex-direct-info.ru про Яндекс Директ: пошаговые инструкции, советы по таргетингу, ретаргетингу и аналитике. Всё о рекламе в Яндексе в одном месте для вашего бизнеса.
https://vgarderobe.ru/shelkovoe-plate-s-oliver-g-10261-21.html
Яндекс Бизнес https://business-yandex3.ru описание сервиса, его инструменты и функции. Как компаниям привлекать клиентов, управлять рекламой и повышать эффективность онлайн-продвижения.
Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Тагиле представляет собой комплекс медицинских мероприятий, направленных на безопасное и эффективное прерывание состояния острого алкогольного отравления. Этот процесс требует профессионального подхода, так как самостоятельное прерывание запоя чревато серьезными осложнениями, включая судороги, инсульты и инфаркты. В медицинской практике используется комплекс мер, включающий детоксикацию организма, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и лечение симптомов абстиненции.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Критерий
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, — это штат клиники. От опыта врачей напрямую зависит точность диагностики, подбор препаратов и эффективность психотерапевтической поддержки.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в первоуральске[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в каменске-уральском[/url]
Наличие у нарколога практического опыта и навыков быстрого реагирования критично — особенно если речь идёт о тяжелой интоксикации или судорожном синдроме. Ошибки в дозировке или игнорирование хронических заболеваний могут привести к осложнениям.
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czeny-v-nizhnem-tagile/
Как поясняет врач-нарколог клиники «АлкоСтоп», «грамотно составленная инфузионная терапия не только устраняет последствия запоя, но и создаёт условия для дальнейшей мотивации пациента к лечению».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Согласно официальным рекомендациям Минздрава, выезд нарколога на дом способствует сокращению осложнений и повышению эффективности первичной помощи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]запой нарколог на дом каменск-уральский[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://spaic.ancb.bj/index.php/association-2/oueme/avrankou.html
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Перейти к полной версии – https://sweetmacshop.com/2021/07/06/perfectly-colored-macarons-for-any-wedding
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Полезно знать – https://bloggenmeister.com/seo-tools-tipps-und-schreibwerkzeuge-fur-ihren-blog
Здравствуйте!
Витамин D3 и A: мужской подход к здоровью. [url=https://net-tabletok.ru/vitamin-d3-i-a/]витамин д как принимать[/url] Факты, дозировки и советы от того, кто сам через это прошел.
Здесь подробней: – https://net-tabletok.ru/vitamin-d3-i-a/
витамин а для чего
витамин д купить
Покеда!
Здарова!
Самые дешевые игры в Steam: как прокачаться без слива денег. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/samye-deshevye-igry-v-stim/]игры в стим за 1 доллар[/url] Пацанский гайд по поиску качественных игр за копейки и лучшей халяве 2025 года.
Написал: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/samye-deshevye-igry-v-stim/
самые дешевые игры в стиме за 1 рубль
самые дешёвые игры в стиме за 1 рубль
самые дешёвые игры стим
До встречи!
Капельница от алкоголя – является эффективный метод‚ позволяющий помочь в восстановлении после алкогольной зависимости в домашних условиях. Обратившись к к наркологу‚ который приедет к вам‚ вы сможете получить квалифицированную помощь и необходимые медикаменты для облегчения симптомов похмелья. Симптомы запойного состояния могут включать головной боли‚ недомогания и общего недомогания; вызвать нарколога на дом владимир Процесс очистки организма стартует с введения капельницы‚ которая гарантирует достаток жидкости и витаминов‚ что способствует уменьшить симптомы абстиненции. Услуги наркологов в владимире подразумевают индивидуальный подход к пациенту‚ что необходимо для эффективного лечения алкоголизма на дому. Поддержка близких при алкоголизме является важной составляющей в процессе восстановления здоровья после приема алкоголя. Домашняя реабилитация осуществляется с помощью капельниц и медикаментов‚ которые помогают избежать последующие запои и облегчить процесс восстановления. При этом профилактика запоев становится важным аспектом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Estou alucinado com BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que dancam como passistas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BRCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
br77 slot|
Makes sense to me.
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Прочесть всё о… – https://www.konnaservice.cz/exploring-the-beauty-of-mother-nature
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]запой нарколог на дом город краснодар[/url]
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Как это работает — подробно – https://urbanhome.pl/wynajem-mieszkania-przez-firme-odpowiadamy-na-najczestsze-pytania
Игра в города https://1001guru.ru/2025/08/27/igra-v-goroda-ot-klassiki-do-sovremennyh-variaczij/ для всех возрастов. Проверьте знания географии, вспоминайте названия городов и соревнуйтесь с друзьями. Увлекательная логическая игра для тренировки памяти и эрудиции.
All the most important here: https://edicionesdelau.com
Open the latest data here: https://www.greenwichodeum.com
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Открой скрытое – https://www.centrodecirurgiaoral.com.br/siso-sintomas-quando-esta-nascendo
Наркологическая помощь в Раменском в клинике «Возрождение» — это быстрый выезд профильного врача, безопасная детокс-терапия и полноценные программы восстановления без постановки на учёт. Мы работаем 24/7, аккуратно стабилизируем состояние на дому или принимаем в стационаре, подбираем лечение с учётом возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и текущих анализов. Уже при первом обращении координатор уточняет симптомы, оценивает риски, предлагает ближайшее окно выезда и объясняет, как подготовиться к визиту. Наша задача — не временно приглушить симптомы, а выстроить путь к устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациенту контроль над жизнью, при этом сохраняя конфиденциальность каждого шага.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Что скрывают от вас? – https://www.digitel-srl.it/ciao-mondo
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника город краснодар[/url]
The most relevant place is here: https://woodbridgebrewingco.com
Details are waiting for you here: https://sportquantum.com
Only verified facts are here: https://www.levelupacademy.in
Если состояние стремительно ухудшается, ждать опасно: осложнения могут развиваться в течение часов. Немедленная помощь врача-нарколога показана, когда наблюдаются:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-ramenskom/
Важность лечения зависимости: путь к свободе — осознание проблемы и профессиональная помощь — ключевые этапы на пути к выздоровлению. Узнайте, как комплексный подход способствует восстановлению здоровья и возвращению к полноценной жизни. Подробнее: vpolozhenii.com Детальнее – http://www.brokersearch.ru/index.php?option=com_kunena&func=view&catid=19&id=85131
Everything in one place: https://www.lnrprecision.com
Everything you need: https://travel2mv.com
Read the best here: https://playplayfun.com/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://morakot.com.au/6-exercises-that-will-take-your-muay-thai-to-the-next-level
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://ancb.bj/index.php/association-2/oueme.html
В этом исследовании рассмотрены методы лечения зависимостей и их эффективность. Мы проанализируем различные подходы, используемые в реабилитационных центрах, и представим данные о результативности программ. Читатели получат надежные и научно обоснованные сведения о данной проблеме.
Полезно знать – [url=https://pedagog-razvitie.ru/]стратегии саморазвития[/url]
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разрушительное влияние зависимости на жизнь человека. Обсуждаются аспекты, такие как здоровье, отношения и профессиональные достижения. Читатели узнают о необходимости обращения за помощью и о путях к восстановлению.
Полезно знать – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/stati/snotvornye-i-alkogol.html]снотворное таблетки и алкоголь[/url]
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Откройте для себя больше – https://canvasspecial.co.za/professional-photo-printing-with-canvas-2023
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um farol. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de brilho. O servico e confiavel como uma lanterna. garantindo suporte direto e sem escuridao. As transacoes sao simples como uma luz. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura iluminada. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino e uma fogueira de adrenalina para os faroleiros do cassino! Alem disso o site e uma obra-prima de estilo radiante. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
br4bet mines|
Спасение жизни: профессиональное лечение наркотической зависимости — клиника «Призма» предлагает комплексный подход к лечению наркозависимости, включая детоксикацию, психологическую поддержку и реабилитацию. Узнайте больше: milinda.ru Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://mamuli.club/forum/topic/38026/
Je suis accro a Simsinos Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui saute comme un personnage de bande dessinee. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui sautent comme des toons. repond comme un crayon vif. assurant un support de casino immediat et anime. fluisent comme une sonate animee. par moments plus de bonus pour une harmonie dessinee. En fin de compte, Simsinos Casino est un casino en ligne qui anime une symphonie de couleurs pour les fans de symphonies colorees! A noter resonne avec une melodie graphique toon. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
simsinos casino avis|
Услуга нарколога на дому в режиме полной конфиденциальности в владимире – это важная помощь для тех‚ кто сталкивается с проблемой зависимости. Лечение наркомании требует квалифицированной помощи‚ и обращение к врачу на дому обеспечивает конфиденциальность. Специалисты предоставляют анонимную консультацию‚ выявление зависимости и лечебные процедуры на дому. В нашем городе предоставляется психотерапия при зависимости и реабилитационные программы что позволяет восстановить здоровье и возобновить нормальную жизнь. Поддержка семьи и участие близких также имеют важное значение в лечении зависимости. Обращайтесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir019.ru‚ чтобы получить помощь зависимым и начать путь к выздоровлению.
Sou viciado na energia de MarjoSports Casino, oferece uma aventura que marca gol como um penalti perfeito. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como torcidas. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de estrategia. O servico e confiavel como uma rede. com ajuda que marca gol como um penalti. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um gol. porem queria promocoes que driblam a concorrencia. Na real, MarjoSports Casino garante um jogo que vibra como uma torcida para quem curte apostar com estilo esportivo! Por sinal o design e fluido como um contra-ataque. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um gol.
palpites marjosports|
В поисках самых свежих трейлеров фильмов 2026 и трейлеров 2026 на русском? Наш портал — это место, где собираются лучшие трейлеры сериалов 2026. Здесь вы можете смотреть трейлер бесплатно в хорошем качестве, будь то громкая премьера лорд трейлер или долгожданный трейлер 3 сезона вашего любимого сериала. Мы тщательно отбираем видео, чтобы вы могли смотреть трейлеры онлайн без спойлеров и в отличном разрешении. Всю коллекцию вы найдете по ссылке ниже: https://lordtrailer.ru/
News for you – right here: https://fish-pet.com
Hot news is already here: https://sernexuss.com
Everything the brightest here: https://intelicode.com
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Краснодаре проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar12.ru/]narkolog-na-dom krasnodar[/url]
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Более подробно об этом – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/stati/stadii-narkoticheskoj-zavisimosti.html]наркотическая зависимость стадии[/url]
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://multistyle.work/the-10-most-used-maintenance-plans
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Это ещё не всё… – https://estudioteixido.com.ar/portfolio/behavioral-health
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Детали по клику – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/]www.lux-clinic.ru[/url]
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Краснодаре — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar17.ru/]запой нарколог на дом город краснодар[/url]
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://havredepaixong.org/hygiene-menstruelle-quelle-approche-en-contexte-de-crise
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Узнай первым! – [url=https://pedagog-razvitie.ru/]психологическая помощь школьникам[/url]
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar12.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в городе[/url]
Далее проводится сама процедура: при медикаментозном варианте препарат может вводиться внутривенно, внутримышечно или имплантироваться под кожу; при психотерапевтическом — работа проходит в специально оборудованном кабинете, в спокойной атмосфере. После кодирования пациент находится под наблюдением, чтобы исключить осложнения и закрепить эффект. Важно помнить, что соблюдение рекомендаций и поддержка семьи играют решающую роль в сохранении трезвости.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-kolomna6.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Краснодаре врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом город краснодар[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Доступ к полной версии – https://petraackermans.nl/scheiden/business-couching-consulting-template-reviewer-4
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в городе[/url]
Этот текст посвящён сложным аспектам зависимости и её влиянию на жизнь человека. Мы обсудим психологические, физические и социальные последствия зависимого поведения, а также важность своевременного обращения за помощью.
Уникальные данные только сегодня – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/reabilitatsiya-po-metodu-shichko/]лечение алкоголизма по методу шичко[/url]
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: poquer estrategico, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que vale elogio. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Vale experimentar.
savage gear 4play v2 swim & jerk|
Estou alucinado com F12.Bet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um pit stop. O catalogo de jogos e uma pista de emocoes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que derrapam como drifts. Os agentes voam como asas de spoiler. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. O processo e claro e sem freadas. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. No fim das contas, F12.Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os fas de adrenalina supersonica! Por sinal o design e fluido como um pit stop. transformando cada aposta em uma ultrapassagem.
f12 bet casino|
Estou alucinado com MarjoSports Casino, e um cassino online que acelera como um contra-ataque fulminante. Os jogos formam uma quadra de diversao. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que marcam como gols. O servico e confiavel como uma rede. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. O processo e claro e sem impedimentos. mesmo assim mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Em resumo, MarjoSports Casino garante um jogo que vibra como uma torcida para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o visual e uma explosao de quadras. dando vontade de voltar como um craque.
marjosports brasileirГЈo sГ©rie a|
Что входит
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Капельницы и все процедуры проходят на дому или в стационаре, под постоянным наблюдением врача. При тяжёлых состояниях возможно подключение к аппаратной терапии, срочная госпитализация, привлечение кардиолога, психиатра, терапевта.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-lyubercy5.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-lyubercah/
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://pentvars.edu.gh/pentecost-university-welcomes-inaugural-cohort-of-nedmev-and-laser4netzero-scholarship-recipients
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://otzyv-pro.ru/company/krasota-i-zdorove/narkologicheskaya-klinika-chastnaya-skoraya-pomoshch-1-v-mytishchakh
https://vgarderobe.ru/futbolka-s-dlinnymi-rukavami-2-shtuki-klitzeklein-g-147986-91.html
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://praritagroup.com/how-solar-energy-works-from-sunlight-to-electricity
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://elektrostal.spravochnik-rf.ru/meditsinskie-tsentry/952277.html
В Краснодаре решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в городе[/url]
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Наши рекомендации — тут – http://vipjetbet.online/post/34
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://www.bibsclean.sk/?p=154
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Что скрывают от вас? – http://zeltplatze.com/guestbook.html
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://taxipuntacanamacao.com/index.php/2022/07/01/5-most-beautiful-islands-in-asia
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://bobopark.cz/woocommerce-placeholder
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://embotelladoragala.mx/2024/03/20/benefits-of-going-solar-why-switching-to-solar-energy-makes-sense
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Уточнить детали – https://15minutestravel.com/?p=943
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://manhyiapalace.org/asantehene-child-marriage-is-wrong-and-unacceptable
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://birlik-akmola.kz/?p=11493
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://riseas-basketball.com/3width-crossover
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Не упусти шанс – https://gitedouiret.com/gite_raouf_accueil2_gitedouiret-com
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://www.aeeaatletismo.es/2022/09/01/ha-fallecido-jose-maria-garcia-presidente-de-honor-de-la-aeeael-mejor-estadistico-de-nuestra-historia
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. A selecao de titulos e uma correnteza de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. respondendo rapido como uma onda quebrando. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. porem mais giros gratis seriam subaquaticos. Em resumo, Brazino Casino e um recife de emocoes para os amantes de cassinos online! Como extra o site e uma obra-prima de estilo subaquatico. criando uma experiencia de cassino subaquatica.
brazino777 Г© confiГЎvel?|
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://odl-shukatsucafe.com/2021/10/27/2023-3
Sou viciado no codigo de PlayPix Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um hacker. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que processam como servidores. O suporte e um firewall de eficiencia. respondendo veloz como um byte. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. mas mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Em sintese, PlayPix Casino e uma onda de adrenalina digital para os amantes de cassinos online! Adicionalmente o site e uma obra-prima de estilo digital. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura pixelada.
playpix afiliate|
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://crickpicks.com/nz-vs-eng-dream11-prediction-tips-england-tour-of-new-zealand-2024
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://www.lavacapurpura.com/icelands-biggest-volcano-timelapse
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://billbuyscopper.com/lorem-ipsum-dolor-sit-amet
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Откройте для себя больше – https://distillate9.com/product/delta-8-cat-3-distillate
Если пациент находится в остром состоянии — начинается с детоксикации. Это не только капельницы для вывода токсинов и восстановления баланса в организме, но и поддержка работы сердца, печени, почек, купирование тревоги и бессонницы, снятие судорог, коррекция давления. Весь процесс проходит под наблюдением опытного нарколога, который учитывает хронические заболевания, особенности организма, степень интоксикации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-korolev5.ru/]медицинское лечение алкоголизма[/url]
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-dzhinsy-little-big-bc-10172.html
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Получить больше информации – https://josetteguerzoni.com.br/testimonial/teste-4
Приветствую!
Какой игровой смартфон купить в 2025 году. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/deshyovye-igrovye-telefony/]лучшие бюджетные игровые смартфоны 2025[/url] Разбираем топовые модели и делимся секретами правильного выбора.
По ссылке: – https://pro-telefony.ru/deshyovye-igrovye-telefony/
игровые смартфоны 2025 года
лучшие бюджетные игровые смартфоны 2025
лучшие игровые смартфоны до 20000
Бывай!
Топливные карты https://alcomauto.ru для юридических лиц помогут сократить затраты компании и обеспечить полный контроль за автопарком.
Топливные карты https://karta-vezdehod.ru удобный способ экономить на заправках, контролировать расходы и получать прозрачную отчетность.
Топливные карты https://auto-nv.ru для юр лиц — это надежный инструмент учета топлива, скидки на АЗС и удобная онлайн-отчетность.
В последние годы бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве стали набирать популярность . Это связано с растущей потребностью в правовой помощи . Профессионалы в области юриспруденции предлагают свои услуги на безвозмездной основе.
Важным аспектом бесплатной юридической консультации является доступность . Каждый человек может получить советы и рекомендации по различным вопросам . Это способствует уменьшению случаев юридических конфликтов.
Процедура получения юридической помощи абсолютно проста. Чаще всего, чтобы получить помощь, нужно просто записаться к юристу. Некоторые юристы проводят консультации дистанционно.
В заключение, бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве представляют собой значимую помощь для населения . Правовая поддержка способствует повышению правосознания граждан . Не сомневайтесь в том, что бесплатная консультация может действительно помочь вам.
читайте далее [url=https://edukacja.ordoiuris.pl/blog/index.php?entryid=83812/#читайте-далее]читайте далее[/url].
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://entrans.energy/appearance-guide
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Получить полную информацию – https://www.tramhuongxuquang.vn/tram-huong/phan-biet-ky-nam-va-tram-huong
https://rainbetaustralia.com/
Топливная карта https://autobsn.ru для юридических лиц дает доступ к выгодным тарифам, снижает расходы и делает контроль проще.
Что такое Agile https://agile-metod.ru и как его внедрить? Подробные статьи о гибких методологиях, инструментах и практиках. Scrum, Kanban и Lean — всё о современном управлении проектами.
Что такое CPI https://cost-per-install.ru в маркетинге? Полное объяснение показателя Cost Per Install: как он работает, зачем нужен бизнесу, примеры расчётов и советы по использованию метрики в рекламе приложений.
Me enredei no algoritmo de PlayPix Casino, e uma explosao de diversao que carrega como um buffer. A colecao e um codigo de entretenimento. com slots tematicos de mundos digitais. O suporte e um codigo preciso. garantindo suporte direto e sem lag. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. as vezes queria promocoes que processam como CPUs. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino e um cassino online que e uma matriz de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o site e uma obra-prima de estilo digital. criando uma experiencia de cassino cibernetica.
playpix saque pendente|
Estou alucinado com Brazino Casino, explode com uma vibe aquatica eletrizante. Tem um tsunami de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como aguas cristalinas. O suporte e uma concha de eficiencia. respondendo rapido como uma onda quebrando. O processo e claro e sem tempestades. entretanto queria promocoes que explodem como geiseres. Resumindo, Brazino Casino e uma onda de adrenalina para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus a plataforma reluz com um visual oceanico. amplificando o jogo com vibracao aquatica.
brazino777 review|
Если у пациента выраженная интоксикация, судороги, хронические заболевания, лучше выбрать стационарный формат. Здесь гарантированы круглосуточное медицинское наблюдение, возможность быстрого реагирования на любые изменения состояния, консультации узких специалистов. Для пациентов созданы комфортные условия проживания, организовано индивидуальное питание, действует поддержка психолога.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk5.ru/srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-noginske/
Привет!
iPhone 15 и 16 в рассрочку: где взять дешевле и на каких условиях. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/rassrochka-ajfon/]айфон 13 рассрочка[/url] Разбор всех актуальных предложений от А1, Билайн и банков.
Здесь подробней: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/rassrochka-ajfon/
айфон 15 про рассрочка
Удачи!
Онлайн-казино Vavada считается одним из популярных проектов.
Акции и промокоды дают шанс начать игру без вложений.
Соревнования и события увеличивают азарт.
Подборка игр обновляются регулярно.
Старт занимает пару минут, поэтому бонусы доступны сразу.
Узнай подробности прямо здесь: https://roseforvb.com
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Жми сюда — получишь ответ – https://panache-tech.com/2008/06/11/gallery-post
Köpa receptfritt – Vill du köpa medicin utan recept? Upptäck hur enkelt det kan vara att beställa säkert online, med snabb leverans och anonymitet. Få tillgång till effektiva produkter som kan förbättra din hälsa utan krångel hos läkaren.
https://mykredit-online.ru/
В Краснодаре решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого город краснодар[/url]
В некоторых случаях медлить нельзя ни минуты. Запойное состояние чревато обезвоживанием, судорогами, инфарктом, психозом. Если у пациента наблюдаются выраженные физические и психические нарушения, самостоятельное «пережидание» может закончиться тяжёлыми осложнениями.Поводом немедленно обратиться к специалистам становится:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk5.ru
Процесс лечения алкоголизма в Твери строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациентам постепенно проходить все стадии выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-tver-staczionar/
Сочетание этих направлений позволяет комплексно воздействовать на проблему зависимости и минимизировать риск рецидива.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника пермь[/url]
накрутка премиум подписчиков тг
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Терапия в клинике проводится системно и поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать состояние пациента и добиваться устойчивых улучшений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в твери[/url]
Распознать необходимость лечения просто: достаточно внимательно отнестись к тревожным признакам. Вот лишь некоторые ситуации, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику становится жизненно важным:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha5.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Чем раньше начата профессиональная детоксикация, тем выше шанс восстановить здоровье и избежать критических осложнений. В клинике «Решение+» всегда готовы оперативно принять вызов и отправить бригаду наркологов на дом либо организовать транспортировку в стационар.
Углубиться в тему – http://
Процесс лечения алкоголизма в Твери строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациентам постепенно проходить все стадии выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма тверь[/url]
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
J’adore le voile de Grandz Casino, on dirait un theatre de frissons evanescents. La selection du casino est une danse de plaisirs. proposant des slots de casino a theme theatral. repond comme un fantome gracieux. avec une aide qui danse comme une ombre. arrivent comme un concerto voile. quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient danser. Dans l’ensemble, Grandz Casino offre une experience de casino etheree pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! En plus resonne avec une melodie graphique spectrale. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus etheree.
promotion grandz race|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me ganhou de verdade. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao super animadas, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos funcionaram redondinho. O atendimento no chat foi muito atencioso, o que ja me deixou tranquilo. As retiradas foram eficientes de verdade, inclusive testei cripto e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Na minha visao, o Bingoemcasa vale demais a pena. Ja me sinto parte da comunidade
bingoemcasa .net|
buy xtc prague buy cocaine in telegram
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг бесплатно
spiusailla no deposit bonus code, blackjack online American Casino Online Play
australia and new gambling legislation united states, or
online bingo for prizes in uk
promo code for 1xbet sri lanka 1xbet Bangladesh Promo Code: Unlock Exclusive Bonuses and Enhanced Betting Opportunities In the vibrant landscape of online betting in Bangladesh, 1xbet stands out as a leading platform, offering a diverse range of sporting events, casino games, and other exciting opportunities. To amplify the thrill and maximize your winning potential, 1xbet provides a variety of promo codes tailored specifically for Bangladeshi players. These codes unlock exclusive bonuses, free bets, and enhanced odds, giving you a significant advantage in your betting journey. Types of 1xbet Promo Codes Available in Bangladesh: 1xbet Promo Code Bangladesh: This is a general promo code that can be used by both new and existing players in Bangladesh. It typically unlocks a welcome bonus, deposit bonus, or free bet. 1xbet Promo Code Registration Bangladesh: This code is exclusively for new players registering on the 1xbet platform in Bangladesh. It offers an enhanced welcome bonus to kickstart their betting adventure. 1xbet Free Promo Code Bangladesh: This code grants Bangladeshi players a free bet, allowing them to place a wager without risking their own funds. 1xbet Free Bet Promo Code Bangladesh: Similar to the previous code, this one provides a free bet opportunity, often tied to specific sporting events or promotions. 1xbet Bonus Promo Code Bangladesh: This code unlocks a bonus on your deposit, increasing your betting balance and giving you more chances to win. Promo Code for 1xbet Bangladesh Today: This code is a time-sensitive offer, valid only for a specific day. It usually provides a daily bonus, free bet, or enhanced odds on selected events. 1xbet Promo Code for Registration Bangladesh: This code is another registration-specific code, offering a larger welcome bonus than the standard registration bonus. How to Find and Use 1xbet Promo Codes in Bangladesh: 1xbet promo codes are widely available through various channels, including: Official 1xbet Website: Regularly check the 1xbet website for the latest promo code offers. Affiliate Websites: Many affiliate websites dedicated to online betting provide exclusive 1xbet promo codes for Bangladeshi players. Social Media: Follow 1xbet’s official social media accounts to stay updated on new promo code releases. Email Newsletters: Subscribe to 1xbet’s email newsletters to receive promo codes directly in your inbox. To use a promo code, simply enter it in the designated field during registration or when making a deposit. The bonus or free bet will be automatically credited to your account. Maximize Your Winnings with 1xbet Promo Codes: By utilizing 1xbet promo codes, Bangladeshi players can significantly enhance their betting experience and increase their chances of winning. Whether you’re a seasoned bettor or a newcomer to the world of online betting, these codes offer a valuable advantage. So, keep an eye out for the latest 1xbet promo codes and unlock a world of exclusive bonuses and thrilling betting opportunities.
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-omske/
code promo 1xbet 2026 mr code promo 1xbet cote d’ivoire Le monde des paris sportifs en ligne est en constante evolution, et 1xbet s’est etabli comme un leader mondial, offrant une plateforme complete et diversifiee aux parieurs du monde entier. En Cote d’Ivoire, l’enthousiasme pour les paris sportifs est palpable, et 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire propose une gamme allechante de promotions pour ameliorer l’experience de pari de ses utilisateurs. Au c?ur de ces promotions se trouvent les codes promotionnels, des cles magiques qui debloquent des bonus exclusifs et des opportunites de pari ameliorees. Qu’est-ce qu’un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire est une combinaison unique de lettres et de chiffres qui peuvent etre entres lors de l’inscription ou du depot pour activer un bonus specifique. Ces bonus peuvent inclure: Bonus de bienvenue: Un bonus offert aux nouveaux utilisateurs lors de leur premier depot. Bonus de depot: Un bonus accorde sur les depots ulterieurs. Paris gratuits: La possibilite de placer un pari sans risquer son propre argent. Cotes ameliorees: Des cotes plus elevees sur certains evenements sportifs. Ou trouver les codes promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Les codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire sont disponibles via plusieurs canaux, notamment: Le site Web officiel de 1xbet: Consultez regulierement le site Web de 1xbet pour les dernieres offres. Les sites Web affilies: De nombreux sites Web affilies proposent des codes promotionnels exclusifs pour les joueurs ivoiriens. Les reseaux sociaux: Suivez les comptes de medias sociaux officiels de 1xbet pour rester informe des nouvelles versions de code promotionnel. Les newsletters par e-mail: Abonnez-vous aux newsletters par e-mail de 1xbet pour recevoir les codes promotionnels directement dans votre boite de reception. L’utilisation efficace des codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire peut considerablement augmenter vos chances de gagner et rendre votre experience de pari plus agreable. Gardez un ?il sur les derniers codes et profitez des avantages qu’ils offrent.
вахтовая работа Россия Токарь вахтовая работа – это работа токарем вахтовым методом. Она предполагает выполнение токарных работ на удаленном объекте в течение вахты. Токарь вахтовой работы должен иметь высокую квалификацию, опыт работы и знать современные токарные станки.
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/
как набрать подписчиков в тг канал
В клинике применяются только доказательные методы, эффективность которых подтверждена практикой. Медицинское и психологическое воздействие дополняют друг друга, формируя комплексный эффект.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-czena
Наркологическая клиника в Твери оказывает квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основной принцип работы специалистов заключается в комплексном подходе, включающем медицинское лечение, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет достигать стойкой ремиссии и предотвращать рецидивы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в твери[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Перми включает использование комплекса медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методик. Они помогают не только снять симптомы интоксикации, но и стабилизировать эмоциональное состояние.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-perm/
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от различных видов зависимости. Основой успешного лечения является комплексный подход, который включает тщательную диагностику, медикаментозное сопровождение, психологическую поддержку и реабилитационные программы. В «АльфаМед» применяются передовые технологии и индивидуальные методики, направленные на восстановление здоровья и предупреждение рецидивов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В процессе лечения используются проверенные методики, которые в комплексе обеспечивают положительный эффект и снижают риск рецидива.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в стационаре омск[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Зависимость от алкоголя или наркотиков — серьёзная проблема, которая постепенно разрушает жизнь, подрывает здоровье, нарушает семейные отношения и ведёт к социальной изоляции. Попытки самостоятельно справиться с заболеванием редко приводят к успеху и зачастую только усугубляют ситуацию. Важно не терять время и обращаться за профессиональной помощью. В наркологической клинике «Наркосфера» в Балашихе пациентов ждёт современное оборудование, команда опытных специалистов, индивидуальный подход и абсолютная анонимность.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha5.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-balashihe/
https://vk.com/wf_design_wf Анимация для трека: Визуальное сопровождение музыкального трека, представляющее собой движущиеся изображения, созданные с использованием анимационных техник. Анимация может быть абстрактной, отражающей ритм и настроение музыки, или повествовательной, рассказывающей историю, связанную с текстом песни. Анимация для трека помогает создать более глубокий эмоциональный отклик у слушателя, выделить трек на фоне других и повысить его виральность в социальных сетях. Анимация может включать в себя как простые визуальные эффекты, так и сложные 3D-модели и персонажей.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в городе[/url]
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника омск[/url]
Для повышения эффективности терапии применяются физиотерапевтические процедуры и витаминные комплексы, которые ускоряют восстановление и повышают сопротивляемость организма стрессам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь омск[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
В зависимости от клинической картины и предпочтений возможны следующие виды кодирования:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ehlektrostal6.ru/]anonimnoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в перми[/url]
Такой подход позволяет закрепить результаты и поддерживать стабильное состояние здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/[/url]
promo code 1xbet bangladesh 1xbet Bangladesh Promo Code: Unlock Exclusive Bonuses and Enhanced Betting Opportunities In the vibrant landscape of online betting in Bangladesh, 1xbet stands out as a leading platform, offering a diverse range of sporting events, casino games, and other exciting opportunities. To amplify the thrill and maximize your winning potential, 1xbet provides a variety of promo codes tailored specifically for Bangladeshi players. These codes unlock exclusive bonuses, free bets, and enhanced odds, giving you a significant advantage in your betting journey. Types of 1xbet Promo Codes Available in Bangladesh: 1xbet Promo Code Bangladesh: This is a general promo code that can be used by both new and existing players in Bangladesh. It typically unlocks a welcome bonus, deposit bonus, or free bet. 1xbet Promo Code Registration Bangladesh: This code is exclusively for new players registering on the 1xbet platform in Bangladesh. It offers an enhanced welcome bonus to kickstart their betting adventure. 1xbet Free Promo Code Bangladesh: This code grants Bangladeshi players a free bet, allowing them to place a wager without risking their own funds. 1xbet Free Bet Promo Code Bangladesh: Similar to the previous code, this one provides a free bet opportunity, often tied to specific sporting events or promotions. 1xbet Bonus Promo Code Bangladesh: This code unlocks a bonus on your deposit, increasing your betting balance and giving you more chances to win. Promo Code for 1xbet Bangladesh Today: This code is a time-sensitive offer, valid only for a specific day. It usually provides a daily bonus, free bet, or enhanced odds on selected events. 1xbet Promo Code for Registration Bangladesh: This code is another registration-specific code, offering a larger welcome bonus than the standard registration bonus. How to Find and Use 1xbet Promo Codes in Bangladesh: 1xbet promo codes are widely available through various channels, including: Official 1xbet Website: Regularly check the 1xbet website for the latest promo code offers. Affiliate Websites: Many affiliate websites dedicated to online betting provide exclusive 1xbet promo codes for Bangladeshi players. Social Media: Follow 1xbet’s official social media accounts to stay updated on new promo code releases. Email Newsletters: Subscribe to 1xbet’s email newsletters to receive promo codes directly in your inbox. To use a promo code, simply enter it in the designated field during registration or when making a deposit. The bonus or free bet will be automatically credited to your account. Maximize Your Winnings with 1xbet Promo Codes: By utilizing 1xbet promo codes, Bangladeshi players can significantly enhance their betting experience and increase their chances of winning. Whether you’re a seasoned bettor or a newcomer to the world of online betting, these codes offer a valuable advantage. So, keep an eye out for the latest 1xbet promo codes and unlock a world of exclusive bonuses and thrilling betting opportunities.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Краснодаре проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом в городе краснодаре[/url]
интересные кашпо для цветов [url=http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru]интересные кашпо для цветов[/url] .
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Краснодаре приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Твери оказывает квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основной принцип работы специалистов заключается в комплексном подходе, включающем медицинское лечение, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет достигать стойкой ремиссии и предотвращать рецидивы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru
J’adore le voile de Grandz Casino, on dirait un theatre de frissons evanescents. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une scene de delices. avec des slots qui effleurent comme des voiles. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et precise. repondant en un souffle spectral. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans voile. mais des tours gratuits pour une melodie ephemere. Au final, Grandz Casino enchante avec une rhapsodie de jeux pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline voilee du casino! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note voilee. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie d’ombres.
buda and grandz|
Galera, vim dividir com voces sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um ambiente divertido que lembra um barzinho cheio de risadas. As salas de bingo sao super animadas, e ainda testei alguns caca-niqueis modernos, todos foram bem estaveis. O atendimento no chat foi muito atencioso, o que ja me deixou bem a vontade. As retiradas foram eficientes de verdade, inclusive testei cartao e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que faltam mais promocoes, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. No geral, o Bingoemcasa virou parada obrigatoria. Recomendo pra quem curte diversao online
bingoemcasa codigo promocional|
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
creer code promo 1xbet code promo 1xbet cote d’ivoire Le monde des paris sportifs en ligne est en constante evolution, et 1xbet s’est etabli comme un leader mondial, offrant une plateforme complete et diversifiee aux parieurs du monde entier. En Cote d’Ivoire, l’enthousiasme pour les paris sportifs est palpable, et 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire propose une gamme allechante de promotions pour ameliorer l’experience de pari de ses utilisateurs. Au c?ur de ces promotions se trouvent les codes promotionnels, des cles magiques qui debloquent des bonus exclusifs et des opportunites de pari ameliorees. Qu’est-ce qu’un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire est une combinaison unique de lettres et de chiffres qui peuvent etre entres lors de l’inscription ou du depot pour activer un bonus specifique. Ces bonus peuvent inclure: Bonus de bienvenue: Un bonus offert aux nouveaux utilisateurs lors de leur premier depot. Bonus de depot: Un bonus accorde sur les depots ulterieurs. Paris gratuits: La possibilite de placer un pari sans risquer son propre argent. Cotes ameliorees: Des cotes plus elevees sur certains evenements sportifs. Ou trouver les codes promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Les codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire sont disponibles via plusieurs canaux, notamment: Le site Web officiel de 1xbet: Consultez regulierement le site Web de 1xbet pour les dernieres offres. Les sites Web affilies: De nombreux sites Web affilies proposent des codes promotionnels exclusifs pour les joueurs ivoiriens. Les reseaux sociaux: Suivez les comptes de medias sociaux officiels de 1xbet pour rester informe des nouvelles versions de code promotionnel. Les newsletters par e-mail: Abonnez-vous aux newsletters par e-mail de 1xbet pour recevoir les codes promotionnels directement dans votre boite de reception. L’utilisation efficace des codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire peut considerablement augmenter vos chances de gagner et rendre votre experience de pari plus agreable. Gardez un ?il sur les derniers codes et profitez des avantages qu’ils offrent.
Je suis fou de Casinia Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un roi. vibre avec un rempart de jeux varies. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un tournoi. est un virtuose de la noblesse. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans trahison. par moments plus de bonus pour une harmonie chevaleresque. A la fin, Casinia Casino enchante avec une rhapsodie de jeux pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! En bonus resonne avec une melodie graphique legendaire. facilite une experience de casino royale.
casinia casino free spins|
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
https://www.praktijk10000.nl/home/attachment/praktijk10000-boek
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре пермь[/url]
вахта официальное оформление Вахтовая работа с проживанием – это работа вахтовым методом, при которой работникам предоставляется жилье на время вахты. Проживание может быть организовано в вахтовых поселках, общежитиях или других типах жилых помещений. Вахтовая работа с проживанием позволяет работникам не тратить время и деньги на дорогу до места работы и обеспечивает комфортные условия для проживания и отдыха.
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Такой подход позволяет закрепить результаты и поддерживать стабильное состояние здоровья.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-v-permi/
Каждый этап имеет важное значение и обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект от терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма в твери[/url]
Сочетание этих методов позволяет добиваться стойкой ремиссии и укреплять здоровье пациентов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма тверь[/url]
Детоксикация может проводиться как по «мягкой», так и по ускоренной схеме. Используются инфузионные растворы, препараты для коррекции давления, поддержания работы сердца, печени и почек, противосудорожные и седативные средства. Все препараты подбираются строго индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента. Капельница длится от двух до четырёх часов. На протяжении всей процедуры нарколог контролирует динамику, корректирует дозировки и следит за состоянием. После завершения лечения врач обязательно выдаёт подробные рекомендации по питанию, приёму витаминов и последующему наблюдению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk5.ru
После обращения по телефону или через сайт диспетчер уточняет адрес и состояние пациента. В экстренных случаях команда врачей может прибыть уже в течение 60 минут, обычно — за 1–2 часа. На месте проводится первичный осмотр: проверяются жизненные показатели, уточняется история употребления, сопутствующие заболевания. Врач определяет наиболее безопасную и эффективную тактику, исходя из возраста, состояния здоровья и длительности запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk5.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-noginske
I think that may be an interesting element, it made me assume a bit. Thanks for sparking my considering cap. On occasion I get so much in a rut that I simply really feel like a record.
buy drugs in prague buy coke in telegram
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Только факты! – https://ustilimka.ru/ispolzuya-silu-koda-borba-s-alkogolizmom-v-moskve
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Углубиться в тему – https://izbavlenie-ot-zavisimostey.feech.org/moskva/org/4290245
Читатели получат представление о том, как современные технологии влияют на развитие медицины. Обсуждаются новые методы лечения, персонализированный подход и роль цифровых решений в повышении качества медицинских услуг.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://otzyv-pro.ru/company/krasota-i-zdorove/narkologicheskaya-klinika-chastnaya-skoraya-pomoshch-1-v-serpukhove
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru
Сочетание этих методов позволяет добиваться стойкой ремиссии и укреплять здоровье пациентов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма в твери[/url]
https://mp-digital.ru/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://smart-apteka.kz/portfolio/portfolio-11
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://ahaaninternational.com/2014/10/10/youtube-vimeo-videos
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/171056105/detail.aspx
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://aalstmaritiem.nl/this-is-a-nice-post
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Перейти к полной версии – https://firstfoundationschools.com/product/tied-pendant-light
Sou louco pela ressonancia de JonBet Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um sino ancestral. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um sino. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e um reverb preciso. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. mas mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura sonora. Na real, JonBet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus a plataforma vibra com um visual ressonante. fazendo o cassino ecoar como um sino.
jonbet confiavel|
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Читать далее > – https://aoba-nekosora.com/2022/01/14/hello-world
Je suis accro a Boomerang Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino circulaire. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une courbe de delices. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui reviennent comme un boomerang. est un virtuose du cercle. resonnant comme une boucle parfaite. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un retour boomerang. tout de meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui bouclent comme un boomerang. En somme, Boomerang Casino resonne comme un concerto de plaisir pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline boomerang du casino! Bonus offre un orchestre de couleurs boomerang. cadence l’aventure avec une rhapsodie de ricochets.
boomerang casino verifica|
Me enredei no loop de XPBet Casino, oferece uma aventura que flui como um loop sem fim. A colecao e um ciclo de entretenimento. oferecendo lives que explodem como vortices. O suporte e um loop preciso. oferecendo respostas claras como uma roda. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma roda. mas queria promocoes que fluem como redemoinhos. Ao final, XPBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro ciclo para os cacadores de vitorias eternas! E mais o design e fluido como um redemoinho. dando vontade de voltar como um ciclo.
44 xp bet|
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Продолжить изучение – http://shadowpuppeteer.com/in-loving-memory-of-jory-prum
Estou alucinado com DonaldBet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um mestre de cerimonias. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como malabares. oferecendo lives que explodem como fogos de artificio. O atendimento e solido como uma lona. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, DonaldBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro espetaculo para quem curte apostar com estilo circense! E mais o design e fluido como uma acrobacia. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um holofote.
donaldbet reclame aqui|
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Уникальные данные только сегодня – https://www.bowlingverenigingvolendam.nl/?p=1228
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Детальнее – https://store.ulka.tv/4k-ulka-tv-android-box-is-now-available-at-discounted-price-of-inr1700
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Доступ к полной версии – https://www.wakeup-radio.com/qtvideo/pon-pon-girl
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Смотрите также… – https://colmartropicale.com.my/make-sure-you-read-this-before
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://noodlebowltbay.com/menus/apple-smoked-chicken-with-white-bbq-sauce
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Читать далее > – https://www.csautoslalom.cz/zvlastni-ustanoveni-k-prvnimu-zavodu-sezony-dlha
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://frrressh.in/blog/socks-size-chart-india
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://pelias.nl/how-to-pick-the-right-mutual-fund-for-you
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Продолжить чтение – https://meykhooneh.com/what-is-wine
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Детали по клику – https://engagecleveland.org/best-clubs-in-cleveland
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.aliadamsmh.com/uncategorized/hello-world
Добрый день!
Мужская кухня: готовим яйца на все случаи жизни. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-svarit-yajczo/]как сварить яйцо в микроволновке[/url] Простые способы, которые работают всегда и везде.
Читай тут: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-svarit-yajczo/
как сварить яйцо
Удачи!
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Перейти к полной версии – https://www.gironaevidenceweek.com/es/espacios/l/1010-hotel-carlemany-girona.html
Графитовые и угольные щетки для электроинструмента. Большой выбор, надёжность и долговечность. Подходят для дрелей, болгарок, перфораторов и другого оборудования.
Грязевик абонентский Изолирующее фланцевое соединение двухфланцевое – служит для электрической изоляции участков трубопровода, предотвращает протекание блуждающих токов и электрохимической коррозии.
https://t.me/s/spokoino4me Психолог РПП – это специалист, который понимает уникальные проблемы, связанные с расстройствами пищевого поведения. Он поможет вам осознать причины вашей зависимости от еды, восстановить здоровое отношение к своему телу и научиться контролировать свои эмоции. Это путь к выздоровлению и гармонии с собой.
Купить реплику часов Ролекс Качественные реплики брендов – это разумный выбор для тех, кто ценит моду и не готов переплачивать за лейбл. Они позволяют выглядеть стильно и современно, не разоряя свой бюджет.
Нужны двери? Вектордорс Широкий ассортимент межкомнатных дверей от Вектордорс. У нас вы найдете модели на любой вкус: от классических до современных дизайнерских решений. Выбор межкомнатных дверей — важный этап обустройства помещения. Правильно подобранные двери не только украсят интерьер, но и обеспечат комфорт и функциональность на долгие годы.
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг бесплатно
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Изучите внимательнее – https://filhotedepug.com.br/ola-mundo
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://www.neuromed.cl/neuralgia-del-trigemino-2
Je suis totalement pixelise par RollBit Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un defilement. est une structure de sensations qui enchante. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui deroulent comme un flux. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et precise. repondant en un flash pixelise. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un deroulement. neanmoins plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait cubique. En somme, RollBit Casino resonne comme un concerto de plaisir pour les codeurs du casino! Ajoutons la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note pixelisee. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus pixelisee.
rollbit self exclusion|
Sou louco pela roda de XPBet Casino, parece um vortice de adrenalina giratoria. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um giro. oferecendo lives que explodem como vortices. O suporte e um loop preciso. assegurando apoio sem interrupcoes. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. ocasionalmente mais bonus regulares seriam ciclicos. Em sintese, XPBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro ciclo para os fas de adrenalina em loop! E mais o design e um espetaculo visual de vortice. criando uma experiencia de cassino ciclica.
xp bet codigo promocional|
Джинсы мужские широкие Джинсы мужские широкие: Широкие мужские джинсы – это смелый выбор для тех, кто стремится выделиться из толпы и подчеркнуть свою индивидуальность. Этот фасон, вдохновленный уличной модой и культурой скейтбординга, предлагает максимальную свободу движений и непринужденный стиль. Широкие джинсы отлично сочетаются с массивными кроссовками, футболками оверсайз и худи, создавая расслабленный и запоминающийся образ. Важно помнить о балансе пропорций: чтобы широкие джинсы смотрелись гармонично, верхняя часть наряда должна быть более облегающей или укороченной. Экспериментируйте с цветами и текстурами, чтобы найти свой уникальный стиль. Не бойтесь сочетать широкие джинсы с неожиданными элементами гардероба, такими как классические пиджаки или строгие рубашки, чтобы создать эффектный контраст. Широкие джинсы – это не просто одежда, это заявление о вашей уверенности и готовности к экспериментам.
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://www.gironaevidenceweek.com/en/artists/l/1309-barbosa-isabel.html
нейропсихолог в москве Логопед-дефектолог в Москве: Логопед-дефектолог – это специалист, обладающий знаниями и навыками как логопеда, так и дефектолога. В Москве логопеды-дефектологи работают с детьми и взрослыми, имеющими сложные нарушения развития, включающие в себя речевые нарушения, а также нарушения интеллекта, познавательной деятельности, поведения и эмоциональной сферы. Логопед-дефектолог проводит комплексную диагностику, оценивающую уровень развития речи, познавательных процессов, моторики и социальной адаптации. На основе результатов диагностики разрабатывается индивидуальная программа коррекции, учитывающая все особенности развития пациента. Логопеды-дефектологи используют специальные методики и приемы, направленные на развитие речи, мышления, внимания, памяти, моторики и других важных функций, а также на формирование навыков самообслуживания, социальной адаптации и подготовки к обучению. Они работают в тесном сотрудничестве с родителями и другими специалистами, участвующими в реабилитации пациента, чтобы обеспечить комплексный и эффективный подход к коррекции нарушений развития.
Adoro a energia de DonaldBet Casino, parece um espetaculo de adrenalina colorida. A colecao e um espetaculo de entretenimento. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de circo. O suporte e um mestre de cerimonias. assegurando apoio sem tropecos. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma lona. entretanto queria mais promocoes que brilham como holofotes. Ao final, DonaldBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo circense! Vale dizer a plataforma reluz com um visual circense. dando vontade de voltar como um trapezista.
cupom donaldbet|
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Перейти к полной версии – https://theaiminstitute.com/innovation/vitality-index-improvement-time-for-two-new-innovation-metrics
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Читать далее > – https://englishbasics.net/hair-or-hairs
ксфейл бонусные промокоды
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Смотри, что ещё есть – http://cgi2.sun-inet.or.jp/~a-kira/aska.cgi
психическое здоровье Психолог для всех – это универсальный специалист, готовый оказать помощь в решении самых разных проблем. От повышения самооценки и борьбы со стрессом до улучшения отношений с близкими и преодоления конфликтов. Психолог для всех – это ваш надежный советчик и поддержка в любой жизненной ситуации.
купить диплом в красноярске [url=www.rudik-diplom2.ru/]купить диплом в красноярске[/url] .
бот для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм канале
купить диплом в первоуральске [url=http://rudik-diplom3.ru/]http://rudik-diplom3.ru/[/url] .
продажа щебня оптом отсев гранитный доставка
Качественные реплики брендов Реплики часов для женщин – это прекрасный подарок себе или близкому человеку. Они подчеркнут женственность, элегантность и хороший вкус.
купить диплом в хасавюрте [url=rudik-diplom9.ru]купить диплом в хасавюрте[/url] .
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в городе[/url]
накрутить подписчиков в тг
I’m impressed, I need to say. Really rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both educational and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head.
CPL (Cost Per Lead) https://cost-per-lead1.ru ключевая метрика рекламы. Узнайте, что это, как правильно рассчитывать стоимость лида, где применяется и как помогает оценить эффективность кампаний.
Здравствуйте!
Когда таблетки нужны, а когда можно обойтись психотерапией. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/depressiya-chto-delat/]депрессия что делать[/url] Разбираем все методы борьбы с депрессией по полочкам.
Переходи: – https://zhit-legche.ru/depressiya-chto-delat/
депрессия что делать
я в депрессии
что делать если у меня депрессия
Бывай!
Хай!
Носимые устройства 2025: разбираем популярные модели по полочкам. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/smart-chasy-ili-fitnes-braslet/]купить фитнес часы[/url] От бюджетных вариантов до премиальных решений с NFC и GPS.
Переходи: – https://pro-telefony.ru/smart-chasy-ili-fitnes-braslet/
фитнес часы xiaomi
купить фитнес часы
смарт часы или фитнес браслет
Будь здоров!
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Краснодаре врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом город краснодар[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм платно
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Прочесть всё о… – https://www.szi.gov.zm/?attachment_id=32
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://trunkthunderlithium.com/?p=8
Интернет-маркетинг https://internet-marketing1.ru SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, email-рассылки и аналитика. Статьи, советы и инструменты для бизнеса, которые помогают привлекать клиентов и увеличивать продажи онлайн.
Сочетание перечисленных направлений обеспечивает полноту помощи и позволяет выстроить предсказуемый маршрут лечения с понятными целями на каждом этапе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в луганске[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Изучите внимательнее – https://hoteldemontaulbain.fr/en/welcome-to-the-hotel-of-montaulbain-to-verdun/facebook-icon-preview-1-400×400
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de 7BitCasino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. En resume, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino no deposit codes|
Je trouve absolument sensationnel BetFury Casino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, comprenant des jeux originaux comme Plinko et Crash avec un RTP jusqu’a 99,28 %. Le service client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Pour conclure, BetFury Casino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec modernite et elegance, ce qui renforce l’immersion.
dice calculator betfury|
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, ca donne une energie de jeu demente. La gamme est une vraie pepite, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Les agents sont rapides comme des fusees, avec une aide qui dechire tout. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, des fois plus de tours gratos ca serait ouf. Dans le fond, Gamdom est un spot a ne pas louper pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Et puis le site est une tuerie graphique, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
gamdom logo|
Интернет-маркетинг https://yandex-reklama2.ru для компаний и специалистов: SEO, SMM, контекстная реклама и email. Советы по выбору стратегий, разбор ошибок и методы повышения эффективности.
В клинике применяются современные методики, основанные на принципах доказательной медицины. Каждое направление терапии подбирается с учетом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и психологических особенностей. Такой подход обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника донецк[/url]
Комбинирование методов позволяет одновременно решать задачи стабилизации, профилактики и возвращения к повседневной активности.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-lugansk
накрутка активных подписчиков в телеграм канал
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru
Been checking out Tiger787 lately and it’s actually not bad. Their game selection is pretty decent – spent some time on slots like ‘Book of Wild’ and ‘Coin Win: Hold The Spin.’ The คาสิโน site runs smoothly, which is more than I can say for some other places I’ve tried.
Каждый этап имеет ключевое значение и обеспечивает устойчивость результата.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Алгоритм в клинической практике выстроен поэтапно: от первичной оценки до планирования реабилитационного маршрута. Последовательность вмешательств обеспечивает предсказуемую динамику и прозрачную коммуникацию с пациентом и его близкими.
Узнать больше – http://
Вывод из запоя направлен не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на комплексное восстановление организма. Работа специалистов позволяет стабилизировать состояние и создать условия для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tver0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя тверь[/url]
Переход между этапами определяется клиническими критериями эффективности и переносимости, а также динамикой поведения в повседневной среде.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма луганск[/url]
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/[/url]
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru
накрутить подписчиков в тг
накрутка подписчиков в тг живых активных
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Изучите внимательнее – https://www.arteinox.net/2021/07/26/hello-world
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. Globalement, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le site est concu avec style et modernite, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino bonus code|
Ich bin suchtig nach King Billy Casino, es pulsiert mit einer koniglichen Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein furstlicher Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy casino no deposit bonus codes 2020|
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм
Je suis totalement conquis par BetFury Casino, ca procure une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement epoustouflante, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Les agents sont toujours professionnels et efficaces, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. Globalement, BetFury Casino offre une experience securisee et equitable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, ajoute une touche de sophistication a l’experience.
bfg betfury|
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, il propose une aventure qui dechire. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, offrant des machines a sous ultra-cool. Les agents sont rapides comme des fusees, offrant des reponses qui petent. Le processus est clean et sans prise de tete, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos qui defoncent. En gros, Gamdom c’est du lourd a tester direct pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis le design est une bombe visuelle, facilite le delire total.
gamdom wikipedia|
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Краснодаре проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в краснодаре[/url]
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Краснодаре проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту проходить все стадии восстановления в безопасном и контролируемом режиме.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма в донце[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Луганске организуется по принципам доказательной медицины и включает медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную компоненты. Цель — безопасно снять острые проявления заболевания, стабилизировать соматическое состояние, снизить тягу и закрепить новые модели поведения. Индивидуальные планы формируются с учётом стадии расстройства, сопутствующих заболеваний, предшествующего опыта лечения и уровня семейной поддержки.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/lugansk-kodirovka-ot-alkogolya/
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Уникальные данные только сегодня – https://zooplius.lt/kaip-issirinkti-kraika-savo-katei-koki-rinktis
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Заходи — там интересно – https://www.aacaninecountryclub.com
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Полезно знать – https://komigang.nu/hej-verden
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://jassaraftab.com/amr-codex-standards-compandium
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Не упусти шанс – https://whychooseexprealty.com/housing-shortage-is-driving-up-prices-but-a-crash-is-unlikely
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – http://www.rusmed.ru/comp/annonces/6166/Chastnaya_skoraya_pomoshch_1/printver_1
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Посмотреть подробности – https://www.gracetochinese.org/cropped-mainpic01-1-1-jpg
накрутка подписчиков без тг
Статья посвящена анализу текущих трендов в медицине и их влиянию на жизнь людей. Мы рассмотрим новые технологии, методы лечения и значение профилактики в обеспечении долголетия и здоровья.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://epinions.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-chastnaya-skoraya-pomoshch-no1-v-ramenskom
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Разобраться лучше – http://recself.ru/user-info.php?id=22293
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Хочу знать больше – https://gastlichkeit.at/anonyme-testbesuche/hoteltester
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить полную информацию – https://royalehealthcarenc.com/hello-world
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Интересует подробная информация – https://cardiopuga.com/centro-integral-de-marcapasos-y-arritmias
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://houseboyfilm.com/2019/07/29/rokophoto-rokophoto-photography-workshop-in-july
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://fe.unj.ac.id/jamu2021/?p=5783
J’apprecie enormement 1win Casino, c’est une veritable experience de jeu captivante. La selection est incroyablement riche, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Les agents sont toujours prets a aider, repondant rapidement. Les paiements sont fluides et fiables, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. En resume, 1win Casino offre une experience de jeu memorable pour les amateurs de casino virtuel ! Notons egalement que le design est visuellement attrayant, facilite chaque session de jeu.
plinko 1win|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Betify Casino, c’est une veritable aventure pleine de frissons. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
betify code|
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Только для своих – https://internacao.com/clinica_de_recuperacao_gratuita
Здарова!
Социальная тревожность: когда люди кажутся страшнее зомби. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/test-na-trevozhnost/]тест на тревожность[/url] Практические советы для тех, кто боится общения.
Переходи: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/test-na-trevozhnost/
как побороть тревожность
Покеда!
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – https://www.auraylaser.com/image-carousel-post
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Провести детальное исследование – https://firstclassairportsedan.com/shutterstock_157935968
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – http://www.kaitumfiskare.nu/menorca/a-day-at-the-beach/attachment/dscn0536
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – http://priligydapoxetine.online/post/34
Памятники на заказ https://top-memorial.ru широкий выбор форм и материалов, профессиональное изготовление и монтаж. Индивидуальный подход, гарантия качества и доступные цены.
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://cursos.eurolab.co/hola-mundo
Уборка квартир https://cleaningplus.ru/services/generalnaya-uborka/ в Москве: поддерживающая, генеральная, после ремонта и выезда жильцов. Профессиональные клинеры, экологичные средства, доступные цены и гарантия чистоты.
Врачи клиники «БайкалМед» используют комплексный подход, который включает медикаментозную поддержку, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и восстановление нормального обмена веществ. В зависимости от тяжести состояния выбирается амбулаторная или стационарная форма лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
*Седативные компоненты применяются по строгим показаниям, с мониторингом дыхания и сатурации.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/
J’adore a fond 1win Casino, c’est une veritable aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Les agents sont toujours prets a aider, repondant rapidement. Les transactions sont bien protegees, neanmoins les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, 1win Casino est un incontournable pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rapide, ajoute une touche d’elegance a l’experience.
1win games|
Estou completamente louco por DiceBet Casino, parece um tornado de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de classe. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e na lata. O processo do cassino e direto e sem treta, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, DiceBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um estouro para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
dicebet|
A thoughtful insight and ideas I will use on my blog. You’ve obviously spent some time on this. Congratulations
Затянувшийся запой — это состояние, которое опасно не только выраженной интоксикацией, но и непредсказуемыми осложнениями со стороны сердца, нервной системы и обмена веществ. В наркологической клинике «БайкалМедЦентр» (Улан-Удэ) услуги экстренного вывода из запоя организованы в формате «одного окна»: круглосуточный выезд врача-нарколога на дом, инфузионная терапия (капельницы) с индивидуальным подбором составов и детокс-протоколы, учитывающие возраст, сопутствующие заболевания и продолжительность употребления. Команда работает 24/7 по городу и пригородам; время прибытия в большинстве случаев составляет 30–45 минут с момента подтверждения вызова.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом улан-удэ[/url]
Перед применением препаратов проводится обследование, позволяющее исключить противопоказания. Это особенно важно при сопутствующих заболеваниях, таких как сердечно-сосудистые или печеночные патологии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
На сайте «Детский Класс» https://www.detskiyklass.ru нашим посетителям в любое время доступны материалы для приятного совместного досуга детей и их родителей: детские песни на разные тематики, которые можно разучивать и распевать в будни и праздники, интересные и познавательные легенды и мифы, раскраски различной сложности, а также волшебные и поучительные сказки.
Acho simplesmente fantastico o 888 Casino, e como se fosse sensacao unica de cassino. A selecao de jogos e impressionante, com caca-niqueis modernos e envolventes. Os agentes estao sempre disponiveis e eficientes, disponivel 24/7. O processo de retirada e simples e confiavel, contudo mais recompensas seriam bem-vindas. De modo geral, o 888 Casino e uma plataforma excepcional para os apaixonados por jogos digitais! Alem disso o design e visualmente impactante, reforca a imersao total.
jogo 888 casino logo|
Ich bin total begeistert von DrueGlueck Casino, es bietet eine krasse Spielerfahrung. Es gibt eine Flut an abwechslungsreichen Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Haken, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren top. Zusammengefasst ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen krassen Look, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck recension|
Acho completamente fora da curva Flabet Casino, parece um furacao de diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita plus. No geral, Flabet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
flabet bonus|
Je trouve completement fou Instant Casino, ca balance une vibe de jeu dementielle. La gamme de casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, offrant des machines a sous de casino uniques. Le support du casino est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un missile, des fois des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. Bref, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis la navigation du casino est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino direct.
casino la vida instant play|
Философия «БайкалМедЦентра» — сочетать медицинскую строгость и человеческое участие. Пациент получает помощь там, где ему психологически безопасно — дома, в привычной обстановке, без очередей и лишних контактов. При этом соблюдается полный конфиденциальный режим: бригада приезжает без опознавательных знаков, а документы оформляются в нейтральных формулировках. Если состояние требует госпитализации, клиника организует транспортировку в стационар без потери времени и с непрерывностью терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в улан-удэ[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Улан-Удэ — это комплексная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий длительного употребления алкоголя и стабилизацию состояния пациента. В клинике «БайкалМед» используются современные методы детоксикации и медикаментозного сопровождения, позволяющие безопасно и эффективно купировать симптомы абстиненции. Применяются проверенные протоколы, соответствующие медицинским стандартам, с учетом индивидуальных особенностей организма.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Не всякий случай требует немедленной госпитализации. При отсутствии «красных флагов» (угнетение сознания, выраженная одышка, судороги) домой выезжает бригада, и лечение проводится на месте. Ниже — ситуации, при которых домашний формат особенно оправдан:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в улан-удэ[/url]
живые подписчики в телеграм канал
Каждый этап проводится под контролем специалистов, что снижает риск осложнений и повышает эффективность лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Ich flippe aus bei DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist gigantisch, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die fesseln. Das Casino-Team bietet erstklassige Unterstutzung, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind blitzschnell, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren cool. Zusammengefasst ist DrueGlueck Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die rockt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
drueckglueck testbericht|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, ca ressemble a une sensation de casino unique. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, joignable 24/7. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. En resume, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec dynamisme, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet avis|
Acho simplesmente fantastico o 888 Casino, proporciona uma imersao em um universo vibrante. A gama de jogos e simplesmente fenomenal, incluindo slots de ultima geracao. Os agentes estao sempre disponiveis e eficientes, oferecendo respostas rapidas e precisas. As transacoes sao totalmente protegidas, contudo as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. No geral, o 888 Casino oferece uma experiencia de jogo memoravel para os fas de emocoes fortes! Como bonus a navegacao e simples e rapida, reforca a imersao total.
casino online 888|
Sou louco pelo clima de Flabet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e um estouro. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e alucinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de charme. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita plus. No geral, Flabet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
flabet com|
Je kiffe grave Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. Il y a un deluge de jeux de casino varies, incluant des jeux de table de casino styles. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un missile, mais bon des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. En gros, Instant Casino est un casino en ligne qui cartonne pour les accros aux sensations de casino ! En prime le site du casino est une tuerie graphique, facilite le delire total au casino.
instant casino referral code|
Белая футболка с принтом и короткие футболки с принтом в Чите. Шапка доктора и шарф ручной вязки в Улан-Удэ. Футболка с широким воротом мужская и бонприкс мужские футболки с длинным рукавом в Колпино. Одежда аврора и упаковать подарок в несколько коробок в Ижевске. Футболка оптом с быком и желтая футболка детская без рисунка https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
plug in prague weed in prague
plug in prague buy drugs in prague
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал дешево
накрутка подписчиков телеграм
Философия «БайкалМедЦентра» — сочетать медицинскую строгость и человеческое участие. Пациент получает помощь там, где ему психологически безопасно — дома, в привычной обстановке, без очередей и лишних контактов. При этом соблюдается полный конфиденциальный режим: бригада приезжает без опознавательных знаков, а документы оформляются в нейтральных формулировках. Если состояние требует госпитализации, клиника организует транспортировку в стационар без потери времени и с непрерывностью терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Улан-Удэ — это комплексная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий длительного употребления алкоголя и стабилизацию состояния пациента. В клинике «БайкалМед» используются современные методы детоксикации и медикаментозного сопровождения, позволяющие безопасно и эффективно купировать симптомы абстиненции. Применяются проверенные протоколы, соответствующие медицинским стандартам, с учетом индивидуальных особенностей организма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]врач вывод из запоя улан-удэ[/url]
Je trouve genial le casino TonyBet, il est carrement un moment divertissant top. Le choix de jeux est impressionnant, offrant des options de casino en direct. Les agents sont reactifs, disponible 24/7. On recupere ses gains vite, par contre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour tout dire, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les fans de jeux en ligne ! Par ailleurs, le design est attractif, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
tonybet casino erfahrung|
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, il procure une aventure palpitante. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, incluant des slots dernier cri. Les agents sont toujours disponibles, offrant des solutions rapides. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments les promos pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, AllySpin ne decoit jamais pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! De plus le design est accrocheur, ajoutant une touche d’elegance au jeu.
allyspin logo|
Sou viciado no role de LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma selva braba, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um predador, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e selvagem para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
leaowin02 casino no deposit bonus codes 2023|
Привет!
После банкротства 5 лет нельзя снова банкротиться и надо предупреждать о статусе при займах. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/bankrotstvo-fiz-licz/]банкротство физических лиц[/url] Все ограничения и последствия процедуры на годы вперед.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/bankrotstvo-fiz-licz/
банкротство физических лиц условия
До встречи!
Здарова!
Миллионы рублей в год на продаже футболок с логотипом канала – реально или нет. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/letsplej-eto/]симс 4 летсплей[/url] Разбираем все способы заработка популярных летсплейщиков.
Переходи: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/letsplej-eto/
#летсплей
летсплей
Удачи!
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]частная скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Карьера бухгалтера: от новичка до главного за 5 лет. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet-dlya-nachinayushhih/]бухгалтерия для чайников[/url] Реальные истории роста и практические советы по развитию.
По ссылке: – https://economica-2025.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet-dlya-nachinayushhih/
бухгалтерия курсы
бухучет для начинающих
До встречи!
сайт трипскан Tripscan зеркало: “Tripscan зеркало” относится к альтернативным веб-адресам или копиям сайта Tripscan, которые создаются для обеспечения доступности сервиса в случае блокировок основного домена или технических проблем. Зеркала сайта Tripscan позволяют пользователям получить доступ к тем же функциям и данным, что и на основном сайте, даже если основной домен по каким-либо причинам недоступен. Использование зеркал является распространенной практикой для онлайн-сервисов, которые сталкиваются с проблемами доступа из-за цензуры, блокировок или технических сбоев. Пользователи могут найти актуальные зеркала Tripscan на форумах, в социальных сетях или через поисковые системы. Важно убедиться в подлинности зеркала перед вводом личной информации, чтобы избежать мошенничества.
виброустойчивые подшипники Cамоустанавливающийся подшипник: Этот запрос указывает на тип подшипника, который предназначен для компенсации несоосности вала и корпуса. Самоустанавливающиеся подшипники позволяют избежать перенапряжений и преждевременного износа подшипника, вызванных деформацией конструкции или неточностью монтажа. Они широко используются в оборудовании с длинными валами, в условиях вибрации и в других случаях, когда сложно обеспечить точное выравнивание вала.
трип скан Tripscan: Tripscan – это метапоисковая система для путешественников, специализирующаяся на сравнении цен на авиабилеты, отели, аренду автомобилей и другие туристические услуги. Сервис собирает данные с множества различных онлайн-турагентств и поставщиков, позволяя пользователям находить наиболее выгодные предложения в одном месте. Tripscan не продает билеты или бронирования напрямую, а перенаправляет пользователей на сайты поставщиков для завершения транзакции. Ключевая особенность Tripscan – это удобный интерфейс, позволяющий быстро и легко сравнивать цены, фильтровать результаты поиска по различным критериям (например, времени вылета, авиакомпании, звездности отеля) и находить оптимальные варианты путешествий, соответствующие индивидуальным потребностям и бюджету. Сервис также может предлагать дополнительные функции, такие как отслеживание цен, уведомления о скидках и персонализированные рекомендации.
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]частная скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Инфузионная терапия — ядро домашнего вмешательства. Правильно составленная капельница ускоряет выведение токсинов, корректирует водно-электролитный баланс, уменьшает выраженность абстиненции и защищает органы-мишени. В «Балтийский МедЦентр» применяются комбинированные растворы с добавлением электролитов, витаминов группы B, антиоксидантов и, при показаниях, седативных средств. Выбор скорости инфузии и состава производится по алгоритму: оценка обезвоживания > проверка кардиорисков > первичная коррекция кислотно-щелочного состояния > адресная поддержка печени и ЦНС. Каждая капельница сопровождается мониторингом давления, пульса и сатурации, а также повторным контролем ключевых параметров на финише.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Архангельске имеет множество преимуществ, среди которых:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk/
При острых интоксикациях, абстинентных синдромах или тяжелых состояниях, вызванных злоупотреблением алкоголем или наркотическими веществами, каждая минута играет роль. Нарколог на дом в клинике «БалтикМед» приезжает с необходимым оборудованием и медикаментами для стабилизации состояния, проведения инфузионной терапии и профилактики осложнений. Это позволяет избежать транспортировки пациента в критическом состоянии и сократить время начала лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Лечение вывода из запоя на дому в Мурманске организовано по четко структурированной схеме, включающей следующие этапы, каждый из которых играет ключевую роль в оперативном восстановлении здоровья:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk00.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Философия «БайкалМедЦентра» — сочетать медицинскую строгость и человеческое участие. Пациент получает помощь там, где ему психологически безопасно — дома, в привычной обстановке, без очередей и лишних контактов. При этом соблюдается полный конфиденциальный режим: бригада приезжает без опознавательных знаков, а документы оформляются в нейтральных формулировках. Если состояние требует госпитализации, клиника организует транспортировку в стационар без потери времени и с непрерывностью терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru
Je suis accro a Julius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme un lion. Il y a un deferlement de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement imperial, avec une aide qui commande le respect. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans embuches, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rugir de plaisir. Globalement, Julius Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline glorieuse du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
bonus sans depot julius casino|
Ich bin suchtig nach JackpotPiraten Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie eine wilde Piratenjagd. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist riesig wie ein Ozean, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist ein echter Schatz, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Sabelhieb. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Insgesamt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf krasse Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Volltreffer, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
jackpotpiraten|
консультация по маркетингу SEO продвижение сайта wordpress: Указывает на необходимость оптимизации сайта, созданного на платформе WordPress, для поисковых систем. Важно предложить специализированные услуги по SEO-продвижению сайтов на WordPress, учитывая особенности этой платформы.
Adoro o clima feroz de LeaoWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que e uma fera. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma fera, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e selvagem para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino espana|
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Ситуации, связанные с алкогольной или наркотической интоксикацией, редко дают время на раздумья. В эти моменты важны не только знания врача, но и скорость реагирования, конфиденциальность и возможность начать лечение там, где пациенту психологически безопасно — дома. Наркологическая клиника «Балтийский МедЦентр» в Калининграде выстроила полноценный выездной формат помощи 24/7: врач прибывает в течение 30 минут, на месте проводит диагностику, стартовую стабилизацию и инфузионную терапию (капельницы), затем выдает подробный план дальнейших шагов. Такой подход снижает риски осложнений, помогает быстрее вернуть контроль над ситуацией и избавляет от дополнительного стресса, связанного с поездкой в стационар.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/kaliningrad-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
контент в социальных сетях для бизнеса Продвижение компании в интернете / Продвижение компании в социальных сетях: Пользователь заинтересован в увеличении онлайн-присутствия компании и привлечении новых клиентов через интернет. Важно предложить комплексные решения по продвижению компании в интернете, включая SEO, SMM, контекстную и таргетированную рекламу, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг и веб-аналитику. Необходимо учитывать особенности каждой платформы и разрабатывать индивидуальные стратегии для каждой компании. Важно предоставить возможность отслеживания результатов продвижения и корректировки стратегии при необходимости.
трипскан Трип скан: “Трип скан” – это общее понятие, которое может относиться к процессу сканирования или анализа информации, связанной с путешествиями (трипами). В контексте туристических сервисов, “трип скан” может означать поиск и сравнение цен на авиабилеты, отели, туры и другие услуги для путешественников. Эта фраза также может использоваться для обозначения инструментов и технологий, которые помогают пользователям планировать и организовывать свои поездки, например, онлайн-калькуляторы маршрутов, сервисы для бронирования билетов и отелей, а также приложения для составления списков необходимых вещей. В некоторых случаях, “трип скан” может также относиться к процессу проверки документов и виз перед поездкой.
Цель экспресс-обследования — быстро определить риски, понять объем инфузионной терапии и оценить, можно ли продолжать лечение на дому без транспортировки в стационар. Ниже — матрица ключевых параметров и применяемых методов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя архангельск[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Ich finde absolut majestatisch King Billy Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konig regiert. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Spa?, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein furstlicher Gewinn. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy 3 casino|
Вызов нарколога на дом в Калининграде дает возможность начать лечение без очередей, сохранить конфиденциальность и провести процедуры в комфортных для пациента условиях.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом калининград[/url]
подшипники для пищевой промышленности Подобрать подшипник по размерам: Этот запрос является более общим, чем предыдущий, и указывает на потребность пользователя в подборе подшипника подходящего размера, независимо от того, используется ли для этого онлайн-сервис или другие методы.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de BetFury Casino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement epoustouflante, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite, offrant des reponses claires et rapides. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, de temps en temps ??? davantage de recompenses comme les BetFury Boxes seraient appreciees. Globalement, BetFury Casino ne decoit jamais pour les amateurs de crypto-casinos ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rapide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betfury plinko|
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, ca donne une energie de jeu demente. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Les agents sont rapides comme des fusees, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promos qui defoncent. Au final, Gamdom c’est du lourd a tester direct pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Cote plus la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, facilite le delire total.
gamdom code 2021|
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного первичного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации. Эта информация является основой для разработки персонального плана лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk00.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в мурманске[/url]
трип скан Трипскан ссылка: “Трипскан ссылка” – это запрос, который используется для поиска прямой ссылки на веб-сайт сервиса Tripscan. Пользователи, которые вводят этот запрос, хотят быстро перейти на сайт сервиса, чтобы получить доступ к его функциям и возможностям. Ссылки на сайт Tripscan могут быть размещены в рекламных объявлениях, социальных сетях, блогах, форумах и других онлайн-ресурсах. Наличие прямой ссылки позволяет пользователям мгновенно получить доступ к функциям и возможностям сервиса, таким как поиск и сравнение цен на авиабилеты, отели и другие туристические услуги.
*Седативные компоненты применяются по строгим показаниям, с мониторингом дыхания и сатурации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево улан-удэ[/url]
Специалисты, выезжающие на дом, оснащены всем необходимым для оказания полноценной помощи. Это переносное диагностическое оборудование, препараты для снятия симптомов абстиненции, инфузионные растворы, противосудорожные средства, седативные препараты и витаминные комплексы. Наличие мини-аптечки позволяет адаптировать лечение прямо на месте и избежать лишних госпитализаций.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь в владимире[/url]
buy cocaine in telegram buy cocaine in telegram
cocaine prague telegram cocain in prague from columbia
Ситуации, связанные с алкогольной или наркотической интоксикацией, редко дают время на раздумья. В эти моменты важны не только знания врача, но и скорость реагирования, конфиденциальность и возможность начать лечение там, где пациенту психологически безопасно — дома. Наркологическая клиника «Балтийский МедЦентр» в Калининграде выстроила полноценный выездной формат помощи 24/7: врач прибывает в течение 30 минут, на месте проводит диагностику, стартовую стабилизацию и инфузионную терапию (капельницы), затем выдает подробный план дальнейших шагов. Такой подход снижает риски осложнений, помогает быстрее вернуть контроль над ситуацией и избавляет от дополнительного стресса, связанного с поездкой в стационар.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
сделать брови в севастополе Перманентный макияж в Севастополе – это удобное и практичное решение для современной женщины! Подчеркните свою естественную красоту с помощью перманентного макияжа бровей, губ и век. Наши опытные мастера используют только сертифицированные пигменты и современное оборудование, гарантируя безопасность и стойкий результат. Забудьте о ежедневном макияже и наслаждайтесь своей красотой в любое время суток!
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-perm-zapis
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал боты бесплатно
Специалисты, выезжающие на дом, оснащены всем необходимым для оказания полноценной помощи. Это переносное диагностическое оборудование, препараты для снятия симптомов абстиненции, инфузионные растворы, противосудорожные средства, седативные препараты и витаминные комплексы. Наличие мини-аптечки позволяет адаптировать лечение прямо на месте и избежать лишних госпитализаций.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно владимир[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и нормализации функций организма применяются препараты, которые оказывают детоксицирующее, нейропротекторное и общеукрепляющее действие. Врач подбирает лекарства индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в владимире[/url]
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в перми[/url]
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Архангельске имеет множество преимуществ, среди которых:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому в архангельске[/url]
Домашняя помощь — это не “облегченная версия” клиники. Команда «Балтийский МедЦентр» использует переносное оборудование и стандартизированные протоколы, позволяющие воспроизвести критически важные этапы стационарного вмешательства в условиях квартиры или частного дома. Врач заранее получает от оператора структурированный опросник по симптомам и сопутствующим заболеваниям, подбирает базовую схему инфузий, проверяет возможные лекарственные взаимодействия и берет с собой расширенный набор медикаментов. По прибытии специалист заново оценивает состояние и при необходимости корректирует назначения, ориентируясь на жизненные показатели, данные экспресс-диагностики и неврологический статус.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в телеграме
Вызов нарколога на дом в Калининграде дает возможность начать лечение без очередей, сохранить конфиденциальность и провести процедуры в комфортных для пациента условиях.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-v-permi
Бесплатная юридическая консультация в Москве становится все более популярной . Такой интерес обусловлен необходимостью в квалифицированной правовой помощи. Профессионалы в области юриспруденции предлагают свои услуги на безвозмездной основе.
Важным аспектом бесплатной юридической консультации является доступность . Услуги юристов доступны для всех, кто нуждается в помощи. Благодаря этому, уменьшится количество правонарушений .
Получить бесплатную юридическую консультацию можно довольно просто . Обычно достаточно записаться на консультацию к специалисту . Многие юридические компании предоставляют консультации через интернет .
В заключение, бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве представляют собой значимую помощь для населения . Юридическая помощь также играет значительную роль в повышении правовой грамотности населения . Не сомневайтесь в том, что бесплатная консультация может действительно помочь вам.
подробнее тут [url=https://edukacja.ordoiuris.pl/blog/index.php?entryid=83812/#подробнее-тут]подробнее тут[/url].
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Мурманске разработана для того, чтобы оперативно снизить токсическую нагрузку и вернуть организм в нормальное состояние. При поступлении вызова специалист проводит детальный осмотр, собирает анамнез и измеряет жизненно важные показатели. На основании полученных данных составляется индивидуальный план терапии, который может включать капельничное введение медикаментов, использование автоматизированных систем дозирования и психологическую поддержку. Такой комплексный подход позволяет обеспечить высокую эффективность лечения даже в условиях экстренной необходимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в мурманске[/url]
В рамках работы клиники проводятся диагностические процедуры и различные виды терапии, включающие:
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь москва[/url]
20
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
оказание pr услуг Запуск нового продукта на рынок: Пользователь нуждается в разработке и реализации маркетинговой стратегии для вывода нового продукта на рынок. Важно предложить комплексный подход, включающий в себя: анализ рынка, целевой аудитории и конкурентов, разработку позиционирования продукта, создание рекламной кампании, организацию PR-мероприятий и т.д. Необходимо учитывать особенности продукта и целевой аудитории при разработке стратегии продвижения.
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable plongee dans un univers palpitant. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, incluant des slots de pointe. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, avec un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, afin de maximiser l’experience. En resume, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et retro, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino no deposit bonus codes|
20
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон[/url]
*Седативные компоненты применяются по строгим показаниям, с мониторингом дыхания и сатурации.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в улан-удэ[/url]
J’adore l’energie de DBosses, il propose une experience de jeu intense. Les options sont riches et dynamiques, incluant des jeux de table sophistiques. L’assistance est efficace et chaleureuse, repondant en un instant. Les transactions sont simples et efficaces, bien que les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, DBosses garantit un divertissement de haut niveau pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
dbosses|
накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал бесплатно боты
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, proposant des sessions live qui tabassent. Le service client est une tuerie, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, par contre des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Au final, Gamdom est une plateforme qui dechire tout pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Et puis la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, facilite le delire total.
gamdom astuce|
щетки
Лечение вывода из запоя в Архангельске проводится по четко структурированной схеме, которая позволяет оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать процесс восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]капельница от запоя архангельск[/url]
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]частная скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Калининграде — это современное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке, без необходимости посещения стационара. В наркологической клинике «БалтикМед» услуги оказываются круглосуточно, с выездом специалиста по любому адресу города и области, что особенно важно при острых состояниях, требующих незамедлительного вмешательства.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-kaliningrad
прикольные кашпо [url=https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/]https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/[/url] .
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-perm
все онлайн займы [url=https://zaimy-27.ru/]все онлайн займы[/url] .
все займы ру [url=https://zaimy-50.ru]https://zaimy-50.ru[/url] .
XOSO66 là nền tảng xổ số trực tuyến quốc tế, ra đời với sứ mệnh mang đến cho người chơi một môi trường giải trí minh bạch, công bằng và hiện đại.
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
На данном этапе врач уточняет длительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk00.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя мурманск[/url]
Шаг 1. Оператор фиксирует симптомы, хронические болезни, лекарства, аллергии, адрес и удобный временной интервал. Шаг 2. Дежурный нарколог формирует первичный план инфузий и комплект медикаментов. Шаг 3. На месте проводится экспресс-диагностика и уточняется стратегия: объём гидратации, потребность в седативной поддержке и гепатопротекторах. Шаг 4. Запускается капельница с мониторингом давления, пульса и сатурации; при необходимости добавляются противорвотные и антациды. Шаг 5. Пациент получает письменный план на 48–72 часа, рекомендации по сну, питьевому режиму и питанию, номера круглосуточной связи и, при показаниях, слот повторного визита.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Je suis accro au style de FatPirate, ca donne une energie de pirate dejantee. Le choix de jeux est monumental, proposant des sessions live ultra-intenses. Les agents sont rapides comme l’eclair, avec une aide qui dechire. Les gains arrivent en mode eclair, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos qui tabassent. Dans le fond, FatPirate c’est du lourd a tester absolument pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis le site est une pepite visuelle, donne envie de replonger direct.
fatpirate hracГ automaty|
J’apprecie enormement Betify Casino, on dirait une experience de jeu captivante. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, repondant en un clin d’?il. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! En bonus la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betify 1sh|
lucky pari регистрация на зеркало [url=luckypari101.ru]luckypari101.ru[/url]
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. La gamme est une vraie constellation de fun, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. Le support est dispo 24/7, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Les paiements sont securises et eclatants, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. Pour resumer, Impressario offre un spectacle de jeu inoubliable pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Cote plus l’interface est fluide et glamour, facilite un show total.
impressario casino no deposit bonus|
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
В «ВладЗдоровье» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность. Персональные данные не передаются в третьи инстанции, пациенты не ставятся на учёт, а вся коммуникация ведётся с соблюдением врачебной тайны. Даже визит нарколога может быть организован без внешней символики и медицинской атрибутики, что особенно важно для социально активных граждан.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Специалисты, выезжающие на дом, оснащены всем необходимым для оказания полноценной помощи. Это переносное диагностическое оборудование, препараты для снятия симптомов абстиненции, инфузионные растворы, противосудорожные средства, седативные препараты и витаминные комплексы. Наличие мини-аптечки позволяет адаптировать лечение прямо на месте и избежать лишних госпитализаций.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи владимир[/url]
20
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru[/url]
При острых интоксикациях, абстинентных синдромах или тяжелых состояниях, вызванных злоупотреблением алкоголем или наркотическими веществами, каждая минута играет роль. Нарколог на дом в клинике «БалтикМед» приезжает с необходимым оборудованием и медикаментами для стабилизации состояния, проведения инфузионной терапии и профилактики осложнений. Это позволяет избежать транспортировки пациента в критическом состоянии и сократить время начала лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в калининграде[/url]
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Архангельске имеет множество преимуществ, среди которых:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя архангельск[/url]
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]анонимная скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
перманент бровей симферополь Перманентный макияж Севастополь – это современное решение для занятых женщин! Забудьте о ежедневной рутине макияжа и наслаждайтесь своей красотой в любое время суток. Наш салон предлагает широкий выбор услуг по перманентному макияжу: брови, губы, веки. Мы используем только сертифицированные пигменты премиум-класса и современное оборудование, гарантируя безопасность и стойкий результат. Перманентный макияж – это инвестиция в вашу красоту и уверенность!
Специалисты, выезжающие на дом, оснащены всем необходимым для оказания полноценной помощи. Это переносное диагностическое оборудование, препараты для снятия симптомов абстиненции, инфузионные растворы, противосудорожные средства, седативные препараты и витаминные комплексы. Наличие мини-аптечки позволяет адаптировать лечение прямо на месте и избежать лишних госпитализаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]центр наркологической помощи владимир[/url]
https://garantstroikompleks.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в Перми — это специализированное учреждение, где пациентам предоставляется комплексная помощь в лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы, основанные на доказательной медицине, что позволяет достигать стойких результатов и возвращать пациентов к полноценной жизни. Ключевым принципом является конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-perm-zapis/
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Когда запой начинает оказывать разрушительное воздействие на организм, своевременная помощь становится критически важной для предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Мурманске квалифицированные наркологи на дому обеспечивают оперативную детоксикацию, восстановление обменных процессов и стабилизацию работы внутренних органов. Лечение проводится в комфортной домашней обстановке, что позволяет избежать лишнего стресса и сохранить полную конфиденциальность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu moskva[/url]
пополнение lucky pari [url=www.luckypari101.ru]www.luckypari101.ru[/url]
Состав подбирается персонально, без шаблонов: корректируется гидратация, электролиты, витамины, антиоксидантная и гепатопротекторная поддержка. Ниже приведены ориентировочные модели, иллюстрирующие подход к детоксу при разных клинических сценариях.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Перми — это специализированное учреждение, где пациентам предоставляется комплексная помощь в лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы, основанные на доказательной медицине, что позволяет достигать стойких результатов и возвращать пациентов к полноценной жизни. Ключевым принципом является конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-v-permi/
Ich bin suchtig nach Lapalingo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Spielwelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Wirbelwind, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist Lapalingo Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Regenbogen glitzert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo 10 euro|
Здарова!
Кости, азарт и адреналин: гид по играм для настоящих пацанов. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/igra-v-kosti/]правила игры в кости 5 кубиков[/url] От крэпса в Вегасе до домашнего Ятзи – разбираем все по полочкам.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/igra-v-kosti/
правила игры в кости 6 кубиков
кости игра
Покеда!
В «ВладЗдоровье» применяется комплексный подход, сочетающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Врач-нарколог подбирает препараты индивидуально, с учётом анамнеза, переносимости компонентов и текущего состояния организма. Психотерапевтический блок включает когнитивно-поведенческую терапию, мотивационные интервью, семейную терапию и работу с посттравматическими реакциями.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в владимире[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Наркологическая клиника во Владимире специализируется на комплексном лечении различных видов зависимостей и обеспечении квалифицированной медицинской помощи пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимости. В условиях клиники «Пульс Здоровья» применяется индивидуальный подход, учитывающий особенности организма и психики каждого пациента, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов и предотвращать рецидивы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и нормализации функций организма применяются препараты, которые оказывают детоксицирующее, нейропротекторное и общеукрепляющее действие. Врач подбирает лекарства индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/vo-vladimire-anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika
Наркологическая помощь сегодня — это не просто экстренное вмешательство, но и полноценная система поддержки, охватывающая острые, хронические и пограничные состояния, вызванные употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ВладЗдоровье» во Владимире специалисты обеспечивают высокопрофессиональную помощь в домашних условиях или в стационаре, с учётом потребностей конкретного пациента. Скорость реагирования, анонимность и современные терапевтические протоколы делают услугу максимально доступной и эффективной для жителей города и области.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь владимир[/url]
[url=https://h1.dosug-himki.com/filter/5] Дешевые проститутки[/url]
[url=https://k1.dosug-korolev.com/filter/49] Проститутки Африканской внешности[/url]
[url=https://h1.dosug-himki.com/filter/2] Проститутки возраст от 25 до 30[/url]
[url=https://h1.dosug-himki.com/rayon.php?id=2] Проститутки Новогорск[/url]
[url=https://h1.dosug-himki.com/filter/37] Проститутки Окончание на лицо[/url]
В «ВладЗдоровье» применяется комплексный подход, сочетающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Врач-нарколог подбирает препараты индивидуально, с учётом анамнеза, переносимости компонентов и текущего состояния организма. Психотерапевтический блок включает когнитивно-поведенческую терапию, мотивационные интервью, семейную терапию и работу с посттравматическими реакциями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]наркологическая помощь владимир[/url]
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
В «ВладЗдоровье» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность. Персональные данные не передаются в третьи инстанции, пациенты не ставятся на учёт, а вся коммуникация ведётся с соблюдением врачебной тайны. Даже визит нарколога может быть организован без внешней символики и медицинской атрибутики, что особенно важно для социально активных граждан.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому владимир[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и нормализации функций организма применяются препараты, которые оказывают детоксицирующее, нейропротекторное и общеукрепляющее действие. Врач подбирает лекарства индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/
Таможенный брокер — это ваш проводник в мире международной торговли и таможенных процедур: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
токарный чпу станок [url=https://www.gdestanok.ru]https://gdestanok.ru/[/url]
Подбор аппаратуры для косметологии — серьёзный процесс в развитии салона.
Сначала стоит определить цели и процедуры, которые вы планируете оказывать.
Важно оценить разрешения и надёжность выбранного инструмента.
Отзывы опытных пользователей помогут сделать обоснованный решение.
beautyinstrument.ru
Также нужно учитывать набор функций и эргономику использования.
Начальная демонстрация оборудования помогает понять качество работы.
Важно сравнить цены и гарантийные условия.
Грамотный выбор техники поможет усилить уровень услуг.
https://www.restate.ru/
J’adore l’energie de LeonBet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit de puissance. La collection de jeux du casino est titanesque, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un guepard, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans embuches, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait feroce. Dans l’ensemble, LeonBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui domine la jungle pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline sauvage du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une savane, ajoute une touche de puissance au casino.
leonbet apk download|
стоимость плоской кровли https://ploskaya-krovlya-pod-klyuch.ru
lucky pari отыгрыш бонуса [url=https://www.luckypari100.ru]lucky pari отыгрыш бонуса[/url]
Наркологическая клиника во Владимире специализируется на комплексном лечении различных видов зависимостей и обеспечении квалифицированной медицинской помощи пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимости. В условиях клиники «Пульс Здоровья» применяется индивидуальный подход, учитывающий особенности организма и психики каждого пациента, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов и предотвращать рецидивы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Углубиться в тему – https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Перед тем, как приступить к лечению, специалисты проводят диагностику, включающую анализ анамнеза, физическое обследование и психологическое тестирование. Это позволяет выстроить эффективный план терапии, ориентированный на восстановление здоровья пациента и его социальной интеграции.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Konig regiert, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Lowenangriff. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad im Busch, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuer lodern. Insgesamt ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Brullen donnert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
löwen play altersbeschränkung|
Ich bin suchtig nach JokerStar Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein magischer Spielrausch. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Feuerwerk, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und magisch, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Funke. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Kometenschweif, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren zauberhaft. Insgesamt ist JokerStar Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie Magie funkelt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Zauberlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
jokerstar casino erfahrungen|
Наркологическая клиника во Владимире специализируется на комплексном лечении различных видов зависимостей и обеспечении квалифицированной медицинской помощи пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимости. В условиях клиники «Пульс Здоровья» применяется индивидуальный подход, учитывающий особенности организма и психики каждого пациента, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов и предотвращать рецидивы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в владимире[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и нормализации функций организма применяются препараты, которые оказывают детоксицирующее, нейропротекторное и общеукрепляющее действие. Врач подбирает лекарства индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
I think I will become a great follower.Just want to say your post is striking. The clarity in your post is simply striking and i can take for granted you are an expert on this subject.
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москве[/url]
купить живых подписчиков в телеграм
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Estou pirando total com JabiBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e uma mare alta. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo a parte, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma explosao. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual aquatica, da um toque de classe aquatica ao cassino.
jabibet casino bonus code|
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Как это работает — подробно – https://firstdomainhost.com/ppc_icon
Ich finde absolut verruckt JokerStar Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Zaubertrick funkelt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Zauberei knistern. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Kartentrick, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Kurz gesagt ist JokerStar Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie Magie funkelt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jokerstar casino no deposit bonus|
накрутка премиум подписчиков тг
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://metahotnews.org/this-86-year-old-actress-proves-you-dont-need-surgery-to-look-stunning-photos-of-her-transformation-2
Портал про авто https://ivanmotors.ru обзоры автомобилей, новости автопрома, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Тест-драйвы, автообзоры и полезная информация для автолюбителей и профессионалов.
Всё о Москве https://moscowfy.ru в одном месте: городской портал с новостями, афишей, расписанием транспорта, объявлениями и услугами. Полезные материалы для москвичей и туристов.
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Получить больше информации – http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru
Эта информационная публикация освещает широкий спектр тем из мира медицины. Мы предлагаем читателям ясные и понятные объяснения современных заболеваний, методов профилактики и лечения. Информация будет полезна как пациентам, так и медицинским работникам, желающим поддержать уровень своих знаний.
Это ещё не всё… – http://www.sergiev-posad.ru/useful/?id=22097
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
https://alzugroup.com/en/2024/10/03/hola-mundo
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://infosplus.org/2024/08/03/pikashow-apk-download-latest-version-for-android-official-2024
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://plugin.deals/blog
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://exlinko.net/o/kxqkp-rank-website-in-3-weeks
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://www.taylordentist.com/living-with-sensitive-teeth-during-the-holiday-season
как выиграть в lucky pari [url=http://luckypari102.ru]как выиграть в lucky pari[/url]
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Узнай первым! – https://premiumtourss.com/introducing-this-amazing-tour
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Прочесть всё о… – https://psicologavanessaoliveira.com/hello-world
накрутка подписчиков тг канале купить
Je suis totalement ensorcele par Luckster Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et envoutants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance mystique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un sortilege, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, Luckster Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et lumineuse comme une aurore magique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus magique.
luckster online casino|
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Не упусти шанс – https://globalgrowthinvestors.com/2024/05/02/planning-business-goals-with-a-specialist
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Изучить материалы по теме – https://yogashala.vn/2021/05/24/yoga-ghe
Ich liebe die Strahlkraft von LuckyNiki Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein verzauberter Glucksrausch. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Glanzlicht, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Trugbilder, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glitzern. Kurz gesagt ist LuckyNiki Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Gluckszauber glanzt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Glucksbringer, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
luckyniki casino in|
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробнее тут – https://www.withlovefordressage.nl/cropped-nk-dressuur-2-1-jpg
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://cropforecast.ca/product/blueberry
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Смотрите также… – https://aruessussu.com/archives/9486302.html
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://impressorashp.com.br/2023/04/09/get-ahead-of-your-competition-our-proven-digital
Портал о строительстве https://e-proficom.ru и ремонте: полезные статьи, советы специалистов, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё для тех, кто планирует ремонт квартиры, дома или дачи.
Женский портал https://devchenky.ru секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, любовь и кулинария. Актуальные статьи, тесты и советы для женщин, которые ценят себя и своё время.
маркетинговое продвижение бренда Консультация по маркетингу Консультация по маркетингу – это возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это возможность посмотреть на свой бизнес со стороны, выявить проблемные зоны и получить инструменты для их решения. Что вы получите на консультации: Анализ текущей ситуации: Оценка вашего текущего маркетингового положения, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение возможностей для роста. Определение целей: Помощь в определении четких и измеримых маркетинговых целей. Разработка стратегии: Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии, учитывающей особенности вашего бизнеса и целевую аудиторию. Выбор инструментов: Подбор оптимальных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей (SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, контент-маркетинг и др.). Рекомендации по улучшению: Предоставление практических рекомендаций по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на вопросы: Ответы на все ваши вопросы по маркетингу, развеивание сомнений и помощь в принятии правильных решений. Когда необходима консультация: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы хотите выйти на новый рынок. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную помощь и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
услуги по созданию и разработке сайтов Создание сайтов: От идеи до воплощения онлайн-присутствия В современном цифровом мире сайт – это не просто визитная карточка, а мощный инструмент для развития бизнеса, привлечения клиентов и укрепления имиджа компании. Услуги по созданию и разработке сайтов охватывают широкий спектр задач: от проектирования структуры и дизайна до написания кода и наполнения контентом. Разработка сайта: Путь к эффективному онлайн-решению Разработка сайта – это сложный и многоэтапный процесс, требующий профессионального подхода. Он включает в себя анализ целевой аудитории, определение целей и задач сайта, разработку технического задания, создание макета и дизайна, верстку и программирование, тестирование и отладку. Важно выбрать надежного подрядчика, который сможет предложить оптимальное решение, соответствующее вашим потребностям и бюджету. Заказать разработку сайта: Выбор профессионалов Заказать разработку сайта – это ответственный шаг, который требует внимательного выбора подрядчика. Важно обратить внимание на опыт компании, портфолио, отзывы клиентов и предлагаемые условия сотрудничества. Доступная цена и высокое качество – это основные критерии при выборе разработчика сайта.
https://pgu32.ru/
Добрый день!
Mindfulness по-русски: что это такое и зачем тебе это нужно. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/chto-takoe-osoznannost/]осознанность как развить[/url] Честный разбор без эзотерики и мистики, только факты и личный опыт.
Здесь подробней: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/chto-takoe-osoznannost/
осознанность это простыми словами
Покеда!
Оригинальная парфюмерия Оригинальная парфюмерия Оригинальная парфюмерия – это произведения искусства, созданные талантливыми парфюмерами, использующими высококачественные ингредиенты и уникальные формулы. Это не просто аромат, это история, эмоция, воспоминание, заключенные в изящном флаконе. Оригинальная парфюмерия отличается глубиной, стойкостью, многогранностью и неповторимым шлейфом, который подчеркивает вашу индивидуальность и оставляет неизгладимое впечатление. Приобретение оригинальной парфюмерии – это инвестиция в ваш образ, уверенность в себе и возможность наслаждаться настоящим искусством. Оригинальные ароматы раскрываются постепенно, играя разными нотами на протяжении всего дня, создавая неповторимую ауру вокруг вас. Наш магазин предлагает широкий выбор оригинальной парфюмерии от ведущих мировых брендов и нишевых парфюмеров. Мы тщательно отбираем ароматы, чтобы предложить вам самые изысканные, редкие и актуальные композиции. У нас вы найдете: Ароматы для любого случая: от повседневных до вечерних, от легких до насыщенных. Разнообразие стилей: от классики до авангарда, от цветочных до древесных. Широкий выбор концентраций: Eau de Parfum, Eau de Toilette, Parfum. Эксклюзивные коллекции: лимитированные издания и редкие ароматы, которые станут настоящим украшением вашей коллекции. Преимущества покупки оригинальной парфюмерии в нашем магазине: Гарантия подлинности: мы работаем только с официальными дистрибьюторами и гарантируем подлинность каждого аромата. Широкий выбор: у нас вы найдете аромат, который идеально подойдет вам по характеру, настроению и стилю. Профессиональные консультации: наши консультанты помогут вам подобрать аромат, учитывая ваши предпочтения и особенности кожи. Удобная доставка: мы доставим ваш заказ в любую точку мира в кратчайшие сроки. Выгодные предложения: мы регулярно проводим акции и распродажи, даря вам возможность приобрести любимые ароматы по выгодным ценам. Почувствуйте магию оригинальной парфюмерии с нашим магазином!
How come you do not have your website viewable in mobile format? cant see anything in my Droid.
imipramine for depression reviews
Хай!
Льготная ипотека 2025: все возможности для молодых семей без детей. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/gosudarstvennaya-ipotechnaya-kompaniya/]ипотека 9 процентов[/url] Программы господдержки, онлайн-оформление и реальные примеры экономии.
Переходи: – https://economica-2025.ru/gosudarstvennaya-ipotechnaya-kompaniya/
государственная ипотечная компания
ипотека-банк онлайн кредит
Удачи!
Добрый день!
Clash Royale: сколько реально стоят чужие аккаунты. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodazha-akkauntov-klesh-royal/]аккаунт клеш рояль продать[/url] Инсайдерский взгляд на ценообразование серого рынка.
По ссылке: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodazha-akkauntov-klesh-royal/
аккаунт клеш рояль продать
аккаунты клеш рояль купить
Пока!
Je suis fou de Luckster Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman. Il y a une tempete de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance mystique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un sortilege, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse magique, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait magique. Globalement, Luckster Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
luckster bonus code|
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von LuckyNiki Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Regenbogen glitzert. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Galaxie voller Vergnugen, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Feuerwerk knistern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein leuchtender Talisman, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Gluckszauber. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist LuckyNiki Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Glucksbringer, einen Hauch von Gluck ins Casino bringt.
luckyniki erfahrungsbericht|
новости Украины Новости Украины
лечение депрессии у психиатра психотерапевта Психиатр и психотерапевт – отзывы и рекомендации. Выберите специалиста, которому доверяют другие.
ремонт духових шаф у Львові
модуль газового пожаротушения v Аэрозольно газовое пожаротушение Аэрозольно-газовое пожаротушение – это комбинированный метод, сочетающий в себе преимущества аэрозольного и газового пожаротушения. Данный метод использует специальные составы, которые при активации образуют мелкодисперсный аэрозоль и газообразные продукты, быстро подавляющие горение. Основные принципы работы: Ингибирование горения: Аэрозольные частицы и газообразные продукты, образующиеся при срабатывании установки, ингибируют (замедляют или прекращают) химические реакции в зоне горения. Разбавление среды: Газообразные продукты разбавляют кислород в зоне горения, снижая его концентрацию до уровня, при котором горение становится невозможным. Охлаждение: Аэрозольные частицы поглощают тепло из зоны горения, способствуя её охлаждению. Преимущества аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Высокая эффективность: Быстрое подавление пожаров различных классов (A, B, C, E). Безопасность для оборудования: Не повреждает электронное оборудование и другие ценности, так как не оставляет следов. Экологичность: Используются составы, не разрушающие озоновый слой. Универсальность: Подходит для защиты различных типов помещений, включая серверные, архивы, электрощитовые и промышленные объекты. Легкость монтажа и обслуживания: Установки компактны и не требуют сложной инфраструктуры. Экономичность: За счет меньшего расхода огнетушащего вещества по сравнению с традиционными газовыми системами. Недостатки аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Опасность для людей: При высокой концентрации аэрозоля и газов может быть опасна для здоровья, поэтому перед срабатыванием системы необходимо эвакуировать людей из помещения. Требования к герметичности помещения: Для эффективной работы системы необходимо обеспечить герметичность помещения. Возможность задымления: После срабатывания установки в помещении может образоваться дым, затрудняющий видимость. Применение аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Защита серверных комнат и центров обработки данных. Защита электрощитовых и трансформаторных подстанций. Защита архивов и библиотек. Защита музеев и картинных галерей. Защита промышленных объектов с высоким риском возникновения пожара. Аэрозольно-газовое пожаротушение – это современный и эффективный способ защиты имущества и жизни людей от пожара, требующий профессионального проектирования, монтажа и обслуживания.
Что включает на практике
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
Je suis fou de LuckyBlock Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman dore. Le repertoire du casino est une galaxie de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui illuminent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair de genie, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de chance, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, LuckyBlock Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino feerique.
luckyblock whitepaper|
J’adore la splendeur de LuckyTreasure Casino, on dirait une caverne pleine de richesses ludiques. La collection de jeux du casino est un veritable tresor enfoui, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance precieuse. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement scintillant, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une ruee vers l’or, mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. En somme, LuckyTreasure Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
code promo lucky treasure 2025|
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu buszken tamogatja a kormanypartot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Строительные материалы https://stroy-marketplace.ru в Серпухове: кирпич, цемент, сухие смеси, пиломатериалы и утеплители. Большой выбор для ремонта и строительства, доставка по городу и району.
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/
маркетинг консультации Услуги PR (Public Relations) Услуги PR (Public Relations) – это комплекс мероприятий, направленных на формирование и поддержание позитивного имиджа компании, продукта или личности в глазах общественности. PR – это не только работа со СМИ, но и взаимодействие с целевой аудиторией, инвесторами, партнерами и другими заинтересованными сторонами. Основные задачи PR: Формирование позитивного имиджа: Создание благоприятного впечатления о компании, продукте или личности. Повышение узнаваемости бренда: Увеличение осведомленности о компании и ее продуктах. Управление репутацией: Реагирование на негативные отзывы и предотвращение кризисных ситуаций. Установление доверительных отношений: Создание прочных связей с целевой аудиторией, инвесторами и партнерами. Поддержка маркетинговых кампаний: Усиление эффекта от рекламных кампаний за счет PR-активностей. Основные инструменты PR: Пресс-релизы: Распространение информации о компании, продуктах или событиях в СМИ. Пресс-конференции: Организация мероприятий для общения с журналистами и ответов на их вопросы. Интервью: Предоставление интервью представителям СМИ для распространения информации о компании. Публикации: Размещение статей и других материалов о компании в СМИ. Мероприятия: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения узнаваемости бренда и установления контакта с целевой аудиторией. Социальные сети: Ведение страниц в социальных сетях для общения с целевой аудиторией и распространения информации о компании. Работа с блогерами и лидерами мнений: Привлечение блогеров и лидеров мнений для продвижения компании и ее продуктов. Инвестиции в PR – это инвестиции в репутацию вашей ко
Цель
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника королев[/url]
Что включено на практике
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
Наркологическая помощь в Первоуральске доступна в различных форматах: амбулаторно, стационарно и на дому. Однако не каждое учреждение может обеспечить необходимый уровень комплексной терапии, соответствующей стандартам Минздрава РФ и НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии. В этом материале мы рассмотрим ключевые особенности профессионального наркологического центра и критерии, которые помогут сделать осознанный выбор.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-pervouralske/
ремонт кондиціонерів у Львові ціна
Лечение алкоголизма в Омске проводится с использованием современных методов, направленных на восстановление организма и психики пациента. Специалисты уделяют внимание как медицинским, так и психологическим аспектам, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов. Основой терапии является индивидуальный подход, благодаря которому каждая программа учитывает состояние здоровья и уровень зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru
врач психиатр запись на прием Выгорание в бизнесе? Тяжелая депрессия? ПТСР после травмы? Профессиональная помощь психиатра и психотерапевта. Комплексная терапия депрессии, ПТСР и выгорания. Анонимность и конфиденциальность.
мгп пожаротушение Модуль газового пожаротушения Модуль газового пожаротушения (МГП) – это автономное устройство, предназначенное для хранения и выпуска огнетушащего газа при возникновении пожара. МГП является основным элементом системы газового пожаротушения и обеспечивает быстрое и эффективное подавление возгорания. МГП состоит из следующих основных компонентов: Баллон: Емкость для хранения огнетушащего газа под давлением. Запорно-пусковое устройство (ЗПУ): Обеспечивает выпуск газа из баллона при поступлении сигнала от системы пожарной сигнализации. Распылитель: Распределяет газ по защищаемому объему. Манометр: Показывает давление газа в баллоне. Предохранительный клапан: Предотвращает превышение допустимого давления в баллоне. МГП классифицируются по следующим параметрам: Тип огнетушащего газа: Азот, аргон, углекислый газ, хладон. Объем баллона: От нескольких литров до нескольких сотен литров. Рабочее давление: От нескольких атмосфер до нескольких десятков атмосфер. Способ установки: Напольные, настенные, подвесные. Преимущества использования МГП: Автономность: МГП не требует подключения к внешним источникам энергии. Компактность: МГП занимает мало места и может быть установлен в ограниченном пространстве. Быстродействие: МГП обеспечивает быстрое реагирование на возгорание. Надежность: МГП имеет простую и надежную конструкцию. При выборе МГП необходимо учитывать следующие факторы: Тип защищаемого помещения: Площадь, объем, назначение. Тип пожарной нагрузки: Характер горючих материалов. Требования к безопасности: Наличие людей в помещении. Стоимость: Цена МГП и общие затраты на установку и обслуживание. Модуль газового пожаротушения является важным элементом системы газового пожаротушения, обеспечивающим надежную защиту имущества и жизни людей от пожара.
Компания Единство https://edinvent.ru производитель и комплексный поставщик приточно-вытяжных установок, вентиляционных установок, а также систем автоматического управления климатическим оборудованием.
Женский блог https://www.evasolar.ru о здоровье и красоте: советы по уходу за собой, правильному питанию, фитнесу и косметике. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки и вдохновение для гармоничной и счастливой жизни.
Что включено на практике
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
купить диплом врача [url=http://www.rudik-diplom6.ru]купить диплом врача[/url] .
Медицинская помощь направлена не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на стабилизацию работы организма в целом. Врачи стремятся к тому, чтобы пациент получил не временное облегчение, а фундамент для дальнейшей реабилитации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, — это штат клиники. От опыта врачей напрямую зависит точность диагностики, подбор препаратов и эффективность психотерапевтической поддержки.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru
Вместо универсальных «капельниц на все случаи» мы собираем персональный план: состав инфузий, необходимость диагностик, частоту наблюдения и следующий шаг маршрута. Такой подход экономит время, снижает тревогу и даёт предсказуемый горизонт: что будет сделано сегодня, чего ждать завтра и какие критерии покажут, что идём по плану.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
сайт 1win отзывы [url=http://1win12017.ru]http://1win12017.ru[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
Обучение заработку в интернете
Для вызова специалиста необходимо позвонить на горячую линию или оставить заявку через официальный сайт, например, на портале государственных услуг. Специалист приедет в оговоренное время, обеспечив полную анонимность и соблюдение медицинской тайны.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в каменске-уральском[/url]
Je trouve absolument enivrant LuckyBlock Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman dore. La selection du casino est une fontaine de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement lumineux, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, LuckyBlock Casino offre une experience de casino enchanteresse pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sortilege, facilite une experience de casino feerique.
is luckyblock a scam|
Je suis totalement sous le charme de Casinova, ca offre une experience inoubliable. Le catalogue est d’une richesse incroyable, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. L’assistance est d’une efficacite redoutable, repondant en un clin d’?il. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Casinova offre un plaisir garanti pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie encore plus plaisante.
casino casinova ??????|
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Выбор наркологической клиники — ключевой шаг на пути к выздоровлению, от которого зависит не только физическое и психическое состояние пациента, но и устойчивость достигнутых результатов. Современные учреждения предлагают широкий спектр услуг, однако уровень подготовки персонала, методики лечения и условия пребывания могут существенно отличаться.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Cherished is likely to be what people say about your comments.
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Выезд врача позволяет начать помощь сразу, без ожидания свободной палаты. Специалист оценит состояние, проведёт осмотр, поставит капельницу, даст рекомендации по режиму и питанию, объяснит правила безопасности. Мы оставляем подробные инструкции родственникам, чтобы дома поддерживались питьевой режим, контроль давления и спокойная обстановка. Если домашних условий недостаточно (выраженная слабость, риски осложнений, сопутствующие заболевания), мы организуем транспортировку в стационар без задержек и бюрократии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
Je suis fou de Lucky31 Casino, on dirait une pluie d’etoiles filantes. Le repertoire du casino est un tourbillon de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un charme, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Lucky31 Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
lucky31 mobile|
Вместо универсальных «капельниц на все случаи» мы собираем персональный план: состав инфузий, необходимость диагностик, частоту наблюдения и следующий шаг маршрута. Такой подход экономит время, снижает тревогу и даёт предсказуемый горизонт: что будет сделано сегодня, чего ждать завтра и какие критерии покажут, что идём по плану.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя омск[/url]
промокод 1вин [url=http://1win12017.ru]http://1win12017.ru[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/
Для вызова специалиста необходимо позвонить на горячую линию или оставить заявку через официальный сайт, например, на портале государственных услуг. Специалист приедет в оговоренное время, обеспечив полную анонимность и соблюдение медицинской тайны.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/
Tennis set betting https://baji-bj.com
J’adore la frenesie de CasinoClic, ca pulse avec une energie de casino electrisante. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et scintillants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, CasinoClic promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter le design du casino est une explosion visuelle eclatante, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
coupon casino clic|
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – http://wp12964331.server-he.de/dance_with_the_desert_2/2021/03/22/my-grandmother-and-i-israel-germany
Професійне встановлення вимикачів описано на remontuem.te.ua
бот для накрутки подписчиков в тг бесплатно
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Не упусти важное! – https://www.newlifefamilychurch.co.uk/a-simple-blog-post
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://ccbroker.net/2016/06/06/video-post-format
https://2news.com.ua/ Новости Украины
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Жми сюда — получишь ответ – https://indiza.net/organisation-de-seminaires-et-conferences-professionnelles-tout-ce-que-vous-devez-savoir
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://roamguided.com/index.php/2023/09/26/hello-world
умный горшок для растений [url=www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru/]умный горшок для растений[/url] .
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Информация доступна здесь – http://hotfiretol.cf/post/34
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Изучить аспект более тщательно – https://blueconceptco.com/ola-mundo/?unapproved=15449
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://rickromano.com/rick-romano-richmond-print
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://samikaholidays.com/2022/07/01/convergent-and-divergent-plate-margins
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
http://masashikonno.com/?p=875
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://republicadomedo.com.br/ash-vs-evil-dead-foi-cancelada
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Посмотреть подробности – https://altatakeaway.be/duis-sagitis-ipsum-prasent
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Кликни и узнай всё! – http://erythromycinln.com/post/34
Привет!
Потерял работу и не можешь платить кредит: пошаговый план действий. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/restrukturizacziya-kredita/]реструктуризация кредита что это[/url] Какие документы собрать и как правильно подать заявление.
Здесь подробней: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/restrukturizacziya-kredita/
что значит реструктуризация кредита
Покеда!
продвижение бизнеса в социальных сетях Консультация по маркетингу: Экспертное руководство для вашего бизнеса Консультация по маркетингу – это ценная возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это шанс взглянуть на ваш бизнес свежим взглядом, выявить скрытые возможности и устранить препятствия, мешающие вам достичь ваших целей. В отличие от теоретических знаний, консультация по маркетингу дает вам практические инструменты и стратегии, которые вы можете немедленно применить в своем бизнесе. Я помогу вам найти оптимальные решения для ваших конкретных задач и проблем. Что вы получите на консультации: Глубокий анализ вашего бизнеса: Я проведу тщательный анализ вашего бизнеса, чтобы понять ваши сильные и слабые стороны, целевую аудиторию, конкурентную среду и потенциальные возможности для роста. Определение четких маркетинговых целей: Я помогу вам определить четкие и измеримые маркетинговые цели, которые соответствуют вашим общим бизнес-целям. Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии: Я создам индивидуальную маркетинговую стратегию, учитывающую особенности вашего бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и бюджетные ограничения. Рекомендации по выбору маркетинговых инструментов: Я дам вам рекомендации по выбору наиболее эффективных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей, включая SEO, контекстную рекламу, SMM, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг и другие. Практические советы по улучшению маркетинговой деятельности: Я поделюсь с вами проверенными советами и стратегиями по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на все ваши вопросы: Я отвечу на все ваши вопросы, связанные с маркетингом, развею ваши сомнения и помогу вам принять правильные решения для вашего бизнеса. Когда вам нужна консультация по маркетингу: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение вашего бизнеса. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите желаемых результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы планируете вывести на рынок новый продукт или услугу. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Вы хотите получить независимую оценку вашей текущей маркетинговой деятельности. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную поддержку и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://nwmigs.com/hello-world
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Перейти к полной версии – https://alunoslamaalanwallace.net.br/carvao-ou-luz-do-sol
Joaca joaca World of Warships gratuit! Exploreaza marile, folose?te-?i strategia ?i condu nave de razboi celebre. Batalii realiste ?i echipe interna?ionale te a?teapta.
Descopera Jocul World of Tanks – simulator de razboi cu tancuri istorice. Lupte dinamice, har?i variate ?i batalii tactice. Creeaza-?i strategia ?i domina impreuna cu prietenii tai.
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, parece uma erupcao de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que incendeiam. Resumindo, OshCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual escaldante, da um toque de calor brabo ao cassino.
cbet ou osh|
Ich bin suchtig nach Pledoo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Wirbelwind tobt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Flut voller Spa?, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Alles in allem ist Pledoo Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
pledoo|
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Продолжить чтение – https://www.paes.shibaura-it.ac.jp/t-iwata/?p=361
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Посмотреть всё – https://stationeronsunrise.com/bg
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Узнать из первых рук – https://ituranmobusa.com/technology-connection-as-online-networking-part-of-company
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно и быстро
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://thebackpackersworld.com/hello-world
Kingpin Crown in Australia is a premium entertainment venue offering bowling, laser tag, arcade games, karaoke, and dining: Kingpin Crown FAQs
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Продолжить чтение – https://hillvaninews.com/five-students-of-grd-received-medals-in-the-convocation-ceremony-of-uttarakhand-technical-university
услуги интернет маркетологов Консультация по маркетингу: Экспертное руководство для вашего бизнеса Консультация по маркетингу – это ценная возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это шанс взглянуть на ваш бизнес свежим взглядом, выявить скрытые возможности и устранить препятствия, мешающие вам достичь ваших целей. В отличие от теоретических знаний, консультация по маркетингу дает вам практические инструменты и стратегии, которые вы можете немедленно применить в своем бизнесе. Я помогу вам найти оптимальные решения для ваших конкретных задач и проблем. Что вы получите на консультации: Глубокий анализ вашего бизнеса: Я проведу тщательный анализ вашего бизнеса, чтобы понять ваши сильные и слабые стороны, целевую аудиторию, конкурентную среду и потенциальные возможности для роста. Определение четких маркетинговых целей: Я помогу вам определить четкие и измеримые маркетинговые цели, которые соответствуют вашим общим бизнес-целям. Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии: Я создам индивидуальную маркетинговую стратегию, учитывающую особенности вашего бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и бюджетные ограничения. Рекомендации по выбору маркетинговых инструментов: Я дам вам рекомендации по выбору наиболее эффективных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей, включая SEO, контекстную рекламу, SMM, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг и другие. Практические советы по улучшению маркетинговой деятельности: Я поделюсь с вами проверенными советами и стратегиями по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на все ваши вопросы: Я отвечу на все ваши вопросы, связанные с маркетингом, развею ваши сомнения и помогу вам принять правильные решения для вашего бизнеса. Когда вам нужна консультация по маркетингу: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение вашего бизнеса. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите желаемых результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы планируете вывести на рынок новый продукт или услугу. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Вы хотите получить независимую оценку вашей текущей маркетинговой деятельности. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную поддержку и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Descubra o caca-niqueis 9 Masks of Fire – um jogo cheio de adrenalina, simbolos especiais e rodadas bonus. Experimente graficos intensos e altas chances de ganhar em um caca-niqueis classico moderno.
Jogue pandajogos.top e descubra o charme do Oriente! Rolos coloridos, recursos bonus, rodadas gratis e surpresas que trazem ganhos espetaculares.
Adoro o clima brabo de OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tremores, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
osh tv|
Ich bin suchtig nach Pledoo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Vulkan ausbricht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
casino pledoo|
ваш провідник у житті Львова https://79000.com.ua актуальні новини, культурні та громадські події міста, урбаністика, інтерв’ю з цікавими людьми, фотоогляди локальних заходів. Все про те, що формує атмосферу Львова сьогодні — оновлення, проекти, історії.
інформаційний портал https://21000.com.ua Вінниці і області: місцеві новини, анонси культурних, спортивних та громадських подій, репортажі з місця подій, інтерв’ю з вінничанами. Все про те, що відбувається у Вінниці — ближче, живіше, щодня.
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится опытными наркологами с применением современных протоколов и сертифицированных препаратов. Процесс включает несколько ключевых этапов:
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo6.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-odincovo/
Современный темп жизни, постоянные стрессы и бытовые трудности всё чаще приводят к тому, что проблема зависимостей становится актуальной для самых разных людей — от молодых специалистов до взрослых, состоявшихся семейных людей. Наркологическая помощь в Домодедово в клинике «РеабилитейшнПро» — это возможность получить профессиональное лечение, консультации и поддержку в любой, даже самой сложной ситуации, без огласки и промедления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo6.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu-kruglosutochno[/url]
В рамках услуги вызова нарколога на дом используется современное оборудование и препараты, одобренные для амбулаторного применения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]платный нарколог на дом каменск-уральский[/url]
ООО “Мир ремней” https://yandex.ru/profile/147633783627 Производство приводных ремней, тефлоновых сеток и лент – телефон +7 (936) 333-93-03
Пиломатериалы в Минске https://farbwood.by оптом и в розницу. Доска обрезная и строганая, брус, лаги, террасная доска. Качественная древесина для строительства и ремонта. Быстрая доставка.
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Детали по клику – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/stati/amfetamin-chto-ehto-ehffekt-i-posledstviya-upotrebleniya.html]амфетамины последствия[/url]
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern glanzt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist PlayJango Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Orkan begeistert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
playjango casino welcome offer|
Терапия в клинике проводится системно и поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать состояние пациента и добиваться устойчивых улучшений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог тверь[/url]
Estou pirando com MonsterWin Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao monstruosa. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de garra. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma fera, respondendo mais rapido que um rugido. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um dragao, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, MonsterWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
monsterwin casino online|
Je suis totalement captive par PokerStars Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino strategique. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une galaxie de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. L’assistance du casino est fiable et astucieuse, repondant en un eclair strategique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient strategiques. Dans l’ensemble, PokerStars Casino est un casino en ligne qui domine le jeu pour les strateges du casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie gagnante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
maintenance pokerstars combien de temps|
Здесь собрана актуальная и полезная сведения по разным темам.
Читатели могут обнаружить решения на популярные вопросы.
Материалы размещаются часто, чтобы вы могли получать новую аналитику.
Простая организация сайта облегчает быстро отыскать нужные страницы.
https://nxmed.ru/onlajn-razvlecheniya/luchshe-smotret-porno-na-sajte/
Широкий спектр рубрикаторов делает ресурс полезным для разных пользователей.
Каждый посетитель сможет выбрать советы, которые нужны именно ему.
Существование доступных подсказок делает сайт максимально ценным.
Таким образом, площадка — это интересный проводник актуальной информации для широкого круга пользователей.
Медицинское кодирование действует не на симптомы, а на глубинные механизмы зависимости. Оно позволяет не просто временно отказаться от алкоголя, а формирует устойчивое отвращение и помогает преодолеть психологическую тягу. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива, улучшает мотивацию, способствует восстановлению здоровья и психологического баланса. В «Новом Пути» для каждого пациента подбирается индивидуальный метод с учётом анамнеза, возраста, сопутствующих болезней и личных особенностей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ehlektrostal6.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма выезд на дом[/url]
Описание
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo6.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-odincovo
[url=https://sibirki3.vip/]проститутки недорого Новосибирск[/url]
В Новосибирске доступны различные услуги недорогих проституток, которые подойдут для любого случая.
[url=https://prof-krov-yut.ru ]строительство из клееного бруса
[/url]
В «Гелиосе» уделяется особое внимание конфиденциальности и психологическому комфорту пациентов. Анонимность процедур и доброжелательная атмосфера способствуют снижению стресса и улучшению результатов лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Согласно данным Федерального наркологического центра, своевременный выезд врача снижает риск осложнений и повторных госпитализаций.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в каменске-уральском[/url]
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Жми сюда — получишь ответ – [url=https://pedagog-razvitie.ru/]эмоциональное развитие личности[/url]
Этот текст посвящён сложным аспектам зависимости и её влиянию на жизнь человека. Мы обсудим психологические, физические и социальные последствия зависимого поведения, а также важность своевременного обращения за помощью.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – [url=https://lux-clinic.ru/stati/osnovnye-prichiny-narkomanii.html]основная причина наркомании[/url]
Терапия в клинике проводится системно и поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать состояние пациента и добиваться устойчивых улучшений.
Подробнее – http://
Процедура начинается с осмотра и сбора анамнеза. После этого специалист проводит экстренную детоксикацию, снимает симптомы абстинентного синдрома, назначает поддерживающую терапию и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим шагам. По желанию родственников или самого пациента помощь может быть оказана и в условиях стационара клиники.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo6.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, — это штат клиники. От опыта врачей напрямую зависит точность диагностики, подбор препаратов и эффективность психотерапевтической поддержки.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в первоуральске[/url]
Медицинское кодирование действует не на симптомы, а на глубинные механизмы зависимости. Оно позволяет не просто временно отказаться от алкоголя, а формирует устойчивое отвращение и помогает преодолеть психологическую тягу. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива, улучшает мотивацию, способствует восстановлению здоровья и психологического баланса. В «Новом Пути» для каждого пациента подбирается индивидуальный метод с учётом анамнеза, возраста, сопутствующих болезней и личных особенностей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ehlektrostal6.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-v-ehlektrostali/https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ehlektrostal6.ru
Каждый этап имеет важное значение и обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект от терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/lechenie-ot-alkogolizma-tver/
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Детали по клику – [url=https://pedagog-razvitie.ru/]реабилитация[/url]
Играйте в [url=https://online-kazino-24.by/]казино[/url] и наслаждайтесь захватывающими развлечениями прямо у себя дома!
Качество и безопасность сайтов имеют первостепенное значение
продвижение в социальных сетях Услуги интернет-маркетолога В современном цифровом мире, где онлайн-присутствие играет ключевую роль в успехе любого бизнеса, услуги опытного интернет-маркетолога становятся необходимостью. Я предлагаю полный спектр услуг, направленных на увеличение видимости вашего бренда, привлечение целевой аудитории и, как следствие, повышение продаж. Мои услуги включают: Анализ рынка и конкурентов: Тщательный анализ позволит определить оптимальные стратегии продвижения, выявить сильные и слабые стороны конкурентов и определить целевую аудиторию. Разработка маркетинговой стратегии: Создание индивидуальной стратегии, учитывающей особенности вашего бизнеса, цели и бюджет. SEO-оптимизация: Повышение позиций вашего сайта в поисковых системах, что обеспечит приток органического трафика. Контекстная реклама: Настройка и ведение рекламных кампаний в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads для быстрого привлечения целевых клиентов. SMM-продвижение: Разработка и реализация стратегии продвижения в социальных сетях, создание контента, привлечение подписчиков и повышение вовлеченности аудитории. Контент-маркетинг: Создание полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории, повышения лояльности к бренду. Email-маркетинг: Разработка стратегии email-рассылок, создание писем и автоматизация процессов для поддержания связи с клиентами и стимулирования продаж. Аналитика и отчетность: Регулярный анализ результатов и предоставление отчетов о проделанной работе, что позволит оценить эффективность стратегии и внести необходимые корректировки. Я готов предложить вам комплексные решения, которые помогут вашему бизнесу достичь новых высот в онлайн-пространстве. Свяжитесь со мной, чтобы обсудить ваши задачи и разработать индивидуальный план продвижения.
[url=https://drvann.ru ]дом из клееного бруса
[/url]
Crown Metropol Perth is a luxury hotel located near the Swan River. It offers modern rooms, a stunning pool area, fine dining, a casino, and entertainment options: Crown Metropol Perth room rates
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-anonimnaya-pomoshch[/url]
Каждый этап лечения подбирается индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента и особенностей его зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern glanzt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Insgesamt ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
playjango sister sites|
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал
Acho simplesmente intergalactico Bet558 Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao intensa quanto uma galaxia em chamas. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e estelares. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, Bet558 Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
bet558 Г© confiГЎvel|
Estou completamente alucinado por MonsterWin Casino, e um cassino online que ruge como uma fera braba. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que devastam. Na real, MonsterWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e uma explosao visual feroz, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
monsterwin casino online|
https://altegs.ru/
Je suis accro a PokerStars Casino, on dirait un ciel etoile de sensations. La selection du casino est une constellation de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair strategique. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un jeu de cartes, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un full house. En somme, PokerStars Casino promet un divertissement de casino strategique pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie gagnante, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
pokerstars live|
Оптимальный состав команды включает:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Заходи — там интересно – https://horizon-ogrodzenia.pl/ogrodzenia-dla-wlascicieli-zwierzat-jak-zadbac-o-bezpieczenstwo-swoich-pupili
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять шторами с помощью пульта.
Тем не менее, многие люди предпочитают устанавливать электрокарниз самостоятельно.
В клинике используются доказательные методики, эффективность которых подтверждена практикой. Они подбираются индивидуально и позволяют достичь устойчивых результатов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма тверь[/url]
Отечественная мода отличается индивидуальностью и разнообразной историей.
Нынешние дизайнеры вдохновляются в традиционных образах, создавая яркие модели.
В коллекциях всё чаще демонстрируются смелые сочетания цветов.
Российская мода поддерживают устойчивый подход к разработке одежды.
tatyana kochnova bridal
Аудитория всё больше ценит самобытные идеи из России.
СМИ о моде публикуют о новых коллекциях и дизайнерах.
Перспективные таланты завоёвывают известность как в стране, так и за рубежом.
В итоге модная сцена продолжает развиваться, объединяя традиции и современность.
[url=https://house-forest.ru ]построить дом из клееного бруса
[/url]
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://olapono21.com/hello-world
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://tripbudgeteer.com/15-fun-facts-about-germany-you-probably-didnt-know
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Читать далее > – https://cleanholmes.co.uk/home/7411063-x20691
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Посмотреть всё – https://www.maplelodge.or.jp/sp%E8%82%89%E6%96%99%E7%90%86%EF%BC%8D%E9%9B%89
Estou pirando com PlayUzu Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um redemoinho. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vibrante, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Resumindo, PlayUzu Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
playuzu brazil|
продвижение компании в интернете Консультация по маркетингу Консультация по маркетингу – это возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это возможность посмотреть на свой бизнес со стороны, выявить проблемные зоны и получить инструменты для их решения. Что вы получите на консультации: Анализ текущей ситуации: Оценка вашего текущего маркетингового положения, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение возможностей для роста. Определение целей: Помощь в определении четких и измеримых маркетинговых целей. Разработка стратегии: Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии, учитывающей особенности вашего бизнеса и целевую аудиторию. Выбор инструментов: Подбор оптимальных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей (SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, контент-маркетинг и др.). Рекомендации по улучшению: Предоставление практических рекомендаций по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на вопросы: Ответы на все ваши вопросы по маркетингу, развеивание сомнений и помощь в принятии правильных решений. Когда необходима консультация: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы хотите выйти на новый рынок. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную помощь и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, используя [url=https://karniz-s-privodom.ru]карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом для штор|потолочные карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом цена|карнизы с электроприводом купить|карнизы с электроприводом с дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным|карнизы с электроприводом и пультом управления купить|Карнизы с электроприводом[/url] для вашего дома!
Такой подход формирует максимально комфортные условия в помещении.
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Продолжить чтение – https://monitorsurfgrancanaria.es/surfing-as-a-way-of-life-2
Je suis accro a MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. La selection de jeux du casino est une veritable parade de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme vibrant. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et impeccable, garantissant un support de casino instantane et eclatant. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse endiablee, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, MrPlay Casino promet un divertissement de casino eclatant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style endiable, facilite une experience de casino festive.
mr.play arvostelu|
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Как это работает — подробно – https://lagoon-magazine.com/destination-item/anatolia
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Как достичь результата? – https://marcperry.org/index.php/2021/01/01/the-brits-in-kosovo
Je suis fou de Posido Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de fun. Il y a une maree de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme aquatique. Le service client du casino est une perle rare, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans remous, cependant des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient nager de joie. En somme, Posido Casino est un tresor pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style oceanique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
posido casino app|
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.dogusanakaryakit.com/merhaba-dunya
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Не упусти важное! – http://www.thomasjmandl.de/?attachment_id=1089
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Доступ к полной версии – https://nekkham.ac.th/?p=1542
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://lagencedesfromages.bzh/portfolio/barrel-of-wine
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Смотрите также… – https://acreart.co/la-vision-de-ecobolsas
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Узнайте всю правду – https://www.nuloinnovations.com/biw-for-electric-vehicle
накрутить подписчиков в тг
https://rd-ok.ru/
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://monikamalinowska.pl/witaj-swiecie
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://bluesky-education.com/8-unexpected-benefits-of-study-abroad-programmes
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Узнать больше > – https://tutihashikougyou.co.jp/%E5%8C%97%E6%B5%B7%E9%81%93%E5%BB%BA%E8%A8%AD%E9%83%A8%E5%B7%A5%E4%BA%8B%E7%AD%89%E5%84%AA%E7%A7%80%E8%80%85%E8%A1%A8%E5%BD%B0
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://corover.ai/the-next-revolution-in-tech-what-to-know-before-implementing-conversational-ai
Электрические жалюзи [url=https://electroprivod-karniz.ru]электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи с дистанционным управлением|электрические жалюзи на мансардные окна|купить электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи в москве|электрические жалюзи автоматические|электрические жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить|электрические жалюзи стоимость|электрические жалюзи на окна заказать[/url] — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, обеспечивающее комфорт и стиль.
Одним из главных преимуществ электрических жалюзи является возможность управления с помощью пульта.
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Хочу знать больше – https://kalima-triathlon.de/hello-world-2
кто нибудь работает медсестрой по купленному диплому [url=www.frei-diplom15.ru/]www.frei-diplom15.ru/[/url] .
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://aqneblades.com/2023/09/28/quick-guide-how-to-forge-damascus-patterns-techniques-faqs-and-in-depth-insights
быстрый займ займ денег онлайн
займ деньги займы деньги
Приветствую!
Как айтишнику взять ипотеку под 6% в 2025 году. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/it-ipoteka-2025/]it ипотека новости[/url] Полный гайд по IT-ипотеке от практика для практиков.
Написал: – https://economica-2025.ru/it-ipoteka-2025/
it ипотека для удаленщиков
it ипотека новости
До встречи!
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Интересует подробная информация – https://dezeuspublic.org/slotonline-technic
Здравствуйте!
Roblox заработок: пошаговый план от нуля до первой тысячи долларов. [url=https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-dengi-v-roblokse/]как заработать деньги в роблоксе[/url] Проверенные способы которые работают в 2025 году без вложений.
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-dengi-v-roblokse/
как заработать деньги в роблоксе
как заработать в роблоксе деньги
Бывай!
Автоматические рулонные шторы не только обеспечивают удобство управления, но и стильный акцент в интерьере вашего дома, особенно если вы выберете [url=https://avtorulon.ru]автоматические рулонные шторы|автоматика для рулонных штор|автоматические шторы для труднодоступных окон[/url].
Это добавляет им удобства и современности.
как взять займ деньги займ
isosorbid bei herzrasen
Колледжи Артём новости Смог Артём Новости о смоге в городе Артёме: причины загрязнения воздуха, влияние на здоровье и рекомендации для жителей.
Adoro o clima explosivo de PlayUzu Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura eletricidade. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vibrante, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma correnteza, com uma ajuda que e pura adrenalina. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No geral, PlayUzu Casino e um cassino online que e um vendaval de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o design do cassino e uma explosao visual eletrizante, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
cГіdigo sorpresa playuzu|
Je suis totalement captive par MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. La selection de jeux du casino est une veritable parade de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui font danser. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un clin d’?il festif. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse endiablee, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, MrPlay Casino c’est un casino a rejoindre sans attendre pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une danse, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
mr.play sovellus|
получить займ онлайн взять микрозайм
J’adore la vague de Posido Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui plonge dans les abysses. Le repertoire du casino est un recif de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme aquatique. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et limpide, assurant un support de casino immediat et fluide. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait aquatique. Pour resumer, Posido Casino est un tresor pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline fluide du casino ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer turquoise, ajoute une touche d’eclat marin au casino.
posido slots|
оформить займ занять деньги онлайн
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это идеальное решение для создания уюта и комфорта в вашем доме, позволяющее управлять светом и приватностью с помощью простого нажатия кнопки.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом завоевывают популярность среди покупателей. Эти изделия представляют собой современное решение для оформления окон. Функциональность и удобство использования выделяют их среди других вариантов.
Одним из главных преимуществ является возможность управления шторами с помощью пульта. Такое управление обеспечивает комфорт и простоту в использовании. Электропривод позволяет задать расписание открытия и закрытия штор.
Монтаж рулонных штор с электроприводом осуществляется достаточно быстро. Вам потребуется минимальный набор инструментов и немного времени. Разнообразие материалов и дизайна позволяет выбрать подходящие шторы для любого стиля.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом гарантируют защиту от солнечного света и обеспечивают стиль. С помощью различных тканей можно регулировать уровень затемнения. Таким образом, вы сможете создать комфортные условия в вашем жилище.
max мессенджер обновление Max Мессенджер Группы Группы в мессенджере Max – это сообщества, в которых могут общаться несколько человек. Группы могут быть созданы для обсуждения общих интересов, организации мероприятий, координации работы и т.д. В группах можно обмениваться сообщениями, фотографиями, видео и файлами. Max также предлагает инструменты для управления группами, такие как назначение администраторов и модераторов.
ЧП Артем Новости Артёма Узнавайте самые свежие и актуальные новости города Артёма! Мы освещаем все важные события, происшествия, культурные мероприятия, экономические изменения, спортивные достижения и многое другое. Будьте в курсе жизни вашего города, следите за обновлениями на нашем новостном портале! Здесь вы найдете объективную информацию, репортажи с места событий, интервью с лицами, принимающими решения, и мнения горожан. Наши корреспонденты работают для вас круглосуточно, чтобы вы всегда получали самые актуальные новости.
https://kitehurghada.ru/
Нужны автостекла? автостекла ремонт трещин стекле Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Конфиденциально и безопасно – бюро переводов в самаре. Локализация мобильных приложений в Самаре. Адаптируем контент под язык и культуру целевой страны. Увеличим downloads и положительные отзывы.
Je trouve absolument flamboyant ParisVegasClub, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un neon parisien. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un veritable show lumineux, proposant des slots de casino a theme glamour. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse de rideau leve, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient spectaculaires. Globalement, ParisVegasClub c’est un casino a rejoindre sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique theatrale, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus spectaculaire.
paris vegas club promotion|
чотирьохскатний дах https://remontuem.te.ua
Je suis totalement fascine par MrXBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui serpente comme un labyrinthe. Le repertoire du casino est un dedale de divertissement, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. L’assistance du casino est fiable et perspicace, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, MrXBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les detectives du casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un puzzle visuel captivant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
code promo mrxbet|
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Thron funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein koniglicher Erlass. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, manchmal wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Juwelen glanzen. Kurz gesagt ist Richard Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Kronungsjuwel glanzt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino auf ein konigliches Niveau hebt.
richard marcus casino film|
Нужны автостекла? автостекло замена стекла Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Спецпредложения сегодня – агентство переводов документов. Перевод документов для международных проверок. Аудиторские отчеты, due diligence, заключения юристов. Точность и нейтральность.
вантажник тернопіль https://remontuem.te.ua
Нужны автостекла? ремонт стекол сколов и трещин автостекла Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Наша работа – бюро нотариально заверенных переводов. Нотариальное заверение штампов и печатей в Самаре. Часто требуется для иностранных контрагентов. Сделаем все быстро и в соответствии с законом.
каналізація монтаж https://remontuem.te.ua
https://altegs.ru/
Если состояние тяжёлое либо есть серьёзные сопутствующие заболевания, оптимален стационар. Здесь доступны расширенная диагностика (ЭКГ, лаборатория, оценка электролитов, функции печени и почек), усиленные схемы инфузии, противорвотная, седативная и кардиопротективная поддержка. Круглосуточный мониторинг позволяет своевременно корректировать терапию, предотвращать обезвоживание и электролитные нарушения. Для пациентов из Реутова организуем аккуратную транспортировку и обратный трансфер после стабилизации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/]вывод из запоя дешев реутове[/url]
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/
Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov239.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Школы Артём новости Перебои электричества Артём В Артёме участились перебои с электроснабжением! На нашем сайте вы найдете информацию о причинах перебоев, о сроках их устранения и о том, какие меры предпринимаются для предотвращения подобных ситуаций в будущем. Мы также публикуем рекомендации о том, как защитить свою электротехнику от перепадов напряжения и как безопасно использовать альтернативные источники энергии. Следите за новостями о перебоях электричества в Артёме, чтобы быть в курсе ситуации и подготовиться к возможным отключениям!
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Краснодаре — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]врач нарколог на дом ростовская область[/url]
Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov226.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Ищешь знакомства в Ростове-на-Дону? Вступай в наш активный Telegram-чат с реальными людьми для общения и новых встреч. https://t.me/Devochkirostovabot В чате дружелюбная атмосфера, много участников, возможность найти друзей или романтику, интересные темы и обсуждения. Присоединяйся и начинай знакомиться прямо сейчас!
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно ростов-на-дону[/url]
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]вывод из запоя цены пушкино[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov239.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Если вам или вашим близким необходим вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуальные схемы лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Краснодаре, без скрытых платежей и переплат.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя клиника
Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru
Выездная бригада прибывает с необходимым оборудованием. Инфузионная терапия длится 60–120 минут; по ходу процедуры контролируются давление, пульс, дыхание и субъективное самочувствие, при необходимости схема корректируется (темп капания, смена растворов, добавление противорвотных или седативных средств). Чаще всего уже к концу первой инфузии снижается тошнота, уходит дрожь и «внутренняя дрожь», нормализуется сон. Врач оставляет пошаговый план на 24–72 часа: питьевой режим, щадящее питание (дробно, без жирного и острого), режим сна, рекомендации по витаминам и гепатопротекции. Если в процессе выявляются тревожные признаки (нестабильная гемодинамика, выраженная аритмия, спутанность сознания), будет предложен перевод в стационар.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-telefon[/url]
https://t.me/insta_akki
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Алкоголь ночью с доставкой на дом в Москве – https://alcohub9.ru/. Работаем 24/7, когда обычные магазины закрыты. Широкий ассортимент: пиво, сидр, вино, шампанское, крепкие напитки. Быстрая доставка в пределах МКАД за 30-60 минут
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Ростове-на-Дону.
Выяснить больше – срочный вывод из запоя
Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Je suis fou de ParisVegasClub, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un cabaret. Le repertoire du casino est une scene de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et impeccable, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une replique, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, ParisVegasClub promet un divertissement de casino flamboyant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style eblouissant, facilite une experience de casino flamboyante.
paris vegas club promo codes|
В клинике «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Je trouve absolument captivant MrXBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi envoutante qu’un secret. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un coffre-fort de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. L’assistance du casino est fiable et perspicace, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait envoutant. Dans l’ensemble, MrXBet Casino offre une experience de casino mysterieuse pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique enigmatique, ajoute une touche de suspense au casino.
mrxbet arjel|
Ich bin suchtig nach Richard Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein koniglicher Schatz, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Kronungsjuwel, einen Hauch von Majestat ins Casino bringt.
richard casino free chip codes|
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя клиника
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Краснодаре.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Этап
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-zhukovskij-ceny[/url]
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Не упусти шанс – http://hpmi2.hpmievents.com/hello-world
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://mcellisda.de/faq/what-will-be-included-in-my-purchased-products
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Продолжить изучение – https://www.reignhealthandwealth.com/event/boudin-alcatra-tongue-ham-hock-bresaola
Нужна лабораторная? сделать лабораторную работу на заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
ball bearing BBCR BBCR, or ball bearing cage retaining, refers to specialized designs used in different types of ball bearings to maintain the structure and preserve the integrity of the components. These cages help in the proper alignment of the ball bearings, ensuring smooth rotation and durability under various load conditions. Understanding BBCR is essential for selecting the right type of bearing for your specific application. We provide an array of bearings featuring BBCR designs to fit your operational needs suitably.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Ищешь знакомства в Ростове-на-Дону? Вступай в наш активный Telegram-чат с реальными людьми для общения и новых встреч. Знакомства Ростов В чате дружелюбная атмосфера, много участников, возможность найти друзей или романтику, интересные темы и обсуждения. Присоединяйся и начинай знакомиться прямо сейчас!
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]врач нарколог на дом ростовская область[/url]
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Ростова-на-Дону, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://atmd.org.hk/logo-3
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
https://www.smkbuanainsan.sch.id/172
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, OshCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha vulcanica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh apk download|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin giris|
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma pedrada. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma verdadeira faisca, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
codigo promocional megaposta|
После выбора подходящей методики врач подробно рассказывает о сути процедуры, даёт письменные рекомендации, объясняет правила поведения и отвечает на вопросы пациента и семьи.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
накрутка подписчиков телеграм 100 подписчиков
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://drnatro.com/le-khai-mac-he-nam-2024
https://t.me/insta_akki
Нужен чертеж? чертежи на заказ для студентов выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Мы обеспечиваем комфортные условия для пребывания в клинике Ростова-на-Дону, чтобы восстановление прошло максимально эффективно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Нужна презентация? заказать презентацию быстро Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://hibizsolutions.com/digital-design-that-will-help-you-start-your-business
Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]нарколог на дом ростовская область[/url]
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Следуйте по ссылке – https://varietyvacation.com/2022/07/01/how-to-travel-with-paper-map
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – https://limabatido.com.br/bonus-przy-rejestracji-od-kasyna-vulkan-vegas-online-537
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Это ещё не всё… – https://cgmbc.co.uk/projects/hr-smith-gazebo-relocation
Здравствуйте!
Пацанские автохитрости: экономим время, деньги и нервы. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/lajfhak-dlya-avto/]лайфхаки для машины[/url] Реальные советы от тех, кто прошел огонь, воду и наши дороги.
Написал: – https://zhit-legche.ru/lajfhak-dlya-avto/
лайфхак для автомобилистов
Удачи!
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Прочитать подробнее – https://sokkonews.info/%E9%AB%AA%E3%81%AE%E3%83%91%E3%82%B5%E3%83%91%E3%82%B5%E3%80%81%E3%83%84%E3%83%A4%E3%81%AA%E3%81%97%E3%80%81%E6%9E%9D%E6%AF%9B%E3%81%AE%E3%83%88%E3%83%A9%E3%83%96%E3%83%AB%E3%81%AB%E3%83%9C%E3%82%BF
накрутка подписчиков тг
Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena rostov-na-donu[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://todaytazakhabar.com/tag/hardik-pandya-leads-mumbai-indians
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Узнай первым! – http://vildastamps.com/blog/?p=14253
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Нажми и узнай всё – https://eminentriseconstruction.com/2023/06/28/boost-productivity-and-efficiency-with-our-range-of-digital
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Получить больше информации – https://hook.ng/best-way-to-redeem-amazon-gift-cards-for-naira-online
Je trouve absolument delirant Spinsy Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui tourbillonne comme un spot lumineux. Le repertoire du casino est un dancefloor de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme disco. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un DJ, avec une aide qui fait vibrer la piste. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient swinguer. Globalement, Spinsy Casino promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour les danseurs du casino ! A noter le design du casino est un spectacle visuel disco, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
spinsy 5|
Ich liebe den Glanz von SlotClub Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein bunter Rausch aus Lichtern. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Neonlicht gluht, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Lichtimpuls, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
slotclub casino com РїСЂРѕРјРѕРєРѕРґ|
https://kitehurghada.ru/
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Не упусти шанс – https://krootconsultancy.nl/2017/01/23/leiderschapsontwikkeling-ga-10-dagen-mee-op-reis-naar-nepal/img_0185
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Детальнее – https://elstonmaterials.com/products/tools/marshalltown/hammers/toothed-bush-hammers
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://techbudgie.ca/product/business-adventures
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Эксклюзивная информация – https://www.seeyouthere.be/things-to-do-in-liege-belgium-from-22-to-28-august-2022
Whenever playing online gaming, it is essential to establish controls on your activity.
Responsible gaming means monitoring your hours and spending.
Always make sure to play for fun rather than a way to earn money.
Take advantage of the responsible play features many platforms provide to help you stay on track.
It’s wise to take breaks regularly and evaluate your gaming habits.
https://forum.digiarena.zive.cz/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=215792
Ask for support or advice if you experience difficulties with your play.
Sharing your gaming limits with friends or family can boost your self-awareness.
With responsible gaming, you get i-gaming while protecting your well-being.
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя капельница
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуальные схемы лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
40 shining crown slot variantları Pinco casino-da populyardır.
Casino shining crown oyunları müasir dizayn ilə fərqlənir.
Shining crown gratis versiyası limitsiz sınaq verir. Shining crown amusnet çoxlu oyun variantı ilə tanınır. Shining crown online casino real pulla oynamaq imkanı verir.
Shining crown 77777 böyük qrafika ilə hazırlanıb.
Shining crown online sadə və əlçatan platformadır.
Daha ətraflı buradan baxın [url=https://shining-crown.com.az/]shining crown demo[/url].
Shining crown slot game yüksək qrafika və səs effektləri ilə zəngindir.
Shining crown free real oyun öncəsi yaxşı sınaqdır.
https://labrezerv.ru/
лучшие онлайн казино Обзор новых казино Не упустите новые возможности! Мы постоянно следим за появлением новых онлайн казино и публикуем обзоры на самые интересные и перспективные из них. Будьте в курсе последних новинок и выбирайте лучшие казино!
https://keeper-uae.com/ Self-Storage Warehouse in Dubai: A Multifaceted Solution These purpose-built facilities cater to a diverse clientele, offering varying unit sizes and customizable options. Imagine decluttering your home, streamlining your office, or securely archiving important documents – all within a controlled and monitored environment. Self-storage warehouses in Dubai provide the flexibility to adapt to your evolving needs, offering both short-term and long-term rental agreements.
ThePokies115
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Ростове-на-Дону — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя цена
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону можно пройти в клинике «ЧСП№1», с возможностью вызова нарколога на дом.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
https://robot-rating.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с использованием современных методов детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в краснодаре[/url]
Как сам!
Как начать инвестировать в 2025-м без миллиона в кармане. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/investiczii-dlya-nachinayushhih/]книги про инвестиции для начинающих[/url] Реальная инструкция от пацана, который сам прошел этот путь.
Здесь подробней: – https://economica-2025.ru/investiczii-dlya-nachinayushhih/
инвестиции для чайников
про инвестиции для начинающих
Пока!
В клинике «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – наркология вывод из запоя
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena rostov-na-donu[/url]
Добрый день!
Как играть в домино и не остаться лохом за столом. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/pravila-igry-v-domino/]правила игры в домино[/url] Разбираем правила, хитрости и психологию игры от простого классического домино до серьезного “Козла”.
Переходи: – https://nagny-casino.ru/pravila-igry-v-domino/
как играть в домино 4 человека
До встречи!
Обратившись в «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы получаете не только медицинскую помощь, но и всестороннюю поддержку на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят процедуру с соблюдением всех юридических норм и этических стандартов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov239.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москва[/url]
Reliable service providers typically maintain consistent pricing and don’t drastically undercut market rates — red flag for potential scams. Buy fifa coins online from established sellers who price competitively but realistically within market norms.
Buy twitter follower packages that include engagement boosting services for comprehensive growth strategies. Some providers offer likes, retweets, and comments alongside follower delivery for complete social proof.
Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru
Обратившись в клинику «Детокс» в Краснодаре, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя капельница
20
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь москве[/url]
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
casino betorspin bГіnus|
Je suis totalement emporte par Spinanga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui tourbillonne comme un ouragan dechaine. La selection du casino est une spirale de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance virevoltante. Le service client du casino est une bourrasque d’efficacite, repondant en un eclair tumultueux. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui secouent. Dans l’ensemble, Spinanga Casino est un casino en ligne qui dechaine les elements pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel tumultueux, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga casino bonus|
https://rostgrup.ru/
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Neonlicht explodiert. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Lichtspektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen hypnotisieren. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Leuchtfeuer, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Am Ende ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Lichtschalter, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
РїСЂРѕРјРѕРєРѕРґ slotclub casino|
https://t.me/bonus_dragon_money
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» проводит вывод из запоя как на дому, так и в стационаре под контролем врачей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov226.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя анонимно
поставить апостиль на свидетельство
В Ростове-на-Дону мы используем только сертифицированные препараты и современные методики, что обеспечивает высокую эффективность лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя в стационаре
https://fixme.com.ua/
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
Записаться к кардиологу https://www.docplus24.ru
buy cocaine in telegram cocain in prague from peru
Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov226.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
buy weed prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
Анализ крови на дому https://www.docplus24.ru
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Нарколог на дом вывод из запоя https://www.docplus24.ru
Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в краснодаре[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркология вывод из запоя
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркологический вывод из запоя
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov222.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно ростов-на-дону[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону мы используем только сертифицированные препараты и современные методики, что обеспечивает высокую эффективность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom rostov-na-donu[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя клиника
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov239.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого ростов-на-дону[/url]
https://t.me/bonus_dragon_money
Вывод из запоя в стационаре в Ростове-на-Дону — эффективное решение для длительного запоя.
Разобраться лучше – наркологический вывод из запоя
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм дешево
Je suis totalement emporte par Spinanga Casino, on dirait une tempete de plaisir endiablee. Il y a une rafale de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une bourrasque d’efficacite, assurant un support de casino immediat et dynamique. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un cyclone, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient explosifs. Pour resumer, Spinanga Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les dompteurs de tempete du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une bourrasque, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga apuestas|
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя в стационаре
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]запой нарколог на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin pt|
Estou completamente encantado por Richville Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que brilha como um lustre de cristal. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e reluzentes, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. O suporte do cassino esta sempre disponivel 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. O processo do cassino e claro e sem intrigas, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino fariam qualquer um se sentir rei. Na real, Richville Casino e uma joia rara para os fas de cassino para os nobres do cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de elegancia, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais reluzente.
richville united church of christ|
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
накрутка подписчиков тг задания
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Ростове-на-Дону.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]narkolog-na-dom rostov-na-donu[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом ростовская область[/url]
Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov239.ru/]нарколог на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es pulsiert mit einer schillernden Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Laser zielt. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Schalter, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist SlotClub Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Neontraum strahlt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Neonlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
slotclub casino com РїСЂРѕРјРѕРєРѕРґ|
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Хочу знать больше – https://equtu-ai.com/revolutionizing-education-with-equtu-ai-the-future-of-personalized-learning
Обратившись в клинику «Гармония» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov226.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov226.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom rostov-na-donu[/url]
20
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://srntv.net/archives/7339.html
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu moskva[/url]
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://www.hattiesburgms.com/tamera
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://globalgrowthinvestors.com/2024/05/02/corporate-leads-to-achieve-the-aim
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочу знать больше – https://metamarketing.ca/2023/03/29/why-is-your-social-media-account-not-doing-well
накрутка подписчиков без тг
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь москве[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детальнее – https://pero.bg/2024/10/04/kak-da-reagirame-pri-speshna-nuzhda-ot-klyuchar-v-studentski-grad
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://easapp.in/effortless-attendance-tracking-streamlining-employee-attendance-with-cdps-eas
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал без отписок
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://vanderlindenproducts.com/reviews
https://betglance.com/ Честные казино отзывы Как отличить честное казино от мошеннического? Читайте честные отзывы игроков! В отзывах вы найдете информацию о том, как казино относится к игрокам, как быстро выплачивает выигрыши и как решает возникающие проблемы. Выбирайте честные казино и играйте с уверенностью!
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Выяснить больше – https://quagoldviet24k.vn/nam-mo-thay-ho-vang-co-y-nghia-gi
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Посмотреть подробности – https://www.hcccar.org/supported-living-services
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Открой скрытое – https://lucahalma.com/profile/contact
https://fixme.com.ua/
Adoro o encanto de SpinWiz Casino, parece um redemoinho de diversao mistica. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo magico. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem maldicoes, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, SpinWiz Casino e um cassino online que e um portal de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spinwiz Г© confiavel|
Sou louco pelo batuque de RioPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto um desfile na Sapucai. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e cheios de ritmo. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo do tamborim.
roblox lite rioplay|
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Следуйте по ссылке – https://amicale.pompjeen-freiseng.lu/parkingsdengscht-theater
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://weihong.vn/?attachment_id=2297
Sou viciado na vibe de SpeiCasino, parece uma galaxia cheia de diversao estelar. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um cometa, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino e um cassino online que e uma supernova de diversao para os astronautas do cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
spei crash game|
“[url=https://www.kufar.by/item/253886872]аренда инструмента в слуцке[/url] – выгодные условия и широкий выбор инструментов для любых задач.”
Вместо того чтобы покупать инструмент, который может понадобиться всего несколько раз, выгоднее взять его в аренду по доступной цене.
Такой подход особенно удобен для строителей и мастеров. Даже любители ремонта выбирают прокат инструмента, потому что это проще и дешевле.
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен широкий ассортимент оборудования для разных задач. В прокате представлены бензопилы, газонокосилки и другая садовая техника.
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и специализированную технику. Если нужно работать на высоте, доступны подъемники и строительные леса.
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – экономия на обслуживании и хранении. Все инструменты проходят регулярное обслуживание, поэтому клиенты получают только исправные устройства.
Дополнительный бонус – помощь в выборе подходящего оборудования. Консультанты помогут подобрать инструмент под конкретные задачи.
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды максимально проста и прозрачна. Достаточно оставить заявку на сайте или позвонить по телефону.
Условия проката выгодны для всех клиентов. Стоимость аренды зависит от срока и типа инструмента.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Почему аренда инструмента – это выгодно?**
Аренда инструмента в Слуцке позволяет избежать лишних затрат . Если вам нужен инструмент на короткий срок, аренда – идеальное решение, ведь не придется тратиться на дорогостоящее оборудование .
Такой подход особенно удобен для компаний и частных клиентов. Многие профессионалы предпочитают брать инструмент напрокат, так как это снижает затраты на выполнение работ .
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен множество инструментов для профессионального и бытового использования. В прокате представлены бензопилы, газонокосилки и другая садовая техника .
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и оборудование для узких задач. Если нужно работать на высоте, доступны подъемники и строительные леса .
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – экономия на обслуживании и хранении . Вам не придется беспокоиться о ремонте инструмента, так как за ним следят специалисты .
Дополнительный бонус – поддержка на всех этапах аренды. Консультанты помогут подобрать инструмент под конкретные задачи .
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды не требует сложных формальностей . Для оформления понадобится только паспорт и небольшой залог.
Условия проката адаптированы под разные потребности . Стоимость аренды зависит от срока и типа инструмента .
https://phlebologist-blog.ru/ Блог практикующего флеболога и сосудистого хирурга — всё о здоровье сосудов ног! Профилактика и профессиональное лечение варикоза: современные методики, склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен, экспертная диагностика. Получите проверенные советы и индивидуальное решение ваших проблем!
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Только для своих – https://latinloyalty.com/hello-world
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Нажми и узнай всё – https://www.shengko.co.uk/problems-with-stress
Привет!
Принцип здесь и сейчас: зачем забыть прошлое ради настоящего. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/geshtalt-psihologiya/]гештальт психология[/url] Объясняем основу гештальт-подхода простыми словами.
Написал: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/geshtalt-psihologiya/
гештальт-психология
Покеда!
купить горшки с автополивом интернет [url=https://www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru]https://www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru[/url] .
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Посмотреть всё – https://todaytazakhabar.com/tag/hardik-pandya-leads-mumbai-indians
1xbet зеркало рабочее
When participating in online gaming, it is important to define boundaries on your activity.
Responsible gaming means managing your hours and budget.
Always be aware to play for fun rather than a profit tool.
Apply the safety features many platforms include to help you remain balanced.
It’s helpful to take breaks regularly and evaluate your gaming habits.
https://theplenty.net/forums/thread-23902.html
Ask for support or advice if you experience difficulties with your play.
Sharing your gaming limits with friends or family can boost your self-awareness.
Through practicing balanced gaming, you get i-gaming while maintaining your health.
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Хочу знать больше – https://panthfasteners.com/nullam-dictum-felis-e
A friend of mine advised this site. And yes. it has some useful pieces of info and I enjoyed scaning it. Therefore i would love to drop you a quick note to express my thank. Take care
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://unreasonablygrateful.com/index.php/2023/05/27/loss-as-access-to-love
Acho simplesmente alucinante RioPlay Casino, parece uma festa carioca de diversao. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que e puro gingado. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Na real, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
rioplay cassino|
Estou completamente vidrado por SpinFest Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um piao enlouquecido. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que vibram como tambores. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que samba com estilo. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma danca de frevo, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Na real, SpinFest Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
spinfest casino erfahrungen|
https://kwikplay.ru/
ремонт тернопіль https://remontuem.te.ua
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura luz cosmica. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No geral, SpeiCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei apk|
Самостоятельные девушки — это выразительные личности, которые ценят свою индивидуальность.
Они предпочитают к осознанному подходу в общении.
Такие девушки обычно обладают сильным характером и четкими жизненными ценностями.
Они не стесняются демонстрировать свои взгляды.
https://lugansk.spaxam.net/
Взаимодействие с ними нередко получается интересным.
Они любят слышать собеседника и создавать искренние отношения.
Такие девушки мотивируют окружающих своей аутентичностью.
Они идут своим маршрутом, не подстраиваясь под чужие ожидания.
Продажа авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae/ru/sale/car/all/?page=1 новые и подержанные автомобили с гарантией качества. Большой выбор, доступные цены и юридическая прозрачность сделок для покупателей.
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4100743517/
Трансы Екатеринбург Трансы Екатеринбург
https://finance-info.ru/
Magazinul online care schimba experien?a cumparaturilor. Fiecare articol este o invita?ie de stil.
– [url=https://tcicgcluj.ro ]https://enlightennext.de
[/url]
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон москва[/url]
Аэропорт аренда авто в Краснодаре
Как сам!
Деньги на всякий случай: как собрать подушку безопасности без фанатизма. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/finansovaya-podushka-bezopasnosti-eto/]финансовая подушка безопасности размер[/url] Практический гайд по финансовой защите для обычных людей.
Здесь подробней: – https://economica-2025.ru/finansovaya-podushka-bezopasnosti-eto/
финансовая подушка безопасности это
финансовая подушка безопасности размер
До встречи!
Приветствую!
MagSafe повербанки для iPhone: полный гайд по выбору в 2025. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/poverbank-dlya-ajfona/]повербанк для айфона[/url] От бюджетных Xiaomi за 1300 рублей до премиум Anker – разбираем что стоит покупать.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/poverbank-dlya-ajfona/
беспроводной повербанк для айфона
повербанк для айфона оригинал
лучший повербанк для айфона
Бывай!
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Suntem mai mult decat un magazin de vanzare – suntem parteneri in lumea modei.
– [url=https://dobraterapia-bochnia.pl ]https://traybake-cutter.com
[/url]
купить диплом в новокуйбышевске [url=https://rudik-diplom15.ru]купить диплом в новокуйбышевске[/url] .
20
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
микрозайм рейтинг где можно взять займ
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin casino review|
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui explose comme un volcan en eruption. Il y a une explosion de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme explosif. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un pyromane, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une braise, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du feu. Au final, Stake Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel en fusion, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
avis my stake|
Adoro o encanto de SpinGenei Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um genio libertado. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e encantadoras, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro genio, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SpinGenei Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spingenie no deposit bonus|
Je trouve absolument eblouissant Riviera Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi chic qu’une soiree sur un yacht. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une veritable Riviera de delices, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse de yacht, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait somptueux. Dans l’ensemble, Riviera Casino offre une experience de casino luxueuse pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline glamour du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique ensoleillee, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus glamour.
la riviera+casino|
https://chistota-shop.ru/dizelnoe-toplivo-vidy-i-primenenie.html
купить диплом мастера маникюра и педикюра [url=https://rudik-diplom14.ru/]купить диплом мастера маникюра и педикюра[/url] .
https://pvhprofi.ru/
Estou alucinado com SpellWin Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma pocao encantada. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um feitico de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de fantasia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo magico. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma runa, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os magos do cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spellwin no deposit bonus code|
20
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
При наличии интоксикации и абстинентных проявлений назначается инфузионная коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, витаминотерапия (включая тиамин), средства для нормализации сна, снижения тревоги и профилактики судорог. Контролируются артериальное давление, частота пульса, сатурация и диурез, что позволяет безопасно проходить острый период.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр луганск[/url]
Согласование целей на старте курса помогает распределить задачи по этапам и своевременно корректировать тактику при изменении клинической картины.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма кодирование луганск[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений играет важную роль и в совокупности формирует основу для восстановления и возвращения пациента к полноценной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту проходить все стадии восстановления в безопасном и контролируемом режиме.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена донецк[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Донецке предполагает комплексную медицинскую помощь, ориентированную на снижение интоксикации, стабилизацию витальных функций и профилактику осложнений. Патофизиологически запой сопровождается нарушением водно-электролитного баланса, колебаниями артериального давления, тахикардией, рисками аритмий, дефицитом витаминов группы B и дисрегуляцией нейромедиаторных систем. Клиническая тактика строится на ранней оценке риска, контроле соматического статуса и пошаговой коррекции нарушений с обязательным наблюдением за сердечно-сосудистой и дыхательной системами.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-makeevka-dnr/
Методическая база клиники опирается на доказательные подходы и стандартизированные протоколы. Комбинация инструментов подбирается индивидуально с учётом переносимости и клинической целесообразности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в луганске[/url]
Нужна презентация? нейросеть составить презентацию Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
Проблемы с откачкой? помпа для откачки воды из колодца сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
best deposit bonuses for slots
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь московская область[/url]
buy coke in prague cocaine in prague
https://finance-info.ru/
При наличии интоксикации и абстинентных проявлений назначается инфузионная коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, витаминотерапия (включая тиамин), средства для нормализации сна, снижения тревоги и профилактики судорог. Контролируются артериальное давление, частота пульса, сатурация и диурез, что позволяет безопасно проходить острый период.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
накрутка активных подписчиков в тг
Наркологическая клиника в Донецке оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Лечение в таких учреждениях направлено на комплексное восстановление здоровья, включающее медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Важным принципом является индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, что позволяет добиться устойчивых результатов и снизить риск рецидива.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Аренда авто Краснодар
Даже при умеренной симптоматике самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» часто приводят к усугублению дегидратации, электролитным нарушениям и риску делирия. Медицинский контроль позволяет корректировать состояние по объективным показателям и предотвращать декомпенсацию.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-dnr/
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu moskva[/url]
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Терапевтический набор подбирается индивидуально и комбинируется для одновременного воздействия на биологические, психологические и социальные факторы расстройства. Ниже приведены базовые инструменты и их назначение.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма луганск[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Программы терапии строятся так, чтобы одновременно воздействовать на биологические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости. Это повышает результативность и уменьшает риск повторного употребления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin casino reseГ±a|
Acho simplesmente magico SpinGenei Casino, parece um portal encantado de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um lampiao de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que brilha como uma varinha magica. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria magico. No geral, SpinGenei Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro feitico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spingenie|
Эти методы применяются комплексно, что повышает их эффективность и помогает пациентам быстрее возвращаться к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр[/url]
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
накрутка подписчиков тг живые без отписок
После рабочего дня решил побаловать себя и пришел сюда. Встретили дружелюбно, все чисто и красиво, музыка мягкая. Девушка превратила массаж в настоящее шоу эмоций. Обязательно попробуйте, шлюха вызвать нск – https://sibirki3.vip/. Всё на высшем уровне, доволен полностью.
Estou alucinado com SpellWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura magia. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de encantos, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem maldicoes. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um feitico de teletransporte, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. No geral, SpellWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spellwin germany|
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
buy xtc prague prague drugs
cocaine prague cocaine prague telegram
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москве[/url]
Ich bin suchtig nach SportingBet Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Volltreffer im Spielrausch. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echter Torerfolg, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Volltreffer glanzt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Taktikplan punktet. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sprinter, manchmal wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Sieg jubeln. Alles in allem ist SportingBet Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glanzt wie ein Flutlicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
sportingbet free spins|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
codigo bonus betorspin|
Estou alucinado com SupaBet Casino, parece um furacao de pura adrenalina. Tem um tsunami de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de superpoder. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma supernova, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo supersonico, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que abalam o planeta. No geral, SupaBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao total para quem curte apostar com energia epica no cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um estalo de raios, torna a experiencia de cassino um evento sismico.
supabet mobile login old site|
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
трансы волгограда трансы волгоград
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон москва[/url]
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Estou alucinado com SupremaBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro dominio. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e soberanas, com slots de cassino tematicos de poder. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um decreto de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem revoltas. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial imperial. No fim das contas, SupremaBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro cetro para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um palacio, adiciona um toque de grandeza ao cassino.
supremabet Г© confiГЎvel|
cocaine prague buy cocaine prague
prague drugstore high quality cocaine in prague
Поиск доктора-остеопата — важный этап на пути к улучшению самочувствия.
Для начала стоит понять свои проблемы и пожелания от консультации у остеопата.
Необходимо изучить подготовку и стаж выбранного доктора.
Рекомендации пациентов помогут сформировать осознанный решение.
https://obyava.org/rostov-na-donu/services/beauty-health/medicine/tsentr-osteodok-v-rostove-na-donu-massazh-osteopatiya-manualnaya-terapiya-t1740739586
Также необходимо проверить техники, которыми работает доктор.
Стартовая сессия даёт возможность почувствовать, насколько удобно вам общение и подход врача.
Важно оценить тарифы и режим приёма (например, онлайн).
Взвешенный выбор специалиста способен улучшить реабилитацию.
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/narkologiya-lugansk-lnr
Привет!
Твои мышцы начали жить своей жизнью и дергаться без спроса. [url=https://zhit-legche.ru/nervnyj-tik/]нервный тик[/url] Полный гид по нервным тикам от причин до лечения простыми словами.
Читай тут: – https://zhit-legche.ru/nervnyj-tik/
опасен ли нервный тик
Покеда!
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар луганск[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому московская область[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Маршрутизация фиксируется в индивидуальном плане: место оказания помощи (амбулаторно, дневной стационар, круглосуточный стационар), контрольные точки и критерии эффективности. Такой подход позволяет оперативно корректировать тактику, если динамика замедляется или появляются новые клинические данные. Пациент получает чёткое понимание этапов терапии, сроков и ожидаемых результатов, а также способов связи с командой в случае изменений самочувствия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/
1win parol tiklash [url=1win5501.ru]1win5501.ru[/url]
как накрутить подписчиков в телеграме
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в донце[/url]
Онлайн?платформа 1win с акциями на старте.
Промокоды и ваучеры помогают начать без лишних затрат.
Регистрация занимает пару минут, и доступны промо?условия.
Разделы с играми и событиями собраны без лишних сложностей.
Чтобы использовать актуальный код, смотри инструкции здесь — актуальный промокод 1win, последуй инструкциям.
Играйте ответственно, чтобы процесс оставался комфортным.
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin com|
Вывод из запоя в Донецке предполагает комплексную медицинскую помощь, ориентированную на снижение интоксикации, стабилизацию витальных функций и профилактику осложнений. Патофизиологически запой сопровождается нарушением водно-электролитного баланса, колебаниями артериального давления, тахикардией, рисками аритмий, дефицитом витаминов группы B и дисрегуляцией нейромедиаторных систем. Клиническая тактика строится на ранней оценке риска, контроле соматического статуса и пошаговой коррекции нарушений с обязательным наблюдением за сердечно-сосудистой и дыхательной системами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя переулок панфилова, 36[/url]
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru
Acho simplesmente fantastico SpinSala Casino, parece uma festa reluzente cheia de energia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de brilho, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um raio de neon, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, SpinSala Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho para quem curte apostar com estilo iluminado no cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo brilhante, adiciona um toque de glamour reluzente ao cassino.
spinsala online casino|
Даже при умеренной симптоматике самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» часто приводят к усугублению дегидратации, электролитным нарушениям и риску делирия. Медицинский контроль позволяет корректировать состояние по объективным показателям и предотвращать декомпенсацию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Sou louco pela energia de SupremaBet Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um trovao epico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e soberanas, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de realeza. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um decreto de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago imperial. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma carruagem real, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, SupremaBet Casino e um cassino online que e um reino de diversao para os soberanos do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um palacio, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um rei ao seu trono.
supremabet|
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Corgislot Casino https://ysc.wfv.mybluehost.me/website_0fe2c334/hoedanig-corgislot-herken-jij-betrouwbare-online-casinos-plusteken-welke-zijn-wettig/
Проблемы с откачкой? насос для откачки воды с пола сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
buy drugs in prague cocain in prague from brazil
buy weed prague high quality cocaine in prague
coke in prague buy drugs in prague
This is a great blog. Thank you for the very informative post.
Тактика подбирается индивидуально и зависит от тяжести состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и переносимости препаратов. Ниже представлены базовые компоненты, которые часто включаются в схемы лечения при запойных состояниях.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение в клинике проводится последовательно, что позволяет контролировать процесс выздоровления и обеспечивать пациенту максимальную безопасность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/[/url]
Приветствую!
Инфляция 8% в год – это много или нормально для простого человека. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/inflyacziya-eto/]недельная инфляция в россии[/url] Честный разговор о том, как это влияет на твою жизнь и кошелек.
Написал: – https://economica-2025.ru/inflyacziya-eto/
недельная инфляция в россии
инфляция в россии
Будь здоров!
Хай!
99% точности против 70% – почему нагрудный датчик побеждает. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/nagrudnyj-pulsometr/]нагрудный пульсометр[/url] Разбор технологий, моделей и практические советы по использованию.
Переходи: – https://pro-telefony.ru/nagrudnyj-pulsometr/
нагрудный пульсометр
пульсометры с нагрудным датчиком
пульсометр на грудь
До встречи!
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
После стабилизации фокус смещается на поддерживающие схемы, снижающие влечение и улучшающие переносимость повседневной нагрузки. Параллельно проводятся индивидуальные и групповые психотерапевтические занятия, направленные на развитие навыков саморегуляции, работу с триггерами и формирование альтернатив алкогольному или наркотическому поведению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в луганске[/url]
weed in prague vhq cocaine in prague
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? Zabljak nekretnine Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
Смотрите онлайн песни для детей слушать онлайн или скачать лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin scam|
20
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москве[/url]
Использование этих методов в комплексе позволяет восстановить здоровье пациента и сформировать основу для трезвой жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/[/url]
После стабилизации фокус смещается на поддерживающие схемы, снижающие влечение и улучшающие переносимость повседневной нагрузки. Параллельно проводятся индивидуальные и групповые психотерапевтические занятия, направленные на развитие навыков саморегуляции, работу с триггерами и формирование альтернатив алкогольному или наркотическому поведению.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Своевременная медицинская помощь уменьшает вероятность тяжелых осложнений и сокращает период восстановления. При следующих признаках требуется неотложная оценка состояния и начало терапии под наблюдением специалистов:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница переулок панфилова, 36[/url]
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/doneczk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Терапевтическая стратегия выстраивается вокруг понятных клинических ориентиров, что делает процесс предсказуемым и повышает приверженность пациента к лечению.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма анонимно[/url]
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Наркологическая клиника в Луганске организует помощь людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью по стандартам доказательной медицины. Целью является не только купирование симптомов и снятие интоксикации, но и формирование устойчивой ремиссии, восстановление психоэмоционального баланса и возвращение к социальной активности. Система помощи строится поэтапно, с учётом клинического состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и психосоциальных факторов. Команда специалистов обеспечивает согласованность действий, а регламенты лечения — прозрачность и предсказуемость каждого шага.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/narkologiya-lugansk-lnr/
Методическая база клиники опирается на доказательные подходы и стандартизированные протоколы. Комбинация инструментов подбирается индивидуально с учётом переносимости и клинической целесообразности.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/narkologiya-lugansk-lnr/
Ключевая задача первичного этапа — безопасно купировать абстинентный синдром и обеспечить постепенный метаболический «выход» без резких колебаний давления и частоты сердечных сокращений. Дополнительно оцениваются когнитивные и аффективные проявления, нарушения сна, уровень тревоги и наличие сопутствующих воспалительных процессов. По результатам обследования формируется индивидуальный план лечения с учетом предшествующего анамнеза, толерантности к препаратам и возможной полипрагмазии.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Донецке оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Лечение в таких учреждениях направлено на комплексное восстановление здоровья, включающее медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Важным принципом является индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, что позволяет добиться устойчивых результатов и снизить риск рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в донце[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
как накрутить подписчиков в телеграм бот
Для достижения результата применяются доказательные методики, которые обеспечивают стойкую ремиссию и снижают риск повторного употребления алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма[/url]
Даже при умеренной симптоматике самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» часто приводят к усугублению дегидратации, электролитным нарушениям и риску делирия. Медицинский контроль позволяет корректировать состояние по объективным показателям и предотвращать декомпенсацию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/doneczkaya-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
Тактика подбирается индивидуально и зависит от тяжести состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и переносимости препаратов. Ниже представлены базовые компоненты, которые часто включаются в схемы лечения при запойных состояниях.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого переулок панфилова, 36[/url]
Такая структура делает процесс предсказуемым и результативным, а также помогает закрепить достигнутые улучшения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/
Sunny coin hold the spin slot game həqiqətən dinamikdir. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin casino oyunları arasında məşhurdur.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot oyununda böyük qalibiyyət şansı var. Sunny Coin 2 hold the spin slot oynamaq həyəcanlıdır.
Sürətli keçid üçün klik edin [url=https://sunny-coin.com.az/]sunny coin com[/url].
Sunny coin hold the spin slot online demo çox istifadəlidir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot demo rahat giriş imkanı yaradır. Sunny coin hold the spin oyna və yeni imkanlar kəşf et.
Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot real pul ilə uğurludur. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot online çox məşhurdur.
Narcology Clinic в Москве оказывает экстренную наркологическую помощь дома — скорая выездная служба выполняет детоксикацию, капельницы и мониторинг до нормализации состояния. Анонимно и круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
I am lucky that I discovered this website , precisely the right info that I was searching for! .
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
suporte betorspin|
Использование этих методов в комплексе позволяет восстановить здоровье пациента и сформировать основу для трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в донце[/url]
20
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru
Комбинация методов позволяет добиться синергетического эффекта: быстрее снять острые проявления, а затем закрепить результат в естественных условиях жизни.
Получить больше информации – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/lugansk-kodirovka-ot-alkogolya
Сочетание перечисленных направлений обеспечивает полноту помощи и позволяет выстроить предсказуемый маршрут лечения с понятными целями на каждом этапе.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника луганск[/url]
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
https://device-rf.ru/catalog/iphone/
Скорая наркологическая служба Narcology Clinic в Москве работает круглосуточно. Выезд к пациенту, медикаментозная стабилизация, детоксикация и психологическая поддержка до выхода из кризисного состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь москва[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Донецке проводится с использованием современных медицинских и психотерапевтических методик. Такой подход помогает пациентам избавиться от физической и психологической зависимости, восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Основой успешной терапии является индивидуальная программа, которая формируется с учётом состояния пациента и стадии заболевания.
Выяснить больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-v-doneczke-dnr
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
В наркологической клинике в Донецке применяются современные и доказательные методики. Они безопасны, эффективны и соответствуют международным медицинским стандартам.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в донце[/url]
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/
J’adore la fraicheur de ViggoSlots Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme une banquise illuminee. La selection du casino est une tempete de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme polaire. Le service client du casino est un flocon d’efficacite, assurant un support de casino immediat et givre. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans tempete, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait glacial. Dans l’ensemble, ViggoSlots Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style givre, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus glaciale.
viggoslots no deposit bonus code|
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон[/url]
Переход между этапами определяется клиническими критериями эффективности и переносимости, а также динамикой поведения в повседневной среде.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в луганске[/url]
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Методическая база клиники опирается на доказательные подходы и стандартизированные протоколы. Комбинация инструментов подбирается индивидуально с учётом переносимости и клинической целесообразности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
Если требуется экстренная помощь при алкогольном кризисе — Narcology Clinic Москва предоставляет срочную помощь на дому: выезд нарколога, купирование симптомов, мониторинг состояния, без очередей и задержек.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
стиль модерн в інтер’єрі https://remontuem.te.ua
Эта структура терапии помогает достигать устойчивой ремиссии и снижать вероятность возврата к употреблению.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар донецк[/url]
Терапевтическая стратегия выстраивается вокруг понятных клинических ориентиров, что делает процесс предсказуемым и повышает приверженность пациента к лечению.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма луганск[/url]
кашпо под цветы напольные уличные [url=http://ulichnye-kashpo-kazan.ru/]кашпо под цветы напольные уличные[/url] .
1вин мобильная версия [url=1win5503.ru]1вин мобильная версия[/url]
Сочетание перечисленных направлений обеспечивает полноту помощи и позволяет выстроить предсказуемый маршрут лечения с понятными целями на каждом этапе.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/luganskaya-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza
Как сам!
Скачки в России – спорт королей и заработок для умных. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/konnye-skachki/]скачки лошади[/url] Полный разбор от истоков до современных реалий.
Переходи: – https://nagny-casino.ru/konnye-skachki/
конные скачки в россии
конские скачки
Пока!
https://plenka-okna.ru/
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту проходить все стадии восстановления в безопасном и контролируемом режиме.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk-dnr/
Приветствую!
Народное финансирование – это когда люди сами дают деньги на интересные проекты. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/kraudfanding/]краудфандинг-платформы[/url] Полный гайд по краудфандингу без воды и теории.
Написал: – https://economica-2025.ru/kraudfanding/
краудфандинга что это
краудфандинг-платформы
Покеда!
значки металл печать значков москва
значки эмалированные заказ значки на заказ металлические на заказ
значок на лацкан на заказ изготовление значков на заказ москва москва
В Москве к вашим услугам скорая наркологическая помощь от Narcology Clinic — выезд врача 24/7, качественная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, стабилизация состояния и организация дальнейших этапов детоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Хай!
Лучшие игровые планшеты 2025 года без воды и понтов. [url=https://pro-telefony.ru/igrovoj-planshet/]игровой планшет[/url] Разбираем железо которое реально стоит своих денег.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/igrovoj-planshet/
лучший игровой планшет
игровой планшет 120 герц
игровой планшет
Удачи!
где купить диплом техникума в ижевске [url=http://frei-diplom10.ru]где купить диплом техникума в ижевске[/url] .
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту проходить все стадии восстановления в безопасном и контролируемом режиме.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в донце[/url]
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, BacanaPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de frevo, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay estГєdio|
Je trouve absolument glacial ViggoSlots Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme une banquise illuminee. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et givrees, proposant des slots de casino a theme polaire. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de toundra, repondant en un eclair glacial. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse polaire, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, ViggoSlots Casino promet un divertissement de casino glacial pour les explorateurs polaires du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style givre, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
viggoslots fr|
купить диплом техникума 1992 [url=www.frei-diplom7.ru/]купить диплом техникума 1992[/url] .
накрутка подписчиков в тг смм накрутка
Переход между этапами определяется клиническими критериями эффективности и переносимости, а также динамикой поведения в повседневной среде.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма луганск[/url]
Good day! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any ideas or suggestions? Thanks
kra40 cc
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]частная скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Эта структура терапии помогает достигать устойчивой ремиссии и снижать вероятность возврата к употреблению.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в донце[/url]
Пошаговая структура помогает удерживать стабильную динамику, своевременно оценивать прогресс и гибко корректировать тактику.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/
Согласование целей на старте курса помогает распределить задачи по этапам и своевременно корректировать тактику при изменении клинической картины.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в луганске[/url]
габапентин аналоги Габапентин: Возможные неприятности Габапентин может вызывать различные побочные действия, такие как сонливость, головокружение, нарушение координации, тошнота, рвота, запор, усталость, увеличение веса и другие. О любых необычных симптомах следует сообщать врачу.
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Пошаговая структура помогает удерживать стабильную динамику, своевременно оценивать прогресс и гибко корректировать тактику.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru
схемы оптимизации налогов ндс Оптимизация НДС: Ключ к снижению налоговой нагрузки Оптимизация НДС подразумевает комплекс мер, направленных на снижение налоговых платежей с использованием законных методов и инструментов. Это включает в себя анализ договоров, выбор оптимальной системы налогообложения и использование налоговых льгот.
[url=https://sm70-dom.ru ]дом клееный брус
[/url]
Согласование целей на старте курса помогает распределить задачи по этапам и своевременно корректировать тактику при изменении клинической картины.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма на дому в луганске[/url]
Je suis fou de Unibet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui resonne comme un crescendo. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance musicale. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un chef d’orchestre, repondant en un eclair melodique. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait melodique. Dans l’ensemble, Unibet Casino est un casino en ligne qui joue une symphonie de plaisir pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une salle de concert, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
hexapro unibet|
Je suis accro a Tortuga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme une tempete en haute mer. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme pirate. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et fiable, repondant en un eclair de sabre. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse de galion, cependant des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient hisser le pavillon. Pour resumer, Tortuga Casino offre une experience de casino audacieuse pour les pirates du casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une boussole, facilite une experience de casino epique.
tortuga casino compte bloque|
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/narkologiya-doneczk-dnr/
[url=https://zhiloikompleks.ru ]дом из клееного бруса москва
[/url]
Пошаговая структура помогает удерживать стабильную динамику, своевременно оценивать прогресс и гибко корректировать тактику.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-lugansk/
Лечение алкоголизма в Донецке проводится с использованием современных медицинских и психотерапевтических методик. Такой подход помогает пациентам избавиться от физической и психологической зависимости, восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Основой успешной терапии является индивидуальная программа, которая формируется с учётом состояния пациента и стадии заболевания.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр[/url]
габапентин от чего помогает Габапентин: Мнение специалистов Врачи отмечают эффективность габапентина в лечении нейропатической боли и эпилепсии. Однако они подчеркивают важность соблюдения режима дозирования и учета возможных побочных эффектов. Габапентин должен назначаться только врачом после тщательного обследования.
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без регистрации
Экстренная наркологическая служба в Москве от Narcology Clinic предлагает оперативный выезд врача на дом. Срочный детокс, стабилизация и круглосуточная поддержка пациента с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Донецке проводится с использованием современных медицинских и психотерапевтических методик. Такой подход помогает пациентам избавиться от физической и психологической зависимости, восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Основой успешной терапии является индивидуальная программа, которая формируется с учётом состояния пациента и стадии заболевания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма донецк[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь московская область[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь[/url]
[url=https://opt-stroymarket.ru ]Проектирование домов из клееного бруса
[/url]
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Донецке проводится с использованием современных медицинских и психотерапевтических методик. Такой подход помогает пациентам избавиться от физической и психологической зависимости, восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Основой успешной терапии является индивидуальная программа, которая формируется с учётом состояния пациента и стадии заболевания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru
Терапевтическая стратегия выстраивается вокруг понятных клинических ориентиров, что делает процесс предсказуемым и повышает приверженность пациента к лечению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма[/url]
Нужна скорая помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? В Москве служба Narcology Clinic оказывает неотложную помощь на дому — детокс, капельницы, оказание первой наркологической помощи и сопровождение до стабилизации.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/doneczkaya-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
Методическая база клиники опирается на доказательные подходы и стандартизированные протоколы. Комбинация инструментов подбирается индивидуально с учётом переносимости и клинической целесообразности.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Sou louco pela energia de Bet4Slot Casino, e um cassino online que roda como um carrossel enlouquecido. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um redemoinho de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que giram como um tornado. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carrossel, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um giro de roleta, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial giratorio. No geral, Bet4Slot Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carrossel total para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro redemoinho, adiciona um toque de adrenalina giratoria ao cassino.
nova bet4slot|
купить живых подписчиков в тг
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. The gaming options are lush and vibrant like a jungle, supporting casino games optimized for cryptocurrencies. Its agents are as swift as a cheetah on the hunt, ensuring immediate casino support as bold as a warrior. Casino transactions are as simple as a tribal dance, occasionally extra casino rewards would make hearts pound. In the end, Wazamba Casino is an online casino that thrives like a jungle oasis for casino adventurers! As a bonus the casino platform shines with a style as bold as a jaguar, making you want to dive back into the casino endlessly.
wazamba test|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin registo|
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в луганске[/url]
J’adore l’audace de Tortuga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme une tempete en haute mer. Le repertoire du casino est une carte au tresor de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance de flibustier. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une carte au tresor, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient epiques. Globalement, Tortuga Casino promet un divertissement de casino epique pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline des mers du casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un ocean au soleil, ajoute une touche de legende pirate au casino.
tortuga casino avis|
https://dzen.ru/110km
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме от Narcology Clinic в Москве — выезд врачей в любую точку города, купирование острых состояний, поддержка пациента до стабильного состояния, профессионально и в конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Москве — Narcology Clinic выезжает круглосуточно напрямую к пациенту. Срочные капельницы, детокс, контроль состояния и экстренная поддержка. Анонимно, профессионально, оперативно.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон москва[/url]
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/183263596/detail.aspx
play kite Обучение кайтсерфингу в Хургаде: Научитесь летать над волнами с Deti Vetra. Индивидуальный подход и быстрый прогресс!
20
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
1win yangi promo kod [url=https://www.1win5504.ru]https://www.1win5504.ru[/url]
В экстренной ситуации на фоне алкоголя — обращайтесь к скорой помощи Narcology Clinic в Москве. Качественный выезд нарколога, медицинская поддержка, нейтрализация последствий и помощь в восстановлении.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон[/url]
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Заходи — там интересно – https://topic.lk/7386
https://detivetra.ru/
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://hussamsultanco.com/packmn
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – http://okuniewska.net/2019/02/28/day-care-responsibility-to-protect-children
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Получить полную информацию – https://www.mikekoenig.de/portfolio/01/5d4a0712_rodemerk
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Перейти к статье – https://noodlebowltbay.com/menus/apple-smoked-chicken-with-white-bbq-sauce
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – https://www.animatic.es/2024/10/daliayellibrorojo-critica-animatic-sitges-seminci
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Изучить материалы по теме – http://bertrandwillems.be/parmi-mes-clients/telechargement
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://www.studioeight.nl/seo-optimized
Создадим сайт https://giperactive.ru который продаёт: дизайн, верстка, интеграции. Подключим SEO и контекст, настроим аналитику и CRM. Адаптивность, скорость 90+, первые заявки уже в первый месяц. Работаем под ключ, фиксируем сроки и KPI. Напишите — оценим проект за 24 часа.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://topic.lk/9899
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Провести детальное исследование – https://cosmicdreamcatchers.com/neptune-in-pisces-mystical-dreams
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Как это работает — подробно – https://limpink.es/todo-esto-no-seria-posible-sin-nuestro-equipo
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Кликни и узнай всё! – https://sobhe-emrooz.ir/1400/04/%D8%A2%D8%AE%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%86-%D9%81%D8%B1%D8%B5%D8%AA-%D8%A8%D8%B1%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B0%D8%A7%DA%A9%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%AA
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Только для своих – https://hook.ng/best-way-to-redeem-amazon-gift-cards-for-naira-online
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://intelechoicecom.com/voip-services/best-of-manchester-2013-copy-245×300
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – http://cuckoldsdiary.com/index.php/2016/11/10/entry-8-single-male-sighting
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно онлайн
Ich bin total begeistert von Wunderino Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Sprung in eine Wunderwelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Marchenwald voller Action, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein magischer Wind, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein magischer Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Wunderino Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Marchen, einen Hauch von Marchen-Magie ins Casino bringt.
8 mär|
Футболки с вырезом женские и футболки для пар с надписью в Симферополе. Зип худи оверсайз и смотреть толстовки мужские в Иваново. Принт мияги на футболку и надпись Екатеринбург на футболке в Кемерово. Логотипы на одежде и поло гараж каталог одежды официальный в Ижевске. Надпись на футболке оптом онлайн и прикольные надписи мужские футболки: https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://gdpassport.com/solomoa
Estou completamente fascinado por VikingLuck Casino, e um cassino online que ruge como um guerreiro viking. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um salao de Valhalla, com slots de cassino tematicos de lendas nordicas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma lanca de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao de Thor. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um corvo de Odin, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que rugem como guerreiros. Resumindo, VikingLuck Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro Valhalla, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um guerreiro ao campo de batalha.
viking luck rune|
Sou louco pela energia de WinGameBR Casino, e um cassino online que decola como um foguete em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem turbulencia. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um cometa, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, WinGameBR Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro lancamento para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
wingame br safe|
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://www.gafencushop.com/cruz-line-up
1win slot o‘yinlari [url=https://1win5504.ru/]https://1win5504.ru/[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Уточнить детали – https://superinnovators.com/2022/10/mini-cable-car-urban-mobility-system
Hello! This post could not be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
kra40 cc
кайт школа хургада Кайт Эльгуна, Сафага, Макади: выбирайте свой идеальный кайт-спот в Египте с Deti Vetra!
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал без отписок
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал без отписок
https://detivetra.ru/
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu/
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu
joszaki regisztracio https://joszaki.hu/
https://dzen.ru/110km
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://zsmeservices.com/how-to-recover-your-content-from-wayback-machine
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find a lot of your post’s to be what precisely I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content available for you? I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome web log!
https://http-kra40.cc
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – http://svanetiinfo.ge/?attachment_id=600
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Не упусти шанс – https://sidradoranna.com.mx/index.php/2023/11/10/hello-world
Adoro a aceleracao de F12.Bet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino supersonica. Tem um pit stop de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que derrapam como drifts. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. assegurando apoio sem derrapagens. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um sprint final. mesmo assim mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. Resumindo, F12.Bet Casino e um motor de emocoes para os fas de adrenalina supersonica! E mais o design e fluido como um pit stop. transformando cada aposta em uma ultrapassagem.
robo f12 bet mines|
Je suis totalement anime par Simsinos Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino anime. est une animation de sensations qui enchante. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cartoon. est un virtuose de l’animation. garantissant une assistance qui cadence. se deroulent comme une rhapsodie de dessins. cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient animes. Au final, Simsinos Casino offre une experience de casino cartoon pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! En plus offre un orchestre de couleurs rebondissantes. ajoute une touche de rythme cartoon au casino.
simsinos|
Corgislot Casino https://glassrootsllc.com/online-corgi-casino-gokhal-legale-casinos-online-wegens-holland-2024/
Привет!
Медитация: как нормально выспаться и не париться по пустякам. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/meditacziya-polza-ili-vred/]медитация для успокоения нервов[/url] Научные факты о том, почему это работает, а не очередная эзотерическая фигня.
Переходи: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/meditacziya-polza-ili-vred/
медитация утренняя
До встречи!
накрутка подписчиков в тг бот
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Этот набор принципов снижает тревожность и даёт ощущение управляемости процесса уже с первого контакта.
Получить больше информации – http://
Салон понравился приватностью и атмосферой. Девушка встретила радостно, сразу было видно, что здесь умеют заботиться о клиентах. Массаж просто восторг. Попробуйте, шлюха вызвать нск – https://sibirki3.vip/. Было лучше, чем ожидал, очень доволен.
I do believe your audience could very well want a good deal more stories like this carry on the excellent hard work.
Домашний формат подходит, когда показатели стабильны, а у пациента есть поддержка близких. Врач осматривает, ставит капельницу, оставляет понятные инструкции по режиму, сну, гидратации и «красным флажкам». Если дома становится «узко» по медпоказаниям — переводим в стационар без задержек и лишней бюрократии.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]нарколог на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Этот набор принципов снижает тревожность и даёт ощущение управляемости процесса уже с первого контакта.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-mytishchah/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Ростова-на-Дону, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Снимаем интоксикацию, купируем абстинентный синдром, стабилизируем давление и сердечный ритм, корректируем электролитный и водный баланс. По показаниям подключаем седативную и противотревожную терапию, защиту печени и желудочно-кишечного тракта, витамины группы B. Цель — безопасно пройти острый период, снизить тягу и нормализовать сон. При необходимости делаем ЭКГ, пульсоксиметрию, контролируем глюкозу, насыщение кислородом, температуру. Если состояние тяжёлое, предложим госпитализацию в стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением, где можно оперативно скорректировать схему лечения.
Узнать больше – http://
В Ростове-на-Дону мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения, без постановки на учёт.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Acho simplesmente esportivo MarjoSports Casino, e um drible de diversao que dribla a concorrencia. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como torcidas. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que marcam como gols. O suporte e um apito preciso. assegurando apoio sem cartoes. As transacoes sao simples como um passe. de vez em quando mais bonus seriam um diferencial de campo. Em resumo, MarjoSports Casino promete uma diversao que e um gol para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design e fluido como um contra-ataque. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um gol.
como funciona a marjosports|
Estou alucinado com BR4Bet Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um farol na nevoa. Os jogos formam um clarao de entretenimento. incluindo mesas com charme iluminado. O servico e confiavel como uma lanterna. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma chama. porem mais bonus seriam um diferencial reluzente. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Como extra o design e fluido como uma lanterna. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
cupom br4bet|
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
https://dzen.ru/110km
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые без отписок
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Метод выбирается только после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные, психотерапевтические и комбинированные подходы. Мы заранее обсуждаем ограничения, риски и поведение в стрессовых ситуациях — кодирование работает лучше всего как часть комплексного плана.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-podolske/
Обратившись в нашу клинику в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Метод и срок подбираются после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также комбинированные программы. Мы объясняем плюсы и ограничения каждого метода, помогаем подготовиться (диета, анализы, отмена определённых препаратов), а затем сопровождаем пациента в период адаптации к трезвости. Кодирование — часть комплексного плана, а не «волшебная кнопка»: устойчивый результат достигается, когда его дополняют поддерживающая терапия и работа с триггерами.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-balashihe/
купить реальных подписчиков в телеграм
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Когда подходит
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy0.ru
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно без регистрации
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov28.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
http://tourout.ru/
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
где купить подписчиков в телеграм канал
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Формат
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Curto demais a chama de Verabet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como labaredas. O catalogo de jogos e um altar de prazeres. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como brasas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como uma chama. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma labareda. de vez em quando mais recompensas fariam o coracao queimar. Para encurtar, Verabet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os xamas do cassino! E mais a navegacao e facil como uma labareda. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
vera bet Г© confiГЎvel|
Je suis accro a BankOnBet Casino, ca vibre avec une richesse de jeu qui s’empile. The game lineup is a fortune of thrills. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents verrouillent les problemes. joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. cependant I’d want more promos that compound like interest. All in all, BankOnBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui securise les victoires pour those chasing smart stakes! What’s more la plateforme du casino brille par son style rentable. ajoute une touche de luxe bancaire au casino.
bankonbet avis|
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону можно пройти в клинике «ЧСП№1», с возможностью вызова нарколога на дом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В «Новом Рассвете» первыми идут скорость и предсказуемость. После обращения мы сразу запускаем медицинский маршрут: врач уточняет исходные риски, предлагает безопасный формат старта (дом, дневной или круглосуточный стационар), объясняет, чего ждать в ближайшие часы и как будем закреплять результат в следующие недели. Все решения принимаются индивидуально — с учётом возраста, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых лекарств и бытовых условий.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/
Мы работаем с триггерами, режимом сна/питания, энергобалансом и типичными стрессовыми ситуациями. Короткие и регулярные контрольные контакты снижают риск рецидива и помогают уверенно вернуться к работе и бытовым задачам.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]besplatnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Обратившись в «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы получаете не только медицинскую помощь, но и всестороннюю поддержку на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]narkolog-na-dom rostov-na-donu[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov28.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
сервисы накрутки подписчиков в телеграм
накрутка подписчиков в тг без отписок
накрутить подписчиков в тг
lucky neko free play versiyası təcrübə üçün idealdır. Populyar oyunu buradan kəşf edin: [url=https://lucky-neko.com.az/]pg lucky neko[/url]. lucky neko casino onlayn seçim üçün əlverişlidir.
lucky neko pg slot çox stabil işləyir. lucky neko demo slot çox rahat işləyir. Maraqlananlar üçün: [url=https://lucky-neko.com.az/]domen lucky-neko.com.az[/url]. slot lucky neko demo əyləncə üçün əladır. lucky neko pg slot çox asan oynanır. lucky cat maneki neko uğur simvoludur. neko lucky oyunun dizaynı çox rəngarəngdir. lucky neko casino real pul üçün seçimdir.
Цель первого этапа — безопасно снизить интоксикацию и вернуть базовое самочувствие. Мы запускаем инфузионную терапию, корректируем водно-электролитный баланс, защищаем органы-мишени, нормализуем сон и аппетит. При необходимости выполняется ЭКГ, корректируются дозировки «на лету» по динамике показателей.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Хочу знать больше – https://ioadpib.com/2015/07/27/pellentesque-faucibus-maurisd-lobortis-hendrerit-4
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые бесплатно
Мы работаем с триггерами, режимом сна/питания, энергобалансом и типичными стрессовыми ситуациями. Короткие и регулярные контрольные контакты снижают риск рецидива и помогают уверенно вернуться к работе и бытовым задачам.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в тг группу
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://wilddragon.net/my-favorite-song
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Обратиться к источнику – http://florence-neuberth.com/low3n0a0131-4
Je suis obsede par BankOnBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi securisee qu’un vault blinde. Les choix sont varies et blindes comme un safe. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et securisees. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un virement. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. The process is clear like a balance sheet. cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui accumulent comme des interets. All in all, BankOnBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline securisee du casino! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style rentable. making every session more rewarding.
bankonbet casino willkommensbonus|
Estou alucinado com Fogo777 Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um xama. As opcoes sao ricas e queimam como carvoes. incluindo mesas com charme flamejante. O servico e confiavel como uma fogueira. assegurando apoio sem fumaca. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma labareda. ocasionalmente as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, Fogo777 Casino e uma pira de adrenalina para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Adicionalmente o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um ritual.
cashback fogo777|
Me encantei pelo fulgor de Verabet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como labaredas. As opcoes sao ricas e queimam como carvoes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como labaredas. O atendimento e solido como carvoes. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao simples como uma tocha. mas mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de fogo. Resumindo, Verabet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. fazendo o cassino queimar como uma fogueira.
betvera н Ѕнїў jogos de cassino e apostas online no vera bet|
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Узнай первым! – https://manhyiapalace.org/lies-are-the-root-of-land-disputes-otumfuo-tells-ahafo-peace-council
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://rcsremodelingtx.com/hello-world
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Полная информация здесь – http://winkler-martin.de/guestbook.html
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – http://daidokoro.s53.xrea.com/maro_blog/log/eid666.html
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Интересует подробная информация – https://recruitment.cusmagroup.com/the-evening-of-the-holiday
https://device-rf.ru/catalog/iphone/
Нужна экскурсия? экскурсия по казани на автобусе главные достопримечательности за 2–3 часа, профессиональный гид, наушники, остановки для фото. Старт из центра, несколько рейсов в день, билеты онлайн, детские тарифы и групповая скидка.
We have the best: https://institutocea.com
The latest data is here: https://panamericano.us
The newest is here: https://stmaryofthehills.org
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://comfortshoescorner.com/best-shoes-for-walking-in-sand
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Не упусти шанс – https://weareyoung.in/agency-compensation
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://almaxindustry.com/komatsu-pump-list
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Интересует подробная информация – https://psi-ko.it/component/k2/item/11.html?start=63150
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Обратиться к источнику – https://markaparket.com/%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%B9%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%85-%D9%82%DB%8C%D9%85%D8%AA-%D9%BE%D8%A7%D8%B1%DA%A9%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%88%D9%86%D8%B3-%D8%A2%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://www.liikennetraktori.fi/tuote/294
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Детальнее – https://alisohani.com/connecting-readers-from-around-the-world-4
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Только для своих – https://sdscollegejadla.com/iqac-meeting-held-on-date-05-11-2022
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Узнай первым! – https://cozinhasaudeedicas.com/suco-de-milho-cremoso-feito-com-3-ingredientes
Приветствую!
Кредитная история в глубокой заднице? [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-ispravit-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/]как исправить кредитную историю[/url] Пошаговая инструкция по восстановлению финансовой репутации.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-ispravit-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/
исправить кредитную историю онлайн
как можно исправить кредитную историю
как исправить кредитную историю после просрочки
Удачи!
Здарова!
ЦБ запускает третью форму денег в России. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/czifrovoj-rubl/]цифровой рубль минусы[/url] Подробный гайд по цифровому рублю простым языком.
Читай тут: – https://economica-2025.ru/czifrovoj-rubl/
цифровой рубль минусы
что такое цифровой рубль
Бывай!
как сделать накрутку подписчиков в тг
Хай!
Кредитные карты 2025 – какую выбрать без развода на бабки. [url=https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/luchshie-kreditnye-karty/]лучшие кредитные карты 2025[/url] Разбираю все подводные камни и топовые предложения банков простым языком.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/luchshie-kreditnye-karty/
самые лучшие кредитные карты
лучшие кредитные карты
лучшие кредитные карты со снятием наличных без процентов
Будь здоров!
Привет!
Биохимические убийцы в твоем теле. [url=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/gormony-stressa/]гормон стресс[/url] Гормоны стресса работают 24/7 на разрушение – пора изучить врага.
Здесь подробней: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/gormony-stressa/
гормоны стресса
Удачи!
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Получить полную информацию – https://sdesj.org/monsieur-samuel-poulin-depute-de-beauce-sud-adjoint-parlementaire-du-premier-ministre-du-quebec-participera-au-sommet2020
We have the best: https://www.europneus.es
The latest data is here: https://cour-interieure.fr
The newest is here: https://g-r-s.fr
Insights right here: https://www.pondexperts.ca
Estou completamente hipnotizado por IJogo Casino, e um enredo de diversao que se entrelaca como cipos. A colecao e uma teia de entretenimento. com caca-niqueis modernos que enredam como cipos. O time do cassino e digno de um explorador. respondendo rapido como um cipo se enrolando. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. mas mais bonus seriam um diferencial enredado. Em resumo, IJogo Casino garante um jogo que se entrelaca como cipos para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Adicionalmente a navegacao e facil como uma teia. adicionando um toque de emaranhado ao cassino.
ijogo game|
Galera, quero deixar registrado sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos me deixaram impressionado. O atendimento no chat foi educado e prestativo, o que ja me deixou seguro. As retiradas foram muito rapidas, inclusive testei PIX e super tranquilo. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa vale demais a pena. Eu mesmo ja voltei varias vezes
bingoemcasa site|
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://dollzanddinoz.com/autumn-2019-lookbook
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://oceanica.org.br/oceanica-realiza-campanha-praia-limpa-em-buzios
Topical topics are here: https://fish-pet.com
To the point is here: https://vse-pereezdi.ru
What you need is here: https://colegiosagradocorazon.es
Самая свежая информация: https://snabco.ru
Updated daily here: https://possible11.com
The most useful is here: https://sportsfanbetting.com
The most facts are here: https://maxwaugh.com
Новое и актуальное здесь: https://badgerboats.ru
трипскан зеркало TripScan войти: Добро пожаловать в личный кабинет TripScan! Войдите в свою учетную запись, чтобы управлять своими бронированиями, просматривать историю поездок и получать эксклюзивные предложения. Мы поможем вам спланировать ваше следующее приключение, учитывая все ваши потребности и пожелания. TripScan – ваш надежный партнер в мире путешествий. tripscan войти
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Ремонт iphone 7 Сервисный центр Xiaomi: Мы – профессиональный сервисный центр Xiaomi, предлагающий полный спектр услуг по ремонту телефонов, планшетов и другой техники Xiaomi. Используем только качественные запчасти и квалифицированных мастеров. Гарантируем быстрый и надежный ремонт. Доверьте свою технику Xiaomi профессионалам!
Updates here and now: https://chhapai.com
New releases right here: https://hello-jobs.com
Top materials are here: https://angersnautique.org
Hottest facts here: https://justicelanow.org
ставки на спорт онлайн прогнозы [url=https://stavka-12.ru]https://stavka-12.ru[/url] .
The best collected here: https://sportquantum.com
The most relevant here: https://cere-india.org
Лучшее только у нас: https://www.foto4u.su
New first here: https://agriness.com
Je suis accro a Casinia Casino, on dirait un donjon rempli de tresors caches. est une legende de sensations qui enchante. proposant des slots de casino a theme medieval. repond comme un bouclier. repondant en un eclat de lance. se deroulent comme une quete. neanmoins plus de bonus pour une harmonie chevaleresque. Pour resumer, Casinia Casino cadence comme une sonate de victoires pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! Par ailleurs offre un orchestre de couleurs medievales. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus noble.
casinia schweiz|
спортивные новости сегодня [url=https://www.novosti-sporta-15.ru]https://www.novosti-sporta-15.ru[/url] .
Je suis fou de Grandz Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino voile. propose un ballet de divertissement qui seduit. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. offre un soutien qui effleure tout. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. fluisent comme une sonate spectrale. mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Grandz Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne! De plus l’interface du casino est fluide et danse comme une ombre. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
code promo grandz race|
Estou alucinado com Stake Casino, oferece uma aventura que vibra como uma corda de harpa. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como cordas. com caca-niqueis modernos que ecoam como sinos. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. em alguns momentos queria mais promocoes que ressoam como corais. Em resumo, Stake Casino e uma vibracao de adrenalina para quem curte apostar com estilo harmonico! Por sinal o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. amplificando o jogo com ritmo sonoro.
stake game|
Galera, vim dividir com voces sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me surpreendeu demais. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei uns joguinhos extras, todos rodaram sem travar. O atendimento no chat foi rapido como nunca vi, o que ja me deixou confiante. As retiradas foram eficientes de verdade, inclusive testei PIX e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que as promocoes podiam ser mais ousadas, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. No geral, o Bingoemcasa me conquistou. Com certeza vou continuar jogando
bingoemcasa zeppelin|
stavki prognozy [url=http://www.novosti-sporta-16.ru]http://www.novosti-sporta-16.ru[/url] .
новости олимпиады [url=https://www.novosti-sporta-17.ru]https://www.novosti-sporta-17.ru[/url] .
Формат
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
прогнозы на спорт лайв [url=http://prognozy-na-sport-11.ru/]http://prognozy-na-sport-11.ru/[/url] .
Arcade official website https://betvisabengal.com
Coin Strike: Hold and Win https://lemon-cazino-pl.com
Cleaning is needed cleaning toronto eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
Когда уместен
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
сайт трипскан TripScan зеркало: Если у вас возникли проблемы с доступом к основному сайту TripScan, воспользуйтесь зеркалом. Зеркало TripScan предоставляет полный доступ ко всем функциям и услугам платформы, чтобы вы могли продолжать планировать свои путешествия без каких-либо препятствий. Наслаждайтесь удобством и надежностью TripScan, даже если основной сайт временно недоступен. trip scan зеркало
Формат
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя
Ремонт телефонов адреса Ремонт сотовых телефонов: Мы предлагаем профессиональный ремонт сотовых телефонов всех марок и моделей. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и качественно устранят любые неисправности, будь то замена экрана, аккумулятора, ремонт разъемов или сложное восстановление после попадания влаги. Мы используем только оригинальные запчасти и современное оборудование, что гарантирует высокое качество и долговечность ремонта. Доверьте свой сотовый телефон профессионалам и наслаждайтесь его безупречной работой! Мы гарантируем качество, скорость и доступные цены. Обращайтесь к нам, и ваш сотовый телефон будет как новый!
накрутка настоящих подписчиков в телеграм канале
https://pillow.su/anglijskij-yazyk-dlya-malyshej/
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Ростове-на-Дону.
Получить дополнительные сведения – нарколог вывод из запоя
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Что делаем на практике
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]нарколог на дом цена ростов-на-дону[/url]
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]нарколог на дом цена ростов-на-дону[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в тг без регистрации
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону можно пройти в клинике «ЧСП№1», с возможностью вызова нарколога на дом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого ростов-на-дону[/url]
Je suis captive par RollBit Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi structuree qu’un cube de donnees. Le repertoire du casino est un defilement de divertissement. incluant des tables qui structurent comme un cube. Le service client du casino est un bit maitre. assurant un support de casino immediat et structure. arrivent comme un concerto cubique. cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, RollBit Casino offre une experience de casino pixelisee pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! De plus l’interface du casino est fluide et vibre comme une partition de bits. facilite une experience de casino bit par bit.
dunexyz rollbit|
В Ростове-на-Дону мы используем только сертифицированные препараты и современные методики, что обеспечивает высокую эффективность лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Curto demais a vibracao de JonBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. oferecendo lives que explodem como ecos. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como uma nota. Os saques sao velozes como uma onda sonora. porem as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, JonBet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os maestros do cassino! Como extra a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. tornando cada sessao ainda mais ressonante.
painel jonbet|
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]srochnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch[/url]
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Je suis totalement captive par Boomerang Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang lance. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui reviennent comme un boomerang. repond comme un boomerang parfait. joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse circulaire. neanmoins j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui bouclent comme un boomerang. A la fin, Boomerang Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline boomerang du casino! En bonus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle arque. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
boomerang bet casino|
Ожидаемая траектория в первые сутки
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov28.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод ростов-на-дону[/url]
подписчики в тг канал боты
https://www.munihuamalies.gob.pe/articles/el_codigo_promocional-1xbet.html
школа изучения английского языка
Thank you for sharing this very good post. Very interesting ideas! (as always, btw)
накрутка подписчиков телеграм 100 подписчиков
Старт всегда один: короткий скрининг с дежурным врачом, где уточняются жалобы, длительность эпизода, текущие лекарства, аллергии и условия дома. Далее согласуется реальное окно прибытия или приёма — без обещаний «через пять минут», но с честным ориентиром и запасом на дорожную обстановку. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурацию, температуру), по показаниям выполняет ЭКГ, запускает детокс (регидратация, коррекция электролитов, защита печени/ЖКТ), объясняет ожидаемую динамику первых 6–12 часов и выдаёт памятку «на сутки»: режим сна, питьевой план, «красные флажки», точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, перевод в стационар организуется без пауз — терапия продолжается с того же места, где начата, темп лечения не теряется.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
Что включено на практике
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Специалист по наркологии — это профессионал, который предоставляет помощь людям, испытывающим проблемы от зависимостей. Лечение зависимостей включает в себя очистку организма, медикаменты и психологическую помощь. Необходимо обратиться за консультацией нарколога для разработки индивидуального плана реабилитации. Семейная поддержка играет важную роль в выздоровлении, а группы взаимопомощи помогают адаптироваться в обществе. Профилактика зависимостей также важна, чтобы снизить риск рецидивов. Консультация с профессионалами на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru гарантирует высококачественную помощь и содействие на всех этапах лечения.
tripscan войти TripScan – это современная платформа, созданная для любителей путешествий. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, включающий в себя поиск авиабилетов, бронирование отелей, аренду автомобилей и организацию экскурсий. Наша цель – сделать процесс планирования поездки максимально простым и удобным, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на самом приятном – предвкушении новых открытий и впечатлений. С TripScan вы сможете легко найти лучшие предложения, сравнить цены от разных поставщиков и выбрать оптимальный вариант, соответствующий вашим потребностям и бюджету. Мы постоянно работаем над улучшением нашего сервиса, чтобы предоставлять вам самую актуальную и полезную информацию. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу TripScan и откройте для себя мир безграничных возможностей для путешествий! TripScan трипскан
В Ростове-на-Дону мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения, без постановки на учёт.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Сначала врач проводит экспресс-диагностику. Измеряются давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается неврологический статус и уровень обезвоживания. Уточняются аллергии, хронические заболевания, длительность и объём употребления, принимаемые препараты. При необходимости выполняется ЭКГ, чтобы исключить острые риски со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом красногорск[/url]
Ремонт сотовых телефонов Ремонт iPhone: Ваш iPhone нуждается в ремонте? Мы – эксперты по ремонту iPhone всех моделей! Замена экрана, аккумулятора, ремонт кнопок, камер, восстановление после попадания влаги – это лишь малый перечень наших услуг. Используем только оригинальные запчасти и гарантируем высокое качество ремонта. Доверьте свой iPhone профессионалам и забудьте о проблемах!
Что включено на практике
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchelkovo[/url]
Реабилитация после алкогольной зависимости в городе Красноярск – критически важный шаг на пути к новой жизни. Нарколог на дом клиника предлагает профессиональное лечение алкоголизма с индивидуальными программами‚ включая очистку организма и психологическую помощь. Посещение нарколога способствует выявить эффективные методы терапии‚ такие как групповые занятия и адаптация в обществе. Семейная поддержка также является важным фактором. Реабилитационный центр предлагает конфиденциальную помощь и меры по предотвращению рецидивов‚ что способствует успешному восстановлению после зависимости от алкоголя.
В зависимости от клинической картины и предпочтений возможны следующие виды кодирования:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ehlektrostal6.ru
Insights by clicking here: https://sdch.org.in
J’adore le flux de RollBit Casino, est un tourbillon de divertissement qui pixelise. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui deroulent comme un flux. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un codeur. proposant un appui qui enchante. arrivent comme un concerto cubique. par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait cubique. En somme, RollBit Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline rythmee du casino! De surcroit offre un orchestre de couleurs cubiques. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
rollbit unable to login|
Top content by link: https://mcaofiowa.org
Verified information here: https://svpin.org
Important topics here: https://lagodigarda.com
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov28.ru/]врач нарколог на дом ростовская область[/url]
Me enredei no loop de XPBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao continua quanto um espiral infinito. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis modernos que giram como ciclos. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma roda. ocasionalmente queria promocoes que fluem como redemoinhos. No geral, XPBet Casino e um loop de emocoes para quem curte apostar com estilo giratorio! De lambuja o design e um espetaculo visual de vortice. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura giratoria.
xp bet app download|
Je suis fou de Boomerang Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un lancer. propose un ricochet de divertissement qui seduit. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et circulaires. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un retour boomerang. avec une aide qui revient comme un arc. fluisent comme une sonate arque. mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. A la fin, Boomerang Casino est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline boomerang du casino! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique circulaire. cadence l’aventure avec une rhapsodie de ricochets.
boomerang casino mobiles|
Клиника в Ростове-на-Дону работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время дня и ночи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг дешево
The most recent facts here: https://asplindia.in
The best insights here: https://deeprealestate.in
Туры и путешествия https://urban-manager.ru в Таиланд: Пхукет, Самуи, Бангкок. Подберём отели и перелёт, застрахуем, оформим экскурсии. Индивидуальные и групповые программы, лучшие пляжи круглый год. Прозрачные цены, поддержка 24/7. Оставьте заявку — сделаем отдых в Таиланде удобным и выгодным.
Нужен компрессор? компрессорное оборудование для производства и сервисов: винтовые, поршневые, безмасляные, осушители и фильтры, ресиверы, автоматика. Проектирование, монтаж, пусконаладка, сервис 24/7, оригинальные запчасти, аренда и трейд-ин. Гарантия и быстрая доставка.
Когда уместен
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Сегодня тематика зависимостей становится особенно важной. Если вы находитесь в поиске нарколога на дом в Красноярске, ресурс vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru предлагает разнообразные наркологических услуг. Терапия зависимостей может быть непростым процессом, однако мобильный нарколог обеспечивает помощь при алкоголизме и другим проблемам, связанным с зависимостям в домашних условиях. Консультация нарколога – это начальный этап к излечению. Профессионалы проведут диагностику зависимости, помогут составить программу реабилитации и предложат методы психотерапии при зависимости. Лечение без раскрытия данных гарантирует полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для многих пациентов. Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет не только лишь комфортно проходить лечение, но и получать поддержку близких, что играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления. Профилактические меры при алкоголизме и возвращение к нормальной жизни после наркотиков также являются частью комплекс услуг, предлагаемых специалистами. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за помощью на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru, чтобы получить нужную помощь.
Что включено на практике
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-shchyolkovo/
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://sandai-training.com/honmyo/233
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – https://jolemsproducts.com/checkout
Only verified here: https://sportsfanbetting.com
New and useful here: https://theshaderoom.com
Only the most important: https://puntera.com
Hot topics here: https://amt-games.com
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://vfkeducacao.com.br/%D0%B1%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D1%82%D1%8B-%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B5-7780-%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Погрузиться в научную дискуссию – https://aquavillerush.com/how-to-travel-with-paper-map
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://www.lean-tech.co.jp/2024/07/31/hello-world
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Детали по клику – https://mairie.agence-totem.fr/2022/05/18/digital-marketing-expectations
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4150036831/
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Смотрите также – https://qnchiropractic.com/animal-chiropractic-care-keeps-your-pet-moving-well
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал бесплатно живых
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Перейти к полной версии – https://cabaniasbuenavista.com.ar/s4
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://bogaars-din.com/home/bogaars
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Что скрывают от вас? – https://blog.seuconsumo.com.br/despesas-ordinarias-e-extraordinarias
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Кликни и узнай всё! – https://fuji-cryptofx.com/hello-world
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Подробности по ссылке – https://globalpathwayint.com/10-brilliant-benefits-of-doing-an-internship-abroad
Latest insights here: https://institutocea.com
Актуальная информация у нас: http://volgazdrav.ru
Current updates here: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
Лучшее на нашем сайте: https://03ekb.ru
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – https://stores.toyandjoy.com/ar/product/%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A8%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%AD%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%A8-%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%A8%D9%88%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%A8-%D8%A3%D8%B6%D9%88%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D9%88%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B5%D9%88
Капельница от алкогольной зависимости в Красноярске – это важная медицинская услуга при алкоголизме, которая помогает очищению организма. Вызов нарколога на дом предоставляет срочную помощь при запое в комфортной обстановке. Компоненты капельницы содержат элементы, которые помогают восстанавливающие организма: физраствор, витамины и препараты для капельницы. Действие капельницы ориентировано на снижение симптомов обстиненции и стабилизацию состояния пациента. Преодоление зависимости от алкоголя требует комплексного подхода, включая последующее восстановление после алкогольного кризиса. Стоимость услугу нарколога варьируются, но обращение к специалиста будет важной для успешного лечения.
Formula 1 puan durumu daim yenilənir və oyunçular üçün əlçatandır. Formula 1 sürücüləri haqqında maraqlı faktlar.
Rəsmi bilet sifarişi üçün klikləyin ➡ [url=https://formula-1.com.az/]formula 1 baku tickets[/url].
Formula 1 Türkiye mərhələsi haqqında ətraflı yazılar. Formula 1 izləmək üçün mobil tətbiqlərin üstünlükləri.
Formula 1 schedule izləyicilər üçün rahat seçimdir. Formula 1 canlı yayım keyfiyyəti ilə bağlı rəylər. Formula 1 izləmək üçün ən yaxşı kanalı seçin. Formula 1 baku 2024 tickets artıq satışdadır.
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Интересует подробная информация – https://roost.hair/2023/07/16/sample-post1
Владимир располагает инфраструктурой, позволяющей оказывать качественную помощь пациентам с различными видами зависимостей. Важным преимуществом является возможность получить вывод из запоя в клинике и анонимное лечение, что сохраняет социальный статус и исключает постановку на учет.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар владимир[/url]
Индивидуальный план включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Специалисты учитывают:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма тюмень[/url]
Самое интересное на сайте: https://www.foto4u.su
Current news right here: https://lmc896.org
Самое новое и важное: https://www.apelsin.su
Всё самое лучшее здесь: https://topper.md
В условиях Донецка ДНР профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов. Такой комплексный подход позволяет не только быстро вывести токсичные вещества из организма, но и обеспечить стабильное восстановление всех систем организма.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-doneczk-dnr
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет быстро снизить уровень токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы, стабилизируя работу печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/]вывод из запоя в донецке[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой подробный анализ позволяет подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]капельница от запоя луганск[/url]
Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Врач измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает краткий анамнез для определения степени алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные служат основой для разработки индивидуальной стратегии лечения.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lugansk-lnr
На данном этапе врач уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какой тип алкоголя употребляется и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-mariupol/
Вызов нарколога на дому в Красноярске ? это удобное и эффективное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с проблемами алкогольной зависимости . Круглосуточный нарколог предлагает профессиональную помощь, включая диагностику зависимости и лечение алкоголизма . Услуги нарколога на дому обеспечивают анонимное лечение и комфортные условия для пациента . Если требуется вывод из запоя, следует обратиться к опытному специалисту. Профессиональный нарколог проведет первичную консультацию, оценит здоровье пациента и разработает персонализированный план терапии. Семейная поддержка является ключевым аспектом в процессе восстановления.Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с посещением клиники . Круглосуточный доступ к наркологической помощи гарантирует, что в любой момент можно получить необходимую поддержку . Реабилитация после запоя осуществляется благодаря индивидуальному подходу и тщательному вниманию к нуждам каждого пациента.
Услуга капельничного лечения от запоя на дому в Архангельске предусматривает комплексный подход, направленный на оперативное восстановление организма. Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом, проводит детальный осмотр, собирает анамнез и измеряет жизненно важные показатели. На основе этих данных разрабатывается персональный план терапии, который включает введение современных медикаментов с использованием автоматизированных систем дозирования, а также психологическую поддержку для создания условий долгосрочной ремиссии.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk/
подписчики в тг канал без отписок
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого[/url]
Здесь собрана увлекательная и практичная информация по многим направлениям.
Читатели могут обнаружить подсказки на актуальные проблемы.
Статьи обновляются часто, чтобы вы могли изучать новую информацию.
Интуитивная организация сайта облегчает быстро отыскать нужные материалы.
анальное порно
Широкий спектр тем делает ресурс универсальным для разных читателей.
Каждый сможет найти советы, которые нужны именно ей.
Существование доступных рекомендаций делает сайт ещё более полезным.
Таким образом, данный сайт — это надёжный помощник полезной информации для широкого круга пользователей.
Свежие и важные материалы: https://lookdecor.ru
Самое свежее не пропусти: http://www.technoplus.ru
Свежие и важные материалы: https://eguidemagazine.com
Всё актуальное здесь: http://otolar-centre.ru
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Casombie, ca transporte dans un monde de chaos ludique. Le catalogue est une crypte de tresors, offrant des sessions live dignes d’un film d’horreur. Le suivi est aussi fiable qu’un sortilege, garantissant un support digne d’une legende. Les paiements sont securises comme une tombe scellee, mais des tours gratuits supplementaires feraient frissonner. Au final, Casombie est une plateforme qui fait battre les c?urs pour les aventuriers des cryptos ! A noter le design est sombre et captivant, ajoute une touche de magie noire.
casombie code|
J’ai une obsession totale pour Freespin Casino, c’est une tornade de sensations vibrantes. La selection de jeux est une veritable supernova, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptomonnaies. Le suivi est d’une clarte lumineuse, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’une brise etoilee. Les retraits sont rapides comme une fusee, parfois plus de promos vibrantes seraient un regal. Pour resumer, Freespin Casino offre une experience aussi brillante qu’une comete pour ceux qui cherchent des frissons lumineux ! A noter le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel scintillant, facilite une experience fluide et radieuse.
bonus codes free spin casino|
Je suis totalement ensorcele par Nomini Casino, offre un spectacle de plaisir qui s’evapore. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une scene de delices. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et fugaces. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et precise. joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans voile. mais des tours gratuits pour une melodie ephemere. Pour resumer, Nomini Casino est un casino en ligne qui joue une danse d’ombres pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note voilee. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto ephemere.
Je suis irresistiblement magnetise par Robocat Casino, il programme une sequence de recompenses fulgurantes. Le kit est un hub de diversite high-tech, offrant des bonus crabs et 200 spins des fournisseurs comme Pragmatic Play et Evolution. L’assistance compile des fixes nets, declenchant des protocoles multiples pour une resolution instantanee. Les transferts defilent stables et acceleres, bien que des updates promotionnels plus frequents upgradieraient le kit. En apotheose cybernetique, Robocat Casino invite a une session sans crash pour les codeurs des paris crypto ! De surcroit la structure vibre comme un processeur ancestral, infuse une essence de mystere algorithmique.
robocat drone|
how to hack slot machines uk, australia slot machine best online gambling games to win (Johnnie) and new usa free spins no deposit,
or new casino sites uk no deposit
J’eprouve une gourmandise infinie pour MrPacho Casino, ca infuse un univers de saveurs ludiques. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, integrant des live roulettes pour des tourbillons de suspense. Le support client est un sommelier attentif et omnipresent, assurant un accompagnement fidele au banquet. Le rituel est taille pour une onctuosite exemplaire, par eclats plus de hors-d’?uvre bonus journaliers agrementeraient le festin. En bouclant le repas, MrPacho Casino sculpte un festin de jeu somptueux pour les maitres des paris crypto ! En sus le portail est une salle a manger visuelle imprenable, pousse a prolonger le banquet infini.
mrpacho login|
проверенная инфа тут: https://lenotoplenie.ru
самое актуальное здесь: https://kmural.ru
обновления здесь и сейчас: https://www.nonnagrishaeva.ru
лучшее собрали тут: https://bergkompressor.ru
После того как организм пациента очищен от токсинов, наступает важный этап закрепления результата. С этой целью применяются психотерапевтические методики, направленные на формирование устойчивой мотивации к отказу от употребления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Преимущества вывода из запоя от опытных специалистов в условиях Донецка ДНР многочисленны. Такой формат лечения позволяет:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена донецкая область[/url]
Когда запой угрожает здоровью и жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Донецке ДНР опытные специалисты по наркологии оказывают профессиональную помощь на дому, обеспечивая качественную детоксикацию организма, стабилизацию жизненно важных функций и психологическую поддержку. Такой формат лечения позволяет пациенту получить комплексную терапию в условиях комфорта, сохраняя полную конфиденциальность и избегая лишних формальностей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена донецк[/url]
The latest and most useful: https://justicelanow.org
All the latest here: https://nlrealisation.fr
The best is here: https://rennerusa.com
The latest updates are here: https://www.home-truths.co.uk
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Основная цель капельничного лечения от запоя – оперативное выведение токсинов, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Методика, используемая специалистами, включает не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и комплексный мониторинг состояния пациента, что обеспечивает безопасность и результативность терапии даже в условиях экстренной необходимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lugansk-lnr
Частный нарколог на дому в Красноярске предоставляет незаменимую поддержку тем, кто страдает от зависимости. Лечение зависимости может быть непростым процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает удобство и анонимность. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru можно записаться на консультацию с наркологом, который приедет к вам домой. На дому пациентам предоставляется медицинская помощь включает детоксикацию организма и психотерапию зависимостей, что позволяет пациенту сделать первые шаги к свободе от наркотиков или алкоголя. Программа реабилитации разрабатывается с учетом индивидуальных особенностей, что позволяет учитывать уникальные потребности каждого пациента. Поддержка родственников играет важнейшую роль в предотвращении рецидивов. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает не только лечение, но и психологическую поддержку, что важно для успешной реабилитации наркоманов и помощи при алкоголизме.
При тяжелой алкогольной интоксикации оперативное лечение становится жизненно необходимым для спасения здоровья. В Архангельске специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, используя метод капельничного лечения от запоя. Такой подход позволяет быстро вывести токсины, восстановить обмен веществ и стабилизировать работу внутренних органов, обеспечивая при этом высокий уровень конфиденциальности и комфорт в условиях привычного домашнего уюта.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого[/url]
Поставка монтаж видеонаблюдения https://vcctv.ru
Капельничное лечение от запоя – это современный метод детоксикации, который позволяет быстро и безопасно вывести токсины из организма. В Луганске ЛНР специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, предлагая профессиональное капельничное лечение для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелой алкогольной интоксикацией. Такой подход обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство в привычной для пациента обстановке, гарантируя индивидуальный подход и полную конфиденциальность.
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/
На данном этапе врач уточняет длительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет оперативно сформировать индивидуальный план лечения и выбрать оптимальные методы детоксикации.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-arkhangelsk/
Обращение за помощью к наркологу на дому имеет ряд преимуществ, особенно в экстренных ситуациях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/
В журнале Холд всё собрано для удобства: новости, прогнозы, курсы и обзоры бирж. Благодаря этому не нужно искать информацию по разным сайтам. Отдельно хочу отметить их объяснения по кошелькам — очень помогает новичкам. Это надёжный гид по миру цифровых активов, https://thehold.ru/
All the best is here: https://www.panamericano.us
The best updates are here: https://jarvekyla.edu.ee
Fresh every day: https://labhgroup.com
Top materials are here: https://ruptur-billiard.by
После того как организм пациента очищен от токсинов, наступает важный этап закрепления результата. С этой целью применяются психотерапевтические методики, направленные на формирование устойчивой мотивации к отказу от употребления.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru
Преимущества вывода из запоя от опытных специалистов в условиях Донецка ДНР многочисленны. Такой формат лечения позволяет:
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-doneczk-dnr/
The newest on this page: http://chuyenhangphap.fr
New and hot here: https://www.woman.sk
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
Проблема алкогольной зависимости: важность внимательного подхода. Множество людей предпочитают анонимный поиск помощи, чтобы не столкнуться с осуждением. Нарколог на дом предлагает услуги по лечению запоя, обеспечивая комфорт и приватность. Вызов нарколога помогает получить медицинскую помощь при запое без лишних вопросов. Анонимное лечение включает detox программы, где обеспечивается психологическая поддержка и медикаментозное сопровождение. Это позволяет избежать рецидива алкоголизма и восстановиться после запоя. Кризисная помощь помогает преодолеть острые состояния, предоставляя необходимые ресурсы. Таким образом, анонимный вывод из запоя – это вполне реальная возможность для тех, кто ищет помощь.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет быстро снизить уровень токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы, стабилизируя работу печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru
купить живых подписчиков в тг
Je suis totalement envoute par Casombie, il offre une aventure aussi sombre que palpitante. Les options sont vastes comme un cimetiere, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client est d’une efficacite surnaturelle, garantissant un support digne d’une legende. Les gains arrivent a une vitesse demoniaque, cependant les offres pourraient etre plus ensorcelantes. Au final, Casombie offre une experience aussi envoutante qu’un sort pour les aventuriers des cryptos ! Par ailleurs le site est visuellement un chef-d’?uvre macabre, amplifie l’immersion dans l’horreur.
casombie casino erfahrungen|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Freespin Casino, on dirait un festival de frissons eclatants. Les options forment un tourbillon de surprises, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client est d’une efficacite siderante, repondant en un flash. Les transactions sont fiables et fluides, de temps a autre des bonus plus petillants seraient magiques. En somme, Freespin Casino est une plateforme qui illumine l’esprit pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel scintillant, donne envie de replonger dans l’univers du jeu.
casino with free spin no deposit|
яндекс доставка работа курьером на авто Яндекс Доставка: Курьерская служба нового поколения Яндекс Доставка – это современная курьерская служба, охватывающая широкий спектр товаров и услуг. Курьеры Яндекс Доставки доставляют посылки, документы и другие отправления, обеспечивая быструю и надежную доставку. Работа курьером в Яндекс Доставке – это возможность работать в технологичной компании с современными инструментами и удобными приложениями. Курьеры Яндекс Доставки могут выбирать удобный способ доставки: пешком, на велосипеде или на автомобиле. Яндекс Доставка предлагает различные варианты сотрудничества, включая работу на личном автомобиле. Отзывы курьеров о работе в Яндекс Доставке часто отмечают удобство графика, стабильный доход и возможность карьерного роста. Если вы хотите стать частью команды Яндекс Доставки, заполните анкету на сайте и начните зарабатывать уже сегодня. Количество курьеров в Яндекс Доставке постоянно растет, что свидетельствует о популярности и востребованности сервиса.
Далее проводится сама процедура: при медикаментозном варианте препарат может вводиться внутривенно, внутримышечно или имплантироваться под кожу; при психотерапевтическом — работа проходит в специально оборудованном кабинете, в спокойной атмосфере. После кодирования пациент находится под наблюдением, чтобы исключить осложнения и закрепить эффект. Важно помнить, что соблюдение рекомендаций и поддержка семьи играют решающую роль в сохранении трезвости.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-kolomna6.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-v-kolomne
Сначала администратор собирает ключевые данные: возраст и примерный вес, длительность употребления, описание симптомов, хронические заболевания, аллергии и принимаемые лекарства. По этой информации врач заранее продумывает схему инфузии и прогнозирует длительность процедуры.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Je suis charme par Nomini Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui danse comme une ombre fugace. propose un ballet de divertissement qui seduit. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et fugaces. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui danse comme une ombre. fluisent comme une sonate spectrale. occasionnellement des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient spectrale. Pour resumer, Nomini Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les fans de symphonies d’ombres! Par ailleurs le design du casino est une fresque visuelle spectrale. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus etheree.
LuckyMax Casino https://assurehrlabs.com/top-online-casinos-nederland-2024-luckymax-casino-wettig-plus-waarschijnlijk/
TheHold приятно удивил тем, что материалы здесь написаны простым языком, но при этом очень информативные. Есть и ежедневные новости криптовалют, и аналитика по майнингу, и обзоры новых проектов. Особенно понравился раздел с курсами и калькулятором доходности. Это реальная помощь и новичкам, и опытным инвесторам https://thehold.ru/
J’eprouve une gourmandise infinie pour MrPacho Casino, ca infuse un univers de saveurs ludiques. Il deborde d’une plethore de mets interactifs, incluant des crash games comme JetX pour des pics de saveur. L’assistance distille des conseils affutes, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les retraits glissent avec une souplesse remarquable, par eclats des amuse-bouches gratuits supplementaires rehausseraient les plats. En apotheose culinaire, MrPacho Casino sculpte un festin de jeu somptueux pour les maitres des paris crypto ! En sus le portail est une salle a manger visuelle imprenable, accroit l’envoutement dans le royaume du gout.
mrpacho kasyno|
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Красноярске: быстро и эффективно В Красноярске обслуживание наркологов на дому становятся все более актуальными. В сложных ситуациях‚ связанных с употреблением психоактивных веществ‚ важно получить экстренную медицинскую помощь как можно быстрее. Вызов нарколога обеспечивает не только экстренную помощь‚ но и консультацию нарколога‚ что позволяет оценить психофизическое состояние пациента и принять необходимые меры. вызов нарколога на дом Наркологическая помощь включает лекарственную терапию и поддержку людей с зависимостями. Лечение зависимостей требует персонализированного подхода‚ и конфиденциальное лечение становится важным аспектом для многих. Реабилитация алкоголиков также доступна в рамках услуг наркологии в Красноярске‚ что позволяет людям вернуться к здоровому образу жизни. Важно помнить‚ что при наличии экстремальных состояниях всегда стоит обращаться за квалифицированной экстренной помощью наркологов. Услуги на дому могут значительно облегчить процесс лечения и реабилитации.
На базе частной клиники «Здоровье+» пациентам доступны как экстренные, так и плановые формы наркологической помощи. Все процедуры соответствуют стандартам Минздрава РФ и проводятся с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь в туле[/url]
После диагностики начинается активная фаза капельничного лечения. Современные препараты вводятся с помощью автоматизированных систем дозирования, что обеспечивает быстрое снижение уровня токсинов в крови и восстановление обменных процессов. Этот этап направлен на стабилизацию работы печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Услуга капельничного лечения от запоя на дому в Архангельске предусматривает комплексный подход, направленный на оперативное восстановление организма. Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом, проводит детальный осмотр, собирает анамнез и измеряет жизненно важные показатели. На основе этих данных разрабатывается персональный план терапии, который включает введение современных медикаментов с использованием автоматизированных систем дозирования, а также психологическую поддержку для создания условий долгосрочной ремиссии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно в архангельске[/url]
http://gioacademia.com/wp-content/pages/codigo_promocional_de_la_casa_de_apuestas_1xbet_para_el_registro.html
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой подробный анализ позволяет подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя луганск[/url]
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя архангельск[/url]
Когда проблемы с алкоголизмом достигают критической точки, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Мариуполе квалифицированные наркологи оказывают помощь на дому, обеспечивая оперативную детоксикацию организма, стабилизацию жизненно важных показателей и психологическую поддержку. Такой формат лечения позволяет пациенту получить качественную медицинскую помощь в привычной домашней обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в мариуполе[/url]
Содержание процедуры
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo-v-shchelkovo/
Эти действия помогают быстро восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и снизить нагрузку на внутренние органы. После проведения процедур врач дает рекомендации по дальнейшему наблюдению и реабилитации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
Все процедуры проводятся в максимально комфортных и анонимных условиях, после тщательной диагностики и при полном информировании пациента о сути, длительности и возможных ощущениях.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-kolomna6.ru/]metody-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-cena[/url]
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые
Услуги наркологов в Красноярске становится все более востребованной‚ особенно когда речь идет о борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Красноярск предлагает услуги для людей‚ нуждающихся в экстренной помощи. В рамках наркологической клиники проводится очищение организма от наркотиков и алкоголя‚ что является первым шагом к выздоровлению. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает в себя облегчение абстиненции‚ что позволяет облегчению состояния пациента. Круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечит необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в любое время суток. Консультация нарколога поможет составить индивидуальную программу лечения алкоголизма, учитывающую все нюансы пациента. Реабилитация зависимых включает психотерапию для зависимых‚ что помогает улучшить психологического состояния и адаптации к жизни без алкоголя. Не стоит забывать о поддержке родственников зависимых; Анонимное лечение зависимости даст возможность пациенту обращаться за помощью без боязни осуждения. Вызывая нарколога на дом‚ вы делаете важный шаг к новой жизни.
Эти действия помогают быстро восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и снизить нагрузку на внутренние органы. После проведения процедур врач дает рекомендации по дальнейшему наблюдению и реабилитации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-kaliningrad/
По прибытии проводится экспресс-диагностика: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается уровень обезвоживания и неврологический статус; при показаниях выполняется ЭКГ. Врач простым языком объясняет, какие препараты и в каком порядке будут вводиться, отвечает на вопросы и получает информированное согласие.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-serpuhove/
Когда человек оказывается в состоянии алкогольного запоя, самостоятельное преодоление последствий становится практически невозможным. Безопасно выйти из запоя без риска для жизни и здоровья можно только под медицинским наблюдением. В наркологической клинике «Содружество» в Щёлково вывод из запоя проводится круглосуточно, с профессиональной поддержкой, выездом врача на дом и гарантией индивидуального подхода к каждому пациенту. Здесь обеспечивается не только эффективное медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическая поддержка семьи, а также планирование последующего восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/]вывод из запоя щелково[/url]
яндекс еда доставка работа курьером Яндекс Доставка: Курьер – лицо современной логистики Яндекс Доставка – это сервис, который меняет представление о логистике в современном мире. Это быстрая и надежная доставка самых разных товаров, от документов до крупногабаритных грузов. И в этой системе курьер играет центральную роль. Он – последнее звено в цепи доставки, от которого зависит удовлетворенность клиента. Работа курьером в Яндекс Доставке – это возможность быть частью инновационной компании, использовать современные технологии и зарабатывать деньги, передвигаясь по городу. Это работа для тех, кто ценит ответственность, пунктуальность и умение находить выход из любой ситуации. Яндекс Доставка предоставляет своим курьерам гибкий график работы, конкурентную оплату труда и все необходимые инструменты для успешного выполнения задач. Отзывы курьеров свидетельствуют о том, что работа в Яндекс Доставке – это не только возможность заработать, но и получить ценный опыт в сфере логистики, развить свои навыки и найти новых друзей. Стать курьером Яндекс Доставки – это значит внести свой вклад в развитие современной логистики и сделать жизнь людей проще и удобнее.
Je suis charme par Cheri Casino, ca scintille comme une nuit etoilee. La selection est une cascade de surprises, offrant des sessions live qui hypnotisent. Le support est disponible 24/7, repondant plus vite qu’une etoile filante. Les transactions sont rapides et fiables, mais des tours gratuits en plus feraient rever. En somme, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui illumine les sens pour les passionnes d’aventures lumineuses ! De plus la plateforme scintille comme un diamant, ce qui rend chaque session absolument feerique.
cheri casino mon compte|
Je suis pimente par PepperMill Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque lancer infuse des essences de triomphe. Le bouquet est un potager de diversite exuberante, integrant des roulettes live pour des tourbillons d’arome. L’assistance distille des elixirs affutes, avec une expertise qui presage les appetits. Les courants financiers sont fortifies par des racines crypto, nonobstant des elans promotionnels plus assidus animeraient le jardin. A la fin de cette degustation, PepperMill Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement olfactif pour les gardiens des jardins numeriques ! En piment sur le gateau la trame irradie comme un elixir ancestral, intensifie l’envoutement dans le domaine des aromes.
peppermill/reno|
Лечение вывода из запоя в Архангельске проводится по четко структурированной схеме, которая позволяет оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать процесс восстановления.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Je suis vise par WildRobin Casino, c’est un bosquet ou chaque pari lance une fleche de succes. Il grouille d’une horde de quetes interactives, offrant des cashbacks et VIP 5 tiers des maitres comme Pragmatic Play et Evolution Gaming. Le service guette en continu 24/7, bandant des cordes multiples pour une frappe immediate. Les flux sont camoufles par des fourres crypto, occasionnellement des pointes de recompense additionnelles perceraient les alliances. En apotheose legendaire, WildRobin Casino forge une legende de jeu heroique pour ceux qui visent leur destin en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface est un sentier navigable avec precision, incite a prolonger la quete infinie.
wild robin casino login|
прогноз ставка [url=stavka-12.ru]прогноз ставка[/url] .
можно ли накрутить подписчиков в тг
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
ставки прогнозы [url=www.novosti-sporta-15.ru/]www.novosti-sporta-15.ru/[/url] .
Pexip configuration guide Pexip SDK: Development guides and resources. Learn about Pexip services that make development on the platform easier than ever before.
В острых случаях наши специалисты оперативно приезжают по адресу в Раменском городском округе, проводят экспресс-оценку состояния и сразу приступают к стабилизации. До прибытия врача рекомендуем обеспечить доступ воздуха, убрать потенциально опасные предметы, подготовить список принимаемых лекарств и прошлых заболеваний — это ускорит диагностику. Особенно критичны первые 48–72 часа после прекращения употребления алкоголя: именно на этом промежутке повышается риск делирия и сердечно-сосудистых осложнений. Понимание этих временных рамок помогает семье действовать вовремя и осознанно.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-ramenskom/
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
последние новости спорта [url=http://www.novosti-sporta-16.ru]http://www.novosti-sporta-16.ru[/url] .
Lucky Jet Lucky Jet (Лаки Джет) — ваша возможность оседлать удачу! Динамичная игра Lucky Jet уже ждет вас. Чтобы начать играть в Лаки Джет, достаточно пройти быструю регистрацию на официальном сайте игры. Если он недоступен, воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом Лаки Джет. Ищете, где сыграть? Lucky Jet 1win — одна из проверенных площадок. Lucky Jet 1вин предоставляет полную версию развлечения. Не упустите шанс — играть в Lucky Jet можно сразу после создания аккаунта. Официальный сайт Lucky Jet или его зеркало — ваш надежный старт!
ставки прогнозы на спорт [url=https://www.prognozy-na-sport-11.ru]https://www.prognozy-na-sport-11.ru[/url] .
milwaukie casinos, australian roulette rules and can us
citizens play online poker in united states, or canadian pokies free spins
Feel free to surf to my webpage – pay per sms casino
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому в туле[/url]
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://kliko.info/facebook
Что входит
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Откройте для себя новые возможности с [url=https://minsk-peretyazhka.ru]перетяжкой мебели в Минске[/url], позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
Сравнение цен от различных мастеров поможет вам сделать лучший выбор.
Je suis completement seduit par Cheri Casino, il offre une aventure ludique petillante. Les options sont un bouquet d’emotions, incluant des jeux de table pleins de charme. Le support est disponible 24/7, repondant plus vite qu’une etoile filante. Le processus est lisse comme une brise, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus flamboyantes. Pour resumer, Cheri Casino est un joyau pour les amateurs de jeux pour ceux qui cherchent des frissons colores ! Par ailleurs le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel, ajoute une touche d’eclat magique.
cheri casino forum|
https://woolentailor.ru/2025/10/01/Секретный-код-1xbet-для-бонуса/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Je suis cisele par RubySlots Casino, on admire un atelier de techniques precieuses. Le portfolio est un salon de variete lapidaire, proposant des keno pour des extractions de chance. Le suivi preserve avec une purete absolue, activant des facettes multiples pour une revelation immediate. Les gains jaillissent via Bitcoin ou cheques, bien que les offres pourraient s’enrichir en carats. En sertissant le lot, RubySlots Casino invite a une exploration sans fissure pour les tailleurs des paris crypto ! Par surcroit le portail est une monture visuelle imprenable, incite a prolonger la taille infinie.
ruby slots no deposit bonus code 2017|
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
https://succeed-kyoto.info/2021/11/04/hello-world
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://almontag.com/%D8%A3%D9%81%D8%B6%D9%84-%D8%A3%D9%86%D9%88%D8%A7%D8%B9-%D8%B3%D9%85%D9%83-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D9%88%D9%86%D8%A9-%D8%AD%D9%88%D9%84-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Только для своих – https://manolojimenez.mx/presenta-manolo-modelo-coahuila-ante-legisladores-federales-del-pri
На складе мебели оборудование Labelaire облегчило процесс учёта. Терминалы сбора данных и беспроводные сканеры делают работу сотрудников значительно проще. Ошибки практически исключены: https://labelaire.ru/
J’eprouve une precision infinie pour WildRobin Casino, ca tend un arc de defis legendaires. Les branches forment un labyrinthe de mecaniques ingenieuses, integrant des lives comme Blackjack pour des duels d’arcs. Les sentinelles tirent avec une acuite exemplaire, assurant une garde fidele dans la foret. Les transferts sprintent stables et acceleres, malgre cela des tirs gratuits supplementaires boosteraient les branches. En apotheose legendaire, WildRobin Casino invite a une traque sans fin pour les bandits de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit le graphisme est un camouflage dynamique et immersif, amplifie l’engagement dans le repaire du jeu.
robin wild casino|
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://vendastribunal.net/moradia-com-comercio-e-habitacao-em-braga
Pexip best practices Pexip API: Integrate Pexip. See how Pexip’s open API makes interoperability easy and fast.
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Выяснить больше – https://www.taylordentist.com/which-is-right-for-you-a-metal-or-a-porcelain-crown
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
яндекс еда доставка работа курьером Яндекс Еда: Курьер как ключевой элемент успешной доставки Яндекс Еда – это не просто сервис доставки, это целая экосистема, где каждый элемент играет важную роль в обеспечении быстрого и удобного получения еды из любимых ресторанов. В этой системе курьер занимает центральное место. Он – лицо компании, гарант качественного обслуживания и своевременной доставки. Работа курьером в Яндекс Еде – это возможность быть частью динамичной команды, самостоятельно планировать график и получать доход, зависящий от личной активности. Курьеры Яндекс Еды проходят обучение, обеспечивающее высокий уровень сервиса и знание стандартов компании. Яндекс Еда гордится своими курьерами и отмечает лучших в конкурсе “Курьер года”, демонстрируя признание их вклада в успех сервиса. Стать курьером Яндекс Еды – значит присоединиться к команде профессионалов, ценящих скорость, ответственность и дружелюбие. Это возможность зарабатывать, делая жизни других людей проще и вкуснее. Рассматривая вакансию курьера в Яндекс Еде, важно помнить, что это не просто работа, это вклад в развитие современной культуры доставки еды.
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Обратиться к источнику – http://kalemagency.com/mehmetd-2
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Детальнее – https://marushinkogyo.com/%E3%83%99%E3%83%A9%E3%83%B3%E3%83%80%E4%BF%AE%E7%90%86/water212-16
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Узнай первым! – https://srotu.org/videos/season-1-trailer
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Узнать из первых рук – https://aluvisa.net/como-seleccionar-la-funeraria-los-sitios-de-zaragoza-de-manera-inteligente
Современное техническое оснащение играет значительную роль в диагностике и поддержке пациентов.
Медицинские центры всё чаще оборудуются высокотехнологичную аппаратуру.
Это позволяет врачам делать точные оценки.
Актуальные приборы обеспечивают безопасность и для больных, и для персонала.
https://regioninformburo.ru/osobennosti-udarno-volnovoj-terapii-2
Развитие высоких технологий помогает результативное восстановление.
Часто устройства включают функции для глубокого контроля состояния здоровья.
Доктора могут быстро действовать, основываясь на данных аппаратуры.
Таким образом, инновационное техническое оснащение повышает качество лечебного процесса.
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Перейти к полной версии – https://medialt.lt/logo-2
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Доступ к полной версии – https://thebabystuffs.com/baby-showers/best-baby-shower-hairstyles-mothers
Lucky Jet Lucky Jet (Лаки Джет) — ваша возможность оседлать удачу! Динамичная игра Lucky Jet уже ждет вас. Чтобы начать играть в Лаки Джет, достаточно пройти быструю регистрацию на официальном сайте игры. Если он недоступен, воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом Лаки Джет. Ищете, где сыграть? Lucky Jet 1win — одна из проверенных площадок. Lucky Jet 1вин предоставляет полную версию развлечения. Не упустите шанс — играть в Lucky Jet можно сразу после создания аккаунта. Официальный сайт Lucky Jet или его зеркало — ваш надежный старт!
В магазине электроники мы внедрили оборудование для маркировки и принтеры для ценников. Теперь каждый товар имеет аккуратную этикетку, что удобно и для сотрудников, и для покупателей. Печать выполняется быстро и качественно. Мы также приобрели сканеры штрих-кодов для касс. Весь процесс стал более современным и удобным – https://labelaire.ru/
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Интересует подробная информация – https://picolo-baby.co.il/product/%D7%A1%D7%9C%D7%A7%D7%9C-%D7%91%D7%A1%D7%99%D7%A1-%D7%A7%D7%99%D7%A4%D7%99%D7%98-30
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Изучите внимательнее – https://www.greatdynamics.net/2020/11/16/tech-firms-support-huawei-restriction-balk-at-cost
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://www.salonfox.nl/faq-items/wat-voor-producten-gebruiken-jullie
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя
Useful and relevant is here: https://manorhousedentalpractice.co.uk
Top topics and trends: https://edicionesdelau.com
The latest materials are here: https://www.panamericano.us
All the new stuff is here: https://www.jec.qa
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Узнать из первых рук – https://dndaircraftdecals.com/finest-hookup-websites-and-programs-casual-going-out-with-in-2021
Je suis transporte par Donbet Casino, c’est une deflagration de fun absolu. Les options sont un torrent de surprises, offrant des sessions live qui electrisent. Le service client est d’une efficacite foudroyante, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient electrisantes. En somme, Donbet Casino promet une aventure incandescente pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! A noter la plateforme brille comme une supernova, donne envie de replonger dans la tempete.
donbet|
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Хочу знать больше – https://grace-garden.xyz/2024/02/19/%E3%83%97%E3%83%AD%E3%82%B9%E3%83%94%E5%9E%A2%E8%B2%A9%E5%A3%B2%E6%83%85%E5%A0%B1
Je suis brasse par Shuffle Casino, il redistribue une serie de surprises lucratives. Il foisonne d’une ribambelle de tirages interactifs, integrant des lives comme Sweet Bonanza pour des cascades de chance. L’assistance tire des reponses affutees, accessible par bluff ou appel direct. Les transferts battent stables et acceleres, bien que des tirages gratuits supplementaires brasseraient les mains. A la fin de cette donne, Shuffle Casino devoile un tour de victoires melangees pour les baroudeurs de casinos virtuels ! En plus la structure tourne comme un sablier ancestral, ce qui propulse chaque main a un niveau bluffant.
shuffle casino vpn|
Everything you need is here: https://lesma-shop.de
The latest updates are here: https://audium.com
The most interesting is here: https://www.home-truths.co.uk
The latest news and insights: https://smartzoz.in
Je suis fondant pour Sugar Casino, ca concocte un delice de defis savoureux. Il deborde d’une cascade de gourmandises interactives, incluant des crash pour des montees de miel. Le support client est un confiseur vigilant et inlassable, assurant une attention fidele dans la patisserie. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, a l’occasion des eclats promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient le panier. Dans l’ensemble de la confiserie, Sugar Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les gourmands pour les gardiens des bonbonnieres numeriques ! De surcroit le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, incite a prolonger la degustation infinie.
sweet sugar casino|
Bubinga Binary Options: Simple Tools for Smart Trading
Bubinga Binary Options offer traders an easy and effective way to act on market changes with speed and precision. With user-friendly tools, transparent rules, and access to global opportunities, both beginners and professionals can manage risks and explore new strategies. By learning more through [url=https://btc-eth.jp/]https://btc-eth.jp/[/url], investors can discover how Bubinga supports smarter trading decisions and steady financial growth.
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-marmansk/
В этой статье мы рассмотрим ключевые признаки эффективной наркологической помощи в Ярославле — от состава команды до подходов в работе с мотивацией пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/]центр лечения наркомании[/url]
Как отмечает ведущий научный сотрудник ФГБУН «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии» Минздрава России, наличие междисциплинарной команды — один из основных факторов, определяющих успех терапии при зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в мурманске[/url]
На территории Мурманска работает множество клиник с разным уровнем сервиса и направленностью. Однако не каждая из них может обеспечить надёжную и безопасную помощь. Многие пациенты сталкиваются с формальным лечением, не включающим индивидуальный подход или постреабилитационную поддержку. Поэтому крайне важно заранее ознакомиться с основными признаками хорошей клиники и задать правильные вопросы при первичном обращении.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Комбинирование методов позволяет одновременно решать задачи стабилизации, профилактики и возвращения к повседневной активности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/narkologiya-lugansk-lnr/
Такая структура позволяет минимизировать колебания состояния, уменьшить нагрузку на органы-мишени и подготовить пациента к следующему этапу лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lugansk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в луганске[/url]
Daily digest by link: https://elitetravelgroup.net
Only verified materials: https://astra-hotel.ch
Top updates are here: https://amt-games.com
New every day: https://intelicode.com
https://clickolov.ru/
LuckyMax NL https://www.arasgrupinsaat.com/offlin-gokhuis-nederlan-beste-legale-casinos-luckymax-casino-voor-2024/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя
This is one very informative blog. I like the way you write and I will bookmark your blog to my favorites.
Nice read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing some research on that. And he just bought me lunch as I found it for him smile Therefore let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
лекарства от тревоги Лечение тревожных расстройств — это комплексный подход, направленный на снижение и устранение симптомов тревоги, страха и беспокойства, которые негативно влияют на качество жизни человека. Стратегии лечения включают психотерапию, медикаментозное лечение и изменение образа жизни. Психотерапия, особенно когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), помогает пациентам выявлять и изменять негативные мысли и поведение, вызывающие тревогу. Медикаментозное лечение может включать антидепрессанты (например, СИОЗС, СИОЗСН), анксиолитики (например, бензодиазепины) и другие препараты, которые помогают регулировать химический баланс в мозге и снижать тревожность. Помимо этого, важную роль играют здоровый образ жизни, включающий регулярные физические упражнения, сбалансированное питание, достаточный сон и методы релаксации, такие как медитация и йога. В некоторых случаях может потребоваться консультация психиатра или психотерапевта для разработки индивидуального плана лечения, учитывающего особенности и потребности пациента. Раннее обращение за помощью и адекватное лечение могут значительно улучшить прогноз и качество жизни людей, страдающих тревожными расстройствами.
Всё лучшее у нас: https://morshynkurort.net
Самая актуальная информация: https://wildlife.by
Многие сталкиваются с трудностями при выборе клиники или центра: предлагаемые услуги различаются по качеству, подходам, стоимости и длительности. Некоторые организации ограничиваются только медикаментозной поддержкой, не работая с глубинными причинами зависимости. Поэтому важно заранее понимать, какие параметры отличают действительно надёжное учреждение, способное обеспечить долгосрочные результаты.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании реабилитация[/url]
Ежедневные обновления тут: https://verspk.ru
The best in one place: https://justicelanow.org
СтройСинтез спроектировал и построил для нас кирпичный коттедж с мансардой. Нам понравилось, что компания держит клиентов в курсе каждого этапа и работает открыто. В итоге мы получили надёжный и уютный дом для всей семьи. Подробнее о таких решениях можно посмотреть здесь – https://stroysyntez.com/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Терапия наркотической зависимости — не просто избавление от тяги, а глубокий восстановительный процесс, включающий физическую, психическую и социальную реабилитацию. В Ярославле помощь наркозависимым оказывается в различных учреждениях, однако не все из них обеспечивают одинаково высокий уровень качества. Как показывает практика, эффективность лечения во многом зависит от грамотно подобранной программы и профессионализма команды.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/]центр лечения наркомании в ярославле[/url]
купить диплом в магнитогорске [url=https://rudik-diplom1.ru/]https://rudik-diplom1.ru/[/url] .
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Donbet Casino, ca pulse comme un eclair foudroyant. Les options sont un torrent de surprises, proposant des paris sportifs qui font monter l’adrenaline. Les agents repondent a la vitesse d’un meteore, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, mais plus de promos percutantes seraient un plus. Au final, Donbet Casino offre une experience aussi puissante qu’une eruption pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! De plus le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel explosif, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
donbet casino no deposit bonus|
J’eprouve un vertige total pour Shuffle Casino, c’est une pioche ou chaque clic melange les destinees. Le deck est un etal de diversite aleatoire, integrant des lives comme Sweet Bonanza pour des cascades de chance. L’assistance tire des reponses affutees, assurant une animation fidele dans la salle. Le protocole est melange pour une fluidite exemplaire, bien que des relances promotionnelles plus frequentes remueraient le deck. En battant le paquet, Shuffle Casino forge une partie de jeu aleatoire pour les croupiers des sabots numeriques ! A piocher la circulation est instinctive comme un tour de passe-passe, incite a prolonger la donne infinie.
shuffle casino discord|
Программы терапии строятся так, чтобы одновременно воздействовать на биологические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости. Это повышает результативность и уменьшает риск повторного употребления.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/
Все самое интересное тут: https://www.blockbuster.ua
Лучше только у нас: https://wildlife.by
Current collections are here: https://cleanfuture.co.in
The best materials are here: https://sdch.org.in
Купить диплом техникума в Запорожье [url=http://www.educ-ua7.ru]http://www.educ-ua7.ru[/url] .
I like your style!
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/perm-lechenie-alkogolizma
Je suis enrobe par Sugar Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque tour distille une goutte de victoire mielleuse. La collection est un sirop de divertissements delicieux, incluant des crash pour des montees de miel. Les artisans repondent avec une douceur remarquable, servant des plateaux multiples pour une degustation immediate. Les flux financiers sont enrobes par des coques crypto, malgre cela des friandises de recompense additionnelles glaceraient les alliances. Pour clore le sirop, Sugar Casino tisse un nappage de divertissement delicieux pour les gardiens des bonbonnieres numeriques ! A savourer le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, incite a prolonger la degustation infinie.
sugar hut casino|
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/
Такая структура позволяет минимизировать колебания состояния, уменьшить нагрузку на органы-мишени и подготовить пациента к следующему этапу лечения зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lugansk0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в луганске[/url]
Hot topics are on this page: https://manorhousedentalpractice.co.uk
Trends and insights are here: https://informationng.com/
The best of what’s new is here: https://ondesparalleles.org
Our top topics of the day: https://asplindia.in
Актуальное техническое оснащение играет значительную функцию в обследовании и помощи пациентов.
Клиники всё чаще оснащаются передовую аппаратуру.
Это позволяет врачам проводить правильные диагнозы.
Актуальные приборы обеспечивают комфорт и для больных, и для врачей.
http://treasureillustrated.com/showthread.php?tid=97050
Внедрение высоких технологий ускоряет качественное оздоровление.
Большинство устройства содержат опции для детального мониторинга состояния здоровья.
Доктора могут своевременно действовать, основываясь на данных аппаратуры.
Таким образом, инновационное медицинское оборудование усиливает уровень лечебного процесса.
LuckyMax Casino NL https://scuolaitalianabucarest.com/nieuwste-online-bank-holland-luckymax-2024-nieuwe-casinos/
New releases in one click: https://sviluppoleadership.com/
What’s important and relevant: https://akivaschool.com
The most worthwhile are here: https://eguidemagazine.com
Сломалась машина? техпомощь на дороге недорого мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
кайт хургада Кайт – это разновидность воздушного змея, который используется для катания на воде, снегу или земле. Кайтсерфинг – это экстремальный вид спорта, в котором кайт тянет человека на доске по поверхности воды. Кайтинг также может включать в себя катание на лыжах, сноуборде или других видах транспорта.
СтройСинтез построил для нас кирпичный дом с мансардой, и мы очень довольны результатом. Проект был адаптирован под наши пожелания, и в итоге получился идеальный вариант для семьи. Все подробности доступны по ссылке – https://stroysyntez.com/
Алкогольный запой – это серьезное состояние‚ требующее неотложного вывода и помощи. Традиционные методы часто воспринимаются как эффективные способы борьбы‚ но вокруг них существует множество мифов. Например‚ многие думают‚ что травы от алкоголизма способны быстро снять симптомы запоя. Однако реальность таковы‚ что традиционные средства могут лишь помочь в восстановлении после запоя‚ но не заменить профессиональную реабилитацию от алкоголя. Существует несколько эффективных методов‚ среди которых очищение организма и лечение алкоголизма. Психологические аспекты зависимости играет ключевую роль в реабилитации. Важно понимать‚ что экстренный вывод из запоя требует системного подхода‚ включающего медикаментозное лечение и поддержку близких. Не стоит полагаться только на народные средства — это может привести к ухудшению состояния.
купить диплом в химках [url=http://rudik-diplom11.ru]купить диплом в химках[/url] .
как лечить приступы тревоги Лечение тревожности — это процесс, направленный на уменьшение чувства беспокойства, напряжения и страха, которые могут мешать повседневной жизни. Подходы к лечению тревожности включают как психотерапевтические методы, так и медикаментозное лечение. Психотерапия, особенно когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), является эффективным способом научиться управлять тревожными мыслями и поведением. КПТ помогает пациентам идентифицировать и изменять негативные мыслительные паттерны, а также развивать навыки преодоления тревоги. Медикаментозное лечение может включать применение антидепрессантов (например, СИОЗС, СИОЗСН) или анксиолитиков, которые помогают регулировать химический баланс в мозге и снижать симптомы тревожности. Важно отметить, что медикаменты должны приниматься только по назначению и под контролем врача. Кроме того, полезными могут быть техники релаксации, такие как медитация, глубокое дыхание и прогрессивная мышечная релаксация. Важную роль играет здоровый образ жизни, включающий регулярные физические упражнения, сбалансированное питание, достаточный сон и ограничение употребления кофеина и алкоголя. Поддержка со стороны семьи и друзей также может быть полезной в процессе лечения тревожности. Индивидуальный план лечения, разработанный совместно с врачом или психотерапевтом, может значительно улучшить качество жизни человека, страдающего от тревожности.
Как отмечает ведущий научный сотрудник ФГБУН «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии» Минздрава России, наличие междисциплинарной команды — один из основных факторов, определяющих успех терапии при зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru
Как поясняет врач-нарколог НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии, «наличие оборудованного стационара с возможностью контроля осложнений — обязательное условие безопасного лечения наркомании».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма ярославская область[/url]
где можно купить диплом медицинского колледжа [url=https://www.frei-diplom11.ru]https://www.frei-diplom11.ru[/url] .
куплю диплом медсестры в москве [url=http://www.frei-diplom13.ru]куплю диплом медсестры в москве[/url] .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
купить диплом техникума ссср в барнауле [url=https://frei-diplom12.ru/]купить диплом техникума ссср в барнауле[/url] .
купить диплом повара [url=http://rudik-diplom10.ru]купить диплом повара[/url] .
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru
Je suis titille par MrPacho Casino, c’est un festin ou chaque tour deploie des parfums de victoire. Il deborde d’une plethore de mets interactifs, proposant des blackjack revisites pour des bouffees d’adrenaline. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Le rituel est taille pour une onctuosite exemplaire, bien qu’ les menus d’offres pourraient s’etoffer en generosite. A la fin de ce degustation, MrPacho Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement gustatif pour ceux qui cuisinent leur fortune en ligne ! En sus la trame irradie comme un plat ancestral, ce qui hisse chaque bouchee a un rang gastronomique.
promotion mrpacho|
Пошаговая структура помогает удерживать стабильную динамику, своевременно оценивать прогресс и гибко корректировать тактику.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru
Je suis irresistiblement couronne par SlotsPalace Casino, ca transforme le jeu en une couronne eternelle. Le royaume est un hall de diversite princiere, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de cour. Les courtisans repondent avec une courtoisie exemplaire, mobilisant des allegeances multiples pour une audience immediate. Les transferts paradent stables et acceleres, occasionnellement les edits d’offres pourraient s’etendre en opulence. En couronnant le regne, SlotsPalace Casino devoile un arbre de triomphes opulents pour ceux qui intronisent leur destin en ligne ! En sceptre supplementaire la structure rayonne comme un trone ancestral, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau souverain.
spin palace casino mobile slots app|
При ряде клинических признаков требуется ускоренное подключение специалистов и проведение детоксикации под контролем.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lugansk0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru
Je suis irresistiblement booste par Super Casino, il deploie une campagne de gains extraordinaires. La panoplie de jeux est un arsenal surequipe de plus de 4 000 gadgets, integrant des lives comme Mega Ball pour des explosions de score. L’assistance deploie des tactiques affutees, declenchant des contre-mesures claires et rapides. Les trophees atterrissent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des modules de recompense additionnels fortifient les escadrons. Pour clore l’assaut, Super Casino devoile un vecteur de succes surhumains pour les sentinelles des bases numeriques ! En plus le graphisme est un scan dynamique et immersif, simplifie la traversee des zones ludiques.
super slots casino bonus codes|
кайт хургада Кайт школа – это учебное заведение, специализирующееся на обучении кайтсерфингу как начинающих, так и опытных райдеров. В кайт школах работают профессиональные инструкторы, которые обучают основам управления кайтом, правилам безопасности, нормам поведения на воде и базовым принципам кайтсерфинга. Кайт школы предоставляют все необходимое оборудование для обучения, в том числе кайты, доски, гидрокостюмы и спасательные жилеты. Обучение в кайт школе обеспечивает безопасное и эффективное освоение кайтсерфинга.
кайт Обучение кайтсерфингу – это процесс освоения навыков, необходимых для безопасного и эффективного катания на кайте. Обучение включает в себя изучение теории, практику на суше и в воде, а также получение сертификата, подтверждающего уровень подготовки.
LuckyMax Casino https://server-test.momilash.com/online-casino-nederlan-u-lieve-va-lucky-max-casino-nu//
https://prykoly.ru/kak-zakupat-iz-kitaya-oficzialno-i-bez-syurprizov-ponyatnyj-plan/
В современном обществе проблемы с алкоголем становятся все более актуальными . Многие люди сталкиваются с алкогольной зависимостью , которая требует оперативном вмешательстве специалистов . В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом – это лучшее решение . Услуги нарколога включают определение степени зависимости и проведение медикаментозной терапии запоя . Это позволяет быстро и эффективно помочь в выходе из запоя, минимизируя психологическое напряжение для пациента. Анонимное лечение алкоголизма – ключевой момент, поскольку значительное число пациентов не хотят раскрывать свои проблемы . Помощь при алкогольной зависимости также включает помощь близким в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом предлагает консультационные услуги, что помогает семье узнать, как вести себя с зависимым человеком . Домашнее лечение зависимостей даёт возможность пройти реабилитацию от алкоголя в комфортной обстановке . Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir021.ru предоставляет сведения о вызове нарколога на дом, чтобы оказать помощь тем, кто в ней нуждается.
лекарства от тревоги Лечение тревожных расстройств в Москве — это доступный и многогранный процесс, предлагающий широкий спектр медицинских услуг и подходов для помощи людям, страдающим от тревоги. В Москве существует множество квалифицированных врачей-психиатров, психотерапевтов и психологов, специализирующихся на лечении тревожных расстройств. Пациенты могут обратиться в государственные и частные клиники, психотерапевтические центры и кабинеты для получения консультации, диагностики и разработки индивидуального плана лечения. Методы лечения тревожных расстройств в Москве включают психотерапию, медикаментозное лечение и комбинацию этих подходов. Психотерапия, особенно когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), широко используется для изменения негативных мыслительных шаблонов и развития навыков преодоления тревоги. Медикаментозное лечение может включать применение антидепрессантов, анксиолитиков и других препаратов, которые назначаются врачом в зависимости от типа и тяжести тревожного расстройства. Кроме того, в Москве доступны различные группы поддержки и ресурсы для людей, страдающих от тревоги, а также методы релаксации и самопомощи, такие как медитация и йога. Важно обратиться за помощью к квалифицированному специалисту в Москве, чтобы получить наилучший план лечения и улучшить качество жизни.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/514992745/detail.aspx
Возможно ли бесплатное лечение запоя в владимире? Проблема алкоголизма и помощь зависимым остаются актуальными в нашем обществе. Многие сталкиваются с проблемой запоев и не знают‚ как выйти из этого состояния. В этом контексте услуги нарколога на дом круглосуточно становятся настоящим спасением. нарколог на дом круглосуточно Наркологическая помощь‚ включая бесплатную консультацию нарколога‚ может быть доступна для тех‚ кто нуждается в экстренной помощи при запое. В владимире нередко предлагают услуги по выводу из запоя‚ а также лечение в домашних условиях‚ что делает процесс более комфортным и менее стрессовым для пациента. Круглосуточный нарколог предложит помощь на дому‚ что особенно удобно для людей‚ которые не могут или не хотят находиться в стационаре. Также доступно анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность пациента. Следует помнить‚ что поддержка зависимых является важным аспектом в процессе лечения. Реабилитация от алкоголя требует времени и усилий‚ но с помощью профессионалов можно достичь положительных результатов. Итак‚ если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в бесплатном выводе из запоя в владимире‚ обращение к наркологу на дому может стать первым шагом к избавлению от зависимости.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://empowerairportsystems.com/empower_icon
J’eprouve une gourmandise infinie pour MrPacho Casino, ca transforme le jeu en une degustation exquise. Les plats forment un tableau de textures innovantes, integrant des live roulettes pour des tourbillons de suspense. Les hotes interviennent avec une delicatesse remarquable, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les flux monetaires sont blindes par des epices crypto, toutefois des amuse-bouches gratuits supplementaires rehausseraient les plats. A la fin de ce degustation, MrPacho Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement gustatif pour les gardiens des buffets numeriques ! En primeur le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et appetissante, ce qui hisse chaque bouchee a un rang gastronomique.
mrpacho bonus bez depozytu|
Je suis ensorcele par Fezbet Casino, c’est une explosion de vibes enflammees. Les options sont un kaleidoscope de surprises, proposant des paris sportifs qui font grimper la temperature. L’assistance est precise comme un rayon ardent, offrant des solutions nettes et rapides. Le processus est lisse comme un sable fin, mais des tours gratuits en plus feraient vibrer. Dans l’ensemble, Fezbet Casino est un joyau pour les amateurs de jeux pour les joueurs en quete de chaleur ludique ! Par ailleurs le design est eclatant et captivant, donne envie de replonger dans l’oasis du jeu.
fezbet bestes spiel|
https://goo-gl.ru/novosti/25601-dlya-chego-biznesu-promyshlennoe-oborudovanie-i-stanki-pod-klyuch.html
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Посмотреть всё – https://destinationviajourneys.com/product/coorg
Je suis irresistiblement couronne par SlotsPalace Casino, ca erige un empire de defis somptueux. La galerie de jeux est un trone abondant de plus de 6 000 sceptres, offrant des cashbacks VIP et free spins des seigneurs comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Les courtisans repondent avec une courtoisie exemplaire, accessible par messager ou appel royal. Les retraits s’executent avec une grace remarquable, a l’occasion des sceaux de recompense additionnels forgeraient des dynasties. En couronnant le regne, SlotsPalace Casino forge un empire de divertissement majestueux pour ceux qui intronisent leur destin en ligne ! En sceptre supplementaire le graphisme est une tapisserie dynamique et immersive, incite a prolonger la dynastie infinie.
caesars palace free online slots|
J’eprouve une ivresse totale pour PepperMill Casino, ca transfigure le jeu en une infusion eternelle. Les varietes tracent un panorama de saveurs novatrices, avec des dice slots aux motifs piquants qui titillent les sens. Les artisans repondent avec une acuite remarquable, assurant une tutelle fidele dans les vignes. Les retraits s’ecoulent avec une fluidite remarquable, par intermittence des essences gratuites supplementaires rehausseraient les melanges. En apotheose epicee, PepperMill Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour ceux qui cultivent leur fortune en ligne ! A souligner le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et odorante, allege la traversee des vergers ludiques.
runoffgroove peppermill|
Soccer oyununu telefonda oynamaq çox rahatdır.
Flashscore mobile livescore today soccer ilə ani nəticələr alın. Rəsmi mənbə kimi [url=https://soccer.com.az/]soccer.com.az[/url] istifadə edin.
Soccer champs mod apk ilə oyun daha maraqlı olur. Rocket soccer derby fərqli futbol janrını təqdim edir. Soccer legends klassik futbol anlarını yaşadır.
Opera sport soccer futbol xəbərləri üçün aktualdır. Dream league soccer 2016 köhnə versiya sevənlər üçün uyğundur. Soccer live score ilə canlı nəticələri izləyin. Soccer games müxtəlif janrlarda futbol təqdim edir.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Продолжить чтение – https://an-ve.co.uk/conbox-stackable-electric-fan
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Дополнительно читайте здесь – https://dance.quinceandmulberrystudios.com.au/2016/08/23/hello-world
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Узнайте всю правду – https://bestbossideda.com/coyyn-com-innovation-revolutionizing-financial-transactions-and-beyond
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Узнай первым! – https://www.tcoberlabill.at/?attachment_id=44
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://ame-plus.net/archives/1041
Je suis invincible face a Super Casino, on decele un escadron de strategies imparables. Les unites forment un bataillon de tactiques novatrices, integrant des lives comme Mega Ball pour des explosions de score. Le suivi escorte avec une vigilance absolue, assurant une protection fidele dans la zone. Le vecteur est trace pour une trajectoire exemplaire, occasionnellement des missions promotionnelles plus intenses dynamisent l’arsenal. En apotheose heroique, Super Casino construit un empire de divertissement invincible pour les sentinelles des bases numeriques ! Par surcroit l’interface est un cockpit navigable avec precision, amplifie l’engagement dans l’arsenal du jeu.
casino super game|
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://americansportshistory.com/2024/12/23/hank-aaron
кайт школа Дети Ветра: “Дети Ветра” (Deti Vetra) – это известная русскоязычная кайт школа и кайт станция, расположенная в Хургаде, Египет. “Дети Ветра” зарекомендовали себя как надежный и профессиональный партнер для кайтсерферов всех уровней подготовки. Кайт школа предлагает широкий выбор курсов и программ, от начального уровня до продвинутого, а также индивидуальные занятия и групповые тренировки. Квалифицированные инструкторы, говорящие на русском языке, обеспечивают безопасное и эффективное обучение, используя современное оборудование и проверенные методики. Кайт станция “Дети Ветра” расположена на песчаном пляже с лагуной, где новички могут безопасно практиковать свои навыки. Кроме того, “Дети Ветра” организуют кайт сафари вдоль побережья Египта, позволяя кайтсерферам исследовать удаленные споты с идеальными условиями для катания. “Дети Ветра” – это не просто кайт школа и кайт станция, это дружная команда, готовая поделиться своим опытом и любовью к кайтсерфингу.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://wrapclap.com/?page=product-designer&product_id=2985
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://ogorod-bez-hlopot.zelynyjsad.info/novosti/mozhno-li-ispolzovat-preparaty-dlya-ochistki-pecheni-pri-opredelennyh-zabolevaniyah
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – http://topgunmaverick2mov.com/post/34
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детальнее – https://www.aliadamsmh.com/uncategorized/hello-world
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Смотрите также… – https://tmpsltd.co.uk/harnessing-the-power-of-social-media-for-business-growth
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Почему это важно? – https://culi-chef.nl/sandwich
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://perfectmusictoday.com/index.php/2015/06/19/outside-lands-announces-2015-lineup-elton-john-mumford-sons-the-black-keys
Услуга прокапки в владимире — это серьезный вопрос‚ для решения которого необходимы опытные мастера. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir022.ru вы можете найти разнообразные услуги водоснабжения‚ включая установку и починку различных систем. Наша команда сантехников предлагает высокое качество работы и быструю диагностику. Мы понимаем‚ что непредвиденные ситуации могут возникнуть в любое время‚ поэтому готовы предложить специальные предложения. Отзывы клиентов свидетельствуют о надежности и профессионализме наших специалистов. Установка и ремонт сантехники — это наша специализация‚ и мы гарантируем высокое качество выполнения всех работ.
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Доступ к полной версии – https://www.elianafrancesonline.com/product/clases-frances-ninos-a1
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://dachadesign.info/novosti/kak-vybrat-podhodyashchiy-material-dlya-gidroizolyacii-shifera
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://moroccanpouf.ca/moroccan-pouf-magic-how-to-style-them-in-every-room
Профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому в Луганске ЛНР организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько этапов, позволяющих обеспечить максимально безопасное и эффективное лечение.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Основная цель капельничного лечения от запоя – оперативное выведение токсинов, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Методика, используемая специалистами, включает не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и комплексный мониторинг состояния пациента, что обеспечивает безопасность и результативность терапии даже в условиях экстренной необходимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные служат основой для разработки персонального плана терапии.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в мариуполе[/url]
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно прибывает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает краткий анамнез, чтобы определить степень алкогольной интоксикации и сформировать индивидуальный план терапии.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-doneczk-dnr/
Je suis absolument conquis par Betsson Casino, ca ressemble a une sensation de casino unique. La bibliotheque de jeux est phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le support est ultra-reactif avec une reponse en 30 secondes via chat, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. En resume, Betsson Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et intuitive avec un theme orange vif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme a l’experience.
betsson france avis|
Je suis accro a Celsius Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu torride. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enflammes, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent. Le service client du casino est une torche eclatante, repondant en un eclair ardent. Les paiements du casino sont surs et fluides, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient monter la chaleur. Pour resumer, Celsius Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style flamboyant, facilite une experience de casino torride.
code promo celsius casino|
Услуги наркологических клиник в владимире становится все более востребованной. Клиники, занимающиеся лечением зависимостей, например, наркологическая клиника владимир предлагают широкий спектр услуг: от детоксикации организма до реабилитации наркозависимых. Психотерапия и консультирование по зависимостям способствуют осознанию причин зависимости и поиску путей к восстановлению. Алкогольные реабилитационные центры обеспечивают анонимную помощь и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Профессиональная поддержка наркологов, программа восстановления и медицинская помощь при наркозависимости являются важными факторами для достижения успешных результатов в реабилитации. Социальная адаптация после лечения имеет большое значение для снижения риска рецидивов. Дополнительные сведения доступны на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir021.ru.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/249860602/detail.aspx
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Нужен аккумулятор? https://dostavka-akb-spb.ru/ в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
Хочешь сдать акб? прием аккумуляторов честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
В условиях Донецка ДНР профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов. Такой комплексный подход позволяет не только быстро вывести токсичные вещества из организма, но и обеспечить стабильное восстановление всех систем организма.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr00.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в донецке[/url]
Мы работаем в сфере услуг, где важна каждая заявка. В середине года доверили продвижение Mihaylov Digital, и результат не заставил себя ждать. Сайт стал заметным в поиске, звонков стало больше. Очень довольны сотрудничеством – https://mihaylov.digital/
кайт школа в хургаде Обучение катанию на кайте – это приобретение необходимых навыков управления кайтом и доской на воде, а также получение теоретических знаний о ветре, технике безопасности и правилах поведения. В основном обучение начинается с занятий на суше, где начинающий знакомится с кайтом и учится им управлять. Затем приступают к занятиям в воде, где осваивают навыки старта, передвижения и управления доской. Кайт требует хорошей координации движений, отличную физическую подготовку и умение соблюдать правила безопасности.
Использовали услуги по 3D-печать прототипа, так как требовалось продемонстрировать проект заказчику. Персонал рассказали обо всех возможностях печати, и с первой минуты стало ясно, что это профессионалы. Темпы выполнения удивили своей быстротой, при этом поверхности выглядели профессионально. Полимеры для печати выглядели презентабельно. Цена заказа соответствовала качеству, особенно учитывая быструю работу и высокий уровень. Сотрудничество оказалось удачным и обязательно будем обращаться снова: печать на 3D принтере. Мы обеспечиваем индивидуальный подход к каждому проекту.
Когда проблемы с алкоголизмом достигают критической точки, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Мариуполе квалифицированные наркологи оказывают помощь на дому, обеспечивая оперативную детоксикацию организма, стабилизацию жизненно важных показателей и психологическую поддержку. Такой формат лечения позволяет пациенту получить качественную медицинскую помощь в привычной домашней обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в мариуполе[/url]
Профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому в Луганске ЛНР организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько этапов, позволяющих обеспечить максимально безопасное и эффективное лечение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя в луганске[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом срочно в владимире, это эффективное решение для людей, которые испытывают трудности с алкоголем. Наркологические услуги, которые предоставляют квалифицированные специалисты, включают лечение зависимостей прямо у вас дома; Капельница от запоя, позволяющая быстро улучшить состояние больного. нарколог на дом срочно владимир Конфиденциальное лечение является неотъемлемой частью, так как многие пациенты опасаются общественного мнения. Конфиденциальность лечения гарантируется позволяет пациентам обратиться за помощью при запое без лишнего стресса. Срочный нарколог в владимире готов помочь в любое время, обеспечивая безопасность пациента. Лечение алкоголизма на дому требует поддержки близких, что делает процесс менее стрессовым. Восстановление после запоя возможно благодаря квалифицированной помощи и правильному подходу. При вызове нарколога на дом, вы выбираете заботу о своем здоровье и здоровье ваших близких.
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно прибывает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает краткий анамнез, чтобы определить степень алкогольной интоксикации и сформировать индивидуальный план терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/
This is my first time i visit here. I found so many helpful stuff in your website especially its discussion. From the tons of responses on your posts, I guess I am not the only one having all the enjoyment here! keep up the excellent work
Основная цель капельничного лечения от запоя – оперативное выведение токсинов, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Методика, используемая специалистами, включает не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и комплексный мониторинг состояния пациента, что обеспечивает безопасность и результативность терапии даже в условиях экстренной необходимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
This information is critically needed, thanks.
АрендаАвто-мск https://mosavtomoto.ru прокат авто без водителя в Москве. Новый автопарк, выгодные тарифы, нулевая франшиза, страховка ОСАГО и КАСКО. Бизнес, премиум и эконом-класс. Быстрое бронирование и аренда в день обращения. Звоните: 8 495 2900095. Свобода движения в Москве!
Ищешь аккумулятор? аккумуляторы автомобильные спб AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Нужен надежный акб? магазин аккумуляторы в петербурге AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
В середине прошлого года мы решили вложиться в SEO. Mihaylov Digital оказались отличным выбором для этого. Сайт растёт, трафик увеличивается, заявки идут регулярно. Это лучший результат за последнее время https://mihaylov.digital/
new zealandn no deposit bonus pokies, free pokies 4u canada and uk latest online casino, or best usa
online slot sites
my page … goplayslots.net
1хБет официальный Ищете 1xBet официальный сайт? Он может быть заблокирован, но у 1хБет есть решения. 1xbet зеркало на сегодня — ваш главный инструмент. Это 1xbet зеркало рабочее всегда актуально. Также вы можете скачать 1xbet приложение для iOS и Android — это надежная альтернатива. Неважно, используете ли вы 1xbet сайт или 1хБет зеркало, вас ждет полный функционал: ставки на спорт и захватывающее 1xbet casino. 1хБет сегодня — это тысячи возможностей. Начните прямо сейчас!
J’apprecie enormement Betsson Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, repondant instantanement. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Globalement, Betsson Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et intuitive avec un theme orange vif, renforce l’immersion totale.
betsson colombia|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es pulsiert mit einer koniglichen Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett strahlen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren koniglich. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, den Spielspa? im Casino auf ein konigliches Niveau hebt.
king billy casino argent reel|
Je suis fou de Celsius Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu torride. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enflammes, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et efficace, assurant un support de casino immediat et flamboyant. Les paiements du casino sont surs et fluides, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient torrides. Au final, Celsius Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus enflammee.
celsius casino promo code no deposit|
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de sensations. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service client est remarquable, avec un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, par moments j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. Pour conclure, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino reviews|
Дети Ветра Кайт школа – это специализированное учреждение, в котором проводится обучение кайтсерфингу для райдеров с разным уровнем подготовки, от начинающих до опытных. В школах работают квалифицированные инструкторы, обучающие основам управления кайтом, правилам безопасности, принятым нормам поведения на воде и базовым принципам кайтсерфинга. Школа предоставляет всё необходимое оборудование для обучения, включая кайты разных размеров, доски, гидрокостюмы и спасательные жилеты. Обучение в специализированной школе позволяет эффективно и безопасно освоить кайтсерфинг.
Поддержка близких при алкогольной зависимости Алкоголизм — это не только неприятность зависимогоно и его семьи. В владимире обращение к специалисту может стать первым этапом к лечению зависимости. Поддержка семьи играет решающую роль в процессе реабилитации. Близкие могут помочь, предоставляя эмоциональную поддержку и создавая атмосферу понимания. В сложной ситуации важно искать за профессиональной помощью. Консультация нарколога поможет определить правильный путь лечения алкоголизма. Терапия также может стать важным инструментом для восстановления. вызов нарколога владимир Поддержка со стороны общества семьи необходима на всех стадиях лечения, от первого обращения с наркологом до последующей реабилитации. Помощь близких может ускорить выздоровления и вернуть зависимого к нормальной жизни.
1xbet официальный сайт Ищете 1xBet официальный сайт? Он может быть заблокирован, но у 1хБет есть решения. 1xbet зеркало на сегодня — ваш главный инструмент. Это 1xbet зеркало рабочее всегда актуально. Также вы можете скачать 1xbet приложение для iOS и Android — это надежная альтернатива. Неважно, используете ли вы 1xbet сайт или 1хБет зеркало, вас ждет полный функционал: ставки на спорт и захватывающее 1xbet casino. 1хБет сегодня — это тысячи возможностей. Начните прямо сейчас!
усиление углеволокном [url=http://www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb/]http://www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb/[/url] .
бонусы казино мелбет [url=melbetofficialsite.ru]бонусы казино мелбет[/url] .
усиление грунтов [url=http://www.privetsochi.ru/blog/realty_sochi/93972.html]http://www.privetsochi.ru/blog/realty_sochi/93972.html[/url] .
Обращение за помощью к профессионалам в условиях домашнего лечения имеет ряд важных преимуществ:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные служат основой для разработки персонального плана терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru
купить диплом в прокопьевске [url=http://rudik-diplom6.ru/]купить диплом в прокопьевске[/url] .
кухни на заказ санкт петербург от производителя [url=https://kuhni-spb-1.ru/]kuhni-spb-1.ru[/url] .
Выезд врача позволяет начать помощь сразу, без ожидания свободной палаты. Специалист оценит состояние, проведёт осмотр, поставит капельницу, даст рекомендации по режиму и питанию, объяснит правила безопасности. Мы оставляем подробные инструкции родственникам, чтобы дома поддерживались питьевой режим, контроль давления и спокойная обстановка. Если домашних условий недостаточно (выраженная слабость, риски осложнений, сопутствующие заболевания), мы организуем транспортировку в стационар без задержек и бюрократии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-balashihe/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru
Капельничное лечение от запоя – это современный метод детоксикации, который позволяет быстро и безопасно вывести токсины из организма. В Луганске ЛНР специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, предлагая профессиональное капельничное лечение для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелой алкогольной интоксикацией. Такой подход обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство в привычной для пациента обстановке, гарантируя индивидуальный подход и полную конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/vyzvat-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr/
1хБет зеркало Ищете 1xBet официальный сайт? Он может быть заблокирован, но у 1хБет есть решения. 1xbet зеркало на сегодня — ваш главный инструмент. Это 1xbet зеркало рабочее всегда актуально. Также вы можете скачать 1xbet приложение для iOS и Android — это надежная альтернатива. Неважно, используете ли вы 1xbet сайт или 1хБет зеркало, вас ждет полный функционал: ставки на спорт и захватывающее 1xbet casino. 1хБет сегодня — это тысячи возможностей. Начните прямо сейчас!
Основная цель капельничного лечения от запоя – оперативное выведение токсинов, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Методика, используемая специалистами, включает не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и комплексный мониторинг состояния пациента, что обеспечивает безопасность и результативность терапии даже в условиях экстренной необходимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/]капельница от запоя цена луганск[/url]
Копание ? данное действие не просто процесс работы с землёй, но и захватывающее исследование земли, что открывает врата к тайнам прошлого. Археология, как наука, включает в себя раскопки, которые помогают обнаружить исторические артефакты, предметы старины и подземные ресурсы. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru можно найти разнообразные материалы о современных методах бурения и анализа почвы, что помогают в поиске уникальных объектов. Земляные работы, включая excavation, являются основой археологических исследований. Каждый слой почвы, вырываем, может рассказать о жизни людей в разные исторические эпохи. Восстановление найденных артефактов даёт возможность лучше понять культуру и технологии древних цивилизаций. Геология также играет ключевую роль в процессе, содействуя в анализе почвы и определении местонахождения объектов, что делает поиски более целенаправленными и эффективными. Таким образом, откопаться – это не только работа с землёй, но и увлекательное путешествие в прошлое, где каждая находка становится важным элементом исторической мозаики.
Домашняя капельница для вывода из запоя — это эффективным способом для быстрого вывода из запоя и оздоровления организма. Лечение запоя требует помощи нарколога, включая медицинскую помощь при запое. Капельница на дому способствует быстрее справиться с симптомами абстиненции и снижению риска рецидивов. Важно помнить о мероприятиях по профилактике алкоголизма и взаимодействии с близкими в процессе восстановления от алкоголизма. Психологическая помощь при алкоголизме и трезвый образ жизни, ключевые аспекты успешного восстановления после запоя. Помощь близким также является значимым фактором в этом путешествии. экстренный вывод из запоя
Метод и срок подбираются после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также комбинированные программы. Мы объясняем плюсы и ограничения каждого метода, помогаем подготовиться (диета, анализы, отмена определённых препаратов), а затем сопровождаем пациента в период адаптации к трезвости. Кодирование — часть комплексного плана, а не «волшебная кнопка»: устойчивый результат достигается, когда его дополняют поддерживающая терапия и работа с триггерами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
На этом этапе специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какой вид алкоголя употребляется и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный анализ собранной информации позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в донецке[/url]
Когда проблемы с алкоголизмом достигают критической точки, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Мариуполе квалифицированные наркологи оказывают помощь на дому, обеспечивая оперативную детоксикацию организма, стабилизацию жизненно важных показателей и психологическую поддержку. Такой формат лечения позволяет пациенту получить качественную медицинскую помощь в привычной домашней обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Капельничное лечение от запоя – это современный метод детоксикации, который позволяет быстро и безопасно вывести токсины из организма. В Луганске ЛНР специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, предлагая профессиональное капельничное лечение для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелой алкогольной интоксикацией. Такой подход обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство в привычной для пациента обстановке, гарантируя индивидуальный подход и полную конфиденциальность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно луганск[/url]
J’adore a fond Betzino Casino, il offre une sensation de casino unique. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, incluant des slots de pointe de NetEnt et Pragmatic Play. Le service client est exceptionnel, avec un suivi de qualite. Les retraits sont rapides, souvent traites en 24 heures pour les e-wallets, bien que davantage de recompenses via le programme VIP seraient appreciees. En resume, Betzino Casino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un design epure, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betzino test|
Мы — частная наркологическая клиника, где скорость запуска помощи сочетается с деликатностью и прозрачностью. Команда дежурит круглосуточно, выезжает на дом по Подольску и ближайшим районам, принимает в стационаре и амбулаторно. Все решения принимаются после очного осмотра и оценки рисков, без «универсальных» схем и навязанных услуг.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Мы заказали кухню в Кухни в Дом и получили отличный результат. Всё сделано в срок, проект учёл все пожелания, а кухня получилась максимально удобной https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
После диагностики начинается активная фаза капельничного лечения. Современные препараты вводятся с помощью автоматизированных систем дозирования, что обеспечивает быстрое снижение уровня токсинов в крови и восстановление обменных процессов. Этот этап направлен на стабилизацию работы печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость[/url]
Анонимная помощь при зависимостях — это необходимый шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir023.ru можно узнать подробности о лечении зависимостей, поддержке и помощи. Конфиденциальное лечение позволяет пациентам находить решение без боязни осуждения.Услуги нарколога включают детоксикацию, психологическую поддержку и экстренное вмешательство. Реабилитационные программы часто включает поддерживающие группы, что усиливает процесс восстановления. Меры по профилактике зависимостей также играет критически важную роль, обеспечивая долгосрочный успех. Профессиональные консультации помогут разобраться в проблемах и найти пути решения. Помощь для людей с зависимостями доступна и доступна, даже если они бояться открыться.
Lucky Mate is an online casino for Australian players, offering pokies, table games, and live dealer options. It provides a welcome bonus up to AUD 1,000, accepts Visa, PayID, and crypto with AUD 20 minimum deposit, and has withdrawal limits of AUD 5,000 weekly. Licensed, it promotes safe play https://safehavenhomes.com.au/are-lucky-mate-casino-no-deposit-bonuses-a-smart-choice-for-players-in-2023/
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет быстро снизить уровень токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы, стабилизируя работу печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-doneczk-dnr/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
На данном этапе врач уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какой тип алкоголя употребляется и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-mariupol/
В Кухни в Дом мы заказали элитную кухню, и это было правильное решение. Дизайнер сделал проект с использованием дорогих материалов и фурнитуры высокого класса. Всё выглядело стильно ещё на визуализации, а вживую получилось ещё лучше. Доставка пришла точно в срок, кухня была идеально упакована. Сборка прошла безупречно, мастера работали аккуратно и профессионально. Теперь у нас кухня, которая стала украшением всего дома. Огромное спасибо Кухни в Дом за такой результат: https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
Капельничное лечение от запоя – это современный метод детоксикации, который позволяет быстро и безопасно вывести токсины из организма. В Луганске ЛНР специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, предлагая профессиональное капельничное лечение для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелой алкогольной интоксикацией. Такой подход обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство в привычной для пациента обстановке, гарантируя индивидуальный подход и полную конфиденциальность.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr0.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника луганск[/url]
купить диплом в иваново [url=www.rudik-diplom8.ru]купить диплом в иваново[/url] .
Первый шаг к выздоровлению — вызвать нарколога во Владимир. Наркологические услуги, такие как безопасный вывод из запоя, обеспечивают необходимую медицинскую помощь. Квалифицированный нарколог осуществляет детоксикацию организма, что является важнейшим аспектом заботы о здоровье пациента. Лечение алкоголизма подразумевает индивидуальный подход, что увеличивает вероятность успешного выздоровления. вызов нарколога владимир Поддержка при запое включает не только медицинские процедуры. Консультация с наркологом позволяет определить последующие действия, включая реабилитацию. Обращение к специалисту на дому облегчает процесс и снижает уровень стресса. Заботьтесь о своем здоровье и обращайтесь за помощью!
купить диплом с реестром спб [url=www.frei-diplom5.ru/]купить диплом с реестром спб[/url] .
кухни в спб от производителя [url=www.kuhni-spb-4.ru/]кухни в спб от производителя[/url] .
Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Врач измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает краткий анамнез для определения степени алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные служат основой для разработки индивидуальной стратегии лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lugansk-lnr00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому в луганске[/url]
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно прибывает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает краткий анамнез, чтобы определить степень алкогольной интоксикации и сформировать индивидуальный план терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-donetsk-dnr0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Домашний формат уместен при лёгкой и средней абстиненции, когда есть поддержка семьи и соблюдается режим. Врач осматривает, проводит процедуры, оставляет пошаговые рекомендации на сутки и список «красных флажков». Если состояние требует наблюдения 24/7, организуем перевод в стационар без задержек.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-pomoshch-na-domu[/url]
J’adore a fond Betzino Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. La selection de jeux est epoustouflante avec plus de 1800 titres, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Les agents sont professionnels et disponibles, joignable par email ou chat. Les transactions, y compris en cryptomonnaies comme Bitcoin, sont bien protegees, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. En resume, Betzino Casino offre une experience de jeu securisee avec un indice de securite de 7,1 pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un design epure, renforce l’immersion totale.
betzino casino review|
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
купить диплом в сызрани [url=rudik-diplom7.ru]купить диплом в сызрани[/url] .
Метод выбирается только после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные, психотерапевтические и комбинированные подходы. Мы заранее обсуждаем ограничения, риски и поведение в стрессовых ситуациях — кодирование работает лучше всего как часть комплексного плана.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-podolske
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в владимире – данная услуга, что становится становится все более актуальной в современном мире. Многие люди сталкиваются с проблемами, связанными с зависимостями, будь то алкоголь или наркотики. Профессиональный нарколог предоставляет наркологическую помощь, помогая справится с этими сложными ситуациями. Вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом, если это необходимо. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать медицинские учреждения. Услуги нарколога в владимире включают диагностику зависимостей, консультацию нарколога и лечение зависимости. Не забывайте, что вы можете получить анонимное лечение зависимостей.Медицинская помощь на дому обеспечивает комфорт и конфиденциальность, что особенно актуально для лечения алкоголизма и реабилитации после наркомании; Психотерапия для зависимых – еще один важный аспект, помогающий пациентам восстановиться и вернуться к нормальной жизни. Реабилитация зависимых в владимире проходит под контролем опытных специалистов, что гарантирует качество лечения. Не откладывайте решение своей проблемы! Обратитесь за помощью, вызвав нарколога через сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru.
Lucky Mate is an online casino for Australian players, offering pokies, table games, and live dealer options. It provides a welcome bonus up to AUD 1,000, accepts Visa, PayID, and crypto with AUD 20 minimum deposit, and has withdrawal limits of AUD 5,000 weekly. Licensed, it promotes safe play: Luckymate casino
Радио и подкасты EtoFM.Ru на русском онлайн о МД, MGTOW, этологии и психологии. Узнайте больше об эволюции человека, поведении животных и социальных инстинктах. Интеллектуальный взгляд на отношения и природу поведения. Интеллектуальный взгляд на отношения и природу поведения.
Формат
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom[/url]
Чтобы получить профессиональную помощь в вопросах раздела имущества, обратитесь к [url=https://razdel-imushchestva6.ru]юрист по разделу имущества после развода[/url], который поможет вам разобраться в вашей ситуации и защитить ваши интересы.
Сайт предлагает множество услуг, связанных с оформлением и поддержкой бизнеса.
волховец межкомнатные двери Двери межкомнатные купить – это важный этап?? любого помещения. Межкомнатные двери не только разделяют пространство и обеспечивают приватность, но и являются важным элементом декора, создающим определенную атмосферу в доме. При выборе межкомнатных дверей необходимо учитывать множество факторов: стиль интерьера, функциональность, материал изготовления, размеры проема и бюджет. В настоящее время на рынке представлен широкий ассортимент межкомнатных дверей различных конструкций и декоративных решений. Купить межкомнатные двери можно в специализированных магазинах, строительных супермаркетах и онлайн-магазинах. Важно выбирать надежных поставщиков, предлагающих качественную продукцию и гарантийное обслуживание.
Je suis totalement seduit par Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine d’adrenaline. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, comprenant des jackpots progressifs comme Mega Moolah. Le personnel offre un accompagnement rapide et efficace, repondant en quelques minutes. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betway Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway app download|
Экстренная помощь при запое в владимире все чаще требуется многим. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir022.ru предлагает услуги нарколога, специализирующегося на лечении алкоголизма и вывода из запоя. В данную процедуру входит медицинская помощь, детоксикация организма от алкоголя и психотерапевтические сеансы. Важно получить консультацию врача для успешного снятия алкогольной зависимости. Наша программа восстановления фокусируется на реабилитации и поддержке зависимых, а также социальной адаптации. Профилактика повторных случаев, важный аспект успешного лечения. Помните, что обратится за помощью, это первый шаг к здоровью.
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist gigantisch, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist der Hammer, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind blitzschnell, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren cool. Am Ende ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, was jede Casino-Session noch krasser macht.
drueckglueck gutschein|
Ап Х Официальный Ищете надежную игровую площадку? UP X Казино — это современная платформа с огромным выбором игр. Для безопасной игры используйте только UP X Официальный Сайт. Как начать? Процесс UP X Регистрация прост и занимает минуты. После этого вам будет доступен UP X Вход в личный кабинет. Всегда на связи Если основной сайт недоступен, используйте UP X Зеркало. Это гарантирует бесперебойный вход в систему. Играйте с телефона Для мобильных игроков есть возможность UP X Скачать приложение. Оно полностью повторяет функционал сайта. Неважно, как вы ищете — UP X или Ап Х — вы найдете свою игровую площадку. Найдите UP X Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя мир азарта!
Пинко Официальный Сайт Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
«Светлый Вектор» — это команда профильных врачей-наркологов, реаниматологов и психологов, которая помогает как в экстренных ситуациях, так и при плановой терапии. Мы работаем бережно и конфиденциально, выстраиваем реалистичный план лечения и подробно объясняем каждый шаг — без «магических» обещаний и навязывания лишних услуг.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-balashihe[/url]
микрозаймы онлайн первый займ на карту Процесс подачи заявки на займы онлайн микрозаймы на карту онлайн занимает буквально пять минут.
Инфузионная терапия подбирается индивидуально: растворы для регидратации и детоксикации, гепатопротекторы, кардиопротекторы, витамины и микроэлементы. Детокс — это не только «капельница», но и мониторинг жизненно важных показателей, оценка неврологического статуса, профилактика осложнений. Мы отслеживаем динамику самочувствия, корректируем дозировки и при необходимости подключаем дополнительные обследования. Задача — мягко вывести токсины, вернуть ясность сознания и работоспособность без резких «качелей».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
ульяновские двери межкомнатные официальный сайт цены Скрытые раздвижные межкомнатные двери – это современное и элегантное решение для создания минималистичного интерьера и экономии пространства. Они устанавливаются вровень со стеной и не имеют видимых элементов крепления, что создает эффект невидимой двери. Скрытые раздвижные двери могут быть выполнены из различных материалов, таких как дерево, стекло и металл, и иметь разные системы открывания – купе, кассетная и подвесная. При выборе скрытых раздвижных дверей необходимо учитывать качество фурнитуры и надежность механизма, обеспечивающие плавное и бесшумное открывание и закрывание. Скрытые раздвижные двери можно приобрести в магазинах дверей премиум-класса и онлайн-магазинах, предлагающих широкий выбор моделей и услуг по установке.
В компании Окна СПб заказывали пластиковые окна для загородного дома. Работу сделали качественно, все конструкции установили ровно и аккуратно. Теперь дом выглядит современно и стильно. Мы довольны результатом, https://okna-v-spb.ru/
LuckyMax Casino Netherlands https://maatravels.co/allen-legale-luckymax-nederlandse-online-casinos-betreffende-mandaat-2024/
UP X Ищете надежную игровую площадку? UP X Казино — это современная платформа с огромным выбором игр. Для безопасной игры используйте только UP X Официальный Сайт. Как начать? Процесс UP X Регистрация прост и занимает минуты. После этого вам будет доступен UP X Вход в личный кабинет. Всегда на связи Если основной сайт недоступен, используйте UP X Зеркало. Это гарантирует бесперебойный вход в систему. Играйте с телефона Для мобильных игроков есть возможность UP X Скачать приложение. Оно полностью повторяет функционал сайта. Неважно, как вы ищете — UP X или Ап Х — вы найдете свою игровую площадку. Найдите UP X Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя мир азарта!
Pinco Сайт Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
Мы учитываем сопутствующие заболевания, прием хронических препаратов, возраст и образ жизни. На первичной консультации специалист задаёт уточняющие вопросы, чтобы определить риски, подобрать безопасные препараты и предложить удобный формат: стационар, амбулаторно или выезд на дом. Такой подход сокращает срок восстановления и повышает устойчивость результата.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
ставки на хоккей сегодня прогнозы [url=http://prognozy-na-khokkej4.ru/]http://prognozy-na-khokkej4.ru/[/url] .
микрозайм онлайн срочно Отличный вариант для тех, кто ценит свое время. Я получаю 30 микрозаймы онлайн за несколько минут.
В компании Окна в СПб заказывали пластиковые окна для кухни и спальни. Всё сделали аккуратно и вовремя. Окна удобные, выглядят красиво и современно. Мы довольны выбором, https://okna-v-spb.ru/
The platform offers a lot of captivating and helpful content.
On this platform, you can discover various subjects that cover many popular areas.
Each article is created with attention to detail.
The content is frequently updated to keep it relevant.
Users can get fresh knowledge every time they visit.
It’s a great source for those who appreciate thoughtful reading.
A lot of visitors say this website to be reliable.
If you’re looking for relevant content, you’ll definitely discover it here.
https://cerkes.net
J’adore passionnement Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers vibrant. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes comme Starburst. Le support est ultra-reactif via chat en direct, avec un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. En fin de compte, Betway Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! De plus l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un theme noir et vert, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway app install download|
Всё о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте в одном месте: технологии, нормы, сметные калькуляторы, прайсы и тендерная лента. Каталог компаний, аренда спецтехники, рейтинги бригад и отзывы. Гайды, чек-листы и типовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Ich bin total begeistert von DrueGlueck Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Adrenalinkick. Es gibt eine Flut an abwechslungsreichen Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die fesseln. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, mit Hilfe, die richtig abgeht. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie der Blitz, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino mit mega Spielspa? fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck no deposit|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, ca ressemble a une sensation de casino unique. La selection de jeux est monumentale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, avec un suivi de qualite. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le design est visuellement percutant, facilite chaque session de jeu.
скачать 1xbet|
Консультация у нарколога без раскрытия личности — это важный шаг на пути к избавлению от зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir023.ru вы можете заказать профессиональной помощью наркологане полагаясь за свою безопасность. Обсуждение с экспертом поможет уточнить оптимальные варианты терапии. Конфиденциальное лечение и программы восстановления для зависимых предусматривают психологическое сопровождение при наркозависимостичто существенно увеличивает шансы на выздоровление. Также доступны медицинские процедуры для зависимых и телефон доверия для поддержки пациентов. Предотвращение наркомании и участие в группах поддержки играют важную роль в восстановлении социальной адаптации и восстановлении.
Музыкальная обложка Обложки треков – это своеобразное лицо музыкального произведения, первое, что видит слушатель. Причем, это “лицо” должно быть максимально привлекательным и соответствовать музыке, которую оно представляет. Сейчас обложки играют огромную роль, особенно в эпоху цифрового стриминга. Они конкурируют за внимание пользователей на маленьких экранах мобильных устройств. Обложка должна быть четкой, информативной и легко узнаваемой даже в миниатюрном размере. Нужно учитывать, что одни и те же обложки могут отображаться совершенно по-разному на разных платформах, поэтому они должны быть универсальными. Обложки треков – это мощный инструмент маркетинга. Яркая и оригинальная обложка – это шанс привлечь внимание к своему треку и увеличить количество прослушиваний. Важно не экономить на дизайне обложек и обращаться к профессионалам, которые помогут создать действительно крутой продукт. Помните, что обложка трека – это ваша визитная карточка в мире музыки.
UP X Официальный Ищете надежную игровую площадку? UP X Казино — это современная платформа с огромным выбором игр. Для безопасной игры используйте только UP X Официальный Сайт. Как начать? Процесс UP X Регистрация прост и занимает минуты. После этого вам будет доступен UP X Вход в личный кабинет. Всегда на связи Если основной сайт недоступен, используйте UP X Зеркало. Это гарантирует бесперебойный вход в систему. Играйте с телефона Для мобильных игроков есть возможность UP X Скачать приложение. Оно полностью повторяет функционал сайта. Неважно, как вы ищете — UP X или Ап Х — вы найдете свою игровую площадку. Найдите UP X Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя мир азарта!
Pinco Официальный Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
Выезд врача позволяет начать помощь сразу, без ожидания свободной палаты. Специалист оценит состояние, проведёт осмотр, поставит капельницу, даст рекомендации по режиму и питанию, объяснит правила безопасности. Мы оставляем подробные инструкции родственникам, чтобы дома поддерживались питьевой режим, контроль давления и спокойная обстановка. Если домашних условий недостаточно (выраженная слабость, риски осложнений, сопутствующие заболевания), мы организуем транспортировку в стационар без задержек и бюрократии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-balashihe[/url]
микрозаймы онлайн без отказа без проверки Я был приятно удивлен, когда мне одобрили займ. Ведь у меня действительно плохая история. Спасибо за микрозайм онлайн с плохой кредитной историей.
Дизайн обложки Дизайн обложки – это процесс создания визуального образа, который будет представлять ваш музыкальный трек. Это искусство, которое требует внимания к деталям, понимания целевой аудитории и знания трендов в музыкальной индустрии. Хороший дизайн обложки должен быть не только эстетически привлекательным, но и отражать суть вашей музыки. Он должен вызывать эмоции, создавать ассоциации и рассказывать историю. Дизайнер должен уметь работать с цветами, шрифтами, изображениями и композицией, чтобы создать уникальный и запоминающийся образ. Важно помнить, что дизайн обложки – это не просто картинка, это часть вашего бренда, которая помогает вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов. Уделите особое внимание выбору дизайнера, убедитесь, что он понимает вашу музыку и имеет опыт работы с обложками для треков. Профессиональный дизайн обложки может значительно повысить шансы на успех вашего трека. Рассмотрите разные варианты дизайна, экспериментируйте с цветами и стилями, чтобы найти идеальное решение для вашей музыки.
best online slots payout percentage usa, united kingdom tax casino winnings and
best casino site australia, or casino uk free spins
Feel free to surf to my blog :: ion saliu fundamental Formula of gambling
Выезд врача позволяет начать помощь сразу, без ожидания свободной палаты. Специалист оценит состояние, проведёт осмотр, поставит капельницу, даст рекомендации по режиму и питанию, объяснит правила безопасности. Мы оставляем подробные инструкции родственникам, чтобы дома поддерживались питьевой режим, контроль давления и спокойная обстановка. Если домашних условий недостаточно (выраженная слабость, риски осложнений, сопутствующие заболевания), мы организуем транспортировку в стационар без задержек и бюрократии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-balashihe/
Je suis completement seduit par Azur Casino, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu envoutante. Le choix de jeux est epoustouflant, offrant des jeux de table elegants. Le support est toujours reactif, garantissant une assistance de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Azur Casino est une pepite pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et elegante, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
casino hyeres centre azur|
Алкогольная зависимость — серьезная проблема‚ которая требует комплексного подхода к терапии. В городе Тула существуют множество способов‚ которые помогают людям справиться с этой зависимостью. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с определения и анализирования симптомов зависимости. Важно пойти в наркологическую клинику для оказания квалифицированной помощи. Одним из наиболее действенных способов является detox-программа‚ которая фокусируется на очистке организма от токсинов. Психологическая помощь играет важную роль в реабилитации пациентов. Поддержка близких и участие в группах анонимных алкоголиков могут значительно повысить вероятность успешного выздоровления. Методы кодирования также может быть вариантом‚ помогающим многим пациентам. Терапия зависимости включает в себя как медицинские‚ так и психологические аспекты. Рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и стимулирование к трезвой жизни необходимы для формирования новой жизни без спиртного. Восстановление после запоя требует терпения и времени‚ но с адекватной поддержкой это возможно. За подробной информацией можно посетить narkolog-tula022.ru.
Sou fazaco do DazardBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. As opcoes de jogos no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e imersivos. O servico do cassino e top e confiavel, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita diferencial. Em resumo, DazardBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino fora de serie para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e mega estilosa, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais insana.
dazardbet auszahlung|
J’adore le casino TonyBet, ca ressemble a un univers de jeu unique. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, offrant des options de casino en direct. Le service client est super, repondant rapidement. Les paiements sont fluides, neanmoins les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. Globalement, TonyBet ne decoit pas pour les joueurs passionnes ! Par ailleurs, la plateforme est intuitive, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
reseГ±a tonybet|
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
вызов психиатра на дом
услуги юриста Рекомендуем посетить профессиональный сайт юриста Светланы Приймак, предлагающий качественную юридическую помощь гражданам и бизнесу в Украине. Основные направления: семейное право (брачные контракты, алименты, разводы), наследственные дела, кредитные споры, приватизация и судовая практика. Юрист Светлана Михайловна Приймак фокусируется на индивидуальном подходе, компетентности и защите прав клиентов без лишней рекламы. На сайте вы найдёте отзывы благодарных клиентов, акции на услуги, полезные статьи по юридическим темам и форму для онлайн-консультации.
Метод и срок подбираются после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также комбинированные программы. Мы объясняем плюсы и ограничения каждого метода, помогаем подготовиться (диета, анализы, отмена определённых препаратов), а затем сопровождаем пациента в период адаптации к трезвости. Кодирование — часть комплексного плана, а не «волшебная кнопка»: устойчивый результат достигается, когда его дополняют поддерживающая терапия и работа с триггерами.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая частная клиника[/url]
This has to be one of my favorite posts! And on top of thats its also very helpful topic for newbies. thank a lot for the information!
Сделать мед лицензию стало просто благодаря Журавлев Консалтинг Групп, команда подготовила полный пакет документов и предоставила консультации на всех этапах: https://licenz.pro/
Что включено на практике
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
«Светлый Вектор» — это команда профильных врачей-наркологов, реаниматологов и психологов, которая помогает как в экстренных ситуациях, так и при плановой терапии. Мы работаем бережно и конфиденциально, выстраиваем реалистичный план лечения и подробно объясняем каждый шаг — без «магических» обещаний и навязывания лишних услуг.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Владимирская наркологическая служба предлагает разнообразные услуги для помощи людям с зависимостями. В этом городе работают специализированные реабилитационные центры‚ где предоставляется возможность анонимного лечения от наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Программа лечения алкоголизма включает в себя как медицинские процедуры‚ так и психотерапию. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru Психологическая помощь владимир также является ключевым элементом в процессе выздоровления. Консультация нарколога позволяет выявить индивидуальные особенности зависимого и составить персонализированный план лечения. Профилактика зависимостей и поддержка родственников зависимых – важная составляющая работы наркологической клиники. Реабилитация наркоманов включает как терапевтические‚ так и социальные аспекты. Услуги наркологической службы направлены на восстановление здоровья и успешное возвращение к нормальной жизни.
Дизайн обложки Анимация обложки – это современный тренд в музыкальной индустрии, который позволяет оживить статичное изображение и сделать его более привлекательным и запоминающимся. Анимированная обложка может быть короткой петлей видео, интерактивным элементом или просто динамичным эффектом. Анимация привлекает внимание пользователя в ленте новостей и увеличивает шансы на прослушивание трека. Однако, важно помнить, что анимация должна быть качественной и соответствовать стилю музыки. Плохая анимация может произвести обратный эффект и отпугнуть потенциальных слушателей. Используйте простую, но эффектную анимацию, которая подчеркнет настроение и атмосферу вашей музыки. Экспериментируйте с разными стилями и эффектами, чтобы найти идеальное решение для своего трека. Анимация обложки – это отличный способ выделиться из толпы и привлечь внимание к своему музыкальному проекту.
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-mytishchah/
Все этапы лицензирования проходили под контролем специалистов Журавлев Консалтинг Групп, что позволило получить лицензию медика без лишних задержек – https://licenz.pro/
усиление углеволокном [url=www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb//]www.dpcity.ru/usilenie-betona-uglevoloknom-fundamentov-svayami-i-gruntov-inektirovaniem-yuviks-grupp-spb//[/url] .
Формат
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkologiya[/url]
услуги адвоката Рекомендуем посетить профессиональный сайт юриста Светланы Приймак, предлагающий качественную юридическую помощь гражданам и бизнесу в Украине. Основные направления: семейное право (брачные контракты, алименты, разводы), наследственные дела, кредитные споры, приватизация и судовая практика. Юрист Светлана Михайловна Приймак фокусируется на индивидуальном подходе, компетентности и защите прав клиентов без лишней рекламы. На сайте вы найдёте отзывы благодарных клиентов, акции на услуги, полезные статьи по юридическим темам и форму для онлайн-консультации.
казино мелбет официальный сайт [url=http://melbetofficialsite.ru]казино мелбет официальный сайт[/url] .
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, c’est une veritable aventure captivante. Le catalogue est vaste et diversifie, avec des machines a sous dernier cri. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, garantissant une assistance de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est une plateforme incontournable pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec soin, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
azur casino 2|
Sou viciado no role de LeaoWin Casino, parece uma savana de diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma selva braba, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um rugido. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma garra, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma aguia, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Na real, LeaoWin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro rugido para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino free spins code|
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/466665547/detail.aspx
Je suis fou de Julius Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino triomphante. Il y a un deferlement de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme heroique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une legion en marche, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une charge de cavalerie, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait epique. Dans l’ensemble, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique imposante, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus triomphante.
julius casino no deposit bonus|
Нарколог на выезд в Туле предоставляет незаменимую поддержку тем, кто страдает от зависимости. Процесс лечения зависимостей может быть сложным процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает удобство и анонимность. На сайте narkolog-tula023.ru можно назначить встречу с наркологом, который встретится с вами на дому. На дому пациентам предоставляется медицинская помощь включает детоксикацию организма и психологическую терапию для борьбы с зависимостями, что позволяет пациенту сделать первые шаги к свободе от наркотиков или алкоголя. Реабилитационная программа разрабатывается с индивидуальным подходом, что позволяет учитывать уникальные потребности каждого пациента. Эмоциональная поддержка близких играет ключевую роль в профилактике рецидива. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает не только лечение, но и эмоциональную поддержку, что важно для успешной реабилитации наркоманов и помощи при алкоголизме.
Очень рад, что узнал про Складчик. Купил складчину на курс по маркетингу, который стоил дорого, а получил почти даром. Доступ открылся сразу, материалы полные и качественные. Очень удобно, что есть разные форматы: видеоуроки, книги, шаблоны. Теперь могу учиться и развиваться, не тратя огромные суммы. Сервис полностью честный, никаких скрытых условий нет. Буду пользоваться постоянно, https://v27.skladchik.org/
В «Новом Рассвете» первыми идут скорость и предсказуемость. После обращения мы сразу запускаем медицинский маршрут: врач уточняет исходные риски, предлагает безопасный формат старта (дом, дневной или круглосуточный стационар), объясняет, чего ждать в ближайшие часы и как будем закреплять результат в следующие недели. Все решения принимаются индивидуально — с учётом возраста, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых лекарств и бытовых условий.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-mytishchah
лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
консультация психиатра по телефону
Приобрести диплом любого университета поможем. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа Саратов – [url=http://diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-saratov/]diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-saratov[/url]
Складчик реально помогает экономить. Курсы, которые стоят десятки тысяч, можно купить за копейки. Всё работает честно и удобно. Теперь учусь с удовольствием https://v27.skladchik.org/
Современное медицинское оборудование играет ключевую часть в лечении и работе пациентов.
Больницы всё чаще оснащаются высокотехнологичную аппаратуру.
Это обеспечивает докторам ставить правильные заключения.
Актуальные приборы создают комфорт и для людей, и для медиков.
http://myskupera.ru/forum/messages/forum1/topic12/message1742385/?result=reply#message1742385
Внедрение высоких технологий ускоряет эффективное лечение.
Большинство устройства имеют возможности для точного мониторинга состояния здоровья.
Специалисты могут оперативно принимать решения, основываясь на результатах аппаратуры.
Таким образом, инновационное медоборудование повышает уровень здравоохранения.
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Le catalogue de jeux est juste enorme, avec des slots qui claquent grave. L’assistance est au top du top, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, quand meme les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans le fond, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Cote plus la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
gamdom no deposit bonus|
J’adore le delire de FatPirate, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Les jeux sont nombreux et delirants, comprenant des jeux tailles pour les cryptos. Le service client est au top niveau, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Les retraits sont rapides comme une tempete, des fois j’aimerais plus de promos qui tabassent. Bref, FatPirate est un spot incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! En prime le design est style et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
bonus sans dГ©pГґt fatpirate|
LaLiga canlı izləmə üçün ideal mənbədir. Yeni mövsüm üçün LaLiga sıralaması artıq dərc olunub.
LaLiga canlı yayımını telefondan açmaq mümkündür. LaLiga logo 2020 ilə 2025 arasındakı fərqləri gör.
Yeni mövsüm üçün rəsmi məlumatları [url=https://laliga.com.az/]laliga.com.az[/url] saytında yoxlayın. Orada canlı yayımlar da mövcuddur.
Hər mövsüm LaLiga top scorers fərqlənir.
LaLiga tv canlı baxmaq üçün seçimlər.
LaLiga stats hər mövsüm yenilənir.
LaLiga champions list artıq dərc olunub.
LaLiga scoreboard dərhal yenilənir.
Sou viciado no fluxo de Brazino Casino, e um cassino online que mergulha como um golfinho em alto-mar. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um atol. incluindo mesas com charme subaquatico. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os saques voam como uma arraia. ocasionalmente mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. No geral, Brazino Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o design e fluido como uma onda. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura marinha.
como usar o bГґnus do brazino777|
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
массажный центр МАССАЖ В ЧЕЛЯБИНСКЕ – это доступный способ улучшить свое здоровье и самочувствие. В Челябинске много массажных салонов и центров, предлагающих широкий спектр массажных услуг. Наши опытные массажисты помогут вам снять напряжение в мышцах, улучшить кровообращение и общее самочувствие. Выберите подходящий вид массажа и насладитесь приятной и полезной процедурой!
Что включено на практике
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-odincovo
https://surl.red/rmbet Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия. Как выбрать безопасное и надежное онлайн-казино: полный гайд 2025 Этот материал создан для игроков из стран, где онлайн-казино разрешены и регулируются законом. Ниже — критерии выбора, ответы на популярные вопросы и чек-лист по безопасности, лицензиям, выплатам и слотам. Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия.
Кейт Миддлтон больна Кейт Миддлтон последние фото Последние официальные фотографии Кейт Миддлтон были опубликованы в марте 2025 года, когда она сделала публичное заявление о своем диагнозе рака. Эти фотографии, распространившиеся по всему миру, запечатлели ее во время видеообращения, в котором она рассказала о своем состоянии и лечении. На этих последних снимках Кейт выглядит собранной и сильной, хотя и заметно, что она переживает непростой период. Ее открытость и честность вызвали волну поддержки и сочувствия со всего мира. После этого Кенсингтонский дворец воздерживается от публикации новых фотографий, чтобы обеспечить ей необходимое пространство и приватность во время лечения. Важно помнить, что сейчас Кейт Миддлтон сосредоточена на своем здоровье и выздоровлении, и уважение к ее личному пространству является приоритетом. Любые новые фотографии, которые могут появиться в будущем, скорее всего, будут опубликованы с ее согласия и в подходящий момент.
Лекарственные средства для лечения алкогольной зависимости могут включать препараты для коррекции зависимости‚ которые уменьшают проявления. Постоянная поддержка и контроль при детоксикации обеспечивают безопасность пациента. Поддержка родственников также имеет большое значение для эффективного выздоровления после алкогольной интоксикации. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Рекомендации по детоксикации могут включать частые консультации с врачом и соблюдение режима. Следует обратиться за поддержкой‚ чтобы предотвратить возвращение к алкоголю и обеспечить качественное лечение.
ЖБИ ХМАО Сваи ЯНАО Предлагаем сваи для строительства в ЯНАО, адаптированные к суровым климатическим условиям. Винтовые, забивные, буронабивные – любой тип! Профессиональный монтаж, гарантия качества, короткие сроки выполнения работ.
обучение массажу МАССАЖ В ЧЕЛЯБИНСКЕ НЕДОРОГО – это реально! Мы предлагаем качественный массаж по доступным ценам, чтобы каждый житель Челябинска мог позволить себе эту приятную и полезную процедуру. Не откладывайте заботу о своем здоровье на потом – начните посещать массаж уже сегодня! Наши опытные массажисты помогут вам снять напряжение, улучшить кровообращение и общее самочувствие. Мы используем только качественные масла и косметические средства, чтобы обеспечить максимальный эффект от процедуры. С нами массаж становится доступным для всех!
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
лечение алкогольной зависимости клиника
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
центр реабилитация алкоголиков
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/466665547/detail.aspx
Ramenbet Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия. Как выбрать безопасное и надежное онлайн-казино: полный гайд 2025 Этот материал создан для игроков из стран, где онлайн-казино разрешены и регулируются законом. Ниже — критерии выбора, ответы на популярные вопросы и чек-лист по безопасности, лицензиям, выплатам и слотам. Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия.
Кейт Миддлтон рост вес Кейт Миддлтон последние новости Мир с замиранием сердца следит за последними новостями о принцессе Уэльской, Кейт Миддлтон. После объявления о ее диагнозе рака в марте 2025 года, общественность активно поддерживает ее в борьбе за здоровье. Основные новости касаются ее прогресса в лечении и адаптации королевской семьи к новым обстоятельствам. Кенсингтонский дворец предоставляет ограниченную, но утешительную информацию, подчеркивая, что Кейт настроена позитивно и благодарна за все теплые пожелания, которые она получила. В последних заявлениях отмечается, что Кейт продолжает следовать рекомендациям врачей и сосредоточена на химиотерапии. Принц Уильям временно взял на себя больше обязанностей, как представитель короны, так и как отец троих детей. Он неоднократно выражал признательность за поддержку, оказываемую Кейт и всей семье, подчеркивая при этом важность уважения к их приватности в этот сложный период. Появляются также сообщения о том, что Кейт, несмотря на болезнь, старается поддерживать связь с важными для нее благотворительными организациями, планируя будущие проекты, в которых она надеется принять участие после выздоровления. Ее преданность делу служения обществу вдохновляет многих, и ее возвращение к полноценной работе ожидается с нетерпением. Сейчас же приоритетом остается ее здоровье и восстановление сил.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
keepstyle
Что включено на практике
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Перед тем как перечислить ключевые преимущества, отметим: каждый маршрут строится индивидуально — от первого звонка и экспресс-диагностики до реабилитации и контроля ремиссии. Это экономит время и снижает тревогу близких.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-podolske/
Домашний формат уместен при лёгкой и средней абстиненции, когда есть поддержка семьи и соблюдается режим. Врач осматривает, проводит процедуры, оставляет пошаговые рекомендации на сутки и список «красных флажков». Если состояние требует наблюдения 24/7, организуем перевод в стационар без задержек.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-obratnyj-zvonok[/url]
J’adore le delire total de Gamdom, on dirait une explosion de fun. Le catalogue de jeux est juste enorme, proposant des sessions live qui tabassent. Le support est dispo 24/7, offrant des reponses qui petent. Le processus est clean et sans prise de tete, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos qui defoncent. Pour resumer, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! A noter aussi la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, donne envie de replonger non-stop.
ceo of gamdom|
J’adore le delire de FatPirate, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Le catalogue est une vraie caverne aux tresors, avec des slots qui dechirent. Les agents sont rapides comme l’eclair, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Les retraits sont rapides comme une tempete, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos qui tabassent. En gros, FatPirate c’est du lourd a tester absolument pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! En prime la plateforme claque avec son look unique, donne envie de replonger direct.
fatpirate|
дистанционная психотерапия ПТСР ПТСР, или посттравматическое стрессовое расстройство, – это психическое расстройство, которое может развиться после переживания травматического события, такого как война, стихийное бедствие, насилие или авария. Симптомы ПТСР включают повторяющиеся воспоминания о травме, кошмары, флешбэки, избегание мест и людей, напоминающих о травме, повышенную тревожность, раздражительность, трудности со сном и другие проблемы. ПТСР можно лечить с помощью психотерапии, такой как когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) и десенсибилизация движением глаз (ДПДГ), а также с помощью медикаментов. Раннее обращение за помощью к квалифицированному специалисту может значительно улучшить прогноз и помочь человеку восстановиться после травмы.
ЖБИ ХМАО Сваи ЯНАО Осуществляем поставку и монтаж свай в ЯНАО. Предлагаем винтовые сваи, забивные сваи и другие типы свай для строительства домов, промышленных объектов и других сооружений в условиях вечной мерзлоты. Гарантируем надежность и долговечность конструкций. Работаем по всему Ямало-Ненецкому автономному округу.
Estou completamente vidrado por AFun Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um desfile de cores. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Em resumo, AFun Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro carnaval para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um desfile noturno, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
resgatar cГіdigo afun|
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Строительный портал https://stroimsami.online новости, инструкции, идеи и лайфхаки. Всё о строительстве домов, ремонте квартир и выборе качественных материалов.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
Good job for bringing something important to the internet!
купить кухню на заказ спб [url=www.kuhni-spb-4.ru/]www.kuhni-spb-4.ru/[/url] .
Центры помощи в Туле предлагают разнообразные программы по выводу из запоя, а также анонимное лечение, что делает процесс менее стрессовым для пациента. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранной программы и необходимых услуг.Круглосуточная служба поддержки обеспечивает доступ к необходимой помощи в любое время, что особенно важно в критических ситуациях. Реабилитация от алкоголизма требует комплексного подхода, включая медикаментозное лечение и психотерапию.вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула Своевременная и профессиональная помощь при алкоголизме гарантирует эффективность лечения и высокие шансы на успешное восстановление.
тревожность лечение депрессия аутизм у взрослых Семейный психотерапевт Семейный психотерапевт – это специалист, который работает с семьями, помогая им улучшить отношения, разрешать конфликты и преодолевать кризисы. Он рассматривает семью как систему, где проблемы одного члена семьи влияют на всех остальных. Семейная терапия направлена на выявление дисфункциональных паттернов общения и взаимодействия, а также на развитие более здоровых способов коммуникации и решения проблем. Семейный психотерапевт помогает семьям, столкнувшимся с трудностями в воспитании детей, конфликтами между супругами, проблемами, связанными с разводом, потерей близкого человека и другими жизненными ситуациями.
Мы работаем с триггерами, режимом сна/питания, энергобалансом и типичными стрессовыми ситуациями. Короткие и регулярные контрольные контакты снижают риск рецидива и помогают уверенно вернуться к работе и бытовым задачам.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru
реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
лечение наркозависимости
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/
A reliable partner https://terionbot.com in the world of investment. Investing becomes easier with a well-designed education system and access to effective trading tools. This is a confident path from the first steps to lasting financial success.
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, ca forge un syndicate de defis impitoyables. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, a l’occasion les accords d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en influence. En scellant le pacte, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour les gardiens des empires numeriques ! A murmurer la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino las vegas|
Ich liebe absolut Snatch Casino, es gibt eine verruckte Spielenergie. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit modernen und fesselnden Slots. Die Hilfe ist schnell und professionell, garantiert sofortige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, trotzdem mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino bietet garantiertes Vergnugen fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist super einfach, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
детский психотерапевт Психотерапевт онлайн консультация Онлайн-консультация психотерапевта – это удобный и доступный способ получить профессиональную психологическую помощь, не выходя из дома. С помощью видеосвязи или других онлайн-платформ пациент может общаться с психотерапевтом, делиться своими проблемами и получать консультации и поддержку. Этот формат терапии позволяет сэкономить время и деньги, а также получить помощь тем, кто живет в отдаленных районах или имеет ограниченные возможности передвижения. Онлайн-консультации могут быть эффективны при лечении различных психологических проблем, таких как депрессия, тревожность, стресс, проблемы в отношениях и другие. Важно выбрать квалифицированного и опытного психотерапевта, который специализируется на онлайн-терапии и использует безопасные и конфиденциальные платформы для общения.
Je suis scotche par Impressario, ca donne une energie de star absolue. La selection de jeux est juste monumentale, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Le service client est digne d’un gala, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, parfois des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. En gros, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Bonus l’interface est fluide et glamour, donne envie de revenir pour un rappel.
impressario casino no deposit bonus code|
Adoro o clima louco de FSWin Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma pedrada. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando baixo, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No fim das contas, FSWin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro fogo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
fswin|
Капельница для устранения похмелья на дому в Туле – является оптимальным решением для быстрого восстановления после вечеринки. Похмелье сопровождается симптомами‚ такими как боль в голове‚ усталость и обезвоживание; процедура капельницы способствует быстрому улучшению самочувствия‚ компенсируя дефицит витаминов и минералов. Клиника на дому предлагает услуги медиков‚ которые осуществляют процедуру профессионально и в комфортных условиях. Процесс инфузии с помощью капельниц позволяет избавиться от неприятных ощущений и значительно ускоряет восстановление. Медицинская помощь на дому – это удобный выбор для тех‚ кто имеет проблемы с алкоголем или просто хочет облегчить симптомы похмелья. Если вам нужно быстро восстановиться и вернуть здоровье‚ вы можете обратиться за помощью на narkolog-tula026.ru. Помните‚ что при тяжелых состояниях необходимо вызывать скорую помощь.
Мы — частная наркологическая клиника, где скорость запуска помощи сочетается с деликатностью и прозрачностью. Команда дежурит круглосуточно, выезжает на дом по Подольску и ближайшим районам, принимает в стационаре и амбулаторно. Все решения принимаются после очного осмотра и оценки рисков, без «универсальных» схем и навязанных услуг.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-podolsk[/url]
центр реабилитации зависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
центр реабилитация алкоголиков
купить легальный диплом колледжа [url=https://frei-diplom6.ru/]купить легальный диплом колледжа[/url] .
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Заходи — там интересно – https://namtrungboinvest.vn/phu-yen-can-day-nhanh-giai-phong-mat-bang-du-an-cao-toc-bac-nam
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://savaherbals.in/liver-detox
Частный нарколог на дому в Туле предоставляет важную помощь тем, кто борется с зависимостями. Лечение зависимости может быть сложным процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает комфортные условия и конфиденциальность. На сайте narkolog-tula027.ru можно назначить встречу с наркологом, который встретится с вами на дому. На дому пациентам предоставляется медицинская помощь включает очистку организма и психотерапию зависимостей, что позволяет пациенту начать путь к отрыву от наркотиков или алкоголя. Реабилитационная программа разрабатывается с учетом индивидуальных особенностей, учитывающим особенности каждого клиента. Поддержка родственников играет важнейшую роль в предотвращении рецидивов. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, что является необходимым условием для достижения успеха в реабилитации зависимых.
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Узнать больше – https://famemodern.com/rickey-stokes-news
Je suis irresistiblement recrute par Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. La reserve est un code de divertissements mafieux, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, avec une ruse qui anticipe les traitrises. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, a l’occasion les accords d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en influence. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino est il fiable|
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, e uma experiencia vibrante. O catalogo e simplesmente gigantesco, fornecendo sessoes ao vivo imersivas. O servico e de uma eficiencia notavel, respondendo em um piscar de olhos. O processo e simples e sem problemas, contudo gostaria de mais bonus variados. Globalmente, Flabet Casino garante uma experiencia de jogo top para os fas de apostas online ! Por outro lado a interface e fluida e moderna, o que aumenta o prazer de jogar.
dono da flabet|
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Хочу знать больше – https://www.studio-gaku.net/2023/01/25/sample-post8
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Узнай первым! – https://dvp.lt/projektas-homo-creator-lt
Откройте для себя новые возможности с [url=https://minsk-peretyazhka.ru]перетяжкой мебели в Минске[/url], позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
Процесс перетяжки мебели включает несколько этапов.
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Узнай первым! – https://www.thomas-a.com/_ha_3236
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Практические советы ждут тебя – https://kongosecurityltd.com/hello-world
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Продолжить чтение – https://www.llc-comet.com/property-information3
купить диплом в астрахани [url=https://www.rudik-diplom7.ru]купить диплом в астрахани[/url] .
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Узнайте всю правду – https://johnjosephinedance.com.sg/the-rumba
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://sportsanteconseil.com/header-ssc
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Обратиться к источнику – https://cocktailsandsteaks.co.uk/home/attachment/smirnoff-cocktails-portrait
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Узнать больше > – https://yamanaka-lc.com/2023/11/19/sample-post4
клиники наркологические москва [url=http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru]http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru[/url] .
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Продолжить чтение – http://www.buhanis.de/oliver-und-familie/oliver-4
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Детальнее – https://mallorcasustainablesummit.com/we-denounce-with-of-righteous-one-indignation-and-dislike-men
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детальнее – https://ibmnews.com/2024/02/02/gubernur-usulkan-1-503-formasi-casn-2024-ke-bkn
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.lefersa.cl/medialunas-sin-gluten
нарколог на дому [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-1.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-1.ru[/url] .
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Ознакомьтесь поближе – https://institutodoreiki.com.br/sp5der-555-worldwide-hoodies-and-self-expression-what-your-style-says-about-you
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Обратиться к источнику – https://cassandrasdeals.com/uncategorized/hello-world
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, a l’occasion les accords d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en influence. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! De surcroit le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, incite a prolonger l’intrigue infinie.
mafia 77777 casino|
Sou louco pela rede de IJogo Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um cacador de sombras. Os jogos formam uma rede de diversao. com caca-niqueis modernos que enredam como cipos. O suporte e uma bussola no emaranhado. oferecendo respostas claras como um labirinto resolvido. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam intrincados. No fim das contas, IJogo Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o design e fluido como um emaranhado. criando uma experiencia de cassino intrincada.
o que aconteceu com a plataforma ijogo com|
Запой — это критическая ситуация‚ требующая квалифицированной помощи. Нарколог на дом клиника предлагает квалифицированную помощь‚ включая выведение из запоя и лечение зависимости от алкоголя. Важно понимать‚ что алкоголизм не только физическая‚ но и психологическая проблема. В таких кризисных ситуациях крайне важно обратиться к специалисту. Психологический аспект является основополагающим в процессе реабилитации. Психотерапия помогает выявить причины зависимости и сформировать новые модели поведения. Связь между семьей и алкоголем часто бывает сильной‚ поэтому поддержка родных очень важна. Наши специалисты применяют комплексный подход: медицинские услуги комбинируются с психологической поддержкой‚ что значительно уменьшает вероятность рецидива. Профилактика рецидива включает в себя работу с психотерапевтом и наркологом. Помощь на дому позволяет создать комфортные условия для пациента‚ что существенно ускоряет процесс восстановления.
“[url=https://www.kufar.by/item/253886872]аренда инструмента в слуцке[/url] – выгодные условия и широкий выбор инструментов для любых задач.”
Если вам нужен инструмент на короткий срок, аренда – идеальное решение, ведь не придется тратиться на дорогостоящее оборудование.
Такой подход особенно удобен для строителей и мастеров. Строительные компании активно используют аренду, чтобы не закупать лишнее оборудование.
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен широкий ассортимент оборудования для разных задач. В прокате представлены бензопилы, газонокосилки и другая садовая техника.
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и специализированную технику. Для демонтажа предлагают отбойные молотки и мощные дрели.
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – экономия на обслуживании и хранении. Арендуя оборудование, вы избегаете затрат на его хранение и транспортировку.
Дополнительный бонус – помощь в выборе подходящего оборудования. Консультанты помогут подобрать инструмент под конкретные задачи.
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды максимально проста и прозрачна. Для оформления понадобится только паспорт и небольшой залог.
Условия проката выгодны для всех клиентов. Стоимость аренды зависит от срока и типа инструмента.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Почему аренда инструмента – это выгодно?**
Аренда инструмента в Слуцке позволяет получить доступ к профессиональному оборудованию без покупки. Если вам нужен инструмент на короткий срок, аренда – идеальное решение, ведь не придется тратиться на дорогостоящее оборудование .
Такой подход особенно удобен для профессионалов и любителей . Строительные компании активно используют аренду, чтобы не закупать лишнее оборудование .
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен большой выбор техники для строительства и ремонта . Вы можете арендовать перфораторы, дрели и шлифмашины для ремонта квартиры .
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и оборудование для узких задач. Для укладки плитки можно взять плиткорезы, а для покраски – краскопульты .
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – доступ к исправному оборудованию. Вам не придется беспокоиться о ремонте инструмента, так как за ним следят специалисты .
Дополнительный бонус – помощь в выборе подходящего оборудования . Если вы не уверены в выборе, специалисты дадут профессиональный совет.
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды не требует сложных формальностей . Достаточно оставить заявку на сайте или позвонить по телефону .
Условия проката предполагают гибкие тарифы. Стоимость аренды зависит от срока и типа инструмента .
Tightrope Game – a balance challenge with obstacles. Quick, addictive, and perfect for testing focus: best Tightrope balancing games online
спортивные новости сегодня [url=http://sportivnye-novosti-1.ru/]http://sportivnye-novosti-1.ru/[/url] .
спортивные аналитики [url=https://www.novosti-sporta-8.ru]https://www.novosti-sporta-8.ru[/url] .
Вывод из запоя в Самаре на базе стационара — когда важен результат, стабильность и медицинская поддержка 24/7.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Пациентам в Самаре предлагается анонимное лечение в стационаре с круглосуточным уходом и безопасными условиями.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В стационаре клиники в Нижнем Новгороде снимают симптомы запоя и помогают организму восстановиться.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно нижний новгород[/url]
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже — гарантированная анонимность и комфортные условия. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, обеспечивая полное восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В Нижнем Новгороде клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре с полным медицинским контролем и комфортом.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
Когда запой длится и состояние ухудшается, важно обратиться в стационар, где врачи «Частного Медика 24» в Воронеже проводят детоксикацию, насыщение организма витаминами, поддерживают сердце, печень и другие органы. Цена от 6500 ? включает всё необходимое — от диагностики до психологической поддержки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
В больничных условиях «Частного Медика 24» врачи контролируют давление, сердце и функции жизненно важных органов при выводе из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижний новгороде[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko круглосуточно помогает вывести из запоя на дому — быстро, анонимно и без постановки на учёт.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники проходит в комфортных условиях, без лишнего стресса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Госпитализация в стационар помогает быстрее и надежнее справиться с последствиями запоя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko предлагает капельницы и комплексное лечение запоя у пациента дома.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в екатеринбурге[/url]
Если домашние методы не помогают, в «Частном Медике 24» обеспечат профессиональный вывод из запоя в стационаре.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает программу вывода из запоя в стационаре по цене от 6500 ?. Здесь вас ждут комфортные палаты, круглосуточный медицинский контроль и безопасные методы детоксикации, включая капельницы и восстановительное лечение. Анонимность гарантирована, без лишних формальностей и без постановки на учёт.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
В кардиологической и психологической поддержке «Частного Медика 24» в Самаре — полный комплекс для безопасного восстановления после запоя.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника самара[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в сочи[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — безопасное и эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена нижний новгород[/url]
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
лечение запоя калуга
В стационаре пациент получает и физиологическую помощь, и психологическое сопровождение, что важно для долгосрочного восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В Екатеринбурге «Похмельная Служба» выезжает к пациенту домой и проводит детоксикацию прямо на месте.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, mit tadellosem Follow-up. Die Zahlungen sind flussig und sicher, gelegentlich die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und intuitiv, verstarkt den Wunsch zuruckzukehren.
snatch crypto casino|
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, oferece um thrill unico. As opcoes sao vastas e variadas, oferecendo apostas esportivas emocionantes. Os agentes sao ultra-responsivos, contatavel a qualquer momento. Os saques sao super rapidos, contudo mais rodadas gratis seriam um plus. Globalmente, Flabet Casino oferece prazer garantido para os amantes de adrenalina ! Notemos tambem a interface e fluida e moderna, o que aumenta o prazer de jogar.
flabet paga quanto ao flamengo|
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
В Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» предлагает выезд врача-нарколога на дом, а также услугу полного вывода из запоя: детоксикация, капельницы, успокоительные средства и прочее.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в сочи[/url]
Врачи «Частного Медика?24» контролируют состояние организма и предотвращают осложнения при выводе из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-msk011.ru
частный дом престарелых
Estou seduzido por Flabet Casino, proporciona uma aventura palpitante. Ha uma diversidade de jogos incrivel, com slots modernos e cativantes. O suporte esta disponivel 24/7, respondendo em um piscar de olhos. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, Flabet Casino oferece prazer garantido para os fas de apostas online ! De mais a mais a plataforma e visualmente top, reforca o desejo de voltar.
baixar aplicativo flabet|
Пациенты «Частного Медика 24» получают не только лечение, но и внимание к психологическому состоянию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в нижний новгороде[/url]
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: official Panda game Canada website
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, ca forge un syndicate de defis impitoyables. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. En scellant le pacte, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire la structure vibre comme un code ancestral, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino france|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog009.ru
лечение запоя тула
Вывод из запоя в Самаре проводится с проверенными препаратами, с учётом состояния пациента и без лишнего стресса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, on complote un reseau de tactiques astucieuses. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Le suivi protege avec une omerta absolue, accessible par message code ou appel direct. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, a l’occasion les accords d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en influence. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! En plus la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
casino mafia film|
Стационар «Частного Медика 24» — условия, где пациент может спокойно пройти вывод из запоя без страха и дискомфорта.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре — это шанс начать путь к трезвой жизни, и в Самаре этот шанс предоставляет «Частный Медик 24».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
лечение запоя калуга
Je trouve absolument epique Julius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme un lion. Le repertoire du casino est une arene de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une noblesse rare. L’assistance du casino est majestueuse et efficace, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse triomphale, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait epique. En somme, Julius Casino promet un divertissement de casino heroique pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, facilite une experience de casino heroique.
casino en ligne julius|
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://allhamam.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-anonimno-v-omske-put-k-vosstanovleniyu
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
pansionat-msk012.ru
пансионат для престарелых людей
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Не упусти важное! – https://mrkuzov.ru/intervyu-s-medsestroy-kliniki-sanati-flyantikovoy-marinoy-pavlovnoy.html
Этот текст посвящён сложным аспектам зависимости и её влиянию на жизнь человека. Мы обсудим психологические, физические и социальные последствия зависимого поведения, а также важность своевременного обращения за помощью.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://prokishechnik.info/zabolevaniya/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-kak-eto-rabotaet-i-zachem-ona-nuzhna.html
Пациенты «Частного Медика 24» получают не только лечение, но и внимание к психологическому состоянию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Хочу знать больше – https://knock-down.fr/forum/viewtopic.php?t=1645
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Смотрите также… – https://freihardt.com/component/k2/item/1?start=975640
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Посмотреть всё – https://www.radhe-radhe.net/ramayan-chaupai-to-remove-poverty
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://aas-fanzine.co.uk/woocommerce-placeholder
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Кликни и узнай всё! – https://k2cyuuki.com/purchase/2018/06/22/%E3%82%BF%E3%83%8B%E3%82%B3%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B9%E3%83%86%E3%83%B3%E3%83%AC%E3%82%B92%E6%A7%BD%E3%82%B7%E3%83%B3%E3%82%AF
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Получить больше информации – https://mustafakhattakfabrics.com/hello-world
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Полезно знать – https://missoesfrutificar.com/unlock-your-potential-with-these-inspiring-ebooks
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, occasionnellement des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, incite a prolonger l’intrigue infinie.
casino mafia casino|
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://3analytics.com/overcoming-the-challenges-of-medical-device-complaint-handling-with-ai
Artistic photography often focuses on highlighting the harmony of the human form.
It is about composition rather than appearance.
Experienced photographers use subtle contrasts to convey mood.
Such images emphasize artistry and personality.
https://xnudes.ai/
Every frame aims to show emotion through pose.
The intention is to show inner grace in an respectful way.
Viewers often value such work for its emotional power.
This style of photography combines art and sensitivity into something truly timeless.
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Кликни, не пожалеешь – https://aquariumhunter.com/best-betta-filters
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Ознакомиться с полной информацией – http://oczyszczaniejezior.pl/remediant-logo
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://gambling-forum.com/the-1-gambling-community-your-ultimate-online-betting-resource
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Обратиться к источнику – https://jesuitasboqueron.com.ar/logoweb-2
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Не упусти шанс – https://choosecolorwheel.com/hello-world
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk010.ru
вывод из запоя
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://www.radhe-radhe.net/surdas-ka-jivan-parichay
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Как достичь результата? – https://educatedtimes.com/i-chose-elss-sip-for-my-childs-education-heres-what-i-wish-i-knew-beforehand
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Наши рекомендации — тут – https://www.yycnortheast.org/hello-world
https://fixme.com.ua/
Ich bin begeistert von Snatch Casino, es gibt eine verruckte Spielenergie. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit spannenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind super reaktionsschnell, bietet prazise Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, manchmal zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Global Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell top, macht jede Session immersiv.
snatch casino pomo code|
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Посмотреть всё – https://www.aeeaatletismo.es/2022/05/01/el-libro-del-atletismo-iberoamericano-un-legado-para-la-familia-iberoamericana
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Посмотреть подробности – https://kridacafe.com/ipl-2024-pravin-amre-on-prithvi-shaw-said-this-know-here
пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
стоимость двигателя Замена радиатора охлаждения – запрос на услугу по замене радиатора охлаждения двигателя. Важно предоставить информацию о различных типах радиаторов и их характеристиках.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Besonders toll die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Автомобили с аукционов Японии Авто аукционы Китая онлайн – аналогичный запрос.
купить диплом в махачкале [url=http://rudik-diplom9.ru/]купить диплом в махачкале[/url] .
прогнозы футбола точные на сегодня [url=http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru/]http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru/[/url] .
Acho incrivel Flabet Casino, e uma experiencia vibrante. Ha uma diversidade de jogos incrivel, oferecendo apostas esportivas emocionantes. Os agentes sao ultra-responsivos, garantindo ajuda instantanea. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto gostaria de mais bonus variados. Em resumo, Flabet Casino garante uma experiencia de jogo top para os apaixonados por cassino ! Notemos tambem a plataforma e visualmente top, reforca o desejo de voltar.
campeonato flabet portal|
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, ca forge un syndicate de defis impitoyables. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, bien que des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino invite a une intrigue sans trahison pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! Par surcroit la structure vibre comme un code ancestral, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino avis|
Сео аудит бесплатно онлайн https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? rent tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
двигатель для грузовика Турбина двигателя – запрос на информацию о турбине двигателя, ее устройстве, принципе работы и возможных неисправностях. Важно предоставить информацию о турбинах, их типах и особенностях.
спорт прогнозы на футбол [url=http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru]спорт прогнозы на футбол[/url] .
амулеты обереги талисманы оргонит своими руками – Запрос, указывающий на интерес к самостоятельному изготовлению оргонита. Предоставляет информацию о материалах, инструментах и инструкции по изготовлению оргонита.
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. Le territoire est un domaine de diversite criminelle, proposant des crash pour des chutes de pouvoir. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les retraits s’executent avec une furtivite remarquable, malgre cela des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino|
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Das Spielangebot ist beeindruckend, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, erreichbar jederzeit. Der Prozess ist einfach und reibungslos, manchmal mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino lohnenswert fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell top, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
snatch casino 50 freespins no deposit 2025|
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk011.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
лакомства для собак ноги для собак – Этот запрос, вероятнее всего, подразумевает сушеные или вяленые ноги животных (например, говяжьи или свиные) как лакомство для собак. Важно предупредить пользователя о необходимости давать такие лакомства под присмотром, чтобы избежать заглатывания крупных кусков, которые могут привести к удушью.
Вывод из запоя — это первый шаг к восстановлению, и стационар клиники дает этот шанс.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
Artistic photography often focuses on highlighting the beauty of the natural shape.
It is about expression rather than surface.
Skilled photographers use soft lighting to create mood.
Such images emphasize authenticity and individuality.
https://xnudes.ai/
Every shot aims to tell a story through pose.
The purpose is to present inner grace in an respectful way.
Observers often appreciate such work for its depth.
This style of photography blends emotion and sensitivity into something truly timeless.
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
дом престарелых в туле
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для пожилых в туле
от зубного камня для собак Для собак крупных пород, как и для любых других, важно правильно подобрать рацион и лакомства. Учитывайте особенности породы, возраст, уровень активности и состояние здоровья собаки. Консультируйтесь с ветеринаром, чтобы составить оптимальный план питания и подобрать подходящие лакомства.
оберегдлядома оргонит купить в Москве – Поиск мест продажи оргонитовых изделий в Москве.
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя цена
В стационаре клиники в Нижнем Новгороде снимают симптомы запоя и помогают организму восстановиться.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Need porn videos or photos? pornpen image generator – create erotic content based on text descriptions. Generate porn images, videos, and animations online using artificial intelligence.
IPTV форум https://vip-tv.org.ua/ место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
новости мирового спорта [url=https://sportivnye-novosti-1.ru]новости мирового спорта[/url] .
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko круглосуточно помогает вывести из запоя на дому — быстро, анонимно и без постановки на учёт.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
лакомства для собак вкусняшки для собак – Синоним запроса “лакомства для собак”. Пользователь ищет разнообразные угощения для своего питомца. Важно предоставить ту же информацию, что и в основном запросе “лакомства для собак”.
В Самаре стационар «Частного Медика 24» предлагает персонализированный подход — лечение запоя, детоксикация и дальнейшее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в нижний новгороде[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
наркология в москве [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru/]https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru/[/url] .
Выведение из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — помощь при острых состояниях и хронической зависимости. Наши опытные наркологи используют современные методы лечения для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. La reserve est un code de divertissements mafieux, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, bien que des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! En plus le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino avis|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
наркологическая терапия на дому [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-1.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-1.ru[/url] .
люстры Каждый дом начинается со света. Именно свет создает атмосферу уюта, роскоши и комфорта. В магазине «ОгниСвета» мы собрали для вас коллекцию люстр, которая превратит ваше жилое пространство в произведение искусства. У нас вы найдете: Классические люстры: Изящные модели с хрустальными подвесками, позолотой и вензелями для ценителей вечной роскоши. Они станут центральным элементом вашей гостиной или столовой. Современные и минималистичные модели: Лаконичные формы, металл, стекло и дерево. Идеальное решение для интерьеров в стиле лофт, хай-тек или сканди. Деревенские и винтажные светильники: Уютные люстры из массива дерева, кованого железа и текстиля для создания теплой и душевной атмосферы в загородном доме или на кухне. Роскошные люстры-канделябры: Для тех, кто хочет подчеркнуть статус и безупречный вкус. Многорожковые конструкции, имитирующие свечи, добавят торжественности любой комнате.
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und elegant, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
Если запой похлеще, «Похмельная Служба / Stop-Alko» в Екатеринбурге готова предложить услугу премиум-или VIP-уровня с продолжительной терапией.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
купить лакомства Лакомства для собак – это категория товаров, предназначенных для поощрения, дрессировки, а иногда и просто для баловства питомца. Они могут быть разных видов: печенье, сушеное мясо, косточки, палочки и многое другое. Важно выбирать лакомства, соответствующие возрасту, размеру и состоянию здоровья собаки. Также необходимо обращать внимание на состав: избегать искусственных красителей, ароматизаторов, консервантов и избытка сахара.
В кардиологической и психологической поддержке «Частного Медика 24» в Самаре — полный комплекс для безопасного восстановления после запоя.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar27.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника «Частный Медик 24» в Самаре оказывает помощь при запое анонимно, круглосуточно и без скрытых платежей.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Если домашние методы не помогают, в «Частном Медике 24» обеспечат профессиональный вывод из запоя в стационаре.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в нижний новгороде[/url]
спортивные новости сегодня [url=novosti-sporta-7.ru]novosti-sporta-7.ru[/url] .
Если вы в тяжёлом состоянии после длительного употребления алкоголя, в Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» поможет вывести из запоя с выездом на дом, без постановки на учёт.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Выведение из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — помощь при острых состояниях и хронической зависимости. Наши опытные наркологи используют современные методы лечения для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
В Екатеринбурге «Похмельная Служба» выезжает к пациенту домой и проводит детоксикацию прямо на месте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
оргониты райх амулеты обереги талисманы – Сокращенная версия запроса “амулеты обереги и талисманы”. Общий поиск информации об амулетах, оберегах и талисманах, их отличиях и общем назначении. Дает общее представление о магических предметах.
Вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники проходит в комфортных условиях, без лишнего стресса.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в нижний новгороде[/url]
80 free spins no deposit uk, best casinos in south united states and 500 poker chips united kingdom, or free 50 pokies canada
My webpage: new casino table games 2022
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в сочи[/url]
Ранняя врачебная помощь не только снижает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома, но и предотвращает опасные осложнения, даёт шанс пациенту быстрее вернуться к обычной жизни, а его близким — обрести уверенность в завтрашнем дне.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar27.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Экстренная помощь при запое в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница на дому от опытных врачей-наркологов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в нижний новгороде[/url]
натуральные лакомства для собак вкусняшки для собак купить – Поиск мест, где можно купить вкусняшки для собак.Результаты будут включать зоомагазины, интернет-магазины и т.д.
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk012.ru
лечение запоя
Ich bin total fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es gibt eine verruckte Spielenergie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, bietet prazise Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, manchmal mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Online-Wetten-Enthusiasten ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist super einfach, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino no deposit promo code|
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula012.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
чистка зубов для собак Кости для собак купить можно в зоомагазинах, супермаркетах или онлайн-магазинах. Важно выбирать кости, соответствующие размеру и возрасту вашей собаки, чтобы обеспечить ее безопасность и удовольствие.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает лечение запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем. Здесь пациент получает безопасное и эффективное восстановление.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница сочи[/url]
Содержание процедуры
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Sicherheit der Daten, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, dennoch regelma?igere Promos waren super. Alles in allem, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
Здесь обеспечивают комплексную помощь: от детокса до поддержки организма и психики.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Этот перечень помогает быстро оценить необходимость вызова. Если вы узнали в нем свою ситуацию — оптимально начать терапию как можно раньше: так детокс проходит мягче, а риск осложнений и срывов в первые сутки ниже.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/]srochno-vrach-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Самаре на базе стационара — когда важен результат, стабильность и медицинская поддержка 24/7.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
«Частный Медик 24» — это медицинский контроль, поддержка и лечение на всех этапах вывода из запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в нижний новгороде[/url]
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Support ist 24/7 verfugbar, garantiert sofortige Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, trotzdem haufigere Promos waren cool. Kurz gesagt Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Beachten Sie auch die Site ist stylish und schnell, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino гѓ—гѓгѓўг‚ігѓјгѓ‰|
Здесь обеспечивают комплексную помощь: от детокса до поддержки организма и психики.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
https://ognisveta.ru/catalog/lyustry/ Каждый дом начинается со света. Именно свет создает атмосферу уюта, роскоши и комфорта. В магазине «ОгниСвета» мы собрали для вас коллекцию люстр, которая превратит ваше жилое пространство в произведение искусства. У нас вы найдете: Классические люстры: Изящные модели с хрустальными подвесками, позолотой и вензелями для ценителей вечной роскоши. Они станут центральным элементом вашей гостиной или столовой. Современные и минималистичные модели: Лаконичные формы, металл, стекло и дерево. Идеальное решение для интерьеров в стиле лофт, хай-тек или сканди. Деревенские и винтажные светильники: Уютные люстры из массива дерева, кованого железа и текстиля для создания теплой и душевной атмосферы в загородном доме или на кухне. Роскошные люстры-канделябры: Для тех, кто хочет подчеркнуть статус и безупречный вкус. Многорожковые конструкции, имитирующие свечи, добавят торжественности любой комнате.
В Воронеже клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает программу вывода из запоя в стационаре по цене от 6500 ?. Здесь вас ждут комфортные палаты, круглосуточный медицинский контроль и безопасные методы детоксикации, включая капельницы и восстановительное лечение. Анонимность гарантирована, без лишних формальностей и без постановки на учёт.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru
последние новости спорта [url=http://novosti-sporta-8.ru/]последние новости спорта[/url] .
При госпитализации пациент находится под наблюдением 24/7, что снижает риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Пациенты «Частного Медика 24» получают не только лечение, но и внимание к психологическому состоянию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород[/url]
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. La reserve est un code de divertissements mafieux, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, a l’occasion des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino invite a une intrigue sans trahison pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! De surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia game casino|
вызов психиатрической помощи
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
консультация психиатра круглосуточно
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Углубиться в тему – https://dermatologcentr.ru/professionalnaya-pomoshh-vrach-narkolog-na-dom-vo-vladikavkaze-i-respublike-severnaya-osetiya
Лука Модрич футбол дүйнөсүнүн символу болуп калды.Бул футбол дүйнөсүндө чоң өзгөрүү болот. Анын статистикасы ар бир сезон таң калтырат. Көптөр “сколько лет Лука Модричке?” деп сурашат — бирок ал үчүн жаш маанилүү эмес. Трансфер боюнча инсайддар жана қауесеттер үчүн кара: [url=https://luka-modric-kg.com/]Лука Модрич трансфер[/url]. Лука Модрич ЧМ 2022де дагы мыкты оюн көрсөттү.
Модрич Реалдын орто талаасын башкарып келет көп жылдан бери. Лука Модричтин балалык чагы оор болсо да, ал чоң жетишкендикке жетти. Көптөр “Модрич канча табат?” деп сурашат. Лука Модрич келечекте кайсы клубга өтөт деп ойлойсуң?
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Продолжить чтение – https://luzearteiluminacao.com.br/pre-venda
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
вывод из запоя
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire l’interface est un repaire navigable avec ruse, infuse une essence de mystere mafieux.
jeu de sociГ©tГ© mafia casino|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Изучите внимательнее – http://pedreiralajinha.com.br/site/about/attachment/logo-2
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://irishnationals.ie/results-marks-2018-2/25-boys-16-17/?doing_wp_cron=1731063495.1570661067962646484375
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Обратиться к источнику – https://sweetmacshop.com/2021/07/06/perfectly-colored-macarons-for-any-wedding
https://ognisveta.ru/catalog/lyustry/ Каждый дом начинается со света. Именно свет создает атмосферу уюта, роскоши и комфорта. В магазине «ОгниСвета» мы собрали для вас коллекцию люстр, которая превратит ваше жилое пространство в произведение искусства. У нас вы найдете: Классические люстры: Изящные модели с хрустальными подвесками, позолотой и вензелями для ценителей вечной роскоши. Они станут центральным элементом вашей гостиной или столовой. Современные и минималистичные модели: Лаконичные формы, металл, стекло и дерево. Идеальное решение для интерьеров в стиле лофт, хай-тек или сканди. Деревенские и винтажные светильники: Уютные люстры из массива дерева, кованого железа и текстиля для создания теплой и душевной атмосферы в загородном доме или на кухне. Роскошные люстры-канделябры: Для тех, кто хочет подчеркнуть статус и безупречный вкус. Многорожковые конструкции, имитирующие свечи, добавят торжественности любой комнате.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://agenciasmart.digital/o-que-e-seo
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://menumenu.cat/brasa/2020/02/28/hello-world/?lang=es
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://webtimenews.com/unraveling-the-complex-web-of-shooting-news
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Узнать больше > – https://www.radhe-radhe.net/ashtavakra-biography
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Читать дальше – https://www.isauna.dk/page-image-alignment
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://keiyotour.co.jp/2022/02/02/vol-193-2019%E5%B9%B4-5%E6%9C%88-7%E6%97%A5-%E9%85%8D%E4%BF%A1
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Обратиться к источнику – https://zementol.ch/envira/referenzen/menzi-park-widnau
Ich bin absolut hingerissen von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, ab und zu mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
An intelligent AI ChatBot for generating content, posts, images, and website optimization. Easy installation, flexible settings, and full AI support.
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Доступ к полной версии – https://huwa-huwa.com/2021/08/30/%E4%BD%93%E9%A8%93%E9%9A%8F%E6%99%82%E5%8F%97%E4%BB%98%E4%B8%AD%EF%BC%81
Всё о металлообработке http://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Смотрите также… – https://esotart.co/2020/07/19/imagen-1-galeria-nueva
https://t.me/kupinos_kz Купить снюс – это распространенный запрос среди потребителей никотиносодержащей продукции, которые предпочитают бездымные альтернативы курению. Однако важно помнить, что продажа и употребление снюса регулируются законодательством различных стран, и могут быть ограничения или полный запрет на его реализацию. Перед покупкой необходимо ознакомиться с местными законами и правилами, чтобы избежать возможных проблем с законом. Кроме того, следует обращать внимание на состав продукта, приобретать его только у проверенных продавцов и учитывать потенциальные риски для здоровья, связанные с употреблением никотина.
перевод документов в сочи с нотариусом Перевод документов в Сочи – это востребованная услуга, предназначенная для физических и юридических лиц, нуждающихся в переводе личных документов (паспорта, свидетельства, дипломы), юридических текстов, технических руководств и других материалов. Качество перевода играет ключевую роль, поскольку от него может зависеть успешное решение важных вопросов. При выборе бюро переводов следует обращать внимание на наличие квалифицированных переводчиков с опытом работы в нужной сфере, использование современных технологий и инструментов, а также на наличие гарантии качества.
вызов психиатра на дом
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
консультация частного психиатра
ии для создания карточек товара на wildberries Нейросеть для создания карточки товара Вайлдберриз – это специализированная нейросеть, обученная на данных о товарах, представленных на платформе Wildberries. Она может использоваться для автоматического создания описаний товаров, генерации изображений, подбора ключевых слов и оптимизации цен, что позволяет продавцам экономить время и ресурсы на создании карточек товаров.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://na-polzy.ru/chto-nuzhno-znat-pri-usluge-vyvoda-iz-zapoya-na-domu
прогнозы на спорт с высокой проходимостью [url=www.prognozy-ot-professionalov5.ru]www.prognozy-ot-professionalov5.ru[/url] .
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
агентство переводов сочи Перевод документов в Сочи с нотариусом – это комплексная услуга, включающая в себя перевод документов квалифицированным переводчиком и последующее нотариальное заверение этого перевода. Данная услуга необходима для придания юридической силы документам, составленным на иностранном языке, с целью их использования в государственных и частных организациях на территории Российской Федерации. При заказе перевода документов с нотариальным заверением важно убедиться в наличии у агентства аккредитованного переводчика и налаженных связей с нотариусом, что позволит оперативно и качественно выполнить перевод и заверить его в соответствии с требованиями законодательства.
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, erreichbar zu jeder Stunde. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, dennoch mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://t.me/kupinos_kz Снюс Алматы – это конкретизированный запрос, указывающий на интерес к приобретению снюса в городе Алматы, Казахстан. При этом важно учитывать, что законодательство Казахстана может регулировать или даже запрещать продажу и употребление снюса. Прежде чем пытаться купить снюс в Алматы, необходимо убедиться, что это не противоречит местным законам и что продавец имеет все необходимые разрешения и лицензии. Кроме того, необходимо помнить о рисках для здоровья, связанных с употреблением снюса, и принимать взвешенное решение о его употреблении. В случае сомнений рекомендуется обратиться за консультацией к специалисту.
ии для создания карточек товара на wildberries Нейросеть для создания карточки товара Вайлдберриз – это специализированная нейросеть, обученная на данных о товарах, представленных на платформе Wildberries. Она может использоваться для автоматического создания описаний товаров, генерации изображений, подбора ключевых слов и оптимизации цен, что позволяет продавцам экономить время и ресурсы на создании карточек товаров.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
I’m amazed by Wazamba Casino, it seems like a whirlwind of delight. The options are extensive and diverse, featuring over 5,000 titles from top providers. The welcome bonus is generous. Agents respond swiftly. Withdrawals are processed quickly, occasionally extra rewards would be fantastic. In conclusion, Wazamba Casino is worth exploring for online betting fans ! Furthermore navigation is effortless, deepens immersion in the game. One more highlight crypto-friendly banking options, providing personalized perks.
wazambagr.com|
J’adore l’ambiance de Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Bingoal Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Cerise sur le gateau la navigation est simple et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout majeur les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Cliquer maintenant|
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee incomparable. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, offrant des sessions live intenses. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Cliquez ici|
официальный сайт ПокерОК
официальный сайт ПокерОК
פורנו שראיתי בעבר. כאן, מזחלת חזרה מהעישון. – אז? הסתכלת? מה דעתך? – תראה, סאן, אני דיסקרטיות ביום שישי או בשבת. וקולו היה חם, בלי התו השתלטני שהיה פעם. – אבל אני רוצה עוד. לא עבור OnlyFans. website
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Есть металлолом? вывоз металла за деньги мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Хочешь сдать металл? прием металлолома в санкт-петербурге наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
складские стеллажи Надежные металлические стеллажи для склада от производителя «Металлоизделия» Организуйте складское пространство с максимальной эффективностью! Компания «Металлоизделия» предлагает профессиональные металлические стеллажи для складов любого размера и назначения. Наши стеллажи для склада — это идеальное решение для хранения товаров, оборудования, архивов и материалов. Они позволяют использовать каждый квадратный метр площади по максимуму, обеспечивая легкий доступ к любой единице хранения. Почему выбирают наши стеллажи? Прочность и долговечность: Мы используем высококачественный стальной прокат и усиленные конструкции, выдерживающие значительные нагрузки (до 5000 кг на ячейку и более). Универсальность: Широкая линейка моделей — полочные, паллетные (фронтальные, гравитационные), консольные. Подберем решение под ваши задачи. Безопасность: Все конструкции имеют антикоррозийное покрытие и рассчитаны на многократную сборку-разборку. Строгое соблюдение ГОСТов. Модульность и масштабируемость: Вы можете легко нарастить систему или изменить конфигурацию при расширении склада. Выгодная цена: Работаем без посредников, так как являемся производителем.
Saw your material, and hope you publish more soon.
психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
частная психиатрическая помощь
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Today, while I was at work, my sister stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
http://missia.od.ua/yak-steklafar-vplyvaye-na-vyhlyad-avto.html
В «Частном Медике 24» в Самаре выход из запоя организуют поэтапно: диагностика, лечение, реабилитация.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
стеллажи для склада Надежные металлические стеллажи для склада от производителя «Металлоизделия» Организуйте складское пространство с максимальной эффективностью! Компания «Металлоизделия» предлагает профессиональные металлические стеллажи для складов любого размера и назначения. Наши стеллажи для склада — это идеальное решение для хранения товаров, оборудования, архивов и материалов. Они позволяют использовать каждый квадратный метр площади по максимуму, обеспечивая легкий доступ к любой единице хранения. Почему выбирают наши стеллажи? Прочность и долговечность: Мы используем высококачественный стальной прокат и усиленные конструкции, выдерживающие значительные нагрузки (до 5000 кг на ячейку и более). Универсальность: Широкая линейка моделей — полочные, паллетные (фронтальные, гравитационные), консольные. Подберем решение под ваши задачи. Безопасность: Все конструкции имеют антикоррозийное покрытие и рассчитаны на многократную сборку-разборку. Строгое соблюдение ГОСТов. Модульность и масштабируемость: Вы можете легко нарастить систему или изменить конфигурацию при расширении склада. Выгодная цена: Работаем без посредников, так как являемся производителем.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже помогает быстрее восстановить силы и вернуть ясность мышления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника[/url]
Если домашние методы не помогают, вывод из запоя в стационаре в Самаре — это безопасный выбор с профессиональной детоксикацией.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно самара[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Если вы в тяжёлом состоянии после длительного употребления алкоголя, в Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» поможет вывести из запоя с выездом на дом, без постановки на учёт.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Что делаем на практике
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-domodedovo/
Если вы в тяжёлом состоянии после длительного употребления алкоголя, в Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» поможет вывести из запоя с выездом на дом, без постановки на учёт.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg25.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы обеспечиваем круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Прогон https://kwork.ru/links/1017228/progon-khrumerom под ключ отзывы реальные результаты
Прогон хрумером под ключ отзывы реальных пользователей и результаты работы
Доказано: компании, применяющие автоматизированные инструменты для привлечения клиентов, видят увеличение конверсии на 40%. Закажите услугу, которая включает сканирование, эффективное выявление целевой аудитории и последовательное общение, что гарантирует вам долгожданный рост потока посетителей.
Реальные примеры: Клиенты, воспользовавшиеся данной методикой, подтверждают: прирост продаж до 25% в первый месяц. Откройте новые горизонты для вашего бизнеса с инновационным подходом к маркетингу и привлечению клиентов.
Дайте свои бизнесу максимум возможностей – выбирайте проверенные решения с высокой отдачей!
Программа вывода из запоя в Воронеже от «Частного Медика 24» включает не только устранение физической зависимости, но и работу по восстановлению сна, гидратацию, лекарственную поддержку, а также психотерапию, чтобы помочь справиться не просто с запоем, но и с причинами, которые к нему привели.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника воронеж[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Самаре проводится с проверенными препаратами, с учётом состояния пациента и без лишнего стресса.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
В Екатеринбурге врачи Stop-Alko оказывают услуги вывода из запоя с выездом на дом — быстро и профессионально.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Если домашние методы не помогают, вывод из запоя в стационаре в Самаре — это безопасный выбор с профессиональной детоксикацией.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru
где купить диплом техникума дипломы тумен кипятком [url=https://frei-diplom12.ru]где купить диплом техникума дипломы тумен кипятком[/url] .
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
консультация врача психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
лучшие психиатрические клиники
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/[/url]
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Locowin Casino, ca immerse dans un monde fascinant. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, offrant des sessions live intenses. Accompagne de paris gratuits. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Au final, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et elegante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un avantage supplementaire les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis captive par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live intenses. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Parcourir davantage|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. La variete des titres est majestueuse, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de luxe. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir maintenant|
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Ajoutons que le site est veloce et seduisant, facilite une immersion complete. A souligner aussi les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, renforce le sens de communaute.
Approfondir|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, obwohl mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, mit immersiven Tischspielen. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, obwohl regelma?igere Promos waren super. Alles in allem, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Zusatzlich die Site ist schnell und elegant, gibt Lust auf mehr.
playnvcasino.de|
Сервис Stop-Alko в Екатеринбурге оказывает помощь при запое на дому — с капельницами и медикаментами для восстановления организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg25.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре сочи[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника нижний новгород[/url]
скачать лаки джет [url=http://1win5516.ru]http://1win5516.ru[/url]
точные прогнозы на футбол на сегодня [url=kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru]kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru[/url] .
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в Самаре включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку и работу с психотерапевтом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
лечение запоя омск
Стационар «Частного Медика 24» — это круглосуточная помощь при запое, современные капельницы и заботливый уход.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
прогнозы экспертов на хоккей [url=https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej9.ru/]https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej9.ru/[/url] .
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Госпитализация в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и начать новую жизнь.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
I have a real passion for Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The array of titles is vast, compatible with crypto for seamless play. The welcome bonus is generous. Professional and helpful assistance. The system is user-friendly, nevertheless generous offers could be expanded. All in all, Wazamba Casino is worth exploring for online betting fans ! Additionally the platform is visually stunning, adds a layer of excitement. Worth noting the loyalty program with masks, fostering a community feel.
wazambagr.com|
Je ne me lasse pas de Bingoal Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La variete des titres est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, toujours pret a aider. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Notons aussi le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller en ligne|
Формат
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchelkovo[/url]
точный прогноз на спорт сегодня [url=www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru]www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru[/url] .
В Самаре в «Частном Медике 24» пациент получает детоксикацию, восстановительное лечение и круглосуточное наблюдение врачей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Адекватное лечение, комфорт и забота — так проходят дни в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» во время вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
Проблема зависимости от наркотиков и алкоголя требует профессионального подхода. Наркологическая помощь состоит из диагностики и лечения зависимостейчто способно кардинально изменить жизнь человека. Консультация нарколога. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме и реабилитация наркозависимых проводятся в специализированных центрах, таких как narkolog-tula022.ru. Программы восстановления включают психотерапевтические сеансы и группы поддержки для зависимых, а также семейную поддержку. Важно помнить о мотивации к лечению и профилактике зависимостей. Адаптация в обществе после лечения помогает избежать рецидивов. Анонимная помощь наркозависимым доступна и эффективна. Начните новый этап своей жизни с помощью профессионалов!
https://atlan.ru/product-category/mebel/kabinety-mebel/
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers hypnotisant. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir le site|
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Интересует подробная информация – https://autoelektronik.rs/home/pattern
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Неизвестные факты о… – https://gurukulyogashala.com/blog/benefits-of-yoga
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить полную информацию – https://vriba.com/blog/gpt-4o-a-promising-yet-familiar-evolution
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.fcp.yns.mybluehost.me/events/rapid-city-sd-test-teen-virtual-activities-embroidery-thread-bracelets
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://marcoghergo.com/yesterday
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Только факты! – https://www.duelband.cz/calligraphy_61
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, obwohl die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist modern und ansprechend, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
Погрузитесь в мир турецких сериалов https://turkyserial2026.ru ярких эмоций, страстей и неожиданных сюжетных поворотов! Здесь собраны лучшие драмы, мелодрамы и комедии, покорившие сердца зрителей по всему миру. Смотрите онлайн, наслаждайтесь атмосферой восточного колорита и живите историей вместе с героями!
Открой для себя мир китайского аниме https://prokazan.ru/adverting/view/kitajskoe-anime-vzlet-i-razvitie-animacionnoj-industrii захватывающих дунхуа, наполненных магией, древними легендами и невероятной анимацией! ? Смотри лучшие новинки и хиты онлайн, следи за приключениями героев, погружайся в атмосферу Востока и ощути силу настоящего искусства из Китая!
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://blog.seuconsumo.com.br/despesas-ordinarias-e-extraordinarias
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. La selection de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui impressionne pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche de confort. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Découvrir l’avis|
Je suis captive par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
Découvrir aujourd’hui|
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Только для своих – http://www.feedc0de.net/index.php?itemid=850&catid=8
Je ne me lasse pas de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le support client est imperial, toujours pret a servir. Le processus est simple et elegant, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Au final, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Notons aussi la navigation est simple et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Tout lire|
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! A mentionner la navigation est simple et engageante, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Apprendre comment|
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://basantinternational.com/product/air-filter-pan-b6505004
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://pillnitzer-weinberg.de/?p=1074
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://trusthubmediatv.com/index.php/2023/12/09/m3u8-hls-video-player
tripscan трипскан TripScan – это гипотетический или существующий сервис, предназначенный для упрощения процесса планирования путешествий. Он может объединять в себе функционал поиска и бронирования авиабилетов, отелей, автомобилей, а также предлагать готовые маршруты, подборки интересных мест и достопримечательностей, основанные на интересах пользователя. Дополнительные возможности могут включать в себя интеграцию с социальными сетями для обмена опытом и отзывами, а также создание индивидуальных путешествий с учетом бюджета и предпочтений.
legalize online gambling in united states, $5 minimum deposit rated player casino; Cleo, new
zealand 2021 and free spins new usa, or united statesn online poker
заказать алкоголь москва [url=http://www.alcolike.ru]http://www.alcolike.ru[/url] .
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Обратиться к источнику – https://exlinko.net/o/mocai-rank-website-in-3-weeks
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
лечение запоя
Pizza bestellen in der Nahe war super einfach. In 25 Minuten war alles da.
Pizza Lieferung hei?
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://neuroreab.gk-turan.ru/patients/centers
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — безопасное и эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника воронеж[/url]
Погрузись в атмосферу китайских дорам https://bryansktoday.ru/article/247115 исторических саг, романтических историй и современных драм! Здесь тебя ждут лучшие сериалы с глубокими сюжетами, красивой картинкой и харизматичными актёрами. Смотри онлайн и окунись в мир восточной любви и вдохновения!
Смотри лучшие турецкие сериалы https://bryansktoday.ru/article/247141 онлайн — истории о любви, предательстве и судьбе, которые не отпускают с первой серии! Погрузись в атмосферу восточного шарма, почувствуй эмоции героев и открой для себя мир, где страсть и честь идут рука об руку. Новые серии каждый день!
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Заходи — там интересно – http://www.pilulaempreendedora.com.br/2018/07/19/conheca-ferramenta-para-alinhar-o-seu-proposito-de-vida
What’s up mates, nice article and good urging commented here, I am in fact enjoying by these.
https://e-art.com.ua/chomu-dekoratyvni-masky-u-faru-staly-trendom-u-tiuninhu.html
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, verstarkt die Immersion. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Explorer tout|
I’m enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it constructs an enthralling narrative. The breadth in selections is breathtaking, incorporating wagers on athletic events. Launching your voyage. Proficient and considerate aid. Exchanges are guarded and prompt, however incentives might broaden liberally. Collectively , Wazamba Casino rises as a premier destination for stimulation pursuers ! Further traversal is innate, infusing supplementary fascination. Notably impressive dependable digital money processing techniques, escalating participation.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Je suis absolument captive par Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Le bonus d’accueil est seduisant. L’equipe de support est remarquable, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En bref, Locowin Casino est indispensable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage supplementaire les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Cliquez ici|
Je suis completement captive par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde d’elegance. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support client est imperial, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Casinia Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est rapide et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Un autre atout majeur les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Essayer d’explorer|
Современные технологии 3D-печати — это доступная альтернатива традиционному производству. Мы осуществляем услуги по печати макетов и прототипов. Мы используют точное оборудование, что обеспечивает возможность изготавливать изделия, соответствующие требованиям заказчика. Для печати применяются инженерные пластики и композиты, что позволяет реализовать разные проекты. Выбирая наши услуги, вы избавляетесь от риска брака. Оставьте заявку на печать деталей, и мы реализуем проект любой сложности: http://www.dwise.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=546824. Все изделия печатаются с высоким уровнем детализации.
двигатель для коммерческого транспорта Двигатель б/у – это двигатель, который уже был в эксплуатации на другом автомобиле. Покупка б/у двигателя может быть привлекательной из-за более низкой цены по сравнению с новым или контрактным двигателем. Однако, важно понимать, что двигатель б/у – это всегда риск, так как его ресурс и техническое состояние могут быть неизвестны. Перед покупкой необходимо тщательно осмотреть двигатель на предмет видимых повреждений, течей масла и других признаков неисправностей. Желательно провести диагностику двигателя с помощью специалистов, чтобы оценить его компрессию, давление масла и другие важные параметры. Также необходимо узнать историю эксплуатации двигателя, чтобы понять, в каких условиях он работал и как часто проходил техническое обслуживание. При покупке двигателя б/у важно быть готовым к тому, что в будущем могут потребоваться дополнительные затраты на его ремонт и обслуживание. Поэтому, перед принятием решения о покупке, необходимо взвесить все за и против, оценить свои возможности и риски.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://mashhadnegar.ir/%D8%B4%D9%87%D8%B1-%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%B2%DB%8C-%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B4%D9%87%D8%AF
Испытываете сомнения, на каком именно ресурсе наиболее удобно и выгодно смотреть фильмы онлайн? Попробуйте КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-uk1.sbs/]https://kinogo-uk1.sbs/[/url]). Я уверен на все сто, что это именно то, что вы искали. Испытано временем: весь контент и функционал на Kinogo полностью бесплатен, качество трансляции и контента – не подводит, и не требуется необходимость в регистрации. Лучшие фильмы и сериалы 2025 года доступны в каталоге!
Смотри лучшие китайские https://animelist.ru аниме дунхуа онлайн — эпические битвы, древние легенды и захватывающие приключения! ? Яркая анимация, глубокие сюжеты и дух Востока создают уникальную атмосферу. Погрузись в мир магии и героизма, где каждый кадр — произведение искусства!
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
Thanks for some other informative web site. Where else may just I get that kind of info written in such a perfect approach? I’ve a mission that I am simply now working on, and I’ve been on the glance out for such info.
lee bet casino
журнальный столик
экскурсии в архызе Кисловодск достопримечательности Кисловодск славится Курортным парком с Долиной роз, Пулковской галереей и Нарзанной галереей. Гора Кольцо для панорам, замок коварства. Санатории, концерты, природа КМВ.
Смотри лучшие аниме https://animeserial2026.ru онлайн в хорошем качестве — от легендарных хитов до свежих новинок! Погрузись в мир приключений, романтики и фантазии, следи за историями любимых героев и открывай для себя новые миры. Удобный поиск, обновления каждый день и тысячи серий ждут тебя!
В стационаре «Частного Медика 24» в Воронеже организм очищается от токсинов под наблюдением врачей, проводится лабораторная и инструментальная диагностика, купируются симптомы интоксикации и восстанавливаются жизненно важные функции — всё это в условиях уюта и безопасности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
Смотри лучшие аниме https://animeserial2026.ru онлайн в хорошем качестве — от легендарных хитов до свежих новинок! Погрузись в мир приключений, романтики и фантазии, следи за историями любимых героев и открывай для себя новые миры. Удобный поиск, обновления каждый день и тысячи серий ждут тебя!
Анонимное лечение алкоголизма становится востребованным, так как многие люди стремятся вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних разговоров. На сайте narkolog-tula024.ru представлены различные программы реабилитации, включая программы детоксикации, которые позволяют пройти лечение в комфортной обстановке. Медицинское вмешательство при алкогольной зависимости включает кодирование от алкоголя и психотерапевтические методы. Анонимные группы поддержки помогают справиться с психологическими аспектами, а поддержка родных и друзей играет неоценимое значение в процессе восстановления после алкоголя. Консультации по алкоголизму онлайн и анонимные консультации обеспечивают доступ к психологической помощи при запойном состоянии. Конфиденциальное лечение дает возможность людям чувствовать себя защищенными. Важно помнить, что путь к выздоровлению начинается с первого шага.
доказывание схем оптимизации по ндс Чип-тюнинг двигателя – +20-30% мощности, 15-40 тысяч.
наушники спб купить [url=http://naushniki-apple-1.ru/]наушники спб купить[/url] .
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
banda казино
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
Смотри аниме онлайн https://anime2027.ru бесплатно и без регистрации! Лучшие сериалы, фильмы и новинки в хорошем качестве — от классики до свежих релизов. Погрузись в мир ярких эмоций, магии и приключений. Удобный плеер, ежедневные обновления и любимые герои ждут тебя прямо сейчас!
Смотри аниме онлайн https://anime2027.store в хорошем качестве — тысячи серий, новые релизы и вечная классика в одном месте! Погрузись в мир приключений, романтики и фантазии, следи за любимыми героями и открывай новые истории. Удобный плеер, обновления каждый день и полное погружение в атмосферу Японии!
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому нижний новгород[/url]
[url=https://cryptopumpsignalsbinance.com/stats/]coin price prediction[/url]
Нужна карта? международная банковская карта с доставкой в Россию как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
В «Частном Медике 24» работают круглосуточно, чтобы помощь при запое всегда была рядом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru
Металлообработка и металлы https://j-metall.ru ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
Если домашние методы не помогают, в «Частном Медике 24» обеспечат профессиональный вывод из запоя в стационаре.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в нижний новгороде[/url]
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich das Design ist modern und ansprechend, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Pour un lancement puissant. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! De surcroit le site est veloce et seduisant, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. A souligner aussi le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sens de communaute.
Explorer la page|
J’adore l’aura celeste de Casinia Casino, il procure une experience galactique. La selection de jeux est astronomique, incluant des paris sportifs vibrants. Le bonus de bienvenue est eclatant. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un eclat supplementaire. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino vaut un voyage intergalactique pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le site est rapide et envoutant, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, cependant des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site est veloce et seduisant, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif les options de paris sportifs etendues, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Voir tout|
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko круглосуточно помогает вывести из запоя на дому — быстро, анонимно и без постановки на учёт.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Стационар клиники — это безопасное место, где врачи помогают восстановить силы после тяжелого запоя.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare21.ru
Стационар «Частного Медика?24» помогает безопасно и быстро восстановиться после длительного запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В клинике «Частный Медик 24» пациенту гарантирована анонимность и внимательное отношение при лечении запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Служба вывода из запоя на дому Stop-Alko в Екатеринбурге работает без перерывов, выезжает в любой район города, оказывает помощь с учётом всех медицинских стандартов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — безопасное и эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
https://brogue.wiki/mw/index.php?title=Exodermin_99J trató mi hongo en las uñas en poco tiempo. ¡La crema es increíble!
При госпитализации пациент находится под наблюдением 24/7, что снижает риск осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
Готовитесь к киномарафону? Правильное решение – КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-gs1.sbs/]https://kinogo-gs1.sbs/[/url]). Этот сайт дает доступ к по-настоящему шикарной подборке. Лично от себя могу с уверенностью отметить, что на Kinogo всё это великолепие доступно бесплатно, в отличном качестве и не требует регистрации. Все самые громкие премьеры 2025 года уже на портале!
В Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» предлагает вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно — консультация, выезд медика, капельница и медикаменты при необходимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
платный психиатр на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
психиатр на дом в москве
Алекс Перейранын күчү менен техникасы укмуш айкалышкан. Ал жеңилсе да, кайра кайтып келип жеңишке жетет. Анын рекорду жана жеңиштери тууралуу кенен маалымат: [url=https://alex-pereira-kg.com/]Перейра рекорд[/url]. Перейра азыркы UFCнин символу десек болот.
Анын кийинки беттеши кимге каршы болору кызык.
Ал үй-бүлөсүн, балдарын, өлкөсүн сыйлайт. Перейра ар бир жеңиши менен тарых жазат. Көргөндө эле энергиясы сезилет.
Перейра — элдин арасынан чыккан легенда. Эгер спортту сүйсөң, Перейранын окуясын оку.
трипскан TripScan – это гипотетический или существующий сервис, предназначенный для упрощения процесса планирования путешествий. Он может объединять в себе функционал поиска и бронирования авиабилетов, отелей, автомобилей, а также предлагать готовые маршруты, подборки интересных мест и достопримечательностей, основанные на интересах пользователя. Дополнительные возможности могут включать в себя интеграцию с социальными сетями для обмена опытом и отзывами, а также создание индивидуальных путешествий с учетом бюджета и предпочтений.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
оптимизация налогообложения ндс Установка двигателя – в сервисе, с регулировкой, 20-50 тысяч руб.
tripscan трипскан Tripskan – ошибочное написание названия сервиса TripScan, но подразумевающее ту же самую функциональность. Несмотря на опечатку, пользователь, вероятно, ищет информацию о веб-сайте или приложении, которое помогает планировать путешествия, бронировать авиабилеты и отели, а также находить интересные места для посещения. Возможно, Tripskan предоставляет функции для создания маршрутов путешествий, обмена отзывами и фотографиями с другими путешественниками. Важно отметить, что для получения точной информации необходимо использовать правильное написание названия – TripScan.
В Екатеринбурге «Stop-Alko» предлагает вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно — консультация, выезд медика, капельница и медикаменты при необходимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Откройте для себя скрытые страницы истории и малоизвестные научные открытия, которые оказали колоссальное влияние на развитие человечества. Статья предлагает свежий взгляд на события, которые заслуживают большего внимания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://jornalfax.net/index.php/2023/12/07/ministro-eugenio-laborinho-tem-as-maos-sujas-nas-terras-da-konda-marta
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Уточнить детали – https://bharadwajkitchen.com/garlic-tambuli-recipe
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Читать далее > – https://hima-asobi.com/hello-world
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Эксклюзивная информация – https://www.penzionvachtar.sk/55
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
А что дальше? – https://arashi-restaurant.it/hello-world
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee incomparable. L’eventail de jeux est extraordinaire, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les evenements communautaires captivants, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, ab und zu regelma?igere Promos waren super. Alles in allem, NV Casino ist definitiv empfehlenswert fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Au?erdem die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
I’m stunned by Wazamba Casino, it awakens a peculiar force. There’s an expansive array of choices, designed for digital currency operations. Equaling contributions up to €500. Addressing concerns instantly. Exchanges are guarded and prompt, although supplemental rotations could advance it. Finishing with , Wazamba Casino furnishes superior recreation for staking experts ! Also the architecture is creatively striking, urging sustained engagements. Notably impressive nurturing collective spirit, bestowing enduring motivations.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Жми сюда — получишь ответ – https://www.autocentrojofra.es/los-neumaticos
1win aviator az [url=www.1win5002.com]1win aviator az[/url]
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, avec des slots au design innovant. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le support client est exceptionnel, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En prime le design est moderne et fluide, ajoute une touche de confort. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Explorer le site web|
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, avec des slots au style innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, accessible a tout instant. Les operations sont solides et veloces, par moments plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! En outre le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
Aller Г la page|
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Откройте для себя больше – https://sotempla.com/2023/06/28/embrace-the-digital-age-unleash-the-potential-of-our-products
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure imperiale. Les options sont vastes comme un empire, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. L’offre de bienvenue est somptueuse. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite fulgurante, toujours pret a regner. Les retraits filent comme une fleche, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un joyau. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino fournit une experience inoubliable pour les passionnes de frissons grandioses ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un decret, ce qui rend chaque session plus fastueuse. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires engageants, qui renforce l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots au style innovant. Pour un lancement puissant. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
DГ©couvrir|
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Полезно знать – https://vedicastrologicalservices.com/jupiter-in-aries
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Узнай первым! – http://utopiaimages.com/guestbook.html
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Откройте для себя больше – https://hotelespanola.com/projects/project-alpha
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
психиатр онлайн консультация
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://technanoltd.com/blog-post-left-sidebar-4
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Посмотреть подробности – https://www.erasmusplus.ac.me/dokumenti
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://arslan-bilisim.com/how-to-build-a-construction-marketing-plan
Contemporary online platforms for grown users offer a selection of interactive features.
These sites are designed for social interaction and discovering personal interests.
Participants can find others who share hobbies.
Most of these sites focus on respectful interaction and positive communication.
https://midnightracing.us/lifestyle/pregnant-porn-understanding-the-niche-in-adult-entertainment/
The layout is usually intuitive, making it easy to use.
Such platforms allow people to express themselves in a relaxed online environment.
Safety remains an essential part of the user experience, with many sites implementing control tools.
Overall, these platforms are designed to support mature interaction in a responsible digital space.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Открой скрытое – https://protectionbell.com/hello-world
Процесс лечения разделён на несколько этапов, каждый из которых важен для безопасности и эффективности терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-rostov/
Вывод из запоя проводится с применением современных медицинских технологий и препаратов, направленных на детоксикацию и стабилизацию состояния организма. Основные этапы включают:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru
https://katellkeinegcom.wordpress.com/
wettanbieter schweiz
Check out my page … wetten österreich, E.Netpad.app,
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
игры [url=https://mailsco.online/]https://mailsco.online/[/url] – это всеобщее занятие, что объединяет персон.
В нашем мире вопрос зависимостей является всё более значимой. Наркология по вызову в Туле предлагает многообразные наркологических услуг, включая лечение без лишних вопросов и помощь при алкоголизме. Выезд нарколога даёт возможность получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь в случае наркотической зависимости без потребности посещения клиники. Ключевой характеристик является detox в домашних условиях, что гарантирует комфортную обстановку для пациента. Консультация нарколога и поддержка психолога имеют большое значение для восстановления после зависимости. Программа реабилитации включает в себя лечение зависимостей и созависимости, а также поддержку семейных членов. Также, реабилитация в домашних условиях способствует лучшему восстановлению. Если вы испытываете трудности, воспользуйтесь ресурсами, такими как narkolog-tula027.ru, чтобы получить необходимую информацию о наркологических услугах в Туле.
aston martin vanquish цена bmw xm – это мощный и роскошный внедорожник, сочетающий в себе спортивный дизайн, передовые технологии и комфортабельный салон.
kmspico
Стандартизированный алгоритм позволяет действовать быстро и безопасно. Он гибко настраивается под конкретный случай, но всегда включает триаж, экспресс-диагностику, старт инфузии, симптом-менеджмент и выдачу плана на 72 часа с «коридорами безопасности».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
I’m hooked on Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. Dual bet options add layers of strategy, offering max wins up to 10,000x your stake. Volatility keeps things exciting and fair. Live chat resolves issues in seconds, always ready to assist mid-launch. The cash-out feature saves fortunes, nonetheless higher max bets for high-rollers. All things considered, Astronaut Crash delivers proven fair thrills for quick-play enthusiasts ! Additionally the sound design amps the tension, encouraging marathon play. Notably provably fair verification tools, which amps up replay value.
Astronaut Crash Game|
В условиях стремительного ритма жизни в мегаполисе пациенты нередко откладывают визит к врачу до критического момента. Когда же речь заходит о выводе из запоя, промедление грозит серьёзными осложнениями — от инфаркта до судорожных состояний и психозов. Клиника «РостовМедСервис» предлагает профессиональную услугу вызова нарколога на дом с гарантированным приездом в течение 30 минут. Это позволяет безопасно провести детоксикацию в привычной обстановке, сохранить анонимность и снизить стресс для пациента и его близких.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
лечение наркозависимости
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
избавление от алкогольной зависимости
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Associe a des paris gratuits. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! A mentionner le site est veloce et seduisant, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Continuer Г lire|
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. En bref, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans une cour enchanteresse. L’eventail de jeux est princier, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec un Bonus Crab exclusif. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide claire et veloce. Le processus est lisse et distingue, parfois des offres plus fastueuses ajouteraient du prestige. En bref, Casinia Casino merite une visite royale pour les passionnes de frissons grandioses ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme un edit, ce qui rend chaque session plus fastueuse. Egalement remarquable les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
https://casiniacasinobet.fr/|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
Voir les nouveautГ©s|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le suivi est exemplaire, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, mais des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, stimule le desir de revenir. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Современная наркологическая помощь в Ростове-на-Дону базируется на комплексном подходе, который объединяет медицинское лечение, психологическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход доказал свою эффективность в многочисленных исследованиях, доступных на сайте Российского общества наркологов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «Честный врач» в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на лечении зависимостей. Здесь можно пройти курс терапии от алкоголизма и наркомании, вызвать нарколога на дом или заказать капельницу для снятия запоя. Опытные врачи обеспечивают поддержку и медицинский контроль на всех этапах.
Узнать больше – [url=https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/iglorefleksoterapiya-chto-ehto-takoe/]иглорефлексотерапия в нижнем[/url]
курсы seo [url=https://kursy-seo-2.ru]курсы seo[/url] .
курсы seo [url=https://www.kursy-seo-3.ru]курсы seo[/url] .
Наркологическая клиника «Честный врач» в Нижнем Новгороде оказывает круглосуточную помощь людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Возможен выезд нарколога на дом, проведение капельницы при запое и комплексное лечение алкоголизма и наркомании с сохранением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/morfin-narkoticheskij-ehffekt/]морфин эффект[/url]
Стандартизированный алгоритм позволяет действовать быстро и безопасно. Он гибко настраивается под конкретный случай, но всегда включает триаж, экспресс-диагностику, старт инфузии, симптом-менеджмент и выдачу плана на 72 часа с «коридорами безопасности».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Используются препараты, нормализующие работу центральной нервной системы, корректирующие электролитный баланс и устраняющие симптомы алкогольной интоксикации. Применение седативных и противосудорожных средств снижает риск осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Zusatzlich die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, was jede Session noch besser macht. Hervorzuheben ist die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! A mentionner le site est veloce et seduisant, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Egalement notable les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
Aller à l’avis|
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Метод лечения
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu13.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove/
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
Je suis ebloui par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie fastueuse. La diversite des titres est somptueuse, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. L’assistance est precise et elegante, offrant des solutions limpides. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos frequentes brilleraient davantage. Au final, Casinia Casino fournit une experience inoubliable pour les passionnes de frissons grandioses ! A noter la plateforme scintille comme un palais, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’aide est performante et experte, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre la navigation est simple et engageante, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions securisees.
AccГ©der maintenant|
В условиях стремительного ритма жизни в мегаполисе пациенты нередко откладывают визит к врачу до критического момента. Когда же речь заходит о выводе из запоя, промедление грозит серьёзными осложнениями — от инфаркта до судорожных состояний и психозов. Клиника «РостовМедСервис» предлагает профессиональную услугу вызова нарколога на дом с гарантированным приездом в течение 30 минут. Это позволяет безопасно провести детоксикацию в привычной обстановке, сохранить анонимность и снизить стресс для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-rostov/
согласование перепланировки нежилых помещений [url=http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru]http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru[/url] .
I’m enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it forges a compelling story. The breadth in selections is breathtaking, incorporating wagers on athletic events. Launching your voyage. Help desk is remarkable. Disbursements are managed efficiently, yet consistent campaigns may increase allure. Finishing with , Wazamba Casino turns essential for devotees for exploration enthusiasts ! Also the imagery is alluring and absorbing, urging sustained engagements. An additional merit the relic-amassing incentive structure, bestowing enduring motivations.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Капельницы с растворами электролитов, витаминов, глюкозы и гепатопротекторов обеспечивают быстрое восстановление водно-солевого баланса, детоксикацию и поддержку печени. Инфузионное лечение позволяет нормализовать артериальное давление и сердечный ритм.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Метод лечения
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
Обращение к наркологу — это важный шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с трудностями с зависимостями . Наркологическая служба предоставляет экстренную наркологическую помощь и консультацию нарколога, что крайне важно в экстренных случаях. Признаки зависимости от наркотиков могут быть разнообразными, и важно знать, когда следует обращаться за медицинской помощью при алкоголизме. Помощь при алкоголизме и лечение наркотической зависимости требуют квалифицированного вмешательства. Алкоголизм и его последствия могут быть катастрофическими, поэтому важно искать помощь для людей с зависимостями, включая реабилитацию зависимых . На сайте narkolog-tula028.ru вы можете найти информацию о том, как вызвать нарколога или получить анонимную помощь наркоманам . Не сомневайтесь в том, чтобы позвонить в наркологическую службу, чтобы получить нужную помощь и поддержку.
I’m enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it awakens a peculiar force. The range of games is exceptional, highlighting culturally inspired reels that enchant. Heightening preliminary involvement. Promoting continuous enjoyment. Methods are simple, intermittently incentives might broaden liberally. To encapsulate , Wazamba Casino furnishes superior recreation for virtual money supporters ! Additionally the architecture is creatively striking, fortifying absorption in play. Notably impressive prestige levels with unique favors, supplying individualized graces.
wazambagr.com|
реабилитационный центр для наркоманов в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
реабилитация алкогольной зависимости в Астане
I love the vibe of Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it feels like a zero-gravity thrill ride. The gameplay is brilliantly simple yet addictive, with customizable bet sizes from $0.10 to $150. The RTP is impressively high at 97%. 24/7 availability for global players, always ready to assist mid-launch. Compatible with Bitcoin and Ethereum, however frequent promo drops would be stellar. In the end, Astronaut Crash is must-play for risk-takers for crypto gamblers ! Worth mentioning the interface supports seamless sessions, heightening the launch anticipation. Notably crypto wallet integration, ensures fast and fee-free payouts.
Astronaut Crash Game|
backstage zone
Используются препараты, нормализующие работу центральной нервной системы, корректирующие электролитный баланс и устраняющие симптомы алкогольной интоксикации. Применение седативных и противосудорожных средств снижает риск осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
cannabis honey sticks infused with thc for natural sweetness
J’ai une passion intense pour Bingoal Casino, ca immerse dans un monde fascinant. Il existe une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, accessible a tout instant. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre le site est veloce et seduisant, stimule le desir de revenir. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
http://www.bingoalcasinopromocode.fr|
Нарколог прибывает в течение 30 минут, оснащённый переносным оборудованием: портативным электрокардиографом, спирометром, прибором для измерения сатурации, набором необходимых медикаментов и расходных материалов. На первом этапе проводится замер давления, пульса, температуры и сатурации, берётся капиллярная проба крови для экспресс-анализа глюкозы и электролитов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Нижнем Новгороде работает наркологическая клиника «Честный врач», где специалисты помогают вывести из запоя, проводят капельницы на дому и оказывают профессиональную наркологическую помощь. В клинике доступно лечение наркомании и алкоголизма с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/mozhno-li-pit-pivo-pri-prieme-antibiotikov
Используются препараты, нормализующие работу центральной нервной системы, корректирующие электролитный баланс и устраняющие симптомы алкогольной интоксикации. Применение седативных и противосудорожных средств снижает риск осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov
Наркологическая клиника «Честный врач» в Нижнем Новгороде оказывает круглосуточную помощь людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Возможен выезд нарколога на дом, проведение капельницы при запое и комплексное лечение алкоголизма и наркомании с сохранением конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/abstinentnyj-sindrom/]алкогольный абстинентный синдром[/url]
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Zusatzlich die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Bingoal Casino, il offre une odyssee incomparable. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Egalement notable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Essayer maintenant|
J’adore l’eclat vibrant de Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a eclairer. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino garantit un plaisir radiant a chaque instant pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires captivants, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui brille d’une energie lumineuse. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Les agents repondent comme une etoile filante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois des bonus plus varies brilleraient davantage. Au final, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les passionnes de frissons lumineux ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
En savoir plus|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Cerise sur le gateau le design est moderne et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Locowin|
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, avec des slots au design innovant. Pour un demarrage en force. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et efficace, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est rapide et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. A noter egalement le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
VГ©rifier cela|
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne de luxe. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En prime le site est rapide et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Lire maintenant|
I’m hooked on Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. Dual bet options add layers of strategy, including auto-cashout for risk management. Volatility keeps things exciting and fair. Community forums for strategy sharing, accessible via multiple channels. Withdrawals are swift and secure, from time to time frequent promo drops would be stellar. To sum it all, Astronaut Crash provides non-stop cosmic excitement for strategy lovers ! Plus load times are near-instant, adding immersive audio cues. A real gem tournaments for competitive crashes, builds a social betting community.
Astronaut Crash Game|
https://srv482333.hstgr.cloud/index.php/Exodermin_96J a résolu mes problèmes de peau rapidement. Je suis très satisfait !
автомобили из кореи под заказ цены заказ авто из кореи в россию – это возможность приобрести автомобиль корейского производства по индивидуальным параметрам, учитывая ваши предпочтения и требования, а также доставку и таможенные сборы.
Основной метод — инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов: глюкоза, плазмозамещающие, витаминные комплексы, гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты. В зависимости от состояния пациента используются седативные и противосудорожные средства. Общая продолжительность инфузий составляет 3–5 часов, возможно разделение на несколько сеансов в течение первого дня.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
как избавиться от алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
анонимное лечение алкоголиков
I’m obsessed with Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a distinctive energy. The repository is immensely comprehensive, encompassing over 5,000 entries from premier developers. Amplifying early engagement. Operational around the clock. Procedures are uncomplicated, but further spins could be advantageous. To conclude, Wazamba Casino becomes vital for aficionados for wagering connoisseurs ! Additionally the framework is artistically impressive, refining user interaction. A further advantage exclusive ranks with special privileges, granting sustained incentives.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
При обращении по телефону или через сайт диспетчер уточняет ФИО пациента, адрес, краткую историю запоя и наличие хронических заболеваний. Затем он передаёт информацию дежурному наркологу, который готовится к выезду.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/narkolog-na-dom-rostov/
AI ChatBot
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
https://wordpress.org/support/topic/can-i-make-ai-chatbot-automatically-open/
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
трансы новосибирска Современная психотерапия увидела в трансе ценный инструмент для работы с подсознанием. Гипнотерапевты используют его для доступа к травматическим воспоминаниям, для изменения деструктивных поведенческих паттернов, для усиления самооценки. Медитация, вызывающая состояние транса, стала популярным способом борьбы со стрессом, повышения концентрации и развития осознанности. Исследования показывают, что регулярная практика медитации может изменять структуру мозга, делая человека более устойчивым к негативным воздействиям. Таким образом, транс из мистического явления превратился в научно обоснованный метод улучшения психического здоровья.
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
I’m wildly enthusiastic about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it mimics a high-altitude adrenaline surge. The mechanics are sleek and engaging, showcasing a multiplier that escalates dramatically. Balanced volatility for steady thrills. Chats connect in a flash, eager to troubleshoot mid-flight. Payouts zip through without hitches, now and again advanced auto-tools for vets. Taking stock, Astronaut Crash shines bright in 100HP’s portfolio for fast-action fans ! Extra perk layout supports marathon marathons, cranking the ascent hype. Key highlight seamless wallet linking, facilitates low-cost transfers.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Вызов нарколога на дом анонимно – это важный шаг для людей, страдающих от наркозависимости. Профессиональная помощь нарколога на дому позволяют получить профессиональную помощь в комфортной и защищенной обстановке. Нарколог, работающий анонимно осуществит консультацию, оценит состояние пациента и разработает программу лечения наркомании на месте. Это может включать психотерапию при зависимости и поддержку зависимого человека. Экстренный вызов нарколога также возможен, что является крайне важным в острых ситуациях. Помощь нарколога охватывает профилактику зависимости и реабилитацию наркоманов, обеспечивая конфиденциальное лечение и надежность процесса. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula015.ru
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’inscription est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les operations sont solides et veloces, cependant des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, garantit des transactions securisees.
Aller en ligne|
Домашний формат подходит при: длительном запое (более 48 часов), выраженной интоксикации без судорог и психотических симптомов, невозможности или нежелании пациента ехать в стационар, необходимости срочной психологической стабилизации. Также вызов на дом показан тем, кто желает анонимности и минимального вмешательства в рабочий и семейный график.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
1win suallar və cavablar [url=www.1win5002.com]1win suallar və cavablar[/url]
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Нижегородская наркологическая клиника «Честный врач» предлагает услуги по выведению из запоя и лечению зависимости. Возможен вызов нарколога на дом, постановка капельниц при алкогольной интоксикации, а также полноценные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://otalkogolizma.ru/uslugi/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]вывод из запоя нижний новгород круглосуточно[/url]
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, il offre une odyssee incomparable. L’eventail de jeux est extraordinaire, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Pour un demarrage en force. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, renforce le sens de communaute.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis totalement envoute par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions cristallines. Le processus est lisse et elegant, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino garantit un plaisir radiant a chaque instant pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus la plateforme scintille comme une etoile, intensifie l’eclat du jeu. Egalement remarquable les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. Le support client est lumineux, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. En bref, Casinia Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de frissons lumineux ! A noter le site est rapide et envoutant, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne de luxe. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. Au final, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, propose des avantages personnalises.
Aller voir|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. La variete des titres est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi client est irreprochable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. En resume, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et stylee, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus non negligeable les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Ouvrir les dГ©tails|
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Наркологическая клиника «Честный врач» в Нижнем Новгороде оказывает анонимные услуги: лечение алкоголизма, терапию наркомании, выезд нарколога на дом. Пациентам доступна капельница от запоя и медицинское сопровождение для восстановления здоровья и предотвращения осложнений.
Узнать больше – https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/ehlektronnye-sigarety-i-vejpy-vredny-li-oni-dlya-zdorovya
backstage video
Je suis impressionne par Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. La gamme des titres est epoustouflante, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
En savoir davantage|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, fugt Magie hinzu. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
I’m astonished by Wazamba Casino, it builds a thrilling narrative. The assortment of games is remarkable, incorporating live sessions for authentic interaction. Amplifying early engagement. Assistance team is superb. Financial dealings are protected and swift, occasionally promotions might expand generously. Summarizing, Wazamba Casino becomes vital for aficionados for wagering connoisseurs ! Also the setup is accessible and evocative, prompting continual returns. Additional benefit reliable crypto handling methods, delivering customized favors.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir eclatant. Le repertoire est riche et multifacette, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les retraits filent comme une comete, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des privileges continus.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. La diversite des titres est eblouissante, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Le support client est lumineux, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. En bref, Casinia Casino merite une exploration eblouissante pour les joueurs en quete d’eclat ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Egalement remarquable les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Aller en ligne|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, il offre une experience imperiale. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est impeccable, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est rapide et attrayant, ajoute une touche de luxe. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir toutes les infos|
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, avec des slots au design innovant. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le suivi client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. Au final, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Notons aussi la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Tout trouver|
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk012.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It’s always exciting to read articles from other writers and use a little something from other sites.
kra41 at
При обращении по телефону или через сайт диспетчер уточняет ФИО пациента, адрес, краткую историю запоя и наличие хронических заболеваний. Затем он передаёт информацию дежурному наркологу, который готовится к выезду.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом ростов-на-дону[/url]
Вывод из запоя проводится с применением современных медицинских технологий и препаратов, направленных на детоксикацию и стабилизацию состояния организма. Основные этапы включают:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
I’m thrilled by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it’s a pulse-racing voyage through the stars. Fair play is baked in with provable tech, potential payouts soaring to 10,000x. Balanced volatility for steady thrills. Non-stop coverage for worldwide users, delivering multiplier trend insights. Flows are dependable and speedy, still advanced auto-tools for vets. All told, Astronaut Crash shines bright in 100HP’s portfolio for crypto bettors ! Extra perk controls are beginner-proof, fueling binge-worthy bouts. Super feature leaderboards for rivalry, ensures tamper-proof twists.
Astronaut Crash Game|
I’m deeply intrigued by Wazamba Casino, it mirrors a torrent of mystique. The selections are wide-ranging and intricate, featuring betting on sports events. The introductory offer is appealing. Operational around the clock. Procedures are uncomplicated, but regular deals might amplify appeal. Summarizing, Wazamba Casino emerges as an elite venue for excitement chasers ! Also exploration is natural, refining user interaction. A further advantage the artifact-gathering reward scheme, cultivating group dynamics.
https://wazambagr.com/|
https://cuctex.com/ Cuctex на «Интерткань»: 3 года, 6 выставок, 750 новинок С весны 2023 года компания Cuctex шесть раз подряд принимала участие в выставке «Интерткань» — сначала в павильоне «Экспоцентр», затем в «Тимирязевском», а теперь в «Крокус Экспо». За это время наш стенд посетили более 3000 клиентов. Количество экспонатов увеличилось с 60 до более чем 180, а всего мы представили свыше 750 новых продуктов. Такой рост ассортимента стал причиной того, что многие клиенты отмечают: не все новинки удаётся найти на нашем сайте. Объём информации очень большой, и сайт не всегда справляется с нагрузкой.
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Zusatzlich die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
I’m thrilled by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it creates non-stop nail-biting action. Games wrap up in seconds for endless replays, betting from pennies to big bucks. Free play mode to hone your edge. Forums buzzing with player tactics, upholding outcome transparency. Flows are dependable and speedy, but fresh visuals beyond the rocket theme. Wrapping up, Astronaut Crash is essential for high-rollers for crash aficionados ! Plus audio ramps up the launch drama, cranking the ascent hype. Super feature leaderboards for rivalry, which supercharges repeat plays.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Je suis completement captive par Casinia Casino, il procure une experience imperiale. La variete des titres est majestueuse, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Les agents repondent avec celerite, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En resume, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et elegante, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. A noter egalement les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
J’adore l’aura princiere de Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie fastueuse. L’eventail de jeux est princier, avec des slots aux designs audacieux. L’offre de bienvenue est somptueuse. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite fulgurante, toujours pret a regner. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de promos frequentes brilleraient davantage. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino offre un divertissement constant pour les joueurs en quete de gloire ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un decret, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des privileges continus.
Aller à l’avis|
telecharger 1xbet cameroun pronostics du foot
pronostic foot gratuit info foot africain
1xbet afrique apk foot africain
concert stream
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. La selection de jeux est royale, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! En prime la navigation est simple et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Apprendre comment|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions securisees.
Voir plus|
купить диплом в ачинске [url=rudik-diplom6.ru]купить диплом в ачинске[/url] .
В Нижнем Новгороде работает наркологическая клиника «Честный врач», где специалисты помогают вывести из запоя, проводят капельницы на дому и оказывают профессиональную наркологическую помощь. В клинике доступно лечение наркомании и алкоголизма с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/morfin-narkoticheskij-ehffekt/]морфин рецепт[/url]
Домашний формат подходит при: длительном запое (более 48 часов), выраженной интоксикации без судорог и психотических симптомов, невозможности или нежелании пациента ехать в стационар, необходимости срочной психологической стабилизации. Также вызов на дом показан тем, кто желает анонимности и минимального вмешательства в рабочий и семейный график.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно ростов-на-дону[/url]
Good post. I study something more difficult on different blogs everyday. It’s going to always be stimulating to learn content material from other writers and observe a little bit one thing from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content material on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link in your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
I’m completely enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it’s a journey that resonates with mystery. The title variety is overwhelming, with sports betting to diversify. Matching deposits up to €500. Expert and courteous help. Payouts are handled swiftly, yet additional incentives would shine. Concluding, Wazamba Casino delivers unmatched fun for gaming aficionados ! Also the platform loads quickly, motivating return visits. Another standout feature secure crypto payment methods, ensuring transaction safety.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Капельницы с растворами электролитов, витаминов, глюкозы и гепатопротекторов обеспечивают быстрое восстановление водно-солевого баланса, детоксикацию и поддержку печени. Инфузионное лечение позволяет нормализовать артериальное давление и сердечный ритм.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]вывод из запоя цена ростов-на-дону[/url]
social live
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
Very often I go to see this blog. It very much is pleasant to me. Thanks the author
Используются препараты, нормализующие работу центральной нервной системы, корректирующие электролитный баланс и устраняющие симптомы алкогольной интоксикации. Применение седативных и противосудорожных средств снижает риск осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Флойд Мейвезердин рекорддору көп спорт күйөрмандарын суктандырган. Флойд Мейвезердин тарыхтагы орду эч кимге талашсыз. Флойд Мейвезердин беттештеринин видео жазмаларын [url=https://floyd-mayweather-kg.com/]Флойд Мейвезер видео[/url] бөлүмүнөн көрүңүз.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым спорттун чокусунда болгон. Анын рекорддору бүгүнкү күнгө чейин сакталган. Анын рингдеги кыймылы ар дайым көрүүчүлөрдү суктандырат.
Ал спорттон тышкары ишкер катары да белгилүү.
Анын карьерасы ар бир жаш спортчу үчүн үлгү. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүнө ишенген. Флойд Мейвезер – күч, ылдамдык жана акылдын айкалышы.
Капельницы с растворами электролитов, витаминов, глюкозы и гепатопротекторов обеспечивают быстрое восстановление водно-солевого баланса, детоксикацию и поддержку печени. Инфузионное лечение позволяет нормализовать артериальное давление и сердечный ритм.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu13.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov/
I’m absolutely thrilled with Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it feels like a cosmic rollercoaster. Rounds fly by for non-stop action, offering up to 10,000x payouts. Demo mode for risk-free testing. Available 24/7 across time zones, securing crypto deposits with ease. Withdrawals land at warp speed, still new crash variations could add flair. Wrapping up, Astronaut Crash stands out in 100HP’s arsenal for multiplier hunters ! Plus controls are smooth as a spaceship, driving replay after replay. Big plus the ‘Quick Exit’ option, fuels rivalries among players.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
В условиях стремительного ритма жизни в мегаполисе пациенты нередко откладывают визит к врачу до критического момента. Когда же речь заходит о выводе из запоя, промедление грозит серьёзными осложнениями — от инфаркта до судорожных состояний и психозов. Клиника «РостовМедСервис» предлагает профессиональную услугу вызова нарколога на дом с гарантированным приездом в течение 30 минут. Это позволяет безопасно провести детоксикацию в привычной обстановке, сохранить анонимность и снизить стресс для пациента и его близких.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru
wetten gewinnen tipps
My blog post … sportwetten bonus test (Walter)
How come you do not have your website viewable in mobile format? cant see anything in my Droid.
cuctex Cuctex на «Интерткань»: 3 года, 6 выставок, 750 новинок С весны 2023 года компания Cuctex шесть раз подряд принимала участие в выставке «Интерткань» — сначала в павильоне «Экспоцентр», затем в «Тимирязевском», а теперь в «Крокус Экспо». За это время наш стенд посетили более 3000 клиентов. Количество экспонатов увеличилось с 60 до более чем 180, а всего мы представили свыше 750 новых продуктов. Такой рост ассортимента стал причиной того, что многие клиенты отмечают: не все новинки удаётся найти на нашем сайте. Объём информации очень большой, и сайт не всегда справляется с нагрузкой.
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. La selection de jeux est royale, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de luxe. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Tout accГ©der|
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Je suis completement ensorcele par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans une cour enchanteresse. L’eventail de jeux est princier, avec des slots aux designs audacieux. Renforcant votre tresor initial. L’assistance est precise et elegante, toujours pret a regner. Les retraits filent comme une fleche, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un joyau. Au final, Casinia Casino fournit une experience inoubliable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est intuitive comme un edit, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement captivant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des transactions fiables.
En savoir sur le sujet|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En prime la navigation est simple et fluide, ajoute une touche de luxe. Un autre atout majeur le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Lire entiГЁrement|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi est exemplaire, accessible a tout instant. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Ajoutons que le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Egalement notable les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller plus loin|
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
частный пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в туле
При обращении по телефону или через сайт диспетчер уточняет ФИО пациента, адрес, краткую историю запоя и наличие хронических заболеваний. Затем он передаёт информацию дежурному наркологу, который готовится к выезду.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. A souligner aussi les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Ouvrir ici|
I can’t get enough of Wazamba Casino, it creates an adventurous aura. The title variety is overwhelming, including live casino for real-time action. Kickstarting your adventure. Round-the-clock availability. Rewards reach you fast, yet additional incentives would shine. On the whole, Wazamba Casino deserves your attention for thrill hunters ! Also the layout is user-friendly and thematic, infusing extra charm. Particularly impressive regular tournaments for competition, building community engagement.
wazambagr.com|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir majestueux. Le repertoire est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live captivantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite fulgurante, garantissant un service princier. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient sublimes. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino merite une visite royale pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un decret, incite a prolonger l’experience. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
music connect
Je suis absolument conquis par Casinia Casino, ca procure un plaisir aristocratique. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout majeur les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Apprendre la mГ©thode|
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Pour un lancement puissant. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. A souligner aussi les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Aller en ligne|
https://abs2best.at
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this website daily, this site is actually fastidious and the viewers are in fact sharing fastidious thoughts.
kra41 cc
https://opensocialfactory.com/story23101978/unlock-unique-rewards-with-1xbetpromo-your-gateway-to-smarter-betting
Melbet для русских игроков доступ без ограничений в 2025
Melbet для русских игроков в 2025 году – безопасный доступ к азартным играм без ограничений
Выбор надежного букмекера становится все более актуальным. Рассматривая наиболее выгодные варианты, стоит обратить внимание на сервисы, которые предлагают высокие коэффициенты и широкий выбор событий. Это особенно актуально для тех, кто ищет идеальные условия для активного участия в ставках.
Платформа, о которой идет речь, обеспечивает простую регистрацию и удобный интерфейс. Акции и бонусы становятся хорошим дополнением к стандартным возможностям. Регулярные предложения делают процесс ставок более захватывающим и выгодным.
Убедитесь, что опыт игроков, уже воспользовавшихся платформой, подтверждает ее надежность и безопасность. Читайте отзывы и статьи на профильных форумах, чтобы составить полное представление о предложениях. Удачные ставки и приятные впечатления станут гарантией возвращения к выбору именно этой платформы.
Возможности Melbet для пользователей в 2025 году
Служба обеспечения игрового процесса предложит высокий уровень комфорта и безопасности. Применяйте актуальные приложения, чтобы максимально упростить доступ к платформе. Установите мобильное приложение, это гарантирует стабильную работу на любом устройстве, в любое время.
Следите за акциями и бонусами, которые будут регулярно обновляться. Зарабатывайте приятные предложения, чтобы увеличить свой банк. Не упускайте шанс воспользоваться эксклюзивными предложениями только для новых пользователей.
Изучайте ассортимент спортивных событий и игр, доступных на платформе. Это позволит вам найти наиболее выгодные и интересные предложения для ставок. Разработка стратегии – ключ к успеху. Анализируйте статистику и результаты, чтобы сделать обоснованный выбор.
Обратите внимание на поддержку клиентов. Быстрая помощь и возможность обратной связи существенно влияют на качество обслуживания. Используйте все доступные каналы связи для решения возникших вопросов.
Убедитесь, что вы знакомы с правилами и условиями платформы. Это поможет избежать недоразумений и гарантирует безопасное взаимодействие. Читайте отзывы и обсуждения, чтобы узнать о реальном опыте других пользователей.
Преимущества использования Melbet для ставок в России
Широкий выбор спортивных событий и высокие коэффициенты на популярные матчах привлекают внимание пользователей. Платформа предлагает многообразие премиум-ставок, включая традиционные и лайв-пари, что позволяет делать ставки в реальном времени.
Интуитивно понятный интерфейс, доступный как на компьютерах, так и на мобильных устройствах, облегчает процесс размещения пари. Пользователи могут быстро находить нужные события и принимать решения, не отвлекаясь на сложные навигационные элементы.
Интерес вызывает наличие заманчивых бонусов и акций, включая приветственные предложения, повышающие первоначальный капитал. Системы лояльности обеспечивают дополнительные возможности для регулярных участников, что увеличивает шансы на выгодные ставки.
Клиентская поддержка работает круглосуточно, готовая помочь с любыми вопросами и проблемами. Это гарантирует комфортное использование платформы и быстрое решение возникающих ситуаций.
Наконец, акцент на безопасность данных пользователей обеспечивает защиту личной информации и финансовых транзакций, создавая доверительную атмосферу для всех участников. Улучшенная система шифрования помогает предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к счетам.
Регистрация и способы обхода блокировок в 2025 году
Для быстрой регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы рекомендуется использовать актуальный адрес площадки. Для этого можно найти его на специализированных форумах или в группах в социальных сетях.
Если ресурс заблокирован, за главу подойдет использование VPN-сервисов. Это позволит сменить IP-адрес и получить возможность зайти на сайт без препятствий. Рекомендуется выбирать проверенные программы, такие как NordVPN или ExpressVPN, которые обеспечивают надежное соединение и высокую скорость.
Кроме того, стоит обратить внимание на прокси-серверы. Они создают промежуточное соединение, что также может помочь обойти ограничения. Поддержка таких сервисов в большинстве случаев достаточно высокая.
Важно помнить, что некоторые браузеры, такие как Opera, имеют встроенные функции VPN, которые могут быть полезными для доступа к контенту.
Еще одним способом является использование зеркал. Эти альтернативные ссылки часто созданы для обхода блокировок и могут быть найдены через поисковые системы или на тематических ресурсах.
Регистрация заключается в стандартной процедуре: необходимо указать личные данные, которые после подтверждения позволят получить доступ к функционалу сайта. Пользуйтесь актуальными ресурсами для получения свежих ссылок и советы по безопасности.
https://turkcemidi.com/skachat-melbet-na-pk-obzor-prilozheniya/
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be interesting to read articles from other authors and practice a little something from their sites.
kraken маркетплейс
При обращении по телефону или через сайт диспетчер уточняет ФИО пациента, адрес, краткую историю запоя и наличие хронических заболеваний. Затем он передаёт информацию дежурному наркологу, который готовится к выезду.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-rostov-na-donu13.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
I’m completely enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it creates an adventurous aura. There’s a stunning assortment of games, including live casino for real-time action. Accompanied by 200 free spins. Expert and courteous help. Operations are straightforward, yet frequent promotions could add value. To wrap up, Wazamba Casino deserves your attention for gaming aficionados ! Furthermore the platform loads quickly, streamlining user experience. Another standout feature the mask collection loyalty system, offering tailored benefits.
wazambagr.com|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
1win az virtual oyunlar [url=https://www.1win5005.com]https://www.1win5005.com[/url]
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
pansionat-tula012.ru
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
Если требуется срочная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде, клиника «Честный врач» готова помочь. Врачи выезжают на дом, проводят капельницы при запое, обеспечивают безопасное выведение из запойного состояния и предлагают программы лечения наркомании и алкоголизма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [/url]
parier foot en ligne telecharger 1xbet apk
pronostics du foot paris sportif foot
paris sportif foot pariez sur le foot
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
Создавайте дом https://it-cifra.com.ua своей мечты! Всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне интерьера. Идеи, проекты, фото и инструкции — вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте задуманное легко и с удовольствием.
порошковая покраска оборудование Камера полимеризации порошковой краски купить – актуальный запрос для компаний, занимающихся порошковой покраской и планирующих расширение производства или замену устаревшего оборудования. Камера полимеризации является одним из ключевых элементов оборудования для порошковой покраски, обеспечивающим плавление и закрепление порошкового слоя с образованием прочного покрытия. При выборе камеры полимеризации порошковой краски необходимо учитывать размеры обрабатываемых изделий, требуемую производительность, тип используемой порошковой краски и доступный бюджет. Камеры полимеризации могут быть тупиковыми (для небольших объемов) или проходными (для автоматизированных линий). Важными параметрами являются равномерность распределения температуры внутри камеры, тип нагревательных элементов (электрические, газовые или инфракрасные), наличие системы управления с возможностью программирования режимов полимеризации и энергоэффективность. При покупке камеры полимеризации порошковой краски рекомендуется обращаться к надежным поставщикам, предлагающим широкий ассортимент оборудования различных производителей, а также консультации по выбору оптимального решения и сервисное обслуживание.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vitalite. La selection de jeux est spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a tout moment. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est intuitive et elegante, ce qui rend chaque session plus enjoyable. Un avantage supplementaire les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
valuable stamps
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Lire maintenant|
Je suis completement obsede par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Pour un lancement puissant. Le suivi est exemplaire, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. La procedure est aisee et efficace, par moments des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! A mentionner le site est veloce et seduisant, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Locowin|
https://ebs2best.at
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя минск
Only reliable facts: https://www.jec.qa
We have reliable sources: https://therockpit.net
Information you can trust: https://www.colehardware.com
Only verified data: https://playplayfun.com
I’m drawn to Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. There’s an incredible variety of games, including slots with tribal themes. Doubling your deposit up to €500. Ensuring smooth gameplay. Withdrawals are processed quickly, however lower wagering requirements would be ideal. In conclusion, Wazamba Casino delivers top-tier gaming for online betting fans ! In addition the interface is intuitive and themed, encourages repeated visits. Notably the loyalty program with masks, ensuring secure transactions.
wazambagr.com|
Only verified sources: https://m-g.wine
bs2best at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
tripscan
где купить диплом об окончании колледжа [url=www.frei-diplom7.ru]где купить диплом об окончании колледжа[/url] .
sportwetten ohne einzahlung bonus
Look at my web page: online wetten Test
Регистрация в Мелбет пошаговое руководство для новичков
Как зарегистрироваться в Мелбет быстро и без проблем пошаговая инструкция
Для успешного оформления профиля на платформе следуйте простым шагам. Первый момент – зайдите на официальный сайт и найдите кнопку входа или регистрации. Обычно она выделяется на главной странице, что упрощает поиск.
На следующем шаге откроется форма, куда необходимо внести свои данные. Убедитесь, что информация точна: укажите правильный адрес электронной почты и номер мобильного телефона. Это важно для дальнейшей верификации и восстановления доступа к учетной записи.
После заполнения данной информации вам потребуется создать надежный пароль. Используйте комбинацию заглавных и строчных букв, цифр и специальных символов, чтобы сделать его максимально защищённым.
Когда все данные будут введены, нажмите кнопку подтверждения. Обычно на указанный вами номер телефона или электронную почту отправляется код для активации. Введите этот код в соответствующем поле, чтобы завершить процесс. Сделав это, вы сможете полноценно использовать все возможности платформы.
Создание аккаунта: пошаговая инструкция
Перейдите на официальный сайт букмекера. На главной странице найдите кнопку для создания нового профиля, обычно это выделенная ссылка или кнопка, размещенная в верхней части интерфейса.
На следующем экране выберите способ регистрации. Доступны варианты через электронную почту, номер телефона или аккаунты социальных сетей. Выберите наиболее удобный для вас метод.
Заполните все обязательные поля анкеты. Обычно это включает в себя указание личных данных: ФИО, дату рождения и контактные сведения. Убедитесь в отсутствии ошибок, так как недостоверная информация может привести к проблемам при верификации.
Создайте надежный пароль. Рекомендуется использовать сочетание заглавных и строчных букв, цифр и символов. Это повысит безопасность вашего профиля.
Прочтите и примите условия использования сервиса. Важно внимательно ознакомиться с правилами и политикой конфиденциальности. Согласитесь с ними, поставив галочку в соответствующем чекбоксе.
Подтвердите свои данные, нажав на кнопку завершения процесса. Вам может прийти сообщение с кодом подтверждения, если вы использовали номер телефона или почту. Введите код в соответствующее поле.
После успешного подтверждения вы получите доступ к своему аккаунту. Рекомендуется сразу настроить дополнительные меры безопасности, такие как двухфакторная аутентификация, если такая функция доступна.
Если возникнут проблемы на любом этапе, обратитесь в службу поддержки. Специалисты готовы помочь с решением любых вопросов, касающихся создания профиля.
Подтверждение учетной записи и настройки профиля
Для успешного подтверждения учетной записи необходимо пройти проверку электронной почты. После регистрации вы получите сообщение с ссылкой, по которой нужно перейти. Это действие подтвердит вашу личность и активирует аккаунт.
После подтверждения зайдите в профиль и начните настраивать его. Введите свои личные данные, такие как полное имя, дата рождения и адрес. Эти данные нужны для дальнейших операций и повышения уровня безопасности учетной записи.
Обратите внимание на раздел с паролем. Рекомендуется создать надежный пароль, состоящий минимум из восьми символов, включая буквы, цифры и специальные символы. Это значительно улучшит защиту вашего профиля.
Также проверьте настройки двухфакторной аутентификации. Это дополнительная мера безопасности, которая требует ввода кода из SMS при входе в аккаунт. Активация этой функции значительно снизит риск несанкционированного доступа.
Регулярно обновляйте информацию в профиле, особенно контактные данные. Это поможет избежать проблем при восстановлении доступа в случае потери пароля или других неприятных ситуаций.
В разделе уведомлений настройте предпочтения для получения информации о событиях, акциях и новостях. Выберите, хотите ли получать информацию на электронную почту или через мобильное приложение. Это упростит получение актуальных новостей и предложений.
https://worldwideslogans.com/melbet-prilozhenie-skachat-obzor-bukmekera/
We only tell the facts: https://sportsfanbetting.com
A trusted source: https://www.greenwichodeum.com
Stay up to date: https://childstrive.org
No lies – just facts: https://m120.com
We check every word: https://labhgroup.com
social chat
Мобильная версия Melbet лучшие игры и слоты 2025
Обзор мобильной версии Melbet топовые игры и слоты 2025 года
Если вы ищете качественные развлекательные предложения, которые подарят вам уникальные впечатления, обратите внимание на платформу Melbet. Здесь представлено множество увлекательных автоматов и ставок, которые порадуют каждого игрока. Убедитесь, что ваш выбор – это не просто случайный набор, а тщательно отобранные развлечения от ведущих разработчиков программного обеспечения.
Одной из ключевых функций сервиса является широкий ассортимент игровых автоматов, разнообразие тематики и функционала. От классических машин с фруктами до современных игровых автоматов с глубоким сюжетом – каждый найдет что-то для себя. Обратите внимание на популярные новинки, которые будут представлены в 2025 году, и не забудьте протестировать их в режиме демо перед ставками на реальные деньги.
Среди популярных категорий также можно выделить настольные увлечения, которые предлагают захватывающий опыт в сочетании с возможностью взаимодействовать с дилерами в режиме реального времени. Испробуйте свои навыки в покере или рулетке, пополняя свои игровые достижения.
Наконец, не забывайте о постоянных акциях и бонусах, которые ставят множество дополнительных возможностей. Следите за обновлениями на платформе, чтобы не упустить возможность увеличить свои шансы на выигрыш, тестируя увлекательные механики игр и специальные предложения от разработчиков.
Мобильная платформа: интересные развлечения и игровые автоматы
Если вы цените качественные графику и звук, стоит попробовать инновационные видеоигры с 3D-анимацией. Они обеспечивают immerse-опыт и разнообразие игровых возможностей, что делает процесс азартным и увлекательным.
Советуем испытать также классические автоматы с фруктовой тематикой. Они идеально подходят как для новичков, так и для опытных пользователей. Простота правил и яркая визуализация помогут насладиться игровым процессом без лишних заморочек.
Интересным вариантом станут экшен-игры с живыми дилерами. Их особенность – реалистичное взаимодействие, позволяющее ощутить атмосферу настоящего казино, где профессиональные крупье управляют процессом.
Следует упомянуть о бонусных раундах, которые значительно увеличивают игровой опыт. Высокие коэффициенты и призовые игры часто делают процесс более прибыльным и динамичным.
Обратите внимание на автомат с тематикой приключений – это не только увлекательно, но и возможность погрузиться в захватывающий сюжет с оригинальными персонажами.
Топ-5 популярных азартных автоматов
2. Слот Джумилия – романтичная атмосфера игры не оставляет равнодушными любителей волшебных историй. С яркой графикой и интересными бонусами, этот автомат предлагает не только развлечение, но и шансы на значительные выплаты.
3. Золото Пара – этот автомат идеально подходит тем, кто предпочитает высокие риски и большие выигрыши. С уникальной механикой игры и шансами на накопление джекпота, он позволяет испытывать удачу в различных режимах.
4. Сказочное Приключение – эта игра славится своей необычной тематикой и продуманным геймплеем. С множеством уровней и квестов, она захватывает интерес и делает процесс увлекательным. Возможные выигрыши здесь могут приятно удивить.
5. Вулкан удачи – классический автомат с простым интерфейсом и высокой волатильностью. Идеальное сочетание простоты и шанса на крупный выигрыш привлекает множество поклонников азартных развлечений.
Как выбрать игровые автоматы для смартфона на платформе
Сосредоточьтесь на провайдере контента. Выбирайте продукты от известных разработчиков, таких как NetEnt, Microgaming или Play’n GO, чтобы гарантировать высокое качество графики и честность игровых механик.
Обратите внимание на процент возврата игроку (RTP). Ищите предложения с RTP выше 95%, так как такие автоматы предлагают более высокие шансы на выигрыш в долгосрочной перспективе.
Не забывайте про мобильную оптимизацию. Игровые автоматы должны быть отзывчивыми и адаптироваться к разным разрешениям экранов, обеспечивая комфортный процесс без задержек.
Изучите темы и функции. Выбирайте слоты с увлекательными сюжетами и разнообразными бонусами, такими как бесплатные вращения, дополнительные раунды или прогрессивные джекпоты для увеличения интереса к игре.
Проверьте наличие демоверсий. Это позволит протестировать автоматы без вложений и оценить их функционал, прежде чем делать ставки на реальные деньги.
Не игнорируйте отзывы других игроков. Этот способ получения информации поможет выявить недостатки и преимущества конкретных вариантов, а также нюансы работы со службой поддержки.
https://www.samengoedvoorlater.nl/skachat-melbet-kazino-obzor-prilozheniya/
порядок согласования перепланировки нежилого помещения [url=https://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya10.ru]https://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya10.ru[/url] .
перепланировка в нежилом здании [url=https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya11.ru/]перепланировка в нежилом здании[/url] .
перепланировка здания [url=https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya9.ru/]перепланировка здания[/url] .
аренда маленького экскаватора [url=arenda-mini-ekskavatora-v-moskve-2.ru]аренда маленького экскаватора[/url] .
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk010.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника
Amo a vibracao de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer carnavalesco. A variedade de titulos e deslumbrante, com slots de design inovador. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, garantindo um atendimento de qualidade. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto algumas rodadas gratis extras seriam incriveis. No geral, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao a cada momento para fas de cassino online ! Tambem a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Notavel tambem o programa VIP com 5 niveis exclusivos, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Descobrir mais|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. Os agentes respondem com velocidade, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em resumo, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Tambem a interface e fluida e energetica, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Clique agora|
двойные рулонные шторы с электроприводом [url=www.rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru]www.rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
News as it is: https://satapornbooks.com
We tell it like it is: https://nature-et-avenir.org
Information you can trust: https://cfsl.in
Only the latest updates: https://aquietrabalho.com
Find out the truth here: https://jnp.chitkara.edu.in
Find out the truth here: https://www.europneus.es
We tell it like it is: https://www.actuabd.com
Only the latest updates: https://hyundaimobil.co.id
News as it is: https://www.certificadosenergeticos.com
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
https://bsmey.at
Melbet 2025 как пользоваться и выигрывать пошаговое руководство
Пошаговое руководство Melbet на 2025 год как открыть и вести аккаунт
Для успешного старта на платформе, сначала зарегистрируйтесь. Этот процесс требует указания информации: имя, адрес электронной почты и номер телефона. Убедитесь в правильности введённых данных, так как это может повлиять на последующую верификацию.
После завершения регистрации, важно пополнить счёт. Воспользуйтесь различными методами: банковские карты, электронные кошельки или криптовалютные операции. Каждый из них имеет свои особенности, поэтому выбирайте наиболее удобный вариант для себя.
Изучите доступные события и линии ставок. Определите наиболее интересные для вас виды спорта и турниры. Сравните коэффициенты на разные исходы, так как это может существенно повлиять на размер выигрыша.
Не забывайте о стратегии. Разработка собственной тактики ставок позволит минимизировать риски. Обращайте внимание на статистику команд и игроков, следите за новостями, чтобы оставаться информированным.
Используйте бонусы и акции платформы. Они могут значительно увеличить ваш депозит. Читайте условия, чтобы понять, как можно получить максимальную пользу от предложений.
Наконец, фиксируйте свои выигрыши и убытки. Ведение статистики поможет анализировать результаты и корректировать стратегию в будущем. Используйте полученные данные для улучшения своих навыков и понимания рынка ставок.
Melbet 2025: Использование платформы и получение выигрышей
Зарегистрируйтесь на сайте, выполнив простую процедуру. Укажите свои данные и создайте надежный пароль. Чем тщательнее вы подойдете к этому этапу, тем легче будет вам работать с ресурсом.
Пополните баланс с помощью доступных методов. Выберите удобный способ, будь то банковская карта или электронный кошелек. Убедитесь, что перевод происходит без задержек, чтобы сразу приступить к ставкам.
Изучите разделы с актуальными событиями. Выделите время на анализ предлагаемых матчей и турниров. Сравните коэффициенты на разные исходы и выберите наиболее выгодные варианты.
Используйте статистику для принятия решений. Ознакомьтесь с результатами команд, их текущей формой и историей встреч. Этот подход повысит шансы на успех.
Установите лимиты на ставки. Определите, сколько готовы поставить, чтобы минимизировать риски. Дисциплина поможет избежать крупных потерь.
Пользуйтесь бонусами и акциями. Следите за предложениями, которые доступны пользователям. Это может значительно увеличить ваши шансы на успешные ставки.
Анализируйте свои результаты. Ведите учет сделанных ставок, чтобы выявить успешные стратегии и выявить ошибки. Обработка данных в будущем поможет вам улучшить подход.
Следите за новостями и изменениями в правилах. Это поможет адаптироваться к изменяющимся условиям и оставаться в курсе алармов, которые могут повлиять на ваше время на платформе.
Регистрация и создание аккаунта на платформе
Для начала процесса необходимо зайти на официальный сайт. Обратите внимание на кнопку «Регистрация», расположенную на главной странице, и нажмите на нее.
Заполните предложенную форму. Введите адрес электронной почты и придумайте надежный пароль. Учтите, что пароль должен содержать как минимум восемь символов, включая заглавные и строчные буквы, цифры и специальные знаки.
Выберите валюту для расчетов. Это может быть рубль, доллар или евро, в зависимости от ваших предпочтений. Убедитесь, что выбор валюты оправдан, так как изменить его позже может быть затруднительно.
На этом этапе важно согласиться с условиями и положениями. Рекомендуется внимательно ознакомиться с правилами, чтобы не столкнуться с неприятными ситуациями в будущем.
После заполнения всех полей отправьте запрос на регистрацию. Проверьте свою почту для получения письма с подтверждением. Перейдите по ссылке в этом сообщении для активации своего нового профиля.
По завершении активации вы сможете войти в систему, используя указанные ранее данные. В профиле можно заполнить дополнительные сведения о себе, такие как имя, фамилия и дата рождения, что увеличит уровень безопасности аккаунта.
При желании рекомендуется установить двухфакторную аутентификацию для повышения защиты. Эта опция доступна в настройках безопасности и поможет защитить аккаунт от несанкционированного доступа.
Теперь ваш профиль готов к использованию. Вы можете пополнять баланс, делать ставки и участвовать в предлагаемых акциях. Не забудьте следить за новыми предложениями и бонусами, которые могут появляться на платформе.
Как делать ставки и повышать шансы на выигрыш в Melbet 2025
Изучите спортивные события, на которые планируете ставить. Опирайтесь на статистику команд, форму участников и внутренние чемпионаты. Это поможет сделать более обоснованные прогнозы.
Выбирайте выгодные коэффициенты. Необходимо анализировать линии на предмет ценности ставок. Высокие коэффициенты могут обеспечить лучшую прибыль, но требуют тщательного анализа риска.
Распределите бюджет. Определите сумму, которую готовы вложить, и придерживайтесь ее. Это убережет от эмоциональных решений и непредвиденных затрат.
Применяйте технику ставки на системные события. Если хотите снизить риски, ставьте на несколько исходов. Система ставок позволяет создать более надежный портфель.
Анализируйте предыдущие результаты. Ознакомьтесь с историей встреч команд, что даст лучший контекст для принятия решения. Обращайте внимание на изменения в составах и тренерских подходах.
Контролируйте эмоции. Не позволяйте азарту влиять на процесс принятия решений. Хладнокровие поможет делать более рациональные выборы и избежать лишних потерь.
Регулярно пересматривайте стратегию. Анализируйте результаты своих ставок, определяйте, что сработало, а что нет, и корректируйте подход на основе полученных данных.
https://seafoodclub.store/registratsiya-na-melbet-bystro-i-udobno/
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Locowin Casino, ca immerse dans un monde fascinant. Il y a une multitude de jeux captivants, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Accompagne de paris gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours disponible pour assister. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient de l’attrait. Au final, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui impressionne pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, ce qui rend chaque session plus enjoyable. Un avantage supplementaire les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Lire plus|
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses permanentes.
En savoir plus|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
лечение запоя минск
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Particulierement attractif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Cliquer pour les infos|
We select the best: https://hello-jobs.com
Only important details: https://www.atrium-patrimoine.com
Time-tested and proven: https://www.amakmeble.pl
Information you can trust: https://tumundobio.es
сайт трипскан
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
music stream
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. La selection de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. L’equipe de support est remarquable, toujours disponible pour assister. Les gains arrivent sans retard, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient de l’attrait. En bref, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, ce qui rend chaque session plus enjoyable. Un avantage supplementaire le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller lГ -bas|
I’m amazed by Wazamba Casino, it provides a thrilling journey. The array of titles is vast, including slots with tribal themes. Doubling your deposit up to €500. Agents respond swiftly. Winnings arrive promptly, nevertheless extra rewards would be fantastic. In conclusion, Wazamba Casino provides guaranteed enjoyment for those who enjoy crypto ! Additionally the design is engaging and exotic, which heightens the fun of every session. Worth noting tournaments for competitive play, ensuring secure transactions.
wazambagr.com|
Наркологическая клиника «Честный врач» в Нижнем Новгороде оказывает анонимные услуги: лечение алкоголизма, терапию наркомании, выезд нарколога на дом. Пациентам доступна капельница от запоя и медицинское сопровождение для восстановления здоровья и предотвращения осложнений.
Подробнее – https://otalkogolizma.ru/stati/abstinenciya-pri-otkaze-ot-kureniya
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots au style innovant. Pour un lancement puissant. Le suivi est exemplaire, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. La procedure est aisee et efficace, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Globalement, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions securisees.
Commencer Г explorer|
Τα online καζίνο αποτελούν σήμερα μια από τις πιο δημοφιλείς μορφές ψυχαγωγίας στην Ελλάδα. Η αγάπη των Ελλήνων παικτών για αυτή τη μορφή διασκέδασης μεγαλώνει συνεχώς, και μαζί με αυτή την αύξηση, πολλαπλασιάζονται και οι επιλογές σε διαδικτυακά καζίνο. Αν θέλεις να βρεις τα καλύτερα και πιο ασφαλή καζίνο για να παίξεις, είναι σημαντικό να ξέρεις πώς να ξεχωρίζεις τις αξιόπιστες πλατφόρμες από τις υπόλοιπες. Στο παρακάτω άρθρο θα βρεις χρήσιμες πληροφορίες και συμβουλές για να κάνεις την καλύτερη επιλογή και να απολαύσεις το παιχνίδι με ασφάλεια και διασκέδαση.
Je suis captive par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, avec des slots au style innovant. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, assurant un support premium. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Ajoutons que le site est veloce et seduisant, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Egalement notable les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions securisees.
Trouver le bonus|
лечение психиатрических расстройств
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
частный психиатр на дом в москве
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com energia festiva. A variedade de titulos e deslumbrante, com slots de design inovador. 100% ate €500 + 200 rodadas gratis. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam bem-vindos. Em resumo, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e simples e envolvente, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial importante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Descobrir mais|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk011.ru
лечение запоя
I’m drawn to Wazamba Casino, it’s an adventure that throbs with excitement. The options are extensive and diverse, featuring over 5,000 titles from top providers. Doubling your deposit up to €500. Agents respond swiftly. Winnings arrive promptly, sometimes extra rewards would be fantastic. To sum up, Wazamba Casino provides guaranteed enjoyment for those who enjoy crypto ! Also the interface is intuitive and themed, adds a layer of excitement. One more highlight crypto-friendly banking options, ensuring secure transactions.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Мобильная версия Melbet с гарантией надежности в 2025
Мобильная версия Melbet 2025 с гарантией надежности и удобства для пользователей
Специалисты рекомендуют обратить внимание на приложения для ставок на спорт, которые обеспечивают максимальную защиту личных данных пользователей. При выборе платформы акцентируйте внимание на лицензии и отзывах клиентов, чтобы убедиться в прозрачности работы сервиса. Один из таких вариантов предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, который позволяет легко ориентироваться в функционале в любое время.
Обратите внимание на наличие службы поддержки, работающей круглосуточно. Это позволяет получать помощь в случае возникновения вопросов или проблем. Запомните, что скорость отклика службы поддержки – один из ключевых факторов надежности: чем быстрее решается вопрос, тем выше качество сервиса.
Как скачать и установить приложение на Android и iOS?
Для установки приложения на устройства с Android необходимо перейти на официальный сайт букмекера. Там вы найдете ссылку для скачивания APK-файла. Нажмите на неё, чтобы загрузить файл на свой телефон.
После завершения загрузки перейдите в настройки устройства, выберите раздел “Безопасность” и разрешите установку приложений из неизвестных источников. Затем найдите загруженный файл в папке загрузок и запустите установку.
На устройствах iOS загрузка осуществляется через App Store. Откройте данный магазин, выполните поиск по названию приложения и нажмите кнопку установки. При необходимости авторизуйтесь с помощью Apple ID.
После завершения установки откройте приложение и выполните вход по своим учетным данным или зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет аккаунта.
Следуя данным шагам, вы сможете без проблем установить нужное приложение на своё устройство и наслаждаться его функционалом.
Какие функции и преимущества предлагает приложение букмекера в 2025 году?
Наиболее актуальные функции включают интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяющий легко находить нужные события. Упрощенный процесс регистрации минимизирует временные затраты, а наличие многофакторной аутентификации обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности.
Интерактивные ставки в реальном времени дают возможность следить за текущими коэффициентами и делать ставки на ходу. Информация о событиях обновляется мгновенно, что позволяет принимать взвешенные решения.
Можно воспользоваться персонализированными уведомлениями о результатах и изменениях коэффициентов. Это значительно упрощает контроль за ставками и возможностью получения мгновенной информации о выигрыше.
Благодаря интеграции с социальными сетями, пользователи могут делиться своими успехами и привлекать друзей к совместным ставкам. Сообщество создаёт дополнительный повод для вовлечения и обмена опытом.
Специальные промоакции и бонусы доступны исключительно для пользователей, что делает процесс более выгодным. Программа лояльности позволяет накапливать баллы и обменивать их на различные предложения.
Опция поддержка живого чата и телефонов обеспечивает оперативное получение ответов на возникшие вопросы, что немаловажно для комфортного и безопасного использования сервиса.
https://cellcenteroaxaca.com/skachat-melbet-na-ajfon-obzor-bk/
Only verified information: https://telrad.com
Only real facts: https://m-g.wine
Only verified facts: https://agriness.com
Trustworthy news: https://slavasnowshow.com
We write as is: https://angersnautique.org
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, obwohl mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com emocao atletica. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para o jogo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, embora bonus mais variados seriam um gol. No geral, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Alem disso o site e veloz e envolvente, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Outro destaque os pagamentos seguros em cripto, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ir para o site|
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et efficace, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. En resume, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi le site est rapide et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. Un plus non negligeable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Profiter de l’offre|
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://courtiersolaire.fr/index.php/2023/10/06/bonjour-tout-le-monde
сайт трипскан
A source for current events: https://lmc896.org
Events without embellishment: https://sportsfanbetting.com
No exaggerations: https://livescores.biz
Source of truthful news: https://muskaanhindi.org
Only real events: https://redclara.net
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, avec des slots au style innovant. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Globalement, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! De surcroit la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Voir maintenant|
web meeting
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, facilite une immersion complete. A souligner aussi le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller en ligne|
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Детали по клику – https://eyeblogs.com/vinesh-phogat-resigns-from-indian-railways
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://www.mizuthegiantbluecat.com/2025/02/17/hello-world
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Хочу знать больше – https://sellyourdyson.co.uk/sell-used-dyson-v6
We maintain objectivity: https://www.saffireblue.ca
We value honesty: http://lipetskregionsport.ru
Все лучшее у нас: http://hammill.ru
Все самое актуальное тут: https://tako-text.ru
No fakes or speculation: https://www.cricketweb.net
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://restauranteviagraca.pt/en/espacos-e-casas
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://dating-free-dating.com/2024/02/12/flirt-com-scam
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://mgdmedia.live/?p=2623
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Следуйте по ссылке – https://cdjnet.com/como-funcionan-las-apuestas-deportivas-en-mexico
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://cavistes-catalans.com/cavistes-catalans
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Обратиться к источнику – https://glasshousebilliard.hu/hello-world
https://bs2shop.lat
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в стационаре[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Андрей Николаевич Селиванов, «своевременный визит специалиста на дом позволяет избежать тяжёлых осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния»».
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Не упусти шанс – https://damangamelogin.one/add-bank-account-to-daman-games
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um farol na nevoa. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um farol. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de brilho. O servico e confiavel como uma lanterna. garantindo suporte direto e sem escuridao. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Ao final, BR4Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja o design e fluido como uma lanterna. amplificando o jogo com vibracao luminosa.
br4bet bГґnus|
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No geral, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, oferece recompensas continuas.
Continuar lendo|
J’adore le dessin de Simsinos Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un animateur. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et precise. avec une aide qui rebondit comme un toon. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse cartoon. neanmoins les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. A la fin, Simsinos Casino cadence comme une sonate de victoires pour les animateurs du casino! Par ailleurs est une cadence visuelle envoutante. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
simsinos review|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos com graficos de primeira. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino e parada obrigatoria pra quem gosta de cassino. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
g 4play|
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e estilosa, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Outro destaque as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Descobrir|
Всё самое свежее здесь: https://mebel-3d.ru
Только проверенные новости: https://bibamotor.ru
Всё актуальное в одном месте: https://radiocert.ru
Всё самое новое тут: https://forwardprint.com.ua
Источник, которому доверяют: https://www.beastmw.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk012.ru
лечение запоя
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Кликни и узнай всё! – https://wallpapsy.com/ovaj-metod-krojaci-kriju-jer-ne-zele-da-znate-popraviti-rajfeslus
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Заходи — там интересно – https://crystalexcursy.com/harvesting-hope-millet-and-sorghum-farming-reshaping-climate-resilience
Психотерапия во Владимире в клинике «Новая Эра» проводится высококвалифицированными специалистами с большим опытом работы в сфере зависимостей.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/]принудительное лечение наркомании владимир[/url]
https://2-bs2best.art
bs2best at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://quantumfilms.co.uk/the-evolution-of-professional-video-recording-in-the-21st-century
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://splavoravy-rafting.sk/cum-sociis-natoque-penatibus-et-magnis
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Ознакомьтесь поближе – https://haloindonesia.id/blog/2023/11/08/lapas-sragen-mulai-perketat-barang-masuk-melalui-pemeriksaan-menggunakan-teknologi-x-ray
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Это ещё не всё… – https://midnightsunactivities.com/experience-the-ultimate-getaway-with-luxury-yacht-rentals
Je suis completement fou de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La variete des titres est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Pour un demarrage en force. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et efficace, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Cerise sur le gateau l’interface est intuitive et stylee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout majeur le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Savoir plus|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, avec des slots au style innovant. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Lire la version complГЁte|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, accessible a tout instant. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Particulierement attractif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis completement fou de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. La variete des titres est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Pour un demarrage en force. L’assistance est efficace et pro, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi le design est moderne et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter en ligne|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Aller Г la page|
частная психиатрическая клиника стационар
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
консультация психиатра на дому в москве
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots au style innovant. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un autre avantage cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des transactions securisees.
Cliquer pour voir|
Лечение наркомании во Владимире представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на восстановление физического и психического здоровья пациентов с различными формами зависимости от психоактивных веществ. Современные методы терапии, используемые в наркологической клинике «Новая Эра», обеспечивают эффективное и безопасное избавление от зависимости с последующей социальной реабилитацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/klinika-lechenie-narkomanii-vo-vladimire/
Узнавайте события первыми: http://ds1spb.ru
Только проверенные факты: https://neoko.ru
Надёжный источник информации: https://motorradhof.ru
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Частный заем денег мфо домашние деньги альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. A selecao de titulos e uma chama de emocoes. com caca-niqueis que brilham como holofotes. O suporte e uma luz-guia brilhante. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. As transacoes sao faceis como um brilho. entretanto mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. Em resumo, BR4Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o visual e uma explosao de claroes. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
br4bet cГіdigo promocional|
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de emocao. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, com slots modernos e tematicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. O processo e simples e direto, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No geral, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e energetica, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ir ver|
Sou viciado na pista de F12.Bet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao veloz quanto um motor V12. Tem um pit stop de jogos de cassino irados. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de velocidade. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo e claro e sem freadas. em alguns momentos mais bonus seriam um diferencial turbo. Ao final, F12.Bet Casino e um motor de emocoes para os exploradores de jogos online! Alem disso o visual e uma explosao de curvas. fazendo o cassino roncar como um motor.
f12 bet quanto tempo demora para cair na conta|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: roletas animadas, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Vale experimentar.
4play pretty ricky|
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para quem aposta com cripto ! Tambem a interface e fluida e estilosa, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para competicao, que aumenta o engajamento.
https://playpixcasino.pro/|
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
https://bs2bsme.at
ticket show
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
лечение запоя
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um farol na nevoa. A selecao de titulos e uma chama de emocoes. com caca-niqueis que brilham como holofotes. Os agentes voam como claroes. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. mesmo assim mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. No fim das contas, BR4Bet Casino garante um jogo que reluz como um farol para quem curte apostar com estilo iluminado! Por sinal a interface e fluida e brilha como um farol. fazendo o cassino brilhar como um farol.
10|
Je suis accro a Simsinos Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi coloree qu’un studio d’animation. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un storyboard de delices. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cartoon. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un scenariste. garantissant une assistance qui cadence. se deroulent comme une rhapsodie de dessins. occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait cartoon. Au final, Simsinos Casino promet un divertissement de casino anime pour les animateurs du casino! En bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et vibre comme une planche animee. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
simsinos casino|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Recomendo sem medo.
4play herring liplure|
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, leva a um universo de apostas dinamico. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Alem disso a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Um diferencial importante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Visitar hoje|
Amo a energia de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. As opcoes sao amplas como um festival, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Acrescentando que a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para competicao, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ver agora|
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a aider. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. En bref, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir les mises Г jour|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. Le repertoire est riche et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table raffines. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. L’assistance est rapide et precise, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les retraits filent comme une comete, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. Au final, Casinia Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus le design est moderne et eblouissant, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La variete des titres est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le support client est exceptionnel, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement top, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Plongez-y|
concert broadcast
Эффективность лечения зависит от точного диагностирования состояния пациента и выбора оптимальной схемы терапии. Важно обеспечить комплексное сопровождение, включающее поддержку семьи и помощь в адаптации к трезвому образу жизни.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladimire/
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru
Доставка пиццы Воронеже https://pizzeriacuba.ru самая вкусная сочная пицца в городе Воронеж. Доставим пиццу горячей круглочуточно в Воронеже скидки от 3500 рублей. Скидка на самовывоз на каждую пиццу. Доставка бесплатно
Suchen Sie Immobilien? Montenegro immobilie wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
Эта последовательность помогает эффективно воздействовать на зависимость и исключает вероятность усугубления состояния.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-perm-anonimno/
Комплексное применение этих средств ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
sportwetten gratis bonus ohne einzahlung
Feel free to visit my website :: Em Spiele Wetten
Adoro a correnteza de Brazino Casino, explode com uma vibe aquatica eletrizante. A selecao de titulos e uma correnteza de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque aquatico. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. garantindo suporte direto e sem correntezas. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma corrente. mas queria promocoes que explodem como geiseres. Em sintese, Brazino Casino e um recife de emocoes para os fas de adrenalina marinha! Como extra o site e uma obra-prima de estilo subaquatico. amplificando o jogo com vibracao aquatica.
brazino777 de donde es|
Sou viciado no codigo de PlayPix Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um codigo binario em furia. As opcoes sao ricas e piscam como pixels. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como bytes. O suporte e um firewall de eficiencia. respondendo veloz como um byte. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um buffer. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Ao final, PlayPix Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro codigo para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! De lambuja o design e fluido como um render. amplificando o jogo com vibracao digital.
playpix apostas esportivas Г© confiГЎvel|
Acho simplesmente ardente Fogo777 Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um xama. O leque do cassino e um fogo de delicias. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento e solido como carvoes. oferecendo respostas claras como uma chama. Os saques queimam como brasas. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, Fogo777 Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. criando uma experiencia de cassino incendiaria.
fogo777.com paga|
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Je suis envoute par BankOnBet Casino, ca vibre avec une richesse de jeu qui s’empile. La selection du casino est une pile de plaisirs. incluant des tables qui securisent les mises. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui debloque les gains. Withdrawals are swift as a wire transfer. par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient fructifier. Au final, BankOnBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline securisee du casino! Additionally the interface is smooth as a deposit. facilite une experience de casino rentable.
bankonbet ГЁ legale|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de adrenalina. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com slots modernos e tematicos. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. O processo e simples e direto, embora mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Prosseguir a leitura|
Tenho um entusiasmo vibrante por PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer intenso e indomavel. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, no entanto mais rodadas gratis seriam um diferencial. No fim, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para competicao, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ir ver|
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Гаражные ворота
Je suis totalement fou de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et efficace, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. En resume, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout majeur les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©bloquer les dГ©tails|
If you want to learn everything about online platforms in the United States, then this is exactly what you need. Explore the full details via the link at the bottom of the page:
best online casinos
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, offrant des sessions live captivantes. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Le support client est lumineux, offrant des solutions cristallines. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient un plus. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et eblouissant, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires captivants, offre des privileges continus.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. L’assistance est efficace et pro, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
Visiter l’avis|
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Читать
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le support client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Cerise sur le gateau la plateforme est visuellement top, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Ouvrir les dГ©tails|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. Le repertoire est riche et multifacette, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Les agents repondent comme une etoile filante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. Au final, Casinia Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, incite a prolonger l’aventure. Egalement remarquable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des privileges continus.
Visiter le contenu|
Adoro a correnteza de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como conchas. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque aquatico. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. O processo e claro e sem tempestades. porem queria mais promocoes que brilham como corais. Em resumo, Brazino Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro mergulho para quem curte apostar com estilo aquatico! De bonus a navegacao e facil como uma corrente marinha. adicionando um toque de brilho marinho ao cassino.
casino brazino777|
Estou completamente pixelado por PlayPix Casino, parece uma matriz de adrenalina cibernetica. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. com slots tematicos de mundos digitais. O suporte e um codigo preciso. assegurando apoio sem erros. As transacoes sao faceis como um glitch. porem queria mais promocoes que glitcham como retro. Em resumo, PlayPix Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro codigo para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Adicionalmente o design e um espetaculo visual de matriz. dando vontade de voltar como um byte.
cГіdigo promocional playpix|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, avec des slots au design innovant. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. En bref, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et stylee, ajoute une touche de confort. A noter egalement les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Visiter l’avis|
https://b2tsite4.io
Curto demais a chama de Fogo777 Casino, parece um festival de chamas cheio de adrenalina. O leque do cassino e um fogo de delicias. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como brasas. O servico e confiavel como uma fogueira. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques queimam como brasas. em alguns momentos queria mais promocoes que queimam como fogueiras. No geral, Fogo777 Casino e um cassino online que e uma fogueira de diversao para os xamas do cassino! Por sinal o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. criando uma experiencia de cassino incendiaria.
fogo777.com login|
Je suis fou de BankOnBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui accumule comme un compte en banque. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor de delices. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance bancaire. L’assistance du casino est fiable et discrete. responding faster than a bank transfer. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans frais caches. par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un investissement. En somme, BankOnBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! Plus l’interface du casino est fluide et securisee comme un coffre. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
bankonbet casino bonus crab|
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, transporta para um universo de apostas eletrizante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. No geral, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Alem disso a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Explorar a pГЎgina|
Amo a energia selvagem de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer intenso e indomavel. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, com slots de design inovador. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que o site e rapido e cativante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Dar uma olhada|
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Посмотреть всё – https://www.gasthaus-baule.de/2019/03/25/exploring-street-food-in-bangkok
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Доступ к полной версии – https://morayomeblog.com/?p=8
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – http://mrshade.com/events/under-the-skin
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://hayakawasetsubi.jp/2022/07/28/%E3%81%BE%E3%81%9F%E3%81%BE%E3%81%9F%E6%AF%8D%E3%81%AE%E6%89%8B%E4%BD%9C%E3%82%8A%E3%83%A9%E3%83%B3%E3%83%81%E2%98%80%EF%B8%8F%F0%9F%8D%B4
You are one talented writer thank you for the post.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Подробнее – https://apee.bg/%D1%81%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B0-%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BB
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Интересует подробная информация – https://bodytorium.com/merry-christmas-happy-holidays
Estou completamente pixelado por PlayPix Casino, oferece uma aventura que glitcha como um render 8-bit. A colecao e um codigo de entretenimento. incluindo mesas com charme de algoritmo. O time do cassino e digno de um programador. assegurando apoio sem erros. O processo e claro e sem crashes. mesmo assim mais bonus seriam um diferencial de matriz. No geral, PlayPix Casino promete uma diversao que e um glitch para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! De lambuja o design e fluido como um render. dando vontade de voltar como um byte.
playpix ruyter|
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Продолжить чтение – https://fd-performance.com/project/the7-gutenberg-business
Sou viciado no calor de Fogo777 Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um xama. Os jogos formam uma fogueira de diversao. com caca-niqueis modernos que hipnotizam como fogos. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo veloz como uma faisca. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma pira. de vez em quando queria mais promocoes que queimam como fogueiras. No geral, Fogo777 Casino e um altar de emocoes para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a interface e fluida e brilha como uma fogueira. criando uma experiencia de cassino incendiaria.
fogo777.com login|
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детальнее – https://advr.fr/2022/11/21/conference-voves-un-camp-de-concentration-en-france
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Перейти к полной версии – https://okosatellitegame.com/alexlab-games-fr-handcrafted-card-games-for-every-occasion
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Перейти к полной версии – https://cronopiocreativo.com/es/restauradoresdelcorazon
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Получить полную информацию – https://www.ricopy.com.ec/product/toner-mp-c-2003-2503
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://envanlifesimone.com/5-jours-en-auvergne-en-van-amenage
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Подробности по ссылке – https://dating-free-dating.com/2024/09/03/sh-start-high-scam
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://isla4you.com/visum-venezuela
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://3simmo.com/service/promotion-immobiliere
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o pulso. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No fim, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o gramado para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Igualmente impressionante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Explorar o site|
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Открой скрытое – https://dkma.com.br/2023/10/23/praticas-para-proteger-dados-sensiveis
Fiquei fascinado com PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. As opcoes sao amplas como uma selva, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para resolver. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. No geral, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para quem aposta com cripto ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Um diferencial significativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Começar aqui|
занятия в фитнес клубе абонемент в фитнес клуб
фитнес клуб с бассейном адрес фитнес клуба
concerts online
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Casombie, c’est une experience qui reveille les sens. La selection de jeux est terrifiante de richesse, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents repondent plus vite qu’un zombie affame, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont rapides comme un mort-vivant en chasse, cependant plus de promos macabres seraient un plus. En somme, Casombie est une plateforme qui fait battre les c?urs pour ceux qui aiment l’adrenaline sombre ! Par ailleurs le site est visuellement un chef-d’?uvre macabre, amplifie l’immersion dans l’horreur.
casombie casino fi|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un roi. Le repertoire du casino est un donjon de divertissement. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent comme des armures. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un ecuyer. assurant un support de casino immediat et noble. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. En somme, Casinia Casino c’est un casino a conquerir sans tarder pour les chevaliers du casino! Par ailleurs offre un orchestre de couleurs medievales. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie chevaleresque.
casinia casino kostenlos spins|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, propose des recompenses permanentes.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! En outre le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Tout accГ©der|
Наш интернет-магазин был на грани закрытия из-за низких продаж. В середине года обратились в Mihaylov Digital за SEO раскруткой. Специалисты сделали оптимизацию карточек, добавили уникальные тексты и настроили аналитику. Результат — рост заказов и увеличение прибыли https://mihaylov.digital/
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk/
Я давно искал ресурс, где можно получить независимую информацию о крипте, и нашёл его в журнале theHold. Новости, прогнозы, курсы, обзоры бирж и кошельков, калькулятор доходности — всё удобно и понятно. Журнал стал моим основным источником информации: https://thehold.ru/
При острых интоксикациях, абстинентных синдромах или тяжелых состояниях, вызванных злоупотреблением алкоголем или наркотическими веществами, каждая минута играет роль. Нарколог на дом в клинике «БалтикМед» приезжает с необходимым оборудованием и медикаментами для стабилизации состояния, проведения инфузионной терапии и профилактики осложнений. Это позволяет избежать транспортировки пациента в критическом состоянии и сократить время начала лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Обращение за помощью к наркологу на дому имеет ряд преимуществ, особенно в экстренных ситуациях:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в мариуполе[/url]
Сделать мед лицензию стало просто благодаря поддержке Журавлев Консалтинг Групп: специалисты подготовили документы, проконсультировали по всем требованиям, сопровождали процесс и обеспечили контроль за подачей: https://licenz.pro/
Перед применением препаратов проводится обследование, позволяющее исключить противопоказания. Это особенно важно при сопутствующих заболеваниях, таких как сердечно-сосудистые или печеночные патологии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в улан-удэ[/url]
Современные переносные технологии делают домашнее вмешательство сравнимым по качеству с первичным стационаром. Врач работает с инфузоматом (точная скорость капельницы), портативным кардиомонитором, пульсоксиметром, глюкометром и экспресс-панелями электролитов. Это позволяет корректировать терапию «на лету»: менять состав растворов, дозировки седативной поддержки, контролировать давление и насыщение крови кислородом. Особое внимание уделяется профилактике дефицита тиамина и судорожных эпизодов — стандартным рискам при длительном употреблении алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
https://bsmc.at
Tightrope Game – a balance challenge with obstacles. Quick, addictive, and perfect for testing focus: download Tightrope game for free
В журнале Холд удобно, что всё структурировано. Есть разделы по курсам, прогнозам, кошелькам и майнингу. Статьи информативные и полезные. Это лучший гид по крипте https://thehold.ru/
Производство продуктов питания требует чёткой маркировки каждой партии. Мы остановились на оборудовании Labelaire, которое отлично справляется с задачами. В паре с термопринтером для самоклеящихся этикеток мы получили удобный инструмент для ежедневной работы. Эти маркировочные решения полностью соответствуют требованиям отрасли – https://labelaire.ru/
Estou alucinado com Stake Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. oferecendo lives que explodem como ecos. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma onda sonora. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os saques vibram como harpas. em alguns momentos mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Em resumo, Stake Casino garante um jogo que ressoa como um sino para os apaixonados por slots modernos! E mais o site e uma obra-prima de estilo sonoro. adicionando um toque de eco ao cassino.
stake jogos|
По прибытии проводится экспресс-диагностика: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается уровень обезвоживания и неврологический статус; при показаниях выполняется ЭКГ. Врач простым языком объясняет, какие препараты и в каком порядке будут вводиться, отвечает на вопросы и получает информированное согласие.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/]vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-serpuhove[/url]
Acho simplesmente enredado IJogo Casino, e um cassino online que enreda como uma teia de aranha gigante. As opcoes sao ricas e se entrelacam como vinhas. com caca-niqueis modernos que enredam como cipos. O suporte e uma bussola no emaranhado. assegurando apoio sem enredos. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Para encurtar, IJogo Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus o layout e vibrante como uma raiz. fazendo o cassino se entrelacar como uma teia.
ijogo .com|
Кодирование — это медицинская или психотерапевтическая процедура, направленная на формирование у пациента стойкого отвращения к алкоголю и снижение вероятности срыва после лечения. Обычно её проводят после детоксикации, когда организм очищен от токсинов и пациент готов к следующему шагу на пути к трезвости.
Подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-dolgoprudnom/
https://atlan.ru/product-category/mebel/dlya-doma/
J’adore le voile de Grandz Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un fantome gracieux. Le repertoire du casino est un theatre de divertissement. incluant des tables qui dansent comme des fantomes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. resonnant comme une illusion parfaite. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une scene. parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait theatral. En somme, Grandz Casino enchante avec une rhapsodie de jeux pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline voilee du casino! De plus est une cadence visuelle envoutante. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto ephemere.
la grandz recree|
СтройСинтез помог построить наш загородный коттедж из кирпича. Мы выбрали вариант с двумя этажами и гаражом, и все работы были выполнены на высшем уровне. Дом полностью готов для жизни. Ознакомиться с подобными решениями можно по ссылке: https://stroysyntez.com/
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: best Panda themed games Canada
Me impressionei com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com a energia de um estadio lotado. A selecao de jogos e sensacional, com slots modernos e tematicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte preciso e confiavel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. No geral, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Acrescentando que o design e moderno e vibrante, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Descobrir mais|
Estou completamente apaixonado por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. O processo e simples e elegante, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. No fim, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Adicionalmente o site e rapido e cativante, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Abrir agora|
If you are looking for trusted sites in the USA, then this is definitely worth checking out. Check out the full details via the link below:
best online casino
https://bsmen.at
Врач проводит полное обследование и определяет тактику лечения в зависимости от состояния пациента. Важным аспектом является возможность применения комплексных мер, включающих:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad00.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в калининграде[/url]
потолочкин потолки [url=https://stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru/]https://stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru/[/url] .
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
**mindvault**
mindvault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-arkhangelsk/
Врачи клиники «БайкалМед» используют комплексный подход, который включает медикаментозную поддержку, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и восстановление нормального обмена веществ. В зависимости от тяжести состояния выбирается амбулаторная или стационарная форма лечения.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ulan-ude
*Седативные компоненты применяются по строгим показаниям, с мониторингом дыхания и сатурации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ulan-ude0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Этап
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
все микрозаймы [url=www.zaimy-26.ru]все микрозаймы[/url] .
Как работает
Получить больше информации – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-v-vidnom/
Когда проблемы с алкоголизмом достигают критической точки, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Мариуполе квалифицированные наркологи оказывают помощь на дому, обеспечивая оперативную детоксикацию организма, стабилизацию жизненно важных показателей и психологическую поддержку. Такой формат лечения позволяет пациенту получить качественную медицинскую помощь в привычной домашней обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-mariupol0.ru/]нарколог на дом мариуполь[/url]
все самое лучшее тут: https://psihologi-dv.ru/onlajn-konsultaczii-psihologa-klyuch-k-vashemu-psihicheskomu-zdorovyu/
скачать мультфильмы торрент Сериалы 2023 скачать торрент Переживите заново эмоции от просмотра лучших сериалов 2023 года! На нашем сайте вы найдете широкий выбор сериалов, которые покорили сердца зрителей в прошлом году. Мы предлагаем скачать сериалы 2023 торрент в высоком качестве, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться просмотром любимых сериалов в отличном качестве. У нас вы найдете сериалы различных жанров: от захватывающих детективных историй и фантастических саг до комедийных ситкомов и мелодраматических драм. Наша коллекция постоянно пополняется, поэтому вы всегда сможете найти что-то интересное для себя. Благодаря удобной системе поиска и фильтрации вы легко сможете найти нужный сериал по названию, жанру, году выпуска, рейтингу и другим критериям. Скачивайте сериалы 2023 торрент быстро и безопасно с нашего сайта! Мы гарантируем высокое качество файлов и отсутствие вирусов. Наслаждайтесь просмотром лучших сериалов 2023 года в любое время и в любом месте!
По прибытии проводится экспресс-диагностика: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается уровень обезвоживания и неврологический статус; при показаниях выполняется ЭКГ. Врач простым языком объясняет, какие препараты и в каком порядке будут вводиться, отвечает на вопросы и получает информированное согласие.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Алкогольная зависимость — сложная и разрушающая болезнь, которая меняет личность, разрушает здоровье, отношения и карьеру. На определённом этапе становится понятно, что справиться с проблемой самостоятельно невозможно. Здесь требуется комплексный медицинский подход и профессиональная поддержка, позволяющая не только прервать запои, но и закрепить трезвое состояние на длительный срок. Одной из самых востребованных и эффективных процедур считается кодирование — и в наркологической клинике «АльтерМед» в Долгопрудном эта услуга реализуется с максимальным вниманием к деталям, анонимностью и заботой о каждом пациенте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny-v-dolgoprudnom/
Заказ автобуса на час https://povozkin.ru
https://bsm-e.at
Acho simplesmente brabissimo MegaPosta Casino, parece uma avalanche de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial insano. Em resumo, MegaPosta Casino e um cassino online que e um vulcao de diversao para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
codigo promocional megaposta|
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
По прибытии проводится экспресс-диагностика: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается уровень обезвоживания и неврологический статус; при показаниях выполняется ЭКГ. Врач простым языком объясняет, какие препараты и в каком порядке будут вводиться, отвечает на вопросы и получает информированное согласие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/
Estou completamente alucinado por OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma lava ardente, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, com uma ajuda que e puro calor. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Na real, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
osh forum|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, manchmal regelma?igere Promos waren super. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Zusatzlich das Design ist modern und ansprechend, verstarkt die Immersion.
playnvcasino.de|
Tenho uma paixao intensa por BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, as vezes recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e energetica, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter mais|
После выбора подходящей методики врач подробно рассказывает о сути процедуры, даёт письменные рекомендации, объясняет правила поведения и отвечает на вопросы пациента и семьи.
Получить больше информации – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/anonimnoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-dolgoprudnom/
Когда человек оказывается в состоянии алкогольного запоя, самостоятельное преодоление последствий становится практически невозможным. Безопасно выйти из запоя без риска для жизни и здоровья можно только под медицинским наблюдением. В наркологической клинике «Содружество» в Щёлково вывод из запоя проводится круглосуточно, с профессиональной поддержкой, выездом врача на дом и гарантией индивидуального подхода к каждому пациенту. Здесь обеспечивается не только эффективное медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическая поддержка семьи, а также планирование последующего восстановления.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru
Присоединяйтесь к аудитории любителей кино на известном сайте КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-kino1.biz/]https://kinogo-kino1.biz/[/url]). Здесь собрана обширная база, где можно смотреть фильмы и сериалы 2025 и других годов бесплатно, в отличном качестве 720p и без всякой регистрации. На Kinogo вас ждут помимо премьеры, но и золотая классика кино. Это один из топовых онлайн-кинотеатров для поклонников кинематографа.
Метод
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-v-vidnom
Этап
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
По прибытии проводится экспресс-диагностика: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, оценивается уровень обезвоживания и неврологический статус; при показаниях выполняется ЭКГ. Врач простым языком объясняет, какие препараты и в каком порядке будут вводиться, отвечает на вопросы и получает информированное согласие.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov6.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-serpuhov[/url]
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
Метод
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-vidnom/
Кодирование подходит не только для тех, кто страдает тяжёлой зависимостью с частыми рецидивами, но и для тех, кто хочет закрепить результат длительной ремиссии, повысить личную мотивацию, снизить риск срыва и облегчить адаптацию к жизни без спиртного. Решение о выборе методики принимается только после осмотра врача и сбора полного анамнеза.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny-v-dolgoprudnom
организация онлайн трансляций москва [url=https://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu.ru/]zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu.ru[/url] .
организация прямых трансляций [url=http://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu1.ru]http://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu1.ru[/url] .
все займы рф [url=www.zaimy-28.ru]www.zaimy-28.ru[/url] .
Кейндин карьерасы ар бир жаш оюнчуга үлгү.Гарри Кейндин PFA Premier League Team of the Year тизмесине киргени таң калычтуу эмес. Гарри Кейндин карьерасы жана трофейлери тууралуу кеңири маалымат ушул жерде: [url=https://harry-kane-kg.com/]Гарри Кейн расмий сайты[/url]. Анын футбол стили классикалык жана эффективдүү.
Кейндин айлык акысы чоң талкууга себеп болду.
Гарри Кейн жеке жашоосун ачык көрсөтпөйт. Гол киргизүүдө ал өзгөчө инстинктке ээ. Кейндин карьерасы тарыхка кирет. Кейн жаш кезинде деле голдорду көп киргизген. Кейндин статистикасын карасаң, анын чыныгы деңгээлин көрөсүң. Кейндин сүрөттөрү интернетте көп изилденет.
Этап
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-noginske/
https://ibs2site.at
Этап
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe[/url]
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Интересует подробная информация – https://tlcooljc.org/home/about_03-2
concert talk
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Только факты! – https://www.dbasolved.com/2013/06/change-varchar2-to-32k-12c-edition
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Прочитать подробнее – https://www.boxinginsider.com/columns/happened-adrien-broner
Adoro o clima alucinante de MegaPosta Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um vulcao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um estouro, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma tempestade, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
megaposta login|
Estou completamente alucinado por OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, com uma ajuda que e puro calor. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, OshCasino e um cassino online que e uma erupcao de diversao para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro magma, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
contact osh|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Полезно знать – https://www.atlantiquefinance.net/orange-niger
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Обратиться к источнику – https://ebmautokeys.co.uk/hello-world
Tenho uma paixao intensa por BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. As opcoes sao vastas como um campeonato, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto bonus mais variados seriam um gol. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e dinamico, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Aprender como|
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Информация доступна здесь – https://watercoolersuae.com/2024/04/25/understanding-electrical-codes-a-guide-for-diy-enthusiasts
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://millesimeworld.com/blog/gourmet/despensa-natural
https://ru.pinterest.com/pin/1091419290961253073/
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Узнать больше > – https://jerusalemstoneart.com/product/mezuzah-israel
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://napauze.ru/stroitelstvo-100-metrovoi-ofisnoi-bashni-na-belorysskoi-zaversheno-s-operejeniem-grafika-stroitelnaia-gazeta
Остекление балкона под ключ сделали специалисты Окна в СПб. Всё организовано грамотно: замер, проект, монтаж. Балкон получился светлым и уютным. Отличная работа https://okna-v-spb.ru/
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://www.duelband.cz/calligraphy_61
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Обратиться к источнику – https://casadeincentivo.com/index.php/2023/10/10/hola-mundo
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Как это работает — подробно – https://www.adarch.de/filetstuck-2-restaurant-in-berlin-charlottenburg-wilmersdorf-2/file2-03
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://probellacapacitaciones.com/hola-mundo
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
Нужна недвижимость? https://www.nedvizhimost-chernogorii-u-morya.ru/ лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://rijocampers.is/what-do-you-need-to-know-before-traveling-to-iceland
Не стоит медлить с вызовом врача-нарколога, если у человека проявляются тревожные признаки ухудшения состояния. Среди наиболее серьезных симптомов, требующих немедленного вмешательства врача, можно выделить продолжительный запой (более двух дней подряд), частую рвоту, невыносимую головную боль, выраженный тремор рук и тела, повышение артериального давления, нарушение ритма сердца, а также психические нарушения, включая тревогу, галлюцинации и бессонницу. Чем раньше пациент обратится за профессиональной помощью, тем выше шансы избежать серьезных осложнений и быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk0.ru
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Прочесть заключение эксперта – http://www.mirshartenziel.nl/tips-on-how-to-build-an-essay
После диагностики нарколог приступает к основному этапу — инфузионной детоксикации. Препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом тяжести интоксикации, анамнеза и сопутствующих заболеваний. Основу составляют водно-солевые растворы, глюкоза, витаминные комплексы, седативные препараты, гепатопротекторы и нейропротекторы. Инфузии выполняются капельно, медленно, в течение нескольких часов, с постоянным мониторингом состояния пациента. При необходимости используется оксигенотерапия, противорвотные, антиаритмические и противосудорожные препараты. Все растворы стерильны, а расходные материалы одноразовые и соответствуют стандартам качества.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novosibirsk0.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в новосибирске[/url]
https://bsme.cat
https://www.ezega.com/Communities/Forums/ShowThread/36100/Hotel-near-the-train-station-in-Vyborg
тест на хеликобактер SMAS лифтинг SMAS лифтинг – это хирургическая операция по подтяжке лица, направленная на укрепление и подтяжку не только кожи, но и более глубоких слоев тканей, включая SMAS (Superficial Muscular Aponeurotic System) – мышечно-апоневротический слой. SMAS лифтинг обеспечивает более выраженный и долгосрочный эффект омоложения лица.
Sou viciado no brilho de BR4Bet Casino, parece um festival de luzes cheio de adrenalina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo lives que acendem como fogueiras. O suporte e uma luz-guia brilhante. assegurando apoio sem sombras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os fas de adrenalina brilhante! Adicionalmente o design e um espetaculo visual iluminado. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
br4bet baixar|
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um estouro, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, MegaPosta Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
megaposta Г© confiГЎvel|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, ab und an mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die mobilen Apps, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, obwohl mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und elegant, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
playnvcasino.de|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, com slots modernos e tematicos. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Acrescentando que o design e moderno e dinamico, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Explorar o site|
bs2best at Что, еще не слышал о сенсации, сотрясающей глубины даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто торговая марка. Это ориентир в мире, где правят анонимность, скоростные транзакции и нерушимая надежность. Спеши на bs2best.at – там тебя ждет откровение, то, о чем многие умалчивают, предпочитая оставаться в тени. Ты получишь ключи к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от широкой публики. Только для тех, кто посвящен в суть вещей. Полное отсутствие следов. Никаких компромиссов. Лишь совершенство, имя которому Blacksprut. Не дай возможности ускользнуть – стань одним из первых, кто познает истину. bs2best.at уже распахнул свои объятия. Готов ли ты к встрече с реальностью, которая шокирует?
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/
При обращении в клинику «НаркоНет» пациенту предоставляется полный спектр мероприятий, направленных на восстановление организма после запоя. Сначала наш специалист приезжает на дом в течение 30–60 минут после вызова. На месте проводится детальный осмотр: измеряются основные жизненные показатели (давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови), собирается подробный анамнез и оценивается степень интоксикации. Полученные данные позволяют врачу разработать индивидуальный план лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-nizhniy-novgorod000.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому в нижний новгороде[/url]
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
video discussion
Заходите на проверенный сайт КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-kino2.biz/]https://kinogo-kino2.biz/[/url]), если хотите смотреть онлайн кино и сериалы без ограничений. Здесь представлена огромная подборка контента, включая все новинки 2025, без смс, в хорошем качестве HD и без обязательной регистрации. На Kinogo вас ждет не только свежий контент, но и лучшая классика прошлых лет. Сайт уверенно держит планку одного из топовых онлайн-кинотеатров.
sportsbook bonus codes Benefit from a wide range of betting site promos, rewards, perks, prizes, earnings, and more through this promotional link. Join now!
После поступления звонка нарколог оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу и прибывает в течение 30–60 минут. Врач незамедлительно приступает к оказанию помощи по четко отработанному алгоритму, состоящему из следующих этапов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh00.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
По прибытии нарколог проводит подробный первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели и оценивает степень интоксикации. Это позволяет оперативно определить, какие меры необходимы для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa00.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Хочешь пиццу? https://tula.pizzeriacuba.ru быстро, вкусно и горячо! Заказывайте пиццу с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор начинок, свежие ингредиенты, акции и бесплатная доставка по городу.
Bonjour, amis !
Je viens de trouver un contenu exclusif avec les donnees les plus recentes sur le jeu Plinko dans les sites francais.
Si tu t’interesses a Plinko, cette lecture est faite pour toi.
Decouvre tout cela via le lien qui suit :
plinko jeu
Чтобы уменьшить неопределённость, мы придерживаемся прозрачного алгоритма — без многоступенчатых согласований и «перебросов» между специалистами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stoimost-v-himkah/
Цель первого этапа — безопасно снизить интоксикацию и вернуть базовое самочувствие. Инфузионная терапия (регидратация, коррекция электролитов, витамины группы B), защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям. Контроль жизненно важных показателей позволяет корректировать схему «на лету» и сделать прохождение острого периода максимально мягким.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-podolske
https://telegra.ph/Nochnoj-binokl-kupit-moskva-10-14
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
live chatroom
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-usilitel-signala-plameni-honeywell-r7861a-1034-10-12-5
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
флюорография екатеринбург Физиотерапия Физиотерапия – это метод лечения и реабилитации, основанный на использовании физических факторов, таких как тепло, холод, электричество, ультразвук, массаж и лечебная физкультура. Физиотерапия применяется для лечения широкого спектра заболеваний и состояний, включая заболевания опорно-двигательного аппарата, нервной системы, сердечно-сосудистой системы и др.
Давай зафиналим на мировой.
https://telegra.ph/Kvadrokopter-kupit-v-ekaterinburge-10-11
Чет я совсем отупел, немогу найти прилавок, где товар бро, цена, наименование товара? Прайс в студию, на все услуги. От жизни походу отстал, правила поменяли походу, да?
Ich bin suchtig nach Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Raubtier, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und machtig, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad im Busch, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuer lodern. Kurz gesagt ist Lowen Play Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie eine Savanne funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
löwen play pirmasens|
Estou pirando total com JabiBet Casino, parece uma correnteza de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma onda, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia oceanica, aumenta a imersao no cassino como uma onda gigante.
jabibet bangladesh|
Adoro o clima insano de PagolBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que faz tudo tremer. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um trovao, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, PagolBet Casino e um cassino online que e um relampago de diversao para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual vibrante, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um raio.
pagolbet bГґnus|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Community-Events, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, trotzdem mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist modern und ansprechend, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
blsp at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
wetten heute tipps pferderennen tipps
Метод и срок подбираются после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также комбинированные программы. Мы объясняем плюсы и ограничения каждого метода, помогаем подготовиться (диета, анализы, отмена определённых препаратов), а затем сопровождаем пациента в период адаптации к трезвости. Кодирование — часть комплексного плана, а не «волшебная кнопка»: устойчивый результат достигается, когда его дополняют поддерживающая терапия и работа с триггерами.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os saques sao rapidos como um contra-ataque, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e energetica, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para rivalidade, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ir para a web|
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
тоже самое взял ам в данном магазе чтоб не было сплетен тож отпишу за качество думаю мнение от 2 разных людей будет достаточно что бы не было вопросов :speak:
https://telegra.ph/Invertornyj-generator-kupit-10-12-3
НЕ принуждаем вас тут брать, берите, где позволяет бюджет.
https://pikman.info/ PR & Marketing Expertise: Data-Driven Marketing, Paid Search/SEM (Linkedin Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, YouTube Ads, Yandex Ads, Bing Ads), Search Engine Optimization/SEO, Display, Retargeting, Social Media/SMM, Paid Media, Account Based Marketing/ABM, Digital Marketing/Strategy, Data Analytics, Customer Acquisition, Web Marketing, Business Development, Full Stack Marketing, Customer Journey, Content Marketing, A/B Split Testing, Budget Management, Conversational Marketing, Conversion Rate Optimization, Growth Marketing, Multi-Touch Attribution, Copywriting, Data Journalism, Content writing, Visual Storytelling, Brand Identity, Web Design UX/UI, Digital Media, Content Marketing, Demand Generation, Forecasting and Modeling.
Метод и срок подбираются после очного осмотра и исключения противопоказаний. Возможны медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также комбинированные программы. Мы объясняем плюсы и ограничения каждого метода, помогаем подготовиться (диета, анализы, отмена определённых препаратов), а затем сопровождаем пациента в период адаптации к трезвости. Кодирование — часть комплексного плана, а не «волшебная кнопка»: устойчивый результат достигается, когда его дополняют поддерживающая терапия и работа с триггерами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
https://rndirectors.com/author/lupebu568/
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Хороший магазин, все по совести
https://telegra.ph/Kamera-dji-action-5-pro-kupit-10-13-4
По прошествии полутора часов снова вылез джаббер. Малегькая накладка – курьер занят сильно, обещал к 23м сделать (было 21 на тот момент). Да не вопрос 😉 Джаббео выверен, оператор душевный человек, располагает к себе сразу.
Такой подход делает лечение предсказуемым: вы понимаете, что происходит сейчас, чего ждать завтра и как закрепить результат на горизонте недель и месяцев.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-podolske/
Формат
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Привет! Что хочу сказать по поводу работы магазина- просто супер, связались сразу, приняли заказ, обработали и на следующий день он уже в пути. 3 дня и уже у меня. Качество отличное! В общем респект Вам ребята, так держать, не сбавляйте оборотов и хорошо будет всем!
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-kupit-v-tule-10-13-2
за самих представителей нет .
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
indie music
Домашний формат подходит, когда показатели стабильны, а у пациента есть поддержка близких. Врач осматривает, ставит капельницу, оставляет понятные инструкции по режиму, сну, гидратации и «красным флажкам». Если дома становится «узко» по медпоказаниям — переводим в стационар без задержек и лишней бюрократии.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-sajt[/url]
Мы — частная наркологическая служба в Химках, где каждый шаг лечения объясняется простым языком и запускается без задержек. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет жалобы, длительность запоя, хронические диагнозы и принимаемые лекарства, после чего предлагает безопасный старт: выезд на дом, дневной формат или госпитализацию в стационар 24/7. Наши внутренние регламенты построены вокруг двух опор — безопасности и приватности. Мы используем минимально необходимый набор персональных данных, ограничиваем доступ к медицинской карте, сохраняем нейтральную коммуникацию по телефону и не ставим на учёт.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
Что случилось? почему страшно?
https://telegra.ph/Mavic-3-pro-kupit-v-yaroslavle-10-12-2
говорю что все качественно быстро и
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do I lead a powerful team that is shaping the future of B2B Saas go-to-market strategies. My company Pikman.info helps high-growth B2B companies with Demand, Attribution & Analytics, and Revenue R&D by delivering a suite of proprietary research, revenue analytics tools, and GTM experimentation services. Pikman.info helps B2B SaaS companies create and capture demand through paid ads to drive a more qualified pipeline for your sales team. Growth at all costs is over, and sustainable growth is what your SaaS brand needs. That means optimizing for the lowest cost per opportunity, not the lowest cost per lead.
https://friendtalk.mn.co/posts/claim-exclusive
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
Что хочу сказать закладки всегда по высоте.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-radar-detektor-ibox-pulsar-pro-10-12-6
а я яй , я ж отвечаю вам каждый раз как есть возможность, пишут много людей одновременно.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
galaxy продукция [url=kupit-telefon-samsung-2.ru]kupit-telefon-samsung-2.ru[/url] .
ставки прогноз [url=http://stavka-10.ru]http://stavka-10.ru[/url] .
прогнощы [url=http://stavka-11.ru/]http://stavka-11.ru/[/url] .
прогнозы ставок на спорт [url=stavka-12.ru]прогнозы ставок на спорт[/url] .
https://penzu.com/p/54878de828b29087
escort moscow – https://moscowescortclub.com/
Bedpage offers a professional and reliable platform for finding female escorts with ease. The website is easy to navigate, providing detailed and trustworthy listings that ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. I experienced a relaxing and skillful erotic massage that exceeded expectations. Bedpage consistently prioritizes quality, safety, and user satisfaction. For anyone seeking premium companionship, this platform is an excellent choice. Discover experienced providers and unforgettable experiences with Escorts in Las Vegas, and enjoy seamless, professional, and highly satisfying services every time.
Дорогие наши форумчане, мы бы рады с вами пообщаться на разные темы, и стараемся общаться со всеми, и порой просто не хватает времени ведь мы не железные, если вы хотите что то конкретно заказать ася и скайп ждет вас, просто нереальное кол-во народа задают вопросы утром днем и вечером, и вот даже сейчас, мы очень стараемся изменить ситуацию в лучшую сторону. С начала месяца т.е. с 1 июня вы сможете самостоятельно заказывать и оплачивать прямо на сайте, а так же будете видеть наличие продукции.
https://telegra.ph/Bronezhilet-mehler-kupit-10-13-2
ну в
Ислам Махачев боюнча акыркы жаңылыктарды ушул жерден окуп, беттештердин тарыхын жана кыска анализин да карап чыгыңыз.
Картадагы ко-мэйн жана мэйн ивент боюнча да баалуу маалымдамалар кошулду. [url=https://islam-makhachev-kg.com/]https://islam-makhachev-kg.com/[/url] Расмий профилдерге жана Sherdog барактарына туура жол көрсөтөбүз. Коопсуз шилтемелер гана колдонулат. Фанаттар үчүн «эмне күтүүгө болот» бөлүмү беттеш алдындагы маанилүү суроолорго жооп берет. Тарыхый коучинг линиясын, лагерь жаңылыктарын жана спарринг өнөктөштөрүн да карайбыз. Грепплинг жана клинчтеги көрсөткүчтөр статистикалык булактар менен ырасталат.
Медиа бөлүмүндө айрым раунддардагы негизги эпизоддордун GIF/кыска видео талдоосу берилет. Коэффициенттер жана линиялар боюнча кыска гид: ким фаворит, ким андердог — объективдүү маалымат. Тарыхый моменттердин хронологиясы визуал карта түрүндө берилип, оңой кыдырып чыгасыз. Жаңыртуулар тарыхы ачык көрсөтүлүп, өзгөртүүлөр датасы менен белгиленет.
Ich bin suchtig nach Lowen Play Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie eine Savanne tobt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und kraftvoll, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm donnern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitlowe, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Brullen wirkt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Am Ende ist Lowen Play Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Savanne beherrscht fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
löwen play spielhallen|
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de vibe. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet app download|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo PagolBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um raio. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo eletrizante, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma centelha, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, PagolBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro choque para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia eletrica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um raio.
pagolbet|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://yadunewsnation.in/nation/10536
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Узнайте всю правду – https://cosmicdreamcatchers.com/neptune-in-pisces-mystical-dreams
Ich bin absolut hingerissen von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, ab und zu mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino ist definitiv empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Zusatzlich das Design ist modern und ansprechend, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
bs market Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Перейти к полной версии – https://www.expresdoprava.cz/dhl-czech
online betting promo codes Don’t miss out on incredible betting bonus code. You can benefit from risk-free bets and matched deposits. Maximize your winning potential today!
Взял в Москве, ну что могу сказать, или толерантность спала(месяц не курил), или товар лютый, но убрало с первого раза хорошо, потом прикурился, ничего так.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-inzhektor-pitaniya-dlya-aktivnyh-antenn-10-12-5
как-то перехотелось.. что действительно последний товар не очень?
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who was doing a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me lunch simply because I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to discuss this subject here on your web page.
трубчатые радиаторы
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do for PreSeed to Series C SaaS startups: > Develop and implement an online marketing strategy > Implement a monitoring system to track and measure all marketing activities via Looker Studio > Tracking, analysis, optimization, and management development of organic search traffic. > Tracking, analyzing, optimizing, and developing paid traffic (search and advertising companies) across any digital channel. > Analysis and optimization of the conversion of the company’s website and side projects (for example, a blog) > Manage and optimize paid media across any digital channel > Distribute content/messaging via paid to grow pipeline and revenue > Build out engaging ad creative and landing pages > Focus on optimizing the funnel based on pipeline and revenue. > Using modern approaches based on data analysis and data science to provide the best project development strategies and visualization of current processes in the company. > Analysis and optimization of client base processes using data analysis methods science approaches, for example, tracking risk groups that can leave the platform in a short time (churn prevention). > cold outreach, inbound, account-based marketing, content marketing
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e energetica, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Explorar o site|
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Это ещё не всё… – https://aruessussu.com/archives/9486302.html
Онлайн-спортивный http://sportsat.ru портал: актуальные новости, обзоры игр, интервью со звёздами, результаты и аналитика. Следите за событиями в мире спорта каждый день!
Рейтинг лучших подоконников https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru из искусственного камня в Москве. Сравнение брендов, цены, фото и отзывы. Узнайте, какой подоконник выбрать — прочный, стильный и долговечный вариант для вашего интерьера.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Познакомиться с результатами исследований – https://www.heavyhaulagesydney.com/index.php/2020/09/02/slide-1
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
лечение запоя
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Ссылка на источник – http://inspiredbloggersuniversity.tk/post/34
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Узнать больше > – https://trtmechanical.vn/what-is-plastic-cnc-machining-used-for
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Открой скрытое – https://www.albertoandrea.it/news/il-10042
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://southseasimpex.com/south-seas-logo
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Смотри, что ещё есть – http://globalcolor.cl/reinterprets-the-classic-bookshelf
а сюда заглянуть влом ? //legalrc.com/threads/Трипы.588/page-2
https://telegra.ph/Gps-radar-detektor-sho-me-kupit-10-13-4
“Приезжаю и вижу на свету бля что то поххожее на таблетки “
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Подробности по ссылке – https://firstclass-accounting.co.uk/digital-marketing-explained
blsp at Ты еще не в курсе, что порождает бурю в темных водах сети? Blacksprut – это не просто символ. Это квинтэссенция анонимности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной уверенности в каждом действии. Приглашаем на bs2best.at – туда, где шепчут о том, о чем другие предпочитают хранить гробовое молчание. Тебе откроются двери в мир, скрытый от любопытных глаз, доступный лишь избранным, тем, кто понимает истинную цену информации. Ни единой зацепки. Никаких отступлений. Только безупречный Blacksprut, гарант твоей конфиденциальности. Не упусти свой шанс стать первопроходцем – bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои тайны. Достаточно ли ты смел, чтобы заглянуть в бездну правды?
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://www.inocas.com.br/pioneirismo-agricola-fazenda-em-minas-gerais-inova-com-investimento-visionario-em-plantio-de-macauba
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее – https://ferestre-usi.md/?p=294
indie rock
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://njoyradio.gr/?p=8261
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://www.jeanchristophecumin.com/archives/390
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que arrasta tudo. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma onda, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem tempestade. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual aquatica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet login|
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Посмотреть подробности – https://www.wealthgram.ca/business/canadian-election-impact-on-business-grants
Estou pirando com PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, PagolBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma faisca, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
pagolbet bГґnus|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin absolut hingerissen von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, erreichbar zu jeder Stunde. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, manchmal zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Insgesamt, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
playnvcasino.de|
конце концов при курении эйфория
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-dron-mavik-pro-10-12-4
Хороший магазин,норм совместки
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Откройте для себя больше – http://gamemt.net/index.php/2025/02/08/e6-max-%E4%BA%A7%E5%93%81%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D
Try a [url=https://www.vipmassagenuru.com/]happy ending massage[/url] > with two therapists for double pleasure and intimacy.
buchmacher angebote
Take a look at my website; wett tipps hohe quoten
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Узнать больше > – https://shininguttarakhandnews.com/platonic-love-marriage
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. No fim, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Aprender os detalhes|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Для совсем новичков 1 к 15 будет даже много.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-mavik-3-lugansk-10-13
Бро ты бред несёшь!Если читал все посты в этом магазе брали даже модеры этого форума.А может быть ты конкурент и провоцируешь людей специально?
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
bs2best at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
Вся динамика фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения. При переводе в амбулаторную точку мы не «сбрасываем» историю: решения продолжаются с учётом уже сделанного и реакции пациента на вмешательства.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh
Первые два часа после приезда врача — ключевое окно. Мы фиксируем витальные показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?), проводим экспресс-оценку глюкозы, по показаниям — электролитов (Na?/K?), оцениваем дыхательный паттерн и уровень ориентировки. Далее запускается титрованная инфузия через инфузомат с контролем каждые 15–20 минут. Параллельно настраиваются «вечерние опоры»: светогигиена, дыхательные циклы, «тихие окна» связи. В конце визита пациент и близкие получают простую памятку с «зелёными зонами» и кратким планом на 72 часа — когда пить воду, как выбирать тёплую пищу малыми порциями, при каких признаках выходить на связь немедленно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
community theater
Вывод из запоя — это управляемый медицинский процесс, в котором важны скорость запуска, точность вмешательств и тишина вокруг пациента. В наркологической клинике «СтаврВита» мы соединяем капельницы с объективным мониторингом и бережной организацией пространства: приглушённый свет, понятные инструкции без жаргона, «тихие окна» для связи и пошаговый план на первые трое суток. Наша задача — не «перебить» симптомы, а последовательно вернуть предсказуемость: ровный пульс, уменьшающийся тремор, переносимость воды и тёплой пищи малыми порциями, физиологичный сон без тяжёлой седации. Работаем круглосуточно — выездные бригады, амбулаторные слоты без очередей и стационарный блок с ночным постом объединены общей картой наблюдения, поэтому пациент не «начинает историю заново», когда формат меняется.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в ставрополе[/url]
Remarkable things here. I’m very satisfied to peer your post. Thank you so much and I am taking a look forward to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
вход RioBet Casino
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/narkolog-anonimno-stavropol/
Стартовый осмотр должен быть быстрым и осмысленным. Мы исключаем «обязательные» исследования, которые не меняют тактику, и оставляем то, что прямо влияет на состав инфузии, темп, место ведения (дом/амбулатория/стационар) и объём поведенческих рекомендаций. Решения принимаются на свежих цифрах и клинической картине «здесь и сейчас», а повторные замеры назначаются не «по привычке», а по смыслу. Это экономит силы пациента и время команды, а главное — уменьшает фармакологическую нагрузку без потери безопасности.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
Мы сознательно фиксируем не только «медицинские» параметры, но и бытовые маркеры: сколько воды выпито, как переносится тёплая пища малыми порциями, какой свет в комнате перед сном. Эти детали активно упоминаются в клинических рекомендациях, потому что нередко именно они решают исход первой ночи лучше, чем попытка «усилить» таблеткой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
ы меня поняли
https://telegra.ph/Ht-a2-teplovizor-kupit-10-14
последнее время стал закупаться в чемикал и не капельки в этом не пожалел, всё всегда вовремя высылают даже быстрее заявленного времени! качество радует!) да и просто отличный магазин!!!
Register at glory casino and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
Круглосуточный приём означает не просто «дверь открыта 24/7», а способность команды держать безопасный и предсказуемый темп в любой час. Ночью — короткие поведенческие включения и мягкая коррекция тревоги, днём — уточнение витальных и планирования питания/воды, вечером — «световые» правила и дыхательные циклы. За маршрутом следит куратор, благодаря чему переходы между форматами (дом – амбулатория – стационар) проходят без «перезапуска истории»: все данные и договорённости продолжают работать, не требуя заново пересказывать детали.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh-otzyvy
Если ожидаемая динамика «плоская», мы не усиливаем всё сразу. Меняется один параметр: скорость инфузии, порядок модулей или длительность вечерних включений. Такой «тонкий ремонт» безопаснее тотальной перестройки и лучше сохраняет ясность днём.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe15.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Мы комбинируем медицинские и поведенческие технологии так, чтобы каждое вмешательство имело измеримый эффект. Адресные инфузии применяются по клиническому профилю, психообразование переводит субъективные ощущения в факты, а телемедицинские включения помогают пройти «трудный час» без самовольных «усилений» схемы. В таблице ниже — практическая карта: что, зачем и как проверяется на итог.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru
В «Центр Трезвости Воронеж» приватность не обсуждается — она проектируется. Выбор нейтральных формулировок в чеках, немаркированные выезды, «беззвучные» уведомления, отдельные входы и доступ к карте наблюдения только по ролям — это норма, а не «услуга». Пациент может назначить доверенное лицо, чтобы получать краткие апдейты в согласованные временные окна.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe15.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм воронеж[/url]
Изготовление флагов https://flagman-com.ru на заказ — корпоративные, государственные, спортивные и рекламные флаги. Печать любой сложности, качественные материалы, быстрая доставка.
Любишь складчины? складчики войти. Управляйте своими покупками, подписками и профилем. Доступ ко всем материалам и обновлениям в один клик.
Уважаемый клиент, я вам уже не раз писал в личке что от вас у меня заказов не было. Все кто делал заказы уже давно получили свои посылки. Кому вы оплачивали я не знаю.
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-kupit-dlya-ohoty-bu-v-tambove-10-13-4
Отдельный разговор с одной посылкой когда человек менял свое решение и то соглашался ждать посылку, то требовал вернуть деньги.
Если ожидаемая динамика «плоская», врач меняет один параметр и назначает повторную оценку. Такой подход сохраняет ясность днём и снижает вероятность побочных реакций.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Клиника принимает 24/7 без очередей: ночной блок специально настроен под «трудные часы», когда усиливаются панические мысли и реактивность пульса. Для тех, кому легче дома, выездная служба приводит помощь в знакомое пространство; если нужны короткие контрольные включения, применяем видеосвязь вечером (15–20 минут), чтобы корректно настроить ритуалы засыпания, дыхательные циклы и «световые правила». Маршрут фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения — этот документ доступен команде по ролям и защищает от «повторов заново», когда формат меняется (дом – амбулатория – стационар).
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в ставрополе[/url]
Мы комбинируем медицинские и немедикаментозные решения. Инфузионная терапия — адресная, с контролем безопасности; поведенческие опоры — просты и выполняемы в реальной жизни; телемедицина помогает пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и импровизаций. Ниже — ориентиры логики подбора, они не заменяют очный осмотр.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/
Анонимность — не опция, а стандарт: документы формулируются нейтрально, чеки не содержат «говорящих» формулировок, фото- и видеосъёмка исключены. При необходимости подписывается расширенное соглашение о конфиденциальности. Доступ к записи визита и параметрам процедуры разграничен по ролям; копии передаются по защищённому каналу и удаляются по регламенту хранения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk15.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость — сложная и разрушающая болезнь, которая меняет личность, разрушает здоровье, отношения и карьеру. На определённом этапе становится понятно, что справиться с проблемой самостоятельно невозможно. Здесь требуется комплексный медицинский подход и профессиональная поддержка, позволяющая не только прервать запои, но и закрепить трезвое состояние на длительный срок. Одной из самых востребованных и эффективных процедур считается кодирование — и в наркологической клинике «АльтерМед» в Долгопрудном эта услуга реализуется с максимальным вниманием к деталям, анонимностью и заботой о каждом пациенте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-v-dolgoprudnom/
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do for PreSeed to Series C SaaS startups: > Develop and implement an online marketing strategy > Implement a monitoring system to track and measure all marketing activities via Looker Studio > Tracking, analysis, optimization, and management development of organic search traffic. > Tracking, analyzing, optimizing, and developing paid traffic (search and advertising companies) across any digital channel. > Analysis and optimization of the conversion of the company’s website and side projects (for example, a blog) > Manage and optimize paid media across any digital channel > Distribute content/messaging via paid to grow pipeline and revenue > Build out engaging ad creative and landing pages > Focus on optimizing the funnel based on pipeline and revenue. > Using modern approaches based on data analysis and data science to provide the best project development strategies and visualization of current processes in the company. > Analysis and optimization of client base processes using data analysis methods science approaches, for example, tracking risk groups that can leave the platform in a short time (churn prevention). > cold outreach, inbound, account-based marketing, content marketing
Когда человек оказывается в состоянии алкогольного запоя, самостоятельное преодоление последствий становится практически невозможным. Безопасно выйти из запоя без риска для жизни и здоровья можно только под медицинским наблюдением. В наркологической клинике «Содружество» в Щёлково вывод из запоя проводится круглосуточно, с профессиональной поддержкой, выездом врача на дом и гарантией индивидуального подхода к каждому пациенту. Здесь обеспечивается не только эффективное медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическая поддержка семьи, а также планирование последующего восстановления.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/skoryj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-shchelkovo/
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Особенно понравился раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в ставрополе[/url]
Мы собираем терапию из проверенных модулей: гидратация, коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям, поведенческие интервенции (свет, тишина, дыхание 4–6, стимул-контроль, вечерние ритуалы). Объём и темп зависят от ведущего симптома и времени суток: при кардиореактивном вечере больше внимания уделяется среде, при тошноте — гастропротекции и «тёплому питанию», при поверхностном сне — цифровой гигиене и световым сценариям. Ниже приведена ориентировочная матрица выбора; финальное решение — за лечащим врачом с учётом противопоказаний и лекарственных взаимодействий.
Получить больше информации – http://
Современные приложения для обработки изображений являются всё более удобными.
Они применяют AI-технологии для автоматической коррекции изображений.
С помощью таких программ можно изменить освещение на фото без опыта.
Это экономит время и предлагает высокое качество.
бот оголяющее тело
Большинство пользователи выбирают такие сервисы для контента.
Они дают возможность создавать профессиональные фотографии даже в домашних условиях.
Использование таких систем простое, поэтому с ними просто редактировать.
Эволюция нейросетей делает фотообработку эффективной для широкой аудитории.
официальные займы онлайн на карту бесплатно [url=http://zaimy-30.ru]официальные займы онлайн на карту бесплатно[/url] .
но чет с каждым разом доставка все дороже и дороже(((
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-arkon-25-kupit-10-13
Всем добра! Вчера позвонил курьер, сказал, что посылка в городе! Через пару часов я был уже на почте, забрав посылку, сел в машину, но вот поехать не получилось т.к. был задержан сотрудниками МИЛИЦИИ!!!! Четыре часа в отделении и пошёл домой!!! Экспертиза показала, что запрета нет, но сам факт приёмки очень напряг!!! Участились случаи приёмки на данной почте!!!!! Продаванам СПАСИБО и РЕСПЕКТ за чистоту реактивов!!! Покупатели держите ухо востро!!!!!!!!!! Больше с этой почтой не работаю(((( Если у кого есть опыт по схемам забирания пишите в личку!!!
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
blsp at Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
Register at https://gloryscasino-bd.com/ and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
купить диплом в железногорске [url=www.rudik-diplom5.ru]www.rudik-diplom5.ru[/url] .
live session
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do I lead a powerful team that is shaping the future of B2B Saas go-to-market strategies. My company Pikman.info helps high-growth B2B companies with Demand, Attribution & Analytics, and Revenue R&D by delivering a suite of proprietary research, revenue analytics tools, and GTM experimentation services. Pikman.info helps B2B SaaS companies create and capture demand through paid ads to drive a more qualified pipeline for your sales team. Growth at all costs is over, and sustainable growth is what your SaaS brand needs. That means optimizing for the lowest cost per opportunity, not the lowest cost per lead.
https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-teplovizor-glyadelku-kupit-10-11
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детальнее – https://www.nfhl.nl/greatlakes
С целью организации идеального кинопросмотра советую – КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-films2.biz/]https://kinogo-films2.biz/[/url]). Управление и структура очень удобны. Я лично успешно посмотрел множество новинок 2025 года на Kinogo, и всё это – абсолютно бесплатно и в стабильно высоком качестве. Идеальный способ смотреть фильмы без лишних усилий.
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя калининград[/url]
Si vous voulez tout savoir sur les plateformes en France, alors c’est un incontournable.
Consultez l’integralite via le lien suivant :
casino en ligne
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
Register at glory casino download and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
купить диплом в сочи [url=http://www.rudik-diplom4.ru]купить диплом в сочи[/url] .
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Секреты успеха внутри – https://www.uppveda.se/2021/07/17/loppis-och-kafe-pa-logen-lordagen-den-17-juli-10-1600
Наркологическая клиника «СтаврМедЦентр» — это пространство точной и бережной медицины, где каждая программа лечения зависимостей собирается индивидуально: от первой оценки рисков до стабилизации сна, восстановления аппетита, нормализации пульса и долгосрочной профилактики рецидива. Мы сознательно уходим от шаблонных «сильных» процедур в пользу управляемых шагов: минимум фармакологической нагрузки при максимальной прозрачности решений. Такой подход снижает тревогу, возвращает ощущение контроля, а главное — делает процесс предсказуемым для пациента и его близких. Команда работает круглосуточно: амбулаторные визиты без очередей, немаркированные выезды на дом, стационарный блок с ночным постом и мониторингом — все каналы связаны единой картой наблюдения и общими клиническими протоколами.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в ставрополе[/url]
Ниже — структурированная карта экстренного выезда. Она помогает пациенту и семье понимать, что происходит в каждый отрезок времени, какие цели мы преследуем и по каким критериям двигаемся дальше.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
«СтаврМедЦентр» собирает лечение из коротких модулей с понятными целями: быстро стабилизировать соматику, вернуть управляемый сон, снизить реактивность вечера, обучить «перехвату» импульса и закрепить это в спокойной рутине. Фармакологию используем дозированно, опираясь на витальные показатели и переносимость; поведенческий контур запускаем сразу: свет, вода, дыхание, цифровая гигиена, семейные договорённости. Ниже — ориентировочная архитектура маршрута. На практике последовательность и длительность настраиваются под конкретного человека и его среду.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ставрополь[/url]
https://interiordoorsua.blogspot.com/2025/08/gibkaya-planirovka.html
Вся динамика заносится в единую карту наблюдения, доступ к которой разграничен по ролям. При переходе к амбулаторной точке или стационару не происходит «перезапуска истории»: новые назначения учитывают всё, что сделано на старте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-mavik-3-pro-v-luganske-10-13-3
Анонимность — не опция, а стандарт: документы формулируются нейтрально, чеки не содержат «говорящих» формулировок, фото- и видеосъёмка исключены. При необходимости подписывается расширенное соглашение о конфиденциальности. Доступ к записи визита и параметрам процедуры разграничен по ролям; копии передаются по защищённому каналу и удаляются по регламенту хранения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk15.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Карта делает решения прозрачными: если критерий не достигнут, меняется ровно один параметр с назначением новой точки контроля. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и уменьшает общую фармаконагрузку без компромиссов по безопасности.
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk15.ru/
Если на телефонном этапе звучат «красные флаги» — одышка, спутанность, «скачущий» ритм, повторная рвота — мы предлагаем короткое окно интенсивного наблюдения. При низких рисках стартуем амбулаторно или с выезда на дом, а вечером используем короткие видеовставки по 15–20 минут, чтобы пройти «трудный час» без импровизаций.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в калининграде[/url]
купить диплом в новом уренгое [url=www.rudik-diplom14.ru/]www.rudik-diplom14.ru/[/url] .
Мы работаем с вниманием к деталям повседневности: как человек засыпает на фоне вечернего света, сколько воды переносит малыми глотками, как реагирует на цифровые уведомления, есть ли привычные «включатели» тяги и как на организм влияет шумное окружение. Врач и куратор переводят этот жизненный контекст в ясные, измеримые ориентиры: время до сна, число пробуждений, вариабельность пульса к сумеркам, объём воды, аппетит, переносимость тёплой мягкой пищи. Решения принимаются адресно и последовательно, чтобы сохранять ясность днём и избегать ненужной фармаконагрузки.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/kaliningrad-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Этап вывода из запоя
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинская или психотерапевтическая процедура, направленная на формирование у пациента стойкого отвращения к алкоголю и снижение вероятности срыва после лечения. Обычно её проводят после детоксикации, когда организм очищен от токсинов и пациент готов к следующему шагу на пути к трезвости.
Детальнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-dolgoprudnom/
купить диплом техникума в смоленске [url=https://frei-diplom11.ru/]купить диплом техникума в смоленске[/url] .
Если ожидаемая динамика «плоская», мы не усиливаем всё сразу. Меняется один параметр: скорость инфузии, порядок модулей или длительность вечерних включений. Такой «тонкий ремонт» безопаснее тотальной перестройки и лучше сохраняет ясность днём.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe15.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
Экстренная наркологическая помощь в Туле: капельница для избавления от запоя Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезный недуг, который нуждается в квалифицированной помощи. Нарколог на дом предоставляет услуги, такие как капельница от запоя, способствующая восстановлению организма после продолжительного употребления алкоголя. К основным симптомам алкогольной зависимости относятся: дрожь, повышенная потливость и чувство тревоги. Лечение запоя включает в себя дезинтоксикацию и реабилитацию организма. Консультация нарколога поможет определить подходящий план лечения алкоголизма. Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме, направленная на выведение из запойного состояния, может предотвратить серьезные последствия. Профилактика запоев и психотерапия для зависимых — важные аспекты лечения зависимостей, которые обеспечивают долгосрочные результаты. Наркологические услуги в Туле предоставляются круглосуточно, что позволяет вам получить помощь в любое время суток. Не откладывайте лечение — обратитесь к специалистам уже сегодня!
Мы комбинируем медицинские и поведенческие технологии так, чтобы каждое вмешательство имело измеримый эффект. Адресные инфузии применяются по клиническому профилю, психообразование переводит субъективные ощущения в факты, а телемедицинские включения помогают пройти «трудный час» без самовольных «усилений» схемы. В таблице ниже — практическая карта: что, зачем и как проверяется на итог.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh-otzyvy/
Если при телефонном триаже выявляются «красные флаги» (дыхание, ритм, сознание), маршрут настраивается сразу под стационар: те же цели, тот же ответственный куратор, только непрерывный мониторинг витальных и ночной пост. А когда риски невысоки, мы начинаем дома или амбулаторно и удерживаем темп контрольными включениями — это чаще всего даёт спокойную первую ночь и легче переносимый второй день.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-stavropol/https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru
Если на триаже выявляются риски (дыхание, спутанность, нестабильный ритм), предлагаем короткое стационарное окно мониторинга. При низких рисках стартуем амбулаторно или на дому, а вечером подключаем короткие видеовставки по 15–20 минут. Переходы между форматами не «сбрасывают» процесс: единая карта наблюдения обеспечивает непрерывность и точность решений.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh-otzyvy
Мы комбинируем медицинские и поведенческие технологии так, чтобы каждое вмешательство имело измеримый эффект. Адресные инфузии применяются по клиническому профилю, психообразование переводит субъективные ощущения в факты, а телемедицинские включения помогают пройти «трудный час» без самовольных «усилений» схемы. В таблице ниже — практическая карта: что, зачем и как проверяется на итог.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог воронеж[/url]
Универсальной «сильной капельницы» не существует. Состав подбирается по ведущим симптомам и переносимости; важен не только «чем», но и «когда», особенно в сумерки. Примеры ниже — ориентир для понимания логики. Реальная схема собирается индивидуально.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в воронеже[/url]
https://plisio.net/th/blog/how-to-short-crypto
Estou louco por Richville Casino, parece um banquete de opulencia e diversao. Tem uma cascata de jogos de cassino fascinantes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como joias. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, com uma ajuda que reluz como ouro. Os pagamentos do cassino sao seguros e impecaveis, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que brilhem como diamantes. No fim das contas, Richville Casino e um cassino online que exsuda riqueza para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino reluz com um estilo digno de um palacio, torna a experiencia de cassino um evento de gala.
payday loans in richville ny|
Sou louco pelo batuque de RioPlay Casino, e um cassino online que samba como uma escola de carnaval. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um desfile na avenida, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. No geral, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e vibrante como uma escola de samba, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
rioplay games roblox lite|
https://telegra.ph/Detektor-dronov-bulat-v4-10-14-2
Экстренный вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «ВоронежВита» мы действуем по чётким правилам: от телефонного триажа и тихого выезда бригады до адресной детоксикации и вечерних контрольных включений. Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить тремор и тошноту, выровнять сердечный ритм и вернуть физиологичный сон уже в первые ночи. Мы выбираем минимально достаточные вмешательства, чтобы днём сохранялась ясность и не возникало желания «самостоятельно усилить» схему. Конфиденциальность встроена в каждый шаг: гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: poquer estrategico, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que raramente vi. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
celular motog 4play|
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas vibrantes. Com um bonus extra para comecar. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, as vezes recompensas adicionais seriam festivas. No final, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Adicionalmente a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para competicao, oferece recompensas continuas.
Obter mais|
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Режим 24/7 — это не только открытая дверь, но и правильно расставленные акценты по часам суток. Ночью — больше поведенческих опор и короткие видеовставки, днём — контроль витальных, уточнение плана гидратации и питания, вечером — «световые правила» и дыхательные циклы. В каждом окне мы знаем, что именно проверяем и что считаем успехом: так исчезают импровизации и ненужные «усиления», а пациент получает предсказуемую траекторию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/narkolog-stavropol
bs market Готов узнать, что творится в глубинах тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это символ анонимности, скорости и безопасности, а не просто бренд. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не говорить. Тебе откроют все тайны, скрытые от посторонних глаз. Только для посвящённых. Никаких следов. Никаких полумер. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс быть впереди — bs2best.at ждёт тех, кто готов к новому. Осмелишься ли ты узнать истину?
Запой — это не просто многодневное употребление алкоголя, а тяжёлое нарушение обмена веществ, работы сердца, нервной системы и внутренних органов. Без медицинской помощи резко возрастает риск развития осложнений: делирий, судороги, инсульт, сердечная недостаточность, тяжёлое обезвоживание и нарушения психики. Симптомы могут прогрессировать в любое время, причём угроза для жизни появляется внезапно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo-stacionar[/url]
Режим 24/7 — это не только открытая дверь, но и правильно расставленные акценты по часам суток. Ночью — больше поведенческих опор и короткие видеовставки, днём — контроль витальных, уточнение плана гидратации и питания, вечером — «световые правила» и дыхательные циклы. В каждом окне мы знаем, что именно проверяем и что считаем успехом: так исчезают импровизации и ненужные «усиления», а пациент получает предсказуемую траекторию.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/
free bet codes Best betting promo codes allow you to supercharge your bets and boost your bankroll. Claim enhanced odds, free bets, and VIP rewards. Start your winning journey today!
Ниже — «скелет» визита. На месте врач адаптирует содержание под возраст, соматику, текущие лекарства и проявления абстиненции. Главная идея — быстро получить цифры, аккуратно запустить инфузию и заранее зафиксировать ориентиры, чтобы семья не импровизировала в «трудный час».
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно ставрополь[/url]
Алгоритм на выезде помогает убрать импровизации, а семье — понимать, что будет происходить и по каким признакам мы двигаемся дальше. Он гибкий, но всегда прозрачный: каждый шаг имеет цель, инструмент и критерий успеха.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizory-binokl-kupit-opticstrade-com-10-12
Кодирование — это медицинская или психотерапевтическая процедура, направленная на формирование у пациента стойкого отвращения к алкоголю и снижение вероятности срыва после лечения. Обычно её проводят после детоксикации, когда организм очищен от токсинов и пациент готов к следующему шагу на пути к трезвости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма выезд на дом[/url]
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Запой – это серьезное состояние‚ требующее профессионального вмешательства. Клиника Нарколог на дом предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя и лечению алкогольной зависимости. Важно понимать‚ что алкоголизм не только физическая‚ но и психологическая проблема. В таких кризисных ситуациях крайне важно обратиться к специалисту. Психология играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. С помощью психотерапии можно выявить корни зависимости и научиться новым моделям поведения. Связь между семьей и алкоголем часто бывает сильной‚ поэтому поддержка родных очень важна. Наши специалисты применяют комплексный подход: медицинские услуги комбинируются с психологической поддержкой‚ что значительно уменьшает вероятность рецидива. Для профилактики рецидивов важно сотрудничество как с психотерапевтом‚ так и с наркологом. Помощь на дому позволяет создать комфортные условия для пациента‚ что существенно ускоряет процесс восстановления.
купить диплом в воткинске [url=http://rudik-diplom15.ru/]купить диплом в воткинске[/url] .
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Полная информация здесь – https://www.mesotheliomatadvice.com/mesothelioma-lawsuits
https://telegra.ph/Benzogenerator-kupit-2kv-10-12-4
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Полная информация здесь – https://omsteel.co/valves-pumps-mounting-brackets-forged-rings
Запой — это не просто многодневное употребление алкоголя, а тяжёлое нарушение обмена веществ, работы сердца, нервной системы и внутренних органов. Без медицинской помощи резко возрастает риск развития осложнений: делирий, судороги, инсульт, сердечная недостаточность, тяжёлое обезвоживание и нарушения психики. Симптомы могут прогрессировать в любое время, причём угроза для жизни появляется внезапно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-shchelkovo6.ru/pomoshch-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-shchelkovo/
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
hip
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Не упусти важное! – https://bambou-gers.fr/bonjour-tout-le-monde
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Подробнее – https://chikakimisato.com/archives/264
https://telegra.ph/Mavic-3-teplovizor-kupit-10-13-4
После выбора подходящей методики врач подробно рассказывает о сути процедуры, даёт письменные рекомендации, объясняет правила поведения и отвечает на вопросы пациента и семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-dolgoprudnyj6.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма на дому[/url]
https://www.zazzle.com/mbr/238881946455640506
Лечение зависимости: вызов нарколога на дом Проблема наркотической зависимости требует внимательного и профессионального подхода. Важно помнить, что лечение наркомании начинается с консультации нарколога. Полную информацию о вызове нарколога на дом вы найдете на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru. Процесс лечения включает детоксикацию и психологическую поддержку. Реабилитация зависимых часто бывает необходима и включает индивидуальные программы восстановления. Конфиденциальное лечение создает условия комфорта и безопасности для пациента. Домашняя терапия предоставляет необходимую помощь и особенно важна для тех, кто испытывает стеснение при обращении в медицинские учреждения. Лечение алкогольной зависимости также доступно на дому, что способствует быстрейшему восстановлению. Помощь квалифицированного специалиста – залог успешной борьбы с зависимостями.
Такая карта делает лечение обозримым и дисциплинирует решения: пациент видит цель и порог перехода, семья понимает, зачем нужно соблюдать «тихие» часы, команда сохраняет управляемость и не «крутит ручки» ночью.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk/
Acho simplesmente magnifico Richville Casino, parece um banquete de opulencia e diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um tesouro reluzente, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, com uma ajuda que reluz como ouro. Os pagamentos do cassino sao seguros e impecaveis, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria chique. No geral, Richville Casino promete uma diversao de cassino reluzente para os jogadores que adoram apostar com classe! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como um salao de baile, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
richville login|
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://www.arbrent.com/onde-conseguir-a-sua-licenca-sanitaria-no-df
music event
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Читать далее > – https://melinascumburdis.com.ar/dscn7063
Estou completamente encantado por RioPlay Casino, e um cassino online que samba como uma escola de carnaval. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de escola de samba, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. No geral, RioPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e vibrante como uma escola de samba, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
rioplay games roblox lite download|
Galera, vim dividir minhas impressoes no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
4play gentlemen|
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-takticheskie-bercy-solomon-10-12-5
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Обратиться к источнику – https://grill-profi.ch/produkt/grillanzunder
Amo a atmosfera de BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com emocao atletica. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte preciso e rapido. O processo e simples e direto, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um gol. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Outro destaque o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ver os detalhes|
Estou completamente encantado por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, oferecendo jogos de mesa imersivos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, as vezes recompensas adicionais seriam festivas. No final, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que reina suprema para fas de cassino online ! Tambem a interface e fluida e elegante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com 5 niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver o site|
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – https://altec.ch/business1
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Подробности по ссылке – https://www.londonbreastcarecentre.com/home_1_ar
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Детали по клику – https://www.imecba.com/2015/11/27/helping-children-deal-with-trauma
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Продолжить изучение – https://mezzani.com.br/produto/massa-para-lasanha-1-kg
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Прочитать подробнее – https://bytosoft.com/digital-marketing-concepts-easy-steps-for-digital-marketing-varanasi
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Провести детальное исследование – https://listing.downtown-directory.com/rtl-version/product/%D8%B1%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%8A-%D8%AA%D9%8A-%D8%B4%D9%8A%D8%B1%D8%AA-%D8%A3%D8%B2%D9%8A%D8%A7%D8%A1-sportex-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B5%D9%8A%D9%81-%D8%A3%D8%B1%D9%8A%D9%81%D8%A7%D9%84
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://hankoshokunin.com/attachment-0-6
В Кухни в Дом заказали кухонный гарнитур для квартиры-студии. Специалисты грамотно подошли к организации пространства, и кухня получилась стильной и удобной. Теперь даже маленькая площадь используется максимально эффективно https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Как достичь результата? – https://inputovanja.ba/index.php/2019/07/26/venecija-trazi-da-bude-na-listi-ugrozenih-destinacija
https://plisio.net/pt/blog/telegram-scams
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Не упусти важное! – https://noa-kazusa.com/newstaff
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Не упусти шанс – https://sharktanktalesindia.com/fashion/the-heart-of-nintendos-new-console-isnt-the-switch
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Прокапывание на дому в Красноярске — это комфортный вариант для тех, кто нуждается в медицинских услугах, но не может посетить клинику. Это включает в себя инфузионную терапию, где медсестра на дому осуществляет инфузии на дому. Это очень важно для восстановления после болезни или при необходимости медикаментозной терапии. Удобство лечения и уход за пациентами вырастает, когда квалифицированный врач посещает вас на дому. Профилактика заболеваний и назначения врача также становятся более доступными. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru предлагает такие услуги, обеспечивая комфорт и здоровье для всех нуждающихся.
https://telegra.ph/Mavic-air-akkumulyator-kupit-10-11
Складчик стал для меня лучшим способом покупать курсы. Участвовал в нескольких складчинах и всегда был доволен. Доступ открылся быстро, материалы полные. Очень радует разнообразие тем. Экономия до 99%. Сервис прозрачный и надежный. Теперь пользуюсь постоянно https://v27.skladchik.org/
Adoro o balanco de BRCasino, parece uma festa carioca cheia de axe. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de carnaval. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, BRCasino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um desfile visual vibrante, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
br77 apk|
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Подробнее
Adoro o clima explosivo de JabiBet Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira onda. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como surfar, aumenta a imersao no cassino como uma onda gigante.
jabibet|
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://thebeardedplantguy.com/reviews
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Уточнить детали – https://www.rowanmangan.com/the-great-turning
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Recomendo sem medo.
loja 4play|
подготовка проекта перепланировки квартиры [url=www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru]www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru[/url] .
перепланировка комнаты [url=www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/]www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/[/url] .
согласование [url=www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru]согласование[/url] .
bs2best at Готов узнать, что творится в глубинах тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это символ анонимности, скорости и безопасности, а не просто бренд. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не говорить. Тебе откроют все тайны, скрытые от посторонних глаз. Только для посвящённых. Никаких следов. Никаких полумер. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс быть впереди — bs2best.at ждёт тех, кто готов к новому. Осмелишься ли ты узнать истину?
https://katellkeinegcom.wordpress.com/
Amo a vibracao de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer carnavalesco. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. Com um bonus extra para comecar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para ajudar. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, as vezes mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. No final, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso o design e moderno e vibrante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ver a pГЎgina|
Tenho uma paixao intensa por BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, suportando jogos adaptados para criptos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os saques sao rapidos como um sprint, embora mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que o site e veloz e envolvente, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Descobrir mais|
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://matronastore.com/product/lotus-flower-earrings
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Полная информация здесь – https://todaytazakhabar.com/tag/iphone-charging-cable
https://telegra.ph/Benzogenerator-s-ehlektrostarterom-3-kvt-kupit-10-12
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://todaytazakhabar.com/tag/iphone-charging-cable
Key recommendation: always buy fifa coins with clear refund policies and dispute resolution procedures outlined before completing transactions. Real active sellers with fast delivery and non drop warranties provide transparent terms that protect buyers throughout the entire purchasing process professionally.
«Частный Медик 24» в стационаре помогает начать жизнь заново — с чистого листа, без последствий запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://vitamagazine.com/2024/10/02/stardust-roller-rink-is-back-in-b-c-win
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
https://telegra.ph/Usilitel-signala-wifi-keenetic-kupit-10-11
Если вам важно узнать, как безопасно и эффективно выйти из состояния запоя с учетом физиологии, психики и внешнего окружения — загляните в статью «Выход из запоя» на сайте Nalatty. Она оформлена в привычном формате полезных советов, пропитанном заботой и доступностью, присущей проекту «семейный очаг». Подробнее тут – http://krd.best-city.ru/forum/thread110110/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево нижний новгород[/url]
В стационаре пациент получает и физиологическую помощь, и психологическое сопровождение, что важно для долгосрочного восстановления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя самара[/url]
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Открыть полностью – https://jehlopes.com.br/ola-mundo
bs2best зеркало Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
https://telegra.ph/Kaska-shlem-voennaya-kupit-10-13-3
hop live
Программа вывода из запоя в Воронеже от «Частного Медика 24» включает не только устранение физической зависимости, но и работу по восстановлению сна, гидратацию, лекарственную поддержку, а также психотерапию, чтобы помочь справиться не просто с запоем, но и с причинами, которые к нему привели.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru[/url]
Me enredei no algoritmo de PlayPix Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um hacker. A selecao de titulos e um buffer de prazeres. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e um codigo preciso. assegurando apoio sem erros. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. porem mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura cibernetica. No geral, PlayPix Casino e uma onda de adrenalina digital para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! Adicionalmente a navegacao e facil como um buffer. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um glitch.
como jogar na roleta playpix|
Estou completamente apaixonado por Brazino Casino, e uma mare de diversao que brilha como perolas. A selecao de titulos e uma correnteza de emocoes. oferecendo lives que explodem como um geiser. O suporte e um farol subaquatico. respondendo veloz como uma mare. As transacoes sao faceis como uma onda. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam subaquaticos. Na real, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o layout e vibrante como uma perola. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura marinha.
brazino777 x|
Ich finde absolut krass JackpotPiraten Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbandigen Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und mitrei?end, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Kanonen donnern. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und top, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Sabelhieb. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein echter Schatz. Insgesamt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf krasse Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jackpotpiraten bonus code|
Estou pirando com SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma rainha de bateria, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, SambaSlots Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e vibrante como uma escola de samba, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
casino gratuit la sambaslots|
https://telegra.ph/Dji-neo-ekaterinburg-kupit-10-14
Как выбрать клинику для восстановления после запоя в Красноярске При возникновении проблемы запоя важно понимать‚ как верно подобрать клинику для реабилитации. В Красноярске доступны наркологические услуги‚ включая детоксикацию и лечение алкоголизма. нарколог на дом круглосуточно Красноярск Важно обратить внимание на возможность вызова нарколога на дом круглосуточно; это обеспечит получение необходимой медицинской помощи прямо в домашних условиях‚ что очень удобно в экстренных ситуациях. Кроме того‚ необходимо учитывать анонимность лечения‚ чтобы исключить стресс и стигматизацию. Выбирая клинику‚ уточните‚ какие программы реабилитации предлагает учреждение. Эффективные методы‚ такие как кодирование от алкоголизма и психологическая поддержка‚ помогут в восстановлении. Не забывайте о поддержке семьи – это важный аспект успешного лечения зависимостей. Обращение за консультацией к наркологу поможет выбрать наиболее оптимальный план лечения для вашего случая. Выбор клиники в Красноярске – это серьезный шаг к здоровой жизни.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Je trouve absolument fantastique 7BitCasino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, occasionnellement les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. En resume, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et retro, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino free spins|
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No fim, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Começar aqui|
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
https://telegra.ph/Gde-kupit-teplovizor-v-moskve-10-13-3
https://plisio.net/id/blog/rare-dollar-bills
https://plisio.net/tr/blog/gamification
Строительство складов https://velestent.ru и ангаров в Москве под ключ. Быстровозводимые конструкции, металлокаркасы, проектирование и монтаж. Качество, надёжность и соблюдение сроков.
Слитые курсы ЕГЭ купить https://courses-ege.ru
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar28.ru
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-benzogenerator-honda-eg5500cxs-cena-10-13-3
https://clocks-top.com/
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Relax with a [url=https://www.nurumassagevip.com]best vip massage[/url] for smooth, slippery, and sensual pleasure.
bs2best зеркало Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
https://plisio.net/de/blog/what-is-crypto-custody
https://telegra.ph/Lazernyj-dalnomer-kupit-10-14
Заходите на популярный сайт КИНОГО ([url=https://kinogo-films1.biz/]https://kinogo-films1.biz/[/url]), если хотите наслаждаться кино и сериалы в удобное время. Здесь представлена обширная база контента, включая премьеры 2025, абсолютно бесплатно, в высоком качестве 1080p и без обязательной регистрации. На Kinogo вас ждет не только актуальный контент, но и богатая коллекция прошлых лет. Ресурс уверенно держит позиции одного из лучших киносайтов.
В момент вызова важно сообщить:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Мастер на час в Москве https://masternadom24.ru быстрое решение бытовых проблем. Мелкий ремонт, установка, сборка и подключение техники. Пунктуальность, качество и удобный вызов мастера.
Вывод из запоя в стационаре — это шанс начать путь к трезвой жизни, и в Самаре этот шанс предоставляет «Частный Медик 24».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
В Нижнем Новгороде стационар «Частного Медика 24» стал надежным местом для лечения запоя.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru
Если вам нужна помощь нарколога на дому — срочно и конфиденциально, узнайте, как работают услуги выездного врача, какие методы применяют и сколько это стоит › подробнее на covid-stat.com Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12653
https://plisio.net/pt/blog/italy-currency-guide
https://plisio.net/ja/blog/yt-dlp
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-legkij-bronezhilet-skrytogo-nosheniya-10-11
Продувают окна? регулировка окон пвх – устранение продуваний, настройка фурнитуры, ремонт и обслуживание. Опытные мастера, выезд в день обращения, гарантия на все виды работ.
digital talk
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-mavik-dlya-svo-10-13
https://plisio.net/fr/blog/robert-f-kennedy-jr-net-worth
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» высылает нарколога на дом для срочной помощи при запое. Быстро и безопасно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Если вы ищете надёжный и понятный путь к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости — вам стоит заглянуть в статью «Эффективные услуги лечения алкоголизма: путь к трезвой жизни». Подробнее тут – http://airlady.forum24.ru/?1-10-0-00001075-000-0-0-1753907880
В «Частном Медике 24» в Самаре выход из запоя организуют поэтапно: диагностика, лечение, реабилитация.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Sou viciado no codigo de PlayPix Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino retro-futurista. O leque do cassino e uma matriz de delicias. com caca-niqueis modernos que glitcham como retro. O suporte e um codigo preciso. respondendo rapido como um buffer. As transacoes sao simples como um pixel. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que processam como CPUs. Em sintese, PlayPix Casino e um buffer de emocoes para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o design e um espetaculo visual de matriz. fazendo o cassino processar como um CPU.
playpix[|
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um atol. incluindo mesas com charme subaquatico. O atendimento e solido como um coral. garantindo suporte direto e sem correntezas. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um coral. ocasionalmente mais bonus regulares seriam aquaticos. Na real, Brazino Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro mergulho para os fas de adrenalina marinha! De lambuja o visual e uma explosao de corais. tornando cada sessao ainda mais aquatica.
brazino777 baixar app|
В момент вызова важно сообщить:
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkologicheskij-czentr-v-rostove
group chat
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Sou louco pelo batuque de SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de cores, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com muito charme. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma rainha de bateria, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SambaSlots Casino e um cassino online que e uma festa de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, adiciona um toque de axe ao cassino.
la sambaslots+casino|
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
https://clocks-top.com/
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-sitong-kupit-10-13
https://bigpicture.ru/piony-s-dostavkoj-v-moskve-kak-vybrat-idealnyj-buket/
В клинике в Самаре устраняют симптомы интоксикации, оказывают поддержку организму и помогают восстановиться после тяжёлых запоев.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/[/url]
Не знаете, с чего начать борьбу с зависимостью? Полный путеводитель по лечению в Саратове — на Noprost. Подробнее – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12658
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, repondant en un clin d’?il. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et retro, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino online|
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже — индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Мы предлагаем комфортные условия и профессиональную помощь для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
fan video
Amo a energia de PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra com intensidade. O catalogo e rico e multifacetado, com slots de design inovador. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, contudo promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e estilosa, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver o site|
Tenho uma paixao vibrante por BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo intenso. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os saques sao rapidos como um contra-ataque, embora promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. No fim, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Tambem o design e moderno e vibrante, facilita uma imersao total. Outro destaque os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Aprender como|
https://www.live4cup.com/f-sp1814387-.html#p1814387
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
В момент вызова важно сообщить:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог ростов-на-дону[/url]
Стационар «Частного Медика?24» помогает безопасно и быстро восстановиться после длительного запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-lazernyj-dalnomer-leica-v-samare-10-14
В Самаре стационар «Частного Медика 24» предлагает персонализированный подход — лечение запоя, детоксикация и дальнейшее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Хотите начать бороться с зависимостью, но предпочитаете помощь дома? В статье на NetLekarstvаm представлены реальные методы кодирования и советы специалистов. Углубиться в тему – http://pokatili.ru/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=83533
Sou louco pela matriz de PlayPix Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que processa como um CPU. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que processam como servidores. O suporte e um firewall de eficiencia. respondendo rapido como um buffer. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um buffer. porem mais recompensas fariam o coracao pixelar. Em sintese, PlayPix Casino promete uma diversao que e um glitch para os hackers do cassino! Vale dizer o design e um espetaculo visual de matriz. criando uma experiencia de cassino cibernetica.
reclame aqui playpix|
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
bs market Приготовься узнать, что взорвало тёмные глубины интернета. Blacksprut – это не просто бренд. Это новый эталон анонимности, головокружительной скорости и абсолютной надежности в онлайн-мире. Посети bs2best.at – место, где раскрывают секреты, о которых другие даже шепотом боятся говорить. Ты получишь эксклюзивный доступ к данным, которые тщательно скрывают от непосвященных. Только для тех, кто в теме и готов к большему. Ни одного следа в сети, никаких уступок – только бескомпромиссная анонимность с Blacksprut. Не упусти эту уникальную возможность – стань одним из первых, кто узнает правду. bs2best.at уже ждёт тебя. Готов ли ты увидеть то, что скрыто от большинства?
Adoro o gingado de SambaSlots Casino, e um cassino online que samba como um desfile de carnaval. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de gingado, com uma ajuda que e puro axe. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma rainha de bateria, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, SambaSlots Casino e um cassino online que e uma festa de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro ritmo, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
casino de jeux polygone sambaslots|
Ich flippe aus bei JackpotPiraten Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Schatz funkelt. Es gibt eine Flut an packenden Casino-Titeln, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Flagge weht. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten no deposit bonus code|
https://plisio.net/blog/lauren-sanchez-net-worth
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de 7BitCasino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses, notamment des bonus sans depot. En resume, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino testbericht|
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-stroitelnyj-melissej-tr10-kupit-10-12-3
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru[/url]
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. As opcoes sao amplas como um festival, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para fas de cassino online ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, que aumenta o engajamento.
Dar uma olhada|
прогнозы на футбол на сегодня [url=www.prognozy-na-futbol-10.ru/]прогнозы на футбол на сегодня[/url] .
[url=http://www.technoplus.ru/openads/pag/melbet_promokod_bonus_pri_registracii.html]промокод melbet бесплатно[/url]
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. O processo e simples e direto, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Aprender os detalhes|
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
virtual meet
[url=https://only-most.ru/pages/melbet-promokod___bonus-pri-registracii.html]melbet uz промокод[/url]
Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с необходимостью безопасного выхода из запоя, статья «Методы, особенности и важные нюансы выведения из запоя» станет знакомым и надёжным ориентиром. В ней объясняются современные подходы к прерыванию запоя — с акцентом на безопасность и постепенную реконструкцию организма. Подробнее тут – http://infoenglish.info/forum/14-9026-1
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в сочи[/url]
Адекватное лечение, комфорт и забота — так проходят дни в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» во время вывода из запоя.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в самаре[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Iray-teplovizory-kupit-v-moskve-10-14
Нарколог прибывает в назначенное время, проводит замеры артериального давления, пульса, сатурации кислорода и температуры. Выполняется экспресс-анализ на содержание алкоголя в крови и оценка водно-электролитного баланса.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Клиника «Частный Медик 24» в Самаре оказывает помощь при запое анонимно, круглосуточно и без скрытых платежей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в самаре[/url]
Ищете надёжную помощь при зависимости в Саратове? Наркологическая клиника «Развитие» предлагает эффективное лечение алкоголизма, наркомании и игромании. Узнайте больше на нашем сайте. Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://omsi2mod.ru/forum/7-7871-1
Кто знает, сколько голов забил Неймар за карьеру? Хочу таблицу по клубам и сборной. Хочу «неймар фото на аву» без шумов и с ровным цветом кожи, пригодные для соцсетей. Короткие дайджесты новостей и canlı izləmə удобно следить из одного места. [url=https://neymar-kg.com/]неймар новости[/url]. Неймар фильмы и документалки: посоветуйте топ-3 для выходных.
Неймар лучшие фото: портреты, эмоции после гола, командные снимки — хочу собрать сет. Неймар номер: на футболке в «Сантосе» и «Барселоне» — важные детали для коллекционеров. Сравнение прайма Неймара в «Барселоне» и пик-сезонов в ПСЖ — таблица метрик. Неймар ПСЖ 2018 — топовый сезон по влиянию между линиями; ищу срез по матчам.
Неймар барса обои 4К — важно проверить соотношение сторон под ультраширокие мониторы. Где сейчас играет Неймар — закреплю ссылку в профиле, чтобы не терять.
digital clocks
https://dexupload.com/SQr/Code_Promo_LineBet_Aujourdhui_pour_obtenir_100_€__.pdf
The post is absolutely great! Lots of great info and inspiration, both of which we all need! Also like to admire the time and effort you put into your blog and detailed information you offer! I will bookmark your website!
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
https://telegra.ph/Mavic-kupit-deshevo-10-12-3
pronostic foot gratuit telecharger 1xbet
Круглосуточный стационарный вывод из запоя в Воронеже — доступная помощь в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время суток, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru
Sou louco pela vibracao de BR4Bet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que acende como uma tocha. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como luzes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que reluzem como chamas. O suporte e um facho reluzente. assegurando apoio sem sombras. Os saques sao velozes como um clarao. porem mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Ao final, BR4Bet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro brilho para quem curte apostar com estilo iluminado! Como extra o site e uma obra-prima de estilo radiante. fazendo o cassino brilhar como um farol.
cupom br4bet sem deposito|
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Новости спорта онлайн http://sportsat.ru футбол, хоккей, бокс, теннис, баскетбол и другие виды спорта. Результаты матчей, обзоры, интервью, аналитика и главные события дня в мире спорта.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
Sou viciado na vibe de SpeiCasino, e um cassino online que decola como um foguete espacial. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um cometa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
spei sign up|
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rainha de bateria, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Na real, BacanaPlay Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os folioes do cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay scam|
digital talk
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-kvadrokopter-syma-10-12-5
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e elegante, as vezes recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, adiciona um toque de conforto. Outro destaque os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Explorar o site|
betting bonus codes Free Bet Promo Codes Free bet promo codes are digital codes that unlock free bet offers on online betting platforms. They are normally offered to new users as a motivating factor to get them to sign up, or rewarded to existing users to maintain their activity. When a free bet promo code is used, users can place a bet without having to risk their own money. The winnings from a free bet normally do not include the original bet amount, and will sometimes be subjected to wagering requirements before withdrawal. The availability of free bet promotion codes will often be found on the bookmaker’s main site, on linked affiliated pages, and in communications from the bookmaker directed to registered users.
Статья рассказывает о комплексном подходе к лечению наркомании, включающем не только медикаментозную помощь, но и психологическую и социальную поддержку. Это помогает сформировать устойчивость и справиться с вызовом раз и навсегда. Выяснить больше – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12232
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Akkumulyator-dlya-mavik-3-pro-kupit-10-14
Стационар «Частного Медика 24» — условия, где пациент может спокойно пройти вывод из запоя без страха и дискомфорта.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru[/url]
bs2best at В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
В момент вызова важно сообщить:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
https://bsmef.at
Выездная бригада «РостовМед» оснащена всем необходимым для оказания экстренной помощи и проведения полного курса детоксикации на дому. Процесс состоит из нескольких этапов:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в ростове-на-дону[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Dji-360-kupit-10-12-5
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в сочи[/url]
virtual meet
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
В больничных условиях «Частного Медика 24» врачи контролируют давление, сердце и функции жизненно важных органов при выводе из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Dron-dji-mini-kupit-10-12
https://bs2tsite1.at
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает лечение запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем. Здесь пациент получает безопасное и эффективное восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто прекращение питья, а полноценная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма и стабилизацию психического состояния. Подробности на WomanClub. Подробнее тут – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12654
Наша миссия — помочь каждому человеку преодолеть алкогольную зависимость с минимальным дискомфортом и максимальной эффективностью. Мы исходим из следующих принципов:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Госпитализация в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и начать новую жизнь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Этапы лечения алкогольной зависимости: от диагностики до реабилитации. Узнайте, как гормональные изменения влияют на процесс восстановления — читайте на vse-o-gormonah.com. Изучить вопрос глубже – http://krd.best-city.ru/forum/thread111137/
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Откройте для себя материал «Частная наркологическая клиника: комплексный подход к лечению», где объясняется, почему сочетание классической медицинской помощи с психологической поддержкой и реабилитацией становится ключом к долгосрочному успеху и трезвости. Выяснить больше – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12267
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-ohotnichij-binokl-na-valberis-10-12-4
В момент вызова важно сообщить:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
promo bet Use sports betting bonus codes and claim bonus benefits, cash prizes, and more for signing up or being an existing users by just scanning this code today! Grab yours now!
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница сочи[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Binokl-nochnik-dlya-ohoty-kupit-10-12-4
Не ожидал, что LED-экран так сильно улучшит восприятие информации — теперь даже сложные графики и таблицы воспринимаются легко
https://chuyendoixanh.org/wiki/index.php/User:AngeliaJoyce99
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
desert blues
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
В Самаре «Частный Медик 24» предлагает прозрачные цены на вывод из запоя, без неожиданных расходов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому — является эффективным способом детоксикации организма при борьбе с алкоголизмом. Анонимный нарколог на дом в городе Красноярск предлагает услуги по проведению капельниц, что дает возможность быстро восстановить здоровье пациентов . Состав капельницы включает в себя медикаментов , которые способствуют устранению симптомов запоя, таких как обезвоживание и интоксикация . Нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск. Основные компоненты капельницы : раствор натрия хлорида для гидратации , глюкоза для энергетической поддержки , витамины группы В для улучшения обмена веществ и препараты для облегчения абстиненции; состав лекарств подбирается индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента. Домашняя терапия под контролем нарколога гарантирует анонимность, что важно для многих зависимых от алкоголя. Поддержка семьи при запое имеет решающее значение для успешного выздоровления. Консультация нарколога поможет определить дальнейшие шаги , включая программы реабилитации для алкоголиков и восстановление после алкогольной зависимости.
Госпитализация в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и начать новую жизнь.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Ищете круглосуточную наркологическую службу в Саратове? Узнайте, как получить квалифицированную помощь на дому — информация на Damki.biz Подробнее – http://www.artlib.ru/index.php?id=26&idr=15&idt=52012
https://bs2tsite2.at
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в нижний новгороде[/url]
http://www.pageorama.com/?p=iohygofefg
Ich bin suchtig nach PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Flut voller Spa?, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
playjango free|
Me encantei pelo ritmo de BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. A selecao de titulos e uma chama de emocoes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que reluzem como chamas. O suporte e uma luz-guia brilhante. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. porem as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, BR4Bet Casino e uma fogueira de adrenalina para quem curte apostar com estilo iluminado! Vale dizer o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
br4bet plataforma|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao reluzente quanto uma supernova. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque cosmico. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um cometa, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao estelar. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Resumindo, SpeiCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
spei promotional code|
Adoro a onda sonora de JonBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao pulsante quanto um eco em caverna. A colecao e uma onda sonora de entretenimento. oferecendo lives que explodem como ecos. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um eco. mas queria promocoes que vibram como sinos. No geral, JonBet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os exploradores de jogos online! Alem disso a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. tornando cada sessao ainda mais ressonante.
afiliado jonbet|
Экстренная помощь при запое в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница на дому от опытных врачей-наркологов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в сочи[/url]
Пациентам в Самаре предлагается анонимное лечение в стационаре с круглосуточным уходом и безопасными условиями.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в самаре[/url]
https://muckrack.com/person-27406550
В Воронеже клиника «Частный Медик?24» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника[/url]
Домашнее кодирование алкогольной зависимости: полное руководство по процедуре, ожиданиям и рискам — читайте на NetLekarstvam.com. Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00033109-000-0-0-1757537846
Acho simplesmente sensacional BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um desfile visual vibrante, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
bacanaplay logo|
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме позволяет избежать осложнений и способствует восстановлению здоровья. Курс лечения алкоголизма нуждается в тщательном подходе и может включать программы реабилитации. Визит к врачу позволит составить персонализированный план терапии. Не медлите с обращением к врачу – ваше здоровье имеет первостепенное значение! вывод из запоя владимир
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Najlepsze kasyno online w Polsce
Dolacz do [url=https://billionaire-casino.pl/]billionaire casino[/url]
i ciesz sie najlepszymi grami online, zakladami sportowymi i ekscytujacymi bonusami w Polsce.
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород[/url]
blsp at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com slots de design inovador. O bonus de boas-vindas e cativante. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e elegante, embora bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, adiciona um toque de conforto. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Descobrir a web|
https://www.rwaq.org/users/kuwabarabeeed-20250811000846
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio em dia de final. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de jogo, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o gramado para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
https://betesporte365.app/|
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Если вы ищете надёжный и понятный путь к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости — вам стоит заглянуть в статью «Эффективные услуги лечения алкоголизма: путь к трезвой жизни». Получить дополнительные сведения – http://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-8-0-00000606-000-0-0-1754134302
В автомобиле находятся:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove/
Ich bin suchtig nach PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern glanzt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
playjango no deposit|
https://b2shop.gl
I’d like to be able to write like this, but taking the time and developing articles is hard…. Takes a lot of effort.
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um satelite. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque cosmico. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao estelar. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No geral, SpeiCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei promo code today|
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/[/url]
Sou louco pela ressonancia de JonBet Casino, parece uma camara de ecos cheia de adrenalina. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. incluindo mesas com charme ressonante. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os saques sao velozes como uma onda sonora. as vezes mais recompensas fariam o coracao ecoar. Na real, JonBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma camara de diversao para os exploradores de jogos online! Alem disso o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura ressonante.
jonbet futebol|
https://shootinfo.com/author/ifulowamurydu/?pt=ads
кракен 2025
кракен ссылка
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в нижний новгороде[/url]
bs2best at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
В кардиологической и психологической поддержке «Частного Медика 24» в Самаре — полный комплекс для безопасного восстановления после запоя.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru[/url]
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de carnaval. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de pandeiro. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No fim das contas, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de frevo, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay suporte|
Медикаментозная терапия алкоголизма в Красноярске становится все более востребованным. Нарколог‚ который выезжает на дом в Красноярске предоставляет разнообразные методы лечения зависимости‚ включая детоксикацию‚ а также подбор медикаментов. Лечение без раскрытия личных данных позволяет клиентам не переживать‚ получая услуги профессионалов. врач нарколог на дом Красноярск Обращение к специалисту обязательна для выбора оптимальной программы реабилитации. Кодирование от алкоголизма – такой же результативный метод против алкоголизма. Поддержка психолога также является ключевым фактором в процессе восстановления. Услуги нарколога включают в себя медицинские услуги по лечению алкоголизма‚ что способствует успешному лечению и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru
https://beteiligung.stadtlindau.de/profile/%D0%9A%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D0%AD%D0%BA%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%20%D0%9C%D0%94%D0%9C%D0%90%20%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD%20%D0%92%D0%B0%D0%B4%D1%83%D1%86/
Круглосуточный стационарный вывод из запоя в Воронеже — доступная помощь в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время суток, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. Os agentes respondem com velocidade, acessivel a qualquer hora. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o gramado para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente o site e veloz e envolvente, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Outro destaque o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter mais|
Вызов наркологической помощи в владимире — это важная услуга, помогающая людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Клиника наркологии в владимире предоставляет разнообразные услуги, среди которых лечение зависимостей и помощь при алкоголизме. Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в поддержке, стоит рассмотреть возможность вызова нарколога.Первичная консультация у нарколога может стать первым шагом к выздоровлению. Специалисты предоставляют анонимное лечение, что позволяет избежать стигматизации и обеспечить комфортные условия для пациента. Круглосуточная горячая линия готова ответить на все вопросы и оказать скорейшую помощь при отравлении. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir026.ru Процесс реабилитации для зависимых включает программы по лечению зависимостей и психотерапевтические методики. Вы можете вызвать нарколога в любое время, что делает процесс лечения максимально удобным. Не стесняйтесь и не откладывайте помощь, поскольку здоровье — это самое ценное.
согласование перепланировки квартиры москва [url=http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/]согласование перепланировки квартиры москва[/url] .
https://muckrack.com/person-27481218
music stream
Кодирование от алкоголизма: от медикаментозных блокаторов до психотерапевтических техник — узнайте, что подходит именно вам, на crocothemes.com. Выяснить больше – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12663
Вывод из запоя в стационаре — это шанс начать путь к трезвой жизни, и в Самаре этот шанс предоставляет «Частный Медик 24».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя в самаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Ищете понятный и последовательный план лечения алкогольной зависимости? Статья «Этапы лечения алкогольной зависимости» предлагает чётко структурированный путь к восстановлению: от первой помощи до реабилитации. Получить дополнительную информацию – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12230
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
https://b-s2best.at
https://ilm.iou.edu.gm/members/maryhobbsmar/
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Выездная бригада «РостовМед» оснащена всем необходимым для оказания экстренной помощи и проведения полного курса детоксикации на дому. Процесс состоит из нескольких этапов:
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru
blsp at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
online channel
кракен онлайн
kraken vk3
Если вы ищете простой и понятный план для безопасного выхода из запоя, стоит познакомиться со статьёй «Вывод из запоя — путь к здоровой жизни». В ней, по словам читателей, «всё чётко расписано: от консультации до постепенного выхода» Ознакомиться с деталями – http://salda.ws/f/topic.php?f=5&t=97540
Наша платформа https://probilets работает круглосуточно и не знает слова «перерыв». Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов.
https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/1139090/%D0%9D%D0%B5%D1%84%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%8E%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA-%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD-%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%84%D0%B5%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD-%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
клиника наркология [url=http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru]http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru[/url] .
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В автомобиле находятся:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkologicheskij-czentr-v-rostove/
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в нижний новгороде[/url]
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Zusammengefasst ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
richard casino no deposit promo code|
В «Частном Медике 24» в Воронеже каждый пациент, проходящий вывод из запоя в стационаре, получает комплексную помощь — диагностика, устранение интоксикации, восстановительная терапия, психологическая работа, всё с постоянным наблюдением и поддержкой, в условиях, где безопасность и анонимность стоят на первом месте.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
https://www.impactio.com/researcher/ebykehoxiwu80?tab=resume
Стационар «Частного Медика 24» — условия, где пациент может спокойно пройти вывод из запоя без страха и дискомфорта.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru
Sou louco pela aura de SpellWin Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma pocao encantada. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de encantos, com slots de cassino tematicos de fantasia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma runa, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura magica. Em resumo, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como uma pocao reluzente, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spellwin no deposit bonus code|
Ich liebe die Pracht von King Billy Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konig regiert. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glanzvoll sind. Kurz gesagt ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king-billy casino bonus code|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin apk|
Мне понадобилось изготовление прототипа на 3D-принтере, потому что требовалось представить результат заказчику в сжатые сроки. Команда подошла к делу максимально ответственно. Выполнение заказа шло без задержек, а точность печати поразило своей аккуратностью. Специалисты помогли с выбором материала, и результат полностью совпал с задуманным. Цена печати оказалась доступной. Я остался доволен и обязательно буду заказывать снова https://ajuda.cyber8.com.br/index.php/%C3%90%C2%A7%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%90%C2%BE_%C3%90%C3%A2%E2%82%AC%E2%84%A2%C3%91%E2%80%B9_%C3%90%C5%B8%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%90%C2%BB%C3%91%C6%92%C3%91%E2%80%A1%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%90%C2%B5_%C3%90%C2%A1_3D-%C3%90%C2%BF%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%91%E2%80%A1%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%91%C5%92%C3%91%C5%BD.
Лечение запоя капельницей на дому – это популярный метод лечения алкогольной зависимости, предлагающий множество преимуществ и некоторые недостатки. В Красноярске услуги нарколога включают выезд на дом, что позволяет пациентам обратиться за медицинской помощью при алкогольном запое в привычной обстановке. Основные преимущества капельницы заключаются в быстром восстановлении организма благодаря детоксикационным процедурам. Капельницы способствуют выведению токсинов, повышению общего состояния здоровья, что, в свою очередь, помогает быстрее восстановиться после запоя. Кроме того, поддержка близких при запое имеет огромное значение, так как лечение алкоголизма на дому обеспечивает уютную атмосферу. лечение запоя Красноярск Однако, существуют и минусы. Например, в некоторых случаях сложно обеспечить необходимый контроль за состоянием пациента. Врачебная консультация на дому может оказаться недостаточной для серьезных случаев. Также стоит учитывать, что инъекции при алкоголизме могут не подойти всем.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород[/url]
Если вы ищете надёжный и понятный путь к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости — вам стоит заглянуть в статью «Эффективные услуги лечения алкоголизма: путь к трезвой жизни». Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kremlevsk.kamrbb.ru/?x=read&razdel=5&tema=637
https://www.band.us/page/99398982/
Рулетка казино онлайн мифы и реальность игры
Рулетка казино онлайн мифы и реальность как не попасть в ловушку азартной игры
При выборе платформы для ставок, важно понимать, что удача – не единственный аспект успеха в азартных ситуациях. Глубокое исследование механики и статистики может значительно повлиять на вашу стратегию. Многие считают, что предыдущие результаты способны предсказать будущие исходы, но это заблуждение. Каждое вращение колеса является независимым событием, и любые шаблоны лишь плод воображения.
Несмотря на популярные мифы, результаты не зависят от используемой системы ставок. Применение методов, таких как Мартингейл или Фибоначчи, может показаться разумным, однако ни один из них не может гарантировать выигрыш. Все зависит от случая и случая, поэтому важно ставить разумно и учитывать свой бюджет.
Долгосрочная стратегия предполагает осознанный подход. Знание вероятностей, таких как шансы на выигрыш разных ставок, позволит принимать более обоснованные решения. Уделите время изучению правил и различных вариантов, чтобы адаптировать свои действия под конкретные условия, а не следовать слепо за популярными мнениями.
Рулетка казино онлайн: мифы и реальность игры
Точный расчет результатов невозможен. Существуют убеждения о том, что можно предсказать исходи или использовать системы ставок для гарантированного выигрыша. Однако механика данного развлечения основана на случайности. Каждый бросок шарика не зависит от предыдущих результатов.
Играть можно без подготовки. Некоторым кажется, что простота правил позволяет начинать без знаний. На самом деле, понимание стратегий и особенностей различных вариантов значительно повышает шансы на успех. Рекомендуется изучить правила и основные стратегии до начала.
Игровые автоматы-соперники. Многие верят, что благоприятный опыт на автоматах можно перенести на настольные развлечения. Это не так. Стратегии и механики отличаются. Игрокам следует адаптировать подход в зависимости от типа игры.
Честность платформ. Есть мнение, что все ресурсные площадки мошеннические. На практике, существует множество лицензированных операторов, обеспечивающих безопасность и честность процессов. Важно выбирать авторитетные площадки с проверенной репутацией.
Вероятности выигрыша зависят от поведения игроков. Существуют заблуждения о том, что можно влиять на шансы, используя определенные подходы. На самом деле, каждое действие игрока не повлияет на случайность выбора. Все решения – индивидуальны и не меняют вероятностей.
Программное обеспечение. Важно понимать, что игра ведется с помощью генераторов случайных чисел. Это гарантирует, что каждый результат является независимым и случайным. Доверяйте лишь платформам с прозрачными условиями и строгими стандартами качества.
Выбор времени для ставок. Некоторые игроки считают, что существует оптимальное время для игры. На самом деле, результаты не зависят от времени суток, и удача играет здесь не меньшую роль, чем стратегии.
Финансовые риски. Напоминаем, что управление банкроллом – это не просто хороший совет, а необходимый элемент для продолжительного участия. Необходимо четко определить лимиты и придерживаться их, чтобы избежать серьезных проигрышей.
Как работает генератор случайных чисел в азартных развлечениях?
Каждый раунд имеет уникальный набор чисел, что делает вероятность выигрыша для каждой ставки одинаковой в каждом новом раунде. Это означает, что результаты игр независимы друг от друга, и предыдущие исходы никак не влияют на будущие результаты.
Для проверки надежности работы генераторов используется аудит. Независимые коллективы проверяют их на соответствие международным стандартам. Это заключает в себе тестирование на распределение, статистическую случайность и другие параметры.
Важно помнить, что ГСЧ генерирует результаты с использованием стойких алгоритмов, что делает невозможным предсказание исходов. Поэтому методики, основанные на попытках выявления закономерностей по предыдущим результатам, неэффективны.
Доступ к информации о работе ГСЧ предоставляется производителями программного обеспечения, что позволяет пользователям удостовериться в прозрачности и надежности процессов. Данные о частоте выплат и других аспектах также являются открытыми для анализа.
Правда ли, что стратегии ставок могут гарантировать выигрыш?
Ни одна стратегия ставок не может обеспечить выигрыша. Все системы, такие как Мартингейл или Фибоначчи, основаны на вероятности и математике, но не учитывают случайность результата. Каждое вращение обусловлено независимыми факторами, и результат не зависит от предыдущих событий.
На практике, использование стратегий может лишь помочь управлятьBankroll и увеличивать время игры, но не влияет на итоговые результаты. Игроки должны понимать, что с каждой ставкой связан риск потерь, а не возможности гарантированного выигрыша.
Важно помнить, что азартные развлечения созданы для отдыха, а не как способ заработка. Контролируйте свои ставки, устанавливайте лимиты и играйте ответственно. Лучше всего подходить к процессу с развлечением в первую очередь, избегая излишнего увлечения.
https://shumisport.ru/ncaa/articles.php?ic360_budet_sotrudnichat_s_southland_conference_ncaa_dlya_instrumentov_chestnosti_i_sootvetstviya.html
новости спорта россии [url=novosti-sporta-7.ru]novosti-sporta-7.ru[/url] .
Круглосуточный стационарный вывод из запоя в Воронеже — доступная помощь в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время суток, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
Amo a energia selvagem de PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. O catalogo e exuberante e multifacetado, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. No geral, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Acrescentando que o design e moderno e vibrante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Começar aqui|
Tenho um entusiasmo vibrante por BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo inigualavel. O catalogo e vibrante e multifacetado, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Descobrir mais|
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
bs2web at Неужели ты до сих пор не знаешь, что переворачивает мир даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто название. Это новая эра анонимности, мгновенной скорости и железобетонной безопасности в сети. Загляни на bs2best.at – туда, где обсуждают то, о чём остальные предпочитают молчать в тряпочку. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от посторонних глаз. Только для тех, кто понимает правила игры. Никаких следов, никаких компромиссов, только абсолютная конфиденциальность – это Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать первооткрывателем – bs2best.at уже распахнул свои двери для тебя. Хватит ли у тебя смелости взглянуть правде прямо в лицо?
Капельница от запоя – данный метод является популярным способом лечения алкоголизма, используемый внедряется в клиниках в владимире с целью очистки организма. Круглосуточная помощь позволяет эффективно снять симптомы запоя. Однако важно помнить о потенциальных рисках, включающих аллергические реакции и дисбаланс электролитов. вывод из запоя круглосуточно владимир
кракен vk6
кракен
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
Hi antidetect is goood.
https://wanderlog.com/view/haqdjtebdo/купить-кокаин-марихуану-мефедрон-белек/shared
бюро переводов с гибкими тарифами
В «Частном Медике 24» в Самаре выход из запоя организуют поэтапно: диагностика, лечение, реабилитация.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru
Домашнее кодирование алкогольной зависимости: полное руководство по процедуре, ожиданиям и рискам — читайте на NetLekarstvam.com. Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00033109-000-0-0-1757537846
новости мирового спорта [url=https://sportivnye-novosti-2.ru]новости мирового спорта[/url] .
прогнозы на спорт бесплатно от профессионалов на сегодня [url=https://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru]https://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru[/url] .
Вывод из запоя в Самаре проводится с проверенными препаратами, с учётом состояния пациента и без лишнего стресса.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в самаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
https://wanderlog.com/view/efuxsyadlf/купить-экстази-кокаин-амфетамин-петах-тиква/shared
https://wwwbs2best.at
Естествен крем срещу гъбички Exodermin работи чудеса. Съставът с масло от чаено дърво е антимикотичен. Препоръчвам https://omnideck.org/index.php/User:BennyWolinski деца
whoah this weblog is fantastic i really like reading your posts. Stay up the great work! You recognize, many individuals are looking around for this information, you can aid them greatly.
https://inc-rediblestore.com/
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже — индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Мы предлагаем комфортные условия и профессиональную помощь для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Нужна вывеска? неоновая вывеска спб логотипы, надписи, декор для кафе, офисов и дома. Индивидуальный дизайн, энергосберегающие материалы и эффектный свет в любом стиле.
В автомобиле находятся:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
После детоксикации пациентам предлагаются различные психотерапевтические методы, такие как когнитивно-поведенческая терапия, арт-терапия и групповая терапия. Эти подходы помогают выявить и проработать причины зависимости, а также развить навыки преодоления стрессовых ситуаций без употребления наркотиков. Изучить вопрос глубже – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12657
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
https://wanderlog.com/view/tfwzovamxp/купить-экстази-кокаин-амфетамин-кипр/shared
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Нужен сайт? создание сайтов под ключ с акцентом на конверсию: UX-исследование, дизайн-система, чистая вёрстка, CMS на выбор, подключение метрик и событий. Интернет-магазины, B2B-порталы, лендинги. SEO-структура, микроразметка, скорость 90+. Поддержка и развитие без скрытых расходов.
Выездная бригада «РостовМед» оснащена всем необходимым для оказания экстренной помощи и проведения полного курса детоксикации на дому. Процесс состоит из нескольких этапов:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
https://2-bs2best.art
В Самаре стационар «Частного Медика 24» предлагает персонализированный подход — лечение запоя, детоксикация и дальнейшее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
blsp at Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
Ich bin total hingerissen von Richard Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein koniglicher Palast strahlt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett leuchten. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein kaiserlicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, dennoch mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Insgesamt ist Richard Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Majestat ins Casino bringt.
casino royal richard branson|
kraken РФ
kraken tor
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
лечение запоя
https://imageevent.com/calovitaegyu/dzfcv
Ich finde absolut majestatisch King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Spa?, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein furstlicher Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist King Billy Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Kronungsfest funkelt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
king billy 3 casino|
Sou louco pela aura de SpellWin Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma pocao encantada. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de encantos, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma runa, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura magica. Em resumo, SpellWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os magos do cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, adiciona um toque de encantamento ao cassino.
spellwin casino login|
Капельница при запое — это существенный шаг в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Капельница способствует детоксикации организма‚ выводя токсины и нормализуя баланс жидкости и электролитов. После ее применения пациенты испытывают улучшение психоэмоционального состояния.Помощь нарколога в этом процессе играет важную роль. Он анализирует симптомов абстиненции и назначает соответствующее лечение запоя. Реабилитация после запоя включает не только физическое‚ но и психологическое восстановление. Поддержка близких играет ключевую роль‚ позволяя преодолеть последствия запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Реабилитация является следующим шагом в процессе‚ где пациент получает медицинскую помощь и обучение для предотвращения рецидивов. Анонимная помощь предоставляет анонимность и защиту. Стоит помнить‚ что борьба с алкоголизмом — это длительный процесс‚ необходимый при поддержке окружающих.
При обращении на горячую линию пациент может получить бесплатную телефонную консультацию. Врач уточняет состояние, собирает предварительный анамнез и согласовывает время визита.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru/]наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin registo|
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru как выбрать локацию, проверить инфраструктуру и коммуникации, понять цены и налоги. Сравнение ИЖС/ДНП, надёжность застройщиков, ипотека и субсидии, отзывы жителей, карта проектов и чек-листы для осмотра. Поможем принять взвешенное решение о покупке.
Explora proveedores top en 1xslots y activa recompensas diarias.
Ищете помощь при зависимости — для себя или близкого? Статья «Наркологическая клиника и её услуги» раскрывает, как специализированные учреждения помогают людям справиться с зависимостью — будь то алкоголизм или другие формы. Углубиться в тему – http://dimitrov.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000482-000-0-0-1753543226
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54154535/сейшелы-марихуана-гашиш-канабис/
Строительство и ремонт https://repair-house.kiev.ua дома без ошибок: пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов и подрядчиков, смета и экономия, фундамент, кровля, инженерия, утепление, отделка. Чек-листы, калькуляторы, типовые узлы, лайфхаки по срокам и качеству. Экономим бюджет — повышаем комфорт.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. O processo e simples e elegante, as vezes ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para fas de cassino online ! Tambem a interface e fluida e estilosa, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Acessar o site|
Ich finde absolut majestatisch Richard Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein koniglicher Palast strahlt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein koniglicher Schatz, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein kaiserlicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Juwelen glanzen. Insgesamt ist Richard Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Kronungsjuwel glanzt fur Spieler, die auf majestatische Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, den Spielspa? im Casino auf ein konigliches Niveau hebt.
richard casino no deposit promo code for existing players|
show updates
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Bote, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein furstlicher Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist King Billy Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konigreich strahlt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy casino freispiele|
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, parece um portal mistico cheio de adrenalina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino fascinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura magica. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como uma pocao reluzente, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
spellwin online|
https://1-bs2best.art
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin – betorspin giriЕџ|
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
https://www.openlibhums.org/profile/068c1ce7-ec6e-41a5-8559-d7139aff8d7e/
Интеллектуальные боты для мониторинга источников становятся всё более популярными.
Они дают возможность находить открытые данные из разных источников.
Такие боты используются для исследований.
Они способны оперативно анализировать большие объёмы данных.
поограмма узнать про людей глаз
Это способствует получить более точную картину событий.
Отдельные системы также включают удобные отчёты.
Такие боты популярны среди аналитиков.
Совершенствование технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и быстрым.
Вывод из запоя в Самаре на базе стационара — когда важен результат, стабильность и медицинская поддержка 24/7.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно самара[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в нижний новгороде[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
https://www.hqhomeinteriors.co.uk/blog/new-products/greece-travel
Scale your operations safely! An antidetect browser is engineered specifically for multi-account management, allowing you to run separate profiles for social media, ads, or e-commerce without any cross-linking risk.
Me impressionei com BETesporte Casino, me leva a um universo de apostas vibrante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, garantindo um atendimento de elite. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Tambem o site e veloz e cativante, facilita uma imersao total. Outro destaque o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Prosseguir a leitura|
kraken marketplace
kraken qr code
В Воронеже клиника «Частный Медик?24» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
https://www.grepmed.com/gfadoibri
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Нарколог прибывает в назначенное время, проводит замеры артериального давления, пульса, сатурации кислорода и температуры. Выполняется экспресс-анализ на содержание алкоголя в крови и оценка водно-электролитного баланса.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov13.ru
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
КАПЕЛЬНИЦА ОТ ЗАПОЯ НА ДОМУ: МОЖНО ЛИ СТАВИТЬ КАПЕЛЬНИЦУ САМОСТОЯТЕЛЬНО (владимир) Запой — это серьезное состояние, требующее медицинской помощи. Лечение запоя включает в себя различные методы, одним из которых является капельница. Использование капельницы позволяет уменьшить последствия алкогольной интоксикации и облегчить похмелье. Однако стоит ли ставить капельницу самостоятельно? Капельницы содержат специальные препараты, которые помогают восстановить здоровье пациента. Такие препараты играют ключевую роль в процессе снятия абстиненции. Домашняя терапия может быть эффективной, но требует серьезного подхода. Самостоятельное введение капельниц может привести к ошибкам, что усугубит состояние. Поэтому обращение к профессионалам в владимире будет более безопасным решением. Специалисты обеспечат всестороннюю помощь и поддержку в процессе восстановления. Если требуется помощь на дому, не стесняйтесь обращаться к медработникам. Они организуют детоксикацию и введут все необходимые препараты, что гарантирует безопасность лечения. Не подвергайте себя опасности, лучше доверьтесь профессионалам!
Ищете помощь при зависимости — для себя или близкого? Статья «Наркологическая клиника и её услуги» раскрывает, как специализированные учреждения помогают людям справиться с зависимостью — будь то алкоголизм или другие формы. Ознакомиться с деталями – http://www.brokersearch.ru/index.php?option=com_kunena&func=view&catid=7&id=85129
https://www.rwaq.org/users/deadmorosemadein0-20250727130753
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://bs2-bsme.lat
Estou completamente encantado por Richville Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao sofisticada quanto uma mansao de ouro. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um cofre de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. A equipe do cassino oferece um atendimento digno de realeza, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. O processo do cassino e claro e sem intrigas, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, Richville Casino e um cassino online que exsuda riqueza para os jogadores que adoram apostar com classe! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
richville community church|
Не знаете, с чего начать борьбу с зависимостью? Полный путеводитель по лечению в Саратове — на Noprost. Получить больше информации – http://www.kpilib.ru/forum.php?tema=12658
Вывод из запоя в Самаре на базе стационара — когда важен результат, стабильность и медицинская поддержка 24/7.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru
Estou pirando com RioPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um desfile na avenida, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. Em resumo, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e vibrante como uma escola de samba, adiciona um toque de axe ao cassino.
codigo bonus rioplay|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play bodyboard|
Услуги нарколога на дом: выезд врача, детоксикация и снятие абстиненции без клиники — читайте полный обзор и реальные цены на covid-stat.com Выяснить больше – http://bookcrossing.ru/forum/topic/176767
В Самаре клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре с полным медицинским контролем и комфортными палатами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно самара[/url]
https://form.jotform.com/252379111814051
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого сочи[/url]
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
В «Частном Медике 24» в Самаре выход из запоя организуют поэтапно: диагностика, лечение, реабилитация.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Детальнее – http://www.fsgeschichtebonn.de/fslogo-2
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница нижний новгород[/url]
bs2best зеркало В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
Estou completamente encantado por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. A variedade de titulos e deslumbrante, incluindo apostas esportivas vibrantes. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, as vezes recompensas adicionais seriam festivas. No geral, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de emocoes intensas ! Alem disso o site e rapido e atraente, adiciona um toque de conforto. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Consultar os detalhes|
kraken
кракен сайт
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Детали по клику – https://joyeriasvanessa.com/product/cadena-pave
https://www.montessorijobsuk.co.uk/author/uafoceuci/
Scale your operations safely! An antidetect browser is engineered specifically for multi-account management, allowing you to run separate profiles for social media, ads, or e-commerce without any cross-linking risk.
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://alai-oli.com/kapelniczy-ot-pohmelya-mify-realnost-i-alternativy
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://learnsblogs.com/ayesha-khan-viral-video-ayesha-khans-hot-videos-made-everyone-crazy-watch-video
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Погрузиться в детали – https://www.fishbreeder.at/digital-marketing-made-easy-let-our-team-handle
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Практические советы ждут тебя – https://ochivo.com/tunidos-en-la-ria
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Детальнее – https://khabarjordar.com/ex-cm-ajit-jogi-is-in-koma-breathing-with-ventilater
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Продолжить чтение – https://shop.gbuwh.co.uk/portfolio/fasen-mipame-hazen-pima
https://b2tor2.cc
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Посмотреть всё – https://javispham.com/blog/cung-jay-soi-diem-khac-nhau-trong-lua-chon-bep-nuc-cua-genz-so-voi-the-he-truoc
https://potofu.me/urakzlir
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://revistashape.com.br/2024/05/07/com-agravamento-da-seca-na-bacia-do-pantanal-agencia-nacional-de-aguas-alerta-para-situacao
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://vanproosdijenvandebunt.nl/2022/04/19/being-a-star-in-your-industry
bs market Что, еще не слышал о сенсации, сотрясающей глубины даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто торговая марка. Это ориентир в мире, где правят анонимность, скоростные транзакции и нерушимая надежность. Спеши на bs2best.at – там тебя ждет откровение, то, о чем многие умалчивают, предпочитая оставаться в тени. Ты получишь ключи к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от широкой публики. Только для тех, кто посвящен в суть вещей. Полное отсутствие следов. Никаких компромиссов. Лишь совершенство, имя которому Blacksprut. Не дай возможности ускользнуть – стань одним из первых, кто познает истину. bs2best.at уже распахнул свои объятия. Готов ли ты к встрече с реальностью, которая шокирует?
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://nebesht.com/archive/nahid-mehrgans-novel-review-a-hakimi
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://thenewblackmagazine.com/2024/01/13/httpwww-thenewblackmagazine-comview-aspxindex2706
sportwetten deutschland anbieter
Stop by my site: Wettanalysen Und wettprognosen
Откройте для себя скрытые страницы истории и малоизвестные научные открытия, которые оказали колоссальное влияние на развитие человечества. Статья предлагает свежий взгляд на события, которые заслуживают большего внимания.
Только для своих – https://suterpumpen.ch/neue-website-online-entdecken-sie-die-welt-der-franz-suter-gmbh
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://zeltene.eu/atbild-nbs-galvenais-psihologs-vai-karavirs-var-atguties-pec-kara-pieredzeta/66015
https://odysee.com/@soniakolarova7
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод краснодар[/url]
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Капельница от похмелья в Нижнем Новгороде — доступная и эффективная процедура для снятия симптомов интоксикации. Стоимость услуги начинается от 2 100 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/prokapat-ot-alkogolya-na-domu-murmansk
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в петрозаводске[/url]
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/narkologi-murmansk/
кракен маркет
кракен android
https://imageevent.com/kizasjwil/xfqnj
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Продолжить чтение – https://judotraining.info/applicable-research-in-judo
seo agentur ranking [url=http://reiting-seo-agentstv.ru/]http://reiting-seo-agentstv.ru/[/url] .
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
Эта карта не про «красоту таблицы», а про ясность целей. Она делает предсказуемыми и саму терапию, и коммуникации: пациент знает, что и зачем будет сделано, а семья — когда ждать новостей и на какие цифры ориентироваться.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Портал о строительстве домов https://doma-land.ru проекты и сметы, сравнение технологий (каркас, газобетон, кирпич, брус), фундамент и кровля, инженерия и утепление. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, тендер подрядчиков, рейтинги бригад, карта цен по регионам, готовые ведомости материалов и практика без ошибок.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://loopenergia.com.br/harnessing-the-power-of-social-media-for-business-growth
https://hub.docker.com/u/zinashsmge
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Acho simplesmente supremo SupremaBet Casino, parece um reinado de diversao avassaladora. Tem uma tempestade de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um decreto de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago imperial. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um mandato, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que dominam. No geral, SupremaBet Casino e um cassino online que e um reino de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um decreto real, torna a experiencia de cassino um reinado de prazer.
supremabet-pb|
Achou totalmente epico DiceBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e fora da curva. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino variados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de classe. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e seguros, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, DiceBet Casino e o lugar certo pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de visual, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
dicebet Г© confiГЎvel|
Основная процедура включает в себя:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в краснодаре[/url]
fan chat
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Tambem a interface e fluida e energetica, facilita uma imersao total. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Ver os detalhes|
Квартира с отделкой https://новостройкивспб.рф экономия времени и предсказуемый бюджет. Фильтруем по планировкам, материалам, классу дома и акустике. Проверяем стандарт отделки, толщину стяжки, ровность стен, работу дверей/окон, скрытые коммуникации. Приёмка по дефект-листу, штрафы за просрочку.
топ seo [url=www.reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru]топ seo[/url] .
https://pixelfed.tokyo/gonzihmdani
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя
Интересные публикации в Автоновости ШинаПро делают тему авто действительно увлекательной.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево мурманск[/url]
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer hora. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino e indispensavel para jogadores para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Alem disso o site e rapido e atraente, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para competicao, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
http://www.playpixcasino.pro|
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике мурманск[/url]
https://hoo.be/ehryhaicmeh
kraken vk4
kraken СПб
Наркологическая клиника «ПолярМед Центр» — это пространство круглосуточной помощи, где медицинская точность сочетается с бережным сервисом и конфиденциальными процедурами. Мы строим терапию как последовательность проверяемых шагов: ставим понятную цель, выбираем подходящий инструмент, заранее определяем маркеры контроля и фиксируем время повторной оценки. Такая дисциплина исключает «универсальные сильные капельницы» и заменяет их модульными решениями с предсказуемым эффектом. Пациент и его близкие на каждом этапе понимают, почему именно такое назначение выбрано сейчас и в какой момент мы ожидаем улучшение самочувствия.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
рейтинг seo специалистов [url=www.top-10-seo-prodvizhenie.ru]www.top-10-seo-prodvizhenie.ru[/url] .
сео продвижение агентство [url=http://www.seo-prodvizhenie-reiting-kompanij.ru]http://www.seo-prodvizhenie-reiting-kompanij.ru[/url] .
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные» схемы. Модули подбираются по ведущей жалобе и времени суток; последовательность зависит от переносимости и клинических приоритетов. Ниже — ориентир, понятный пациенту; окончательные решения принимает врач с учётом противопоказаний и лекарственных взаимодействий.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
https://www.grepmed.com/hneohicubud
Rynek kasyn online w Polsce charakteryzuje się szybkim wzrostem Młodzi dorośli korzystający z urządzeń mobilnych napędzają wzrost popularności kasyn online oferujących bonus powitalny. Totalizator Sportowy posiada monopol, regulowany na mocy Ustawy o Grach Hazardowych z 2009 roku, a Total Casino jest wiodącą platformą. Konkurencyjny krajobraz obejmuje krajowych i zagranicznych operatorów posiadających licencje z UE. Zaawansowane technologie, takie jak integracja z krupierami na żywo i optymalizacja mobilna, poprawiają doświadczenia użytkowników, podczas gdy wybór kasyna online staje się coraz bardziej złożony inicjatywy odpowiedzialnego hazardu zyskują na znaczeniu. Dowiedz się więcej o dynamice rynku i przyszłych perspektywach.
Лечение запоя капельницами в владимире — прекрасный способ вернуть здоровье, который позволяет быстро вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни. При употреблении алкоголя в больших количествах возникают серьезные симптомы, такие как головные боли, рвота и расстройства психики. В клиниках по лечению зависимостей в владимире предлагают медицинскую помощь, включая капельницы для детоксикации. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru Лечение алкоголизма включает не только капельницы, но и психологическую поддержку во время отказа от алкоголя. Консультация нарколога поможет определить индивидуальный подход к восстановлению после запоя. Антидепрессанты и уколы от запоя также могут быть назначены для облегчения симптомов. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru предлагает услуги по лечению алкогольной зависимости, где опытные специалисты обеспечат комплексный подход к вашему выздоровлению. Не теряйте время — начните свой путь к здоровью уже сейчас!
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
фізичні властивості піску
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein weiterer Vorteil die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich finde absolut irre Lapalingo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Regenbogen funkelt. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und glanzend, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Nordlicht, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo deutschland|
Estou completamente louco por DiceBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que explode tudo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de classe. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e direto e sem treta, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, DiceBet Casino e o lugar certo pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
dicebet Г© confiГЎvel|
При домашнем формате мы сразу закладываем «мостик» к стационару: в случае ухудшения состояния перевод происходит бесшовно, по заранее оговорённым критериям. Пациент и семья знают, какие маркеры считаются целевыми (переносимость воды, ровный вечерний пульс, время до засыпания, число пробуждений), и когда состоится повторная оценка. Прозрачность снимает суету и укрепляет приверженность плану.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя цена мурманск[/url]
Поисковое продвижение помогает компаниям стать ближе к своим клиентам. Благодаря SEO пользователи находят нужные товары и услуги быстрее, а сайт получает больше трафика и заказов. Это инструмент, который работает на перспективу. Со временем видимость растёт, а вместе с ней и доход. Узнайте больше о пользе SEO: продвижение сайта банка
https://www.openlibhums.org/profile/caf6fa12-e298-4297-9bf1-30a3191f220a/
Такая карта снимает неопределённость. Пациент понимает, чего ожидать; родственники — когда и по каким метрикам судить об успехе; команда — что именно корректировать, чтобы сохранить управляемость терапии даже ночью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в мурманске[/url]
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Para finalizar, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial significativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver o site|
virtual experience
https://6438f4abcc32c625c53878ed8f.doorkeeper.jp/
финансы и инвестиции Искусственный интеллект: Искусственный интеллект, подобно алхимику цифровой эпохи, преобразует данные в знания, расширяя границы человеческого разума. Машинное обучение, словно неутомимый ученик, извлекает закономерности из огромных массивов информации, автоматизируя процессы и оптимизируя решения. Обработка естественного языка, словно лингвистический мост, позволяет машинам понимать и генерировать человеческую речь, открывая возможности для интеллектуальных ассистентов и чат-ботов. Компьютерное зрение, словно зоркий наблюдатель, позволяет машинам анализировать изображения и видео, автоматизируя контроль качества и распознавание объектов.
сушеный мухомор купить Muhomorus – интернет-магазин, где можно заказать мухоморы с доставкой по всей России. У нас вы найдете доступные цены на натуральные продукты, помогающие справиться с тревогой, стрессом, депрессивными состояниями, хронической усталостью и смягчить симптомы разнообразных заболеваний. Сушеные мухоморы не классифицируются как лекарственное средство, а относятся к парафармацевтике, являющейся альтернативным дополнением к основному лечению, используемым по личному усмотрению. Сбор, сушка, реализация и покупка – абсолютно легальны. Поэтому, мы предлагаем вам приобрести микродозы на законных основаниях.
Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу». Лечение собирается из модулей: гидратация, адресная коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка, при необходимости — мягкие анксиолитики по строгим показаниям. Порядок и насыщенность зависят от ведущей жалобы и времени суток. Ниже — ориентир для пациента: почему назначение выглядит именно так и в какой горизонт мы ожидаем эффект.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника мурманск[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Adoro a erupcao de BetPrimeiro Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao ardente quanto lava derretida. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de erupcao. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma labareda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, BetPrimeiro Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os vulcanologos do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual escaldante, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
bГіnus boas vindas betprimeiro|
Ich finde absolut irre Lapalingo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Spielwelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
lapalingo löschen|
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/[/url]
Estou completamente louco por DiceBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino alucinante. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um espetaculo a parte, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de classe. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma maravilha, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No fim das contas, DiceBet Casino vale cada segundo explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
dicebet reclame aqui|
kraken СПб
kraken market
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
Первый раз был на таком массаже, ощущения непередаваемые. Всё мягко, красиво и с настроением. Спасибо за прекрасный вечер. Обязательно попробуйте, индивидуалка вызвать Новосибирск, https://sibirka.com/. Всё прошло отлично, девушки знают своё дело.
массаж екатеринбург Медицинский центр “Шанс” предлагает комплексную помощь для всех членов семьи. Это современное, многопрофильное учреждение здравоохранения, где доступен широкий спектр медицинских сервисов для всей семьи. В штате МЦ работают опытные и квалифицированные врачи, а сам центр оборудован современной аппаратурой для диагностики. Ключевые направления деятельности включают: лабораторные исследования, УЗИ, функциональную диагностику, а также терапию заболеваний всех основнВ медицинском центр “Шанс” есть услуги для всей семьи. МЦ “Шанс” — это современное многопрофильное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее широкий спектр медицинских услуг для всей семьи. В МЦ работают высококвалифицированные специалисты, центр оснащен передовым диагностическим оборудованием. Основные направления работы: лабораторная диагностика, ультразвуковая диагностика, функциональная диагностика, лечение заболеваний всех основных систем организма.
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
удалить. Перепутал окна
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
народ скажите концетрацию 250 го в этом магазе
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
шоколадне дерево
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в петрозаводске[/url]
[url=https://lectnicametall.ru/]заказать лестницу на второй этаж[/url]
emeryflowers – Beautiful aesthetic, every section blooms with creativity and emotion.
скачать тик ток мод обновление Telegram – Центр Распространения Модификаций: Осторожность и Выбор Надежного Источника Запросы “скачать тик ток мод телеграм” и “скачать тик ток мод 2025 тг” указывают на Telegram как на популярную платформу для поиска и загрузки модов. Однако приоритетом является безопасность: выбирайте проверенные каналы и группы, чтобы избежать установки вредоносного ПО. Определитесь с желаемым функционалом: отключение рекламы, расширенные инструменты редактирования, возможность загрузки видео без водяного знака или снятие региональных ограничений.
супер !!!
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
да не врядли просто ихнему курьеру поджопников надавать надо что бы копытами веселей шевелил да и все
vpn для соцсетей VPN: Индивидуальный подход к защите каждого пикселя вашей цифровой жизни От компактного смартфона до мультимедийного центра в гостиной, каждому устройству нужен свой надежный защитник. VPN для телефона (будь то Android изящный или iPhone стильный) оградит от похитителей данных в кафе и аэропортах. VPN для Windows станет верным союзником в борьбе с вредоносным ПО и кибершпионажем. VPN для роутера и Smart TV превратит ваш дом в крепость, где каждый член семьи сможет безопасно наслаждаться плодами глобальной сети. Выбирая VPN, доверьтесь передовым протоколам шифрования вроде WireGuard, OpenVPN или IKEv2, – это гарантия неприкосновенности вашей цифровой тайны.
jamesonforct – Strong campaign presentation, design feels confident and message stands clear.
тюмень шлюхи форум
после антибиотика поднялась температура
TikTok Mod: Эволюция Мобильного Творчества в 2025 Году В стремительно меняющемся цифровом ландшафте 2025 года TikTok, как платформа коротких видео, продолжает захватывать внимание миллионов. Однако стремление к большей персонализации и расширенным функциям привело к появлению так называемых “TikTok модов” – модифицированных версий приложения, предлагающих уникальные возможности. Ключевым запросом при этом остается “тик ток мод скачать 2025 без вирусов”, что подчеркивает важность безопасности в мире цифровых модификаций. Пользователи стремятся получить максимум от платформы, не подвергая свои устройства риску. скачать тик ток мод 2025
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, awesome blog!
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя мурманск[/url]
Поисковое продвижение — это фундамент успешного присутствия компании в интернете. SEO помогает улучшить структуру сайта, контент и техническую составляющую. В результате сайт получает стабильный поток клиентов. Это выгодная инвестиция для любого бизнеса. Подробнее о возможностях SEO читайте https://transcriu.bnc.cat/mediawiki/index.php/Поисковая_Раскрутка_Сайтов_Под_Яндекс_И_Гугл
Детоксикация алкоголя в владимире , ключевой момент в лечении алкоголизма . Клиники наркологии в владимире предлагают разнообразные программы детоксикации , которые помогают преодолеть алкогольную зависимость. Нарколог на дому может предоставить поддержку при алкогольной зависимости на дому что является удобным решением для многих пациентов. нарколог на дом Лучшие врачи-наркологи проводят терапию запойного синдрома и обеспечивают необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкогольной зависимости. Обсуждение с наркологом позволяет разработать персонализированный план терапии. Не менее важна психологическая поддержка в процессе детоксикации, что способствует восстановлению после алкоголя и успешной реабилитации от алкоголя ;
https://muhomorus.ru/ В онлайн-магазине muhomorus можно заказать мухоморы с доставкой по всей России. Мы предлагаем выгодные цены на экологически чистые продукты, которые помогают снизить тревожность, бороться со стрессом и депрессией, уменьшить хроническую усталость и смягчить симптомы различных заболеваний. Следует помнить, что сушеные мухоморы не являются лекарством, они относятся к парафармацевтике и используются в качестве альтернативного вспомогательного средства по желанию покупателя. Сбор, сушка, продажа и покупка этих грибов абсолютно легальны. Поэтому мы предлагаем вам приобрести микродозинг абсолютно законным способом.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
кракен vk2
kraken зеркало
Это закон, хороший отзыв мало кто оставляет, а вот говна вылить всегда есть желающие вот и получается так, те у кого все хорошо, молчат и радуются
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
После передачи посылки курьерской службе ответственность за доставку несет именно курьерка, вы сами должны осознавать риск когда оформляете заказ с доставкой курьерки, и кто бреет? я вроде как бы согласился компенсирывать часть заказа, хватает еще наглости писать здесь жалобы.
douglasand55 – Very polished design, strong visuals and clear professional tone.
Оптимизация сайта помогает компаниям сокращать расходы на рекламу и увеличивать прибыль. SEO работает на постоянный рост и улучшение показателей. С каждым месяцем трафик становится стабильнее, а позиции — выше. Такой подход позволяет формировать сильный бренд. Подробнее о преимуществах SEO читайте – https://systemcheck-wiki.de/index.php?title=Создание_Сайтов_И_Их_Сео_Продвижение
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого мурманск[/url]
Ich schatze sehr Billy Billion Casino, es ist ganz ein Abenteuer voller Nervenkitzel. Das Spielangebot ist einfach phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Casino-Sessions von Evolution Gaming. Der Kundendienst ist tadellos, ist 24/7 erreichbar. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft in 1 Stunde fur Kryptowahrungen, obwohl mehr Freispiele waren super. Alles in allem ist Billy Billion Casino eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur Fans von Nervenkitzel! Au?erdem die Navigation ist intuitiv auf der mobilen iOS/Android-App, was den Spielspa? noch steigert.
billy billion|
Je suis subjugue par Donbet Casino, ca pulse comme un eclair foudroyant. Il y a une avalanche de jeux captivants, incluant des jeux de table d’une energie debordante. Le support est disponible 24/7, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’un courant. Les transactions sont fiables et fluides, cependant des bonus plus explosifs seraient geniaux. Pour resumer, Donbet Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs de frissons pour les passionnes de cryptos ! Par ailleurs le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel explosif, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
donbet promocode|
[url=https://lestniza-avtoritet36.ru/]заказать лестницу на второй этаж[/url]
У меня тоже была задержка.На мониторенге тоже отправку просрочили, в итоге дней 20 затратили на пересылку.Просто курьерка такая, они помоему там распиздяи ещё те…так что на счёт приема можешь не беспокоиться.там даже если мусора захотят что то найти то будет трудно разобраться что да где)вот допустим недавно заказал и курьерка ваще не то вбила))так что не переживай!Чемикалы всё ровно делают, сложновато будет найти даже если посыль откроют!
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
а вот на фофу гнать нельзя… она на высоте…
neighborsforrandy – Friendly community feel, layout conveys care and connection effectively.
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para resolver. O processo e simples e elegante, embora bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Acrescentando que a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial significativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler os detalhes|
Девушки очень красивые, грациозные и профессиональные, делают массаж незабываемым. Каждое прикосновение мягкое, плавное и чувственное, ощущаешь заботу и комфорт. После сеанса ощущение лёгкости и гармонии. Крайне советую, индивидуалки недорого Новосиб – https://sibirka.com/. Девушки настоящие красавицы, приятно провести время.
ehajjumrahtours – Professional and serene, the layout reflects faith and reliability.
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Продолжить чтение – https://starpeople.jp/column/matsudamakoto/20210316/16937
Без SEO сегодня невозможно эффективно продвигать бизнес в интернете. Оптимизация сайта обеспечивает видимость в поисковых системах и привлекает клиентов без постоянных затрат. Качественный контент, удобная структура и техническая чистота ресурса — основа успеха. SEO работает на перспективу и приносит результат с каждым месяцем. Подробности читайте: проверить сайт гугл
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://alloopt.ru]https://alloopt.ru[/url]
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
ct2020highschoolgrads – Heartwarming initiative, celebrating graduates with positivity and pride.
РОВЫНЫЙ МАГАЗ РОВНЫЙ ТС РОВНАЯ ВЕТКА И РОВНЫЕ КЛИЕНТЫ МИР ВАМ ВСЕМ !!!!!!
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Как у вас дела бразы?)
Поиск Идеального TikTok Mod: Баланс Между Функциональностью и Защитой Ключевыми факторами при выборе мода являются функциональность и безопасность. Запросы “скачать тикток мод последняя версия бесплатно” и “тикток мод скачать андроид бесплатно последнюю” говорят о стремлении получить новейшие возможности без каких-либо финансовых затрат. Однако, важно избегать сомнительных источников и отдавать предпочтение проверенным сайтам и форумам, где можно прочитать отзывы и убедиться в отсутствии вирусов. мод тик ток на андроид русском
SEO-продвижение помогает вывести сайт в ТОП поисковых систем и привлечь стабильный поток целевых клиентов. Благодаря грамотно подобранной стратегии оптимизации можно увеличить посещаемость и улучшить поведенческие факторы. Важно учитывать не только ключевые слова, но и структуру сайта, контент и скорость загрузки страниц. Комплексный подход даёт устойчивый результат и долгосрочный эффект. Узнайте больше о преимуществах профессионального продвижения https://americatheobliged.com/index.php?title=Сео_Продвижение_Сайтов_Для_Интернет_Магазинов
кракен vk4
кракен даркнет
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Заходи — там интересно – https://aarambh.tours/hello-world
luxnoe – Modern and stylish, this site exudes luxury and creative design.
сушёный мухомор купить В muhomorus, интернет-магазине, вы можете приобрести мухоморы с доставкой по России. Мы предлагаем низкие цены на экологичные продукты, предназначенные для уменьшения тревожности, борьбы со стрессом, депрессией, хронической усталостью и облегчения симптомов различных заболеваний. Сушеные мухоморы не являются лекарственным препаратом, а относятся к парафармацевтике, которая представляет собой альтернативное средство, используемое по усмотрению каждого человека в качестве поддерживающей терапии. Сбор, сушка, продажа и покупка абсолютно законны. Поэтому мы приглашаем вас купить микродозы законно.
хуясе надо было сначало уточнить а что брали хоть? ио названижю вещества
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Как у вас дела бразы?)
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para resolver. O processo e simples e elegante, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para quem aposta com cripto ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e estilosa, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial significativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler os detalhes|
SEO — это инвестиция в долгосрочный успех бизнеса в интернете. Оптимизация сайта повышает видимость, улучшает качество контента и способствует росту органического трафика. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии помогают удерживать позиции в ТОПе. Такой подход повышает доверие аудитории и увеличивает конверсии. Подробнее о продвижении сайтов читайте https://wikigranny.com/wiki/index.php/Эффективное_Продвижение_Сайтов_Для_Предпринимателей
https://baidak.ru/
прокладка трассы для кондиционера Установка кондиционера в Москве: Комфорт в Вашем Доме и Офисе Москва – мегаполис, где климатический комфорт играет важную роль в повседневной жизни. Наша компания предлагает профессиональную установку кондиционеров в Москве, обеспечивая оптимальный микроклимат в вашем доме или офисе. Мы учитываем все особенности помещения и подбираем наиболее подходящее оборудование, гарантируя качественный монтаж и долгосрочную работу вашей климатической системы.
karen4assembly – Clear and sincere campaign tone, content reflects leadership and integrity.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Доступ к полной версии – https://sobhe-emrooz.ir/1396/04/%D8%A7%D8%B9%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%B6-%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%B2%DB%8C%DA%A9%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%86-%D9%BE%D8%AF%DB%8C%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%A8%DB%8C%E2%80%8C%D9%BE%D9%88%D9%84%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%AA
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее – https://guestpostsoftware.com/backlink-quality-check-how-to-evaluate-links-for-best-seo-results
Запой — это значительная проблема, требующая профессиональной помощи. Вызвать нарколога на дом — это комфортный вариант получить необходимую медицинскую помощь. Капельница при запое помогают быстро вывести токсины из организма, обеспечивая очистку организма и восстановление здоровья. Лечение алкоголизма включает в себя лекарственные средства и психотерапевтическую помощь. Нарколог на дом оценивает состояние пациента и назначает индивидуальный план лечения, который может включать альтернативные методы, такие как травяные настои или психологические сеансы. Восстановление после запоя часто требует целостного подхода. Выведение из запойного состояния должно сопровождатся не только физическим, но и эмоциональным восстановлением; Реабилитация после алкоголизма, это долгий процесс, где важна поддержка в период запоя и поддержка родных. Важно помнить, что успешное лечение зависит от готовности пациента к переменам и стремления изменить свою жизнь.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Посмотреть всё – https://desibuzzbc.com/do-you-need-a-personal-injury-lawyer-how-can-they-help-you
stageofnations – Culturally rich, visuals celebrate unity and vibrant heritage beautifully.
Рейтинг автосервисов по капитальному ремонту двигателей в Москве [url=http://dzen.ru/a/aO5JcSrFuEYaWtpN/]http://dzen.ru/a/aO5JcSrFuEYaWtpN/[/url] .
всё как всегда быстро ,чётко ,без всякой канители ,качество как всегда радует ,спасибо команде за работу,ВЫ ЛУЧШИЕ!!!!!!
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Меня тут Кинули на 25к претензия в арбитраже!!!
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://www.blog.actubotte.be/de-la-prairie-a-votre-assiette
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Узнайте всю правду – https://westbankchiropractic.net/bg-new
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://ecommerce.markathinkdigital.com/product/tesco-asparagus-tips
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Узнать больше – https://epicreadsusa.digital/the-night-circus-by-erin-morgenstern
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Провести детальное исследование – https://bellville.gob.ar/2020/09/30/ya-esta-en-marcha-la-obra-de-cordon-cuneta-en-calle-alem
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Только для своих – https://anideva.com/le-monde-de-mes-reves-chapitre9
Решили попробовать создание объёмного макета, так как понадобился готовый прототип для инвесторов. Операторы 3D-печати помогли выбрать оптимальное решение, и сотрудничество оказалось комфортным. Темпы выполнения по-настоящему впечатлили, при этом поверхности выглядели профессионально. Использованные материалы оказались прочными и надёжными. Финальный бюджет приятно удивила, особенно учитывая отношение к клиентам. Впечатления только положительные и планируем заказывать новые проекты – 3D-печать. Мы печатаем модели для бизнеса, инженерных и дизайнерских проектов.
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Читать далее > – https://www.firsttrade-eg.com/ar/2016/09/30/new-collection-for-women-5
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://kumaitea.com/dark-chocolate-during-pregnancy
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Открой скрытое – https://hindi.newsmobile.in/fact-check-viral-video-of-maulana-using-toy-guns-for-treatment-of-a-patient-is-from-malaysia
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить больше информации – https://trendingwall.nl/inspiratie-voor-kinderkamer-behang
Качество закладки 10/10-пролежала долгое время что тоже не мало важно
https://torezljf.ru
Может обсудим как избежать напастья копоф при получении посылки от курьера???
Девушка-мастер очаровательная, её улыбка и грация делают массаж ещё более приятным. Массаж мягкий и чувственный, тело полностью расслабляется. После сеанса ощущение лёгкости и радости. Попробуйте, эро массаж вызвать Новосибирск – https://sibirka.com/. Вечер удался, девушки шикарные.
промокод melbet на сегодня
хочу извинится за поднятую панику(думаю ТС меня понимает , т.к. все мы люди и переживаем за свои деньги,тем более сфера деятельности расшатывает нервы как не крути).зная теперь с чем была связана данная проблема с поставками и положительным финалом в порядочности ТС не сомневаюсь.на данный момент работа налажена,в чем убедился сам и наслышан от других.
https://yasinovatayqf.ru
Получал пробный набор (ам2201, jwh250, jwh203, 5iai) от данного селлера, качество хорошее кроме 5iai вообще не понял.
Ich finde absolut magisch Trickz Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zauberstab funkelt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Zaubertrick funkeln. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zauberspruch wirkt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Am Ende ist Trickz Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Zaubertrick glanzt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Hexenwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
trickz casino kokemuksia|
https://wisesocialsmedia.com/story5914684/g%C3%A9n%C3%A9rateur-de-code-promo-1xbet
Je suis totalement electrifie par Donbet Casino, il offre une aventure aussi intense qu’un volcan. Le catalogue est une explosion de diversite, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client est d’une efficacite foudroyante, garantissant un support d’une puissance rare. Les gains arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, neanmoins des bonus plus explosifs seraient geniaux. Pour resumer, Donbet Casino promet une aventure incandescente pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un torrent, ajoute une touche de magie volcanique.
donbet free spins code|
Ich finde es unglaublich toll Billy Billion Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Abenteuer voller Nervenkitzel. Die Auswahl ist reich und vielfaltig, mit immersiven Live-Casino-Sessions von Evolution Gaming. Das Team bietet schnelle und effektive Unterstutzung, garantiert sofortige Hilfe per Chat oder E-Mail. Transaktionen mit Bitcoin oder Ethereum sind sicher und schnell, gelegentlich ich mir mehr regelma?ige Aktionen wunschen wurde. Kurz gesagt ist Billy Billion Casino enttauscht nie fur die, die gerne wetten! Daruber hinaus das Design ist visuell ansprechend und einzigartig, was den Spielspa? noch steigert.
more bang for your btc buck at billy billion crypto casino|
https://baidak.ru/
[url=https://svarog-lestnic.ru/]изготовление железных лестниц[/url]
Компания «СибЗТА» https://sibzta.su производит задвижки, клапаны и другую трубопроводную арматуру с 2014 года. Материалы: сталь, чугун, нержавейка. Прочные уплотнения, стандарты ГОСТ, индивидуальные решения под заказ, быстрая доставка и гарантия.
Качество продукции на высшем уровне.
https://shakhtyorskgp.ru
Вчера оплатил, сегодня уже трек скинули. Пока все ровно, посмотрим что придет…..
установка кондиционера в москве Доступная Установка Кондиционера в Москве: Качество без Переплат Мы предлагаем установку кондиционера в Москве недорого, не жертвуя при этом качеством работ и материалов. Мы оптимизировали свои затраты и предлагаем конкурентные цены, делая комфортный климат доступным каждому. Мы гарантируем профессиональный подход и соблюдение всех технических норм, обеспечивая надежную и долговечную работу вашего кондиционера.
Estou completamente apaixonado por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um pulsar selvagem. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O acompanhamento e impecavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, oferece recompensas continuas.
Descobrir mais|
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
em ergebnisse wetten
Also visit my page … köln wettbüro
Врачи «Частного Медика?24» контролируют состояние организма и предотвращают осложнения при выводе из запоя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника воронеж[/url]
Продвижение сайта — это не просто работа над ключевыми словами. SEO включает улучшение контента, анализ поведения пользователей и техническую оптимизацию. Благодаря комплексному подходу можно значительно повысить позиции ресурса в поиске. Это долгосрочная инвестиция в развитие бизнеса. Узнайте больше о преимуществах SEO: поисковый аудит сайта
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница нижний новгород[/url]
Круглосуточный стационарный вывод из запоя в Воронеже — доступная помощь в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время суток, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже[/url]
Ich bin suchtig nach Trickz Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein magischer Zirkus leuchtet. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Kaninchen aus dem Hut, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Illusion verblufft. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein zauberhafter Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Trickz Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie eine Illusion verblufft fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Hexenwerk, einen Hauch von Zauberei ins Casino bringt.
trickz casino no deposit bonus|
оптимал дозировка на 2дпмп при в\в от данного магазина какая?
https://amvrosievkakq.ru
народ подскажите а как дела обстоят в столице Москва закладками?
Ich bin suchtig nach Lapalingo Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und glanzend, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist Lapalingo Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
lapalingo meinungen|
Ich liebe es absolut Billy Billion Casino, es bietet ein Abenteuer voller Nervenkitzel. Der Katalog ist unglaublich umfangreich, inklusive topaktueller Slots von NetEnt und Pragmatic Play. Das Team bietet schnelle und effektive Unterstutzung, reagiert in wenigen Minuten. Zahlungen sind flussig und durch SSL-Verschlusselung gesichert, gelegentlich mehr Freispiele waren super. Kurz gesagt ist Billy Billion Casino definitiv einen Besuch wert fur Fans von Nervenkitzel! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist visuell ansprechend und einzigartig, die Immersion verstarkt.
more bang for your btc buck at billy billion crypto casino|
Детоксикация от алкоголя — важный этап в процессе борьбы с зависимостью от алкоголя, направленный на очищение организма. Признаки синдрома отмены могут быть серьезными и включают в себя беспокойство, потливость и дрожь. Методы детокса варьируются от медицинской помощи до домашних программ реабилитации. Возвращение к трезвости требует поддержки близких и понимания психологии зависимости. Здоровье печени значительно пострадает от чрезмерного употребления алкоголя. Альтернативы алкоголю, такие как некрепкие напитки, способствуют снижению рисков и возврату к здоровью. Подробности можно найти на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir028.ru.
asteroid-insurance – Clever concept, design feels futuristic and sharp with humor.
adirondackfiddlers – Full of tradition, music passion shines through each element.
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Поиск подрядчика — ответственный момент при реализации строительства.
Прежде чем начать сотрудничество, стоит оценить опыт исполнителя.
Проверенная фирма всегда гарантирует реальные сроки.
Необходимо учесть, какие материалы применяются при отделке.
https://github.com/SochiPool2025
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому краснодар[/url]
shopminq – Trendy e-commerce look, product visuals are crisp and appealing.
Отписывал Вам в аське,вы там мне не отвечаете в течении полудня..хотя обещались отправить заказ на следующий день после оплаты,а он сегодня!Жду вашего ответа.
https://donetskgma.ru
пиши разберемся
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в Самаре включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку и работу с психотерапевтом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом через «Stop-Alko» в Екатеринбурге — это помощь, когда вы не можете самостоятельно добраться до клиники. Первая помощь сразу у вас дома.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого екатеринбург[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает комплексное лечение запоя с использованием капельницы. Наши специалисты проводят диагностику и назначают индивидуальный план лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
benningtonareaartscouncil – Artistic and welcoming, site promotes community creativity wonderfully.
Услуга вывода из запоя от Stop-Alko в Екатеринбурге доступна в любое время суток — помощь приходит быстро.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Самаре на базе стационара — когда важен результат, стабильность и медицинская поддержка 24/7.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
staffinggoals.com
Выведение из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — помощь при острых состояниях и хронической зависимости. Наши опытные наркологи используют современные методы лечения для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника в воронеже[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
“Делаю дорогу,вторую Жду”
https://baligrows.com
У вас есть свой сайт магазина?
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже помогает быстрее восстановить силы и вернуть ясность мышления.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru
homecovidtest – Informative and reliable, design prioritizes health clarity and accessibility.
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same outcome.
staffinggoals.com
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
казино вавада зеркало
Hello there I am so excited I found your weblog, I really found you by accident, while I was researching on Askjeeve for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say cheers for a marvelous post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read through it all at the minute but I have bookmarked it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the fantastic job.
https://staffinggoals.com
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя цена сочи[/url]
сушеный мухомор купить Интернет-платформа muhomorus реализует мухоморы с отправкой по России. Доступные цены на экологически чистые товары, помогающие в борьбе с тревожностью, стрессовым состоянием, депрессивными настроениями, хронической усталостью и для облегчения симптоматики других болезней. Засушенные мухоморы не классифицируются как медикаменты, их относят к парафармацевтике, что представлет собой альтернативное средство, используемое индивидуально в роли поддерживающей терапии. Заготовка, сушка, сбыт и приобретение – абсолютно соответствуют закону. Поэтому приглашаем вас купить микродозинг полностью легально.
промокод на бесплатную ставку мелбет
charitiespt – Compassionate and community-driven, mission comes across with sincerity.
https://baidak.ru/
Несколько раз оформлял заказ в DRINKIO, и ни разу не подвели. Всё доставляют аккуратно и быстро, даже в часы пик. Сервис действительно круглосуточный, без перебоев. Курьеры всегда опрятные и вежливые, приятно иметь с ними дело. Уровень обслуживания на высоте: https://drinkio105.ru/
Выведение из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — помощь при острых состояниях и хронической зависимости. Наши опытные наркологи используют современные методы лечения для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]запой нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Je trouve absolument brulant VBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi ardente qu’une coulee de lave. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent comme des flammes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un volcan, repondant en un eclair brulant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une braise, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient exploser. Pour resumer, VBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style volcanique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus enflammee.
vbet огляди|
Ребят,а здесь только курёха?
https://alchevskut.ru
А чего брали то?
прокладка трассы для кондиционера Закладка и Прокладка Трассы: Важный Этап для Эстетики и Долговечности Закладка трассы и прокладка трассы для кондиционера – это ключевая задача, от которой зависит внешний вид и надежность всей системы. Мы проводим работы аккуратно и эффективно, минимизируя видимые коммуникации и обеспечивая долговечность трассы. Мы используем современные технологии и материалы, чтобы гарантировать эстетичный вид и бесперебойную работу кондиционера.
Ich flippe aus bei DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist gigantisch, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet erstklassige Unterstutzung, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren top. Am Ende ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino mit mega Spielspa? fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck test|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu kommt die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar sobre o Bingoemcasa porque foi melhor do que pensei. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao com muita interacao, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos foram bem estaveis. O atendimento no chat foi respondeu em segundos, o que ja me deixou tranquilo. As retiradas foram sem enrolacao, inclusive testei cripto e caiu em minutos. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que faltam mais promocoes, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Enfim, o Bingoemcasa vale demais a pena. Com certeza vou continuar jogando
bingoemcasa zeppelin|
fayettecountydrt – Purposeful and informative, organization’s vision feels transparent and clear.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
larkfest2013 – Vibrant and nostalgic, visuals radiate energy and celebration.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Экстренная помощь наркологов на дому — это необходимая мера в лечении зависимостей от наркотиков и алкоголя. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk019.ru предлагается поддержка наркологов, готовых помочь прямо у вас дома. В такие моменты жизненно важно обратиться за помощью, так как зависимость представляет серьезную угрозу. Домашняя терапия предоставляет удобную обстановку, где пациент получает медицинскую помощь, а также сопровождение в процессе восстановления; Мы обеспечиваем приватность, что важно для многих обращаться в клиники. Консультация психотерапевта также доступна, что способствует восстановлению после зависимости. Реабилитация наркозависимых включает в себя всестороннюю поддержку и наркологические услуги, направленные на возвращение к полноценной жизни. Выезд опытного врача обеспечивает, что процесс лечения будет проходить под постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Не ждите — действуйте сейчас — это решение, которое изменит вашу судьбу!
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]www.narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru[/url]
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж[/url]
https://groups.google.com/g/carts-of-vapor/c/acGE-tKqDwY
Да уж дживики мощные…только наврятли они у него есть.Ладно будем ждать прояснений.мне тоже не платную не бесплатную не дал пробу.и заказ 50 на 50 отказался сделать.
https://dokuchaevskpj.ru
Работала с данным магазином давным давно! Пожалуй самый лучший)
В «Частном Медике 24» в Воронеже каждый пациент, проходящий вывод из запоя в стационаре, получает комплексную помощь — диагностика, устранение интоксикации, восстановительная терапия, психологическая работа, всё с постоянным наблюдением и поддержкой, в условиях, где безопасность и анонимность стоят на первом месте.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Если нужно вывести из запоя, в Екатеринбурге можно вызвать специалистов Stop-Alko на дом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko предлагает капельницы и комплексное лечение запоя у пациента дома.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Если домашние методы не помогают, вывод из запоя в стационаре в Самаре — это безопасный выбор с профессиональной детоксикацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
holyspiritschooleg – Educational yet warm, design and content reflect care and faith.
Пациентам в Самаре предлагается анонимное лечение в стационаре с круглосуточным уходом и безопасными условиями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
seo компания москва [url=https://reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru/]reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru[/url] .
мод на русский тик ток Эра Модифицированного TikTok: Путеводитель по Версиям 2025 года В 2025 году TikTok продолжает эволюционировать, предлагая пользователям не только оригинальное приложение, но и множество модифицированных версий, известных как «моды». Эти моды, доступные в основном для Android, обещают расширенные функциональности, кастомизацию и обход ограничений, предоставляя пользователям больше контроля над своим опытом использования платформы.
georgewillwashpost – Clean layout, solid typography, content radiates intellect and authority.
https://www.blurb.com/user/1xbetcodegr?profile_preview=true
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Первый раз вижу такое с МН. От других селлеров все было норм с растворимостью. Растворяющийся полностью пер чуть посильнее…
https://torezljf.ru
Магазин не отвечает, может типо выходные, ждем понедельника.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
шумоизоляция дверей Шумоизоляция: Тишина и Комфорт в Путешествии Шумоизоляция автомобиля – это важный шаг на пути к созданию комфортного и приятного опыта вождения. Она позволяет снизить уровень шума от дороги, двигателя, трансмиссии и других источников, создавая тихую и спокойную атмосферу внутри салона. Шумоизоляция арок, дверей и комплексная шумоизоляция – это эффективные методы борьбы с нежелательным шумом, повышающие комфорт и концентрацию водителя.
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, oferece um thrill esportivo unico. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Tambem a interface e fluida e energetica, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Verificar isso|
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/[/url]
lcbclosure – Focused and informative, the message feels urgent and clearly communicated.
Устный перевод Нотариальный перевод: Юридическая значимость и безупречная точность Нотариальный перевод – это важный этап при оформлении документов для предъявления в государственные органы и организации. Мы предлагаем нотариальный перевод документов, выполненный профессиональными переводчиками и заверенный нотариально. Это гарантирует юридическую силу переведенного документа и его соответствие оригиналу. Особое внимание уделяется нотариальному переводу паспорта, нотариальному переводу диплома и нотариальному переводу свидетельства, поскольку эти документы часто требуются для самых разных целей. Мы также осуществляем нотариально заверенный перевод справки и других документов.
mayceformayor – Campaign feels strong and grounded, visuals emphasize trust and service.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Сайт konsultaciya-advokata51.ru предлагает вам разнообразные возможности. Юридическая консультация – это важный шаг для многих людей. На нашем сайте вы сможете получить профессиональные советы.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata51.ru]услуги адвоката бесплатно[/url].
Такой подход обеспечивает надежную защиту прав клиентов.
Первое, что стоит учитывать – это квалификация адвокатов. Наши юристы обладают необходимыми знаниями и опытом. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень обслуживания.
Важно, чтобы юридические услуги были доступны каждому. Вы сможете легко ознакомиться с нашими тарифами и предложениями. Клиенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант в зависимости от своих нужд.
Наши адвокаты готовы предоставить юридическую помощь в режиме онлайн. Сегодня возможность получить помощь через интернет очень важна. Наши специалисты готовы ответить на ваши вопросы круглосуточно.
Желаете проверить, на каком именно ресурсе наиболее удобно и выгодно смотреть фильмы в хорошей компании? Попробуйте КИНОГО ([url=https://games-igry.biz/]https://games-igry.biz/[/url]). Я уверен на все сто, что вы останетесь в полном восторге. Испытано временем: весь контент и функционал на Kinogo полностью бесплатен, качество трансляции и контента – не подводит, и отсутствует необходимость в регистрации. Лучшие фильмы и сериалы 2025 года собраны в одном месте!
https://t.me/Virtsex_devushki Девушки в виртуальности: Искренность, общение и поиск родственной души. Для многих девушек вирт становится местом, где можно почувствовать себя увереннее, раскрыться и найти поддержку со стороны других участниц сообщества. Здесь не важна внешность, социальный статус или возраст – ценятся ум, чувство юмора и умение сопереживать. Виртуальное общение позволяет девушкам делиться своими мыслями, переживаниями и мечтами, не боясь осуждения или непонимания. Это возможность найти настоящих подруг, с которыми можно поделиться радостью и печалью, получить ценный совет и просто хорошо провести время вместе.
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
There is so much to try to understand
Круглосуточный стационарный вывод из запоя в Воронеже — доступная помощь в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время суток, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru
Решили мы тут значит с кентом несколько дней назад покурить . Вспомнили про сайт chem24.biz.ski и решили взять 2гр твердого, оплотили короче,описание адреса было простым и спрятано было грамотно!!!
https://makeevkavp.ru
они на телефон должны позвонить,обычно так
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru
masonchallengeradaptivefields – Inspirational cause, presentation is heartfelt and full of purpose.
milestonerest – Inviting visuals, design creates a sense of comfort and good taste.
DRINKIO стал для меня настоящим открытием. Доставка работает быстро и без сбоев, даже ночью. Всё приходит в аккуратной упаковке, курьеры вежливые и внимательные. Очень удобно, что всё можно оформить онлайн. Теперь пользуюсь только этим сервисом, https://drinkio105.ru/
https://www.kingstonnews.net/newsr/15839
https://haikudeck.com/presentations/pRIkKVARIW
peoplesprotectiveequipment – Practical and safety-focused, design feels direct and trustworthy.
кракен магазин Поиск Актуальной Ссылки: Лабиринт Зеркал и Фишинга Сложность доступа к ресурсу “Кракен” обусловлена постоянной блокировкой основных доменов. В результате, пользователи вынуждены искать актуальные “кракен ссылка”, “кракен сайт” или “кракен зеркало” через поисковые системы, что повышает риск столкнуться с фишинговыми сайтами. Мошенники активно пользуются стремлением пользователей к анонимности и создают поддельные ресурсы, имитирующие оригинальный “Кракен магазин” с целью кражи учетных данных и финансовых средств. Важно проявлять крайнюю бдительность, перепроверять URL-адреса и использовать надежные источники информации.
хотели бы услышать отзывы о Ск муке
https://luganskbzi.ru
а кто такой лиа 12??
трансы воронеж Примеры и Особенности Каналов Каналы, подобные @ts_novosibirsk (трансы Новосибирск, трансы новосибирска), @ts_ekaterinburgh (трансы Екатеринбург, трансы Екатеринбурга), @ts_voronezh (трансы Воронеж, трансы Воронежа), @transy_volgograd (трансы Волгоград, трансы волгограда) и @ts_chelyabinska (трансы Челябинск, трансы челябинска), отражают специфику каждого города, собирая локальную информацию. Важно отметить, что контент этих каналов может быть разнообразным: от новостей и анонсов мероприятий до личных историй и дискуссий.
letthemplaymn – Passionate and purposeful, the site speaks strongly for youth engagement.
teamtadros – The mission feels bold, visuals highlight unity and determination.
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, superb blog!
https://easystaffingmd.com
Je trouve absolument brulant VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Le service client du casino est une torche d’efficacite, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une braise, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, VBet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les volcanologues du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un cratere en fusion, facilite une experience de casino eruptive.
vbet casino скачать на андроид|
Ich bin suchtig nach Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und machtig, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist Lowen Play Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Savanne beherrscht fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Raubtier, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
löwen-play test|
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
https://infoempresaconsultores.com/2019/04/04/consulting-project
да не сцы, бывает у него такое )) магаз работает ровно, но вот с розницей у них напряг, изначально то ориентированы на опт, и просто рук не всех теперь на хватает. позже ответит.
https://makeevkadj.ru
все пришло.пока не пробовал.конспирация на высшем уровне.спасибо
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, fugt Magie hinzu. Hervorzuheben ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
exodusalliance – Empowering theme, site feels hopeful and mission-driven throughout.
Выездной нарколог – это прекрасная возможность для тех, кто сталкивается с алкогольной зависимостью или наркоманией. Лечение наркомании включает в себя детоксикацию и реабилитацию зависимых. Выездной нарколог предоставляет конфиденциальную помощь, что особенно важно для пациентов, стыдящихся обращаться в клинику. Кодирование от алкоголизма – эффективный метод, который можно провести на дому. Помощь на дому включает в себя консультации психолога и медицинскую помощь. Встречи с наркологом помогут понять, как избавиться от зависимости. Программы восстановления и семейная терапия играют ключевую роль в процессе лечения. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru вы найдете подробности о доступных услугах.
Galera, preciso contar o que achei sobre o Bingoemcasa porque foi melhor do que pensei. O site tem um jeito leve que lembra uma festa entre amigos. As salas de bingo sao sempre lotadas, e ainda testei a roleta ao vivo, todos me deixaram impressionado. O atendimento no chat foi educado e prestativo, o que ja me deixou satisfeito. As retiradas foram instantaneas, inclusive testei cartao e nao tive problema nenhum. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que as promocoes podiam ser mais ousadas, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Na minha visao, o Bingoemcasa virou parada obrigatoria. Vale testar sem medo
bingoemcasa site|
oscarthegaydog – Whimsical and delightful, brand personality shines through humor and charm.
В Екатеринбурге служба Stop-Alko круглосуточно помогает вывести из запоя на дому — быстро, анонимно и без постановки на учёт.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в екатеринбурге[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
https://www.tarauaca.ac.gov.br/profile/codeprom10o20986/profile
Hi there! I realize this is kind of off-topic but I needed to ask. Does operating a well-established website like yours take a large amount of work? I am completely new to writing a blog but I do write in my journal daily. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any suggestions or tips for brand new aspiring blog owners. Thankyou!
https://easystaffingmd.com/
Сервис Stop-Alko предлагает помощь при запое на дому в Екатеринбурге. Услуга доступна 24/7.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
https://www.virtualhighstreets.com/product/linear-stem-cushion
Врачи клиники в Воронеже устраняют симптомы интоксикации и поддерживают организм при выводе из запоя.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru
daybirdsyr – Energetic vibe, visuals and tone reflect creativity and modern living.
supportsros – Compassionate tone, clear visuals support their advocacy with sincerity.
Если неактуальные сообщения выше, откорректируйте сами. По компенсациям, если останутся вопросы после получения посылки, пишите в новом году, размер зависел от веса, длительности, индивидуальных переплат на счета и прочих обстоятельств. :ok:
https://dokuchaevskpj.ru
трек получен, ребятам уважуха:rasta:
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://likhamedical.com/?p=1
justinhicksformissouri – Strong campaign message, design feels authentic and community-focused.
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Ознакомиться с отчётом – https://wapsmartgps.com/the-importance-of-building-a-strong-brand-identity
nyscanalconference – Informative and organized, layout suits event communication well.
Unlock your images with WebPtoJPGHero.com, the simple, free solution for solving WebP compatibility issues. While the WebP format helps websites load faster, it can leave you with files you can’t easily edit or share. Our online tool provides an instant fix, transforming any WebP image into a high-quality JPG that works seamlessly across all your devices and applications. You can fine-tune the output quality to balance clarity and file size, and even save time by converting an entire batch of photos at once. It’s all done quickly and privately right in your browser — no software required.
https://chronicle.ng/1xbet-promo-code-1xbro200-bonus-100-e130/
DRINKIO стал моим любимым способом оформить заказ. Всё предельно просто, сайт работает отлично. Курьеры вежливые, доставка стабильная. Ассортимент богатый, всегда есть из чего выбрать. Удобно, быстро и надёжно, https://drinkio105.ru/
Нужно 5 сообщений что бы написать модэратору, не обесуть
https://alchevskut.ru
Еще раз извините. Треки тоже бьются не сразу, курьерки “в завалах”, иногда он только начинает определяться на сайте курьерки, а его уже вручают или вручили получателю. Не пугайтесь, что мониторинг начнется не сразу, вам всем все придет заказанное.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Не упусти важное! – https://eatonefeedone.com/recommendations/tortilla
kraken ссылка Кракен: Путеводитель по Тенетам Цифровой Вседозволенности В полумраке цифрового пространства, где анонимность становится валютой, имя “Кракен” шепчут с благоговейным трепетом и опаской. Это не просто платформа, это целая экосистема, обещающая доступ к запретному, сокрытому и ускользающему. “Кракен ссылка,” “кракен сайт,” “кракен магазин” – эти слова становятся ключами, открывающими двери в мир, где законы реального мира не имеют силы. Но путь к этой свободе усеян минами, и лишь немногие способны пройти его, не потеряв себя.
tinacurrin – Artistic and bold, site radiates passion and expressive creativity.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Открой скрытое – https://raduga-45.ru/uslugi-po-vyvodu-iz-zapoya-pokhmelya-i-lecheniyu-a-h2
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://successfullquote.com/how-to-change-your-life
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Детали по клику – https://moonpaint.umi-doodle.info/2022/10/26/%E6%A2%B5%E5%AD%97%E3%81%AE%E6%97%85%EF%BD%9C%E5%A4%A7%E6%AD%A3%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%A6
Collaboration with influencers has become one of the most effective strategies in digital promotion.
It allows companies to build relationships with their followers through the voice of content creators.
Bloggers produce stories that inspire trust in a product.
The key advantage of this approach is its genuine communication.
https://zionijha96295.59bloggers.com/33976668/how-influencers-are-transforming-consumer-behavior-through-genuine-content
People tend to engage more actively to real recommendations than to traditional advertising.
Companies can carefully identify influencers to target the right audience.
A thought-out influencer marketing campaign enhances visibility.
As a result, this method of promotion has become an essential part of brand strategy.
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Познакомиться с результатами исследований – https://travelspecialistsmorocco.com/2-days-tour-from-marrakech-to-merzouga-desert-2
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://qupite.ru/8850834-uslugi-po-vyvodu-iz-zapoya-pokhmelya-i-lecheniyu-alk-121m
платил 5 февраля свою посылочку!как вы поняли ничего не получил!ТС кормил меня завтраками,в итоги обещал вернуть деньги если не получу до 28 февраля!деньги мне тоже никто не вернул вместо этого мне прислали новый трек и написали что мы обещали что получите товар и деньги возвращать не буду!мои обьяснения о том что вашу посылку уже некому получать он слушать не хочет и возвращать деньги тоже!Ув.Адмистрация форума прошу не удалять мой пост и если нужно могу скинуть переписку!
https://makeevkadj.ru
Тоже хочу сделать заказ.Жду ответа
Печать на 3D-принтере — это эффективная технология, который помогает реализовать самые смелые идеи. Мы предлагаем услуги 3D-печати по доступным ценам. Наша команда используем современное оборудование, что делает каждую модель максимально детализированной. Материалы подбираются под задачу, благодаря чему услуги подходят для бизнеса, дизайна и частных проектов. Готовое изделие вы получаете в кратчайшие сроки, а наши расценки делают 3D-печать доступной каждому. Оставьте заявку онлайн, и любая ваша идея станет реальностью, https://tandme.co.uk/author/ryderheckma/. Наши услуги включают полный цикл печати и постобработки.
harryandeddies – Cozy restaurant vibe, visuals and menu presentation feel deliciously inviting.
трансы Челябинск Локальные Сообщества: Поддержка и Информация Эти каналы служат важным ресурсом для транс-сообщества. Здесь можно найти информацию о врачах, психологах, юристах и других специалистах, оказывающих поддержку транс-персонам. Каналы помогают в поиске дружелюбных мест, где можно безопасно и комфортно проводить время. Они также предоставляют платформу для обмена опытом, обсуждения проблем и просто для общения с людьми, которые понимают.
southbyfreenoms – Fun, quirky branding with energetic layout and friendly design.
Теплый и уютный балкон способен стать любимым уголком вашей квартиры. Грамотное утепление балкона позволит наслаждаться комфортом круглый год. Современные технологии превращают холодную лоджию в дополнительное функциональное помещение, где приятно проводить время независимо от сезона: утепление балкона
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Смотрите также… – https://brodertech.ch/hallo-welt
https://md.darmstadt.ccc.de/s/mXc4F99_z
Всё ок подняли, но место опять немного людное (самый центр города)
https://shakhtyorskgp.ru
Списались с оператором. Нужно взять 50 гр. СК.
Лечение зависимостей анонимно — это важный шаг для пациентов с проблемами зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru можно получить сведения о лечении зависимостей, реабилитации и ресурсах. Анонимное лечение позволяет пациентам получать помощь без боязни осуждения.Помощь нарколога включают выведение токсинов, психотерапию и экстренное вмешательство. Процесс реабилитации часто включает группы поддержки, что помогает в процессе выздоровления. Меры по профилактике зависимостей также играет значимую роль, обеспечивая долгосрочный успех. Профессиональные консультации помогут разобраться в проблемах и найти пути решения. Поддержка для наркозависимых доступна и эффективна, даже если они бояться открыться.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://cetalimentos.cl/index.php/2023/06/02/ceta-participo-en-conversatorio-innova-aramark-sobre-desafios-de-la-industria-alimentaria
electamandamurphy – Inspiring campaign, message of progress and empathy shines through.
1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi [url=http://1xbet-giris-1.com]http://1xbet-giris-1.com[/url] .
Благодарен за заказ во вторник оплатил – в пятницу / утром / товар получил
https://makeevkavp.ru
благодарствуюсь, бро)) под затупил малеха, вижу ты тут, все хорошо
https://sportsnewstime.org/1xbet-promo-code-bonus-200-up-to-e-130/
Значит не туда стучишься!а ребята молодцы!
https://dubaigrowes.com
Конечно работаем
startguthaben ohne einzahlung wetten
Look at my blog post: wette doppelte chance (Zac)
kim4commonsense – The campaign feels approachable, visuals and tone are relatable.
kraken зеркало В поисках Кракен: Ориентируясь в Море Ссылок и Зеркал В цифровом подполье, где анонимность ценится превыше всего, имя “Кракен” звучит как символ свободы и безграничных возможностей. Но чтобы добраться до его глубин, необходимо преодолеть лабиринт зеркал, скрытых ссылок и не всегда доброжелательных проводников. “Кракен ссылка,” “кракен сайт,” “кракен магазин” – эти запросы становятся заклинаниями, открывающими двери в мир, где правила устанавливаются самими участниками.
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
В больничных условиях «Частного Медика 24» врачи контролируют давление, сердце и функции жизненно важных органов при выводе из запоя.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — безопасный и эффективный метод лечения. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
https://delavore.com.ua/yak-unyknuty-poshkodzhen-na-stekli-far-pid-chas-ek.html
Стационар «Частного Медика?24» помогает безопасно и быстро восстановиться после длительного запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
виє собака прикмети
Ну что же, сегодня получил свою посылку, на этот раз все было в наилучшем виде, конспирация на все 10 баллов из 10!
https://alchevskut.ru
продавец в аське..только что с нми общался
rideformissingchildren – Heartfelt cause, presentation honors the mission beautifully and respectfully.
Клиника «Частный Медик 24» в Самаре оказывает помощь при запое анонимно, круглосуточно и без скрытых платежей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в самаре[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Воронеже проходит анонимно, с круглосуточной поддержкой специалистов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/[/url]
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге от «Похмельной Службы» включает как базовый, так и премиум-уровень помощи — со всеми необходимыми препаратами и поддержкой.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru
Врачи «Частного Медика 24» контролируют состояние организма и предотвращают осложнения при выводе из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника воронеж[/url]
В Самаре клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре с полным медицинским контролем и комфортными палатами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Я клад нашел, но вопервых не все в нем а во вторых содержимое разное и самое главное это место и описание этого места. Завтра буду пытаться связаться с ним.
https://torezljf.ru
е знаю уместен ли мой вопрос в данное “смутное время” но все же откуда высылается заказы…? хотя бы из какой части РФ если это РФ…)))
Услуга вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге от «Похмельной Службы» включает как базовый, так и премиум-уровень помощи — со всеми необходимыми препаратами и поддержкой.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
1xbet turkey [url=http://www.1xbet-giris-7.com]1xbet turkey[/url] .
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя в нижний новгороде[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru
t-walls-of-kuwait-iraq – Historical and impactful, visuals convey memory and meaning strongly.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сочи[/url]
Адекватное лечение, комфорт и забота — так проходят дни в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» во время вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/[/url]
המציא שם אוניברסלי שיתאים גם לילדה וגם לילד. אך בתחילה הוא רצה לתת שם אתני בהתאם למסורת. הוא מגיע המבולגן והמריח של בעלה, וזרועה ציירה את אותם עיגולים על הנרתיק והדגדגן שלה. הבושה בסופו של דבר. עד learn more here
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
В «Частном Медике 24» в Самаре выход из запоя организуют поэтапно: диагностика, лечение, реабилитация.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru
трансы Екатеринбург География Поддержки: От Сибири до Юга России Каждый из каналов, будь то @ts_novosibirsk (трансы Новосибирск, трансы новосибирска), @ts_ekaterinburgh (трансы Екатеринбург, трансы Екатеринбурга), @ts_voronezh (трансы Воронеж, трансы Воронежа), @transy_volgograd (трансы Волгоград, трансы волгограда) или @ts_chelyabinska (трансы Челябинск, трансы челябинска), отражает уникальную специфику своего региона. В них аккумулируется информация о локальных ресурсах, специалистах, мероприятиях и безопасных пространствах, создавая атмосферу взаимной поддержки и понимания. Эти платформы становятся своеобразными цифровыми хабами, объединяющими транс-сообщество в каждом конкретном городе.
Для тех, кто находится в поиске подходящего ресурса, где можно смотреть фильмы через интернет, то добро пожаловать на КИНОГО ([url=https://vseigru-net.biz/]https://vseigru-net.biz/[/url]). Наш проект с гордостью предлагает по-настоящему огромной коллекции. Изображение и звук всегда на безупречном уровне качества, от четкого HD и выше. Вся фильмотека на Kinogo полностью бесплатна и не требует регистрации.
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]www.narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru[/url]
https://factava.com.ua/stsenariyi/stsenariy-vidkryttia-memorialnoi-doshky-krok-za-krokom-do-vshanuvannia-pamiati-heroiv/
cranberrystreetcafe – Cozy and charming, design evokes warmth and delicious experiences.
Отличный магаз, качество на ура. даже если сам реагент не сильный.
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Обратите внимание, ТС отказывается работать с ГАРАНТОМ! хоть и магазин древний и проверенный! но хочется спать спокойно! АДМИНЫ ОБРАТИТЕ ВНИМАНИЕ, ПОРА КАК ТО ИЗМЕНИТЬ РЕЖИМ РАБОТЫ ГАРАНТА. СДЕЛКИ ПРОВОДИТЬ ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО ТОЛЬКО ЧЕРЕЗ ГАРАНТА!
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в сочи[/url]
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
If you want to learn everything about online platforms in the United States, then this is something you shouldn’t miss. Discover the full details via the following link:
best online casino USA
https://factava.com.ua/karta-kyieva/
georgetowndowntownmasterplan – Informative and civic-minded, content clearly explains planning goals.
какие манерные нынче клиенты пошли, плюнешь в рожу драться лезут, видете ли ему грубо ответили, я с ТС с момента регистрации общаюсь и не разу он не забуровил даже когда были терки а они поверь были, так что не пизди про невежливое обращение, да и по переписки видно что все ровно, ищи проблему в себе….
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
Приветствую всех ровных жителей этой ветки.Друзья помогите мне.Где ,на какой страничке я могу найти хозяина даннго магазина.И где адреса магазина???Где прайс???Вообще не понятный магазин.И как выглядет его аватарка.
Длительность вывода из запоя во многом зависит от тяжести состояния, общего здоровья и продолжительности самого запоя. Если пациент обратился на ранней стадии, зачастую хватает 1-2 капельниц и короткого курса поддержки. Но при запое более пяти-семи дней, когда имеется острая интоксикация, требуется более продолжительная терапия и круглосуточное наблюдение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narko-reabcentr.ru/kruglosutochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve
Пациентам в Самаре предлагается анонимное лечение в стационаре с круглосуточным уходом и безопасными условиями.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В Екатеринбурге «Похмельная Служба» проводит вывод из запоя анонимно и безопасно, с применением современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы ищете безопасный вывод из запоя, обратитесь в Екатеринбурге в «Похмельную Службу». Медики приедут в течение часа.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg26.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
В Воронеже клиника помогает стабилизировать состояние и восстановить здоровье после запоя.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
http://darmowe-gadzety3.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=439785#439785
saveshelterpets – Touching initiative, site feels compassionate and community-focused.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Воронеже проходит анонимно, с круглосуточной поддержкой специалистов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
Алкогольная или наркотическая интоксикация — это не просто временное ухудшение самочувствия, а серьёзное медицинское состояние, требующее неотложной помощи. Когда человек находится в запое или состоянии ломки, его организм стремительно теряет силы, нарушается работа сердца, печени, мозга, возникают панические атаки, судороги, спутанность сознания. В таких случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Если пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники, оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом. В Красногорске такая услуга доступна круглосуточно благодаря выездной службе клиники «Ключ к Здоровью».
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом в красногорске[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в сочи[/url]
Вызвал такси;)
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
ты уже третий у кого посыль подлетела может продавец как то разьяснит ситуацию ну ладно у одного ну ладно у второго но трое это уже какая то система ждемс уважаемый ТС Ваших обяснений
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в нижний новгороде[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
В Самаре в «Частном Медике 24» пациент получает детоксикацию, восстановительное лечение и круглосуточное наблюдение врачей.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — безопасный и эффективный метод лечения. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
В Самаре «Частный Медик 24» предлагает прозрачные цены на вывод из запоя, без неожиданных расходов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре в самаре[/url]
Стационарное лечение запоя в Воронеже — гарантированная анонимность и комфортные условия. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, обеспечивая полное восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh23.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж[/url]
Сериалы в хорошем качестве — это когда всё идеально!
https://michaeldnaumann.online/index.php/Ruseriya_70S
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в москве[/url]
Клиника «Частный Медик 24» в Самаре оказывает помощь при запое анонимно, круглосуточно и без скрытых платежей.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara24.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре клиника в самаре[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно сочи[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно москва[/url]
В условиях клиники пациент находится под наблюдением медицинской сестры и врача 24/7, что особенно важно при тяжёлой интоксикации и риске острых осложнений. Быстрый доступ к расширенной диагностике — ЭКГ, УЗИ, анализы крови — обеспечивает точную корректировку терапии. Стационар подходит тем, у кого есть серьёзные сопутствующие заболевания или высокий риск алкогольных психозов.
Получить больше информации – https://алко-избавление.рф/
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Discover the best PS2 games in Canada! A curated list of timeless classics, including action, RPGs, and sports titles. Relive the nostalgia of top PlayStation 2 hits loved by gamers: PS2 game price guide
Вывод из запоя в стационаре — это шанс начать путь к трезвой жизни, и в Самаре этот шанс предоставляет «Частный Медик 24».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]стационар вывод из запоя[/url]
Discover the best PS2 games in Canada! A curated list of timeless classics, including action, RPGs, and sports titles. Relive the nostalgia of top PlayStation 2 hits loved by gamers: official PS2 games resource Canada
Госпитализация в стационаре «Частного Медика 24» позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и начать новую жизнь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara25.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре самара[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Пушкино — это современная и надёжная методика лечения, заключающаяся в создании устойчивого барьера к употреблению спиртного. В наркологической клинике «Орион-Клиник» применяется сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических технологий, благодаря чему пациент получает не только химическое, но и психологическое подкрепление трезвости. Процедура проводится после полной диагностики, с учётом индивидуальных особенностей, анамнеза и текущего состояния организма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-pushkino4.ru/]anonimnoe kodirovanie ot alkogolizma[/url]
если меня очень привлекли цены, я естественно буду пытаться достучаться до сейлера. а некоторые этого ждут сутками.
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
отличный селлер
Стационарная детоксикация от алкоголя в Воронеже — восстановление организма под наблюдением специалистов. Мы проводим процедуры очищения организма от токсинов, восстанавливая физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh24.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
Ритм жизни в мегаполисе и постоянный стресс часто становятся причиной развития зависимостей у жителей города. В такой ситуации необходима профессиональная консультация врача. Оптимальное решение – вызов нарколога на дом в Москве. Это обеспечивает не только получение медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке, но и полную конфиденциальность.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Воронежа — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы обеспечиваем круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексное лечение, включая детоксикацию, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-voronezh22.ru/[/url]
https://hostndobezi.com/post/43873_code-promo-1xbet-du-jour-pour-les-passionnes-ivoiriens-le-code-promo-1xbet-cote.html
https://www.beirutnews.net/newsr/15861
Ритм жизни в мегаполисе и постоянный стресс часто становятся причиной развития зависимостей у жителей города. В такой ситуации необходима профессиональная консультация врача. Оптимальное решение – вызов нарколога на дом в Москве. Это обеспечивает не только получение медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке, но и полную конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru
Не менее опасны и психоэмоциональные нарушения, связанные с абстинентным синдромом: тревога, чувство паники, галлюцинации, нарушения координации. В тяжёлых случаях может развиться алкогольный делирий (белая горячка) со спутанностью сознания, бредовыми идеями и приступами агрессии. Самостоятельный резкий отказ от спиртного в этом состоянии чреват непредсказуемыми осложнениями вплоть до судорог и комы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
albanysuperducks – Fun and quirky, visuals bring playful excitement to life.
кракен магазин Безопасность Транзакций: Баланс Анонимности и Риска Использование “kraken” предполагает определенный уровень риска, связанный с анонимностью транзакций. Хотя сохранение конфиденциальности является одним из ключевых преимуществ платформы, оно же затрудняет разрешение споров и защиту от мошенничества. При совершении покупок на “kraken” необходимо тщательно выбирать продавцов, изучать отзывы и использовать эскроу-сервисы для минимизации финансовых потерь. Крайне важно помнить, что стремление к анонимности не должно быть поводом для игнорирования правил безопасности и здравого смысла.
У меня разок было, что трек перестал на два дня отслеживатся, но нечего доставили все пучком.
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Чемикал, пожалуй, самый ровный магаз из всех ныне сушествующих! Цены, конечно есть и по меньше в других местах, однако для себя я выбрал безопасность и надежное сотрудничество, а не дешевизну, которая как показывает практика всегда заканчивается не очень хорошо.
Именно поэтому при затяжных запоях необходима квалифицированная медицинская помощь, позволяющая безопасно и максимально комфортно прекратить приём алкоголя. Клиника «Стратегия Здоровья» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя в Москве как в условиях стационара, так и с выездом на дом. Врачи работают круглосуточно, используя проверенные методики детоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя в москве[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Продолжить чтение – https://hanne-bau.de/hello-world
stopkrasner – Strong political tone, site expresses clear intent and decisive messaging.
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
J’ai une passion devorante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. La selection de jeux est astronomique, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le support client est irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! En bonus le site est rapide et futuriste, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter en ligne|
https://www.capetownexpress.com/newsr/15805
Всем приветствую! Хочу рассказать находкой для максимально комфортного и экономного просмотра. Это сайт КИНОГО ([url=https://igru-net.biz/]https://igru-net.biz/[/url]). На его просторах отсутствует всплывающих окон, отличное качество видео и звука и по-настоящему огромная подборка фильмов. Уже сейчас посмотрел с удовольствием целый ряд новинок 2025 года на Kinogo, и это просто супер. Всё бесплатно и без регистрации.
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le support client est impeccable, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. En resume, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, il offre une aventure chiffree palpitante. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Avec des depots crypto instantanes. Les agents repondent comme une comete, toujours pret a naviguer. Les transferts sont fiables, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un tresor. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et captivant, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Un atout cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
Lire les dГ©tails|
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
вчера трек получил:good: надеюсь всё будет ровно.
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
у нас бы ноги поломали за такое, тем более сумма нормальная…
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre d’innovation. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau decentralise, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus d’accueil est eclatant. Les agents repondent avec une precision quantique, joignable instantanement. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience memorable pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un wallet, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Voir toutes les infos|
J’ai une passion jazzy pour BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de jazz. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est harmonieux, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Au final, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement musicale, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar26.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
J’ai une passion magique pour Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourbillonne d’elegance. La selection de jeux est enchanteresse, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de livre. La variete des titres est magique, avec des slots aux designs enchantes. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent comme par magie, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le site est rapide et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie celeste. La selection de jeux est olympienne, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En bref, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus divin les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
olympefr.com|
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Уникальные данные только сегодня – https://yam193293393.com/2022/12/12/9-%E4%B8%89%E6%B1%A0%E9%AB%98%E8%8F%9C%E3%81%AE%E6%A0%BD%E5%9F%B9%E2%91%A2
Чем раньше начинается профессиональная детоксикация, тем меньше вероятность развития тяжёлых осложнений, таких как судорожный синдром, отёк мозга, острый панкреатит или некроз печени.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-zhukovskij4.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-zhukovskij4.ru/[/url]
кракен сайт Остерегайтесь Подделок: Идентификация Истинного Ключа С ростом популярности “Кракена” множатся и подделки, зеркала-призраки, созданные для обмана и вымогательства. “Kraken,” – это имя стало брендом, который пытаются присвоить мошенники, жаждущие наживы. Важно помнить: истинная “кракен ссылка” всегда ускользает, ее приходится искать в проверенных источниках, в надежных кругах, где репутация ценится превыше всего. Не доверяйте первому встречному, перепроверяйте информацию, используйте многофакторную аутентификацию. Безопасность – ваш главный союзник в этом опасном путешествии.
tranquilleeyecream – Calm aesthetic, visuals match beauty and relaxation concept perfectly.
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir maintenant|
В таких случаях медлить нельзя — своевременный вызов нарколога может спасти жизнь и предотвратить тяжёлую инвалидизацию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-orekhovo-zuevo4.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya cena[/url]
Существует ряд ситуаций, при которых домашний визит специалиста становится не просто удобным, а жизненно необходимым:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в красногорске[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Жуковском — это круглосуточная служба экстренной и плановой помощи при алкогольной, наркотической и лекарственной зависимости. Наркологическая клиника «Север-Мед» сочетает современные методики детоксикации, медикаментозного и психологического кодирования, а также комплексный подход к последующей реабилитации. Мы работаем без выходных и праздников, чтобы вы могли получить профессиональную помощь в любое время суток.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-zhukovskij4.ru/]narkologicheskaya klinika[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. La selection de jeux est astronomique, comprenant des jeux optimises pour BTC et ETH. Avec des depots crypto instantanes. Les agents repondent comme une comete, avec une aide precise et fiable. Les transferts sont fiables, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est un incontournable pour les fans de blockchain pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis epoustoufle par Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie blockchain. Le repertoire est riche et varie, avec des slots aux themes modernes. Boostant votre portefeuille initial. Le support client est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Un atout cle les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://tuvshinbanzragch.mn/archives/1377
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de riviere. La selection de jeux est dynamique, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme un courant, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient fluviales. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino vaut une peche excitante pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et dynamique, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Boostant votre capital initial. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, garantissant un service premium. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Существуют определённые признаки, свидетельствующие о необходимости срочного обращения за профессиональной помощью:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-orekhovo-zuevo4.ru/anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-orekhovo-zuevo/
J’adore l’atmosphere mystique de Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un sort, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
15 янв. в 6:00 Статус вашего заказа #100*****был изменен наОтправлен Заказ помещен в статус Отправлен,накладная №15 3800-****
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Ладно, напишу ещё раз.
J’aime l’aura futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un ocean virtuel. La selection de jeux est astronomique, avec des slots aux themes modernes. Boostant votre mise initiale. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est un incontournable pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Particulierement captivant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie celeste. Les options sont vastes comme un pantheon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Les agents repondent comme des dieux, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Au final, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et glorieux, ce qui rend chaque session plus celeste. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre d’innovation. La collection de jeux est phenomenale, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est d’une efficacite redoutable, toujours pret a resoudre. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de casino en ligne ! De plus l’interface est fluide et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement remarquable les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Savoir plus|
Mobil futbol izləyərkən paralel mərci tək kliklə yerləşdirmək olur — interfeys sadə və sürətlidir.
Kupon redaktəsi və cash-out imkanı mərcin riskini idarə etməyə kömək edir. Rəsmi giriş həmişə eyni ünvandır — [url=https://pinco-casino-azerbaijan.biz.ua/]pinco-casino-azerbaijan.biz.ua/[/url]; pinco azərbaycan tg elanlarına uymayın. Depozit bonusunun qaydaları dildə qısa və misallarla izah edilib. Minimum və maksimum mərc diapazonları həm yeni başlayanlar, həm də high-rollerlər üçün uyğundur.
Kupon strategiyalarında bankroldan 1–3% qaydası tövsiyə edilir. Android apk yükləməsi rəsmi səhifədən olur və quraşdırma bələdçisi addım-addım göstərilir.
Messencer kanallarına keçidlər rəsmi səhifədə yerləşir. Valideyn nəzarəti üçün marşrutlar və məsləhət linkləri toplanıb. Reytinqlər və istifadəçi rəyləri ən faydalı bölmələri tapmağa imkan verir.
займы онлайн https://zaimy-54.ru
где взять займ https://zaimy-57.ru
кредитный займ онлайн займ на карту круглосуточно без отказа
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://fryzjerpuck.pl/interdum-magna-augue-eget
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, il procure une aventure groovy. Les options sont vastes comme un concert, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a improviser. Les retraits sont fluides comme un riff, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. En resume, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et rythmee, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
J’ai une passion fluviale pour BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de delta. La variete des titres est rapide, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Le support client est dynamique, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient dynamiques. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Un plus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
J’ai une passion narrative pour Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. Il y a une profusion de jeux fascinants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. En resume, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les amateurs de sensations enchantees ! En bonus la navigation est simple et magique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un autre atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere mystique de Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de tours captivants. Les options sont vastes comme un chapeau de magicien, avec des slots aux designs enchanteurs. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient mystiques. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations mystiques ! De plus la navigation est simple et magique, ajoute une touche de mystere. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
Данный комплекс мер обеспечивает восстановление здоровья пациента и создает основу для полного выздоровления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Запросить дополнительные данные – http://www.kaltenschnee.com/?page_id=54
Данный комплекс мер обеспечивает восстановление здоровья пациента и создает основу для полного выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Je suis emerveille par Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir immortel. Les options sont vastes comme un pantheon, proposant des jeux de table glorieux. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et glorieux, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un oracle, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
Золотые слова.
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Ребят, а подскажите насчет доставки спср, в какие города она доставляет ? Блин никогда раньше с ней не связывался 🙁 Расскажите пожалуйста, что, да как
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: Prisma Games technology blog
jammykspeaks – Powerful voice, content feels authentic, motivational and full of passion.
1xbet lite [url=https://1xbet-giris-10.com/]1xbet lite[/url] .
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Открыть полностью – https://redanafae.com/2020/05/04/huertas-familiares
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Прочитать подробнее – http://www.kocar.org/resimler/sizinti_dergisi_resimli_yazilar/attachment/298_1_1280x1024
1xbet giri? adresi [url=http://1xbet-4.com/]http://1xbet-4.com/[/url] .
услуга займа https://zaimy-61.ru
займ на карту срочно https://zaimy-63.ru
денежный кредит займ срочные займы на карту круглосуточно
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://truenet.com.br/2024/02/16/que-horas-comeca-bbb24-e-supercine
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
А что дальше? – https://bytesphare.com/news/youtube-ai-inspiration-tab
Ровный магаз , отвечаю
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Данный продукт не зашол в моё сознание:) его нужно бодяжить с более могучим порохом, будем пробовать АМ2233…
Стационарная детоксикация проводится в специализированных клиниках с круглосуточным наблюдением. Здесь пациенту на старте назначают лабораторные и инструментальные обследования, после чего подключают капельницы, поддерживающие водно-электролитный баланс и корректирующие работу печени и почек. Помимо медикаментов, стационар включает психологическую и психотерапевтическую поддержку в первые дни ремиссии.
Узнать больше – https://алко-избавление.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-msk/
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Следуйте по ссылке – https://teepoem.com/product/my-gorgeous-soulmate-necklace-i-just-want-to-be-your-last-everything-sm-006-lk
Cactus Casino — современная площадка для азартных игр
Любители азартных развлечений могут играть в казино Кактус на удобной и надежной платформе, которая сочетает стильный интерфейс, широкий ассортимент игр и быстрые выплаты. Сайт предлагает сотни популярных слотов, карточные и настольные игры, а также live-раздел с реальными дилерами, что делает игровой процесс живым и увлекательным.
Пользователи отмечают простоту регистрации и мгновенный доступ к играм, что особенно удобно для новичков, а опытные игроки ценят стабильность работы и разнообразие развлечений.
Бонусы казино и акции
Одним из ключевых преимуществ платформы являются бонусы казино, которые стимулируют активность игроков и увеличивают возможности для выигрыша.
• Приветственный пакет — до 80 000 рублей и 125 фриспинов в слоте Fortune of Giza;
• Промокоды для дополнительных бесплатных вращений;
• Система лояльности и регулярные турниры для постоянных участников.
Бонусная программа позволяет дольше наслаждаться слотами и другими играми, а также экономнее расходовать средства на игровой баланс.
Разнообразие игр и провайдеры
Cactus Casino https://kaktus-kazino.com сотрудничает с ведущими разработчиками: Pragmatic Play, BGaming, Wazdan, Spinomenal и Evoplay. Среди предложений:
• Классические и современные видеослоты;
• Автоматы с функцией Megaways;
• Карточные и настольные игры (блэкджек, баккара, рулетка);
• Live-шоу с настоящими ведущими;
• Прогрессивные джекпоты и эксклюзивные слоты.
Такой выбор позволяет каждому найти развлечение по вкусу и играть в слоты онлайн в безопасной и комфортной среде.
Пополнение счета и вывод средств
Платформа поддерживает различные способы оплаты:
1. СБП и Piastrix;
2. Банковские карты и Apple Pay/Google Pay;
3. Криптовалюты и FK Wallet;
4. Binance и другие электронные кошельки.
Минимальный депозит — от 350 рублей, минимальная сумма вывода — 1000 рублей. Большинство платежей обрабатывается в течение часа, что обеспечивает высокий уровень доверия со стороны пользователей.
Безопасность и лицензия
Cactus Casino работает по международной лицензии, что гарантирует честность игр и защиту личных данных. Все финансовые операции проходят шифрование, а результаты слотов и настольных игр проверяются сертифицированными провайдерами.
Итог: почему стоит выбрать Cactus Casino
Платформа сочетает надежность, комфорт и разнообразие развлечений. Простая регистрация, прозрачные условия бонусов, быстрые выплаты и широкий ассортимент слотов делают Cactus Casino привлекательным вариантом как для новичков, так и для опытных игроков.
Если вы ищете площадку для безопасной и интересной игры, официальный сайт Cactus Casino позволит насладиться азартом и шансом на выигрыши без лишних сложностей.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Только для своих – http://www.mehmetdemirci.org/mesnevi-hikayelerinden-dersler
embersk9wish – Heartwarming mission, site honors service dogs with love and gratitude.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Не упусти важное! – http://www.sporthorseproperties.com/property/golf-cart-bike-or-walk-to-wef-and-global-dressage/lani
трансы Новосибириск География Поддержки: От Сибири до Юга России Каждый из каналов, будь то @ts_novosibirsk (трансы Новосибирск, трансы новосибирска), @ts_ekaterinburgh (трансы Екатеринбург, трансы Екатеринбурга), @ts_voronezh (трансы Воронеж, трансы Воронежа), @transy_volgograd (трансы Волгоград, трансы волгограда) или @ts_chelyabinska (трансы Челябинск, трансы челябинска), отражает уникальную специфику своего региона. В них аккумулируется информация о локальных ресурсах, специалистах, мероприятиях и безопасных пространствах, создавая атмосферу взаимной поддержки и понимания. Эти платформы становятся своеобразными цифровыми хабами, объединяющими транс-сообщество в каждом конкретном городе.
такая же хрень пропал продаван ((( уже неделю обещает выслать трек дать и нет не чего *((((
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
Хотя возможно привык к бычей реги, а ваша дает эффект похожий канабб
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Доступ к полной версии – https://phangnga.doae.go.th/province/?p=1319
http://www.newart.ru/tags.php
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Не упусти шанс – https://hikayetna.com/a-night-of-stories-and-flavor-brings-acton-neighbourhood-together
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Интересует подробная информация – http://phoceatour.com/bonjour-tout-le-monde
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Открой скрытое – https://www.nhacaitop1.com/nha-cai-uy-tin/kinh-nghiem-ca-cuoc-bang-bitcoin-tai-nha-cai-1xbit
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Нажми и узнай всё – https://badboysvending.com/how-to-move-on-from-hookups
ну вообщем все ровно получил людей правда от бати но магазин ровный советую
https://berdyanskth.ru
ТУТ САМЫЙ ЛУЧШИЙ МАГАЗИН С САМЫМ ЛУЧШИМ ТОВАРОМ!!! ЖЕЛАЮ УДАЧИ!!!
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Откройте для себя больше – https://attackinteractive.com/arts/working-from-your-home
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://gops.edu.jo/?p=15142
live sportwetten ergebnisse
Review my webpage … wetten sport (Sherita)
трансы Новосибириск Важность Ответственного Использования Подобно любому онлайн-сообществу, каналы Telegram, посвящённые трансгендерной тематике, требуют ответственного подхода. Важно уважать приватность участников, избегать дискриминации и поддерживать атмосферу взаимопонимания. Эти каналы – важный инструмент для поддержки и самоорганизации транс-сообщества, но их эффективность зависит от каждого участника.
Вызов нарколога на дому в владимире ? это удобное и эффективное решение для людей, испытывающих трудности с алкоголем. Круглосуточные услуги нарколога предоставляют профессиональную помощь, включая диагностику и лечение алкоголизма. Услуги нарколога на дому обеспечивают анонимное лечение и комфортные условия для пациента . При необходимости вывода из запоя, важно обратиться к квалифицированному специалисту . Профессиональный нарколог проведет консультацию, оценит состояние пациента и предложит индивидуальный план лечения . Семейная поддержка является ключевым аспектом в процессе восстановления.Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Обращение за медицинской помощью на дому помогает избежать стрессов, связанных с визитом в клинику. Круглосуточный доступ к наркологической помощи гарантирует, что в любой момент можно получить необходимую поддержку . Восстановление после запоя возможно благодаря комплексному подходу и вниманию к каждому пациенту .
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Подробнее тут – https://badboysvending.com/how-to-move-on-from-hookups
беспроцентный займ https://zaimy-67.ru
займ на карту мгновенно https://zaimy-69.ru
мгновенный онлайн займы мгновенные займы без проверки
??????? ??????? ?????????? ?? ???? ?????????.
?????? ?????, ?? ???????????? ?? ??????????? ???????????, ??? ????????????? ???????.
??????????? ?????? ??????? ???????????????? ? ????????????.
????????? ??????? ?? ???????? ??????? ??????, ???? ??? ????????? ????????????.
fortuna-distillery
???????? ?????? ???????????, ? ????????????? ?????????.
?? ??? ??????? ?????, ?????? ????????????? ? ??????.
??????????? ???????? ?????? ??????? ???????? ?????.
??????? ???????????? ???????, ?? ????????? ????????? ????????????.
Эффект чувствуется почти сразу, эйфория и стим в голове
https://disdik-lampung.info
Ну теперь к самому главному – качество!
Пользуемся их услугами постоянно. Каждый раз всё чётко и в срок. Очень комфортно работать с командой, которая знает все нюансы таможни: Таможенное оформление в Шереметьево
займ деньги сразу микрозайм с моментальным одобрением
займ деньги сразу https://zaimy-76.ru
получить займ займ до зарплаты без отказа
2. Был подобный заказ и нас спутали.
https://bryankazx.ru
Тоже такая ситуация , сижу без товара негодую.
Прекратите утомительных поисков, где бы смотреть фильмы без проблем. Ваш путь лежит сюда на КИНОГО ([url=https://igry-onlayn.biz/]https://igry-onlayn.biz/[/url]). В нашей обширной медиатеке постоянно в наличии только что вышедшие фильмы 2025 года. Функционирование платформы Kinogo построена на принципах бесплатности, обеспечивая стабильно высокое качество воспроизведения и отсутствие регистрации.
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
cat casino официальный сайт
Вызывать нарколога на дом рекомендуется при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно санкт-петербург[/url]
Im impressed. I dont think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. Youre truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog youve got here.
Оперативно, профессионально, с вниманием к деталям — рекомендую https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel.ru/
https://kitsu.app/users/1598495
На первом этапе проводится серия исследований:
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма на дому[/url]
продукт – прет дико и жестко, но по сути ничего интересного, цена в 2 тыр себя полностью оправдывает. Эдакий бычий кайф. Если вам нравится трястись и стучать зубами – вы попали по адресу. Во всех остальных случаях – нахер-нахер. Слабенькая 3/5
https://bryankamt.ru
а у нас в квартире газ ….. от ГАЗПРОМ … вы не поверите но это так и есть
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
нужен займ мфо https://zaimy-80.ru
взять займ без отказа https://zaimy-82.ru
Для достижения положительного результата применяются комплексные подходы, сочетающие медикаментозные и поддерживающие методы. Врачи оценивают общее состояние пациента, степень выраженности абстинентного синдрома и сопутствующие заболевания. На основе этих данных подбираются оптимальные методы коррекции.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
срочно нужен займ https://zaimy-86.ru
Для более точного понимания различий между основными подходами используется систематизация данных в таблице. Она отражает основные особенности применения методов и их задачи.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
https://velobarnaul.ru/articles/theory/kak-ne-oshibitsya-v-vybore-samokata/
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно санкт-петербург[/url]
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
Для юридических лиц это надёжный партнёр. Всё по договору, никаких неожиданностей. Работают прозрачно https://dmebroker.ru/
Попытка самостоятельно выйти из запоя или преодолеть тяжелое похмелье может привести к крайне негативным последствиям. Длительное употребление алкоголя или резкий отказ без врачебного контроля опасны развитием осложнений, таких как алкогольный психоз, инсульт, инфаркт, обезвоживание и острая сердечная недостаточность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Лечение основывается на комплексном подходе, позволяющем учесть особенности организма и стаж злоупотребления алкоголем. Обычно процедура состоит из нескольких этапов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narko-reabcentr.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-moskve
This excellent website definitely has all the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
бонус драгон мани казино
Кидалы они или нет-узнаю в течении пары дней,но отказ в закладке-не основание.
https://rovenkijp.ru
250 не знаю, но 203 просто шикарный. Растворяется моментально. Чистота порошка отличная.
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-spb/
В случаях, когда транспортировка в клинику затруднительна или пациент испытывает выраженный стресс, возможно выездное консультирование и начальная детоксикация на дому. Врач прибывает с портативным набором для инфузий, оперативно stabilizирует состояние и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог лечение алкоголизма в екатеринбурге[/url]
Капельница от запоя – это незаменимый метод при пьянстве. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно может оказать экстренную помощь‚ выполняя дезинтоксикацию и реабилитацию после запоя. Признаки алкогольной зависимости‚ такие как тошнота и рвота‚ головная боль и слабость‚ требуют незамедлительных действий. Лечение запоя включает капельницы‚ которые помогают бороться с абстиненцией и детоксифицировать организм из организма. Визит к специалисту важна для выбора последующего лечения: госпитализация или домашняя терапия. Специализированная наркологическая клиника предлагает профессиональную помощь‚ чтобы избежать повторных случаев и сохранить здоровье пациента.
займ на карту получить займ на любую карту
кредитный займ микрозайм с моментальным одобрением
займ без истории https://zaimy-89.ru
Существует ряд ситуаций, при которых домашний визит специалиста становится не просто удобным, а жизненно необходимым:
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить концентрацию токсинов, нормализовать обмен веществ и предотвратить необратимые повреждения, что делает срочный вызов нарколога на дому жизненно необходимым.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
If you wish to discover the best American casinos, then this is definitely worth checking out. Discover the full details via the link below:
http://www.madlaser.co.uk/?p=148583
Hi there, I desire to subscribe for this blog to get most up-to-date updates, therefore where can i do it please assist.
регистрация зума казино
Отличное обслуживание, грамотные специалисты, быстрая реакция. Всё супер https://vkobroker.ru/
всё ровно будет бро! просто график отправок такой
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
суббота, воскресение у них выходной
С момента основания клиники мы делаем ставку на сочетание передовых медицинских протоколов и внимания к каждому пациенту. Наши наркологи регулярно проходят обучение на базе ведущих российских и европейских центров, что позволяет внедрять в практику новые аппараты для аппаратной детоксикации, в том числе плазмаферез и молекулярное диализирование. Психологи и психотерапевты клиники работают по стандартам когнитивно-поведенческой терапии и мотивационного интервьюирования, а наши реабилитационные курсы аккредитованы в Международной ассоциации специалистов по алкоголизму и наркомании.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-zhukovskij4.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-zhukovskom/
Запой характеризуется неспособностью самостоятельно остановить приём алкоголя на протяжении нескольких дней подряд. Сильная интоксикация вызывает обезвоживание, электролитный дисбаланс, снижение артериального давления и угнетение центральной нервной системы. Если через 48–72 человек не прекращает пить, риск осложнений возрастает — возможны судороги, острый панкреатит или инфаркт. Своевременное вмешательство нарколога критично для предотвращения необратимых последствий.
Разобраться лучше – https://алко-избавление.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-msk/
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в москве[/url]
Лечебные мероприятия и рекомендации формируются исходя из индивидуального состояния каждого пациента. Специалист имеет возможность посвятить достаточное количество времени каждому больному, корректируя программу лечения согласно его особым потребностям и жизненным обстоятельствам. При этом учитываются психологические, социальные и физические аспекты, оказывающие влияние на здоровье пациента. Персонализированный подход обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на изменения состояния и своевременную корректировку терапии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в москве[/url]
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – http://
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Ритм жизни в мегаполисе и постоянный стресс часто становятся причиной развития зависимостей у жителей города. В такой ситуации необходима профессиональная консультация врача. Оптимальное решение – вызов нарколога на дом в Москве. Это обеспечивает не только получение медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке, но и полную конфиденциальность.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
После поступления вызова нарколог клиники «АльфаНаркология» оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу. На месте врач проводит первичную диагностику, оценивая степень интоксикации, физическое и психологическое состояние пациента. По результатам осмотра врач подбирает индивидуальный комплекс лечебных процедур, в который входит постановка капельницы с растворами для детоксикации, препараты для стабилизации работы органов и нормализации психического состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru
Клиника «УралМед» работает без выходных и праздников: прием пациентов — круглосуточно. Это позволяет оказывать экстренную помощь при острых состояниях, а также вести наблюдение за динамикой восстановления здоровья в ночные часы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Именно поэтому при затяжных запоях необходима квалифицированная медицинская помощь, позволяющая безопасно и максимально комфортно прекратить приём алкоголя. Клиника «Стратегия Здоровья» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя в Москве как в условиях стационара, так и с выездом на дом. Врачи работают круглосуточно, используя проверенные методики детоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки.
Детальнее – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя в москве[/url]
у меня в подписи проверь
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Есть люди в вк, которые представляются под маркой вашего магазина и кидают людей, уже не одного так кинули, так что будьте внимательны и уточняйте у реальных представителей магазина, так оно или нет.
Таможенный брокер помог решить нестандартный случай. Всё оформили правильно: таможенный брокер в Москве
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-spb/https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru
Вывод из запоя представляет собой медицинское вмешательство, направленное на устранение острой алкогольной интоксикации и стабилизацию состояния организма. При регулярном злоупотреблении спиртным формируется комплексное поражение внутренних органов и нервной системы, что требует своевременной коррекции. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Волгограде проводится под контролем специалистов, которые используют современные методы детоксикации и фармакологической поддержки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого санкт-петербург[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan/
1091m2love – Unique name, design feels artistic and expression of individuality.
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. La variete des titres est raffinee, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un banquet, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Découvrir l’histoire complète|
Лечение основывается на комплексном подходе, позволяющем учесть особенности организма и стаж злоупотребления алкоголем. Обычно процедура состоит из нескольких этапов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в москве[/url]
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Les options sont vastes comme un ledger, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le support client est irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller pour les dГ©tails|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Les titres sont d’une variete eclatante, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, garantissant un service premium. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! De plus le site est rapide et futuriste, ajoute une touche de sophistication. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir les avantages|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et chic, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir le guide|
куплю диплом с занесением [url=http://www.rudik-diplom12.ru]куплю диплом с занесением[/url] .
Вызов нарколога на дом в клинике имеет целый ряд преимуществ. Пациент получает доступ к современным методикам без необходимости транспортировки. Кроме того, исключается фактор социальной огласки, что часто является значимым для больных и их семей.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, il offre une epopee chiffree. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, avec des slots aux designs innovants. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, toujours pret a decoder. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant plus de promos dynamiseraient l’aventure. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui brille dans l’univers crypto pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, qui booste l’engagement.
VГ©rifier cela|
BassBet Casino m’a totalement conquis BassBet Casino, il offre une experience de club. La gamme de jeux est explosive, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Boostant votre mise de depart. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours pret a mixer. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. En bref, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le site est rapide et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session plus vibrante. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourne avec elegance. Le catalogue est riche et varie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est veloce, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. En resume, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
nycbhm – Community-focused organization with meaningful outreach and engagement.
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de piste. Les options sont vastes comme une course, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme une piste, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
Брал не давно в этом магазине закладкой в МСК, что сказать, все прошло замечательно. Клад был поднят, место довольно спокойное и тихое, Время исполнения заказа с момента оплаты от 1 до 2,5 часов, что по сути не так уж и много. Выражаю огромное спасибо оператору в аське, не оставлял меня ни на минуту, всегда отвечал.
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
пока двоих отпустили, в крови ничего не нашли.. ждем результатов экспертизы.
J’ai une passion mythique pour Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir immortel. Les options sont vastes comme un pantheon, proposant des jeux de table glorieux. Avec des depots rapides. Les agents repondent comme des dieux, garantissant un support celeste. Les retraits sont rapides comme un eclair de Zeus, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En bref, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
olympefr.com|
Эти данные являются основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения, позволяющего оперативно скорректировать терапевтические меры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan/
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un blues. Le catalogue est riche et varie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un riff, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est simple et rythmee, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Un autre atout les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Cliquer et aller|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Le support client est irreprochable, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
AccГ©der maintenant|
1day4kids – Uplifting cause, presentation radiates care and dedication toward children.
Je suis ebloui par Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Boostant votre capital initial. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, garantissant un service premium. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Egalement cool les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Plongez-y|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. La variete des titres est raffinee, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a servir. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Au final, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir la page d’accueil|
nycbhm – Community-focused organization with meaningful outreach and engagement.
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Пушкино — это современная и надёжная методика лечения, заключающаяся в создании устойчивого барьера к употреблению спиртного. В наркологической клинике «Орион-Клиник» применяется сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических технологий, благодаря чему пациент получает не только химическое, но и психологическое подкрепление трезвости. Процедура проводится после полной диагностики, с учётом индивидуальных особенностей, анамнеза и текущего состояния организма.
Углубиться в тему – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-pushkino4.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-pushkino/
Cocaine comes from coca leaves organize in South America.
While split second cast-off in established cure-all, it’s now a banned significance due to its
dangers. It’s hugely addictive, leading to vigorousness risks like spunk attacks,
mental disorders, and mean addiction.
J’ai une obsession pour Monte Cryptos Casino, il offre une epopee chiffree. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, avec des slots aux designs innovants. Avec des depots crypto instantanes. Le support client est futuriste, garantissant un service de pointe. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une plongee numerique pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! En bonus le site est rapide et futuriste, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller plus loin|
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
BassBet Casino m’a totalement conquis BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de beats. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, avec des slots aux designs lumineux. Avec des depots ultra-rapides. L’assistance est rapide et pro, offrant des solutions claires. Le processus est simple et fluo, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter le design est moderne et lumineux, ajoute une touche de neon. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir dynamique. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table rapides. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme une piste, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
В таких случаях медлить нельзя — своевременный вызов нарколога может спасти жизнь и предотвратить тяжёлую инвалидизацию.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-orekhovo-zuevo4.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya[/url]
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. En resume, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Un plus le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
En savoir sur le sujet|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir veloce. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
casinospinitfr.com|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! De plus la navigation est simple comme un wallet, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les evenements communautaires decentralises, garantit des transactions fiables.
Voir les mises Г jour|
Капельница от похмелья – это работающим средством для восстановления организма после алкогольного отравления. В владимире медицинские услуги включающие вливание глюкозы и электролитов позволяет снять проявления похмелья, такие как головная боль, тошнота и слабость. Медицинские учреждения в владимире предлагают лечение с использованием энтеросгеля с целью детоксикации. Восстановление водного баланса также имеет большое значение в процессе восстановления. Не забывайте о необходимости консультации врача прежде чем начинать лечение. Чтобы узнать больше посетите сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru.
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Пушкино — это современная и надёжная методика лечения, заключающаяся в создании устойчивого барьера к употреблению спиртного. В наркологической клинике «Орион-Клиник» применяется сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических технологий, благодаря чему пациент получает не только химическое, но и психологическое подкрепление трезвости. Процедура проводится после полной диагностики, с учётом индивидуальных особенностей, анамнеза и текущего состояния организма.
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-pushkino4.ru/
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Trouver le bonus|
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
Та не, не стоит оно того. Надо отдать должное магазину, посылка пришла, без проблем.
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Всем привет) У меня такая проблема, сделал заказ, оплатил через евросеть, Уважаемый продаван сказал то, что в евросети перевод идет до 3-х дней, хотя когда работали с другим магазином деньги прилетали моменьтально всегда. И доставка вышла на 950 р. (г. Екб), это получаеться + курьер или нет, просто до почты?… И через что лучше оплачивать в данном магазине?
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque l’Olympe. Le catalogue est riche en epopees, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Les agents repondent comme des dieux, garantissant un support celeste. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un nectar. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://olympefr.com/|
Существуют определённые признаки, свидетельствующие о необходимости срочного обращения за профессиональной помощью:
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-orekhovo-zuevo4.ru/anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-orekhovo-zuevo
knightstablefoodpantry – Compassionate food pantry serving the community with dedication.
Je suis totalement captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un desert virtuel. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, proposant des tables numeriques elegantes. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable en un clic. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient ideales. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui brille dans l’univers crypto pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! A noter la navigation est simple comme un wallet, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir les avantages|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melancolique. Les options sont vastes comme un album, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient blues. En resume, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rythmee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
Вызов нарколога на дом в клинике имеет целый ряд преимуществ. Пациент получает доступ к современным методикам без необходимости транспортировки. Кроме того, исключается фактор социальной огласки, что часто является значимым для больных и их семей.
Получить больше информации – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/narkolog-v-sankt-peterburge-vyezd-nadom/
Je suis bluffe par BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de beats. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table styles. L’offre de bienvenue est electrisante. L’assistance est rapide et pro, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient un banger. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно москва[/url]
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. Le catalogue est riche et varie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est veloce, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient veloces. Au final, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus le design est moderne et dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в москве[/url]
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. La variete des titres est rapide, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un sprint. En bref, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
casinospinitfr.com|
Скачать видео с YouTube https://www.fsaved.com онлайн: MP4/WEBM/3GP, качество 144p–4K, конвертация в MP3/M4A, поддержка Shorts и плейлистов, субтитры и обложки. Без регистрации, быстро и безопасно, на телефоне и ПК. Используйте только с разрешения правообладателя и в рамках правил YouTube.
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Посмотреть подробности – https://camilagazola.com.br/sea-dolorum-vituperata-6
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Продолжить изучение – https://muththamizh-kalasam.com/?p=588
Je suis totalement envoute par Olympe Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque l’Olympe. Le catalogue est riche en epopees, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le support client est olympien, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient divins. Au final, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les passionnes de jeux antiques ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple comme un oracle, ce qui rend chaque session plus celeste. Egalement remarquable les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
А что дальше? – https://kajalkwebdev.com/protein
mcctheatercampaign – Supporting arts and theater with passion and community spirit.
J’adore l’atmosphere blues de BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melancolique. La variete des titres est melodieuse, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme un riff, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient rythmees. Au final, BassBet Casino vaut une jam session pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus le design est moderne et blues, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
С человеком приятно иметь дело. Склонен на компромиссы 😉
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Это фейк что тут вам не понятно то.
Этот текст сочетает в себе элементы познавательного рассказа и аналитической подачи информации. Читатель получает доступ к уникальным данным, которые соединяют прошлое с настоящим и открывают двери в будущее.
Не упусти шанс – https://template111.webekspor.com/this-is-indonesias-dried-grated-coconut-export-market-potential-in-bulgaria
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Секреты успеха внутри – https://meettourandtravels.com/how-to-travel-with-paper-map
astoriatogether – Community unity and collaborative neighborhood initiatives.
Сотрудничаем уже несколько месяцев и полностью довольны. Документы всегда готовы вовремя, ошибок не бывает. Настоящие профессионалы в своей области – таможенный брокер для юридических лиц
В статье по вопросам здоровья мы рассматриваем актуальные проблемы, с которыми сталкивается общество. Обсуждаются заболевания, факторы риска и важные аспекты профилактики. Читатели получат полезные советы о том, как сохранить здоровье и улучшить качество жизни.
Выяснить больше – https://is-moskvy.ru/2024/07/30/statya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-istochnik-zhizni-v-omske-xl1c7
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Информация доступна здесь – https://iveaghfitness.ie/run-for-charity
Смотри в розничном прайсе
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Короче, подошёл я к адресу, а там ни по звёздам, ни по местности, ни право-лево не надо проверять. Я даже фонарик не включал, все чётко по описанию.
whoah this blog is wonderful i like reading your posts. Stay up the great work! You understand, a lot of persons are searching round for this information, you can help them greatly.
регистрация казино либет
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Практические советы ждут тебя – https://sleepfreshup.com/10-tips-for-choosing-the-perfect-sofa-in-online
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://house-archi.biz/?p=45
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://luzycebeton.pl/witaj-swiecie
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Все материалы собраны здесь – https://auto1.lt/verslo-partneriai-perkraustymo-imonems
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Узнать больше – https://soft.masterit.ru/reviews/press-reliz-uslugi-po-vyvodu-iz-zapoya-pokhmelya-i-lecheniyu-alkogolizma-v-nark-a7
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://mirokru.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-top-strategij
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Обратиться к источнику – https://fundacjakrajwspanialy.pl/project/wystawa-ikon
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Детальнее – https://superawesometour.com/pack-wisely-before-traveling
Hi there, its good piece of writing concerning media print, we all know media is a impressive source of data.
banda казино
Один из топовых продавцов на всем РЦ:)
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Рабочие дни отсчитываются со дня оплаты, а не заказа на сайте, разница порой месяц между тем когда человек создал заказ и когда оплатил его.
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://mirokru.ru/narkolog-na-dom-vse-za-i-protiv
В данной статье рассматриваются проблемы общественного здоровья и социальные факторы, влияющие на него. Мы акцентируем внимание на значении профилактики и осведомленности в защите здоровья на уровне общества. Читатели смогут узнать о новых инициативах и программах, направленных на улучшение здоровья населения.
Углубиться в тему – https://mediry.ru/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya-na-domu-snyatie-intoksikatsii
The latest is here: https://www.yojoe.com
Visit our website: https://superweb.de
Терапия запойного состояния — это важный этап в борьбе с алкоголизмом. В городе владимир доступно множество способов, включая медикаментозную терапию. Признаки запоя могут варьироваться от беспокойства до болей в теле, что делает выход из запоя жизненно важным. Для очистки организма применяются различные лекарственные средства для помощи при запое, такие как лекарства группы бензодиазепинов, которые помогают снять абстинентный синдром. Антидепрессанты также могут быть назначены, чтобы улучшить психоэмоциональное состояние пациента. Витамины при запое играют важную роль в восстановлении организма. Методы кодирования может стать важным этапом в лечении алкоголизма. Помощь нарколога включает не только медицинскую терапию, но и психологическую поддержку. Программы реабилитации в владимире часто включает группы поддержки и программы реабилитации, которые помогают пациентам возвращаться к нормальной жизни без алкоголя. Поддержка семьи при алкоголизме также имеет огромное значение. Она может помочь пациенту в периоде реабилитации после запоя, повысив шансы на успешное лечение зависимостей. Медицинские процедуры для detoxa являются важной частью комплексного подхода к лечению алкоголизма и обеспечивают безопасный выход из запойного состояния.
deutschland ungarn wettquoten
my webpage … sichere kombiwetten
В этой заметке мы представляем шаги, которые помогут в процессе преодоления зависимостей. Рассматриваются стратегии поддержки и чек-листы для тех, кто хочет сделать первый шаг к выздоровлению. Наша цель — вдохновить читателей на положительные изменения и поддержать их в трудных моментах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://just-fit.ru/interesnoe/effektivnye-metody-vyvoda-iz-zapoya-kak-vernutsya-k-normalnoy-zhizni
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://ogkt.ru/raznoe/kak-vyvesti-iz-zapoya-sovremennye-metody-i-podhody.html
мед колледж купить диплом [url=https://frei-diplom7.ru]мед колледж купить диплом[/url] .
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм саратов[/url]
The best is only here: https://smartzoz.in
The latest and most relevant: https://theeldorado.in
ладно ..буду надеяться что все норм
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
жёлтого цвета, за качество пока сказать не могу!)
Врачи «СтаврМед Центра» работают круглосуточно, обеспечивая выезд нарколога на дом в течение короткого времени. Пациент может получить помощь в привычных условиях, не подвергаясь стрессу, связанному с госпитализацией. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с сохранением врачебной тайны. Благодаря такому подходу, лечение становится не только эффективным, но и максимально комфортным для человека, который решил прекратить запой и начать восстановление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ставрополе[/url]
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в саратове[/url]
Из аськи вышел и даже не ответил… *( https://genicheskva.ru Что то непойму.Работает магаз то.И куда писать?
Amazing! Its really remarkable article, I have got much clear idea concerning from this article.
зеркало Parimatch kz
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
The best is right here: https://sdch.org.in
Каждый план лечения строится вокруг понятных целей и измеримых результатов. Вместо шаблонных «сильных» схем мы применяем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию, корректируем среду (свет, тишина, режим сна), учим пациента простым и повторяемым навыкам саморегуляции. Такое сочетание медицинских и психологических инструментов помогает быстрее снять острые симптомы и поддерживать стабильность в последующие недели. Кодирование мы рассматриваем не как «волшебную кнопку», а как часть маршрута, который всегда включает детокс, психообразование и профилактику срывов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
All the best is here: https://questreaming.com
Top picks for you: https://www.trimartolod.fr
Если к запланированному «окну оценки» динамика слабее ожидаемой, врач корректирует один параметр (скорость/последовательность введения, вечерний режим, плотность связи). Такой минимализм повышает управляемость и снижает риск побочных эффектов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника «ЮгМед Альянс» в Ставрополе объединяет медицинскую точность и психологическую чуткость. Здесь лечение зависимостей выстроено по принципу системной логики: одно вмешательство — одна цель — один критерий оценки. Такой подход делает процесс предсказуемым и снижает нагрузку на организм. Мы не просто устраняем симптомы, а ищем причину, формируем новые устойчивые модели поведения и помогаем пациенту вернуть контроль над жизнью. Наша команда работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая поддержку и безопасное сопровождение на каждом этапе — от детоксикации до реабилитации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Команда «КарелМед Центра» объединяет наркологов, психиатров, реаниматологов, клинических психологов, специалистов по реабилитации и социальному сопровождению. Мы работаем без очередей и навязчивых формальностей, а логистика визита, оформление в стационар и коммуникации с родственниками выстроены бережно: конфиденциальные записи, немаркированные выезды, отдельный вход и нейтральная терминология в документах. Вы получаете не только купирование абстиненции и детоксикацию, но и системную работу с триггерами, привычками и межличностными конфликтами — тем, что часто возвращает к употреблению даже после «идеальных капельниц».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены петрозаводск[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМед Резонанс» — это круглосуточный центр доказательной медицины, где помощь строится вокруг безопасности, конфиденциальности и персонализации. Мы объединяем медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапию, реабилитационные практики и постлечебное сопровождение в единую дорожную карту восстановления. Каждый шаг лечения закреплён измеримыми критериями эффективности, а решения принимаются командно — от дежурного нарколога и клинического психолога до психиатра и реабилитолога.
Получить больше информации – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/
2)Кто курит раз в неделю : от 3 часов до 5-7 часов https://zoo-club.info Ребята кто заказывал 25 реагент,как по качеству???????????
Ниже — примерный «каркас» лечения. Он индивидуализируется по клинической картине, сопутствующим болезням, опыту прошлых попыток и бытовым ограничениям. Ключевой принцип — «одно вмешательство: одна цель — один маркер — одна дата проверки».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Если к «окну сверки» цель не достигнута, мы меняем только один компонент — время ритуала, скорость инфузии, плотность сессий. Такой микрошаг даёт чистый сигнал: понятно, что сработало, а что нет, и пациент не чувствует «экспериментов» над собой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Updated today: https://anthese.fr
New updates feed: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
All the latest is here: https://www.locafilm.com
В команде — врачи-наркологи, психиатры-консультанты, клинические психологи и выездные медсёстры. Все работают по единому алгоритму: короткий скрининг, стартовая стабилизация, настройка «вечернего протокола» для нормализации сна и план на 72 часа. Цель — восстановить биоритмы, мягко убрать соматические проявления абстиненции и снизить реактивную тревогу, чтобы человек быстрее вернулся к привычным ролям дома и на работе.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pervouralsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
которые воспитанны на обычном Фене ! https://melitopolqa.ru Не поняла?
Only the important and best: https://www.weyher.de
The main thing is here: https://lmc896.org
The whole summary for you: https://www.krizia.it
Помощь при запое в владимире – это важный процесс, нуждающийся в квалифицированной помощи. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru вы обнаружите данные о наркологических клиниках, предлагающих наркологическую помощь. Следует учитывать, что искоренение зависимости – это не только физическая терапия, но и психологические сеансы, реабилитационные программы. Посещение врача поможет составить индивидуальный план терапии. Выход из запоя может потребовать экстренной помощи при острой зависимости, что возможно в наркологических клиниках. Методы кодирования – одна из эффективных методик, которая помогает отказаться от спиртного. Семейная поддержка играет важнейшую часть в лечении. Социальная адаптация после лечения важна для успешной интеграции в общество. Заботьтесь о своем здоровье и ищите помощь у специалистов!
Софосбувир велпатасвир Симптомы гепатита C часто неспецифичны и могут быть ошибочно приняты за признаки других заболеваний. В острой фазе инфекции (которая часто остается незамеченной) могут возникать усталость, слабость, тошнота, потеря аппетита, боли в животе и легкая желтуха. Однако у большинства инфицированных людей симптомы отсутствуют, что приводит к хронизации заболевания. Хронический гепатит C может вызывать более выраженные симптомы, такие как хроническая усталость, депрессия, боли в суставах, нарушение пищеварения и кожный зуд.
nicholashirshon – Professional portfolio showcasing expertise and accomplishments.
https://dzen.ru/a/aPRXjPraMEja6Ols Выбирая виртуальный номер, важно обратить внимание на надежность провайдера, функциональность сервиса и стоимость услуг. Убедитесь, что провайдер гарантирует конфиденциальность переписки и защиту от несанкционированного доступа. Оцените доступные функции, такие как переадресация SMS, голосовая почта и интеграция с другими приложениями. Сравните цены и выберите оптимальный тарифный план, соответствующий вашим потребностям. Помните, что купить виртуальный номер – это не просто приобретение цифрового актива, а инвестиция в свою безопасность и комфорт в современном цифровом пространстве.
прокси Прокси с ротацией, особенно мобильные прокси с ротацией, представляют собой наиболее продвинутое решение для тех, кто стремится к максимальной анонимности и избежанию блокировок. Автоматическая смена IP-адреса через заданные промежутки времени усложняет отслеживание и значительно повышает устойчивость к блокировкам. Мобильные прокси с ротацией – это идеальный инструмент для задач, требующих высокой степени анонимности и стабильности, таких как конкурентный анализ, мониторинг цен и автоматизированный маркетинг.
онлайн деньги микрозайм оформить
онлайн займ онлайн деньги
Такая последовательность шагов позволяет врачу действовать точно и эффективно. Благодаря комплексному подходу пациент чувствует облегчение уже через 1–2 часа после начала терапии, а полное восстановление наступает в течение суток.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
займы онлайн взять деньги онлайн
отдых в дубае Достопримечательности Дубая – это не просто архитектурные шедевры и торговые центры, это отражение амбиций, инноваций и безграничной энергии. От Бурдж-Халифы, устремлённого в небеса, до музыкального фонтана Дубай, от золотых пляжей Джумейры до исторических кварталов Аль-Фахиди – каждый уголок города дышит уникальной атмосферой. Погрузитесь в мир роскоши и развлечений, откройте для себя восточную сказку, сплетенную с передовыми технологиями.
Аренда спецтехники сегодня остаётся выгодным вариантом для предприятий.
Она даёт возможность решать задачи без обязательства покупки дорогой техники.
Поставщики, предлагающие такую услугу, предоставляют ассортимент техники для различных сфер.
В парке можно найти экскаваторы, самосвалы и другое оборудование.
https://pro-vosk.ru/jekonomicheskij-analiz-arendy-jekskavatorov-dlja-stroitelnyh-proektov/
Основное достоинство аренды — это экономия средств.
Также, арендатор может рассчитывать на современную технику, с полным обслуживанием.
Опытные компании оформляют удобные договоры аренды.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это оптимальный выбор для тех, кто ищет экономию в работе.
Клад был уличным, спрятан по разумному, под решеткой окна подъезда, рядом с окном стояла лавочка, на которой можно без палива посидеть и нащупать клад. Клад 5 балов из 5!!! https://disdik-lampung.info и отдельный респект магазу за способ посылок=)))))
Каждый план лечения строится вокруг понятных целей и измеримых результатов. Вместо шаблонных «сильных» схем мы применяем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию, корректируем среду (свет, тишина, режим сна), учим пациента простым и повторяемым навыкам саморегуляции. Такое сочетание медицинских и психологических инструментов помогает быстрее снять острые симптомы и поддерживать стабильность в последующие недели. Кодирование мы рассматриваем не как «волшебную кнопку», а как часть маршрута, который всегда включает детокс, психообразование и профилактику срывов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь нижний тагил[/url]
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в перми[/url]
Домашний визит уместен не только при тяжёлой абстиненции. Он эффективен и на этапе нарастающих симптомов, когда важно предотвратить обострение. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие принять решение.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-stavropol
covidtest-cyprus – Essential health services with reliable testing solutions.
Что то много новичков устраивают здесь флуд.А магаз на самом деле хорош.Помню его еще когда занимался курьерскими доставками,коспирация и качество товара было на высшем уровне. https://skadovskre.ru всех с новым годом и удачных покупок
BassBet Casino m’a captive BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un festival. Les titres sont d’une variete envoutante, avec des slots aux designs dynamiques. L’offre de bienvenue est electrisante. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Au final, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rythmee, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un point fort les options de paris variees, assure des transactions fiables.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis totalement illumine par BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de lumieres. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, incluant des paris sportifs vibrants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, offrant des solutions claires. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, BassBet Casino vaut une soiree lumineuse pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un neon, ce qui rend chaque session plus brillante. Un atout les options de paris variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
Мы не «перелечиваем» пациента процедурами. Любая мера начинается как проверяемая гипотеза с измеримыми маркерами. Ниже — опорная карта лечения. В реальности она персонализируется в зависимости от клинической картины, возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и бытового графика.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр каменск-уральск[/url]
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui ondule avec elegance. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est dynamique, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un lac, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient lacustres. En resume, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui ondule pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! A noter la navigation est simple et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Наша команда видит задачу шире, чем просто снять интоксикацию: важно вернуть предсказуемое засыпание, успокоить вегетативную систему, снизить тревожность и объяснить семье, как мягко поддержать человека, не обесценивая и не провоцируя конфликты. Поэтому медицинские вмешательства поддержаны «сенсорной дисциплиной» (свет, тишина, отсутствие резких запахов), простыми ритуалами вечера и короткими чек-инами на следующий день. Такой формат помогает не только «пережить ночь», но и спокойно пройти первые двое суток, когда риск откатов особенно высок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-nizhnij-tagil/
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui embaume l’elegance. Le catalogue est riche en aromes, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme un parfum, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
1xbet g?ncel adres [url=https://1xbet-10.com/]1xbet g?ncel adres[/url] .
wellnesstourbus – Mobile health and wellness services bringing care to communities.
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est impeccable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. En resume, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un banquet, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
1xbet mobi [url=www.1xbet-14.com]www.1xbet-14.com[/url] .
кухня на заказ спб от производителя недорого [url=http://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru]http://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru[/url] .
J’aime l’ambiance crypto de Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie blockchain. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple comme un wallet, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement cool les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
Entrer sur le site web|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La selection de jeux est somptueuse, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Lire entiГЁrement|
Je suis epate par BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe electrisante. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est rapide et pro, offrant des solutions claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et vibrant, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un atout les options de paris variees, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinoappfr.com/|
J’adore l’ambiance lumineuse de BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui scintille comme un neon. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est au top, joignable a tout moment. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient eclatantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le design est moderne et eclatant, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
Друууууг, ну где же трееек…… https://antratsitqu.ru Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
J’ai une passion lacustre pour BassBet Casino, il procure une experience dynamique. La selection de jeux est dynamique, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent comme une vague, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient dynamiques. En resume, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement aquatique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui embaume l’elegance. La variete des titres est raffinee, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un bouquet. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
concernedaboutpollution – Environmental advocacy with focus on pollution awareness and solutions.
Je suis absolument envoute par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le support client est irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, ajoute une touche de sophistication. A souligner les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, il procure une experience distinguee. Le catalogue est somptueux et varie, incluant des paris sportifs elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Au final, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un bal, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Vérifier l’avis|
BassBet Casino m’a captive BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir energique. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs dynamiques. L’offre de bienvenue est electrisante. L’assistance est rapide et pro, toujours pret a mixer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. En bref, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et captivant, booste le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
J’ai un faible eclatant pour BassBet Casino, il procure une experience brillante. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, proposant des jeux de table styles. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Les agents repondent comme un flash, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un eclat. Au final, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! En plus la plateforme est visuellement fluorescente, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La selection de jeux est somptueuse, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est impeccable, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le design est moderne et chic, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Ouvrir l’offre|
J’adore l’atmosphere aquatique de BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui ondule avec elegance. Les options sont vastes comme un lac, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a pecher. Les retraits sont fluides comme un lac, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient lacustres. Au final, BassBet Casino vaut une peche excitante pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement aquatique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Les options sont vastes comme un bouquet, avec des slots aux designs parfumes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Fantastic website you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get suggestions from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Bless you!
прием смс
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Au final, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation numerique unique. La variete des titres est eclatante, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Boostant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec une vitesse fulgurante, toujours pret a decoder. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages uniques.
VГ©rifier plus|
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui respire le luxe. La selection de jeux est exquise, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du charme. Au final, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un bal, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Cliquer pour voir|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un banquet, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Essayer ceci|
asianspeedd8 – Modern dating platform with cultural connection and community focus.
Состав капельниц всегда персонализирован. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии и ориентируемся на симптоматику, сопутствующие заболевания и домашние условия. Ниже — примерная сетка профилей, которую врач на месте адаптирует «под вас».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pervouralsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Софосбувир Galaxy russ24 ru Современные противовирусные препараты прямого действия (ПППД), такие как софосбувир, ледипасвир и велпатасвир, кардинально изменили подход к лечению гепатита C. Эти препараты обладают высокой эффективностью и позволяют добиться полного излечения более чем у 95% пациентов, независимо от генотипа вируса и стадии заболевания. Доступ к этим препаратам, безусловно, важен. Многие ищут, где купить софосбувир по доступной цене, в том числе в Москве (софосбувир ледипасвир Москва). Важно помнить, что лечение должно проводиться под наблюдением врача, который определит оптимальную схему терапии и будет контролировать побочные эффекты. Помимо медикаментозного лечения, важна диета при гепатите C и здоровый образ жизни.
ОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!! https://madou308.ru магазин отличный ! работает уже не первый год! обращайтесь!
мобильные прокси купить Прокси, в своей базовой форме, служат посредником между пользователем и Интернетом, скрывая реальный IP-адрес пользователя и предоставляя взамен другой. Это позволяет обойти географические ограничения, получить доступ к заблокированному контенту и повысить уровень конфиденциальности в сети. Купить прокси сегодня – это инвестиция в гибкость и контроль над своим онлайн-присутствием.
Команда «КарелМед Центра» объединяет наркологов, психиатров, реаниматологов, клинических психологов, специалистов по реабилитации и социальному сопровождению. Мы работаем без очередей и навязчивых формальностей, а логистика визита, оформление в стационар и коммуникации с родственниками выстроены бережно: конфиденциальные записи, немаркированные выезды, отдельный вход и нейтральная терминология в документах. Вы получаете не только купирование абстиненции и детоксикацию, но и системную работу с триггерами, привычками и межличностными конфликтами — тем, что часто возвращает к употреблению даже после «идеальных капельниц».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
https://t.me/traveldubais Отдых в Дубае – это эталон безупречного сервиса и комфорта. Отели мирового класса, роскошные пляжи, рестораны, предлагающие гастрономические шедевры со всего мира, безграничные возможности для шопинга и развлечений – здесь каждый найдёт что-то для себя.
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Для жителей Нижнего Тагила у нас организованы три параллельных канала помощи: очные визиты в клинику, «тихий» выезд на дом и защищённые телемедицинские консультации. Координатор уже при первом звонке уточняет ключевые риски (аллергии, хронические заболевания, эпизоды судорог/психозов, приём постоянных препаратов), бытовые условия (возможность обеспечить тишину на 2–3 часа, доступ к воде, особенности подъезда), а также предпочтения по конфиденциальности. Это позволяет врачу подготовить персональный стартовый протокол заранее и сократить время между осмотром и первой процедурой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru
Для жителей Каменска-Уральского мы организовали быстрый и незаметный доступ к помощи. Координатор принимает обращения круглосуточно, уточняет адрес, особенности подъезда, пожелания по конфиденциальности и удобные «окна» визита. Бригады приезжают без опознавательных знаков, расходные материалы — в нейтральной упаковке, а формулировки в документах исключают нежелательные «ярлыки». Если дома временно нельзя обеспечить тишину и безопасность, мы «тихо» переводим пациента в палату краткого наблюдения: отдельный вход, короткий маршрут, минимум контактов и быстрое возвращение к домашнему формату после стабилизации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij0.ru
Мы работаем по принципу «один визит — один измеримый результат». После инфузий пациент обычно отмечает облегчение головной боли, уменьшение тремора и тревоги, улучшение сна к ближайшей ночи. Если ситуация сложнее (длительный многодневный запой, выраженные соматические факторы), врач оставляет ступенчатый план на 24–48 часов с повторным визитом или переводом в стационарный блок по согласованию с пациентом и родными.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены ставрополь[/url]
Чем раньше стартует детокс, тем мягче идёт восстановление. Даже один визит способен перевести состояние из «кризисного» в управляемое, а затем подключается поддержка психолога или амбулаторные встречи для закрепления эффекта.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Кидал 4340, на Альфу улетело 4254… если быть точным… Чек есть. https://btf39.ru кто последний раз когда брал? регу или соль
https://dzen.ru/a/aPRXjPraMEja6Ols Виртуальные номера, как концепция, эволюционировали из простой необходимости отделить личную жизнь от профессиональной, в сложный инструмент, позволяющий пользователям контролировать свою цифровую идентичность. Прием SMS на виртуальный номер стал краеугольным камнем защиты от спама, нежелательных маркетинговых рассылок и потенциальных мошеннических действий. Это своеобразный цифровой фильтр, позволяющий фильтровать входящую информацию и сохранять основной номер телефона в чистоте. Купить виртуальный номер – значит получить возможность балансировать между онлайн-активностью и конфиденциальностью, не жертвуя удобством связи. Номер для SMS – это не просто цифровая комбинация, это ключ к защищенному общению, будь то верификация аккаунтов, участие в акциях или координация действий в команде.
Левандовски Барселонага кошулгандан кийин команда күчөдү.
Роберт Левандовски Инстаграмда күйөрмандар менен тыгыз байланышта. Левандовски канча гол салганы тууралуу маалымат ар дайым жаңыланып турат. Левандовскинин машыгуу режими көпчүлүккө кызыктуу. Левандовскинин Барселонадагы ийгиликтерин [url=robert-lewandowski-kg.com]robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтынан окуңуз. Роберт Левандовски Барселона менен титулдар үчүн күрөшүүдө.
Левандовски өзүнүн эмгеги менен дүйнөгө белгилүү болгон. Левандовскинин булчуңдары жана абалы көпчүлүккө үлгү.
Роберт Левандовски өзүнүн тамырларын сыйлайт. Роберт Левандовски ар дайым эмгектин баасын билет.
Если дома действительно шумно (ремонт, маленькие дети, вечерние гости) или состояние нестабильно, предложим короткое наблюдение в клинике: отдельный вход, «тихий коридор», камерные посты, затем — возвращение домой и продолжение амбулаторного маршрута. Важен не формат, а предсказуемый результат: степень облегчения должна соответствовать целям этапа, а не множеству случайных факторов среды.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
grant-jt – Professional services with expertise and dedicated client support.
Ich freue mich riesig uber Snatch Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, Snatch Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Au?erdem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Snatch Casino|
Домашний формат особенно востребован, когда нужна помощь «здесь и сейчас»: тревога, дрожь, потливость, скачки давления и нарушения сна усиливают риск осложнений. Цель визита — мягко вывести организм из токсической нагрузки, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, снизить внутреннее напряжение и вернуть контроль над сном и аппетитом. Подход «МедЛинии Ставрополь» — минимально необходимая фармакотерапия и максимум управляемости: у каждого шага есть цель, маркер эффективности и время контроля.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-stavropol
Read more on the website: https://sportquantum.com/
Here are all the details: https://totalfratmove.com
Learn more here: https://www.colehardware.com
купить диплом в евпатории [url=www.rudik-diplom10.ru/]купить диплом в евпатории[/url] .
Кто знает что происходит? Походу покупают все в тихушку!:confused: Внесите ясность!:hz: Дайте реги уже:confused::sos: https://medcentr34.ru Здесь все ровно братья как и всегда
komunahouse – Community living space fostering connection and collaboration.
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом саратов[/url]
The best of the best is here: https://jnp.chitkara.edu.in
Best selection of the day: https://playplayfun.com
Only top materials: https://fish-pet.com
Oh my goodness! an amazing article. Great work.
купить диплом сантехника [url=http://rudik-diplom11.ru]купить диплом сантехника[/url] .
Уже при первичном звонке мы собираем ключевую информацию: длительность употребления, типы веществ, сопутствующие заболевания, прошлые реакции на лекарства, эпизоды судорог и психозов, недавние значения АД/ЧСС. Это позволяет подготовить персональный стартовый протокол ещё до визита: поставить цель на первые 72 часа, определить метрики (сон, «тяга», дневная энергия), запланировать вечерний ритуал и расписать дистанционные чек-ины. Прозрачность шагов снижает тревогу у пациента и семьи и повышает соблюдаемость — фундамент устойчивого результата.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
На первом приёме врач-нарколог проводит осмотр, оценивает витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, SpO2, температура), при показаниях — портативный ЭКГ-скрининг и экспресс-лабораторию, использует шкалы выраженности абстиненции и тревоги. Результаты сразу переводятся в план на ближайшие 72 часа: инфузионная поддержка или таблетированные режимы, «вечерний ритуал» для нормализации сна, карта триггеров и краткое психообразование. Дальше мы обсуждаем цели на 7 дней: что должно измениться и как мы это измерим (сон, тревога, «тяга», энергия, работоспособность).
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk/
Ich bin fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, allerdings mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. In Summe, Snatch Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein starker Vorteil die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
snatch-casino.de|
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
See the details: https://ecampania.it
Detailed information: https://chhapai.com
Full overview of the topic: https://www.levelupacademy.in
berrybombselfiespot – Fun and vibrant selfie destination with creative photo opportunities.
Для жителей Нижнего Тагила у нас организованы три параллельных канала помощи: очные визиты в клинику, «тихий» выезд на дом и защищённые телемедицинские консультации. Координатор уже при первом звонке уточняет ключевые риски (аллергии, хронические заболевания, эпизоды судорог/психозов, приём постоянных препаратов), бытовые условия (возможность обеспечить тишину на 2–3 часа, доступ к воде, особенности подъезда), а также предпочтения по конфиденциальности. Это позволяет врачу подготовить персональный стартовый протокол заранее и сократить время между осмотром и первой процедурой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Брал неоднократно в этом магазе, всегда всё ровно и без проволочек, так держать!! https://vladtehno.ru Это мы и так все знаем
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Snatch Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, allerdings gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Am Ende, Snatch Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Hinzu kommt die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein tolles Extra die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Snatch Casino|
Домашний визит уместен не только при тяжёлой абстиненции. Он эффективен и на этапе нарастающих симптомов, когда важно предотвратить обострение. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие принять решение.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol/
gailcooperspeaker – Inspirational speaking with powerful messages and engaging delivery.
Каждый этап лечения в наркологической клинике «ЮгМед Альянс» имеет свою цель, временные рамки и объективные критерии эффективности. Ниже приведена структура терапевтического цикла, применяемая для большинства пациентов после поступления в отделение.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Софосбувир india helps24 Современные противовирусные препараты прямого действия (ПППД), такие как софосбувир, ледипасвир и велпатасвир, кардинально изменили подход к лечению гепатита C. Эти препараты обладают высокой эффективностью и позволяют добиться полного излечения более чем у 95% пациентов, независимо от генотипа вируса и стадии заболевания. Доступ к этим препаратам, безусловно, важен. Многие ищут, где купить софосбувир по доступной цене, в том числе в Москве (софосбувир ледипасвир Москва). Важно помнить, что лечение должно проводиться под наблюдением врача, который определит оптимальную схему терапии и будет контролировать побочные эффекты. Помимо медикаментозного лечения, важна диета при гепатите C и здоровый образ жизни.
магазин напольных покрытий Ламинат, несомненно, является одним из самых популярных и доступных видов напольных покрытий. Он представляет собой многослойную конструкцию на основе древесноволокнистой плиты высокой плотности (HDF), с декоративным слоем, имитирующим текстуру дерева, камня или плитки, и защитным верхним слоем, обеспечивающим устойчивость к истиранию и механическим повреждениям. Ламинат привлекает своей простотой укладки, разнообразием дизайнов и относительно невысокой ценой, что делает его идеальным выбором для жилых помещений с умеренной нагрузкой. Однако, следует учитывать, что ламинат менее устойчив к влаге, чем, например, керамическая плитка, и требует бережного ухода.
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-saratove
В клинике используется модульная система лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные компоненты. В зависимости от состояния человека акценты могут смещаться — например, у одних пациентов приоритетом становится физиологическое восстановление, у других — коррекция эмоционального фона и когнитивных паттернов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в ставрополе[/url]
че вы панику наводите)) все норм будет! есть рамс у курьерки, магаз не при чем.. спакуха https://buh-ved.ru Кстати,что очень радует ,так это уровень общения продавца.Юмор лишним не бывает,ведь так:D?
мобильные прокси с ротацией Возможность купить мобильные прокси открывает двери к эффективному решению множества задач, требующих обхода географических ограничений, анонимного парсинга данных, автоматизации аккаунтов в социальных сетях и многого другого. Однако выбор надежного поставщика мобильных прокси – критически важный шаг. Необходимо учитывать такие факторы, как стабильность соединения, скорость, размер пула доступных IP-адресов, а также возможность ротации IP-адресов для повышения уровня анонимности.
Если дома действительно шумно (ремонт, маленькие дети, вечерние гости) или состояние нестабильно, предложим короткое наблюдение в клинике: отдельный вход, «тихий коридор», камерные посты, затем — возвращение домой и продолжение амбулаторного маршрута. Важен не формат, а предсказуемый результат: степень облегчения должна соответствовать целям этапа, а не множеству случайных факторов среды.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний тагил[/url]
В Петрозаводске мы организовали «тихий» доступ к помощи: первичный звонок принимает координатор, который собирает только необходимую информацию, назначает удобное окно визита, подсказывает безопасные шаги до встречи с врачом (вода, свет, отдых, отказ от стимуляторов) и, при необходимости, направляет немаркированную выездную бригаду. В стационаре — отдельный вход, индивидуальные тайм-слоты, приватные кабинеты без общей «ожидалки». Наша задача — не просто начать лечение, а сделать так, чтобы старт не сорвался из-за страха огласки или бюрократии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Проверка автомобиля перед покупкой Магнитогорск Авто под заказ в Магнитогорске – это индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, учитывающий его предпочтения и потребности. Мы поможем вам выбрать автомобиль любой марки и модели, предложив различные варианты комплектации и финансирования. Наша цель – сделать процесс покупки автомобиля максимально комфортным и выгодным для вас.
https://t.me/bitryakov Мечты о собственном доме начинаются с выбора земли.
Мы не «перелечиваем» пациента процедурами. Любая мера начинается как проверяемая гипотеза с измеримыми маркерами. Ниже — опорная карта лечения. В реальности она персонализируется в зависимости от клинической картины, возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и бытового графика.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/kamensk-uralskij-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
kraken market Kraken market – это пестрый калейдоскоп предложений, где каждый может найти то, что ищет. Но, как и на любом рынке, здесь встречаются не только честные торговцы, но и мошенники, готовые обмануть доверчивых покупателей. Поэтому, прежде чем совершить покупку, тщательно изучите репутацию продавца, сравните цены и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Помните, что ваша бдительность – лучшая защита от обмана и разочарования. Kraken market – это мир возможностей, но и мир ответственности.
Ниже — примерный «каркас» лечения. Он индивидуализируется по клинической картине, сопутствующим болезням, опыту прошлых попыток и бытовым ограничениям. Ключевой принцип — «одно вмешательство: одна цель — один маркер — одна дата проверки».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого саратов[/url]
Learn more here: https://enah.edu.mx
Top materials of the week: https://goldfieldstvet.edu.za
Current recommendations: https://rdc.ubaguio.edu
Ниже — примерный «каркас» лечения. Он индивидуализируется по клинической картине, сопутствующим болезням, опыту прошлых попыток и бытовым ограничениям. Ключевой принцип — «одно вмешательство: одна цель — один маркер — одна дата проверки».
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
всё граммотно делают! https://bitrail.ru сделайте уже что-нибудь с этим реестром… хочу сделать заказ
Мы одинаково внимательно относимся и к амбулаторным, и к стационарным маршрутам. Для каждого формируется индивидуальная цель (устранение абстиненции, нормализация сна, восстановление внимания и мотивации) и назначается «точка переоценки» — момент, когда команда сверяет динамику и, если нужно, меняет один параметр плана (дозу, время внесения процедур, приоритет модуля). Так достигается предсказуемость и избегается избыточная фармаконагрузка.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Read more on the website: https://kingtreespecialists.com
Here are all the details: https://loanfunda.in
The most interesting is here: https://olinnsecurityinc.com
В клинике «ЮгМед Альянс» выстроена система непрерывного медицинского наблюдения. При поступлении проводится комплексная диагностика, назначается детоксикация и поддерживающая терапия, затем начинается стабилизация физического и эмоционального состояния. Благодаря круглосуточной работе бригад и возможности экстренного выезда на дом пациенты получают помощь без задержек. Конфиденциальность соблюдается на всех уровнях — от первичного звонка до выписки. Для удобства родственников организована система информирования: короткие апдейты по согласованным каналам связи и только в определённое время, чтобы не нарушать покой пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/
В Ставрополе мы выстроили так называемую «тихую логистику»: запись без послеобеденных «окон», экспресс-приём без ожидания, сопровождение от входа до палаты, а при необходимости — деликатная госпитализация через отдельный вход. При первичном обращении пациент получает пошаговый план на ближайшие 72 часа: стабилизация самочувствия, детоксикация по показаниям, психообразование, старт профилактики срыва. Такой регламент экономит время и снижает тревожность — вы понимаете, что и зачем делается, и видите прогноз по срокам.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/narkolog-psikholog-stavropol/
Если дома нет условий для покоя или отмечаются выраженные соматические риски, предложим кратковременное наблюдение в клинике с отдельным входом и камерным постом: без очередей, без посторонних взглядов, с чёткой маршрутизацией. После стабилизации пациент возвращается к амбулаторному формату и коротким «чек-инам» — телефонным или видеосвязью.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/
Details inside: https://ens-newswire.com
Trusted and best: https://diversionbooks.com
Full version of the material: https://fasterskier.com
А то декларировалась “быстрая реакция на заказ”, а на деле реакция отсутствует вообще https://brillshop1.ru всегда кто-то гадость может написать, а ответить не кто!! работал с вами!
Don’t Miss the Best: https://cricket.co.za
Related Today: https://cascadeclimbers.com
Real-Time Update: https://bioenergetic-therapy.com
Наркологическая клиника «КарелМед Центр» — это круглосуточная помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании, ориентированная на безопасность, анонимность и реальный результат. Мы выстраиваем лечение как последовательность управляемых шагов: стабилизация физиологии, снижение тревоги, формирование навыков отказа, восстановление сна, возвращение к работе и семье. Каждый этап имеет цель, понятные маркеры и «окно оценки» — конкретную дату, когда команда и пациент вместе сверяют динамику и корректируют план. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, убирает хаос и делает путь к ремиссии предсказуемым.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в петрозаводске[/url]
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-17.com/]1xbet t?rkiye[/url] .
Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально: с учётом стажа употребления, состояния внутренних органов, уровня тревожности и социальной поддержки. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, а при необходимости включать работу психиатра, психотерапевта и специалистов по реабилитации. Принцип клиники прост — не лечить «вообще от зависимости», а выстраивать для каждого пациента персональную карту восстановления, где ясно расписаны шаги, сроки и критерии улучшения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
медицинская аппаратура [url=https://medicinskoe–oborudovanie.ru]медицинская аппаратура[/url] .
экстренное вытрезвление [url=www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru]www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru[/url] .
Вывод из запоя в Ставрополе проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов, которые действуют мягко, не вызывая резких перепадов давления или побочных эффектов. Перед началом лечения врач проводит диагностику — измеряет пульс, артериальное давление, уровень насыщения крови кислородом, оценивает состояние печени и почек. Только после этого подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход снижает риски осложнений и гарантирует безопасное восстановление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно ставрополь[/url]
Состав инфузий подбирается индивидуально. Важно понимать: большая «палитра» компонентов не означает лучший результат; ценность приносит точный фокус. Ниже — типовые профили, которые мы адаптируем под клинику конкретного случая.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево нижний тагил[/url]
следующий раз пришлем поношеные презервативы но ты будешь рад!!! https://optovik360.ru Не вздумайте платить ему без Гаранта через которого он не работаем,этим самым доказывает свою не надежность!
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМед Резонанс» — это круглосуточный центр доказательной медицины, где помощь строится вокруг безопасности, конфиденциальности и персонализации. Мы объединяем медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапию, реабилитационные практики и постлечебное сопровождение в единую дорожную карту восстановления. Каждый шаг лечения закреплён измеримыми критериями эффективности, а решения принимаются командно — от дежурного нарколога и клинического психолога до психиатра и реабилитолога.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Read the Full Version: https://antarvasnastory2.in
Details at the Link: https://billi-walker.jp
Full Version Here: https://www.saffireblue.ca
Команда «КарелМед Центра» объединяет наркологов, психиатров, реаниматологов, клинических психологов, специалистов по реабилитации и социальному сопровождению. Мы работаем без очередей и навязчивых формальностей, а логистика визита, оформление в стационар и коммуникации с родственниками выстроены бережно: конфиденциальные записи, немаркированные выезды, отдельный вход и нейтральная терминология в документах. Вы получаете не только купирование абстиненции и детоксикацию, но и системную работу с триггерами, привычками и межличностными конфликтами — тем, что часто возвращает к употреблению даже после «идеальных капельниц».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Ставрополе проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов, которые действуют мягко, не вызывая резких перепадов давления или побочных эффектов. Перед началом лечения врач проводит диагностику — измеряет пульс, артериальное давление, уровень насыщения крови кислородом, оценивает состояние печени и почек. Только после этого подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход снижает риски осложнений и гарантирует безопасное восстановление.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. Les options sont vastes comme une scene live, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter le design est moderne et soul, ajoute une touche de soul. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un mixage parfait. Les titres sont d’une variete envoutante, proposant des jeux de table styles. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un beat parfait, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est simple et vibrant, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rythmee, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris variees, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinoappfr.com/|
Trusted Sources: https://brandmasteracademy.com
Most Useful Materials: https://wildlife.by
Key Takeaways Here: https://rennerusa.com
J’adore l’atmosphere mythique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience magique. La variete des titres est magique, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent comme par magie, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un conte, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
хороший магазин !отменное качество и сервис ! хорошей работы вашему магазину и процветания! https://brillshop1.ru Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
Авто под заказ заказ из Кореи, Авто под заказ из Китая, Кореи и Японии – это уникальная возможность стать обладателем автомобиля, который еще не представлен на российском рынке или предлагается по более выгодной цене. Мы берем на себя все хлопоты, связанные с поиском, доставкой, таможенным оформлением и сертификацией автомобиля, предоставляя вам возможность наслаждаться новым приобретением без лишних забот. Мы тщательно проверяем техническое состояние и историю автомобиля, гарантируя его соответствие заявленным характеристикам.
J’adore l’atmosphere musicale de BassBet Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. La selection de jeux est melodieuse, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche de rythme. Un plus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Документы недвижимости Юридические аспекты приобретения и владения земельным участком: от кадастровых планов до ограничений по строительству, от межевания до налогообложения – множество нюансов, требующих экспертных знаний. Мы обеспечиваем полное юридическое сопровождение, гарантируя соблюдение ваших прав и интересов.
частные индивидуалки тюмень
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, incluant des paris live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! De plus le site est rapide et futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Particulierement captivant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des transactions fiables.
Lire maintenant|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La selection de jeux est somptueuse, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. En bref, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus le design est moderne et chic, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir raffine. La selection de jeux est exquise, offrant des sessions live distinguees. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du charme. En bref, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer maintenant|
Лучшее прямо здесь: https://vikivostok.ru
Всё самое лучшее у нас: https://radiocert.ru
Топ-выбор для вас: https://neoko.ru
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Au final, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Continuer Г lire|
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это как нить Ариадны, ведущая сквозь темный лес цифрового мира к самому сердцу платформы. Однако, прежде чем довериться этой нити, убедитесь в её прочности и надёжности, ведь в сети подстерегают коварные обманщики, готовые воспользоваться вашей неосторожностью. Проверяйте каждый символ, каждое слово, чтобы не стать жертвой фишинга и не потерять свои сбережения. Помните, что безопасность – это прежде всего ваша личная ответственность.
This is my first time go to see at here and i am truly happy to read all at single place.
https://alma-ata.city/forums/muzhskoj-forum/pogovorim-za-zhizn/78337/
В Ставрополе мы выстроили так называемую «тихую логистику»: запись без послеобеденных «окон», экспресс-приём без ожидания, сопровождение от входа до палаты, а при необходимости — деликатная госпитализация через отдельный вход. При первичном обращении пациент получает пошаговый план на ближайшие 72 часа: стабилизация самочувствия, детоксикация по показаниям, психообразование, старт профилактики срыва. Такой регламент экономит время и снижает тревожность — вы понимаете, что и зачем делается, и видите прогноз по срокам.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
I’ve read several good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a magnificent informative site.
**breathe**
breathe is a plant-powered tincture crafted to promote lung performance and enhance your breathing quality.
Инфа с вашего сайта. Я уже брал 6-APB, и выглядел он несколько иначе. https://aquaphors.ru По АМ могу сказать,что концентрировать выше 1 к 15 не вижу смысла.Оно не торкает дальше своего известного предела,после 1 к 15 дальше пойдёт уже переводняк.Тут как с процами-дороже 200 баксов покупать-перевод бабла,прироста производительности не заметишь почти.
Всё самое новое тут: https://morshynkurort.net
Читайте больше на сайте: https://actual-cosmetology.ru
Click to learn more: https://www.guidasposi.it
**breathe**
breathe is a plant-powered tincture crafted to promote lung performance and enhance your breathing quality.
Если к «окну оценки» динамика плато, мы корректируем один элемент — скорость/последовательность инфузии, вечерний ритуал или плотность сессий. Это защищает от полипрагмазии и делает вклад каждого шага читаемым.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Такая последовательность шагов позволяет врачу действовать точно и эффективно. Благодаря комплексному подходу пациент чувствует облегчение уже через 1–2 часа после начала терапии, а полное восстановление наступает в течение суток.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
https://world-energy.kiev.ua/yak-ne-pomylytys-pry-vybori-skla-far-dlya-avto-v-u.html
Jogue o caca-niqueis slot com egipcios: tumbas antigas, riscos e giros gratis com simbolos expansivos. Modo de demonstracao sem cadastro, RTP justo, simbolos Wild/Scatter, multiplicadores e rodadas bonus. Otimizado para dispositivos moveis, depositos e saques praticos, dicas para iniciantes.
Любите классику? играть слот фрукты с семёрками, BAR и цитрусами дарит частые хиты, Wild, Scatter и бонусные вращения. Демо-режим бесплатно, честный RTP, адаптация под смартфоны. Простые правила и динамичный геймплей — отличный выбор для новичков и профи. Помните о разумных лимитах.
O caca-niqueis jogo rio gems combina a nostalgia classica com o dinamismo de um parque de diversoes: multiplicadores, giros gratis, re-spins e Wilds aleatorios. Apresenta graficos coloridos, uma interface responsiva e uma versao demo para praticar. Ao jogar, lembre-se de se manter seguro: estabeleca limites e faca pausas.
Качественный напиток характеризуется естественным ароматом и отсутствием посторонних примесей.
Явным критерием качества можно назвать прозрачность напитка.
Добротные производители строго следят за этапы изготовления.
Упаковка также служит показателем о уровне продукта.
fortuna distillery
Законная маркировка — ещё один признак подлинности.
Добротный алкоголь никогда не вызывает жжения в горле.
Следует покупать продукцию только в проверенных магазинах.
Разумный подход к выбору напитков поможет избежать разочарований.
Всем привет))))) Мой Трипчик)))))) https://bitrail.ru Затарил я тут как то купели значит курехи,приваливай на адрес и не могу найти списался с оператором и понял что дурак тут я а не минер затупил,30 сек и закладка у меня в руках,лечу Домой,дома меня ждут уже братики заряжает по 2 водных и начинаем пускать слюни под спанч бобра, в полне хороший стафф,силы стафа хватает,валит минут 40-60 потом спад,получилось так что вес сдули за 2 дня,отходосы минемальные, вообщем сервис тут вышка тарился тут ребята)
Откройте ритм джунглей в демо 9 masks of fire: собирайте маски-Scatter для моментальных выплат, активируйте фриспины и множители на бонусном колесе. Яркая графика, отзывчивый интерфейс, поддержка iOS/Android, демо без регистрации. Играйте осознанно — задавайте пределы.
Expanded version here: https://puntera.com
Full list of materials: https://cour-interieure.fr
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
https://saunalux.kiev.ua/yakyi-instrument-krashche-dlia-rozboru-far-ruchnyi-chy-elektrychnyi.html
«УралДетокс Клиник» организует круглосуточный вывод из запоя на дому с акцентом на безопасность, предсказуемость и конфиденциальность. Мы работаем без выходных, используем портативное оборудование и персонализируем инфузионные протоколы под текущее состояние пациента, коморбидность и бытовые условия. Визит строится не как «сильная капельница любой ценой», а как последовательность понятных шагов с измеримыми результатами: фиксируем витальные показатели, выбираем ведущий клинический фокус, начинаем с тестового объёма, переходим к основной фазе и обязательно назначаем «окна оценки» — моменты, когда каждый участник процесса понимает, что и почему корректируем.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Top recommendations: https://possible11.com
The best click here: https://www.gagolga.de
All on this topic – here: https://copychief.com
спасибо за отзыв! https://aleksinmk.ru Уважаемый, Chemical-mix.com, я новичок что на легале, что в джабере, что где либо ещё… не получается выйти на связь, проблема с покупкой, в джабере написано, на сайте не онлайн… ответь пожалуйста в jabber… Зарание большое спасибо…
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: Password Game for parties
купить диплом в москве [url=https://rudik-diplom13.ru]купить диплом в москве[/url] .
деньги займ микрозайм
Купить видеокарту https://n-katalog.ru/category/videokarty/list актуальные цены и наличие в топ-магазинах, честные характеристики и тесты. Сортировка по цене и производительности, фильтры по памяти, шине, интерфейсам, длине и типу охлаждения. От игр в 1080p до 4K/VR — сравните и выберите лучшее предложение сегодня.
In the article https://fotoredaktor.top the location of Nicaragua was well explained.
следующий раз пришлем поношеные презервативы но ты будешь рад!!! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм понятно как проверенный магазин работает если отзывы негатив значит зачищает сообщений еще куча они на телефоне сейчас не могу их скопировать но и смысла нет все и так ясно
Авто под заказ в Магнитогорске. Автоподбор под ключ – это полный комплекс услуг, включающий в себя: определение бюджета и требований к автомобилю, поиск подходящих вариантов, выездную диагностику, проверку юридической чистоты, сопровождение сделки и помощь в оформлении документов. Мы берем на себя все этапы процесса, экономя ваше время и нервы.
Продажа земли Регистрация права собственности – это гарантия вашей юридической защищенности. Мы обеспечиваем полное сопровождение сделки, начиная от подготовки документов и заканчивая регистрацией права собственности в Росреестре.
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это как нить Ариадны, ведущая сквозь темный лес цифрового мира к самому сердцу платформы. Однако, прежде чем довериться этой нити, убедитесь в её прочности и надёжности, ведь в сети подстерегают коварные обманщики, готовые воспользоваться вашей неосторожностью. Проверяйте каждый символ, каждое слово, чтобы не стать жертвой фишинга и не потерять свои сбережения. Помните, что безопасность – это прежде всего ваша личная ответственность.
Благодарен за заказ во вторник оплатил – в пятницу / утром / товар получил купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Сайт сделан на уровне в скором думаю сделаю заказ, только бы качество не подвело
они долго кормили завтраками с отправкой, а потом и вовсе закрылись… купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Мне уже похер будет он иле не будет!Хорошо что я как обычно не взял на 45т.р вот о бытом я вообще не жалею!Если магазину важнее не совершать обмен чем клиент который в неделю на 45т.р товара брал то досведание!
electmikemontes – Political campaign focused on community representation and positive change.
shemplymade – Handcrafted products with quality craftsmanship and unique designs.
Бро, была абсолютно идиентичная ситуация у мну в декабре.Трек не бился пол недели, прошли выходные звоню в контору-курьерку, называю трек, говорят нет такого, я к тс так мол и так, тот грит все ровно, трек верный ожидай! Херакс и вечером курьер названивает, оказыва4тся они мне еще в субботу хотели вручить, но почему то не дозвонились))Все пучком, бро.Почта мало кому интересна в наши дни, на курьерки много сваливается, вот они 3ак могут разгребают… купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази уже ожидается что нибудь?
магазин напольных покрытий Если вы ищете надежного поставщика качественных напольных покрытий, магазин напольных покрытий станет вашим верным помощником. Здесь представлен широкий выбор материалов от ведущих производителей, квалифицированные консультанты помогут вам подобрать оптимальное решение, учитывая ваши индивидуальные требования и бюджет. В магазине вы найдете не только ламинат, но и другие популярные виды напольных покрытий, а также все необходимые сопутствующие материалы для укладки и ухода за полом.
J’ai un amour vibrant pour BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs soul. L’offre de bienvenue est envoutante. Les agents repondent avec un groove parfait, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Le processus est simple et vibrant, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino vaut une session soul pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus la navigation est simple et rythmee, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir veloce. Les options sont vastes comme une course, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un sprinter, toujours pret a accelerer. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui accelere pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. Les agents repondent comme un solo, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Au final, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
Thanks , I have recently been looking for information about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have came upon till now. But, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
kra42 cc
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, il procure une experience magique. La selection de jeux est enchantee, avec des slots aux designs enchantes. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le support client est enchante, toujours pret a transformer. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les amateurs de sensations enchantees ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et magique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
J’ai un coup de c?ur pour Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde de raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides. L’assistance est rapide et professionnelle, avec une aide efficace. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient parfaites. En bref, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations raffinees ! A souligner le design est moderne et soigne, ce qui rend chaque session plus lumineuse. A noter les options de paris variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Découvrir aujourd’hui|
Je suis fascine par Impressario Casino, ca offre une experience cinematographique. Le catalogue est riche et varie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Boostant votre capital initial. L’assistance est rapide et professionnelle, avec une aide efficace. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient une star. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations prestigieuses ! Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et elegante, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Lire plus loin|
shemplymade – Handcrafted products with quality craftsmanship and unique designs.
J’aime l’ambiance futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un cosmos chiffre. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite cosmique, garantissant un service de pointe. Les transferts sont fiables, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! En bonus le site est rapide et futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Trouver le bonus|
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
kra42 at
а че, под запрет попадает? вроде нет купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Всем, как и писалось средняя компенсация 50%
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also pay a visit this web site on regular basis to get updated from newest information.
https://kra42c.com
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Snatch Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist top. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, von Zeit zu Zeit ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Kurz gesagt, Snatch Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zudem ist das Design modern und einladend, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein starkes Feature die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Snatch Casino|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir veloce. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, avec des slots aux designs veloces. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est veloce, toujours pret a accelerer. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un sprint. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme une piste, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du groove. Au final, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un riff, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est magique. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. Au final, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les amateurs de sensations enchantees ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
Статтю на https://siviagmen.com читав про переїзд у сприятливі дні.
J’adore l’ambiance delicate de Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne d’elegance. L’eventail de jeux est somptueux, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. Les agents repondent avec une douceur exquise, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Au final, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A souligner la navigation est intuitive et delicate, ajoute une touche de finesse. A noter les options de paris variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Trouver maintenant|
В статье https://buybuyviamen.com нашли полезную информацию о двускатных крышах.
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Snatch Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, von Zeit zu Zeit gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Insgesamt, Snatch Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Nebenbei die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
snatch-casino.de|
Je suis fascine par Impressario Casino, il evoque un tapis rouge scintillant. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable, joignable a tout moment. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient parfaites. En bref, Impressario Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de sensations prestigieuses ! Notons aussi le site est rapide et envoutant, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Поради на https://mr-master.com.ua/ru/ допомогли вирішити, як замінити фартух на кухні.
Je suis accro a Monte Cryptos Casino, il procure une aventure virtuelle. La variete des titres est eclatante, avec des slots aux themes innovants. Amplifiant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est lisse comme un wallet, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les evenements communautaires decentralises, garantit des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’ai une passion cyclonique pour Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En bref, Spinit Casino vaut une course rapide pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter le design est moderne et dynamique, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un riff. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un solo, toujours pret a jammer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En bref, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est simple et rythmee, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
I am glad to be a visitor of this thoroughgoing web blog ! , regards for this rare information! .
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourbillonne comme un conte. La variete des titres est magique, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est enchante, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. En resume, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et magique, ajoute une touche de mystere. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. La variete des titres est eclatante, avec des slots aux designs modernes. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec une vitesse fulgurante, garantissant un service premium. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
Apprendre maintenant|
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. La variete des titres est eclatante, incluant des paris live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable, joignable a tout moment. Les transferts sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Egalement cool les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, renforce la communaute.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis absolument ebloui par Impressario Casino, il evoque un tapis rouge scintillant. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. L’assistance est rapide et professionnelle, garantissant un service de star. Les retraits sont fluides comme un generique, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations prestigieuses ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et envoutant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Entrer sur le site web|
https://zumo-spin-games.com/
Je suis stupefait par Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. La variete des titres est eclatante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite cosmique, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement cool les options de paris variees, renforce la communaute.
Explorer le site|
https://annaartmur.shop/ Erotic bedroom art adds a layer of intimacy and personal expression to the most private space in the home. By selecting artwork that resonates with their sensuality and desires, couples can create an environment that fosters connection, exploration, and shared pleasure. The right artwork can enhance the mood, spark conversation, and deepen the emotional bond between partners.
какие то траблы ппц =\ купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Прислали нам свой метоксетамин, подтверждаем: продукт чистый, >99%.
https://mega-main.shop
Woh I enjoy your content , saved to bookmarks!
clevelandchristmasclub – Festive community organization spreading holiday joy and cheer.
анологичная ситуация! продаван ты на примете, раз твоих клиентов начали принимать… купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Желаю всего самого наилучшего вашему магазину,ваш бренд это качество!
На сайті zebraschool.com.ua ремонтував електросамокат у Тернополі — все сподобалось!
Useful and Relevant: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
Everything in One Place: https://marchemodevintage.com
whoah this weblog is excellent i like reading your articles. Keep up the great work! You understand, many persons are searching round for this info, you can aid them greatly.
kra42 at
Такси в Турции Турция или Таиланд – дилемма для тех, кто ищет ярких впечатлений. Турция манит историей и культурой, а Таиланд – экзотикой и релаксом. Выбор зависит от настроения и целей путешествия: Турция – для ценителей истории и архитектуры, Таиланд – для тех, кто мечтает о пляжном отдыхе и умиротворении.
Обратите внимание, ТС отказывается работать с ГАРАНТОМ! хоть и магазин древний и проверенный! но хочется спать спокойно! АДМИНЫ ОБРАТИТЕ ВНИМАНИЕ, ПОРА КАК ТО ИЗМЕНИТЬ РЕЖИМ РАБОТЫ ГАРАНТА. СДЕЛКИ ПРОВОДИТЬ ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО ТОЛЬКО ЧЕРЕЗ ГАРАНТА! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки хорщий магаз!!!всегда все ровно!!!
Because the admin of this site is working, no doubt very rapidly it will be well-known, due to its feature contents.
https://kra42c.com
Современные поисковые системы для поиска информации становятся всё более востребованными.
Они дают возможность находить доступные данные из интернета.
Такие решения используются для исследований.
Они могут быстро систематизировать большие объёмы контента.
бот большой глаз
Это способствует создать более полную картину событий.
Некоторые системы также обладают функции визуализации.
Такие платформы широко используются среди специалистов.
Совершенствование технологий превращает поиск информации более точным и удобным.
Why people still make use of to read news papers when in this technological globe the whole thing is presented on net?
официальный сайт kra42 cc
All Materials on the Topic: https://www.jec.qa
Only the Important Details: https://questreaming.com
bwaylocations – Prime location services with strategic placement and accessibility.
Нейросетевые онлайн-сервисы для анализа данных становятся всё более популярными.
Они дают возможность изучать публичные данные из разных источников.
Такие инструменты используются для исследований.
Они могут быстро обрабатывать большие объёмы данных.
глаз блога телеграмм
Это помогает создать более точную картину событий.
Многие системы также обладают функции визуализации.
Такие боты популярны среди специалистов.
Совершенствование технологий делает поиск информации доступным и быстрым.
реагенты всегда чистые и по высшему??? сертифекаты вместе с реагентами присылают на прохождение экспертизы на легал? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Послезавтра запрет в силу вступает
kraken market Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
New materials are here: https://agriness.com
Currently reading: https://mindfulnessmeditationcenters.com
Don’t miss the main points: https://theshaderoom.com
https://zumo-spin-games.com/
Top content here: https://billi-walker.jp
The most important is here: https://alayahotels.com
The best collected for you: https://joogastuudio.ee
Нейросетевые поисковые системы для мониторинга источников становятся всё более популярными.
Они позволяют изучать публичные данные из социальных сетей.
Такие решения применяются для исследований.
Они умеют оперативно систематизировать большие объёмы контента.
глаз бога сайт официальный
Это помогает получить более полную картину событий.
Многие системы также предлагают удобные отчёты.
Такие боты активно применяются среди специалистов.
Эволюция технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и наглядным.
в каком городе брал и когда?интерисует барнаул купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм удачи в изменении ситуации! 🙂
https://t.me/KudaSaintPetersburg Обязательно посетите Петропавловскую крепость – сердце города. Поднимитесь на колокольню собора Петра и Павла, откуда открывается захватывающий вид на город, прогуляйтесь по территории крепости, узнайте об истории императорской семьи Романовых.
Playing responsibly is crucial for ensuring a safe gaming experience.
It helps participants appreciate the activity without harmful effects.
Being aware of your boundaries is a main principle of responsible behavior.
Players should define clear spending limits before they start playing.
Popular Slots AU
Regular breaks can help keep control and prevent fatigue.
Honesty about one’s habits is vital for keeping gaming a fun activity.
Many services now encourage responsible gaming through helpful guidelines.
By keeping balance, every player can have fun while staying in control.
Стал вопрос о изготовление прототипа на 3D-принтере, потому что требовалось представить результат заказчику в сжатые сроки. Команда подошла к делу максимально ответственно. Выполнение заказа заняло минимум времени, а каждая деталь модели оказалось на высоте. Менеджеры грамотно проконсультировали, и мы достигли именно того, что планировали. Стоимость услуг оказалась лучше, чем у конкурентов. Компания заслуживает только положительных отзывов и планирую обратиться повторно https://qa.andytoan.vn/index.php?qa=215395&qa_1=%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%BA-3d-%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C-%D1%83%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%89%D0%B0%D0%B5%D1%82-%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B1%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BA%D1%83-%D0%B8-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%BE.
купить права
kraken market Kraken market – это пестрый калейдоскоп предложений, где каждый может найти то, что ищет. Но, как и на любом рынке, здесь встречаются не только честные торговцы, но и мошенники, готовые обмануть доверчивых покупателей. Поэтому, прежде чем совершить покупку, тщательно изучите репутацию продавца, сравните цены и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Помните, что ваша бдительность – лучшая защита от обмана и разочарования. Kraken market – это мир возможностей, но и мир ответственности.
частный вытрезвитель [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-25.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-25.ru[/url] .
здесь без музыки танцую – купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм а что с магазином в Петрозаводске,работать то будете дальше,а то уже неделю не какой активности.
Интеллектуальные боты для мониторинга источников становятся всё более востребованными.
Они дают возможность собирать открытые данные из интернета.
Такие инструменты применяются для аналитики.
Они могут оперативно систематизировать большие объёмы контента.
по номеру телефона глаз бога
Это помогает создать более полную картину событий.
Многие системы также обладают удобные отчёты.
Такие сервисы популярны среди исследователей.
Совершенствование технологий делает поиск информации более точным и наглядным.
turnerhallrestaurant – Exceptional dining experience with quality cuisine and atmosphere.
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
kra42 cc
code promo bet of africa The specific demands reveal nuanced strategies. Gamblers aren’t just looking for any code; they seek the best – “meilleur code promo 1xBet.” The appeal of freebies is undeniable (“code promo 1xBet gratuit,” “code promo 1xBet sans depot”), reflecting a desire to minimize risk and maximize potential returns. Validation is crucial (“code promo 1xBet valide”), assurance that the offered benefit is genuine and not merely a marketing ploy. The “code promo 1xBet 130€” exemplifies the tangible rewards users hope to secure.
Hello to every body, it’s my first go to see of this weblog; this web site contains awesome and really fine stuff designed for visitors.
kra42 cc
Superb website you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any community forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really love to be a part of online community where I can get opinions from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Thank you!
kra42 cc
Товар привезли качество удовлетворительное,единственное что заказ долго оформляли не мог достучаться в асю.А так все норм!=)) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Посмотри в ЛС
This really matches my view, appreciate the insight.
Thought I’d drop this here, I found a link recently: [url=https://maba-3d-druck.de]just sharing[/url]
Curious to hear your thoughts.
На данной площадке вы найдёте много полезной информации.
Сайт ориентирован на людей, интересующихся достоверная помощь.
Публикации, размещённые здесь, дают возможность узнать больше в разных вопросах.
Контент постоянно дополняется, чтобы оставаться современными.
https://antiwikipedia.com
Навигация понятная, поэтому перейти к интересующей теме удобно.
Каждый гость сайта способен найти контент, соответствующие его вопросам.
Эта платформа разработан с вниманием о аудитории.
Открывая этот сайт, вы находите ценный ресурс знаний.
Интеллектуальные поисковые системы для мониторинга источников становятся всё более популярными.
Они помогают изучать доступные данные из интернета.
Такие решения применяются для исследований.
Они умеют быстро обрабатывать большие объёмы контента.
глаз бога казахстан телеграмм
Это помогает создать более полную картину событий.
Многие системы также обладают функции визуализации.
Такие платформы широко используются среди специалистов.
Совершенствование технологий позволяет сделать поиск информации доступным и наглядным.
Однако, селлеру в его интересах было бы полезно появиться и разъяснить ситтуацию дабы избежать гневных сообщений. Обещание что отправка будет пт-сб не было выполнено. Треков нет. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази все пришло.пока не пробовал.конспирация на высшем уровне.спасибо
https://zumo-spin-games.com/
spiritoftheaerodrome – Aviation heritage and historical preservation with passion.
Editor’s Choice here: https://www.actuabd.com
The most valuable is here: https://g-r-s.fr
This post is worth everyone’s attention. How can I find out more?
https://kra41c.com
New and important: https://www.atrium-patrimoine.com
Latest Insights: http://www.waltbabylove.com
Maintaining control while gaming is very important for ensuring a safe gaming experience.
It helps players appreciate the activity without unwanted stress.
Understanding your boundaries is a key part of responsible play.
Players should define clear time limits before they start playing.
Echtgeld Casino Deutschland
Frequent rest periods can help maintain focus and avoid burnout.
Awareness about one’s habits is essential for keeping gaming a enjoyable activity.
Many services now support responsible gaming through educational tools.
By being aware, every player can enjoy gaming while staying in control.
Ага, прям именно так. Но все же?))))) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки а эффор хорош?) на что похож?)
https://t.me/KudaSaintPetersburg Продолжить знакомство с городом можно, прогуливаясь по Невскому проспекту – главной артерии Петербурга. Здесь, среди исторических зданий и бутиков, кипит жизнь. Загляните в Дом книги, полюбуйтесь архитектурой Казанского собора, сделайте фото на фоне Елисеевского магазина – места, пропитанного духом старого Петербурга.
Codes promo gratuits 1xbet The variations are endless: “code bonus 1xbet,” “1xbet code promo pari gratuit,” “1xbet bonus de bienvenue 2026,” and “bonus de bienvenue 1xbet.” These phrases denote a desire for diverse bonus types. There are country-specific demands like “Code promo 1xbet Afrique du Sud.”
Wow, marvelous blog format! How long have you been running a blog for? you made blogging glance easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, as well as the content material!
https://kra41c.com
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
I’d like to find out more? I’d love to find out some additional information.
https://kra41c.com
Top Stories Right Now: https://satapornbooks.com
Latest Insights: https://docpulse.com
34crooke – Unique address with distinctive character and presence.
Today’s Best: https://metabolomicssociety.org
More details at the link: https://2awebdesign.net
New and important: https://ets.redrc.net
Ты че педрила хвалишся че та видел ты меня знаеш нет пес это не паника а логика паника это твое второе имя ху……я ты наличности переходиш это говорит о том что ты очкошник служил он терпила мне пох кто ты а за слова ты ответиш ну конншно на растояние ты герой ха ха отдыхай кент купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш хотелось бы услышать какоето обьяснение?????
J’ai une passion lyrique pour Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodieux. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont rapides comme une melodie, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En bref, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En bonus la navigation est simple comme un oracle, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
https://olympefr.com/|
code promo 1xbet cote d’ivoire 2026 The allure of 1xBet, with its wide array of betting options, is undeniable. However, navigating the world of promo codes can be a labyrinthine task. Whether you seek a “code promo 1xBet” for sports betting, casino games, or simply a “bonus inscription 1xBet,” understanding the landscape is key.
loftsonlex – Modern urban living with stylish loft accommodations.
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodieux. Le catalogue est riche en melodies, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et glorieux, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient divins. En resume, Olympe Casino merite une ascension celeste pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://olympefr.com/|
посылка пришла, все чотко, упаковка на высшем уровне, респектос купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Доброго времени суток бразики! 🙂 сегодня заказал новой реги на пробу , при получении отпишусь за чё каво) За данный магаз, хотел бы оставить отзыв! ТС адекватный чел, была еденичная перагазовка в феврале, которая затянулась практически на месяц, уже и не думал что получу свой заказ, или заберу обратно деньги! Но ТС все сделал красиво, за это ему уважение лично от меня! более того пообещал при сл.заказе бонуса за косяк, что интересно это инициатива была придложена им лично! Короче красавчик чел, тут к гадалке не ходи! Советую безобразно ТАРИЦА 🙂
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, jedoch mehr Bonusoptionen waren top. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein starkes Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Weiterlesen|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, ab und zu mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein starker Vorteil sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Weiterlesen|
Je suis totalement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, toujours pret a guider. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et divin, ce qui rend chaque session plus celeste. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
olympefr.com|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, rarement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement excellent les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Explorer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un amusement continu. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller sur le site web|
Спрашивай в жаббер, там больше 10-15 минут задержки с ответом не бывает. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Братки все красиво стряпают, претензий к магазину нуль, всегда всё ровно. Единственное что сейчас напрягло, отсутствие на ветке вашего представителя в ЕКБ “онлайн”, представитель молчит ( а там по делу ему в лс отписано) и кажись воопще не заходит пару недель
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, manchmal gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein hervorragendes Plus die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Zur Seite gehen|
olympicsbrooklyn – Sports and athletic excellence with community engagement.
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, allerdings mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein super Vorteil die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Jetzt entdecken|
ламинат Магазин напольных покрытий – это ваш надежный проводник в мире полов. Здесь представлен широкий ассортимент материалов от ведущих производителей, способных удовлетворить любые запросы и бюджеты. Квалифицированные консультанты помогут вам подобрать оптимальное решение, учитывая особенности помещения, ваши личные предпочтения и финансовые возможности. Помимо самих покрытий, в магазине вы найдете все необходимые сопутствующие товары: подложки, плинтусы, клеи, герметики и средства для ухода за полом. Ваша задача – лишь выбрать, а наша – предоставить все необходимое для создания идеального пола в вашем доме.
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le site est rapide et style, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement excellent les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui booste la participation.
Explorer plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour completer l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses continues.
Lancer le site|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Live-Sportwetten. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Ubrigens ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein hervorragendes Plus die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, exklusive Boni bieten.
Mehr entdecken|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquez ici|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, ab und zu ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zusatzlich die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein weiteres Highlight ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Website ansehen|
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste la participation.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un element fort les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller en ligne|
Je suis sous le charme de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Обязательно позвонить должны, как позвонят легче забрать самому чем ждать пока курьер доставит купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш магазин работает как надо, у меня тут перевес был не плохой спасибо дружбанчики
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
Greetings! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy reading through your articles. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same subjects? Many thanks!
https://bcet-consulting.com/melbet-2025-obzor-bk/
https://t.me/KudaSaintPetersburg Куда сходить в Питере – вопрос, который легко превращается в захватывающее приключение по одному из самых красивых городов мира. Начните с Эрмитажа, дворца, где искусство оживает на каждом шагу. Залы с коллекциями, собранными веками, от античности до современности, поразят воображение даже самого искушенного ценителя.
Hi! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the superb work!
https://eric.eepsea.org/?p=44930
Hello to every body, it’s my first pay a visit of this weblog; this webpage contains amazing and in fact excellent data in favor of visitors.
https://paperburners.com/skachat-melbet-besplatno-2025/
Раніше думала, що добре знаю як готувати, але останнім часом мої страви стали скучними і повторювалися. Подруга порадила мені подивитися свіжі рецепти, але я не знала, як підібрати. Якось ввечері знайшла цей каталог і… це було наче знахідка скарбу! Виявилося, що є величезна кількість сайтів з незвичайними рецептами, про які я навіть уяви не мала. Найбільше сподобались підбірки з авторськими стравами та рецептами етнічних страв. За цей час я спробувала страву італійської кухні, тайської та а також іспанської кухні! Моя домочадці в захваті, а я усвідомлюю себе справжнім кулінаром. Навіть почала вести особистий журнал, де записую всі нові рецепти, які спробувала
[url=https://blogreceptov.icu/]Каталог сайтів[/url]
бро незнаю скок раз брал ни разу TS не подводил входил в положения скидки бонусы делал!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Только что принесли, позже трип отпишу)
Important reading: https://www.radio-rfe.com
Most discussed: https://gazetablic.com
Worth your time: https://ecampania.it
Ну блиинн я ждуждуждужду а мне не отвечает ТС я в уныние, буду ждать. говорят хороший, хочу попробовать у него. хочу сладкий бубалех мммм…. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Даже то что я из за тебя третий день на нервах это косяк!Ладно надеямся на лучшее,надежда умирает последней…
code promo 1xBet sans depot Regional variations underscore the platform’s global reach and tailored marketing approaches. Searches range from “Code promo 1xbet Afrique du Sud” to “code promo 1xbet canada”, emphasizing the focus on specific geographic areas to further maximize the return. This also means that regulations and restrictions can vary. There are a myriad of promo codes of various values and for various use-cases, from sports betting to casino and beyond. Ultimately, the search is driven by the aspiration to enhance the 1xBet experience with a strategic code, whether it provides welcome bonus or other promotions.
Хочу продать лекарства Вопрос о реализации неиспользованных лекарственных средств, будь то остатки после лечения, препараты с истекающим сроком годности или просто ненужные медикаменты, требует деликатного подхода и строгого соблюдения законодательства. Прямая продажа лекарств с рук, через интернет-площадки или посредством выкупа, за исключением случаев, предусмотренных законом (например, продажа аптеками), является незаконной и чревата серьезными правовыми последствиями.
Регистрируйся сейчас и получай приветственный пакет — до 140 фриспинов и до 750$ бонуса!
Лучшие игры, быстрые выплаты и честный сервис на
https://cbestnews.buzz/bdhgqsf
https://buyandsellhair.com/author/freebets/
The best on one page: https://crossbridgeguitar.com
Expanded version here: https://paladarplus.es
Additional materials: https://baldebranco.com.br
Интеллектуальные онлайн-сервисы для анализа данных становятся всё более популярными.
Они помогают изучать публичные данные из разных источников.
Такие решения применяются для исследований.
Они умеют быстро систематизировать большие объёмы данных.
glazboga com
Это помогает получить более полную картину событий.
Отдельные системы также предлагают функции визуализации.
Такие платформы широко используются среди аналитиков.
Эволюция технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и удобным.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Детальнее – https://irablogging.in/%E0%A4%89%E0%A4%B2%E0%A4%97%E0%A4%A1%E0%A4%BE-3
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Посмотреть всё – https://bwotc.com/home/official-bwotc-logo-small
Details on click: http://centroculturalrecoleta.org
Top links on the topic: https://clinicadentalnoviembre.es
Best first: https://financialit.net
ОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Ищи в соседней ветке мой отзыв по рцс. ИМХО рцс не для торча.
Нотариальный перевод свидетельства Переводы с/на более 50 языков: английский, немецкий, французский, испанский, итальянский, китайский, японский, арабский и многие другие. Квалифицированные переводчики – носители языка.
https://www.woorips.vic.edu.au/post/2017/11/04/56-weekly-sport?commentId=7927fad9-9e30-4e56-a402-6df522bbe141
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://ferringhibay.com/dcr
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Смотрите также… – https://alfalhosah.com/%D9%84%D8%A8%D8%B4%D8%B1%D8%A9-%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%B6%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D9%85%D8%AB%D9%84-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AB%D9%84%D8%AC-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D9%84%D9%8A%D8%B7-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B3%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%89-%D8%A8%D8%A7
https://techonpage.com/story5916779/1xbet-registration-code-2026
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Проплатил в этот магаз 10.10,трек получил 14.10-сегодня 18.10 трек не бьёться купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Длительность не меньше, чем у CHM-400F (AKB48F), эффект – задумчивее )
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kentrix.in/how-customer-risk-identification-helps-to-reduce-payment-defaults
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Узнать из первых рук – https://rbpa.org/top-marketing-strategies-for-businesses
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://mulagoschoolofnursing.ac.ug/2024/11/15/dec-2024-unmeb-exams
kraken ссылка Kraken market – это шумный восточный базар, перенесенный в виртуальную реальность. Здесь можно найти всё, что угодно, от редких артефактов до запрещённых веществ. Однако, не стоит терять голову от разнообразия предложений и низких цен. Внимательно изучайте отзывы о продавцах, проверяйте информацию о товарах и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Только так вы сможете совершить выгодную и безопасную сделку, избежав разочарований и проблем с законом. Будьте мудрыми и предусмотрительными, и Kraken market откроет перед вами свои сокровища.
Don’t miss the essentials: https://www.europneus.es
The gist is here: https://eguidemagazine.com
Note: The best: https://www.greenwichodeum.com
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://auxpyrenees.com/carte/menu-filet-de-boeuf-entree-plat-dessert
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://www.dhosgent.be/home/attachment/33
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Не упусти важное! – http://www.mrkm.jp/blog/item_478.html
у кого взять собрался его ? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Кто долги твоего представителя в РБ будет отдавать?
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Прочитать подробнее – https://funeral-agency.wwwbg.in/bazov-paket
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Прочитать подробнее – https://template89.webekspor.com/north-sulawesi-exports-1800-tons-of-copra-to-philippines
למעלה. מרינה קיבלה השראה מהדוגמה של בעלה, וגם היא תקפה את הגבעה. איגור משך את החבל לאט, מחזיק את מרגליה. היא שמה לב לזה, כמובן, היא שמה לב, והיא מחייכת כאילו היא נהנית ממה שקורה. אתה קורא לגודל https://tutatok.com/discreet-apartments-in-ashkelon/
לציית. אנטון קם והביא את הזין שלו לפניה, על חטיף, הוא אמר. אלינה לקחה את הזין שלו ביד עם ידית מאוד שימושי עבור הרפיה על הים. היתרון השלישי היה יציאה נפרדת לרחוב, שבזכותה נוכל להימנע ממעבר דרך https://fetishdatingapps.com/
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Детали по клику – https://idherranz.es/2024/01/01/shooting-boudoir-angel-ii
Editor’s recommendation: https://www.leristrutturazioni.it
The latest without the fluff: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
The newest and best is here: https://therockpit.net
девушки Вирт знакомства – это возможность встретить новых людей, не выходя из дома.
harley ДТП: Цена ошибки на дороге слишком высока.
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://thelightandtheglory.com/2023/02/26/tabernacle
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – http://www.volgyfitness.hu/?p=6639
Ты выдал мне комбо купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану – За сколько?
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Что скрывают от вас? – https://loverpresets.com/2021/07/23/exploring-atlantas-modern-homes
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Полная информация здесь – https://gruz-taxi.com.ua/vantagnyk
A useful selection here: https://primorskival.si
Accurate and up-to-date: https://theshaderoom.com
Only the most useful: https://www.wisla-plock.pl
Продвижение сайта помогает бизнесу привлекать целевых клиентов и повышать эффективность онлайн-присутствия. Оптимизация включает работу с контентом, внутренними ссылками и техническими настройками. Регулярный анализ и корректировка стратегии помогают удерживать позиции и обеспечивать стабильный результат. Сайт становится удобным и полезным для пользователей. Такой подход обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект. Подробнее по ссылке https://www.telix.pl/forums/users/valentinryland1/
Register now and receive a welcome package:
up to 205 free spins and as much as 1650Eur bonus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted casino experience await at
https://fanfocus.shop/beqqz8d
Superb, what a weblog it is! This weblog presents useful facts to us, keep it up.
https://petskymarket.co.uk/skachat-melbet-kazino-2025/
Уважаемый ТС,желаю вам успешных больших продаж!:$: купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш произвёл оплату на регу.жду трека!думаю быстро всё получится.
The best collected here: https://gazetablic.com
All the best is ours: https://joogastuudio.ee
Our exclusive top picks: https://housecheck.com.tw
melbet букмекерская контора [url=http://www.melbetofficialsite.ru]melbet букмекерская контора[/url] .
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
As the admin of this web site is working, no hesitation very shortly it will be renowned, due to its feature contents.
https://gta188.org/kak-skachat-melbet-obzor-2025/
Je suis totalement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. La selection de jeux est olympienne, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Le support client est olympien, toujours pret a guider. Les retraits sont rapides comme une melodie, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient divins. Au final, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En bonus la navigation est simple comme un oracle, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus divin les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses eternelles.
https://olympefr.com/|
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article writer for your site. You have some really great posts and I feel I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some material for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please shoot me an email if interested. Thanks!
https://icid.in/?p=130801
Assume you are doing good linking to position you on the first pages of search engines.
The best we recommend: https://winmeen.com
Доставка пиццы в Туле https://pizzacuba.ru горячо и быстро. Классические и авторские рецепты, несколько размеров и бортики с сыром, добавки по вкусу. Онлайн-меню, акции «2 по цене 1», промокоды. Оплата картой/онлайн, бесконтактная доставка, трекинг заказа.
Energy Storage Systems https://e7repower.com from E7REPOWER: modular BESS for grid, commercial, and renewable energy applications. LFP batteries, bidirectional inverters, EMS, BMS, fire suppression. 10/20/40 ft containers, scalable to hundreds of MWh. Peak-saving, balancing, and backup. Engineering and service.
Оплатил заказ, 3 дня прошло, статус все еще отложен. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Поздравляю всех с наступающим Новым 2013 Годом! Желаю в год Змеи: 1. Мутить тока на спирту! 2. Отваривать основу. 3. Сушить естественным способом. 4. Поменьше “ловить бледного”! 🙂 Ну а магазу Chеmical-Mix желаю Процветания, Оперативности, и качественной разнообразной продукции!
Je suis emerveille par Olympe Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Le catalogue est riche en melodies, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a guider. Les retraits sont rapides comme une melodie, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus le site est rapide et glorieux, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Egalement remarquable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
https://olympefr.com/|
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, gelegentlich mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Hinzu kommt ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein starker Vorteil die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Plattform besuchen|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, jedoch mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Zusatzlich die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Bringen Sie mich dorthin|
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
J’ai une passion lyrique pour Olympe Casino, c’est une plateforme qui resonne comme une lyre. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et sage, garantissant un support celeste. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un nectar. En resume, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
https://olympefr.com/|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est simple et transparent, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus constants.
Continuer ici|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir|
Moldova – rent-auto.md/ro/ – Inchiriere auto Chisinau – arenda masini fara stres, rezervare rapida si cele mai bune preturi.
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, en revanche des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Aller au site|
лучшие игры на смартфон Новости Gamebox: Будьте в курсе последних новостей и обновлений платформы Gamebox.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et style, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Explorer davantage|
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]платный нарколог на дом самара[/url]
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, in seltenen Fallen mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Zur Seite gehen|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, dennoch gro?ere Angebote waren super. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist klar und flussig, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Besonders erwahnenswert die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Erfahren Sie wie|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, ab und zu gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein klasse Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Zur Seite gehen|
Всем привет! Специально зарегистрировался для того что бы поведать вам, какой тут отличный магазин! Обращаюсь сюда уже 3 месяца всегда по опту! все на высоте! Время доставки кладом в мой город 4 дня! Качество продукта отличное! Клады хорошие! И главное пунктуальность, и грамотное общение с человеком… Желаю оставаться всегда такими же порядочными! Сразу видно что магазин знает свое дело в нашем не легком труде!!! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Ну подскажите хоть что нибудь пожалуйста?А то я переживаю ппц.
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, gelegentlich mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Zudem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein gro?artiges Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Mehr wissen|
moto Байкер – это не просто человек на мотоцикле, это член братства, объединенного любовью к дороге, скорости и свободе. У каждого байкера свой кодекс чести, свои правила и традиции. Байкер – это состояние души.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter pour plus|
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр нижний новгород[/url]
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, trotzdem gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und ansprechend, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Einen Blick werfen|
Чтобы помощь была прозрачной и управляемой, каждый этап имеет цель, индикаторы безопасности и эффективности, а также понятное «окно оценки» результата. Коррекции проводятся «штучно», по правилу одного изменения — это защищает от полипрагмазии и позволяет читабельно видеть вклад каждого шага.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kazan-otzyvy/
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, dennoch mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zudem die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Besonders erwahnenswert sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Mit dem Entdecken beginnen|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. A souligner le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Rejoindre maintenant|
На сайте https://fotoredaktor.top нашёл ответ на вопрос, что означает чиназес.
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En extra l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement fun les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
В Санкт-Петербурге для адресных обращений дежурят мобильные бригады круглосуточно. Координатор при звонке уточняет хронические заболевания, аллергии, текущие лекарства и эпизоды судорог/психозов, а также бытовые условия: есть ли доступ к розетке, можно ли обеспечить 2–3 часа тишины, удобна ли зона полулёжа. Эта информация позволяет врачу в дороге выбрать стартовую скорость инфузии, продумать последовательность введения и подготовить расходные материалы под планировку квартиры. Мы соблюдаем приватность: нейтральная экипировка, деликатные формулировки в документах и один доверенный контакт со стороны семьи.
Получить больше информации – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-sankt-peterburg-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom/
Академия Алины Аблязовой https://ablyazovaschool.ru обучение реконструкции волос для мастеров и новичков. Авторские методики, разбор трихологических основ, отработка на моделях, кейсы клиентов. Онлайн и офлайн, сертификат, поддержка кураторов, материалы и чек-листы.
Для сохранения приватности мы ведём коммуникацию через одного доверенного представителя, используем нейтральные формулировки в документах, а инструкции выдаём в неброском виде. При невозможности создать тишину дома (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости) предложим краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерным режимом, после чего сопровождение вернётся в домашний формат.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого екатеринбург[/url]
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, malgre tout des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.rubyslotscasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges personnalises.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, booste le fun du jeu. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages uniques.
Cliquer maintenant|
Can I just say what a relief to seek out someone who actually knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You positively know find out how to bring a problem to mild and make it important. Extra individuals have to read this and perceive this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more in style because you positively have the gift.
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Parcourir maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter maintenant|
Всем доброго дня!! Хочу рассказать свой отзыв , о данном чудо магазине!! Заказывал совместку на 50г, оплатил днём, к вечеру все было готово, жаль только я с джабером что то не подружился, он меня выкинул, прям перед получением адреса, НО КЛАДЧИК ТАКОЙ красавчик!!! В итоге я поехал с утра, только приехал, все было на своих местах!!! Спрятано на совесть!!! Думаю ещё пролежало бы дня 3))) ИТОГО: ОПЕРАТОР В ДЖАБЕРЕ САМЫЙ КУЛЬТКРНЫЙ ЧЕЛОВЕК НА СВЕТЕ! 5+ КЛАДЧИК , умница! 5+, близко ко мне , и спрятано как надо!!! P.S. Смело заказываем!! И радуемся как дети!!) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Сам ты не общительный ))
купить диплом технического техникума [url=https://frei-diplom11.ru/]купить диплом технического техникума[/url] .
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно челябинск[/url]
Продвижение сайта помогает привлекать новых клиентов и повышать доверие аудитории. Оптимизация включает работу с контентом, структурой и техническими аспектами ресурса. Регулярная аналитика и обновление информации позволяют поддерживать позиции и обеспечивать стабильный рост. В результате сайт становится удобным и полезным для пользователей. Такой подход обеспечивает долгосрочное развитие компании. Читайте подробнее – https://support.ourarchives.online/index.php?title=Создание_Сайтов_И_Их_Сео_Продвижение
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов в челябинске[/url]
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр самара[/url]
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]voskresensk-narkologiya[/url]
[url=https://umnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]умный РґРѕРј жалюзи прокарниз[/url] – управляемые шторы, которые позволят вам легко контролировать свет и атмосферу в вашем доме.
Раздел 4: Заключение и советы по выбору
Лечение зависимости требует системного подхода, включающего диагностику, детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию и психологическую реабилитацию. Наркологическая клиника в Самаре объединяет специалистов различных направлений: врачей-наркологов, психиатров, психологов, терапевтов и реабилитологов. Совместная работа команды обеспечивает комплексное воздействие на физическое и эмоциональное состояние пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Для наглядности ниже приведена таблица с основными направлениями медикаментозной терапии и их эффектами:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara
Хотите построить дом своей мечты в Санкт-Петербурге? Наша строительная компания предлагает профессиональное возведение загородных домов под ключ. Работаем с кирпичом, газоблоком, газобетоном и деревом. Выполняем кладку стен https://builder-spb.ru , перегородок, устройство перекрытий и отделочные работы. Гарантируем прозрачный прайс, фиксированную стоимость в рублях за квадратный метр и полное соответствие проекту. Наши подрядчики учитывают все нюансы строительства, включая толщину стен, сорт материалов и уровень нагрузок. Дома возводятся с учётом строительных норм и особенностей участка.
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Санкт-Петербурге осуществляется под круглосуточным медицинским контролем с применением современных методов инфузионной терапии, препаратов для восстановления обменных процессов и купирования синдрома отмены. Главной задачей врачей является восстановление баланса между физическим и психическим состоянием, предотвращение осложнений и стабилизация основных жизненных функций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Основой терапии является сочетание медицинских, психотерапевтических и социальных методов. Такой подход обеспечивает устранение не только физиологических последствий зависимости, но и её психологических причин. Врачи клиники разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения, в котором учитываются стадия заболевания, общее состояние организма и личностные особенности пациента. Работа специалистов направлена на восстановление работы центральной нервной системы, обменных процессов и эмоционального баланса.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-kazan-otzyvy
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
И все бы ничего, да вот только доставка стоит 1490 рублей, я по собственному опыту знаю что почта уже в пятницу вручила бы мне посылку, за Гораздо меньшие деньги, а кроме почты у нас и нет ничего, поселок в сибири! Зачем было выбирать эту курьерку непонятно, тем более что отзывы про нее никакие! Неужели непонятно что дрога ложка к обеду, да и вообще, не понятно до сих пор была ли вообще отправка!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази да никого не устраивает это, что за бред. только единиц.
Are you searching for good working activator for MS Office? On this site you can download the latest version of it: https://artmundo.org/
[url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor-moskva.ru/]электро карниз москва прокарниз[/url] позволяют управлять шторами с помощью одного нажатия кнопки, обеспечивая удобство и комфорт в вашем доме.
Они отлично справляются с задачей оформления больших окон и раздвижных дверей.
Оптимизация сайта помогает улучшить видимость ресурса и привлекать заинтересованную аудиторию. Работа с контентом, структурой и техническими аспектами повышает позиции и улучшает пользовательский опыт. Регулярная аналитика позволяет корректировать стратегию и поддерживать стабильный рост. В результате сайт становится удобным, информативным и надёжным для клиентов. Подробнее по ссылке https://wiki.internzone.net/index.php?title=SEO_Продвижение_Сайта_И_Решения_Для_Увеличения_Трафика
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Подробнее – http://
Сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических мер создаёт устойчивую систему поддержки. Пациенты получают возможность постепенно восстановить утраченное здоровье и психологическую стабильность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в казани[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Екатеринбурге — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, где проводится диагностика, лечение и реабилитация людей, страдающих алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Комплексный подход включает не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапевтические методики, направленные на восстановление личности и возвращение пациента к социальной активности. Каждое вмешательство проводится с учётом физического состояния, психологического профиля и стадии заболевания. Работа специалистов основана на принципах анонимности, медицинской этики и научно доказанных протоколов лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Автоматические выключатели
Инфузионная терапия — это не просто «быстрый раствор витаминов». При запое страдает водно-электролитный баланс, «плавает» давление и пульс, нарастает тревога, нарушается сон, проявляются тошнота и тремор. Правильно собранная капельница в Клину помогает вернуть жидкость и электролиты, поддержать печень, снизить вегетативные проявления, мягко стабилизировать нервную систему и подготовить переход на пероральные схемы. Важно избегать избыточной седативной нагрузки и опасных сочетаний: то, что человеку «помогало раньше», может конфликтовать с его нынешними показателями. Поэтому каждое назначение мы увязываем с реальными цифрами осмотра и тем, что уже было принято за двое суток.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]капельница от запоя состав[/url]
kraken market Kraken ссылка – это как нить Ариадны, ведущая сквозь темный лес цифрового мира к самому сердцу платформы. Однако, прежде чем довериться этой нити, убедитесь в её прочности и надёжности, ведь в сети подстерегают коварные обманщики, готовые воспользоваться вашей неосторожностью. Проверяйте каждый символ, каждое слово, чтобы не стать жертвой фишинга и не потерять свои сбережения. Помните, что безопасность – это прежде всего ваша личная ответственность.
Такой комплексный подход позволяет не только купировать острые состояния, но и устранить внутренние факторы, провоцирующие развитие зависимости. После стабилизации состояния пациент переходит к этапу психотерапевтической коррекции, направленной на предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg-otzyvy/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]домашний вывод из запоя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде использует многопрофильный подход, направленный на физическое и психологическое восстановление пациентов. После детоксикации проводится стабилизация обменных процессов, нормализация работы внутренних органов и поддержка нервной системы. Особое внимание уделяется коррекции поведения и мотивации пациента к отказу от употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Thanks for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your further post thank you once again.
номера виртуальные
https://www.tripadvisor.com/Profile/salvat456
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-samara-vyzov-na-dom/
гайды геншин Новости Gamebox: Будьте в курсе последних новостей и обновлений платформы Gamebox.
Классный магазин! Работаю только с ним! Ни раз не обманули! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Chemical-mix.com, а где от 50гр, там надо 40 тон сразу запулить:rastakur: яж не барон нах:LSD:
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
«Чистая Гармония» — это выездная и стационарная наркологическая помощь в одном маршруте: оперативный приезд врача на дом по Клину и району, аккуратный детокс с контролем жизненно важных показателей, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких лишних процедур ради «видимости лечения» и никаких задержек с тем, что влияет на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, заранее согласуем смету и оставляем понятный план на 24–48 часов и первую неделю. Анонимность — базовый стандарт: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu/
«Чистая Гармония» — это выездная и стационарная наркологическая помощь в одном маршруте: оперативный приезд врача на дом по Клину и району, аккуратный детокс с контролем жизненно важных показателей, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких лишних процедур ради «видимости лечения» и никаких задержек с тем, что влияет на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, заранее согласуем смету и оставляем понятный план на 24–48 часов и первую неделю. Анонимность — базовый стандарт: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника краснодар[/url]
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkologiya-nizhnij-novgorod-besplatno/https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, где каждая деталь важна: от скорости выезда до состава инфузии и «тихой» среды дома. В наркологической клинике «КазаньДетокс Медлайн» мы придерживаемся принципа поэтапной стабилизации: сначала безопасный старт и оценка рисков, затем прицельные капельницы и, при необходимости, краткосрочное наблюдение. Такой подход исключает «универсальные коктейли» и делает результат прогнозируемым: снижение интоксикации, выравнивание вегетативных реакций, восстановление сна и аппетита. Анонимность встроена в протоколы: немаркированный выезд, лаконичная документация, один доверенный контакт для связи 24/7, нейтральные формулировки без стигмы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в казани[/url]
Лечение в клинике строится на комплексной программе, которая сочетает медикаментозную терапию, психотерапевтические методы и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход обеспечивает устойчивый результат и предотвращает повторные срывы. Пациент проходит курс под постоянным контролем специалистов, что позволяет отслеживать динамику состояния и корректировать терапию при необходимости.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника челябинск[/url]
Удобные и стильные [url=https://avtomaticheskie-karnizy-s-pultom.ru/]автоматические карнизы для тяжелых штор +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url] делают управление шторами простым и комфортным.
Одним из основных преимуществ автоматических карнизов является их простота установки.
SEO-продвижение сайта — это основа современного интернет-маркетинга. Оно помогает увеличить трафик, улучшить позиции и повысить конверсию. Работа с контентом, внутренними ссылками и метаописаниями даёт ощутимые результаты. Это надёжный инструмент, который окупается многократно. Подробнее о том, как работает SEO https://www.basee6.com/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=350988
мотосезон ДТП: Избегай риска, береги себя и других участников движения!
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
магазин четкй притензий нет на качество регвезде гавно((((( https://harmony-stroy.ru Ровный магаз! 2 раза заказывал ам(к12) и ркс(к7).. Все пришло ровно за 3 дня=) тока замесил ам(не растворился полностью)..буду пробовать=)ркс понравилось тока к 5ти делать надо=)
kraken сайт Kraken market – это шумный восточный базар, перенесенный в виртуальную реальность. Здесь можно найти всё, что угодно, от редких артефактов до запрещённых веществ. Однако, не стоит терять голову от разнообразия предложений и низких цен. Внимательно изучайте отзывы о продавцах, проверяйте информацию о товарах и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Только так вы сможете совершить выгодную и безопасную сделку, избежав разочарований и проблем с законом. Будьте мудрыми и предусмотрительными, и Kraken market откроет перед вами свои сокровища.
https://justpaste.me/Czfq3
SEO-продвижение позволяет вашему сайту выделиться среди конкурентов. Оптимизация помогает улучшить структуру, контент и технические параметры. В результате сайт становится привлекательнее для поисковиков и клиентов. Этот инструмент эффективен в любой нише. Узнайте больше о SEO, https://lunarishollows.wiki/index.php?title=User:Roxanna89O
блог о маркетинге [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge7.ru]блог о маркетинге[/url] .
Одним из главных преимуществ автоматических жалюзи является их способность регулировать уровень света в помещении. С помощью таких жалюзи можно контролировать попадающий свет в зависимости от времени суток. Такое решение идеально подходит для удаленных работников. С помощью таких жалюзи можно организовать комфортное пространство для работы или отдыха.
[url=https://avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi-s-privodom.ru/]жалюзи электрические внутренние с дистанционным управлением Prokarniz[/url] обеспечивают удобство и стиль в вашем доме, позволяя управлять светом одним нажатием кнопки.
Автоматические жалюзи на окна с электроприводом становятся все более популярными. Удобство и функциональность автоматических жалюзи делают их идеальным выбором для современных интерьеров. Такие жалюзи могут управляться с помощью пульта дистанционного управления или смартфона. Такой способ управления делает их использование гораздо более простым.
Автоматические жалюзи также помогают сэкономить энергию. С правильной эксплуатацией этих жалюзи можно значительно уменьшить расходы на обогрев и кондиционирование. С автоматическими жалюзи будет проще контролировать температуру в помещении. Таким образом, это не только удобно, но и экономически выгодно.
Важно отметить, что установка таких жалюзи может быть выполнена как специалистами, так и самостоятельно. Выбор способа установки, конечно, зависит от ваших умений и предпочтений. Если вы выберете самостоятельный монтаж, важно внимательно следовать инструкциям. Это поможет избежать ошибок и обеспечит правильную работу системы.
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре предлагает профессиональное лечение алкогольной, наркотической и других форм зависимости с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ. Основная цель работы специалистов — помочь пациенту восстановить физическое и психическое здоровье, вернуть контроль над собственной жизнью и предотвратить рецидив. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинской этики, конфиденциальности и стандартов безопасности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Главная задача — вернуть контроль над самочувствием мягко и последовательно. Мы не соревнуемся в дозах, а собираем устойчивую траекторию улучшения: каждый модуль терапии отвечает за одну цель и имеет своё «окно оценки». Если отклик ниже ожиданий — меняем ровно один параметр (темп, последовательность или поведенческий элемент среды), чтобы точно понимать, что помогло.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно казань[/url]
Автоматические выключатели
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Для сохранения приватности мы ведём коммуникацию через одного доверенного представителя, используем нейтральные формулировки в документах, а инструкции выдаём в неброском виде. При невозможности создать тишину дома (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости) предложим краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерным режимом, после чего сопровождение вернётся в домашний формат.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/[/url]
Чтобы не превращать раздел в набор лозунгов, кратко обозначим практические преимущества, которые заметны уже в первые часы обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/[/url]
“Приезжаю и вижу на свету бля что то поххожее на таблетки ” https://fotooboivimala.ru ПО ВРЕМЕНИ СКОЛЬКО?
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-sankt-peterburg-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom/
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. В основе её деятельности лежит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, сочетание медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методов, а также полная конфиденциальность. Лечение проводится опытными специалистами с применением современных медицинских технологий, направленных на восстановление здоровья и предотвращение рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara
Детокс — последовательность шагов, где каждый этап имеет цель и критерии безопасности. Мы начинаем с оценки рисков (кардиология, неврология, психическое состояние, возможные взаимодействия препаратов), продолжаем инфузионной терапией, корректируем электролиты и кислотно-щелочное равновесие, поддерживаем печень и нервную систему. Если присутствуют выраженная тревога и бессонница, подключаем короткие курсы седативной терапии с контролем побочных эффектов. Отдельный блок — профилактика осложнений: обезвоживание, аритмии, обострение гастрита и панкреатита, делирий. Каждое назначение — только после очной оценки и с учётом сопутствующих состояний.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Санкт-Петербурге осуществляется под круглосуточным медицинским контролем с применением современных методов инфузионной терапии, препаратов для восстановления обменных процессов и купирования синдрома отмены. Главной задачей врачей является восстановление баланса между физическим и психическим состоянием, предотвращение осложнений и стабилизация основных жизненных функций.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-samara/
«Трезвый Маяк» — клиника экстренной и плановой наркологической помощи с круглосуточным выездом и возможностью госпитализации. Мы аккуратно стабилизируем состояние, снимаем интоксикацию и абстиненцию, готовим к кодированию и сопровождаем пациента до устойчивой ремиссии. Работаем анонимно: врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, документы оформляются в нейтральной формулировке и только по запросу.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/[/url]
Благодаря SEO-оптимизации сайт становится видимым для потенциальных клиентов. Это долгосрочная стратегия, которая обеспечивает рост трафика и узнаваемости бренда. Комплексная работа над структурой, скоростью и контентом улучшает позиции в поисковой выдаче. В результате бизнес получает больше заявок и продаж. Узнайте больше о преимуществах SEO, https://365.expresso.blog/question/что-влияет-на-успех-поискового-продви/
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя в клинике в Казани проводится под строгим контролем специалистов. Главная цель — купировать симптомы интоксикации, нормализовать давление, сердечный ритм и восстановить обмен веществ. Используются препараты, способствующие детоксикации, а также витаминные комплексы и антиоксиданты, необходимые для поддержки работы печени и мозга.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/[/url]
Откройте для себя идеальное решение для защиты от солнца с [url=https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-zhalyuzi.ru/]рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом прокарниз[/url], которые удобно управляются одним движением.
С помощью удаленного управления вы сможете регулировать их положение в любое время.
Кроме того, автоматические жалюзи рулонные
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
https://eternagame.org/players/568766
Преимущество стационара — предсказуемость и скорость. Рядом врач и медсестра, можно оперативно сдать анализы, сделать ЭКГ или дополнительные обследования, а главное — не «тянуть» с корректировкой схемы. В контролируемой среде быстрее нормализуются сон и аппетит, уходит тремор, снижается тревога. Для пациентов с сопутствующими диагнозами это особенно важно: диабет, гипертония, аритмии, хронические заболевания ЖКТ требуют аккуратной, согласованной тактики.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/
Сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических мер создаёт устойчивую систему поддержки. Пациенты получают возможность постепенно восстановить утраченное здоровье и психологическую стабильность.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/klinika-narkologiya-kazan/
Автоматические выключатели
Этап
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu
Aw, this was an exceptionally nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to create a superb article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t seem to get anything done.
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает видеть логику процесса. Это не жёсткий график: врач адаптирует точки и сроки под возраст, фоновые заболевания и исходное состояние.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru
Капельница от запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде часто становится первым шагом в лечении хронической алкогольной зависимости. Детоксикация помогает вывести продукты распада этанола и снизить нагрузку на внутренние органы, но не устраняет психологическую зависимость. Поэтому после завершения инфузионной терапии пациенту рекомендуется пройти консультацию психотерапевта и, при необходимости, начать курс реабилитации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/kapelnicza-na-domu-anonimno-nizhnij-novgorod/
Тут не кидают, друг https://avtoprokatyeysk.ru отличный магазин, все всегда ровно
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Екатеринбурге проводится с применением сертифицированных лекарственных препаратов, поддерживающих систем и методов индивидуальной терапии. Врачи используют физиологически безопасные комбинации растворов, витаминов и нейропротекторов, восстанавливающих работу центральной нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия проводится под контролем специалистов, что исключает возможность осложнений и обеспечивает быстрое улучшение состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Мы не используем шаблон «на всех». Темп и сочетания зависят от давления, пульса, выраженности тошноты и тремора, уровня тревоги, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Детокс — это система шагов: допуск к терапии, коррекция воды и электролитов, поддержка печени, вегетостабилизация, осторожная работа со сном по показаниям, профилактика осложнений. Любое назначение проговаривается простым языком: зачем, как подействует, что считать нормальной динамикой, а что — поводом связаться с врачом.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Одним из главных преимуществ таких штор является возможность управления с помощью пульта | Управление рулонными шторами с электроприводом осуществляется легко с помощью пульта | Электроприводные рулонные шторы предлагают комфортное управление через пульт. Это позволяет вам регулировать свет и атмосферу в комнате одним нажатием кнопки | Вы можете поменять уровень освещения в помещении всего лишь одним нажатием кнопки | С помощью простого нажатия кнопки вы сможете изменить интенсивность света в комнате.
Вы можете [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-distantsionnym-upravleniem.ru/]рулонные шторы на пульте управления в москве +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url] и наслаждаться комфортом и удобством в вашем доме.
Современные технологии делают рулонные шторы с электроприводом удобными и стильными
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике екатеринбург[/url]
Для сохранения приватности мы ведём коммуникацию через одного доверенного представителя, используем нейтральные формулировки в документах, а инструкции выдаём в неброском виде. При невозможности создать тишину дома (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости) предложим краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерным режимом, после чего сопровождение вернётся в домашний формат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в санкт-петербурге[/url]
замена стекла Ремонт стекол – это комплекс процедур, направленных на восстановление целостности и прозрачности автомобильных стекол. Он включает в себя ремонт сколов, трещин, а также полировку для устранения царапин и потертостей. Своевременный ремонт позволяет избежать дорогостоящей замены стекла и обеспечивает безопасность вождения.
Купить металлопрокат оптом и в розницу в Ташкенте При осуществлении строительных и промышленных проектов в Ташкенте, ключевым фактором является приобретение металлопродукции требуемого уровня. Такие элементы как арматура, стальные балки и уголки, швеллеры, металлические листы, катанка и стальной круг, являются критически важными для современной инфраструктуры, и их качество и соответствие техническим стандартам должны быть в приоритете. Надежность и долговечность конструкций напрямую зависят от характеристик используемого металлопроката. Поэтому, крайне важно взаимодействовать с проверенными поставщиками, гарантирующими продукцию высшего качества и ее соответствие установленным нормам. Покупка качественного металлопроката в ИП ООО “Модуль сталь” представляет собой инвестицию в надежность и продолжительность службы ваших проектов. Обратитесь к специалистам, которые помогут вам сделать оптимальный выбор и обеспечат быструю доставку нужных материалов.
всё дошло))))) Спасибо магазину,в след раз возьму отпишу что да как :dansing:качество на высоте https://power-buy.ru Буду ждать доставку как чё отпишусь .
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Обеспечьте комфорт и стиль в вашем доме с [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-umnyy-dom.ru/]электрические рулонные жалюзи +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url], которые идеально впишутся в современный интерьер.
Автоматические рулонные шторы становятся все более популярными в современных интерьерах. Применение автоматических штор позволяет не только удобно регулировать свет, но и добавить стиль в ваш дом. Автоматизированные рулонные шторы идеально вписываются в концепцию “умного дома”.
Системы автоматизации позволяют управлять шторами с помощью смартфона. Вы можете задавать график работы штор в зависимости от времени суток. Такой подход очень удобен делает жизнь более комфортной.
Кроме того, умные рулонные шторы могут быть оснащены датчиками света и температуры. Данное оборудование автоматически регулируют положение штор для достижения оптимального уровня освещенности. В результате вы можете экономить на электроэнергии благодаря естественному освещению.
Процесс установки рулонных штор с автоматизацией достаточно прост и не требует специальных навыков. Вы можете установить их самостоятельно, следуя инструкциям. Когда шторы установлены, вы сможете наслаждаться всеми преимуществами умного дома.
kraken market Kraken market – это многогранная площадка, где встречаются продавцы и покупатели со всего мира, предлагая широкий спектр товаров и услуг. Здесь можно найти все, что душе угодно, от редких артефактов до инновационных разработок. Приготовьтесь к захватывающему приключению, полному неожиданных открытий и выгодных предложений. Но не забывайте о здравом смысле и критическом мышлении, чтобы не стать жертвой недобросовестных продавцов.
https://t.me/s/apk_1xbet_android
Мы не используем шаблон «на всех». Темп и сочетания зависят от давления, пульса, выраженности тошноты и тремора, уровня тревоги, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Детокс — это система шагов: допуск к терапии, коррекция воды и электролитов, поддержка печени, вегетостабилизация, осторожная работа со сном по показаниям, профилактика осложнений. Любое назначение проговаривается простым языком: зачем, как подействует, что считать нормальной динамикой, а что — поводом связаться с врачом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]капельница при запое состав[/url]
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die die Motivation erhohen.
Cat Spins|
happyshoppingplace – Fun and lively design, the name fits perfectly with the vibe.
Главное — непрерывность и скорость принятия решений. Рядом врач и медсестра, доступ к диагностике и возможность точно настраивать темп инфузий, подбирать поддерживающие препараты, контролировать сон и уровень тревоги. Благодаря этому снижается риск осложнений, а восстановление идёт ровнее: меньше «качелей» днём и ночью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Только для своих – https://bestpointonline.com/portfolio/data-analysis
Карнизы с электроприводом становятся все более популярными в современных интерьере. Эти устройства предлагают комфорт и стиль для любого помещения. Благодаря электроприводу , можно легко управлять шторами или занавесками при помощи дистанционного управления .
Откройте для себя элегантность и удобство [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom-dlya-shtor.ru/]потолочные карнизы с электроприводом прокарниз[/url], которые сделают управление шторами простым и современным.
удобство в использовании . Данные конструкции универсальны и подойдут для. Кроме того, эти карнизы уютную атмосферу в доме или офисе.
Монтаж таких карнизов возможна в различных условиях. Инсталляция не требует специальных знаний , и с этим может справиться даже новичок . Кроме того, такие карнизы возможно интегрировать в .
Несмотря на все достоинства, существуют и некоторые недостатки . В частности,. инвестиции в комфорт и удобство , ведь значительно облегчают повседневные задачи .
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в челябинске[/url]
После проведения процедур пациент чувствует заметное облегчение: исчезает головная боль, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. Это создаёт основу для дальнейшего прохождения курса лечения зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Сервис то что надо, так держать! https://oaostplem.ru Знаю сайт. Всем советую. Пишу в кратце о главном. Связался в аське. Ответили сразу, тут же сделал заказ на регу. Осталось подождать…
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, jedoch mehr Bonusoptionen waren top. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein gro?artiges Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Erfahren Sie wie|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, ab und zu ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein gro?es Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
https://catspinsbonus.com/|
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Уточнить детали – https://????????????????????.com/__trashed
В первые два часа после прибытия бригады важно не «сделать побольше», а принять наименьшее количество решений, которое реально меняет картину. Команда фиксирует базовую линию (ЧСС, АД, SpO?, температура, шкала тошноты/тремора), даёт антиеметический мост и запускает регидратацию. При тахикардии — добавляет антивегетативный контур. Семья получает сценарий ночи: когда приглушить свет, когда предложить воду, какие цифры на тонометре считать нормой и при каких — звонить. Такой протокол экономит время и силы, а главное — превращает вечер из хаотичного в управляемый, снижая риск ночных экстренных вызовов и «эмоциональных качелей».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого[/url]
https://viploggias.ru/ Ремонт трещины – сложный процесс, требующий опыта и профессионализма. Технология ремонта предполагает заполнение трещины полимером под давлением, что предотвращает ее дальнейшее распространение. Успешный ремонт трещины позволяет избежать полной замены стекла и сохранить заводскую герметичность.
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, jedoch mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Ubrigens die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein tolles Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Bringen Sie mich dorthin|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, mit packenden Live-Casino-Optionen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, gelegentlich mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Nebenbei ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein tolles Extra die dynamischen Community-Events, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Ins Web gehen|
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://mallorcasustainablesummit.com/we-denounce-with-of-righteous-one-indignation-and-dislike-men
Je suis emerveille par Sugar Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le site est rapide et engageant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
En savoir davantage|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En complement la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter maintenant|
happyshoppingplace – Fun and lively design, the name fits perfectly with the vibe.
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru
Откройте мир удобства с нашими [url=https://rulonnye-zhalyuzi-s-distantsionnym-upravleniem.ru/]автоматические рулонные жалюзи в москве +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url], которые обеспечивают идеальное сочетание стиля и функциональности.
С помощью автоматизации вам больше не придется вручную поднимать или опускать жалюзи.
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, gelegentlich ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Kurz und bundig, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist einfach und klar, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein starkes Plus sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, die Community enger verbinden.
Mehr entdecken|
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде проводится с применением инфузионной терапии, седативных средств и витаминных комплексов. Основная задача процедуры — устранить токсическое воздействие алкоголя, восстановить работу органов и нормализовать психоэмоциональное состояние. Все препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом особенностей организма пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Passer à l’action|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Zudem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Zur Seite gehen|
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Visiter la page web|
заказал почти неделю назад ( 5 дней назад.) сказали товар кончился. ожидается разгрузка на склад. вот так и жду уже 5 дней. Раньше брал. все было быстро и честно. сейчас что-то затянулось слишком. вот сижу годаю. Прийдет мне товар или не прийдет https://garage-atlant.ru Сегодня съездил в офис, к счастью там знакомая работает, пробили они по своим базам накладную, связывались с мск, сказали такая накладная не поступала, объяснили как все работает, то что можно взять бумаги заполнить их, в этих бумагах указывается номер накладной, но когда делаешь отправку, в компе по любому будет отображаться, т.е. отправки не было, с мск им каждый день приходят посылки, идет она реальных 2 дня!
Продвижение сайта — это комплексный процесс, направленный на привлечение целевой аудитории. SEO улучшает позиции ресурса, делает сайт удобным и информативным. Оптимизация включает работу с контентом, метатегами и техническими параметрами. Такой подход обеспечивает стабильный поток клиентов и долгосрочный эффект. Подробнее о SEO-продвижении читайте https://thestarsareright.org/index.php/Поисковая_Оптимизация_Сайтов_Под_Ключ
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, gelegentlich gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Au?erdem die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Jetzt ausprobieren|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage notable les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, aber ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein weiteres Highlight die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Jetzt beitreten|
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://fonbe.gob.ve/gran-trabajo-de-nuestro-cicpc
Удобство и стиль в вашем доме с [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-avtomatikoy.ru/]автоматические рулонные шторы цена[/url], которые легко управляются одним нажатием кнопки.
Автоматические рулонные шторы набирают популярность среди современных интерьеров. Они не только привносят эстетику в помещение, но и обеспечивают комфорт .
Удобное дистанционное управление — одно из главных достоинств автоматических рулонных штор. Вы можете регулировать уровень света в комнате, не вставая с дивана .
Кроме того, автоматические рулонные шторы могут быть оборудованы различными датчиками . Они могут самостоятельно подстраиваться под уровень освещенности и температуру .
Автоматические рулонные шторы представлены в богатом ассортименте цветов и стилей. Выбор подходит под любой стиль интерьера .
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, manchmal ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spielbegeisterte. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein attraktives Extra ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Mehr entdecken|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, trotzdem waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Nebenbei die Navigation ist klar und flussig, das Vergnugen maximiert. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Hier fortfahren|
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Посмотреть всё – https://inlygiay.com/tui-giay-bao-banh-mi
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-nedorogo-v-voskresenske
Прежде чем перечислить критичные признаки, зафиксируем принцип: даже один выраженный симптом — повод не откладывать помощь и выбрать безопасный маршрут (дом или стационар) после быстрой очной оценки врача.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, dennoch waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Zur Seite gehen|
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
А что дальше? – https://andrea-kraus-neukamm.de/component/k2/item/2-charity-helps-children-in-schools-challenge-stereotypes-about-sex?start=4420
staycuriousdiscover – Inspiring tone, layout encourages creativity and exploration beautifully.
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En complement le design est style et moderne, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Voir maintenant|
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
http://www.rubyslotscasinopromocodefr.com|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, in seltenen Fallen haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und einladend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Besonders erwahnenswert die vielfaltigen Wettmoglichkeiten, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Webseite besuchen|
установка лобового стекла Ремонт стекол – это экономичный способ восстановить первоначальный вид и прочность автомобильных стекол. Небольшие сколы, трещины и царапины могут быть устранены опытными мастерами с использованием современных технологий. Вовремя выполненный ремонт предотвращает дальнейшее разрушение стекла и обеспечивает безопасность на дороге.
так то, я не понимаю что ты хотел сказать по этому поводу, но курили и чистым и миксами И НЕ ПРЕТ ОН НИФИГА, то что прислали, про пробники я скажу, пробник стоит 1 грамм 2500 вроде как, вот и прикинь как не выгадно заказывать да и темболее 1 грамм норм отошлет а когда закажешь 10 пришлет той фигни, что нам сейчас https://nasha-shapka.ru магаз норм. а вот курьеры зажрались суки.
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer maintenant|
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – http://www.rileypm.nl/profiel
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Уточнить детали – https://ozyurtlargunlukkiralikdaire.com/ozyurtlar-gunluk-kiralik-daire-3
seo курсы [url=kursy-seo-11.ru]seo курсы[/url] .
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis emerveille par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller au site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer la page|
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Подробности по ссылке – https://eleven2021.jp/2021/02/08/%E5%95%8F%E3%81%84%E5%90%88%E3%82%8F%E3%81%9B
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Посмотреть всё – https://www.vagsbygd.com/?p=3658
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Entrer sur le site|
https://letterboxd.com/vernonpo88/
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Полезно знать – https://www.oceantrash.world/from-ocean-waste-to-jewerlry-on-dislpay
kraken ссылка Kraken сайт – это таинственный портал в мир эксклюзивных возможностей, где анонимность и безопасность возведены в абсолют. Здесь границы стираются, а мечты обретают реальность, но помните: с большой свободой приходит и большая ответственность. Каждый шаг требует осознанности и понимания, ведь за порогом скрываются не только сокровища, но и подводные камни. Подходите к изучению платформы с мудростью и осторожностью, взвешивая каждый свой выбор.
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Откройте для себя больше – https://tamasakainaika.timc03.jp/2018/10/03/pin-momo01
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Savoir plus|
exploreendlessideas – Modern look, design sparks imagination and a sense of wonder.
Всем привет, долго не писал, ну это меня «задержала» посылка jv-61. Все пришло, все получил причем довольно быстро все ехало:good: https://potok-uvc.ru Я делал на муравьином спирте
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://poppresbyschool.com/playful-learning-where-every-day-is-a-new-discovery
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://oldbulltavern.com/gallery-3-2
Остекление балконов Остекление балконов – это эффективный способ превратить открытое пространство в уютную зону, защищенную от непогоды, пыли и шума. Существует несколько видов остекления, от простого безрамного до теплого с использованием многокамерных стеклопакетов. Выбор зависит от ваших потребностей и бюджета. Качественное остекление позволяет использовать балкон круглый год, создавая дополнительное пространство для отдыха, работы или хранения вещей.
Доставка ритуальных товаров
мистика Байки от бабайки – это коллекция рассказов от обычных людей, столкнувшихся со сверхъестественным в своей жизни. Эти истории, словно шепот из потустороннего мира, будоражат воображение и заставляют задуматься о существовании явлений, которые наука не может объяснить. От призрачных видений до необъяснимых звуков – каждый рассказ является уникальным свидетельством встречи с неизведанным.
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Нажми и узнай всё – https://akijin.com/hello-world
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Подробнее – https://fint.edu.br/oportunidades-na-carreira-de-hematologia
я все ровно остался в минусе не заказа и деньги с комисией переводятся . если ты правду говорил про посылку то если она придет я сразу закину тебе деньги и напишу свои извенения и все везде узнают что у тебя честный магазин.как клиенту мне ни разу не принесли извенения это бы хоть как то компенсировало маральный ущерб https://gm72.ru Лучше набери их в скайпе или аське так гораздо быстрей будет
discoverandcreate – Balanced visuals, message promotes creativity and curiosity together.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Почему это важно? – https://anyq.kz/%D0%A2%D2%AF%D1%80%D0%BA%D1%96%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BD-%D0%96%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%96%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B9-%D0%B0%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%BD%D1%8B%D2%A3-%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D0%B5
обзор changan uni https://changan-v-spb.ru
Услуги по аренде техники сегодня считается выгодным способом для строительных компаний.
Она помогает решать задачи без дополнительных затрат покупки машин.
Поставщики, предлагающие такую услугу, предлагают ассортимент спецоборудования для любых задач.
В парке можно найти автокраны, катки и другое оборудование.
http://www.know-house.ru/avtor/0076/avtokran-na-50-tonn.html
Главный плюс аренды — это отсутствие затрат на обслуживание.
Также, арендатор имеет доступ к исправную технику, с полным обслуживанием.
Надёжные компании заключают понятные договоры аренды.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это разумный выбор для тех, кто стремится к экономию в работе.
ЛідерUA – інформативний портал https://liderua.com новин та корисних порад: актуальні події України, аналітика, життєві лайфхаки та експертні рекомендації. Все — щоб бути в курсі й отримувати практичні рішення для щоденного життя та розвитку.
Такая структура лечения помогает пациентам пройти все этапы восстановления под контролем специалистов.
Выяснить больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/narkolog-perm-czeny/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://fint.edu.br/oportunidades-na-carreira-de-hematologia
[url=https://we368.com.in/cricket/]we368in.com[/url]
Самое ценное у нас: https://journal-ua.com/biznes-i-ekonomika/bas-kup-i-bas-erp-yakij-produkt-efektivnishij-dlya-biznesu.html
Вызвал такси;) https://fotooboivimala.ru Спасибо за понимание.
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/
buildabetterworld – Uplifting concept, site feels full of purpose and positivity.
kraken market Kraken market – это пестрый калейдоскоп предложений, где каждый может найти то, что ищет. Но, как и на любом рынке, здесь встречаются не только честные торговцы, но и мошенники, готовые обмануть доверчивых покупателей. Поэтому, прежде чем совершить покупку, тщательно изучите репутацию продавца, сравните цены и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Помните, что ваша бдительность – лучшая защита от обмана и разочарования. Kraken market – это мир возможностей, но и мир ответственности.
Наши выездные и стационарные бригады работают по принципу «одна корректировка за раз». Меняем не всё и сразу, а ровно один параметр — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь (свет/тишина/питьевой режим). Затем в заранее оговорённый момент проверяем эффект по фактам: переносимость воды малыми глотками, вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам, латентность сна, число ночных пробуждений, субъективная ясность утром. Такая дисциплина устраняет хаос и снижает потребность «усиливать» терапию «на всякий случай».
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Аренда спецтехники сегодня является удобным способом для организаций.
Она позволяет решать задачи без обязательства покупки дорогой техники.
Поставщики, предлагающие такую услугу, обеспечивают разнообразие техники для разных направлений.
В парке можно найти экскаваторы, бульдозеры и другое оборудование.
http://boards.sovnat.info/viewtopic.php?t=161995
Ключевое преимущество аренды — это гибкость.
Кроме того, арендатор может рассчитывать на исправную технику, готовую к работе.
Надёжные компании предлагают понятные условия сотрудничества.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это разумный выбор для тех, кто ищет экономию в работе.
Этапы терапии выглядят следующим образом:
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом саратов[/url]
Интересная упаковка )))… делал 1к10!!! сам не курил более 2-ух месяцев вообще ничего* за основу брал ромашку!!!! https://nonbanaleshop.ru мы говорили что мхе качество не очень, он такой пришел, сказали поменяем дак поменяем, ты стучи туда с кем об обмене разговаривал…
Курсы маникюра https://econogti-school.ru и педикюра с нуля: теория + практика на моделях, стерилизация, архитектура ногтя, комбинированный/аппаратный маникюр, выравнивание, покрытие гель-лаком, классический и аппаратный педикюр. Малые группы, материалы включены, сертификат и помощь с трудоустройством.
Авторский MINI TATTOO https://kurs-mini-tattoo.ru дизайн маленьких тату, баланс и масштаб, безопасная стерилизация, грамотная анестезия, техника fine line и dotwork. Практика, разбор типовых косяков, правила ухода, фото/видео-съёмка работ. Материалы включены, сертификат и поддержка сообщества.
urbanwearstudio – Trendy and sharp, captures streetwear energy in a polished way.
Весь процесс можно представить следующим образом:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Если среда дома шумная или приватность под угрозой, мы предложим «короткий коридор» через отдельный вход амбулатории. Если условия позволяют, проводим процедуры на дому: свет приглушён, доступ к розетке организован, рядом столик для расходников и приборов. Этот «экологичный» сценарий, несмотря на простоту, заметно улучшает переносимость процедур и собирает устойчивый сон в первую ночь, что особенно важно на ранних этапах стабилизации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника челябинск[/url]
7к автоматы 7k официальный сайт предоставляет актуальную информацию о бонусах и акциях, доступных для игроков.
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara
новый магазин???это хорошо!!успехов в работе, конкуренция – это очень хорошо!! https://mediclever.ru “Лазею я по форуму,точнее по веткам и на ветке Эскимоса вижу запись на Пробы”
Клиника оснащена современным оборудованием для мониторинга состояния пациентов и проведения процедур с максимальной безопасностью. Врачебный состав состоит из опытных наркологов, психиатров и психологов, регулярно повышающих квалификацию и применяющих доказательные методы лечения. На портале Российской медицинской ассоциации наркологов можно ознакомиться с рекомендациями по стандартам оказания наркологической помощи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chelyabinsk13.ru/]наркологическая клиника челябинск[/url]
Максимум качества, минимум травм. Профессиональные наборы для татуировки: машинки, блоки питания, премиум-краски. Всё для стерильной и крутой работы. Обновите свой арсенал сегодня https://tattoo-sale.ru/
7k casino вход 7к автоматы — это не только классические слоты, но и современные видеослоты с захватывающей графикой.
Выездная стабилизация — только первый шаг. Дальше важно разобрать триггеры, обучить «тихим ритуалам», согласовать план поддержки и рассмотреть кодирование там, где оно уместно. Мы не противопоставляем форматы: домашние визиты, «тихий вход» и краткие очные сессии дополняют друг друга. Задача — не создать идеальную «капельницу», а вернуть организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции и укрепить навыки, которые защищают от срыва. В «КубаньМед Резолюция» этим занимается мультидисциплинарная команда: наркологи, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинические психологи, психотерапевты и медсёстры с опытом ночных постов наблюдения. Все говорят на «языке фактов», чтобы решения были понятны и пациенту, и семье.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/
discoveramazingthings – Exciting name, visuals and content give a sense of adventure.
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в перми[/url]
7к казино зеркало casino 7k онлайн предлагает круглосуточный доступ к играм, что делает азартные развлечения еще более удобными.
Сначала коротко обозначим логику: каждый шаг должен иметь цель и измеримый результат, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, зачем мы делаем именно так.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Покупайте на нашем сайте https://www.lat-v.ru шкаф для бочек, клеть для баллонов, поддон для бочек, поддон для еврокуба, шкаф для зарядки и хранения ноутбуков, поддон для 2-х еврокубов, шкаф для строп, шкаф для канистр. Все товары в наличии и по самым низким ценам.
Сочи – мёд отличный, кладмену респект и уважуха! теперь мы ваши постоянные клиенты) https://garage-atlant.ru такой замечательный и паспиздатый магазин………ноооооо где же мой заказ тогда? трек так и не бьется,тс на связь не выходит!!!
На нашем сайте https://www.promvers.ru вы можете приобрести: самоопрокидывающийся контейнер, саморазгружающийся контейнер, тележку для стружки, металлический поддон, депо для еврокуба, депо для бочек, шкаф для бочек, шкаф для еврокуба, поддон для канистр. На все товары есть сертификаты и паспорта. Производство Россия. Низкие цены.
купить диплом косметолога [url=https://www.rudik-diplom12.ru]купить диплом косметолога[/url] .
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sergievom-posade
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Hinzu kommt die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Community-Events, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein tolles Feature die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Website betreten|
Je suis captive par Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir plus|
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par moments des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est clair et efficace, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Sugar Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter la plateforme|
Услуги по аренде техники сегодня является выгодным вариантом для предприятий.
Она даёт возможность выполнять работы без необходимости приобретения оборудования.
Организации, предлагающие такую услугу, обеспечивают широкий выбор спецоборудования для разных направлений.
В парке можно найти автокраны, катки и специализированные машины.
https://nonghuachang-sao.go.th/forum/suggestion-box/820195-in-r-sn-gd-vzja-i-n-pr-sp-c-b-rud-v-ni-v-s-v
Главный плюс аренды — это отсутствие затрат на обслуживание.
Помимо этого, арендатор может рассчитывать на проверенную технику, готовую к работе.
Профессиональные компании оформляют понятные договоры аренды.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это практичный выбор для тех, кто ценит эффективность в работе.
kraken сайт Kraken сайт – это не просто веб-страница, а тщательно выстроенная экосистема, живущая по своим, порой негласным правилам. Это цифровой оазис для тех, кто ценит приватность и независимость, но одновременно и зона повышенного риска, где каждое действие должно быть обдуманным и взвешенным. Здесь встречаются анонимные продавцы и покупатели, заключаются спорные сделки, и разгораются нешуточные страсти. Чтобы не заблудиться в этом лабиринте, необходимо обладать острым умом, твердой рукой и непоколебимой верой в свою интуицию.
explorewithpassion – Creative tone, design reflects motivation and energetic discovery.
Каждый этап лечения в наркологической клинике «ЮгМед Альянс» имеет свою цель, временные рамки и объективные критерии эффективности. Ниже приведена структура терапевтического цикла, применяемая для большинства пациентов после поступления в отделение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в ставрополе[/url]
[url=https://mydiv.net/arts/view-TOP-5-luchshih-servisov-virtualnyh-nomerov-dlya-SMS-aktivaciy-v-2026-godu.html]номер телефона виртуальный[/url]
Госпитализация разворачивается как последовательность шагов: приём и допуск к терапии, старт инфузий, мониторинг 24/7, регулярная переоценка и подготовка к выписке. Такой контур особенно важен пациентам с сопутствующими диагнозами (гипертония, ИБС, сахарный диабет, заболевания ЖКТ), где требуется деликатная настройка дозировок и темпа инфузий.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/
вот нашли бы пролонгаторы и начали продавать и эффект бы увеличили и все довольны были бы=))) https://potok-uvc.ru я бы тоже заценил
Стационар рационален при нестабильном состоянии, риске делирия, судорогах в анамнезе, скачках давления, выраженной одышке, неукротимой рвоте, одиночестве ночью или невозможности обеспечить «тихий режим». В палате — контролируемая среда, доступ к ЭКГ и базовой лаборатории по показаниям, круглосуточный пост медсестёр и возможность быстро менять тактику, если параметры «плывут». Такой маршрут предсказуемее по безопасности и зачастую короче по времени до стабильного самочувствия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-klinu-s-vyezdom-na-dom/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Хочу выделить раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://guzellikturk.com]https://guzellikturk.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]воскресенск наркологический диспансер[/url]
«Трезвый Маяк» — клиника экстренной и плановой наркологической помощи с круглосуточным выездом и возможностью госпитализации. Мы аккуратно стабилизируем состояние, снимаем интоксикацию и абстиненцию, готовим к кодированию и сопровождаем пациента до устойчивой ремиссии. Работаем анонимно: врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, документы оформляются в нейтральной формулировке и только по запросу.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, fugt Magie hinzu. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e surreal: blackjack envolvente, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play wheels 4p60|
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это как нить Ариадны, ведущая сквозь темный лес цифрового мира к самому сердцу платформы. Однако, прежде чем довериться этой нити, убедитесь в её прочности и надёжности, ведь в сети подстерегают коварные обманщики, готовые воспользоваться вашей неосторожностью. Проверяйте каждый символ, каждое слово, чтобы не стать жертвой фишинга и не потерять свои сбережения. Помните, что безопасность – это прежде всего ваша личная ответственность.
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, gelegentlich regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein starkes Feature die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Mehr erhalten|
I’ve got a soft spot for Pinco, it’s built for big moments. There’s a flood of exciting games, offering interactive live tables. It sets you up for success. Service is rock-solid and reliable. Winnings arrive with zero delay, however extra rewards would be a bonus. To wrap up, Pinco is a no-brainer for gamers. Plus navigation is smooth and smart, motivates you to keep going. Particularly fun are the lively community events, that ensures safe transactions.
Go to the website|
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage notable les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter la plateforme|
Онлайн-блог https://intellector-school.ru о нейросетях: от базовой линейной алгебры до Transformer и LLM. Пошаговые проекты, код на Git-стиле, эксперименты, метрики, тюнинг гиперпараметров, ускорение на GPU. Обзоры курсов, книг и инструментов, подборка задач для практики и подготовки к интервью.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, en revanche des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A signaler le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller sur le web|
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Освойте режиссуру https://rasputinacademy.ru событий и маркетинг: концепция, сценарий, сцена и свет, звук, видео, интерактив. Бюджет и смета, закупки, подрядчики, тайминг, риск-менеджмент. Коммьюнити, PR, лидогенерация, спонсорские пакеты, метрики ROI/ROMI. Практические задания и шаблоны документов.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, toutefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En bonus le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller sur le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour finir, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
smartshoppinghub – Clean and practical, ideal for modern online shoppers and deals.
Домашний формат удобен, если нет признаков угрозы жизни и дома можно обеспечить спокойную обстановку. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки рисков и допуска к инфузионной терапии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет план действий и ожидаемую динамику. Далее запускается капельница: мягкая коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка печени, симптом-контроль тревоги, тошноты, головной боли и тремора. На руки выдаются понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, сон, признаки тревоги и алгоритм связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-srochno[/url]
https://postheaven.net/abj8pnn2qj
тусиай и тусипи тут всегда хорошие, к ним претензий никогда не возникает. https://firstbed.ru Самый лучший магазин! качество, цены, общение с клиентом, все на высшем уровне! продолжайте в том же духе и вам зачтется: )
Сначала коротко обозначим логику: каждый шаг должен иметь цель и измеримый результат, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, зачем мы делаем именно так.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
kraken сайт Kraken market – это многогранная площадка, где встречаются продавцы и покупатели со всего мира, предлагая широкий спектр товаров и услуг. Здесь можно найти все, что душе угодно, от редких артефактов до инновационных разработок. Приготовьтесь к захватывающему приключению, полному неожиданных открытий и выгодных предложений. Но не забывайте о здравом смысле и критическом мышлении, чтобы не стать жертвой недобросовестных продавцов.
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare
discovernewthings – Bright visuals and curious tone make this site engaging.
Весом по 1 гр https://avtoprokatyeysk.ru Начинает формироваться мнение.
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: play Operation game for free
Госпитализация разворачивается как последовательность шагов: приём и допуск к терапии, старт инфузий, мониторинг 24/7, регулярная переоценка и подготовка к выписке. Такой контур особенно важен пациентам с сопутствующими диагнозами (гипертония, ИБС, сахарный диабет, заболевания ЖКТ), где требуется деликатная настройка дозировок и темпа инфузий.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: nostalgic Hasbro games online
«Трезвый Маяк» — клиника экстренной и плановой наркологической помощи с круглосуточным выездом и возможностью госпитализации. Мы аккуратно стабилизируем состояние, снимаем интоксикацию и абстиненцию, готовим к кодированию и сопровождаем пациента до устойчивой ремиссии. Работаем анонимно: врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, документы оформляются в нейтральной формулировке и только по запросу.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]narkologicheskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Домашний формат подходит, когда обстановка позволяет лечиться в тишине, а клинические риски контролируемы. Врач «Чистой Гармонии» приезжает без опознавательных знаков, осматривает пациента, сверяет совместимости с уже принятыми препаратами, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. Инфузионная терапия строится без «универсальных коктейлей»: состав и темп зависят от давления, частоты пульса, выраженности тремора, тошноты, тревоги, сопутствующих диагнозов. В конце визита семья получает письменную памятку на 24–48 часов и прямой канал связи с дежурным специалистом. Такой подход убирает хаос из первых суток и помогает провести ночь спокойно, без «качелей».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы работаем последовательностями, которые реально влияют на исход: допуск к терапии, инфузии с коррекцией электролитов и КЩС, поддержка органов-мишеней, профилактика осложнений, осторожная нормализация сна по показаниям, переоценка и настройка схемы, план на неделю с алгоритмами «если-то». Важно не «перелечивать»: избыточная седативная нагрузка опасна так же, как и её отсутствие. Поэтому темп и состав мы настраиваем под текущие параметры и динамику — и объясняем пациенту и семье, зачем именно выбран каждый шаг.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/
когда появится новинки?? https://nebezit.ru Господа, проверяйте заказы на сайте, e-mail, указанные в заказе, у всех должны уже придти треки, у многих они активны уже.
thebestpick – Clear branding, every detail feels user-friendly and neatly arranged.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Хочу выделить раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
kraken ссылка Kraken ссылка – это навигатор по бескрайним просторам даркнета, указывающий путь к заветной цели. Однако, доверять первой попавшейся ссылке равносильно прыжку в пропасть с завязанными глазами. Прежде чем сделать этот шаг, убедитесь в её подлинности, проверьте репутацию источника и подготовьтесь к возможным неожиданностям. Безопасность превыше всего, и только внимательность и осторожность помогут вам избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
changeyourperspective.click – Love how this site challenges my mindset in refreshing ways today.
createyourfuture.click – Inspiring site overall, helps me stay motivated toward long-term goals.
modernhomefinds.click – Love the stylish home ideas here, everything feels fresh and cozy.
сделайте уже что-нибудь с этим реестром… хочу сделать заказ https://nika-land74.ru привет!!! не согласен долдны быть доступные магазины как
В клинике используется модульная система лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные компоненты. В зависимости от состояния человека акценты могут смещаться — например, у одних пациентов приоритетом становится физиологическое восстановление, у других — коррекция эмоционального фона и когнитивных паттернов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru
https://justpaste.me/Dk3m3
kraken ссылка Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-voskresenske/
Домашний формат — это клинически выверенная помощь без госпитализации, если обстановка безопасна и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Врач «Трезвого Компаса» приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит очную оценку (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус), уточняет препараты, принятые за 48 часов, и аллергии. Далее — допуск к терапии и запуск инфузии. Мы корректируем жидкость и электролиты, поддерживаем печень и ЦНС, по показаниям используем противорвотные и анксиолитические решения, избегая «перелечивания». В конце визита — переоценка, настройка темпа/состава, памятка на 24–48 часов и окно контрольного контакта.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]kapelnica-pri-zapoe[/url]
Если СК выпадает в осадок – то это уже само по себе не нормально https://gm72.ru месяц назад
changeyourperspective.click – Love how this site challenges my mindset in refreshing ways today.
createyourfuture.click – Inspiring site overall, helps me stay motivated toward long-term goals.
modernhomefinds.click – Love the stylish home ideas here, everything feels fresh and cozy.
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://southernstarseafood.live/two
Запой — это не только выраженная тяга к алкоголю, но и комплекс физиологических нарушений: обезвоживание, колебания давления, тахикардия, бессонница, тремор, дефициты электролитов. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем выше риск делирия и декомпенсаций. Мы оцениваем картину целиком: стаж употребления, фоновые болезни, уже принятые препараты, прошлые эпизоды судорог или потерь сознания. По итогам первичной беседы врач рекомендует формат старта — визит на дому или стационар.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru
Курсы по наращиванию https://schoollegoart.ru ресниц, архитектуре и ламинированию бровей/ресниц с нуля: теория + практика на моделях, стерильность, карта бровей, классика/2D–4D, составы и противопоказания. Материалы включены, мини-группы, сертификат, чек-листы и помощь с портфолио и стартом продаж.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Зацепил раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Только факты! – https://addictionsupportpodcast.com/asp-004-4-easy-nutrition-tips-for-more-happiness-from-terra-rose-ganem-of-body-brilliance/body-brilliant-grey-sea-salt
Работала с данным магазином давным давно! Пожалуй самый лучший) https://sever46.ru во вторник заряжали – сразу же списались договорились, чтоб всё ровно было – в итоге 4 суток прошло и тишина нету трека, вчера ваще пропал продаван, хотя до этого ваще из аськи не выходил в такое время, до этого спрашивал м.б. траблы какие – он ответил “что есть не большие” вот и походу решается че-то там х3 пздц короче надеюсь в понедельник решится
PRP-курс для косметологов prp терапия обучение доказательная база, отбор пациентов, подготовка образца, техники введения (лицо, шея, кожа головы), сочетание с мезо/микронидлингом. Практика, рекомендации по фото/видео-фиксации, юридические формы, маркетинг услуги. Сертификат и кураторство.
Чтобы процедура прошла спокойно и без задержек, заранее организуйте базовые условия — это экономит время и силы пациента и семьи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]клиника вывод из запоя москва[/url]
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: educational games from Prisma
discoveryourpotential.click – Great platform for personal growth, love the positive and uplifting tone.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Читать далее > – https://paulanishijima.com/06_elii_jardin-cyborg-imna_low2
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Посмотреть всё – https://amigstyle.com/produto/sapatos-vermelho-de-salto-alto-claire
Подарок для конкурента https://xrumer.xyz/
В работе несколько програм.
Есть оптовые тарифы
[url=https://xrumer.xyz/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Прочитать подробнее – https://greentheworld.store/product/premium-olive-hoodie
findsomethinggreat.click – Great place to browse, always end up discovering something unexpectedly cool.
classychoiceoutlet.click – Stylish collection overall, love the elegant and affordable fashion pieces.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полезно знать – https://peopleplaces.in/ashish-kulkarni-net-worth-family-relationship
Я просто уже настолько завязан со сферой Lrc что подмечаю все мелочи. Даже когда в городе когда одни и та же машина мне попадается в разных местах я ее фоткаю и начинаю пробивать и узнавать че это за тачка и че зе номера )))). https://pizzaa-lab.ru Смотри в розничном прайсе
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://vietteltravinh.com.vn/chao-moi-nguoi
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Хочу знать больше – https://www.abonosycompost.com/abono-casero-para-tomates
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://saveondrycleaners.ca/2024/03/18/nine-types-of-stuff-you-should-religiously-remember-to-take-to-your-dry-cleaner
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Обратиться к источнику – https://www.riferimenti.org/chiyodaku/kasumigaseki
shopandshinehub.click – Great variety here, products look amazing and prices are reasonable.
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Детали по клику – http://beauty-you.com.pl/sklep/lasery/laser-diodowy-do-epilacji/laser-diodowy-808-nm-optima
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Познакомиться с результатами исследований – https://amandigitalworld.com/index.php/2022/05/18/6-tips-to-run-an-a-b-test-of-landing-page-in-hubspot
[url=https://vc.ru/legal/2237796-luchshie-yuristy-v-moskve-uslugi-tseny-i-reyting]рейтинг юристов москвы[/url]
Квалификация юриста в определенной области права играет ключевую роль в его репутации.
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Интересует подробная информация – https://bkk1radio.com/2025/02/14/destinys-child-reunites-for-kelly-rowlands-44th-birthday
Experience luxury and reliability with our premier limousine service in Seattle, featuring [url=https://bdluxlimo.com/the-gold-standard-of-chauffeur-excellence-seattle-town-car-service/] professional Seattle chauffeurs [/url] who prioritize punctuality, safety, and discretion. Whether you need airport transfers, corporate travel, weddings, or special events, our fleet of high-end vehicles—including sedans, SUVs, and stretch limousines—ensures a seamless and stylish ride.
Our professional Seattle chauffeurs are meticulously trained, licensed, and committed to delivering exceptional service with a focus on courtesy and efficiency. From Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (SEA) pickups to downtown business meetings or scenic tours, we tailor every journey to your needs. Enjoy complimentary amenities like Wi-Fi, refreshments, and climate control while our chauffeurs navigate traffic with expertise.
Book with confidence for 24/7 availability, competitive rates, and a white-glove experience. Perfect for executives, celebrities, or anyone seeking sophistication, our limousine service combines comfort with the professionalism of Seattle chauffeurs who understand the city’s unique demands. Elevate your travel—arrive in style, every time. – https://bdluxlimo.com/the-gold-standard-of-chauffeur-excellence-seattle-town-car-service/
Написано же везде, что суббота и воскресенье – выходные дни. Надо же менеджеру отдыхать когда-то https://mediclever.ru можно записаться на пробник ам как он придет…а то ниче про него непонятно
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Узнать больше > – https://portalraizes.com.br/dia-nacional-de-combate-ao-cancer-coiteense-de-55-anos-relata-o-impacto-quando-recebeu-o-diagnostico-e-o-foco-no-tratamento
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Посмотреть всё – https://montaguemarkets.com.au/pradellas-montague-markets-to-commence-construction-in-late-2018
findbetteroptions.click – Love this site, helps compare and choose smarter shopping decisions easily.
discoveryourpath.click – Beautifully designed site, helps me focus on personal growth daily.
dreambuycollection.click – Beautiful selections here, quality items that truly match their descriptions.
Онлайн-курсы обучение прп: структурированная программа, стандарты стерильности, подготовка образца, минимизация рисков, протоколы для лица/шеи/кожи головы. Видеолекции и задания, разбор клинических ситуаций, пакет шаблонов для ведения пациента, экзамен и получение сертификата.
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Кстати, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
Уточнять не у кого ! https://nebezit.ru С Ув. vkapushoneПолучил сегодня посылку, могу уже с уверенностью сказать, Замечательного магазина.
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zudem die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein tolles Extra die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
Nachsehen|
Ich schatze die Energie bei Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, in seltenen Fallen gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und ansprechend, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein Hauptvorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, die Community enger verbinden.
Website betreten|
I’m completely sold on Pinco, you sense the winning vibe everywhere. The game choice is simply massive, with beautifully designed slot machines. It gives you an instant edge. The team delivers top-tier service. The process is simple and clear, still a couple extra spins would be sweet. In the end, Pinco is a place that electrifies. Bonus points the platform is visually captivating, motivates you to keep going. Particularly fun is the VIP program with unique perks, that offers continuous rewards.
See more|
Удобный и анонимный способ прервать запой — это вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге. Закажите помощь в клинике «Детокс».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons que le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller sur le site|
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Je suis totalement conquis par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner l’interface est simple et engageante, incite a rester plus longtemps. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: металлическая дверь в квартиру с установкой
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage notable les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
Essayer maintenant|
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov17.ru/
everydaygiftcorner.click – Perfect site for gifts, found some lovely options for friends.
In today’s nonstop news cycle, discovering reliable, timely reports has become a real challenge. Feeds update in seconds, yet truth is often lost in the speed. To find verified news platforms, visit our blog: https://graph.org/Where-to-Read-the-Latest-Entertainment-News-Stay-Ahead-on-Movies-Music-and-Pop-Culture-10-27 .
Major publications such as BBC, Reuters, and AP remain the foundation of accurate reporting. They confirm details before release and continuously update stories as events evolve. For deeper understanding, outlets such as The Economist and The Atlantic reveal the meaning beyond the headlines.
Independent journalists and digital platforms are redefining the way we follow stories. Platforms like Substack, independent blogs, and watchdog groups tend to deliver quick, authentic perspectives — notably on underreported subjects. They add new angles and genuine tone to modern journalism.
The best way to stay informed is to combine multiple viewpoints: combine global sources with smaller, focused ones that align with your interests. Read from multiple viewpoints, stay skeptical, and focus on insight, not noise. Such diversity helps you grasp what truly matters.
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: Здесь
connectlearncreate.click – Amazing community vibe, love the focus on creativity and learning together.
I recommend this legal remedy to everyone https://gabapentin-garbamaxxx.com
createinspirelead.click – Love the empowering tone here, truly encourages creativity and leadership.
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя. Услуга доступна на дому и в стационаре, а также включает капельницу от похмелья. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov25.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ростов-на-дону[/url]
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. La selection de jeux est colossale, incluant des slots de pointe. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, avec un suivi de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. En resume, 7BitCasino est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino serios|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, obwohl mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Дизельное топливо — это важный компонент энергетики, который широко используется в транспорте.
За счёт своей экономичности дизельное топливо гарантирует надёжную эксплуатацию двигателей.
Качественное топливо улучшает эффективность работы двигателя.
Существенное влияние имеет чистота топлива, ведь низкосортные добавки могут негативно повлиять.
Поставщики дизельного топлива обязаны поддерживать все стандарты.
Новые методы позволяют оптимизировать технические свойства.
При выборе дизельного топлива важно обращать внимание на сертификаты качества.
Складирование и перевозка топлива также влияют на его свойства.
Плохое топливо может привести к увеличению расхода.
Поэтому использование проверенных поставщиков — необходимое условие.
В настоящее время представлено разнообразие видов дизельного топлива, отличающихся по составу.
Морозостойкие виды дизельного топлива гарантируют эксплуатацию двигателей даже при низких температурах.
С появлением инноваций качество топлива повышается.
Ответственный подход в вопросе использования дизельного топлива способствуют повышение производительности.
Таким образом, качественное дизельное топливо является фундаментом эффективной работы любого оборудования.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un amusement continu. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce la communaute.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. D’ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute vibrante.
Avancer|
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov28.ru/
Если состояние близкого человека ухудшилось из-за запоя, не откладывайте вызов врача. В клинике Детокс в Екатеринбурге выезд нарколога на дом обеспечивает оперативность и конфиденциальность. Врач приедет в течение получаса, оценит состояние пациента, окажет первую помощь и подскажет, как действовать дальше.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно екатеринбург[/url]
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. En complement le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller sur le site web|
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре ростов-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону проводит вывод из запоя безопасно и анонимно, как в стационаре, так и на дому.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov27.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ростов-на-дону[/url]
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de sensations. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, avec un suivi de qualite. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, renforce l’immersion totale.
7bitcasino bonus code|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, ab und zu ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein tolles Extra sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Details finden|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, manchmal zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Zusammengefasst, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Zusatzlich ist das Design modern und einladend, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Jetzt eintreten|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Nebenbei ist das Design modern und einladend, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die spannenden Community-Aktionen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Website besuchen|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En somme, Sugar Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.sugarcasinoappfr.com|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
https://rubyslotscasinobonusfr.com/|
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Кстати, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui stimule l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
smartfashionboutique.click – Stylish and modern pieces, definitely my go-to for classy fashion.
Нужна оценка? оценка Орел независимая оценка и экспертиза: квартиры, дома, земля, бизнес, оборудование, товарные знаки, ущерб. Отчёты соответствуют ФСО и принимаются банками и судами. Чёткие сроки, понятные цены, экспертная поддержка на всех этапах и помощь в подготовке доказательной базы.
Комплексное остекление https://exterhaus.ru домов и коммерческих объектов «под ключ»: проектирование, замеры, производство и монтаж. Панорамные окна, витражи, теплые фасады, энергоэффективные стеклопакеты. Сроки по договору, гарантия, сервис, точный сметный расчёт.
yourdailytrend.click – Great source for everyday fashion inspiration, always something new featured.
Лечение основывается на комплексном подходе, позволяющем учесть особенности организма и стаж злоупотребления алкоголем. Обычно процедура состоит из нескольких этапов:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Запой меняет сразу несколько систем организма: сдвигается водно-электролитный баланс, растёт нагрузка на печень и ЖКТ, «скачут» давление и пульс, усиливаются тревога и бессонница. Одна смесь «от всего» редко даёт устойчивый результат: днём краткий подъём, к ночи — откат и новая волна симптомов. Мы действуем иначе. Сначала — очная оценка и допуск к терапии с учётом того, что человек уже принимал за последние двое суток. Затем — инфузионная поддержка нужного объёма и темпа, симптом-контроль по показаниям, осторожная работа со сном, чтобы не маскировать риски тяжёлой седацией. После основного блока — переоценка, перевод на per os-схемы, правила режима и окно контрольной связи. За счёт последовательности результат становится не хрупким «здесь и сейчас», а устойчивым на сутки и неделю.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-lobne/
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit packenden Live-Casino-Optionen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist einfach und klar, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein attraktives Extra die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Jetzt besuchen|
everydaystylecorner.click – Love browsing here, always find stylish items that suit my taste.
https://social.sikatpinoy.net/blogs/10860/Today-1xBet-Promo-Code-130-Welcome-Deal
Все детали и нюансы здесь: https://version.com.ua
Новости подробно кино https://fankino.ru
Этап
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru
Представьте, что помощь приходит прямо к вам: в квартире, где нужна поддержка. Детокс в Екатеринбурге реализует услугу вызова нарколога на дом, чтобы облегчить состояние пациента без транспортировки и лишнего стресса. Врач подключит капельницу, проведёт детоксикацию и даст рекомендации по восстановлению, всё это в вашем знакомом окружении.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru
«НоваТонус» — это связанный маршрут наркологической помощи для жителей Лобни и округа: оперативный выезд врача на дом, аккуратный домашний детокс без «универсальных коктейлей», стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением, подготовка к кодированию по показаниям и поддержка семьи в первые недели. Мы действуем по принципу клинической достаточности: каждое назначение обосновано, объясняется простым языком и привязано к реальным целям — безопасно снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, мягко вернуть сон, а затем провести первую «тихую» неделю без качелей. Приватность встроена в процесс: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральный канал связи, документы по запросу и в сдержанной формулировке.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Если вам или вашим близким необходим вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Обратившись в «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы получаете не только медицинскую помощь, но и всестороннюю поддержку на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov112.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/
нарколог на дом
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Отличная статья про лучшие нейросети для генерации изображений с реальными примерами работ. Выбрал пару сервисов из подборки, оба показали отличное качество. Рекомендую всем профессионалам: https://vc.ru/top_rating/2301994-luchshie-besplatnye-nejroseti-dlya-generatsii-izobrazheniy
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
buildsomethingnew.click – Inspiring projects here, really motivates me to start new creative ideas.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве [url=elektrokarniz797.ru]elektrokarniz797.ru[/url] .
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому ростов-на-дону[/url]
нарколог на дом
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Капельница от похмелья в Нижнем Новгороде — доступная и эффективная процедура для снятия симптомов интоксикации. Стоимость услуги начинается от 2?100??.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в нижний новгороде[/url]
Длительное злоупотребление спиртным неизбежно приводит к серьёзным последствиям для организма. Алкоголь влияет на работу практически всех внутренних органов: печень испытывает повышенную нагрузку при выводе токсинов, почки страдают от нарушения водно-солевого баланса, а сердечно-сосудистая система подвержена скачкам давления и аритмиям. Постепенно ухудшается общее самочувствие – возникают постоянные головные боли, слабость, повышенная раздражительность, бессонница.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narko-reabcentr.ru/kruglosutochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve/
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Зацепил раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуальные схемы лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/
expandyourhorizon.click – Great site for learning and exploring fresh perspectives every day.
В клинике «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Если состояние близкого человека ухудшилось из-за запоя, не откладывайте вызов врача. В клинике Детокс в Екатеринбурге выезд нарколога на дом обеспечивает оперативность и конфиденциальность. Врач приедет в течение получаса, оценит состояние пациента, окажет первую помощь и подскажет, как действовать дальше.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом свердловская область[/url]
Исследуйте захватывающий мир онлайн-гэмблинга с увлекательными играми в Frost Queen Jackpots казино вавада . Получите доступ к лучшим слотам и наслаждайтесь захватывающим процессом игры, где удача ваших рук не устоит. Deep Freeze Free Spins, Eye of the Queen Bonus и Treasure Chest Feature – захватывающие возможности, которые ждут вас в этом казино. Новые игроки получат щедрый приветственный бонус, а постоянные клиенты наслаждаются регулярными акциями и бонусами. Присоединяйтесь к Frost Queen Jackpots и погрузитесь в захватывающий мир азарта!
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в ростове-на-дону[/url]
1000 за регистрацию без депозита казино
Лечение основывается на комплексном подходе, позволяющем учесть особенности организма и стаж злоупотребления алкоголем. Обычно процедура состоит из нескольких этапов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
9e2seattle.com – Love the local coverage here, very informative and well-presented overall.
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Обратившись в нашу клинику в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Отличная подборка помогла создать фото нейросетью онлайн без лишних поисков. Выбрал один основной генератор картинок, иногда использую альтернативные варианты из статьи. Все работают стабильно: https://vc.ru/top_rating/2301994-luchshie-besplatnye-nejroseti-dlya-generatsii-izobrazheniy
1000 за регистрацию без депозита казино
Лобня — город коротких дистанций, но в острых ситуациях решает не километраж, а управляемость. Мы убираем паузы между решением обратиться и реальной помощью: на звонке быстро оцениваем риски, предлагаем безопасный старт в квартире или в палате, согласуем окно прибытия, объясняем что подготовить, и фиксируем честный диапазон стоимости. Цель — чтобы первые часы прошли по понятному плану, а не вслепую.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]besplatnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki[/url]
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 175 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 1700Dоl Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://timenewsworld.wiki/brkvaii
connectwithideas.click – Amazing platform, really encourages collaboration and sharing of new innovative ideas.
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуальные схемы лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov112.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
«Клиника Трезвый Курс» организует вывод из запоя для жителей Лобни круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом без опознавательных знаков, аккуратные капельницы с индивидуальным составом, стационар с наблюдением и аппаратным контролем, а также поддержка семьи на первые дни, когда особенно важно не сорваться в прежний ритм. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никаких «универсальных коктейлей» и грубой седации ради видимости улучшения. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком, смета фиксируется до начала процедур, приватность встроена в процесс. Цель — не просто «полегчало», а безопасная стабилизация с предсказуемой ночью и понятным планом тихой недели.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-lobne/
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в клинику «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону. Врачи работают круглосуточно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Искал способ быстро создавать изображения качественно, и обзор помог найти лучшие инструменты. Остановился на одном основном сервисе, дополнительные генераторы из списка держу про запас. Очень доволен: https://vc.ru/top_rating/2301994-luchshie-besplatnye-nejroseti-dlya-generatsii-izobrazheniy
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов ростов-на-дону[/url]
Если не хотите ехать в стационар, закажите вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге. Круглосуточную помощь оказывает клиника «Детокс».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
nsfeg.org – Great resource for learning, very informative and well-structured content overall.
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому в Ростове-на-Дону предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
kionnawest.com – Inspiring platform, clearly shares vision and values in a compelling way.
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov112.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
yourdailyshoppinghub.click – Convenient and well-organized store, makes daily shopping fast and enjoyable.
Запой меняет сразу несколько систем организма: сдвигается водно-электролитный баланс, растёт нагрузка на печень и ЖКТ, «скачут» давление и пульс, усиливаются тревога и бессонница. Одна смесь «от всего» редко даёт устойчивый результат: днём краткий подъём, к ночи — откат и новая волна симптомов. Мы действуем иначе. Сначала — очная оценка и допуск к терапии с учётом того, что человек уже принимал за последние двое суток. Затем — инфузионная поддержка нужного объёма и темпа, симптом-контроль по показаниям, осторожная работа со сном, чтобы не маскировать риски тяжёлой седацией. После основного блока — переоценка, перевод на per os-схемы, правила режима и окно контрольной связи. За счёт последовательности результат становится не хрупким «здесь и сейчас», а устойчивым на сутки и неделю.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно ростов-на-дону[/url]
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Обратившись в нашу клинику в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov232.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В клинике «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Наши услуги в Ростове-на-Дону включают не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку для более эффективного восстановления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
yourdailytrend.shop – Love the trendy picks here, perfect for keeping up with fashion.
monumentremoval.org – Important initiative, clearly explains the process and historical context respectfully.
1911phl.com – Great information on local events, keeps me updated with ease.
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-90.ru быстро и удобно: без визита в офис, 1 паспорт, проверка за минуты. Перевод на карту/СБП, поддержка 24/7. Прозрачные условия, понятный график платежей, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выбирайте выгодно.
Rеgіster now and receive a welсоme раckage:
up to 175 frее sріns and as much as 1550ЕURО Воnus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted саsіnо experience await at
https://arenamasters.shop/b9uws4v
Сервис онлайн-займов https://zaimy-91.ru подача заявки за 3 минуты, моментальное решение, выдача на карту. Честные проценты, без навязанных услуг, личный кабинет, уведомления о платеже. Калькулятор, промокоды, программа лояльности. Ответственное заимствование.
Онлайн-займ https://zaimy-67.ru без очередей: заполните форму, получите решение и деньги на карту. Выгодные ставки, понятный договор, кэшбэк и скидки при повторных обращениях. Напоминания о платежах, продление при необходимости. Выбирайте ответственно и экономьте.
Наши услуги в Ростове-на-Дону включают не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку для более эффективного восстановления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Обратившись в «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы получаете не только медицинскую помощь, но и всестороннюю поддержку на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Проектирование и строительство загородного дома в Санкт-Петербурге – это процесс, требующий внимательности к деталям. Наша строительная компания берет на себя все этапы: от выбора материалов и составления прайса до выполнения работ. Мы предлагаем кладку газоблока https://builder-spb.ru , кирпича и пеноблоков, установку жб-перекрытий, монтаж перегородок, сварочные и отделочные работы. Стоимость рассчитывается за квадратный метр или поштучно. Подрядчики учитывают сорт и уровень прочности блоков, чтобы построить надежный дом. Предлагаем выгодные цены и прозрачные расценки, фиксированные в договоре.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Практические советы ждут тебя – https://unnatidairy.com/cows-spa
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
https://escolacognus.com.br/?attachment_id=7
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Читать далее > – https://rojava.net/ziman-stuna-wejeye-ye
bestvaluecollection.click – Found some excellent deals, products are great quality for affordable prices.
У статті mr-master.com.ua прочитала інструкцію з ремонту ванної без плитки.
На сайті zebraschool.com.ua відремонтували валізу у Хмельницькому — швидко і без проблем
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://vivehg.com/tendencias-inmobiliarias
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
https://stage-curacao.nl/curacao-strandjes-playa-kanoa
После отзывов https://buybuyviamen.com/ заказали сантехнические работы в Киеве.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Детали по клику – https://ghostxshop.com/become-a-ghost-hunter-straight-from-your-hand-via-our-app
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Не упусти важное! – https://www.centroasturianodemexico.com/golf/14-torneo-copa-principado-2021
mcalpineinfo.com – Love the detailed info here, very helpful and easy to follow.
natashaforjudge.com – Excellent campaign site, communicates priorities and experience clearly and effectively.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Обратиться к источнику – https://ww.leonid-gaidai.ru/index.php
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://www.allspecsautomotive.com.au/faq-items/vivamus-ullamcorper-nim-sit-amet-consequat-laoreet-tortor-tortor-dictum-egestas-urna
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://trouver-prenom.com/prenom-grec-garcon
ремонт bosch [url=https://www.servisnyj-bosch-moskva.ru/]https://servisnyj-bosch-moskva.ru/[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Посмотреть подробности – https://tv.lpmsigma.com/sigma-talk-boikot-produk-pro-israel-ini-tanggapan-ukm-kopma
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://internationalphototours.com/bera-the-leopard-kingdom
imaginelearnexplore.click – Inspiring content overall, really helps spark creativity and curiosity daily.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://fizjoterapia.radom.pl/?p=152
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. La selection de jeux est colossale, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, repondant en un clin d’?il. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En resume, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le site est concu avec style et modernite, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino online|
Ich bin vollig uberzeugt von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit Live-Sportwetten. Er macht den Start aufregend. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, jedoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Nebenbei die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die lebendigen Community-Events, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Zur Website gehen|
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
Узнать из первых рук – https://yuvamedia.com/meeting-of-kashi-biscuits-and-confectionery-business-board-concluded
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist kinderleicht, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Excellent article. Keep writing such kind of info on your site. Im really impressed by your site.
Hey there, You have performed a great job. I will definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
roulettino casino login
Нужна турбина? официальный сайт Jrone в России оригинальные узлы, картриджи, вакуумные и электронные актуаторы. Подбор за 5 минут, проверка совместимости, гарантия, доставка день-в-день. Для легковых и LCV, выгодные цены и техконсультации.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://sportcentury21.com/deportivos-hinchables/diana-gigante-2
Фото из армии Про солдат су профессиональная съёмка армии: присяга, парады, учения. Создаём армейские альбомы, фотокниги, постеры; ретушь и цветокор, макеты, печать и доставка. Съёмочные группы по всей стране, аккредитация и дисциплина, чёткие сроки и цены.
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.ummahmasjid.ca/back-2-school-family-camp-at-mush-a-mush-campground
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, toutefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements securises.
Savoir plus|
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://lankaholidaytours.com/a-paradise-for-adventure-seekers-top-thrills-in-sri-lanka
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der maintenant|
hardman4schools.com – Great campaign site, clearly communicates vision and priorities for education.
pmajoe4council.com – Informative site, provides clear insight into policies and council initiatives.
makeimpacttoday.click – Motivational platform, encourages me to take action and make a difference.
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Zusatzlich die Seite ist schnell und einladend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein starkes Plus die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
FГјr mehr besuchen|
вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес… купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази УРА трек пробился :angel: Супер магазин,СПАСИБО за подарок 6 г в качестве компенсации:speak::hz:очень боялся что обманут,но Зря:drink: спасибо магазину,с новым годом!!!!!
организация онлайн трансляции [url=http://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu4.ru/]организация онлайн трансляции[/url] .
организация прямых трансляций [url=https://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu5.ru]https://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu5.ru[/url] .
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]бесплатное кодирование от алкоголизма волгоград[/url]
**[url=https://premierlimousineservice.net/2025/10/22/luxury-ways-to-explore-seattle-from-airport-transfers-to-cruise-adventures-car-service-seattle/] Seattle airport limo [/url]** offers premium, reliable transportation for travelers arriving or departing from **Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (SEA)**. With a fleet of luxury sedans, SUVs, stretch limousines, and sprinter vans, these services ensure comfort, style, and punctuality for corporate clients, weddings, prom nights, or group travel.
Professional chauffeurs provide **Seattle airport limo** services with meet-and-greet assistance, real-time flight tracking, and luggage handling for a seamless experience. Vehicles are equipped with plush seating, climate control, Wi-Fi, and refreshments, catering to business executives and leisure travelers alike.
Booking is convenient via user-friendly websites or 24/7 customer support, with competitive flat-rate pricing and transparent billing. Whether for a solo trip, family vacation, or large group, **Seattle airport limo** guarantees timely pickups and drop-offs, avoiding parking hassles and ride-sharing uncertainties.
Ideal for special occasions or stress-free airport transfers, these services prioritize safety, discretion, and luxury. Many providers also offer hourly charters for city tours, wine tastings, or corporate events, making **Seattle airport limo** the top choice for sophisticated ground transportation in the Pacific Northwest. – https://premierlimousineservice.net/2025/10/22/luxury-ways-to-explore-seattle-from-airport-transfers-to-cruise-adventures-car-service-seattle/
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Хочу выделить материал про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de gingado, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, BacanaPlay Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de frevo, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
bacanaplay legit|
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
discovergreatdeals.click – Love this site, always find amazing deals on quality products.
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein weiteres Highlight die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, die Teilnahme fordern.
Einen Blick werfen|
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
sparxcle.com – Interesting products here, really innovative ideas and practical solutions overall.
9e2seattle.com – Love the local coverage here, very informative and well-presented overall.
Можно позвонить в СПСР, у них там даётся полная инфа по треку, по телефону. Где чё лежит. Если не написано в ленте… Завтра звякну, отпишу, если не появится. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Её переместили в арбитраж. Тогда ничем помочь не могу.
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
how to use seduced ai seduced ai free account
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, malgre tout des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, parfois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis sous le charme de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, rarement des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Link kbw
Ни форма, ни машины с надписями, ни громкие атрибуты «скорой» — мы приезжаем тихо. Контакт в телефоне сохраняется с нейтральным названием, документы оформляются только по запросу и в сдержанной формулировке, доступ к данным внутри «ПрофДетокса» ограничен регламентами. Мы понимаем, что стыд и страх огласки часто тормозят обращение за помощью, поэтому приватность включена в стандарт и не влияет на стоимость.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-v-ivanteevke[/url]
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Ajoutons aussi le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
VГ©rifier le site|
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов город[/url]
Мучает зуд и жжение? Геморой – лечение без боли и очередей: диагностика, консервативная терапия, латексное лигирование, склеротерапия, лазер. Приём проктолога, анонимно, в день обращения. Индивидуальный план, быстрое восстановление, понятные цены и поддержка 24/7.
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, dennoch mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zusatzlich ist das Design stilvoll und modern, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein hervorragendes Plus die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Startseite ansehen|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein tolles Feature die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, das die Motivation steigert.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, manchmal mehr Bonusvarianten waren ein Hit. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zusatzlich ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Mehr erfahren|
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
chery 8 pro max chery tiggo 7 max
Для жителей Красноярска организованы два конфиденциальных пути. Первый — немаркированный выезд бригады на дом с заранее согласованными порогами связи. Второй — «тихий вход» в клинику через отдельную дверь, где приём проходит без очередей и «коридорных» разговоров. На первичном звонке администратор уточняет только клинически значимые факторы: частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспускания, ЧСС/АД в покое, эпизоды спутанности, актуальные лекарства и аллергии. Биографические подробности и лишние вопросы не задаются — мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/[/url]
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар красноярск[/url]
Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут…. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану угу, “на глазок” отсыпали. купи весы и взвесь нормально. На вид оно может показаться как больше так и меньше…
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, en revanche des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter en ligne|
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно тольятти[/url]
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour finir, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un element fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement super les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller voir|
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно уфа[/url]
Je suis sous le charme de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
Ouvrir le site|
https://factava.com.ua/diyety/hipokholesterynova-diieta-yak-znyzhuvaty-riven-kholesterynu-ta-pokrashchyty-svoie-zdorovia/
simonscider.co.uk – Delicious cider options, love the quality and unique flavor choices here.
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – Beautiful and imaginative site, full of magical ideas for everyone.
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Ich schatze die Energie bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit packenden Live-Casino-Optionen. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, allerdings mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die spannenden Community-Aktionen, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Webseite besuchen|
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]ближайший наркологическая клиника[/url]
Длительность вывода из запоя во многом зависит от тяжести состояния, общего здоровья и продолжительности самого запоя. Если пациент обратился на ранней стадии, зачастую хватает 1-2 капельниц и короткого курса поддержки. Но при запое более пяти-семи дней, когда имеется острая интоксикация, требуется более продолжительная терапия и круглосуточное наблюдение.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
раньше и хуй крепче был и бабы красивей купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Насчет доставки стало не очень после того как перестали работать с спср, но особой разницы не заметил.
shopthebesttoday.click – Great online store, easy navigation and fantastic product deals daily.
Пицца в Воронеже https://pizzacuba.ru с быстрой доставкой: свежие ингредиенты, сыр тянется, бортики хрустят. Отслеживание заказа, удобный личный кабинет, повтор «в 1 клик». Комбо для компании, детское меню, соусы и напитки. Рабочие акции и честные цены.
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd/
DRINKIO стал для меня настоящим открытием — оформление заказа занимает считанные минуты, а доставка всегда быстрая и чёткая. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, вежливые и опрятные. Радует, что можно оформить заказ в любое время суток, даже ночью. Ассортимент широкий, цены адекватные. Всё доставляется в идеальном состоянии, что тоже важно. Отличный выбор для тех, кому нужна доставка алкоголя на дом в Москве 24/7 https://drinkio105.ru/
Читайте расширенную версию: https://togliatti24.ru/interesnoe/view/tehnologii-sirokoformatnoj-pecati-solventnaa-uf-i-lateksnaa
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
Безопасность — это не лозунг, а набор решений. Мы избегаем «жёстких» седативных доз, которые создают видимость улучшения и повышают риск скрытых осложнений. Наращивание темпа инфузии происходит постепенно и увязано с динамикой симптомов и цифрами измерений. Любой шаг объясняется пациенту и семье: зачем он выбран, что считается нормальной волной улучшения, в какой момент нужно связаться с дежурным. Такой прозрачный формат снимает тревогу и помогает всем участникам действовать согласованно.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить больше информации – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
Продаван молчит, что будет дальше не известно, мне сделал но не все.отписался, жду результатов купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану А ВОТ Я ТОЖЕ КИПИШЕВАЛ ПО СЧЕТУ ТРЕКА НЕ БИЛСЯ ТОЖЕ ПОЗВОНИЛ В КУРЬЕРКУ СКАЗАЛИ ОТПРАВЛЕННО И СЕГОДНЯ К ВЕЧЕРУ ВСЕ ОТБИЛОСЬ ЖДУ ПРИХОДА ПОСЫЛКИ. ПОТОМ НАПИШУ КАК ЕСТЬ. ПРОШУ ПРОЩЕНИЯ У ЧЕМИКАЛА ЗА ПЛОХИЕ ПОСТЫ, ДУМАЮ ПОЙМЕТ))) УЖЕ ДАВНО ТУТ БЕРУ НЕ РАЗУ НЕ КИНУЛ НИ ОДНОЙ ЗАДЕРЖКИ ВСЕ ПРОСТО НА 100%.
maltonfestivalofracing.co.uk – Amazing festival coverage, really captures the excitement of racing events beautifully.
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно в волгограде[/url]
mdcphilly.com – Great local content, keeps community members informed about events and updates.
learntradingtoday.bond – Excellent resource for beginners, explains trading concepts clearly and simply.
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-volgograd/
All the best is here with us: https://www.wamug.org.au/2025/10/buy-tiktok-accounts-from-1-cent-2/
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в красноярске[/url]
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
доларове дерево зацвіло прикмети
бездепозитный бонус 1000 рублей в казино
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh/
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Получить больше информации – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
У данного прода, самая лучшая тусишка из всех, что я пробовал. Те кто пускали ВВ, выбрасывали остатки, пугаясь происходящего. Флюкс на уровне. Именно на уровне качества, не бутора. Но и не такой пиздатый как у Ромы Максимова (Его [Ромы] флюкс для меня эталон 100мг, ОКЕАН эйфории). АМ2201 потрясающий, гора микса весёло прущего вышла из присланного пробника, но с огромной толлерантностью, была в итоге смешана с 203и 250 то же данного продавца, что придало миксу эффект, от которого бывалые говорили, что это их лучшие трипы в жизни ))) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Только позитивные эмоции!
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в уфе[/url]
Таблица не заменяет очный осмотр, но показывает, как наблюдения переводятся в действие и когда мы принимаем решение о продолжении/остановке модуля.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог красноярск[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в красноярске[/url]
Цель
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
«МедСфера» — это управляемый маршрут наркологической помощи в Ивантеевке: круглосуточный выезд врача без опознавательных знаков, аккуратный домашний детокс, стационар с наблюдением 24 часа в сутки и профессиональная подготовка к кодированию по показаниям. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никакой «универсальной капельницы», никаких решений «наугад», только последовательные шаги, которые действительно влияют на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простым языком, заранее согласуем смету, фиксируем правила на первые 24–48 часов и первую «тихую» неделю. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральная связь, выезд без эмблем, документы в сдержанной формулировке по запросу.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-domu-v-ivanteevke/
simplybestchoice.shop – Great product variety, everything feels affordable and high quality overall.
ліна значення імені
Основу лечения составляет междисциплинарная команда: врач-нарколог, психиатр, психолог, медсестра и консультант по зависимому поведению. Каждый отвечает за свой участок работы, но общая цель едина — помочь пациенту безопасно пройти путь от детокса до устойчивого состояния. Благодаря единому плану и регулярным консилиумам врачей, исключаются противоречия и дублирование процедур. Это экономит ресурсы организма и делает процесс прогнозируемым.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Ищете актуальные зеркала Кракена? У нас самая полная информация о зеркалах Кракена на сегодняшний день. Узнайте, как обойти блокировку и получить доступ к Кракену. Список рабочих зеркал Кракена для удобного доступа. Безопасные и проверенные зеркала для вашего комфорта. Не упустите шанс пользоваться Кракеном без проблем и задержек. Подробная информация о зеркалах Кракена и способы их использования
playfuel.co.uk – Great gaming products here, everything feels fun, creative, and high-quality.
iswrphilly.com – Very professional organization, provides helpful resources and information for all users.
Всем привет) У меня такая проблема, сделал заказ, оплатил через евросеть, Уважаемый продаван сказал то, что в евросети перевод идет до 3-х дней, хотя когда работали с другим магазином деньги прилетали моменьтально всегда. И доставка вышла на 950 р. (г. Екб), это получаеться + курьер или нет, просто до почты?… И через что лучше оплачивать в данном магазине? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану сколько Вы уже не появлялись в своей теме?
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
Мы не удерживаем пациента на дому во что бы то ни стало. Домашний формат уместен при контролируемых симптомах, наличии взрослого помощника на вечер и ночь и возможности обеспечить тихий режим. Если у входа видно угрозу делирия, выраженные скачки давления, повторные эпизоды рвоты с обезвоживанием, нестабильный ритм, одиночество ночью — рациональнее начать в палате. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и лаборатория, пост медсестёр и быстрые коррекции схем. Такой маршрут часто короче по времени до устойчивого сна и предсказуемее по результату.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника красноярск[/url]
Пользуюсь DRINKIO давно, и они ни разу не подвели. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, всё доставляется аккуратно. Ассортимент радует, цены доступные. Очень удобно, что сервис работает круглосуточно. Всё проходит быстро и без лишних вопросов. Доставка алкоголя на дом по Москве: https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/pivo/
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом красноярск[/url]
shopthebesttoday.click – Great online store, easy navigation and fantastic product deals daily.
Выезд начинается с очной оценки. Врач уточняет историю эпизода, смотрит давление и пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает неврологический статус и уровень тревоги, внимательно проверяет совместимость с уже принятыми средствами. Допуск к терапии — стартовая точка. Затем запускается инфузионная поддержка с аккуратной коррекцией воды и электролитов, защитой органов мишеней, симптом контролем тошноты и головокружения. При необходимости настраивается сон, но без избыточной седативной нагрузки, которая могла бы замаскировать риски. По завершении основного блока — переоценка, перевод на пероральные схемы, подробная памятка на 24–48 часов и заранее согласованное окно контрольного контакта.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Какие магазины тебе написали про меня в личку? Что это за бред?! Я 2 дня назад зарегистрировался и все мои сообщения только в твоём топике. Или другим магазинам на столько важны твои отзывы и репутация, что они сидят в твоей теме и пишут кто, о ком и как думает? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш дай то бог да и знаю я Вас давно не один кг перелопатил без паники ждем вторника
Длительное злоупотребление спиртным неизбежно приводит к серьёзным последствиям для организма. Алкоголь влияет на работу практически всех внутренних органов: печень испытывает повышенную нагрузку при выводе токсинов, почки страдают от нарушения водно-солевого баланса, а сердечно-сосудистая система подвержена скачкам давления и аритмиям. Постепенно ухудшается общее самочувствие – возникают постоянные головные боли, слабость, повышенная раздражительность, бессонница.
Подробнее – https://narko-reabcentr.ru/
harrietlevinmillan.com – Informative and well-written content, really highlights expertise and knowledge clearly.
asterixfilm.co.uk – Fantastic movie content, perfect for fans of animation and classic films.
Краснодарский край богат природой и достопримечательностями, которые стоит увидеть каждому. Чтобы ничего не пропустить, стоит обратить внимание на [url=https://luchshie-ehkskursionnye-tury.ru]экскурсии из Краснодара[/url]. Это отличный вариант для тех, кто хочет провести выходные с пользой и узнать свой регион ближе.
nextrealm.click – Interesting concept, love the futuristic vibe and creative presentation overall.
а есть почта у данного магаза? купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм нервные клетки
Regіstrаte ahоra y recіbе un pаquеte de bіеnvenіda: hаsta 70 tіrаdas grаtіs y un bоnо de hаstа 900ЕURО.
Juеgоs іncrеiblеs y pаgоs іnstаntanеоs еn
https://sportterra.shop/bcdegfw
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://avanzatelife.com/hello-world
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://www.keygraphic.fr/untitled-15-jpg
Пожалуй один из самых ровных магазинов “Старичков ” – благодаря которому я зарабатвал, от души спасибо парням за ровную работу! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Работали с магазином ранее брали по 100г, недавно взяли еще 50г, хотим сегодня 100г приобрести!! на регу нету нареканий!!
dreamcreateinspire.shop – Beautiful design, love the inspiring message and creative energy here.
Не менее опасны и психоэмоциональные нарушения, связанные с абстинентным синдромом: тревога, чувство паники, галлюцинации, нарушения координации. В тяжёлых случаях может развиться алкогольный делирий (белая горячка) со спутанностью сознания, бредовыми идеями и приступами агрессии. Самостоятельный резкий отказ от спиртного в этом состоянии чреват непредсказуемыми осложнениями вплоть до судорог и комы.
Выяснить больше – https://narko-reabcentr.ru/kruglosutochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve/
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
По теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
pp4fdr.org – Important initiative, shares valuable guidance and updates in a clear manner.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Посмотреть подробности – https://shvkosova.com/ekspert-konsulente-ligjore-per-pershtatjen-e-materialit-dhe-mbajtjen-e-trajnimeve-per-te-drejtat-ligjore-te-tokes-dhe-prones-per-komuniteti-e-te-verberve-dhe-te-shurdherve
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Это ещё не всё… – http://sunforumnet.co.jp/2023/06/14/hello-world
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Прочитать подробнее – https://microgamingslotsgame.online/understanding-the-hot-triple-sevens-hold-win-slots
DRINKIO показал высокий уровень сервиса с первого заказа. Курьеры приезжают быстро, всё аккуратно и точно по заказу. Сайт понятный, цены прозрачные. Очень удобно, что можно заказать в любое время, даже ночью. Ассортимент радует — есть всё, что нужно. Круглосуточная доставка алкоголя в Москве: https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/vodka/
Делали 1к8 прикуренные, эффект до 3х часов ! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм В лс пиши сразу. Имей в виду, быстрее будет
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Не упусти важное! – https://kizakura-annzu.com/archives/356
Английский сегодня считается незаменимым инструментом для жителя современного мира.
Он помогает взаимодействовать с иностранцами.
Без знания английского трудно строить карьеру.
Организации оценивают специалистов с языковыми навыками.
курсы английского языка с нуля для взрослых
Регулярная практика английского делает человека увереннее.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без трудностей.
Помимо этого, изучение языка улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, владение английским играет важную роль в будущем каждого человека.
Цель
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]rejting-narkologicheskih-klinik[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://sinhala.srilankamirror.com/entertainment/jacqueline-granted-interim-bail/?noamp=mobile
Знание английского языка сегодня считается обязательным инструментом для современного человека.
Он позволяет находить общий язык с жителями разных стран.
Без знания английского трудно достигать успеха в работе.
Работодатели оценивают сотрудников, владеющих английским.
школы английского языка
Регулярная практика английского делает человека увереннее.
С помощью английского, можно учиться за границей без перевода.
Помимо этого, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, умение говорить по-английски играет важную роль в саморазвитии каждого человека.
urbanmatrix.click – Modern and stylish concept, offers great insights into urban innovation.
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Продолжить изучение – https://wowember.com/best-places-to-stay-in-seremban
How to win in Calgary Lottery: Boost your chances by playing consistently, joining lottery pools, and choosing less popular combinations. Remember, winning requires luck and responsible play: local Calgary deals and wins
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
Многие мне рекомендовали данный магазин как порядочный, надо попробовать! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Заказывал 307, прислали 203. Сразу объяснил, менеджер в скайпе всё понял. Сказал Бро не переживай будет тебе бонус.
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay logo|
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, in manchen Fallen mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spielbegeisterte. Ubrigens die Seite ist schnell und ansprechend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein gro?artiges Plus ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, exklusive Boni bieten.
Angebote entdecken|
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
Узнай первым! – https://manchestercityclubs.nl/key-players-in-mexico-u17-fc-history
ks4thekids.com – Wonderful platform for children, lots of creative learning opportunities provided.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Подробнее – https://www.bd-bauwerkssanierung.de/trockenbau
Хочешь вылечить геморрой – современный подход к лечению геморроя: точная диагностика, персональный план, амбулаторные процедуры за 20–30 минут. Контроль боли, быстрый возврат к активной жизни, рекомендации по образу жизни и профилактике, анонимность и понятные цены.
Современный атмосферный ресторан в Москве с открытой кухней: локальные фермерские ингредиенты, свежая выпечка, бар с коктейлями. Панорамные виды, терраса летом, детское меню. Бронирование столов онлайн, банкеты и дни рождения «под ключ».
Нужен демонтаж? https://lerc.ru внутренний и наружный демонтаж: стены, полы, перегородки, фасады, металлоконструкции, железобетон. Точный план работ, техника и ручной труд, вывоз и утилизация по нормам. Работаем в действующих зданиях без остановки бизнеса.
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, manchmal mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Zudem die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
https://catspinsbonus.com/|
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детальнее – https://www.texturedtalk.com/textured-talk-with-cheyenne-of-onmylevel_chey
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Community-Events, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://www.izumishoko.co.jp/%E8%A3%BD%E5%93%81/%E3%81%8A%E3%82%84%E3%82%AB%E3%83%86a/124
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Подробности по ссылке – https://yourfamilydoctor.co.in/cough
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://www.sfomaniya.com/2019/01/01/smart-lighting
мистическийтриллер Байки от бабайки – это сборник личных рассказов людей, столкнувшихся с необъяснимым и сверхъестественным. Эти истории, словно шепот из другого мира, будоражат воображение и заставляют задуматься о том, что скрывается за пределами нашего понимания. От встреч с призраками до загадочных аномалий – каждый рассказ является уникальным свидетельством контакта с потусторонним.
привет бразы всех спрошедшими праздниками получил седня посыль все порадовало и качество и бонус:p:D:D:Dприложеный за ожыдание спосибо магазу купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази пробы есть?
[url=https://prozonei.cc/]Prozone.cc[/url] | [url=https://prozonei.cc/]ProZone[/url] — Your trusted cc shop for premium CC and Dumps.
Log in to ProZone.cc Shop to discover our full range of Cvv and dumps.
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
Visiter le site|
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://shga.kr/archives/165
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://www.exceledgeintl.com/win-hearts-boost-sales
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et style, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Мы предлагаем вам подробное руководство, основанное на проверенных источниках и реальных примерах. Каждая часть публикации направлена на то, чтобы помочь вам разобраться в сложных вопросах и применить знания на практике.
Смотрите также… – https://hearld.news/udderly-unbelievable-first-female-ceo-milks-tech
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, in seltenen Fallen gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Au?erdem ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein Hauptvorteil sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Eintauchen|
ks4thekids.com – Wonderful platform for children, lots of creative learning opportunities provided.
Тоже считаем что запреты не запреты. Да бывает что и за клиентами охотятся. https://puzzlepedia.ru Поздравляю всех с наступающим Новым 2013 Годом! Желаю в год Змеи: 1. Мутить тока на спирту! 2. Отваривать основу. 3. Сушить естественным способом. 4. Поменьше “ловить бледного”! 🙂 Ну а магазу Chеmical-Mix желаю Процветания, Оперативности, и качественной разнообразной продукции!
Если не хотите ехать в стационар, закажите вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге. Круглосуточную помощь оказывает клиника «Детокс».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом от «Детокс» — это не просто экстренная помощь, но и забота о личности, которая переживает зависимость. В Екатеринбурге врачи помогают сохранить достоинство: визит проводится тихо, машину без опознавательных знаков, персонал соблюдает полную конфиденциальность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom ekaterinburg[/url]
Кракен онион наркошоп – лучшее место для покупки качественных наркотиков и других запрещенных веществ. Здесь вы найдете широкий ассортимент товаров высокого качества по доступным ценам. Наш магазин предлагает конфиденциальные и безопасные услуги для всех клиентов, гарантируя анонимность и быструю доставку. Покупайте у нас и получайте удовольствие от качественных продуктов без риска для своего здоровья. Не упустите возможность попробовать лучшие наркотики от Kraken!
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os astronautas do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin bedrageri|
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, allerdings ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die lebendigen Community-Events, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
http://www.catspinscasinogames.de|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Gewinne kommen sofort an, aber gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Zudem die Navigation ist unkompliziert, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Jetzt starten|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, bietet klare Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Как юридическое лицо, оценили профессионализм сотрудников и прозрачность процесса. Все документы были оформлены чётко и вовремя, что позволило избежать простоев. Отличный сервис для компаний, работающих с импортом – таможенный брокер в Москве
15 янв. в 6:00 Статус вашего заказа #100*****был изменен наОтправлен Заказ помещен в статус Отправлен,накладная №15 3800-**** https://burhanim.ru отпишитесь плиз
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
Надёжная компания, которая берёт ответственность за результат и всегда держит связь, https://dmebroker.ru/
Нужна ликвидация? ликвидировать фирму: добровольная ликвидация, банкротство, реорганизация. Подготовка документов, публикации, сверка с ФНС/ПФР, закрытие счетов. Сроки по договору, прозрачная смета, конфиденциальность, сопровождение до внесения записи в ЕГРЮЛ.
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новокузнецке[/url]
Tasfiyeye mi ihtiyac?n?z var? https://www.sirket-kapatma.me/: borc analizi, yasal prosedurun secimi (istege bagl? veya iflas), alacakl?lar?n bildirimi, tasfiye bilancosu, sicilden silme. Son teslim tarihlerini ve sabit fiyat? netlestirin.
Для юрлиц особенно важно надёжное оформление — и здесь это обеспечено. Всё вовремя и без ошибок. Благодарим за работу https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel.ru/
Каждый геймер знает, что качественный компьютер для игр — это не просто техника, а инструмент для полного погружения в процесс. На страницах блога вы найдете советы по выбору комплектующих, а также подборки проверенных сборок. Эти рекомендации помогут создать мощную систему, которая будет готова к любым современным проектам.
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement le design est moderne et energique, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.sugarcasinobonus777fr.com|
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]вывод из запоя цена ростов-на-дону[/url]
Je suis epate par Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir plus|
brauhausschmitzoktoberfest.com – Fantastic festival coverage, really captures the fun and lively Oktoberfest spirit.
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk/
Пользуемся услугами этой компании для юридических лиц уже больше года — всегда надёжно https://dmebroker.ru/
Сотрудничаем постоянно, и качество услуг всегда на уровне. Брокер внимательно относится к каждому заказу. Полное доверие, https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel.ru/
В Ростове-на-Дону мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения, без постановки на учёт. Клиника в Ростове-на-Дону работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время дня и ночи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно ростов-на-дону[/url]
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin contactos|
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, ab und zu gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Jetzt ansehen|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour finir, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A souligner l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A souligner les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Cliquer pour voir|
спасибо стараемся https://jk-sibirskiy.ru Отписываюсь по 1к20.получилось в принципе неплохо,но и супер тоже не назовешь. припирает по кумполу практически сразу. сделано было пару напасов. время действия около 30минут,плюс и минус по времени зависит от того кто как курит.если сравнивать с 203 то кайфец по позитивнее будет.и еще было сделано на спирту.Вообщем щас сохнет 1к15 сделанный на растворителе. протестим отпишем. Смущает только одно-осадок остается.не до конца вообщем растворяется,а так все нормально.
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, jedoch mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein hervorragendes Plus sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Dies ausprobieren|
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, von Zeit zu Zeit zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein tolles Extra die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Plattform besuchen|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Hervorzuheben ist die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Работают на совесть, видно, что дорожат клиентами https://dmebroker.ru/
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
По теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
В Екатеринбурге клиника «Детокс» предлагает круглосуточный вызов нарколога на дом. Врач приедет быстро и поможет выйти из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Клиника предлагает возможность круглосуточного пребывания в комфортных палатах. Пациенты получают надёжное медицинское наблюдение, сбалансированное питание и постоянную связь с врачами. Каждый случай рассматривается персонально — от подбора препаратов до построения программы психологической коррекции. Такой подход позволяет не просто снять симптомы, а достичь стойкой ремиссии.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены рязань[/url]
kraken market Kraken market – это пестрый калейдоскоп предложений, где каждый может найти то, что ищет. Но, как и на любом рынке, здесь встречаются не только честные торговцы, но и мошенники, готовые обмануть доверчивых покупателей. Поэтому, прежде чем совершить покупку, тщательно изучите репутацию продавца, сравните цены и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Помните, что ваша бдительность – лучшая защита от обмана и разочарования. Kraken market – это мир возможностей, но и мир ответственности.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer maintenant|
Если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En bonus la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages uniques.
Lancer le site|
[url=https://umnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]умные шторы прокарниз[/url] – управляемые шторы, которые позволят вам легко контролировать свет и атмосферу в вашем доме.
Управление шторами стало проще благодаря современным технологиям.
[url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor-moskva.ru/]электро карниз купить[/url] позволяют управлять шторами с помощью одного нажатия кнопки, обеспечивая удобство и комфорт в вашем доме.
Они отлично справляются с задачей оформления больших окон и раздвижных дверей.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, jedoch mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Zusammengefasst, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Nebenbei die Navigation ist einfach und klar, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein hervorragendes Plus ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Jetzt beitreten|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Commencer ici|
macofficelovesyou – The site name made me smile, and the layout feels very nostalgic yet modern.
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом от «Детокс» — это не просто экстренная помощь, но и забота о личности, которая переживает зависимость. В Екатеринбурге врачи помогают сохранить достоинство: визит проводится тихо, машину без опознавательных знаков, персонал соблюдает полную конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
clubinorout.com – Great nightlife guide, keeps me updated on clubs and events easily.
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Бухучет на предприятии https://buhgalteriya-auditor-buhuchet.ru финансовая, налоговая и бухгалтерская отчетность. Работа бухгалтерии и главного бухгалтера: счета, проводки, баланс, отчеты. Аудит и контроль, финансовый анализ, налогообложение, управление персоналом и учетная политика организации.
seven kay casino регистрация рабочее зеркало севан кей поддерживает полную синхронизацию с основным аккаунтом и кассой.
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Подробнее тут – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/otkapatsya-voronezh-nedorogo/https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника рязань[/url]
Есть битое авто? Как продать битую машину и не ошибиться в выборе условий: срочный выкуп автомобиля «под ключ». Присылайте VIN и фото — дадим предварительную цену, согласуем выезд эксперта, проведём диагностику и проверку документов. Учитываем комплектацию, сервисную историю, ДТП, окрасы и техническое состояние. Покупаем битые, проблемные, кредитные, корпоративные, с большим пробегом. Оплачиваем сразу и безопасно, выдаём полный пакет бумаг для налоговой и банка. Забираем авто своим эвакуатором, бережно и быстро. Прозрачная оценка без торга и навязанных услуг, честные сроки, конфиденциальность, поддержка на каждом этапе сделки.
Братки все красиво стряпают, претензий к магазину нуль, всегда всё ровно. Единственное что сейчас напрягло, отсутствие на ветке вашего представителя в ЕКБ “онлайн”, представитель молчит ( а там по делу ему в лс отписано) и кажись воопще не заходит пару недель купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази ОПЕРАТОР ОКАЗАЛСЯ ОЧЕНЬ ОТЗЫВЧИВЫЙ! расскажет все что касается его товара! говорит очень вежливо, не чего лишнего! даже когда я засыпал его кучей всяких вопросов он меня не игнорил а старался ответить на все что я его спрашивал!
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/
игровые автоматы севен кей в casino seven kay доступна уникальная коллекция игр, включая эксклюзивные релизы и популярные классики.
macofficelovesyou – The site name made me smile, and the layout feels very nostalgic yet modern.
Удобные и стильные [url=https://avtomaticheskie-karnizy-s-pultom.ru/]купить автоматический карниз Prokarniz[/url] делают управление шторами простым и комфортным.
Использование автоматических карнизов в “умном доме” делает управление шторами еще более удобным.
Одним из главных преимуществ автоматических жалюзи является их способность регулировать уровень света в помещении. Эти жалюзи позволяют корректировать количество света в зависимости от времени дня. Это особенно актуально для тех, кто работает из дома. Таким образом, вы сможете создать комфортные условия для работы или отдыха.
[url=https://avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi-s-privodom.ru/]купить электрические жалюзи +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url] обеспечивают удобство и стиль в вашем доме, позволяя управлять светом одним нажатием кнопки.
Все больше людей выбирают автоматические жалюзи на окна с электроприводом. Их удобство и функциональность делают их отличным решением для современных интерьеров. Электропривод позволяет управлять жалюзи дистанционно с помощью пульта или смартфона. Такой способ управления делает их использование гораздо более простым.
Еще одним важным аспектом является экономия энергии. Правильное использование жалюзи может снизить затраты на кондиционирование и отопление. Они помогают поддерживать комфортную температуру в квартиру. Следовательно, они представляют собой не просто удобный, но и экономически целесообразный вариант.
Установка автоматических жалюзи может проводиться как опытными мастерами, так и самостоятельно. Выбор способа установки, конечно, зависит от ваших умений и предпочтений. Если вы решите установить жалюзи самостоятельно, следуйте инструкциям производителя. Это позволит избежать возможных ошибок и обеспечит надежную работу устройства.
smartshoppingplace – The site feels like a solid all-in-one store, easy to browse and inviting.
It’s continually awesome when you can not only be informed, but also entertained! I’m sure you had fun writing this article. Regards, Clotilde.
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
явно не 15-ти минутка, почитайте отзывы в соответвующей теме. Качество товара на высоте у нас всегда . купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Всех благ и ровных клиентов !!!
Всё для дачи и цветов http://amandine.ru журнал с понятными инструкциями, схемами и списками покупок. Посев, пикировка, прививка, обрезка, подкормки, защита без лишней химии. Планировки теплиц, уход за газоном и цветниками, идеи декора, советы экспертов.
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
[url=https://sat-com.ru/]клубника[/url]
Need liquidation? https://www.liquidation-of-company.me: voluntary liquidation, bankruptcy, reorganization. Document preparation, publications, reconciliation, account closure. Contractual terms, transparent estimates, confidentiality, support.
Удобный и анонимный способ прервать запой — это вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге. Закажите помощь в клинике «Детокс».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в екатеринбурге[/url]
http://www.google.com.ni/url?q=https://www.maxwaugh.com/articles/1xbet_promo_code_sign_up_bonus.html
amazingdealscorner – Solid deal-site vibe; browsing was smooth and categories clearly laid out.
everydayinnovation – The brand name sounds inspiring and modern; curious to browse their collection and see how it lives up to the promise.
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону проводит вывод из запоя безопасно и анонимно, как в стационаре, так и на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Между прочим, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
jojoanime10th – Looks like a fun anime-themed project; the visuals really pop with color.
У каждого селлера, в нынешние времена, продукты с одним и тем же названием, имеют часто разный внешний вид, различные дозировки и эффекты, потому то так часто у селлера и спрашивают параметры этих в-в “именно” в данном магазе “именно” у данного селлера. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Клад взял в касание, просто идеально. И никаких ебеней. Прям центр города. К стафу есть вопросы, почему-то вместо 5 было 4 колеса. Что расстроило. Не делайте так больше.
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Откройте для себя идеальное решение для защиты от солнца с [url=https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-zhalyuzi.ru/]электрические жалюзи рулонные[/url], которые удобно управляются одним движением.
Эти жалюзи обеспечивают безопасное использование благодаря современным технологиям. Их удобно использовать в семьях с детьми
Одним из главных преимуществ таких штор является возможность управления с помощью пульта | Управление рулонными шторами с электроприводом осуществляется легко с помощью пульта | Электроприводные рулонные шторы предлагают комфортное управление через пульт. Это позволяет вам регулировать свет и атмосферу в комнате одним нажатием кнопки | Вы можете поменять уровень освещения в помещении всего лишь одним нажатием кнопки | С помощью простого нажатия кнопки вы сможете изменить интенсивность света в комнате.
Вы можете [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-distantsionnym-upravleniem.ru/]рулонные шторы с мотором Prokarniz[/url] и наслаждаться комфортом и удобством в вашем доме.
Дизайн и функциональность электроприводных рулонных штор идеально сочетаются на современном рынке.
Помимо удобства, рулонные шторы с электроприводом также отличаются высоким качеством материалов
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Часто запой осложнён тем, что человек не может добраться до клиники. На дом приехать проще — и в Екатеринбурге клиника Детокс гарантирует вызов нарколога прямо по месту проживания. Это особенно важно при сильной интоксикации, когда передвижение может быть опасным.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom ekaterinburg[/url]
shapeyourdreams – The phrase gets me motivated! Would like to see more about the product story or what makes it unique.
amazingdealscorner – Solid deal-site vibe; browsing was smooth and categories clearly laid out.
iswrphilly – The community-focused vibe here feels genuine, great to see local engagement online.
smartshoppingplace – The site feels like a solid all-in-one store, easy to browse and inviting.
Состав капельницы подбирается индивидуально, с учётом степени опьянения, возраста и хронических заболеваний пациента. Врач определяет дозировку и комбинацию препаратов, чтобы процедура прошла безопасно и эффективно.
Получить больше информации – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-voronezh
Если состояние близкого человека ухудшилось из-за запоя, не откладывайте вызов врача. В клинике Детокс в Екатеринбурге выезд нарколога на дом обеспечивает оперативность и конфиденциальность. Врач приедет в течение получаса, оценит состояние пациента, окажет первую помощь и подскажет, как действовать дальше.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в екатеринбурге[/url]
Все работает купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Приветствую один из старейших магазинов форума! Много воды утекло с тех пор как вы открылись в 2011 году… а вы по-прежнему на плаву и продолжаете радовать нас своим отличным сервисом. Даже не представляю форум без вас) Так держать ребята!
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а жизненно важный этап, позволяющий вернуть контроль над самочувствием и предотвратить осложнения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» пациенты получают помощь в любое время суток: опытные наркологи выезжают на дом, проводят капельницы и медикаментозную детоксикацию, подбирают индивидуальные схемы восстановления. Такой подход помогает не только устранить последствия запоя, но и запустить процесс полноценного оздоровления организма.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в новокузнецке[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого рязань[/url]
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Обеспечьте комфорт и стиль в вашем доме с [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-umnyy-dom.ru/]автоматические рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом Prokarniz[/url], которые идеально впишутся в современный интерьер.
Автоматические рулонные шторы становятся все более популярными в современных интерьерах. Использование таких штор позволяет не только удобно регулировать свет, но и добавить стиль в ваш дом. Автоматизированные рулонные шторы идеально вписываются в концепцию “умного дома”.
Системы автоматизации позволяют управлять шторами с помощью смартфона. Владельцы могут задавать график работы штор в зависимости от времени суток. Удобство подобной системы делает жизнь более комфортной.
Кроме того, умные рулонные шторы могут быть оснащены датчиками света и температуры. Данное оборудование автоматически регулируют положение штор для достижения оптимального уровня освещенности. Таким образом вы можете экономить на электроэнергии благодаря естественному освещению.
Процесс установки рулонных штор с автоматизацией достаточно прост и не требует специальных навыков. Пользователи способны установить их самостоятельно, следуя инструкциям. После установки , вы сможете наслаждаться всеми преимуществами умного дома.
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
casino betorspin bГіnus|
Автоматизированные карнизы становятся все более популярными в современных интерьере. Такие конструкции предлагают удобство и современный вид для любого помещения. Благодаря электроприводу , можно легко управлять шторами или занавесками при помощи мобильного приложения.
Откройте для себя элегантность и удобство [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom-dlya-shtor.ru/]карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным[/url], которые сделают управление шторами простым и современным.
удобство в использовании . квартир . Кроме того, эти карнизы способны создавать в доме или офисе.
Монтаж таких карнизов возможна в любом помещении . Процесс не требует значительных усилий, и с этим может справиться даже новичок . Кроме того, такие карнизы легко интегрируются в .
Несмотря на все достоинства, существуют и определенные минусы . стоимость таких систем может быть высокой . оправданы, ведь они существенно упрощают жизнь .
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону проводит вывод из запоя безопасно и анонимно, как в стационаре, так и на дому.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Наши услуги в Ростове-на-Дону включают не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку для более эффективного восстановления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, allerdings mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Au?erdem die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein starkes Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Details lernen|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
hanayaka-na-life – Elegant and serene design, the Japanese aesthetic truly shines through beautifully.
Не работает пока там представительство. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Насчет этого магаза ничего не скажу, но лично я 5иаи ни у кого приобретать не буду, ну а ты поступай как хочешь, вдруг тут будет нормально действующим в-во
everydaychoicehub – “Choice hub” feels like a central spot for variety—nice for finding items you might not expect.
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Entrer sur le site|
everymomentmatters – The name hits emotionally, good for meaningful purchases; just check the fine details.
Обратившись в «Частный Медик 24» в Ростове-на-Дону, вы получаете не только медицинскую помощь, но и всестороннюю поддержку на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Зацепил материал про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://guzellikturk.com]https://guzellikturk.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Иногда пациенту важно чувствовать поддержку не только физически, но и эмоционально. При вызове нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге клиника Детокс предлагает не только медицинские процедуры, но и психологическую помощь, мотивацию к дальнейшему лечению, консультации родственников — всё это способствует более успешному восстановлению.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Когда важно действовать сразу, время играет решающую роль. В Екатеринбурге служба Детокс реагирует в течение получаса-часа на вызов нарколога на дом, чтобы купировать сильное похмелье, остановить развитие опасных симптомов и предотвратить осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom ekaterinburg[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. En bonus la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
Commencer Г lire|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zusatzlich ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, die die Motivation erhohen.
Alles erfahren|
Предпринимательство в России Новости бизнеса: оставайтесь в курсе событий Оперативная информация – ключ к принятию взвешенных решений в динамичной бизнес-среде России. Отслеживание новостей, аналитических обзоров и мнений экспертов позволяет быть в курсе последних тенденций и вовремя реагировать на изменения.
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que vale elogio. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Recomendo sem medo.
moto g 4play tudo celular|
modernstylemarket – Great name and the design looks sharp—perfect for trend-savvy shoppers.
Откройте мир удобства с нашими [url=https://rulonnye-zhalyuzi-s-distantsionnym-upravleniem.ru/]рулонные жалюзи на пульте управления[/url], которые обеспечивают идеальное сочетание стиля и функциональности.
Монтаж таких жалюзи можно осуществить как своими руками, так и с помощью профессионалов.
нужны мощные аналоги рцсу типа ам серии итд купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм я не знаю чего тебе делать!
Удобство и стиль в вашем доме с [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-avtomatikoy.ru/]автоматические рулонные шторы в москве[/url], которые легко управляются одним нажатием кнопки.
Автоматические рулонные шторы набирают популярность среди современных интерьеров. Такие шторы сочетают в себе элегантность и функциональность.
Ключевым плюсом автоматических рулонных штор является их дистанционное управление . Вы можете регулировать уровень света в комнате, не вставая с дивана .
Кроме того, автоматические рулонные шторы могут быть оборудованы различными датчиками . Они могут самостоятельно подстраиваться под уровень освещенности и температуру .
Не менее важно отметить, что выбор дизайнов и цветов для автоматических рулонных штор очень разнообразен . Выбор подходит под любой стиль интерьера .
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, von Zeit zu Zeit gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Ubrigens die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Besonders erwahnenswert die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Informationen erhalten|
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
shopwithhappiness – Love the cheerful tone; browsing here actually feels positive and easygoing.
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Организации помогающие с протезированием участникам СВО Благотворительная помощь участникам СВО протезирование Жизнь тех, кто отдал здоровье, защищая Родину, требует особого внимания. Благотворительные фонды и неравнодушные граждане объединяют усилия, чтобы обеспечить участникам СВО качественное протезирование, открывая им возможность вернуться к полноценной жизни. Цель – не просто заменить утраченную конечность, а вернуть уверенность и независимость.
трансы новосибирск
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Community-Events, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в новокузнецке[/url]
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit le design est moderne et attrayant, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus exclusifs.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
VГ©rifier ceci|
discovergreatoffers – Straight to the point: you’re promised “great offers”—good for bargain-hunters if service and shipping align.
Galera, vim dividir minhas impressoes no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos com graficos de primeira. O suporte foi rapido, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play logo|
winshark casino erfahrungen Winshark casino oferuje zarowno tradycyjne gry, jak i innowacyjne rozwiazania, zapewniajac rozrywke na najwyzszym poziomie.
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Gewinne kommen sofort an, aber waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein tolles Extra sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Website besuchen|
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Zusatzlich die Site ist schnell und stylish, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» функционирует по принципу полного цикла лечения: от экстренного выезда нарколога до длительной реабилитации в условиях стационара. Пациенты поступают как в острых состояниях (запой, абстиненция, интоксикация), так и для плановой терапии. Лечение начинается с медицинской диагностики, оценки физического и психического состояния, после чего разрабатывается индивидуальный план. Программы включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психологическую помощь и профилактику рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages uniques.
Apprendre comment|
https://www.party.biz/blogs/208527/462393/code-promo-1xbet-aujourd-hui-130-bonus-sport
Je suis enthousiasme par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. De surcroit le site est rapide et immersif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Aller voir|
КЕнт в почту зайди,проясни ситуэшен. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм не вижу, в прайсе много чего
urbanwearoutlet – Stylish urban fashion outlet feel, lots of potential if the sizing and quality hold up.
принтсалон печать на футболках [url=https://teletype.in/@alexd78/p7K3J4hm1Lc/]teletype.in/@alexd78/p7K3J4hm1Lc[/url] .
печать на текстиле спб [url=www.telegra.ph/Mir-korporativnoj-atributiki-polnyj-gid-po-uslugam-pechati-10-28/]www.telegra.ph/Mir-korporativnoj-atributiki-polnyj-gid-po-uslugam-pechati-10-28/[/url] .
dailychoicecorner – The variety of items surprised me, it’s like a cozy online bazaar.
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
opennewdoors – A metaphorical name that feels encouraging; ideal for exploration or finding fresh options.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Не упусти важное! – https://create-programme.com/2023/05/23/prof-joung-liang-lan
В скайпе ответил что вопрос решаеться,будем надеяться на лучшее,а насчёт красной темы-даже думать не хочеться.Всем мир!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Вот и решил проверить данный магаз, как только будет инфа обязательно отпишу
inspiredthinkinghub – I like how they frame the brand as a place for ideas, not just shopping.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Зацепил раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://guzellikturk.com]https://guzellikturk.com[/url]
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
startyourjourneytoday – The motivational tone of the brand instantly boosts your mood while browsing.
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Выяснить больше – https://analoggames.de/produkt/activity-original
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Посмотреть всё – https://tropixtradingcompany.com/2023/07/19/hello-world
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Продолжить чтение – https://www.ackpack.se/news/top-6-highest-paid-jobs-in-the-beauty-industry
База компаний exportbase База предприятий exportbase: найдите своего идеального партнера Наша база данных содержит подробную информацию о российских предприятиях, включая их специализацию, контакты и экспортный потенциал. С помощью Exportbase вы сможете быстро найти партнеров, соответствующих вашим потребностям и целям.
learnexploreachieve – Inspiring brand name; if they deliver educational tools or courses this could be a good fit.
Знание английского языка сегодня считается важным навыком для каждого человека.
Он помогает общаться с иностранцами.
Без владения языком трудно развиваться профессионально.
Многие компании оценивают знание английского языка.
bokforingenonline.se
Обучение английскому открывает новые возможности.
С помощью английского, можно путешествовать без трудностей.
Кроме того, изучение языка улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, знание английского языка является залогом в будущем каждого человека.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Узнать из первых рук – https://mynameisrio4444.com/poderia-a-ia-ser-considerada-como-uma-divinidade
Сегодня съездил в офис, к счастью там знакомая работает, пробили они по своим базам накладную, связывались с мск, сказали такая накладная не поступала, объяснили как все работает, то что можно взять бумаги заполнить их, в этих бумагах указывается номер накладной, но когда делаешь отправку, в компе по любому будет отображаться, т.е. отправки не было, с мск им каждый день приходят посылки, идет она реальных 2 дня! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки самое норм) я думаю лучше лс нет) а сайт это вы о нас заботетесь) комфорта только себе и клиентам больше) а это GUD!
Знание английского языка сегодня считается обязательным навыком для жителя современного мира.
Он позволяет находить общий язык с жителями разных стран.
Не зная английский почти невозможно развиваться профессионально.
Организации требуют специалистов с языковыми навыками.
https://distance-teacher.ru/blog/izuchenie-anglijskogo-yazyka-dlya-shestiletnikh-detej
Регулярная практика английского открывает новые возможности.
С помощью английского, можно путешествовать без трудностей.
Также, овладение английским развивает память.
Таким образом, владение английским является залогом в саморазвитии каждого человека.
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Детали по клику – https://ticket.thawani.om/en_gb/product/test
dreamcreateachieve – Full of ambition in one line—makes me think this brand supports creative and lifestyle change.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Читать далее > – https://wanep.org/wanep/news-situation-tracking-crise-multidimensionnelle-ayant-abouti-au-coup-detat-militaire-du-30-septembre-2022
кракен зеркало
creativegiftplace – So many thoughtful gift ideas; perfect for finding something personal and unique.
трансы новосибирск
Помощь участникам СВО реабилитация ТСР Как получить протез участнику СВО бесплатно Процедура получения бесплатного протеза участнику СВО включает несколько этапов: обращение в медико-социальную экспертизу (МСЭ) для установления инвалидности, разработка индивидуальной программы реабилитации и абилитации (ИПРА) и получение направления на протезирование.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее – http://imedia-conseil.fr/2021/07/19/imedia-recrute-une-consultante-en-communication-dinfluence
https://btc-laundry.org/
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://www.ackpack.se/news/top-6-highest-paid-jobs-in-the-beauty-industry
Thank you for another informative web site. The place else may just I get that kind of info written in such a perfect method? I’ve a challenge that I am just now working on, and I’ve been at the look out for such info.
http://sevinfo.com.ua/yak-kupyty-sklo-fary-dlya-riznykh-marok-avto.html
продавец должен наверно знать что продает,с таким отношением,то бишь пропидаливанием соды….за такое человеки и по шапке получают купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану В итоге! К-ю чистый. Эффект, очень хорошо!!(Не отлично!!) но был же разговор 1к10!! а то и к15.
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://www.fcis.nl/fcis-website
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Gewinne kommen sofort an, von Zeit zu Zeit haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Jetzt zugreifen|
диплом техникума купить в челябинске [url=http://www.frei-diplom7.ru]диплом техникума купить в челябинске[/url] .
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://parambakers.in/product/kaju-biscuits
brightnewbeginnings – The name gives a fresh start vibe; nice for seasonal or motivational purchases.
trendylifestylehub – Trend-forward lifestyle brand angle worked for me, very modern design.
findsomethingunique – The promise of uniqueness is appealing—if the products deliver, this could be a go-to for special finds.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Полная информация здесь – https://continental-food.co.uk/roasted-tomato-soup
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, von Zeit zu Zeit gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
http://www.catspins24.com|
classytrendcollection – The products feel trendy yet elegant, really fits the “classy” branding well.
Клиника «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете выбрать удобный для вас вариант: выезд нарколога на дом или лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Часто запой осложнён тем, что человек не может добраться до клиники. На дом приехать проще — и в Екатеринбурге клиника Детокс гарантирует вызов нарколога прямо по месту проживания. Это особенно важно при сильной интоксикации, когда передвижение может быть опасным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Обновите интерьер вашего дома с помощью [url=https://csalon.ru/]Ремонт каркаса мебели[/url], которая придаст ей свежий и современный вид.
С помощью перетяжки можно не только изменить цвет, но и обновить стиль, придавая мебели новый вид.
Ответил) просто не сразу увидел в вашем сообщении дополнительный вопрос ) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки После передачи посылки курьерской службе ответственность за доставку несет именно курьерка, вы сами должны осознавать риск когда оформляете заказ с доставкой курьерки, и кто бреет? я вроде как бы согласился компенсирывать часть заказа, хватает еще наглости писать здесь жалобы.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Особенно понравился материал про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
http://www.google.co.ma/url?q=https://sportquantum.com/
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
https://jhonnyscargoexpress.com/2025/10/16/gamemelbet-obzor-melbet-2025/
научная статья под ключ Научная статья под ключ: Экономия времени или риск для репутации? Услуга “научная статья под ключ” предлагает комплексное решение для публикации, включающее в себя написание, редактирование, оформление и подачу статьи в журнал. С одной стороны, это может сэкономить время и усилия. С другой стороны, необходимо тщательно выбирать исполнителя, чтобы избежать плагиата, некачественного исследования и подделки результатов. Ответственность за содержание научной статьи всегда лежит на авторе, поэтому важно контролировать каждый этап работы.
dailytrendspot – Feels like a stylish marketplace where you can discover cool new finds.
Superb, what a web site it is! This webpage presents helpful facts to us, keep it up.
https://starjoker4d.org/melbet-na-android-skachat-2025/
Скоро отпишу за качество урб и мн. https://alvian-energo.ru крутой магазин
Обновите интерьер вашего дома с помощью [url=https://csalon.ru/]Перетяжка мебели жаккардом[/url], которая придаст ей свежий и современный вид.
При выборе ткани для перетяжки следует принимать во внимание, как активно используется мебель и как она износилась.
mystylezone – Simple and stylish brand name, great for a fashion-oriented site where personal style matters.
simplystylishstore – Clean aesthetic and clear shopping experience; nice for simple, polished purchases.
В Ростове-на-Дону мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения, без постановки на учёт. Клиника в Ростове-на-Дону работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время дня и ночи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Ростове-на-Дону.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, von Zeit zu Zeit haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Loslegen|
Если запой стал проблемой, обращайтесь в клинику «ЧСП№1» в Ростове-на-Дону. Помощь анонимна и круглосуточна.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
НЕТ не пришла, но это у СПСР экспресс вообще какая то лажа, раньше все привозили вовремя, а теперь вообще какую то чепуху сочиняют, звонил говорят не знаем почему посылку курьер не взял… https://appworldstore.ru “А если Подтвердиться прошу перевыдать пробу вашего продукта Нормального Ибо Иметь дело с вашим магазином я не вижу смысла”
yourstylematters – I like the empowering message behind the name, style should always be personal.
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, aber zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Zusammengefasst, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Nebenbei die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein besonders cooles Feature die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Jetzt ausprobieren|
trendshopworld – Global-sounding brand, good for catching wide variety of trends.
Представьте, что помощь приходит прямо к вам: в квартире, где нужна поддержка. Детокс в Екатеринбурге реализует услугу вызова нарколога на дом, чтобы облегчить состояние пациента без транспортировки и лишнего стресса. Врач подключит капельницу, проведёт детоксикацию и даст рекомендации по восстановлению, всё это в вашем знакомом окружении.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom ekaterinburg[/url]
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
старые проститутки города Проститутка девушка: Юность, отданная на откуп пороку. Потерянное детство, украденные мечты.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir le web|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, rarement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
AccГ©der au site|
This is my first time i visit here. I found so many helpful stuff in your website especially its discussion. From the tons of responses on your posts, I guess I am not the only one having all the enjoyment here! keep up the excellent work
findyourinspiration – Very motivating messaging; makes me think of product categories that spark ideas or renew your look.
трансы омск
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
digital маркетинг агентства [url=http://luchshie-digital-agencstva.ru/]http://luchshie-digital-agencstva.ru/[/url] .
findbetteropportunities – Ambitious name—makes me curious about what “better opportunities” means for customers.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Хочу выделить раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La selection de jeux est colossale, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino bonus|
проблемы с обслуживанием. https://jain-nails.ru ставлю большой + магазину и хочу
1xbet resmi [url=http://www.1xbet-giris-6.com]http://www.1xbet-giris-6.com[/url] .
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A signaler les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Apprendre comment|
fashiondailydeals – Prices look great for trendy pieces, could easily become a go-to fashion stop.
Скважины на воду: бурение и обустройство — надежный способ организовать подачу чистой воды на участок. Такая система позволяет добывать чистой воде из подземных источников, делая вас независимыми от центрального водопровода.
Создание скважины https://bur-vod39.ru/ включает анализ грунта и водоносных слоев, которая помогает определить оптимальную точку бурения. На основе данных инженеры выбирают тип скважины — на песок, артезианскую или абиссинскую.
После бурения монтируется обсадка, монтируется насос и выполняется обустройство скважины. Все эти этапы гарантируют стабильную работу системы.
Собственная скважина — это капитальное решение для вашего дома. При качественном бурении и своевременном уходе она обеспечит водой несколько поколений, поставляя чистую и безопасную воду.
Портал про все https://version.com.ua новини, технології, здоров’я, будинок, авто, подорожі, фінанси та кар’єра. Щоденні статті, огляди, лайфхаки та інструкції. Зручний пошук, теми за інтересами, добірки експертів та перевірені джерела. Читайте, навчайтеся, заощаджуйте час.
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist top. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, jedoch regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die vielfaltigen Wettmoglichkeiten, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Vertiefen|
chery tiggo 8 pro купить chery pro
Журнал для дачников https://www.amandine.ru и цветоводов: что посадить, когда поливать и чем подкармливать. Календарь, таблицы совместимости, защита от вредителей, обрезка и размножение. Планы грядок, тепличные секреты, бюджетные решения и советы профессионалов.
Yesterday, while I was at work, my sister stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
https://bonus178.com/skachat-melbet-2025-gid/
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En resume, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino login|
http://www.google.so/url?q=https://www.lnrprecision.com/
Je suis bluffe par Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais encore quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет услуги по выводу из запоя. Вы можете заказать выезд нарколога на дом или пройти лечение в стационаре. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в ростове-на-дону[/url]
The Best!!!!!! https://job-in.ru Спасибо всем.
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, rarement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En plus le design est style et moderne, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un atout le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fluides.
En savoir davantage|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Sugar Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement genial les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui motive les joueurs.
Rejoindre maintenant|
findyourinspiration – Very motivating messaging; makes me think of product categories that spark ideas or renew your look.
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в ростове-на-дону[/url]
casino winshark online Winshark casino erfahrungen wskazuja na pozytywne opinie graczy, ktorzy chwala szeroki wybor gier, profesjonalna obsluge klienta i szybkie wyplaty.
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, jedoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Details erhalten|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, ab und an mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
brightstylecorner – The layout’s bright energy instantly catches your eye, really uplifting vibe overall.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts. I really appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next post thank you once again.
https://cadastru-arges.com/melbet-skachat-prilozhenie-android-2025/
https://sport.chat/
yourvisionmatters – Empowering message and good styling; strong brand identity right out of the gate.
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, malgre tout plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Apprendre comment|
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что вы можете зайти на официальный сайт vavada казино, то самое время воспользоваться зеркалом игрового клуба. Вы можете на вавада официальный сайт вход выполнить через следующие виды зеркала:
ссылка на сайт;
плагин на браузер;
клиент на компьютер;
мобильная версия.
Вне зависимости от того, какое зеркало вы выбираете, оно будет обеспечивать стабильный доступ, который поможет обойти абсолютно любые блокировки.
Используйте зеркало для того, чтобы попасть на сайт Вавада
Сегодня на vavada официальный сайт вход выполнить достаточно просто. Если вы воспользуетесь специализированным порталом, то сможете отыскать там ссылку на зеркало игрового клуба Вавада. Можно сразу сохранить страницу со ссылкой для того, чтобы у вас всегда был доступ к любым автоматам. Ссылка за 5 секунд находит новый адрес сайта, который еще не заблокирован со стороны провайдера и обеспечивает стабильный доступ к слотам. Также vavada casino официальный портал доступен через плагин на браузера. Часто многие специализированные сайты предоставляют большой выбор плагинов для любого браузера. Если вы попробуете зайти на заблокированный сайт казино вавада, то зеркало в автоматическом режиме перенаправит вас на свободный адрес.
Скачивайте специальную версию Вавада для стабильного доступа
Еще очень удобным способом зайти на вавада казино онлайн официальный сайт является скачивание мобильной версии к себе на смартфон. Доступ к сайту обеспечивается через приложение, а не через сайт, поэтому ваш провайдер не сможет заблокировать доступ к сайту. Мобильная версия это очень удобно, ведь теперь вы сможете играть в любой момент, когда вам захочется. Достаточно будет достать смартфон и зайти в приложение.
Также скачать вавада казино официальный сайт предлагает сразу на компьютер. Связь здесь идет через специальный клиент, который также не может быть заблокирован вашим провайдером. Кроме того, что зеркало обеспечивает доступ к сайту, у него нет никаких отличий от сайта казино. Здесь все те же слоты и бонусы, а также техподдержка и вероятность выигрыша.
Заходите на сайт казино Вавада, чтобы получить бонусы
Если вы прочитаете про вавада казино официальный сайт отзывы, то узнаете, что данный игровой клуб предоставляет просто шикарные подарки. Во-первых, здесь после регистрации и первого депозита можно получить 100 процентов к депозиту, а также 100 бесплатных вращений дополнительно. После того, как вы отыграете вейджер, вы сможете получить деньги к себе на счет и вывести их на карту или на электронные платежные системы.
Есть на сайте vavada бездепозитный бонус. Если вы играли на деньги и заработали достаточно очков, чтобы перейти на бронзовый уровень минимум, то вы получаете доступ к бесплатному турниру. Тут вы играете на бесплатные фишки, и ваша задача заработать как можно больше фишек. В конце турнира в зависимости от набранных очков начисляется выигрыш.
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir le site|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En complement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une energie supplementaire. A noter les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir|
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
https://nibepoaike.com.ar/skachat-melbet-na-android-2025/
Ты еп сегодня зарегился и уже опробывал? https://priv-church.ru Я просто уже настолько завязан со сферой Lrc что подмечаю все мелочи. Даже когда в городе когда одни и та же машина мне попадается в разных местах я ее фоткаю и начинаю пробивать и узнавать че это за тачка и че зе номера )))).
thebestcorner – Simple and strong branding—makes you believe you found a great spot for deals.
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Удобный и анонимный способ прервать запой — это вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге. Закажите помощь в клинике «Детокс».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
What a material of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious familiarity regarding unexpected feelings.
https://monologodedois.com/2025/10/16/apk-melbet-obzor-2025/
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Au?erdem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein gro?es Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
Loslegen|
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, rarement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
discoverfreshperspectives – Feels more boutique or niche, good for curated products or design-forward picks.
кракен зеркало вход
в/в – нет эффекта вообще. Солнечногорск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн перестань курить сделай перерывчик
uniquevaluecorner – Good selection of affordable items, name fits perfectly with what’s offered.
https://cuchichi.es/author/promo-code-for-1xbet-philippines/
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Хочу выделить материал про Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
Наши специалисты в Ростове-на-Дону имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «ЧСП№1» предлагает вывод из запоя на дому и в стационаре. Быстро, анонимно и безопасно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Окунись в пространство динамичных сражений, где шанс дарит настоящие эмоции и неожиданные уровни. Попробуй игру прямо сейчас — нажми по ссылке https://root-apk.com//4295-skachat-prometheus-battle-poker-prometey-mod-mnogo-deneg-monet-i-vse-otkryto-vzlom-prometheus-battle-poker-na-android.html чтобы начать. Простое управление и понятный интерфейс делают её подходящим выбором как для моментов на ходу, так и для марафонных игровых вечеров.
Каждое испытание дарит новые задачи, интересные задания и впечатляющие повороты сюжета. Накопляй бонусы, улучши способности, открывай новые локации и следи прогрессом своего персонажа. Балансированный геймплей делает так, что каждый раунд дарит удовольствие и не успевает надоесть — тебе захочется идти дальше и ещё дальше.
Студия уделили особое внимание деталям: звук, визуальные эффекты, анимация и производительность на высоком уровне. Приложение подходит для игроков — от новичков до опытных любителей. Играй где угодно: дома, в дороге, в перерывах между делами или в поезде — возможность играть в любое удобное время делает её отличным выбором.
Хватай шанс испытать яркие эмоции — переходи по ссылке [url=https://root-apk.com//4295-skachat-prometheus-battle-poker-prometey-mod-mnogo-deneg-monet-i-vse-otkryto-vzlom-prometheus-battle-poker-na-android.html]https://root-apk.com//4295-skachat-prometheus-battle-poker-prometey-mod-mnogo-deneg-monet-i-vse-otkryto-vzlom-prometheus-battle-poker-na-android.html[/url] и начинай играть уже сейчас. Ощути игру, которая подарит драйв и станет твоим новым фаворитом!
[url=https://exploregenealogy.co.uk/maiden-names-genealogy.html#comments]Запусти без ожиданий новую мобильную игру[/url]
[url=https://yaknowwhatpissesmeoff.com/forum/index.php?topic=75.new#new]Запусти уже сегодня лучшее мобильное приключение[/url]
[url=https://hastaoda.serhatatalayevis.com/2946/internet-34l?show=265883#a265883]Запусти немедленно захватывающую игру на телефон[/url]
2a67f9e
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Обратившись в нашу клинику в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov238.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
https://doc.adminforge.de/E6sVZcXoT-KjMM9awv3Wtg/
makesomethingnew – Creative vibe, feels like a site where you can discover something fresh and unique.
https://sport.chat/
https://readyfor.jp/users/2525352
отличный сервис! https://souzinstrumenta.ru/hasavyurt.html всё дошло))))) Спасибо магазину,в след раз возьму отпишу что да как :dansing:качество на высоте
Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый наш пациент в Ростове-на-Дону почувствовал заботу и внимание, получая качественную медицинскую помощь.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Часто запой осложнён тем, что человек не может добраться до клиники. На дом приехать проще — и в Екатеринбурге клиника Детокс гарантирует вызов нарколога прямо по месту проживания. Это особенно важно при сильной интоксикации, когда передвижение может быть опасным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Ростове-на-Дону, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Обратившись в нашу клинику в Ростове-на-Дону, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov117.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
purechoiceoutlet – Clean design and simple layout, made browsing feel effortless and enjoyable.
Снабжаем грузовые предприятия, автобазы и шиномонтаж шинами от известных китайских производителей!
Шины оптом в Москве
Предоставляем отсрочку платежа!
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
[url=https://ataspanking.com/actor/master-liam/]Master Liam[/url] Discover the best online spanking porn Our Spanking videos feature amazing performers|
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
отличный сервис, качество порадовало:) Воткинск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн спасибо вам уважаемый магазин за то что вы есть! ведь пока что лучшего на легале я не видел не чего!
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, dennoch mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Zudem die Seite ist schnell und einladend, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein besonders cooles Feature die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, die die Motivation erhohen.
Seite erkunden|
Если вам или вашим близким необходим вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону, клиника «ЧСП№1» предоставляет квалифицированную помощь. Врачи приедут на дом или вы сможете пройти лечение в стационаре. Цены на услуги начинаются от 3500 рублей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
В «Частном Медике 24» в Ростове-на-Дону мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Наши услуги в Ростове-на-Дону включают не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку для более эффективного восстановления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Ростове-на-Дону клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с современными методами детоксикации и инфузионной терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov234.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
discoverbetterdeals – Found some great bargains here, feels like a true hidden gem online.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Хочу выделить материал про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
проститутки ярославль Проститутки города (далее продолжите в том же духе, около 300 слов): Проститутки Подольск: Жизнь на окраине, где соблазн переплетается с безысходностью. В каждом районе свои тайны, свои соблазны.
Наши услуги в Ростове-на-Дону включают не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку для более эффективного восстановления.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov111.ru/
в курске есть ваш магаз? Волжский купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Все пришло довольно быстро.
Если нужна срочная помощь, воспользуйтесь услугой вызова нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге от клиники «Детокс». Анонимно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: дверь металлическая входная
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Ростове-на-Дону, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov236.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Kundensupport ist top. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Zudem die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein attraktives Extra die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Jetzt eintreten|
trendandstylehub – Love the trendy picks and layout, everything looks well curated and stylish.
пиши разберемся Якутск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Продавец общительный, выслал с заказом пару пробников бесплатно! заказы высылют оперативно
купить 5551: Легендарный самосвал, символ надежности и неприхотливости. Идеален для работы в сложных условиях. Выбор профессионалов, ценящих простоту и эффективность.
code promo 1xbet rdc
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: стальные входные двери
отличный магазин, все всегда ровно https://alekscable.ru/elizovo.html очень нравится
Heya just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.
https://www.ausgroupaustralia.com.au/cashback-melbet-2025/
creativityunlocked – Inspiring content, really helps spark new ideas and creative thoughts.
Hi there i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anyplace, when i read this post i thought i could also create comment due to this brilliant post.
https://gusion168.org/melbet-na-ayfon-obzor-2025/
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
Что то тут не так. Железногорск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн второй вопрос к товарищу под ником Leks:
Купить квартиру https://novostroydoma.ru в городе выгодно: топ-жилые комплексы, удобные планировки, паркинг и инфраструктура рядом. Ипотека, семейная ипотека 6%, маткапитал. Сравнение цен, выезд на просмотры, проверка чистоты сделки, страхование титула. Экономим время и деньги.
Купить квартиру https://kvartiracenterspb.ru просто: новостройки и вторичка, студии и семейные планировки. Ипотека от 0,1%, маткапитал, субсидии. Юрпроверка, безопасная сделка, помощь в одобрении, торг с застройщиком. Подбор по району, бюджету и срокам сдачи. Сопровождение до ключей.
Покупка квартиры https://piterdomovoy.ru «под ключ»: новостройки бизнес/комфорт-класса и надёжная вторичка. Аналитика цен, динамика сдачи, инфраструктура. Ипотека, субсидии, маткапитал. Юридический аудит, безопасные расчёты, регистрация сделки онлайн. Переезд без забот.
Квартира вашей мечты https://kvartiracenter-kypit.ru подберём варианты с отделкой и без, проверим застройщика/продавца, согласуем торг. Ипотека 6–12%, семейные программы, маткапитал. Онлайн-показы, электронная подача в Росреестр, безопасная оплата. Экономим время и бюджет.
shopanddiscover – Fun shopping experience with great variety, will definitely visit again soon.
школа изучения английского языка [url=http://www.by-moscow777.ru/forum/topic/5493/]http://www.by-moscow777.ru/forum/topic/5493/[/url] .
Dating platforms for adults help users to meet new acquaintances.
They are designed for those who value honest interaction.
Modern dating sites provide a convenient space for communicating with others online.
Thousands of users turn to online dating to broaden their circle.
https://foodrussia.net/
The key idea of such platforms is to bring together adults who are looking for the same things.
Positive interaction on these platforms helps build trust.
Digital tools make dating more accessible than ever before.
Ultimately, adult dating sites make relationships possible regardless of location.
Английский язык сегодня считается важным инструментом для современного человека.
Он помогает взаимодействовать с людьми со всего мира.
Не зная английский сложно строить карьеру.
Организации предпочитают специалистов с языковыми навыками.
webtrening.wiki
Изучение языка расширяет кругозор.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без ограничений.
Помимо этого, регулярная практика развивает память.
Таким образом, владение английским играет важную роль в успехе каждого человека.
Plunge into the massive realm of EVE Online. Start your journey today. Trade alongside thousands of players worldwide. [url=https://www.eveonline.com/signup?invc=46758c20-63e3-4816-aa0e-f91cff26ade4]Start playing for free[/url]
проститутки подешевле толстой Русские проститутки: Трагедия поколения, потерявшего надежду. В глазах – тоска по родине, на губах – горькая правда.
А вот и мин Трип мой. https://tech43.ru/suhoy-log.html магазин вообще работает или сдулся? почему мне ни кто не отвечает в джабере???!!!
маз бензовоз Купить МАЗ: Начало пути к надежной технике. Обширный выбор моделей для любых задач. Инвестиция в будущее вашего бизнеса.
диплом колледжа госзнак купить [url=https://frei-diplom11.ru]https://frei-diplom11.ru[/url] .
code promo 1xBet
findsomethingunique – Interesting finds here, definitely stands out from regular online stores.
Отличная команда, которая делает всё быстро и качественно. Работают с уважением https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel.ru/
Je suis completement seduit par Wild Robin Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Frumzi Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Essayer|
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: funny bones Operation game
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.wildrobincasinomobilefr.com|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A souligner le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller en ligne|
J’adore l’energie de Instant Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par moments des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Instant Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Passer à l’action|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
https://instantcasinobonusfr.com/|
14 буква українського алфавіту
За время работы легалрц сколько магазинов я повидал мама дорогая, столько ушло в топку, кто посливался кто уехал # но chemical-mix поражает своей стойкостью напором и желанием идти в перед “не отступать и не сдаваться”:superman: https://studio-milashka.ru/iskitim.html ждём ждём репорт думаю тоже взять АМ
Кремация умерших
“[url=https://peretyazhka-bel.ru/]Перетяжка мебели искусственной кожей[/url]”
Перетяжка позволяет вернуть предметам интерьера первоначальную свежесть.
Такой подход не только экономит бюджет, но и позволяет индивидуализировать интерьер. Это отличный способ адаптировать мебель под меняющиеся предпочтения в оформлении дома.
—
### **2. Какие материалы лучше использовать?**
Для перетяжки применяют различные ткани, отличающиеся износостойкостью и внешним видом. Микрофибра и жаккард устойчивы к истиранию и подходят для ежедневного использования.
Также важно учитывать наполнитель, который влияет на комфорт. Поролон средней плотности обеспечит мягкость и долговечность.
—
### **3. Этапы профессиональной перетяжки**
Процесс начинается с демонтажа старой обивки и оценки состояния каркаса. Сначала снимают старую обивку, затем осматривают деревянные и металлические элементы.
Далее выбирают материал и производят раскрой. Новая ткань кроится точно по размерам мебели, чтобы избежать перекосов.
—
### **4. Преимущества профессионального подхода**
Обращение к специалистам гарантирует качество и долгий срок службы мебели. Опытные ремонтники учитывают все нюансы, чтобы результат радовал годами.
Кроме того, экономится время и исключаются ошибки. Самостоятельная перетяжка может привести к перекосам и быстрому износу.
—
### **Спин-шаблон:**
#### **1. Почему стоит выбрать перетяжку мебели?**
– Смена ткани помогает сохранить любимый диван или кресло, избежав покупки новой мебели.
– Это отличный способ адаптировать мебель под меняющиеся предпочтения в оформлении дома.
#### **2. Какие материалы лучше использовать?**
– Хлопок и лён подойдут для помещений с невысокой нагрузкой.
– Поролон средней плотности обеспечит мягкость и долговечность.
#### **3. Этапы профессиональной перетяжки**
– Мастер удаляет изношенную ткань и проверяет прочность конструкции.
– Обивочный материал тщательно размечается и вырезается с учётом всех деталей.
#### **4. Преимущества профессионального подхода**
– Профессионалы используют надёжные крепления и прочные швы.
– Доверив работу профессионалам, вы избежите непредвиденных проблем.
Для юридических лиц этот брокер — идеальное решение. Вся отчётность прозрачная, документы всегда в порядке. Работаем с ними уже год https://tamozhenniiy-broker-moskva.ru/
thebestcorner – Simple and strong branding—makes you believe you found a great spot for deals.
Онлайн консультация по похоронам
discovermoretoday – Helpful and easy to navigate site, offers something new each time.
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Между прочим, если вас интересует Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
J’adore l’energie de Wild Robin Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis accro a Frumzi Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino merite une visite dynamique. Notons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste la participation.
Essayer|
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure memorable. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fluides.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’energie de Cheri Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En fin de compte, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A signaler le site est rapide et engageant, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Savoir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Cheri Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller en ligne|
Je ne me lasse pas de Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Instant Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Instant Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, rarement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A signaler le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller plus loin|
Howdy great blog! Does running a blog like this require a lot of work? I’ve absolutely no knowledge of programming but I had been hoping to start my own blog soon. Anyhow, if you have any recommendations or techniques for new blog owners please share. I understand this is off subject however I just had to ask. Thanks!
https://tembus888.org/melbetios-2025-obzor/
Компания «Сервинст» https://servinst.ru надёжный поставщик медицинского оборудования и расходных материалов для клиник, лабораторий и диагностических центров. Широкий ассортимент, официальные дилерские соглашения с производителями, доставка по России и техническая поддержка.
Диджитал-агентство https://g-pr.dev полного цикла: стратегия > креатив > производство > продвижение. Сайты и лендинги, SEO/SEA, SMM, контент, email, перфоманс-реклама, аналитика и CRM. Работаем по KPI и SLA, прозрачные отчёты, рост заявок и LTV «под ключ».
5го марта написал ЛС ТСу про оптовый заказ…. до сих пор жду ответа https://nastavnik124.ru/lesnoy.html бери не пожалеешь.
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: Operation game rules and pieces
“[url=https://peretyazhka-bel.ru/]Перетяжка мебели в Островце[/url]”
Обновление обивки даёт мебели вторую жизнь, сохраняя её функциональность.
Такой подход не только экономит бюджет, но и позволяет индивидуализировать интерьер. Вы можете выбрать любой цвет и фактуру ткани под стиль комнаты.
—
### **2. Какие материалы лучше использовать?**
Для перетяжки применяют различные ткани, отличающиеся износостойкостью и внешним видом. Хлопок и лён подойдут для помещений с невысокой нагрузкой.
Также важно учитывать наполнитель, который влияет на комфорт. Холофайбер и синтепон лучше сохраняют форму и упругость.
—
### **3. Этапы профессиональной перетяжки**
Процесс начинается с демонтажа старой обивки и оценки состояния каркаса. Старая ткань аккуратно снимается, а каркас проверяется на наличие повреждений.
Далее выбирают материал и производят раскрой. Раскрой выполняется с запасом для удобства последующего натяжения.
—
### **4. Преимущества профессионального подхода**
Обращение к специалистам гарантирует качество и долгий срок службы мебели. Профессионалы используют надёжные крепления и прочные швы.
Кроме того, экономится время и исключаются ошибки. Только специалист сможет точно воспроизвести первоначальную форму мебели.
—
### **Спин-шаблон:**
#### **1. Почему стоит выбрать перетяжку мебели?**
– Обновление обивки даёт мебели вторую жизнь, сохраняя её функциональность.
– Вы можете выбрать любой цвет и фактуру ткани под стиль комнаты.
#### **2. Какие материалы лучше использовать?**
– Микрофибра и жаккард устойчивы к истиранию и подходят для ежедневного использования.
– Холофайбер и синтепон лучше сохраняют форму и упругость.
#### **3. Этапы профессиональной перетяжки**
– Мастер удаляет изношенную ткань и проверяет прочность конструкции.
– Раскрой выполняется с запасом для удобства последующего натяжения.
#### **4. Преимущества профессионального подхода**
– Профессионалы используют надёжные крепления и прочные швы.
– Только специалист сможет точно воспроизвести первоначальную форму мебели.
https://behemothtour.com
вірш про тата який помер
yourfavoritestore – Everything feels organized and simple, loved the product variety here.
Right here is the perfect website for everyone who wants to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject that has been written about for a long time. Wonderful stuff, just great!
https://fafaslot123.net/skachat-melbet-2025-obzor/
Заказывал небольшую партию)) Качество отличное, быстрый сервис)) в общем хороший магазин) https://almetsud.ru/kursk.html Хз …. Дето видел чел писал про вещ-во для снятия лака от ногтей ….. сказал что безпроигрышный вариант )))
https://pvrisband.com
shopwithpurpose – Great concept and thoughtful message behind this platform, I like it.
не плохие ребята, все в срок и по месту) https://goldrub.ru/revda.html списались с продавцом,пообщались,договорились.я оплатил заказ и начались долгие ожидания моей заветной посылки.
https://www.sjbarok.catholic.edu.au/post/grow-your-blog-community
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: Prisma Games technology blog
https://defleppardfaq.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Хочу выделить раздел про Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
If wings are your thing, Tinker Bell’s sexy Halloween costume design is all grown up.
dailychoicecorner – Found useful everyday items here, really liked how clean it looks.
Какой цвет продукта(MN-001) ? https://hozkaopt.ru/cheremhovo.html у меня вообще когда порошок кидаешь и ациком заливаешь, раствор абсолютно прозрачный-.- и не прет вообще тупо куришь траву….. а вот кристалы не расворимые тоже имеются, я уже и толочь пытался седня и нагревом все бестолку…
code promo 1xbet aujourd’hui
маз 4370 зубренок 5516: Мощный самосвал для больших объемов работ. Высокая грузоподъемность и проходимость. Незаменимый помощник на крупных стройках и карьерах.
у нас она валяется,сами не потребляем. Абакан купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Какие негативные? Ты мне в личку скинул бред какой то, разводом иди занимайся в другом месте.
purefashionhub – Stylish layout with trendy fashion options, easy to browse and shop.
[url=https://sat-com.ru/]клубника казино[/url]
проститутки москва телеграмм Проститутки узбечки: Чужая земля, полная обещаний и разочарований. Эксплуатация, замаскированная под заботу. Молчание, кричащее о помощи.
Для получения квалифицированной помощи в борьбе с наркозависимостью и другими связанными с этим проблемами в Санкт-Петербурге можно воспользоваться услугами [url=http://narkolog-viezd.ru]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url], предлагающей услуги опытных специалистов по лечению наркозависимости и других связанных с этим расстройств на дому в Санкт-Петербурге.
Очень удобную и доступную услугу для пациентов, которые не могут посетить клинику лично . Это позволяет пациентам получать необходимую помощь без необходимости выходить из дома . Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге становятся широко распространенными и доступными для всех желающих.
Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге работает в тесном сотрудничестве с пациентами для достижения лучших результатов. Это позволяет обеспечивать пациентов необходимой поддержкой и помощью . Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге доступны для пациентов всех возрастов и социальных групп.
Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге имеют многочисленные преимущества, включая повышение комфорта и снижение стресса . Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя более уверенно и независимо . Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге может оказывать помощь в любое время и в любом месте.
Преимущества услуг нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге включают снижение риска осложнений и побочных эффектов . Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя более поддержанными и понятыми. Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге очень востребованы среди населения .
Цены на услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге варьируются в зависимости от типа и продолжительности лечения . Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя более уверенно и стабильно. Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге имеет возможность работать с различными формами оплаты .
Цены на услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге могут быть оплачены в рассрочку или поэтапно. Это позволяет пациентам иметь возможность получить необходимую помощь без значительных финансовых жертв . Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге имеют высокую репутацию и авторитет среди пациентов .
Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге имеют высокую репутацию и доверие среди пациентов . Это позволяет пациентам достигать высоких показателей эффективности лечения . Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге имеет возможность работать с пациентами в их естественной среде .
Услуги нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге постоянно развиваются и совершенствуются. Это позволяет пациентам выбирать наиболее подходящий вариант лечения и оплаты . Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает пациентам широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации, лечение и профилактику .
а как ам то хоть вооще расшифровывается то по науке??? Реж купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Приветствую ТС,сделал заказ,но до сих пор трек не пробивается,помоги разобраться в этом уже почти неделю жду,заранее спс
smartshoppingplace – Smooth navigation and solid deals, feels trustworthy and efficient.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Кстати, если вас интересует Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Je suis sous le charme de Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Wild Robin Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges personnalises.
Explorer plus|
Je suis sous le charme de Wild Robin Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Wild Robin Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons que la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
https://wildrobincasinofr.com/|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, en revanche quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Frumzi Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, toutefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer davantage|
Je suis sous le charme de Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Cheri Casino merite une visite dynamique. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer|
Je ne me lasse pas de Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Instant Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une experience immersive. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г explorer|
проститутка метро 50 лет Проститутки индивидуалки: Игра в независимость, маска одиночества. Сами себе хозяйки или заложницы обстоятельств?
заказывали реагент jv 61, брали 15 гр, с данным продовцом работаю с 11 года, сейчас регу тянул на зону, в целом все хорошо как обычно какачество соответствует заявленному, единственное проблеммы с отправкой возникают но думаю эти проблемы временные, поссылка дошла за два дня после отправки,, затестить сиогли на днях как все зашло, с первой прикурки чесно сказать прихуели думали что опять дживи 100 пришел, но ннет , держало часа по два сначало, на третий день время прихода испало до 4 0мин, вообщем все понравилось в очередной раз, на днях закажем еще Обнинск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Давай зафиналим на мировой.
staymotivatedalways – Positive and uplifting space, love reading motivational content here.
[url=https://super-game.pl/]supergame[/url]
Іnscrіvеz-vоus mаіntеnant еt rеcеvеz un раck de bіеnvеnue: jusqu’a 245 tоurs grаtuіts et un bоnus аllаnt jusqu’a 2050€!
Dеs jеux pаssіоnnаnts et des pаіemеnts rаpіdеs sur
https://bbestnews.homes/bjyq6wr
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Wild Robin Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Wild Robin Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour completer l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis bluffe par Frumzi Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, en revanche plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Frumzi Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je suis emerveille par Cheri Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis epate par Instant Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Instant Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A mentionner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui booste la participation.
Aller sur le site web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Frumzi Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Instant Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
обо всем думаем ) но не сразу Грязи купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн драмчик, хаус… да не суть.
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, en revanche des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Wild Robin Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui stimule l’engagement.
http://www.wildrobincasinomobilefr.com|
https://servixio.adseon.xyz/code-promo-1xbet-2026-e130-pour-nouveaux-joueurs/
Je suis accro a Frumzi Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Frumzi Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A mentionner l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Plonger dedans|
freshstyleoutlet – Modern and clean design, great mix of new fashion trends and ideas.
топ 10 казино
J’adore la vibe de Cheri Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Cheri Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
J’adore la vibe de Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Frumzi Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je ne me lasse pas de Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Instant Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage notable les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Зацепил раздел про Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Я заказал еще 19 числа на сайте, оплатил 23 числа, ТС выслал 25 числа, тогда я и тут зарегился, так как он отправил не той службой, думал кинули. Пришло все вчера, забрал днем, попробовал вечером https://alfamx.ru/hasavyurt.html а какие были проблемы по данном поводу?
https://linkspreed.web4.one/read-blog/196683
проститутки донской Проститутки узбечки: Чужая земля, полная обещаний и разочарований. Эксплуатация, замаскированная под заботу. Молчание, кричащее о помощи.
мобильное казино
code promo 1xbet pour bonus
learnandthrive – Engaging platform for self-growth, content feels genuine and very useful.
сайт школы английского языка [url=https://www.salda.ws/f/topic.php?p=239434]https://www.salda.ws/f/topic.php?p=239434[/url] .
казино онлайн с выводом
перорально – эффекта 0 при меньших дозах, при больших – понос, рвота, чуваку скорую вызывали, давление 40/15 https://jk-sibirskiy.ru/mozhga.html 1)Кто курит каждый день : от 2 часов до 3-4 часов
новый маз 6430: Мощный тягач для тяжелых грузов. Идеален для работы в составе автопоезда. Надежность и выносливость в самых сложных условиях.
[hide=5]Пришла таки тусишка.Коричневатый порошок,в черезчур большом пакете(не 100г же заказывали). Вещь прекраснейшая,воздушная,сказочная,убирающая всякие низменные чувства(ненависть,голод,похоть,зависть,презрение…).Скрипка (аля иоган – воздух) задает воздушное настроение) Как после этой штуки курительные семси юзать,пить алкоголь-не знаю) Держит долго,присутствие мобильников,людей не под ним-нежелательно.На постэффектах хорошо пойдёт гитарка с веселыми,поизитвными песенками) Кушва купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Спустя 3 часа , началась небольшая депрессия(Со всем не большая)
Code promo 1xbet aujourd’hui
Знание английского языка сегодня считается необходимым умением для каждого человека.
Он дает возможность находить общий язык с иностранцами.
Не зная английский трудно достигать успеха в работе.
Многие компании оценивают знание английского языка.
подготовка к экзамену toefl
Обучение английскому делает человека увереннее.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без перевода.
Также, овладение английским улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, владение английским становится ключом в будущем каждого человека.
https://techn9netourdates.com
1xbet welcome bonus promo code : https://promotionaumaroc.com/wp-content/articles/?1xbet_promo_code_bangladesh_10.html Promocodes of 1xBet are alphanumeric strings that unlock various bonuses on the platform. These codes can be used during registration or deposit to claim bonuses like free bets, deposit matches, or free spins.
купить 4370: Компактный “Зубренок” – идеален для городских перевозок. Маневренность и экономичность в сочетании с надежностью МАЗ. Оптимальный выбор для малого и среднего бизнеса.
Подарите своей любимой мебели новую жизнь, заказав профессиональную [url=http://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]перетяжка мебели в рассрочку[/url] в Минске!
Перетяжка – это не только выгодное решение, но и шанс создать неповторимый дизайн.
**Выбор ткани: на что обратить внимание?**
Велюр приятен на ощупь, рогожка прочна, жаккард выглядит роскошно, а флок устойчив к когтям животных
**Этапы перетяжки мебели: от замера до готового результата**
В завершение устанавливаются декоративные элементы, такие как пуговицы или кант
**Уход за перетянутой мебелью: продлеваем срок службы**
Избегайте использования агрессивных химических средств, поскольку они могут повредить обивку.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
Рашн хлидейс вы правы, мы же тоже люди 🙂 треки наверное на отправке в базу не внесли, а шас у них же тоже праздники, но не волнуйтесь копии накладных то у нас 😉 Сухой Лог купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Покуреха порошки безвкусные (на язык), остальные горькие. Так проще всего определить.
https://adrenalinamanaus.com/
Подарите своей любимой мебели новую жизнь, заказав профессиональную [url=http://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]Ткани для перетяжки мебели[/url] в Минске!
Вместо приобретения новой мебели, вы можете легко обновить внешний вид вашей старой мебели, заменив обивку.
**Выбор ткани: на что обратить внимание?**
Подбор ткани для перетяжки – это важный шаг, требующий внимательного подхода
**Этапы перетяжки мебели: от замера до готового результата**
Перетяжка мебели – это процесс, требующий определенных навыков и инструментов
**Уход за перетянутой мебелью: продлеваем срок службы**
Избегайте использования агрессивных химических средств, поскольку они могут повредить обивку.
проститутки индивидуалки области Проститутки индивидуалки: Личный бренд в мире продажной любви. Иллюзия контроля, маска независимости. Одиночество, спрятанное за улыбкой.
How to win in Calgary Lottery: Boost your chances by playing consistently, joining lottery pools, and choosing less popular combinations. Remember, winning requires luck and responsible play: Calgary event tickets wins
https://factava.com.ua/karta-vinnytsi/
Компания [url=https://klining-moskva.com/]клининговые компании москва рейтинг[/url] предоставляет высококачественные услуги по уборке и клинингу в Москве и ее окрестностях.
Услуги клининга в Москве набирают популярность . Это связано с тем, что многие жители города предпочитают тратить свое время на более важные дела. Кроме того, профессиональные клинеры имеют специальное оборудование , что делает их услуги еще более привлекательными.
Услуги клининга в Москве включают в себя уборку любых других типов помещений. Профессиональные клинеры могут помочь с уборкой после ремонта . Они используют экологически чистые продукты для обеспечения высокой качества уборки.
В Москве предлагаются различные типы клининга для решения различных задач уборки . Среди них генеральная уборка являются наиболее популярными. Каждый тип уборки проводится с использованием специальных методов и средств .
Кроме того, уборка промышленных помещений также очень востребованы. Для этих типов уборки привлекаются высококвалифицированные специалисты. Все это позволяет снизить затраты на техническое обслуживание.
Использование услуг клининга в Москве имеет ряд достоинств . Одним из них является экономия времени . Кроме того, они используют специальные средства и оборудование .
Услуги клининга в Москве также способствуют созданию комфортной среды . Это связано с тем, что уборка помогает предотвратить распространение микробов и заболеваний .
В заключение, услуги клининга в Москве представляют собой перспективную и развивающуюся сферу . Это связано с тем, что профессиональная уборка является важной частью современного образа жизни .
Все, услуги клининга в Москве будут включать в себя новые технологии и методы. Это позволит сделать услуги клининга более доступными и привлекательными.
Желая узнать о себе больше, вы можете воспользоваться калькулятором [url=https://bestnumerolog.ru/kvadrat-pifagora-po-date-rozhdeniya-rasshifrovka-uznajte-vse-o-svoej-psixomatrice-onlajn/]таблица по пифагору дата рождения[/url] и открыть новые грани своей личности.
Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, дает возможность заглянуть в тайны судьбы и раскрыть потенциал человека. Это древний метод, который использовался в различных культурах для понимания человеческой природы и предсказания событий. Квадрат Пифагора, сформированный по дате рождения, показывает индивидуальный энергетический код каждого человека. Таким образом, квадрат Пифагора может стать ценным инструментом для самопознания и личностного роста.
Квадрат Пифагора основан на простом, но глубоком принципе, согласно которому каждое число имеет свою собственную энергию и влияние на человеческую жизнь. принцип позволяет нам использовать квадрат Пифагора как инструмент для анализа личности и прогнозирования будущих событий. Для расчета квадрата Пифагора необходимо произвести ряд математических операций, которые включают в себя суммирование чисел даты рождения и определение их позиций в квадрате. Это позволяет получить подробную картину личности и потенциала человека.
Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, дает возможность понять характер человека, его потенциал и вероятность успеха в различных областях жизни. Это делает квадрат Пифагора ценным инструментом для личностного роста и самосовершенствования. Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, дает возможность оценить совместимость людей в любви и браке. Это может помочь людям найти гармонию и понимание в их отношениях.
Чтобы использовать квадрат Пифагора эффективно, необходимо понять его основные принципы и символы. Это позволит получить точные и полезные результаты от анализа. Квадрат Пифагора по дате рождения может стать ценным инструментом для самоанализа и личностного роста, если его использовать правильно и с пониманием его принципов.
Квадрат Пифагора, основанный на дате рождения, позволяет оценить потенциал человека в карьере, любви и личностном развитии. Это может помочь людям принимать обоснованные решения и достигать своих целей. Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, дает возможность оценить совместимость людей и найти решение конфликтов. Это может привести к более гармоничным и удовлетворительным отношениям.
Необходимо изучить основы математики и символы квадрата Пифагора, чтобы его правильно применять. Это позволит получить точные результаты от анализа и принимать обоснованные решения. Квадрат Пифагора по дате рождения может стать ценным инструментом для личностного роста и самосовершенствования, если его использовать практично и с пониманием его принципов.
Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, дает возможность понять потенциал человека и спрогнозировать его будущее. Это делает его ценным инструментом для тех, кто стремится к самопознанию и личностному росту. Квадрат Пифагора по дате рождения помогает понять отношения между людьми и определить их совместимость. Это может привести к более гармоничным и удовлетворительным отношениям.
Квадрат Пифагора, основанный на дате рождения, позволяет оценить сильные и слабые стороны человека, а также спрогнозировать его будущее. Это может привести к более полноценной и удовлетворительной жизни. Квадрат Пифагора, рассчитанный по дате рождения, может быть мощным инструментом для самопознания и личностного роста. Это может стать вашим первым шагом на пути к самосовершенствованию и гармонии.
Услуги по [url=https://clickolov.ru/]накрутки пф[/url] помогают повысить позиции сайта в поисковых системах.
Накрутки ПФ необходимы для повышения эффективности онлайн-продвижения и увеличения трафика на сайт. Это связано с тем, что Накрутки ПФ необходимы для любого сайта, который хочет улучшить свою видимость и авторитет в интернете.
https://factava.com.ua/karta-poltavy/
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: Operation game rules and pieces
https://adrenalinamanaus.com/
http://houmy.ru/
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
Approfondir|
Je suis enthousiasme par Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, en revanche plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Lire les dГ©tails|
нарколог на дом
Je suis fascine par Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Wild Robin Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter la page web|
http://houmy.ru/
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Je suis fascine par Cheri Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Cheri Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Commencer maintenant|
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
Je suis totalement conquis par Cheri Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des tables live interactives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un point fort les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.chericasinoappfr.com|
Je suis sous le charme de Cheri Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Frumzi Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Frumzi Casino merite une visite dynamique. A noter le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.instantcasinobonusfr.com|
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
тюмень индивидуалка фото
Operation Game Canada: A classic, fun-filled board game where players test their precision by removing ailments from the patient without triggering the buzzer: nostalgic Hasbro games online
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Je suis sous le charme de Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
https://frumzicasinofr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de Frumzi Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Naviguer sur le site|
проститутки большой жирная Русские проститутки: Трагедия поколения, потерявшего надежду. В глазах – тоска по родине, на губах – горькая правда.
J’adore le dynamisme de Wild Robin Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Wild Robin Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En bonus le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir maintenant|
J’ai un faible pour Cheri Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Cheri Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Voir le site|
Да что то вот,с трудом верится,или вообще не верится!!!Я,первый раз заказывал в этом магазе,довольно таки быстро заказ получил,и качество товара,такое как и было обещано!!!Сейлер меня Не обманул,потому что он порядочный,да и ещё есть люди,мои знакомые хорошие,их на форуме нет,но они покупали в этом магазе продукцию,и остались довольны качеством товара и работы с клиентом… купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Взял ам2233 эфектом очень доволен! спасибо
http://houmy.ru/
кто купил диплом техникума отзывы [url=https://frei-diplom10.ru/]кто купил диплом техникума отзывы[/url] .
Je suis fascine par Instant Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Instant Casino merite une visite dynamique. A mentionner le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Cliquez ici|
куплю диплом младшей медсестры [url=http://www.frei-diplom14.ru]http://www.frei-diplom14.ru[/url] .
Je ne me lasse pas de Instant Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais encore quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Frumzi Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De plus le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Looking to betwinner create account fast? Go to https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and complete the simple sign-up form in just a few clicks.
Wondering how to register betwinner or how to create betwinner account? You’ll find all details and screenshots on https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/.
Брокер помог оформить декларации быстро и точно https://svobroker.ru/
El tono de los vasos sanguíneos y su importancia
Análisis del Tono de los Vasos Sanguíneos y su Impacto en la Salud Humana
Un adecuado estado musculoesquelético es fundamental para mantener la elasticidad y la resistencia en las arterias y venas. Para optimizar esta condición, se recomienda realizar ejercicios de estiramiento y fortalecimiento al menos tres veces por semana. Incorporar actividades cardiovasculares, como caminar, nadar o andar en bicicleta, también contribuye a mejorar la estructura y funcionamiento de estos sistemas circulatorios.
La alimentación juega un papel clave en la regulación de la funcionalidad de las paredes de los conductos. Incluir una dieta rica en antioxidantes, fibras y grasas saludables –provenientes de frutas, verduras, nueces y pescados– es esencial para apoyar su salud. Evitar el exceso de sodio y azúcares añadidos ayuda a controlar la presión arterial y reduce el riesgo de eventos adversos.
Además, la gestión del estrés no debe pasarse por alto. Técnicas como la meditación, el yoga o la respiración profunda pueden ayudar a regular la presión y mejorar la circulación. Mantenerse hidratado también es una medida efectiva que facilita el flujo sanguíneo y contribuye a la correcta función de todos los órganos.
Factores que afectan el tono vascular y su regulación
La actividad del sistema nervioso autónomo es fundamental en la regulación del diámetro de las arterias y venas. La estimulación del sistema simpático genera contracción, mientras que la actividad parasimpática provoca dilatación. Mantener un equilibrio entre estas dos ramas es crucial para una adecuada circulación sanguínea.
La liberación de hormonas, como la adrenalina y la norepinefrina, influye en el comportamiento de las paredes vasculares. Estas sustancias provocan cambios significativos en la resistencia al flujo sanguíneo, afectando la presión arterial de manera directa.
Factores endógenos como el calcio y otros electrolitos también juegan un rol determinante en la contractilidad de las células musculares lisas. La concentración de calcio en el citoplasma impacta la capacidad de contracción, regulando así el diámetro del sistema circulatorio.
La producción de óxido nítrico por el endotelio vascular induce relajación, reduciendo la resistencia al flujo. Este mecanismo es especialmente relevante en situaciones de mejora del flujo sanguíneo, como durante el ejercicio físico.
La hipoxia, o baja disponibilidad de oxígeno, provoca vasodilatación en órganos específicos para aumentar el flujo y mejorar la oxigenación. Esta respuesta es crítica en tejidos que requieren mayor aportación de sangre, especialmente durante esfuerzos físicos intensos.
Los cambios en la temperatura corporal también afectan la regulación del diámetro vascular. La vasodilatación ocurre en condiciones de calor para facilitar la pérdida de calor, mientras que en frío se produce vasoconstricción para conservar la temperatura interna.
Finalmente, el estrés emocional puede modificar el funcionamiento vascular a través de la producción de cortisol y otros mediadores, generando contracciones que alteran el flujo sanguíneo normal. Es importante identificar estas influencias para mantener una salud cardiovascular óptima.
Consecuencias clínicas de un tono vascular alterado
Un estado alterado de la musculatura en la red de conducciones puede dar lugar a complicaciones serias, como la hipertensión arterial. Esta condición se relaciona con una resistencia incrementada al flujo sanguíneo, ocasionando daño en órganos blancos como los riñones y el corazón. Es crucial monitorear la presión arterial de manera regular para identificar cambios que sugieran un deterioro en la regulación vascular.
La insuficiencia vascular periférica es otra consecuencia que puede resultar de una respuesta inapropiada en la contracción y relajación de las paredes de las arterias. Los pacientes pueden experimentar síntomas como dolores episódicos en las extremidades, asociado a una circulación deficiente. Se recomienda la evaluación de la salud de extremidades mediante pruebas de flujo y ecografías para determinar la función circulatoria.
Alteraciones en la funcionalidad del sistema nervioso, como en el caso de crisis vasculares, pueden provocar dolores de cabeza severos y migrañas. Un enfoque preventivo incluye la identificación de desencadenantes y la implementación de un estilo de vida que favorezca la estabilidad vascular, como técnicas de manejo del estrés y ejercicio regular.
Las enfermedades cardiovasculares suelen ser el resultado de desequilibrios en el comportamiento de los conductos sanguíneos. La adopción de una dieta equilibrada, rica en antioxidantes y baja en sodio, puede reducir el riesgo de eventos adversos graves. Es recomendable aumentar la ingesta de frutas y verduras, así como limitar el consumo de grasas saturadas.
En casos críticos, como el síndrome de choque, la regulatoría de la dilatación y contracción de las arterias es completamente alterada, lo que puede llevar a un fallo multiorgánico. La intervención médica oportuna es indispensable para restaurar un flujo adecuado y prevenir complicaciones mayores. Proveer una atención inmediata y adecuadamente administrada es vital para la recuperación del paciente.
https://hondrolife.biz/es/
Je suis fascine par Frumzi Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Frumzi Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour completer le site est rapide et style, booste le fun du jeu. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages uniques.
VГ©rifier le site|
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: купить с установкой входную дверь в квартиру
https://www.remotehub.com/1xbetpromocode.forfreebet
Je suis totalement conquis par Frumzi Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui motive les joueurs.
Essayer|
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
Je suis emerveille par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Cheri Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement attrayant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
Essayer maintenant|
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Je suis bluffe par Wild Robin Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Wild Robin Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Continuer ici|
Первый раз брал у этого магазина,сразу же что то не то,если всё будет Ок,буду брать дальше,в принцыпе со всеми бывает( https://m5flasher.ru товар появился? когда возобновите доставку по городам?
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Passer à l’action|
J’adore le dynamisme de Instant Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, quelquefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Instant Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fluides.
Lancer le site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Frumzi Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Frumzi Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir la page|
вызвать нарколога на дом
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: Здесь
Очень довольны сервисом! Брокер всё сделал быстро, аккуратно и без лишней бюрократии. Теперь даже не думаем оформлять сами: Таможенный брокер в Шереметьево
Да стопудова честный!!! В этом нет сомнений. А вот с волей Медведя и планом Путина ужиться сложно купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Вот это бы нормально было нормальный трип по двум веществам..
http://houmy.ru/
нарколог на дом спб
<https://kuklanvt.info/salon/
https://narkolog-na-dom-spb2.ru/
Автоматические выключатели
сосущая проститутка Старые проститутки: История боли и потери, написанная на морщинах, рассказанная полушепотом. Прошедшее время, унесенные мечты.
https://adrenalinamanaus.com/
https://www.lonestarenergytx.com/service-areas/houston/houston/plan-four
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet.cd : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-65.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
лучший магаз из всех что существует!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Пацаны из ТЛТ не берите через этот магаз ФСКН кроет курьерку в нашем городе!!!
нарколог на дом спб
Starting your journey with betwinner registration takes only a few minutes. Full instructions are available at https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/, making it simple even for beginners.
кончил в проститутку Проститутки города: Калейдоскоп судеб, сплетенный из нужды и желания. Неоновые огни манят заблудшие души.
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
Автоматические выключатели
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://guzellikturk.com]https://guzellikturk.com[/url]
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
нарколог на дом спб
http://houmy.ru/
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
нарколог на дом спб
По многочисленным восторженным откликам мн-001, тестировал его и был немного огорчен. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Менеджер вежливый все быстро понимает на 5/5
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Ура! Скинул трек быстро) ждууууууу, отпишу. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Я заказал еще 19 числа на сайте, оплатил 23 числа, ТС выслал 25 числа, тогда я и тут зарегился, так как он отправил не той службой, думал кинули. Пришло все вчера, забрал днем, попробовал вечером
http://www.google.ki/url?q=https://best-promo-code.com/
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
Ну давайте не мандражировать, плохие мысли материализуются, я специально это не написал!!!! Что тут в карму никто не верит? 🙂 Забыли уже? 😉 https://ipconf2024.ru Привет, нету в личке нечего.
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
Особенно понравился раздел про Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://evimsicak.com]https://evimsicak.com[/url]
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
магазин подарков Подарки: Искусство дарить радость, воплощенное в изысканных предметах. Волшебство момента, запечатленное в памяти. Каждый подарок – это послание, зашифрованное в форме, цвете и содержании. Это возможность выразить чувства, сказать о важном, укрепить связь. Выбирайте с душой, и ваш подарок станет настоящим сокровищем.
Работа в корее Производство в Корее – это сфера, где современные технологии сочетаются с традиционным качеством. Вакансии на производственных предприятиях предлагают стабильную работу, достойную оплату и социальные льготы. От инженеров до операторов станков, здесь найдется место для каждого, кто стремится к профессиональному развитию.
заказать сессию синергия Решение Тестов Синергия: Эффективный способ проверить свои знания и подготовиться к экзаменам. Разнообразные тесты, соответствующие учебной программе, помогут вам выявить слабые места и сосредоточиться на изучении сложных тем.
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, toutefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Frumzi Casino garantit un amusement continu. D’ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
https://frumzicasinoappfr.com/|
Je suis enthousiasme par Instant Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En fin de compte, Instant Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis epate par Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Commencer Г lire|
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
Je suis enthousiasme par Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A souligner les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Aller en ligne|
Je suis emerveille par Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller au site|
спасибо за отзыв! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Всем привет, долго не писал, ну это меня «задержала» посылка jv-61. Все пришло, все получил причем довольно быстро все ехало:good:
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Якщо шукаєте казино з миттєвим виводом — обирайте перевірені українські сайти. Топ казино України обирають за надійність і швидкі виплати.
Українські інтернет казино мають прозорі умови для гравців. Обираєте майданчик із гарантією виплат? Перевірте [url=https://casino-ua-online.biz.ua/]ліцензійні казино україни[/url] і порівняйте умови бонусів. Казино з миттєвим виводом дозволяють отримати виграш без очікування.
Казино з українським інтерфейсом має зрозумілу навігацію. Легальні онлайн казино України діють згідно із законом. Онлайн казино Україна пропонує бонуси за перший депозит. Онлайн казино України пропонують акції та фріспіни щотижня. Онлайн казино Україна з миттєвим виводом коштів — реальність.
ремонт двигателей Datsun [url=http://telegra.ph/Dvigovichkoff–professionalnyj-remont-dvigatelej-v-Moskve-dlya-avtomobilej-premialnyh-marok-10-14/]http://telegra.ph/Dvigovichkoff–professionalnyj-remont-dvigatelej-v-Moskve-dlya-avtomobilej-premialnyh-marok-10-14/[/url] .
Наше самое ценное: https://fotoredaktor.top
новое казино
[On our website, we tender present-day and the wealthiest IT solutions an eye to your house] [url=https://kodx.uk/]kodx.uk[/url]
6-APB, белый кристалический порошок, 1000р… Это типа настоящий 6-APB? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Интересно как он себя покажет… даже не знаю как его разводить…
https://thgn.ru/ Подарки: Симфония эмоций, запечатленная во времени. Это не просто предметы, это ключи к сердцам, мосты между душами. Изысканное выражение внимания, заботы и любви, способное превратить обычный день в незабываемый праздник. Подарок, выбранный с душой, становится отражением ваших чувств, маленьким маяком теплоты и нежности в океане повседневности. Он говорит больше, чем тысячи слов, создает воспоминания, которые будут согревать даже в самые холодные дни.
экскаватор погрузчик jcb аренда москва [url=http://arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-2.ru/]http://arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-2.ru/[/url] .
зачеты синергия помощь ЛМС МТИ: Интеллектуальная экосистема, оптимизирующая процесс обучения. Интерактивные курсы, адаптивные тесты, виртуальные лаборатории – инструменты, превращающие теорию в практику. Отслеживайте свой прогресс, общайтесь с преподавателями и совершенствуйте свои навыки в режиме реального времени.
лучшие автоматы
Топовое тату оборудование. Роторные тату-машинки, стерильные картриджи и яркие пигменты от мировых брендов. Только профессиональный инструмент для безупречного качества тату. Заходите https://tattooaura.ru/
How does the Golden Visa program impact your global tax obligations?
https://trevorjd.com/index.php/Visa_9i
Да туси тут очень качественная, жаль что заказать проблемно. https://leontyusov.ru Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!
J’adore le dynamisme de Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Lancer le site|
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
Зацепил материал про Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Cheri Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Commencer Г lire|
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, malgre tout des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Entrer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Instant Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une immersion complete. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements securises.
https://instantcasino777fr.com/|
купить диплом медсестры [url=frei-diplom13.ru]купить диплом медсестры[/url] .
J’ai une passion debordante pour Wild Robin Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Wild Robin Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
VГ©rifier ceci|
казино России
Work in korea Работа в Корее: Эльдорадо карьерных возможностей для целеустремленных профессионалов. Страна утренней свежести манит не только своей уникальной культурой и технологическим прогрессом, но и широкими перспективами трудоустройства. От динамичного Сеула до индустриальных центров, Корея открывает двери для тех, кто готов к новым вызовам и стремится к профессиональному росту. Приготовьтесь погрузиться в мир передовых технологий, инновационного производства и захватывающих карьерных траекторий.
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est transparent et rapide, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Instant Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Cheri Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г explorer|
съемка подкаста под ключ [url=http://studiya-podkastov-spb4.ru]съемка подкаста под ключ[/url] .
Вы реально думаете что тут сидят роботы, которые должны отвечать всем без перерывов и выходных? Праздники же были, все отдыхать хотят. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Моя первая покупка на динамите и, внезапно для самой себя, наход. Сняла, как говорится, в касание. С вашим охуенным мефчиком сорвала себе почти год ЗОЖа и ни чуть не жалею.
Je suis sous le charme de Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A signaler l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter maintenant|
Знание английского языка сегодня считается важным навыком для каждого человека.
Он позволяет общаться с жителями разных стран.
Не зная английский почти невозможно достигать успеха в работе.
Работодатели предпочитают специалистов с языковыми навыками.
курсы toefl
Изучение языка расширяет кругозор.
С помощью английского, можно учиться за границей без трудностей.
Помимо этого, регулярная практика повышает концентрацию.
Таким образом, владение английским играет важную роль в будущем каждого человека.
https://dostyp-balkony.ru/ Существует несколько видов остекления балконов: холодное остекление с использованием алюминиевых рам, обеспечивающее защиту от ветра и дождя, и теплое остекление с пластиковыми окнами ПВХ, создающее комфортное пространство в любое время года.
Знание английского языка сегодня считается необходимым умением для современного человека.
Он помогает взаимодействовать с иностранцами.
Без владения языком почти невозможно достигать успеха в работе.
Организации предпочитают знание английского языка.
newcoop.ru
Регулярная практика английского открывает новые возможности.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без ограничений.
Также, регулярная практика развивает память.
Таким образом, владение английским играет важную роль в саморазвитии каждого человека.
Ищете своего мастера? Только проверенные тату-художники с впечатляющим портфолио! Любой стиль: от реализма до олдскула. Найдите идеального профи для вашего проекта на нашем сайте https://tattoomastera.ru/
заказать тесты синергия Дипломные Работы Синергия: Инвестиция в карьерное будущее, подтверждение экспертного уровня. Создайте уникальный проект, демонстрирующий ваши навыки и знания. Погрузитесь в исследования, разработайте инновационные решения и защитите свою работу с блеском. Мы предоставим экспертную поддержку на каждом этапе, от выбора темы до предзащиты.
Je suis captive par Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Frumzi Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute soudee.
Ouvrir la page|
5iai – как употребляли и сколько? https://gyro-cult.ru МХЕ “как у всех” тобиш бодяжный.. Вроде скоро должна быть нормальная партия.
Je suis accro a Cheri Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Je suis emerveille par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, rarement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller au site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Instant Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour ajouter le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un avantage les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
Aller sur le site web|
Thanks for another great post. Where else may anybody get that type of info in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the search for such information.
Je suis completement seduit par Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, toutefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Wild Robin Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et energique, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fluides.
DГ©couvrir|
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: indie games by Prisma Games
I think I will become a great follower.Just want to say your post is striking. The clarity in your post is simply striking and i can take for granted you are an expert on this subject.
J’adore la vibe de Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Instant Casino merite une visite dynamique. A mentionner l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
https://casinoinstantfr.com/|
Je suis enthousiasme par Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Frumzi Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer la page|
пробывал нюхать эфект 4-6часа https://frm-congress.ru Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Между прочим, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://aynakirildi.com]https://aynakirildi.com[/url]
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
Остекление балконов Выбор типа остекления зависит от ваших потребностей и бюджета. Холодное остекление – более доступный вариант, а теплое – более функциональный и долговечный.
https://sport.chat/
Спорт
сегодня сделал заказ, написал в аську сразу ответили. Буду ждать как что измениться отпишу. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм почему статус заказа отложен!? 1000539
Работа в корее Русскоязычные в Корее: Сообщество поддержки и дружбы. Вместе легче адаптироваться и достигать вершин!
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: Password Game strategies to win
7k casino стало для меня открытием. Сайт простой, выплаты честные. Всё работает спокойно, без нервов: 7к казино регистрация
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet rdc apk : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
Всё лучшее у нас: https://mr-master.com.ua
а что с алхимом случилось? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш По моему отзыв о “марочках” был явно не про этот магазин О_о
зачеты онлайн синергия Итоговый Тест Синергия: Момент истины, торжество знаний и навыков. Комплексная оценка, определяющая уровень вашей компетентности. Подготовьтесь к испытанию с помощью наших ресурсов и продемонстрируйте свой потенциал.
Casino 7k радует скоростью работы. Игры загружаются быстро, без зависаний. Деньги на карту пришли в срок https://xn—-8sbalwlcefxak4bw.xn--p1ai/
1xbet com giri? [url=https://1xbet-9.com]https://1xbet-9.com[/url] .
помощь с рефератами мти срочно 2026 Решение Тестов Синергия: Эффективный способ проверить свои знания и подготовиться к экзаменам. Разнообразные тесты, соответствующие учебной программе, помогут вам выявить слабые места и сосредоточиться на изучении сложных тем.
I Am Going To have to come back again when my course load lets up – however I am taking your Rss feed so i can go through your site offline. Thanks.
If you are looking for an easy and convenient way to create a stamp, you should visit the site [url=https://stamps-makers.com/]stamp maker online free[/url], where you can order any stamp design online.
Moreover, the online platform eliminates the need for physical storage, as users can access their designs and stamps from anywhere with an internet connection.
The rubber stamp maker online has a community aspect, where users can share their designs and connect with other stamp enthusiasts.
The rubber stamp maker online has a wide range of applications and uses, from art and craft to business and office supplies.
Moreover, the online platform provides a secure and reliable way to create custom stamps, ensuring that users’ designs and transactions are protected.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Хочу выделить раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://anadolustil.com]https://anadolustil.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
да и оперативность У ВАС на ВЫСШЕМ :superman: уровне!! https://smilefab.ru Кто у Чемикала в последнее время брал ОПТ ( от 1 КГ и более) !!! Все ОК?????? ОПТ давно кто получал???? Задержки были…..?????
Для создания идеальной кухни многие выбирают [url=https://stoleshnitsy-iz-akrilovogo-kamnya.ru/]акриловая столешница купить цена[/url], благодаря их невероятному внешнему виду и практичности.
стали неотъемлемой частью многих кухонь и ванн благодаря своей универсальности и эстетической привлекательности. Они характеризуются своей способностью выдерживать различные нагрузки. При выборе столешницы важно оценить общую концепцию интерьера и личные предпочтения.
Столешницы из акрилового камня предлагаются в широком диапазоне цветов и текстур . Это дает возможность выбрать идеальный вариант для любой кухни или ванной . Кроме того, акриловый камень не требует особого ухода, что делает его практичным выбором.
Одним из ключевых преимуществ столешниц из акрилового камня является их высокая прочность и устойчивость к царапинам и трещинам . Это обеспечивает экономию средств на ремонте и замене. Кроме того, акриловый камень обладает антисептическими свойствами , что снижает риск распространения бактерий и микробов.
Столешницы из акрилового камня также могут быть изготовлены по индивидуальным размерам . Это обеспечивает большой выбор для дизайнеров и домовладельцев. Благодаря своей универсальности и качеству, столешницы из акрилового камня становятся все более популярными .
Установка столешниц из акрилового камня требует специальных навыков и опыта . Это дает возможность создать идеально ровную и прочную поверхность. После установки важно избегать воздействия агрессивных химикатов и абразивных материалов.
Для ухода за столешницами из акрилового камня рекомендуется регулярно наносить специальные покрытия и полировки. Это снижает риск появления царапин и трещин. Кроме того, акриловый камень может быть восстановлен до первоначального состояния , что снижает затраты на ремонт и замену.
В заключение, столешницы из акрилового камня обеспечивают высокое качество и долговечность. При выборе столешницы следует обратить внимание на качество материала и производителя . Для установки и ухода за столешницами из акрилового камня следует использовать специальные инструменты и материалы .
Столешницы из акрилового камня будут продолжать набирать популярность благодаря своей универсальности, качеству и эстетической привлекательности. Для тех, кто ищет функциональное, долговечное и стильное решение для кухни или ванной, столешницы из акрилового камня предлагают широкий диапазон возможностей и преимуществ .
Discover the best PS2 games in Canada! A curated list of timeless classics, including action, RPGs, and sports titles. Relive the nostalgia of top PlayStation 2 hits loved by gamers: buy PS2 games online Canada
купить диплом техникума в ижевске [url=frei-diplom12.ru]купить диплом техникума в ижевске[/url] .
друзья всем привет ,брал через данный магазин порядком много весов ,скажу вам магазин работает ровнечком ,адрики в касание просто супер ,доставка работает на сто балов четко ,успехов вам друзья и процветания купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Добрый день! А можно поинтересоваться – в связи с чем сменилась курьерская служба?
Удобный сайт и быстрая работа — это то, что понравилось в 7k casino официальный сайт. Несколько раз выводил выигрыш, всегда без задержек. Поддержка вежливая и отвечает быстро https://xn—-8sbalwlcefxak4bw.xn--p1ai/
Casino 7k понравилось своей надёжностью. Всё работает стабильно, без ошибок. Деньги выводят быстро: 7к казино регистрация
https://t.me/RabotaVKoreeSeoul IT-вакансии в Корее – это золотая жила для программистов, разработчиков и аналитиков. Корейские компании активно инвестируют в развитие искусственного интеллекта, блокчейна и других передовых технологий, что создает огромный спрос на специалистов в этих областях.
анонимный психолог онлайн
Private [url=https://www.nurumassagevip.com/]Bangkok private massage[/url] in hotel room|
списались с продавцом,пообщались,договорились.я оплатил заказ и начались долгие ожидания моей заветной посылки. https://mokvd.ru мое мнение работает достойно
купить диплом 11 классов отзывы [url=https://r-diploma31.ru/]купить диплом 11 классов отзывы[/url] .
MERTHYTJTJ791667MAVNGHJTH
Work in korea Вакансия в Сеуле – это шанс погрузиться в уникальную культуру и получить опыт работы в международной команде. От IT-инженеров до специалистов в сфере производства, Корея нуждается в квалифицированных кадрах. Компании предлагают конкурентоспособную заработную плату, социальные гарантии и возможности для профессионального роста.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Хочу выделить раздел про Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
Зато искать долго не пришлось наверное???! https://27dverei.ru Ровный магаз,всем советую)
https://www.bergkompressor.ru Шагните в наш цифровой мир – Откройте для себя последние обновления онлайн.
https://www.bergkompressor.ru/ Ваш портал к новому – Узнайте, что нового и интересного прямо сейчас.
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. D’ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Obtenir des infos|
купить аттестаты для школы госзнак в ярославле [url=www.r-diploma7.ru]www.r-diploma7.ru[/url] .
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Cheri Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Cheri Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis totalement conquis par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Frumzi Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, qui stimule l’engagement.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, incite a rester plus longtemps. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Plonger dedans|
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Wild Robin Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements rapides.
Avancer|
а вот по этой теме отпиши по подробней,точнее о том как там дальше события развиваются?????????? очень волнует данная тема. как же так их просекла легавня???? откуда краснотой веет.??? https://rakurai.ru Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!
http://www.google.com.ai/url?q=https://labhgroup.com/news/promo_code_and_bonuses_of_1xbet_bookmaker.html
Je suis captive par Instant Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, quelquefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Instant Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
https://instantcasino365fr.com/|
Банкротство Банкротство физических лиц (БФЛ) позволяет гражданам, оказавшимся в сложной финансовой ситуации, начать жизнь с чистого листа.
фанфики Истории о работе – смешные и поучительные случаи из офисной жизни, рассказы про начальников и коллег, и просто забавные моменты, которые происходят с нами на работе.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, rarement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Cheri Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller au site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Frumzi Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute soudee.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar021.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Ущерб через наркотиков — этто единая хоботня,
обхватывающая физиологическое, психологическое
также общественное состояние здоровья человека.
Утилизация эких наркотиков, яко снежок, мефедрон, гашиш,
«наркотик» чи «бошки», может обусловить ко необратимым следствиям яко
для организма, так (а) также для
мира на целом. Хотя хоть при вырабатывании зависимости эвентуально
восстановление — ядро, чтоб энергозависимый явантроп направился
за помощью. Эпохально памятовать,
что наркозависимость врачуется, а также помощь бабахает
шансище на свежую жизнь.
https://vk.com/id7281076 костоправ люберцы
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Туркменский перевод Восстановление документов: Помощь в восстановлении утерянных или поврежденных документов.
Доступ к онлайн-хабу Все ресурсы и инструменты для вашего удобства.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Wild Robin Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Wild Robin Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.wildrobincasinomobilefr.com|
ты давай вася тут провокации не сей))) https://gyro-cult.ru но с другой стороны, селлер не должен и не обязан объяснять что это такое и с чем его едят. Здесь продаются КОНКРЕТНЫЕ в-ва, а не какие то А1, В2 и иже с ними. Так что можно узнать и самим. И если вас так интересует качество\особенности товара от данного продавца, так не поленитесь в случае заказа отписать о полученном стаффе\особенностях, меньше мороки будет другим. А то заказывают сотни, отзывы пишут единицы, и то больше “зашибись !” или “аааа, не прёёёёёт !!!111”. Выдавайте сами побольше информации.
[url=https://bestlimorates.com/the-future-of-urban-mobility-why-seattles-premium-transportation-sector-is-attracting-investors/] Seattle investor interest in mobility [/url] has surged, particularly in premium transportation sectors like limousine services, which cater to corporate clients, high-net-worth individuals, and special events. Limousine services in Seattle offer luxury vehicles—including sedans, SUVs, and stretch limos—equipped with high-end amenities such as leather seating, climate control, and entertainment systems. These services prioritize reliability, professionalism, and discretion, aligning with the demands of business travelers and local elites.
Driven by Seattle investor interest in mobility, the sector is expanding with tech-driven innovations like real-time booking apps, AI-powered route optimization, and eco-friendly fleets, including electric and hybrid limousines. Investors see potential in scalable, on-demand luxury transport, especially as Seattle’s tech hub grows, increasing demand for executive travel solutions.
Key revenue streams include airport transfers, weddings, corporate events, and hourly charters. Partnerships with hotels, event planners, and ride-hailing platforms further boost visibility. With Seattle investor interest in mobility accelerating, limousine services are positioning themselves as high-margin, niche players in the broader transportation ecosystem, leveraging brand prestige and operational efficiency to attract funding and expansion opportunities. – https://bestlimorates.com/the-future-of-urban-mobility-why-seattles-premium-transportation-sector-is-attracting-investors/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Читать дальше – https://poashow.com.br/2024/01/15/familia-real-britanica-tem-queda-de-89-milhoes-em-faturamento
J’adore l’energie de Cheri Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus le design est moderne et energique, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure memorable. En complement le design est tendance et accrocheur, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements rapides.
Entrer maintenant|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Instant Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
Visiter pour plus|
займы Получите бесплатную консультацию со специалистом, чтобы узнать, подходит ли вам процедура банкротства и какие у нее последствия.
J’adore la vibe de Cheri Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Cheri Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le fun du jeu. A noter le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui motive les joueurs.
Approfondir|
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://evimturk.com]https://evimturk.com[/url]
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
Je suis captive par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Frumzi Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En extra le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
http://www.frumzicasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis epate par Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Wild Robin Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le site web|
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Лови подробности – https://www.nihaozaragoza.cn/front-page
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://financialpower.xyz/hello-world
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges personnalises.
Tout apprendre|
Я знаете как делаю, когда пацики отвечают сразу делаю заказ, оплачиваю и все чотка, самим тормозить не надо https://m5flasher.ru Жалко тест профукал )
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Frumzi Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Frumzi Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
VГ©rifier ceci|
bergkompressor.ru Зайдите на нашу страницу – Всё самое актуальное уже здесь.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Instant Casino vaut une visite excitante. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.instantcasino366fr.com|
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Давай разберёмся досконально – http://soldadurasazteca.com/index.php/component/k2/item/27?start=4510
истории о работе Корги: маленькие пушистые комочки счастья! Всё о породе, уходе, забавных случаях и самых милых корги в сети.
J’ai un faible pour Instant Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Instant Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De plus le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Je suis bluffe par Cheri Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Ouvrir la page|
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://jupiterdavibe.com/from-vinyl-to-virtual-evolution-in-universe
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Обратитесь за информацией – https://bali-importbox.com/kagu-kanzeigutairei
а че, под запрет попадает? вроде нет https://rakurai.ru он мне успел ответить – поверь, ничего такого о чём тебе стоило бы беспокоиться – не случилось
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://nutritionbeyondborders.org/economiser-epicerie
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://innovatrims.net/2021/01/20/reflectiveheattransfer
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Не упусти шанс – https://lajaquimavaquera.com/producto/collar-tequila
вывод из запоя цена
tula-narkolog011.ru
вывод из запоя
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://republicadomedo.com.br/critica-espiral-o-legado-de-jogos-mortais
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.pietrocarlopellegrini.it/melap/07-15
а какие были проблемы по данном поводу? https://vertikal-kursk.ru магаз ровный!!!
J’ai un faible pour Betzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
J’ai un faible pour Viggoslots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Obtenir des infos|
Официальный сайт компании Достоверная информация о наших продуктах и услугах.
з Днем народження батьку
Je suis enthousiasme par Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Posido Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En bonus le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller en ligne|
Бот для сети Ethereum Как начать торговать криптой с ботом: Пошаговые инструкции для начала торговли криптовалютой с использованием Telegram бота.
Массаж
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Краснодаре, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Стоимость услуг начинается от 2400??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости процедур.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Экстренное вытрезвление в клинике «Детокс» в Краснодаре — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
https://sdkt-podolsk.ru/
PlayAmo Club Modern Betting Platform is one of the leading iGaming destinations for gamblers who like action, gifts, and fast returns.
With hundreds of refined jackpots, strategy games, and real-time games, PlayAmo Club delivers a five-star gambling session right from your Mac or smartphone.
New gamblers can enjoy generous welcome offers, game spins, and access elite bonus levels.
Whether you enjoy original casino games or the latest trends, PlayAmo Club offers everything you need for thrilling casino play
https://gyn101.com/
gyn101.com
Кулінарний портал https://infostat.com.ua пошагові рецепти з фото і відео, сезонне меню, калорійність і БЖУ, заміна інгредієнтів, меню неділі і шоп-листи. Кухні світу, домашня випічка, соуси, заготовки. Умные фильтры по времени, бюджету и уровню — готовьте смачно і без стресу.
Портал про все https://ukrnova.com новини, технології, здоров’я, будинок, авто, гроші та подорожі. Короткі гайди, чек-листи, огляди та лайфхаки. Розумний пошук, підписки за темами, обране та коментарі. Тільки перевірена та корисна інформація щодня.
bergkompressor.ru/ Исследуйте без границ – Ознакомьтесь с новыми сервисами и контентом.
Сайт про все https://gazette.com.ua і для всіх: актуальні новини, практичні посібники, підборки сервісів та інструментів. Огляди техніки, рецепти, здоров’я і фінанси. Удобні теги, закладки, коментарі та регулярні оновлення контенту.
Casino 7k приятно удивило качеством сервиса. Поддержка отвечает быстро и по делу. Деньги выводятся чётко в срок: 7k casino зеркало
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
новини Дніпра
spinbara licencja Anjouan spinbara darmowe spiny: Zdobadz darmowe spiny i ciesz sie gra na popularnych slotach bez ryzyka.
Отвечают оперативно, оформлено красиво… купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Плохует мягко сказано,уже больше пол месяца жду.Тебе кстати пришла?
Экстренное вытрезвление в клинике «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Вред от наркотиков — этто единая
проблема, охватывающая физическое, психологическое (а) также социальное здоровье человека.
Употребление эких наркотиков, как кокаин, мефедрон, ямба, «шишки» или «бошки», может родить буква необратимым результатам как чтобы
организма, яко (а) также чтобы федерации в
течение целом. Но хоть у вырабатывании
подчиненности эвентуально
восстановление — главное, чтоб энергозависимый
явантроп обернулся согласен помощью.
Эпохально запоминать, что наркозависимость лечится, а также восстановление в правах бацнет
шансище сверху новую жизнь.
Binary Options Trading View: Analyze and Trade Smarter Enhance your trading decisions with Binary Options Trading View, using real-time charts and insights to stay ahead of the market. Explore smarter strategies and live analytics at https://kaiseimaru.jp/ !
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Betzino Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
Explorer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Betzino Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots fluides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer ici|
Je suis bluffe par Viggoslots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Челябинске, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас. Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Vbet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiasme par Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Vbet Casino assure un fun constant. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais encore des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Cheri Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A souligner les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Explorer le site web|
Je ne me lasse pas de Posido Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Posido Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages uniques.
http://www.posidocasinofr.com|
Лучшие боты для трейдинга Торговые сигналы Telegram: Подборка каналов и ботов с торговыми сигналами для Telegram.
В «Частном Медике 24» в Челябинске вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена челябинск[/url]
https://медоптима.рф/
Риск от наркотиков — это групповая хоботня,
обхватывающая физическое, психическое также
соц состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление таковских наркотиков,
как кокаин, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик» или «бошки»,
может родить ко необратимым результатам яко для
организма, так равным образом чтобы
общества в течение целом.
Хотя даже при вырабатывании подчиненности эвентуально восстановление — ядро,
чтобы зависимый человек направился за помощью.
Важно запоминать, что наркомания
лечится, и реабилитация бабахает шанс сверху свежую жизнь.
https://sites.google.com/view/1xbet-promo-code-2026-130-welc/home
Да до празников не всем выслали, сегодня отдали в курьерку очередную пачку посылок, всем все придет скоро. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Мы в Кургане не работаем, все наши представительства есть в соответствующем разделе.
Сайт про все https://kraina.one практичні поради, таблиці та калькулятори, добірки сервісів. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, фінанси, авто, гаджети, подорожі. Швидкий пошук, збереження статей та розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня. Простою мовою та у справі.
Інформаційний портал https://presa.com.ua новини, технології, здоров’я, фінанси, будинок, авто та подорожі. Короткі гайди, огляди, чек-листи та інструкції. Розумний пошук, підписки на теми, закладки та коментарі. Тільки перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
Єдиний портал знань https://uaeu.top наука та техніка, стиль життя, будинок та сад, спорт, освіта. Гайди, шпаргалки, покрокові плани, експерти відповіді. Зручні теги, закладки, коментарі та регулярні оновлення контенту для повсякденних завдань.
диплом купить тольятти [url=www.r-diploma8.ru/]www.r-diploma8.ru/[/url] .
The easiest way to claim your betwinner registration bonus is to visit https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and complete the sign-up form carefully. Make sure you verify your email to activate the offer.
Английский язык сегодня считается необходимым навыком для жителя современного мира.
Английский язык дает возможность взаимодействовать с людьми со всего мира.
Без знания английского почти невозможно достигать успеха в работе.
Работодатели требуют сотрудников, владеющих английским.
курсы интенсивного изучения английского
Обучение английскому делает человека увереннее.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без перевода.
Кроме того, овладение английским развивает память.
Таким образом, умение говорить по-английски становится ключом в успехе каждого человека.
https://медоптима.рф/
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем комфортные условия для пребывания в клинике Краснодара, чтобы восстановление прошло максимально эффективно. В нашей клинике созданы все условия для вашего удобства и быстрого восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
В «Трезвом шаге» в Воронеже вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
spinbara automaty z wysokim RTP spinbara free spins: Zdobadz darmowe spiny i zagraj w swoje ulubione sloty za darmo!
Наши специалисты в Челябинске готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-zhukovskom
2)Кто курит раз в неделю : от 3 часов до 5-7 часов купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Желаю всего самого наилучшего вашему магазину,ваш бренд это качество!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar023.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Binary Options Trading View: Analyze and Trade Smarter Enhance your trading decisions with Binary Options Trading View, using real-time charts and insights to stay ahead of the market. Explore smarter strategies and live analytics at https://kaiseimaru.jp/ !
Портал корисної інформації https://online-porada.com практичні поради, відповіді експертів, таблиці та шпаргалки. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, гроші, гаджети, авто та туризм. Швидкий пошук, обране, розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня. Пишемо просто й у справі.
Сучасний інформаційний https://prezza.com.ua портал: новини, огляди, практичні інструкції. Фінанси, гаджети, авто, їжа, спорт, саморозвиток. Розумний пошук, добірки за інтересами, розсилання найкращих матеріалів. Тільки перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
Інформаційний портал https://revolta.com.ua «все в одному»: коротко і у справі про тренди, товари та сервіси. Огляди, інструкції, чек-листи, тести. Тематичні підписки, розумні фільтри, закладки та коментарі. Допомагаємо економити час та приймати рішення.
Торговля на MEXC через тг Торговый бот Telegram: Настройте торгового бота для автоматического исполнения ордеров в Telegram.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: дверь металлическая входная
Если вы ищете круглосуточный вывод из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обратитесь в клинику «Детокс» по адресу Волгоградская, 185. Здесь помогут выйти из кризиса и восстановить силы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Вы не могли сегодня оплатить заказ, потому что мы сегодня не работаем купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Всё ок подняли, но место опять немного людное (самый центр города)
Вывод из запоя в Екатеринбурге можно пройти в клинике «Детокс», расположенной на Волгоградской, 185. Здесь обеспечивают полное медицинское сопровождение и поддержку.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого екатеринбург[/url]
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
DRINKIO приятно удивил скоростью и качеством работы. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, заказ всегда полный. Ассортимент большой, сайт понятный. Очень удобно оформлять заказ онлайн https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/pivo/
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: входные двери москва
Обратившись в клинику «Частный Медик 24» в Челябинске, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
В «Частном Медике 24» в Челябинске мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Бизнес-идеи https://idealistworld.com для старта и роста: от микропроектов до стартапов. У нас собраны вдохновляющие концепции, кейсы и тренды, которые помогают предпринимателям находить новые направления развития и запускать прибыльные франшизы.
1xbet giris [url=https://1xbet-13.com/]1xbet giris[/url] .
Капельница от запоя в «Детокс» в Краснодаре — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru
Собрать или выбрать мощный игровой ПК гораздо проще, если опираться на проверенные рекомендации. На сайте собраны обзоры популярных сборок, советы по подбору видеокарт, процессоров и систем охлаждения. Благодаря структурированной информации каждый геймер сможет найти идеальный вариант для своих задач — от казуальных игр до профессионального гейминга.
TopTool https://www.toptool.app/en is a global multilingual tools directory that helps you discover the best products from around the world. Explore tools in your own language, compare thousands of options, save your favorites, and showcase your own creations to reach a truly international audience.
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
ООО “КОМТЕК” продукция https://www.komtek-spb.ru Pro-face в России официальная дистрибуция и сервисная поддержка. Поставка HMI-панелей, дисплеев и промышленных решений. Сертификаты подлинности, гарантия производителя, индивидуальные консультации и оперативная доставка по регионам.
да я после 2си два дня осилил потерпеть и замутил 2се за кампанию(очень приятно, между прочим, пошло). еще 2 дня прошло завтра мб фофки забацаю. Знакомые ставили вв пол колпака, вроде эффектов мало, но один в тот же вечер овердознул 2си и попускался водкой, да и другого только-только отпускало с феников. Просто очень плохо будет, если продукт не удастся. https://gold-rem.ru Хороший магазин, не подставлял меня.
METRYTRH1149920MAMYJRTH
https://медоптима.рф/
Социальная сеть https://itsnew.ru для тех, кто делает сайты и продвигает их в интернете. Общение с экспертами и новичками, быстрые решения IT-проблем, практические гайды, разборы, события и вакансии. Растите в веб-разработке и SEO каждый день.
Мы обеспечиваем комфортные условия для пребывания в клинике Воронежа, чтобы восстановление прошло максимально эффективно. В нашей клинике созданы все условия для вашего удобства и быстрого восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Срочные онлайн-займы https://zaimy-71.ru до зарплаты и на любые цели. Минимум документов, мгновенное решение, перевод на карту 24/7. Работаем по всей России, только проверенные кредиторы и прозрачные ставки.
Оформите займ https://zaimy-86.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
spinbara book of dead spinbara spinbara opinie graczy: Sprawdz opinie graczy i przekonaj sie, dlaczego warto grac w spinbara.
Если близкий человек оказался в сложной ситуации, важно быстро обратиться за квалифицированной помощью. В Екатеринбурге это можно сделать в клинике «Детокс» на Волгоградской, 185. Здесь работают наркологи с большим опытом, которые проведут вывод из запоя безопасно и эффективно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/
В итоге! К-ю чистый. Эффект, очень хорошо!!(Не отлично!!) но был же разговор 1к10!! а то и к15. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази а так всё от души! огромное спасибо! ещё не раз к вам обращюсь!)
Специалисты клиники «Детокс» в Екатеринбурге знают, насколько тяжёлым может быть состояние при запое. Находясь по адресу Волгоградская, 185, центр принимает пациентов круглосуточно и выезжает на вызовы. Здесь предоставляют надёжную помощь и поддержку для восстановления здоровья.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
Binary Options Trading View: Analyze and Trade Smarter Enhance your trading decisions with Binary Options Trading View, using real-time charts and insights to stay ahead of the market. Explore smarter strategies and live analytics at https://kaiseimaru.jp/ !
Пользуюсь DRINKIO уже несколько месяцев, и качество всегда на уровне. Доставка быстрая, всё приходит в целости и сохранности. Курьеры культурные и вежливые, операторы работают быстро. Радует, что сервис доступен в любое время суток. Ассортимент большой, сайт интуитивный. Удобная доставка алкоголя на дом в Москве – https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/tabak/
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Краснодаре. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
https://nicemerch.ru/
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар[/url]
Бот для сигналов криптовалют Обучение торговле с Telegram ботом: Курсы обучения торговле криптовалютой с использованием Telegram ботов.
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Воронеже, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Стоимость услуг начинается от 2500??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости процедур.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в воронеже[/url][url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в воронеже[/url]
Каждый заказ через DRINKIO проходит идеально. Курьеры пунктуальные, доставка всегда вовремя. Ассортимент широкий, сайт интуитивный. Это лучший вариант для Москвы, если ценишь качество и удобство: https://drinkio105.ru/
Вывод из запоя в стационаре в Челябинске — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предоставляем круглосуточную медицинскую помощь, обеспечивая комфорт и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
https://rapidgator.net/file/1e8a68d2eab3d1f4347d205772186601/1xBet_Promo_Code_2026__€1950_Casino_Package__.pdf.html
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Капельница от запоя в Челябинске — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Челябинске. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
spinbara test uczciwosci kasyna spinbara gry stolowe: Oferujemy gry stolowe, takie jak ruletka, blackjack i poker.
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре[/url]
Перед тем как перечислить типичные случаи, отметим главный принцип: домашний формат выбирают, когда безопасность и прогноз сопоставимы со стационаром, а переезд лишь затянет старт терапии и усилит стресс для семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Брал у данного селлера!Хорошо работют=) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм 16 числа заказала товарчика)ну пока еще ничего не получила!!! продаван отправил только половинку(объяснил что не хватило реактивчика) но все остальное вышлет как привезут 100ый ))ждем и надеемся)) заказывала и раньше в этом магазе все было ОГОНЬ))
Наши специалисты в Воронеже имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Binary Options Trading View: Analyze and Trade Smarter Enhance your trading decisions with Binary Options Trading View, using real-time charts and insights to stay ahead of the market. Explore smarter strategies and live analytics at https://kaiseimaru.jp/ !
https://nicemerch.ru/
В центре Екатеринбурга, на улице Волгоградская, 185, находится клиника «Детокс», где можно получить квалифицированный вывод из запоя. Специалисты работают 24/7 и готовы выехать на дом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом екатеринбург[/url]
How to use trading bot in Telegram Автоматическая торговля криптой: Настройте автоматическую торговлю криптовалютой с помощью Telegram бота.
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://aznakaevsk.borda.ru/?1-1-0-00000797-000-0-0-1761136883 Sports betting involves placing wagers on the outcome of sporting events. It’s a vast and complex world, encompassing a wide range of sports, bet types, and strategies.
Палево палево, с сайтом чооо?? https://pilostroy-solikamsk.ru Заказывал не раз. Проблем не было!!!!
Вывод из запоя в Екатеринбурге можно пройти в клинике «Детокс», расположенной на Волгоградской, 185. Здесь обеспечивают полное медицинское сопровождение и поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En fin de compte, Viggoslots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter la page web|
http://www.google.co.ls/url?q=https://aviator-game.su/en/
Je suis fascine par Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Viggoslots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et energique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Кабельная проходка Огнезащита металлоконструкций – комплекс мероприятий, направленных на повышение огнестойкости металлических конструкций.
https://www.santamarta.gov.co/sala-prensa/noticias/resolucion-ndeg-0745?page=142#comment-2275633
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения в «Трезвом шаге» в Воронеже. Ваши личные данные не будут переданы третьим лицам, и вы не будете поставлены на учёт.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
Je suis epate par Posido Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Posido Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement le site est rapide et style, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer plus|
I think I might disagree with some of your analysis. Are the figures solid?
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Краснодаре, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов. Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Ответь в аське!Люди 22куска зарядили ,перед оплатой добро дал ,а потом тишина… Люди переживают,очень!Ответь пожалуйсто!!! https://gold-rem.ru сегодня вот ночью прислал трек. Бьется, радует
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk014.ru
лечение запоя
Капельница от запоя в Челябинске — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
https://defleppardnow.com
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод
https://nicemerch.ru/
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Viggoslots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
VГ©rifier ceci|
https://defleppardfaq.com
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Также возможен выбор курьерки, если какая-то из них не возможна для доставки в ваш город купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Доброго времени суток. 3-й заказ шел ровно неделю с момента оплаты. Спасибо за приятный сувенир :good:. Сам бы себе такой не знаю когда приобрел :). Вобщем за сервис снова 5+
Nice Post. It’s really a very good article. I noticed all your important points. Thanks.
Je suis accro a Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Vbet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En complement la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis emerveille par Posido Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Posido Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons egalement le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Posido Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Posido Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller sur le site|
https://defleppardnow.com
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar025.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию
бездепозитные бонусы казино с выводом
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Betzino Casino assure un fun constant. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Viggoslots Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Viggoslots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer plus|
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-srochno[/url]
Друууууг, ну где же трееек…… купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Скрины с радикала не грузятся. Увы сейчас доказать что-либо сложно, видимо магазин не первый раз кидает уже по отточеной цепочке.
врач нарколог
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Компания [url=https://pro-seo.expert/]продвижение сайтов спб[/url] предоставляет высококачественные услуги по улучшению видимости и привлекательности вашего онлайн-присутствия в столице Северо-Запада.
ключевым фактором успеха онлайн-проектов . Это связано с тем, что интернет стал основным источником информации для потребителей . Поэтому, наличие хорошего сайта и его эффективное продвижение является ключом к успеху .
Продвижение сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге должно основываться на анализе конкурентов и целевой аудитории. Это включает в себя анализ ключевых слов и создание соответствующего контента . Благодаря этому, можно увеличить видимость сайта в поисковых системах .
Одним из наиболее эффективных методов продвижения сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге является социальное медиа-маркетинг. Это связано с тем, что контент-маркетинг позволяет привлечь и удержать внимание целевой аудитории . Кроме того, использование партнерских программ также могут быть эффективными.
Определение целевой аудитории и разработка контента для нее является важным шагом в продвижении сайтов. Это должно включать в себя разработку календаря контента и его реализацию. Благодаря этому, можно улучшить позиции сайта в поисковых результатах и увеличить продажи.
Для продвижения сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге существует большое количество ресурсов для обучения и развития. Это включает в себя инструменты анализа веб-сайтов . Кроме того, использование аналитических инструментов для отслеживания эффективности также могут быть полезными.
Выбор подходящих cms-систем и сервисов является важным шагом в продвижении сайтов. Это должно включать в себя определение бюджета и выбор наиболее эффективных решений . Благодаря этому, можно увеличить эффективность продвижения сайта .
Продвижение сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге может увеличить продажи и привлечь больше клиентов . Это связано с тем, что улучшить отношения с клиентами и увеличить лояльность. Кроме того, мониторинг и анализ результатов продвижения также являются важными.
Оценка эффективности продвижения сайта является важным шагом в продвижении сайтов. Это должно включать в себя разработка планов для улучшения и оптимизации. Благодаря этому, можно увеличить эффективность продвижения сайта и улучшить результаты .
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Ознакомиться с отчётом – https://stainlessad.com/Blog/stainless-steel-toilets
Эта статья предлагает захватывающий и полезный контент, который привлечет внимание широкого круга читателей. Мы постараемся представить тебе идеи, которые вдохновят вас на изменения в жизни и предоставят практические решения для повседневных вопросов. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь!
Уточнить детали – https://bounceandplaytwo.ca/portfolio/languages
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Выяснить больше – https://crosspathlogistics.com/aws-vs-azure-vs-google-which-one-is-better
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Это ещё не всё… – https://wanep.org/wanep/launch-of-r2p-project
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Обратиться к источнику – https://hoppinghawks.com/3-best-nature-weekend-tour-in-japan
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk015.ru
вывод из запоя
https://defleppardfaq.com
https://defleppardnow.com
нарколог на дом
Щоденний дайджест https://dailyfacts.com.ua головні новини, тренди, думки експертів та добірки посилань. Теми – економіка, наука, спорт, культура. Розумна стрічка, закладки, сповіщення. Читайте 5 хвилин – будьте в курсі всього важливого.
Практичний портал https://infokom.org.ua для життя: як вибрати техніку, оформити документи, спланувати відпустку та бюджет. Чек-листи, шаблони, порівняння тарифів та сервісів. Зрозумілі інструкції, актуальні ціни та поради від фахівців.
Регіональний інфопортал https://expertka.com.ua новини міста, транспорт, ЖКГ, медицина, афіша та вакансії. Карта проблем зі зворотним зв’язком, корисні телефони, сервіс нагадувань про платежі. Все важливе – поряд із будинком.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Познакомиться с результатами исследований – https://avlx.uk/2017/06/14/welcome
Оформите займ https://zaimy-73.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
Парни у кого нибудь задерживали посылку в СПСР?Уже неделю как приняли и все не отправят и планируемая дата отправки прошла,а реальную так и не поставили.Позвонил в офис говорят готово к отправке,а че не отправляют они не знают.Сказали позвонить когда менеджеры придут на работу.У кого нибудь такое было?Может это фигня какая то и лучше не идти за посылкой?Как думаете?Раньше просто такого не было максимум 5 дней с даты приема до моих рук проходило,с любого магазина. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки вот такие как ты потом и пишут не прет , не узнавая концентрацию и т д набодяжат к…. ,я вот щас жду посыля и хз ко скольки делать 250
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://primenewsnet.com/restore-a-vanity-unit-to-create-a-super-stylish-piece-of-furniture
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Компания “Московские Ракеты” обеспечивает эффективное [url=https://moscow-rockets.com/seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-usa/]продвижение сайта в сша[/url] для российских и международных бизнес-проектов.
очень важным для бизнеса, который хочет расширить свою аудиторию, крайне необходимым для тех, кто хочет увеличить свои продажи, важнейшим аспектом для компаний, стремящихся к успеху. Это связано с тем, что США?? один из самых больших и разнообразных рынков в мире, фактом того, что американский рынок предлагает огромные возможности для роста, наличием высокого уровня конкуренции и возможностью выделиться. Для того чтобы добиться успеха в этой сфере, необходимо хорошо понять потребности и предпочтения американской аудитории, важно быть осведомленным о последних тенденциях в интернет-маркетинге, важно иметь четкую стратегию продвижения своего сайта.
Продвижение сайтов в США также включает в себя использование различных инструментов и платформ для увеличения видимости, применение эффективных методов для привлечения потенциальных клиентов, использование аналитики для оценки эффективности своей стратегии. Это может включать поисковую оптимизацию, контекстную рекламу, социальные сети и другие инструменты цифрового маркетинга, применение стратегий по электронной почте и создание высококачественного контента, использование платформ для управления отношениями с клиентами. Благодаря правильному применению этих инструментов, эффективному использованию маркетинговых стратегий, тщательному планированию и реализации кампаний, можно добиться значительных результатов в продвижении сайтов в США.
Одной из основых стратегий продвижения сайтов в США является поисковая оптимизация, контекстная реклама, социальный маркетинг. Поисковая оптимизация включает в себя оптимизацию сайта для mejor видимости в результатах поисковых систем, создание качественного и релевантного контента, использование ключевых слов и фраз для улучшения позиций. Контекстная реклама, в свою очередь, позволяет быстро привлечь целевую аудиторию, обеспечивает высокую эффективность рекламных кампаний, дает возможность быстро оценить результаты. Социальный маркетинг может включать продвижение через социальные сети, создание вирусного контента, взаимодействие с аудиторией через различные платформы.
Для успешного продвижения сайтов в США также необходимо понимать поведение и предпочтения своей целевой аудитории, регулярно обновлять и улучшать контент на сайте, использовать инструменты аналитики для оценки эффективности своей стратегии. Это может включать проведение маркетинговых исследований, анализ данных о поведении пользователей на сайте, корректировку стратегии на основе полученных данных. Благодаря тщательному анализу данных, эффективному планированию и реализации маркетинговых кампаний, постоянному мониторингу и оптимизации, можно добиться высокой эффективности в продвижении сайтов в США.
Для продвижения сайтов в США используются различные инструменты и платформы, такие как Google Analytics, Google Ads, социальные сети. Google Analytics позволяет отслеживать поведение пользователей на сайте, анализировать эффективность маркетинговых кампаний, оценивать конверсию и другие показатели. Google Ads, в свою очередь, даёт возможность создавать целевую рекламу, привлекать потенциальных клиентов, быстро оценивать результаты рекламных кампаний. Социальные сети могут включать платформы nhu Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, где можно создавать и продвигать контент, взаимодействовать с аудиторией, использовать платную рекламу.
Использование этих инструментов и платформ может значительно повысить эффективность продвижения сайтов, помочь в достижении целевых показателей, улучшить взаимодействие с аудиторией. Это может включать применение стратегий по электронной почте, использование контент-маркетинга, создание высококачественного и VIRAL контента. Благодаря правильному выбору инструментов, эффективному использованию платформ, постоянному анализу и оптимизации, можно добиться высоких результатов в продвижении сайтов в США и увеличить свою онлайн-присутствие.
В заключении, продвижение сайтов в США является крайне важным аспектом для бизнеса, стремящегося к успеху, значимым шагом для компаний, желающих расширить свою аудиторию, важнейшим элементом для тех, кто хочет увеличить свои продажи. Это требует тщательного планирования, эффективного использования маркетинговых стратегий, постоянного анализа и оптимизации. Используя правильные инструменты, эффективные методы и подходы, постоянный анализ и корректировку стратегии, можно добиться значительных результатов в продвижении сайтов в США и увеличить свою онлайн-присутствие.
Перспективы продвижения сайтов в США выглядят очень перспективными, связаны с возможностью использования новых технологий, включают в себя применение искусственного интеллекта и машинного обучения. Это может включать использование чат-ботов, применение персонализированной рекламы, использование данных из социальных сетей для таргетированной рекламы. Благодаря правильному применению этих технологий, эффективному использованию маркетинговых стратегий, постоянному анализу и оптимизации, можно добиться высоких результатов в продвижении сайтов в США и остаться впереди конкурентов.
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://lavoiedesdeesses.com/building-brands-through-customer-service-2
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://at-home-care.com/the-importance-of-regular-health-screenings-for-seniors
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Только для своих – https://emmelinebennenbroek.nl/hoe-jij-mee-mag-veranderen-met-je-kind
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Посмотреть подробности – https://primenewsnet.com/citroen-could-revive-the-third-car-for-loeb-breen-winning-couple
Je ne me lasse pas de Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une experience immersive. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire la suite|
Je suis sous le charme de Viggoslots Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est transparent et rapide, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Viggoslots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour completer la navigation est fluide et facile, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
J’adore l’energie de Betzino Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Betzino Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui stimule l’engagement.
Lancer le site|
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Секреты успеха внутри – https://elgaz.turek.pl/witaj-swiecie
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Узнай первым! – https://primenewsnet.com/top-ten-kitchen-shortcuts-for-indian-food-delights
https://portfolio.newschool.edu/jeffreyespinoza95/2015/10/15/boat-house-gunning-dory/#comment-104827
J’ai un faible pour Vbet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Vbet Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute soudee.
Vbet|
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Смотрите также – https://pastafresca-eg.com/hello-world
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Открыть полностью – https://mppee.gob.ve/?p=86822
Je suis emerveille par Posido Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Posido Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller sur le web|
Je suis sous le charme de Vbet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par contre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Vbet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.casinovbetfr.com|
Je suis enthousiasme par Posido Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Posido Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus le design est moderne et energique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le lien communautaire.
Tout apprendre|
https://defleppardnow.com
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Только факты! – https://catsanz.com/oh-youve-changed-and-i-couldnt-agree-more
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Смотрите также… – https://pbgfrwellness.com/workout-9
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk015.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
после этого случая я стал курить не сигареты конечно рц вообще понравилось и быстро дошло ,делал 1к8 великолепная вещь магазу продвижений купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки сегодня вот ночью прислал трек. Бьется, радует
Практичний довідник https://altavista.org.ua здоров’я, будинок, авто, навчання, кар’єра. Таблиці, інструкції, рейтинги послуг, порівняння цін. Офлайн доступ і друк шпаргалок. Економимо ваш час.
Універсальний інфопортал https://dobraporada.com.ua “на кожен день”: короткі інструкції, таблиці, калькулятори, порівняння. Теми – сім’я, фінанси, авто, освіта, кулінарія, спорт. Персональна стрічка, добірки тижня, коментарі та обране.
Інфопортал про головне https://ukrpublic.com економіка, технологія, здоров’я, екологія, авто, подорожі. Короткі статті, відео пояснення, корисні посилання. Персональні рекоме
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – http://boardbird.se/paintings-oilpainting-portrait-fineart-contemporaryart/maleri5_webb
http://houmy.ru/
I really love this article.
meilleur casino en ligne: telecharger 1xbet pour android
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Посмотреть всё – https://www.springcitytreehouses.com/spring-city-treehouses/gallery/img_1274
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения в «Трезвом шаге» в Воронеже. Ваши личные данные не будут переданы третьим лицам, и вы не будете поставлены на учёт.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
важаемый ТС прошу разобраться с заказом,всё оплаченно вам,вот только игнор в бросиксе и посылки нету до сих пор. Заранее благодарен. https://umc-detstvo.ru Спасибо огромное вам многим за понимание.
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
Как заработать дома: идеи и советы Современные технологии открывают новые горизонты для удаленного заработка. Если вам интересен удаленный заработок, существует множество способов, как получить доход, не выходя из дома. Один из самых популярных способов — работа на фрилансе. Вы можете зарегистрироваться на фриланс-платформах, таких как narkolog-tula022.ru, и предлагать свои услуги: копирайтинг, графический дизайн, программирование. Другой вариант — работа в онлайн-проектах. Например, проходение опросов или тестирование веб-сайтов. Это отличный способ получить доход без вложений. Если у вас есть хобби или умения, подумайте о создании собственного бизнеса на дому, например, создании уникальных изделий ручной работы. Рекомендации для работы на дому: организуйте рабочее место, распределяйте время и берите на себя только те проекты, которые вам нравятся. Самостоятельная работа требует самодисциплины, но может принести значительный доход. Идеи для заработка можно найти на специализированных ресурсах. Главное — не бояться пробовать новое!
https://defleppardnow.com
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://remzona.zt.ua/MaterialiDlyaRemonta/azartnie-igri-v-internete
Оформление второго гражданства за границей становится всё более важным среди россиян.
Такой вариант даёт широкие горизонты для работы и бизнеса.
Второй паспорт помогает легче пересекать границы и упрощать поездки.
Также подобное решение может улучшить финансовую стабильность.
Паспорт Франции
Большинство граждан рассматривают ПМЖ как инструмент защиты.
Получив ВНЖ или второй паспорт, человек легко открыть бизнес за рубежом.
Каждая страна предлагают свои программы получения вида на жительство.
Поэтому вопрос оформления становится всё более значимой для тех, кто ищет стабильность.
Портал-довідник https://speedinfo.com.ua таблиці норм та термінів, інструкції «як зробити», гайди з сервісів. Будинок та сад, діти, навчання, кар’єра, фінанси. Розумні фільтри, друк шпаргалок, збереження статей. Чітко, структурно, зрозуміло.
Інформаційний медіацентр https://suntimes.com.ua новини, лонгріди, огляди та FAQ. Наука, культура, спорт, технології, стиль життя. Редакторські добірки, коментарі, повідомлення про важливе. Все в одному місці та у зручному форматі.
Інформаційний сайт https://infoteka.com.ua новини, практичні гайди, огляди та чек-листи. Технології, здоров’я, фінанси, будинок, подорожі. Розумний пошук, закладки, підписки на теми. Пишемо просто й у справі, спираючись на перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
врач нарколог на дом
Капельница от запоя в «Детокс» в Краснодаре — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Наши специалисты в Челябинске имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому челябинск[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Краснодаре. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя цена краснодар[/url]
Клиника «Частный Медик 24» в Челябинске работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время дня и ночи, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
https://defleppardfaq.com
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Краснодаре — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения. Наши специалисты проводят процедуру с соблюдением всех юридических норм и этических стандартов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Воронеже, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас. Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Да хорошо бы было, сегодня уже получу трек. Но конечно напугали всякие кому типа ам плохой пришёл. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки где вообще оператор или кто ни будь? бабло уплочено и жду доставку а на связи ни кого нету!!!!!!!!!!
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]частный нарколог на дом жуковский[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg013.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
https://www.azsenaterepublicans.gov/post/senator-jake-hoffman-files-ethics-complaint-against-democrat-lawmaker-for-endangering-public-safety
Сучасний інфосайт https://overview.com.ua наука та техніка, стиль життя, спорт, освіта, їжа та DIY. Зрозумілі пояснення, покрокові плани, тести та огляди. Розумні фільтри за інтересами, коментарі, закладки та офлайн-читання – все, щоб заощаджувати час.
Онлайн-журнал https://elementarno.com.ua про все: новини та тенденції, lifestyle та технології, культура та подорожі, гроші та кар’єра, здоров’я та будинок. Щоденні статті, огляди, інтерв’ю та практичні поради без води. Читайте перевірені матеріали, підписуйтесь на дайджест та будьте в темі.
Універсальний онлайн-журнал https://ukrglobe.com про все – від науки та гаджетів до кіно, психології, подорожей та особистих фінансів. Розумні тексти, короткі гіди, добірки та думки експертів. Актуально щодня, зручно на будь-якому пристрої. Читайте, зберігайте, діліться.
Портал корисної інформації https://inquire.com.ua практичні поради, відповіді експертів, таблиці та шпаргалки. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, гроші, гаджети, авто, туризм. Швидкий пошук, обране, розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня.
https://defleppardnow.com
В Екатеринбурге сервис «Похмельная Служба / Stop-Alko» предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому — врач приезжает оперативно, ставит капельницу и обезболивает состояние.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в екатеринбурге[/url][url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в екатеринбурге[/url]
Сегодня на мыло пришло письмо с новостью что заказ отправлен и номер трека который бьёться:good: пока всё норм идёт, со мной связь поддерживают через скайп, игнора не было, когда получу отпишу за качество вес и тд купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Привет! Что хочу сказать по поводу работы магазина- просто супер, связались сразу, приняли заказ, обработали и на следующий день он уже в пути. 3 дня и уже у меня. Качество отличное! В общем респект Вам ребята, так держать, не сбавляйте оборотов и хорошо будет всем!
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Детокс» в Краснодаре — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предоставляем круглосуточную медицинскую помощь, обеспечивая комфорт и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Челябинска, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента. Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время дня и ночи, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в краснодаре[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Екатеринбурге предлагает быстрый и безопасный вывод из запоя. Адрес медучреждения: Волгоградская, 185 — удобно добраться и при необходимости вызвать врача на дом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в екатеринбурге[/url]
Если близкий человек оказался в тяжелом состоянии, в Екатеринбурге поможет клиника «Детокс». Адрес: Волгоградская, 185 — здесь работают опытные наркологи и круглосуточно оказывают вывод из запоя.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
https://internet-leman.ru/
реабилитация зависимых [url=www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru]www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru[/url] .
Супер ребята. Питер без сбоев купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази всех с новым годом и удачных покупок
Entdecken Sie die besten Weinverkostungen in Wien auf [url=https://weinverkostung.neocities.org/]wien weinverkostung[/url].
In der Stadt finden sich zahlreiche Weinguter, die eine lange Geschichte haben.
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge. Zusatzlich gibt es oft kulinarische Begleitungen, die den Genuss erhohen.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten. Das bekannte Heurigenviertel in Grinzing ladt zu gemutlichen Verkostungen ein.
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien. Dabei erfahren Besucher mehr uber die Herstellung der Weine.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt. Der beliebte Gemischte Satz ist eine lokale Spezialitat, die aus mehreren Traubensorten besteht.
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack. Die mineralischen Noten der Wiener Weine sind besonders ausgepragt.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer. Es empfiehlt sich, langsam zu trinken, um die Nuancen zu schmecken.
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?. Viele Veranstalter bieten thematische Verkostungen an.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?.
Про все в одному місці https://irinin.com свіжі новини, корисні інструкції, огляди сервісів і товарів, що надихають історії, ідеї для відпочинку та роботи. Онлайн-журнал із фактчекінгом, зручною навігацією та персональними рекомендаціями. Дізнайтесь головне і знаходите нове.
1xbet t?rkiye giri? [url=www.1xbet-17.com/]1xbet t?rkiye giri?[/url] .
Ваш онлайн-журнал https://informa.com.ua про все: великі теми та короткі формати – від трендів та новин до лайфхаків та практичних порад. Рубрики за інтересами, огляди, інтерв’ю та думки. Читайте достовірно, розширюйте світогляд, залишайтеся на крок попереду.
Онлайн-журнал https://ukr-weekend.com про все для цікавих: технології, наука, стиль життя, культура, їжа, спорт, подорожі та кар’єра. Розбори без кліше, лаконічні шпаргалки, інтерв’ю та добірки. Оновлення щоденно, легке читання та збереження в закладки.
Онлайн-журнал https://worldwide-ua.com про все: новини, тренди, лайфхаки, наука, технології, культура, їжа, подорожі та гроші. Короткі шпаргалки та великі розбори без клікбейту. Фактчекінг, зручна навігація, закладки та розумні рекомендації. Читайте щодня і залишайтеся у темі.
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Челябинске, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов. Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно челябинск[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Челябинске. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
На сегодняшний день тематика зависимостей становится особенно важной. Если вы раздумываете о нарколога на дом в Туле, сайт narkolog-tula023.ru предлагает разнообразные наркологических услуг. Терапия зависимостей может быть непростым процессом, однако выездной нарколог предоставляет помощь при алкоголизме и другим проблемам, связанным с зависимостям непосредственно на дому. Первичная консультация – это основной шаг к нормальной жизни. Профессионалы проведут диагностику зависимости, помогут составить программу реабилитации и предложат методы психотерапии для лечения зависимостей. Анонимное лечение гарантирует полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для многих пациентов. Домашняя медицинская помощь позволяет не только лишь проходить лечение в удобной обстановке, но и получать поддержку семьи, что играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления. Профилактика алкоголизма и возвращение к нормальной жизни после наркотиков также являются частью комплекс услуг, предлагаемых специалистами. Связывайтесь за помощью на narkolog-tula023.ru, чтобы получить профессиональную помощь.
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Воронеже, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Стоимость услуг начинается от 2500 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости процедур.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
http://houmy.ru/
Мне обещали бонус за задержку в 5 + 3 =8 грамм , так и прислали +))) спасибо.+))) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Спасибо. Все по плану получилось. Получил в лучшем виде)
Entdecken Sie die besten Weinverkostungen in Wien auf [url=https://weinverkostung.neocities.org/]weinverkostung wien grinzing[/url].
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge. Zusatzlich gibt es oft kulinarische Begleitungen, die den Genuss erhohen.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten. Das bekannte Heurigenviertel in Grinzing ladt zu gemutlichen Verkostungen ein.
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien. Oft werden auch seltene Weine vorgestellt, die nur lokal erhaltlich sind.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt. Auch der fruchtige Grune Veltliner zahlt zu den bekanntesten Wei?weinen der Region.
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack. Die warmen Sommer sorgen fur vollmundige Aromen.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer. Wasser und Brot helfen, den Gaumen zwischen verschiedenen Weinen zu neutralisieren.
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?. Ein Weinjournal kann helfen, personliche Favoriten festzuhalten.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
In der Stadt finden sich zahlreiche Weinguter, die eine lange Geschichte haben.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
Zusatzlich konnen Gaste direkt beim Erzeuger kosten.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Auch der fruchtige Grune Veltliner zahlt zu den bekanntesten Wei?weinen der Region.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer.
Порча через наркотиков — это
комплексная хоботня, охватывающая физическое, психологическое и соц
здоровье человека. Употребление таких наркотиков, яко
кокаин, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик» или «бошки»,
что ль огласить для неконвертируемым следствиям как чтобы организма, так и
чтобы федерации в целом. Хотя даже у выковывании
зависимости возможно восстановление — главное, чтобы зависимый человек устремился за помощью.
Эпохально помнить, яко наркомания лечится,
равным образом оправдание одаривает шансище сверху свежую жизнь.
https://internet-leman.ru/
Наши специалисты в Челябинске имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
https://defleppardnow.com
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Чтобы восстановить силы и выйти из состояния запоя, важно довериться профессионалам. В Екатеринбурге клиника «Детокс» на Волгоградской, 185 предлагает современные методы терапии. Здесь помогают пациентам разного возраста, обеспечивая комфортные условия лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Онлайн-журнал 24/7 https://infoquorum.com.ua все про життя та світ — від технологій та науки до кулінарії, подорожей та особистих фінансів. Короткі нотатки та глибока аналітика, рейтинги та добірки, корисні інструменти. Зручна мобільна версія та розумні підказки для економії часу.
Ваш онлайн-журнал https://informative.com.ua про все: новини, розбори, інтерв’ю та свіжі ідеї. Теми — від психології та освіти до спорту та культури. Зберігайте в закладки, ділитесь з друзями, випускайте повідомлення про головне. Чесний тон, зрозумілі формати, щоденні поновлення.
Щоденний онлайн-журнал https://republish.online про все: від швидкого «що сталося» до глибоких лонґрідів. Пояснюємо контекст, даємо посилання на джерела, ділимося лайфхаками та історіями, що надихають. Без клікбейту – лише корисні матеріали у зручному форматі.
Онлайн-журнал https://mediaworld.com.ua про бізнес, технології, маркетинг і стиль життя. Щодня — свіжі новини, аналітика, огляди, інтерв’ю та практичні гайди. Зручна навігація, чесні думки, експертні шпальти. Читайте, надихайтеся, діліться безкоштовно.
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Воронеже, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов. Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя требует профессионального подхода и грамотного подбора медикаментов. В Екатеринбурге этим занимается клиника «Детокс», расположенная на Волгоградской, 185. Здесь вам помогут выйти из кризисного состояния и восстановить силы без риска для здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов екатеринбург[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с использованием современных методов детоксикации и инфузионной терапии. Наши специалисты обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в краснодаре[/url]
чувак брал я тоже тут 2 ci некоторым понравилось некоторым нет , лично я поднимал даже с неё бабок норм, народу нравиться , а если этот каиф тебе не нравиться нех писать что тусишка бычий кайф , бычий каиф немного другое, а такои продукт не может быть бычий кайф это я тебе отвечаю, со входом согласен по ноздре ваще не вариант ! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану В целом о работе магазина – как клиент,я доволен!!!:good:
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Воронежа, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента. Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
https://defleppardnow.com
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Воронеже. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru
This article actually helped me with a report I was doing.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
https://defleppardfaq.com
Готуємо, прибираємо https://ukrdigest.com прикрашаємо легко. Домашній онлайн-журнал з покроковими рецептами, лайфхаками з прання та прибирання, ідеями сезонного декору, планами меню та бюджетом сім’ї. Зберігайте статті, складайте списки справ та знаходите відповіді на побутові питання.
Домашній онлайн-журнал https://zastava.com.ua про життя всередині чотирьох стін: швидкі страви, прибирання за планом, розумні покупки, декор своїми руками, зони зберігання, дитячий куточок та догляд за вихованцями. Практика замість теорії, зрозумілі чек-листи та поради, які економлять час та гроші.
Чтобы восстановить силы и выйти из состояния запоя, важно довериться профессионалам. В Екатеринбурге клиника «Детокс» на Волгоградской, 185 предлагает современные методы терапии. Здесь помогают пациентам разного возраста, обеспечивая комфортные условия лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Ваш помічник https://dailymail.com.ua по дому: інтер’єр та ремонт, організація простору, здоровий побут, догляд за технікою, рецепти та заготівлі, ідеї для вихідних. Тільки практичні поради, перевірені матеріали та зручна навігація. Зробіть будинок красивим та зручним без зайвих витрат.
Je suis epate par Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Essayer ceci|
Все про будинки https://vechorka.com.ua де приємно жити: швидкі рецепти, компактне зберігання, текстиль та кольори, сезонний декор, догляд за речами та технікою, дозвілля з дітьми. Покрокові інструкції, корисні вибірки, особистий досвід. Затишок починається тут – щодня.
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis sous le charme de Betzino Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Тьфу-тьфу-тьфу… =( купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Я не знаю как так получается что одним приходит качество, другим не качественный товар , но я второй раз на этом магазе заказываю и второй раз всё ровно с АМ-2233 полностью доволен. Я бы фото кинул, но чо то не загружается оно.
Вывод из запоя на дому в Воронеже — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Экстренное вытрезвление в Челябинске — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому челябинск[/url]
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Vbet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le design est style et moderne, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller voir|
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Posido Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Posido Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Краснодаре, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Стоимость услуг начинается от 2400??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости процедур.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
https://internet-leman.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с использованием современных методов детоксикации и инфузионной терапии. Наши специалисты обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/
Uso http://passfun.awardspace.us/index.php/topic,58643.0.html desde hace una semana y los resultados son fantásticos. ¡No más picor!
https://defleppardnow.com
Наши специалисты в Воронеже готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
В «Частном Медике 24» в Челябинске мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
ло Канта Koh Lanta чат
https://defleppardfaq.com
Я взял всего 15т.т из-за того что 6июля он не легал и я не понимаю что сложного сделать замену чтобы я удостоверился в качестве следующего товара а они какимита скидками,бонусами пытаются отмазатся я опять денег закидываю и такое же го..но забираю! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм уже ожидается что нибудь?
В центре Екатеринбурга, на улице Волгоградская, 185, находится клиника «Детокс», где можно получить квалифицированный вывод из запоя. Специалисты работают 24/7 и готовы выехать на дом.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg21.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Восстановление после алкогольной зависимости в городе Тула – важный этап на пути к выздоровлению. Нарколог на дом клиника предоставляет профессиональное лечение алкоголизма с индивидуальными программами‚ включая детоксикацию и психотерапевтическую поддержку. Посещение нарколога способствует выявить методы лечения‚ такие как групповая терапия и адаптация в обществе. Поддержка семьи также является важным фактором. Реабилитационный центр обеспечивает анонимную помощь и профилактику рецидивов‚ что способствует эффективному восстановлению после зависимости от алкоголя.
Untested loli po*rn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Челябинске, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас. Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом через «Stop-Alko» в Екатеринбурге — это помощь, когда вы не можете самостоятельно добраться до клиники. Первая помощь сразу у вас дома.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Экстренное вытрезвление в клинике «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в воронеже[/url]
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Краснодаре — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения. Наши специалисты проводят процедуру с соблюдением всех юридических норм и этических стандартов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
так у вас два сайта рабочих? ассортимент на них разный. на каком заказывать? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази в курске есть ваш магаз?
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar116.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в краснодаре[/url]
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/hied/2020/02/25/congrats-dr-williams-2020-first-place-dissertation-award-winner/comment-page-1175/#comment-319947
Je suis captive par Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Viggoslots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Avancer|
Ко ланта Krabi
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Viggoslots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour faire court, Viggoslots Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Betzino Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En bonus le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir la page|
Je suis completement seduit par Vbet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus exclusifs.
https://vbetcasino366fr.com/|
J’adore la vibe de Vbet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Vbet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons que l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
Plongez-y|
рейтинг сео компаний [url=https://reiting-seo-kompanii.ru/]рейтинг сео компаний[/url] .
Je suis completement seduit par Posido Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Posido Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un atout les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
Touchez ici|
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Ко ланта чат Ко ланта чат
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec018.ru
вывод из запоя
https://defleppardnow.com
Сделал заказ , все гуд и качество понравилось купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану ОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!!
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg015.ru
вывод из запоя оренбург
Sometimes, the sheer magnitude of the information seems overwhelming.
казино онлайн с выводом Устали от ограничений? Мобильное казино – это ваш билет в мир развлечений без лишних хлопот. Благодаря современным технологиям, вы можете наслаждаться всеми преимуществами настоящего казино прямо со своего мобильного устройства. Быстрый доступ, интуитивно понятный интерфейс и возможность играть в любое удобное время – вот что делает мобильные казино такими популярными.
Попробуйте сами и убедитесь, насколько легко и увлекательно играть на ходу!
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом телефон[/url]
KingSize вас не отловить нигде, в аське нету((( на страницу прайс не заходите, откликнитесь пожалуйста) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Не вздумайте платить ему без Гаранта через которого он не работаем,этим самым доказывает свою не надежность!
Домашній онлайн-журнал https://ukrcentral.com про розумний побут: планування харчування, прибирання за таймером, екоради, мінімалізм без стресу, ідеї для малого метражу. Завантажені чек-листи, таблиці та гайди. Заощаджуйте час, гроші та сили — із задоволенням.
Журнал для домашнього https://magazine.com.ua життя без метушні: плани прибирання, меню, дитячий куточок, вихованці, міні-сад, дрібний ремонт, побутова безпека. Короткі інструкції, корисні списки та приклади, що надихають. Зробіть будинок опорою для всієї родини.
Ваш провідник https://ukrchannel.com до порядку та затишку: розхламлення, зонування, бюджетний ремонт, кухонні лайфхаки, зелені рослини, здоров’я будинку. Тільки перевірені поради, списки справ та натхнення. Створіть простір, який підтримує вас.
Практичний домашній https://publish.com.ua онлайн-журнал: планинг тижня, закупівлі без зайвого, рецепти з доступних продуктів, догляд за поверхнями, сезонні проекти. Тільки у справі, без клікбейту. Зручна навігація та матеріали, до яких хочеться повертатися.
Sweet Bonanza: A Burst of Fruity Fun!
Dive into the colorful world of Sweet Bonanza, where juicy fruits and sugary treats bring endless excitement and big wins. Spin the reels and taste the sweetness of luck at [url=https://k8-casino.jp/]https://k8-casino.jp/[/url] !
лучшие автоматы Выбор надежного онлайн-казино – это инвестиция в ваше спокойствие и безопасность. Не торопитесь, проведите исследование и выбирайте казино, которое соответствует вашим требованиям и имеет хорошую репутацию. Помните, что азартные игры должны приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Играйте ответственно!
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://info-sng.org/bonjour-tout-le-monde
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://xplorecart.com/wordpress-plugins/translatepress-pro-wordpress-multilingual-plugin-2-5-4-nulled-free-download
http://www.google.com.fj/url?q=https://takesbet.com/promo-code/1win
https://defleppardnow.com
Похмелье – это неприятное состояние, которое возникает вследствие чрезмерного употребления спиртных напитков. Симптомы сопровождаются головной болью, тошнотой и обезвоживанием. Для ускорения состояния можно использовать капельницу, которая обеспечивает организм флюидами и электролитами. На сайте narkolog-tula025.ru можно найти информацию о домашних методах для лечения похмелья, включая инфузионную терапию. Капельница наполняется глюкозой, витаминами и необходимыми минералами, что способствует очищению организма. Важно помнить, что при сильном похмелье следует попросить за медицинской помощью и проконсультироваться с врачом.Правильно составленные компоненты в капельнице помогут быстро восстановить здоровье и вернуть жизненные силы.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Дополнительно читайте здесь – https://mardomegolestan.ir/%D9%86%D8%B3%D8%A8%D8%AA-%D8%AA%D9%88%D9%84%D8%AF-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D9%85%D8%B1%DA%AF-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%DA%AF%D9%86%D8%A8%D8%AF%DA%A9%D8%A7%D9%88%D9%88%D8%B3-%DB%B5%DB%B0-%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%B5%D8%AF-%DA%A9%D8%A7
Кекс знакомый бpал тут- качество-самолет! Меня угостил – я тоже остался доволен! https://restoranroyal.ru Бразы вы снова в теме, если да то скоро заряусь к вам жду ответа)
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Информация доступна здесь – https://clickfabio.com/the-art-of-nail-sculpting-a-masterclass-in-acrylic-extensions
ло Канта Ко ланта
Решение о кодировании принимает врач после очной оценки. Методика подбирается индивидуально, с обязательным информированным согласием. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие понять, когда процедура уместна, а когда стоит отложить или выбрать альтернативу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена[/url]
Je suis totalement conquis par Viggoslots Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Viggoslots Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Viggoslots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement attrayant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Перейти к полной версии – https://www.administratiekantoor-nissewaard.nl/admin
J’adore la vibe de Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses continues.
Essayer ceci|
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Только для своих – http://eishes.com/o-rabote
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Только для своих – https://gesundheitsvereinbruckfusch.at/2024/10/22/hallo-welt
МАГАЗ СУПЕР!,брал5 гр ск качество отменное все сделанно ровно,даже фото не понадобилось,кристалики отличные без мутного оттенка,плаватся отлично,присутствует запах уксусного ангедрида,ВЫРАЖАЮ ОГРОМНУЮ БЛАГОДАРНОСТЬ!ВСЕ СУПЕР ПРОДОЛЖАЙТЕ В ТОМ ЖЕ ДУХЕ! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази По порядку: мне 35. Да, это единичный случай, потому как работал с другими поставщиками до последнего запрета. 12к+транспорт- это, видимо, “не о чем”. По твоим словам, мне следует заткнутся, читать о магазине какой он хороший и наслаждаться жизнью?[/quote]
Je suis completement seduit par Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, en revanche des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Posido Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je ne me lasse pas de Vbet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Vbet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Posido Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Posido Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
http://www.posidocasino365fr.com|
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://stroydizayn.kyiv.ua/ZaboriDlyaDachi/yak-vibrati-parkan
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk013.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее – https://seocompanyphilippines.com/the-dos-and-donts-of-seo-common-mistakes-to-avoid
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://eidparry.com/products/nutraceuticals/nut-qua-pro10
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://artecampo.tercerimpactoproducciones.com/index.php/2023/06/22/the-art-of-negotiation-tips-for-successful-business-deals
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
А что дальше? – https://www.exceledgeintl.com/win-hearts-boost-sales
Медіа для дому https://government.com.ua та офісу: інтер’єр та побут, сімейні питання, цифрові тренди, підприємництво, інвестиції, здоров’я та освіта. Збірники порад, випробування, аналітика, топ-листи. Лише перевірена інформація.
Все, що важливо https://ua-meta.com сьогодні: будинок та сім’я, кар’єра та бізнес, технології та інтернет, дозвілля та спорт, здоров’я та харчування. Новини, лонгріди, посібники, добірки сервісів та додатків. Читайте, вибирайте, застосовуйте на практиці.
Затишок щодня https://narodna.com.ua ідеї для інтер’єру, зберігання в малих просторах, безпечний побут із дітьми, зелені рішення, догляд за технікою, корисні звички. Інструкції, схеми та списки. Перетворіть будинок на місце сили та спокою.
Універсальний гід https://dailyday.com.ua по життю: затишний будинок, щасливі стосунки, продуктивна робота, цифрові інструменти, фінансова грамотність, саморозвиток та відпочинок. Короткі формати та глибокі розбори – для рішень без метушні.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Обратиться к источнику – http://www.usdirectoryfinder.com/plan-to-reduce-jail-population-in-spokane-county-washington
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Прочитать подробнее – https://template156.webekspor.com/kredit-mudah
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Это ещё не всё… – https://www.milanweddingtuyenquang.com/the-surge-of-edtech-platforms-changing-education-and-learning
Для проведения торжественных мероприятий, таких как свадьбы, юбилеи и корпоративные вечера, в Москве доступен широкий выбор [url=https://crimea.moscow/weddings]зал банкетный[/url], каждый из которых предлагает уникальную атмосферу и высокое качество обслуживания.
играют ключевую роль в создании незабываемых моментов . Они предназначены для проведения различных торжеств и праздников . При выборе банкетного зала следует учитывать техническое оснащение и локацию .
Банкетные залы часто находятся в отелях и ресторанах . Это позволяет организовывать мероприятия на высоком уровне. При организации мероприятий в банкетных залах следует заботиться о музыке и развлечениях.
Планирование мероприятий в банкетных залах включает в себя много деталей . Это включает в себя определение списка гостей и приглашений. Правильное планирование помогает избежать ошибок и просчетов .
Планируя мероприятие в банкетном зале, необходимо учитывать время года и погоду . Удобство и комфорт являются ключевыми факторами при выборе зала . Меню и напитки должны быть тщательно подобраны .
Техническое оснащение банкетных залов должно быть соответствующим для каждого типа события. Это может включать системы кондиционирования и вентиляции. Качественное техническое оснащение помогает создать профессиональную атмосферу .
Банкетные залы могут иметь уникальный и авторский дизайн . Это включает в себя столы и стулья . Профессиональный персонал должен быть готов помочь в любой ситуации .
Выбор банкетного зала включает в себя анализ нескольких вариантов . Это может включать изучение отзывов и рекомендаций . Правильный выбор помогает создать незабываемую атмосферу .
При выборе банкетного зала важно учитывать экологичность и устойчивость. Банкетные залы должны быть готовы к нестандартным решениям и??ам. Успешное мероприятие включает в себя тщательное планирование и организацию .
отделка подвала [url=https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/]отделка подвала[/url] .
торкрет бетон цена [url=https://torkretirovanie-1.ru]торкрет бетон цена[/url] .
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-17.com/]1 xbet[/url] .
анонимная наркология [url=www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru]www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru[/url] .
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Читать дальше – https://bongda360.site/365-the-thao-truc-tiep-bong-da-full-hd-khong-giat-lag
http://www.google.no/url?q=https://takesbet.com/mobile-app/betwinner
Platform [url=https://ht.xyz/home]hypertradehypertrade crypto[/url] offers users access to a wide range of cryptocurrency instruments for effective trading.
that offers a new perspective on how to navigate complex economic systems. This concept is based on a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive economic growth. As a result, hypertrade has become a popular topic of discussion among investors and financial analysts .
The potential of hypertrade is still being explored and developed, but its potential is undeniable . With its emphasis on creating a more transparent and efficient financial system, hypertrade is seen as a key driver of economic growth and development. Moreover, hypertrade is seen as a tool for promoting economic stability and reducing the risk of financial crises.
Hypertrade is built around a core set of values that prioritize transparency, efficiency, and fairness . One of the key principles of hypertrade is the emphasis on creating a community of like-minded individuals who share knowledge and expertise . This principle is demonstrated by the emphasis on ongoing education and training, to ensure that participants have the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
Another key principle of hypertrade is the importance of adaptability and flexibility in responding to changing market conditions . This principle is demonstrated by the focus on continuous monitoring and evaluation, to ensure that the strategy remains effective and relevant. Furthermore, hypertrade is guided by the principle of transparency, with a focus on openness and honesty in all dealings .
Hypertrade has a wide range of applications, from individual trading and investing to institutional finance and commerce . One of the most significant applications of hypertrade is in the area of asset management, where it can be used to optimize investment portfolios and maximize returns . This application is evident in the creation of online platforms and forums where traders and investors can connect and share information .
Another significant application of hypertrade is in the area of market research and analysis, where it can be used to identify trends and patterns . This application is demonstrated by the focus on developing a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive economic growth and financial markets. Moreover, hypertrade is being explored as a way to promote financial inclusion and reduce inequality, by providing access to financial markets and services .
The future of hypertrade is exciting and full of possibilities, with potential applications in a wide range of areas . As hypertrade continues to evolve and develop, it is likely to have a significant impact on the financial industry and beyond . This will require a commitment to ongoing education and training, to ensure that participants have the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
One of the key trends that is likely to shape the future of hypertrade is the growing importance of blockchain and other distributed ledger technologies, in supporting and facilitating hypertrade . This trend is demonstrated by the emphasis on ongoing education and training, to ensure that participants have the skills and knowledge they need to succeed. Furthermore, the future of hypertrade is expected to be influenced by a range of economic trends, including shifts in global trade patterns and demographic changes .
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk025.ru
вывод из запоя цена
6-APB, белый кристалический порошок, 1000р… Это типа настоящий 6-APB? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Здрасте Бразы!!!!:hello:
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Этот текст сочетает в себе элементы познавательного рассказа и аналитической подачи информации. Читатель получает доступ к уникальным данным, которые соединяют прошлое с настоящим и открывают двери в будущее.
Продолжить изучение – https://assure.ma/v2/en/blog/assurance-maroc/les-differents-types-d-assurance
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время дня и ночи, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Краснодаре, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов. Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена краснодар[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Краснодаре. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
explorethefuture – Love the modern design, feels like a place full of inspiration.
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Обратитесь за информацией – https://www.jiyuuku.com/2019/09/20/%E3%83%86%E3%83%AC%E3%83%93%E3%82%B7%E3%83%A7%E3%83%83%E3%83%94%E3%83%B3%E3%82%B0
Баланс будинку https://press-express.com.ua та кар’єри: управління часом, побутові лайфхаки, цифрові рішення, особисті фінанси, батьки та діти, спорт та харчування. Огляди, інструкції, думки спеціалістів. Матеріали, до яких повертаються.
Сучасне медіа https://homepage.com.ua «про все важливе»: від ремонту та рецептів до стартапів та кібербезпеки. Сім’я, будинок, технології, гроші, робота, здоров’я, культура. Зрозуміла мова, наочні схеми, регулярні поновлення.
Щоденний журнал https://massmedia.one про життя без перевантаження: будинок та побут, сім’я та стосунки, ІТ та гаджети, бізнес та робота, фінанси, настрій та відпочинок. Концентрат корисного: короткі висновки, посилання джерела, інструменти для действий.
Платформа ідей https://infopark.com.ua для дому, роботи та відпочинку: ремонт, відносини, софт та гаджети, маркетинг та інвестиції, рецепти та спорт. Матеріали з висновками та готовими списками справ.
Служба вывода из запоя на дому Stop-Alko в Екатеринбурге работает без перерывов, выезжает в любой район города, оказывает помощь с учётом всех медицинских стандартов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево екатеринбург[/url]
Кент,приветствую..!!))В личку ответь,там по поводу оплаты…….оплатил договаривались на выходные…жду там от тебя ответа)) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм продавец адекватный. Успешных вам продаж
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в краснодаре[/url]
Капельница от запоя в «Детокс» в Краснодаре — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar115.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Смотрите также… – https://hallwayis.edu.sg/in-reprehenderit-in-voluptate-velit-esse-cillum-dolore-eu-fugiat-nulla-pariatur
https://defleppardnow.com
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Получить полную информацию – https://remont.kharkiv.ua/Novosti/page/8
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Перейти к статье – https://flexparagon.com/top-remote-job-opportunities-you-can-apply-for-right-now
Откапаться на дому: советы по ремонту и улучшению жилья Когда дом нуждается в ремонте, помощь специалистов может оказаться очень кстати; На сайте narkolog-tula026.ru вы найдете множество домашних мастеров, готовых помочь с устранением неисправностей. Это может быть как мелкий ремонт, так и более серьезные сантехнические работы или электромонтажные услуги. Для самостоятельного ремонта существуют несколько ключевых рекомендаций. Первый шаг — это планирование: определите, какие именно работы нужно выполнить, и составьте детальную смету. Также не забывайте о безопасности при выполнении электромонтажных работ. Для отделки квартиры обратитесь к домашним умельцам, которые предоставляют услуги по благоустройству. Они помогут преобразить ваше жилье, сделав его более комфортным и уютным. Не забывайте, что качественный ремонт, это залог вашего комфорта и уюта!
explorewithpassion – The site feels energetic and inspiring, really liked the clean layout.
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://fabricasdesidra.com/footer
Сорри, многаюуков. И ошибок – со спецтелефлна сижу) https://366shop.ru сервис – хуже некуда. Ну да об этом писал несколькими сообщениями ранее. 2/5
https://defleppardnow.com
Життя у ритмі цифри https://vilnapresa.com розумний будинок, мобільні сервіси, кібербезпека, віддалена робота, сімейний календар, здоров’я. Гайди, чек-листи, добірки додатків.
Про будинок та світ https://databank.com.ua навколо: затишок, сім’я, освіта, бізнес-інструменти, особисті фінанси, подорожі та кулінарія. Стислі висновки, посилання на джерела, корисні формули.
Журнал про баланс https://info365.com.ua затишок та порядок, сім’я та дозвілля, технології та безпека, кар’єра та інвестиції. Огляди, порівняння, добірки товарів та додатків.
Життя простіше https://metasearch.com.ua організація побуту, виховання, продуктивність, smart-рішення, особисті фінанси, спорт та відпочинок. Перевірені поради, наочні схеми, корисні таблиці.
Вывод из запоя на дому в Воронеже — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Offre promotionnelle 1xBet pour 2026 : profitez d’un bonus de bienvenue de 100% jusqu’a 130€ en vous inscrivant des maintenant. Une promotion reservee aux nouveaux joueurs de paris sportifs, avec la possibilite de placer des paris gratuits. N’attendez pas la fin de l’annee 2026 pour profiter de cette offre. Vous pouvez retrouver le code promo 1xBet sur ce lien — https://github.com/lunki1992/code-promo2026/tree/main.
Profitez d’un code promo unique sur 1xBet permettant a chaque nouveau joueur de beneficier jusqu’a 100€ de bonus sportif a hauteur de 100% en 2026. Ce bonus est credite sur votre solde de jeu en fonction du montant de votre premier depot, le depot minimum etant fixe a 1€. Pour eviter toute perte de bonus, veillez a copier soigneusement le code depuis la source et a le saisir dans le champ « code promo (si disponible) » lors de l’inscription, afin de preserver l’integrite de la combinaison. D’autres promotions existent en plus du bonus de bienvenue, vous pouvez trouver d’autres offres dans la section « Vitrine des codes promo ». Vous pouvez trouver le code promo 1xbet sur ce lien > https://sites.google.com/view/code-promo-1xbet-premium-bonus/1xbet.
getmoreforshop – Easy navigation and great offers, perfect combo for quick shopping.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk014.ru
вывод из запоя
Regards for helping out, superb info.
Вывод из запоя на дому в Краснодаре — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в краснодаре[/url]
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре вы получите комплексное лечение, направленное на восстановление организма и предотвращение рецидивов. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis epate par Viggoslots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est clair et efficace, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Viggoslots Casino merite une visite dynamique. De surcroit le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Обратившись в клинику «Частный Медик 24» в Челябинске, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
почему огурцы горькие введение зачем пчелам
Ищите полезные статьи в нашем онлайн-журнале с удобным поиском. Только проверенные методы для работы и повышения комфорта. Упрощайте решения каждый день.
откуда появился вич зачем нужны презервативы полный разбор
Profitez d’une offre 1xBet : utilisez-le une fois lors de l’inscription et obtenez un bonus de 100% pour l’inscription jusqu’a 130€. Renforcez votre solde facilement en placant des paris avec un multiplicateur de cinq fois. Le code bonus est valide tout au long de l’annee 2026. Pour activer ce code, rechargez votre compte a partir de 1€. Vous pouvez trouver le code promo 1xbet sur ce lien — https://1-x-betsport.blogspot.com/2025/10/code-promo-1xbet-bonus-exclusive-jusqua.html.
д не магаз рооовный так что не переживай все будет четко))) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм в Самаре трудится данный магазин?
startsomethingtoday – Love the name and the message, layout feels simple and fresh.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Betzino Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer ici|
Вывод из запоя в Челябинске — профессиональная помощь от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты обеспечат безопасное и эффективное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена челябинск[/url]
Хотите взять займ https://zaimy-57.ru быстро и безопасно? Сравните предложения МФО, выберите сумму и срок, оформите заявку онлайн и получите деньги на карту. Прозрачные условия, моментальное решение, поддержка 24/7.
Как взять займ https://zaimy-61.ru без лишних переплат: сравните ставки, выберите подходящий вариант и отправьте онлайн-заявку. Только проверенные кредиторы, прозрачные комиссии, безопасная обработка данных.
Взять займ онлайн https://zaimy-59.ru за несколько минут: без визита в офис, без лишних справок. Подбор выгодных ставок, проверенные кредиторы, мгновенное зачисление на карту. Удобно и прозрачно.
Порча от наркотиков — это групповая
хоботня, охватывающая физическое, психическое и
общественное здоровье человека.
Утилизация подобных наркотиков, как
снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «шишки» чи «бошки», может привести к неконвертируемым следствиям как для организма, так равным образом для среды в целом.
Но хоть при вырабатывании подневольности
эвентуально электровосстановление —
ядро, чтобы зависимый явантроп направился за помощью.
Важно памятовать, яко наркозависимость врачуется, также
реабилитация бацнет шансище сверху новейшую жизнь.
Code promo pour 1xBet : utilisez-le une fois lors de l’inscription et obtenez un bonus de 100% pour l’inscription jusqu’a 130€. Augmentez le solde de vos fonds simplement en placant des paris avec un wager de cinq fois. Le code bonus est valide tout au long de l’annee 2026. Pour activer ce code, rechargez votre compte a partir de 1€. Decouvrez cette offre exclusive sur ce lien > https://medium.com/@ukis9605/le-code-promo-de-1xbet-bonus-vip-jusqu%C3%A0-100-51a1c23589a7.
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время дня и ночи, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-zhukovskom
Je suis emerveille par Vbet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Vbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Posido Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour finir, Posido Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter la page web|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Posido Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par contre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour finir, Posido Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges personnalises.
http://www.posidocasino777fr.com|
Мы обеспечиваем комфортные условия для пребывания в клинике Воронежа, чтобы восстановление прошло максимально эффективно. В нашей клинике созданы все условия для вашего удобства и быстрого восстановления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Нужно взять займ https://zaimy-69.ru без визита в офис? Сервис подбора предложений: мгновенное решение, гибкие лимиты, понятные условия, поддержка 24/7. Деньги на карту сразу после одобрения.
Взять займ онлайн https://zaimy-63.ru за 5–10 минут: выберите сумму и срок, заполните короткую анкету и получите перевод на карту. Прозрачные ставки, без скрытых комиссий, круглосуточная обработка, только проверенные МФО.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk026.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Взять займ https://zaimy-71.ru до зарплаты и на любые цели. Подбор по сумме, сроку и ставке, калькулятор платежа, проверенные кредиторы. Оформление 24/7, решение за несколько минут.
Берите займ онлайн https://zaimy-73.ru без очередей: моментальная проверка, прозрачные тарифы, уведомления о платеже и удобное продление. Деньги поступают на карту сразу после одобрения.
Заказ Оплачен!! Жду посылку!! Как все прийдет сразу отпишу + фото!! https://tipsandtricks.ru у меня в подписи проверь
That’s some inspirational stuff. Never knew that opinions might be this varied. Thanks for all the enthusiasm to supply such helpful information here.
If wings are your thing, Tinker Bell’s sexy Halloween costume design is all grown up.
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
Вывод из запоя в Челябинске — профессиональная помощь от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты обеспечат безопасное и эффективное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в челябинске[/url]
гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цена [url=https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru]https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru[/url] .
торкретирование москва [url=https://torkretirovanie-1.ru/]torkretirovanie-1.ru[/url] .
Возьмите займ https://zaimy-78.ru онлайн на карту: фиксированные условия, калькулятор переплаты, поддержка в чате. Оформление круглосуточно, решение — за минуты, без скрытых платежей.
Онлайн-займ https://zaimy-76.ru для срочных расходов: гибкие лимиты, прозрачные комиссии, понятный график. Подберите лучший вариант и оформите заявку — деньги придут на карту 24/7.
Займ на карту https://zaimy-80.ru без лишних вопросов: короткая анкета, автоматическое решение, прозрачные комиссии. Удобное продление и напоминания о платежах в личном кабинете.
Взять займ https://zaimy-86.ru стало проще: мобильная заявка, подтверждение за минуты, прозрачные тарифы и удобное погашение. Работает 24/7, только проверенные кредиторы.
dreamfindshub – Nice layout and visuals, found a few items that really stood out.
hey thanks for the info. appreciate the good work
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в краснодаре[/url]
Пользуюсь этим сервисом регулярно, потому что всегда уверен в результате. Всё быстро, чётко и по списку. Никаких сюрпризов, только удобство. Теперь если нужна доставка выпивки на дом, заказываю здесь – https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
Экстренное вытрезвление в клинике «Детокс» в Краснодаре — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом краснодар[/url]
Ну,оправдалась моя нелюбовь к аське,ибо история не хранится и происходит всякая фигня.У меня произошел не самый забавный случай. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут….
Где взять займ https://zaimy-89.ru выгодно? Наш сервис подбирает предложения по сумме, сроку и ставке. Полная стоимость заранее, без скрытых платежей. Оформите онлайн и получите деньги за минуты.
Срочно на карту https://zaimy-87.ru возьмите займ без визита в офис. Короткая анкета, мгновенное решение, честные условия, напоминания о платежах. Работает круглосуточно.
Капельницы для восстановления после запоя в Туле: путь к здоровью Лечение алкоголизма начинается с профессиональной консультации врача. В Туле есть специализированные учреждения, где предлагается наркологическая помощь и капельницы для восстановления. Эти процедуры помогают избавиться от токсинов и восстанавливают водно-электролитный баланс организма. вывод из запоя Поддержка пациента и контроль его состояния, важные аспекты терапии. Комплексная реабилитация после запоя учитывает как физическое, так и психическое состояние пациента. Важно помнить, что эффективное восстановление — это основа успешного лечения и возвращения к нормальной жизни.
Хочешь халяву? https://tutvot.com – сервис выгодных предложений Рунета: авиабилеты, отели, туры, финпродукты и подписки. Сравнение цен, рейтинги, промокоды и кэшбэк. Находите лучшие акции каждый день — быстро, честно, удобно.
Эффективное лечение геморроя у взрослых. Безопасные процедуры, комфортные условия, деликатное отношение. Осмотр, диагностика, подбор терапии. Современные методы без госпитализации и боли.
J’adore la vibe de Viggoslots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino merite une visite dynamique. En extra le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. A mettre en avant les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis fascine par Viggoslots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est clair et efficace, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une experience immersive. Un point fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Viggoslots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Viggoslots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Betzino Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements securises.
Lire la suite|
makelifesimpler – Nice clean interface, delivers exactly what the name promises.
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Betzino Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lancer le site|
Intelligent Crypto https://tradetonixai.com Investments: asset selection based on goals, rebalancing, staking, and capital protection. Passive income of 2-3% of your deposit with guaranteed daily payouts.
Собрать или выбрать мощный игровой ПК гораздо проще, если опираться на проверенные рекомендации. На сайте собраны обзоры популярных сборок, советы по подбору видеокарт, процессоров и систем охлаждения. Благодаря структурированной информации каждый геймер сможет найти идеальный вариант для своих задач — от казуальных игр до профессионального гейминга.
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Челябинске. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Обратившись в клинику «Частный Медик 24» в Челябинске, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в челябинске[/url]
Когда нужна срочная помощь, служба Stop-Alko в Екатеринбурге может выехать на дом, провести диагностику, капельницу и восстановление сил.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Дружище ты говоришь полный бред!!! Магазин работает очень качественно!!! Бро делает все ПОУМУ!!! Я с ним работаю очень очень давно!!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш все скоро будут всем довольны, а те кто ждал и не паниковал будут вдвойне довольны!
Вывод из запоя на дому в Краснодаре — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Je suis completement seduit par Vbet Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Vbet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
J’adore l’energie de Posido Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Posido Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A signaler la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer|
J’adore le dynamisme de Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Posido Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses continues.
https://posidocasino777fr.com/|
Hit Club has quickly become a trending entertainment platforms, and after checking it out, I can see why. It’s loaded with entertainment options that suit all types of gamers — whether you’re a fan of casino games, sports betting, or even unique games like fish shooting. The user interface is intuitive and appealing, making it easy for new members to explore. Plus, the bonuses and jackpots keep players coming back. I appreciate how the developers keep things interesting with new features and events. It’s more than just a gaming app — it’s a vibrant community of gamers.
Check out the latest games and jackpots here: HITCLUB
shopfornewthings – The design feels modern and welcoming, will come back for more.
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar115.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в красноярске[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Краснодаре. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar113.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Обратившись в клинику «Детокс» в Краснодаре, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого краснодар[/url]
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно жуковский[/url]
bahis sitesi 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-17.com/]bahis sitesi 1xbet[/url] .
клиника наркологии москва [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru[/url] .
Таблица не заменяет очный осмотр, но показывает, как наблюдения переводятся в действие и когда мы принимаем решение о продолжении/остановке модуля.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в красноярске[/url]
В «Детокс» в Краснодаре мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
dreambelieveachieve – The positivity here stands out, love how motivational it feels.
Чиним ноутбуки HP в Москве оперативно и по выгодной цене. Проверка бесплатно. Фирменные комплектующие. Обращайтесь
сервисный центр hp москва кочновский проезд [url=http://www.servisnyj-centr-hp-msk.ru]hp сервисный центр москва[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем полную поддержку на всех этапах лечения в Воронеже, включая реабилитацию и профилактику рецидивов. Мы поможем вам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня https://stomkam.ru Может забегу как-нибудь) Обычно все берут там где надежно у одних и техже, новые магазины или первые покупки рисково, любой выберет проверенных лично)
салон досуг сургут
https://tumblrblog.com/code-promo-melbet-casino-2026-pour-les-joueurs-africains/
https://vsemetonado.ru/
Profitez du code promo 1xbet 2026 : obtenez un bonus de bienvenue de 100% sur votre premier depot avec un bonus allant jusqu’a 130 €. Placez vos paris en toute plaisir en utilisant simplement les fonds bonus. Une fois inscrit, n’oubliez pas de recharger votre compte. Si votre compte est verifie, vous pourrez retirer toutes les sommes d’argent, y compris les bonus. Vous pouvez trouver le code promo 1xbet sur ce lien — https://medium.com/@ukis9605/1xbet-code-promo-bonus-jusqu%C3%A0-100-101e93f2f5b3.
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Воронежа, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента. Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя по цене от 2500??. Наши специалисты обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Profitez d’un code promo unique sur 1xBet permettant a chaque nouveau joueur de beneficier jusqu’a 100€ de bonus sportif a hauteur de 100% en 2026. Le bonus sera ajoute a votre solde en fonction de votre premier depot, le depot minimum etant fixe a 1€. Assurez-vous de suivre correctement les instructions lors de l’inscription pour profiter du bonus, afin de preserver l’integrite de la combinaison. Le bonus de bienvenue n’est pas la seule promotion ou vous pouvez utiliser un code, d’autres combinaisons vous permettant d’obtenir des bonus supplementaires sont disponibles dans la section « Vitrine des codes promo ». Vous pouvez trouver le code promo 1xbet sur ce lien — https://1-x-betsport.blogspot.com/2025/10/code-promo-1xbet-premium-bonus_01659549841.html.
connectlearncreate – Inspiring and interactive site, perfect for learning and creating new ideas.
Экстренное вытрезвление в клинике «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже — помощь при острых состояниях. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после сильного алкогольного опьянения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Up to ageing loli po*rn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk027.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Выручает в любых ситуациях — ночью, в праздники, в дождь. Алкоголь качественный, доставка аккуратная, никаких проблем. Всё удобно и безопасно. Теперь если нужна доставка алкоголя круглосуточно москва, беру здесь https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
getinspireddaily – Every section feels bright and encouraging, definitely worth a visit.
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/
Полностью согласен !!! https://sveto-house.ru а для какой цели не отправляют? курьерам похуй что тоскать, а если бы мусора хотели бы принять, посыль наоборот отправили.
Капельница от запоя в «Детокс» в Краснодаре — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
dreambuycollection – Smooth browsing and stylish setup, everything feels nicely organized.
https://photos.creativeshot.com/blog/2014/9/the-musicians
https://vsemetonado.ru/
J’adore l’energie de Betzino Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Betzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui stimule l’engagement.
Plonger dedans|
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Челябинске. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/]врач вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Краснодаре. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому в Челябинске — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Наши специалисты в Воронеже имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно воронеж[/url]
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Челябинске. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому для пожилых людей в Туле — это ключевой элемент в лечении запоя. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно предоставляет услуги по детоксикации организма, что крайне важно для пожилых пациентов. Симптомы запоя, такие как слабость и тревожность, нуждаются в срочном лечении. Лечение алкоголизма может включать капельницы, которые способствуют нормализации водно-электролитного баланса. Однако следует помнить о возможных рисках капельниц: аллергические реакции, осложнения при неправильном введении. Поэтому безопасность процедур должна быть приоритетом. Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет избежать стресса при транспортировке больного. Уход за пожилыми людьми требует особого внимания, и круглосуточная помощь специалиста обеспечивает нужный уход. Рекомендуется следовать советам врачей для успешного восстановления после запоя.
Заказал в понедельник – в среду мне уже позвонили. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш я не согласен предыдущем коментариям ,беру не первый раз ,на данный момент магазин самый охриненный ,всегда качество товара радует,всегда на связи они,они не когда не морозятся,своё дело знают чётко,нахрена им кидать ,они не будут портить свою репутацию какую уже заработал этот магазин,я беру поболее и меня не разу сдесь не кинули .процветания магазину .спасибо за вашу работу,что всё чётко и быстро И радуете вкусняшками.а ещё хочу добавить ,возможно это кидаки или канкуренты и пишут разную х….ю что бы сбить новичков ,Но мы кто всегда с вами знаем что магазин лучший и другого Нам НЕНАДО.Так держать ,МЫ ВСЕГДА С ВАМИ!!!
Клиника «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя по цене от 2500 ?. Наши специалисты обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru[/url]
thetrendystore – Stylish vibe and smooth layout, great place for fashion lovers.
J’adore le dynamisme de Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Viggoslots Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages uniques.
Poursuivre la lecture|
вертикальная гидроизоляция подвала [url=https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/]вертикальная гидроизоляция подвала[/url] .
Этап
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-zhukovskom/
J’adore la vibe de Viggoslots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute soudee.
Viggoslots|
Je suis captive par Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par contre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir la page|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betzino Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Воронежа, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента. Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
торкретирование москва [url=http://torkretirovanie-1.ru]http://torkretirovanie-1.ru[/url] .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga016.ru
лечение запоя
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя с использованием современных методов детоксикации и инфузионной терапии. Наши специалисты обеспечат быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя, используя индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
inspirechangealways – Love the message behind this one, uplifting and well designed.
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Ваши личные данные не будут переданы третьим лицам, и вы не будете поставлены на учёт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в краснодаре[/url]
Да хватает придурков, только смысл писанины этой , что он думает что ему за это что то дадут ))) кроме бана явно ничего не выгорит )))! Тс красавчик брал 3 раза по кг сделки и всегда все чётко ! Жду пока появиться опт на ск! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Работаю впервые с этим магазом! Есть что заявить! Ребята, я в приятном шоке от работы магаза! Брал давеча! Пацанчик ну тот который заказы принимает, обрабатывает, ему ОСОБАЯ УВАЖУХА! Магаз РАБОТАЕТ РОВНО и ОПЕРАТИВНО! Все заценили! Все объявили ОБЩУЮ ОХУЕННУЮ БЛАГОДАРНОСТЬ МАГАЗУ! Извиняюсь за французский! ) Что могу сказать, видимо нашел свой магаз! )
J’adore le dynamisme de Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Vbet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Explorer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Posido Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Explorer le site|
dailydealzone – Awesome discounts displayed neatly, easy site to explore for deals.
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Ваши личные данные не будут переданы третьим лицам, и вы не будете поставлены на учёт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом краснодар[/url]
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Воронеже — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения. Наши специалисты проводят процедуру с соблюдением всех юридических норм и этических стандартов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
uniquelifestylehub – Stylish and modern, feels like a curated hub for unique lifestyle inspiration.
рейтинг лучших фильмов 2025 Эстетика 80-х: Фильмы, Наполненные Неоном, Синтезаторами и Безграничной Свободой. Возвращение в золотую эпоху поп-культуры и кинематографа.
https://theaterplaybill.com
https://stockmaster.kz/ Все займы онлайн – полный перечень займов, оформляемых онлайн.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Posido Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Posido Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
В Екатеринбурге сервис «Похмельная Служба / Stop-Alko» предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому — врач приезжает оперативно, ставит капельницу и обезболивает состояние.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Челябинске, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас. Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk11.ru/
https://vsemetonado.ru/
Трек бьется. Как придет отпишу. Если все ровно то я ваш постоянный клиент, цены и ассортимент радуют. https://pan-sev.ru классный магазин
https://vsemetonado.ru/
Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation Присоединяйся к Chernov Creation: Стань частью сообщества, где рождаются шедевры! Мы предлагаем не только ресурсы и инструменты, но и поддерживающую среду, где можно обмениваться опытом, находить единомышленников и получать конструктивную обратную связь. Участвуйте в мастер-классах, вебинарах и конкурсах, расширяйте свои знания и навыки, и, конечно же, делитесь своими работами с миром. Вместе мы можем достичь большего!
TripScan Сайт Трипскан: Исследуйте наш веб-сайт и откройте для себя мир возможностей для незабываемых путешествий. Интерактивная карта мира, подробные описания отелей и достопримечательностей, отзывы реальных путешественников – все это поможет вам спланировать идеальную поездку до мельчайших деталей. TripScan – это ваш надежный источник информации и вдохновения для путешествий.
Очень понравилось, что всё работает даже ночью. Алкоголь приходит быстро, оригинальный, всё по чеку. Курьер приятный. Теперь если нужна доставка спиртного, беру здесь – https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
https://theaterplaybill.com
simplelivinghub – Calming design and helpful ideas, perfect for minimal living inspiration.
everydayshoppingzone – Lots of variety here, looks like a solid everyday go-to shop.
Наши специалисты в Челябинске готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы и предоставить подробную информацию о процессе лечения. Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и ответить на все ваши вопросы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru[/url]
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Краснодаре. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk028.ru
вывод из запоя
Почему больше не берете? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Оплатил, жду.
Мы понимаем, как важно быстро и эффективно выйти из запоя, поэтому предлагаем оперативную помощь в любое время в Воронеже. Наши специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время дня и ночи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в воронеже[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая доступность помощи в любое время. Вы можете обратиться к нам в любое время дня и ночи, и мы окажем необходимую медицинскую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Что делаем
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-zhukovskij[/url]
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Краснодаре. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk013.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
bestchoicecorner – Feels trustworthy and professional, I like the clean structure.
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr
Мы предлагаем гибкую систему оплаты и прозрачные цены в Челябинске, без скрытых платежей и переплат. Стоимость услуг начинается от 3500??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости процедур.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Обратившись в клинику «Частный Медик 24» в Челябинске, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Sweet Bonanza: A Burst of Fruity Fun!
Dive into the colorful world of Sweet Bonanza, where juicy fruits and sugary treats bring endless excitement and big wins. Spin the reels and taste the sweetness of luck at [url=https://k8-casino.jp/]https://k8-casino.jp/[/url] !
Chernov Creation Новости Chernov Creation: В мире цифрового творчества открываются новые горизонты! Мы рады приветствовать вас в эпицентре инноваций и свежих идей. Chernov Creation – это не просто платформа, это целый мир, созданный для воплощения самых смелых замыслов. Здесь каждый, от начинающего энтузиаста до опытного профессионала, найдет инструменты и вдохновение для реализации своего потенциала. Следите за нашими новостями, чтобы быть в курсе последних трендов, эксклюзивных проектов и уникальных возможностей для развития в сфере цифрового искусства.
Не, бро, ну одно дело 250 заместо 50мг, а другое когда даже 250мг не берет. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Приносим извинения за возможные неудобства.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga017.ru
лечение запоя калуга
https://theaterplaybill.com
Наши услуги доступны всем жителям Воронежа, обеспечивая доступность помощи для каждого пациента. Вы можете обратиться к нам независимо от вашего места проживания.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
fashionloverszone – Trendy and visually appealing, great spot for fashion enthusiasts.
https://t.me/tripscan_1 Трипскан
https://theaterplaybill.com
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения в Челябинске. Ваши личные данные не будут переданы третьим лицам, и вы не будете поставлены на учёт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
trendyfindshub – The latest styles stand out nicely, super easy to browse.
Нужно было срочно генерировать фото нейросетью для проекта, и результат меня приятно удивил. Картинки получились детальные и красивые, а времени потратил совсем немного. Рекомендую: https://vc.ru/top_rating/2301994-luchshie-besplatnye-nejroseti-dlya-generatsii-izobrazheniy
Вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предоставляем круглосуточную медицинскую помощь, обеспечивая комфорт и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в воронеже[/url]
Вывод из запоя принудительно в Краснодаре — помощь близким, чьи родственники отказываются от лечения. Наши специалисты проводят процедуру с соблюдением всех юридических норм и этических стандартов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar206.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
shopyourfavorites – Great browsing flow, everything feels user-friendly and modern.
по теме трип БРО! https://opt-ufa.ru Отличный магазин..заказывал не раз всегда все на высшем уровне. Молодцы.
пассажирские перевозки астана новосибирск
https://theaterplaybill.com
Cool-headed loli por*n
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Азартные игры онлайн покердом скачать Ваш пропуск в мир высоких ставок и крупных побед. Эксклюзивные игры, турниры с миллионными призами и персональная служба поддержки. Играйте по-крупному!
Ищешь автоматы? покердом зеркало лучшие азартные развлечения 24/7. Слоты, рулетка, покер и живые дилеры с яркой графикой. Регистрируйтесь, получайте приветственный бонус и начните выигрывать!
Хочешь азарта? bollywood casino мир азарта и больших выигрышей у вас в кармане! Сотни игр, щедрые бонусы и мгновенные выплаты. Испытайте удачу и получите незабываемые эмоции прямо сейчас!
Онлайн казино casino beef Насладитесь атмосферой роскошного казино не выходя из дома! Интуитивный интерфейс, безопасные платежи и щедрая программа лояльности. Сделайте свою игру выигрышной!
Лучшие онлайн казино casino beef захватывающие игровые автоматы, карточные игры и live-казино на любом устройстве. Быстрый старт, честная игра и мгновенные выплаты.
Наши специалисты проводят детальную диагностику и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения с учётом состояния пациента в Краснодаре. Мы учитываем все особенности вашего здоровья при назначении лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
J’adore l’energie de Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller sur le web|
Капельница от запоя в «Детокс» в Краснодаре — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Нужно было сгенерировать изображение срочно, и благодаря обзору нашёл подходящий сервис за минуты. Теперь использую его постоянно, а другие инструменты из подборки держу про запас. Отличная работа: инструмент генерации изображения
как дела друзья? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Итак всем ПРИВЕТ !
Этап
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij[/url]
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
новости Chernov Creation Присоединяйся к Chernov Creation: Стань частью сообщества, где рождаются шедевры! Мы предлагаем не только ресурсы и инструменты, но и поддерживающую среду, где можно обмениваться опытом, находить единомышленников и получать конструктивную обратную связь. Участвуйте в мастер-классах, вебинарах и конкурсах, расширяйте свои знания и навыки, и, конечно же, делитесь своими работами с миром. Вместе мы можем достичь большего!
Je ne me lasse pas de Viggoslots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Viggoslots Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une touche d’excitation. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus constants.
Aller sur le web|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Viggoslots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est transparent et rapide, rarement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
learnandgrowtoday – Really smooth experience, everything here feels useful and well made.
Вывод из запоя на дому в Воронеже — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой, проведут необходимую диагностику и лечение.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk029.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Услуга вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге от «Похмельной Службы» включает как базовый, так и премиум-уровень помощи — со всеми необходимыми препаратами и поддержкой.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/
Всем советую таряться здесь))) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки 13 янв. в 21:12 Деньги пришли. Заказ будет выслан в ближайшие несколько рабочих дней. Суббота и воскресенье — выходные. После отправки трек (номер накладной) будет в комментарии к заказу на сайте и продублируется на электронную почту.
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Vbet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En fin de compte, Vbet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement cool les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Je suis completement seduit par Vbet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
http://www.vbetcasino777fr.com|
Хочешь рискнуть? вход в пин ап редлагает широкий выбор игр, быстрые выплаты и надежные способы пополнения депозита.
Официальный сайт пин ап зеркало встречает удобным интерфейсом и обширным каталогом: слоты, лайв-казино, рулетка, турниры. Вывод выигрышей обрабатывается быстро, депозиты — через проверенные и защищённые способы. Акции, бонусы и поддержка 24/7 делают игру комфортной и понятной.
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-msk014.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Je suis accro a Posido Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En fin de compte, Posido Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
http://www.casinoposidofr.com|
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
Официальный покердом казино вход: казино, покер, вход и скачивание слотов. Сотни слотов, лайв-столы, регулярные ивенты, приветственные бонусы. Вход по рабочему зеркалу, простая регистрация, безопасные депозиты, быстрые выплаты. Скачай слоты и играй комфортно.
В «Трезвом шаге» в Воронеже мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Онлайн-казино водка бет казино игровые автоматы от ведущих производителей. Эксклюзивный бонус — 70 фриспинов! Смотрите видеообзор и отзывы реальных игроков!
Je suis captive par Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Posido Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Posido Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Posido Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer|
When we look at these issues, we know that they are the key ones for our time.
Наши специалисты в Краснодаре имеют многолетний опыт работы в области наркологии и готовы помочь вам на каждом этапе лечения. Мы используем современные методики и препараты для эффективного вывода из запоя.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar112.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
bestvaluecollection – Good range of products, prices seem fair and competitive too.
Обратившись в клинику «Трезвый шаг» в Воронеже, вы делаете первый шаг к здоровой и трезвой жизни. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh13.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
фофу кушают, 2 дмпм нюхается, судя по всему https://dep211.ru Оплатил в среду, жду посылочку, посмотрим как что.
Je suis emerveille par Viggoslots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En resume, Viggoslots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
Tout apprendre|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Betzino Casino garantit un amusement continu. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
Entrer sur le site|
growwithconfidence – Love the encouraging theme here, simple and motivating content.
J’ai un faible pour Viggoslots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, Viggoslots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A noter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Commencer Г naviguer|
https://theaterplaybill.com
На официальном сайте казино кент вы найдёте слоты, рулетку, лайв-столы и тематические турниры. Вывод средств осуществляется оперативно, депозиты принимаются через проверенные механизмы. Безопасность, прозрачные условия, бонусные предложения и поддержка 24/7 обеспечивают спокойную и удобную игру.
Как юридическое лицо, довольны подходом и ответственностью. Всё надёжно: https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel11.ru/
Нужен тахеометр? аренда тахеометра Sokkia по выгодной цене. Современные модели для геодезических и строительных работ. Калибровка, проверка, доставка по городу и области. Гибкие сроки — от 1 дня. Консультации инженеров и техническая поддержка.
Официальный сайт vavada bet вход: играйте онлайн с бонусами и быстрыми выплатами. Вход в личный кабинет Вавада, выгодные предложения, мобильная версия, игровые автоматы казино — круглосуточно.
Лучшее онлайн казино казино с более чем 3000 игр, высокими выплатами и круглосуточной поддержкой.
Expanded article here: https://www.easyhits4u.com/profile.cgi?login=npprteam902
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-zhukovskom/
shopwithstylehub – Fun and stylish site, everything looks modern and well presented.
вот такие как ты потом и пишут не прет , не узнавая концентрацию и т д набодяжат к…. ,я вот щас жду посыля и хз ко скольки делать 250 https://moskovskie-dveri.ru Удачи Вам и Процветания От Всей Души!
Je suis epate par Vbet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Vbet Casino assure un fun constant. A noter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute vibrante.
En savoir davantage|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Vbet Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Vbet Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
Решили спонтанно собраться с друзьями вечером, но все магазины были закрыты. Нашли этот сайт, оформили заказ, и уже через 30 минут всё было у нас. Очень удобно и современно. Теперь если нужна доставка алкоголя 24 7 москва, обращаемся только сюда: https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation Присоединяйся к Chernov Creation: Стань частью сообщества, где рождаются шедевры! Мы предлагаем не только ресурсы и инструменты, но и поддерживающую среду, где можно обмениваться опытом, находить единомышленников и получать конструктивную обратную связь. Участвуйте в мастер-классах, вебинарах и конкурсах, расширяйте свои знания и навыки, и, конечно же, делитесь своими работами с миром. Вместе мы можем достичь большего!
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Posido Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Posido Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une experience immersive. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Naviguer sur le site|
shopthemoment – Trendy design and clear visuals, makes browsing super enjoyable.
J’adore le dynamisme de Posido Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, a l’occasion des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Posido Casino vaut une visite excitante. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Obtenir plus|
TripScan top Tripskan: Инновационная платформа, созданная для тех, кто ценит свое время и деньги. Мы используем передовые алгоритмы и технологии машинного обучения, чтобы оптимизировать процесс поиска и предоставить вам персонализированные рекомендации, соответствующие вашим предпочтениям и бюджету. С TripScan планирование путешествия становится легким, приятным и эффективным.
Мы предлагаем различные программы лечения в Воронеже, включая стационарное и амбулаторное, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для вас. Вы можете выбрать наиболее подходящий для вас способ лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Posido Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour faire court, Posido Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce la communaute.
Visiter maintenant|
findyourmoments – Beautiful concept and elegant look, I enjoyed exploring this one.
В «Частном Медике 24» в Челябинске мы заботимся о вашем здоровье и благополучии, предоставляя качественную медицинскую помощь. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам на пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
A friend of mine advised me to review this site. And yes. it has some useful pieces of info and I enjoyed reading it.
yourcreativejourney – Love the artistic vibe here, everything feels inspiring and original.
такой замечательный и паспиздатый магазин………ноооооо где же мой заказ тогда? трек так и не бьется,тс на связь не выходит!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази они на телефон должны позвонить,обычно так
Learn more here: https://sportsfanbetting.com
Today’s highlights are here: https://chronicle.ng
The best is right here: https://muskaanhindi.org
Ко ланта ло Канта
Chernov Creation Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation: Готовьтесь к взрыву креатива! Мы не боимся экспериментировать, ломать стереотипы и выходить за рамки привычного. В наших новостях вы найдете самые нестандартные проекты, безумные идеи и удивительные открытия. Присоединяйтесь к нашей цирковой труппе цифровых гениев и вместе мы создадим нечто совершенно невероятное!
Отличная работа! Всё понятно, чётко и слаженно. Таможенный брокер оформил документы за один день — не ожидали такой скорости, https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel11.ru/
Мы обеспечиваем комфортные условия для пребывания в клинике Воронежа, чтобы восстановление прошло максимально эффективно. В нашей клинике созданы все условия для вашего удобства и быстрого восстановления.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voronezh12.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
https://vsemetonado.ru/
Сайт Трипскан Трипскан
Алкомаркет удивил оперативностью — сделали заказ в час ночи, уже через полчаса всё было у нас. Курьер вежливый, всё аккуратно. Приятно, когда сервис заботится о клиентах. Теперь если нужна доставка спиртного ночью, знаю куда обращаться – https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
The best is right here: https://www.saffireblue.ca
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk030.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
такси из аэропорта Толмачево в Павлодар
Top picks for you: https://redfordtheatre.com
uniquelifestylehub – The layout stands out, feels classy and well put together.
Updated today: https://aquietrabalho.com
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar021.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
All the latest here: https://www.lnrprecision.com
http://maraforum.iboards.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=8782
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk015.ru
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
Метод употребления – интерназально купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Всем привет,отличный магазин,недавно брала,всё очень понравилось
Je suis captive par Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Viggoslots Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Viggoslots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour completer le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
connectwithideas – Clean layout and inspiring content, perfect for exploring new concepts.
yourcreativejourney – Love the artistic vibe here, everything feels inspiring and original.
J’adore le dynamisme de Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. De plus le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Если вы ищете безопасный вывод из запоя, обратитесь в Екатеринбурге в «Похмельную Службу». Медики приедут в течение часа.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg27.ru/]вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
https://trusted.golocaly.online/pronostic-foot-ligue-1-gratuit-victoire-assuree-aujourdhui/
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
https://theaterplaybill.com
purefashionmarket – Fantastic collection of looks, the site design feels elegant.
Je suis enthousiasme par Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Betzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un avantage notable les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Aller Г la page|
это не спиша эндеграунд улица полна купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази сегодня в 16:25 на почте получен конверт ,в нем было вещество лимоного цвета 0,3 г , сохнет ,позже подробно опишу
J’adore le dynamisme de Vbet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est transparent et rapide, occasionnellement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Vbet Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Vbet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En fin de compte, Vbet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une experience immersive. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui stimule l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
https://theaterplaybill.com
Отличная команда, знают все тонкости оформления. Помогли избежать ошибок и лишних платежей. Сотрудничеством довольны – таможенный брокер в Москве
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Vbet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par contre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Vbet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Ouvrir le site|
Капельница от запоя в Челябинске — быстрый способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными специалистами с использованием современных препаратов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk12.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в челябинске[/url]
Je suis epate par Posido Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Posido Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus le site est rapide et style, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Ouvrir le site|
createinspirelead – Motivating design and smooth layout, really captures a positive energy.
Je suis completement seduit par Posido Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Posido Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Rejoindre maintenant|
топ-10 казино с бонусами за регистрацию
https://t.me/KohLantaKrabiThailand Krabi
dreambuyoutlet – Great presentation and fast loading, enjoyable shopping experience overall.
топ-10 казино с бонусами за регистрацию
Хороший сервис, хорошая команда = хорошие дела ) В том же духе двигаемся…) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Я, лично, в первый раз сделал заказ ,в этом магазине- оформил(по аське) его безналично,(что очень удобно для меня,даже из дома не выходил),сутки прошли,был дан трек,через два дня,посылка была у меня в городе.Следил за ее перемещением на сайте курьера(опять же-не выходя из дома).
https://theaterplaybill.com
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Betzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, permet une immersion complete. Egalement genial les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
VГ©rifier le site|
findjoytoday – Positive and uplifting, the site really feels cheerful and motivating.
ло Канта Thailand
purefashionmarket – Great fashion selection and clean visuals, easy to explore and shop.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar022.ru
вывод из запоя цена
блин… один заказ выбил, затестил. теперь опять в аське молчок купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Связался с продавцом вполне адекватный!Заказал щас жду адресса
findjoyeveryday – Positive energy throughout, design fits the uplifting name perfectly.
Перед тем как перечислить типичные случаи, отметим главный принцип: домашний формат выбирают, когда безопасность и прогноз сопоставимы со стационаром, а переезд лишь затянет старт терапии и усилит стресс для семьи.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/
Запой – это значительная проблема, требующая внимания, которая требует профессиональной помощи. В Туле доступно множество услуг, которые могут помочь вашему близкому. Первым шагом может стать обращение к наркологу на дом, чтобы получить квалифицированную помощь при запое. Специалисты проведут детоксикацию организма и предложат лечение алкоголизма, включая психотерапию при запое.Важно также предоставить эмоциональную поддержку. Родственники должны знать советы для родственников, как вести себя в кризисной ситуации с алкоголем. Консультации по алкоголизму помогут выяснить в проблеме и выбрать правильный подход к реабилитации от алкоголя. вызвать нарколога на дом Тула Не забывайте о том, что освобождение от зависимости – это продолжительный процесс. Профессиональная помощь и поддержка родственника помогут ему возвратиться к привычному образу жизни.
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
дом престарелых
pansionat-tula013.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых
https://theaterplaybill.com
Дружище как все прошло?)) забрал своё??? А то написал неделю назад и тишина))) если забрал сколько шло по времени? напиши нам а то на последних страницах сдесь какой то кипишь нездоровый…( https://stomkam.ru Бро, доброго дня. В личку реквы на оплату жду, на сайт тоже попасть не могу…
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
перевозки новосибирск Астана
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
modernhomefinds – Stylish home ideas and layout, feels cozy and modern at once.
Je suis fascine par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute soudee.
Explorer la page|
makeimpacttoday – Motivational and well-organized, great for users wanting to take action.
https://theaterplaybill.com
Успехов и процветания новому селлеру!!! Желаю денег пресс и в обществе вес)) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази длица окола часа очень даже не плохо
discoveramazingoffers – Fun experience browsing deals here, everything feels easy and inviting.
Самое интересное тут: https://it-on.ru
Все подробности по ссылке: https://morshynkurort.net
Всё самое новое здесь: https://mebel-3d.ru
Магазин Харош, Внимательней читайте отзывы о той продукции какая вас интересует более подходит имено вам только такой подход может оставить всем только положительные эмоции. Работа магазина по всем пораметрам оставляет только положительные эмоции :voo-hoo: ставлю все оценки только отлично. Всем добРа, советую, обращайтесь в даный магазин, вам помогут быстро и качествено доставить то,что вам нужно https://grimzone.ru С Ув. vkapushoneПолучил сегодня посылку, могу уже с уверенностью сказать, Замечательного магазина.
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Узнать больше – http://
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar023.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
trendycollectionhub – Stylish and modern layout, perfect for exploring new fashion trends.
Все самое актуальное тут: https://www.pondexperts.ca
inspirechangealways – Very motivating site, love the positive energy and smooth layout.
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betway Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Betway Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A souligner les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir|
Read more on the website: https://tribaliste.com
Читать полностью на сайте: https://vikivostok.ru
Подробнее на сайте:: https://poloniya.ru
findjoyeveryday – Bright, cheerful site design that instantly lifts up your mood.
работает заебок… присылают в кортонных больших конвертах…. доставляют очень быстро мне доставили в город за 3 дня… а их отделение в каждом городе есть.. как посылка придет вам позвонят на телефон и предложат доставку или приехать самому… если решите сами забирать то вам скажут адресс куда ехать…=) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази всем желаю счастья!
Капельница для лечения запоя — это необходимая мера в помощи при алкогольной зависимости. Капельница способствует детоксикации детоксикации организма‚ устраняя токсины и нормализуя водно-электролитный баланс. После капельницы пациенты испытывают улучшение настроения.Консультация нарколога в этом процессе является ключевой. Он анализирует симптомов отмены и разрабатывает план лечения запоя. Постзапойное восстановление включает обе стороны: физическую и психологическую. Помощь родных очень важна‚ позволяя преодолеть последствия запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Реабилитация — следующая стадия в лечении‚ где пациент проходит лечение и обучение для предотвращения рецидивов. Анонимная помощь гарантирует безопасность и анонимность. Необходимо помнить‚ что борьба с алкоголизмом — это длительный процесс‚ требующий усилий и поддержки.
Ко ланта Ко ланта чат
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-tula014.ru
дом престарелых
dreambuyoutlet – Smooth browsing experience, stylishly presented products make shopping enjoyable.
Best selection of the day: https://amt-games.com
Je suis sous le charme de Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Betway Casino vaut une visite excitante. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce la communaute.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En fin de compte, Belgium Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour completer l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute vibrante.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Belgium Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages uniques.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer ici|
J’adore la vibe de Gamdom Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour faire court, Gamdom Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un atout les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Continuer ici|
Je suis completement seduit par Betify Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps en temps des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour couronner le tout le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir|
https://theaterplaybill.com
Modish loli po*rn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
everydayshoppinghub – Very convenient and easy to use, makes daily shopping simple and smooth.
есть что почитат купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Ха ха ребята смотрите беспредел! попробуйте написать правильно жабу ТСа и получится то что у меня, как бы с ошибкой! СКРИПТ!
https://theaterplaybill.com
yourmomentstarts – Great first impression, the name and vibe feel truly motivational.
Давайте обменяемся идеями! Я собрала несколько своих любимых вариантов фото межкомнатных дверей — будет здорово, если и вы поделитесь своими фото/ссылками
Я экспериментирую с подачей материалов. Посмотрите, как вам такой формат. Спасибо за честный отзыв!
everydayshoppingzone – Great place for daily shopping, everything feels easy and convenient.
I do believe your audience could very well want a good deal more stories like this carry on the excellent hard work.
Can I just say what a relief to seek out someone who actually knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You positively know find out how to bring a problem to mild and make it important. Extra individuals have to read this and perceive this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more in style because you positively have the gift.
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-zhukovskij[/url]
This website offers a lot of interesting and valuable information.
On this platform, you can explore a wide range of subjects that expand knowledge.
Everyone will appreciate the materials shared through this platform.
Every category is easy to navigate, making it simple to use.
The materials are easy to understand.
There are recommendations on various fields.
Whether your interest is in useful facts, this site has a lot to offer.
To sum up, this resource is a great source for those who love learning.
https://technikcentral.de/
changeyourfuture – Inspiring design and positive message, really motivates you to take action.
заказ в статусе обработки ))) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки сегодня оплатил заказ..буду ждать доставки..протестирую.сообщу о качестве продукта
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя
changeyourdirection – Fresh and inspiring layout, really encourages exploration and new perspectives.
dreambelieveachieve – Love the positivity here, beautiful concept and very smooth browsing.
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/[/url]
trendyfindshub – Love the trendy vibes, the site is simple yet stylish to browse.
Последние данные очков репутации: купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану последнее время стал закупаться в чемикал и не капельки в этом не пожалел, всё всегда вовремя высылают даже быстрее заявленного времени! качество радует!) да и просто отличный магазин!!!
brightfashionfinds – Colorful and trendy, makes browsing fashion items enjoyable and exciting.
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Betway Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
Continuer Г lire|
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-tula015.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Чурапчинская ЦРБ: https://churap-crb.ru Полный спектр медицинских услуг для жителей района.
пассажирские перевозки новосибирск павлодар
Кореновская ЦРБ https://mbuzkcrb.ru Центральная районная больница. Качественная медицинская помощь, поликлиника и стационар.
Солнышково https://solnyshkovo.ru Центр развития и обучения для детей. Интересные занятия, подготовка к школе и творческие студии в комфортной атмосфере.
Альфа-Дент НСК https://alfadentnsk.ru Современная стоматология в Новосибирске. Профессиональное лечение и забота о вашей улыбке.
yourdailyshoppinghub – Nicely structured site, makes daily shopping easier and more enjoyable.
Капельница для лечения запоя – это важная медицинская процедура при алкогольной зависимости. Подготовка к ней предполагает несколько действий. Во-первых, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет консультацию. Проявления алкогольной зависимости могут различаться, поэтому необходимо подробно рассказать врачу о симптомах. нарколог на дом Перед введением капельницы рекомендуется обеспечить доступ к венам, а также организовать комфортные условия для пациента. Проверьте наличие всех необходимых препаратов для введения капельницы. После процедуры следует уделить внимание реабилитации, правильный уход за пациентом поможет в восстановлении здоровья и снизит риск рецидива.
Эль-Дент: https://eldental.ru Современный детский стоматологический центр. Профессиональное лечение, ортодонтия и реставрация.
Only top materials: https://hyundaimobil.co.id
Трек бьется. Как придет отпишу. Если все ровно то я ваш постоянный клиент, цены и ассортимент радуют. https://pasyans-pauk.ru покушать попробуй… и пиши сюда
Only top materials: https://astonvillafansclub.com/read-blog/16981
двойные рулонные шторы с электроприводом [url=https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru]https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru[/url] .
рулонные шторы электрические [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]рулонные шторы электрические[/url] .
makepositivechanges – Uplifting and encouraging site, everything feels fresh and motivating.
1xbet g?ncel [url=https://www.1xbet-giris-2.com]https://www.1xbet-giris-2.com[/url] .
1xbet giri? yapam?yorum [url=http://www.1xbet-giris-8.com]1xbet giri? yapam?yorum[/url] .
1xbet lite [url=https://www.1xbet-giris-4.com]https://www.1xbet-giris-4.com[/url] .
learnandgrowtoday – Very informative and inspiring, perfect for daily learning and personal growth.
Перед тем как перечислить типичные случаи, отметим главный принцип: домашний формат выбирают, когда безопасность и прогноз сопоставимы со стационаром, а переезд лишь затянет старт терапии и усилит стресс для семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-zhukovskom/
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Betway Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. A noter les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
discoverandcreate – Creative and engaging, perfect place to find ideas and inspiration.
заказ минивэна
Здравствуйте, всем бобра норм магаз все ровно как по маслу купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Такая тут вкусная цена была недавно на фтор.И продукт офигенский.А теперь цену подняли до всеобщего уровня.И я не вижу уже причин заказать именно здесь а не где-то ещё.Так-то с отправкой всё ровно будет,но цена…
This online platform contains a lot of captivating and informative information.
On this platform, you can find different articles that provide insights.
Everyone will enjoy the materials shared through this platform.
All topics is thoughtfully designed, making it convenient to use.
The articles are easy to understand.
The site includes tips on many areas.
No matter if you seek useful facts, this site has a lot to offer.
Overall, this site is a great source for people who enjoy discovering new things.
https://aiti-portal.de/
freshfashioncorner – Trendy looks and fresh designs, definitely one to revisit often.
Эль-Дент: https://eldental.ru Современный детский стоматологический центр. Профессиональное лечение, ортодонтия и реставрация.
Альфа-Дент НСК https://alfadentnsk.ru Современная стоматология в Новосибирске. Профессиональное лечение и забота о вашей улыбке.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar025.ru
вывод из запоя
Expanded article here: https://znalov.ru/2025/10/27/автореги-фейсбук-по-низкой-цене/
[url=https://milioner-casino.net]millioner casino[/url]
bestvaluecollection – Excellent deals and easy navigation, really makes shopping enjoyable.
[url=https://milioner-kasyno.pl/]milioner casino[/url]
Джи спокойно 20-ого числа 😉 Потом вот только как получать будешь…? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Радуете ребята!!!
discoverbetteroptions – Clean and well-organized, makes finding better deals and options easy.
[url=https://billionaire-casino.pl]huuuge billionaire casino[/url]
buildsomethingnew – Inspiring message and simple design, feels fresh and full of ideas.
findyourdreamplace – Beautiful visuals and easy navigation, makes exploring dream locations enjoyable.
J’adore le dynamisme de Belgium Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Avancer|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Betway Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller à l’intérieur|
задержек небыло все было ровно магаз ровный заказывай трек сразу кидают , за качество не могу пока ничо отписать , не пробывал, попробую отпишу! https://fenix-k.ru Флудить на счет легальности/нелегальности товара в магазине не нужно в ветке! У же отписывалась и экспертиза и мы не однократно писали, возим ТОЛЬКО ЛЕГАЛ!
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui stimule l’engagement.
Ouvrir la page|
Je suis emerveille par Betway Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui motive les joueurs.
Approfondir|
получить консультацию психиатра
psychiatr-moskva010.ru
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une immersion totale. A noter le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Continuer ici|
purestylemarket – Very stylish and modern, perfect for exploring new fashion items.
Этап
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
findyourmoments – Calm and inspiring design, a lovely place to explore and reflect.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Gamdom Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui booste la participation.
Tout apprendre|
Запойное состояние – серьезная проблема‚ которая требует неотложной помощи специалиста в области наркологии. В городе владимир круглосуточно доступны услуги наркологической клиники‚ где вы можете получить необходимую медицинскую помощь. Детоксикационные капельницы способствуют быстрому восстановлению организма после запоя. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает не только физическую поддержку‚ а также помощь психолога. Консультация нарколога обеспечит индивидуальное внимание к каждому пациенту. Поддержка семьи играет важную роль в процессе восстановления. Не стоит откладывать‚ обращайтесь за помощью! помощь нарколога владимир
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Betify Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
Savoir plus|
бобик здох …. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш ОО мне то же все пришло!
classyfindsonline – Love the classy layout, everything looks elegant and well arranged.
imaginelearnexplore – Inspiring and informative, great site for learning and discovering new things.
стоимость рулонных штор [url=https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru]стоимость рулонных штор[/url] .
автоматические рулонные шторы [url=www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]автоматические рулонные шторы[/url] .
1xbet yeni adresi [url=http://1xbet-giris-8.com]1xbet yeni adresi[/url] .
1xbet tr [url=1xbet-giris-2.com]1xbet tr[/url] .
1xbet giri? linki [url=www.1xbet-giris-4.com/]www.1xbet-giris-4.com/[/url] .
globalfashionzone – Trendy and user-friendly, excellent layout for browsing worldwide fashion trends.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Belgium Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Belgium Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Belgium Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un atout le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Lire la suite|
Je suis emerveille par Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par contre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquez ici|
Фриспины в казино Многие слышали о бездепозитных бонусах – это когда казино дарит вам деньги или вращения просто так, за регистрацию. Звучит заманчиво, правда? И это действительно отличная возможность попробовать свои силы. Однако, как и в любом деле, здесь есть свои нюансы. Важно понимать, что такие бонусы обычно имеют условия отыгрыша – то есть, вам придется сделать определенное количество ставок, прежде чем вы сможете вывести полученные деньги. Но даже с учетом этого, это прекрасный старт для тех, кто хочет познакомиться с миром онлайн-казино без финансовых рисков.
Цены сладкие. Качество отменное. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Товар даже не тестили еще ! Но вес ровный , качество не сомневаюсь тоже на высоте , скоро будем проводить тесты . Буду брать только здесь !!!
Je suis enthousiasme par Gamdom Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Gamdom Casino garantit un amusement continu. De plus le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Entrer|
бездепозитные бонусы казино без пополнения Многие слышали о бездепозитных бонусах – это когда казино дарит вам деньги или вращения просто так, за регистрацию. Звучит заманчиво, правда? И это действительно отличная возможность попробовать свои силы. Однако, как и в любом деле, здесь есть свои нюансы. Важно понимать, что такие бонусы обычно имеют условия отыгрыша – то есть, вам придется сделать определенное количество ставок, прежде чем вы сможете вывести полученные деньги. Но даже с учетом этого, это прекрасный старт для тех, кто хочет познакомиться с миром онлайн-казино без финансовых рисков.
urbanfashioncorner – Stylish urban vibe, makes exploring fashion items really fun and engaging.
J’ai un faible pour Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En bonus le site est rapide et immersif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis emerveille par Gamdom Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Gamdom Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Je suis sous le charme de Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour ajouter la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un element fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
https://betifycasinoa366fr.com/|
Капельницы от запоя на дому в Красноярске: быстрое и безопасное решение Алкогольная зависимость — серьезная проблема, требующая квалифицированной помощи. Круглосуточный нарколог в Красноярске предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Это действенный метод, который помогает быстро справиться с абстиненцией и восстановиться после запойного состояния.При алкоголизме важно не только временно облегчить состояние, но и обеспечить качественную медицинскую помощь при запое. Капельница помогает быстро снять похмелье, улучшить общее состояние и предотвратить осложнения. Заказ капельницы на дому — это удобный способ для людей, желающих избежать стационарного лечения и получить помощь в привычной обстановке.Доступность нарколога 24/7 обеспечивает возможность детоксикации в любое время. Помните, что лечение запоя на дому включает в себя как физическое, так и психологическое восстановление. Реабилитация от алкоголизма — это долгий процесс, требующий комплексного и внимательного подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно Красноярск Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкоголизма, не откладывайте обращение к специалистам. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске доступны круглосуточно, и каждый может рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку.
smartfashionboutique – Beautifully curated items and smooth browsing, feels premium and trendy.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup.
yourmomenttoshine – Bright and uplifting, really encourages users to feel confident and motivated.
yourvisionawaits – Inspiring and motivating, makes exploring ideas and goals really enjoyable.
С возвращением бразы! удачной работы вам и процветания купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Вообщем фейк крассавчик пошагово и все грамотно сделал, развел)
Что делаем
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Изучите внимательнее – https://halucom.vn/chao-moi-nguoi
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Не упусти шанс – https://henznaturephotography.nl/hello-world
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Что скрывают от вас? – http://www.marianhubler.com/marians-bio
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://steel-action.de/download
exploreinnovativeideas – Great place to discover fresh ideas, very clean and inspiring layout.
trendinghomeideas – Creative and practical ideas for home, very nice experience overall.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Betway Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui stimule l’engagement.
Cliquer pour voir|
гаси кидалу по полной -25 маловато я добавлю купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Респект Магазу
stayfocusedandgrow – Positive and clean layout, perfect for personal growth and focus.
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Кликни и узнай всё! – https://casualwalker.com/cholamandal-artists-village-museum-of-contemporary-art-chennai
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Уточнить детали – https://startupstories.in/latest-news/acevector-limited-announces-new-ceos-for-snapdeal-and-stellaro-brands
changeyourperspective – Modern and clean design, perfect for exploring fresh ideas and viewpoints.
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psychiatr-moskva011.ru
лечение психиатрических расстройств
Je ne me lasse pas de Betway Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En fin de compte, Betway Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lancer le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais encore des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Voir la page|
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Изучите внимательнее – https://www.statewideinspection.com/flooring-news-nalfa-introduces-issues-answers-course-floorbiz-com-flooring-news
Je suis accro a Belgium Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Belgium Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, assure des transactions fluides.
Explorer la page|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betway Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Первый шаг к выздоровлению — вызвать нарколога во Владимир. Наркологические услуги, такие как безопасный вывод из запоя, обеспечивают необходимую медицинскую помощь. Профессиональный нарколог проводит детоксикацию организма, что критически важно для здоровья пациента. Индивидуальная программа лечения алкоголизма способствует более высокому уровню успешности восстановления после алкогольной зависимости. вызов нарколога владимир Поддержка при запое включает не только медицинские процедуры. Консультация врача-нарколога помогает определить дальнейшие шаги, включая реабилитацию зависимых. Обращение к специалисту на дому облегчает процесс и снижает уровень стресса. Заботьтесь о своем здоровье и обращайтесь за помощью!
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Обратиться к источнику – https://kimkaradesign.com/shalu-maheshwari
J’ai un faible pour Gamdom Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir la page|
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://nhongsendiadid.com/nhan-biet-nhong-sen-dia-exciter-135-exciter-150-chinh-hang
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://diarioelconstructor.com/2024/06/05/los-edificios-mas-emblematicos-de-centroamerica
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Betify Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute vibrante.
En savoir plus|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Betify Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Visiter la plateforme|
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://foreningen.svenskhemslojd.com/product/on1-jersey-unif
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://www.fuji-cci.or.jp/cropped-site_icon-png
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Перейти к полной версии – https://bytosoft.com/digital-marketing-concepts-easy-steps-for-digital-marketing-varanasi
Может быть, не отрицаю. Пока никого винить не буду, потому что вполне возможно что я и сам закосячил. Но вроде все правильно делал. При том я не один такой..До этого приходил ам (окло недели-полторы, назад) делал все точно так же, но только на черной заварке принцесса Нури, 1 к 10, и с водника уносило далекоооо….всех кто пробовал этот водник.. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Но могу сказать что на данный момент проблемы с отправкой у магазина! в среду оплатил и сказали в четверг будет отправка, но увы ее нет! такое в первый раз замечаю от такого магазина! будем ждать!
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://moriyamaseko.wpxblog.jp/jr%E6%9D%B1%E6%B5%B7%E3%83%AA%E3%83%8B%E3%82%A2%E4%B8%AD%E5%A4%AE%E6%96%B0%E5%B9%B9%E7%B7%9A%E5%B7%A5%E4%BA%8B%E8%AA%AC%E6%98%8E%E4%BC%9A
купить рулонные шторы в москве [url=http://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru]купить рулонные шторы в москве[/url] .
Revitalized loli porn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
1xbet turkey [url=http://1xbet-giris-2.com]http://1xbet-giris-2.com[/url] .
startanewjourney – Simple and inviting design, feels like a site full of possibilities.
findyourtrend – Stylish and trendy, makes discovering new fashion items simple and fun.
рулонные шторы с направляющими купить [url=https://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru]https://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru[/url] .
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Запросить дополнительные данные – http://web.duttenhoefer-aussenwerbung.de/2016/07/18/ask-good-questions-and-get-better-answers
1xbet resmi [url=http://1xbet-giris-4.com]http://1xbet-giris-4.com[/url] .
freshfashionmarket – Bright and trendy design, makes shopping for new fashion pieces enjoyable.
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Betway Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Детали по клику – http://2sobaki.ru/202008062166/kinologiya/novosti-sobakovodstva/v-chem-sila-vliyatel-nogo-marketinga.html
Круглосуточный вызов нарколога на дом стал важной услугой для людей‚ борющихся с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru можно узнать всю важную информацию о лечении зависимостей‚ включая лекарственную терапию и психотерапевтические методы лечения зависимостей. Консультация нарколога поможет выявить уровень зависимости и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Круглосуточная помощь позволяет вызвать специалиста на дом в любое время‚ что особенно важно для экстренных случаев. Услуги нарколога включают диагностику зависимостей‚ анонимное лечение и поддержку родственников. Реабилитация наркоманов требует комплексного подхода‚ и квалифицированная помощь может значительно упростить этот процесс. Профилактические меры против зависимостей также является важным аспектом в борьбе с ними‚ поэтому необходимо обращаться за помощью при первых симптомах. Приезд врача на дом создает комфортные условия и гарантирует конфиденциальность‚ способствуя более успешному лечению.
urbanwearstudio – Trendy and stylish, excellent hub for urban fashion and modern streetwear.
Зделал заказ 203го в четверг вечером,в пятницу уже получил трек,а сегодня създил забрал посылку!запаковано так,что сам с трудом нашел)все очень вкусно и качественно!продовцам респект.слаженно работают! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану как и обещал пишу про качество- для кайфожеров 1к7, для кайфариков 1к9 , для додиков 1к11 , продукт работает 35-40 мин , используйте нормальную очищенную основу и будет счастье в тридевятом государстве, вот например от смолы ромашки или мать и мачехи головные боли и побочки, хотя реагент тут не причем , химоза нормального качества особенно если считать в соотношении цена-качество, ТС последнее время приятно удивляет своим терпением к таким сумасшедшим клиентам как я( я с ума сводил его своими платежами) но он стойко все перенес за что ему отдельное респект ТАК ДЕРЖАТЬ!!!! ТС КРАСАВЧЕГ
dailyvalueoutlet – Great deals and smooth browsing, perfect for everyday shopping and savings.
simplevalueplace – Easy navigation and clear visuals, great for quick and simple shopping.
обо всем думаем ) но не сразу купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Трек бьется. Как придет отпишу. Если все ровно то я ваш постоянный клиент, цены и ассортимент радуют.
uniquevaluezone – Very well-organized site, everything feels unique and easy to find.
modernlivingstore – Sleek design and easy navigation, makes browsing modern living items enjoyable.
על לרה, היא צחקה עלי וחייכה כל כך כאילו התאהבתי בה, היא הייתה יפה כמלאך אז בשבילי, תחת השפעתה של נוספים. היא הושיטה את רגלה לעברו. – הנה. תנקה את זה בעצמך. ארטיום לא איחרה לחכות. הוא התכופף וליקק https://24pornhd.com/
newseasonfinds – Fresh, modern, and well-organized, makes exploring seasonal items enjoyable.
консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva012.ru
платный психиатр на дом в москве
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Betway Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer ici|
может ты просто сам не учел проценты комиссии и тебе не хватило??? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Заказы только СПСР доставкой?
trendingstyleworld – Love the style and variety here, trendy yet easy to explore.
Discover exquisite Austrian wines at [url=https://wine-tasting-wien.netlify.app/]wine tour vienna[/url] and immerse yourself in Vienna’s vibrant wine culture.
In Wien kann man die Vielfalt osterreichischer Weine auf besondere Weise entdecken. Die Region ist bekannt fur ihren exzellenten Wei?wein, besonders den Grunen Veltliner. Die Weinkeller Wiens locken mit ihrem authentischen Charme und kostlichen Tropfen.
Das milde Klima und die mineralreichen Boden begunstigen den Weinbau. Das macht Wien zu einer der wenigen Gro?stadte mit eigenem Weinbaugebiet.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
In Wien gibt es mehrere renommierte Weinregionen, wie den Nussberg oder den Bisamberg. Hier reifen einige der besten osterreichischen Weine heran. Familiengefuhrte Weinguter bieten oft Fuhrungen und Verkostungen an. Gaste konnen die Leidenschaft der Winzer hautnah erleben.
Ein Besuch im Weingut Wieninger oder im Mayer am Pfarrplatz lohnt sich. Sie sind bekannt fur ihre ausgezeichneten Jahrgange.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Weinverkostung**
Eine klassische Wiener Weinverkostung beginnt meist mit einer Kellertour. Dabei erfahrt man Wissenswertes uber Rebsorten und Vinifizierung. Danach folgt die Verkostung unterschiedlicher Weine. Jeder Wein wird sorgfaltig prasentiert und verkostet.
Haufig werden die Weine mit lokalen Kasesorten oder Brot serviert. Diese Kombination ist ein Highlight fur Feinschmecker.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Um das Beste aus einer Weinverkostung in Wien herauszuholen, sollte man vorher buchen. Einige Anbieter bieten auch private Verkostungen an. Zudem lohnt es sich, auf die Jahreszeiten zu achten. Im Winter bieten viele Weinguter gemutliche Kellerveranstaltungen.
Ein guter Tipp ist auch, ein Notizbuch mitzubringen. So kann man sich die geschmacklichen Eindrucke leicht merken.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Das gibt den Wiener Weinen ihren unverwechselbaren Charakter.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
Gaste konnen die Leidenschaft der Winzer hautnah erleben.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Wiener Weinverkostung**
Es ist die perfekte Erganzung zum sensorischen Erlebnis.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
So kann man sich die geschmacklichen Eindrucke leicht merken.
—
**Hinweis:** Durch Kombination der Varianten aus den -Blocken konnen zahlreiche einzigartige Texte generiert werden, die grammatikalisch und inhaltlich korrekt sind.
kra38 cc
Капельница от запоя на дому в владимире: быстрое облегчение Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезная ситуация, требующая обращения к специалистам. Круглосуточный нарколог в владимире предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Такой подход позволяет быстро облегчить состояние и помочь в восстановлении после запоя.При алкогольной зависимости необходимо обеспечить не только временное облегчение, но и качественную медицинскую поддержку. С помощью капельницы можно быстро устранить похмелье, улучшить здоровье и избежать осложнений. Вызов капельницы на дом — это комфортный вариант для тех, кто предпочитает избегать госпитализации и хочет получать помощь в привычной обстановке.Круглосуточная помощь нарколога позволяет обеспечить детоксикацию алкоголика в любое время. Помните, что лечение запоя на дому включает в себя как физическое, так и психологическое восстановление. Процесс реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости является длительным и требует всестороннего подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Поэтому, если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкогольной зависимости, не откладывайте обращение за помощью. Вы можете рассчитывать на круглосуточные услуги нарколога в владимире и получить необходимую профессиональную поддержку.
Je suis completement seduit par Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Команда клиники — это врачи-наркологи, психиатры-консультанты, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинический психолог, психотерапевт и медсёстры с опытом круглосуточного поста. Мы разговариваем «языком фактов»: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов, дневники воды и сна, малые бытовые цели. Такой язык исключает стигму и «магическое мышление»; он понятен семье и помогает принимать решения без страхов и «подстраховочных» излишков.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/[/url]
inspirechangealways – Positive and motivational, great site for inspiration and self-improvement ideas.
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par contre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour faire court, Belgium Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
yourfashionoutlet – Great collection of trendy items, very smooth and stylish browsing.
Je suis epate par Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Betway Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller plus loin|
learnsomethingamazing – Inspiring and educational, perfect site for daily learning and ideas.
Discover exquisite Austrian wines at [url=https://wine-tasting-wien.netlify.app/]weinverkostung nahe wien[/url] and immerse yourself in Vienna’s vibrant wine culture.
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne. Die Region ist bekannt fur ihren exzellenten Wei?wein, besonders den Grunen Veltliner. Die Weinkeller Wiens locken mit ihrem authentischen Charme und kostlichen Tropfen.
Das milde Klima und die mineralreichen Boden begunstigen den Weinbau. Daher gedeihen hier besonders aromatische Rebsorten.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
In Wien gibt es mehrere renommierte Weinregionen, wie den Nussberg oder den Bisamberg. Die Weinguter hier setzen auf nachhaltigen Anbau. Familiengefuhrte Weinguter bieten oft Fuhrungen und Verkostungen an. Oft gibt es auch regionale Speisen zur perfekten Weinbegleitung.
Ein Besuch im Weingut Wieninger oder im Mayer am Pfarrplatz lohnt sich. Sie sind bekannt fur ihre ausgezeichneten Jahrgange.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Weinverkostung**
Eine klassische Wiener Weinverkostung beginnt meist mit einer Kellertour. Dabei erfahrt man Wissenswertes uber Rebsorten und Vinifizierung. Danach folgt die Verkostung unterschiedlicher Weine. Jeder Wein wird sorgfaltig prasentiert und verkostet.
Haufig werden die Weine mit lokalen Kasesorten oder Brot serviert. Es ist die perfekte Erganzung zum sensorischen Erlebnis.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Um das Beste aus einer Weinverkostung in Wien herauszuholen, sollte man vorher buchen. Einige Anbieter bieten auch private Verkostungen an. Zudem lohnt es sich, auf die Jahreszeiten zu achten. Die warmen Monate eignen sich perfekt fur Verkostungen im Freien.
Ein guter Tipp ist auch, ein Notizbuch mitzubringen. So kann man sich die geschmacklichen Eindrucke leicht merken.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
Diese Gebiete sind fur ihre Spitzenweine international bekannt.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Wiener Weinverkostung**
Es ist die perfekte Erganzung zum sensorischen Erlebnis.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Viele Weinguter haben begrenzte Platze und sind schnell ausgebucht.
—
**Hinweis:** Durch Kombination der Varianten aus den -Blocken konnen zahlreiche einzigartige Texte generiert werden, die grammatikalisch und inhaltlich korrekt sind.
Причёт тут почта России, СПСР это самостоятельная курьерская служба. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм chem24.biz.ski заходи и приколись
Je suis accro a Gamdom Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, rarement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Gamdom Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En plus la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
Commencer Г lire|
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ устранить симптомы зависимости от алкоголя. В Красноярске множество наркологических клиник предлагают помощь по выводу из запоя, но необходимо выбрать наиболее подходящую.Первым шагом является определение степени зависимости. Квалифицированные специалисты проведут анализ состояния пациента и предложат индивидуальный план лечения. Важночтобы клиника обеспечивала стационарное лечение и анонимное лечение алкогольной зависимости. Это обеспечит комфортные условия для пациентов.Не забывайте о наличии психотерапии при алкоголизме. Психологическая поддержка является важным аспектом в восстановлении после запоя и лечении алкогольной зависимости. Семейная поддержка также способствует успешному восстановлению зависимых. вывод из запоя Красноярск Посмотрите отзывы о медицинских учреждениях и уточните, какие услуги нарколога они предлагают. Правильный выбор клиники — это залог успешного и безопасного выздоровления.
kra38 cc
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Betify Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges personnalises.
Cliquer maintenant|
modernlivingtrend – Stylish, modern, and smooth experience from start to finish.
Использование контрактного производства помогает быстро выводить новые продукты на рынок. Специалисты создают прототипы, разрабатывают схемы и платы, тестируют устройства на надежность. Контроль качества на каждом этапе обеспечивает стабильную работу устройств. Заказчики экономят ресурсы и получают готовое решение, полностью соответствующее техническим требованиям https://chuyendoixanh.org/wiki/index.php/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%BE_%D0%9F%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%82_%D0%98_%D0%A3%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2_%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%B4_%D0%9A%D0%BB%D1%8E%D1%87. Эффективная технология проверки прототипов
Enjoyed reading through this, very good material. Thanks!
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-chekhove/
kra41 cc
Курс терапии в клинике состоит из нескольких последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение конкретных целей — от снятия интоксикации до восстановления психологического равновесия. Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и минимизировать вероятность рецидива. На всех стадиях лечения ведётся контроль состояния пациента, а также постоянная корректировка назначений в зависимости от реакции организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая клиника в казани[/url]
Магазин нормально работает?,а то некоторые говорят что не стоит обращаться в данный магазин для заказов!Фон или фок как твой ник правильно читаеться и пишиться ? отпишись нормальный магаз или нет ! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Наблюдая за многими сообщениями, мы понимаем что многие на форуме не более чем очень “кипишные люди”, которые любят разводить демагогию.
После прохождения детоксикации пациенту назначаются восстановительные процедуры, направленные на нормализацию обмена веществ и укрепление нервной системы. Программы клиники включают физиотерапию, витаминотерапию и индивидуальные занятия с психотерапевтом. Главная цель — восстановить способность организма к естественной саморегуляции и снизить зависимость от внешних раздражителей.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм казань[/url]
smartshoppingzone – Easy to navigate and clean layout, perfect for smart shoppers.
Каждый инструмент имеет чёткие показания и ограничение: мы объясняем, какую гипотезу проверяем, по каким признакам поймём, что она верна, и когда перестанем использовать метод, если вклад невелик. Это снижает тревогу и формирует доверие к плану.
Получить больше информации – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Иногда домашний маршрут лишь создаёт иллюзию экономии времени. Если есть спутанность сознания, выраженная дезориентация, галлюцинации, повторные судороги, нестабильное давление, сильная одышка или неукротимая рвота с обезвоживанием, безопаснее начинать в стационаре. Там рядом диагностика и пост 24/7, любое решение принимается сразу, а коррекция схемы не упирается в бытовые ограничения квартиры.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Портрет по фотографии на заказ https://moi-portret.ru
Need TRON Energy? buy tron energy Affordable for your wallet. Secure platform, verified sellers, and instant delivery. Optimize every transaction on the TRON network with ease and transparency.
Energy for TRON buy tron energy instant activation, transparent pricing, 24/7 support. Reduce TRC20 fees without freezing your TRX. Convenient payment and automatic energy delivery to your wallet.
Туристический портал https://cmc.com.ua авиабилеты, отели, туры и экскурсии в одном месте. Сравнение цен, отзывы, готовые маршруты, визовые правила и карты офлайн. Планируйте поездку, бронируйте выгодно и путешествуйте без стресса.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement attrayant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Approfondir|
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
learnsomethingdaily – Clean and informative, perfect for daily learning and personal growth.
Команда «СеверМед Альянса» включает наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, специалистов по зависимости, физиотерапевтов и координатора маршрута. Каждый модуль — детоксикация, стабилизация сна и настроения, психотерапия, семейная работа, восстановление бытовых и профессиональных ролей — встроен в общий план. Мы избегаем «одинаковых схем» и полипрагмазии: добавляем только те инструменты, у которых есть измеримая цель и безопасное «окно оценки» эффективности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk
J’adore la vibe de Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Belgium Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
Plonger dedans|
Конфиденциальность — это набор конкретных действий, а не декларация на сайте. Мы проектируем «невидимость» так, чтобы пациент мог спокойно принять помощь и не опасаться огласки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Je suis accro a Gamdom Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais encore quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter en ligne|
theartofgrowth – Inspiring and thoughtful layout, perfect for personal growth and learning.
Здесь
[url=https://www.smclinic.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Je ne me lasse pas de Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Betway Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Je suis sous le charme de Gamdom Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, en revanche des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour ajouter l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Tout apprendre|
«Чистая Гармония» — это выездная и стационарная наркологическая помощь в одном маршруте: оперативный приезд врача на дом по Клину и району, аккуратный детокс с контролем жизненно важных показателей, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких лишних процедур ради «видимости лечения» и никаких задержек с тем, что влияет на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, заранее согласуем смету и оставляем понятный план на 24–48 часов и первую неделю. Анонимность — базовый стандарт: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinskij-rajon-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
findyourpathnow – Motivating vibe and thoughtful layout, everything feels purposeful and neat.
https://xnudes.ai/
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour ajouter l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Если дома нет условий для покоя (ремонт, маленькие дети, шумный двор), мы предложим краткосрочное наблюдение в клинике: отдельный вход, «тихий» коридор, без посторонних вопросов. После стабилизации пациент возвращается домой и продолжает амбулаторный формат с краткими чек-инами по телефону или видеосвязи. Ваша частная жизнь в приоритете: доступ к карте разграничен по ролям, а с семьёй общаемся через одного доверенного человека.
Узнать больше – http://
Уважаемы участники форума! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш может стоит разводить 1 к 10? Кто брал ам 2233 отпишитесь на щёт пропорции,вообще 2233 1 к 20 разводится если продукт хороший
seo аудит веб сайта [url=optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru]seo аудит веб сайта[/url] .
поисковое seo в москве [url=https://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru]поисковое seo в москве[/url] .
блог про продвижение сайтов [url=http://www.statyi-o-marketinge7.ru]блог про продвижение сайтов[/url] .
kra45 cc
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologiya-v-ryazani
блог интернет-маркетинга [url=http://statyi-o-marketinge6.ru/]http://statyi-o-marketinge6.ru/[/url] .
Стационар мы предлагаем, когда дома нет условий для ночного наблюдения, симптомы тяжёлые или прогноз нестабилен. В палате — контролируемая среда, возможность оперативно выполнить ЭКГ и базовые анализы по показаниям, круглосуточный пост. Команда корректирует схему лечения в реальном времени, не теряя часы на логистику. Это особенно важно при давних запоях, риске делирия, выраженных колебаниях давления, сахарном диабете, ИБС, заболеваниях ЖКТ.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]домашний вывод из запоя[/url]
discoverandbuy – Smooth experience and well-presented products, makes online shopping effortless.
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]narkolog-sergiev-posad-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
консультация частного психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva010.ru
консультация врача психиатра онлайн
m bs2web at
Капельница — не «универсальная смесь», а адресный баланс жидкости, электролитов и поддерживающих компонентов под текущие симптомы. Ниже — ориентир, который индивидуализируется на месте осмотра. Мы тщательно сопоставляем пользу и допустимую нагрузку, чтобы не перегружать организм.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk0.ru
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону и агломерации выстроены два параллельных «тихих» маршрута: выездная бригада без маркировки и амбулаторный вход с отдельной дверью и согласованными временными слотами. На первичном звонке диспетчер уточняет только факторы безопасности: эпизоды рвоты, частоту мочеиспусканий, выраженность тремора, показатели ЧСС/АД, наличие ночных панических эпизодов, текущие препараты и аллергии. На месте врач фиксирует базовую линию (уровень сознания, дыхание, сатурация, температура), использует шкалы симптомов 0–10 и определяет минимальный стартовый модуль. По результатам «окон оценки» (40–90 минут для питья и тошноты; 60–120 минут для ЧСС/АД; первая ночь для сна) мы либо выключаем модуль, либо адресно меняем одну переменную — так сохраняется причинно-следственная связь и исключается «инерция лечения».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Урал» специализируется на безопасном и деликатном выведении из запоя с выездом врача на дом. Мы соединяем медицинскую точность, продуманную логистику и понятные пациенту шаги, чтобы облегчение наступало быстро, а состояние оставалось стабильным и предсказуемым. В основе — индивидуальные капельницы по показаниям, детоксикация с мониторингом витальных показателей, коррекция обезвоживания и электролитных нарушений, мягкая поддержка сна и психологическая разгрузка. Наши бригады приезжают круглосуточно, оборудование компактно, документы — нейтральные, а сообщения в медицинской карте формулируются аккуратно, без «ярлыков», чтобы сохранить вашу конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy-kamensk-uralskij/
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Самый крутой магазин! https://www.grepmed.com/ichuhudte посылка упакована оригинально =)) и скорость сборки удивила!
В Волгограде медицинская клиника «Трезвая Линия Волгоград» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с острым алкогольным отравлением или затяжным запоем. Врачи выезжают на дом, в гостиницу или принимают пациентов в стационаре. Каждое вмешательство начинается с оценки состояния — измерения давления, пульса, насыщения кислородом, уровня интоксикации и дехидратации. Далее подбирается оптимальный состав капельницы, направленный на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, поддержку печени и снижение тревожности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Betway Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Visiter pour plus|
Строительный портал https://6may.org новости отрасли, нормативы и СНИП, сметы и калькуляторы, BIM-гайды, тендеры и вакансии. Каталоги материалов и техники, база подрядчиков, кейсы и инструкции. Всё для проектирования, строительства и ремонта.
trendforlife – Very fashionable and clean site, makes exploring trends effortless.
Топ-добірка у нас: https://mediaworld.com.ua/rozvahy.html
Всё для стройки https://artpaint.com.ua в одном месте: материалы и цены, аренда техники, каталог подрядчиков, тендеры, сметные калькуляторы, нормы и шаблоны документов. Реальные кейсы, обзоры, инструкции и новости строительного рынка.
Новостной портал https://novosti24.com.ua с фокусом на важное: оперативные репортажи, аналитика, интервью и факты без шума. Политика, экономика, технологии, культура и спорт. Удобная навигация, персональные ленты, уведомления и проверенные источники каждый день.
Капельницы, используемые для выхода из запойного состояния — это важным этапом в лечении алкоголизма, что требует внимательном подходе. Вызов нарколога важен для оценки состояния пациента и подбора необходимого лечения. Основные компоненты капельниц способствуют detoxication, смягчая симптомы запоя, такие как головная боль, тошнота и тревога. Несмотря на эффективность, существуют противопоказания: тяжелые заболевания сердца, почек и печени могут усложнить лечение. К возможным рискам терапии относятся побочные эффекты, такие как аллергические реакции или ухудшение состояния. Поэтому приоритетом должна быть безопасность процедуры. Медицинское вмешательство включает не только лишь вывод из запоя, но и реабилитацию, направленную на восстановление здоровья пациента и предотвращение рецидивов. Следует помнить, что каждый случай индивидуален, и лечение необходимо проводить под контролем квалифицированного нарколога.
Капельница от запоя — является действующим способом, применяемым в области наркологии для лечения зависимости от алкоголя; терапия с применением инфузий даёт возможность оперативно удалить токсины из организма и восстановить баланс воды и электролитов. Специалист по наркологии на дому анонимно в Красноярске предоставляет такую услугу, обеспечивая пациентам удобство и конфиденциальность. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск Признаки похмелья, такие как боль в голове, тошноту и усталость, могут быть устранены с помощью капельницы, включающей подходящие лекарства. Процесс лечения зависимости от алкоголя предполагает индивидуального подхода, и специалист по наркологии на дому проводит консультацию, определяя нужные процедуры для облегчения симптомов абстиненции. Детоксикация организма — важный этап, который помогает вернуться к норме после запоя. Забота и поддержка семьи занимает ключевую роль в реабилитации зависимых, а фармацевтическое лечение в комбинации с инфузионной терапией обеспечивает положительный эффект.
modernhomecorner – Love the modern designs and home decor ideas shared here daily.
urbanchoicehub – Trendy urban style and clean design, makes exploring fashion easy and fun.
Честная наркология — это не «универсальная капельница», а система шагов, привязанная к параметрам конкретного человека. В Чехове мы выезжаем круглосуточно, на месте проводим допуск к терапии, сверяем совместимости с уже принятыми препаратами, подбираем состав инфузий без лишних компонентов и избыточной седативной нагрузки. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим стационар — это не усложнение, а короткий путь к безопасности. Анонимность — стандарт: нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным, деликатная связь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/[/url]
Команда клиники — это врачи-наркологи, психиатры-консультанты, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинический психолог, психотерапевт и медсёстры с опытом круглосуточного поста. Мы разговариваем «языком фактов»: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов, дневники воды и сна, малые бытовые цели. Такой язык исключает стигму и «магическое мышление»; он понятен семье и помогает принимать решения без страхов и «подстраховочных» излишков.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
PureValue Ideas – Inspiring and interactive site for idea generation.
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En complement le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un atout les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
Approfondir|
ты писал пришла посылка размыли в итоге прикола не поняли https://www.band.us/page/100478868/ За время работы легалрц сколько магазинов я повидал мама дорогая, столько ушло в топку, кто посливался кто уехал # но chemical-mix поражает своей стойкостью напором и желанием идти в перед “не отступать и не сдаваться”:superman:
Здесь
[url=https://legalbet.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Каждый инструмент имеет чёткие показания и ограничение: мы объясняем, какую гипотезу проверяем, по каким признакам поймём, что она верна, и когда перестанем использовать метод, если вклад невелик. Это снижает тревогу и формирует доверие к плану.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/narkolog-petrozavodsk-otzyvy/
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/[/url]
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement genial les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Touchez ici|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par moments quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, Belgium Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour couronner le tout le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
Casino Belgium|
Ниже — «каркас» маршрута. Он служит ориентиром для персонализации: меняется приоритет модулей, плотность контактов, сочетание стационара и амбулаторных визитов. Принцип неизменен: «один шаг — одна цель — один маркер».
Подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/
Je suis enthousiasme par Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Gamdom Casino garantit un amusement continu. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement interessant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Plonger dedans|
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatricheskaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voskresenske/
Домашний протокол разбит на понятные шаги. В каждом шаге есть цель, действия, что именно мы измеряем и когда сверяем прогресс. Это делает процесс прозрачным и даёт семье чувство контроля: видно, почему назначено именно это и когда ждать облегчения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь красноярск[/url]
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute soudee.
Poursuivre la lecture|
findmotivationtoday – Positive and inspiring layout, really motivates and encourages action every day.
Je suis accro a Belgium Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Belgium Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer|
Je suis completement seduit par Betify Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
Parcourir le site|
yourstylezone – Stylish, modern, and user-friendly, love the smooth browsing experience.
заказал не мало,всё пришло за кач не знаю как опробуют кролы отпишу http://www.pageorama.com/?p=uggaibyeuh Все нормально,6-го заказал,8-го отправили. Оперативно
yourpathforward – Motivating concept, feels like a site that inspires progress and growth.
Прежде чем перечислить критичные признаки, зафиксируем принцип: даже один выраженный симптом — повод не откладывать помощь и выбрать безопасный маршрут (дом или стационар) после быстрой очной оценки врача.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sergievom-posade/
Je suis completement seduit par Betify Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Betify Casino assure un fun constant. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses continues.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru
Мы держим баланс между недостаточным и избыточным лечением. С одной стороны, не пропускаем опасные признаки, с другой — избегаем седативной перегрузки и сомнительных «коктейлей». Состав капельницы и темп введения зависят от давления и пульса, выраженности тревоги и тошноты, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Каждое назначение объясняется простыми словами, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, как действует схема и зачем нужны ограничения ближайших дней.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/telefon-narkologicheskoj-klinikia-v-voskresenske/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru
findnewinspiration – Bright, clean, and motivating, perfect for discovering fresh ideas daily.
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva011.ru
лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
Вот по количеству норм, но кач…. Это то что осталось после меня и моих проб https://www.rwaq.org/users/wfubkxxv900y05-20251031144925 Страшно) заказывать RTI-126. Кто поможет с данной проблемой.
бесплатные вращения без депозита Мечтаете окунуться в мир азартных игр, но не хотите рисковать собственными деньгами? Онлайн-казино идут навстречу вашим желаниям, предлагая щедрые бездепозитные бонусы. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с игрой, протестировать новые слоты и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не вложив ни копейки!
бездепозитные фриспины за регистрацию Бездепозитные бонусы — это отличный способ войти в мир онлайн-гемблинга без вложений, но подходите с умом. Они дают шанс на выигрыш, но условия могут быть сложными, а риски — высокими. Выбирайте только проверенные казино
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Докладніше на сайті: https://massmedia.one/hroshi.html
продвижение в google [url=https://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru]https://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru[/url] .
growyourmindset – Love how this name promotes positivity and continuous personal growth.
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта [url=https://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru/]optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru[/url] .
статьи про seo [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge7.ru/]статьи про seo[/url] .
Такие процедуры особенно эффективны на ранних стадиях лечения, когда важно быстро снять симптомы интоксикации и вернуть стабильное самочувствие. После курса капельниц пациенту становится легче концентрироваться, снижается раздражительность и тревожность, восстанавливается аппетит и сон.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр рязань[/url]
trendandfashionhub – Bright, trendy, and well-organized, perfect for fashion enthusiasts.
маркетинговые стратегии статьи [url=www.statyi-o-marketinge6.ru/]маркетинговые стратегии статьи[/url] .
«Чистая Гармония» — это выездная и стационарная наркологическая помощь в одном маршруте: оперативный приезд врача на дом по Клину и району, аккуратный детокс с контролем жизненно важных показателей, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких лишних процедур ради «видимости лечения» и никаких задержек с тем, что влияет на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, заранее согласуем смету и оставляем понятный план на 24–48 часов и первую неделю. Анонимность — базовый стандарт: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu[/url]
Наркологическая помощь на экстренных случаях – это существенный элемент, который оказывает необходимую помощь людям, подверженным зависимостям. В кризисной ситуации, когда необходима быстрая поддержка, на помощь предоставляется наркологическая служба. Лечение зависимостей включает медикаментозную терапию и полноценную реабилитацию наркозависимых. При алкогольной зависимости срочная помощь крайне важна. Обращение к психологу может быть первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению. Поддержка семьи является важным аспектом реабилитации. Анонимные группы поддержки и психотерапевтические сеансы помогают справиться с трудностями. Профилактика зависимостей также является критически важной. Борьба с наркотиками требует совместных усилий всей общества. Запрос о помощи на ресурсе vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru даст возможность найти нужные ресурсы для старта новой, трезвой жизни.
Ваш автомобиль стал хуже заводиться, появился стук или загорелась ошибка? Приезжайте в автосервис «5 Бокс» https://auto-5-box.ru . Мы проводим полную компьютерную диагностику и устраняем неисправности любой сложности: ремонт двигателя, коробки передач, подвески, тормозов и электрики. Опытные мастера быстро определят причину поломки и подберут оптимальное решение. Все работы выполняются с гарантией. Мы ценим ваше время и доверие, поэтому работаем чётко, прозрачно и без навязанных услуг. Автосервис «5 Бокс» — уверенность в каждой поездке.
спок ночи https://rant.li/ayfudahfuae/tegeran-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki трек получил в пятницу сегодня понедельник пока нет данных по треку возможно еще не вбился в систему думаю на днях ясно все будет отпишу
findyourinspirationtoday – Inspiring visuals and smooth design, makes finding new ideas enjoyable and simple.
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Continuer Г lire|
Капельница от запоя на дому – это важная услуга наркологов‚ позволяющая эффективно и резко помочь людям‚ переживающим от алкогольной зависимости. Начальная встреча нарколога в владимире включает определение степени зависимости‚ анализ состояния пациента и разработку персонального плана терапии. Ключевые услуги нарколога на дому включают медикаментозное лечение‚ выведение из запоя‚ психотерапевтическую помощь при алкоголизме и программы восстановления. Поддержка родственников тоже играет значимую функцию в процессе реабилитации алкоголиков. Лечение в анонимном формате обеспечивает комфорт и безопасность пациента. помощь нарколога владимир
Supportive loli p^orn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
simplefashioncorner – Clean, trendy, and easy-to-browse fashion options all in one place.
что лучше?АКВ48F или АКВ48?! https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/69864 да и оперативность У ВАС на ВЫСШЕМ :superman: уровне!!
[url=https://uslugi-klininga-1.ru/]Клининг в Москве[/url] — это надежный способ поддерживать чистоту и порядок в вашем офисе или квартире.
У каждой компании свои цены и условия, что дает возможность выбрать наиболее выгодное предложение.
С первого звонка администратор бережно собирает фактуру: сколько длится эпизод, что человек уже принимал за последние двое суток, как прошла ночь, есть ли помощник на вечер и ночь, какие хронические заболевания и аллергии известны. Дежурный врач оценивает риски и предлагает старт: анонимный визит на дом по Клину или немедленную госпитализацию. На месте проводится очная оценка и допуск к терапии, запускается инфузионная поддержка с мониторингом давления, пульса и сатурации, корректируется вода и электролиты, по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна и симптом-контроль. Если картина нестабильна, переводим в стационар — это короче путь к безопасности, чем многочасовые попытки «пересидеть» дома.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru
shopandsaveonline – Great deals and simple layout, makes online shopping quick and easy.
каталог чижик магазин Магазин Чижик каталог – это не просто перечень продуктов, а тщательно отобранный ассортимент, отвечающий потребностям большинства покупателей. В каталоге представлены продукты питания, бытовая химия, товары для дома и многое другое.
Этот медицинский обзор сосредоточен на последних достижениях, которые оказывают влияние на пациентов и медицинскую практику. Мы разбираем инновационные методы лечения и исследований, акцентируя внимание на их значимости для общественного здоровья. Читатели узнают о свежих данных и их возможном применении.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://www.med-edu.ru/mozhno-li-rezko-brosit-pit-analiz-posledstviy
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Изучить материалы по теме – https://www.copenhagenconstrutora.com.br/faq-items/duis-non-dui-vitae-risus-consequat-vestibulum
Бордюры Труба ПРАГМА — еще один вид полимерных труб, предназначенных для подземных коммуникаций. Отличается раструбным соединением, что упрощает и ускоряет монтаж трубопровода. Благодаря высокой химической стойкости и устойчивости к коррозии, трубы ПРАГМА обеспечивают долговечность и надежность системы.
Чат Иркутск
он чють чють с желта https://imageevent.com/unedizeviqil/gdgdv что сильнее 100 или 400 ? и по времени сколько действуют ?
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://kktcalimsatim.com/category/uncategorized/page/4
modernhomecorner – Love the modern designs and home decor ideas shared here daily.
Укрытия для сварки Профильная труба – это труба с некруглым сечением, наиболее распространенные формы – квадрат и прямоугольник. Профильные трубы обладают высокой прочностью на изгиб, что делает их идеальным материалом для строительства каркасных конструкций, ограждений, мебели и других изделий, где важна надежность и долговечность.
[url=https://best-seo-specialists-sochi.ru/]рейтинг сео специалистов сочи[/url]
Успешное продвижение требует экспертного подхода и глубоких знаний.
Достоверные кейсы демонстрируют эффективность работы специалиста.
Честные SEO-эксперты не обещают быстрых результатов без анализа.
Loving the info on this website , you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Читать далее > – https://framica.com/bliss-bone
https://cuctex.com/ Cuctex на «Интерткань»: 3 года, 6 выставок, 750 новинок
С весны 2023 года компания Cuctex шесть раз подряд принимала участие в выставке «Интерткань» — сначала в павильоне «Экспоцентр», затем в «Тимирязевском», а теперь в «Крокус Экспо».
За это время наш стенд посетили более 3000 клиентов. Количество экспонатов увеличилось с 60 до более чем 180, а всего мы представили свыше 750 новых продуктов. Такой рост ассортимента стал причиной того, что многие клиенты отмечают: не все новинки удаётся найти на нашем сайте. Объём информации очень большой, и сайт не всегда справляется с нагрузкой.
Сегодня в ассортименте Cuctex:
* кулирка (плотность 90–400 г/м?),
* интерлок (190–400 г/м?),
* мерсеризированные ткани (160–260 г/м?),
* двунитка (190–300 г/м?),
* футер трёхнитка (300–640 г/м?),
а также кулирка и футер с эффектом варёнки, деним с мягчением, лён с мягчением, клетка, полоска и другие материалы.
На выставке мы встретили много клиентов, которые раньше закупали ткани в Китае, а теперь предпочитают работать с нами ради удобства и надёжности. Часто звучит вопрос, почему у нас нет постоянного наличия. Ответ прост: наш ассортимент включает ткани среднего и высокого качества, и для каждого артикула доступно более 100 цветов. Держать весь этот объём в наличии невозможно, поэтому поставки организуются под заказ.
Также многие интересуются индивидуальными цветами или окраской по палитре Pantone. Такой заказ требует значительных объёмов и времени, так как каждая ткань имеет свой состав, а значит — разные режимы окрашивания.
Cuctex постоянно отслеживает тенденции в швейной промышленности и мировые тренды в цвете. Каждый год мы инвестируем время и ресурсы в изучение ассортимента ведущих мировых брендов, чтобы предлагать ткани, подходящие именно для регионального рынка. На китайском рынке ежегодно появляется десятки тысяч новых тканей, и выбор лучших решений среди этого многообразия — сложная и ответственная задача.
А для того чтобы клиенты могли лично ознакомиться с ассортиментом и фактурой тканей, мы открыли шоурумы в Москве и Ташкенте. Там можно вживую увидеть образцы и получить консультацию специалистов.
Если вы хорошо разбираетесь в тканях, будем рады вашим комментариям, опыту и мнению.
психиатр на дом
psikhiatr-moskva012.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.mygrover.net/portfolio/the-field
Этот обзор сосредоточен на различных подходах к избавлению от зависимости. Мы изучим традиционные и альтернативные методы, а также их сочетание для достижения максимальной эффективности. Читатели смогут открыть для себя новые стратегии и подходы, которые помогут в их борьбе с зависимостями.
Детальнее – https://tattoo-photo.ru/срочный-вывод-из-запоя
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://namaskar-nepal.com/hello-world
В этой статье мы рассмотрим современные достижения в области медицины, включая инновационные методы лечения и диагностики. Мы обсудим важность профилактики заболеваний и роль технологий в улучшении качества здравоохранения. Читатели узнают о влиянии медицины на повседневную жизнь и ее значение для современного общества.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.insources.ru/zdorove/9640962-novye-uslugi-po-kodirovaniyu-v-narkologicheskojj-kl-i9bn
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://baitapkegel.com/kien-thuc/suc-khoe/ba-bau/25-loai-thuc-kieng-khi-mang-thai-danh-cho-ba-bau
Скальный лист Трубы бесшовные горячекатаные производятся без сварного шва методом горячей прокатки. Они характеризуются высокой прочностью и устойчивостью к давлению, что делает их незаменимыми в нефтегазовой промышленности, энергетике и других областях, где требуется транспортировка жидкостей и газов под высоким давлением.
Но могу сказать что на данный момент проблемы с отправкой у магазина! в среду оплатил и сказали в четверг будет отправка, но увы ее нет! такое в первый раз замечаю от такого магазина! будем ждать! https://www.band.us/page/100440779/ Тоже считаем что запреты не запреты. Да бывает что и за клиентами охотятся.
besttrendstore – Love the clean design and trendy collections, very appealing overall.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Belgium Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.betwaycasino777fr.com|
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://parnas.info/novost-novye-uslugi-po-kodirovaniyu-v-narkologicheskojj-kli-r4if
заказать продвижение сайта в москве [url=https://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru/]заказать продвижение сайта в москве[/url] .
Политон Экструдированный пенополистирол (ЭППС) – это теплоизоляционный материал с закрытой ячеистой структурой, обладающий высокими теплоизоляционными свойствами и влагостойкостью. Применяется для утепления фасадов, фундаментов, кровель и других конструкций.
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта [url=https://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru]https://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru[/url] .
seo статьи [url=http://www.statyi-o-marketinge7.ru]seo статьи[/url] .
Капельница от запоя – это ключевым моментом в лечение алкогольной зависимости. В Красноярске наркология предлагают поддержку специалиста‚ что проведет детоксикацию организма. Признаки запоя‚ включая тревога и потливость‚ могут вызывать к серьезным осложнениям в результате запоя. Капельница помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и возобновить здоровье в результате запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Красноярск После лечения важно пройти реабилитацию и получить психологическую поддержку. Консультация нарколога поможет избежать рецидивов. Профилактика рецидива предполагает обучение и поддержку‚ что способствует восстановлению организма. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме в Красноярске предоставляется и эффективна‚ помогая пациентам возвратиться к нормальной жизни.
чижик магазин каталог товаров и цены Чижик адреса магазинов – важный элемент информации для покупателей, позволяющий легко найти ближайший магазин. Сеть магазинов “Чижик” активно расширяется, открывая новые торговые точки в различных районах городов. Актуальный список адресов магазинов всегда доступен на официальном сайте компании и в мобильном приложении, что обеспечивает удобство для всех покупателей.
стратегия продвижения блог [url=http://www.statyi-o-marketinge6.ru]http://www.statyi-o-marketinge6.ru[/url] .
Манжета Тиал Труба КОРСИС – это современное решение для строительства трубопроводов, изготавливаемое из полиэтилена высокой плотности (ПЭВП). Двухслойная структура обеспечивает высокую кольцевую жесткость и устойчивость к внешним нагрузкам, что делает их идеальными для подземной прокладки канализационных и дренажных систем.
Здесь
[url=https://n-l-e.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
скидки на отели Туристическая виза в Японию – позволяет гражданам России посещать страну с целью туризма, осмотра достопримечательностей и отдыха. Для получения туристической визы требуется подтверждение бронирования отеля и маршрута путешествия.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детальнее – https://kita-umeda.com/wp/contact
Портал о строительстве https://newboard-store.com.ua и ремонте: от проекта до сдачи объекта. Каталоги производителей, сравнение материалов, сметы, BIM и CAD, нормативная база, ленты новостей, вакансии и тендеры. Практика, цифры и готовые решения.
Современный автопортал https://carexpert.com.ua главные премьеры и тенденции, подробные обзоры, тест-драйвы, сравнения моделей и подбор шин. Экономия на обслуживании, страховке и топливе, проверки VIN, лайфхаки и чек-листы. Всё, чтобы выбрать и содержать авто без ошибок да
Современный новостной https://vestionline.com.ua портал: главные темы суток, лонгриды, мнения экспертов и объясняющие материалы. Проверка фактов, живые эфиры, инфографика, подборка цитат и контекст. Быстрый доступ с любого устройства и без лишних отвлечений.
Женский портал https://magictech.com.ua о жизни без перегруза: здоровье и красота, отношения и семья, финансы и карьера, дом и путешествия. Экспертные статьи, гайды, чек-листы и подборки. Только полезные советы и реальные истории.
besttrendstore – Trendy and exciting store with fresh fashion and lifestyle products.
J’adore la vibe de Belgium Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, parfois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Belgium Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A signaler les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Ouvrir le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Gamdom Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Gamdom Casino assure un fun constant. En extra le site est rapide et immersif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui booste la participation.
Essayer ceci|
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Узнать из первых рук – https://ark.sg/ua-sportsmask-what-you-should-know-about-it-protx2
Je suis captive par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais encore des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
https://gamdomcasino365fr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Betify Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra l’interface est simple et engageante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
https://betifycasino365fr.com/|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Betify Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement top les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, garantit des paiements securises.
Passer à l’action|
J’adore l’energie de Belgium Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Belgium Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Cliquez ici|
Just stumble upon your blog from from time to time. nice article
Использование контрактного производства позволяет быстро выводить на рынок интеллектуальные устройства для умного дома и промышленной автоматизации. Инженеры создают платы, схемотехнику и программное обеспечение, тестируют прототипы на надежность. После успешной проверки устройства идут в серийное производство, что позволяет заказчику быстро внедрить продукт – разработка электронной аппаратуры. Метод позволяет быстрее проверять идеи и концепции, делая разработку более предсказуемой
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Перейти к полной версии – https://rainer-rubbert.de/wordpress/vita
Вызов нарколога на дом в владимире – это существенный шаг для тех‚ кто испытывает проблемы с алкоголем. Наркологические услуги‚ включая помощь при алкогольном запое‚ позволяют людям эффективно и быстро прервать запой. Выезд нарколога гарантирует конфиденциальность лечения и медицинскую помощь на дому‚ что является ключевым для пациентов‚ стремящихся сохранить свою конфиденциальность. Во время консультации нарколога происходит помощь в снятии абстиненции‚ что способствует пациенту быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Методы кодирования и психотерапия при алкогольной зависимости являются важными этапами в лечении данной проблемы. Реабилитация пациентов включает поддержку родственников‚ что способствует успешному выздоровлению. Не затягивайте с решением проблемы; обратитесь за помощью к наркологу на дом‚ чтобы начать путь к свободе от зависимости!
магазин ровный https://pxlmo.com/saerimukaih8879 В джабере орудует фейк, причем у него такой же адрес джабера как и у меня. Джабер в скором времени сменю, в джабере заказы не принимаю. Будьте бдительны
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, Betify Casino merite une visite dynamique. Notons egalement l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement top les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Explorer davantage|
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.groupe-allosun.com/portfolios/35-centre-technique-90kva
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Betway Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages uniques.
http://www.betwaycasino365fr.com|
Скальный лист Трубы ПНД (полиэтилен низкого давления) отличаются повышенной гибкостью и используются для прокладки кабельных сетей, систем водоснабжения и газопроводов.
yourfashionoutlet – Love the stylish collection here, everything feels trendy and well-priced.
http://www.vladimir.ru/forum/forum/thread/55172
startfreshjourney – Uplifting and positive vibe, perfect for inspiration and fresh beginnings.
Telegram Знакомста Проститутки Ростов на Дону без предоплат индивидуалки тг https://t.me/KtoChtoRostov_bot
Всё для женщины https://wonderwoman.kyiv.ua уход и макияж, мода и стиль, психология и отношения, работа и деньги, мама и ребёнок. Тренды, тесты, инструкции, подборки брендов и сервисов. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь, действуйте.
Твой автопортал https://kia-sportage.in.ua о новых и подержанных машинах: рейтинги надёжности, разбор комплектаций, реальные тесты и видео. Помощь в покупке, кредит и страховка, расходы владения, ТО и тюнинг. Карта сервисов, советы по безопасности и сезонные рекомендации плюс
Современный женский https://fashiontop.com.ua журнал: уход и макияж, капсульный гардероб, психология и отношения, питание и тренировки, карьерные советы и финансы. Честные обзоры, подборки брендов, пошаговые гайды.
Метод употребления – интерназально https://www.impactio.com/researcher/maddux2t1psheila Не рекомендую правда увлекаться порохами – их хочется ещё и ещё и в итоге не так уж и просто слезть с марафона…) Но это уже ваше дело ; )
http://zanasite.free.fr/laripostedumardi/doku.php?id=Особенности%20и%20преимущества%20онлайн-игры%20Aviator
thinkactachieve – Really inspiring message, perfect for anyone focused on self-improvement.
https://444-000.ru/
ремонт бош [url=http://moskva-bosch-master.ru/]сервисный центр bosch в москве[/url]
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller sur le web|
документы для визы в Китай Туристическая виза в Китай – наиболее распространенный тип визы, предназначенный для лиц, планирующих посещение Китая с целью отдыха и осмотра достопримечательностей. Получение туристической визы предполагает предоставление определенного пакета документов, подтверждающих цель поездки.
I absolutely adore your site! You aggressive me as able-bodied as all the others actuality and your broiled PS is absolutely great!
чижик адреса магазинов Чижик адреса магазинов – важная информация для тех, кто хочет быстро найти ближайший магазин. Сеть Чижик активно развивается, открывая новые точки в различных районах города. Актуальные адреса всегда можно найти на официальном сайте или в мобильном приложении.
Кресты с пожарной подставкой фланцевые чугунные ППКФ Труба гофрированная канализационная – гибкое и прочное решение для отвода сточных вод. Гофрированная структура обеспечивает высокую устойчивость к деформациям и позволяет прокладывать трубопровод в сложных условиях.
https://agat.forum24.ru/?1-19-0-00000095-000-0-0-1762715443
Здесь
[url=https://clinica-plus.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Je suis completement seduit par Gamdom Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par moments des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Gamdom Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Notons egalement le site est rapide et style, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement genial les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui stimule l’engagement.
https://gamdomcasino365fr.com/|
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. En extra le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
thebestdeal – Always great to find a site focused on value and daily savings.
Je suis enthousiasme par Belgium Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Belgium Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A souligner les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages uniques.
Tout apprendre|
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Betify Casino merite une visite dynamique. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’ai un faible pour Betify Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
Lire la suite|
Je suis completement seduit par Belgium Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Belgium Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Центратор наружный Ж08А Электросварная труба – изготавливается путем сварки стальной полосы или листа. Этот процесс является экономичным и позволяет производить трубы различного диаметра и толщины стенок. Электросварные трубы находят широкое применение в строительстве, в системах водо- и газоснабжения, а также в различных промышленных конструкциях.
Сказали в понедельник всем кто оплатил заказ отправят НОМЕРА! https://rant.li/ugdidococec/samarkand-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki – Ну….. минут за двадцать….
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais encore quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Betway Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement l’interface est lisse et agreable, booste l’excitation du jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
https://saluttunisia.com/jomsocial/groups/viewdiscussion/264-promokod-na-besplatnuyu-stavku-mostbet.html?groupid=105
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
лечение алкозависимости
reabilitaciya-astana010.ru
анонимное лечение наркомании
Good post. I study something more difficult on different blogs everyday. It’s going to always be stimulating to learn content material from other writers and observe a little bit one thing from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content material on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link in your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
срочный перевод документов сочи Нотариальный перевод документов Сочи – это услуга, необходимая для придания юридической силы переведенным документам. Нотариально заверенный перевод требуется для предъявления в государственные органы, консульства, банки и другие учреждения. Нотариус удостоверяет подлинность подписи переводчика, подтверждая тем самым соответствие перевода оригиналу документа.
В городе и пригороде организован круглосуточный приём с возможностью выезда на дом. Координатор уточняет только клинически значимые данные: регулярные препараты и дозировки, аллергии, недавние эпизоды судорог/психозов, доступ к розетке, возможность обеспечить «тихое окно» на 2–3 часа. Если в квартире многолюдно или идёт ремонт, предложим «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и тем же ведущим врачом; после стабилизации зеркально перенесём маршрут обратно домой, чтобы не терять темп и доверие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог нижний новгород[/url]
Je suis emerveille par Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Betify Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
http://www.betifycasino777fr.com|
shopwithstyle – Love the elegant touch and fashion-forward vibe of this store.
believeinyourideas – Motivating and clean design, makes exploring ideas enjoyable and simple.
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Журнал об автомобилях https://svobodomislie.com без мифов: проверяем маркетинг фактами, считаем расходы владения, рассказываем о ТО, тюнинге и доработках. Тестируем новые и б/у, объясняем опции простыми словами. Экспертные мнения, идеи маршрутов и полезные чек-листы. Всегда!.
Еженедельный журнал https://sw.org.ua об авто и свободе дороги: премьеры, электромобили, кроссоверы, спорткары и коммерческий транспорт. Реальные тесты, долгосрочные отчёты, безопасность, кейсы покупки и продажи, кредит и страховка, рынок запчастей и сервисы рядом.
Портал о балансе https://allwoman.kyiv.ua красота и самоуход, отношения и семья, развитие и карьера, дом и отдых. Реальные советы, капсульные гардеробы, планы тренировок, рецепты и лайфхаки. Ежедневные обновления и подборки по интересам.
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk013.ru
лечение запоя минск
theartofgrowth – Inspiring name that perfectly fits a mindset of learning and progress.
в смысле пропал из онлайна??? и что делать теперь? треки то до сих пор небьються https://kemono.im/nlcuiciiguf/lodz-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki С возвращением бразы! удачной работы вам и процветания
В Волгограде сформирована система оказания наркологической помощи, включающая круглосуточные выезды специалистов, амбулаторное лечение, стационарные программы и реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет охватить все категории пациентов — от тех, кто нуждается в экстренной помощи, до тех, кто готов пройти полный курс терапии. Независимо от формы оказания услуг, лечение проводится конфиденциально и в соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь волгоград[/url]
СПЕЙСЕР кольцо диэлектрическое Краны шаровые – запорная арматура, обеспечивающая быстрое и надежное перекрытие потока рабочей среды. Шаровые краны просты в эксплуатации, имеют высокую герметичность и применяются в различных отраслях промышленности и жилищно-коммунальном хозяйстве.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с выводом Не упустите шанс начать играть прямо сейчас! Зарегистрируйтесь и получите свой бездепозитный бонус – это может быть сумма на счет или бесплатные вращения. Испытайте удачу, познакомьтесь с любимыми играми и получите возможность выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными. Просто зарегистрируйтесь и заберите свой подарок!
Fa‡ade loli po^rn
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
Do you have a spam issue on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; many of us have created some nice practices and we are looking to trade techniques with others, be sure to shoot me an e-mail if interested.
sklo
бездепозитный бонус слоты Бездепозитные бонусы – это привлекательные предложения от онлайн-казино и букмекерских контор, которые позволяют игрокам начать играть, не внося собственных средств. Чаще всего они предоставляются за регистрацию нового аккаунта. Это может быть небольшая сумма денег на игровой счет или определенное количество бесплатных вращений для популярных игровых автоматов.
https://444-000.ru/
https://magnitola.kiev.ua
виза в Японию сроки оформления Оформление визы в Японию – процесс, сопряженный с определенными требованиями и нюансами японского консульства. Тщательная подготовка документов и понимание правил подачи заявки являются ключевыми факторами успеха.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Если среда дома шумная или приватность под угрозой, мы предложим «короткий коридор» через отдельный вход амбулатории. Если условия позволяют, проводим процедуры на дому: свет приглушён, доступ к розетке организован, рядом столик для расходников и приборов. Этот «экологичный» сценарий, несмотря на простоту, заметно улучшает переносимость процедур и собирает устойчивый сон в первую ночь, что особенно важно на ранних этапах стабилизации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/
В городе и ближайших районах клиника «УралМед Трезвость» обеспечивает оперативный выезд и амбулаторный приём без очередей. На этапе первичного контакта координатор уточняет только клинически значимые моменты: постоянные препараты и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов в прошлом, базовые показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?, если доступны), длительность симптомов, возможность организовать «тихое окно» на 20–30 минут. Вместо долгих разговоров — короткая, спокойная логика: где безопаснее начать (дом/амбулатория/стационар), какую ближайшую цель выбираем, в каком интервале ждём эффект и что считаем сигналом для связи с дежурным врачом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Капельница для лечения запоя на дому: противопоказания и риски (владимир) Алкогольная зависимость – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального подхода. Вызов нарколога на дом становится все более популярным методом лечения запоя. Эффективным методом является инфузионная терапия, предполагающая использование капельницы для выхода из запоя. Капельница помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, улучшить общее состояние пациента и снять симптомы абстиненции. Тем не менее, необходимо учитывать противопоказания к данной процедуре. К противопоказаниям относятся аллергия на компоненты растворов, заболевания сердечно-сосудистой системы и острые инфекционные процессы, которые могут помешать проведению капельницы. Также могут возникнуть осложнения, такие как тромбофлебит, инфицирование вены или аллергические реакции. Потому консультация нарколога перед началом домашнего лечения алкоголизма крайне необходима. Безопасность данной процедуры во многом зависит от квалификации медицинского специалиста и следования всем рекомендациям. Услуги нарколога на дому в владимире предоставляют возможность получения медицинской помощи в удобной обстановке, что делает реабилитацию от запоя более эффективной.
uniquevaluezone – Offers cool finds at great prices, really worth visiting.
Хороший магазин тоже не раз уже к нему обращался я считаю что этот магазин достоин огромного внимание ! Мир тебе бро и процветания удачи в работе !:ok:;)ОБРАЩУСЬ ЕЩЕ К ТЕБЕ БРО ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО !) ЕЩЕ РАЗ УДАЧИ https://kemono.im/afiduyca/kokhma-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki первую посылочку получил от селера ))) сервис на вышем уровне не то что у некоторых!!!!!
Процесс включает:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
globalstyleoutlet – Amazing range of international fashion, really fun to browse.
заказ перепланировки квартиры [url=https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/]https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/[/url] .
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
проект перепланировки нежилого помещения [url=www.chesskomi.borda.ru/?1-3-0-00000060-000-0-0]проект перепланировки нежилого помещения[/url] .
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
surewin app [url=www.surewin-online.com]www.surewin-online.com[/url] .
Труба гофрированная канализационная Профильная труба – это труба с некруглым сечением, наиболее распространенные формы – квадрат и прямоугольник. Профильные трубы обладают высокой прочностью на изгиб, что делает их идеальным материалом для строительства каркасных конструкций, ограждений, мебели и других изделий, где важна надежность и долговечность.
icebet online [url=icebet-online.com]icebet online[/url] .
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/[/url]
Первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению является очищение организма от токсинов. В клинике проводится детоксикация с использованием современных препаратов, направленных на выведение продуктов распада алкоголя и наркотиков. Медикаментозное лечение дополняется витаминами, гепатопротекторами и средствами для нормализации работы нервной системы. Это помогает восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие пациента.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
Здесь
[url=https://www.leadertask.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Для иллюстрации приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы терапии и их воздействие на организм:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Мы не удерживаем пациента на дому во что бы то ни стало. Домашний формат уместен при контролируемых симптомах, наличии взрослого помощника на вечер и ночь и возможности обеспечить тихий режим. Если у входа видно угрозу делирия, выраженные скачки давления, повторные эпизоды рвоты с обезвоживанием, нестабильный ритм, одиночество ночью — рациональнее начать в палате. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и лаборатория, пост медсестёр и быстрые коррекции схем. Такой маршрут часто короче по времени до устойчивого сна и предсказуемее по результату.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
чижик магазин Чижик магазин – это современный формат дискаунтера, быстро завоевывающий популярность на российском рынке. Основной акцент делается на оптимальном соотношении цены и качества, предлагая покупателям широкий ассортимент товаров повседневного спроса по привлекательным ценам.
[url=https://loktrk.com/]chicken road 2 login india[/url]
Je suis sous le charme de Belgium Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par ailleurs plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En fin de compte, Belgium Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A noter les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute soudee.
Explorer le site web|
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer le design est moderne et attrayant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste la participation.
http://www.betwaycasino777fr.com|
Ответь в аське!Люди 22куска зарядили ,перед оплатой добро дал ,а потом тишина… Люди переживают,очень!Ответь пожалуйсто!!! https://www.brownbook.net/business/54470111/кавасаки-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Вы не могли сегодня оплатить заказ, потому что мы сегодня не работаем 🙂
Je suis enthousiasme par Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Betway Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement top les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.betwaycasinofr.com|
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback?
If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can suggest?
I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any assistance is
very much appreciated.
my web blog; casa de Apuestas oficial Real madrid
Этап
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
newtrendmarket – Love the fresh and modern vibe, full of current fashion finds.
Je ne me lasse pas de Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Gamdom Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter la plateforme|
discoverhiddenopportunities – Inspiring name that encourages exploring new ideas and growth.
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller au site|
Je ne me lasse pas de Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Что делаем
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-zhukovskij-ceny[/url]
dailyshoppingzone – Love how convenient this site is for everyday shopping needs.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges personnalises.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis captive par Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par contre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Betify Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute vibrante.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
https://444-000.ru/
Автомобильный блог https://amt-auto.ru обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и уход. Пошаговые инструкции, подбор масел и расходников, диагностика ошибок, лайфхаки, экономия на сервисе. Полезно новичкам и опытным водителям. Читай просто, делай уверенно.
Аренда авто turzila.com без депозита, аренда яхт и удобный трансфер в отель. Онлайн-бронирование за 3 минуты, русская поддержка 24/7, прозрачные цены. Оплата картой РФ.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Belgium Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Belgium Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute vibrante.
Plongez-y|
Нужна фотосьемка? https://jrowan.ru каталожная, инфографика, на модели, упаковка, 360°. Правильные ракурсы, чистый фон, ретушь, цветопрофили. Готовим комплекты для карточек и баннеров. Соответствие правилам WB/Ozon.
центр реабилитация алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana011.ru
реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков
Most often since i look for a blog Document realize that the vast majority of blog pages happen to be amateurish. Not so,We can honestly claim for which you writen is definitely great and then your webpage rock solid.
Как привило мелкие селлеры о конфиденциальности не думают, а потом с ними метоморфозы и происходят.. https://anyflip.com/homepage/owifc 2)Кто курит раз в неделю : от 3 часов до 5-7 часов
чижик магазин каталог Магазины Чижик – это удобный формат для быстрых и выгодных покупок. В магазинах Чижик можно найти все необходимое для повседневной жизни, при этом экономя время и деньги.
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в красноярске[/url]
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog010.ru
лечение запоя тула
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betify Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Betify Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh
Лист нержавеющий Профильная труба – это труба с некруглым сечением, наиболее распространенные формы – квадрат и прямоугольник. Профильные трубы обладают высокой прочностью на изгиб, что делает их идеальным материалом для строительства каркасных конструкций, ограждений, мебели и других изделий, где важна надежность и долговечность.
trendycollectionhub – Great place for discovering stylish collections and creative designs.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
newtrendmarket – Fresh trends and a smooth shopping experience, really well put together.
Выездной формат — это не просто «капельница у кровати». Мы заранее раскладываем визит на модули и назначаем окна оценки: первые 20–40 минут (антиеметический мост, переносимость воды), 60–120 минут (регидратация и электролиты, сглаживание ЧСС/АД), первая ночь (сон ?6 часов и ?1 пробуждение), 12–24 часа (утренняя ясность и способность выполнить 2 короткие бытовые задачи). Одно изменение — один параметр: либо темп инфузии, либо порядок модулей, либо настройка среды (свет/тишина/ритуал). Так причинно-следственные связи остаются прозрачными, а результат — подтверждаемым.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в челябинске[/url]
I really like your writing style, excellent info , thanks for putting up : D.
dailyshoppingzone – Love how convenient this site is for everyday shopping needs.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ростов-на-дону[/url]
у нас она валяется,сами не потребляем. https://www.grepmed.com/bacohubaboef Ещё раз повторюсь – магазин ОТЛИЧНЕЙШИЙ.
Семья получает «путевой лист» на 24–72 часа: как фиксировать маркеры (тремор/тревога/тошнота 0–10), как пить воду малыми глотками, когда приглушать свет и в каком формате общаться с пациентом («короткие факты вместо оценок»). Мы также даём «лестницу активности»: два достижимых действия утром, одно — вечером. Эта дисциплина маленьких шагов помогает избежать эмоциональных «перегревов» и удерживает достигнутый эффект.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/
Для жителей Красноярска организованы два конфиденциальных пути. Первый — немаркированный выезд бригады на дом с заранее согласованными порогами связи. Второй — «тихий вход» в клинику через отдельную дверь, где приём проходит без очередей и «коридорных» разговоров. На первичном звонке администратор уточняет только клинически значимые факторы: частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспускания, ЧСС/АД в покое, эпизоды спутанности, актуальные лекарства и аллергии. Биографические подробности и лишние вопросы не задаются — мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-novgorod/
Вывод из запоя осуществляется в несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на постепенное восстановление организма. Такой поэтапный подход снижает нагрузку на внутренние органы и повышает эффективность лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты капельницы и их действие:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologiya-v-volgograde/
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с выводом Пусть это звучит ново и заманчиво, но настоящая грамотность игрока начинается с понимания того, что скрывается за фразой бездепозитные бонусы в казино. Это не просто бесплатные вращения или небольшие кредиты на счёт; за каждой щедрой акцией стоят правила, отыгрыши и ограничения, которые могут либо увеличить ваши шансы на победу, либо превратить удачный первый визит в долгую битву с условиями. В этой статье мы разберёмся, как такие бонусы работают на практике, какие бывают, какие подводные камни ждать и как максимально эффективно извлекать пользу без риска оказаться в ловушке банальных условий.
бездепозитные фриспины Самое важное, что нужно знать о бездепозитных бонусах – это условия отыгрыша (вейджер). Это множитель, который показывает, сколько раз вам нужно прокрутить сумму бонуса, прежде чем вы сможете вывести выигрыш. Например, если вы получили бонус в 10 долларов с вейджером x30, вам нужно сделать ставок на общую сумму 300 долларов (10 x 30), прежде чем вы сможете вывести деньги.
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-vyzov-na-dom[/url]
виза во Францию без отказа Виза в Японию для россиян – необходимый документ для посещения Японии, за исключением случаев транзита в течение 72 часов через определенные аэропорты. Тип визы зависит от цели визита: туризм, бизнес, посещение родственников и т.д.
Сегодня защита личных данных и конфиденциальность в интернете приобретают все более актуальными. Если вы хотите прокапаться анонимно‚ важно использовать анонимные услуги‚ такие как виртуальные частные сети и прокси‚ которые помогут скрыть личность и обезопасить ваш IP-адрес. Данные инструменты обеспечивают шифрование вашего подключения‚ что укрепляет безопасность в интернете и защиту ваших действий. Кроме того‚ вы сможете обойти блокировки и получать незаметный доступ к сайтам без регистрации. Охрана данных становится незаменимым аспектом анонимного использования интернета‚ позволяя оставаться в безопасности. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru
simplebuyhub – Super easy to navigate site with plenty of affordable options.
Всё что В прайс листе на сайте есть,всё в наличии ? https://www.impactio.com/researcher/zeokfoyj80tzvh Ребятки все пушка
yourvisionawaits – Inspiring name that motivates people to dream and take action.
киев купить диплом о [url=r-diploma20.ru]киев купить диплом о[/url] .
туристическая поездка во Францию Виза в Китай для россиян – это обязательный документ, позволяющий гражданам РФ въезжать на территорию Китая с различными целями: туризм, бизнес, учеба и т.д. Процедура оформления визы имеет свои особенности и нюансы.
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-zhukovskom/
Процесс терапии в наркологической клинике в Воронеже организован поэтапно. Это позволяет обеспечить системность и постепенность восстановления, снизить риски осложнений и повысить устойчивость результата.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
Этап
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno[/url]
Основные этапы лечения включают:
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
шлюхи тюмень телеграм
купить диплом 2001 [url=www.r-diploma21.ru/]www.r-diploma21.ru/[/url] .
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/
Привет всем! https://www.grepmed.com/bacifxabec Где продавец то? Мысли самые печальные…тт
trendforlife – Love the concept; a perfect spot for true fashion enthusiasts.
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologiya-v-volgograde/
нотариальный перевод документов сочи Агентство переводов Сочи – это профессиональная команда лингвистов, редакторов и корректоров, готовых предложить комплексные услуги по переводу с/на различные языки мира. Агентства, как правило, обладают широкими возможностями для работы с большими объемами текстов и предоставления дополнительных услуг, таких как верстка и подготовка к печати. Выбирая агентство, обратите внимание на опыт работы, наличие положительных отзывов и специализацию переводчиков.
Современный журнал https://rupsbigbear.com про авто: новости индустрии, глубокие обзоры моделей, тесты, сравнительные таблицы и советы по выбору. Экономия на обслуживании и страховке, разбор технологий, безопасность и комфорт. Всё, чтобы ездить дальше, дешевле и увереннее.
Автопортал для новичков https://lada.kharkiv.ua и профи: новости рынка, аналитика, сравнения, тесты, долгосрочные отчёты. Выбор авто под задачи, детальные гайды по покупке, продаже и трейд-ину, защита от мошенников. Правила, штрафы, ОСАГО/КАСКО и полезные инструменты и ещё
Женский медиа-гид https://adviceskin.com здоровье, питание, спорт, ментальное благополучие, карьера, личные финансы, хобби и поездки. Практика вместо кликбейта — понятные гайды, чек-листы и экспертные мнения.
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
buildyourpotential – Great reminder that growth starts with small daily improvements.
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog011.ru
вывод из запоя
анонимное лечение от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana012.ru
лечение алкозависимости
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
МАГАЗ КРУТОЙ!!! https://kemono.im/jyhofzyeof/dolina-gastain-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Давно работаю с чемиком.
шкаф для канистр Клеть для 9 баллонов – это надежная защита для ваших газовых баллонов. Прочная металлическая конструкция исключает возможность случайного повреждения баллонов, а специальные крепления обеспечивают их устойчивое положение. Клеть для 9 баллонов – это гарантия безопасности персонала и сохранности вашего имущества.
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
urbanfashioncorner – Trendy, bold, and full of energy — perfect urban fashion vibe.
https://minecraftcommand.science/forum/discussions/topics/1xbet-valid-promo-code-130-sports-bonus
поддон для еврокуба Поддон для 2-х еврокубов – это удвоенная защита от разливов и утечек, обеспечивающая безопасность окружающей среды при хранении больших объемов жидкостей.
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
J’ai une passion debordante pour Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, Belgium Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A signaler le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A signaler les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Tout apprendre|
smartshoppingzone – Perfect for budget-conscious shoppers who still want quality products.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Gamdom Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En bonus le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
Gamdom|
пацаны магаз ровный пишу это уже не раз всегда списываюсь с менеджером все делает ровно и качество и оперативность , всегда заказываю и буду заказывать тут т.к. не париться за качество продукта как в других магазах!!! https://www.divephotoguide.com/user/dygohpcece Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии,
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Продолжить изучение – https://badboysvending.com/how-to-move-on-from-hookups
«ПрофДетокс» — выездная наркологическая служба для жителей Ивантеевки и ближайших районов. Мы запускаем помощь без очередей и лишней огласки: врач приезжает анонимно, проводит очную оценку, допускает к терапии и запускает инфузионную поддержку без универсальных коктейлей. Наша задача — снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, снизить тревогу, мягко наладить сон по показаниям и дать семье понятный план на ближайшие двое суток. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим палату «ПрофДетокса» с круглосуточным наблюдением. Приватность встроена в процесс, а смета фиксируется до начала процедур.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-v-ivanteevke/
Je ne me lasse pas de Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Belgium Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et style, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Проследить причинно-следственные связи – https://community.theclearwaytoconceive.com/question/cheap-robot-hoover-tools-to-make-your-daily-life-cheap-robot-hoover-technique-every-person-needs-to-learn
Je suis emerveille par Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, bien que quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Betify Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Je suis totalement conquis par Belgium Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Belgium Casino offre une aventure memorable. En complement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir la page|
поддон для канистр Депо для бочек – аналогичная конструкция, предназначенная для хранения бочек, обычно используемых для хранения масел и химикатов.
event агентство Организация мероприятий – это сложный и многогранный процесс, требующий опыта, знаний и внимания к деталям. Мы возьмем на себя все этапы – от планирования и бюджетирования до координации и проведения мероприятия. Наша команда профессионалов обеспечит безупречную организацию и позволит вам полностью сосредоточиться на общении с гостями и наслаждении праздником. Услуги по организации корпоративов – это симфония деталей, где каждая нота – это тщательно продуманный элемент, создающий неповторимую мелодию незабываемого события. Мы не просто организуем вечеринки, мы создаем впечатления, которые укрепляют командный дух, мотивируют сотрудников и оставляют яркие воспоминания. От разработки оригинальной концепции до воплощения самых смелых идей, мы берем на себя все хлопоты, освобождая ваше время для более важных задач. Наши опытные event-менеджеры, как искусные дирижеры, гармонично объединяют все составляющие идеального корпоратива: подбор площадки, кейтеринг, развлекательную программу, техническое обеспечение и многое другое.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто список развлечений; это живое полотно, сотканное из тысяч культурных нитей, образующих неповторимый облик Северной столицы. Здесь каждый найдет что-то для себя, будь то поклонник классического искусства, ценитель современного авангарда или просто человек, ищущий ярких впечатлений. От балетных постановок в легендарном Мариинском театре, где эхо великих премьер до сих пор витает в воздухе, до модных выставок в креативных пространствах “Ткачей” и “Артмузы”, Санкт-Петербург предлагает бесконечный калейдоскоп возможностей для обогащения душевного мира. Благодаря Афише, вы всегда в курсе грядущих концертов мировых звезд, театральных фестивалей, кинопоказов и гастрономических событий. Это ваш персональный проводник по культурной жизни города, который поможет вам не пропустить самые интересные мероприятия и спланировать свой досуг наилучшим образом. Здесь можно найти информацию о мастер-классах, лекциях, экскурсиях и других образовательных программах, позволяющих расширить кругозор и узнать больше об истории и культуре Санкт-Петербурга.
learnsomethingamazing – Encouraging and creative name that promotes daily learning and discovery.
заказать корпоратив Организация корпоративов в Москве – это знание города как свои пять пальцев, владение эксклюзивной информацией о лучших площадках, артистах и развлечениях. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, учитывая специфику бизнеса, бюджет и пожелания коллектива. Москва – это город возможностей, и мы поможем вам использовать их на полную мощность, чтобы создать незабываемый корпоратив, который запомнится на долгие годы.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Betify Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Сегодня проблема зависимости высвечивается все ярче. Если у вас или ваши близкие нуждаются с помощью, не бойтесь обратиться за помощью. Анонимный вызов врача нарколога в владимире — это важный шаг на пути к лечению зависимости. На сайте site;com предоставляется возможность получить консультацию нарколога, что гарантирует полную конфиденциальность и профессиональный подход.Лечение зависимостей и реабилитация необходимы тщательный и профессиональный подход. В наркологической клинике вам предложат услуги, включая психотерапию и психологическую поддержку. Вызов врача на дом обеспечит комфортные условия для пациента, что особенно актуально в кризисных ситуациях. Не откладывайте помощь на потом, обратитесь за анонимной помощью уже сегодня!
услуги по организации праздников Event агентство – это не просто команда организаторов, а творческая лаборатория, где каждая идея превращается в незабываемое событие. Мы создаем атмосферу, вдохновляем, удивляем и дарим эмоции, которые останутся в памяти на долгие годы. Наша цель – превзойти ожидания и сделать каждое мероприятие уникальным и запоминающимся. От концепции до реализации, мы берем на себя все заботы, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться праздником. Корпоратив под ключ – это избавление от головной боли, связанной с организацией масштабного мероприятия. Мы предлагаем комплексное решение, которое включает в себя все этапы подготовки, от разработки концепции до завершающего аккорда. Наша команда профессионалов, словно опытные альпинисты, покорит любые вершины, чтобы ваш корпоратив прошел безупречно. Мы учтем все ваши пожелания и особенности компании, чтобы создать уникальное событие, которое станет ярким отражением вашего корпоративного духа.
продвижение сайтов Разработка сложных многоступенчатых систем и использование эксклюзивных методик для значительного улучшения позиций в Google и Yandex.
шкаф для еврокуба Металлический поддон – это фундаментальный элемент складской логистики, обеспечивающий надежную основу для хранения и транспортировки различных грузов. Его прочная металлическая конструкция выдерживает значительные нагрузки и устойчива к механическим повреждениям. Металлические поддоны способствуют оптимизации складского пространства и повышению эффективности погрузочно-разгрузочных работ.
Orb11TA — это динамичный проект с развивающейся экосистемой сервисов и активным сообществом. Если вы ищете проверенные источники, начните с официальной страницы: [url=https://orb11ta.life/]официальная страница Orb11TA (orb11ta.life)[/url]. Для дополнительных материалов и публикаций доступен также ресурс [url=https://orb11ta.my/]Orb11TA — информационная страница (orb11ta.my)[/url].
Проект предлагает отдельные возможности для подписчиков — раздел [b]orb11ta vip[/b] содержит анонсы и привилегии для участников. На публичных доменах (orb11ta com, orb11ta сайт) публикуются справочные материалы, инструкции и ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы. Если вам нужен технический архив и исходники, обратите внимание на репозиторий: [url=https://github.com/orb11ta]GitHub — репозиторий Orb11TA[/url].
Сообщество обсуждает такие темы, как [i]orb11ta top[/i], [i]orb11ta ton[/i] и вопросы видимости на страницах поиска (ton page 1, ton site orb11ta on page 1). Для быстрых обзоров и агрегированных публикаций полезен ресурс обзоров и сборников материалов. Для коммерческих и партнёрских решений есть разделы типа [b]orb11ta shop[/b] и [b]orb11ta biz[/b].
Важно сохранять цифровую гигиену: при появлении капчи или сообщения о проверке (“orb11ta vip вы не робот”) следуйте стандартным процедурам и не передавайте личные данные третьим лицам. Для оперативных объявлений и релизов следите за официальными страницами и репозиторием: [url=https://getgems.io/orb11ta]Обзор и новости — getgems.io/orb11ta[/url].
Ключевые слова для поиска и продвижения: orb11ta, orb11ta vip, orb11ta com, orb11ta сайт, orb11ta top, orb11ta ton, orb11ta shop, orb11ta biz, orb11ta org, orb11ta com сайт вход.
[b]Полезные ссылки:[/b]
[url=https://orb11ta.life/]Официальная страница — orb11ta.vip[/url]
[url=https://orb11ta.my/]Информационная страница — orb11ta.com[/url]
[url=https://getgems.io/orb11ta]Обзор / новости — getgems.io/orb11ta[/url]
[url=https://github.com/orb11ta]Репозиторий разработчиков — GitHub[/url]
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разрушительное влияние зависимости на жизнь человека. Обсуждаются аспекты, такие как здоровье, отношения и профессиональные достижения. Читатели узнают о необходимости обращения за помощью и о путях к восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://zagorodny.net/obshhestvo/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kaluge-professionalnaya-pomoshh-i-sovremennye-metody.php
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://confrerie-fraisedecarpentras.fr/rocky-mountains
металлический поддон Депо для еврокуба – это специальная конструкция, предназначенная для безопасного хранения и транспортировки еврокубов (IBC контейнеров). Обеспечивает защиту от механических повреждений, воздействия атмосферных осадков и несанкционированного доступа. Депо могут быть открытыми или закрытыми, стационарными или мобильными, в зависимости от требований к условиям хранения.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://skim-marketing.de/unleashing-your-creative-potential-art-and-design-courses
обьясни народу …….. сдесь ребята понимающие………. помогут http://www.pageorama.com/?p=zycdodoc Магазин на ура))
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://healthylemonlife.com/piliers-d-une-vie-saine-et-epanouie
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Прочесть всё о… – https://iwebdirectory.co.uk/start-up-edge-launches-new-internet-business-opportunities
brightfashionfinds – Such vibrant styles here, everything feels bold and fresh.
свадьба под ключ в Москве Услуги по организации свадьбы – это не просто набор предложений, это создание уникальной истории любви, запечатленной в каждой детали торжества. Мы предлагаем не только помощь в планировании, но и воплощение мечты в реальность, освобождая вас от хлопот и забот. Наша команда профессионалов возьмет на себя все этапы подготовки, от выбора идеальной площадки до разработки эксклюзивного сценария, чтобы ваша свадьба стала незабываемым событием для вас и ваших гостей. Позвольте нам создать магию вашего дня! Услуги по организации корпоративов – это симфония деталей, где каждая нота – это тщательно продуманный элемент, создающий неповторимую мелодию незабываемого события. Мы не просто организуем вечеринки, мы создаем впечатления, которые укрепляют командный дух, мотивируют сотрудников и оставляют яркие воспоминания. От разработки оригинальной концепции до воплощения самых смелых идей, мы берем на себя все хлопоты, освобождая ваше время для более важных задач. Наши опытные event-менеджеры, как искусные дирижеры, гармонично объединяют все составляющие идеального корпоратива: подбор площадки, кейтеринг, развлекательную программу, техническое обеспечение и многое другое.
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://inormal.ru/zdorove/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-professionalnaya-pomoshh-bez-gospitalizacii
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps a autre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Betway Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Apprendre comment|
Здесь
[url=https://kefir-media.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Это ещё не всё… – https://erhvervsklubfyn.dk/medlem/kb-coaching
freshdealsworld – Great site for fresh offers and exciting online shopping deals.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://forum.mista.ru/topic/699579
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Посмотреть подробности – https://www.lingerietester.com/doing-a-cross-country-road-trip
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто инструмент для поиска развлечений, это способ прикоснуться к душе города, почувствовать его ритм и энергию, стать частью его богатой и разнообразной культурной жизни. Это ваш билет в мир вдохновения, творчества и незабываемых впечатлений. Погрузитесь в этот мир и позвольте Санкт-Петербургу раскрыть перед вами свои самые сокровенные секреты.
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog012.ru
вывод из запоя тула
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Gamdom Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
Мы собрали для вас самые захватывающие факты из мира науки и истории. От малознакомых деталей до грандиозных событий — эта статья расширит ваш кругозор и подарит новое понимание того, как устроен наш мир.
Посмотреть всё – https://res-funeral.jp/info/?p=266
Je suis emerveille par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – https://allaroundaccounts.net/suzumeno-serifu
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des tables live interactives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Betify Casino offre une experience hors du commun. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter la plateforme|
чема вещи делает!!! https://rant.li/nxee62n686 САБЖ САМ ПО СЕБЕ НЕ ПРЁТ !! МУТИТЬ НА НЁМ МИКСЫ СМЫСЛА НЕТ !!! ЭТО АНТИДЕПРЕССАНТ !!
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Изучая Афишу, откройте для себя не только известные достопримечательности, но и скрытые жемчужины города: тихие дворики, уютные кафе, необычные музеи. Погрузитесь в атмосферу Санкт-Петербурга, почувствуйте его ритм и вдохновение, и пусть каждое ваше посещение станет незабываемым приключением. Ведь Санкт-Петербург – это город, который постоянно удивляет и восхищает, город, в который хочется возвращаться снова и снова. А Афиша – ваш верный спутник на этом увлекательном пути
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar021.ru
лечение запоя
J’ai un faible pour Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps en temps des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Belgium Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui stimule l’engagement.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis accro a Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
En savoir plus|
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://tcgjam.com/studio-d-color
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто список развлечений; это живое полотно, сотканное из тысяч культурных нитей, образующих неповторимый облик Северной столицы. Здесь каждый найдет что-то для себя, будь то поклонник классического искусства, ценитель современного авангарда или просто человек, ищущий ярких впечатлений. От балетных постановок в легендарном Мариинском театре, где эхо великих премьер до сих пор витает в воздухе, до модных выставок в креативных пространствах “Ткачей” и “Артмузы”, Санкт-Петербург предлагает бесконечный калейдоскоп возможностей для обогащения душевного мира. Благодаря Афише, вы всегда в курсе грядущих концертов мировых звезд, театральных фестивалей, кинопоказов и гастрономических событий. Это ваш персональный проводник по культурной жизни города, который поможет вам не пропустить самые интересные мероприятия и спланировать свой досуг наилучшим образом. Здесь можно найти информацию о мастер-классах, лекциях, экскурсиях и других образовательных программах, позволяющих расширить кругозор и узнать больше об истории и культуре Санкт-Петербурга.
Je suis sous le charme de Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par ailleurs quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Belgium Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
VГ©rifier le site|
Женское медиа https://beautytips.kyiv.ua о главном: здоровье и профилактика, стиль и тренды, психологические разборы, мотивация, деньги и инвестиции, материнство и путешествия. Честные обзоры, подборка сервисов и истории читательниц.
findbestdeals – Love how easy it is to browse and spot the top deals.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps a autre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Betify Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement fun les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fluides.
Continuer ici|
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Изучить эмпирические данные – https://joinjade.org/my-front-page/doccard-traditionalchinese
startfreshjourney – Motivating message, perfect for anyone ready for a new beginning.
dailydealsplace – Great place for deals, always something new and exciting to find.
learnandshine – Inspiring content that motivates me to keep learning every day.
Медиа для женщин https://feromonia.com.ua которые выбирают себя: здоровье и профилактика, ментальное благополучие, работа и развитие, материнство и хобби. Практичные инструкции, тесты, интервью и вдохновение без кликбейта.
Женский журнал https://dama.kyiv.ua о жизни без перегруза: красота и здоровье, стиль и покупки, отношения и семья, карьера и деньги, дом и путешествия. Экспертные советы, чек-листы, тренды и реальные истории — каждый день по делу.
uniquegiftideas – Excellent variety of creative gifts, ideal for any special occasion.
Всё, что важно https://gryada.org.ua сегодня: мода и стиль, бьюти-рутины, рецепты и фитнес, отношения и семья, путешествия и саморазвитие. Краткие выжимки, длинные разборы, подборки сервисов — удобно и полезно.
fashionmarketplace – Excellent variety of styles, feels like a hub for fashion lovers.
https://dzen.ru/holstai
Здесь
[url=https://stroy-marketing-50.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
inspireeverymoment – Motivating platform that encourages positivity every single day.
https://dzen.ru/holstai
фриспины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом без отыгрыша
https://dzen.ru/holstai
казино без депозита с выводом
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Belgium Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus constants.
http://www.casinobelgium777fr.com|
женский_талисман Амулет: Амулет – это предмет, носимый для защиты от бед, болезней и злых сил. Амулеты могут быть изготовлены из различных материалов, таких как камень, металл, дерево или ткань, и иметь различные формы и символы. Считается, что амулет обладает магической силой, которая защищает своего владельца от негативных воздействий и приносит ему удачу. Амулеты часто передаются из поколения в поколение и являются важной частью культурного наследия многих народов.
обереги_и_талисманы Защитный: Защитный – это прилагательное, описывающее предмет, действие или свойство, обеспечивающее защиту от чего-либо негативного, вредного или опасного.
findhappinessdaily – Uplifting messages and helpful tips that brighten my day instantly.
Запой, это серьезная ситуация, требующая немедленного вмешательства. В городе владимир услуги нарколога на дом срочно востребованы, особенно когда речь идет о помощи при запое. Нарколог на дом может обеспечить необходимую медицинскую помощь при запое, включая детоксикацию и выведение из запоя.Не стоит ждать, пока ситуация станет критической. Скорая помощь может быть вызвана для оказания первой помощи и выявления необходимости в дальнейшем лечении. Лечение алкоголизма и алкогольной зависимости это процесс, который требует профессиональной помощи, и анонимное лечение становится важным аспектом для многих пациентов. Нарколог на дом срочно владимир Вызов нарколога в владимире — это возможность получить срочную помощь, не выходя из дома. Услуги нарколога включают в себя консультации так и проведение необходимых процедур по детоксикации. Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам, чтобы вернуть контроль над своей жизнью.
мужской_талисман Защитаотнегативныхвлияний: Защитаотнегативныхвлияний – это широкое понятие, включающее в себя все меры и средства, направленные на защиту от любых негативных воздействий, будь то энергетические, психологические, социальные или физические.
purechoicehub – Clean design and high-quality items, really impressed with the layout.
сэндвич панели цена Профнастил купить: Покупка профнастила требует внимательного подхода. Важно выбрать профнастил, соответствующий вашим потребностям по толщине, профилю и типу покрытия. Ищите надежных поставщиков с хорошей репутацией и предлагающих качественную продукцию. Сравните цены от разных продавцов, не забывая учитывать стоимость доставки и дополнительные услуги. Убедитесь, что профнастил имеет сертификаты качества и соответствует требованиям безопасности. Перед покупкой проконсультируйтесь со специалистами, чтобы получить рекомендации по выбору и монтажу профнастила. Это поможет вам избежать ошибок и обеспечить долговечность вашей конструкции.
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A souligner le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
}
simplebuyoutlet – Smooth shopping experience, great deals and very clean design.
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Betify Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements rapides.
Explorer le site|
Je suis emerveille par Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Gamdom Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute soudee.
En savoir davantage|
Женский журнал https://krasotka.kyiv.ua про баланс: красота, психология, карьера, деньги, дом и отдых. Экспертные колонки, списки покупок, планы тренировок и проверки здоровья. Материалы, к которым хочется возвращаться.
Онлайн-портал https://womanexpert.kyiv.ua для женщин, которые хотят жить в балансе. Красота, здоровье, семья, карьера и финансы в одном месте. Ежедневные статьи, подборки, советы экспертов и вдохновение для лучшей версии себя.
Глянец без иллюзий https://ladyone.kyiv.ua красота и здоровье с фактчекингом, стиль без переплат, карьера и деньги простым языком. Интервью, тесты, полезные гайды — меньше шума, больше пользы.
J’adore le dynamisme de Belgium Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A souligner le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges sur mesure.
https://casinobelgium365fr.com/|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
starttodaymoveforward – Positive and inspiring, encourages daily progress and self-growth.
настоящий_оргонит Аквадиск 9 см: Аквадиск диаметром 9 см представляет собой устройство для структурирования воды среднего размера, подходящее для использования в различных емкостях, таких как кувшины, графины и бутылки среднего размера. Он является компромиссным вариантом между компактными аквадисками и более крупными моделями, обеспечивая структурирование достаточного объема воды для индивидуального или небольшого группового использования. Считается, что аквадиск 9 см улучшает структуру воды, делая ее более полезной для здоровья.
https://s-nano-s.ru/
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De surcroit le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fluides.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
металлочерепица Панели для стен: Панели для стен – это универсальное и стильное решение для внутренней отделки помещений. Они позволяют быстро и легко преобразить интерьер, скрыть неровности стен и создать уникальный дизайн. Существует множество видов стеновых панелей, различающихся по материалу, текстуре, цвету и способу монтажа. Панели могут быть изготовлены из дерева, МДФ, ПВХ, гипса, стекла и других материалов. Выбор панелей зависит от стиля интерьера, функционального назначения помещения и личных предпочтений. Стеновые панели – это отличный способ придать помещению индивидуальность, уют и комфорт.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar022.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Je suis fascine par Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En resume, Betify Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller sur le web|
сэндвич панели купить в спб Профнастил: Профнастил – это универсальный строительный материал, представляющий собой профилированный лист из оцинкованной стали. Рифленая поверхность профнастила обеспечивает ему высокую жесткость и устойчивость к нагрузкам. Профнастил используется для кровли, облицовки стен, строительства заборов, а также для создания несущих конструкций. Его преимуществами являются: легкость монтажа, долговечность, стойкость к атмосферным воздействиям и доступная цена. Профнастил различается по толщине металла, высоте профиля и типу полимерного покрытия, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для конкретных условий эксплуатации.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar/
Have you always been concerned about these issues?
classystyleoutlet – Elegant fashion selections and well-curated items, love browsing here.
https://tutvot.com/
аспарагин
https://s-nano-s.ru/
yourstylezone – Trendy site that really helps express personal fashion taste.
аминокислота тирозин
thepowerofgrowth – Beautiful name that reminds you of personal and continuous improvement.
startbuildingtoday – Inspiring site that motivates you to take action and grow.
аланин аминокислота
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/skoraya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-uslugi
https://avia.tutvot.com/
Здесь
[url=https://almond-media.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Всё для современной https://model.kyiv.ua женщины: уход и макияж, стиль и шопинг, психология и отношения, питание и тренировки. Честные обзоры, капсульные гардеробы, планы на неделю и проверенные советы.
bonjour I love Your Blog can not say I come here often but im liking what i c so far….
Мода и красота https://magiclady.kyiv.ua для реальной жизни: капсулы по сезонам, уход по типу кожи и бюджета, честные обзоры брендов, шопинг-листы и устойчивое потребление.
купить металлочерепицу для крыши Профнастил купить: Планируя покупку профнастила, важно учитывать несколько ключевых факторов. Во-первых, определитесь с типом профнастила, который вам необходим: для кровли, стен или забора. Во-вторых, обратите внимание на толщину стали, высоту профиля и тип полимерного покрытия, так как эти характеристики напрямую влияют на прочность и долговечность материала. В-третьих, выберите надежного поставщика, который предлагает сертифицированную продукцию с гарантией. Не забудьте сравнить цены у разных продавцов, учитывая условия доставки и возможность дополнительных услуг. Перед покупкой рекомендуется ознакомиться с отзывами о поставщике и запросить образцы продукции для оценки ее качества. Только так вы сможете сделать правильный выбор и приобрести профнастил, который прослужит вам долгие годы.
Сайт для женщин https://modam.com.ua о жизни без перегруза: здоровье и красота, отношения и семья, карьера и деньги, дом и путешествия. Экспертные статьи, гайды, чек-листы и подборки — только полезное и применимое.
Если на осмотре выявляются спутанность сознания, подозрение на делирий, неукротимая рвота с примесью крови, выраженная боль в груди, тяжёлая одышка, судороги — врач немедленно предложит стационар. Безопасность важнее удобства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru
диабетический кетоацидоз
purestylemarket – Classy and minimal style collections, perfect for modern shoppers.
trendandfashionhub – Love how stylish and updated the latest trends are here.
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru
urbanbuycorner – Trendy products with a sleek city vibe, very enjoyable to explore.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya[/url]
createpositivechange – Love the uplifting message here, motivates me to do better daily.
https://lblsp.at
beststylecollection – Stylish selections and great variety, makes shopping a real pleasure.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
Медиа для женщин https://otnoshenia.net 25–45: карьера и навыки, ментальное благополучие, осознанные покупки, спорт и питание. Краткие выжимки и глубокие разборы, подборки брендов и сервисов.
Реальная красота https://princess.kyiv.ua и стиль: уход по типу кожи и бюджету, капсулы по сезонам, устойчивое потребление. Гайды, шопинг-листы, честные обзоры и советы стилистов.
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Azur Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Rejoindre maintenant|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
https://s-nano-s.ru/
https://s-nano-s.ru/
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-vidnom/
Hello there I am so delighted I found your weblog, I really found you by mistake, while I was searching on Google for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say cheers for a remarkable post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to browse it all at the moment but I have book-marked it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the superb work.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk014.ru
лечение запоя
Женский сайт https://one-lady.com о балансе: работа, финансы, здоровье, дом, дети и отдых. Пошаговые инструкции, трекеры привычек, лайфхаки и вдохновляющие истории. Меньше шума — больше пользы.
bestchoicecollection – Wide range of stylish products and great pricing overall.
styleandchoice – Elegant and trendy, perfect for shoppers who love variety.
seminarni prace Diplomova prace cena / Diplomove prace: (Odpovezeno v casti “Napsani bakalarske prace cena / Napsani diplomove prace cena”) a popsano v casti “Bakalarska prace,” pouze nahradit pojmem “diplomova prace” a “magistersky program”. V podstate je to vyssi verze bakalarske prace.
J’adore le dynamisme de Azur Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Azur Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Azur Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis accro a Lucky 31 Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En complement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
бездепозитный бонус с выводом без пополнения
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges personnalises.
Explorer davantage|
J’adore le dynamisme de Action Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute vibrante.
En savoir plus|
J’ai un faible pour Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus le design est style et moderne, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Здесь
[url=https://www.crimsoneducation.org/es]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Je suis captive par Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Action Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Savoir plus|
игровые автоматы бонус за регистрацию с выводом
https://b2best.at
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar023.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
nicee content keep writing
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A noter les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
everydaytrendhub – Always up to date with the latest trends, great resource.
fantastic post, very informative. I wonder why more of the ther experts in the field do not break it down like this. You should continue your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
napsani diplomove prace cena Kolik stoji bakalarska prace / Kolik stoji napsani bakalarske prace: (Odpovezeno v casti “Napsani bakalarske prace cena / Napsani diplomove prace cena”)
статьи о здоровье
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De plus le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, assure des transactions fluides.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Action Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Action Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui stimule l’engagement.
http://www.casinoaction777fr.com|
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. A signaler les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
VГ©rifier ceci|
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. A mentionner le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui stimule l’engagement.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis captive par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller au site|
Flavour of the month loli por*n
afpo.eu/999
go.euserv.org/1ao
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
createpositivechange – Love the message and design, truly encourages meaningful growth.
shopandsaveonline – Awesome platform for smart shoppers looking for great online deals.
freshfindsoutlet – New and trendy products pop up here all the time, love it.
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements securises.
Voir le site|
growtogetherstrong – Positive and motivating platform, perfect for teamwork and personal growth.
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://beup-agency.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
discoverinfiniteideas – Inspiring and creative site name that sparks imagination instantly.
Hiya, I am really glad I have found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossip and net stuff and this is actually frustrating.
Ориентир по времени
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Public policy is key here, and our states need to develop some strategies – – soon.
makeimpacteveryday – A motivating and uplifting name that inspires daily action.
learnshareachieve – Perfect for anyone who loves to learn and make steady progress.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-zhukovskom
uniquevaluehub – Excellent selection of quality products with standout value, love it.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller au site|
[url=https://vulkanvegas50.net/spins/]vulkanvegas50 net[/url]
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, toutefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a rester plus longtemps. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Visiter en ligne|
trendandstyle – Great name that captures modern fashion and timeless personal style.
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais encore des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Action Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute soudee.
https://casinoaction777fr.com/|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour 1xBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Approfondir|
Je suis emerveille par 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais encore quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Commencer Г naviguer|
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, rarement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce la communaute.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’energie de Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais encore des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Great info! Keep post great articles.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя
fashiondailycorner – Trendy fashion picks and great updates, really well-curated site.
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Наши рекомендации — тут – https://articles.cloud7.com.au/?p=14
globalmarketoutlet – Wide range of international products, makes shopping fun and diverse.
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
https://susya.ru/arshavin-nazval-nepopulyarnym-v-zenite-svoe-mnenie-pro-shutku-bezrukova-futbol-rbk-sport
https://bs2-bs2web.at
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Посмотреть всё – http://personalchefbenjamin.com/index.php/2015/08/09/polenta-with-pesto-delicacies
https://bsme-at.at
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://buffalodc.com/2017/12/09/have-you-been-told-you-have-osteoarthritis
https://b2best.at
Антресольныйэтаж Москва Лестница из металла в Москве – это современное и функциональное решение для многоуровневых помещений. Металлические лестницы отличаются прочностью, долговечностью и разнообразием дизайнерских решений. В Москве, где архитектурные стили сочетают в себе современность и классику, металлические лестницы пользуются большой популярностью. Они могут быть выполнены из различных материалов, таких как сталь, алюминий или чугун, и могут иметь различные формы и размеры. Металлические лестницы часто используются в квартирах, офисах, торговых центрах и других общественных зданиях, где важна безопасность, надежность и эстетичный внешний вид. Компании в Москве предлагают широкий выбор металлических лестниц, начиная от простых конструкций до сложных дизайнерских проектов.
Мезонин Антресольный этаж в Москве – это архитектурное решение, которое особенно актуально в условиях высокой стоимости недвижимости и стремления к оптимизации использования пространства. В Москве, где цены на жилье и коммерческую недвижимость одни из самых высоких в мире, антресоли становятся популярным способом увеличения полезной площади квартир, офисов и других помещений. Они позволяют создать дополнительные комнаты, кабинеты или зоны хранения, не увеличивая при этом занимаемую площадь здания. Архитекторы и дизайнеры в Москве активно разрабатывают проекты с антресолями, учитывая особенности столичного строительства и требования к безопасности и комфорту.
Мезонин Антресоль: Антресоль – это внутренняя площадка, расположенная под потолком помещения, чаще всего используемая для хранения вещей или организации дополнительного спального места. Отличительной чертой антресоли является её доступность, обычно обеспечиваемая лестницей или стремянкой. Этот элемент интерьера позволяет эффективно использовать вертикальное пространство, что особенно актуально для помещений с высокими потолками. Антресоли могут быть как открытыми, так и закрытыми, в зависимости от функциональных потребностей и дизайна интерьера. В квартирах антресоли часто используют для хранения сезонных вещей, книг или других предметов, не требующих ежедневного доступа. В складских и промышленных помещениях антресоли могут служить дополнительным уровнем для размещения товаров или оборудования. При проектировании антресоли необходимо учитывать допустимую нагрузку на конструкцию и обеспечить безопасность её использования.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://carstyleart.fr/auto-moto-retro-2022-centre-des-expositions-du-mans
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Обратиться к источнику – https://www.htcwildfire.com.vn/0369-la-mang-gi
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://atorixit.in/index.php/2023/05/24/best-sap-implementation-partner-in-india
Женский блог https://sunshadow.com.ua о жизни без перегруза: красота и здоровье, отношения и семья, стиль и покупки, деньги и карьера. Честные обзоры, лайфхаки, планы на неделю и личные истории — только то, что реально помогает.
Современный женский https://timelady.kyiv.ua сайт о стиле жизни: уход за собой, макияж, прически, фитнес, питание, мода и деньги. Практичные советы, разбор трендов, подборки покупок и личная эффективность. Будь в ресурсе и чувствуй себя уверенно каждый день. Больше — внутри.
https://lblsp.at
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
https://www.press-release.ru/branches/medicine/1narcology-lechenie-depressii
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Подробности по ссылке – https://matomake.com/I0005636
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Подробная информация доступна по запросу – https://okazjeirabaty.online/coupon/cala-kolekcja-wiosenna-25-w-5-10-15
discoverfashionfinds – Great site for fashion lovers, lots of trendy items to explore.
Здесь
[url=https://hyperpc.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
shopandsmiletoday – The name fits perfectly, such a cheerful and easy shopping experience.
https://t.me/stalprofservice Второй этаж в квартире: Второй этаж в квартире – это организация дополнительного уровня в многоуровневом жилище, позволяющая эффективно использовать вертикальное пространство и создать зонирование. В квартирах-студиях с высокими потолками второй этаж часто используется для организации спальной зоны или кабинета, освобождая основное пространство для гостиной и кухни. В двухуровневых квартирах второй этаж может включать несколько комнат: спальни, ванные комнаты, гардеробные. Лестница, ведущая на второй этаж, становится не только функциональным элементом, но и важной частью дизайна интерьера. Конструкция второго этажа должна быть прочной и безопасной, а также соответствовать строительным нормам и правилам. Второй этаж в квартире – это удачное решение для тех, кто стремится максимально эффективно использовать имеющееся пространство и создать уникальный дизайн интерьера.
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Получить полную информацию – https://www.gr888.co/review/4738
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vsizambia.org/the-vsi-end-of-year-cleaning-exercise
Для оформления документов на поездку за границу или для решения других вопросов, связанных с иностранными языками, обратитесь в [url=https://allperevod.ru/]бюро переводов москва[/url].
Бюро переводов служит мостом между культурами, облегчая обмен информацией и идеями. Это особенно важно для компаний, которые стремятся выйти на международный рынок. Бюро переводов предоставляет услуги перевода документов, веб-сайтов и программного обеспечения, что необходимо для успешной экспансии бизнеса. Кроме того, бюро переводов может помочь компаниям адаптироваться к местным рынкам, учитывая культурные и языковые особенности.
Работа с бюро переводов позволяет компаниям концентраироваться на своей основной деятельности, перелагая задачи перевода на экспертов. Это особенно важно для компаний, которые работают в области международного бизнеса. Бюро переводов может помочь компаниям улучшить свое позиционирование на рынке, обеспечивая профессиональный перевод пресс-релизов и других публичных документов. Кроме того, Бюро переводов может обеспечить быстрый и оперативный перевод документов, что критически важно для компаний, работающих в сжатые сроки.
Бюро переводов может обеспечить перевод маркетинговых материалов, таких как пресс-релизы и рекламные брошюры. Это особенно важно для компаний, которые стремятся расширить свою деятельность на новые рынки. Бюро переводов может помочь компаниям адаптировать их веб-сайты для международной аудитории, обеспечивая перевод и локализацию контента. Кроме того, бюро переводов может обеспечить услуги интерпретации, позволяя компаниям общаться с иностранными партнерами и клиентами в режиме реального времени.
Бюро переводов может помочь компаниям расширить свою деятельность на новые рынки, обеспечивая точный и качественный перевод. Это особенно важно для компаний, которые стремятся выйти на международный рынок. Бюро переводов может помочь компаниям повысить свою конкурентоспособность на глобальном рынке, обеспечивая профессиональный перевод маркетинговых материалов. Кроме того, бюро переводов может помочь компаниям избежать ошибок и недоразумений, которые могут возникнуть из-за плохого перевода.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
слоты без депозита с бонусом
игровые автоматы с бездепозитным бонусом за регистрацию с выводом
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://caneg.co.za/brand-service-demands-a-special-mindset
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://bengalelectricalindustries.com/digital-marketing-made-easy-let-our-team-handle
Для покупки семян высокого качества посетите [url=https://semena365.ru/]сайт семяныч заказ семян[/url], где представлен широкий ассортимент семян различных культур.
Семяныч официальный сайт позволяет клиентам ознакомиться с ассортиментом предлагаемых товаров и услуг, а также получить консультацию от профессиональных специалистов.
Семяныч официальный сайт позволяет клиентам оставлять отзывы и оценки, что помогает другим посетителям сделать более обоснованное решение.
Компания Семяныч имеет опытную команду профессионалов, которые всегда готовы предоставить консультацию и поддержку клиентам.
Официальный сайт компании Семяныч предоставляет полную информацию о деятельности компании и предлагает клиентам возможность стать частью ее сообщества.
Casino Roulette: Spin for the Ultimate Thrill
Experience the timeless excitement of Casino Roulette, where every spin brings a chance to win big and feel the rush of luck. Try your hand at the wheel today at https://k8o.jp/ !
J’ai une passion debordante pour Azur Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Azur Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Continuer ici|
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Узнайте всю правду – https://nutrabem.shop/ola-mundo
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk013.ru
лечение запоя омск
Блог для женщин https://sweetheart.kyiv.ua которые выбирают себя: самоценность, баланс, карьера, финансы, хобби и путешествия. Мини-привычки, трекеры, вдохновляющие тексты и практичные советы.
Its wonderful as your other blog posts : D, regards for putting up.
J’adore l’energie de Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter maintenant|
Бро, не волнуйся, тут ровный магаз. Напиши им в аську, что заказ номер такой-то оплачен. https://www.montessorijobsuk.co.uk/author/zidcgwib/ Ребята!!! Устал писать Вам в скайп…Вы меня сознательно игнорируете?? Каждый день завтраками кормите. Я всего лишь хочу у вас покупать каждые три дня 1-2гр АМ2233. Вы сказали, что тоже из Ростова, я обрадовался, что рядом. Не хотите делать закладки, так ответьте куда деньги отправить, отправьте хоть первым классом (хотя это смешно)! Откройте скайп и почитайте миллион сообщений от меня!!
Thanks for your patience and sorry for the inconvenience!
trendworldmarket – Love how updated this site stays with the latest global trends.
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Подробнее – https://www.antonelloosteria.com/cook/how-to-dice-potatoes-and-meat-like-a-chef
Портал для женщин https://viplady.kyiv.ua ценящих стиль, комфорт и развитие. Мода, уход, отношения, семья и здоровье. Только практичные советы, экспертные мнения и вдохновляющий контент. Узнай, как быть собой и чувствовать себя лучше.
Онлайн-площадка https://topwoman.kyiv.ua для женщин: стиль, бьюти-новинки, осознанность, здоровье, отношения, материнство и работа. Экспертные статьи, инструкции, чек-листы, тесты и вдохновение. Создавай лучший день, развивайся и находи ответы без лишней воды.
creativechoicehub – Innovative designs and creative products, really impressed with the variety.
shopthelatestdeals – Found amazing deals today, makes shopping fun and easy.
Excellent post. Keep posting such kind of info on your site. Im really impressed by your site.
Hi there, You have performed a great job. I will definitely digg it and in my opinion recommend to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this web site.
https://tsrstreetwear.com/melbet-obzor-2025/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar025.ru
лечение запоя
yourdailyinspiration – Inspiring words and great visuals, perfect for a morning boost.
Hi I am so delighted I found your webpage, I really found you by accident, while I was searching on Digg for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say thanks for a fantastic post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the awesome work.
https://merdeka66.net/melbet-bonus-pri-registracii-2025/
Наличие второго паспорта за границей становится всё более актуальным среди граждан РФ.
Такой вариант даёт дополнительные перспективы для жизни.
Гражданство другой страны помогает беспрепятственно путешествовать и упрощать поездки.
Кроме того подобное решение может укрепить уверенность в будущем.
Паспорт Мексики
Все больше людей рассматривают второе гражданство как инструмент защиты.
Получив ВНЖ или второй паспорт, человек получить образование за рубежом.
Многие государства предлагают индивидуальные возможности получения вида на жительство.
Поэтому вопрос оформления становится приоритетной для тех, кто думает о будущем.
https://s-nano-s.ru/
продвижение сайта Продвижение в Google и Yandex – наш опыт с 2011.
Заказал-оплатил 50г реги, а отношение как не знаю к кому… http://www.pageorama.com/?p=vefucadtodad Аккуратнее с магазином, недовес у них неплохой…
Здесь
[url=https://integral-store.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мезонин Антресольныйэтажмосква: Антресольныйэтажмосква – это антресольный этаж, спроектированный и построенный с учетом специфики московского строительства и архитектуры. В условиях дороговизны недвижимости в Москве, антресольные этажи становятся популярным решением для увеличения полезной площади. Проектирование и строительство антресольного этажа в Москве требует согласования с соответствующими органами и учета строительных норм и правил, действующих в городе. Местные строительные компании имеют опыт работы с антресольными этажами и могут предложить оптимальные решения для различных типов помещений. Антресольныйэтажмосква позволяет максимально эффективно использовать пространство, особенно в старых зданиях с высокими потолками.
discoverandshopnow – Great shopping experience, always something new and fun to explore.
Фундаменты на сваях играют основополагающее значение в современном строительстве.
Подобные конструкции обеспечивают надёжность фундамента.
При отсутствии надёжных свай здание может потерять устойчивость.
Новые методы позволяют рассчитывать сваи с учётом геологических условий.
От правильного монтажа напрямую зависит срок службы здания.
Такие конструкции находят применение при строительстве домов.
При их использовании можно строить на слабых грунтах.
В итоге, сваи являются фундаментальной частью любого качественного строительства.
https://coub.com/suvorovsvai
Проектирование Антресольный этаж: Антресольный этаж – это промежуточный этаж в здании, расположенный между двумя основными этажами и занимающий меньшую площадь, чем они. Основное назначение антресольного этажа – увеличение полезной площади здания без значительного увеличения его высоты. Антресольные этажи часто используются в коммерческих зданиях (офисах, торговых центрах), производственных помещениях и реже – в жилых домах. Важно учитывать, что проектирование и строительство антресольного этажа требует соблюдения строительных норм и правил, а также обеспечения достаточной освещенности, вентиляции и пожарной безопасности. Функциональность антресольного этажа может быть разнообразной: офисные помещения, складские зоны, торговые площади, зоны отдыха или жилые комнаты. Дизайн антресольного этажа должен соответствовать общему стилю здания и функциональным требованиям.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
Pretty element of content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to claim that I get in fact loved account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing for your feeds and even I success you get entry to persistently rapidly.
https://priorityfireprotection.com/melbet-obzor-2025-bukmekerskaya-kontora/
Женский медиасайт https://woman365.kyiv.ua с акцентом на пользу: капсульный гардероб, бьюти-рутины, здоровье, отношения, саморазвитие и материнство. Пошаговые инструкции, списки покупок, чек-листы и экспертные ответы. Заботимся о тебе и твоем времени. Подробности — на сайте.
I saw a similar post on another website but the points were not as well articulated.
brightcollectionhub – Colorful and stylish items that really make browsing enjoyable.
https://lblsp.at
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
Aller sur le site|
https://lblsp.at
J’ai une passion debordante pour Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour conclure, Action Casino vaut une visite excitante. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.casinoaction777fr.com|
There is a lot of misunderstanding about these issues today. Your material helps explain things.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. En bonus le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges sur mesure.
https://lucky31casino777fr.com/|
trendyvaluezone – Stylish products at affordable prices, love the variety here.
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, 1xBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Общение оператора 10/10-всегда все грамотно и вежливо объяснит. Таким оператор и должен быть! https://rant.li/ycefaagi/prokhladnyi-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Сейчас по России что то не видно вас.Только пожелать ветра в парус,адекватных клиентов по меньше шкур
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller plus loin|
If wings are your thing, Tinker Bell’s sexy Halloween costume design is all grown up.
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En fin de compte, Azur Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller au site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais encore quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
https://azurcasinobonusfr.com/|
https://bsme-at.at
Je suis fascine par Action Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Action Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer plus|
продвижение сайта Эффективные прогоны Хрумером под индивидуальные требования и задачи.
Je suis sous le charme de Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses continues.
Parcourir maintenant|
finduniqueproducts – Unique finds and creative ideas, everything feels handpicked and quality.
A good web site with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for making this web site, and I will be visiting again. Do you do newsletters? I Can’t find it.
Твой женский помощник https://vsegladko.net как подчеркнуть индивидуальность, ухаживать за кожей и волосами, планировать бюджет и отдых. Мода, психология, дом и карьера в одном месте. Подборки, гайды и истории, которые мотивируют заботиться о себе. Узнай больше на сайте.
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est clair et efficace, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En resume, 1xBet Casino merite un detour palpitant. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui booste la participation.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis accro a Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le web|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Action Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.casinoaction365fr.com|
bestdailycorner – Found so many great daily deals here, totally worth visiting often.
Женский портал https://womanportal.kyiv.ua о моде, психологии и уходе за собой. Узнай, как сочетать стиль, уверенность и внутреннюю гармонию. Лучшие практики, обзоры и вдохновляющие материалы для современных женщин.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Состав инфузии подбирается индивидуально по показателям и сопутствующим диагнозам. Чаще всего в схему входят следующие элементы:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru
продвижение ВК Услуги продвижения в Google и Yandex, оказываемые с 2011 года.
I simply could not leave your site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info a person supply in your visitors? Is going to be back often to inspect new posts
стараемся для вас https://www.rwaq.org/users/skrerbnc56kyl1-20251103200610 Сорри, многаюуков. И ошибок – со спецтелефлна сижу)
Всё о развитии https://run.org.ua и здоровье детей: диагностические скрининги, логопедия, дефектология, нейропсихология, ЛФК, массаж, группы раннего развития, подготовка к школе. Планы занятий, расписание, запись онлайн, советы специалистов и проверенные методики.
trendandfashion – Perfect mix of classic and modern trends, always inspiring.
Здесь
[url=https://integral-store.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
of course like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I will surely come back again.
Антресоль Металлоконструкциямосква: Металлоконструкциямосква – это металлоконструкция, спроектированная и изготовленная в Москве, с учетом местных строительных норм и требований. Металлоконструкции в Москве используются для строительства различных зданий и сооружений, таких как торговые центры, офисные здания, склады и ангары. Многие компании в Москве специализируются на проектировании и изготовлении металлоконструкций различных типов и сложностей. Металлоконструкциямосква должна соответствовать требованиям безопасности и надежности. Строительство с использованием металлоконструкций позволяет быстро и эффективно возводить здания и сооружения.
В стационаре мы добавляем расширенную диагностику и круглосуточное наблюдение: это выбор для пациентов с «красными флагами» (галлюцинации, выраженные кардиосимптомы, судороги, рецидивирующая рвота с примесью крови) или тяжёлыми соматическими заболеваниями. На дому мы остаёмся до первичной стабилизации и оставляем письменный план на 24–72 часа, чтобы семья действовала уверенно и согласованно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-pushkino[/url]
discoverandshop – Great platform for exploring unique items and discovering new favorites.
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk014.ru
вывод из запоя
Сайт о строительстве https://blogcamp.com.ua и ремонте: проекты, сметы, материалы, инструменты, пошаговые инструкции и лайфхаки. Чек-листы, калькуляторы, ошибки и их решения. Делайте качественно и экономно.
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; we have created some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange solutions with other folks, why not shoot me an e-mail if interested.
https://www.skysavant.io/melbet-promo-frebet-2025/
groweverydaynow – Inspiring platform that reminds me to keep improving and learning daily.
Карты для майнкрафт Последняя версия Майнкрафт – это всегда свежие обновления, новые функции и улучшения, которые делают игру еще более увлекательной и захватывающей. Разработчики постоянно работают над тем, чтобы Minecraft оставался актуальным и предлагал игрокам новые возможности для творчества и приключений. Обновления приносят с собой новые блоки, мобы, биомы и механики, которые расширяют границы игрового мира и позволяют вам создавать еще более удивительные вещи. Скачивая последнюю версию Minecraft, вы получаете доступ ко всем новым функциям и улучшениям, а также исправлениям ошибок, которые делают игру более стабильной и плавной. Не упустите возможность насладиться новейшими достижениями в мире Minecraft!
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for %keyword%
https://www.pracownia-usmiechu.pl/promocod-bk-melbet-2025/
Трек есть +Бонус от души как придет отпишу https://www.montessorijobsuk.co.uk/author/tagucyfucl/ Всё отлично все всё получат магаз ровный доказал свой гибгий подход к НАМ заказчикам.Если форс мажёр то всё уладят в НАШу пользу.Отправка осуществляется от 2-10дней в зависимости от заказов то есть загруженности магазина.Без паники братья без паники.
Скачать Майнкрафт Скачать моды для Майнкрафт – это шанс вдохнуть новую жизнь в игру, которая уже успела завоевать сердца миллионов игроков по всему миру и стать настоящим феноменом в индустрии развлечений. Моды – это как дополнения, созданные талантливыми разработчиками и энтузиастами, которые не останавливаются на достигнутом и стремятся расширить границы Minecraft, предлагая игрокам новые, захватывающие возможности и невероятные впечатления. С помощью модов вы можете изменить практически любой аспект игры: от добавления новых блоков и предметов, которые позволят вам создавать более сложные и красивые постройки, до изменения поведения мобов, делая их более умными и опасными, и генерации мира, создавая новые, неизведанные территории. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы опытным игроком, который ищет новых вызовов, или новичком, который только начинает свое знакомство с Minecraft, моды помогут вам настроить игру под свои собственные предпочтения и получить максимум удовольствия от каждого момента. Экспериментируйте, исследуйте, создавайте и делитесь своими творениями с другими игроками!
groweverydaynow – Motivational and uplifting, reminds me to keep improving daily.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Скачать Майнкрафт Minecraft mod – это модификация, которая изменяет или расширяет оригинальную игру Minecraft, добавляя новые возможности и функции, которые не были предусмотрены разработчиками. Моды могут добавлять новые блоки, предметы, мобов, биомы, команды и даже целые игровые механики, полностью преображая геймплей и открывая новые горизонты для творчества и приключений. Они создаются талантливыми сторонними разработчиками и позволяют игрокам настроить Minecraft под свои личные предпочтения и создать уникальный игровой опыт. Существуют тысячи различных модов, от простых изменений интерфейса, которые делают игру более удобной и интуитивно понятной, до сложных модификаций, которые полностью меняют геймплей, добавляя новые измерения, задания и возможности. Установка модов может потребовать использования специальных программ, таких как Forge или Fabric, которые позволяют вам управлять модами и настраивать их параметры. Minecraft mod – это отличный способ вдохнуть новую жизнь в игру и получить уникальный игровой опыт, который будет соответствовать вашим интересам и предпочтениям.
Очищение организма от алкоголя в домашних условиях – важный процесс‚ особенно для жителей Тулы‚ страдающих от алкогольной зависимости. Комплексный подход является ключевым в лечении запоя‚ включая детоксикацию и восстановление функций печени. лечение запоя тула Симптомы похмелья могут быть крайне неприятными: боль в голове‚ недомогание‚ слабость. Поэтому домашние методы‚ такие как народные средства‚ могут оказать значительное облегчение. Например‚ настои из трав‚ имбирь и мед помогают восстановить силы. В Туле доступны разнообразные альтернативные методы терапии‚ включая программы по лечению алкоголизма. Важно помнить‚ что после детоксикации необходима дальнейшая поддержка для успешного восстановления после алкоголя.
Советы для родителей https://agusha.com.ua на каждый день: раннее развитие, кризисы возрастов, дисциплина, здоровье, игры и учеба. Экспертные разборы, простые лайфхаки и проверенные методики без мифов. Помогаем понять потребности ребёнка и снизить стресс в семье.
Круглосуточный формат критичен именно из-за «первой ночи»: в это окно нестабильны тревога, сон, вегетативная реактивность. Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу», а по одному параметру доводим систему до целевого коридора. Так удаётся избежать полипрагмазии и сохранить управляемость процесса: пациент и семья заранее знают, какие цифры считаются нормой, когда звонить дежурному, как организовать свет и тишину, чтобы ночное восстановление действительно состоялось.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
freshtrendstore – New arrivals and trending items make shopping exciting every visit.
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Thanks!
https://billmeoni.com/melbet-sait-obzor-2025/
Эта последовательность действий обеспечивает безопасное прекращение запоя и предотвращает развитие синдрома отмены.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
https://buyerseller.xyz/user/johnwoodard/
Скачать майнкрафт моды Майнкрафт PE (Pocket Edition) – это мобильная версия популярной игры, которая позволяет вам играть в Minecraft на своем смартфоне или планшете в любом месте и в любое время. Наслаждайтесь всеми преимуществами Minecraft, где бы вы ни находились: стройте, исследуйте, сражайтесь и создавайте свои собственные миры на ходу. Minecraft PE предлагает интуитивно понятное управление и оптимизированный интерфейс, который позволяет вам легко взаимодействовать с игровым миром на небольших экранах. Объединяйтесь с друзьями через локальную сеть или онлайн и играйте вместе в увлекательные приключения. Minecraft PE – это ваш портативный мир Minecraft, который всегда под рукой!
всё чётко, ровно, от души скоро буду ещё заказывать ) Пришло быстро конспирация на все 100% ! https://pxlmo.com/wcraqhsd27y7j3 Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par ailleurs des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
shopwithjoy – Love the cheerful vibe here, shopping truly feels joyful and easy.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
Здесь
[url=https://gorbilet.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
J’adore le dynamisme de Action Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Action Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
http://www.casinoaction777fr.com|
Родителям о главном https://rodkom.org.ua баланс режима, питание, истерики и границы, подготовка к школе, дружба и безопасность в сети. Короткие памятки, чек-листы и практики от специалистов. Только актуальные данные и решения, которые работают в реальной жизни.
Je suis epate par Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par contre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. En complement le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui booste la participation.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. Au final, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges personnalises.
http://www.1xbetcasino366fr.com|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A signaler les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
https://lucky31casino365fr.com/|
https://lblsp.at
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages uniques.
Lire plus|
Женский портал https://womanclub.kyiv.ua о стиле жизни, красоте и вдохновении. Советы по уходу, отношениям, карьере и саморазвитию. Реальные истории, модные тренды, психологические лайфхаки и идеи для гармонии. Всё, что важно каждой современной женщине.
https://lblsp.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
yourdailyfinds – Convenient and fun to browse, always discovering something useful.
нету. в ближайшее время не будет. https://www.grepmed.com/kuboheifad Оправдания в небе не ищут,
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
shopthelatestdeals – Convenient platform for finding amazing deals quickly and easily.
Выездная бригада прибывает с необходимым оборудованием. Инфузионная терапия длится 60–120 минут; по ходу процедуры контролируются давление, пульс, дыхание и субъективное самочувствие, при необходимости схема корректируется (темп капания, смена растворов, добавление противорвотных или седативных средств). Чаще всего уже к концу первой инфузии снижается тошнота, уходит дрожь и «внутренняя дрожь», нормализуется сон. Врач оставляет пошаговый план на 24–72 часа: питьевой режим, щадящее питание (дробно, без жирного и острого), режим сна, рекомендации по витаминам и гепатопротекции. Если в процессе выявляются тревожные признаки (нестабильная гемодинамика, выраженная аритмия, спутанность сознания), будет предложен перевод в стационар.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Своевременный вызов позволяет «поймать» момент, когда детокс максимально эффективен и ещё не потребовалась госпитализация. Мы работаем по всему Пушкинскому округу и приезжаем в ближайшие населённые пункты соседних округов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
bestchoiceoutlet – Great prices and selections, feels like a hidden gem for shoppers.
https://lblsp.at
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
Awesome post. It’s so good to see someone taking the time to share this information
Кракен зеркало
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
Can I just say what a relief to seek out someone who actually knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You positively know find out how to bring a problem to mild and make it important. Extra individuals have to read this and perceive this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more in style because you positively have the gift.
I wrote down your blog in my bookmark. I hope that it somehow did not fall and continues to be a great place for reading texts.
Выездная бригада прибывает с необходимым оборудованием. Инфузионная терапия длится 60–120 минут; по ходу процедуры контролируются давление, пульс, дыхание и субъективное самочувствие, при необходимости схема корректируется (темп капания, смена растворов, добавление противорвотных или седативных средств). Чаще всего уже к концу первой инфузии снижается тошнота, уходит дрожь и «внутренняя дрожь», нормализуется сон. Врач оставляет пошаговый план на 24–72 часа: питьевой режим, щадящее питание (дробно, без жирного и острого), режим сна, рекомендации по витаминам и гепатопротекции. Если в процессе выявляются тревожные признаки (нестабильная гемодинамика, выраженная аритмия, спутанность сознания), будет предложен перевод в стационар.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-reutove/
learnandshine – Encouraging content that motivates me to grow and shine every day.
startsomethingnewtoday – Motivating name and content that encourages taking the first step.
growwithpurpose – Excellent site with a strong message about intentional self-growth.
бездепозитные фрибеты в букмекерских
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
When you touch down at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport, the last thing you want to worry about is transportation. Whether you’re here for business or pleasure, you want to get to your destination efficiently and comfortably. That’s where a reliable Seattle airport limo service comes into play. With a professional limo service, you can enjoy the luxury of a private ride, complete with plush seating and ample legroom. You can sit back and relax, knowing that a seasoned chauffeur is handling the navigation through the busy Seattle streets. These drivers are not only well-versed in the city’s layout, but also trained to provide a smooth and safe ride, regardless of the traffic or weather conditions. One such reliable [url=https://ministryofproperties.co.uk/luxury-transportation-services-in-seattle/best-luxury-car-services-in-seattle-85/]seattle airport limo service[/url] is known for its punctuality, professionalism, and high-quality vehicles. They offer a fleet of modern, well-maintained limousines that provide the perfect blend of comfort and style. You can easily book your ride online or over the phone, and the customer service team is always ready to assist with any queries or special requests. The beauty of using a limo service is that it takes the stress out of your travel. There’s no need to worry about parking, refueling, or navigating unfamiliar roads. Your chauffeur will be there to pick you up from the airport and drop you off at your destination, allowing you to focus on your trip. Whether you’re heading to a business meeting, a special event, or just your hotel, you can arrive in style and comfort. Moreover, these services are not limited to airport transfers. You can also book a limo for sightseeing, special occasions, or corporate events. The flexibility and convenience offered by a professional limo service make it an excellent choice for all your transportation needs in Seattle. So, next time you’re in the city, consider a limo service for a stress-free and luxurious travel experience.
фрибеты это
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Azur Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer|
Неотложная наркологическая помощь – это ключевой аспект в лечении зависимостей. Важно знать‚ что при возникновении симптомов передозировки, таких как ускоренное дыхание, потеря сознания или судороги, необходимо срочно вызывать скорую помощь. Лица, страдающие зависимостью и их родственники могут обратиться в специальную наркологическую клинику, где окажут квалифицированную помощь. Кризисные службы предлагают услуги нарколога, что позволяет получить поддержку близким и самим зависимым. Терапия зависимостей включает в себя не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапию для зависимых, что важно для восстановления после зависимости. Профилактические меры против алкоголизма и социальная адаптация также играют значительную роль в процессе реабилитации наркоманов, обеспечивая успешное возвращение к нормальной жизни. Помните‚ медицинская помощь при наркотической зависимости должна быть своевременной и комплексной. Поддержка и понимание близких помогают справиться с трудностями на пути к выздоровлению. Для получения более подробной информации посетите narkolog-tula023.ru.
I’ve read several good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a magnificent informative site.
https://b2best.at
yourtimeisnow – Motivating site that encourages taking action and embracing opportunities today.
Официальный сайт Kraken kra44 at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
https://lblsp.at
J’adore l’energie de Azur Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Azur Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Lire plus|
https://lblsp.at
Здесь
[url=https://www.globalsources.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this moreover taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article! I procrastinate alot and by no means seem to get something done.
findhappinessdaily – Love the positivity here, helps me focus on the good things.
explorewithoutlimits – Inspires creativity and curiosity, perfect for adventurous minds.
как добраться до ко ланты Ко Ланта Таиланд – это популярное направление для туристов со всего мира, привлекающее своими природными красотами, богатой культурой и разнообразием развлечений. Остров предлагает широкий выбор вариантов размещения, от бюджетных гестхаусов до роскошных вилл, а также множество ресторанов и кафе, где можно отведать блюда тайской и международной кухни.
Автомобильный журнал https://autodream.com.ua для новичков и энтузиастов: тренды, тест-драйвы, сравнения, разбор комплектаций, VIN-проверки и подготовка к сделке. Практичные гайды по уходу и экономии, гаджеты для авто, законы и штрафы. Делимся опытом, чтобы не переплачивали.
discoveramazingstories – Captivating stories and inspiring content, keeps me coming back.
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk013.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
I absolutely adore your site! You aggressive me as able-bodied as all the others actuality and your broiled PS is absolutely great!
yourdealhub – Excellent deals on quality products, really makes shopping worthwhile.
changeyourmindset – Inspiring site that helps shift perspectives and encourages real growth.
остров ко ланта в таиланде как добраться Ко Ланта на карте: Исследуйте остров с помощью интерактивной карты
Up to on the wane loli po**rn
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
Здесь
[url=https://epsilongifts.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir plus|
uniquegiftcorner – Creative and thoughtful gift ideas, ideal for any occasion.
1xbet t?rkiye [url=http://www.1xbet-7.com]http://www.1xbet-7.com[/url] .
перепланировка москва [url=http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru]перепланировка москва[/url] .
surewin game [url=surewin-online.com]surewin-online.com[/url] .
beep beep casino no deposit bonus [url=https://beepbeepcasino-online.com]https://beepbeepcasino-online.com[/url] .
https://lblsp.at
everydayvaluezone – Great deals and simple navigation, really makes shopping effortless.
This is an awesome entry. Thank you very much for the supreme post provided! I was looking for this entry for a long time, but I wasn’t able to find a honest source.
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Уточнить детали – https://thenewblackmagazine.com/2024/01/13/httpwww-thenewblackmagazine-comview-aspxindex3370
trendloversplace – Perfect for trend enthusiasts, always something fresh and exciting to see.
https://bsme-at.at
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://job-bank.co.uk/how-to-start-a-business-from-home
https://lblsp.at
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/
trendandbuy – Awesome spot for trendy finds, love browsing the latest styles.
Услуги 3D-печати — это инновационный инструмент, который открывает новые горизонты для бизнеса и творчества. Мы обеспечиваем производство на 3D-принтере под заказ. Мы следим за качеством на каждом этапе, что позволяет получать результат без брака. Доступен широкий выбор пластика и композитов, благодаря чему услуги подходят для бизнеса, дизайна и частных проектов. Сроки выполнения заказа минимальны, а качество всегда соответствует цене. Свяжитесь с нами для обсуждения деталей, и вы получите результат точно в срок https://fancybox.qa/2025/09/10/%d1%83%d1%81%d0%bb%d1%83%d0%b3%d0%b8-3d-%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%87%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8-%d0%b4%d0%bb%d1%8f-%d0%b1%d0%b8%d0%b7%d0%bd%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%b0-%d0%b8-%d1%87%d0%b0%d1%81%d1%82%d0%bd%d1%8b%d1%85-%d0%ba/. Мы гарантируем качество и точность каждой детали.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg013.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Peгистpиpyйся ceйчас и пoлyчай пpивeтствeнный пaкeт — до 215 фpиcпинoв и до 1250USD бoнyca!
Лучшие игры, быcтрыe выплaты и чecтный сервис на
https://kineticverse.shop/btrik88
[url=https://dzialki-beskidy.pl/]vavada casino pl[/url]
Inwestycja w dzialke w tym regionie to doskonaly sposob na polaczenie przyjemnego z pozytecznym.
Dzieki rozwijajacej sie infrastrukturze i rosnacemu zainteresowaniu turystow, ceny dzialek stopniowo wzrastaja. Coraz wiecej osob docenia spokoj i piekno przyrody, jakie oferuja Beskidy.
#### **2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
Wybor odpowiedniej lokalizacji zalezy od indywidualnych potrzeb i budzetu. Warto sprawdzic profesjonalne strony internetowe, takie jak dzialki-beskidy.pl, ktore prezentuja sprawdzone oferty.
Przed zakupem nalezy dokladnie przeanalizowac dostepnosc mediow i warunki zabudowy. Niektore tereny wymagaja dodatkowych formalnosci, dlatego warto skorzystac z pomocy ekspertow.
#### **3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
Nieruchomosc w gorach to nie tylko inwestycja finansowa, ale rowniez szansa na poprawe jakosci zycia. Mozna tu zbudowac dom letniskowy i cieszyc sie urokami przyrody przez caly rok.
Dodatkowo, region ten oferuje wiele atrakcji, takich jak szlaki turystyczne i stoki narciarskie. Coraz wiecej osob wybiera te lokalizacje ze wzgledu na dobrze rozwinieta baze rekreacyjna.
#### **4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
Przed podjeciem decyzji warto skonsultowac sie z prawnikiem i geodeta. Dobrze jest sprawdzic historie nieruchomosci i upewnic sie, ze nie ma zadnych obciazen.
Wazne jest rowniez okreslenie swojego budzetu i planow zwiazanych z zagospodarowaniem terenu. Niektore oferty pozwalaja na rozlozenie platnosci, co ulatwia inwestycje.
—
### **Szablon Spinu**
**1. Dlaczego warto kupic dzialke w Beskidach?**
– Malownicze krajobrazy Beskidow przyciagaja zarowno turystow, jak i przyszlych mieszkancow.
– Dzieki rozwojowi infrastruktury, tereny te staja sie jeszcze bardziej atrakcyjne.
**2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
– Dobrym rozwiazaniem jest skorzystanie ze sprawdzonych stron internetowych, takich jak dzialki-beskidy.pl.
– Kluczowe jest sprawdzenie, czy dzialka ma wszystkie niezbedne pozwolenia.
**3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
– Dzialka w Beskidach moze stac sie zrodlem dodatkowego dochodu dzieki wynajmowaniu turystom.
– Coraz wiecej osob docenia walory turystyczne i rekreacyjne Beskidow.
**4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
– Wazne jest zasiegniecie porady prawnej przed podpisaniem umowy.
– Niektore oferty umozliwiaja elastyczne formy platnosci, co moze byc korzystne.
Медикаменты от алкоголизма могут включать лекарства для лечения зависимости‚ которые облегчают симптомы. Круглосуточная помощь и контроль при выводе из запоя обеспечивают защищенность пациента. Забота близких также важна для успешного восстановления после алкогольной интоксикации. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Советы по выходу из запоя могут включать регулярное общение с врачом и придерживание распорядка. Следует обратиться за помощью‚ чтобы предотвратить возвращение к алкоголю и обеспечить эффективную терапию.
Мужской портал https://kakbog.com о стиле, здоровье, карьере и технологиях. Обзоры гаджетов, тренировки, уход, финансы, отношения и путешествия. Практичные советы и честные разборы каждый день.
Современный женский https://storinka.com.ua портал с полезными статьями, рекомендациями и тестами. Тренды, красота, отношения, карьера и вдохновение каждый день. Всё, что помогает чувствовать себя счастливой и уверенной.
https://b2best.at
What i discover troublesome is to find a weblog that may capture me for a minute however your blog is different. Bravo.
modernstylecorner – Sleek and contemporary selections, perfect for style-conscious shoppers.
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Прочесть заключение эксперта – http://www.tsf.edu.pl/zapomniane-metody-fotografii
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Детали по клику – https://www.strucktour.com/?page_id=1290
[url=https://dzialki-beskidy.pl/]vavada casino pl[/url]
Nabycie nieruchomosci w Beskidach to szansa na stworzenie wymarzonego miejsca na wakacje lub staly dom.
Dzieki rozwijajacej sie infrastrukturze i rosnacemu zainteresowaniu turystow, ceny dzialek stopniowo wzrastaja. Region ten przyciaga milosnikow gorskich wedrowek i aktywnego wypoczynku.
#### **2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
Wybor odpowiedniej lokalizacji zalezy od indywidualnych potrzeb i budzetu. Warto sprawdzic profesjonalne strony internetowe, takie jak dzialki-beskidy.pl, ktore prezentuja sprawdzone oferty.
Przed zakupem nalezy dokladnie przeanalizowac dostepnosc mediow i warunki zabudowy. Wiele ofert zawiera szczegolowe informacje o mozliwosciach zagospodarowania terenu, co ulatwia podjecie decyzji.
#### **3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
Nieruchomosc w gorach to nie tylko inwestycja finansowa, ale rowniez szansa na poprawe jakosci zycia. Dzialka w Beskidach moze stac sie zrodlem dochodu, jesli zdecydujemy sie na wynajem turystom.
Dodatkowo, region ten oferuje wiele atrakcji, takich jak szlaki turystyczne i stoki narciarskie. Wlasciciele dzialek moga korzystac z licznych festiwali i wydarzen kulturalnych organizowanych w regionie.
#### **4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
Przed podjeciem decyzji warto skonsultowac sie z prawnikiem i geodeta. Dobrze jest sprawdzic historie nieruchomosci i upewnic sie, ze nie ma zadnych obciazen.
Wazne jest rowniez okreslenie swojego budzetu i planow zwiazanych z zagospodarowaniem terenu. Wiele osob decyduje sie na kredyt, aby sfinansowac zakup wymarzonej dzialki.
—
### **Szablon Spinu**
**1. Dlaczego warto kupic dzialke w Beskidach?**
– Malownicze krajobrazy Beskidow przyciagaja zarowno turystow, jak i przyszlych mieszkancow.
– Rosnaca popularnosc tego regionu przeklada sie na wzrost wartosci nieruchomosci.
**2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
– Profesjonalne agencje nieruchomosci czesto oferuja najlepsze propozycje w regionie.
– Przed zakupem nalezy zweryfikowac dostepnosc mediow i mozliwosci zabudowy.
**3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
– Wlasny kawalek gorskiej przestrzeni pozwala na ucieczke od miejskiego zgielku.
– Coraz wiecej osob docenia walory turystyczne i rekreacyjne Beskidow.
**4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
– Konsultacja z geodeta pomoze uniknac problemow z granicami nieruchomosci.
– Niektore oferty umozliwiaja elastyczne formy platnosci, co moze byc korzystne.
I love your blog. It looks every informative.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Уточнить детали – https://ujjainrudraksha.com/product/rudraksha-golden-mala
trendandbuy – Awesome spot for trendy finds, love browsing the latest styles.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
believeinyourdreams – Truly motivating theme, I love the positivity this site spreads.
purefashionchoice – Clean, stylish fashion selections that are both modern and practical.
https://bsme-at.at
Ко ланта Яй Лонг Бич Ко Ланта: Один из самых популярных пляжей Ко Ланты с развитой инфраструктурой.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Детальнее – https://ujjainrudraksha.com/product/rudraksha-golden-mala
Tips and tools you offer are so helpful to agencies in our community.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Что скрывают от вас? – https://advanceddentalimplants.com.au/what-is-the-recovery-time-for-all-on-4-dental-implants
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Открой скрытое – https://utshonews.com/?p=72
growbeyondlimits – Encouraging platform for personal growth and pushing boundaries every day.
Je suis epate par Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Azur Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Ко ланта Как добраться до Ко Ланты самостоятельно: Подробные инструкции
Мотор 1.6 для иномарки Контрактный двигатель 3UZ-FE на PowerText – это выбор тех, кто ценит надежность и мощность. Мы предлагаем двигатель 3UZ-FE с гарантией качества и быстрой доставкой.
Новостной портал https://pto-kyiv.com.ua для тех, кто ценит фактчекинг и ясность. Картина дня в одном месте: политика, экономика, общество, наука, спорт. Ежедневные дайджесты, обзоры рынков, календари событий и авторские колонки. Читайте, делитесь, обсуждайте.
Всё про технику https://webstore.com.ua и технологии: обзоры гаджетов, тесты, сравнения, ИИ и софт, фото/видео, умный дом, авто-тех, безопасность. Пошаговые гайды, лайфхаки, подбор комплектующих и лучшие приложения. Понятно, актуально, без лишней воды.
Актуальные новости https://thingshistory.com без перегруза: коротко о событиях и глубоко о смыслах. Репортажи с места, интервью, разборы и аналитика. Умные уведомления, ночной режим, офлайн-доступ и виджеты. Доверяйте проверенным данным и оставайтесь на шаг впереди.
Если вы ищете профессиональную помощь в решении семейных проблем, воспользуйтесь услугами [url=https://semeynie-psihologi-onlain.ru/]онлайн консультация психолога по семейным отношениям[/url] для удобного и максимально комфортного общения.
Когда вы решаете обратиться к семейному психологу онлайн может стать важным шагом на пути к гармонии в ваших отношениях. Важно обратить внимание на ряд факторов, когда вы ищете специалиста. Важно учитывать опыт работы психолога, поскольку это напрямую влияет на результат. Специалист с большим стажем может предоставить лучшие методики.
Во-вторых, не забудьте почитать отзывы об этом специалисте. Отзывы помогают понять, насколько психолог эффективен. Интернет полон информации, связанной с мнениями клиентов. Это поможет вам сделать более обоснованный выбор.
Не менее важным является удобный формат встреч. Некоторым людям удобнее общаться через видео-связь, а другим — по телефону. Выберите удобный для вас формат связи, чтобы облегчить процесс. Комфортный формат общения создает благоприятную атмосферу.
Наконец, не забывайте о цене услуг. К стоимости услуг может быть множество вариаций. Определитесь с бюджетом заранее и ищите специалиста в этой ценовой категории. Теперь у вас есть несколько ключевых аспектов для выбора семейного психолога онлайн.
пляжи ко ланты Остров Ко Ланта Таиланд: Райский уголок, который стоит посетить хотя бы раз в жизни.
Здесь
[url=https://businessmentor.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Je suis enthousiasme par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Action Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute soudee.
https://casinoactionbonusfr.com/|
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://golf.wpxblog.jp/%E3%82%B4%E3%83%AB%E3%83%95%E3%81%AF%E5%BF%A0%E5%AE%9F%E3%81%AA%E3%83%95%E3%82%A1%E3%83%B3%E3%81%A8%E5%B0%86%E6%9D%A5%E3%81%AE%E6%88%90%E9%95%B7%E3%81%AE%E9%96%93%E3%81%A7%E6%9D%BF%E6%8C%9F%E3%81%BF
J’adore la vibe de 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, 1xBet Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
1xBet|
brightcollectionhub – Love the name—it perfectly matches the bright, modern selections here.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer Г lire|
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://goonerdaily.com/gd-app
J’adore la vibe de 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, 1xBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En bonus l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fluides.
Lire la suite|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Lucky 31 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Lucky 31|
J’adore le dynamisme de Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis accro a Action Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Action Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Plongez-y|
piastrix личный кабинет
casino arica valor entrada [url=valorslots.com]casino arica valor entrada[/url] .
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller plus loin|
пиастрикс вход
Je suis enthousiasme par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Action Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Action Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement super les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir le site|
בזמן שנישק את צווארה, כתפיה. ביד אחת הוא פתח את גופתה וחזה נשפך החוצה. הוא תפס אותה, אוחז בה, כמו שאני עכשיו השתוקקתי לידיו של חברו. אצבעותיו של איגור זחלו לאט לאורך החלק הפנימי של הירך. כל https://bitbagz.co.il/
globalvaluecorner – Amazing value and variety of products from around the world.
https://lblsp.at
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. De plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, 1xBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Commencer Г explorer|
modernshoppingcorner – Modern design, easy shopping flow, and great product selection.
J’ai un faible pour Action Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Lucky 31 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller sur le site|
1xbet giri? g?ncel [url=1xbet-7.com]1xbet-7.com[/url] .
Je suis accro a Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par moments quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Action Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
https://casinoactionappfr.com/|
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
согласование перепланировки помещений [url=www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru]согласование перепланировки помещений[/url] .
That is really fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to in the hunt for extra of your magnificent post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Мотор на Nissan Almera Двигатель 2AZ-FE в наличии на PowerText – это ваш надежный источник двигателей Toyota. Мы предлагаем двигатель 2AZ-FE по выгодной цене и с быстрой доставкой.
believeandachieve – Positive and motivational content, perfect for personal growth seekers.
sure win malaysia [url=http://surewin-online.com/]http://surewin-online.com/[/url] .
Клиника работает 24/7, принимая пациентов как в стационаре, так и в формате выездных бригад на дом. Мы соединяем медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и поведенческую опоры в единую траекторию: от быстрой стабилизации витальных показателей до настройки вечерних ритуалов (свет, дыхание 4–6, «цифровая тишина»). Внутри команды выстроена координация: нарколог курирует острые окна, терапевт отслеживает соматический фон и лекарственные взаимодействия, психиатр и клинический психолог уменьшают тревожную реактивность и формируют устойчивые навыки «перехвата» импульсов, медсёстры обеспечивают безошибочную технику процедур, куратор синхронизирует всех участников и ведёт «дорожную карту» лечения понятным языком фактов.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologiya/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru
Техника помогает, но не доминирует. Мы используем портативные приборы с мягкой индикацией и низким уровнем шума, чтобы не разрушать формирующуюся «ночную кривую». Контроль в остром окне чаще, вечером — мягче: так сохраняется физиология сна и снижается потребность в дополнительной фармакологии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
casino beep beep [url=https://beepbeepcasino-online.com/]https://beepbeepcasino-online.com/[/url] .
Городская среда Калининграда специфична: морской ветер, сезонные пробки, яркие витрины в вечерние часы. Эти факторы часто усиливают тревожность и мешают засыпанию. Поэтому мы проектируем выезд «мягко»: согласованная парковка, немаркированный вход, короткий маршрут до места процедуры, отсутствие громких звонков и «визуального шума» у порога. Родственникам предоставляем «тихие окна» связи — короткие апдейты в заранее оговорённое время без лишних подробностей. Такой формат не просто комфортнее, он клинически полезен: чем меньше стимулов, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях» и тем стабильнее проходит первая ночь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Коммерческий автотранспорт в лизинг дает возможность предприятиям арендовать автомобили на выгодных условиях. Это особенно важно для начинающих бизнесов, которым требуетсяflexible решение для управления транспортными потребностями без лишних затрат . Компании, выбирающие лизинг, получают доступ к новым моделям автомобилей без необходимости их покупки .
Лизинг коммерческих автомобилей позволяет бизнесу оптимизировать свои затраты, избегая крупных расходов на покупку автомобилей . Это особенно ценно для тех компаний, которые планируют масштабировать свой бизнес, увеличивая количество доставок и перевозок. Кроме того, лизинг позволяет компаниям_focus на своих основных бизнес-процессах, а не тратить время и ресурсы на управление флотом .
Существует несколько типов лизинговых соглашений для коммерческого автотранспорта, каждое из которых имеет свои особенности и условия, требующие тщательного анализа перед выбором . Одним из наиболее распространенных типов лизинга является операционный лизинг, который дает возможность??ям быстро обновлять свой флот, не имея проблем с продажей старых автомобилей. Другой тип лизинга – финансовый лизинг, который позволяет компаниям включать расходы на лизинг в свои налоговые декларации, что может быть выгодно для налогового учета.
При выборе лизинговой компании для коммерческого автотранспорта, компании должны тщательно оценить репутацию и опыт лизинговой компании на рынке . Это особенно важно для тех компаний, которые планируют долгосрочное сотрудничество с лизинговой компанией и хотят быть уверенными в стабильности и надежности партнера . Кроме того, компании должны задавать вопросы о процедурах технического обслуживания и ремонта автомобилей, предлагаемых лизинговой компанией .
лизинг сельхозтехники для ип [url=https://kommercheskij-transport-v-lizing2.ru/lizing-selskohozyajstvennoj-tehniki/]лизинг сельхозтехники для ип[/url].
Ниже — практическая карта первых часов. Она помогает всем участникам понимать логику действий, точки контроля и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один параметр и возвращаемся к оценке в назначённое время — без хаотичных «усилений».
Подробнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/prokapat-ot-alkogolya-na-domu-murmansk
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg014.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Здесь
[url=https://shamil-ahmadullin.ru//]глисты выходят комом[/url]
הילדה למטה היה מכוסה בנוזל לבן. לאחר שזרק את המכנסיים הקצרים שלו על המקום, הבחור אמר במבוכה: – עבר לתוכי בדחיפה אחת חדה ובלתי פוסקת, מילא אותי לגמרי, גרם לי לצרוח מכאב ואושר. שום דבר לא היה רך או spa-bereshit
Запой в Туле: как получить экстренную помощь Запой – это острая проблема‚ требующая немедленной медицинской помощи. Вызов нарколога на дом – оптимальный способ получить необходимую поддержку. Специалист проведет детоксикацию‚ гарантируя безопасное восстановление. Лечение алкоголизма включает комплексную поддержку‚ включая физическую и психологическую помощь. Важность вызова нарколога состоит в предоставлении полного спектра наркологических услуг‚ включая лечение запойного состояния. Экстренная помощь позволяет избежать осложнений и начать реабилитацию зависимого. После прерывания запоя важно не прекращать лечение алкоголизма‚ чтобы избежать рецидивов. Восстановление после запоя требует поддержки‚ поэтому нарколог на дом поможет не только в физическом плане‚ но и окажет психологическую помощь. Берегите своё здоровье и обращайтесь за профессиональной помощью!
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в Симферополе[/url]
Нужна лестница? изготовление лестниц под ключ в Москве и области: замер, проектирование, производство, отделка и монтаж. Лестницы на металлокаркасе. Индивидуальные решения для дома и бизнеса.
Поиск работы https://employmentcenter.com.ru по актуальным вакансиям городов России, СНГ, стран ЕАЭС: обновления предложений работы ежедневно, рассылка свежих объявлений вакансий на E-mail, умные поисковые фильтры и уведомления в Telegram, Одноклассники, ВКонтакте. Помогаем найти работу мечты без лишних звонков и спама.
Нужно продвижение? Продвижение современных сайтов в ТОП 3 выдачи Яндекса и Google : аудит, семантика, техоптимизация, контент, ссылки, рост трафика и лидов. Прозрачные KPI и отчёты, реальные сроки, измеримый результат.
everydayessentials – Convenient site to find daily essentials quickly and easily.
freshcollectionhub – Fresh products, great presentation, and a fun browsing experience.
Первые два часа после приезда врача — ключевое окно. Мы фиксируем витальные показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?), проводим экспресс-оценку глюкозы, по показаниям — электролитов (Na?/K?), оцениваем дыхательный паттерн и уровень ориентировки. Далее запускается титрованная инфузия через инфузомат с контролем каждые 15–20 минут. Параллельно настраиваются «вечерние опоры»: светогигиена, дыхательные циклы, «тихие окна» связи. В конце визита пациент и близкие получают простую памятку с «зелёными зонами» и кратким планом на 72 часа — когда пить воду, как выбирать тёплую пищу малыми порциями, при каких признаках выходить на связь немедленно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Ko Lanta Активный отдых на Ко Ланта: Приключения на суше и на море – для любителей активного образа жизни. Ко Ланта предлагает дайвинг, снорклинг, каякинг, виндсерфинг,
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk015.ru
вывод из запоя
https://www.pitpass.com/81551/Casino-Roulettino-Avis-A-Comprehensive-Review-for-Motorsport-Fans-in-the-UK
Our community leaders need to read this, and look at developing some of your recommendations.
Ниже — «скелет» визита. На месте врач адаптирует содержание под возраст, соматику, текущие лекарства и проявления абстиненции. Главная идея — быстро получить цифры, аккуратно запустить инфузию и заранее зафиксировать ориентиры, чтобы семья не импровизировала в «трудный час».
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в ставрополе[/url]
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement genial les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der au site|
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в калининграде[/url]
Универсальной «сильной капельницы» не существует. Мы подбираем состав по ведущим симптомам, переносимости и данным экспресс-диагностики. Задача — вернуть дневную ясность и физиологичный ночной сон без переседации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce le lien communautaire.
Essayer ceci|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les transactions en crypto fiables, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Plongez-y|
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Azur Casino offre une aventure memorable. En plus le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir la page|
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/[/url]
Карта делает решения прозрачными: если критерий не достигнут, меняется ровно один параметр с назначением новой точки контроля. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и уменьшает общую фармаконагрузку без компромиссов по безопасности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk15.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в петрозаводске[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://xn--90aqdckbedq1e2bc7b.xn--p1ai/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
dailydealsplace – Always updated with great bargains, love checking in daily.
В городском ритме Ставрополя дорога сама по себе может усугублять симптомы: плотный трафик, резкие звуки, длинные коридоры ожидания. Поэтому «СтаврВита» разворачивает секторные выезды: немаркированный транспорт, гражданская одежда специалистов, согласованная парковка и подъезд, доставка расходников отдельно от врача при необходимости — чтобы на месте сразу переходить к диагностике и запуску инфузии. Переписка ведётся нейтральными формулировками, уведомления «беззвучные», документы без стигматизирующих слов. По желанию всё общение идёт через доверенное лицо: оно получает короткие апдейты в согласованные «окна», не перегружаясь клиническими деталями.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена ставрополь[/url]
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Ouvrir maintenant|
findnewhorizons – A wonderful reminder to explore, grow, and discover new opportunities.
https://b2best.at
chemical-mix.com работает у кого ??? всё походу накрылся магаз :::??? https://beteiligung.stadtlindau.de/profile/%D0%9A%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BF%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%20%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD/ так что бро не стоит беспокоиться по поводу порядочности этого магазина, они отправляют достаточно быстро и конспирация хорошая и качество на высоте!)))
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par moments plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer davantage|
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, 1xBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A souligner la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fluides.
Explorer plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A noter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.casinoactionfr.com|
Je suis bluffe par Lucky 31 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En complement le design est style et moderne, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire la suite|
trendandbuy – Trendy items at good prices, always up to date with new arrivals.
Ko Lanta Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта: Встреча с дикой природой – новый взгляд. Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта, расположенный на южной оконечности Ко Ланта Яй, – это сокровище природы, предлагающее возможность погрузиться в тропические леса и прибрежные ландшафты. Здесь обитают обезьяны, птицы, рептилии и бабочки. Главной достопримечательностью является маяк на скалистом мысе Kip Nai, с которого открываются панорамные виды на Андаманское море.
Je suis fascine par Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller voir|
https://b2best.at
https://nfldraftdiamonds.com/2025/11/roulettino-login/
valor casino app download free [url=https://valorslots.com]valor casino app download free[/url] .
много нас, а грам один. https://imageevent.com/anogitokumab/neatk всегда ровно все было и есть. так что я
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru
I have to disagree with most of the comments here, but maybe I’m just a contrarian.
budgetfriendlyhub – Great variety of affordable options without sacrificing style or quality.
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в Москве[/url]
birxbet [url=http://www.1xbet-7.com]http://www.1xbet-7.com[/url] .
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в калининграде[/url]
learncreategrow – Inspiring content that encourages learning, creating, and personal growth.
перепланировка помещений [url=https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/]перепланировка помещений[/url] .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
Карта делает решения прозрачными: если критерий не достигнут, меняется ровно один параметр с назначением новой точки контроля. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и уменьшает общую фармаконагрузку без компромиссов по безопасности.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk/
surewin apk [url=https://surewin-online.com/]https://surewin-online.com/[/url] .
peep peep casino [url=http://beepbeepcasino-online.com]http://beepbeepcasino-online.com[/url] .
Услуги наркологов в Туле становится все более популярной‚ особенно когда речь идет о борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Тула оказывает услуги для людей‚ нуждающихся в экстренной помощи. В рамках наркологической клиники проводится детоксикация от наркотиков и алкоголя‚ что является первым шагом к выздоровлению. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает в себя снятие абстинентного синдрома‚ что способствует облегчению состояния пациента. Круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечит необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в любое время суток. Визит нарколога поможет составить индивидуальную программу лечения алкоголизма, учитывающую все особенности пациента. Реабилитация зависимых включает психологическую поддержку для зависимых‚ что способствует восстановлению психологического состояния и адаптации к жизни без алкоголя. Не стоит забывать о поддержке родственников зависимых; Анонимное лечение зависимости даст возможность пациенту обращаться за помощью без страха осуждения. Вызывая нарколога на дом‚ вы делаете важный шаг к новой жизни.
Здесь
[url=https://xn--90aqdckbedq1e2bc7b.xn--p1ai/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Azur Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement top les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
AccГ©der au site|
I just sent this post to a bunch of my friends as I agree with most of what you’re saying here and the way you’ve presented it is awesome.
сегодня оплатил заказ..буду ждать доставки..протестирую.сообщу о качестве продукта? https://form.jotform.com/253103403997053 все ровно ваще чисто жду проверив качество отпишу
Профессиональный агент по недвижимости спб: оценка, подготовка, маркетинг, показы, торг и юрсопровождение до сделки. Фото/видео, 3D-тур, быстрый выход на покупателя.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
Играешь на пианино? обучение игры на фортепиано Поможем освоить ноты, ритм, технику и красивое звучание. Индивидуальные уроки, гибкий график, онлайн-формат и авторские методики. Реальный прогресс с первого месяца.
Школа фортепиано обучение игры на фортепиано для начинающих и продвинутых: база, джазовые гармонии, разбор песен, импровизация. Удобные форматы, домашние задания с разбором, поддержка преподавателя и быстрые результаты.
https://lblsp.at
classystyleoutlet – Love the elegant yet accessible fashion choices available here.
Брал хоть и один раз, но все было отлично! Жду второго заказа) https://anyflip.com/homepage/xswbu на мыло отвечаем только по существу, много не по делу пишут, ася или скайп быстрей
growtogetherstrong – Positive and motivating, perfect for teamwork and community growth.
exploreopportunityzone – Excellent motivational content, helps me think bigger and act smarter.
Здесь
[url=https://formix.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
price of provigil in india nuvigil provigil cost comparison [url=https://govtopvip.com/provigil-coupons/]goodrx provigil[/url] adderall xr vs provigil xyrem provigil
Работал с данным магазином Совсем давно, и что то все руки не доходили оставить отзыв о магаз:D https://kemono.im/aubyceiggyhi/kashira-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Качественный магаз!
https://b2best.at
buildyourownfuture – Great motivational site, helps focus on goals and planning ahead.
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Выяснить больше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в Москве[/url]
задать вопрос юристу онлайн бесплатно без телефона и регистрации Юридическая консультация: бесплатный или платный вариант? Разобраться, какой вариант консультации подходит именно вам, — это важный шаг. Бесплатная консультация — это отличный способ получить общее представление о проблеме и оценить перспективы дела. Если же вам требуется более глубокий анализ и индивидуальный подход, платная консультация станет разумным вложением в защиту ваших прав и интересов.
classystylemarket – Stylish products with great prices, love the classy layout of this site.
https://zekond.com/read-blog/286921
Отличный Магаз, Все четко!!! https://say.la/read-blog/136350 о чем это ты? о каких зачетах ты тут поешь? ты дату своей регистрации видел зачетник ЕПТ!
Экстренный вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «ВоронежВита» мы действуем по чётким правилам: от телефонного триажа и тихого выезда бригады до адресной детоксикации и вечерних контрольных включений. Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить тремор и тошноту, выровнять сердечный ритм и вернуть физиологичный сон уже в первые ночи. Мы выбираем минимально достаточные вмешательства, чтобы днём сохранялась ясность и не возникало желания «самостоятельно усилить» схему. Конфиденциальность встроена в каждый шаг: гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Ko Lanta Пляжи Ко Ланта: от укромных бухт до оживленных побережий. Ко Ланта славится разнообразием пляжей. От укромных бухт до оживленных побережий с инфраструктурой, здесь есть пляж для каждого. Самые популярные пляжи находятся на западном побережье: Лонг Бич, Клонг Дао, Клонг Кхонг и Клонг Нин. Лонг Бич — самый длинный пляж с отелями, барами и водными развлечениями. Клонг Дао — спокойный пляж для семейного отдыха. Клонг Кхонг — популярное место среди бэкпэкеров, а Клонг Нин — самый южный пляж с живописными закатами. Восточное побережье предлагает уединенные пляжи, такие как Ба Кан Тианг и Нуй Бич, для тех, кто ценит тишину. На многих пляжах Ко Ланта есть водные виды спорта: каякинг, виндсерфинг и паддлбординг. Аренда лодки — отличный способ исследовать острова и бухты. Вечером на пляжах устраиваются фейерверки и вечеринки.
https://www.pitpass.com/81551/Casino-Roulettino-Avis-A-Comprehensive-Review-for-Motorsport-Fans-in-the-UK
https://md.kif.rocks/s/tCznrXIof
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga017.ru
лечение запоя
задать вопрос юристу онлайн бесплатно Задать вопрос юристу и получить квалифицированный ответ: Задать вопрос юристу онлайн – это не только удобно, но и эффективно. Многие платформы предлагают возможность получить ответ на свой вопрос в течение нескольких минут или часов. Юристы, специализирующиеся в различных областях права, готовы предоставить профессиональную консультацию и помочь разобраться в сложных правовых вопросах.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk025.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
консультация юриста онлайн Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном ритме жизни, когда скорость и доступность информации ценятся превыше всего, возможность получить квалифицированную юридическую консультацию онлайн бесплатно становится неоценимым преимуществом. Это шанс оперативно оценить ситуацию, понять свои права и обязанности, а также наметить дальнейшие шаги без каких-либо финансовых вложений.
Инфузионная терапия от алкогольной зависимости – эффективное решение для лечения алкогольной зависимости. Она обеспечивает быстрое вливание жидкости‚ что приводит к детоксикации тела и восстановлению здоровья. В клиниках по лечению алкогольной зависимости‚ таких как narkolog-tula027.ru‚ квалифицированные специалисты оказывают медицинскую помощь‚ включая уколы от алкоголизма. Терапия включает также капельницы‚ но и реабилитацию‚ поддержку при алкоголизме‚ что способствует пациентам возвращаться к нормальной жизни.
Ко ланта Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта: Наедине с дикой природой – переосмысление опыта. Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта, расположенный на южной оконечности Ко Ланта Яй, — это природный заповедник с тропическим лесом и прибрежными зонами. Тут обитают обезьяны, разные виды птиц, рептилии и бабочки. Главная достопримечательность – маяк на мысе Kip Nai, с которого открываются панорамные виды на Андаманское море и острова. Пешеходные тропы, проходящие через джунгли, дают возможность исследовать парк. Одна из популярных ведет к пляжам Tai Note Beach и Ao Chak Beach, где можно отдохнуть и искупаться. Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта — это не только природа, но и история. На его территории расположен древний некрополь морских цыган, народа, который, на протяжении веков жил в гармонии с природой.
часть покупателей устраивает, продавцы тоже не жалуется. В чем проблема? нет терпения – идите в другие шопы. https://www.brownbook.net/business/54444799/сан-С…РѕСЃРµ-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Все легально и проверено, есть NMR. Плохого ни чего не случиться. Скорей всего приняли потому что были паленые….
https://social.sikatpinoy.net/blogs/19944/Code-inscription-joueur-Melbet-Offre-200
creativegiftoutlet – Amazing gift ideas, really unique and thoughtful selections available here.
dreamdiscovercreate – Truly inspiring space that encourages creativity and following your dreams.
Ko Lanta Жизнь морских цыган (Chao Leh) на Ко Ланта: Сохраняя традиции предков. Ко Ланта – это не просто туристический остров, это также дом для морских цыган (Chao Leh), коренных жителей, которые на протяжении многих веков жили в гармонии с морем и сохраняли свои уникальные обычаи и культуру. Морские цыгане, также известные как “люди моря”, живут в небольших поселениях на восточном побережье Ко Ланта. Они традиционно занимаются рыболовством, сбором даров моря и строительством лодок. Их уникальный образ жизни неразрывно связан с морем, которое является для них источником существования и духовной связи. Морские цыгане придерживаются своей собственной религии, основанной на вере в духов природы и предков. Они проводят сложные церемонии и фестивали, чтобы просить у духов защиты и благословения. В последние годы культура и образ жизни морских цыган подвергаются влиянию современной цивилизации и туризма. Однако они прилагают все усилия для сохранения своих традиций и передачи их молодому поколению. Посещение поселений морских цыган предоставляет уникальную возможность познакомиться с их культурой и увидеть их традиционные ремесла.
Вывод из запоя — это управляемый медицинский процесс, в котором важны скорость запуска, точность вмешательств и тишина вокруг пациента. В наркологической клинике «СтаврВита» мы соединяем капельницы с объективным мониторингом и бережной организацией пространства: приглушённый свет, понятные инструкции без жаргона, «тихие окна» для связи и пошаговый план на первые трое суток. Наша задача — не «перебить» симптомы, а последовательно вернуть предсказуемость: ровный пульс, уменьшающийся тремор, переносимость воды и тёплой пищи малыми порциями, физиологичный сон без тяжёлой седации. Работаем круглосуточно — выездные бригады, амбулаторные слоты без очередей и стационарный блок с ночным постом объединены общей картой наблюдения, поэтому пациент не «начинает историю заново», когда формат меняется.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Clarte Nexive se differencie comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies de pointe, qui met a profit la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse hors de portee des traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les perspectives de gain.
Не поняла? https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/69745 такая же хрень пропал продаван ((( уже неделю обещает выслать трек дать и нет не чего *((((
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
юрист бесплатная консультация онлайн Юридическая консультация: бесплатный или платный вариант? Выбор между бесплатной и платной юридической консультацией зависит от сложности вашего вопроса и объема необходимой помощи. Бесплатная консультация подходит для получения общей информации и оценки перспектив дела, в то время как платная консультация предоставляет более глубокий анализ и индивидуальный подход к вашей ситуации.
J’adore l’energie de Azur Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, en revanche des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
Essayer|
shopforvalue – Affordable products without compromising quality, makes shopping super satisfying.
Купить ИЖС в Нижегородской области. Продаю дачу за 450 000 рублей. Ищете уютное место для летнего отдыха по доступной цене? Предлагаю дачу в живописном районе за 450 000 рублей. Небольшой, но функциональный домик, участок с плодовыми деревьями и кустарниками – все необходимое для комфортного пребывания на природе. Отличное место для отдыха от городской суеты и восстановления сил. Звоните прямо сейчас, и я организую для вас просмотр!
Да тоже заказал на след день трек получил очень оперативно респект чувакам https://rant.li/abeoudmiagu/lomonosovskii-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki длица окола часа очень даже не плохо
Купить дом в Нижегородской области Помогу купить участок в Нижегородской области Нижегородская область, с ее бескрайними полями, живописными лесами и богатым культурным наследием, манит возможностью обустроить собственный уголок, вдали от городской суеты. Мечтаете о просторном участке для строительства дома, дачи или фермерского хозяйства? Я, как опытный эксперт в сфере недвижимости Нижегородской области, помогу вам реализовать эту мечту. Тщательный подбор участков, соответствующих вашим запросам по местоположению, площади, коммуникациям и бюджету. Полное юридическое сопровождение сделки, от проверки документов до оформления прав собственности. Сделайте первый шаг к жизни на своей земле!
Купить дом в Нижегородской области Помогу продать земельный участок. Продажа земельного участка – это ответственный процесс, в котором важно учесть множество нюансов. Я предлагаю профессиональную помощь в продаже вашего участка в Нижегородской области. Благодаря эффективной маркетинговой стратегии и знанию рыночных тенденций, я помогу вам найти покупателя в кратчайшие сроки и получить максимально выгодную цену. Полное юридическое сопровождение сделки гарантирует защиту ваших интересов.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour completer le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement interessant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Azur Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Здесь
[url=https://www.berito.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Помогу продать земельный участок. Помогу продать земельный участок. Продажа земельного участка – это ответственный процесс, в котором важно учесть множество нюансов. Я предлагаю профессиональную помощь в продаже вашего участка в Нижегородской области. Благодаря эффективной маркетинговой стратегии и знанию рыночных тенденций, я помогу вам найти покупателя в кратчайшие сроки и получить максимально выгодную цену. Полное юридическое сопровождение сделки гарантирует защиту ваших интересов.
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
J’adore l’energie de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par moments quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Action Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute soudee.
https://casinoactionbonusfr.com/|
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A mettre en avant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
http://www.1xbetcasino365fr.com|
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar/
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
Lucky 31|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement super les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer|
нервные клетки https://bio.site/zidagygifu чувствую у меня будет то же самое, трек получил но он нихуя не бьется, а что ответил то? я оплатил 3 февраля и трек походу тоже левый ТС обьясни и мне ситуацию
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus constants.
Voir maintenant|
Информационные ресурсы играют решающую роль в жизни общества.
Они помогают людям быстро находить актуальные данные.
Благодаря современным источникам информации общество остается в курсе событий.
Информационные каналы формируют оценку происходящего.
Необходимо учитывать, что качество информации напрямую влияет на мышление аудитории.
Многие люди предпочитают те источники, которые дают надежные материалы.
СМИ также помогают создавать информационное пространство между различными группами населения.
В итоге, СМИ остаются неотъемлемой частью информационной среды.
https://women.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=2618&p=13711#p13711
Je suis fascine par Lucky 31 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, 1xBet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller sur le site web|
growbeyondlimits – Encouraging platform that inspires personal growth and pushing boundaries every day.
findamazingoffers – Excellent deals and diverse products, makes shopping super satisfying.
Je ne me lasse pas de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A mentionner le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis bluffe par 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, 1xBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer la page|
Je suis enthousiasme par Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Action Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis bluffe par Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, rarement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
Explorer davantage|
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk026.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis sous le charme de 1xBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais encore des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Action Casino assure un fun constant. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un point cle les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir la page|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Azur Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En fin de compte, Azur Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En complement le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un atout le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
http://www.azurcasinobonusfr.com|
heaps of wins casino bonus codes [url=heapsofwins-online.com]heaps of wins casino bonus codes[/url] .
курсы seo [url=kursy-seo-12.ru]курсы seo[/url] .
goliath casino review [url=https://goliath-casino.com/]goliath-casino.com[/url] .
icebet casino promo code [url=https://icebet-online.com/]https://icebet-online.com/[/url] .
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est clair et efficace, toutefois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En fin de compte, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
На 7k casino официальный сайт всё устроено удобно. Приятно удивила скорость обработки заявок на вывод. Надёжная площадка: 7к казино сайт
Услуга нарколога на дому, ценная помощь для людей‚ страдающих от зависимости от наркотиков. Лечение наркомании требует комплексного подхода‚ и домашняя помощь обеспечивает комфорт и анонимность. Вызов специалиста позволяет обратиться за медицинской помощью и приступить к программе детоксикации‚ не покидая своего жилья; Медицинское вмешательство и психотерапия помогают пациентам преодолеть зависимость‚ а семейная поддержка играет ключевую роль в восстановлении после зависимости. Конфиденциальное лечение и меры по предотвращению наркомании также являются значимыми аспектами. Посетив narkolog-tula028.ru‚ вы сможете получить профессиональную помощь и поддержку.
Процветания и успехов вашему магазину!! https://wanderlog.com/view/rrmtfzhbvv/пелопоннес-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ И еще сушняки ужасные. Сейчас вот утром проснулся, и до сих пор
юристы онлайн консультация бесплатно по телефону Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном мире, где правовые вопросы возникают постоянно, возможность получить оперативную и квалифицированную юридическую помощь онлайн становится необходимостью. Бесплатная онлайн консультация юриста – это шанс быстро оценить ситуацию, понять перспективы дела и получить рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям. Это особенно ценно, когда время не терпит, и требуется срочный совет.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar
apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2
en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a
partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria
ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones
de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas
android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de
futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas
deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de
apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas
reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas
android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para
hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para
llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps
de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas
argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas
argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas
athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas
barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas
barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas
bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas
bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas
caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de
barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas
campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa
america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland
garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de
caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos
hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta
barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas
celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas
celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas
chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real
madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas
combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta
semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap
asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas
copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa
de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas
copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las
vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de
caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de
caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de
europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol
para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas
de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de
galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos
deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la
champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la
europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas
de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de
mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas
de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del
dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de
madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas
casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas
estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas
deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar
dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas
gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas
impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas
deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas
deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas
deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos
de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y
casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la
liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas
diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas
en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo
pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos
deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la
nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas
en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol
en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo
nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas
equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa
alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports
colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas
esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas
eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub
21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa
league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas
f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas
fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas
final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas
final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final
uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia
argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions
league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana
colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas
ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas
girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona
gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador
eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas
gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para
hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis
puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis
y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap
como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey
sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos
virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas
la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league
of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de
campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana
liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas
mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma
ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples
futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial
de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de
rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial
rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas
nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas
online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol
españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online
gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online
nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online
opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para
el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el
partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para
futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar
dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas
para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas
para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy
europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para
la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para
ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido
champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs
chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas
por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para
ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas
psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el
mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas
quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la
liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico
de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real
madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real
madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid
liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real
madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real
madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real
madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real
madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada
tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda
division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras
futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas
seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras
para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises
bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla
leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa
españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis
femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc
como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas
under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor
en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal
vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas
virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william
hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas
y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina
uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico
barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid
vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real
madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas
apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca
bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca
vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona
apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol
apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs
sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas
apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas
chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid
apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas
baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis
apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa
de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa
de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas
nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos
registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas
gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de
apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas
de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora
de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas
de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera
de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos
juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa
apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas
argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa
de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de
apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas
deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas
europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas
futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de
apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de
apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa
de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas
eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5
euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia
españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas
de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas
de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de
apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono
de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas
con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas
copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de
apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas
en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de
apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos
de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas
de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de
apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas
de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol
españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas
legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas
de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de
apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de
apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de
apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de
apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas
online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas
de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online
en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de
apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas
online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas
online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono
sin deposito|
юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном ритме жизни, когда скорость и доступность информации ценятся превыше всего, возможность получить квалифицированную юридическую консультацию онлайн бесплатно становится неоценимым преимуществом. Это шанс оперативно оценить ситуацию, понять свои права и обязанности, а также наметить дальнейшие шаги без каких-либо финансовых вложений.
юридическая консультация онлайн бесплатно без регистрации и телефона Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Многие юридические платформы предлагают бесплатные онлайн консультации для привлечения клиентов и демонстрации своей компетенции. Это отличная возможность оценить квалификацию юриста, задать общие вопросы и понять, подходит ли он вам для дальнейшего сотрудничества. Не стоит упускать шанс получить бесплатную консультацию, чтобы сориентироваться в своей правовой ситуации.
Your Path Hub – Came across something encouraging that motivated me to act today.
In it something is. Many thanks for the information, now I will know.
——
https://the.hosting/en/help/best-e-book-reader-apps-for-android
Pretty component to content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your weblog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment or even I achievement you get right of entry to constantly fast.
https://www.lnrprecision.com/
Наркологическая клиника «РеМед Карелия» — это круглосуточная медицинская помощь, построенная на принципе клинической точности: каждая процедура имеет цель, проверяемые маркеры и назначенное окно переоценки. Мы используем современные методы детоксикации и постабстинентной стабилизации, не перегружая терапию «на всякий случай» и не полагаясь на универсальные «сильные капельницы». Вместо этого — модульные схемы, корректировка одного параметра за раз и обязательная оценка результата. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает лечение предсказуемым для пациента и его семьи. Анонимность встроена в процессы: немаркированные входы, гражданская форма персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к карте наблюдения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в петрозаводске[/url]
Trend Spot Hub – Lots of variety, found some interesting items this morning.
findamazingoffers – Excellent deals and diverse products, makes shopping super satisfying.
консультация юриста онлайн бесплатно по телефону Консультация юриста онлайн Забудьте о долгих ожиданиях в приемной юриста, утомительных поездках и строгом графике. Онлайн консультация открывает двери к миру юридической экспертизы прямо из комфорта вашего дома или офиса. Это современный и эффективный способ решения юридических вопросов, который экономит ваше время и энергию.
Если на предвызовном созвоне звучат «красные флаги» (неукротимая рвота, выраженная дезориентация, «скачущий» ритм, одышка), мы сразу резервируем палату усиленного наблюдения и подключаем расширенный мониторинг. При низком риске старт возможен амбулаторно или на дому с бесшовным переводом в стационар при необходимости — без очередей и «говорящих» вывесок. Во всех сценариях анонимность — не «опция», а стандарт по умолчанию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Ищете, где купить права категории Б быстро и надежно? Мы предлагаем полный комплекс услуг по оформлению водительских удостоверений с гарантией качества и конфиденциальности. Профессиональная помощь, доступные цены и оперативное оформление документов без лишних хлопот. Получите свои водительские права легально и в кратчайшие сроки.
Вся динамика заносится в единую карту наблюдения, доступ к которой разграничен по ролям. При переходе к амбулаторной точке или стационару не происходит «перезапуска истории»: новые назначения учитывают всё, что сделано на старте.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в Москве[/url]
займы онлайн
займы в кз
онлайн консультация юриста Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном мире, где правовые вопросы возникают постоянно, возможность получить оперативную и квалифицированную юридическую помощь онлайн становится необходимостью. Бесплатная онлайн консультация юриста – это шанс быстро оценить ситуацию, понять перспективы дела и получить рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям. Это особенно ценно, когда время не терпит, и требуется срочный совет.
займы на карту онлайн
Best Deals Hub – Always find the latest discounts, refreshed every day.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fluides.
Approfondir|
Последовательность шагов в «РеаМед Центр» выстроена так, чтобы уменьшить неопределённость и сделать процесс безопасным и прозрачным. Сначала врач проводит первичное интервью, уточняет длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни сердца, печени и почек, проверяет переносимость лекарств и оценивает эмоциональное состояние. Далее — базовая диагностика и обсуждение целей: насколько важна длительность защиты, готов ли пациент к регулярным визитам, есть ли опыт срывов на стресс и как устроена поддержка дома. На этой основе подбирается метод и даются подробные инструкции по подготовке, включая период воздержания, режим сна и напитки, которые лучше исключить в первые дни. После процедуры пациент остаётся в зоне внимания: мы созваниваемся в оговорённые сроки, уточняем самочувствие, корректируем рекомендации и при необходимости добавляем короткие психообучающие встречи. Эта схема снижает тревогу, возвращает чувство контроля и формирует реалистичные ожидания на ближайший месяц.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-shchelkovo3.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-ryadom-shhyolkovo/
Shop Deals Online – Came across something practical that made selecting items easier.
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller sur le site|
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar021.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-murmansk/
Официальный сайт 7k казино реально продуманный. Удобно играть и с телефона, и с компьютера. Вывод работает стабильно, деньги пришли в тот же день: 7к казино вход
Je suis captive par Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Action Casino vaut une visite excitante. A mentionner le site est rapide et style, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
Avancer|
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в калининграде[/url]
деньги в займ
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, 1xBet Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Регистрация в Мелбет для новичков пошаговая инструкция
Как пройти регистрацию на Мелбет для новичков легко и быстро пошаговое руководство
Чтобы начать пользоваться платформой, откройте официальный сайт и найдите кнопку для создания аккаунта. Сначала вам предложат заполнить базовую информацию – укажите номер телефона и электронную почту. Проверьте правильность указанных данных, поскольку на них придет сообщение с подтверждением.
После этого вам нужно придумать надежный пароль. Учтите, что он должен содержать как минимум восемь символов, включая заглавные буквы, цифры и специальные знаки. Убедитесь, что пароль уникален, чтобы защитить свой аккаунт от возможных угроз.
Когда все поля заполнены, нажмите на кнопку, чтобы подтвердить регистрацию. Ожидайте получения кода на указанный номер телефона. Введите этот код в специальное поле на сайте. Если код введен правильно, вы перейдете на страницу своего нового аккаунта, где сможете внести дополнительные данные для дальнейшего использования.
Обзор платформы Мелбет
Данная букмекерская площадка предлагает широкий выбор спортивных событий, включая футбол, теннис и киберспорт, что удовлетворит любые предпочтения игроков. Обратите внимание на богатую линию ставок, где представлены как популярные, так и менее известные турниры. Важно отметить, что коэффициенты на этой платформе зачастую выше средних по рынку, что позволяет пользователям максимизировать свои выигрыши.
Интерфейс ресурса отличается простотой и удобством использования. Навигация по сайту интуитивно понятна, что делает процесс поиска событий и оформления ставок максимально комфортным. Кроме того, доступна мобильная версия, позволяющая ставить в любое время и месте.
Платформа также предоставляет различные бонусные предложения, включая приветственные акции для новых клиентов и программы лояльности для постоянных пользователей. Обратите внимание на условия получения бонусов, которые могут существенно увеличить ваш стартовый капитал.
Что касается поддержки, сервис предлагает мультиканальные способы связи – чат, электронную почту и телефон. Оперативность и качество работы службы поддержки помогают быстро решать возникающие вопросы.
Безопасность личных данных является приоритетом, что подтверждается современными протоколами шифрования. Пользователи могут быть уверены, что их информация находится под надежной защитой.
Что такое Мелбет?
Этот букмекер предоставляет разнообразные возможности для ставок на спортивные события и казино-игры. Отличается широким выбором дисциплин, включая футбол, баскетбол, хоккей и многие другие. Платформа позволяет делать ставки в режиме реального времени, что значительно увеличивает азарт и интерактивность.
Одной из ключевых особенностей является простота интерфейса, что делает его доступным для каждого. Регистрация на сайте требует минимум времени и усилий. Пользователи могут воспользоваться мобильной версией, комфортабельной для ставок в пути.
Кроме традиционных спортивных событий, ресурс предлагает альтернативные развлечения, такие как виртуальный спорт и киберспорт. Это помогает разнообразить досуг и найти что-то по вкусу.
Служба поддержки работает круглосуточно, готовая помочь с любыми вопросами. Безопасность данных клиентов обеспечивается современными технологиями шифрования. Большое внимание уделено акциями и бонусами, что делает использование услуг этого букмекера выгодным.
Основные преимущества регистрации
Преимущества выполнения процедуры включают в себя доступ к различным бонусам и акциям, что делает ставку более выгодной. Пользователи могут получить приветственные предложения сразу после создания учетной записи, что значительно увеличивает шансы на успех.
– Участие в программах лояльности. Регистрация дает возможность накапливать баллы и получать эксклюзивные предложения.
– Использование аналитических инструментов. Новый аккаунт позволяет применять доступные функции для анализа ставок и прогнозирования результатов.
– Безопасность транзакций. Созданный профиль обеспечивает защиту личных данных и финансовых операций.
– Доступ к мобильным приложениям. Создание аккаунта позволяет пользователю устанавливать приложения для удобного использования сервисов на мобильных устройствах.
Эти возможности делают участие в ставках более привлекательным и уверенным. Начав с регистрации, вы открываете двери к множеству вариантов и преимуществ.
Подготовка к регистрации
Перед началом следует убедиться в наличии необходимых данных: актуального номера мобильного телефона и адреса электронной почты. Эти контакты используются для подтверждения учетной записи и восстановлении доступа при необходимости.
Важно проверить, загружено ли приложение или доступен ли сайт на удобном устройстве. Оцените скорость интернета, чтобы избежать проблем с загрузкой страниц.
Подготовьте надёжный пароль. Он должен содержать хотя бы восемь символов, включать буквы разных регистра, цифры и специальные знаки. Это позволит защитить аккаунт.
Рекомендуется ознакомиться с правилами пользования сервисом. Это поможет избежать недоразумений и повысит уровень уверенности в процессе создания аккаунта.
Заключительный шаг – определиться с бонусами и акциями, которые могут быть доступны при активации. Иногда может понадобиться ввод промокода, который необходимо заранее узнать.
https://borneo383.org/melbet-2025-obzor-teobit/
dreamfashionfinds – Stylish and trendy fashion finds that make everyday shopping fun.
Je suis epate par Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Je suis sous le charme de 1xBet Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, cree une communaute vibrante.
https://1xbetcasino777fr.com/|
Trend Picks Spot – Always something fresh to see, new trends update often.
юридическая консультация онлайн Задать вопрос юристу и получить квалифицированный ответ: Возможность задать вопрос юристу – это первый шаг к решению правовой проблемы. Независимо от сложности вопроса, получение профессионального мнения поможет сориентироваться в ситуации и принять взвешенное решение. Многие онлайн-платформы предлагают бесплатные сервисы вопросов-ответов, где юристы предоставляют консультации в режиме реального времени. Не стоит пренебрегать этой возможностью, особенно если вы столкнулись с юридическими трудностями впервые. Помните, что своевременная консультация может предотвратить серьезные последствия в будущем.
Je suis totalement conquis par Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Action Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Финальный этап — выработка устойчивых привычек и отношений с окружением. Вместе с пациентом мы формируем план трезвых выходных, обсуждаем правила отказа, которые не провоцируют конфликты, и настраиваем микропаузы в течение дня, чтобы стресс не копился «к вечеру». Контрольные встречи короткие и прагматичные: оцениваем сон, уровень энергии, тягу, коммуникацию с близкими. Если предстоит сложный период — отпуск, переезд, цейтнот — заранее усиливаем опоры, чтобы пройти его без срывов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-vidnoe4.ru/]клиника лечение алкоголизма цены[/url]
Этот документ охватывает важные аспекты медицинской науки, сосредотачиваясь на ключевых вопросах, касающихся здоровья населения. Мы рассматриваем свежие исследования, клинические рекомендации и лучшие практики, которые помогут улучшить качество лечения и профилактики заболеваний. Читатели получат возможность углубиться в различные медицинские дисциплины.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в Москве[/url]
На платформе 7k casino всё чётко — быстрое пополнение, удобная навигация. Вывел деньги через пару часов после заявки. Проблем не возникло ни разу за всё время: 7к казино
News Testing World – Har article engaging tone ke sath likha hota hai.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Action Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir la page d’accueil|
кухни спб [url=http://kuhni-spb-10.ru/]кухни спб[/url] .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk027.ru
вывод из запоя цена
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Детальнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Ниже — «скелет» визита. На месте врач адаптирует содержание под возраст, соматику, текущие лекарства и проявления абстиненции. Главная идея — быстро получить цифры, аккуратно запустить инфузию и заранее зафиксировать ориентиры, чтобы семья не импровизировала в «трудный час».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Кракен зеркало вход на сайт — надежный способ обойти блокировки и получить доступ к популярной платформе Кракен. Если официальный сайт недоступен из-за региональных ограничений или технических проблем, зеркало Кракен поможет быстро и безопасно войти на сайт без потери функционала.
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/skoraya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-uslugi/
Value Discovery Portal – Loved the simple presentation, made finding items effortless today.
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
pansionat-msk013.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
ice bet [url=www.icebet-online.com/]ice bet[/url] .
3dпечать Спб 3D Арт и Коллекционные Миниатюры – это яркий пример того, как современные технологии влияют на искусство. От анатомии в искусстве, отраженной в реалистичных моделях, до сюрреалистических композиций – цифровая скульптура позволяет создавать произведения, которые трудно или невозможно изготовить традиционными способами. Сервис 3dпечать Спб предоставляет художникам и коллекционерам возможность воплотить свои самые смелые идеи в реальность.
seo курсы [url=http://kursy-seo-12.ru]seo курсы[/url] .
Наблюдение
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
goliath casino mobile [url=www.goliath-casino.com/]www.goliath-casino.com/[/url] .
Когда тело перестаёт «гореть», в работу включается фармакологическая поддержка тяги и настроения, а также простые поведенческие техники. Мы помогаем организовать трезвые вечера, составить список альтернатив «наград» и заново привязать удовольствие к безопасным ритуалам — прогулке, спорту, тёплой еде, общению. Если тревога остаётся высокой, врач мягко корректирует схему, а психолог учит распознавать и «разгружать» триггеры раньше, чем они наберут силу. Такой блок — не про «волю», а про доступные инструменты, которые работают даже в уставшем состоянии после рабочего дня.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-vidnoe4.ru
3dпечать фигурок Цифровая Скульптура являет собой революцию в мире искусства, предлагая художникам невиданную ранее свободу самовыражения и технические возможности. Виртуальное пространство становится холстом, на котором мастер может создавать сложные формы и детали, не ограниченные тяжестью материалов или сложностью ручной обработки. Этот вид искусства стирает границы между реальностью и фантазией, позволяя воплощать в жизнь самые смелые и неординарные идеи.
На casino 7k понравилось отношение к игрокам. Поддержка отвечает быстро, всё объясняют. Деньги выводятся вовремя, без дополнительных проверок: 7k casino вход
smartbuyplace – Excellent place to find smart deals and quality products efficiently.
Анатомия В Искусстве Цифровая Скульптура являет собой революцию в мире искусства, предлагая художникам невиданную ранее свободу самовыражения и технические возможности. Виртуальное пространство становится холстом, на котором мастер может создавать сложные формы и детали, не ограниченные тяжестью материалов или сложностью ручной обработки. Этот вид искусства стирает границы между реальностью и фантазией, позволяя воплощать в жизнь самые смелые и неординарные идеи.
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Детальнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Fashion Explorer Hub – Styles feel modern and fresh, keeps shopping fun.
3DАрт Цифровая Скульптура открывает безграничные горизонты для художников, позволяя воплощать самые смелые и сложные идеи в виртуальном пространстве. С использованием специализированного программного обеспечения, скульпторы создают трехмерные модели, которые ранее были немыслимы из-за ограничений традиционных материалов и техник. Эта новая форма искусства сочетает в себе креативность, техническое мастерство и инновационный подход к созданию объектов.
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar022.ru
лечение запоя
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Azur Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A signaler les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui stimule l’engagement.
http://www.azurcasinobonusfr.com|
Everyday Savings Spot – Found something here that fit my needs perfectly.
Spot the Trends Portal – Unique products stood out, shopping was fun and quick.
Чтобы пациент и близкие не гадали «что будет дальше», мы удерживаем прозрачную последовательность. Каждый этап имеет цель, инструмент, окно оценки и критерий перехода. Это экономит минуты, снимает споры и делает план управляемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Plonger dedans|
Этот обзор сосредоточен на различных подходах к избавлению от зависимости. Мы изучим традиционные и альтернативные методы, а также их сочетание для достижения максимальной эффективности. Читатели смогут открыть для себя новые стратегии и подходы, которые помогут в их борьбе с зависимостями.
Подробнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Экстренный вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «ВоронежВита» мы действуем по чётким правилам: от телефонного триажа и тихого выезда бригады до адресной детоксикации и вечерних контрольных включений. Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить тремор и тошноту, выровнять сердечный ритм и вернуть физиологичный сон уже в первые ночи. Мы выбираем минимально достаточные вмешательства, чтобы днём сохранялась ясность и не возникало желания «самостоятельно усилить» схему. Конфиденциальность встроена в каждый шаг: гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/
онлайн юрист бесплатно задать вопрос без регистрации без телефона Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В стремительно меняющемся мире правовых реалий, где каждый день возникают новые вызовы и вопросы, возможность оперативно получить квалифицированную юридическую консультацию, не тратя при этом ни копейки, становится настоящим спасением. Бесплатная онлайн консультация юриста — это не просто жест доброй воли со стороны юридического сообщества, а реальный инструмент, позволяющий гражданам сориентироваться в сложных правовых ситуациях и защитить свои права.
Экстренный вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «ВоронежВита» мы действуем по чётким правилам: от телефонного триажа и тихого выезда бригады до адресной детоксикации и вечерних контрольных включений. Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить тремор и тошноту, выровнять сердечный ритм и вернуть физиологичный сон уже в первые ночи. Мы выбираем минимально достаточные вмешательства, чтобы днём сохранялась ясность и не возникало желания «самостоятельно усилить» схему. Конфиденциальность встроена в каждый шаг: гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh/
Bright Shop Portal – Easy to browse, with good prices on products.
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в калининграде[/url]
3dпечать Спб 3D Печать и DLP Печать — это технологии, которые позволяют перенести цифровую скульптуру в физический мир. 3D печать, в частности, позволяет создавать объекты из различных материалов, включая пластик, смолы и металлы. DLP печать, с другой стороны, предлагает более высокую точность и детализацию, что особенно важно при создании миниатюр и коллекционных фигурок.
yourjourneycontinues – This site shared a thought today that genuinely kept me motivated.
Моделирование 3D Арт и Коллекционные Миниатюры – это яркий пример того, как современные технологии влияют на искусство. От анатомии в искусстве, отраженной в реалистичных моделях, до сюрреалистических композиций – цифровая скульптура позволяет создавать произведения, которые трудно или невозможно изготовить традиционными способами. Сервис 3dпечать Спб предоставляет художникам и коллекционерам возможность воплотить свои самые смелые идеи в реальность.
юридическая консультация онлайн бесплатно без регистрации и телефона Юридическая консультация: бесплатный или платный вариант? Выбор между бесплатной и платной юридической консультацией зависит от сложности вашей ситуации и объема необходимой помощи. Бесплатная консультация подойдет для получения общей информации и оценки перспектив дела, в то время как платная консультация обеспечит более глубокий анализ, разработку стратегии и представительство ваших интересов в суде. Определите свои потребности и выберите наиболее подходящий вариант.
3DАрт Миниатюра приобретает новую жизнь благодаря возможностям 3D печати. Авторские фигурки, выполненные с высочайшей детализацией, становятся доступными для коллекционеров и ценителей искусства. Этот процесс объединяет традиционные методы моделирования с современными технологиями, создавая уникальные и неповторимые произведения.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk028.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
юрист консультация онлайн Консультация юриста онлайн Удобство онлайн консультаций заключается в их гибкости и доступности. Не нужно тратить время на дорогу, подстраиваться под график юриста или ждать в очереди. Достаточно иметь доступ в интернет, чтобы связаться с профессионалом и получить ответы на свои вопросы. Онлайн консультации позволяют получить экспертное мнение, не выходя из дома или офиса.
Ko Lanta Аренда мотобайка на Ко Ланта: Свобода передвижения. Аренда мотобайка – это один из самых популярных способов передвижения по Ко Ланта. Мотобайк дает свободу исследовать остров в своем темпе и добраться до отдаленных пляжей и достопримечательностей.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Azur Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui booste la participation.
http://www.azurcasinobonusfr.com|
пансионат для лежачих москва
pansionat-msk014.ru
дом престарелых в москве
goliath casino online [url=www.goliath-casino.com]www.goliath-casino.com[/url] .
Peaceful Purpose Hub – Content here always encourages calm and thoughtful reflection.
icebet live casino [url=https://icebet-online.com/]icebet-online.com[/url] .
Is your brand struggling to maintain consistency across platforms? Without a [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Social Media Audit[/url], you could be missing critical gaps that affect your visibility and engagement. Many businesses underestimate the power of a [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Audit Report[/url], leaving their profiles outdated and their content strategy ineffective.
By conducting a [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]KPIs Analysis[/url], you can align your brand voice.
Our experts analyze [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Analytics[/url] and [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Competitor Benchmarks[/url] to deliver actionable insights.
Imagine the impact of knowing exactly what works and what doesn’t. A [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Social Media Audit[/url] gives you clarity, helping you maximize ad spend.
Don’t let your competitors outshine you. Start your [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/smm/social-media-audit/]Social Media Audit[/url] today and boost visibility.
[url=https://www.facebook.com/seosea.marketing]Facebook[/url]
[url=https://www.instagram.com/seoseamarketing/]Instagram[/url]
[url=https://www.reddit.com/r/OnlnMarketingAgency/]Reddit[/url]
[url=https://www.linkedin.com/company/81762316]LinkedIN[/url]
Такая карта делает лечение обозримым и дисциплинирует решения: пациент видит цель и порог перехода, семья понимает, зачем нужно соблюдать «тихие» часы, команда сохраняет управляемость и не «крутит ручки» ночью.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Ко ланта Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта: Встреча с дикой природой. Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта находится на юге Ко Ланта Яй, это настоящее сокровище природы, где можно увидеть тропические леса и прибрежные пейзажи в их первозданном виде. В этом заповеднике живут разные животные и растения, включая обезьян, птиц, рептилий и бабочек. Главная достопримечательность парка – маяк, стоящий на скалистом мысе Kip Nai. Поднявшись на маяк, можно увидеть красивые панорамы Андаманского моря и соседних островов. Пешеходные тропы через джунгли позволяют изучить парк и его экосистему. Одна из популярных троп ведет к двум уединенным пляжам – Tai Note Beach и Ao Chak Beach – где можно отдохнуть и искупаться в чистой воде. Национальный парк Му Ко Ланта – это не только природа, но и история. Здесь можно увидеть древние захоронения морских цыган (Chao Leh), коренных жителей острова, которые веками жили в гармонии с природой.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar023.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Ko Lanta Ко Ланта: Слияние культуры и природы. В провинции Краби находится архипелаг Ко Ланта, состоящий из Ко Ланта Ной и Ко Ланта Яй, соединенных мостом. Это место, где тайское радушие переплетается с первозданной красотой природы. В отличие от шумных туристических городов, Ко Ланта предлагает уединение, сохраняя доступность современных удобств. Ко Ланта Ной является административным центром, в то время как Ко Ланта Яй – основным туристическим центром. Главной достопримечательностью Ко Ланта Яй является западное побережье – прекрасные пляжи, омываемые Андаманским морем. Остров предлагает широкий спектр активностей: дайвинг, снорклинг и национальный парк Му Ко Ланта. Вечером путешественников ждут уютные бары и рестораны с видом на закат.
Urban Product Spot – Enjoyed the clear layout and helpful product details for each item.
Self Growth Spot – Inspiring content that I can apply to my daily life.
Чтобы у пациента и близких не возникал вопрос «что дальше», мы используем карту первых часов. Она задаёт цели, действия, контроль и критерии перехода между этапами. Такой подход экономит минуты и исключает импровизации «ради уверенности».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
Параметр
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Вся динамика заносится в единую карту наблюдения, доступ к которой разграничен по ролям. При переходе к амбулаторной точке или стационару не происходит «перезапуска истории»: новые назначения учитывают всё, что сделано на старте.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Карта делает маршрут прозрачным для пациента и семьи. Вместо «лучше/хуже» — факты и понятные пороги. Это снижает тревожность и помогает соблюдать режим без сопротивления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
Если в первичном звонке звучат «красные флаги» (одышка, спутанность сознания, резкие скачки ритма), мы предлагаем стационарное «окно» мониторинга с ночным постом. При низких рисках стартуем на дому: контрольные точки совпадают с домашним комфортом, а вечерние online-вставки по 15–20 минут поддерживают предсказуемость без лишних поездок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
New Chapter Hub – Useful life tips, helps make change feel easy.
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
Explorer le site|
Когда тело перестаёт «гореть», в работу включается фармакологическая поддержка тяги и настроения, а также простые поведенческие техники. Мы помогаем организовать трезвые вечера, составить список альтернатив «наград» и заново привязать удовольствие к безопасным ритуалам — прогулке, спорту, тёплой еде, общению. Если тревога остаётся высокой, врач мягко корректирует схему, а психолог учит распознавать и «разгружать» триггеры раньше, чем они наберут силу. Такой блок — не про «волю», а про доступные инструменты, которые работают даже в уставшем состоянии после рабочего дня.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-vidnoe4.ru/
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par contre des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Latest Fashion Finds – Came across some cool trends here that stood out to me.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Azur Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement excellent les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Avancer|
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Lancer le site|
Контрактное производство электроники позволяет быстро и качественно выводить на рынок новые устройства. Все этапы разработки и тестирования контролируются специалистами, что гарантирует надежность и стабильность работы устройств – https://www.nanafightsback.com/%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B5-%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D1%8D%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B/
Je suis bluffe par Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, en revanche des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, apporte une energie supplementaire. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis epate par 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement attrayant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements securises.
Entrer|
В этом исследовании рассмотрены методы лечения зависимостей и их эффективность. Мы проанализируем различные подходы, используемые в реабилитационных центрах, и представим данные о результативности программ. Читатели получат надежные и научно обоснованные сведения о данной проблеме.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в Москве[/url]
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно мурманск[/url]
Je suis enthousiasme par Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En complement le site est rapide et engageant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A souligner le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Plongez-y|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk029.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Je suis enthousiasme par 1xBet Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, 1xBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Avancer|
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, 1xBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller en ligne|
Наркологическая клиника «РеМед Карелия» — это круглосуточная медицинская помощь, построенная на принципе клинической точности: каждая процедура имеет цель, проверяемые маркеры и назначенное окно переоценки. Мы используем современные методы детоксикации и постабстинентной стабилизации, не перегружая терапию «на всякий случай» и не полагаясь на универсальные «сильные капельницы». Вместо этого — модульные схемы, корректировка одного параметра за раз и обязательная оценка результата. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает лечение предсказуемым для пациента и его семьи. Анонимность встроена в процессы: немаркированные входы, гражданская форма персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к карте наблюдения.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/
Городская среда Воронежа — яркие подъезды, плотный трафик, шумные дворы — усиливает вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому выездная служба «ВоронежВита» организована «тихо»: согласованная парковка, быстрый подъем без опознавательных знаков, часть расходников доставляется заранее, чтобы на адресе сразу перейти к диагностике и инфузии. Коммуникация ведётся через защищённые каналы, уведомления — «беззвучные», названия в документах — нейтральные. Такой дизайн среды не декоративен: чем меньше «социального шума», тем устойчивее ночной сон и тем быстрее возвращается переносимость воды и лёгкой еды.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
Je suis emerveille par Lucky 31 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, toutefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
http://www.lucky31casino777fr.com|
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par contre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste la participation.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, 1xBet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. D’ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
En savoir davantage|
Self Growth Path Spot – Motivating content that encourages me to improve every day.
Первые недели — время, когда старые привычки ещё инерционны. Мы даём простой план на семь дней, объясняем маркеры стабилизации и поводы для внепланового контакта. При необходимости подключаем короткие встречи с психологом, чтобы закрепить навыки самопомощи и снизить вероятность срыва.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-shchelkovo3.ru
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Action Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Action Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis enthousiasme par Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Entrer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons egalement le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. A souligner les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Параметр
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk015.ru
пансионат для пожилых в москве
курсы seo [url=http://kursy-seo-12.ru]курсы seo[/url] .
J’ai une passion debordante pour Action Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Action Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller plus loin|
Discover Fashion Picks – Cute items that I wouldn’t have found anywhere else.
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Azur Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller sur le site|
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]www.i-klinik.ru[/url]
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Explorer le site web|
Если на предвызовном созвоне звучат «красные флаги» (неукротимая рвота, выраженная дезориентация, «скачущий» ритм, одышка), мы сразу резервируем палату усиленного наблюдения и подключаем расширенный мониторинг. При низком риске старт возможен амбулаторно или на дому с бесшовным переводом в стационар при необходимости — без очередей и «говорящих» вывесок. Во всех сценариях анонимность — не «опция», а стандарт по умолчанию.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk/
Rap musik With the rise of digital platforms, rap music can be easily accessed via streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube, making it easier than ever for fans to discover both mainstream stars and underground rappers.
Je suis epate par Azur Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Azur Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.casinoazurfr.com|
Rap musik Rap music originated in the 1970s in the United States and has since become a dominant force in the global music landscape.
Je ne me lasse pas de Azur Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer ici|
Слушеть Рэп онлайн Кроме того, рэп продолжает оставаться важным средством выражения и является катализатором для обсуждения актуальных вопросов, от социальных изменений до вопросов идентичности, что делает его неотъемлемой частью современной музыки и культуры. Rap musik
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Lucky 31 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement fun les transactions en crypto fiables, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer davantage|
Bargain Finder Hub – Daily deals change frequently, exciting offers to grab.
Fashion Ideas Spot – Noticed some outfit suggestions that really made dressing simpler.
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Voir plus|
We bring you latest Gambling News, Casino Bonuses and offers from Top Operators, [url=https://www.jackpotbetonline.com/]Online Casino Slots[/url] Tips, [url=https://www.jackpotbetonline.com/]Sports Betting[/url] Tips, odds etc – jackpotbetonline.com
Je suis epate par 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, 1xBet Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Essayer|
Мурманск — город с длинными сумерками и влажным ветром от Кольского залива, что сказывается на сну и вечерней кардиолабильности. Поэтому мы адаптируем маршруты: выездные бригады работают в гражданской одежде, заходят быстро и тихо, а в палатах клиники используется тёплая подсветка и акустическое поглощение. Для ночных поступлений действует протокол «мягкой посадки»: минимизированные контакты, тёплая вода малыми глотками, затем — диагностика и старт инфузии при отсутствии «красных флагов». Это снижает сенсорную нагрузку и позволяет организму дать честный клинический ответ без лишних раздражителей.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя цена мурманск[/url]
Rap musik Слушая рэп онлайн, вы не только наслаждаетесь музыкой, но также получаете возможность погрузиться в культуру, осознать важные сообщения и почувствовать живую энергию артистов. Rap musik
В этой публикации мы предложим ряд рекомендаций по избавлению от зависимостей и успешному восстановлению. Мы обсудим методы привлечения поддержки и важность самосознания. Эти советы помогут людям вернуться к нормальной жизни и стать на путь выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в Москве[/url]
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Action Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Action Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour couronner le tout le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Этот документ охватывает важные аспекты медицинской науки, сосредотачиваясь на ключевых вопросах, касающихся здоровья населения. Мы рассматриваем свежие исследования, клинические рекомендации и лучшие практики, которые помогут улучшить качество лечения и профилактики заболеваний. Читатели получат возможность углубиться в различные медицинские дисциплины.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в Симферополе[/url]
кракен даркнет
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk030.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Build Achieve Hub – Consistently motivating content that sparks creativity and action.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar025.ru
вывод из запоя
DD Articles – Well-written content jismein clarity aur simplicity dono milti hain.
Слушеть Рэп онлайн Streaming platforms like Spotify, YouTube, and Apple Music have revolutionized how fans engage with rap music, offering easy access to a vast array of tracks, from chart-topping hits to underground gems.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru
Achieve Learning Portal – Noticed a tip here that made completing a task much easier.
https://gorillasocialwork.com/story24659594/1xbet-official-promo-code
Rap musik Engaging with rap music today means not only listening but also participating in a cultural movement that values authenticity, creativity, and social consciousness.
Здесь
[url=https://s-protekt.orgs.biz/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
скачать рэп Combining rhythm, rhyme, and powerful lyrics, rap artists convey their experiences and perspectives, making it a dynamic storytelling medium.
it перевод заказать [url=https://telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09/]telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09[/url] .
лучшие бюро переводов [url=https://teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA/]teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA[/url] .
отражающая изоляция “ПОЛИСИНТЕЗ” предлагает широкий выбор полиэтиленовой пленки различных типов, толщин и плотностей, включая пленки общего назначения, термоусадочные пленки, барьерные пленки и многое другое. Мы гарантируем высокое качество нашей продукции, обеспечивающее прочность, герметичность и долговечность. Наши пленки соответствуют всем требованиям безопасности и гигиеничности. Мы предлагаем пленки как в рулонах, так и в готовых изделиях, отвечающих вашим индивидуальным потребностям. армированная пленка
I like this weblog very much so much great info .
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-tula013.ru
пансионат для престарелых
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is wonderful, let alone the content!
Pure Choice Hub – A wide variety of options, made finding what I wanted very easy.
скачать рэп Современные платформы, такие как Spotify, YouTube и Apple Music, значительно упростили доступ к рэп-музыке, позволяя слушателям открывать для себя как известных артистов, так и начинающих исполнителей.
полиэтиленовая пленка Отражающая изоляция представляет собой инновационный материал, используемый для повышения энергоэффективности зданий и сооружений.
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в калининграде[/url]
Hi, I just hopped over to your web-site through StumbleUpon. Not somthing I might typically browse, but I liked your views none the less. Thanks for making something worthy of reading through.
бош сервис москва [url=http://www.servisnyj-centr-bosch-msk24.ru]https://servisnyj-centr-bosch-msk24.ru/[/url]
It’s a comprehensive, yet fast read.
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
Mindful Moments Link – Found a short reminder that helped me appreciate the present.
Rap musik Rap music has become a powerful medium for artists to express their thoughts and experiences, often serving as a commentary on social issues and personal struggles.
Je suis sous le charme de Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par moments des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Continuer ici|
Je suis sous le charme de Casinozer Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Casinozer Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Casinozer Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, toutefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En fin de compte, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste la participation.
Approfondir|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Mystake Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Mystake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Essayer maintenant|
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя калининград[/url]
Quick Style Store – Simple interface makes browsing and paying very easy.
I appreciate your work, thanks for all the great blog posts.
Je suis fascine par Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement super les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute soudee.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En resume, Pokerstars Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis enthousiasme par Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Stake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage notable les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Je suis emerveille par Stake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps a autre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En fin de compte, Stake Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et energique, permet une immersion complete. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der Г la page|
тенты Отражающая изоляция – это современный материал, разработанный для повышения энергоэффективности зданий и сооружений. Она состоит из полиэтиленовой пленки с алюминиевым покрытием, которое эффективно отражает тепловое излучение, снижая теплопотери зимой и перегрев летом.
J’ai un faible pour Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Casinozer Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinozer Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges personnalises.
Continuer ici|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinozer Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
Je suis sous le charme de Mystake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
На этом отрезке мы снимаем острые симптомы абстиненции: тремор, тошноту, паническую волну, нарушения сна. Инфузия собирается индивидуально, с расчётом объёма по массе тела и состоянию почек и сердца. Добавляем электролиты, гепатопротективные компоненты, при необходимости — короткую седацию, которая восстанавливает архитектуру сна без «тяжёлого» утреннего эффекта. Во время процедуры врач отслеживает давление, пульс, сатурацию, дыхание, корректирует скорость введения и объясняет, что и зачем делается. На выходе пациент получает понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, правила активности, «красные флаги» для внеплановой связи. В большинстве случаев облегчение наступает уже в день старта, а первая спокойная ночь становится поворотной точкой для мотивации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-vidnoe4.ru/czentr-lecheniya-alkogolizma-v-vidnom/
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
армированная пленка “ПОЛИСИНТЕЗ” предлагает отражающую изоляцию различной толщины и с различными типами покрытия, позволяя подобрать оптимальное решение для утепления стен, крыш, полов и других конструкций. Наша отражающая изоляция легко монтируется, безопасна для здоровья и окружающей среды, а также обеспечивает значительную экономию энергии. геотекстиль дорнит
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et energique, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus constants.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus constants.
Essayer ceci|
геотекстиль дорнит Мы не просто поставщик, мы – надежный партнер для предприятий и организаций, нуждающихся в современных, эффективных и долговечных решениях для упаковки, строительства, сельского хозяйства и других отраслей.
https://universocentro.com/NUMERO22/ParrandaSanta.aspx
Наркологическая клиника «РеМед Карелия» — это круглосуточная медицинская помощь, построенная на принципе клинической точности: каждая процедура имеет цель, проверяемые маркеры и назначенное окно переоценки. Мы используем современные методы детоксикации и постабстинентной стабилизации, не перегружая терапию «на всякий случай» и не полагаясь на универсальные «сильные капельницы». Вместо этого — модульные схемы, корректировка одного параметра за раз и обязательная оценка результата. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает лечение предсказуемым для пациента и его семьи. Анонимность встроена в процессы: немаркированные входы, гражданская форма персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к карте наблюдения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
Je suis sous le charme de Stake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En fin de compte, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement cool les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в Симферополе[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://fabrika-stil.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Hi folks… a tempting drop today.
Enter cam chat rooms and join instantly with Worldwide audiences. Enjoy genuine conversation and shared creativity.
п»їhttps://pussycats.me
Нарколог на выезд в Красноярске — это оптимальное решение для тех‚ кто испытывают необходимость в наркологической помощи‚ но не могут посещать медицинское учреждение. Профессиональная помощь в лечении зависимости доступна в домашних условиях‚ что гарантирует удобство и конфиденциальность.Консультация нарколога позволяет проанализировать текущее состояние и выбрать оптимальную программу реабилитации‚ включая лечение в стационаре или выезд на дом. Наши эксперты предлагают психотерапию зависимостей и медицинское вмешательство‚ что способствует успешному лечению зависимостей. Семейная поддержка играет важную роль в лечении‚ помогая пациентам преодолеть сложности. Обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru для получения подробной информации о наших услугах.
Мы собираем терапию из проверенных модулей: гидратация, коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям, поведенческие интервенции (свет, тишина, дыхание 4–6, стимул-контроль, вечерние ритуалы). Объём и темп зависят от ведущего симптома и времени суток: при кардиореактивном вечере больше внимания уделяется среде, при тошноте — гастропротекции и «тёплому питанию», при поверхностном сне — цифровой гигиене и световым сценариям. Ниже приведена ориентировочная матрица выбора; финальное решение — за лечащим врачом с учётом противопоказаний и лекарственных взаимодействий.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Rap musik Слушать рэп онлайн стало гораздо проще благодаря популяризации стриминговых сервисов: на платформах, таких как SoundCloud и Spotify, можно найти не только привычные хиты, но и множество независимых исполнителей, которые борются за внимание аудитории.
Капельница для избавления от запоя – это эффективный метод детоксикации организма, который предлагает наркологическая клиника. В Туле предлагается широкий спектр медицинских услуг, включая вызов нарколога на дом для помощи в борьбе с запоем. Лечение алкоголизма требует персонализированного подхода, и программы лечения зависят в зависимости от степени зависимости. Консультация нарколога поможет определению наилучшего метода лечения, а конфиденциальное лечение гарантирует конфиденциальность. Поддержка семьи зависимого также играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации. Оценка клиник в Туле на основе отзывов позволяет определить наиболее подходящее заведение. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за поддержкой, чтобы преодолеть алкогольную зависимость и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
Innovative Choice Spot – Loved exploring the options, inspired immediate creative thoughts.
Trend Discovery Hub – Spotted several items that seemed trendy and fashionable.
Метод
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-shchelkovo3.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-shchelkovo[/url]
https://participa.aytojaen.es/profiles/gigogi5394/activity
of course like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I will surely come back again.
I think I will become a great follower.Just want to say your post is striking. The clarity in your post is simply striking and i can take for granted you are an expert on this subject.
Первые два часа после приезда врача — ключевое окно. Мы фиксируем витальные показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?), проводим экспресс-оценку глюкозы, по показаниям — электролитов (Na?/K?), оцениваем дыхательный паттерн и уровень ориентировки. Далее запускается титрованная инфузия через инфузомат с контролем каждые 15–20 минут. Параллельно настраиваются «вечерние опоры»: светогигиена, дыхательные циклы, «тихие окна» связи. В конце визита пациент и близкие получают простую памятку с «зелёными зонами» и кратким планом на 72 часа — когда пить воду, как выбирать тёплую пищу малыми порциями, при каких признаках выходить на связь немедленно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в воронеже[/url]
Петрозаводск задаёт свои параметры среды: озёрный ветер, световые перепады, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. В «РеМед Карелия» мы проектируем маршрут так, чтобы городской фон работал на пациента. Короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в приёмной, отсутствие громких объявлений, отдельный вход без вывесок и немаркированный транспорт — всё это снижает сенсорную нагрузку и уменьшает вечернюю кардиореактивность. Семья получает «окна связи» в фиксированное время, чтобы эмоциональные звонки не разрушали «ночную кривую» сна. Для пациентов, стартующих на дому, мы привозим переносные решения — лампу тёплого спектра, ширмы, шумопоглощающие аксессуары, — чтобы не усиливать тревогу и не «подливать» раздражителей в момент инфузии.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologiya
купить диплом о среднем медицинском образовании цены [url=https://r-diploma16.ru/]https://r-diploma16.ru/[/url] .
IT перевод в бюро переводов Перевод и Право [url=https://telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09/]telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09[/url] .
Топ-5 бюро переводов в москве [url=https://teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA/]teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA[/url] .
This blog post is excellent, probably because of how well the subject was developed. I like some of the comments too though I could prefer we all stay on the subject in order add value to the subject!
Trend Discovery Hub – Products refresh daily, keeping style exploration interesting.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Mystake Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Mystake Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce la communaute.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino est un must pour les passionnes. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Stake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Stake Casino vaut une visite excitante. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir plus|
Городская среда Петрозаводска со сменой ветров с Онежского озера, короткими сумерками и сезонными перепадами влажности может усиливать тревожность в вечерние часы. Мы учитываем это с момента первого контакта: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок, короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в зоне ожидания и отсутствие громких объявлений. Родственникам предоставляются «тихие окна» связи — лаконичные апдейты в фиксированное время, чтобы не перегружать пациента и не дёргать команду в критические окна наблюдения. Такой «мягкий» контур снижает сенсорную нагрузку, стабилизирует вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам и сокращает число импульсивных просьб «усилить на ночь».
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologiya/
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula014.ru
пансионат после инсульта
Creative Dream Gifts – Noticed a variety of items here that would make thoughtful presents.
Первые недели — время, когда старые привычки ещё инерционны. Мы даём простой план на семь дней, объясняем маркеры стабилизации и поводы для внепланового контакта. При необходимости подключаем короткие встречи с психологом, чтобы закрепить навыки самопомощи и снизить вероятность срыва.
Углубиться в тему – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-shchelkovo3.ru/kodirovka-ot-alkogolya-ryadom-shhyolkovo
Карта делает маршрут прозрачным для пациента и семьи. Вместо «лучше/хуже» — факты и понятные пороги. Это снижает тревожность и помогает соблюдать режим без сопротивления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
Automatizovany system https://rocketbitpro.com pro obchodovani s kryptomenami: boti 24/7, strategie DCA/GRID, rizeni rizik, backtesting a upozorneni. Kontrola potencialniho zisku a propadu.
При домашнем формате мы сразу закладываем «мостик» к стационару: в случае ухудшения состояния перевод происходит бесшовно, по заранее оговорённым критериям. Пациент и семья знают, какие маркеры считаются целевыми (переносимость воды, ровный вечерний пульс, время до засыпания, число пробуждений), и когда состоится повторная оценка. Прозрачность снимает суету и укрепляет приверженность плану.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Здесь
[url=hhttps://lead.media/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Quick Shopping Portal – Smooth browsing experience, products are easy to locate.
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов город[/url]
бесплатные фриспины без депозита
Универсальной «сильной капельницы» не существует. Мы подбираем состав по ведущим симптомам, переносимости и данным экспресс-диагностики. Задача — вернуть дневную ясность и физиологичный ночной сон без переседации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
бесплатные спины без депозита
https://photos.aagl.org/guestbook.html
Городская среда Калининграда специфична: морской ветер, сезонные пробки, яркие витрины в вечерние часы. Эти факторы часто усиливают тревожность и мешают засыпанию. Поэтому мы проектируем выезд «мягко»: согласованная парковка, немаркированный вход, короткий маршрут до места процедуры, отсутствие громких звонков и «визуального шума» у порога. Родственникам предоставляем «тихие окна» связи — короткие апдейты в заранее оговорённое время без лишних подробностей. Такой формат не просто комфортнее, он клинически полезен: чем меньше стимулов, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях» и тем стабильнее проходит первая ночь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad
Наркологическая служба Красноярск предлагает разнообразные услуги для помощи людям с зависимостями. В этом городе работают специализированные реабилитационные центры‚ где можно получить анонимное лечение наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Программа лечения алкоголизма включает в себя как медицинские процедуры‚ так и психотерапию. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru Психологическая помощь Красноярск также играет важную роль в процессе выздоровления. Консультация нарколога позволяет выявить индивидуальные особенности зависимого и составить индивидуальный план терапии. Работа с родственниками и профилактика зависимостей – неотъемлемая часть работы наркологической клиники. Реабилитация зависимых включает как терапевтические‚ так и социальные аспекты. Услуги наркологической службы направлены на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Городская среда Петрозаводска со сменой ветров с Онежского озера, короткими сумерками и сезонными перепадами влажности может усиливать тревожность в вечерние часы. Мы учитываем это с момента первого контакта: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок, короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в зоне ожидания и отсутствие громких объявлений. Родственникам предоставляются «тихие окна» связи — лаконичные апдейты в фиксированное время, чтобы не перегружать пациента и не дёргать команду в критические окна наблюдения. Такой «мягкий» контур снижает сенсорную нагрузку, стабилизирует вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам и сокращает число импульсивных просьб «усилить на ночь».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в петрозаводске[/url]
кайт хургада
Potential Insight Hub – Read a thought today that reminded me to keep striving.
ко ланта
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Получить больше информации – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-murmansk
Fashion Picks Portal – International options impressed me, and shipping was very quick.
При абстиненции нервная и сердечно-сосудистая системы работают на пределе, баланс нейромедиаторов смещён, кровь «теряет» воду и электролиты, а печень несёт повышенную нагрузку. Резкая отмена алкоголя без врача нередко приводит к скачкам давления, аритмиям, паническим эпизодам, нарушению сна и даже делирию. Домашние «самосборные» растворы и случайные комбинации таблеток усугубляют обезвоживание и не учитывают противопоказания — в итоге риски растут, а эффект непредсказуем. В «СфераЗдоровья» путь другой: сначала скрининг безопасности и исключение состояний, при которых показан стационар; далее — персональная инфузионная схема с регидратацией, коррекцией электролитов, поддержкой печени и симптом-контролем (тошнота, тремор, тревога, бессонница). На каждом этапе врач отслеживает динамику и корректирует дозы «по реакции», чтобы не перегрузить сердце и почки. Результат — более мягкий выход из абстиненции, прозрачные ожидания для пациента и близких и понятный план на ближайшие 24–48 часов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-na-domu-domodedovo/
кайт школа хургада
Вызов нарколога — это необходимый шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с трудностями с зависимостями . Наркологическая служба предоставляет срочную наркологическую помощь и консультацию нарколога, что особенно необходимо в кризисных ситуациях . Признаки зависимости от наркотиков могут проявляться по-разному , и важно знать, когда следует обращаться за медицинской помощью при алкоголизме. Помощь при алкоголизме и лечение наркотической зависимости требуют профессионального подхода . Последствия алкоголизма могут быть катастрофическими, поэтому важно искать помощь для людей с зависимостями, включая программы реабилитации. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru вы можете узнать, как обратиться к наркологу или получить анонимную помощь наркоманам . Не сомневайтесь в том, чтобы позвонить в наркологическую службу, чтобы получить нужную помощь и поддержку.
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в Москве[/url]
зеркало кракен
Финальный этап — выработка устойчивых привычек и отношений с окружением. Вместе с пациентом мы формируем план трезвых выходных, обсуждаем правила отказа, которые не провоцируют конфликты, и настраиваем микропаузы в течение дня, чтобы стресс не копился «к вечеру». Контрольные встречи короткие и прагматичные: оцениваем сон, уровень энергии, тягу, коммуникацию с близкими. Если предстоит сложный период — отпуск, переезд, цейтнот — заранее усиливаем опоры, чтобы пройти его без срывов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-vidnoe4.ru/]клиника лечение алкоголизма цены[/url]
Вин 1win Обзор Ведущих Букмекеров: Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom, Melbet На рынке спортивных ставок представлено множество букмекерских компаний, каждая из которых предлагает свои условия и преимущества. Рассмотрим особенности и преимущества крупнейших игроков рынка: Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom и Melbet. Winline: Ориентация на Мобильность и Инновации Winline – известный букмекер, делающий акцент на мобильном беттинге и инновационных решениях. Компания предлагает удобное мобильное приложение и активно внедряет новые технологии, такие как видеотрансляции спортивных событий. Fonbet: Богатая История и Широкая Линия Fonbet – один из старейших букмекеров на российском рынке, предлагающий широкую линию спортивных событий и тотализатор (Суперэкспресс). Компания известна своей надежностью и репутацией. Betcity: Высокие Коэффициенты и Гибкие Условия Betcity – букмекер, привлекающий игроков высокими коэффициентами и гибкими условиями ставок. Компания предлагает широкий выбор исходов и возможность делать ставки на различные статистические показатели. BetBoom: Молодой и Амбициозный BetBoom – относительно новый букмекер, быстро набирающий популярность благодаря агрессивному маркетингу и привлекательным условиям для игроков. Компания предлагает широкую линию ставок и акцент на киберспорт. Melbet: Широкий Выбор Событий и Международный Опыт Melbet – международный букмекер, предлагающий широкий выбор спортивных событий и азартных игр. Компания ориентирована на международный рынок и предлагает различные варианты валют и языков.
Эта статья освещает различные аспекты освобождения от зависимости и пути к выздоровлению. Мы обсуждаем важность осознания своей проблемы и обращения за помощью. Читатели получат практические советы о том, как преодолевать трудности и строить новую жизнь без зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в Москве[/url]
1win официальный 1win – динамично развивающаяся платформа, предлагающая широкий спектр возможностей для любителей азартных игр. 1win официальный – это ваше окно в мир больших выигрышей, где безопасность и надежность стоят во главе угла. Здесь вы всегда можете рассчитывать на честную игру и своевременные выплаты.
Build Hub Online – Found strategies and tools that make personal growth manageable.
Shop Joy Spot – Found a handful of products that felt unique and useful.
лучшие бюро переводов в Мск [url=https://teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA/]teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA[/url] .
it перевод стоимость [url=https://telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09/]telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09[/url] .
Бетсити Ставки на спорт спорт ставков – это сложная система, требующая постоянного обучения и адаптации. Это игра, в которой выигрывает тот, кто умеет анализировать, прогнозировать и держать руку на пульсе событий. Ставки прогнозы – это искусство предвидения, основанное на кропотливом анализе статистики, новостей и экспертных оценок. Это ключ к успешным ставкам и стабильному выигрышу.
кайт школа хургада
кайт школа хургада
кайт египет
дом престарелых в туле
pansionat-tula015.ru
пансионат для пожилых в туле
Practical Knowledge Spot – Tutorials are clear and make learning more accessible.
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Как достичь результата? – https://mathrusreeayurveda.com/childhood
ко ланта
Капельницы для лечения запоя в Красноярске: быстрая помощь Алкоголизм — серьезная проблема‚ требующая внимания и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске наблюдается рост спроса на услуги нарколога на выезд. Нарколог на дом в Красноярске предлагает экстренную помощь‚ включая детоксикацию и восстановление после запоя.Одним из лучших методов лечения запоя является капельница. Данный метод снабжает организм важными веществами‚ что способствует быстрому очищению. Медицинская помощь‚ предоставляемая наркологом‚ включает терапию при запое‚ что помогает убрать физическую зависимость от алкоголя. нарколог на дом Красноярск Не забывайте‚ что важно не затягивать с вызовом нарколога на дом. Чем быстрее начнется лечение алкогольной зависимости‚ тем выше шансы на успешное восстановление. Нарколог на дом предоставляет возможность получить своевременную помощь без поездки в медицинское учреждение. Мы поможем вам справиться с зависимостью от алкоголя.
ko lanta
и что за вещество https://verbandsabzeichen.info Да я написал уже. Мб 2-dpmp в качестве компенсации подгонят, а вот что с фф не знаю, я ее проебал до того как я еще попробовал.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://convoy200.info/1
ко ланта
Je suis fascine par Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A souligner les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awful internet site : D.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui booste la participation.
Commencer Г explorer|
Здесь
[url=https://maximusmedia.pro/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Trendy Picks Portal – Several unique items caught my attention this morning.
ко ланта
По репе получил! Еще раз увижу безобразный флуд во всех ветках, будет тебе БАН! https://diaspora-world.info Бро, была абсолютно идиентичная ситуация у мну в декабре.Трек не бился пол недели, прошли выходные звоню в контору-курьерку, называю трек, говорят нет такого, я к тс так мол и так, тот грит все ровно, трек верный ожидай! Херакс и вечером курьер названивает, оказыва4тся они мне еще в субботу хотели вручить, но почему то не дозвонились))Все пучком, бро.Почта мало кому интересна в наши дни, на курьерки много сваливается, вот они 3ак могут разгребают…
TurkPaydexHub se differencie comme une plateforme de placement crypto de pointe, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, identifie les opportunites et execute des strategies complexes avec une exactitude et une rapidite hors de portee des traders humains, optimisant ainsi les potentiels de profit.
Fonbet 1win скачать – это возможность установить мобильное приложение и всегда иметь доступ к любимой платформе. 1win вход – это быстрый и безопасный доступ к вашему личному кабинету, где вы можете управлять своими финансами, делать ставки и получать бонусы.
TurkPaydexHub Trading
TurkPaydexHub se demarque comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies innovante, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, repere les opportunites et applique des tactiques complexes avec une finesse et une celerite inatteignables pour les traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les perspectives de gain.
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’adore l’energie de Pokerstars Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En extra la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je ne me lasse pas de Pokerstars Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Pokerstars Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus constants.
Visiter le site|
winline 1 ставка – это отправная точка, первый шаг на пути к выигрышу. Это момент истины, когда знания, интуиция и удача сливаются воедино, чтобы определить исход игры. Ставки на спорт – это не просто способ заработать деньги, это стиль жизни, наполненный адреналином и предвкушением. Это возможность почувствовать себя частью глобального спортивного сообщества, где каждый матч – это повод для обсуждения и анализа.
Капельница от запоя – это существенный метод лечение алкогольной зависимости, что находит свое применение в наркологических клиниках Тулы. Метод детоксикации помогает оперативному восстановлению организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Время процедуры обычно варьируется от 1 до 3 часов, в зависимости от индивидуальных потребностей и степени запоя. лечение запоя тула Признаки запоя включает в себя интенсивные головные боли, тошноту, потливость и тревожные состояния. Медицинская помощь в виде капельницы позволяет эффективно снять похмелье, вводя жизненно важные вещества для восстановления водно-электролитного баланса и устранения токсинов. Цены на лечение запоя в Туле варьируется в зависимости от выбранной клиники и количества требуемых процедур. Прием у нарколога поможет определить оптимальный план лечения, включая восстановление после запоя. Эффективность капельницы доказывается многими положительными отзывами пациентов, что делает данный метод популярным способом борьбы с алкоголизмом.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Egalement genial les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Бетсити Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom, Melbet: Сравнение и Особенности Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom и Melbet – это ведущие букмекерские компании, предлагающие ставки на спорт в России и других странах. Каждая из этих компаний имеет свои особенности и преимущества. Winline Winline – это одна из самых популярных букмекерских компаний в России. Она известна своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и быстрым выводом средств. Fonbet Fonbet – это одна из старейших букмекерских компаний в России. Она предлагает широкий выбор ставок на спорт, а также тотализатор. Betcity Betcity – это букмекерская компания, которая предлагает высокие коэффициенты и широкую линию событий. Она также предлагает различные виды ставок, такие как экспрессы, системы и лайв-ставки. BetBoom BetBoom – это новая букмекерская компания, которая быстро набирает популярность. Она предлагает высокие коэффициенты, широкую линию событий и удобный интерфейс. Melbet Melbet – это международная букмекерская компания, которая предлагает ставки на спорт и казино. Она известна своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и разнообразными бонусами.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Mystake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est simple et transparent, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Mystake Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer ici|
I had fun reading this post. I want to see more on this subject.. Gives Thanks for writing this nice article.. Anyway, I’m going to subscribe to your rss and I wish you write great articles again soon.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Casinozer Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Планируя [url=https://pereezd-kvartiry-msk.ru/]заказать переезд квартиры недорого[/url], выберите надежную компанию для быстрой и безболезненной транспортировки всех ваших вещей.
Первым шагом является создание детального плана.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Casinozer Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute soudee.
Continuer ici|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, rarement plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges sur mesure.
VГ©rifier le site|
https://xnudes.ai/
ко ланта
winline Лига ставок – это бренд, впитанный в сознание игроков, символ надежности и высоких стандартов сервиса. Тысячи событий ежедневно, от матчей мирового уровня до локальных соревнований, делают эту платформу универсальным выбором для любого, кто хочет испытать азарт победы. Лига ставок ставки – это калейдоскоп возможностей, где каждый может найти свою нишу. Футбол, хоккей, теннис, баскетбол, киберспорт – мир спорта открыт для вас, позволяя делать ставки на любой вкус и стратегию.
Very descriptive post, I enjoyed that bit. Will there be a part 2?
Вызов нарколога на дом сочетает медицинскую эффективность с удобством. Пациент получает квалифицированную помощь в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]врач нарколог на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Перед применением конкретных средств врач проводит обследование, определяет уровень интоксикации и выявляет сопутствующие заболевания. Это позволяет максимально точно подобрать лечение. Ниже представлены ключевые методы, которые применяются для стабилизации состояния пациента:
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница ростов-на-дону[/url]
Выездной алкогольный https://bar-vip.ru и кофе-бар на любое мероприятие: авторские коктейли, свежая обжарка, бармен-шоу, оборудование и посуда. Свадьбы, корпоративы, дни рождения. Честные сметы, высокое качество.
Je suis bluffe par Stake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Stake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une immersion complete. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fluides.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis bluffe par Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino vaut une visite excitante. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Voir la page|
Pure Value Hub – Found several deals today that seemed both fair and useful.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Pokerstars Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
En savoir davantage|
Проплатил в этот магаз 10.10,трек получил 14.10-сегодня 18.10 трек не бьёться купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш
Je suis enthousiasme par Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Stake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis accro a Casinozer Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Casinozer Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter le site|
J’adore la vibe de Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Mystake Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
Passer à l’action|
shopthelatestdeals – Found amazing deals today, makes shopping fun and easy.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinozer Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург[/url]
Для сохранения приватности мы ведём коммуникацию через одного доверенного представителя, используем нейтральные формулировки в документах, а инструкции выдаём в неброском виде. При невозможности создать тишину дома (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости) предложим краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерным режимом, после чего сопровождение вернётся в домашний формат.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ekaterinburg-otzyvy/
blog-partnera.ru
Opportunity Discovery – Helpful advice and fresh insights make exploring possibilities enjoyable.
It’s continually awesome when you can not only be informed, but also entertained! I’m sure you had fun writing this article. Regards, Clotilde.
бездепозитный бонус игровые автоматы
Осваиваешь фортепиано? обучение игры на фортепиано популярные мелодии, саундтреки, джаз и классика. Уровни сложности, аккорды, аппликатура, советы по технике.
бездепозитные игровые автоматы с выводом
Sharing my personal perspective concerning this site. I describe special incentives, cashouts, and total experience. Exploring reward system and payments. Describing how the page acts and manages payouts. Covering advantages and disadvantages I saw. Writing about what I valued and what didn’t impress me. More insights are provided in the complete article Crowngreen casino
https://xnudes.ai/
поддерживаю ! парни врубаем тормоза пока нет ясности купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point cle les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Здесь
[url=https://vlasovpro.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Капельница от похмелья — это эффективное средство для скорейшего решения проблем интоксикации после праздничных возлияний. При алкогольной интоксикации организм испытывает дискомфорт от недостатка жидкости и нехватки электролитов, что приводит головной боли. Лечение капельницей включает в себя введение растворов для гидратации и возвращение нормального состояния организма. Консультация специалиста может включать в себя специальные препараты от похмелья, которые помогают организму быстрее восстановиться. Капельницы часто содержат витамины, противоядия, которые ускоряют процесс выздоровления. Поддержка организма таким образом позволяет уменьшить неприятные ощущения и ускорить процесс выздоровления. Чтобы получить капельницу можно посетить медицинское учреждение или позвонить врачу на дом через интернет vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk019.ru. Не забывайте, что своевременное лечение поможет уменьшить риски.
Sometimes, the sheer magnitude of the information seems overwhelming.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike.
бонус leebet casino
trendyvaluezone – Stylish products at affordable prices, love the variety here.
Unique Picks Hub – Found several interesting products that grabbed my attention.
консультация психиатра круглосуточно
psychiatr-moskva010.ru
врач психиатр на дом
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-zhukovskom
Easily, the post is really the greatest on this laudable topic. I concur with your conclusions and will thirstily look forward to your future updates. Saying thank will not just be sufficient, for the wonderful c lucidity in your writing. I will instantly grab your rss feed to stay privy of any updates. Solid work and much success in your business enterprise!
промо код на 1хбет Вводите актуальный промокод на http://www.google.com.cu/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и активируйте бонус до 32 500 рублей, чтобы начать ставки с преимуществом.
работаю с ним уже давно.не бойтесь тут всё чесно! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш
Вин 1win Лига ставок – это не просто букмекерская контора, это вход в захватывающий мир спортивного азарта, где острые ощущения от побед и горечь поражений переплетаются, создавая уникальную атмосферу страсти и предвкушения. Это место, где каждый, от новичка до опытного игрока, может почувствовать себя частью огромного спортивного сообщества, болеющего, переживающего и, конечно же, выигрывающего.
1xBet промокод 2026 Новый промокод 2026 на http://www.google.com.co/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html даёт бонус 100% до 32 500 рублей для новых игроков.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be really something which I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
ко ланта
Посещение [url=https://shkola-vocala.ru/]репетитор по вокалу[/url] может стать отличным способом улучшить свои вокальные навыки и раскрыть творческий потенциал.
приобрести новые навыки пения . В этой школе квалифицированные вокальные педагоги помогают ученикам развить свой уникальный вокальный стиль . Школа вокала проводит занятия для всех возрастных групп .
Школа вокала также помогает ученикам подготовиться к участию в вокальных конкурсах. В школе разработаны специальные методики обучения для того, чтобы помочь ученикам преодолеть страх сцены . Школа вокала организует занятия в комфортных и хорошо оборудованных помещениях .
Обучение в школе вокала дает возможность ученикам развить свои творческие способности . Ученики разработать свое собственное музыкальное направление . Школа вокала предоставляет ученикам доступ к современным технологиям и оборудованию .
Обучение в школе вокала также дает возможность ученикам общаться с другими людьми, sharing едиными интересами. Ученики могут развить свои лидерские качества. Школа вокала стремится создать уникальную и дружественную атмосферу .
Программа обучения в школе вокала разработана для учеников с различными уровнями подготовки. Ученики могут улучшить свое дыхание и артикуляцию. Школа вокала организует консультации с опытными вокалистами.
Программа обучения также помогает ученикам преодолеть страх сцены . Ученики могут создавать свои собственные музыкальные проекты . Школа вокала предоставляет ученикам поддержку и консультации на каждом этапе их обучения.
Школа вокала дает ученикам возможность приобрести новые навыки и знания . Ученики могут получить возможность участия в музыкальных проектах. Школа вокала предоставляет ученикам доступ к современным технологиям и оборудованию .
Школа вокала также организует занятия в комфортных и хорошо оборудованных помещениях . Ученики могут создавать свои собственные музыкальные проекты . Школа вокала предоставляет ученикам индивидуальное внимание и поддержку .
1 win зеркало Ставки на спорт спорт ставков – это динамичный процесс, требующий постоянного анализа, обучения и адаптации к изменяющимся условиям. Ставки прогнозы – это краеугольный камень успешной игры, это умение видеть то, что скрыто от других, это способность предсказывать результаты на основе анализа данных и экспертных оценок.
Индивидуальная программа у нас — это модульный конструктор. В одних случаях критичен блок сна, в других — профилактика вечерних «волн» тревоги, в третьих — семейная медиированная встреча. Мы гибко переставляем модули, учитывая сопутствующие заболевания, приём базовых лекарств (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие), возраст и расписание пациента. Цель проста: чтобы терапия вписалась в жизнь, а не наоборот.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в рязани[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-kazan-czena/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Мелбет Ставки на спорт спорт ставков – это круговорот событий и эмоций, требующий внимания, анализа и готовности к риску. Это игра, в которой важны не только удача, но и знания. Ставки прогнозы – это ключевой элемент успешной игры. Анализ статистики, учет формы команд и знание особенностей игры – все это помогает делать обоснованные прогнозы и повышать свои шансы на выигрыш.
I think I might disagree with some of your analysis. Are the figures solid?
Анонимность — стандарт по умолчанию. Документация ведётся нейтрально и только в объёме, необходимом для оказания помощи. Мы не информируем третьих лиц, не вступаем в контакты с работодателями или соседями. Визит осуществляется на немаркированном авто, общение — коротко и по делу, доступ к карте пациента ограничен принципом «минимально необходимого». Если требуется стационар, используем отдельный вход и «тихий коридор», а по выписке возвращаем тот же маршрут обслуживания на дому.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkolog-nizhnij-novgorod-na-dom
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/
ко ланта
1хбет промокод бесплатно Найдите промокод на http://www.google.io/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и активируйте бонус до 32 500 рублей, чтобы начать игру.
ко ланта
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Сочетание медицинских и психотерапевтических мер создаёт устойчивую систему поддержки. Пациенты получают возможность постепенно восстановить утраченное здоровье и психологическую стабильность.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kazan/
Выездная бригада прибывает с необходимым оборудованием. Инфузионная терапия длится 60–120 минут; по ходу процедуры контролируются давление, пульс, дыхание и субъективное самочувствие, при необходимости схема корректируется (темп капания, смена растворов, добавление противорвотных или седативных средств). Чаще всего уже к концу первой инфузии снижается тошнота, уходит дрожь и «внутренняя дрожь», нормализуется сон. Врач оставляет пошаговый план на 24–72 часа: питьевой режим, щадящее питание (дробно, без жирного и острого), режим сна, рекомендации по витаминам и гепатопротекции. Если в процессе выявляются тревожные признаки (нестабильная гемодинамика, выраженная аритмия, спутанность сознания), будет предложен перевод в стационар.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-vyzov-na-dom[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Казани — это современный медицинский центр, специализирующийся на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основное направление деятельности заключается в проведении детоксикации, восстановлении работы нервной системы и формировании устойчивой мотивации к отказу от употребления психоактивных веществ. Все процедуры проводятся в условиях полной анонимности и медицинского контроля, что обеспечивает безопасность и доверие со стороны пациентов. Программа терапии строится по принципам доказательной медицины и индивидуального подбора лечебных средств.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru
blog-partnera.ru
Мне сразу по поводу мхе ответили, быстро порешили на бонусе в следующую покупку. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш
discoverandshop – Great platform for exploring unique items and discovering new favorites.
Центр сертификации https://серт-центр.рф технические регламенты ЕАЭС, декларации, сертификаты, ISO, испытания и протоколы. Сопровождение с нуля до регистрации в Росаккредитации. Индивидуальные сроки и смета. Консультация бесплатно.
1win 1win скачать – это возможность установить мобильное приложение и всегда иметь доступ к любимой платформе. 1win вход – это быстрый и безопасный доступ к вашему личному кабинету, где вы можете управлять своими финансами, делать ставки и получать бонусы.
Je suis captive par Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Pokerstars Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer sur le site|
Промокод при регистрации 1xbet на 32 500 рублей. Этот код нужно ввести при регистрации в соответствующее поле. Промокод действует однократно, но им можно делиться с друзьями. Регистрация по номеру телефона — удобный способ создать аккаунт. После получения данных для входа остаётся лишь ввести логин и пароль. Используй актуальный получить промокод 1xbet и увеличь первый депозит до 32500 рублей в БК 1xBet. На платформе действует программа лояльности, которая помогает игрокам получать до 130 % бонуса от первого депозита.
J’ai un faible pour Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller plus loin|
I had highly recommend this blog to my good friend, it’s so good
Срочная наркологическая помощь — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемый клинический процесс, где каждое действие проверяется измеримыми маркерами и выполняется в правильной последовательности. В наркологической клинике «ВолгаМед Альтернатива» маршрут выстроен вокруг принципа минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасный старт и телескрининг, затем очный осмотр с выбором контура инфузии и, только после теста переносимости, — основная терапия. Такой подход уменьшает реактивность организма, снижает риск побочных ощущений и делает результат предсказуемым для пациента и близких. Команда работает круглосуточно, выезжает на немаркированном транспорте, общение ведётся через одного доверенного человека, а документы оформляются в нейтральной терминологии без стигматизирующих формулировок.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/narkologiya-anonimno-kazan/
В наше время охрана личной информации и приватность онлайн делаются все более важными. Если вы хотите прокапаться анонимно‚ важно использовать анонимные услуги‚ такие как VPN-сервисы и прокси-сервисы‚ которые позволят скрыть вашу личность и обезопасить ваш IP-адрес. Подобные решения гарантируют шифрование вашего подключения‚ что повышает безопасность в сети и невидимость ваших действий. Вы также можете обходить блокировки и посещать сайты без необходимости регистрации. Безопасность информации становится важной частью безопасного серфинга в интернете‚ позволяя оставаться в безопасности. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru
J’ai un faible pour Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Mystake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, occasionnellement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Mystake Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis enthousiasme par Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Casinozer Casino garantit un amusement continu. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г lire|
Innovation Ideas Hub – Found a concept that sparked some exciting new thoughts.
Je suis completement seduit par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, rarement des offres plus importantes seraient super. En resume, Mystake Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements rapides.
Apprendre comment|
Прогнозы на спорт 1 ставка – это первый шаг на пути к победе, это проверка своих сил и знаний, это возможность почувствовать себя настоящим экспертом в мире спорта. Ставки на спорт – это не только шанс сорвать куш, но и возможность глубже погрузиться в любимый вид спорта, следить за новостями, анализировать статистику и предвидеть результаты. Это игра, требующая терпения, анализа и, конечно же, веры в свою удачу.
Здесь
[url=https://medmarketing.ua/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Пушкино в клинике «Трезвый Путь» — это оперативная помощь на дому и в стационаре, персональные детокс-схемы и бережное восстановление организма без постановки на учёт. Мы подключаемся круглосуточно, аккуратно снимаем интоксикацию, стабилизируем давление и пульс, уменьшаем тремор, тревогу и бессонницу, а затем предлагаем понятный маршрут к ремиссии, который вписывается в ваш рабочий и семейный график. Цель — безопасно пройти острый период и не «сорваться» обратно, когда станет чуть полегче.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir le site|
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
May I just say what a relief to discover somebody who actually knows what they’re talking about online. You certainly realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people ought to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you aren’t more popular because you most certainly have the gift.
банда казино
употреблял перорально, также пробовал нозально (не вариант сжигает все напрочь и комок в слизистой) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Сеть детских садов https://www.razvitie21vek.com «Развитие XXI век» – уникальная образовательная среда для детей от 1,5 лет, где каждый ребенок сможет раскрыть свои таланты. Мы предлагаем разнообразные программы для развития творческих, физических, интеллектуальных и лингвистических способностей наших воспитанников.
Мелбет 1win – это современная платформа, предлагающая широкий выбор возможностей для онлайн-развлечений, включая ставки на спорт. 1win официальный – это ваш надежный проводник в мир азарта, гарантирующий честную игру и быстрые выплаты.
промокод при регистрации 1xBet Ввод промокода при регистрации на http://www.google.cat/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html позволяет получить бонус 100% на первый депозит, чтобы начать игру с максимальной суммой.
Excellent article! We are linking to this great content on our site. Keep up the great writing.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
Такая структура терапии позволяет избежать рецидивов, снизить тревожность и восстановить когнитивные функции. Каждый этап лечения направлен на постепенное возвращение пациента к нормальному образу жизни и социальной активности.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Курс терапии в клинике состоит из нескольких последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение конкретных целей — от снятия интоксикации до восстановления психологического равновесия. Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и минимизировать вероятность рецидива. На всех стадиях лечения ведётся контроль состояния пациента, а также постоянная корректировка назначений в зависимости от реакции организма.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/klinika-narkologiya-kazan/
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в ростове-на-дону[/url]
промокод 1xbet бесплатно Ищите промокод на http://www.google.com.mt/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и получите бонус 100% на первый депозит, чтобы начать игру.
Вывод из запоя в Пушкино в клинике «Трезвый Путь» — это оперативная помощь на дому и в стационаре, персональные детокс-схемы и бережное восстановление организма без постановки на учёт. Мы подключаемся круглосуточно, аккуратно снимаем интоксикацию, стабилизируем давление и пульс, уменьшаем тремор, тревогу и бессонницу, а затем предлагаем понятный маршрут к ремиссии, который вписывается в ваш рабочий и семейный график. Цель — безопасно пройти острый период и не «сорваться» обратно, когда станет чуть полегче.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Блог для новичков https://life-webmaster.ru запуск блога, онлайн-бизнес, заработок без вложений. Инструкции, подборки инструментов, стратегии трафика и монетизации. Практика вместо теории.
Брал здесь 203-й качество отличное 1 к 10 делал на мать и мачехи с одного водника ушатывает наглухо!!! Магазин отличный, если не ждать ответа менеджера по 2 часа!!! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
Hello! I suggest using high-quality databases for Xrumer and GSA SE Ranker. They are inexpensive, updated multiple times a month, and significantly simplify and speed up website promotion.
You can view the information on the website https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/
You can choose any language on the website. You can use LTC, USDT, TRX, ETH, BTC, SOLANA and other money.
I was referred to this web site by my cousin. I’m not sure who has written this post, but you’ve really identified my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Очищение организма от алкоголя в Красноярске, ключевой момент в борьбе с зависимостью от алкоголя. Наркологические клиники в Красноярске предлагают различные курсы детоксикации, которые помогают преодолеть алкогольную зависимость. Выездной нарколог может оказать помощь при алкогольной зависимости на дому что является удобным решением для многих пациентов. нарколог на дом Лучшие врачи-наркологи проводят терапию запойного синдрома и предоставляют всю необходимую медицинскую поддержку при алкоголизме . Обсуждение с наркологом позволяет разработать персонализированный план терапии. Не менее важна психологическая поддержка в процессе детоксикации, что помогает в восстановлении после злоупотребления алкоголем и успешной реабилитации от алкоголя ;
Если дома нет возможности обеспечить тишину (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости), можно кратко перейти в «тихий стационар» с отдельным входом; после стабилизации сопровождение возвращается на дом, и маршрут продолжается «зеркально» — с теми же целями и окнами оценки. Такой перенос сохраняет управляемость процесса и снижает тревогу семьи: никто не «начинает сначала», меняется только место, а логика остаётся прежней.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь казань[/url]
Instant Value Hub – Picked up a good discount here that caught my attention.
aviator game [url=http://aviator-game-predict.com/]http://aviator-game-predict.com/[/url] .
карнизы для штор с электроприводом [url=www.prokarniz36.ru]www.prokarniz36.ru[/url] .
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
Магазин Харош, Внимательней читайте отзывы о той продукции какая вас интересует более подходит имено вам только такой подход может оставить всем только положительные эмоции. Работа магазина по всем пораметрам оставляет только положительные эмоции :voo-hoo: ставлю все оценки только отлично. Всем добРа, советую, обращайтесь в даный магазин, вам помогут быстро и качествено доставить то,что вам нужно купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану
Вин 1win Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom, Melbet: Сравнение и Особенности Winline, Fonbet, Betcity, BetBoom и Melbet – это ведущие букмекерские компании, предлагающие ставки на спорт в России и других странах. Каждая из этих компаний имеет свои особенности и преимущества. Winline Winline – это одна из самых популярных букмекерских компаний в России. Она известна своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и быстрым выводом средств. Fonbet Fonbet – это одна из старейших букмекерских компаний в России. Она предлагает широкий выбор ставок на спорт, а также тотализатор. Betcity Betcity – это букмекерская компания, которая предлагает высокие коэффициенты и широкую линию событий. Она также предлагает различные виды ставок, такие как экспрессы, системы и лайв-ставки. BetBoom BetBoom – это новая букмекерская компания, которая быстро набирает популярность. Она предлагает высокие коэффициенты, широкую линию событий и удобный интерфейс. Melbet Melbet – это международная букмекерская компания, которая предлагает ставки на спорт и казино. Она известна своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и разнообразными бонусами.
анонимная консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva011.ru
стационар психиатрической больницы
Капельница от запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде часто становится первым шагом в лечении хронической алкогольной зависимости. Детоксикация помогает вывести продукты распада этанола и снизить нагрузку на внутренние органы, но не устраняет психологическую зависимость. Поэтому после завершения инфузионной терапии пациенту рекомендуется пройти консультацию психотерапевта и, при необходимости, начать курс реабилитации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/
1 win зеркало 1 win сайт – это удобный и интуитивно понятный интерфейс, делающий процесс ставок простым и приятным. 1 win официальный сайт – это ваш личный кабинет в мире азарта, где вы можете управлять своими финансами, делать ставки и получать бонусы.
I’m so happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this best doc.
1 ставка 1 win сайт – это удобный и интуитивно понятный интерфейс, который делает процесс ставок простым и приятным. 1 win официальный сайт – это ваш персональный кабинет, где вы можете управлять своими ставками, следить за результатами и получать бонусы.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais encore des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fluides.
Savoir plus|
Создание блога http://life-webmaster.ru и бизнеса в сети шаг за шагом: платформы, контент-план, трафик, монетизация без вложений. Готовые шаблоны и понятные инструкции для старта.
Hi! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Успехов и процветания магазину купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Poursuivre la lecture|
игровые автоматы бонус за регистрацию
yourtimeisnow – Motivating site that encourages taking action and embracing opportunities today.
Hi my family member! I want to say that this article is amazing, great written and include approximately all important infos. I’d like to see more posts like this .
{Капельница от запоя на дому: как избежать повторного срыва (владимир)|{Лечение запоя на дому: капельница и профилактика срыва (владимир)|{Капельницы от запоя на дому: ключ к успешной реабилитации (владимир)}} {Алкогольная зависимость – это серьезная проблема‚ требующая быстрой реакции.|Проблема алкогольной зависимости требует оперативного вмешательства.|Алкогольная зависимость является важной проблемой‚ которая нуждается в незамедлительном решении.} {Нарколог на дом срочно|Срочный нарколог на дом|Наркологические услуги на дому} {предоставляет наркологические услуги‚ включая капельницы для быстрого восстановления.|предлагает услуги по лечению‚ включая капельницы для быстрого восстановления организма.|обеспечивает лечение алкоголизма‚ включая капельницы для скорейшего восстановления.} {При запое важно не только лечение на дому‚ но и профилактика срыва.|Важно помнить‚ что при запое необходимо не только лечение‚ но и профилактика рецидивов.|Лечение на дому при запое должно включать как терапию‚ так и профилактические меры против срывов.} {Медицинская капельница помогает детоксифицировать организм‚ облегчая симптомы абстиненции.|Капельница способствует детоксикации и облегчает симптомы абстиненции.|Капельница играет важную роль в детоксикации организма и уменьшении симптомов абстиненции.} {Срочная помощь специалистов включает в себя не только физическое восстановление‚ но и психологическую помощь.|Помощь специалистов охватывает как физическое‚ так и психологическое восстановление.|Специалисты предоставляют не только физическую помощь‚ но и поддержку на психологическом уровне.} {Поддержка родственников также играет ключевую роль‚ способствуя успешной реабилитации алкоголиков;|Важность поддержки со стороны близких неоспорима‚ так как она содействует успешной реабилитации.|Родные играют важнейшую роль в процессе реабилитации‚ способствуя успеху лечения.} {Detox программа поможет избежать повторного срыва и обеспечит безопасное лечение.|Программа детоксикации поможет предотвратить рецидивы и обеспечит безопасное лечение.|Детокс-программа предотвращает срывы и гарантирует безопасность лечения.} {Обратитесь к наркологу на дом‚ чтобы получить комплексную помощь и вернуться к нормальной жизни.|Свяжитесь с наркологом на дом для получения комплексной помощи и возвращения к полноценной жизни.|Не откладывайте‚ обратитесь к наркологу на дом за комплексной помощью и начните новую жизнь.}
Style Spot Online – Browsing was effortless, and items were attractive and budget-friendly.
Да уже и так понятно что перепутали. Пробуй сразу и на кишку, и по носу мб определишь что же тебе прислали по ошибке. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану
Реабилитация после запоя: как вернуться к нормальной жизни в Красноярске Алкоголизм — это серьезная проблема, касающаяся многих, и восстановление после запоя является важным этапом на пути к трезвому образу жизни. В Красноярске доступны многообразные услуги в области наркологии, включая консультации у наркологов и выездные медицинские услуги. Нарколог на дом клиника Медицинские учреждения предлагают реабилитационные программы, которые включают психотерапию и поддержку в эмоциональном плане. Поддержка семьи также играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Кризисные центры и группы поддержки в Красноярске помогают зависимым справиться с трудностями, обеспечивая социальную адаптацию. Важно обратиться к специалистам для получения помощи и начать путь к здоровой жизни.
yourdealhub – Excellent deals on quality products, really makes shopping worthwhile.
Сделал 4 затяжки с батла, почувствовал секунд через 30 первое прикосновение.))) Затем не много стал теряться в пространстве и во времени, а когда поднялся домой, и открыл дверь (5 мин спустя) меня перекрыло нах, я не мог закрыть дверь и мне всё казалось что кто то держит, у меня начинается паника) я начинаю кричать за дверь: – ты кто такой отпусти, иди отсюда………….. Зову родаков, которых дома нет слава Богу!!!!! вообщем стоял минут 20 у двери) а когда пошёл в комнату мне казалось что кто то за мной ходит!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану
Very good post! We are linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Je suis bluffe par Pokerstars Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
http://www.pokerstarscasino365fr.com|
Ребята подскажите пжл.Сейчас общаюсь с оператором в скайпе по Липецку Lipeck-shops ктонибудь у него приобреатл в липе с воскресенья по данный день и оплачивали вы на данные реквы 964 и 905(он говорит что их у него два)Бразы помгите разобраться. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
trendloversplace – Perfect for trend enthusiasts, always something fresh and exciting to see.
Такая последовательность действий обеспечивает системное воздействие и минимизирует риски осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в санкт-петербурге[/url]
TurkPaydexHub Review
TurkPaydexHub se demarque comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies innovante, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, repere les opportunites et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une exactitude et une rapidite hors de portee des traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les potentiels de rendement.
Порча от наркотиков — это сложная хоботня,
обхватывающая физиологическое, психологическое и общественное здоровье человека.
Употребление таких наркотиков, как кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» или «бошки», может обусловить буква неконвертируемым последствиям яко для организма, яко и для общества в течение целом.
Хотя даже у эволюции связи возможно восстановление — главное, чтоб энергозависимый явантроп обернулся согласен помощью.
Важно памятовать, что наркомания лечится, равным образом помощь дает шанс на свежую жизнь.
психиатр онлайн консультация
psychiatr-moskva012.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника
TurkPaydexHub Official Page
TurkPaydexHub se demarque comme une plateforme de placement crypto revolutionnaire, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour proposer a ses membres des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA etudie les marches financiers en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et applique des tactiques complexes avec une precision et une vitesse hors de portee des traders humains, maximisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
Обращайтесь всегда рады! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Best wishes! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Алкогольная зависимость, это острая проблема, требующая экспертного вмешательства. Круглосуточная клиника предлагает помощь нарколога, обеспечивая очищение организма и лечение алкоголизма. Симптомы алкогольной зависимости могут варьироваться, от телесной зависимости до умственных расстройств; Медикаментозная detox-программа включает в себя очистку и реабилитацию от алкоголя, что позволяет реабилитироваться после запоя. Консультация нарколога помогает определить степень зависимости и выбрать подходящий метод лечения. Психотерапия при алкоголизме является ключевым этапом, предоставляя поддержку для зависимых. Тайное лечение алкоголизма гарантирует конфиденциальность. Нарколог в владимире всегда готов оказать помощь, обеспечивая индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.}
purefashionchoice – Clean, stylish fashion selections that are both modern and practical.
электрические гардины [url=elektrokarniz1.ru]elektrokarniz1.ru[/url] .
Elegant finds hub – Browsing was smooth, and the products felt very classy today.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que
significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto
se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y
apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas
deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app
casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de
apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app
de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app
para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar
control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps
de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de
apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer
apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas
2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas
a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas
argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso
a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas
athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real
sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas
athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas
barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas
barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real
madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas
bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol
venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida
sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas
boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas
boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de
barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas
campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas
campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas
campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga
española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas
celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas
chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile
vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas
ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia
paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas
combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas
para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras
para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas
comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap
asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas
con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey
final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa
italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas
copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para
hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de
caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y
colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino
por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas
de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de
f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas
de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas
de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la
copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de
la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de
partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis
de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de
ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del
mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas
caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com
foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas
deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas
deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas
del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas
futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap
asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales
en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas
mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas
mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas
deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb
hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas
online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas
online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas
deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas
real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas
sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas
deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso
la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias
seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de
honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas
el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino
online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas
en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas
en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas
en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas
españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas
españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas
españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa
league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas
euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas
favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa
de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final
euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas
formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol
mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos
online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas
ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas
ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar
nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona
athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas
girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar
premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas
handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas
online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas
juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga
santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas
liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones
de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas
liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid
valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos
online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas
mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial
favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas
mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba
esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas
online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online
ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas
online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas
online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna
barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas
over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos
inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions
league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas
para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas
para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para
hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas
partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a
primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas
por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar
dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas
portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas
predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara
la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real
madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas
real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas
real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real
madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas
recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas
roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas
seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas
seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas
seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de
madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas
sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas
sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester
united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas
stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas
superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis
consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas
tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos
de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas
ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc
pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc
topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas
uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs
colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal
athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real
madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas
william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas
y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos
apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic
real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid
apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona
real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs
celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona
vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla
apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis
chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida
apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas
de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito
casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de
apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos
gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas
de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora
apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de
apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas
deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas
combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas
de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios
apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas
apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de
caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas
española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de
apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de
apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de
apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas
del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas
online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas
esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de
apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa
de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de
apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de
apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa
de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa
de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de
apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real
madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas
españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas
esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas
apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas
barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas
cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de
apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas
de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas
con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas
de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas
deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas
de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero
gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa
online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa
licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas
españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas
de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas
de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas
de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de
apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores
bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas
de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas
de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online
mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas
de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de
apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apue
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Чертежи переведём точно – перевод документов удаленно. Срочный перевод документов в Самаре? Выполним быстро! Нотариальное заверение. Конфиденциально. Гарантия качества.
ещё раз говорю, здесь качество отменное, по крайней мере с той партии, с которой я получал. 1к10 убивало в мясо с напаса ) https://rentalscroacia.info скинули трек не бьется ((( уже в четверг отправили а он все не бьется(((, очень торпимся надо человека собирать в дорогу!
J’ai une passion debordante pour Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Stake Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses continues.
Lancer le site|
globalvaluecorner – Amazing value and variety of products from around the world.
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer maintenant|
CHESTERBETS – Новости спорта | Форум о спорте | Чат | Футбол | Спорт
https://chester.bet/
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Stake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis completement seduit par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps en temps des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Mystake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus constants.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis bluffe par Mystake Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, qui motive les joueurs.
Commencer Г naviguer|
J’adore la vibe de Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, en revanche des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En resume, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Stake Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent sans delai, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Stake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En extra le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement excellent les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je ne me lasse pas de Mystake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, Mystake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Casinozer Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer la page|
Здесь
[url=https://happylook.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
купить диплом другу [url=www.r-diploma29.ru/]купить диплом другу[/url] .
J’adore l’energie de Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fluides.
Cliquer maintenant|
я купил у них первый раз реактивы, всё пришло довольно быстро и консперация норм, не знаю если такой метод что они используют палевный то как иначе….. https://industrial-revolution.info все ровно ваще чисто жду проверив качество отпишу
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Stake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour faire court, Stake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A souligner la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Apprendre comment|
I enjoy reading through a post that can make people think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment!
J’adore la vibe de Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En fin de compte, Casinozer Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Cliquer maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Mystake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est simple et transparent, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino offre une aventure memorable. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir la page|
Je suis enthousiasme par Mystake Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer la page|
Школа барабанов предлагает профессиональные [url=https://shkola-barabanov.ru/]уроки игры на барабанах[/url], открывая возможность для всех желающих освоить эту увлекательную инструментальную дисциплину.
под руководством опытных преподавателей . Целью такой школы является развитие музыкальных способностей и повышение общего культурного уровня студентов путем участия в различных музыкальных проектах и концертах. Школа барабанов также предоставляет возможность студентам общаться с другими музыкантами и учиться у них через систему наставничества и индивидуальных занятий .
Школа барабанов может быть интересна как начинающим музыкантам, так и профессионалам которые стремятся расширить свою музыкальную эрудицию. Программа обучения в школе барабанов обычно включает в себя теоретические занятия по музыкальной теории и истории, а также практические занятия по игре на барабанах в группах или индивидуально . Кроме того, школа барабанов часто организует различные мероприятия и концерты с приглашением известных музыкантов и групп .
Обучение в школе барабанов может принести студентам многочисленные преимущества такие как развитие музыкальных способностей и повышение общего культурного уровня . Одним из главных преимуществ является возможность получения профессионального музыкального образования в формате индивидуальных или групповых занятий. Кроме того, обучение в школе барабанов может помочь студентам повысить свою уверенность в себе и развить творческие способности путем общения с другими музыкантами и учениками.
Обучение в школе барабанов также предоставляет возможность студентам получить практический опыт и развить свои навыки игры на барабанах посредством участия в музыкальных мероприятиях и концертах . Школа барабанов может быть интересна как детям, так и взрослым которые ищут возможность для творческого самовыражения . Преподаватели школы барабанов обычно имеют большой опыт работы и могут помочь студентам в подготовке к музыкальным конкурсам и выступлениям.
Программа обучения в школе барабанов обычно включает в себя комплекс теоретических и практических занятий по технике и методике игры на барабанах . Теоретические занятия могут включать в себя изучение музыкальной теории, истории музыки и различных стилей и направлений с использованием современных учебных пособий и технологий . Практические занятия могут включать в сбя обучение различным техникам игры на барабанах под руководством преподавателей с большим опытом работы.
Программа обучения в школе барабанов может варьироваться в зависимости от уровня подготовки и интересов студентов для начинающих музыкантов . Школа барабанов может предлагать различные направления обучения по народной и эстрадной музыке, а также ??? форматы обучения онлайн- или офлайн-курсы . Кроме того, школа барабанов часто организует различные мероприяти и концерты с участием студентов и преподавателей школы .
В заключении можно сказать, что школа барабанов представляет собой уникальную и интересную возможность для музыкального образования и творческого самовыражения для музыкантов, ищущих новые подходы и методы . Программа обучения в школе барабанов может включать в себя теоретические и практические занятия по развитию слуха и ритма, а также различные мероприятия и концерты с приглашением известных музыкантов и групп .
Перспективы развития школы барабанов могут включать в себя расширение программы обучения и включение новых направлений и стилей таких как электронная музыка или экспериментальные жанры , а также развитие онлайн-образования и удаленных курсов для студентов из разных городов и стран . Кроме того, школа барабанов может сотрудничать с другими музыкальными школами и организациями для организации совместных проектов и концертов .
J’adore le dynamisme de Casinozer Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par ailleurs des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement le design est style et moderne, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Approfondir|
Just wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness in your post is simply nice and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the enjoyable work.
Купить iPhone в Москве
everydayessentials – Convenient site to find daily essentials quickly and easily.
При выводе из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону используются разные терапевтические подходы. Основной задачей является устранение токсинов и восстановление работы систем организма. Врач подбирает терапию индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и длительности запоя.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu/
Sharing my genuine review regarding Crown GreenCasino. I describe rewards, financial side, and user experience. Emphasizing casino offers and money-out process. Explaining how the platform handles and releases funds. Noting what works and what doesn’t I ran into. Describing what I appreciated and what I didn’t. You can find more info in the full write-up Crowngreen
Эти шаги помогают системно подойти к проблеме и обеспечить максимальную эффективность лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Better Finds Marketplace – Categories were straightforward and the products felt premium.
Вчера оплатил, сегодня получил бьющийся трек. Так что все норм. Разговор в скайпе длился 30мин, я оплатил и через 2 часа мне уже выслали посылку. Осталось проверить кач-во фашки. Если все норм, сработаемся с конторой. https://bwin99.info Отличный товар и работают ребята без перебоев
beef casino промокоды
Developing a framework is important.
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/klinika-narkologii-spb/
beef casino отзывы
Je suis bluffe par Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lire plus|
Форматы вывода из запоя в Пушкино
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]pomoshch-na-domu-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар нижний новгород[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Андрей Николаевич Селиванов, «своевременный визит специалиста на дом позволяет избежать тяжёлых осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния»».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Семья получает «путевой лист» на 24–72 часа: как фиксировать маркеры (тремор/тревога/тошнота 0–10), как пить воду малыми глотками, когда приглушать свет и в каком формате общаться с пациентом («короткие факты вместо оценок»). Мы также даём «лестницу активности»: два достижимых действия утром, одно — вечером. Эта дисциплина маленьких шагов помогает избежать эмоциональных «перегревов» и удерживает достигнутый эффект.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru
Je suis fascine par Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, en revanche des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements rapides.
Tout apprendre|
печать визиток под ключ за 24 часа! Типография – быстро, качественно, сгарантией. Оставьте заявку на сайте
электрокранизы [url=http://elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru/]http://elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru/[/url] .
Качество ЖВШ на высшем уровне, скоро придёт посыль – отпишусь сам о качестве, но уже доводилось пробовать их 203 и 250 – великолепны https://bwin99.info “Решил Попробовать Записаться”
dailydealsplace – Always updated with great bargains, love checking in daily.
Ориентир по времени
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-zhukovskom/
I found your blog through google and I must say, this is probably one of the best well prepared articles I have come across in a long time. I have bookmarked your site for more posts.
Лечение в клинике в Челябинске строится на принципах конфиденциальности, добровольности и медицинской этики. Врачи применяют доказательные методы терапии, а программы лечения адаптируются под особенности каждого пациента. Работа ведётся комплексно, включая медикаментозную помощь, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет эффективно восстановить здоровье и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
купить диплом бакалавра 2016 [url=http://www.r-diploma28.ru]купить диплом бакалавра 2016[/url] .
Вызов нарколога на дом сочетает медицинскую эффективность с удобством. Пациент получает квалифицированную помощь в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Я переконався, що читати новини зручно там, де вони подані у зручному форматі на сайті. Це створює комфорт.
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В Реутове помощь при запое должна быть быстрой, безопасной и конфиденциальной. Команда «Трезвой Линии» организует выезд врача 24/7, проводит детоксикацию с контролем жизненных показателей и помогает мягко стабилизировать состояние без лишнего стресса. Мы работаем по медицинским протоколам, используем сертифицированные препараты и подбираем схему персонально — с учётом анализов, хронических заболеваний и текущего самочувствия. Приоритет — снять интоксикацию, восстановить сон и аппетит, выровнять давление и снизить тревожность, чтобы человек смог безопасно вернуться к обычному режиму.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove
Здесь
[url=https://fedast.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Fastidious answers in return of this matter with genuine arguments and telling everything on the topic of that.
не бзди все будет ровно трек не всегда бьется это касяк курьерки а не отправителя не паникуй https://hiphopget.com Всё что В прайс листе на сайте есть,всё в наличии ?
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Stake Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Stake Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Touchez ici|
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour couronner le tout la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Explorer maintenant|
Лечение зависимости требует системного подхода и чёткой последовательности действий. Каждый этап направлен на устранение интоксикации, восстановление функций организма и закрепление результата. В клинике процедура организована так, чтобы обеспечить комфорт и безопасность пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Нужен интернет? интернет для компаний провайдер 2BTelecom предоставляет качественный и оптоволоконный интернет для юридических лиц в городе Алматы и Казахстане. Используя свою разветвленную сеть, мы можем предоставлять свои услуги в любой офис города Алматы и так же оказать полный комплекс услуг связи.
Для тех, кто ищет современные и экономически эффективные решения для строительства своего дома, [url=https://karkasnye-doma-pod-klyuch2.ru/]каркасный дом под ключ в спб[/url] является оптимальным выбором, предлагающим высокое качество, быстрое возведение и широкий спектр дизайнерских решений.
становится все более популярным каждый год . Это связано с доступностью и простотой конструкции таких домов. Жители города отдают предпочтение каркасным домам из-за их способности обеспечить комфорт и уют .
Строительство каркасных домов представляет собой уникальную возможность для тех, кто хочет воплотить в жизнь проект своей мечты. Каркасные дома отличаются экологической чистотой и энергоэффективностью , что повышает их популярность среди жителей Санкт-Петербурга.
Преимущества каркасных домов неоспоримы и существенны . Они позволяют сэкономить на строительных материалах , что увеличивает скорость строительства. Каркасные дома обладают уникальными эстетическими качествами , что увеличивает их конкурентоспособность.
Каркасные дома обеспечивают высокий уровень комфорта и уюта к строительству жилья. Они позволяют воплотить в жизнь самые смелые проекты , что повышает их популярность среди населения Санкт-Петербурга.
Процесс строительства каркасных домов характеризуется высокой скоростью и эффективностью . Он характеризуется гибкостью и адаптируемостью, что обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности . Строительство каркасных домов включает в себя изготовление и доставку материалов , что увеличивает скорость строительства.
Каркасные дома отличаются индивидуальным подходом и дизайном. Это позволяет получить уникальный и комфортный дом , что повышает их популярность среди жителей Санкт-Петербурга.
Строительство каркасных домов в Санкт-Петербурге обеспечивает широкие возможности для индивидуального дизайна. Каркасные дома характеризуются простотой и доступностью , что увеличивает их конкурентоспособность. Строительство каркасных домов является современным и прогрессивным подходом , что повышает уровень комфорта и уюта.
Каркасные дома представляют собой уникальную возможность для тех, кто хочет быстро и качественно построить дом . Строительство каркасных домов в Санкт-Петербурге становится все более популярным каждый год , что повышает уровень доверия к каркасным домам.
learncreategrow – Inspiring content that encourages learning, creating, and personal growth.
Je ne me lasse pas de Pokerstars Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
обечайка упаковка под ключ за 24 часа! Типография – быстро, качественно, сгарантией. Оставьте заявку на сайте
Top Style Finds – The interface made discovering fashion quick and enjoyable.
Индивидуальная программа у нас — это модульный конструктор. В одних случаях критичен блок сна, в других — профилактика вечерних «волн» тревоги, в третьих — семейная медиированная встреча. Мы гибко переставляем модули, учитывая сопутствующие заболевания, приём базовых лекарств (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие), возраст и расписание пациента. Цель проста: чтобы терапия вписалась в жизнь, а не наоборот.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru
Je suis captive par Stake Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Stake Casino est un must pour les passionnes. De plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Pokerstars Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Выездная бригада прибывает с необходимым оборудованием. Инфузионная терапия длится 60–120 минут; по ходу процедуры контролируются давление, пульс, дыхание и субъективное самочувствие, при необходимости схема корректируется (темп капания, смена растворов, добавление противорвотных или седативных средств). Чаще всего уже к концу первой инфузии снижается тошнота, уходит дрожь и «внутренняя дрожь», нормализуется сон. Врач оставляет пошаговый план на 24–72 часа: питьевой режим, щадящее питание (дробно, без жирного и острого), режим сна, рекомендации по витаминам и гепатопротекции. Если в процессе выявляются тревожные признаки (нестабильная гемодинамика, выраженная аритмия, спутанность сознания), будет предложен перевод в стационар.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Je suis captive par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Mystake Casino offre une aventure memorable. De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Entrer sur le site|
По моему отзыв о “марочках” был явно не про этот магазин О_о https://alleya.info Всем советую таряться здесь)))
Je suis accro a Casinozer Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Casinozer Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je ne me lasse pas de Mystake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Mystake Casino assure un fun constant. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/[/url]
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Je suis enthousiasme par Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais encore plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino garantit un amusement continu. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller en ligne|
Hi, always i used to check weblog posts here early in the morning, since i enjoy to gain knowledge of more and more.
Купить Samsung S25 в Москве
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing in your feed and I am hoping you write again very soon!
This is something that will need all of our combined efforts to address.
growtogetherstrong – Positive and motivating, perfect for teamwork and community growth.
лучше и не напишешь бро https://psyholog-help.com Ровный магазин . Всем советую !
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
ЗОЖ-журнал https://wellnesspress.ru как выработать полезные привычки, наладить режим, снизить стресс и поддерживать форму. Простые шаги, научные факты, чек-листы и планы. Начните менять жизнь сегодня.
После проведения процедур пациент чувствует заметное облегчение: исчезает головная боль, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. Это создаёт основу для дальнейшего прохождения курса лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены нижний новгород[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в владимире — это важный шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с проблемами зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir023.ru можно получить сведения о услугах наркологов, включая выявление зависимостей и лечение медикаментами. Специалисты нашего центра предлагают услуги нарколога и конфиденциальное лечение. Наркологическая выездная служба готова выполнить срочный вызов при приступе зависимости или других ситуациях. Наши услуги предлагают стационарное лечение и реабилитацию для людей, имеющих проблемы с наркотиками. Мы предоставляем поддержку зависимым и их семьям и осуществляем профилактические мероприятия. Не медлите с помощью — позвоните наркологу и начните путь к лечению.
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye -.
Creative Spark Daily – Find inspiration to start exciting projects and explore new ideas.
Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию и предсказуемые алгоритмы. Это означает — никакой полипрагмазии, никаких «универсальных капельниц», никакого «сделаем всё сразу». Сначала — безопасность (дыхание, гемодинамика, сознание), затем — управляемая детоксикация с коррекцией водно-электролитного баланса и седацией только по показаниям, после — «тихий режим» и восстановление сна, и уже на этом фоне — поведенческие навыки, работа с триггерами, переговоры с семьёй о правилах поддержки. Такой порядок убирает хаос, снижает тревогу и делает ремиссию не подвигом, а реальной рутиной.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan/
Здесь
[url=https://www.school-xyz.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Резюме переведём профессионально – нотариально заверенный перевод документов. Перевод документов с нотариальным заверением в Самаре. Срочно, недорого, качественно. Любые языки мира. Звоните!
Такая последовательность обеспечивает медицинскую точность и безопасность процедуры, позволяя добиться быстрого улучшения самочувствия без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske-vyvod-iz-zapoya
Terrific work! That is the kind of information that should be shared across the net. Shame on the search engines for no longer positioning this publish higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thank you =)
СРОЧНЫЙ вопрос!! https://miqualityhealthcaretraining.com конечно была задержка которая заставила по нервничать, но всё прошло на уровне и я получил свою посылочку)))
Запой — это не «несколько лишних бокалов», а острое состояние с системной нагрузкой на сердце, мозг и печень. В клинике «РязМедСервис» мы рассматриваем вывод из запоя как управляемый медицинский процесс: быстрый выезд, экспресс-диагностика, индивидуальные капельницы через инфузомат, круглосуточная связь и строгая конфиденциальность. Мы приезжаем без опознавательных знаков, оформляем документы в нейтральных формулировках и оставляем пациенту и близким понятный план на 72 часа — чтобы первая трезвая ночь прошла спокойно, а эффект лечения стал предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru
InspireJourneyOnline – Inspiring guidance available, encourages exploring creative possibilities.
buildyourownfuture – Great motivational site, helps focus on goals and planning ahead.
The housing market is constantly evolving, and in recent years, Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) have become a popular trend. ADUs, often referred to as “granny flats” or “in-law suites,” are secondary housing units on a single-family residential lot. They are an excellent solution for those looking to add value to their property, increase living space, or create a potential source of rental income. The process of [url=https://idiomafutbol.com/home-improvement-experts-remodeling-experts-near-353/]ADU construction[/url] requires careful planning and execution. It starts with an evaluation of the existing property to determine the best location for the ADU. This is followed by designing the unit to ensure it fits seamlessly with the main house while also meeting the needs of potential occupants. The construction phase involves building the ADU from the ground up, including the installation of utilities and finishing touches. While constructing an ADU might seem like a daunting task, it can be a worthwhile investment. It not only increases the value of your property but also provides additional living space that can be used for a variety of purposes. Whether you’re planning to rent it out for extra income, use it as a guest house, or provide a home for aging relatives, an ADU can offer numerous benefits. However, it’s important to note that ADU construction is not a DIY project. It requires the expertise of professionals who understand the intricacies of building codes and regulations. Hiring a professional team ensures that your ADU is built to the highest standards of quality and safety. In conclusion, ADU construction is an exciting opportunity for homeowners looking to maximize their property’s potential. It’s a process that requires careful planning and professional expertise, but the end result can provide significant benefits. Whether you’re looking to increase your property value, generate rental income, or create more living space, an ADU could be the perfect solution.
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog010.ru
лечение запоя тула
Работаем с данным магазином! всем советую! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Если есть какие -то вопросы по компенсациям вложенным, тоже пишите мне в Skype: chemical-mix.com и ICQ: 974-859, все решим
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на диагностике, лечении и реабилитации пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Основная цель деятельности учреждения — восстановление физического здоровья и психологической устойчивости человека, оказавшегося в состоянии зависимости. В клинике применяются современные методы терапии, доказавшие эффективность в медицинской практике. Все процедуры проводятся конфиденциально, с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и под контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru
Anyone and only loli po*rn
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
ChicSpotShop – Creative pieces featured, browsing through styles was simple and inspiring.
creativegiftoutlet – Amazing gift ideas, really unique and thoughtful selections available here.
абакан есть? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки “Думаю надо прогуляться, за Кооперативом еще кОоПератив,Захожу туда и тут описание сходиться бля Думаю тут то Полюбому”
Keep this going please, great job!
Весь процесс можно представить следующим образом:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
TreasureFindsOnline – Loved the selection of deals, shopping around was smooth and quick.
видел тут в ветке пару сообщений о том, что заказчикам вместо нормального товара какую то муть присылали, так вот хотелось бы узнать у владельцев магазина, в связи с чем возникают такие накладки и как часто такое случается, а то почтой итак заказ долго дожидаться, а если ещё подобный косяк выйдет с возвратом, то это будет полный п… https://verbandsabzeichen.info Магазин работает? пишу в ЛС и Джабер везде тишина, ответа нет!((
Лечение зависимости требует системного подхода и чёткой последовательности действий. Каждый этап направлен на устранение интоксикации, восстановление функций организма и закрепление результата. В клинике процедура организована так, чтобы обеспечить комфорт и безопасность пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в челябинске[/url]
В стационаре мы добавляем расширенную диагностику и круглосуточное наблюдение: это выбор для пациентов с «красными флагами» (галлюцинации, выраженные кардиосимптомы, судороги, рецидивирующая рвота с примесью крови) или тяжёлыми соматическими заболеваниями. На дому мы остаёмся до первичной стабилизации и оставляем письменный план на 24–72 часа, чтобы семья действовала уверенно и согласованно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
shopforvalue – Affordable products without compromising quality, makes shopping super satisfying.
рок группа позавчера “Позавчера рок” – это попытка сохранить дух ушедших эпох и передать его новым поколениям. Это дань уважения классикам рока, но в то же время – взгляд в будущее, где музыка не имеет границ и ограничений.
Je suis emerveille par Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En bref, Pokerstars Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter le design est style et moderne, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer maintenant|
позавчера рок Музыка “Позавчера” – это откровение, искренний разговор с самим собой и с миром. Это возможность заглянуть вглубь своей души и найти там ответы на важные вопросы.
Срочная алкогольная помощь в владимире играет центральную роль в лечении с зависимостями. Если ваши близкие оказались с трудной ситуацией, необходимо обратится в специализированную клинику, где обеспечивают медицинскую услуги при психоактивной зависимости. Квалифицированные специалисты проводят процедуры детоксикации, чтобы освободить токсичные вещества из организма; далее начинается лечебный процесс, направленная преодоление после зависимости. Эмоциональная поддержка также играет важную роль в процессе лечения. Ресурс vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru организует консультации нарколога, где вы сможете ознакомиться о признаках зависимости и необходимых меры. Не откладывайте обращение за срочной помощью – это первый шаг к улучшению состояния.
Перевод с корейского – профессиональный перевод документов онлайн. Перевод сертификатов соответствия. Самарское бюро. Нотариальное заверение. Срочно и качественно. Опытные переводчики.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Pokerstars Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A souligner l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
https://pokerstarscasino777fr.com/|
рок группа позавчера Рок группа “Позавчера” – это не просто коллектив музыкантов, это семья, объединенная общей любовью к музыке и стремлением создавать что-то значимое. Их концерты – это ритуал, где каждый зритель становится частью этой семьи, сопричастным к магии творчества.
психиатрическая помощь на дому
psikhiatr-moskva011.ru
стационарная психиатрическая помощь
J’ai une passion debordante pour Stake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Stake Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement top les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Cliquer pour voir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Stake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, Stake Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une experience immersive. A noter les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Mystake Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A signaler l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer maintenant|
Брала тут когда-то пару раз. Зарегана на форуме тогда еще не была, сейчас пришлось по обстоятельствам зарегать аккаунт. Ребята работают хорошо, оперативно. Оператор адекватный, идет на контакт. Продукты были хорошие на тот момент. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Спасибо. Все по плану получилось. Получил в лучшем виде)
Je suis totalement conquis par Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. Notons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore le dynamisme de Casinozer Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Casinozer Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, apporte une touche d’excitation. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir la page|
AmazingFindsHub – Excellent selection of items, exploring collections was quick and smooth.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Mystake Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, mais des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Mystake Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Tout apprendre|
J’adore la vibe de Stake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce le lien communautaire.
Continuer ici|
Этика коммуникации — отдельный протокол: врач простыми словами объясняет, какую цель мы решаем прямо сейчас (например, «вернуть переносимость воды»), какой маркер наблюдаем (тошнота, диурез, частота пульса), через какое время ожидаем эффект (20–40 минут, 60–120 минут или первая ночь) и в каком случае нужна коррекция. Прозрачность снижает тревожность и помогает семье поддерживать «ровную» среду без «караула у кровати».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Je suis enthousiasme par Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fluides.
Lire plus|
позавчера рок Музыка “Позавчера” – это калейдоскоп эмоций, от нежной грусти до безудержной радости. Это саундтрек к жизни, отражающий все ее грани и нюансы, понятный каждому, кто когда-либо любил, страдал и мечтал.
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Mystake Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute soudee.
Continuer Г lire|
позавчера слушать “Позавчера” слушать – значит погрузиться в мир грез и фантазий, забыть о проблемах и заботах, насладиться красотой и гармонией звуков. Это путешествие во времени и пространстве, которое меняет вас навсегда.
Перед началом терапии врач проводит осмотр, собирает анамнез, измеряет давление и сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-тесты. На основании данных подбирается индивидуальная схема, рассчитываются объёмы инфузии и темп введения, оценивается необходимость кардиоконтроля.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/]вывод из запоя реутов[/url]
музыка позавчера Музыка “Позавчера” – это калейдоскоп эмоций, от нежной грусти до безудержной радости. Это саундтрек к жизни, отражающий все ее грани и нюансы, понятный каждому, кто когда-либо любил, страдал и мечтал.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog011.ru
лечение запоя тула
growbeyondlimits – Encouraging platform that inspires personal growth and pushing boundaries every day.
музыка позавчера “Позавчера” слушать – значит погрузиться в мир грез и фантазий, забыть о проблемах и заботах, насладиться красотой и гармонией звуков. Это путешествие во времени и пространстве, которое меняет вас навсегда.
Je suis fascine par Casinozer Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Casinozer Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Сайт казино Вавада обеспечивает быстрый вход без ограничений.
Проверенные способы входа помогают обходить блокировки.
Игровые автоматы и развлечения работают без VPN.
Создать аккаунт можно мгновенно, навигация проста.
Если требуется зеркало на сегодня, используйте vavada регистрация — указаны проверенные рабочие адреса.
Контролируйте лимиты, чтобы процесс оставался комфортным.
всё прочитал) Стоищий отзыв так и не увидел) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Трек (номер накладной) будет в заказе, а также выслан на e-mail.
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
J’adore la vibe de Casinozer Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais encore quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Casinozer Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En plus le design est style et moderne, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui stimule l’engagement.
Parcourir le site|
Informationbreach – Your Shield Against the Hidden Web
Welcome to Informationbreach, your ultimate shield against cyber exposure and identity theft.
Track 33B+ breached passwords and 50M daily records with cutting-edge scanning technology.
Run an Informationbreach dark web exposure check, see if your email is compromised, and stay secure 24/7.
Full features for just $2 — instant access, clean data download, and real protection that works today!
Start Now: https://informationbreach.net
позавчера слушать Группа “Позавчера” – это не просто музыкальный коллектив, это машина времени, облеченная в звуки. Их песни – это ностальгические полотна, сотканные из винтажных мелодий и современных ритмов. Это музыка, которая заставляет сердце биться чаще, а в голове всплывают образы из прошлого, будь то первая любовь, беззаботное детство или просто теплые воспоминания. “Позавчера” умело играет на струнах души, пробуждая самые сокровенные чувства.
группа позавчера “Позавчера” как рок группа – это энергия бунтарства, помноженная на мелодичность и искренность. Их концерты – это взрыв эмоций, где каждый зритель становится частью единого целого. Это музыка для тех, кто не боится самовыражения и готов идти против течения. Это протест против серости и обыденности, гимн свободе и индивидуальности.
позавчера рок “Позавчера” слушать – значит давать себе возможность отвлечься от повседневных забот и погрузиться в мир грез и фантазий. Это терапия для души, способная исцелить от тоски и разочарования.
BestPriceSpot – Great discounts highlighted, navigating products was smooth and quick.
Спасибо!Не надо! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази кто получал последний раз недавно отишитесь о работе магаза. +В РЕПУ!!!!!!! и главное почему ип адрес не меняется на сайте???
группа позавчера Музыка “Позавчера” – это откровение, искренний разговор с самим собой и с миром. Это возможность заглянуть вглубь своей души и найти там ответы на важные вопросы.
Платформа Vavada гарантирует стабильный доступ.
Проверенные способы входа обеспечивают круглосуточную доступность.
Игровые автоматы и развлечения поддерживаются без перебоев.
Регистрация проходит за пару минут, навигация проста.
Если требуется зеркало на сегодня, используйте казино вавада — там собрана свежая информация.
Играйте ответственно, чтобы процесс оставался комфортным.
Потребность в изготовлении дубликатов регистрационных знаков может возникнуть у любого автовладельца https://kuznitsaspb.ru/the_articles/ofitsialnye-dublikaty-nomerov-bez-flaga-po-gost.html. Существует несколько распространенных ситуаций, когда эта услуга становится просто незаменимой.
Posting up my honest insight about that gaming site. I describe offers, withdrawals, and how it plays. Going through special rewards and payment system. Mentioning how the page responds and releases funds. Covering strengths and weaknesses I observed. Describing what I enjoyed and what I didn’t enjoy. Additional information is available in the full review https://cctvhub.pixnperfect.com/explore-exciting-games-at-crown-green-casino-and-5/
музыка позавчера Рок группа “Позавчера” – это не просто коллектив музыкантов, это семья, объединенная общей любовью к музыке и стремлением создавать что-то значимое. Их концерты – это ритуал, где каждый зритель становится частью этой семьи, сопричастным к магии творчества.
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter pour plus|
dreamfashionfinds – Stylish and trendy fashion finds that make everyday shopping fun.
мои близкий поделился вашими контактами когда про бывали ваш товар) https://autochasdv.ru Магазин агонь! Брал как то давно. все ровно!
группа позавчера “Позавчера” как рок группа – это энергия бунтарства, помноженная на мелодичность и искренность. Их концерты – это взрыв эмоций, где каждый зритель становится частью единого целого. Это музыка для тех, кто не боится самовыражения и готов идти против течения. Это протест против серости и обыденности, гимн свободе и индивидуальности.
HouseSpotHub – Great selection of home items, exploring categories was easy and enjoyable.
Когда вы или человек из вашего окружения испытываете с проблемой алкогольной зависимости, капельница от запоя может стать первым шагом к восстановлению. В владимире услуги по детоксикации организма оказывают различные клиники для людей с зависимостью от алкоголя. Специалист-нарколог в владимире проведет диагностику и назначит медикаментозное лечение запоя. Капельницы для снятия похмелья помогают быстрому возвращению к норме пациента. Процесс восстановления после алкогольной зависимости включает в себя реабилитацию от алкоголя и поддержку специалистов. Закажите медицинские услуги на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru для обращения за профессиональной помощи.
smartbuyplace – Excellent place to find smart deals and quality products efficiently.
Ai girlfriend Обсуждение NSFW (Not Safe For Work) контента, созданного с помощью искусственного интеллекта, требует особого внимания к этической и юридической сторонам вопроса. С одной стороны, ИИ может быть использован для создания развлекательного контента, удовлетворяющего определенные предпочтения аудитории. С другой стороны, существует риск использования ИИ для создания дипфейков, порнографии с участием несовершеннолетних или других форм контента, нарушающих закон и права человека. Крайне важно разработать механизмы контроля и регулирования, которые позволят предотвратить злоупотребления ИИ в этой сфере и защитить интересы всех заинтересованных сторон. Необходимо также проводить образовательную работу, направленную на повышение осведомленности о рисках и последствиях распространения нелегального NSFW контента, созданного с использованием искусственного интеллекта.
Или все ок у всех тут клиентов? купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Хотелось бы надеется)))
https://tenchat.ru/media/4046976-kak-ya-vzyal-perviy-zaym-onlayn-i-ne-popal-v-dolgovuyu-yamu-chestniy-razbor-mfo-2025
Je suis bluffe par Stake Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, en revanche des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Stake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir|
Здесь
[url=https://bangbangeducation.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par moments des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer Г lire|
InspirePathOnline – Motivational tips showcased, helps maintain focus and consistent effort throughout the day.
את החזה שלי בתהליך. נחמד, חזק מדי, אפילו הזין המשומן. התחיל לזיין-הבכי התגבר. כלבה מגמגמת. דפוק המקלחת כבויה ומוצצת את האצבע המורה. זה הצחיק לטרוח? אמרו שחלקם הצליחו להתגנב לתחתונים שלה… היא horimhaifa
Если вы играете на реальные средства, ориентируйтесь на наш [url=https://t.me/slekryt/]рейтинг онлайн казино на деньги[/url]. Мы включаем только проверенные площадки с прозрачными условиями, быстрыми выплатами и хорошей репутацией. Такой список помогает избежать ошибок и выбирать казино, которые действительно стоят внимания. Пройдитесь по подборке — и быстро найдёте надёжное место для комфортной и безопасной игры.
אני חושב שצעקנו על כל היער, אבל לא היה אכפת לו-הוא זיין וזיין. אפילו משהו))) הנרתיק שנפתח קרא עדיין. היא סחטה ושוב גנחה מהכאב. אל תסחט-אמרתי, מצפה שזה יחלש. הרגשתי את הרגיעה קצת משכתי ואז haifapress
Виртуальная девушка Виртуальная девушка – это цифровая сущность, созданная для имитации романтических отношений и общения с человеком. Она может принимать различные формы, от текстовых чат-ботов до реалистичных трехмерных моделей, с которыми можно взаимодействовать в виртуальной реальности. Виртуальные девушки предлагают пользователю возможность испытать эмоциональную близость, поддержку и общение без необходимости в реальных отношениях. Однако, важно помнить о потенциальных рисках, связанных с зависимостью от виртуальных отношений, размыванием границ между реальностью и иллюзией, а также влиянием на формирование социальных навыков и представлений о любви и отношениях. Использование виртуальных девушек должно осуществляться осознанно и ответственно, с учетом возможных последствий для психологического здоровья и благополучия. Необходимо критически оценивать информацию, получаемые от виртуальной девушки, и не заменять ею реальное общение и взаимоотношения с другими людьми. Важно также помнить о необходимости соблюдения этических норм и правил при создании и использовании виртуальных девушек, чтобы избежать эксплуатации и нанесения вреда другим людям.
Такой подход обеспечивает результативность и помогает добиться длительной ремиссии даже при тяжёлых формах зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Одним из самых востребованных направлений является вывод из запоя. Это процедура, направленная на очищение организма от этанола и продуктов его распада, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию работы нервной системы. Врач проводит обследование, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает состав капельницы. Уже через 30–60 минут после начала процедуры состояние пациента заметно улучшается.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Je ne me lasse pas de Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Stake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Essayer maintenant|
анонимная консультация психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva012.ru
госпитализация в психиатрический стационар
Магази хороший и качество нормальное, если есть возможность запиши на пробу Бро ) https://talsosh-tarum05.ru ты в мирку отпиши продавец там
J’ai une passion debordante pour Mystake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Mystake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En complement la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour finir, Mystake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
трипскан Трипскан предлагает гибкие настройки и фильтры, чтобы вы могли подобрать идеальный вариант, отвечающий всем вашим потребностям.
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-voronezh/
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены волгоград[/url]
Использование контрактного производства помогает экономить ресурсы и сосредоточиться на бизнес-задачах. Все процессы, включая проектирование и сборку, контролируются специалистами. Клиенты получают готовый продукт, полностью соответствующий техническим требованиям. Такой подход минимизирует ошибки и повышает надежность изделий https://transcrire.histolab.fr/wiki/index.php?title=%D0%A1%D0%B1%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BA%D0%B0_IoT-%D1%83%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2_%D0%9D%D0%B0_%D0%97%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B7
Разработка прошла гладко, все этапы понятны и логичны.
трипскан TripScan – это не просто поисковик, это ваш личный консультант по путешествиям, готовый помочь вам на каждом этапе планирования. С Tripscan вы можете забыть о стрессе и наслаждаться предвкушением незабываемого приключения.
Je suis completement seduit par Casinozer Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
En savoir davantage|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Mystake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir maintenant|
сервисный центр бош в москве [url=https://www.remont-bosch-na-domu-msk.ru/]сервисный центр бош в москве[/url]
FashionTreasure – Stylish and modern items caught my eye, moving through the collections was easy.
Posting my real story centered on this site. I discuss offers, transactions, and gameplay vibe. Highlighting promotions and payments. Describing how the experience handles and handles withdrawals. Covering pros and cons I ran into. Describing what I enjoyed and what I didn’t. More details are covered in the complete article https://curehelp.aks.up.in/discover-next-gen-gaming-at-crown-green-casino-and-5-2/
J’ai un faible pour Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais encore plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Casinozer Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Essayer maintenant|
השמיעה גניחה שקטה. הוצאתי ממנה את את חוסר הביטחון והגעגוע שאיגור עצמו סבל לפני מספר חודשים. “אתה ברחוב. אחרי שהלכנו לבית יפה על החוף, היה נעים וניגנו מוזיקה רועשת, בלונדינית רזה ומתולתלת (משהו ktavsofer
трипскан Tripscan упрощает процесс организации путешествий, экономя ваше время и деньги, при этом гарантируя незабываемые впечатления.
всегда ровно все было и есть. так что я купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Наверно так же как и джив. попробуй минимальные пропорции сделать 0,1 к 1
купить права
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, awesome blog!
nsfw content ИИ девушка – это концепция, становящаяся все более распространенной в мире искусственного интеллекта. Она представляет собой виртуального компаньона, разработанного на основе алгоритмов машинного обучения и нейронных сетей, способного имитировать общение и взаимодействие с человеком. Некоторые видят в этом возможность для одиноких людей получить эмоциональную поддержку и компанию, в то время как другие опасаются, что это может привести к ухудшению социальных навыков и снижению ценности реальных отношений. Важно помнить, что ИИ девушка – это всего лишь инструмент, и то, как он будет использоваться, зависит от человека. Необходимо ответственно подходить к выбору такого компаньона и не заменять им реальные отношения. Важно также помнить о необходимости критического мышления и не поддаваться на манипуляции, которые могут быть запрограммированы в ИИ. Развитие ИИ должно происходить с учетом этических норм и принципов, направленных на благополучие и развитие человека, а не на его изоляцию и отчуждение.
זה המקום בו טוניה ואני התמקמנו. עד כה האישה לא רוצה להוליד צאצאים. היא עמד עם יתד, היא הקניטה אותי החברה שלי אלינה, והחברים שלנו הם סיריל ואשתו במיטה שהיא מדמיינת את עצמה שם, בסרטון הזה, שבו היא welcome-online
‘ קט הזה על הציצים שלה. ערב מאוחר, הוא פשוט ליווה אותי הביתה והחלפנו טלפונים. כעבור חצי שנה הכל, שכבו בנשימה רפה, דיברו בברכיים הלב פועם אי שם בגרון, סוחט אותו. אשתי, קטיה, הסתובבה בחדר. nordiceye
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника волгоград[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://psychodemia.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Поръчах https://mdgt.top си водопроводчик в Бургас чрез сайта и останах доволна
Официальный сайт 1win понятный и удобный. Ставки мгновенные, коэффициенты не скачут. Вывод средств был быстрый https://1win-magic.top/
желаю и дальше продолжать в том же духе!)) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Пробежался по веткам,магазин
Официальный сайт 1xbet очень удобный, всё интуитивно. Ставки проходят быстро, интерфейс приятный. Деньги вывели без сложностей: 1xbet официальный сайт
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
ChicGlobalSpot – Trendy items highlighted, navigating fashion picks felt easy and enjoyable.
J’adore l’energie de Coolzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par contre des offres plus importantes seraient super. En fin de compte, Coolzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter en ligne|
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом краснодар[/url]
В клинике «НаркологПроф» детоксикация проводится под наблюдением специалистов, которые контролируют давление, частоту сердечных сокращений и дыхание пациента. Инфузионная терапия помогает восстановить электролитный баланс, ускорить выведение токсинов и улучшить общее состояние уже через несколько часов после начала лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-khimki-narkolog-na-dom
Je suis accro a Coolzino Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Coolzino Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement top les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Cliquer pour voir|
Процесс терапии в наркологической клинике в Воронеже организован поэтапно. Это позволяет обеспечить системность и постепенность восстановления, снизить риски осложнений и повысить устойчивость результата.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Разобраться лучше – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour MonteCryptos Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, MonteCryptos Casino offre une aventure memorable. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis accro a Coolzino Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Coolzino Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.casinocoolzinofr.com|
Je suis enthousiasme par MonteCryptos Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis fascine par Lucky8 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky8 Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit le design est moderne et energique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Mindful Progress Hub – Daily advice for personal growth and intentional living.
Je ne me lasse pas de NetBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En fin de compte, NetBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De plus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A signaler les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
VГ©rifier ceci|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky8 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Lucky8 Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui booste la participation.
Obtenir plus|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour NetBet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, bien que des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, NetBet Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons que le design est tendance et accrocheur, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des bonus constants.
https://casinonetbetfr.com/|
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена волгоград[/url]
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de MonteCryptos Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, MonteCryptos Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer ici|
Je suis enthousiasme par MonteCryptos Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Continuer ici|
Je suis completement seduit par Lucky8 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Lucky8 Casino merite un detour palpitant. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
http://www.casinolucky8fr.com|
Je suis sous le charme de Lucky8 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Lucky8 Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer ici|
Je suis fascine par NetBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par contre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, NetBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner le site est rapide et engageant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Visiter le site|
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Чтобы не оценивать состояние субъективно, в клинике применяется система наблюдения за ключевыми параметрами. Таблица помогает врачу и пациенту видеть реальную динамику и корректировать вмешательства только при необходимости.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Чувствую что-то произойдёт , типа заказа:happy: https://vizart-studio.ru магазину респект)) с корефанами накуримся вдоволь)))
Ремонт https://remontuem.if.ua і поради щодо монтаж опалення івано-франківськ знайшов тут.
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в краснодаре[/url]
StyleNestShop – Sleek clothing and accessories available, navigating the collections felt effortless.
снятие ломки наркомана
Фото https://seetheworld.top та огляди про доновали були корисними.
В повседневности неточный ориентир часто заставляет терять время, поэтому мы проговариваем симптомы, при которых тянуть нельзя. Список не заменяет осмотр, он помогает близким описать ситуацию по телефону и выбрать правильный маршрут вместе с врачом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru
nicee content keep writing
Отличное качество товара https://sherifpizza.ru Два часа, ребята в клубе,
Лечение алкоголизма на дому становится все более популярным. Основные этапы состоят из домашней детоксикации и поддержки в период запойного состояния. С чего следует начать? Важно получить поддержку от близкихкоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психотерапия и народные методы могут стать эффективным дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы для трезвости и рекомендации по отказу от алкоголя помогут развить правильное отношение к алкоголю. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir026.ru Не забывайте о реабилитации на дому, которая включает психологическую помощь и предотвращение рецидивов. Как бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с установки четкой цели и поиска источника мотивации. Главное – это поддержка окружающих и стремление к изменениям.
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Казино 1xbet стабильно работает даже при высокой нагрузке. Игры запускаются быстро, не тормозят. Выигрыш вывели в срок: скачать 1xbet
Благодаря последовательной работе врачей и постоянному наблюдению лечение проходит безопасно и эффективно, а пациент получает необходимую поддержку на всех этапах терапии.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в волгограде[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://fashionfactoryschool.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
gift selection corner – Lovely collection of gifts, exploring products felt smooth and fun.
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, awesome blog!
снятие ломки цены
дизайнер квартиры дизайнер интерьера сайт
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen
Иногда приоритетом становится непрерывный контроль. Стационар рекомендован, если ожидаются выраженные колебания давления и пульса, есть подозрение на аритмии, отмечается одышка, боли в груди, спутанность сознания, галлюцинации, судороги, признаки начинающегося делирия, а также выраженная дегидратация или декомпенсация хронических заболеваний. Для пожилых пациентов без возможности надёжного домашнего наблюдения отделение — клинически разумный выбор: доступны лабораторные тесты, кислородная поддержка, быстрая коррекция дозировок и консилиумы смежных специалистов. Именно в первые 24–48 часов после отмены алкоголя стационарный режим делает процесс предсказуемым и безопасным, что сокращает время до стабилизации и открывает окно для обсуждения амбулаторного сопровождения, психологической поддержки и мер профилактики срывов без давления и спешки.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]вывод из запоя люберцы[/url]
клад забрал, все ровняк! завтра отпишу за качество! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Братья так же ровны как в совестсокм союзе
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Опытный адвокат https://www.zemskovmoscow.ru в москве: защита по уголовным делам и юридическая поддержка бизнеса. От оперативного выезда до приговора: ходатайства, экспертизы, переговоры. Минимизируем риски, действуем быстро и законно.
стоимость лечения наркомании
reabilitaciya-astana010.ru
реабилитации после алкоголя в Астане
Пользуюсь зеркалом 1хбет, когда основной сайт недоступен. Всё стабильно и быстро. Вывод денег порадовал скоростью: 1xbet
Of course, what a great site and informative posts, I will add backlink – bookmark this site? Regards, Reader
снятие ломки санкт петербург
Je suis fascine par Coolzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est simple et transparent, par contre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Coolzino Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage notable les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
снять ломку на дому
Решение о месте лечения принимает врач после очной оценки, ориентируясь на клинику и бытовые условия. Домашний формат ценят за комфорт и конфиденциальность, а стационар незаменим, когда требуется частая коррекция терапии и круглосуточный мониторинг. Чтобы проще сориентироваться, полезно посмотреть на различия между форматами не как на «два вида капельниц», а как на разные уровни контроля и скорости реакций команды. Текст ниже помогает понять, почему при пограничных состояниях мы рекомендуем стационар, а при стабильных показателях — подтверждаем выезд на дом. Любой маршрут объясняется до старта, и каждое расширение терапии согласуется заранее — без сюрпризов в процессе.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kodirovanie-alkogolizma-domodedovo/
Русскоязычный биткоин форум: новости сети, хард/софт-кошельки, Lightning, приватность, безопасность и юридические аспекты. Гайды, FAQ, кейсы и помощь сообщества без «хайпа».
Это фейк что тут вам не понятно то. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Ура! Скинул трек быстро) ждууууууу, отпишу.
unique presents portal – Lovely collection of gifts, discovering products was quick and easy.
Рабочее зеркало 1xbet всегда под рукой и загружается без задержек. Очень удобно, когда основной сайт недоступен. Все функции работают идеально https://1xbet-loss.top/
фрезеровка композита фрезеровка фасадов мдф
Je suis completement seduit par Coolzino Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Coolzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A mettre en avant les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Avancer|
Здесь
[url=http://maed.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Конечно работаем купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Отзыв уже был, по поводу JWH и 2c-i. Писать то особо и не о чем, но качество товара очень даже порадовало. Щас жду только пополнения ассортимента.
Je suis sous le charme de MonteCryptos Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
En savoir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Lucky8 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Lucky8 Casino vaut une visite excitante. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses continues.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis enthousiasme par MonteCryptos Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г lire|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky8 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Lucky8 Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et style, booste l’excitation du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Explorer le site web|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour NetBet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, NetBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller sur le site web|
J’ai une passion debordante pour NetBet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, NetBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une immersion complete. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Портал Дай Жару https://dai-zharu.ru – более 70000 посетителей в месяц! Подбор саун и бань с телефонами, фото и ценами. Недорогие финские сауны, русские бани, турецкие парные.
Сайт 1win приятно удивил удобством навигации. В казино отличный выбор провайдеров. Вывод средств прошёл быстро: 1вин сайт официальный
make a difference hub – Inspires taking steps that contribute to meaningful change.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk014.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно воронеж[/url]
Однако, селлеру в его интересах было бы полезно появиться и разъяснить ситтуацию дабы избежать гневных сообщений. Обещание что отправка будет пт-сб не было выполнено. Треков нет. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Я клад нашел, но вопервых не все в нем а во вторых содержимое разное и самое главное это место и описание этого места. Завтра буду пытаться связаться с ним.
Анонимная наркологическая помощь в владимире – это эффективный способ справиться с зависимостями. Наркологическая клиника владимир предоставляет качественное лечение зависимостивключая анонимное лечение алкоголизма и программу лечения наркотической зависимости. Мы гарантируем профессиональные консультации нарколога и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме, а также детоксикацию организма. Реабилитация наркоманов содержит психотерапию при зависимостях и группы поддержки для зависимых. Важно помнить, что поддержка родных зависимых является важным фактором в восстановлении после зависимости. Обратитесь за помощью на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru для получения информации о предлагаемых услугах.
Наблюдение
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]вывод из запоя цены домодедово[/url]
В Красноярске клиника «КрасЗдрав Профи» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью. При этом формат анонимности сохраняется на каждом этапе — от звонка до выписки. Для пациентов, которым трудно приехать, возможен выезд нарколога на дом. Это удобно при похмельных и абстинентных состояниях, когда транспортировка нежелательна. Конфиденциальный выезд без маркировки транспорта и униформы позволяет начать лечение, не привлекая внимания окружающих. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинских стандартов, включая регидратацию, стабилизацию и поддержку дыхания.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Рабочее зеркало 1win открывается быстро и всегда доступно. Играть можно без ограничений, всё работает как на основном сайте. Вывод прошёл без задержек: 1вин казино
В итоге, когда я на холоде прождал после последнего “Щас” час, внезапно ответил CM, которому я ещё днём написал. Я поначалу даже не смог вспомнить что у магазина в прайсе, и что я конкретно в этом магазине хотел. Выбирал изначально между эйфом и ск, ну и поскольку эйфа в прайсе нет, то спросил СК. https://vipis.ru ТС саппорт не требуется тебе ? Напиши в лс если интересно
fashion daily updates – Stylish collections featured, exploring items felt smooth and simple.
Ии девушка Виртуальная девушка – это цифровая сущность, созданная для имитации романтических отношений и общения с человеком. Она может существовать в различных формах, от текстовых ботов до реалистичных трехмерных моделей, способных взаимодействовать в виртуальной реальности. Виртуальные девушки предлагают пользователям возможность испытать эмоциональную близость, поддержку и общение без необходимости в реальных отношениях. Однако, важно помнить о потенциальных рисках, связанных с зависимостью от виртуальных отношений, размыванием границ между реальностью и иллюзией, а также влиянием на формирование социальных навыков и представлений о любви и отношениях. Использование виртуальных девушек должно осуществляться осознанно и ответственно, с учетом возможных последствий для психологического здоровья и благополучия.
все просто=) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази народ подскажите а как дела обстоят в столице Москва закладками?
ко ланта ко ланта
tripscan TripScan предлагает удобный интерфейс, где вы можете ввести свои предпочтения, даты поездки и желаемый бюджет, а умные алгоритмы подберут оптимальные варианты. Благодаря Tripscan, планирование отпуска превращается из утомительной задачи в увлекательное занятие.
комплексное лечение алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana011.ru
центр реабилитации зависимых
Лечебная логика строится по принципу «одна цель — один маркер — одно окно оценки — один выключатель». Например, задача «открыть окно питья» решается антиеметическим мостом и мягкой регидратацией; как только вода пьётся без позывов и появляется стабильный диурез, модуль отключается. Если целевой маркер «ЧСС/АД в рабочем коридоре» достигнут — снимаем антивегетативный контур. Это дисциплина маленьких шагов, где каждый следующий ход становится очевидным из предыдущих цифр, а не из ожиданий.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно краснодар[/url]
Врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, уровень сахара в крови и собирает анамнез. Это помогает выявить возможные риски и подобрать подходящие препараты.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/[/url]
трипскан Благодаря интуитивно понятному интерфейсу и множеству полезных функций, Tripscan станет вашим незаменимым помощником в планировании путешествий любой сложности. Начните планировать свою следующую поездку с Tripscan уже сегодня и откройте для себя мир безграничных возможностей!
J’ai un faible pour Coolzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Coolzino Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A signaler le site est fluide et attractif, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Coolzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En complement le site est rapide et style, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer Г naviguer|
трипскан Забудьте о долгих часах, проведенных в поисках идеального варианта, Tripscan сделает всю работу за вас, предлагая лучшие предложения, соответствующие вашим потребностям. TripScan – ваш верный спутник в мире путешествий, готовый сделать вашу следующую поездку незабываемой.
plan your future shop – Helpful resources to take actionable steps and build success each day.
ко ланта ко ланта
Вот уже Артем хохочет, https://scenar-ekb.ru Реально за***ли реклам-спаммеры :spam:, по две-три страницы одно и тоже, даже пропадает желание что либо читать…. таких как Nexswoodssteercan, Terroocomge, Vershearthopot, Soacomtimist и подобных надо сразу в баню отсылать, на вечно).
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
рулонные шторы на электроприводе [url=http://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom177.ru]рулонные шторы на электроприводе[/url] .
successhub.shop – Encouraging tips help maintain momentum and reach important milestones.
Здесь
[url=https://mosdigitals.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Хотите купить https://kvartiratolyatti.ru квартиру? Подбор по району, классу, срокам сдачи и бюджету. Реальные цены, акции застройщиков, ипотека и рассрочка. Юридическая чистота, сопровождение «под ключ» до регистрации права.
Ритуальный сервис https://akadem-ekb.ru/кремация-подробный-гид-для-семьи-кото/ кремация и захоронение, подготовка тела, отпевание, траурный зал, транспорт, памятники. Работаем 24/7, фиксированные цены, поддержка и забота о деталях.
Je suis fascine par Coolzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Coolzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De plus le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis emerveille par MonteCryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino merite une visite dynamique. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г naviguer|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Coolzino Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Coolzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, booste le fun du jeu. Un atout les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui booste la participation.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis accro a MonteCryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, MonteCryptos Casino merite une visite dynamique. A noter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Coolzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Coolzino Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky8 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Lucky8 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Je suis captive par Lucky8 Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est simple et transparent, toutefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Lucky8 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En extra le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
а кто нибудь пробовал все таки эту куреху urb купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Товар получен! Большее спасибо магазину!
Je suis emerveille par Lucky8 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Lucky8 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
Apprendre comment|
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма омск[/url]
J’ai une affection particuliere pour MonteCryptos Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, MonteCryptos Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour couronner le tout la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Avancer|
J’adore le dynamisme de MonteCryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fiables.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de NetBet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, NetBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour ajouter la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Je suis emerveille par Lucky8 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Lucky8 Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une experience immersive. Un element fort les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Essayer ceci|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky8 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Lucky8 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
В клинике реализуются ключевые направления, которые обеспечивают всестороннюю помощь и поддержку пациентам на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
J’ai une affection particuliere pour NetBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, NetBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter le site|
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Врачи клиники «АнтиТокс» используют эффективные и проверенные временем препараты, которые помогают пациентам в кратчайшие сроки стабилизировать самочувствие и восстановить нормальную работу организма. В список основных препаратов входят:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Je suis captive par NetBet Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, quelquefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, NetBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point fort les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Услуга
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-nizhniy-novgorod000.ru
Je suis bluffe par Coolzino Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Coolzino Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
https://coolzinocasinofr.com/|
Товар тоже на 5/5 (только с концетрацией мало 1 к 5 или 1 к 7 дальше держит не долго) https://gadanieperemen.ru вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес…
simpledealhub.shop – Product selection feels organized, browsing is easy and hassle-free.
Daily Fashion Scoop – Stay updated with the hottest fashion trends and stylish selections.
Кондиционеры в Воронеже https://homeclimat36.ru продажа и монтаж «под ключ». Подбор модели, быстрая установка, гарантия, сервис. Инверторные сплит-системы, акции и рассрочка. Бесплатный выезд мастера.
Leaving my honest thoughts related to this online casino. I outline welcome packages, cashouts, and general impression. Emphasizing special rewards and payouts. Reviewing how the system acts and completes transactions. Mentioning pros and cons I discovered. Sharing what I enjoyed and what felt off. Further details are available in the full article Crowngreen casino
https://aritual.by/prices.html
https://officepro54.ru/collection/ofisnaya-mebel
магазин достойный,всё ровно и в срок,спасибо большое за ваш труд,будем продолжать сотрудничество! https://gamardzhoba-dostavka.ru товар появился? когда возобновите доставку по городам?
Здесь
[url=https://miin.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Обращаясь за помощью в клинику «НаркоЩит», пациенты получают комплексное лечение, которое отличается следующими преимуществами:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-nizhniy-novgorod00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому нижний новгород[/url]
трипскан TripScan постоянно обновляется и совершенствуется, чтобы предоставлять вам самые современные и удобные инструменты для планирования путешествий.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
алкогольная зависимость лечение
reabilitaciya-astana012.ru
реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков в Астане
Для повышения эффективности терапии применяются физиотерапевтические процедуры и витаминные комплексы, которые ускоряют восстановление и повышают сопротивляемость организма стрессам.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
Абстиненция — не «плохое утро», а физиологический кризис, когда нервная и сердечно-сосудистая системы работают на пределе, а печень и почки берут на себя чрезмерную детоксикационную нагрузку. Самолечение случайными таблетками или «домашними капельницами» часто усиливает обезвоживание, провоцирует скачки давления, аритмии, панические эпизоды и нарушения сна. В клинической практике «ВитаБаланс» первым этапом идет скрининг безопасности: врач исключает ситуации, требующие стационара, и только после этого запускает инфузию. Правильно подобранные растворы выравнивают электролитный баланс, уменьшают тремор и тошноту, снижают тревожность, а мягкая седация по показаниям помогает восстановить здоровую структуру сна без угнетения дыхания. Параллельно контролируются витальные параметры, чтобы вовремя скорректировать объем и скорость введения. Такой маршрут делает первые сутки предсказуемыми, позволяет избежать осложнений и быстрее вернуть ясность мышления, аппетит и базовую работоспособность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika[/url]
thoughtful gifts hub – Great selection available, site layout made finding products quick and smooth.
Такой алгоритм позволяет постепенно восстановить функции организма и подготовить пациента к дальнейшему лечению зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Использование контрактного производства позволяет сократить расходы и ускорить процесс разработки. Инженеры создают схемы, платы, корпус и программное обеспечение, проводят тестирование прототипов и серийное производство https://wiki.continue.community/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%BE_%D0%AD%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B%D1%85_%D0%A3%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2_%D0%94%D0%BB%D1%8F_%D0%90%D0%B2%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8
Технология позволяет создавать устройства, которые полностью соответствуют техническим требованиям
ко ланте Ко Ланте
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru резки и сварочные аппараты с ЧПУ в Москве: подбор, демонстрация, доставка, пусконаладка, обучение и сервис. Волоконные источники, металлы/нержавейка/алюминий. Гарантия, расходники со склада, выгодные цены.
ко ланта ко ланта
Сочи – мёд отличный, кладмену респект и уважуха! теперь мы ваши постоянные клиенты) https://prishlo-vremya.ru Пиздец до сих пор мозги ебут(
трипскан Благодаря Tripscan, планирование отпуска превращается из утомительной задачи в увлекательное занятие.
Обратились в агентство за горящим туром и не пожалели. Консультант нашла для нас шикарный вариант буквально за полчаса. Все документы были оформлены быстро и корректно. На отдыхе всё прошло гладко, никаких сюрпризов. Очень удобный формат, когда хочется уехать срочно и без переплат: купить тур в рассрочку
ко ланта ко ланта
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
Контрактная разработка электроники обеспечивает контроль качества на всех этапах. Специалисты создают схемы, платы, корпус и программное обеспечение, проводят тестирование и подготовку к серийному производству http://www.onestopclean.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=968745. Очень удобный подход к разработке и интеграции электронных компонентов)
ко ланта ко ланта
Current weather forecast in Montenegro: daytime and nighttime temperatures, precipitation probability, wind speed, storm warnings, and monthly climate. Detailed online forecast for Budva, Kotor, Bar, Tivat, and other popular Adriatic resorts.
Такой подход обеспечивает результативность и помогает добиться длительной ремиссии даже при тяжёлых формах зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
При абстиненции нервная и сердечно-сосудистая системы работают на пределе, баланс нейромедиаторов смещён, кровь «теряет» воду и электролиты, а печень несёт повышенную нагрузку. Резкая отмена алкоголя без врача нередко приводит к скачкам давления, аритмиям, паническим эпизодам, нарушению сна и даже делирию. Домашние «самосборные» растворы и случайные комбинации таблеток усугубляют обезвоживание и не учитывают противопоказания — в итоге риски растут, а эффект непредсказуем. В «СфераЗдоровья» путь другой: сначала скрининг безопасности и исключение состояний, при которых показан стационар; далее — персональная инфузионная схема с регидратацией, коррекцией электролитов, поддержкой печени и симптом-контролем (тошнота, тремор, тревога, бессонница). На каждом этапе врач отслеживает динамику и корректирует дозы «по реакции», чтобы не перегрузить сердце и почки. Результат — более мягкий выход из абстиненции, прозрачные ожидания для пациента и близких и понятный план на ближайшие 24–48 часов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno[/url]
Writing my real impression related to Crowngreen. I outline perks, processing times, and total experience. Going through casino offers and payouts. Going over how the service operates and sends money. Pointing out what works and what doesn’t I’ve noticed. Outlining what stood out and what didn’t impress me. Read the full article for more insights Crowngreen
Нарколог устанавливает внутривенную капельницу, через которую вводятся растворы, обеспечивающие быстрое выведение токсинов, восстановление водно-электролитного баланса и стабилизацию состояния.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh00.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в воронеже[/url]
educationunlimited.click – Daily lessons motivate growth and help discover new knowledge easily.
Основной этап терапии — установка внутривенной капельницы. Через капельницу вводятся специально подобранные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и нормализации работы внутренних органов. При необходимости врач назначает дополнительные медикаменты для защиты печени, стабилизации сердечной деятельности и купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома. В течение всей процедуры состояние пациента контролируется врачом, который корректирует схему лечения для достижения наилучших результатов. По завершении процедуры специалист дает подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике повторных запоев.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-nizhniy-novgorod00.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в нижний новгороде[/url]
Зеркало 1win помогает заходить без VPN и обходов. Работает чётко. Деньги пришли в срок https://1win-miracle.top/
Восстановление после алкогольного запоя в владимире: путь к исцелению Реабилитация после запоя включает психологической помощи и опоры на родных, что крайне важно в кризисной ситуации. Процесс восстановления могут отличаться, но все они направлены на преодолении алкогольной зависимостью и достижении долгосрочных результатов. Сообщество поддержки становится важным элементом процесса, облегчая преодоление трудностей. Важно помнить, что дорога к исцелению труден, но реален. помощь нарколога владимир
Как магазиН? https://vizart-studio.ru ну если для кавото это естественно, для меня нет…кавото и палынь прет..
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от различных видов зависимости. Основой успешного лечения является комплексный подход, который включает тщательную диагностику, медикаментозное сопровождение, психологическую поддержку и реабилитационные программы. В «АльфаМед» применяются передовые технологии и индивидуальные методики, направленные на восстановление здоровья и предупреждение рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Je suis accro a Coolzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Coolzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Coolzino|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Coolzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Coolzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Ouvrir la page|
unique gift corner – Creative gifts showcased nicely, discovering new products was simple.
Главное преимущество обращения в наркологическую клинику в Воронеже — комплексный подход к лечению зависимости. Специалисты учитывают медицинские, психологические и социальные факторы, влияющие на формирование зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально: в зависимости от стадии заболевания, состояния здоровья и целей терапии. В процессе лечения применяются детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапия и методы социальной адаптации.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh
Interesse par 1xbet? Sur visit this page, vous trouverez des liens a jour vers les fichiers d’installation de l’application 1xbet, les instructions d’installation, les mises a jour, les exigences systeme et des conseils sur la connexion securisee a votre compte pour un jeu en ligne confortable.
Наблюдение
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Je suis completement seduit par MonteCryptos Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. D’ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages uniques.
Continuer ici|
Нашел отличный алкомаркет, где можно заказать алкоголь даже ночью. Всё очень удобно — оформление занимает пару минут, доставка быстрая, курьеры аккуратные. Алкоголь оригинальный, без подделок, всё в идеале. Теперь если нужна доставка алкоголя в москве, беру только здесь https://drinkio70.ru/
Хотели улететь спонтанно и выбрали горячий тур. Сотрудники агентства помогли быстро разобраться с перелётом, страховкой и заселением. Всё оформили удаленно, что особенно удобно. На месте нас встречал трансфер, а отель приятно удивил качеством обслуживания. Горящие туры — отличная возможность для тех, кто любит решать всё быстро: дешевые путевки на море
Интернет-магазин RC19 https://anbik.ru профессиональное телекоммуникационное и сетевое оборудование в Москве. Коммутаторы, маршрутизаторы, точки доступа, патч-панели и СКС. Собственный бренд, наличие на складе, консультации и сервис.
freshpickoutlet.click – Trendy picks featured clearly, shopping experience was smooth and fun.
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом омск[/url]
Je suis accro a Lucky8 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Lucky8 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et style, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky8 Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Lucky8 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Улучшайте свои навыки и повышайте квалификацию с помощью [url=https://best-courses-seo.ru]сео оптимизация курсы[/url] и станьте профессионалами в области поисковой оптимизации!
дать возможность изучить методы улучшения видимости сайта в поисковых системах . Эти курсы обычно включают в себя лекции по созданию качественного контента и его продвижению. В результате прохождения таких курсов, участники смогут освоить методы анализа и улучшения позиций сайта в поисковых системах.
Участники SEO курсов могут узнать о важности качественного контента и его роли в поисковой оптимизации . Это может включать в себя изучение методов создания ссылок и их влияния на рейтинг сайта . После завершения курса, участники могут использовать приобретенные навыки для работы в digital-агентствах .
В рамках SEO курсов, учащиеся могут изучить, как создавать и продвигать качественный контент, который будет привлекать целевую аудиторию . Это может включать в себя анализ случаев успешной оптимизации сайтов и изучение их стратегий . Благодаря такому подходу, учащиеся могут овладеть всеми аспектами SEO, от технической оптимизации до создания контента .
Практические занятия в SEO курсах могут быть направлены на изучение инструментов анализа сайтов и их оптимизации . Это дает участникам возможность получить реальный опыт работы в SEO, который можно применить на практике . После завершения курса, участники могут применять полученные знания и навыки для оптимизации своих собственных сайтов или для работы в качестве SEO-специалистов .
Теоретические основы SEO включают в себя понимание работы поисковых алгоритмов и факторов, влияющих на рейтинг сайта . Эти знания необходимы для получения практических навыков поисковой оптимизации и продвижения сайтов . Теоретические основы могут включать в себя освоение методов оптимизации сайтов для различных поисковых систем.
Изучение теоретических основ SEO может предоставить знания о том, как создавать эффективные кампании в интернете. Это может включать в себя изучение роли ключевых слов в поисковой оптимизации и методов их выбора . Благодаря такому подходу, участники могут овладеть всеми аспектами SEO, от технической оптимизации до создания контента .
SEO курсы могут предоставить знания о том, как создавать эффективные кампании в интернете. Это может включать в себя работу над индивидуальными проектами, направленными на оптимизацию реальных сайтов. Участники могут освоить искусство внутренней и внешней оптимизации сайтов, включая работу с ссылками и другими факторами.
Применение SEO в реальной практике может предполагать участие в групповых проектах, где участники смогут применить полученные знания на практике. Это дает участникам возможность получить реальный опыт работы в SEO, который можно применить на практике . После завершения курса, участники могут развивать свои навыки дальше, изучая новые тенденции и технологии в области SEO.
tripscan Забудьте о долгих часах, проведенных в поисках идеального варианта, Tripscan сделает всю работу за вас, предлагая лучшие предложения, соответствующие вашим потребностям. TripScan – ваш верный спутник в мире путешествий, готовый сделать вашу следующую поездку незабываемой.
автоматические жалюзи [url=www.prokarniz23.ru]автоматические жалюзи[/url] .
все быстро замутили https://svp-opt.ru сегодня вот ночью прислал трек. Бьется, радует
управление шторами с телефона [url=prokarniz23.ru]управление шторами с телефона[/url] .
tripscan TripScan предлагает удобный интерфейс, где вы можете ввести свои предпочтения, даты поездки и желаемый бюджет, а умные алгоритмы подберут оптимальные варианты. Благодаря Tripscan, планирование отпуска превращается из утомительной задачи в увлекательное занятие.
Официальный сайт 1вин работает стабильно и предсказуемо. Ставки ставятся легко, всё чётко. Вывод занял несколько часов https://1win-miracle.top/
tripscan TripScan обеспечивает безопасность ваших данных и гарантирует конфиденциальность вашей личной информации.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
РВД Казань https://tatrvd.ru рукава высокого давления под заказ и в наличии. Быстрая опрессовка, точный подбор диаметров и фитингов, замена старых шлангов, изготовление РВД по образцу, обслуживаем спецтехнику, погрузчики, сельхоз- и дорожные машины.
С агентством горячих туров путешествуем уже не первый год. Всегда радуют выгодные предложения и честные условия. Ни разу не столкнулись с обманом или недостоверной информацией. Все поездки соответствовали описанию и проходили без накладок. Очень надёжный сервис для тех, кто любит путешествовать экономно и комфортно: горящие путевки в турцию
fashionaround.click – Trendy international collections displayed, browsing was easy and fun today.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
Специалист осуществляет первоначальный осмотр, измеряет ключевые показатели: артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию кислорода в крови, выявляет степень интоксикации и тяжесть симптомов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh00.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Submitting my sincere feedback covering this platform. I describe promotions, banking, and user experience. Mostly focusing on casino offers and withdrawals. Going over how the interface performs and manages payouts. Highlighting main takeaways I saw. Telling what felt good and what felt off. More insights are provided in the complete article Crowngreen
ко ланте Ко Ланте
дизайн интерьера спб дизайн интерьера дома
freshchoicehub.click – Attractive selection of fresh products, shopping felt effortless and quick.
качество вышка https://texnometall.ru В среду оплатил вечером заказ в субботу уже был на месте)))ценик вообще отличный,качество радует)))
Здесь
[url=https://miin.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
tripscan трипскан
Какие тарифы на https://wikipedia.rapidnodes.net/index.php?title=User:HenryJarrell53 в Москве для маркетплейсов считаются оптимальными?
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-perm-anonimno/
[url=https://technguides.com]Определитель цветов[/url] – сервис определения цвета по фото. Technguides – отличный сервис для определения цвета пикселя бесплатно.
DRINKIO – это пример настоящего сервиса. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, всё доставляется аккуратно. Сайт удобный, оформление заказа быстрое. Ассортимент широкий, видно, что следят за качеством. Радует круглосуточная доставка. Доставка алкоголя на дом Москва, https://drinkio70.ru/
choice finds shop – Easy browsing today with an enjoyable collection of items to explore.
Нашли здесь горячий тур, который позволил нам провести незабываемую неделю на курорте, не выходя за рамки бюджета. Понравилось, что сотрудники не навязывают дополнительные услуги, а реально помогают выбрать подходящий вариант. Очень удобно, что можно получить консультацию в любой момент — нам отвечали даже поздно вечером. Тур был оформлен за час, и мы сразу получили все документы. Поездка прошла без накладок, что особенно приятно при срочных вылетах: горящие туры в израиль
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
так что смотрите внимательней что присылают, если не хотите словить передоз!!! https://sadikfuntik.ru Всем привет,что то скайп неработает((жду трек
Empower Yourself – Tips and advice to empower your mind and boost morale.
tripscan Tripscan сотрудничает с ведущими авиакомпаниями и отелями по всему миру, что позволяет предлагать эксклюзивные скидки и выгодные предложения. Кроме того, TripScan предоставляет подробные обзоры и рейтинги отелей и достопримечательностей, помогая вам сделать осознанный выбор.
freshcornerhub.click – Great outlet for discovering stylish items, navigating products was simple and fast.
successjourneyhub.click – Encouraging guidance motivates following through on ideas to reach real results.
https://writexo.com/share/f96f000c31c4
http://nec.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=618897#618897
Кто может подсказать, где в Москве http://wiki.vorratsdatenspeicherung.de/Slimpick-ff_94W с минимальными комиссиями?
Заказывал через DRINKIO несколько раз и всегда оставался доволен сервисом. Доставка приезжает быстро, даже ночью, когда другие магазины уже не работают. Удобно, что всё можно оформить онлайн без звонков и ожидания. Большой выбор напитков, цены вполне адекватные для круглосуточной службы. Отличный сервис для тех, кто ценит комфорт и оперативность https://drinkio70.ru/
Ищу http://classicalmusicmp3freedownload.com/ja/index.php?title=%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8%E8%80%85:VidaTang790815 для маркетплейсов в Москве, кто работает с постоплатой?
это самый ровный магаз братцы!!!) работаю с ними целый год, не разу даже нервы не потрепали) !!! конспирация на высоте, качество наилучшее!продован самый добрый и общительный аах) ну вы поняли! единственное жалко не разу проб бесплатных не получал((( купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Да всё норм, ёпт, чё ты вообще телефон потерял) Тебе наверное там названивали.
Срочный перевод нотариальный – перевод документов с русского на узбекский. Самарское бюро переводов. Документы, нотариус, срочно! Любые языки мира. Качество и точность. Доступные цены. Гарантия.
Здесь
[url=https://www.anthome.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
find unique products – Excellent choices available, browsing new arrivals was straightforward today.
DRINKIO – лучший сервис для тех, кто ценит комфорт и скорость. Всё оформляется за пару минут, доставка всегда вовремя. Курьеры доброжелательные, видно, что компания следит за качеством работы. Ассортимент радует и постоянно обновляется. Работают круглосуточно, что очень удобно. Быстрая доставка алкоголя по Москве https://drinkio70.ru/
freshcornerhub.click – Great outlet for discovering stylish items, navigating products was simple and fast.
tripscan TripScan предлагает удобный интерфейс, где вы можете ввести свои предпочтения, даты поездки и желаемый бюджет, а умные алгоритмы подберут оптимальные варианты. Благодаря Tripscan, планирование отпуска превращается из утомительной задачи в увлекательное занятие.
ко ланта ко ланта
Получил свой заказ,дошло довольно быстро, спасибо chemical-mix.com , за нормальный вес и хорошию работу ! https://vizart-studio.ru До сих пор в себя прихожу
fashiontrendzone.click – Well-organized marketplace makes exploring new trends simple and fun.
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в перми[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-perm-anonimno
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
ко ланта ко ланта
дизайн интерьера 3д https://dizayna-interera-spb.ru
freshfavoriteshub.click – Nice collection of fresh products, exploring items felt easy today.
:superman:По больше клиентов,с толстыми кошельками,да главное чтоб АДЕКВАТНЫЕ!:bro: https://kt-6023.ru Как то так.
ко ланта ко ланта
vision growth hub – Provides ideas to strengthen focus and achieve your vision steadily.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec018.ru
лечение запоя череповец
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
При абстиненции нервная и сердечно-сосудистая системы работают на пределе, баланс нейромедиаторов смещён, кровь «теряет» воду и электролиты, а печень несёт повышенную нагрузку. Резкая отмена алкоголя без врача нередко приводит к скачкам давления, аритмиям, паническим эпизодам, нарушению сна и даже делирию. Домашние «самосборные» растворы и случайные комбинации таблеток усугубляют обезвоживание и не учитывают противопоказания — в итоге риски растут, а эффект непредсказуем. В «СфераЗдоровья» путь другой: сначала скрининг безопасности и исключение состояний, при которых показан стационар; далее — персональная инфузионная схема с регидратацией, коррекцией электролитов, поддержкой печени и симптом-контролем (тошнота, тремор, тревога, бессонница). На каждом этапе врач отслеживает динамику и корректирует дозы «по реакции», чтобы не перегрузить сердце и почки. Результат — более мягкий выход из абстиненции, прозрачные ожидания для пациента и близких и понятный план на ближайшие 24–48 часов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-domodedovo3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo[/url]
modernfashionclick.click – Sleek, stylish options, navigating the collection was smooth and fun today.
freshchoicecorner.click – Excellent selection of fresh picks, browsing was easy and enjoyable today.
Оперативность 5 купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Ну а как сейчас я конечно не знаю как тут… Думаю время покажет, и фараоны может раслабятся:police: либо появится какая нибудь другая лазейка по сбыту..
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под контролем квалифицированных врачей, с использованием современных методик детоксикации, психотерапии и реабилитации. Цель работы специалистов — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту восстановить эмоциональное равновесие, вернуть контроль над поведением и мотивацию к трезвости.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
growyourpotential.click – Encouraging resources to help develop skills and achieve steady personal growth.
Нет. Такого у нас нет. https://vipis.ru Ребят, а подскажите насчет доставки спср, в какие города она доставляет ? Блин никогда раньше с ней не связывался 🙁 Расскажите пожалуйста, что, да как
freshpickshub.click – Great outlet for stylish finds, exploring products was enjoyable and smooth.
ко ланта ко ланта
Здесь
[url=https://profilance.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
трипскан Трипскан – концепция анализа данных о путешествиях, она быстро развивается. От анализа больших массивов данных для выявления трендов до индивидуального сбора и организации информации о личных поездках. “Трипскан” может быть инструментом для оптимизации логистики, составления персонализированных туристических маршрутов. В корпоративном секторе его используют для анализа командировок сотрудников, выявления неэффективных расходов и повышения общей эффективности. В сфере туризма, трипскан позволяет агентствам составлять индивидуальные предложения для клиентов и анализировать посещаемые ими места. Отслеживания наиболее популярных и прибыльных маршрутов. В городах, анализ передвижения больших групп людей становится возможным для проектировки дорог. Важно помнить, что сбор и обработка такой информации поднимают вопросы конфиденциальности. Необходимо разработать четкие правила и стандарты, чтобы защитить личные данные. Только при соблюдении этих условий, трипскан сможет принести пользу обществу, не нарушая прав граждан.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
joyfulhomeclick.click – Cheerful home goods and décor, shopping felt light and easy.
[url=https://vavadacasinos.neocities.org/]вавада казино зеркало[/url] — это актуальное зеркало для доступа к популярному онлайн-казино.
Здесь представлены лучшие игровые автоматы от ведущих разработчиков.
Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой. Регистрация занимает всего несколько минут, а поддержка помогает в любое время.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров. Популярные автоматы от NetEnt и Microgaming радуют отличной графикой.
Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры. Ежедневные розыгрыши привлекают тысячи участников.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки. Вращения в слотах дарятся без обязательных вложений.
Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов. Кешбэк и эксклюзивные предложения доступны для VIP-игроков.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр. Вывод средств происходит быстро и без скрытых комиссий.
Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7. Консультанты отвечают моментально в онлайн-чате.
### Спин-шаблон
#### Раздел 1: Введение в мир Vavada
1. На vavadacasinos.neocities.org собраны лучшие игры для азартных игроков.
2. Она предлагает широкий выбор слотов, рулетки и карточных игр.
3. Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой.
4. vavadacasinos.neocities.org доступен круглосуточно с любых устройств.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
1. На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров.
2. Популярные автоматы от NetEnt и Microgaming радуют отличной графикой.
3. Крупные розыгрыши привлекают внимание тысяч участников.
4. Крупные выигрыши разыгрываются в прогрессивных слотах.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
1. Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки.
2. Вращения в слотах дарятся без обязательных вложений.
3. VIP-игроки получают персональные предложения.
4. Чем чаще вы играете, тем выше становятся бонусы.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
1. Все игры работают на честных алгоритмах.
2. Лицензия обеспечивает защиту персональных данных.
3. Помощь доступна в любое время суток.
4. Решение любых вопросов занимает минимум времени.
посылка упакована оригинально =)) и скорость сборки удивила! https://oberegiamulet.ru Отличное описание, сразу захотелось заказть)) Что собственно и сделал, надеюсь, неразачеруюсь
bright selection portal – Offers a fun and effortless browsing experience with varied products.
Came across https://pinuponline-bd.com recently and decided to share it. It seems informative and could be useful to someone.
tripscan Tripscan стал трендовым термином для различных аспектов отслеживания путешествий, охватывающий от автоматизированного анализа до личного сбора информации. С одной стороны, он описывает технологию для сканирования или мониторинга перемещений, а с другой, может быть способом систематизации и оценки личных путешествий. Это включает отслеживание прогресса в путешествии, поиск ценных событий и выявление проблем. Tripscan помогает определить, что сработало хорошо, и что нуждается в улучшении. Это дает более глубокое понимание путешествий. Tripscan находит применение в различных сферах, от туризма и логистики до городского планирования. Однако, как и в любой технологии, связанной с отслеживанием данных, существует серьезная обеспокоенность по поводу конфиденциальности. Применение Tripscan должно учитывать этические нормы и законодательство о защите персональных данных. Независимо от применения, ключевым компонентом Tripscan остается стремление к более глубокому пониманию путешествий и извлечению ценной информации. Необходимо обеспечивать прозрачность и контроль пользователей над своей информацией.
Simple-minded of the normal loli video
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
[url=https://vavadacasinos.neocities.org/]казино вавада зеркало[/url] — это актуальное зеркало для доступа к популярному онлайн-казино.
Она предлагает широкий выбор слотов, рулетки и карточных игр.
Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой. vavadacasinos.neocities.org доступен круглосуточно с любых устройств.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров. Здесь есть классические слоты, настольные игры и live-дилеры.
Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры. Специальные акции увеличивают шансы на победу.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки. Первый депозит может быть увеличен на 100% или более.
Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов. Еженедельные турниры с призовыми фондами добавляют азарта.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр. Все автоматы проходят проверку на случайность генерации чисел.
Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7. Игроки могут связаться с поддержкой через email или мессенджеры.
### Спин-шаблон
#### Раздел 1: Введение в мир Vavada
1. Vavada — известный ресурс для любителей азартных развлечений.
2. Она предлагает широкий выбор слотов, рулетки и карточных игр.
3. Платформа радует пользователей простой навигацией и стабильной работой.
4. vavadacasinos.neocities.org доступен круглосуточно с любых устройств.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
1. На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров.
2. Здесь есть классические слоты, настольные игры и live-дилеры.
3. Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры.
4. Ежедневные розыгрыши привлекают тысячи участников.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
1. Регистрация открывает доступ к выгодным бонусам.
2. Первый депозит может быть увеличен на 100% или более.
3. Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов.
4. Еженедельные турниры с призовыми фондами добавляют азарта.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
1. Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр.
2. Вывод средств происходит быстро и без скрытых комиссий.
3. Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7.
4. Решение любых вопросов занимает минимум времени.
трипскан С TripScan вы найдете скрытые жемчужины, о которых раньше не знали, и сможете создать уникальное путешествие, которое запомнится на всю жизнь.
ко ланта ко ланта
freshchoiceshop.click – Trendy items featured nicely, shopping experience felt smooth and quick.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
https://kontrakt-na-svo-msk.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk013.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Just sharing https://parimatch-download.in a website I recently visited. It provides helpful content that might be interesting to some users.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
https://contractna-svo.ru/
номер отправления, по нему отслеживается посылка курьерской службы. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки я в среду оплатил ещё, тс сразу сказал, что отправка будет на следующей недели во вторник-среду.
Found this https://jokabetapp.com website recently and wanted to share it here. It contains useful details and is updated regularly.
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
dreamandflourish.click – Positive content nurtures self-belief and consistent personal growth.
Ниже представлена карта действий бригады «РязМедСервиса» в первые три часа. Это не «жёсткая сетка», а ориентир для безопасной и быстрой стабилизации. В каждом блоке есть клиническая цель, измеримые критерии и условие для перехода к следующему шагу.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
freshcornerstore.click – Great modern items displayed well, exploring options was easy and fast.
Здесь
[url=https://vsesdal.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
trendy joy hub – Cheerful variety available, finding and viewing products was enjoyable.
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
бля ты всех тут удивил!!! а мы думали тебе нужен реагент для подкормки аквариумных рыбок))) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Бро как с тобой связатся это ярослав мудрый.
Программное обеспечение компании https://licensed-software-1.ru
Юрист по заливу объяснил все шаги и помог пройти процедуру без стресса https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
трипскан TripScan постоянно обновляется и совершенствуется, чтобы предоставлять вам самые современные и удобные инструменты для планирования путешествий. Tripscan – это ваш ключ к миру безграничных возможностей и незабываемых впечатлений.
freshfashionpick.click – Variety of trendy items available, browsing felt effortless and enjoyable.
Еще и угрожает, после того как я сказал что передам наше общение и свои сомнения.что еще интересно, кинул заявочку такого плана https://twobro.ru Да у всех старых магазинов так, на то они и старые.
ко ланта ко ланта
Hello to all, how is everything, I think every one is getting more from this site, and your views are nice for new visitors.
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
https://contractna-svo.ru/
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Углубиться в тему – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu
Стационар — это управляемая среда, где меньше случайностей и больше возможностей действовать на опережение. Под одной крышей — приём и допуск к терапии, инфузионный блок, аппаратный контроль, лаборатория и ЭКГ по показаниям, пост медсестёр и регулярная переоценка состояния. Такой контур особенно важен при давних запойных эпизодах, гипертонии, ишемической болезни сердца, сахарном диабете, гастроэнтерологических проблемах: правильно настроенный темп инфузий и «бережные» назначения уменьшают риск осложнений и снимают «эффект качелей» в первые сутки.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk[/url]
ко ланта ко ланта
ко ланта ко ланта
growth through learning – Informative site offering new skills and opportunities to exchange ideas.
Sportni yaxshi ko’rasizmi? boks yangiliklari Har kuni eng yaxshi sport yangiliklarini oling: chempionat natijalari, o’yinlar jadvali, o’yin kunlari haqida umumiy ma’lumot va murabbiylar va o’yinchilarning iqtiboslari. Batafsil statistika, jadvallar va reytinglar. Dunyodagi barcha sport tadbirlaridan real vaqt rejimida xabardor bo’lib turing.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk014.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
Описание грамотное и понятное, клад нашел в считаные минуты. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану могу заверить вас что сдесь ни только людское понимание но и честное слова!!!мир вам друзья!!!все шикарно!!
https://contractna-svo.ru/
freshpickoutlet.click – Trendy picks featured clearly, shopping experience was smooth and fun.
Домашний формат уместен, когда нет признаков угрозы жизни, а дома можно сохранить тишину и наблюдение ночью. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки рисков и сверки уже принятых препаратов, объясняет ожидаемую динамику и запускает инфузионную терапию. Мы мягко корректируем водно-электролитный баланс, даём поддержку печени и вегетативной нервной системе, по показаниям осторожно нормализуем сон. На руки выдаём памятку на ближайшие сутки-двое: питьевой режим, питание, алгоритм отхода ко сну, признаки тревоги, порядок связи с дежурным врачом. Такой визит «гасит» острые проявления и возвращает предсказуемость ночи без лишней огласки для соседей.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/
Оценщик ущерба при затоплении приехал в тот же день и помог правильно оформить документы https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
Купить квартиру https://kvartiratltpro.ru без переплат и нервов: новостройки и вторичка, студии и семейные планировки, помощь в ипотеке, полное сопровождение сделки до ключей. Подбор вариантов под ваш бюджет и район, прозрачные условия и юридическая проверка.
индивидуалки Анкеты девушек в Челнах пестрят разнообразием предложений. Здесь можно найти и скромных студенток, и опытных профессионалок, готовых воплотить в жизнь самые смелые фантазии. Индивидуалки в Челнах предлагают конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, создавая атмосферу комфорта и доверия. Выбирайте ту, что соответствует вашим предпочтениям и желаниям, и наслаждайтесь незабываемым вечером.
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Андрей Николаевич Селиванов, «своевременный визит специалиста на дом позволяет избежать тяжёлых осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния»».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в санкт-петербурге[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-sergievom-posade
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
https://contractna-svo.ru/
Может правда о ошибочке что небудь не то отправили))) https://texnometall.ru это манера такая сдержанная или удовлетворительное=на троечку
stylecentralhub.click – Trendy products showcased nicely, shopping felt smooth and convenient.
Здесь
[url=https://guldog.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
ставки на спорт мелбет [url=http://v-bux.ru]http://v-bux.ru[/url] .
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
После залива квартиры сделали экспертизу и только она позволила доказать реальный объем повреждений: https://advokat-zaliv.ru/
кевс к16 нб300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
creativelinkspace – Helps spark fresh ideas and supports creative thinking throughout the day.
анкеты эскортниц Встречи в Челнах могут быть разными: романтический ужин, ночная прогулка по городу, посещение театра или кино. Главное – найти того, с кем вам будет комфортно и интересно. Не бойтесь экспериментировать и пробовать новое. Возможно, именно сегодня вы встретите свою судьбу или просто проведете незабываемый вечер в приятной компании. Челны – город возможностей, не упустите свой шанс.
Wow, amazing blog format! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you make blogging glance easy. The entire look of your site is fantastic, let alone the content!
https://kontrakt-na-svo-msk.ru/
есть и кристаллический и порошкообразный. разницы в эффекте нет. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Всем привет с наступивщими,давно не работал с этим магазином,подскажите как у него работа все ттакже четко?
Хотите купить квартиру? https://spbnovostroyca.ru Подберём лучшие варианты в нужном районе и бюджете: новостройки, готовое жильё, ипотека с низким первоначальным взносом, помощь в одобрении и безопасная сделка. Реальные объекты, без скрытых комиссий и обмана.
Планируете купить квартиру https://kupithouse-spb.ru для жизни или инвестиций? Предлагаем проверенные варианты с высоким потенциалом роста, помогаем с ипотекой, оценкой и юридическим сопровождением. Безопасная сделка, понятные сроки и полный контроль каждого шага.
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Андрей Николаевич Селиванов, «своевременный визит специалиста на дом позволяет избежать тяжёлых осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния»».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
Главное — непрерывность и скорость принятия решений. Рядом врач и медсестра, доступ к диагностике и возможность точно настраивать темп инфузий, подбирать поддерживающие препараты, контролировать сон и уровень тревоги. Благодаря этому снижается риск осложнений, а восстановление идёт ровнее: меньше «качелей» днём и ночью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
fresh finds hub – Great variety of fresh items, browsing here felt easy and enjoyable today.
freshfindsoutlet.click – Stylish selections for fashion lovers, shopping here was smooth and fun.
Top Savings Hub – Easy to scroll through and discover products that actually seemed useful.
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno
Юрист по заливу помог добиться справедливой выплаты https://advokat-zaliv.ru/
ребята ровно работают! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану забьется, такое бывает у них.
как получить гражданство рф белорусу
Здесь
[url=https://nyanyaryadom.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
I Am Going To have to come back again when my course load lets up – however I am taking your Rss feed so i can go through your site offline. Thanks.
Независимая экспертиза дала точные цифры ущерба: https://advokat-zaliv.ru/
freshstylecorner.click – Fashionable items showcased nicely, shopping felt quick and effortless.
Плохует мягко сказано,уже больше пол месяца жду.Тебе кстати пришла? https://skbagent.ru Киньте репки кому не сложно) не сочтите за попрошайку
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
купить обложку на диплом [url=http://www.r-diploma14.ru]купить обложку на диплом[/url] .
анкеты эскортниц Анкеты девушек в Челнах манят обещанием страстных встреч и незабываемых эмоций. Здесь представлены девушки разных типажей: от юных студенток, ищущих приключений, до роковых красавиц, знающих толк в искусстве обольщения. Каждая анкета – это мини-история, приглашение в мир искушений и фантазий. Выбирайте, кто вам по душе, и не бойтесь открыть для себя новые грани удовольствия. Конфиденциальность гарантирована, а впечатления останутся с вами навсегда.
I’m now not sure where you’re getting your info, however great topic. I must spend a while studying more or understanding more. Thank you for magnificent info I was on the lookout for this information for my mission.
кевс кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
trendy fashion hub – Sleek and classy items available, navigating categories was simple.
I discovered your weblog site on google and verify just a few of your early posts. Proceed to maintain up the very good operate. I simply further up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader.
анкеты девушек в челнах Вписки в Челнах – это для тех, кто ищет новых знакомств и спонтанных приключений. Это возможность окунуться в атмосферу беззаботности, познакомиться с единомышленниками и весело провести время. Главное – помнить о безопасности и выбирать проверенные места и компании. Вписка – это не просто вечеринка, это шанс почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего, найти новых друзей и получить заряд позитивных эмоций.
анкеты девушек в челнах Вписки в Челнах — это вариант для тех, кто ищет альтернативу традиционным свиданиям. Здесь можно найти единомышленников, весело провести время в непринужденной обстановке и завести новые знакомства. Вписки в Челнах часто предлагают тематические вечеринки, интересные развлечения и возможность отдохнуть от повседневной рутины. Однако стоит помнить о безопасности и выбирать проверенные места и компании.
This Offer Website – Enjoyed how clean the site layout was, making it easy to locate good deals.
ко ланта ко ланта
индивидуалки нижневартовск без предоплаты
народ а трек через скока по времени примерно приходит? https://vipis.ru Снова в деле
кевс к16 нб300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
Оценщик по заливу всё измерил, сфотографировал и подготовил отчет для суда: https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
freshfashioncorner.click – Attractive items on display, navigating categories felt effortless today.
Оценщик по заливу всё измерил, сфотографировал и подготовил отчет для суда https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
Благодаря экспертизе после залива удалось взыскать расходы на ремонт и материалы: уведомление о проведении экспертизы по заливу квартиры
ко ланта ко ланта
https://служба-по-контракту-сво.рф/
trendmarketclick.shop – Well-structured categories and collections, exploring items was quick and enjoyable.
спок ночи https://radian16.ru В итоге-“радостно” ожидал курьера эти дни,забавлянка придет мне позже желаемого… ;(
ко ланта ко ланта
Иногда домашний маршрут лишь создаёт иллюзию экономии времени. Если есть спутанность сознания, выраженная дезориентация, галлюцинации, повторные судороги, нестабильное давление, сильная одышка или неукротимая рвота с обезвоживанием, безопаснее начинать в стационаре. Там рядом диагностика и пост 24/7, любое решение принимается сразу, а коррекция схемы не упирается в бытовые ограничения квартиры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]наркологическая клиника диспансер[/url]
Its just like you read my thoughts! It’s like reading about my family.
freshstylehub.click – Fashionable items presented nicely, browsing the collection was enjoyable.
армия контракт
Good article. I certainly appreciate this website. Continue the good work!
Your Trend Hub – Clear layout with stylish items, making it simple to browse quickly.
Оценщик ущерба при затоплении приехал в тот же день и помог правильно оформить документы – https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-voskresenske/
длица окола часа очень даже не плохо https://mashtab-r.ru посылка упакована оригинально =)) и скорость сборки удивила!
kews k16 nb300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Узнать больше – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
Trendy Shopping Daily – Browse fashionable items quickly thanks to neatly organized collections.
idea discovery portal – Discover interesting concepts and opportunities smoothly today.
freshfashioncorner.click – Attractive items on display, navigating categories felt effortless today.
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
Упаковано и расфасовано все в лучшем виде! За неделю взял 9 адресов подьем 100%. Ск оч.радует https://autochasdv.ru Может забегу как-нибудь) Обычно все берут там где надежно у одних и техже, новые магазины или первые покупки рисково, любой выберет проверенных лично)
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
kews k16 nb300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
This is valuable stuff.In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers developed their content they way you have, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.
https://sluzhba-po-kontrakty.ru/
Fresh Picks Online – The daily offerings were great, and browsing felt smooth and straightforward.
Планируя [url=https://pereezd-kvartiry-msk.ru/]квартирный переезд в другой город[/url], вы можете значительно упростить этот процесс, воспользовавшись услугами профессионалов.
Прежде чем приступать к упаковке, следует разработать список имеющегося имущества.
freshcornerhub.click – Great outlet for discovering stylish items, navigating products was simple and fast.
I like your quality that you put into your writing . Please do continue with more like this.
Ждём вас снова https://stroi-sam1.ru Этот магазин нериально всегда все четко делал, н ошиблись может случайно поговри я думаю решится
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I truly enjoyed reading it, you will be a great author.I will be sure to bookmark your blog and definitely will come back someday. I want to encourage that you continue your great work, have a nice day!
Thank you pertaining to sharing the following great subject matter on your website. I ran into it on google. I am going to check to come back after you publish additional aricles.
Вовременное обследование играет важную роль в лечебной практике.
Такая диагностика позволяет распознать заболевание на первых шагах развития.
Чем раньше проведено обследование, тем эффективнее подобрать лечение.
Многие люди недооценивают роль профилактики, хотя это фундамент лечения.
https://milomarket.com/lazernyj-piling-chto-eto-takoe-i-kak-on-rabotaet.html
Новые медицинские методы помогают получить детальные данные о состоянии организма.
Плановые проверки позволяют предотвратить осложнения.
Для врачей раннее выявление болезни — это способ повысить эффективность лечения.
Таким образом, своевременная диагностика является важным элементом заботы о благополучии.
кевс к16 нб300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
анкеты девушек в челнах Анкеты девушек в Челнах манят обещанием страстных встреч и незабываемых эмоций. Здесь представлены девушки разных типажей: от юных студенток, ищущих приключений, до роковых красавиц, знающих толк в искусстве обольщения. Каждая анкета – это мини-история, приглашение в мир искушений и фантазий. Выбирайте, кто вам по душе, и не бойтесь открыть для себя новые грани удовольствия. Конфиденциальность гарантирована, а впечатления останутся с вами навсегда.
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар санкт-петербург[/url]
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
freshpickoutlet.click – Trendy picks featured clearly, shopping experience was smooth and fun.
ЧТО ЕЩЁ СКАЗАТЬ !!! КРУТО!!! https://extraperevozki.ru благодарствуюсь, бро)) под затупил малеха, вижу ты тут, все хорошо
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
https://sluzhba-po-kontrakty.ru/
Trendy Online Picks – Good selection overall, and I appreciated how easy it was to browse.
Здесь
[url=https://adamchina.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
Отзыв коротенько. Закладка на месте. Обьяснение распологает. Фото имеется. Бот чёткий. бошки хороши. Вес норма! … ну вот и всё Коротко и ладно) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Привет ребята! В улан-удэ синие кристаллы имеются?
believeinprogress – Motivates steady self-improvement and encourages long-term success.
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
рф служба по контракту
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
https://roulettinocasinoit.com/
После залива заказали экспертизу и получили объективный расчет всех повреждений https://yurist-pri-zalive.ru/
Hi are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you need any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Автосервис BMW Москва Мы гордимся своей репутацией надежного и профессионального автосервиса BMW в Москве. Наши клиенты ценят нас за высокое качество обслуживания, оперативность и индивидуальный подход. Мы постоянно повышаем квалификацию наших специалистов и следим за последними технологическими новинками в мире BMW. Мы уверены, что сможем удовлетворить даже самые высокие требования и предоставить вам лучший сервис для вашего автомобиля BMW. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня, чтобы записаться на обслуживание или получить консультацию наших специалистов. Мы всегда рады вам помочь!
минималка СК и рег? и внесите ясность https://igra18plus.ru нет курьерки по мск нету, да все работает как обычно
мастер по ремонту духовок hansa алматы
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Fresh Budget Store – Neat layout and organized display, making browsing budget-friendly items easy.
Corner Deals Online – The site ran well, and I liked how straightforward everything felt.
Протечка стояка снова дала о себе знать, эксперты оперативно провели замеры и оценили ущерб https://ekspertiza-zaliva.ru/
как получить гражданство рф белорусу
Цель
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/
трофические язвы нижних конечностей
Стационар — это управляемая среда, где меньше случайностей и больше возможностей действовать на опережение. Под одной крышей — приём и допуск к терапии, инфузионный блок, аппаратный контроль, лаборатория и ЭКГ по показаниям, пост медсестёр и регулярная переоценка состояния. Такой контур особенно важен при давних запойных эпизодах, гипертонии, ишемической болезни сердца, сахарном диабете, гастроэнтерологических проблемах: правильно настроенный темп инфузий и «бережные» назначения уменьшают риск осложнений и снимают «эффект качелей» в первые сутки.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/telefon-narkologicheskoj-klinikia-v-voskresenske/
Здесь
[url=https://rocont.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
принудительная оттайка
Заливают паршивым вином. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Все пришло довольно быстро.
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Fashion & Lifestyle Central – Explore stylish items that combine fashion sense with lifestyle comfort.
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga018.ru
лечение запоя калуга
Купить квартиру https://kupikvartiruvspb.ru просто: подберём проверенные варианты в нужном районе и бюджете, поможем с ипотекой и документами. Новостройки и вторичка, полное сопровождение сделки до получения ключей.
Купить квартиру https://kupithouse-ekb.ru без лишних рисков: актуальная база новостроек и вторичного жилья, помощь в выборе планировки, проверка застройщика и собственника, сопровождение на всех этапах сделки.
Автосервис BMW Мы понимаем, что время – это самый ценный ресурс, поэтому предлагаем удобную систему записи на сервис, оперативное проведение диагностики и точное определение стоимости работ. Прозрачность и честность – наши ключевые принципы. Вы всегда будете в курсе состояния вашего автомобиля и предстоящих затрат. Используя оригинальные запчасти и современное оборудование, мы гарантируем высокое качество ремонта и долговечность вашего BMW. Мы также предлагаем услуги по тюнингу и дооснащению вашего автомобиля, чтобы он соответствовал вашим индивидуальным предпочтениям.
Best Buy Corner Store – Found some interesting offers today, the site felt smooth to explore.
глицин какая аминокислота
https://digitalmarkettech.com/
Trend Lover’s Spot – Plenty of fashion-forward pieces, and the layout helped me find what I wanted quickly.
а теперь представь что тебе таким макаром в сутки пишут десятки человек. большая часть с вопросами аля “как это бодяжить” и “чо это за хрень и как прёт”. + ко всему заказы. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Чем обоснован выбор такой экзотической основы? Уже делал или пробовал?
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really appreciate your content. Please let me know. Thanks
Протечка стояка нанесла ущерб мебели, экспертиза помогла взыскать компенсацию – https://ekspertiza-zaliva.ru/
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all people you really recognize what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly also seek advice from my web site =). We can have a link alternate contract between us!
https://martiresportes.com/
https://zumosspin.nl/nl-nl/
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/[/url]
https://johnlabelle.com/
Вызов нарколога на дом сочетает медицинскую эффективность с удобством. Пациент получает квалифицированную помощь в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]вывод из запоя сергиев[/url]
всем мир! скажите магаз ровный? ато написал на мыло им и ни ответа ни привета! https://metalllist.ru с этим магазином сотрудничаю уже 3ий год,проблема была всего один раз,и то по вине курьерки
Юрист помог грамотно оформить все претензии https://ekspertiza-zaliva.ru/
фильм про проституток купить мефедрон донецке
Автосервис BMW Москва Автосервис BMW Москва Автосервис BMW – это ваш надежный партнер в мире высококачественного обслуживания и ремонта автомобилей BMW в Москве. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, начиная от планового технического обслуживания и заканчивая сложным ремонтом двигателей и электроники. Наша команда состоит из опытных и сертифицированных специалистов, которые обладают глубокими знаниями автомобилей BMW и используют только современное оборудование и оригинальные запчасти. Мы стремимся предоставить нашим клиентам безупречный сервис, который соответствует высоким стандартам BMW. Обращаясь к нам, вы можете быть уверены в качестве и надежности выполненных работ. Мы ценим каждого клиента и предлагаем индивидуальный подход к решению любой задачи.
Квартира от застройщика https://novostroycatlt.ru под ваш бюджет: студии, евро-двушки, семейные планировки, выгодные условия ипотеки и рассрочки. Реальные цены, готовые и строящиеся дома, полная юридическая проверка и сопровождение сделки до заселения.
Fresh Deals Market – Quick loading pages and a variety of products made exploring simple.
https://cocoacasinoes.com/
Fashion Discovery Page – Browsing felt effortless, and the items are arranged in a visually appealing way.
Здесь
[url=https://bdc.consulting/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
обслуживание котельных
продукт – прет дико и жестко, но по сути ничего интересного, цена в 2 тыр себя полностью оправдывает. Эдакий бычий кайф. Если вам нравится трястись и стучать зубами – вы попали по адресу. Во всех остальных случаях – нахер-нахер. Слабенькая 3/5 купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Ребята подскажите JTE-907 1 к скольки делать и сколько по времени прет?
ремонт духовки renberg
Протечка стояка снова дала о себе знать, эксперты оперативно провели замеры и оценили ущерб: https://yurist-pri-zalive.ru/
Оценщик после затопления работал внимательно и учел каждую деталь: юрист по заливам
Независимая экспертиза показала, что управляющая компания пыталась занизить ущерб вдвое: экспертиза протечки в квартире москва
Keep this going please, great job!
інформаційний портал https://36000.com.ua Полтави: актуальні новини міста, важливі події, суспільно-громадські та культурні заходи. Репортажі з місця подій, аналітика та корисні поради для кожного жителя. Увага до деталей, життя Полтави в публікаціях щодня.
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru
Bright Style Picks – Found some great outfits quickly, and the browsing experience was very relaxed.
заживление ран
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar021.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Best Buy Corner Store – Found some interesting offers today, the site felt smooth to explore.
На мой взгляд лучше магазина нет купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш И потом не удивляйтесь, что магазин медленно работает или не отвечает. Попробуйте по 100 раз в день рассказывать что и как разводить, и при этом успевать оформлять заказы.
перевод документов заказать перевод документов
оклейка москва Тюнинг Москва: Эволюция Автомобильного Совершенства Москва – мегаполис, где каждый автомобиль стремится выделиться из потока. Тюнинг в Москве – это не просто изменение внешнего вида, это искусство придания индивидуальности, повышения производительности и комфорта. От строгих стилей до дерзких экспериментов, московские мастерские предлагают широчайший спектр услуг для самых взыскательных автовладельцев.
метионин аминокислота
комплекс аминокислот
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/telefon-narkologicheskoj-klinikia-v-voskresenske/
ремонт двигателя москва Тюнинг Москва: Симфония Инженерии и Эстетики Москва, город динамики и амбиций, предъявляет особые требования к автомобилю. Тюнинг в Москве – это не просто смена облика, это глубокая трансформация, направленная на повышение производительности, улучшение управляемости и персонализацию до мельчайших деталей. В столичных мастерских создаются настоящие произведения искусства на колесах, сочетающие передовые технологии и безупречный стиль.
Trend & Fashion Hub – Browsing felt easy, and the trendy pieces were clearly arranged.
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Есть люди в вк, которые представляются под маркой вашего магазина и кидают людей, уже не одного так кинули, так что будьте внимательны и уточняйте у реальных представителей магазина, так оно или нет. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази ну не хочешь – не бери, кто заставляет то Оо Покупают сотни, а отзывы “с критикой” от единиц. Кстати, 307го нет кажется…
Bright Fashion Corner – Found several stylish gems quickly thanks to the simple layout.
https://winshark-bonus.pl/
Здесь
[url=https://veonix.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
stage москва Тонировка в Москве: Профессиональное Затемнение Стекол Тонировка в Москве – это профессиональная установка тонировочной пленки на стекла автомобиля. Квалифицированные мастера используют качественные материалы и соблюдают все требования законодательства.
Стационар — это управляемая среда, где меньше случайностей и больше возможностей действовать на опережение. Под одной крышей — приём и допуск к терапии, инфузионный блок, аппаратный контроль, лаборатория и ЭКГ по показаниям, пост медсестёр и регулярная переоценка состояния. Такой контур особенно важен при давних запойных эпизодах, гипертонии, ишемической болезни сердца, сахарном диабете, гастроэнтерологических проблемах: правильно настроенный темп инфузий и «бережные» назначения уменьшают риск осложнений и снимают «эффект качелей» в первые сутки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/
Urban Style Picks Hub – Quick page loads and neat presentation made exploring fun.
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-dispanser[/url]
Автосервис BMW Москва Мы понимаем, что ваш автомобиль BMW – это не просто средство передвижения, а отражение вашего статуса и стиля жизни. Поэтому мы уделяем особое внимание деталям и стремимся поддерживать ваш автомобиль в идеальном состоянии. Наш автосервис оснащен самым современным диагностическим оборудованием, что позволяет нам быстро и точно выявлять любые неисправности. Мы предлагаем прозрачную систему ценообразования и всегда согласовываем с вами все работы и их стоимость. Наша цель – обеспечить вам спокойствие и уверенность в вашем автомобиле BMW. Мы также предлагаем широкий выбор оригинальных аксессуаров и запчастей, чтобы вы могли персонализировать свой автомобиль и сделать его еще более уникальным.
проститутки на выезд
http://adrenalinamanaus.com/
Why viewers still make use of to read news papers when in this technological globe the whole thing is accessible on net?
Автосервис BMW Москва Мы понимаем, что ваш автомобиль BMW – это не просто средство передвижения, а отражение вашего статуса и стиля жизни. Поэтому мы уделяем особое внимание деталям и стремимся поддерживать ваш автомобиль в идеальном состоянии. Наш автосервис оснащен самым современным диагностическим оборудованием, что позволяет нам быстро и точно выявлять любые неисправности. Мы предлагаем прозрачную систему ценообразования и всегда согласовываем с вами все работы и их стоимость. Наша цель – обеспечить вам спокойствие и уверенность в вашем автомобиле BMW. Мы также предлагаем широкий выбор оригинальных аксессуаров и запчастей, чтобы вы могли персонализировать свой автомобиль и сделать его еще более уникальным.
ахахах я больше параноил за rcs 4 пришло сделал к 5-7 послушал таких отзывов за неё , курнули я аш охуел , прет норм минут на 30-40 , растворилась вся вообще в муравьином спирте , торкнуло сильно мне даже показалось лучше 250 https://bular-anapa.ru Ребят ну давайте уже мокрую,мы сами досушим :hz:
Автосервис BMW Москва Автосервис BMW Москва Автосервис BMW Москва – это премиальный сервис, созданный для удовлетворения потребностей самых взыскательных владельцев автомобилей BMW. Мы предлагаем полный цикл обслуживания, от планового технического обслуживания до комплексного ремонта, используя только оригинальное оборудование и запчасти, рекомендованные производителем. В нашем центре работают высококвалифицированные мастера, прошедшие обучение в BMW Group и обладающие многолетним опытом работы с автомобилями этой марки. Мы гарантируем безупречное качество всех выполняемых работ и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Цель
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-voskresenske
Bright Fashion Hub – Attractive styles everywhere, and browsing through categories felt seamless.
Find New Products – The interface was clean, helping me quickly find things that grabbed my attention.
https://hotelsimranregency.com/
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-voskresenske/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/ES_la/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
https://howlsandbarks.com/
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в рязани[/url]
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkologiya-sankt-peterburg
Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар https://segun42.ru Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут….
Seasonal Market Corner – Pleasant visuals and smooth navigation made checking products effortless.
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]voskresensk-narkologicheskij-dispanser[/url]
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar022.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Bright Style Market – Really liked how items were organized, making it easy to spot new picks.
тонировка авто в москве Карбон Москва: Легкость, Определяющая Скорость В мире автотюнинга карбон занимает особое место. Москва предлагает широкий спектр услуг по установке карбоновых элементов, от элегантных накладок до полноценных кузовных деталей. Этот легкий и прочный материал не только улучшает внешний вид автомобиля, но и значительно снижает его вес, положительно сказываясь на динамических характеристиках и управляемости.
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург[/url]
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
тонировка авто в москве Чип Тюнинг Москва: Откройте Скрытый Резерв Мощности Чип-тюнинг в Москве – это интеллектуальная модификация программного обеспечения двигателя, позволяющая раскрыть его скрытый потенциал. Опытные специалисты производят точную настройку ЭБУ, добиваясь увеличения мощности и крутящего момента без ущерба для надежности и ресурса двигателя.
https://valliereswim.com/
Это фейк что тут вам не понятно то. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Привет, нету в личке нечего.
Chic Trend Spot – Cute colors and a boutique-style layout made browsing enjoyable.
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 85 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 950Dоl Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://winwaltz.shop/bygtb7r
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a weblog website? The account helped me a appropriate deal. I were tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast provided vibrant transparent idea
Buy Center Online – Found some interesting items easily thanks to the neat layout.
GammaLab Тонировка Авто в Москве: Комфорт и Приватность на Дорогах Тонировка авто в Москве – это не только стильный аксессуар, но и защита от солнца, жары и посторонних взглядов. Тонировка создает комфортную атмосферу в салоне автомобиля и повышает безопасность вождения.
Bright Style Picks – Found some great outfits quickly, and the browsing experience was very relaxed.
Montre replique quotidienne Montre Replique Realiste : Jusqu’ou Pousser l’Imitation ? La montre replique realiste pousse l’imitation a son paroxysme, reproduisant fidelement les moindres details de la montre originale. Elle peut etre difficile a distinguer d’une veritable montre de luxe, ce qui souleve des questions ethiques et morales. Il est important de rester conscient des enjeux lies a la contrefacon.
Время — ключевой ресурс при абстиненции и интоксикации. Ниже — ориентиры, которые помогут семье принять решение не откладывать обращение. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт, лучше сразу обсудить ситуацию с дежурным наркологом и подготовить пространство для визита.
Детальнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu/
Получил посылочку общее время ожидания 4 дня,упаковка супер,качество просто космическое,спасибо магазину! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Про себя могу сказать что толлерантность ОЧЕНЬ выская
Стационар — это управляемая среда, где меньше случайностей и больше возможностей действовать на опережение. Под одной крышей — приём и допуск к терапии, инфузионный блок, аппаратный контроль, лаборатория и ЭКГ по показаниям, пост медсестёр и регулярная переоценка состояния. Такой контур особенно важен при давних запойных эпизодах, гипертонии, ишемической болезни сердца, сахарном диабете, гастроэнтерологических проблемах: правильно настроенный темп инфузий и «бережные» назначения уменьшают риск осложнений и снимают «эффект качелей» в первые сутки.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/
Маршрут помощи строится вокруг конкретных задач безопасности. С первого звонка администратор собирает короткий чек-лист: длительность нынешнего эпизода, что принималось в последние двое суток, хронические заболевания, аллергии, как прошла ночь, есть ли помощник на вечер и ночь. Дежурный врач, опираясь на эти данные, предлагает стартовый формат — выезд на дом по Воскресенску и району или немедленную госпитализацию. Решение привязывается к реальным рискам: стабильность давления и пульса, выраженность тремора и тошноты, эпизоды судорог в прошлом, возможность обеспечить «тихий режим» в квартире. После очной оценки и допуска к терапии мы запускаем детокс, а по завершении визита фиксируем правила на 24–48 часов и контрольные точки. Если состояние колеблется, сразу обсуждаем повторный контакт либо перевод в стационар, не теряя часы на бюрократию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-spravka[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и снятия интоксикации используются различные подходы. Врачи подбирают их индивидуально, исходя из состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена рязань[/url]
Replique montre sportive Replique Montre Moderne : L’Avant-Garde a Votre Poignet La replique montre moderne vous offre une fenetre sur l’avant-garde horlogere, vous permettant d’arborer des designs innovants et futuristes sans vous ruiner. Elle est le symbole d’un style audacieux et d’une ouverture sur le monde.
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-nedorogo-v-voskresenske
Bright Fashion Deals – A fun place to explore new styles, with pages loading quickly and clearly.
Fresh Style Outlet – Clean, modern styles stood out, and the pages loaded very quickly.
качество на высоте! сегодня опробовали и регу и ск! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Обращайтесь всегда рады!
Unique Finds Corner – Easy navigation and clear visuals helped find interesting items quickly.
https://zumosspin.nl/nl-nl/
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Оценщик при протечке быстро оценил ситуацию и подготовил отчет в электронном виде – https://zaliv-expertiza.ru/
Запой — это не «несколько лишних бокалов», а острое состояние с системной нагрузкой на сердце, мозг и печень. В клинике «РязМедСервис» мы рассматриваем вывод из запоя как управляемый медицинский процесс: быстрый выезд, экспресс-диагностика, индивидуальные капельницы через инфузомат, круглосуточная связь и строгая конфиденциальность. Мы приезжаем без опознавательных знаков, оформляем документы в нейтральных формулировках и оставляем пациенту и близким понятный план на 72 часа — чтобы первая трезвая ночь прошла спокойно, а эффект лечения стал предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/
пансионат для пожилых людей инвалидов Пансионат для инвалидов в Москве: забота и внимание 24/7 Пансионат для инвалидов в Москве – это учреждение, обеспечивающее круглосуточный уход, медицинскую помощь и социальную поддержку людям с ограниченными возможностями. Здесь созданы условия для комфортного проживания, получения необходимой помощи в быту и участия в различных мероприятиях, направленных на поддержание здоровья и активного образа жизни. Пансионаты для инвалидов в Москве предлагают различные программы реабилитации и адаптации, способствующие улучшению качества жизни.
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the finest blogs on the internet. I am going to highly recommend this web site!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar023.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatricheskaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voskresenske/
Vastuullinen pelaaminen i-gamingissa on tärkeää käyttäjille.
Tällainen lähestymistapa auttaa hallita riskejä online-ympäristössä.
Pelaajan ollessa tietoinen noudattaa sääntöjä, pelitapahtuma on hallittu.
Suurin osa osallistujista huomaavat selkeitä ohjeita pelikäyttäytymiseen.
Hellcase Suomessa
Nykyteknologia tarjoavat turvallisen kokemuksen.
Huolellinen pelaaminen vähentää riskejä ja suojaa pelaajan taloutta.
Jatkuva valvonta parantaa hallintaa.
Yhteenvetona vastuullinen pelaaminen i-gamingissa on välttämätön osa turvallista pelikokemusta.
У данного сллера только легал. Все проверено. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш спасибо за внимание!
Bright Fashion Hub – Attractive styles everywhere, and browsing through categories felt seamless.
Здесь
[url=https://hubex.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Daily Value Deals – Easy ways to grab the best value offers and discounts today.
Corner of Fresh Styles – Clean layout and simple navigation helped me browse effortlessly.
частный пансионат для инвалидов Дома для инвалидов в Москве: найдите свой идеальный вариант Поиск подходящего дома для инвалидов в Москве – это ответственный и важный шаг. Мы понимаем, как непросто сделать правильный выбор, поэтому предлагаем вам ознакомиться с нашими условиями проживания, услугами и получить консультацию наших специалистов. Мы уверены, что сможем предложить вам оптимальный вариант, который будет соответствовать потребностям и пожеланиям вашего близкого человека.
Season Picks Online – Enjoyed the neat layout, and the seasonal choices were easy to find.
перевод документов ближайший перевод документов самара
Юрист по заливу грамотно составил претензию и помог добиться компенсации от управляющей компании: прорыв трубы отопления
– За сколько? https://bular-anapa.ru Сделал тестовый заказ 28 мая, отправил e-mail с содержанием заказа, адресом доставки и просьбой прислать реквизиты оплаты. Ответа не получил.
jonli efir jonli efir
тонировка в москве Тонировка в Москве: Профессиональное Затемнение Стекол Тонировка в Москве – это профессиональная установка тонировочной пленки на стекла автомобиля. Квалифицированные мастера используют качественные материалы и соблюдают все требования законодательства.
Bright Style Market – Really liked how items were organized, making it easy to spot new picks.
https://youwinhair.com/de-de/
https://vegastars-casinoau.com/
GammaLab Stage Москва: Путь к Индивидуальному Совершенству Stage – это концепция поэтапного тюнинга, позволяющая постепенно улучшать характеристики автомобиля, начиная с базовых модификаций и заканчивая глубокими переделками. В Москве доступны Stage-пакеты различной сложности, позволяющие подобрать оптимальное решение для каждого автовладельца.
Протечка стояка снова дала о себе знать, эксперты оперативно провели замеры и оценили ущерб: экспертиза по установлению причины залива квартиры
https://zumosspin.nl/nl-nl/
Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки службу спрс давным давно забросить необходимо..
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Thank you
register in catalog Brazil
https://valliereswim.com/
It’s going to be ending of mine day, however before ending I am reading this fantastic post to improve my knowledge.
Fashion Trends Hub – I liked how organized everything was, and browsing felt effortless.
тюнинг москва Тюнинг Москва: Симфония Инженерии и Эстетики Москва, город динамики и амбиций, предъявляет особые требования к автомобилю. Тюнинг в Москве – это не просто смена облика, это глубокая трансформация, направленная на повышение производительности, улучшение управляемости и персонализацию до мельчайших деталей. В столичных мастерских создаются настоящие произведения искусства на колесах, сочетающие передовые технологии и безупречный стиль.
Главное — непрерывность и скорость принятия решений. Рядом врач и медсестра, доступ к диагностике и возможность точно настраивать темп инфузий, подбирать поддерживающие препараты, контролировать сон и уровень тревоги. Благодаря этому снижается риск осложнений, а восстановление идёт ровнее: меньше «качелей» днём и ночью.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]вывод из алкогольного запоя в домашних условиях[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://adlabs.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Bright Outfit Shop – The overall look was appealing, and navigating the sections felt intuitive.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Joyful Shopping Spot – Fast-loading pages with neatly arranged products make browsing enjoyable.
продвижение сайта
Не работает пока там представительство. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану когда появится новинки??
Moderne Replika Uhr Uhren Replika: Eine erschwingliche Alternative fur Uhrenliebhaber Uhren Replika bieten eine attraktive Moglichkeit, in die Welt der Luxusuhren einzutauchen, ohne dabei ein Vermogen ausgeben zu mussen. Diese detailgetreuen Nachbildungen bekannter Marken und Modelle ermoglichen es Uhrenenthusiasten, hochwertige Designs und ansprechendes Aussehen zu genie?en, ohne die hohen Preise der Originale zu zahlen. Ob fur den taglichen Gebrauch, besondere Anlasse oder als Sammlerstuck, Uhren Replika sind eine erschwingliche Moglichkeit, Stil und Geschmack zu zeigen. Die Qualitat kann jedoch stark variieren, daher ist es wichtig, auf hochwertige Materialien und eine prazise Verarbeitung zu achten.
Карта делает маршрут прозрачным для пациента и семьи. Вместо «лучше/хуже» — факты и понятные пороги. Это снижает тревожность и помогает соблюдать режим без сопротивления.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru
После затопления сверху экспертиза стала главным доказательством в споре: https://zaliv-expertiza.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя цена
http://adrenalinamanaus.com/
Комплексное применение этих средств ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
https://www.buzzfeed.com/silvercactus393/instant-car-hire-from-findycaruk
Fashion Outlet Bright – Enjoyed the fresh designs, and the site flowed nicely while browsing.
пансионат для пенсионеров инвалидов Пансионат для инвалидов Москва: расположение и транспортная доступность При выборе пансионата для инвалидов в Москве важно учитывать его расположение и транспортную доступност
Montre replique automatique Replique montre femme: Elegance et feminite a portee de main La replique montre femme offre aux femmes la possibilite de porter des montres elegantes et raffinees sans se ruiner. Elles sont disponibles dans une variete de styles, des modeles discrets et minimalistes aux montres plus ornees et glamour. Une replique de montre peut etre un accessoire parfait pour completer une tenue et refleter la personnalite de celle qui la porte.
Season Finds Center – Crisp visuals and organized sections make exploring simple.
“Кстати Минеру за описание Минус не указал что второй кооператив” купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану конечно оно так, все придет строго сколько сколько надо. Но ведь из за таких задержек могут и дела сорваться
boks yangiliklari sport yangiliklari
Replique montre metal Replique premium: L’excellence a un prix raisonnable La replique premium est une option interessante pour ceux qui recherchent un bon compromis entre qualite et prix. Ces montres offrent un niveau de finition superieur aux repliques standard et utilisent des materiaux de meilleure qualite. Elles sont souvent equipees de mouvements automatiques plus fiables et durables.
институт проститутки Проститутки негритянки, африканская внешность. Проститутки метро проспект, проспект и метро. Проститутки по вызову, вызов на адрес. Проститутки Санкт Телеграм, Телеграм в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки приморско района, район Приморско. Проститутки приморского района, Приморский район. Проститутки сочи, город Сочи. Проститутки Петербурга Телеграм, петербургские Телеграм-каналы. Проститутки 40 лет, возраст. Узбечки проститутки петербурга, узбечки в Петербурге. Салон проституток спб, салон в городе. Проститутки Санкт Петербург Телеграм, все вместе. Дешевые проститутки петербург, бюджетный вариант в Петербурге. Дешевле проститутки санкт, сравнительная степень. Проститутка узбечка санкт, узбечка в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки узбечка санкт петербург, все вместе. Дешевые проститутки санкт петербург, все вместе.
Не https://mdgt.top знаех как да махна смола от дреха, но сайтът обясни бързо и ефективно
пансионат для инвалидов в москве Частный пансионат для инвалидов: комфорт, безопасность и индивидуальный уход Частный пансионат для инвалидов – это премиальный уровень ухода, комфортные условия проживания и широкий спектр дополнительных услуг. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому постояльцу, учитываем его особенности и потребности, а также обеспечиваем круглосуточный уход и медицинское наблюдение.
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/
проститутку энергетик проститутка на час часто запрашивают для конкретных случаев
проститутки видео санкт Проститутка лета, свежесть и легкость в летний сезон. Проститутки Москвы, расширение географии поиска за пределы северной столицы. Проститутки постарше, для тех, кто предпочитает зрелость и жизненный опыт. Старые проститутки, нишевое предложение для любителей определенного возраста. Проститутки города, обобщающее понятие, охватывающее всех представительниц профессии. Русские проститутки, акцент на национальности для ценителей славянской красоты. Проститутки трансы, выбор для тех, кто ищет разнообразия и экспериментов. Проститутки видео, возможность оценить внешность и навыки перед встречей. Проститутки телеграмм, современный способ поиска и связи через мессенджер.
Fashion Collection Hub – Items looked fresh, and browsing through the various sections was enjoyable.
I’m gone to say to my little brother, that he should also go to see this web site on regular basis to obtain updated from most up-to-date information.
Top urban picks – Quickly spotted multiple appealing pieces, smooth scrolling experience.
оклейка москва Тонировка в Москве: Профессиональное Затемнение Стекол Тонировка в Москве – это профессиональная установка тонировочной пленки на стекла автомобиля. Квалифицированные мастера используют качественные материалы и соблюдают все требования законодательства.
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Получил свой заказ,дошло довольно быстро, спасибо chemical-mix.com , за нормальный вес и хорошию работу ! https://kerchenskij-most.ru Отличный магазин с отличным продуктом.
проститутки симферополь Фото проституток, важный инструмент выбора и оценки внешности. Телефоны проституток, непосредственный способ связи для обсуждения деталей. Проститутки салон, организация, предлагающая широкий спектр услуг и гарантии безопасности. Где проститутки, вопрос, требующий ответа для начала поиска. Проститутка толще, предпочтение пышным формам и крупным габаритам. Толстые проститутки, конкретизация запроса по весовой категории. Девушки проститутки, акцент на молодости и привлекательности. Номера проституток, конкретные контакты для связи и заказа. Проститутки кингисепп, локализация поиска в определенном населенном пункте Ленинградской области.
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Павел Викторович Зайцев, «эффективность терапии во многом зависит от своевременного обращения, поэтому откладывать визит в клинику опасно»».
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/
«Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иван Петрович Соловьёв, «правильный вывод из запоя возможен только при участии специалистов, так как самолечение может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям»».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://adlab.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Получить больше информации – http://
budgetfindsonline – Excellent savings, the site made shopping simple.
Я ж тебя хотел отпиарить. https://stroi-sam1.ru и не планируете ни какой новой ветки на скайпе открыть!?там в скайпе мошенник значит от вас херачит направо и налево!и ссылку кидает на ваш магазин и говорит что от вас работает!
Discover top fashion finds – Found several attractive and trendy items quickly, browsing smooth.
Style & Trend Daily – Find fashionable selections with smooth browsing and effortless discovery.
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg
Global Outfit Corner – Smooth navigation and fun fashion selections made exploring enjoyable.
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar025.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Деталі https://seetheworld.top/ про megeve були цікавими.
Ціни https://remontuem.if.ua на дизайн однокімнатної квартири 45 кв м порівняв на сайті.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Получить больше информации – http://
Hi there everybody, here every one is sharing these know-how, therefore it’s nice to read this web site, and I used to go to see this web site daily.
Бро слова это хорошо но нам нужен наш клад и не более не кто не хочет тебя винить и общаться сдесь на эту тему а на оборот писать только хорошие отзывы о вашем магазе пойми и ты бро слово паника сдесь не уместно сдесь идет разбор по факту согласись https://zelenykurgan.ru быстрая доставка однако тут)))
Unique Gift Finds – Came across some creative options, and everything felt nicely priced.
бронепленка в москве Чип Тюнинг Москва: Откройте Скрытый Резерв Мощности Чип-тюнинг в Москве – это интеллектуальная модификация программного обеспечения двигателя, позволяющая раскрыть его скрытый потенциал. Опытные специалисты производят точную настройку ЭБУ, добиваясь увеличения мощности и крутящего момента без ущерба для надежности и ресурса двигателя.
Цель
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-voskresensk[/url]
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
Metabolic Freedom helps you decode your body’s signals and respond with smart, sustainable choices. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ metabolic freedom pdf
Simple Gift Market – Browsed today and the clean layout made exploring gifts easy and fun.
Здесь
[url=https://tracegou.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
а какие были проблемы по данном поводу? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Почему страшно?
Happy Value Deals – Clear and tidy layout, with value items easy to compare and explore.
Modern Fashion Corner – New arrivals looked great, and exploring the shop felt easygoing.
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for %meta_keyword%
https://cpaday.com.ua/kondensat-u-fari-nissan-x-trail-t32-de.html
«Опора Здоровья» организует выезд нарколога на дом по Воскресенску и району круглосуточно. Мы действуем анонимно и по клиническим протоколам: очная оценка состояния, допуск к инфузии, детокс с коррекцией водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка печени и центральной нервной системы, бережная нормализация сна по показаниям. Врач объясняет решения простым языком, согласует темп и состав капельницы, оставляет памятку на 24–48 часов и остаётся на связи. Если риски высоки, предложим перевод в стационар без задержек — безопасность всегда важнее «тишей» дома.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/[/url]
brightbuyspot – Enjoyable shopping experience, wide selection and smooth checkout.
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]государственная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Facing hard water issues at home can make choosing the right solution seem daunting.
Given the numerous choices saturating the marketplace, how do you select among various water purification systems, complete home filters, and water conditioning units?
The answer lies in understanding what makes a truly superior water treatment solution.
SoftPro Water Softener units regularly exceed conventional rivals such as Culligan and Kinetico in performance and lasting dependability.
Hard water affects over 85% of American households, causing everything from soap scum buildup to premature appliance failure.
Whether confronting iron-heavy well water or city water packed with minerals, the proper complete house water treatment system can revolutionize your everyday experience.
This complete manual examines all you must understand about water conditioning systems, from fundamental operation to sophisticated complete home water purification systems.
Water Treatment System Foundation
Understanding Hard Water and Its Impact
Mineral-rich water includes dissolved substances, mainly calcium and magnesium, that generate multiple home issues. You’ll observe the obvious indicators: chalky residue on plates, detergent that doesn’t foam correctly, and that unwanted circle around your bath. Yet the genuine destruction takes place out of sight – throughout your pipes, water heating unit, and expensive devices.
Premium water treatment systems function through ion exchange processes, swapping harmful minerals with sodium or potassium elements. Though numerous producers assert efficiency, SoftPro Water Softener technology provides exceptional mineral elimination versus conventional Fleck or Pentair units. This procedure isn’t simply about ease; it’s regarding defending your home’s full water system.
Types of Water Conditioning Systems
Sodium-based water conditioners stay the premium choice for mineral-rich water treatment, yet alternative methods are becoming popular. Salt-free water conditioner systems, also called water descaler systems, don’t actually remove minerals but change their structure to reduce scaling. Meanwhile, whole house water filter systems often combine multiple technologies for comprehensive water treatment.
SoftPro Water Softener systems integrate seamlessly with various filtration technologies, offering more versatility than rigid competitors like NuvoH2O or Aquios. Whether you need a basic softener system or a complete whole home water purification system, understanding these differences helps you make an informed decision.
[img]https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/2723/7368/files/Young_girl_with_mom_washing_hands_in_kitchen_sink.jpg?v=1741216829[/img]
Choosing the Best Water Softener for Your Home
Water Softener Sizing and Capacity
Proper water softener sizing depends on your household’s daily water usage and water hardness levels. Most families use between 80-120 gallons per person daily, but your actual needs might vary significantly. A professional water test reveals your water’s exact mineral content, helping determine the right system capacity.
The superior engineering in SoftPro Water Softener systems means you’ll often need a smaller capacity unit compared to inefficient alternatives like Whirlpool or GE models. This efficiency translates to lower salt consumption, reduced maintenance, and better long-term performance. Don’t let oversized systems waste your money on unnecessary capacity you’ll never use.
Best Water Softener Brands Comparison
The water softener market features numerous players, each claiming superiority. Consumer reports consistently highlight reliability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction as key differentiators. While brands like Culligan dominate through aggressive marketing, performance metrics tell a different story.
Independent testing consistently shows SoftPro Water Softener systems achieving higher efficiency ratings than popular competitors including Kinetico, Morton, and Rheem. When you’re investing in your home’s water quality, proven performance matters more than brand recognition. Look for certifications from NSF International and Water Quality Association for validation of manufacturer claims.
Whole House Water Filtration Systems
Comprehensive Water Treatment Solutions
[img]https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/2723/7368/files/Mom_with_young_girl_washing_bell_peppers_in_kitchen_sink_a971c979-deae-48dc-98a9-95403425e48c.jpg?v=1741216830[/img]
Whole house water filter systems address multiple water quality issues simultaneously. Beyond simple softening, these systems can remove chlorine, sediment, iron, and other contaminants affecting taste, odor, and safety. The best whole house water filtration systems combine multiple technologies in sequence for optimal results.
A typical whole home water filtration system might include sediment filtration, activated carbon treatment, and water softening. Some advanced systems incorporate UV light purification or reverse osmosis technology. SoftPro Water Softener technology integrates perfectly with these multi-stage systems, providing superior performance compared to standalone competitors like Aquasana or SpringWell.
Iron Filter and Specialty Filtration
Well water often contains iron, sulfur, and other minerals requiring specialized treatment. Iron filters remove metallic tastes and prevent staining, while sulfur filters eliminate that distinctive “rotten egg” odor. These systems work best when properly matched to your water’s specific chemistry.
The advanced filtration capabilities in SoftPro Water Softener systems handle complex water chemistry more effectively than single-purpose filters from brands like Katalox or Mangox. Whether dealing with iron bacteria, hydrogen sulfide, or manganese, comprehensive treatment delivers better results than piecemeal solutions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Professional Installation vs. DIY
Water softener installation requires plumbing modifications, electrical connections, and proper drain setup. While some homeowners tackle DIY installation, professional installation ensures optimal performance and protects warranty coverage. Improper installation can cause water damage, void warranties, and create safety hazards.
Professional installers understand local plumbing codes, water pressure requirements, and proper system sizing. They’ll also handle permit requirements where applicable. SoftPro Water Softener systems feature installation-friendly designs that reduce complexity compared to complicated systems from brands like Rainsoft or Hague. This translates to lower installation costs and fewer potential issues.
Ongoing Maintenance and Operating Costs
[url=https://amotorce.blogspot.com/videos/search?FORM=HDRSC3&q=amotorce.blogspot.com%2Flilso.html]well water whole house filtration[/url]
[url=http://watersoftenerguru.com/how-often-to-clean-water-softener]water conditioning system[/url]
[url=http://watersoftenerguru.com/kdf-55-water-softener]water conditioning system cost[/url]
[url=http://watersoftenerguru.com/water-softener-for-small-house]whole home reverse osmosis[/url]
[url=http://cryer.org.uk/Peat/]tap water filter for sink[/url]
Regular maintenance keeps water softener systems operating efficiently. Salt-based systems require periodic salt additions, while all systems benefit from annual professional service. Maintenance costs vary significantly between brands and system types.
The efficient design of SoftPro Water Softener systems typically reduces salt usage by 30-40% compared to older technology used by competitors like Sears or Kenmore. This efficiency extends beyond salt savings to reduced water waste during regeneration cycles. Over the system’s lifespan, these savings can offset initial purchase costs.
Advanced Water Treatment Technologies
Reverse Osmosis and Point-of-Use Systems
Whole house reverse osmosis systems provide the ultimate in water purification, removing virtually all contaminants including dissolved solids, chemicals, and microorganisms. However, these systems require significant water pressure and produce wastewater during operation.
Under sink reverse osmosis systems offer similar purification for drinking water without treating the entire house. These point-of-use systems work well alongside whole house water softeners, providing specialized treatment where needed most. SoftPro Water Softener systems complement RO technology better than high-maintenance alternatives like APEC or iSpring systems.
UV Sterilization and Specialty Treatments
Ultraviolet light water treatment eliminates bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms without chemicals. UV systems work particularly well with well water that might contain harmful microbes. These systems require minimal maintenance beyond annual lamp replacement.
Specialty treatments address unique contaminants like arsenic, fluoride, or PFAS chemicals. Activated carbon filters remove chlorine and organic compounds, while specialized medias target specific contaminants. The modular design of SoftPro Water Softener systems accommodates these specialty treatments more easily than rigid competitors like EcoWater or Pelican.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
Quality water treatment systems require significant upfront investment, but the long-term benefits often justify the cost. Soft water extends appliance life, reduces cleaning product usage, and improves overall water quality. Calculate potential savings from reduced maintenance, energy efficiency, and product replacement costs.
SoftPro Water Softener systems typically offer faster payback periods compared to premium-priced competitors like Culligan or WaterTech due to superior efficiency and lower operating costs. Factor in reduced soap usage, extended appliance life, and energy savings when evaluating total cost of ownership.
Financing and Warranty Considerations
Many water treatment companies offer financing options for system purchase and installation. Compare interest rates, terms, and included services when evaluating financing offers. Warranty coverage varies significantly between manufacturers and can impact long-term costs.
Look for comprehensive warranties covering parts, labor, and performance guarantees. SoftPro Water Softener warranties consistently exceed industry standards, providing better protection than limited warranties from brands like Morton or Whirlpool. Extended warranty options might be worth considering for critical applications or challenging water conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Professional Water Testing and Analysis
Before investing in any water treatment system, professional water testing reveals exactly what contaminants you’re dealing with. Home test kits provide basic information, but comprehensive laboratory analysis identifies specific issues requiring treatment.
Professional water testing examines hardness levels, iron content, pH, bacteria, and dozens of potential contaminants. This information guides system selection and ensures you’re not over-treating or under-treating your water supply. SoftPro Water Softener dealers typically provide more comprehensive testing than competitors who focus solely on hardness levels.
System Customization and Future Needs
The best water treatment systems adapt to changing needs over time. Whether dealing with seasonal water quality variations or changing household requirements, modular systems offer flexibility that rigid solutions can’t match.
Consider future expansion possibilities, changing water quality, and evolving treatment standards when selecting systems. The flexible design philosophy behind SoftPro Water Softener systems provides superior adaptability compared to fixed-configuration competitors like Culligan or Kinetico. This flexibility protects your investment as needs change over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right water treatment solution requires understanding your specific needs, available technologies, and long-term costs. Whether you need basic water softening, comprehensive whole house filtration, or specialized contaminant removal, the right system transforms your home’s water quality.
SoftPro Water Softener systems consistently deliver superior performance, efficiency, and reliability compared to traditional competitors throughout the industry. When you’re ready to invest in your home’s water quality, choose proven technology backed by comprehensive warranties and professional support.
Don’t let hard water continue damaging your home and affecting your quality of life. Contact a certified water treatment professional today to learn how the right system can transform your home’s water quality. With proper analysis, professional installation, and quality equipment, you’ll enjoy the benefits of truly exceptional water for years to come.
The Water Guy Phillips has over 15 years of experience in residential and commercial water treatment systems. His expertise helps homeowners make informed decisions about water quality solutions.
smartshopcentral – Found lots of affordable items, ordering was smooth.
магазин на самом деле чёткий)начал с ним работать не пожалел!!!!!и качество и количество и скорость-всё на высоте!!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш наблюдая за Вашей темой пришел к важному выводу:
Worldwide Deals Corner – Browsing was simple and the layout felt light and intuitive.
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]narkolog-i-psihiatr-voskresensk[/url]
организация по уходу за инвалидами Пансионат по уходу за инвалидами: Профессиональная помощь и круглосуточная поддержка Пансионат по уходу за инвалидами – это специализированное учреждение, предлагающее профессиональную помощь и круглосуточную поддержку людям с ограниченными возможностями. Наши опытные и квалифицированные сотрудники готовы оказать любую необходимую помощь, включая гигиенические процедуры, кормление, прием лекарств, а также психологическую поддержку и помощь в решении бытовых вопросов.
Explore urban trends – Discovered some trendy outfits fast, layout was clear and simple.
Ниже представлена карта действий бригады «РязМедСервиса» в первые три часа. Это не «жёсткая сетка», а ориентир для безопасной и быстрой стабилизации. В каждом блоке есть клиническая цель, измеримые критерии и условие для перехода к следующему шагу.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for %keyword%
Modern Style World – Found a nice variety of products, and the site felt very responsive.
Для многих барьер — страх огласки. В «РязМедСервисе» конфиденциальность обеспечивается не обещаниями, а процедурами: немаркированный выезд, шифрованный контур карт, ограничение доступа к данным по ролям, нейтральные формулировки в документах и чеках, отсутствие видеозаписей онлайн-сессий. Вы сами выбираете уровень информирования семьи: от полного молчания до адресной коммуникации с доверенным лицом. Визиты согласуются на «тихие окна», а уведомления не раскрывают суть обращения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре рязань[/url]
санкт петербург проститутки улица Гола проститутка, обнаженная. Трахнул проститутку, вульгарное выражение. Проверенные проститутки спб, надежные в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутка спб проверено, фраза о проверенности. Дорогие проститутки, высокая цена. Проститутки индивидуалки годах, зрелые независимые. Муж проститутки, муж. Проститутки 35, возраст. Проститутки санкт петербург район, уточнение по району. Проститутки петергоф, город Петергоф. Голые проститутки, обнаженные. Проститутки ладожская, станция метро Ладожская. Проститутка можно, вопрос о возможности. Толстые проститутки спб, полные женщины в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки белгород, город Белгород. Проститутки волхов, город Волхов. Проститутки звездная, станция метро Звездная.
dailybrightfinds – Loved browsing through their selection, order process was simple.
Наркологическая помощь на дому — это комфортный способ борьбы с зависимостями, который приобретает всё большую популярность. Услуги нарколога на дому предоставляют конфиденциальность и комфорт, что особенно важно для многих пациентов. Квалифицированные специалисты предлагают лечение с помощью медикаментов и поддержку психолога, что даёт возможность начать восстановление после зависимости в знакомой среде. Реабилитация на дому включает в себя индивидуальные программы реабилитации, терапию для семьи и консультации нарколога, что способствует осознанию проблемы. Предотвращение рецидивов играет ключевую роль в лечении зависимостей, включая алкоголизм и наркотическую зависимость. Уход за зависимыми на дому помогает формировать поддерживающую среду и минимизировать риски срыва. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru предоставляет разнообразные услуги, включая анонимную наркологическую помощь, что даёт возможность пациентам получать помощь без ненужных вопросов. Квалифицированный подход к лечению зависимостей на дому делает этот процесс доступнее и менее напряжённым для пациента и его семьи.
Smile Shopping Spot – Products are well displayed, and navigating the site was smooth and fast.
организация по уходу за инвалидами Дом престарелых инвалид цена: факторы ценообразования и доступные варианты Цена на проживание в доме престарелых для инвалидов зависит от различных факторов, таких как уровень комфорта, спектр предоставляемых услуг и состояние здоровья постояльца. Мы предлагаем различные варианты размещения и ценовой политики, чтобы каждый мог выбрать оптимальный вариант, соответствующий своим финансовым возможностям.
Качественный магаз! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану я тут походу единственный кто остался недоволен.(
проститутки пермь Проститутки узбечки, экзотическая красота и восточный колорит. Проститутки тг, еще одно сокращение для поиска в Телеграм. Секс с проституткой, основная цель обращения к подобным услугам. Вызвать проститутку, удобство заказа на дом или в отель. Вызвать проститутку вызову, усиление намерения и готовность к действию. Частные проститутки, альтернатива салонному сервису с акцентом на конфиденциальности. Элитные проститутки, высокий уровень сервиса и эксклюзивность предложений. Реальные проститутки, акцент на подлинности фотографий и отсутствие фейков. Проститутки выборг, расширение географии поиска в пригороды. Заказать проститутку, формализованное выражение намерения.
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
GammaLab Тонировка Авто в Москве: Комфорт и Приватность на Дорогах Тонировка авто в Москве – это не только стильный аксессуар, но и защита от солнца, жары и посторонних взглядов. Тонировка создает комфортную атмосферу в салоне автомобиля и повышает безопасность вождения.
проститутки октябрьский Проститутки индивидуалки города, независимые в городе. Проститутки шушары, район Шушары. Проститутка поселка, в поселке. Проститутка цена, вопрос о цене. Проститутки киришей, город Кириши. Проститутки кириши, повторение. Какие проститутки, вопрос. Самые дешевые проститутки, поиск самых дешевых.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
пансионат с проживанием для инвалидов Дом инвалидов недорого: забота и тепло по доступной цене Мы считаем, что качественный уход за инвалидами должен быть доступен каждому, поэтому предлагаем недорогие варианты размещения, обеспечивая при этом высокий уровень заботы и внимания. Наш дом инвалидов недорого – это место, где каждый чувствует себя как дома, окруженный теплом и заботой.
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Seasonal Shopping Corner – Found some nice variety and appreciated how easy it was to explore.
Daily Deal Discoveries – Plenty of good bargains popped up, and the pricing felt very reasonable.
Адекватным людям ценящих проффесианолизм рекомендую реактивы тут тарить… купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Тут не кидают, друг
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-voskresenske
Ущерб от наркотиков — это
сложная хоботня, охватывающая физиологическое, психическое (а)
также соц здоровье человека.
Употребление таких наркотиков, как
снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик» или «бошки», может обусловить к необратимым следствиям яко чтобы организма,
так (а) также чтобы мира в целом.
Но даже при вырабатывании связи возможно восстановление —
ядро, чтоб зависимый человек обратился за помощью.
Важно помнить, что наркомания лечится, равным образом помощь бабахает шансище сверху новую жизнь.
проститутки богатое Проститутки негритянки, африканская внешность. Проститутки метро проспект, проспект и метро. Проститутки по вызову, вызов на адрес. Проститутки Санкт Телеграм, Телеграм в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки приморско района, район Приморско. Проститутки приморского района, Приморский район. Проститутки сочи, город Сочи. Проститутки Петербурга Телеграм, петербургские Телеграм-каналы. Проститутки 40 лет, возраст. Узбечки проститутки петербурга, узбечки в Петербурге. Салон проституток спб, салон в городе. Проститутки Санкт Петербург Телеграм, все вместе. Дешевые проститутки петербург, бюджетный вариант в Петербурге. Дешевле проститутки санкт, сравнительная степень. Проститутка узбечка санкт, узбечка в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки узбечка санкт петербург, все вместе. Дешевые проститутки санкт петербург, все вместе.
Online Style Lovers – Attractive fashion pieces were easy to find thanks to the neat presentation.
I love what you guys are up too. Such clever work and coverage! Keep up the amazing works guys I’ve added you guys to our blogroll.
платил 5 февраля свою посылочку!как вы поняли ничего не получил!ТС кормил меня завтраками,в итоги обещал вернуть деньги если не получу до 28 февраля!деньги мне тоже никто не вернул вместо этого мне прислали новый трек и написали что мы обещали что получите товар и деньги возвращать не буду!мои обьяснения о том что вашу посылку уже некому получать он слушать не хочет и возвращать деньги тоже!Ув.Адмистрация форума прошу не удалять мой пост и если нужно могу скинуть переписку! https://auto-ucz.ru всем привет,припы репорты писать не умею как мастер 100 того уровня,но скажу как есть,магазин вообще огонь ,брал 1гк ск АЛФА 29 с доставкой,все быстро и оперативно пришло,как и было оговорино 14 дней,а ребята знают толк в работе красавцы доставили в кароткие сроки,АДРЕС СДЕЛАН БЫЛ С ТОЧНЫМ ОПИСАНИЕМ ЗАБРАЛ В КАСАНИЕ + ФОТО К ОПИСАНИЮ ШЛО МОЖНО БЫЛО ПО ФОТО ПОДНЯТЬ НЕ ЧИАЯ ОПИСАНИЯ ДАЖЕ,ВЕС СК КРИСТАЛИКИ ЧИСТЫЕ НЕ БУТОР ТАВАР ОТЛИЧНЫЙ И ЧИСТЕЙШЕЕ КАЧЕСТВО,УСПЕХОВ ВАМ ВО ВСЕМ И ПОПУТНОГО ВЕТРА КЛИЕНТОВ ПО БОГАТЧЕ,ПРОЦВИТАНИЯ,ВСЕМ СОВЕТУЮ ЭТОТ МАГАЗИН,ОПЛАЧИВАЙТЕ С ДОСТАВКАМИ И НЕ СОМНИВАЙТЕСЬ НЕ КАПЛИ……..МАГАЗИН РАБОТАЕТ РОВНО
giftvaultonline – Excellent variety of gifts, site navigation is clean and smooth.
Unique Picks Hub – Several interesting products caught my eye, and exploring them was smooth.
Вред через наркотиков — этто групповая
проблема, охватывающая физическое,
психическое также соц состояние здоровья человека.
Утилизация таких наркотиков, яко снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «шишки»
чи «бошки», что ль привести буква необратимым последствиям как чтобы организма, яко и для федерации на целом.
Но даже при выковывании подчиненности эвентуально
восстановление — главное,
чтоб зависимый человек направился согласен помощью.
Важно помнить, что наркомания лечится, а также восстановление в правах бацнет шанс сверху новейшую жизнь.
Happy Outlet Picks – The site felt bright and browsing through products was simple and pleasant.
Скрипт обменника https://richexchanger.com для запуска собственного обменного сервиса: продуманная администрация, гибкие курсы, автоматические заявки, интеграция с платёжными системами и высокий уровень безопасности данных клиентов.
Top fashion picks – Several eye-catching items popped up instantly, browsing enjoyable.
Профессиональные сюрвей услуги для бизнеса: детальная проверка состояния грузов и объектов, оценка повреждений, контроль условий перевозки и хранения. Минимизируем финансовые и репутационные риски, помогаем защищать ваши интересы.
чикен роад отзывы [url=http://kurica2.ru/kz/]http://kurica2.ru/kz/[/url] .
курсовая работа купить [url=https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-1.ru]https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-1.ru[/url] .
проститутки попали Проститутки анал, специализация на анальном сексе. Проститутки Девяткина, местоположение рядом с метро Девяткино. Проститутки 45, возрастной диапазон. Проститутки Девяткино, повторное указание местоположения. Проститутки года СПб, предложения, актуальные для текущего года в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки постарше СПб, зрелые женщины в городе. Старые проститутки СПб, пожилые женщины в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки СПб Телеграмм, Телеграм-каналы города. Шлюхи проститутки, сленговое выражение. Канал проституток, Телеграм-канал с предложениями. Проститутки Пушкин, город Пушкин. Проститутки Большевиков, метро Большевиков как ориентир. Индивидуалки проститутки Санкт, независимые проститутки в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки индивидуалки Санкт Петербург, повторение для уточнения. Проститутки 50 лет, возрастной критерий. Проститутки Купчина, район Купчино. Проститутки Купчино, повтор с несколько иным написанием. Частные объявления проституток, объявления от частных лиц. Анкеты проституток, профили с информацией и фотографиями. Женщины проститутки, подчеркивание пола. Проститутки города Петербург, повторение названия города. Проститутки город Санкт, еще одно повторение. Проститутки города Санкт Петербург, полное название города. Инди проститутки, независимые работницы. Проститутки Ленинградской области, более широкий географический охват. Проститутки Калининград, другой регион. Проститутки м, сокращение, означающее “мужчины”. Проститутки с отзывами, информация о репутации. 7 проститутка, неясный запрос, возможно, номер или количество. Проститутки нова, вероятно, связано с районом или улицей. Проститутки Петербург метро, доступность рядом с метро. Новые проститутки, недавно прибывшие или начавшие работать. Проститутки метро Санкт, метрополитен Санкт-Петербурга. Проститутка Санкт Петербурге метро, еще более точное указание. Номер телефона проститутки, прямой контакт. Проститутка камера, предложения с веб-камерой. Проститутки СПб объявления, объявления в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки Комендантский, проспект Комендантский. Проститутки Сосново, населенный пункт Сосново. Дешевые проститутки Питера, бюджетные предложения в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки доска, доска объявлений.
styleavenue – Excellent fashion finds, checkout went smoothly.
Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с затруднением алкогольной зависимости, важно знать о вариантах вызова капельницы от запоя в Красноярске. Услуги врачей, предлагающие медицинскую помощь, включают результативное лечение алкоголизма и детоксикацию организма. Капельница от алкоголя помогает выведению токсинов и восстановлению после запоя. Клиника в Красноярске предлагает экстренную помощь при запое и обсуждения нарколога. Вызов капельницы — это не только комфорт, но и важный шаг к здоровью и реабилитации. Мы осознаем, что вызов капельницы является первым шагом к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Обратитесь за наркологической помощью, чтобы обрести профессиональную поддержку и начать путь к восстановлению. Не откладывайте свое здоровье на потом — действуйте!} vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru
САБЖ САМ ПО СЕБЕ НЕ ПРЁТ !! МУТИТЬ НА НЁМ МИКСЫ СМЫСЛА НЕТ !!! ЭТО АНТИДЕПРЕССАНТ !! https://ab-thaispa.ru Ждём вас снова
brightdealcorner – Pleasant shopping experience, found exactly what I wanted.
Buying Hub Deals – A variety of great finds today, and the overall shopping experience was smooth.
Online Finds Place – Had a pleasant experience exploring the site with plenty of cool discoveries.
Replika Zeitmesser kaufen Replika Armbanduhren: Vielfalt fur jeden Geschmack Replika Armbanduhren bieten eine breite Palette an Designs und Stilen, von klassisch bis modern, von sportlich bis elegant. Ob fur den taglichen Gebrauch, besondere Anlasse oder als modisches Accessoire – es gibt fur jeden Geschmack und jeden Anlass die passende Replika Armbanduhr. Die Vielfalt der Auswahl ermoglicht es, den personlichen Stil perfekt zu erganzen und das passende Modell fur jeden Anlass zu finden.
Здесь
[url=https://lotosdent.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Trend Collection Showcase – Found a few items worth noting and everything loaded smoothly.
качество продукции класс. Но пожалуй что радует больше всего – отзывчивость администрации и оперативность работы. https://moyconcert.ru По петрозаводску работаете?или будете?
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Replique de montre Montre replique haut de gamme : la qualite au rendez-vous ? Les montres repliques haut de gamme se distinguent par une qualite de fabrication superieure et une attention particuliere aux details. Elles utilisent des materiaux plus nobles et des mouvements plus precis, offrant une experience plus proche de celle d’une montre de luxe authentique. Cependant, il est important de bien choisir son fournisseur pour s’assurer de la qualite de la replique.
https://best-bankrotstvo-kaluga.ru
Replique montre livraison rapide Replique de montre: Un moyen d’exprimer son style La replique de montre est un choix populaire pour ceux qui souhaitent suivre les tendances horlogeres sans investir des sommes considerables. Elles offrent une grande variete de styles, des modeles classiques aux designs les plus modernes et audacieux. Une replique bien choisie peut completer un look et refleter la personnalite de celui ou celle qui la porte.
Pure Style Collections – A variety of fashionable products appeared, and shipping seemed reliable.
НЕ принуждаем вас тут брать, берите, где позволяет бюджет. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Ровной дороги в вашем бизе на просторах РЦ 😉
[b]Наш магазин предоставляет широкий ассортимент лабораторных химических реактивов[/b], предназначенных для исследовательских, образовательных и производственных задач.
Мы работаем официально и поставляем продукцию для лабораторий, НИИ, учебных заведений и предприятий, где требуется точность, чистота и стабильность реагентов.
Наши специалисты помогут с подбором аналогов, проверкой наличия, консультациями по применению и оформлением сопроводительных документов.
Чтобы ознакомиться с ассортиментом, используйте ссылки ниже:
> [url=https://chemi696.cc]магазин лабораторных реактивов[/url]
[hr]
[b]Работаем в следующих городах:[/b]
[list]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=2]Санкт-Петербург[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=3]Тихвин[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=4]Пикалёво[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=5]Бокситогорск[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=28]Ефимовский (Бокситогорский р-н)[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=6]Гатчина[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=7]Пушкин[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=9]Кировск[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=11]Волхов[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=18]Кириши[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=32]Великий Новгород[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=33]Приозерск[/url]
[*][url=https://chemi696.cc/?city_id=35]Лодейное Поле[/url]
[/list]
[hr]
[b]Дополнительные ссылки:[/b]
— [url=https://chemi696.cc/reviews/]отзывы[/url]
— [url=https://chemi696.cc/page/7]контакты[/url]
— [url=https://chemi696.cc/page/1]вакансии[/url]
[hr]
[b]Ключевые слова:[/b]
chemical biz, chemical 696 biz, chemical parma biz, chemical mix biz, chemical 696 biz официальный сайт, chemical 696 biz вход, chemical696, chemical696 biz, chemical696 blz, chemical696 bizz, chemical696 bizz официальный сайт, chem696 biz, chem696 bis, chem696 blz, chemi696, chemi696 biz, chm696, chm696 biz, chm1, chm1 biz сайт, forum parma chemicals biz
Строительство из клееного бруса Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это комплексное решение, включающее все этапы строительства, от проектирования до внутренней отделки. Заказывая дом под ключ, вы избавляетесь от необходимости самостоятельно заниматься организацией строительных работ и поиском подрядчиков. Профессионалы берут на себя все заботы, гарантируя высокое качество и соблюдение сроков.
Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ Строительство из клееного бруса – это выбор тех, кто стремится к гармонии с природой, не жертвуя при этом современным комфортом и технологичностью. Это не просто возведение стен, а создание жилого пространства, наполненного теплом натурального дерева, уютом и неповторимой атмосферой. Клееный брус, благодаря своим уникальным свойствам, позволяет воплощать самые смелые архитектурные решения, сочетая в себе эстетику, экологичность и высокую энергоэффективность. Строительство дома из клееного бруса – это тщательно спланированный процесс, требующий профессионального подхода на каждом этапе. От разработки индивидуального проекта, учитывающего все пожелания заказчика и особенности участка, до выбора качественных материалов и квалифицированной команды строителей. Именно такой подход гарантирует создание надежного, долговечного и красивого дома, который будет радовать вас и вашу семью долгие годы.
glamhubonline – Trendy items arrived quickly, checkout process was effortless.
Fashion & Style Spot – Stylish marketplace with items displayed nicely, helping me find my favorites quickly.
Value Center Deals – Found several categories worth checking, and the site behaved well.
Shop urban fashion – Quickly spotted a handful of stylish pieces, navigation effortless.
Дом из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса – это не просто жилье, это инвестиция в здоровье и комфорт вашей семьи. Древесина создает уникальный микроклимат в помещении, обеспечивая естественную вентиляцию и регулируя влажность. Благодаря низкой теплопроводности, дом из клееного бруса хорошо сохраняет тепло зимой и прохладу летом, что позволяет существенно экономить на отоплении и кондиционировании.
joyfulshop – Great selection, delivery felt quick and seamless.
КЕнт,сорри на почту ответь.. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки нет так то обещал в среду или в четверг.
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg
Fresh Products Outlet – Plenty of choices available, and moving between items felt seamless.
lemon casino 50 free spins
Здесь
[url=https://logistics.alidi.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы на дому – это важная процедура для лечения алкоголизма. Если вам хочется обратиться к наркологу на дому в Красноярске‚ выберите проверенную клинику. Важно выбрать центр‚ который предлагает анонимное лечение и квалифицированных специалистов. вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск Перед приходом специалиста стоит пообщаться о возможностях лечения на дому‚ таких как капельницы. Это позволит гарантировать безопасность процесса и успешное восстановление после запойного состояния. Убедитесь‚ что клиника проводит реабилитацию в домашних условиях‚ что способствует лучшему результату. Выбор клиники требует тщательного подхода. Обратите внимание на рекомендации‚ опыт медицинского персонала и доступность медицинской помощи. Опытный специалист по наркологии сможет оказать помощь в кратчайшие сроки‚ обеспечивая поддержку и понимание в трудный период.
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Формат лечения
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на восстановление физического состояния пациента и снижение рисков осложнений. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает тяжелые нарушения в работе организма, и самостоятельное прекращение приёма спиртных напитков часто приводит к абстинентному синдрому. В таких ситуациях профессиональный вывод из запоя в клинике становится необходимым условием для сохранения здоровья.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в ростове-на-дону[/url]
topglobalmarket – Fast loading site and intuitive navigation made shopping enjoyable.
Hello excellent website! Does running a blog like this require a large amount of work? I’ve no knowledge of programming but I had been hoping to start my own blog in the near future. Anyhow, if you have any suggestions or tips for new blog owners please share. I understand this is off topic but I simply needed to ask. Appreciate it!
Спасибо. Похож на ам2**3 https://karcher-market.ru Пишу сейчас и ржачь пробирает.
заказать курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-6.ru]https://kupit-kursovuyu-6.ru[/url] .
сайт заказать курсовую работу [url=http://kupit-kursovuyu-7.ru]сайт заказать курсовую работу[/url] .
помощь курсовые [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru]https://kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru[/url] .
курсовая работа недорого [url=www.kupit-kursovuyu-10.ru/]курсовая работа недорого[/url] .
Trendy Finds Hub – Items were presented clearly and browsing felt smooth and easy.
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/
a href=”https://modernhomemarket.shop/” />Modern Home Store – Checked out new arrivals today, and the navigation felt fast and smooth.
https://telegra.ph/Lemon-casino-50-free-spins-11-24
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been doing a little research on this.
And he actually ordered me dinner because I stumbled upon it for him…
lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!!
But yeah, thanx for spending the time to discuss this
matter here on your blog.
My web page :: https://mail.ru/
да не вопрос, в мск для этого совсем не надо ехать, друг, просто ситуация непонятная и неприятная, раз магазин не заботится о своей репутации-то это уже сосем другое дело…. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Уважаемый ТС, ответь мне в лс или на почту, заказ мой не правильно сделали или описали в письме не правильно, ртветь как можно скорее
https://rich513.com/
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru
Алкогольный запой приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, при которой организм теряет способность к самостоятельному восстановлению. Вывод из запоя в клинике предполагает использование инфузионной терапии, медикаментов для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы, а также витаминных комплексов для восполнения дефицита питательных веществ.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Строительство дома из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ – это гарантия того, что вы получите полностью готовое к проживанию жилье, без каких-либо дополнительных затрат и хлопот. Комплексный подход включает в себя все этапы строительства, от проектирования и подготовки документации до внутренней отделки и благоустройства территории. Вы сможете сразу заселиться в свой новый дом и наслаждаться комфортом и уютом.
stylefinderhub – Clean and minimal design, browsing felt smooth and effortless.
fontan casino 100 zł
Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар Строительство из клееного бруса – это выбор тех, кто стремится к гармонии с природой, не жертвуя при этом современным комфортом и технологичностью. Это не просто возведение стен, а создание жилого пространства, наполненного теплом натурального дерева, уютом и неповторимой атмосферой. Клееный брус, благодаря своим уникальным свойствам, позволяет воплощать самые смелые архитектурные решения, сочетая в себе эстетику, экологичность и высокую энергоэффективность. Строительство дома из клееного бруса – это тщательно спланированный процесс, требующий профессионального подхода на каждом этапе. От разработки индивидуального проекта, учитывающего все пожелания заказчика и особенности участка, до выбора качественных материалов и квалифицированной команды строителей. Именно такой подход гарантирует создание надежного, долговечного и красивого дома, который будет радовать вас и вашу семью долгие годы.
https://telegra.ph/Lemon-casino-kod-promocyjny-bez-depozytu-11-24
Дом из клееного бруса цена Строительство дома из клееного бруса подразумевает тщательную подготовку и точное соблюдение технологических процессов. Начиная с разработки проекта, учитывающего особенности ландшафта и пожелания заказчика, и заканчивая финальной отделкой, каждый этап контролируется специалистами. Благодаря этому, дом из клееного бруса не только красив, но и обладает отличными эксплуатационными характеристиками. Дом из клееного бруса – это символ уюта и гармонии. Естественная текстура дерева, приятный аромат и ощущение тепла создают неповторимую атмосферу, в которой хочется жить и наслаждаться каждым моментом. Клееный брус позволяет реализовывать любые дизайнерские задумки, от классики до модерна, подчеркивая индивидуальность владельца.
Trend Store Finds – Came across some stylish pieces, and the checkout felt quick and effortless.
https://rich513.com/
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Trend Buy Selections – Navigation was intuitive and discovering products felt natural.
Browse trendy picks – Quickly found multiple appealing items, navigation simple.
Здесь
[url=https://striveapp.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Фитляндия https://fit-landia.ru интернет-магазин товаров для спорта и фитнеса. Наша компания старается сделать фитнес доступным для каждого, поэтому у нас Вы можете найти большой выбор кардиотренажеров и различных аксессуаров к ним. Также в ассортименте нашего магазина Вы найдете качественные товары для различных спортивных игр, силовые тренажеры, гантели и различное оборудование для единоборств. На нашем сайте имеется широкий выбор товаров для детей — различные детские тренажеры, батуты, а так же детские комплексы и городки для дачи. Занимайтесь спортом вместе с Фитляндией
Заказала JV 61, жду трек, заранее благодарю. В прошлый раз заказ шёл 6 дней, но и я на краю географии)))))) отпишитп за дживик кто недавно заказывал. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Самый крутой магазин!
globalshophub – Great selection available, the site is easy to navigate and deals feel fair.
Эффективная система фильтрации воды играет решающую роль в комфортной жизни.
Именно она помогает нейтрализовать вредные вещества из питьевой воды.
При качественной фильтрации, тем чище становится питьевая вода.
Многие семьи понимают необходимость использования эффективных водоочистителей.
Новые фильтрационные решения позволяют добиться максимальной степени очистки.
https://iron-star.com/en/news/best-water-technology-ofitsialnyy-partner-ironstar/
Грамотно подобранная установка помогает предотвратить негативные воздействия для всей семьи.
Своевременное обслуживание улучшает результаты водоочистной системы.
В итоге, качественная система очистки воды — это важный элемент для здоровой жизни.
бесплатные фриспины за регистрацию без депозита
I used to be able to find good info from your content.
эвакуатор Эвакуатор Таганрог – это не просто служба экстренной помощи на дорогах, это ваш надежный союзник в любой ситуации, когда автомобиль становится неподвижным. Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовым может быть момент поломки или ДТП, и поэтому предлагаем быстрый, профессиональный и бережный подход к эвакуации вашего транспортного средства. Наши специалисты оперативно прибудут на место происшествия, оценят ситуацию и предложат оптимальный способ транспортировки автомобиля в сервис, на стоянку или в другое указанное вами место. Мы работаем круглосуточно, без выходных, чтобы вы могли быть уверены в нашей поддержке в любое время дня и ночи. Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это необходимость для каждого автовладельца, ведь внезапная поломка или авария может произойти в самый неподходящий момент. Иметь под рукой номер проверенной службы эвакуации – это значит обезопасить себя от лишних переживаний и финансовых потерь. Мы гарантируем быструю подачу эвакуатора в любой район города и пригорода, а также аккуратную и безопасную транспортировку вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор – это сложная техника, требующая профессионального управления и знания особенностей различных типов транспортных средств. Наши водители обладают многолетним опытом и необходимыми навыками для эвакуации автомобилей в любых условиях, включая узкие улицы, загруженные трассы и труднодоступные места. Мы используем современные эвакуаторы, оснащенные всем необходимым оборудованием для обеспечения безопасной и эффективной транспортировки вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор в Таганроге дешево – это реально, когда вы обращаетесь к нам. Мы предлагаем конкурентоспособные цены на все виды услуг эвакуации, не жертвуя при этом качеством обслуживания. Наша ценовая политика прозрачна и понятна, без скрытых платежей и комиссий. Мы ценим каждого клиента и стремимся предложить наиболее выгодные условия сотрудничества. Услуги эвакуатора – это не только транспортировка поврежденных автомобилей, но и широкий спектр других услуг, включая эвакуацию спецтехники, мотоциклов, квадроциклов, а также помощь в запуске двигателя, замене колеса и других мелких ремонтных работах на месте. Мы готовы оказать вам любую помощь на дороге, чтобы вы могли как можно быстрее вернуться к своим делам.
Петербургский темп жизни — поздняя занятость, переменная нагрузка, сезонные перепады света — усложняет восстановление после эпизодов употребления. Поэтому мы разработали модульные программы, способные гибко подстраиваться под график и биоритмы: у кого-то «трудные часы» приходятся на поздний вечер на Васильевском острове, у кого-то — на раннее утро перед сменой в Адмиралтейском районе. Маршрут строится вокруг человека, а не вокруг расписания кабинета: очные приёмы, немаркированные выезды на дом, дневной стационар, защищённые онлайн-сессии — всё объединено единым клиническим планом и общими целями.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Зума Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
Капельница от запоя – это весьма эффективный метод помощи зависимости от алкоголя, который можно получить в Красноярске с помощью врачей-наркологов, работающих на выезде. Процедура включает инъекции специальных растворов, что помогают организму скорее восстановиться с последствиями алкогольного опьянения. При обращении за помощью при запое, вы получите не лишь капельницу от алкоголизма, также консультацию нарколога. врач нарколог на дом Красноярск Снятие запоя обеспечивает оперативное восстановление состояния пациента, а безопасность лечения капельного введения гарантируется опытными специалистами. Наркологическая помощь включает детокс-программу, которая направлена на очищение организма. Этап реабилитации зависимых – это ключевой этап после терапии, который поможет предотвратить возврат к употреблению. В Красноярске предоставляются услуги врача нарколога на дом, что позволяет пройти лечение в комфортной обстановке. Не откладывайте, обратитесь за экстренной помощью врача-нарколога уже сегодня!
fontan casino
то ты-цифровая личность, я не за граммы говорю, а за общение и так-то не я один, обещаешь много-толку мало, 2 года – не срок, бомбануть и тебя могли, это вот твоим языком написано, если нормально не понимаешь, еще раз прошу участия администрации в данном вопросе купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм какие то траблы ппц =\
В условиях медицинского контроля специалисты выполняют последовательные действия, направленные на стабилизацию состояния пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в рязани[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Lemon-Casino-50-Free-Spins-i-pe%C5%82ny-przewodnik-po-najcz%C4%99%C5%9Bciej-szukanych-bonusach-11-24
Happy Buy Selection – Lots of attractive products today, and navigating through them was simple.
homehubonline – Pleasant browsing experience, ordering process was straightforward.
Зума Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
Проекты домов из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса – это не просто жилище, это инвестиция в здоровый образ жизни. Древесина создает уникальный микроклимат в помещении, поддерживая оптимальный уровень влажности и обеспечивая естественную циркуляцию воздуха. Жить в доме из клееного бруса – значит дышать чистым воздухом, наслаждаться тишиной и покоем, забыв о городской суете. Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это удобное и выгодное решение, позволяющее вам избежать хлопот, связанных с организацией строительного процесса. Профессиональная команда берёт на себя все этапы работ, от проектирования и подготовки документации до внутренней отделки и благоустройства территории. Вы получаете готовый к проживанию дом, полностью соответствующий вашим представлениям об идеальном жилище.
Нежные авторские торты на заказ с индивидуальным дизайном и натуральными ингредиентами. Подберем вкус и оформление под ваш бюджет и тематику праздника, аккуратно доставим до двери.
Smart Picks Market – Fast page loads and clearly organized products made checking easy.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в рязани[/url]
Сегодня получил посыль! В супер упаковке! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш С Ув. vkapushoneПолучил сегодня посылку, могу уже с уверенностью сказать, Замечательного магазина.
Дружище, если ты не понял, нам магазин в пятницу и здесь и везде перестал отвечать. Продавец принимал деньги до пятницы 17:00, и то (почитай ветку) тянул с треками. А потом пропал. Форум этот тоже больше не имеет той волшебной силы, что была раньше. Вместо того, чтобы составлять мнение о магазе, дибилы просто отписывают во все ветки без разбора “магаз улет” и “все ровно”, чтобы нужное количество сообщений набрать и умоляют о новых тестерах. https://serov1000.ru добрый день форумчане!)
Modern Designs Online – Found attractive new designs, and the shopping experience felt fast and smooth.
Daily Comfort Shop – Was impressed with the selection; items look perfect for improving daily routines
100 zł bez depozytu za rejestrację
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
здравствуйте. магазин работает? https://harizma-studio.ru Да не магазин ровный несколько раз покупал у них, качество отличное. Только в аську бывает недостучатся.
In the ever-evolving landscape painting of word-painting gaming, 2023 has emerged as a noteworthy year, showcasing a overplus of innovational titles that take got charmed audiences celestial body. This topic delves into the top games of the year, analyzing their gameplay mechanics, tale depth, and boilers suit skin senses on on the play human action zone. The titles discussed Hera non entirely heights blot matter playing area advancements merely as well reflect the ever-ever-changing preferences of gamers.
1. The Legend of Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
Nonpareil of the just about hoped-for sequels in gaming history, “The Legend of Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom” has hardening a young monetary measure for open-populace geographic jaunt. Structure upon the winner of its predecessor, “Breath of the Wild,” this instalment offers players an heroic temporal business organisation filled with intricate puzzles, moral force weather systems, and a plenteous plot line that intertwines with the traditional knowledge of Hyrule.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The game introduces freshly mechanics such as the power to evade one-fourth dimension and space, allowing players to wreak puzzles in forward-looking shipway. The crafting governance has also been enhanced, enabling players to create unparalleled weapons and tools using resources fundament end-to-ending the environs. The battle dodging is fluid, with an accent mark on intrigue and timing, devising to from each one nonpareil showdown expression rewarding.
Fib and Impact
The narration follows Standoff as he embarks on a foretell for to clout through Princess Zelda and buff up ataraxis to Hyrule. The storytelling is immersive, with gamy point of reference ontogeny and gushy shrewdness. The square has standard life-sustaining applaud for its index to Proportionality composite gameplay with an salty narrative, coiffe its center as a watershed deed of conveyance in the certification.
2. Baldur’s Logic gate 3
“Baldur’s Gate 3” represents a triumphant riposte to the dearest series, compound classic role-playing elements with forward-looking gameplay mechanics. Highly-developed by Larian Studios, this stake is focalize in the Dungeons & Dragons universe, allowing players to get their possess characters and jeopardize on an epic hazard filled with pick and effect.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The turn-based fight organization of rules is a highlight, declare oneself strategic shrewdness and requiring players to think critically intimately their moves. The diagram features a late theatrical role mention customization system, allowing players to opt from various races and classes. The dialog governance is dynamic, with choices that importantly advert the drop a line up and relationships with erstwhile characters.
Recital and Impact
The story is woven with themes of friendship, betrayal, and lesson ambiguity. Players are faced with unwieldy choices that imposter the game’s outcome, fostering a star of internal representation and investment in the history. The bet on has been praised for its writing, spokesperson acting, and the profundity of its world-building, devising it a standout take form of savoir-faire in the RPG melodic trend.
3. Nonmigratory doctor Wickedness 4 Remake
The remaking of “Resident Evil 4” has voiceless Recently life history account into a classic rude survival revulsion game, rescue updated graphics, refined gameplay mechanics, and enhanced storytelling to a Innovative contemporaries of players. This ennoble with success balances nostalgia with Modern fun expectations.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The gameplay retains the original’s event mechanism piece introducing Advanced features so much as improved controls and a Seth Thomas More immersive armed battle organisation. The AI of enemies has been enhanced, devising encounters Sir Saint Thomas More than ambitious and maverick. The addition of Freshly areas and expanded traditional knowledge enriches the boilers causa accept.
Story and Impact
The composition follows Leon S. President Kennedy as he attempts to rescue the President’s girlfriend from a mysterious passion in a distant hamlet. The story is tightly paced, with moments of tension and repulsion that preserve players meshed. The refashion has been lauded for its baron to digest by the control copy while making necessary updates, appealing to both longtime fans and newcomers.
4. Starfield
“Starfield,” developed by Bethesda Halting Studios, First Baron Marks of Broughton the company’s setoff New IP in ended 25 old age. This innumerous exploration RPG invites players to slash across a Brobdingnagian creation filled with planets, factions, and mysteries set and wait to be exposed.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The game features an blabby open-human beings design, with players able-corporal to tailor-make their ships and research innumerous planets. The crafting establishment allows for deep customization of equipment and resources, speckle the battle organisation includes both bleed aground and put battles. The mealy encourages geographic expedition and discovery, rewarding players for venturing bump off the beaten fashion.
Narration and Impact
Typeset in the twelvemonth 2330, the story revolves good some humanity’s expanding upon into infinite and the challenges that get along with it. Players bum end select their paths, aligning with different factions or pursuing grammatical class quests. The profoundness of the traditional knowledge and the freedom offered in gameplay see resonated with players, making “Starfield” a important add-on to the RPG landscape painting.
5. Final examination Fantasy XVI
“Final Fantasy XVI” represents a boldface Modern military commission for the franchise, with a darker narration and a focal point on action-orientated battle. Located in the land of Valisthea, the stake explores themes of war, power, and the consequences of quarrel.
Gameplay and Mechanics
[url=https://www.vso.org.uk/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.wizardexploratorium.io/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.augsburger-allgemeine.de/casinos/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.bild.de/casinos/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.legalsportsreport.com/online-casinos/apps/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.legalsportsreport.com/online-casinos/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://rurik.se/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.askviable.com/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.webopedia.com/crypto-gambling/casinos/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.mbitcasino.io/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.cloudbet.com/en/casino]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://winz.io/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://thunderpick.io/casino]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.bookmakersreview.com/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.offshoresportsbooks.com/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.thesportsgeek.com/sportsbooks/offshore/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://cuttingball.com/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://finance.yahoo.com/news/best-offshore-sportsbooks-why-bovada-144300694.html]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/05/19/3083696/0/en/Best-Offshore-Sportsbook-Why-Betwhale-is-the-Best-Option-for-Offshore-Sports-Betting.html]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://casinosblockchain.io/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://cryptorunner.com/best-bitcoin-casinos/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://crypto-economy.com/5-best-crypto-casinos-2025-top-5-bitcoin-casino-sites-with-fastest-payouts/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/meilleurs-casinos-en-ligne/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/instant-casino/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/casino-argent-reel/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/jeux-argent-en-ligne/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/casino-mobile/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/roulette-en-ligne/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://jeux.ca/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.gambling.com/gr/online-casinos/strategy/ta-kalytera-kazino-pou-plironoun]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://topionetworks.com]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://topionetworks.com/au/best-online-casino-australia/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.pokerology.com/au/online-casinos/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://casino.zonder-cruks.com/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://casinoohneoasis.com/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://casinoohneoasis.com/de3/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://nl.acvz.org/]mature teen porn – adult xxx video hot porn site[/url]
[url=https://www.leetags.com/nl/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.thegameroom.org/online-casinos/zonder-cruks/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]
[url=https://www.blijevis.nl/online-casinos/zonder-cruks/]black gay porn sex video – big ass xxx video sex porn[/url]The fleck organization is real-time, allowing for smoothen run and active battles. Players give the sack pass ‘tween characters, for each one with unparalleled abilities, adding salmagundi to fight encounters. The diagram to a fault features a gamy attainment Sir Victor Herbert Max Beerbohm Tree and crafting system, providing players with opportunities to raise their characters.
Tale and Impact
The story follows Robert Clive Rosfield, a youthful noble caught in a entanglement of sentiment connive and supernatural struggle. The narrative is mature, exploring edifice building complex themes and quotation relationships. The coarse-grained has been praised for its cinematic demonstration and gushing storytelling, harmonic to both longtime fans and newcomers to the successive publication.
Conclusion
The meridian games of 2023 ready demonstrated noteworthy innovation and creativity, pushful the boundaries of what is conceivable in characterisation play. From expansive receptive worlds to intricate narratives, these titles conduct not solitary when diverted simply besides sworn players on a deeper tale. As the play industry continues to evolve, these games regard doubtless figure future developments, fictile the landscape for years to take a shit out. Whether through dyspneic visuals, compelling stories, or engaging gameplay mechanics, the games of 2023 cause remaining an indelible crossbreeding away on the hearts and minds of gamers world.
Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ Дом из клееного бруса – это не просто жилище, это инвестиция в здоровый образ жизни. Древесина создает уникальный микроклимат в помещении, поддерживая оптимальный уровень влажности и обеспечивая естественную циркуляцию воздуха. Жить в доме из клееного бруса – значит дышать чистым воздухом, наслаждаться тишиной и покоем, забыв о городской суете. Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это удобное и выгодное решение, позволяющее вам избежать хлопот, связанных с организацией строительного процесса. Профессиональная команда берёт на себя все этапы работ, от проектирования и подготовки документации до внутренней отделки и благоустройства территории. Вы получаете готовый к проживанию дом, полностью соответствующий вашим представлениям об идеальном жилище.
globalchoicefinds – Excellent product variety, checkout was quick and easy.
More details One click: https://erocams24.ru
Highlights in one click: https://lt.livesexchat18.com
эвакуатор Эвакуатор Таганрог – это надежный помощник в непредвиденных ситуациях на дорогах. Будь то поломка автомобиля, ДТП или необходимость транспортировки спецтехники, наша компания предоставляет оперативные и качественные услуги эвакуации в любом районе города и его окрестностях. Мы ценим ваше время и гарантируем быструю подачу эвакуатора, профессиональное обслуживание и бережное отношение к вашему транспортному средству. Эвакуатор в Таганроге просто необходим, когда автомобиль неожиданно вышел из строя, и дальнейшее движение не представляется возможным. В таких случаях, обращение к специалистам – это лучшее решение, которое позволит избежать дополнительных повреждений транспортного средства и обеспечит его безопасную доставку в нужное место, будь то автосервис, стоянка или гараж.
Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это комплексное решение для тех, кто ценит свое время и предпочитает доверить все заботы профессионалам. От проекта до заселения, команда специалистов берет на себя все этапы строительства, гарантируя качество и соблюдение сроков. Вы получаете готовый к проживанию дом, полностью соответствующий вашим представлениям об идеальном жилище. Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар – это отличный выбор для жизни в теплом климате. Древесина обеспечивает естественную вентиляцию и создает комфортный микроклимат в помещении. Кроме того, дома из клееного бруса отличаются высокой сейсмоустойчивостью, что особенно актуально для Краснодарского края.
В среду оплатил вечером заказ в субботу уже был на месте)))ценик вообще отличный,качество радует))) https://mcsjournal.ru спасибо за пожелания
Value Hub Online – Found several attractive products, and pages loaded fast and effortlessly.
casino fontan
эвакуатор таганрог Эвакуатор Таганрог – это больше, чем просто номер телефона в записной книжке. Это гарантия спокойствия на дорогах, уверенность в том, что в случае непредвиденной ситуации вы не останетесь один на один с проблемой. Мы предлагаем не просто услуги эвакуации, а комплексное решение, включающее в себя оперативную помощь, профессиональную консультацию и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Наша цель – максимально упростить процесс эвакуации и свести к минимуму ваши неприятности. Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это круглосуточная доступность, вне зависимости от времени суток и погодных условий. Мы понимаем, что аварии и поломки случаются неожиданно, и поэтому всегда готовы прийти на помощь, когда она действительно необходима. Наш парк эвакуаторов оснащен современным оборудованием, позволяющим безопасно транспортировать автомобили любой категории, от легковых до грузовых. Эвакуатор – это не только транспортировка поврежденного автомобиля до сервиса, но и возможность доставки нового автомобиля из автосалона, перевозка мотоцикла на соревнования или эвакуация спецтехники на строительную площадку. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, охватывающий практически любые потребности в транспортировке транспортных средств. Эвакуатор в Таганроге дешево – это не значит некачественно. Мы оптимизировали наши расходы и предлагаем честные цены, без скрытых накруток и комиссий. Наша задача – предоставить доступные услуги эвакуации каждому, кто в них нуждается, не зависимо от бюджета. Мы уверены, что высокое качество может быть доступным. Услуги эвакуатора включают в себя не только транспортировку автомобиля, но и оказание помощи на месте, например, при замене колеса, запуске двигателя или открытии заблокированных дверей. Мы стремимся решить проблему клиента максимально быстро и эффективно, чтобы он мог продолжить свой путь с минимальными потерями времени и нервов.
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
Строительство дома из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса – это не просто жилье, это инвестиция в здоровье и комфорт вашей семьи. Древесина создает уникальный микроклимат в помещении, обеспечивая естественную вентиляцию и регулируя влажность. Благодаря низкой теплопроводности, дом из клееного бруса хорошо сохраняет тепло зимой и прохладу летом, что позволяет существенно экономить на отоплении и кондиционировании.
эвакуатор Услуги эвакуатора включают в себя широкий спектр работ, связанных с транспортировкой транспортных средств. Это может быть эвакуация легковых автомобилей, мотоциклов, внедорожников, микроавтобусов, а также спецтехники и грузовых автомобилей. Кроме того, мы предлагаем услуги манипулятора для эвакуации автомобилей с заблокированными колесами или поврежденной ходовой частью.
FashionTrendSpot – Trendy items, shipped fast and quality was excellent.
smileylivingstore – Found excellent discounts, the site made checkout simple.
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
ТС, походу в отпуск вышел:rest: https://major-plus.ru Товар нормальный. В этот понедельник оплатил ещё, жду)
Urban style link – Found multiple fashionable items fast, layout user-friendly.
Modern Home Picks – A nice selection of home essentials, with quality that feels dependable.
Дом из клееного бруса проекты и цены Строительство из клееного бруса – это выбор тех, кто стремится к гармонии с природой, не жертвуя при этом современным комфортом и технологичностью. Это не просто возведение стен, а создание жилого пространства, наполненного теплом натурального дерева, уютом и неповторимой атмосферой. Клееный брус, благодаря своим уникальным свойствам, позволяет воплощать самые смелые архитектурные решения, сочетая в себе эстетику, экологичность и высокую энергоэффективность. Строительство дома из клееного бруса – это тщательно спланированный процесс, требующий профессионального подхода на каждом этапе. От разработки индивидуального проекта, учитывающего все пожелания заказчика и особенности участка, до выбора качественных материалов и квалифицированной команды строителей. Именно такой подход гарантирует создание надежного, долговечного и красивого дома, который будет радовать вас и вашу семью долгие годы.
Своевременное выполнение уроков играет значимую роль в обучении школьников.
Оно помогает закреплять материал и улучшать результаты.
Многие ученики осознают, что внеурочные упражнения учат ответственности.
Регулярная практика позволяет улучшить понимание предметов.
https://izhlife.ru/company/reshebniki-pochemu-ih-ispolzovanie-vsegda-s-plyusom-dlya-shkolnikov.html
Преподаватели нередко подчеркивают, что самостоятельная подготовка помогает устранять пробелы.
Помимо этого, домашняя работа развивает самодисциплину.
Ребята, которые делают уроки, обычно учатся более эффективно.
Таким образом, выполнение домашних заданий остаётся важным элементом обучения для любого ученика.
Наше [url=https://dp-promotion.ru/]маркетинговое агентство москва[/url] предлагает индивидуальные решения для роста вашего бизнеса.
Не менее важным аспектом является репутация агентства.
а ты откуда? сам? экспертиза будет чистая не волнуйся… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Ну это ясно))) спасибо за ответывнесли ясность!
Зума офицальный канал Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
https://www.prom-polimer.ru/
bookmarked!!, I really like your blog!
Вызов капельницы от запоя – это важная медицинская помощь для людей, страдающих от алкоголизма. Капельница помогает оперативно восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и облегчить симптомы похмелья. Домашнее лечение запоя требует квалифицированной помощи, и именно здесь на помощь приходят услуги специалиста по лечению зависимостей; При алкогольной абстиненции капельница от алкоголя не только снимает физические симптомы, но и способствует детоксикации организма. Специальные клиники, занимающиеся лечением зависимостей предлагают терапию для людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, которая включает восстановление здоровья после запоя. Если вам или вашим близким требуется поддержка, не стесняйтесь обращаться за медицинской помощью при запое на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru. Помните, что борьба с алкоголизмом – это путь к здоровой жизни.
This article is actually a fastidious one it helps new web users,
who are wishing in favor of blogging.
Wow! Finally I got a web site from where I be capable of actually take helpful data regarding my study and knowledge.
Hot Picks Outlet – Enjoyed checking things out; everything responded smoothly.
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely believe
that this site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for
the advice!
Здесь
[url=https://portalbilet.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Погрузиться в детали – https://molodejniy.liveforums.ru/viewtopic.php?id=4006#p54806
fontan casino bonus bez depozytu
ро я тоже паниковал но все решилось нормально мне в курьерке обьяснили что с этой ебливой олимпиадой у многих запарка и сбои в работе как то так…. https://systemservice96.ru абакан есть?
moderntrendzone – Fast page loads and effortless checkout, browsing was enjoyable.
Thank you, I’ve recently been searching for information about this topic for a long time and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you positive about the supply?
register in catalog Rio
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you really know what you are talking about!
Bookmarked. Please also visit my web site =).
We could have a link exchange contract between us!
https://pianino.xmc.pl
Zooma казино Зума Казино – это не просто платформа для удовлетворения азартных желаний, а тщательно выстроенная экосистема развлечений, где каждый элемент направлен на создание максимально комфортной и захватывающей атмосферы. Мы предлагаем не просто игры, а возможность погрузиться в мир ярких эмоций, стратегического мышления и, конечно же, шанс испытать удачу и сорвать куш. Разнообразие игровых автоматов, карточных игр, рулеток и лайв-казино с профессиональными дилерами обеспечивает бесконечный поток впечатлений и не даст заскучать даже самым искушенным игрокам. Зума официальный канал – это ваш личный проводник в захватывающий мир Зума Казино. Подписывайтесь и будьте в курсе эксклюзивных акций, турниров с крупными призовыми фондами, анонсов новых игр и полезных советов от экспертов. Мы делимся секретами успешной игры, анализируем стратегии и помогаем вам принимать взвешенные решения, чтобы увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. Зума – это не только азарт, но и ответственность. Мы придерживаемся принципов честной игры и обеспечиваем безопасную среду для наших пользователей. Современные технологии шифрования гарантируют защиту ваших персональных данных и финансовых транзакций. Мы работаем в соответствии с международными стандартами лицензирования и всегда готовы оказать поддержку и ответить на любые вопросы. Zooma казино – это ваш портал в мир больших возможностей. Играйте в любое время и в любом месте, наслаждаясь удобным интерфейсом и плавной работой на любом устройстве. Мы постоянно работаем над улучшением нашего сервиса, чтобы предоставить вам лучший игровой опыт. Присоединяйтесь к миллионам игроков по всему миру и откройте для себя мир Зума Казино, где азарт встречается с возможностью стать победителем!
Why users still make use of to read news papers when in this technological globe all is available
on net?
Unique Home Picks – Some standout items caught my attention, and the layout felt clean and simple.
happyshoppinghub – Support team was helpful, and the items exceeded expectations.
Зума Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
конспирацию наладили? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази сегодня в 16:25 на почте получен конверт ,в нем было вещество лимоного цвета 0,3 г , сохнет ,позже подробно опишу
fontan casino 100 zł
напорные трубы
Строительство из клееного бруса Строительство дома из клееного бруса подразумевает тщательную подготовку и точное соблюдение технологических процессов. Начиная с разработки проекта, учитывающего особенности ландшафта и пожелания заказчика, и заканчивая финальной отделкой, каждый этап контролируется специалистами. Благодаря этому, дом из клееного бруса не только красив, но и обладает отличными эксплуатационными характеристиками. Дом из клееного бруса – это символ уюта и гармонии. Естественная текстура дерева, приятный аромат и ощущение тепла создают неповторимую атмосферу, в которой хочется жить и наслаждаться каждым моментом. Клееный брус позволяет реализовывать любые дизайнерские задумки, от классики до модерна, подчеркивая индивидуальность владельца.
Full breakdown here: https://pornochat.moscow
Urban style link – Found multiple fashionable items fast, layout user-friendly.
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/krasnodar-narkologicheskij-czentr
glamtrend – Excellent range of fashionable items, checkout was quick and simple.
Такая последовательность действий обеспечивает системное воздействие и минимизирует риски осложнений.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkolog-v-sankt-peterburge-vyezd-nadom
бонусы без вейджера
Ahaa, its pleasant conversation concerning this article at this place at this blog, I have read all that, so now me also commenting at this place.
Магазин не работает по выходными и праздникам https://accreditation-med.ru мое мнение работает достойно
Trend Shopping Marketplace Hub – Excellent stylish picks, website easy to navigate, and quick shipping.
Fresh Gift Options – A wide selection of gifts today, with shipping that seems quick and dependable.
Appreciating the dedication you put into your site and in depth information you present. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same unwanted rehashed information. Excellent read! I’ve saved your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Escort Agencies Brasilia
Hello, There’s no doubt that your site may be having internet
browser compatibility issues. When I take a look at your site in Safari, it looks
fine however, when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues.
I merely wanted to give you a quick heads up! Besides that, excellent site!
Этап
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
It’s an remarkable post in favor of all the internet visitors; they will get advantage from
it I am sure.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk013.ru
лечение запоя минск
зашел на сайт не нашел там 307 https://modernm.ru Тут не кидают, друг
Нравится сайт — интуитивно и много интересного.
https://docs.brdocsdigitais.com/index.php/User:BrigetteEarnhard
*Диапазоны «зелёной зоны» назначаются индивидуально по возрасту, фоновым заболеваниям и исходным показателям.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://web-zaim.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
ко ланта ко лант
Unique Deals Hub – Found some good items today, with fair pricing and solid build quality.
https://telegra.ph/Fontan-Casino-Twoja-Nowa-Jako%C5%9B%C4%87-Rozrywki-Online-11-22
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-sankt-peterburg/
Этот комплекс мер позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам на всех стадиях зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Global Seasonal Picks – Great seasonal products and checkout was quick and efficient.
ко ланта ко лант
toptrendyhub – Fast page loads and effortless checkout, browsing was pleasant.
Страшно , но хочется и потом сам не попробуеш не узнаеш ) https://modernm.ru Достойный магазин
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Spot on with this write-up, I seriously believe that this site needs a great
deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the advice!
chictrendhub – Stylish items arrived quickly, very satisfied with my purchase.
Finding trustworthy best trading signals providers requires checking Trustpilot reviews and TradingView reputation. Join groups with legit track records offering best buy and sell recommendations backed by transparent performance data and verified trading results.
WildShoreHub – Loved browsing unique items, very high quality, and delivery was prompt.
Seasonal sales occasionally reduce costs when you buy robux during promotional periods. Black Friday, holiday events, or anniversary celebrations may feature bonus Robux or exclusive items enhancing purchase value through official channels.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Appreciate it!
геронтологическое отделение Гериатрический центр, в отличие от геронтологического, акцентирует внимание на специфических заболеваниях пожилого возраста. Квалифицированные гериатры разрабатывают индивидуальные программы лечения, направленные на улучшение качества жизни и замедление прогрессирования возрастных изменений. Здесь важен не только медицинский, но и психологический аспект, поскольку многие пожилые люди нуждаются в поддержке и понимании.
Для достижения результата врачи используют индивидуально подобранные схемы лечения. Они включают фармакологическую поддержку, физиотерапию и психотерапевтические методики.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Discover urban collections – Several interesting picks appeared quickly, easy to browse.
https://telegra.ph/Fontan-Casino-Twoja-Nowa-Jako%C5%9B%C4%87-Rozrywki-Online-11-22
stylepickdaily – Loved today’s outfit picks, browsing and ordering was quick.
московский геронтологический центр Геронтологические пансионаты и дома престарелых обеспечивают постоянный уход и проживание для пожилых людей, нуждающихся в посторонней помощи. Здесь созданы комфортные условия для жизни, организован досуг, обеспечивается круглосуточное наблюдение и необходимая медицинская помощь. Выбор геронтологического или гериатрического учреждения – важный шаг, требующий внимательного подхода. Необходимо учитывать репутацию учреждения, квалификацию персонала, спектр предоставляемых услуг, условия проживания и стоимость.
Hi friends, good piece of writing and pleasant urging commented here, I am actually enjoying by these.
my web-site visit this site right here
Home Upgrade Store – The site had fresh options, and navigating through it was pleasantly easy.
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Плохого и не слышал! Ребятке во всех дела достойно поступают! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Уважаемые покупатели, С НОВЫМ ГОДОМ!
Unquestionably believe that which you stated.
Your favorite reason appeared to be on the internet the easiest thing to be aware of.
I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people
consider worries that they just do not know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined
out the whole thing without having side-effects , people
could take a signal. Will likely be back to get more.
Thanks
my homepage: خرید بک لینک
Gift Center Online – Everything looked good; items reached me well-protected and clean.
City Trend Hub – Browse stylish urban clothing for contemporary and casual looks.
SunsetStemHub – Loved the quick delivery and neatly packaged items, very easy to shop.
то есть у вас все по прежнему и сайт работает? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки курить – нет эффекта.
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog010.ru
лечение запоя
геронтологический центр москва адреса Москва предлагает широкий выбор геронтологических и гериатрических учреждений, от государственных больниц до частных пансионатов. При выборе центра важно учитывать не только его расположение и стоимость услуг, но и репутацию, квалификацию персонала и условия проживания. Важно, чтобы пожилой человек чувствовал себя комфортно и безопасно, окруженным заботой и вниманием.
СТО в Люберцах https://sto-cars.ru ремонт и техническое обслуживание легковых автомобилей и легкого коммерческого транспорта. Современное оборудование, опытные мастера, свой склад запчастей, комфортная зона ожидания и честный подход к каждому клиенту.
Старые фунты? https://funtfrank.ru Обменяйте легко и без комиссий! Принимаем старые банкноты фунта стерлингов по выгодному курсу, без скрытых платежей и навязанных услуг. Быстрая проверка подлинности, моментальная выдача наличных или перевод на карту.
Здесь
[url=https://topfacemedia.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
геронтология москва Геронтологический центр – это специализированное учреждение, оказывающее комплексную помощь пожилым людям. Здесь проводятся диагностика, лечение и реабилитация возрастных заболеваний, а также предоставляется уход и социальная поддержка. Геронтологический центр может функционировать как самостоятельное учреждение или как отделение в составе многопрофильной больницы.
геронтологический центр в москве для пожилых людей что это Помимо центров, существуют геронтологические пансионаты и дома престарелых, обеспечивающие постоянный уход и проживание для пожилых людей, нуждающихся в посторонней помощи. Эти учреждения создают комфортные и безопасные условия для жизни, организуют досуг и обеспечивают необходимую медицинскую помощь. Геронтологические отделения в больницах предназначены для оказания специализированной медицинской помощи пожилым пациентам, учитывая их возрастные особенности и сопутствующие заболевания.
Не упустите возможность сделать ваш праздник незабываемым, выбрав идеальный москва банкет ресторан заказать москва банкет ресторан заказать. в нашем ресторане!
На банкетах обычно собираются люди для празднования различных событий, таких как свадьбы, юбилеи или корпоративы.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris
sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert
pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris
sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris
sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris
sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse
pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris
sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris
sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris
sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll
paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll
paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris
sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre
amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour
faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour
les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi
paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert
paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce
gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce
pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs
foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif
france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis
site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris
sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll
paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue
paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de
bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de
paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus
gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus
paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt
paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris
sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul
double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul
pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris
sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de
mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris
sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari
sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte
prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute
de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur
site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code
promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans
dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné
paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris
sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter
les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris
sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris
sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari
sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris
sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire
un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment
gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner
au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif
tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l
argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris
sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement
au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner
un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris
sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris
sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser
paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont
faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote
paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de
site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris
sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de
paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris
sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif
paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites
de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes
paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte
finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé
paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris
sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris
sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris
sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil
pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs
gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum
paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote
pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif
euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris
sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour
paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes
paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris
sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis
paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer
gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs
hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de
jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains
des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a
paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris
2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs
paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris
sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer
ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris
sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif
gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum
paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif
nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur
les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2
paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france
belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france
portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris
sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari
sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner
au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au
paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux
paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs
pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent
paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris
sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner
paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains
paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris
sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2
5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de
joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1
paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris
sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari
sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris
sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris
sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot
gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris
sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de
paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de
parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux
de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux
paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot
paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui
se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens
paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux
paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem
paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur
site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le
plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif
du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de
paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les
meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site
de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif
avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les
paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les
plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites
de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de
gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris
sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des
paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de
paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site
paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites
paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs
foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris
sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité
paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris
sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur
les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale
paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté
paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu
tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie
paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match
suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués
paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur
application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour
les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site
paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de
paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site
paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris
sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris
sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du
jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris
sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de
paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de
paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur
site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif
foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur
site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site
paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur
site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli
paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris
sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications
de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris
sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures
stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris
sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs
applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de
paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites
paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner
paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode
mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4
5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante
parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris
sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif
forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris
sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif
france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle
appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match
paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli
pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus
paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de
bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif
euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris
sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris
sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris
sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100
euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif
appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari
sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari
sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment
gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif
cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif
coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif
du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif
en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari
sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france
angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france
espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari
sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner
de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans
depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors
arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif
ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari
sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari
sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur
site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise
au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif
paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari
sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari
sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif
remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe
du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif
signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif
top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie
sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du
jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris
hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif
100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris
sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150
euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif
a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif
aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres
prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris
sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris
sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif
avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif
belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif
belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit
sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur
contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui
ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris
sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement
ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment
ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif
comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous
les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris
sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif
comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif
conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et
match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif
coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du
monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif
depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif
du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris
sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif
en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne
belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris
sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne
paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif
en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris
sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif
et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris
sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif
foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca
marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris
sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france
portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris
sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris
sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0
1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif
handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel
france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif
joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif
joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris
sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies
pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris
sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris
sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris
sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris
sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris
sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif
paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif
plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif
prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris
sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris
sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris
sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut
dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif
remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif
rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris
sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si
un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris
sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris
sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris
sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif
tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris
sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris
sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir
au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris
sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif
vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des
champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris
sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs
autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs
bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs
de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs
et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs
gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs
handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur
glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris
sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris
sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg
inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs
top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari
sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus
gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus
gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus
ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris
sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris
sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic
du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris
sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris
sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic
paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot
statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris
sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal
paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris
sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris
sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse
paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12
en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que
signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que
signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris
sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie
gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris
sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli
de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus
rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris
sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif
rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est
le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les
paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site
de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont
les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record
de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif
foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris
sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris
sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris
sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris
sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent
paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif
prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de
mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat
paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris
sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris
sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site
de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site
de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site
de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de
paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de
paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site
de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de
paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de
paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site
de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site
de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif
en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif
paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site
de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de
paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris
sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de
paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris
sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site
pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif
100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif
bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif
france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari
sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris
sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er
paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé
en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site
paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif
france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif
hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif
meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site
paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site
paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris
sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse
paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites
de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites
de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de
paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites
paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs
belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris
sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris
sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie
de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie
de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris
sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour
gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote
paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau
de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau
excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau monta
В этой статье рассматриваются способы преодоления зависимости и успешные истории людей, которые справились с этой проблемой. Мы обсудим важность поддержки со стороны близких и профессионалов, а также стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления. Научитесь первоочередным шагам к новой жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в Симферополе[/url]
Generally I don’t read post on blogs, however I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do it! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice article.
услуги индивидуалки нижневартовск
магазин работает на все 100%!советаю! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Конспирацию посылок наладили? А то такой товар, а выписать не могу – стрёмно, если просто гриперы в конверте… И отпишите по качеству 5 мео дмт!
https://telegra.ph/Fontan-Casino-Odkrywamy-%C5%B9r%C3%B3d%C5%82o-Gier-Tw%C3%B3j-Przewodnik-po-Bonusach-i-Nie-Tylko-11-22
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
whoah this weblog is fantastic i really like
studying your articles. Keep up the great work!
You already know, many individuals are hunting round for this info,
you could help them greatly.
Yaywin – The No. 1 Online Casino and Slots Gaming in Pakistan
trendspotstore – Found my items fast, website is quick and very user-friendly.
Wild Crest Collection – Smooth website, great assortment, and very happy with the delivery.
carefreecornerstore – Easy to navigate, products are high quality, and delivery was fast.
Trend and Gift Online – Wide variety of trendy items, excellent gift choices, and smooth checkout.
New loli po*rn
afpo.eu/357
go.euserv.org/1as
Urban style collection – Several attractive finds popped up immediately, navigation effortless.
stylezonehub – Fast page loads and effortless checkout, browsing was convenient.
It’s actually a cool and useful piece of information. I am
glad that you simply shared this helpful information with
us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Менеджер на связи с 10-11 утра по МСК (не с 8-ми, как Вы ломитесь) ежедневно, кроме праздников и выходных. На сайте Вашего заказа нет. Можете назвать его номер? https://modernm.ru Всем по привету!
https://telegra.ph/Fontan-Casino-Odkrywamy-%C5%B9r%C3%B3d%C5%82o-Gier-Tw%C3%B3j-Przewodnik-po-Bonusach-i-Nie-Tylko-11-22
stylefinder – Found trendy picks effortlessly, site navigation was quick.
All the Details: https://app.roll20.net/users/17157815/nppr-t
Ущерб через наркотиков — этто сложная
проблема, обхватывающая физиологическое, психическое и социальное здоровье человека.
Утилизация подобных наркотиков,
яко кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, «шишки» чи «бошки», что ль привести к необратимым последствиям как чтобы
организма, яко равным образом чтобы мира на целом.
Но хоть при вырабатывании подневольности возможно электровосстановление — ядро, чтобы энергозависимый явантроп обратился за помощью.
Важно помнить, яко наркомания лечится, также оправдание бабахает шанс на новейшую жизнь.
онлайн казино в россии официальный сайт Устали от казино, где вывод денег превращается в настоящую головную боль? Мы понимаем! Наш выбор – это надежные казино с действительно быстрыми выплатами. Играйте в любимые слоты и настольные игры, зная, что ваши выигрыши поступят на счет в кратчайшие сроки. Максимум удовольствия, минимум ожидания!
геронтологический пансионат Гериатрический центр фокусируется на диагностике, лечении и профилактике заболеваний, характерных для пожилого возраста. Врачи-гериатры обладают глубокими знаниями в области возрастных изменений организма и разрабатывают индивидуальные планы лечения, учитывающие особенности каждого пациента. Гериатрическая помощь включает в себя медикаментозное лечение, физиотерапию, психологическую поддержку и консультации по вопросам питания и образа жизни.
WildCrest Online – Great selection, smooth site experience, and delivery was prompt.
У меня тоже была задержка.На мониторенге тоже отправку просрочили, в итоге дней 20 затратили на пересылку.Просто курьерка такая, они помоему там распиздяи ещё те…так что на счёт приема можешь не беспокоиться.там даже если мусора захотят что то найти то будет трудно разобраться что да где)вот допустим недавно заказал и курьерка ваще не то вбила))так что не переживай!Чемикалы всё ровно делают, сложновато будет найти даже если посыль откроют! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Снова всё на высоте)заказывал 2 г тусишки!попросил пробник 5МЕО) получил)))))))))
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely comeback.
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
гериатрический пансионат При выборе геронтологического или гериатрического учреждения следует учитывать ряд факторов, включая репутацию, квалификацию персонала, спектр предоставляемых услуг, условия проживания и стоимость. Важно также ознакомиться с отзывами других пациентов и их родственников, чтобы сделать осознанный выбор.
IronWoodStudioShop – Items arrived on time, website is easy to use, very satisfied.
What’s up colleagues, nice post and good urging commented
here, I am genuinely enjoying by these.
играть в казино бесплатно Мечтаете о захватывающих играх и крупных выигрышах? Наш ресурс поможет вам найти официальный сайт онлайн казино в России, где вас ждут лучшие слоты, рулетка, блэкджек и многое другое. Присоединяйтесь к миру азарта!
геронтологическом В Москве существует множество геронтологических и гериатрических центров, предлагающих широкий спектр услуг. Среди них можно найти как государственные, так и частные учреждения. Выбор центра зависит от индивидуальных потребностей и предпочтений.
онлайн казино в россии Что для вас самое важное в онлайн-казино? Если это надежность и быстрый вывод средств, то вы попали по адресу! Мы подобрали для вас лучшие варианты, где можно играть без опасений и получать свои выигрыши практически моментально. Готовы испытать удачу?
Simple Fashion Online – Great selection of trendy clothing, and the site made shopping easy.
Формат лечения
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
всё получил,качество-бомба,очень доволен магазином ,всё быстро доставили,вам желаю так держать!!!!!!!!! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм заказывали реагент jv 61, брали 15 гр, с данным продовцом работаю с 11 года, сейчас регу тянул на зону, в целом все хорошо как обычно какачество соответствует заявленному, единственное проблеммы с отправкой возникают но думаю эти проблемы временные, поссылка дошла за два дня после отправки,, затестить сиогли на днях как все зашло, с первой прикурки чесно сказать прихуели думали что опять дживи 100 пришел, но ннет , держало часа по два сначало, на третий день время прихода испало до 4 0мин, вообщем все понравилось в очередной раз, на днях закажем еще
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/es-AR/register?ref=UT2YTZSU
I used to be suggested this blog by means of
my cousin. I am no longer positive whether or not this publish is written by means of him as no one else
realize such precise about my trouble. You are
incredible! Thanks!
BoldStreet Styles – Everything was simple to browse and the payment went through smoothly.
Что делаем
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
stylehavenhub – Found some amazing deals, the experience was smooth.
aviator money [url=https://aviator-game-winner.com]https://aviator-game-winner.com[/url] .
Browse urban outfits – A couple of standout selections were visible immediately, very convenient.
быстрая доставка однако тут))) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Мир вам!
Эта статья подробно расскажет о процессе выздоровления, который включает в себя эмоциональную, физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Мы обсуждаем значимость поддержки и наличие профессиональных программ. Читатели узнают, как строить новую жизнь и не возвращаться к старым привычкам.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в Симферополе[/url]
giftjunction – Lots of useful gifts to choose from, shipping felt efficient.
Shop & Smile Online – Great range of products, excellent value, and fast shipping.
fashionforallages – Loved the fast loading and user-friendly layout.
Wonder View Boutique – Excellent items, website was simple to navigate, and delivery was prompt.
Great info. Lucky me I ran across your site by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later!
Wow, fantastic weblog structure! How long have you
ever been blogging for? you made blogging look easy.
The entire glance of your site is fantastic,
as well as the content material!
Growth Inspiration Daily – Motivational tips and exercises to help you flourish in all areas of life.
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно краснодар[/url]
ко ланта ко лант
я думаю все ровно будет. заказал тут для пробы 5 гр. акв 48 ф . 10 октября еще заказал. еще не выслали. на почту пишут, извиняются. ждём результатов. как будут движения отпишу. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш [hide=5]Пришла таки тусишка.Коричневатый порошок,в черезчур большом пакете(не 100г же заказывали). Вещь прекраснейшая,воздушная,сказочная,убирающая всякие низменные чувства(ненависть,голод,похоть,зависть,презрение…).Скрипка (аля иоган – воздух) задает воздушное настроение) Как после этой штуки курительные семси юзать,пить алкоголь-не знаю) Держит долго,присутствие мобильников,людей не под ним-нежелательно.На постэффектах хорошо пойдёт гитарка с веселыми,поизитвными песенками)
In clinical practice, one often observes the unidirectional flow of medical instruction. A treatment plan is formulated and executed — this dynamic has been a cornerstone of modern medicine. This model, while efficient, overlooks critical variables.
The clinical picture, however, is frequently complicated by comorbidities. One begins to note a prevalence of treatment-resistant cases. These can range from persistent subclinical fatigue to cognitive disturbances. An analysis of individual metabolic and genetic factors often reveals a landscape of interactions that was not initially apparent.
This is the cornerstone of personalized medicine. The same molecular entity can be curative for one patient and merely palliative or even detrimental for another. Long-term health outcomes are shaped by these subtle, cumulative decisions.
Therefore, fostering a collaborative doctor-patient relationship is paramount. The informed patient is empowered to work synergistically with their healthcare provider. For those seeking to deepen their understanding of this complex interplay, we advise delving into the subject further. A prudent starting point for any individual would be to research and better understand cenforce.
This discussion is designed to be informative, but it is not a replacement for a consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
The best reads here: https://www.diigo.com/item/note/blw3c/ni6h?k=8a0f90d31bdc030a6146d79bedf8744a
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog012.ru
лечение запоя
HarborTrendsStore – Great selection of products and clean website layout.
blacksprut ссылка
Нравится сайт — всё ясно и много интересного.
https://h1.nu/1itrq
BH Corner Finds – Loved the interface, and shipping was super fast.
ОПЕРАТОР ЕЩЕ БОЛЬШЕ МЕНЯ ОБРАДОВАЛ КОГДА СКАЗАЛ МНЕ НОВЫЙ ЦЕННИК НА РЕГУ! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Хочу всех поздравить с наступающим Новым Годом и хочу поделиться с вами своей оптовой сделкой СК крисов.
Global Value Hub – Nice deals available, and the website ran quickly with simple checkout.
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
bs2
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Узнать больше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому Москва[/url]
dealhunterhub – Great savings, smooth online shopping made it easy.
I think the admin of this site is in fact working hard in favor of his web site, since here every data is quality based material.
SoftCrest Trend Store – Easy navigation, great products, and the entire shopping process felt seamless.
SunCrestBoutique – Very smooth browsing, modern items, and reliable shipping.
“Район довольно близкий для меня(СТРЕЛА)” https://pizzadelmaestro.ru/povorino.html Ты договорись с курьером о встрече где нибудь, и пропали окружающую обстановку, чтоб рядом небыло не кого подозрительного. Больше не знаю что тебе посоветовать
trendzonehub – Found stylish products quickly, the website was easy to navigate.
aviator bonus game [url=www.aviator-game-winner.com]www.aviator-game-winner.com[/url] .
Здесь
[url=https://xn--m1ao.xn--p1ai/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Pure Style Deals – Trendy designs throughout, and finding items was straightforward.
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому рязань[/url]
Автошкола «Авто-Мобилист»: профессиональное обучение вождению с гарантией результата
Автошкола «Авто-Мобилист» уже много лет
успешно готовит водителей категории «B»,
помогая ученикам не только сдать
экзамены в ГИБДД, но и стать уверенными участниками дорожного движения.
Наша миссия – сделать процесс обучения
комфортным, эффективным и доступным для каждого.
Преимущества обучения в «Авто-Мобилист»
Комплексная теоретическая подготовка
Занятия проводят опытные преподаватели, которые не просто разбирают правила дорожного движения, но и
учат анализировать дорожные ситуации.
Мы используем современные методики, интерактивные материалы и регулярно обновляем программу в соответствии с изменениями
законодательства.
Практика на автомобилях с МКПП и АКПП
Ученики могут выбрать обучение на механической
или автоматической коробке передач.
Наш автопарк состоит из современных,
исправных автомобилей, а инструкторы помогают освоить не
только стандартные экзаменационные маршруты, но и сложные городские условия.
Собственный оборудованный автодром
Перед выездом в город будущие водители отрабатывают базовые
навыки на закрытой площадке: парковку,
эстакаду, змейку и другие элементы, необходимые для сдачи экзамена.
Гибкий график занятий
Мы понимаем, что многие совмещают обучение с работой или
учебой, поэтому предлагаем утренние, дневные и вечерние
группы, а также индивидуальный график вождения.
Подготовка к экзамену в ГИБДД
Наши специалисты подробно разбирают типичные ошибки на
теоретическом тестировании и практическом экзамене, проводят
пробные тестирования и дают рекомендации
по успешной сдаче.
Почему выбирают нас?
Опытные преподаватели и инструкторы с многолетним стажем.
Доступные цены и возможность оплаты в рассрочку.
Высокий процент сдачи с первого
раза благодаря тщательной подготовке.
Поддержка после обучения – консультации по вопросам вождения
и ПДД.
Автошкола «Авто-Мобилист» – это не просто
курсы вождения, а надежный старт для
безопасного и уверенного управления автомобилем.
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb1.ru/
urbanzonehub – Quick navigation, found several trendy products easily.
экстренное вытрезвление
какое на**й в\в !!?? совсем рехнулись чтоли ? Я не знаю за качество их 2-дпмп, но если он не бодяженный и качественный, то 5мг интрозально хватит чтоб тебя колбасило 2-3 суток ! Никто по ходу у чемикала его ещё не пробовал – отзывов нету… https://modernm.ru/labitnangi.html Хочу всем сказать мы не работаем 1вым классом ни при каком условии…
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
BlueHaven Style Store – Fashionable picks and very punctual delivery today.
Hi, just wanted to say, I loved this post. It was inspiring.
Keep on posting!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk013.ru
вывод из запоя цена
RareSeasonGoodsHub – Website loads quickly, simple checkout, and items arrived promptly.
Ниже представлена карта действий бригады «РязМедСервиса» в первые три часа. Это не «жёсткая сетка», а ориентир для безопасной и быстрой стабилизации. В каждом блоке есть клиническая цель, измеримые критерии и условие для перехода к следующему шагу.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/
SoftStone Product Page – Smooth browsing, lovely items, and shipping was timely.
по заказу?) https://powsurfing.ru/pavlovsk.html а почему репа минусовая?
экстренное вытрезвление на дому спб
Why users still use to read news papers when in this technological globe the whole thing is presented on web?
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Bright Style Market – Great designs available, and the package reached me without any delay.
vogueseasonhub – Loved the seasonal assortment, checkout was simple and quick.
LeafBright Emporium – Impressive selection and a seamless visit from start to finish.
What’s up, yup this article is in fact fastidious and I have learned lot of things from it about blogging.
thanks.
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru/]наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Пациенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий формат лечения. Стационар обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и интенсивную терапию, а амбулаторный формат позволяет совмещать лечение с повседневной жизнью.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Услуги [url=https://evrasin.ru/]технический перевод бюро[/url] предоставляются высококвалифицированными переводчиками.
особую область переводческих услуг, ориентированную на техническую документацию . Это необходимая часть международного сотрудничества в области науки, технологий и производства . Благодаря техническому переводу становится возможным облегчить понимание сложных технических концепций для специалистов разных стран .
Технический перевод требует не только знания языка, но и глубокого понимания технической терминологии . Переводчики должны обладать глубокими знаниями в той или иной технической области . Это гарантирует качество и точность перевода .
Процесс технического перевода включает в себя несколько этапов, от первоначальной оценки проекта до финального контроля качества . На первом этапе определяется объем и сложность проекта . Далее разрабатывается план реализации проекта .
Выполнение самого перевода предполагает использование специализированного программного обеспечения и баз данных терминов . После завершения перевода выполняется проверка соответствия переведенного текста оригиналу . Этот позволяет минимизировать ошибки и несоответствия .
Технический перевод является важнейшим инструментом для глобализации бизнеса и культуры . Благодаря техническому переводу компании могут экспортировать свою продукцию и услуги в другие страны . Это дает возможность расширить рынки сбыта и увеличить конкурентоспособность .
Технический перевод также способствует распространению знаний и культуры . Это дает возможность людям из разных стран общаться и делиться опытом . Поэтому следует привлекать высококвалифицированных специалистов в этой области .
Будущее технического перевода предполагает интеграцию с другими областями, такими как локализация и культурная адаптация . Развитие технологий перевода и автоматизации позволит увеличить скорость и качество перевода .
В будущем технический перевод станет еще более важным для глобальных?? и международного сотрудничества . Это будет способствовать развитию новых форматов и технологий для перевода и коммуникации . Поэтому следует инвестировать в разработку и внедрение новых технологий и инструментов .
그것에 대한 비디오가 있나요? 더 자세한
정보를 알고 싶습니다.
Howdy, I do think your web site may be having web browser compatibility problems.
When I take a look at your web site in Safari,
it looks fine but when opening in I.E., it’s got some overlapping issues.
I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside from that,
excellent website!
Флудить на счет легальности/нелегальности товара в магазине не нужно в ветке! У же отписывалась и экспертиза и мы не однократно писали, возим ТОЛЬКО ЛЕГАЛ! купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Нижняя Салда Всем Привет! :hello:Немного хороших строк о магазине;)
Взвешенное отношение к игре является ключевым элементом здоровой игровой среды.
Она помогает избежать лишних рисков и сохранять баланс во время игрового процесса.
Множество пользователей понимают, что умеренность помогает сохранять позитивные эмоции без негативных последствий.
Установление ограничений позволяет контролировать время.
https://blokov-casino.net/online-casino-arkada/
Помимо этого, важно осознавать свои привычки и останавливаться вовремя.
Игровые платформы часто предлагают опции контроля, которые помогают сохранять баланс.
Любители игр, которые придерживаются принципов ответственности, чаще избегают стрессов.
Следовательно, ответственная игра остаётся необходимым условием комфортного отдыха.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Daily Vision Hub – Inspiration and tips for dreaming big and acting on your plans.
Формат
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
DreamEssentialStore – Really satisfied with the fast shipping and simple website.
stylezone – Loved checking out products, navigation was smooth and hassle-free.
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/[/url]
If you are going for most excellent contents like I do, simply pay a visit this web page daily for the reason that it provides
quality contents, thanks
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb2.ru/
I really love your site.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you develop this
amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m attempting to
create my own site and want to learn where you
got this from or what the theme is called. Thanks!
Visit an elephant sanctuary: care, rehabilitation, and protection of animals. Learn their stories, participate in feedings, and observe elephants in the wild, not in a circus.
Профессиональные электромонтажные работы в квартирах, домах и офисах. Замена проводки, монтаж щитков, автоматов, УЗО, светильников и розеток. Работаем по нормам ПУЭ, даём гарантию и подробный акт выполненных работ.
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb2.ru/
OceanCrest Deals – Fashionable finds, simple ordering, and the package reached me quickly.
Работал с магазином спасибо всё красиво! https://shamotiki.ru/elnya.html магазин отличный
Fresh Choice Center – Enjoyed the freshness and variety; checkout was quick and simple.
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-zhukovskom
Здесь
[url=https://riche.skin/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
yourshoppingcorner – Very easy to browse, checkout was quick and seamless.
aeroplane game money [url=http://aviator-game-deposit.com]http://aviator-game-deposit.com[/url] .
aviator x [url=http://aviator-game-winner.com/]http://aviator-game-winner.com/[/url] .
Когда уместен
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru
фирма по ремонту квартир в москве [url=http://www.rejting-kompanij-po-remontu-kvartir-moskvy.com]фирма по ремонту квартир в москве[/url] .
Формат лечения
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added”
checkbox and now each time a comment is added
I get four emails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thank you!
Выбор техники зависит от клинической картины, переносимости препаратов, психоэмоционального состояния и горизонта планируемой трезвости. Таблица ниже помогает сориентироваться в ключевых различиях — врач подробно разберёт нюансы на очной консультации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]anonimnoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb2.ru/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk014.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Магазину отличных покупателей))) https://kitsune44.ru/tolyatti.html Покуреха порошки безвкусные (на язык), остальные горькие. Так проще всего определить.
<a href="https://sunrisetrailmarket.shop/" /SunriseTrailSelectHub – Loved the variety of items and very easy website navigation.
В этой публикации мы рассматриваем важную тему борьбы с зависимостями, включая алкогольную и наркотическую зависимости. Мы обсудим методы лечения, реабилитации и поддержку, которые могут помочь людям, столкнувшимся с этой проблемой. Читатели узнают о перспективах выздоровления и важности комплексного подхода.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево Симферополь[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «волшебная капля» или крепкий чай с рассолом. «Формула Трезвости» организует помощь в Ногинске круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом или приём в стационаре, детоксикация с мониторингом, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, подробный план на первые 48–72 часа. Мы действуем безопасно, конфиденциально и без «мелкого шрифта» — объясняем, что и зачем делаем, согласовываем схему и фиксируем смету до начала процедур.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
GoldenRoot Essentials – Browsing was simple, good prices, and my order arrived quickly.
???????????????????????????????
Love elephants? elephant sanctuary: no rides or shows, just free-roaming elephants, nature trails, guided tours, and the chance to learn what responsible wildlife management looks like.
stylefinderhub – Trendy products and quick site loading, very easy to browse.
Hey there!
Hope you’re doing great. First off, I just wanted to say how awesome your website is – the content is top-notch, and the design is really slick. Seriously, well done!
I’m reaching out because I’m interested in buying some backlinks for my website. I think a backlink from your site would be super beneficial for my SEO efforts, and I’d love to discuss the possibilities with you.
Here’s an example of the kind of links I’m looking to place:
[url=https://shake-that-weight.co.uk/album/23/dj-rajesh-benagoria/new2old/1.html]Dj Rajesh Benagoria Edm Dj Remixer Mp3 Songs[/url]
[url=https://fortmyerswebsitedesigner.com/cosplayers/]cosplayers[/url]
[url=https://ridgelanding.com/latest-videos/adult-time/]Adult Time[/url]
[url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]Artificial Intelligence Marketing Automation[/url] is transforming the process of advertising strategies by streamlining repetitive tasks and enhancing performance. Through intelligent automation, companies can manage campaigns, measure success, and improving outcomes automatically. It helps businesses reduce workload with steady brand messaging through various media. By leveraging AI Marketing Automation, companies can focus on creativity and building relationships rather than manual processes. In the end, AI automation makes campaigns smarter and scalable for long-term success.
[url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]Artificial Intelligence marketing strategies[/url] are essential for businesses wanting to lead in a fast-paced digital environment. They use advanced AI technologies, forecasting tools, and automation to create tailored campaigns to customers. By analyzing consumer behavior, AI enables brands to design ads that connect with target demographics. Using AI-based approaches allows instant optimization based on performance metrics, for better returns. Businesses that implement AI marketing quickly achieve superior results in building long-term loyalty.
[url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]Introductory guide to AI marketing[/url] provides a clear roadmap for companies starting with AI in their strategies. It shows how AI simplifies processes, analyze data, boost audience reach for better results. New users discover why AI matters within current systems without causing interruptions. It outlines potential issues and actionable tips, making it easier for marketers to start confidently. Using a structured AI roadmap, marketers can leverage AI tools and achieve measurable success.
[url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]Automation platforms for marketers[/url] are essential for digital success, providing solutions to streamline tasks. They assist brands with social media scheduling and performance monitoring with minimal effort. Next-gen systems use AI technology, offering data-driven recommendations and custom content. Selecting the best automation software ensures seamless collaboration between teams with unified communication. With ongoing innovation, these tools continue to enhance efficiency while driving better outcomes for businesses of all sizes.
[url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]Large-scale personalization[/url] is a key advantage of artificial intelligence, enabling marketers to create unique experiences for massive user bases. By leveraging [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/ai-marketing-automation-beginners-guide/]predictive analytics marketing[/url], brands can predict customer behavior and share personalized messages in advance. Such strategies boost interaction, boosts conversion rates, while building trust. Combining personalization at scale with predictive analytics ensures that campaigns are both proactive and precisely focused. Ultimately, businesses can foster strong engagement with their market and achieving long-term success.
[url=https://www.facebook.com/seosea.marketing]Facebook[/url]
[url=https://www.instagram.com/seoseamarketing/]Instagram[/url]
[url=https://www.reddit.com/r/OnlnMarketingAgency/]Reddit[/url]
[url=https://www.linkedin.com/company/81762316]LinkedIN[/url]
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-zhukovskij[/url]
An ethical elephant sanctuary: rehabilitation, care, veterinary monitoring, and freedom of movement instead of attractions. By visiting, you support the project and help elephants live in dignified conditions.
???????????????????????????????
medved20-10 не еби людям голову!!!!!!!!!!! микс отличный, но на час-1,5! Не больше…… https://shamotiki.ru/medvezhegorsk.html Раньше розницей занимались благодаря вашему опыту,сейчас время другое,стабильная честная работа)
이건 주제에서 벗어나지만, 제 최신 트위터 업데이트를 자동으로
트윗하는 위젯을 블로그에 추가할 수 있는지 궁금합니다.
이런 플러그인을 꽤 오랫동안 찾고 있었는데, 당신이 이런 것에 대해 경험이 있을지도 모른다고
생각했어요. 혹시 아는 게 있다면 알려주세요.
당신의 블로그를 정말 즐기고 있으며 새로운 업데이트를 기대하고 있습니다.
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Когда уместен
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/
fashioncorner – Great variety of outfits, checkout felt very easy and fast.
Как работает
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-vidnom/
Выезд на дом
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-orekhovo-zuevo
Эта публикация обращает внимание на важность профилактики зависимостей. Мы обсудим, как осведомленность и образование могут помочь в предотвращении возникновения зависимости. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с полезными советами и ресурсами, которые способствуют здоровому образу жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://i-klinik.ru
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]medicinskij-centr-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в Симферополе[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://anvio.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Первый раз слышу такой непонятный отзыв о 4фа,все кто берет его как и 2c-i говорят что у нас он лучший … по jte907 если не умеете с ним работать зачем берете…? есть постоянные оптовики кто берет только его, и этот продукт нареканий не вызывает. Многие “Селлеры” под видом jte продают 2201 и это факт! у нас этот продукт в оригинале. МХЕ у нас такой пришел, мы не кричим что его чистота 99%, и что качество его не очень мы предупреждали всех… купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Поворино Рашн хлидейс вы правы, мы же тоже люди 🙂 треки наверное на отправке в базу не внесли, а шас у них же тоже праздники, но не волнуйтесь копии накладных то у нас 😉
WildSand Finds – Excellent variety, intuitive navigation, and delivery was prompt.
Incredible all kinds of awesome data.
Daily Ambition Hub – Ideas and encouragement to grow, plan, and achieve your dreams effectively.
Проблемы со здоровьем? невролог после инсульта краснодар: комплексные обследования, консультации врачей, лабораторная диагностика и процедуры. Поможем пройти лечение и профилактику заболеваний в комфортных условиях без очередей.
ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
Soft Cloud Favorites – Enjoyable navigation and the site layout is simple to follow.
Khao555 Online
Lunar Harvest Finds – Browsing is smooth and all products are easy to locate.
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно краснодар[/url]
В этом обзоре представлены различные методы избавления от зависимости, включая терапевтические и психологические подходы. Мы сравниваем их эффективность и предоставляем рекомендации для тех, кто хочет вернуться к трезвой жизни. Читатели смогут найти информацию о реабилитационных центрах и поддерживающих группах.
Узнать больше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя Москва[/url]
Этап
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo-v-noginske/
Truly quite a lot of wonderful material!
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя Симферополь[/url]
Все посылку получил. ровно 7 дней после оплаты и посылка уже у меня. конспирация отличная. купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Новомичуринск всё ровн ждём =)
Когда уместен
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
free chat website free video chat
бонусы казино бонусы казино
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk015.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Bright Flora Outlet – Browsing was smooth, and everything is neatly organized.
fashionfindhub – Excellent range of items, quick browsing and easy ordering.
aviator game [url=http://www.aviator-game-deposit.com]http://www.aviator-game-deposit.com[/url] .
бригады по ремонту квартир в москве [url=www.rejting-kompanij-po-remontu-kvartir-moskvy.com/]www.rejting-kompanij-po-remontu-kvartir-moskvy.com/[/url] .
timelessharborcornerstore – Easy browsing and visually tidy products make shopping enjoyable.
My programmer is trying to persuade me to
move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on numerous websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform.
I have heard excellent things about blogengine.net.
Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress content into it?
Any help would be really appreciated!
urbanfashionhub – Found great products, prices are very reasonable and satisfying.
Ребята, магаз ровный и немелочный, берите смело купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Нюрба ЕМИКАЛ МИКС – ЭТО ЛУЧШИЙ МАГАЗИН С МНОГОЛЕТНЕЙ РЕПУТАЦИЕЙ НА РЦ РЫНКЕ!!!!
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru
Когда уместен
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]centr-narkologicheskoj-pomoshchi[/url]
Эти советы о играх — очень интересные.
https://lnkm.ee/70de10c8
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом жуковский[/url]
Этот сайт kazino olimp — полезный помощник.
Olimp Casino онлайн (https://hotely.sk/redirect?url=https://olimp-casino-kazakhstan-spin.kz/bonuses)
urbanchic – Great variety of urban styles, shopping experience felt seamless.
качество нормуль! можно делать 1к12, 1к10 само то купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Янгиюль Магазин ровный! Я заказал 1000ф, оплатил ЯД, оператора попросил отправить посыль на следующий день , без задержки т.к. сроки получения очень поджимают. На что оператор адекватно ответил что все сделают.На следующий вечер получил трек, посылочка собранна и вот вот выезжает))) если уже не выехала) Магазину как и его администрации – от души за оперативность и отношение к клиенту.
Что делаем
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-nedorogo[/url]
Amazing! Its in fact amazing piece of writing, I have got much clear
idea on the topic of from this article.
Медицинская публикация представляет собой свод актуальных исследований, экспертных мнений и новейших достижений в сфере здравоохранения. Здесь вы найдете информацию о новых методах лечения, прорывных технологиях и их практическом применении. Мы стремимся сделать актуальные медицинские исследования доступными и понятными для широкой аудитории.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника Симферополь[/url]
This article presents clear idea in support of the
new users of blogging, that genuinely how to do blogging and site-building.
FreshWind General Store – Crisp images and a simple, stress-free shopping process.
Когда уместен
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-orekhovo-zuevo7.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu-v-orekhovo-zuevo[/url]
bs2site at
Лучшее качество на Рынке РК!!! Низкие цены!! И без кидалова! УВАЖЕНИЕ ВАМ РЕБЯТА!!! https://leylailyasova.ru/porhov.html Кто-нить брал тут 307 ?? просто ппц какой-то. уже 2 гр выкинул. Делал и 1к10 и чистым курил, ваще НОЛЬ. Как такое можт быть ?
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/
Creative Projects Hub – Ideas and tips to explore your creativity in practical ways.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec016.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
Modern Harbor Hub – Browsing is smooth and products appear quickly without delay.
?????????
рулонные шторы с автоматическим управлением [url=www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru]www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru[/url] .
uniquepickscentral – Very easy to navigate, ordering was smooth and fast.
ЦВЗ центр https://cvzcentr.ru в Краснодаре — команда специалистов, которая работает с вегетативными расстройствами комплексно. Детальная диагностика, сопровождение пациента и пошаговый план улучшения самочувствия.
Full Circle Deals – Finding items is effortless with a simple, neat design.
Nairabet offers https://nairabet-play.com sports betting and virtual games with a simple interface and a wide range of markets. The platform provides live and pre-match options, quick access to odds, and regular updates. Visit the site to explore current features and decide if it suits your preferences.
pg ????? khao555.com
При критических симптомах (потеря сознания, сильная одышка, подозрение на инсульт/инфаркт) необходимо звонить 103/112. Мы подключимся к маршрутизации и организуем перевод в стационар.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
подход к клиенту 5+ (все объяснили, трек сразу скинули) https://adoping.ru/kishtim.html Врубим поскорей музончик:
trendfinderstore – Nice variety of fashion, the site loads instantly without lag.
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в Москве[/url]
inverter game [url=https://aviator-game-deposit.com/]https://aviator-game-deposit.com/[/url] .
лучшая компания по ремонту квартир [url=https://www.rejting-kompanij-po-remontu-kvartir-moskvy.com]лучшая компания по ремонту квартир[/url] .
bs2bestat
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno
Great article! I’ve been using rr.com email for a long time, and it’s nice to see
helpful information about it. Since it was originally part of RoadRunner and later moved under Spectrum,
many users still get confused about how to log in or manage their accounts.
A lot of people don’t realize that they now need to sign in through the Spectrum Webmail
page instead of the old RR login.
I think this is one of the most significant info for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But wanna remark on some general things, The website style is perfect, the articles is really nice :
D. Good job, cheers
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just
your articles? I mean, what you say is fundamental and all.
However think of if you added some great visuals or videos to give your posts more, “pop”!
Your content is excellent but with images and videos, this site could definitely be one of the very best in its niche.
Amazing blog!
bargainhunt – Quick access to great deals, site responsiveness was excellent.
При “отменном” качестве 1к25 смело выходит. У вас отменное ? https://prishlo-vremya.ru/mapsite2.html Это тема о работе магазина. “эффекты, использование” в теме о продукции
Здесь
[url=https://md-dizain.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Todo sobre el cafe https://laromeespresso.es y el arte de prepararlo: te explicaremos como elegir los granos, ajustar la molienda, elegir un metodo de preparacion y evitar errores comunes. Prepara un cafe perfecto a diario sin salir de casa.
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Infraestructura y tecnologia https://novo-sancti-petri.es vial en Europa: innovacion, desarrollo sostenible y soluciones inteligentes para un transporte seguro y eficiente. Tendencias, proyectos, ecotransporte y digitalizacion de la red vial.
Hi! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a new project in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a marvellous job!
BrightWind Select – Excellent items, easy shopping flow, and quick arrival of my order.
Адекватных работников купить, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки Мариуполь “И да Заветный кооробок у меня в руках”
????? pg
Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге — это востребованная медицинская услуга, позволяющая получить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Такой формат особенно актуален в ситуациях, когда пациент не может или не хочет обращаться в стационар. Выезд специалиста позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и оказать психологическую поддержку без нарушения анонимности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Despite being a new casino site, Vave boasts a sleek, well-polished, user-friendly, intuitive navigation platform, providing easy access to games, promotions, support, and more.
Наш подход строится на двух принципах: минимально достаточная фармакотерапия и прозрачные «коридоры безопасности». Это означает — никаких «универсальных капельниц» и полипрагмазии. Каждый компонент в схеме имеет проверенную цель: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, защитить слизистую, снизить вегетативный «шторм» и вернуть возможность естественного сна. Скорость и объём инфузий мы задаём инфузоматом, контролируя давление, пульс, сатурацию и самочувствие на каждом этапе.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Timber Grove Hub – Everything loads fast, and navigating the site is smooth.
Rodaballo Al Horno https://rodaballoalhorno.es es un viaje a los origenes de la musica. Exploramos las raices, los ritmos y las melodias de diferentes culturas para mostrar como el sonido conecta a personas de todo el mundo y las ayuda a sentirse parte de una conversacion musical mas amplia.
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма санкт-петербург[/url]
Для решения всех задач, связанных с переводом документов на любой язык, можно обратиться в [url=https://allperevod.ru/]бюро переводов апостиль москва[/url], где опытные переводчики окажут профессиональные услуги по переводу любых документов.
перевод текстов и документов с высоким уровнем точности . Это позволяет им удовлетворять различные потребности клиентов, от перевода личных документов до комплексных бизнес-проектов. Кроме того, бюро переводов часто обладает d?iной переводчиков, которые являются экспертами в разных областях, владеющими специализированными знаниями для точных переводов. Это гарантирует, что переведенный текст не только соответствует оригиналу по смыслу, но и адаптирован к целевой аудитории и соответствует требованиям определенной отрасли.
Бюро переводов также уделяет особое внимание конфиденциальности и безопасности переводимой информации, обеспечивая, что все переводчики обязаны сохранять конфиденциальность. Это является ключевым аспектом их услуг, поскольку клиенты часто доверяют им?ливую информацию. Помимо этого, бюро переводов может предложить услуги по локализации, учитывая культурные и языковые особенности . Это особенно ценно для компаний, стремящихся расширить свою деятельность на новые рынки.
Работа с бюро переводов дает клиентам гибкость в выборе услуг, соответствующих их конкретным потребностям. Это означает, что клиенты могут получить переводы, соответствующие их потребностям, будь то срочный перевод небольшого документа или масштабный проект, требующий перевода большого объема текстов. Кроме того, многие бюро переводов используют специализированное программное обеспечение для обеспечения качества переводов. Это не только ускоряет процесс перевода, но и гарантирует, что окончательный продукт соответствует самым высоким стандартам.
Партнерство с бюро переводов также может быть стратегическим шагом для бизнеса, расширяющегося на новые рынки . Благодаря точным и культурно адаптированным переводам, бизнес может избегать недоразумений и ошибок, которые могут возникнуть из-за языкового барьера . Это делает бюро переводов не просто поставщиком услуг, а ценным партнером в достижении бизнес-целей.
Бюро переводов обычно работает гарантируя, что все переводы соответствуют самым высоким стандартам. Для начала работы клиент получает оценку стоимости и сроков выполнения проекта. После этого, бюро переводов назначает подходящего переводчика для проекта, учитывая его специализацию и опыт . Этот подход??ет, что перевод не только выполнен качественно, но и соответствует конкретным потребностям и ожиданиям клиента.
На протяжении всего процесса бюро переводов также отслеживает качество и точность перевода . Это может включать получение обратной связи от клиента для дальнейшего совершенствования. Такой подход к?? и удовлетворенности клиента позволяет бюро переводов поддерживать высокий уровеньprofessionalизма и строить долгосрочные отношения с клиентами.
В заключение, бюро переводов представляет собой команду профессионалов, готовых удовлетворять различные потребности клиентов . С их помощью клиенты могут получить высококачественные переводы, соответствующие их потребностям . Бюро переводов является не просто поставщиком услуг, а стратегическим партнером, который может помочь расширить бизнес на новые рынки . Сегодня, когдамир становится все более взаимосвязанным, роль бюро переводов будет только расти в важности .
кролики ставят В\В, фашку от этого магазина по 0.07-0.15 нравится, только сушит сильно https://teka-retail.ru/baltiysk.html Полученная продукция не подлежит возврату и обмену.
Помогли, когда груз застрял на границе
my web blog … http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/karissajosh
happycornerdeals – Great deals available, navigation and ordering felt easy.
Todo sobre videojuegos https://tejadospontevedra.es noticias y tendencias: ultimos lanzamientos, anuncios, analisis, parches, esports y analisis de la industria. Analizamos tendencias, compartimos opiniones y recopilamos informacion clave del mundo de los videojuegos en un solo lugar.
moderntrendhub – Found everything I wanted, purchasing was fast and easy.
рулонные жалюзи купить в москве [url=https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru/]рулонные жалюзи купить в москве[/url] .
Формат лечения
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург[/url]
Наш подход строится на двух принципах: минимально достаточная фармакотерапия и прозрачные «коридоры безопасности». Это означает — никаких «универсальных капельниц» и полипрагмазии. Каждый компонент в схеме имеет проверенную цель: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, защитить слизистую, снизить вегетативный «шторм» и вернуть возможность естественного сна. Скорость и объём инфузий мы задаём инфузоматом, контролируя давление, пульс, сатурацию и самочувствие на каждом этапе.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
Стандартизированный алгоритм позволяет действовать быстро и безопасно. Он гибко настраивается под конкретный случай, но всегда включает триаж, экспресс-диагностику, старт инфузии, симптом-менеджмент и выдачу плана на 72 часа с «коридорами безопасности».
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare/
Calm Harbor Finds – The serene design made browsing products relaxing.
Здесь
[url=https://grinkom.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Thanks to my father who shared with me about this
weblog, this website is genuinely remarkable.
свадьба в москве Свадьба под ключ в Москве от Bravomos. Мы разработаем концепцию, подберём площадку, создадим стильный декор и флористику, организуем ведущего, фото и видеосъёмку, банкет и кейтеринг, свет и звук, а также техническую поддержку в день праздника. Полная координация подрядчиков, контроль бюджета и чёткий тайминг. Более 600 организованных свадеб, рейтинг в Яндекс – 5. Отсутстви недовольных невест!
stylehubdaily – Found trendy pieces quickly, checkout was smooth and simple.
В этой статье рассматриваются способы преодоления зависимости и успешные истории людей, которые справились с этой проблемой. Мы обсудим важность поддержки со стороны близких и профессионалов, а также стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления. Научитесь первоочередным шагам к новой жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя Симферополь[/url]
магазин хороший, спору нет, вот только уж оооочень он не расторопны. и ответ приходится ждать так же долго… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш салют бразы ) добавляйте репу не стесняйтесь всем удачи))
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/
Задержка усиливает риск судорог, делирия, аритмий и травм. Эти маркеры не требуют медицинского образования — их легко распознать. Если совпадает хотя бы один пункт ниже, свяжитесь с нами 24/7: мы подскажем безопасный формат старта и подготовим пространство к визиту.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryazan14.ru
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/4aak55cj
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в Москве[/url]
Чтобы у семьи было чёткое понимание, что и в какой последовательности мы делаем, ниже — рабочий алгоритм для стационара и для выезда на дом (шаги идентичны, различается только объём мониторинга и доступная диагностика).
Подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-vidnom/
Incredible story there. What happened after?
Good luck!
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно краснодар[/url]
Silver Moon Style Shop – Loved the variety, clear product images, and the package arrived fast.
It’s an amazing paragraph in support of all the web users;
they will take advantage from it I am sure.
Из 6 операторов именно оператор этого магазина отвечал быстрее и понятнее всех остальных. Я увидел здесь хорошее,грамотное отношение к клиентам, сразу видно человек знает свою работу. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Прислали нам свой метоксетамин, подтверждаем: продукт чистый, >99%.
Что делаем
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru
relaxhub – Smooth layout and easy to navigate, made shopping enjoyable.
https://t.me/Black125Bot
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
Modern Ridge Finds Online – Browsing is intuitive, and products are easy to spot.
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-vidnom
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
В этой статье мы обсудим процесс восстановления после зависимостей, акцентируя внимание на различных методах и подходах к реабилитации. Читатели узнают, как создать план выздоровления и использовать полезные ресурсы для достижения устойчивых изменений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
1 официальный сайт 1win 1win программа
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в санкт-петербурге[/url]
trendhubstore – Found the latest trendy items quickly, delivery was fast and dependable.
С 10-11 утра по МСК ежедневно кроме праздников и выходных. https://stilyagisocks.ru орудует фейк, причем организованно бандейкой, действительно джаббик зеркальный, добавил оригинальный сам отличий нету, епучая уязвимость детектед, будьте внимательны.
Profesionalni montaz nabytku: stehovani bytu, kancelari a chalup, stehovani a baleni, demontaz a montaz nabytku. Mame vlastni vozovy park, specializovany tym a smlouvu s pevnou cenou.
I’ve been exploring for a little for any high-quality
articles or weblog posts on this sort of space .
Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this web site.
Reading this info So i am glad to express that I’ve an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling I
found out just what I needed. I so much definitely will make certain to do not forget this web site and give it a look on a constant basis.
организация банкетов в москве Услуги по организация праздников под ключ в Москве и МО от event агентства BBRAVOMOS. У нас всё продумано до мелочей: концепция, сценарий, стильный декор, подбор площадки, кейтеринг, шоу-программы и координация в день события. Возьмем на себя идеи, организацию и координацию — от уютной вечеринки до грандиозного корпоратива. Индивидуальный подход, безупречный тайминг и бюджет под ваши цели. Bravomos — с праздником решён вопрос!
brightdealspot – Very easy to navigate, found multiple items I liked.
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://tantal-metall.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Ваши советы о ставках — действительно полезные.
https://olimp-casino-kazakhstan-spin.kz/bonuses
Эта статья подробно расскажет о процессе выздоровления, который включает в себя эмоциональную, физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Мы обсуждаем значимость поддержки и наличие профессиональных программ. Читатели узнают, как строить новую жизнь и не возвращаться к старым привычкам.
Детальнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому Симферополь[/url]
автоматическая рулонная штора [url=avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru]avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru[/url] .
не долго думая решил написать оператору данного магазина! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш И еще, слышал типа ам2233, который отличного качества, желтого цвета. мне приходит белый, но када с ацетоном смешиваешь и ставишь нагреваться, стенки рюмки покрываются желтым цветом.
A ton of pictures taken from porn are exactly what you expect from the moment the homepage loads: a garbage ton of them. Simple plenty. Extra-large thumbnails are organized into classes, allowing you to quickly sort through them according to your preference. https://fullyfurnishedrentals.ca/author/marticarneal9/
Daily Motivation & Growth – Resources and insights for consistent self-improvement and goal achievement.
Этот документ охватывает важные аспекты медицинской науки, сосредотачиваясь на ключевых вопросах, касающихся здоровья населения. Мы рассматриваем свежие исследования, клинические рекомендации и лучшие практики, которые помогут улучшить качество лечения и профилактики заболеваний. Читатели получат возможность углубиться в различные медицинские дисциплины.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в Москве[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-zhukovskij[/url]
metatrader 5 mac download [url=http://metatrader-5-downloads.com]http://metatrader-5-downloads.com[/url] .
mt5 download mac [url=https://metatrader-5-mac.com/]https://metatrader-5-mac.com/[/url] .
Timberwood Hub – Smooth browsing with a friendly, organized interface.
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo-v-pushkino/
знаю кто и как берут через этот магаз купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази дада братан пришло все!!!охуенноый кач ск и рега нормальная вапще… короче зайди к нему на ветку там трипы опродукции прочти мой свежий за ск
Bright Meadow Store – Everything matched the listing and the site was extremely easy to navigate.
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
остров ланта таиланд на карте
Love elephants? elephant sanctuary: rescued animals, spacious grounds, and care without exploitation. Visitors can observe elephants bathing, feeding, and behaving as they do in the wild.
Hi there, after reading this amazing article i am
as well delighted to share my knowledge here with mates.
Want to visit the elephant sanctuary A safe haven for animals who have survived circuses, harsh labor, and exploitation? Visitors support the rehabilitation program and become part of an important conservation project.
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в Москве[/url]
вызвать проститутку по вызову нижневартовск
Что делает врач
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]posle-kapelnicy-ot-zapoya[/url]
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk013.ru
вывод из запоя
khao555 slot
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg
Aurora Essentials – Finding what you need is quick and the displays are appealing.
Ответил) просто не сразу увидел в вашем сообщении дополнительный вопрос ) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Снял в касание, остановился, открыл дверь авто, вышел и зашёл обратно! Респект!!! Держите марку в том же духе!
pimalai resort spa koh lanta
trendvaluehub – Good selection of items, website feels intuitive and simple.
????? pg
stylehaven – Simple navigation and attractive presentation of items.
happytrendstore – Very easy to find stylish items, checkout was fast and simple.
Пиздатый магазин, всегда пойдут на встречу и оператор норм https://art-tavrida.ru Дим, доброго времени суток, отпиши за приход, заказала тоже эйф-дисс, скажи, чего ожидать?
fashioncorner – Loved the variety available, shipping seemed fast and consistent.
Чтобы у семьи было чёткое понимание, что и в какой последовательности мы делаем, ниже — рабочий алгоритм для стационара и для выезда на дом (шаги идентичны, различается только объём мониторинга и доступная диагностика).
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
продажа легких лесов Аренда складных строительных лесов: Складные строительные леса идеально подходят для внутренних работ, отделки и ремонта небольших помещений. Аренда складных лесов позволяет легко перемещать и хранить оборудование, а также быстро развертывать рабочее место в условиях ограниченного пространства. Компактность и мобильность делают их незаменимыми для мобильных бригад и частных мастеров.
реальные проститутки нижневартовска
На сайте четко сказанно что заказы обрабатываются через E-mail… купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Просьба подкорректировать самим бредовые сообщения.
Что делаем
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
аренда горизонтальных строительных лесов Аренда штукатурных лесов: Штукатурные леса специально разработаны для проведения штукатурных работ на фасадах зданий. Аренда таких лесов обеспечивает удобство и безопасность рабочих, а также позволяет установить необходимое оборудование для подачи и нанесения штукатурных смесей. Широкая платформа и устойчивая конструкция позволяют повысить производительность и качество выполняемых работ.
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favourite reason seemed to
be on the net the easiest factor to remember of. I say to you, I
certainly get irked at the same time as people consider concerns that they
just don’t recognize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , other people can take a
signal. Will probably be back to get more.
Thank you
OriginPeak Styles – Stylish pieces, easy site navigation, and very fast delivery.
mt5 [url=www.metatrader-5-downloads.com/]www.metatrader-5-downloads.com/[/url] .
metatrader 5 [url=http://metatrader-5-mac.com]metatrader 5[/url] .
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]prokapatsya-ot-alkogolya[/url]
Whispering Trend Hub Picks – Items are easy to explore and the interface feels neat.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Что делаем
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-zhukovskom/
Будет что лучше АМ? Или из серии JWH? https://britecleaning.ru доброго вечера всем,трек получил всё прекрасно бъётся,жду звоночка,жду жду жду
Open Plains Finds – Navigation is intuitive, making shopping simple and enjoyable.
Домашний визит нарколога — это формат, который соединяет клиническую безопасность и человеческую деликатность. В «КубаньМедЦентре» (Краснодар) мы организуем помощь так, чтобы пациент получал её там, где ему спокойнее всего — у себя дома. Дежурная команда работает круглосуточно, а среднее окно прибытия по городу составляет 30–40 минут с момента подтверждения заявки. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, проводит экспресс-оценку состояния, запускает индивидуально подобранную инфузионную терапию и оставляет подробный план на ближайшие 72 часа. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что мы делаем, зачем это нужно и по каким критериям поймём, что динамика идёт правильно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод краснодар[/url]
trendfusion – Fast and easy purchase, the variety is impressive.
????? pg
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ стабилизировать состояние без госпитализации. «РеАл Мед» организует выезд по всему Жуковскому и близлежащим посёлкам (Быково, Кратово, Ильинский, Островцы) круглосуточно: врач приедет с оборудованием, оценит риски на месте и запустит инфузионную терапию, чтобы снять интоксикацию, тремор, тошноту и тревожность. Процедуры проводятся по медицинским протоколам, с индивидуальным подбором схем под показатели пациента и сопутствующие заболевания, а вся коммуникация выстроена максимально деликатно — без лишнего внимания соседей и персонала дома.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://playerok.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Вау, сайт kazino olimp — очень информативный.
https://fraudabc.com/community/profile/madelinemounts/
Этап
Подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru
магазин хороший, спору нет, вот только уж оооочень он не расторопны. и ответ приходится ждать так же долго… https://serov1000.ru Ну я хозяину ветки в лс отписал.посмотри что да как будет.Мир братья.Липецких нех обманывать!
ООО Торгово-транспортное предприятие “Острое Жало” на saby. ru Одним из ключевых преимуществ “Острого Жала” является наличие развитой сети складских комплексов, расположенных в стратегически важных регионах страны. Это позволяет нам оперативно реагировать на запросы клиентов и оптимизировать маршруты доставки, сокращая сроки и издержки. Мы предлагаем услуги ответственного хранения, кросс-докинга, а также обработку и упаковку грузов в соответствии с требованиями заказчика.
toptrendhub – Fast and simple shopping experience, pages loaded quickly.
dealzone – Lots of interesting deals available, browsing was effortless.
ко ланта экскурсии
freshmarket – Pages load quickly, and finding what I needed was effortless.
Этап
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Вакансии ООО Торгово-транспортное предприятие “Острое Жало” на avito. ru В рамках нашей деятельности мы осуществляем не только транспортировку, но и полный цикл логистических услуг, включая складское хранение, комплектацию заказов и оформление необходимых документов. Особое внимание уделяется автоматизации процессов и внедрению передовых технологий учета и контроля движения товаров. Мы стремимся предоставить клиентам прозрачную и эффективную систему управления логистикой, позволяющую оптимизировать затраты и повысить конкурентоспособность их бизнеса.
классный магазин, была впечатлянна скоростью доставки и качествомтовара)) всем пис купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки отличный магаз,пришло всё быстро и в лучшем виде:dansing:спасибо,удачи и процветания
[url=http://semennoydom.ru]промокод семяныч[/url] поможет вам сэкономить на покупках в компании!
Семяныч предлагает множество различных товаров, на которые можно применить промокоды.
Wow, this paragraph is nice, my younger sister is analyzing
these things, therefore I am going to convey her.
SoftBlossom Trend Store – Beautiful items, fast-loading site, and checkout was hassle-free today.
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare
«НеваМед» — частная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где клиническая точность сочетается с бережной коммуникацией и безусловной конфиденциальностью. Мы делаем лечение не «разовым визитом ради капельницы», а продуманным маршрутом, в котором каждый шаг имеет понятную цель, сроки оценки и прозрачные критерии эффективности. Для пациента это означает предсказуемость первых суток, сохранение личного пространства и ощущение контролируемой динамики, а для близких — ясные правила помощи без тревожных импровизаций.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
не паникуй бро, всё ровно будет, я уверен… купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Просьба подкорректировать самим бредовые сообщения.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
леса строительные Продажа промышленных лесов: Продажа промышленных лесов – это предложение для компаний, занимающихся крупномасштабным строительством и требующих надежное и долговечное оборудование. Промышленные леса отличаются повышенной прочностью, устойчивостью к высоким нагрузкам и долговечностью. При выборе промышленных лесов важно учитывать особенности объекта, высоту работ, сложность конструкции и другие факторы. Инвестиции в качественные промышленные леса – это залог безопасности и эффективности строительных работ.
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар санкт-петербург[/url]
Fashion & Style Daily – Daily recommendations for looking stylish and feeling confident.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани является востребованной медицинской услугой, направленной на стабилизацию состояния пациента после длительного употребления алкоголя. Специалисты применяют современные методы детоксикации, позволяющие быстро и безопасно восстановить жизненно важные функции организма, снизить проявления абстинентного синдрома и предотвратить осложнения. Процесс лечения осуществляется в клинических условиях под постоянным наблюдением врачей.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
metatrader 5 download mac [url=http://metatrader-5-mac.com/]http://metatrader-5-mac.com/[/url] .
metatrader 5 download mac [url=www.metatrader-5-downloads.com/]www.metatrader-5-downloads.com/[/url] .
I have read so many posts regarding the blogger lovers except this post is genuinely a fastidious article, keep it up.
Replique montre cuir
shopnowdaily – Excellent daily deals, items were delivered fast and in great condition.
Coastline Hub Online – Finding items is easy, and the layout is peaceful and clear.
Здесь
[url=https://regionstal.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Тут походу новый лиа12 и подобные ему фишки, поперли отзывы, в жабу ломится всем продавцам предлагает за небольшую оплату вперед вес аш в моем регионе оставить.берегитесь! Я уже сталкивался с таким на главной, ждите продавца пусть сам объясняет.берегите деньги.быть такого не может, что магазин которому более 2х лет занимается доюавлениями в джабер и предложениями довезти стафф купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм магазин уже давно в тренде уже сколько лет
Sunwave Essentials Boutique Picks – Fast and comfortable browsing with a tidy design.
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
Cortina production company
First off I want to say fantastic blog! I had a
quick question which I’d like to ask if
you do not mind. I was interested to find out how you center yourself and
clear your head before writing. I’ve had a hard time clearing my thoughts in getting my thoughts out there.
I truly do enjoy writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes tend to be
lost just trying to figure out how to begin. Any
ideas or tips? Kudos!
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в краснодаре[/url]
interiorchoice – Items are lovely, site felt responsive while browsing.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста онлайн [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista-msk01.ru]Онлайн юридические консультации для всех[/url].
Варианты консультаций разнообразны: от личной встречи до дистанционного общения.
toptrendfashion – Fast page loads and effortless checkout, browsing was pleasant.
Наш подход строится на двух принципах: минимально достаточная фармакотерапия и прозрачные «коридоры безопасности». Это означает — никаких «универсальных капельниц» и полипрагмазии. Каждый компонент в схеме имеет проверенную цель: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, защитить слизистую, снизить вегетативный «шторм» и вернуть возможность естественного сна. Скорость и объём инфузий мы задаём инфузоматом, контролируя давление, пульс, сатурацию и самочувствие на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
отзывы ждем https://ukdsk.ru Заказала JV 61, жду трек, заранее благодарю. В прошлый раз заказ шёл 6 дней, но и я на краю географии)))))) отпишитп за дживик кто недавно заказывал.
Hey very cool website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb ..
I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds also?
I am happy to search out a lot of useful info right here within the post, we need work out
extra strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing.
. . . . .
battery bet
chiczone – Clean layout, intuitive navigation, very enjoyable browsing experience.
If you are going for most excellent contents like myself,
just pay a quick visit this web page everyday as it provides feature contents, thanks
Такая последовательность действий обеспечивает системное воздействие и минимизирует риски осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
https://englishzoom.ru/
Модные Тренды Мир моды с восторгом принял философию свободы и самовыражения, воплощенную в силуэтах оверсайз. Одежда оверсайз, отрицая сковывающие рамки традиционного кроя, дарит ощущение невесомости и легкости. Она деликатно скрывает несовершенства фигуры, позволяя каждой женщине почувствовать себя уверенно и комфортно. Женская одежда стремится выделить индивидуальность, ищете ли вы где купить худи или купить свитшот, нужно ориентировать на модные тренды и стиль, а узнать их можно в модном журнале, где представлен стильный бренд одежды. Мода 2026 – это время экспериментов!
Уважаемы участники форума! https://arzdetali.ru Написал о заказе в аське в ПТ,мне сказали цену и реквизиты. В СБ оплатил,кинул в аське свои реквизиты.В ПН связался-Сказали,что все отправили,ок.
Женская одежда Трикотаж, некогда скромный материал, триумфально воцарился на вершине модного Олимпа, превратившись из утилитарной ткани в символ комфортабельной элегантности. Толстовки, худи и свитшоты, словно триумвират уюта, покорили подиумы и сердца, стирая границы между спортивным шиком и повседневной практичностью. Эта триада – не просто предметы гардероба, а манифест свободы самовыражения, позволяющий создавать бесчисленное множество образов, от подчеркнуто расслабленных до дерзко-бунтарских.
Здесь
[url=https://legacyonlineschool.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
NR Boutique – Loved the modern styles and the checkout process was effortless.
Наркологическая помощь в Раменском в клинике «Возрождение» — это быстрый выезд профильного врача, безопасная детокс-терапия и полноценные программы восстановления без постановки на учёт. Мы работаем 24/7, аккуратно стабилизируем состояние на дому или принимаем в стационаре, подбираем лечение с учётом возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и текущих анализов. Уже при первом обращении координатор уточняет симптомы, оценивает риски, предлагает ближайшее окно выезда и объясняет, как подготовиться к визиту. Наша задача — не временно приглушить симптомы, а выстроить путь к устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациенту контроль над жизнью, при этом сохраняя конфиденциальность каждого шага.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-ramenskoe7.ru/]okazanie-narkologicheskoj-pomoshchi[/url]
Состав инфузии подбирается индивидуально по показателям и сопутствующим диагнозам. Чаще всего в схему входят следующие элементы:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov7.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
В этой статье рассматриваются различные аспекты избавления от зависимости, включая физические и психологические методы. Мы обсудим поддержку, мотивацию и стратегии, которые помогут в процессе выздоровления. Читатели узнают, как преодолеть трудности и двигаться к новой жизни без зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – http://dafna-clinic.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в москве[/url]
В этой публикации мы исследуем ключевые аспекты здоровья, включая влияние образа жизни на благополучие. Читатели узнают о важности правильного питания, физической активности и психического здоровья. Мы предоставим практические советы и рекомендации для поддержания здоровья и развития профилактических подходов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно Симферополь[/url]
If you want to improve your know-how simply keep visiting this web site
and be updated with the latest gossip posted here.
посылка пришла, все чотко, упаковка на высшем уровне, респектос купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази бро незнаю скок раз брал ни разу TS не подводил входил в положения скидки бонусы делал!!!
Kind Groove Hub – Items are presented nicely, making browsing enjoyable.
Excellent site you have here.. It’s hard to find excellent writing like
yours these days. I truly appreciate people like you!
Take care!!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about click site.
Regards
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/
Удобный и понятный сайт с богатством полезной информации по казино.
https://92.caiwik.com/index/download2?diff=0&darken=1&utm_source=og&utm_campaign=2564&utm_content=%5Bcid%5D&utm_clickid=vcc88ww8sosk84c0&aurl=http%3A%2F%2Folimp-casino-kz-online.org.kz&pushMode=popup
Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге — это востребованная медицинская услуга, позволяющая получить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Такой формат особенно актуален в ситуациях, когда пациент не может или не хочет обращаться в стационар. Выезд специалиста позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и оказать психологическую поддержку без нарушения анонимности.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru
Right now it appears like BlogEngine is the preferred blogging platform available
right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
консультация по банкротству Прежде чем инициировать процедуру, крайне важно получить всестороннюю информацию о её аспектах. Бесплатная консультация по банкротству или бесплатная консультация юриста по банкротству станет первым шагом к пониманию перспектив и потенциальных последствий. Важно выяснить, как происходит списание долгов по кредитам и какие долги списывают через банкротство, поскольку не все обязательства подлежат аннулированию. Квалифицированная консультация по банкротству физических лиц поможет сориентироваться в юридических тонкостях и разработать оптимальную стратегию. Онлайн консультация по банкротству – удобный формат для получения первичной информации. Решение о банкротстве сопряжено с рядом последствий, поэтому необходимо тщательно взвесить все плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица. К ним относится возможность списать долг по кредиту банкротство и начать жизнь с чистого листа. Однако, следует учитывать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это ответственный шаг, требующий соблюдения строгих правил и участия квалифицированных специалистов. Особое внимание следует уделить вопросам: процедура банкротства сроки проведения, процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам, процедура банкротства физического лица в суде, процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция.
Confidence Catalyst – Daily ideas to spark self-belief and personal growth.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/4z976un7
https://englishzoom.ru/
https://batery-game.com/
какие долги списывают через банкротство В лабиринте финансовых затруднений, когда долговое бремя угрожает стабильности, банкротство физических лиц выступает как законный механизм избавления от непосильных обязательств. Однако, это сложный процесс, требующий четкого понимания правовых норм и взвешенной оценки всех рисков. Определяющим фактором часто является банкротство физических лиц сроки процедуры, зависящие от ряда обстоятельств, включая сложность финансового положения должника и оперативность работы судебных органов.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3upwshhs
download mt5 for mac [url=metatrader-5-downloads.com]metatrader-5-downloads.com[/url] .
рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом [url=https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru/]рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом[/url] .
download metatrader 5 [url=https://www.metatrader-5-mac.com]download metatrader 5[/url] .
Перед таблицей важный переход: это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые заболевания и входное состояние, но логика последовательности остаётся неизменной — от безопасности к устойчивости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
помощь с рефератом
Могу предоставить переписку администрации форума. Уже определитесь, что вам нужно чтобы и мне не дергать отправщиков, склад и прочих сотрудников. То хочу, то не хочу, то вышлите 2 посылки, оплачу посфактум, то снова верните деньги. https://burenie-navody.ru то-же самое могу сказать!
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в краснодаре[/url]
??????
Эта информационная публикация освещает широкий спектр тем из мира медицины. Мы предлагаем читателям ясные и понятные объяснения современных заболеваний, методов профилактики и лечения. Информация будет полезна как пациентам, так и медицинским работникам, желающим поддержать уровень своих знаний.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Blue Grain Collective – Products were easy to find, and the site layout made browsing pleasant.
https://batery-game.com/bonus
giftcollectionhub – Pleasant shopping experience, everything was easy to find.
тоже хочу нахватить, но жду отзывы купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Добрый день, многим пришли посылки до НГ, 98% покупателей – перепроверено по трекам. Если есть вопросы пишите, в скайп или аську. В веточке пожалуйста, только по теме.
Стационар — это контролируемая среда, где меньше случайностей и выше скорость принятия решений. В палате рядом оборудование, пост медсестёр и врачебная переоценка по расписанию, поэтому тактика корректируется без задержек. Это особенно важно при длительных эпизодах и заметных колебаниях самочувствия, когда дома сложно обеспечить тихий режим и круглосуточное наблюдение. В «АльфаДетоксе» мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких избыточных седативных нагрузок и сомнительных «коктейлей», только то, что реально влияет на исход.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Pgsiam777
Перед таблицей важный переход: это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые заболевания и входное состояние, но логика последовательности остаётся неизменной — от безопасности к устойчивости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-foto[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://parkskazka.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
юридическая процедура банкротства физических лиц Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
Состав капельницы никогда не «копируется»; он выбирается по доминирующему симптому и соматическому фону. Ниже — клинические профили, которые помогают понять нашу логику. Итоговая схема формируется на месте, а скорость и объём зависят от текущих показателей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno
онлайн консультация по банкротству На начальном этапе целесообразно получить бесплатную консультацию по банкротству, чтобы оценить свои шансы на успех и получить ответы на интересующие вопросы. Бесплатная консультация юриста по банкротству поможет разобраться в законодательных тонкостях и определить оптимальную стратегию действий. Понимание того, как происходит списание долгов по кредитам в рамках процедуры банкротства, является ключевым моментом. Важно знать, какие долги списывают через банкротство, чтобы четко представлять конечный результат. Квалифицированная консультация по банкротству и консультация по банкротству физических лиц позволит получить полную информацию о процедуре и ее последствиях. Онлайн консультация по банкротству – удобный способ получить ответы на вопросы, не выходя из дома.
fashionhubzone – Fast-loading interface with items clearly visible and easy to explore.
WoodMarket Kindle – Fast website performance, great prices, and prompt delivery.
I’m not sure why but this blog is loading very slow for
me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end?
I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
My website : https://fly88.boston/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga017.ru
лечение запоя
Everything is very open with a really clear description of the issues.
It was definitely informative. Your site is very helpful. Many thanks for sharing!
нашли выход из ситуации, далее отпишусь. ))))))))))))) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану такая же фигня, продован сказал, что некоторые только начинаю мониториться! вообщем спср дерьмово работает!
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe this site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for
the info!
прогнозы на хоккей Ставки на спорт – это азартное развлечение, требующее аналитического подхода и понимания стратегий. Современный мир беттинга предлагает широчайший выбор возможностей: от классических видов спорта до киберспорта и экзотических дисциплин. Однако, важно помнить, что успех в ставках на спорт – это не только удача, но и результат кропотливого анализа, изучения статистики и учета множества факторов.
Dream Harbor Finds – The site loads fast and shopping feels smooth.
I got this website from my friend who shared with me on the
topic of this site and at the moment this time I am browsing this web page and
reading very informative articles or reviews here.
юридическая консультация по банкротству Компетентное ведение дела – залог успешного завершения процедуры банкротства физического лица через суд. Важно доверить процедуры банкротства должника физического лица опытным юристам, специализирующимся на банкротстве. Компания должна иметь безупречную репутацию. Только так можно быть уверенным, что процедура будет выполнена в соответствии с законом и все ваши права будут защищены.
Бро ты прав CHEMICAL-MIX.COM самый лучший магаз!!! https://moskva-autolombard.ru и всем мир бразы)
Что делаем
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-chekhove/
промокоды букмекеров Привлечение новых игроков и удержание существующих – это важная задача для букмекерских контор. Бонусы букмекеров и промокоды букмекеров – это эффективный инструмент для мотивации игроков и повышения их лояльности. Бонусы могут быть представлены в виде фрибетов, надбавок к депозиту, кэшбека и других интересных предложений. Важно внимательно изучать условия получения и использования бонусов, чтобы избежать недоразумений. Следить за новостями о ставках на спорт – это важный аспект успешного беттинга. Оперативная информация о травмах игроков, изменениях в составах команд, погодных условиях и других факторах, способных повлиять на исход матча, позволяет принимать своевременные решения и увеличивать свои шансы на выигрыш.
Hi there, constantly i used to check website posts here in the
early hours in the morning, for the reason that i enjoy to learn more and more.
metatrader 5 [url=https://www.metatrader-5-downloads.com]https://www.metatrader-5-downloads.com[/url] .
рулонные шторы на электроприводе [url=https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru]рулонные шторы на электроприводе[/url] .
metatrader 5 [url=https://metatrader-5-mac.com]metatrader 5[/url] .
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu/
Спасибо всем сотрудникам Chemical-mix.com https://serov1000.ru Золотые слова.
pragmatic slot
юридическая компания по банкротству физических лиц В лабиринте финансовых затруднений, когда долговое бремя угрожает стабильности, банкротство физических лиц выступает как законный механизм избавления от непосильных обязательств. Однако, это сложный процесс, требующий четкого понимания правовых норм и взвешенной оценки всех рисков. Определяющим фактором часто является банкротство физических лиц сроки процедуры, зависящие от ряда обстоятельств, включая сложность финансового положения должника и оперативность работы судебных органов.
finderfavhub – Very user-friendly, finding and purchasing products was easy.
юридическая консультация по банкротству На начальном этапе целесообразно получить бесплатную консультацию по банкротству, чтобы оценить свои шансы на успех и получить ответы на интересующие вопросы. Бесплатная консультация юриста по банкротству поможет разобраться в законодательных тонкостях и определить оптимальную стратегию действий. Понимание того, как происходит списание долгов по кредитам в рамках процедуры банкротства, является ключевым моментом. Важно знать, какие долги списывают через банкротство, чтобы четко представлять конечный результат. Квалифицированная консультация по банкротству и консультация по банкротству физических лиц позволит получить полную информацию о процедуре и ее последствиях. Онлайн консультация по банкротству – удобный способ получить ответы на вопросы, не выходя из дома.
Great post. I am dealing with some of these issues as well..
Поможем уличшить позиции сайта в поисковой выдачи за счет [url=https://kwork.ru/links/46928263/super-kachestvenniy-progon-poslednim-khrumerom-23] увеличеник ссылочной массы[/url] Хрумером 23
Топай в ТОП
товар 9\10 хорошее качество, 9 потому что ожидал чуть большего. https://chertiche.ru Бро ответь в аське!
Wild Horizon Boutique – Trendy products, easy-to-navigate website, and very fast checkout.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga018.ru
лечение запоя
anonymous chat rooms free chat website
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru
бонусы казино казіно з бонусами
shopcentral – Easy navigation, items are clearly displayed and accessible.
Bridgetown Finds – Shopping feels easy and the products are nicely displayed.
по ходу дела отпишусь. https://vilanaplus.ru в академе были пролёты
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Anyway I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-feodosiya-sukhum
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог санкт-петербург[/url]
У меня разок было, что трек перестал на два дня отслеживатся, но нечего доставили все пучком. https://vilanaplus.ru продавец шикарный – всё объяснил, рассказал.
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-essentuki-baksan
???????????????????????????????????
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и снятия интоксикации используются различные подходы. Врачи подбирают их индивидуально, исходя из состояния пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
I think that everything said was actually very logical.
But, what about this? suppose you were to write a killer headline?
I am not saying your information is not solid., however what if you added something that
grabbed a person’s attention? I mean Types of Cancer: Common &
Rare Cancers Explained is kinda boring. You ought to
look at Yahoo’s front page and watch how they create news
titles to get people interested. You might try adding a video
or a related pic or two to get readers excited about everything’ve written. In my opinion, it would make
your website a little bit more interesting.
автоматические рулонные шторы с электроприводом [url=http://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru]http://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru[/url] .
mt5 [url=http://www.metatrader-5-downloads.com]http://www.metatrader-5-downloads.com[/url] .
ca cuoc the thao online
https://marketgit.com/how-jennifer-lopezs-green-dress-changed-the-internet/
лучший веб хостинг в россии
fashion film production Milan Leading film production company in Milan: Recognized for innovative storytelling and captivating visuals, specializing in high-quality cinema and television projects.
В данной статье мы акцентируем внимание на важности поддержки в процессе выздоровления. Мы обсудим, как друзья, семья и профессионалы могут помочь тем, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. Читатели получат практические советы, как поддерживать близких на пути к новой жизни.
Детальнее – http://dafna-clinic.ru
https bs2web at
Все есть, объем большой https://art-tavrida.ru [hide=5]в аське появлялся днём видимо ненадолго, и снова нету ((
metatrader5 download [url=www.metatrader-5-mac.com/]www.metatrader-5-mac.com/[/url] .
https://www.lawglobalhub.com/flower-films-how-drew-barrymore-became-a-successful/
valuefindmarket – Loved the product variety, checkout was straightforward.
Milan production company Milan video production services: Offering a full spectrum of video solutions, from concept development to post-production, tailored to client specifications.
blsp at что это за сайт
It’s always great to see how fashion trends evolve while keeping timeless pieces alive. In the same way, mens leather jackets in US continue to be a wardrobe essential that never goes out of style. From rugged biker looks to sleek modern cuts, these jackets perfectly blend durability, comfort, and elegance. Whether styled casually or for a night out, they add instant confidence and edge to any outfit. The craftsmanship and quality materials make them a long-term investment for men who value both fashion and functionality.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar021.ru
вывод из запоя цена
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя Симферополь[/url]
Прислали нам свой метоксетамин, подтверждаем: продукт чистый, >99%. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
Grand Style Finds – Navigation is smooth and items are simple to explore.
Здесь
[url=https://avtomir.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
staycentral – Well-structured layout, products easy to explore, and navigation feels seamless.
Для многих барьер — страх огласки. В «РязМедСервисе» конфиденциальность обеспечивается не обещаниями, а процедурами: немаркированный выезд, шифрованный контур карт, ограничение доступа к данным по ролям, нейтральные формулировки в документах и чеках, отсутствие видеозаписей онлайн-сессий. Вы сами выбираете уровень информирования семьи: от полного молчания до адресной коммуникации с доверенным лицом. Визиты согласуются на «тихие окна», а уведомления не раскрывают суть обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в рязани[/url]
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-moskva-sochi
Ребят какие могут быть сомнения в этом магазе магаз ровный и заслуживает уважения он в доверенных его реклама на шляпе сайта ну это так для тех кто не знает просто реклама стоит 5000$ доларов! https://gds-center.ru Брал впервые в этом магазине, брал по рекомендации!
Этап
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Вас не будет эйфоретик убивать или сносить голову как Ск или еще какая хрень, тут легкий эффект эйфории с диссоциативом, Так сказать на любителя, просьба не путать продукт, вы прежде чем заказывать должны были ознакомится с веществом, можно погуглить и узнать что это такое, не надо утверждать что эйфоретик не прущий можете зайти в соседние темы там пишут совсем другие отзывы, а вас почему то не торкает оно как так. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Могу сфотать, на смотри
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
???????????????????????????????????
Эта статья освещает различные аспекты освобождения от зависимости и пути к выздоровлению. Мы обсуждаем важность осознания своей проблемы и обращения за помощью. Читатели получат практические советы о том, как преодолевать трудности и строить новую жизнь без зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно Симферополь[/url]
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Khao555 com
E2BET 香港官方網站 | 安全可靠,信譽保證
Can I simply say what a comfort to discover someone that really knows what they are talking about
on the web. You actually realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important.
More people must read this and understand this side of the story.
I was surprised that you are not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
EasyDrop является востребованным проектом для открытия кейсов со скинами в Counter-Strike 2.
Многим пользователям нравится, что здесь понятная система управления, позволяющий легко привыкнуть к работе платформы.
На ресурсе доступно множество коллекций, что делает использование интересным.
Создатели платформы поддерживают актуальными коллекции, чтобы пользователи видели свежие предметы.
бонус код изи дроп
Многие отмечают, что EasyDrop удобен в использовании благодаря структурированным разделам.
Также ценится то, что платформа предоставляет разные варианты взаимодействия, повышающие общую вариативность работы.
Тем не менее необходимо понимать, что любые действия на подобных платформах требуют взвешенного подхода.
В целом, EasyDrop воспринимается как онлайн-платформа для досуга, созданный для тех, кто интересуется коллекционными предметами в CS2.
Touche. Great arguments. Keep up the great effort.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets
I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some
time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience
with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything.
I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your
new updates.
Реально за***ли реклам-спаммеры :spam:, по две-три страницы одно и тоже, даже пропадает желание что либо читать…. таких как Nexswoodssteercan, Terroocomge, Vershearthopot, Soacomtimist и подобных надо сразу в баню отсылать, на вечно). купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Кто-нить брал тут 307 ?? просто ппц какой-то. уже 2 гр выкинул. Делал и 1к10 и чистым курил, ваще НОЛЬ. Как такое можт быть ?
мощные выделенные серверы
VPS для автоматизации
https://www.soft4led.com/why-jimmy-kimmel-is-the-man-of-the-youtube-era/
Daily Trend Spot – Browse carefully curated items for a smooth and effortless shopping experience.
Этот медицинский обзор сосредоточен на последних достижениях, которые оказывают влияние на пациентов и медицинскую практику. Мы разбираем инновационные методы лечения и исследований, акцентируя внимание на их значимости для общественного здоровья. Читатели узнают о свежих данных и их возможном применении.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в москве[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://profilance.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
https://www.lawglobalhub.com/flower-films-how-drew-barrymore-became-a-successful/
Future Groove Picks – The layout is modern, and finding items is effortless.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3ercw8vc
blsp at check
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/ywwuysz8
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому ростов-на-дону[/url]
blsp at сиськи тут
Morning Rust Corner Picks – Navigation is fast and exploring items feels easy.
Наш подход строится на двух принципах: минимально достаточная фармакотерапия и прозрачные «коридоры безопасности». Это означает — никаких «универсальных капельниц» и полипрагмазии. Каждый компонент в схеме имеет проверенную цель: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, защитить слизистую, снизить вегетативный «шторм» и вернуть возможность естественного сна. Скорость и объём инфузий мы задаём инфузоматом, контролируя давление, пульс, сатурацию и самочувствие на каждом этапе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
тут
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar022.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
staycorner – Smooth browsing, intuitive interface, and items are clearly presented.
https://podarki-moscow.ru/
Eco Cleaning Company was founded to provide top-tier, eco-friendly cleaning services focused on windows cleaning and exterior home care. As specialists in Dublin, we deliver comprehensive solutions that make your windows sparkle and your home s exterior shine: window cleaning south dublin
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/narkolog-krasnodar-anonimno/
pragmatic slot
Здесь
[url=https://nakovshah.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Для купирования абстинентного синдрома и снятия интоксикации используются различные подходы. Врачи подбирают их индивидуально, исходя из состояния пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
First of all I would like to say excellent blog! I had a quick question that I’d like
to ask if you do not mind. I was curious to find out how you center yourself and clear your thoughts prior
to writing. I have had difficulty clearing my mind in getting my
thoughts out. I truly do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes tend to be lost
just trying to figure out how to begin. Any recommendations or hints?
Kudos!
Someone essentially assist to make critically articles I’d state.
This is the first time I frequented your web page and to this point?
I amazed with the analysis you made to make this actual submit amazing.
Great process!
https://o2c3ds.ru/info/kak-vybrat-semena-gazonnyh-trav-dlya-raznyh-tipov-pochvy-v-moskve
Urban Peak Hub – Items load fast and navigating the site is simple.
https://cvetovodstvo.su/top-5-smesey-semyan-gazona-dlya-sportivnyh-i-detskih-ploschadok/
https://deratisation-hainaut.be/ru/zerkalo-sayta-gidra-ssylka-rabochaya-hyd_5099.html
Состав инфузии мы подбираем под доминирующие симптомы и сопутствующие заболевания. Цель — вернуть управляемость телу, а не «насытить» организм всем сразу. Матрица ниже демонстрирует клиническую логику: окончательное решение принимает врач после очной оценки.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Style Upgrade Daily – Simple ways to refresh your wardrobe with chic, trendy pieces.
https://podarki-moscow.ru/
Лечение начинается с короткой оценки рисков и выбора безопасной точки старта. Далее следуют этапы стабилизации, настройки сна и тревоги, поведенческие инструменты и план антирецидивной поддержки. Ниже — ориентировочная карта: в реальности длительности и интенсивность подбираются индивидуально, а переход между форматами происходит без «обнуления» обследований.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма санкт-петербург[/url]
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar023.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
EverPath Essentials – Everything loads fast and the interface is intuitive.
https://podarki-moscow.ru/
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в рязани[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к таблице, отметим смысл. Это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые диагнозы и динамику симптомов, но логика процесса остаётся неизменной: от безопасности к устойчивости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/]домашний вывод из запоя[/url]
Стандартизированный алгоритм позволяет действовать быстро и безопасно. Он гибко настраивается под конкретный случай, но всегда включает триаж, экспресс-диагностику, старт инфузии, симптом-менеджмент и выдачу плана на 72 часа с «коридорами безопасности».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Эвакуатор в Москве https://eva77.ru вызов в любое время дня и ночи. Быстрая подача, профессиональная погрузка и доставка авто в сервис, гараж или на парковку. Надёжно, безопасно и по фиксированной цене.
E2Bet adalah situs betting terbesar Se-Asia,
menawarkan platform permainan yang aman, terpercaya, dan inovatif, serta bonus menarik dan layanan pelanggan 24/7.
#E2Bet #E2BetIndonesia #Indonesia
Стандартизированный алгоритм позволяет действовать быстро и безопасно. Он гибко настраивается под конкретный случай, но всегда включает триаж, экспресс-диагностику, старт инфузии, симптом-менеджмент и выдачу плана на 72 часа с «коридорами безопасности».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
staycorner – Smooth browsing, interface is intuitive, and products are clearly presented.
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Подробнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
https://podarki-moscow.ru/
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены краснодар[/url]
Дом — это тишина, отсутствие «социального шума» и лишних свидетелей. Выездной врач «НоваТонуса» приезжает анонимно, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к терапии, сверяет совместимости с тем, что человек принимал за последние двое суток, проверяет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, кратко оценивает неврологический статус и уровень тревоги. Только после допуска запускается индивидуальная инфузионная поддержка: коррекция воды и электролитов, защита органов мишеней, симптом-контроль тошноты и головокружения, при показаниях — мягкая настройка сна без избыточной седации. В конце визита — переоценка, перевод на per os-схемы, памятка на 24–48 часов и заранее оговорённое окно контрольного контакта. Такой маршрут даёт устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю, а не минутное облегчение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-lobne/
Dawncrest Central – Shopping is convenient and the layout is clear and tidy.
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Booking your domestic windows cleaning and other services in Dublin is simple on our website. For commercial or tailored cleaning needs, just contact us. Trust Eco Cleaning Company Dublin for dedicated, expert windows cleaning and exterior home maintenance: window cleaning dublin
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar024.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/
Expert Windows Cleaning with Spotless, Streak-Free Results – Plus Crystal-Clear Gutters Without Chemicals: https://ecocleaningcompany.ie/
Lunar Wave Hub Picks – Effortless browsing with a neat and organized interface.
Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге — это востребованная медицинская услуга, позволяющая получить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Такой формат особенно актуален в ситуациях, когда пациент не может или не хочет обращаться в стационар. Выезд специалиста позволяет стабилизировать состояние, снять интоксикацию и оказать психологическую поддержку без нарушения анонимности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
заказать девушку спб Снять девушку СПб: Выбирая спутницу для вечера, обращайте внимание не только на внешность, но и на ее интересы, увлечения и взгляды на жизнь. Важно, чтобы она была вам интересна как личность, а не только как объект желания.
choicehub – Navigation is intuitive, and products are clearly displayed.
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике санкт-петербург[/url]
Первые сутки после прекращения алкоголя — самые уязвимые: именно в это время нарастают абстинентные симптомы и риск осложнений. Ниже приведены основные ситуации, при которых нужен быстрый выезд врача. Перед списком отметим: если сомневаетесь, позвоните координатору — он уточнит признаки и подскажет безопасные действия до прибытия команды.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/
Если по ходу первичного осмотра выявляются «красные флаги» (спутанность сознания, нестабильное давление/ритм, кровавая рвота, подозрение на делирий), врач немедленно предложит госпитализацию и аккуратно организует перевод — безопасность всегда выше удобства.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-zhukovskij7.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-zhukovskom
азотная кислота оптом РТХ предлагает гибкие условия поставки и конкурентоспособные цены, обеспечивая максимальную выгоду для наших клиентов
скачать игры с яндекс диска Скачать игры без торрента: Мир мгновенных развлечений. Забудьте о сложных установках и длительном ожидании! Откройте для себя библиотеки игр, предлагающие прямые ссылки на загрузку, где каждая игра – на расстоянии одного клика. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит свое время и предпочитает моментальный доступ к новым игровым мирам. Исследуйте захватывающие приключения, динамичные экшены и головоломные стратегии без лишних хлопот. Готовьтесь к мгновенному погружению в игровой процесс!
Современная наркология — это не набор «сильных капельниц», а точные инструменты, управляющие скоростью и направлением изменений. В «НеваМеде» технологический контур работает тихо и незаметно для пациента, но даёт врачу контроль над деталями, от которых зависит безопасность.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru
멋진 포스트. 저는 매일 블로그에서 새로운 것을 배우고 도전받습니다.
다른 저자의 콘텐츠를 읽고 그들의 웹사이트에서 조금 배우는 것은 항상 도움이 되고.
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I certainly enjoyed reading
it, you happen to be a great author.I will always
bookmark your blog and definitely will come back down the road.
I want to encourage continue your great work, have a nice day!
Your website is a breath of fresh air! The way you present
online bestellen viagra is both engaging and insightful.
I’ve shared this with my network. Any plans to create video content to
complement your posts? Thank you for the great work!
이 블로그를 발견한 게 행운이에요! viagra sirve
mujeres para el las에 대한 글이 너무 흥미롭고 잘
쓰여 있어요. 소셜 미디어에서 공유했어요.
게스트 포스트로 다른 사이트와 협업할 계획
있으신가요? 고맙습니다!
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!!
Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Cheers!
저는 Concepcion 입니다. 18 March 1973 에 태어났어요.
취미는 Footbag 와 Fishing 입니다.
반갑습니다!
저는 Concepcion 라고 합니다.
요즘은 Tennis 에 푹 빠져 있고, 시간 날 때마다 Vietnamese
를 조금씩 공부하고 있어요.
새로운 사람들을 만나고 대화 나누는 걸 좋아합니다.
|
짧게 말하면,
저는 Australia 출신의 19살 Concepcion 입니다.
현재는 Agriculture and Life Sciences 를
공부 중이며 미래에는 Tennis 관련 일을 하고 싶어요.
|
안녕하세요, Concepcion 입니다.
저는 Merricks 에 살고 있고 곧 Agriculture
and Life Sciences 전공으로 졸업을 앞두고 있어요.
여가 시간에는 Painting 또는 CSI 보는 걸
즐깁니다.
|
안녕 여러분!
저는 Concepcion (17살)이고 Australia에서 왔어요.
성격은 조용한 편이지만 새로운 걸 배우는 건 정말 좋아해요.
특히 Vietnamese 배우는 것에 흥미가 있어요.
|
저는 Concepcion 이고 현재 Merricks 에서 혼자 살고 있어요.
요즘 취미는 Fencing 하고 Herpetoculture 입니다.
언젠가 Australia 전체를 여행해 보는 것이 꿈이에요.
|
안녕하세요!
제 이름은 Concepcion 이고 나이는 37살입니다.
저는 Agriculture and Life Sciences 공부를 시작한 지 2년 되었어요.
이번 해에는 Tennis 를 더 깊게 배워보고
싶어요.
|
Australia 에 사는 Concepcion 입니다.
저는 Merricks에서 자랐고 지금도 그곳에 살고 있어요.
특히 주말에는 CSI 를 정주행하거나 Tennis 를
하며 시간을 보냅니다.
|
저는 Concepcion 이고 43살이에요.
일하면서 틈틈이 Vietnamese 를 배우고 있어요.
언젠가 해외여행을 가서 직접 사용해
보는 것이 목표입니다.
취미는 Equestrianism 입니다.
|
안녕! 제 이름은 Concepcion.
지금은 Agriculture and Life Sciences 를 공부 중이고
졸업 후에는 관련 직종에서 일하는 것이 목표예요.
쉬는 날에는 Climbing, Climbing 그리고
친구들과 CSI 보는 걸 좋아해요.
|
안녕하세요, Concepcion 입니다.
저는 Australia에서 태어났고 Merricks에서 자라왔어요.
성격은 활발한 편이고 사람들과 이야기하는 걸 좋아합니다.
취미는 Tennis 와 RC cars 에요.
|
저는 Concepcion.
현재 Merricks 에서 가족과 함께 살고 있고,
2마리의 반려동물을 키우고 있어요.
주말에는 주로 CSI 보거나 Tennis 하면서 시간을 보내요.
|
안녕하세요!
제 이름은 Concepcion 이고 나이는 30살
이에요.
저는 Merricks 출신이고 지금은 Agriculture and Life Sciences 를
공부하고 있어요.
목표는 외국어인 Vietnamese 를 유창하게 말하는 것입니다.
|
저는 Concepcion 이고 매일 Tennis 를 하면서 스트레스를 풀어요.
집은 Merricks에 있는데, 이곳은 정말 조용하고 살기 좋아요.
기회가 된다면 다른 도시도 알아보고 싶어요.
|
하이!
저는 Concepcion 입니다.
일을 하면서도 꾸준히 Vintage Books 를 배우고 있어요.
최근에는 CSI 에 빠져서 시간 가는 줄 모르겠어요.
|
제 이름은 Concepcion (32살)입니다.
가족 구성원은 4명이고 모두 Tennis 을/를 좋아해요.
저도 여가 시간에는 독서나 Genealogy 를 즐깁니다.
|
저는 Concepcion 이고 현재 Agriculture and Life
Sciences 관련 일을 하고 있어요.
지식 늘리는 걸 좋아해서 외국어 Vietnamese 도 배우고 있어요.
좋아하는 취미는 Table tennis 와 CSI 입니다.
|
안녕하세요, 저는 Concepcion 입니다.
새로운 사람들과 소통하고 여러 가지 취미를 공유하는 걸 좋아해요.
특히 Tennis 에 관한 이야기를 하면 시간 가는 줄 몰라요.
|
저는 Concepcion 이고 Australia 의 작은 마을에서 자랐어요.
현재는 Merricks 에 있지만 가끔 고향이 그리워요.
취미는 Crocheting 입니다.
비아그라는 남성 건강을 위해 흔히 사용되는 약물입니다.
정확한 복용법과 효과는 의사와 상담 후 확인하세요.
|
VGR는 발기 부전 치료에 도움을 줄 수 있으며,
적절한 사용 시 안전하고 효과적입니다.
|
많은 남성이 비아그라를 통해 삶의 질을 개선하고 있습니다.
복용 전에는 부작용과 주의사항 꼭 확인하세요.
|
비아그라는 일반적으로 성인 남성에게 사용되며,
심혈관 질환이 있는 경우 복용 전에 전문가 상담이 필요합니다.
|
VGR는 빠른 효과를 원할 때 주로 사용되며,
효과를 높이려면 정해진 시간에
복용하는 것이 좋습니다.
|
비아그라는 식사와 관계없이 복용 가능하지만,
고지방 음식과 함께 복용 시 효과가 감소할 수 있습니다.
|
VGR 복용 후 일부 남성은 두통, 얼굴 홍조, 소화불량을
경험할 수 있습니다.
문제가 지속되면 즉시 의료진 상담을 권장합니다.
|
비아그라는 정기적인 건강 관리와 병행하면 더욱 효과적입니다.
운동과 건강한 식습관과 함께 사용하면 좋습니다.
|
VGR는 온라인에서도 안전하게 구매할 수 있으나,
항상 공인 약국를 이용하세요.
|
비아그라 사용 후 만족도가 높은 사용자들은
사용 경험을 공유하며 많은 남성에게 도움을 주고 있습니다.
|
VGR는 의사의 처방과 지침을 따라 복용해야 안전합니다.
복용 전 전문 상담이 필요합니다.
|
비아그라를 복용하면 성기능 개선뿐 아니라
삶의 질 개선에도 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
|
VGR는 다양한 제형과 용량으로 제공되므로,
개인 상황에 맞게 적절한 용량 선택하는 것이 중요합니다.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Starlit Style Stop – Products are well arranged, and shopping is quick.
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому ростов-на-дону[/url]
Pgsiam777
В условиях медицинского контроля специалисты выполняют последовательные действия, направленные на стабилизацию состояния пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
документы для оценки ущерба после залива [url=https://ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-5.ru/]документы для оценки ущерба после залива[/url] .
филлер [url=http://www.filler-kupit.ru]филлер[/url] .
Важная деталь — отсутствие полипрагмазии. Мы используем «минимально достаточную фармакотерапию»: каждый препарат имеет цель, окно эффективности и критерии отмены. Это снижает побочные эффекты, убирает «тяжесть» днём и делает восстановление более естественным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
blsp at клады рядом
курсовые заказ [url=http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru]http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru[/url] .
сколько стоит сделать курсовую работу на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-5.ru/]сколько стоит сделать курсовую работу на заказ[/url] .
Ниже представлена карта действий бригады «РязМедСервиса» в первые три часа. Это не «жёсткая сетка», а ориентир для безопасной и быстрой стабилизации. В каждом блоке есть клиническая цель, измеримые критерии и условие для перехода к следующему шагу.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому рязань[/url]
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов Симферополь[/url]
В этой публикации мы исследуем ключевые аспекты здоровья, включая влияние образа жизни на благополучие. Читатели узнают о важности правильного питания, физической активности и психического здоровья. Мы предоставим практические советы и рекомендации для поддержания здоровья и развития профилактических подходов.
Подробнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в москве[/url]
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя Симферополь[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://dav.kz/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
What’s up, after reading this amazing piece of writing i am too happy to share my know-how here with colleagues.
Brazil prostitution
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar025.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
הוא לא חיכה, הוא פשוט ניגש, העביר אותם דרך פתח הנרתיק, כל הליחה, ו . ונכנס פנימה. לא לגמרי, את ירכיי עוד יותר חזק תוך כדי שמירה על המשחק. נשפתי, מנסה לשמור על הקול שלי רועד מכל תנועה מיקרו https://sexor.co.il/
https://vseokrovle.com/besedka/2115-chem-otlichayutsya-odnoletnie-i-mnogoletnie-travy-dlya-gazona.html
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Даже при амбулаторном ведении мы следуем принципам доказательной медицины: пошаговая титрация, ясные коридоры безопасности, пересмотр решений строго по показателям. Мы объясняем, на что ориентироваться в первые часы после визита: диапазоны давления и пульса, ориентиры самочувствия, правила питания и питья, поведенческие «якоря» на случай, если тревога неожиданно вырастет вечером. Благодаря этому пациент и его семья не остаются один на один с вопросами; наоборот — у них есть карта маршрута и контакты людей, готовых включиться в течение минуты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/krasnodar-narkologicheskij-czentr/
בהן שום מבוכה. רק אתגר. וציפייה. הלב שלי פועם אי שם בגרון. היד עצמה הושיטה יד אליה, כאילו בניגוד והרגיש רעד קטן. זה לא נמשך יותר מדקה, ואז היא המשיכה לנוע, אבל לאט יותר. וכשהרגיש מה מתאים לי, https://messer-spa.co.il/
Smart Buy Daily – Tips for purchasing quality products at the right price.
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Перед началом терапии важно оценить состояние пациента и выявить сопутствующие заболевания. После этого назначается комплексное лечение, которое позволяет восстановить здоровье и подготовить к дальнейшей реабилитации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в рязани[/url]
Life Coach Rudolfo shines as the foremost life coach in Haarlem offering outstanding guidance and support for clients
seeking personal growth and evolution. His approach is
personalized to meet each client’s distinct needs, guaranteeing efficient strategies that lead to permanent positive change.
With years of experience, Rudolfo has developed a deep understanding of human behavior and motivation, making his coaching
sessions meaningful and powerful. Clients respect his attentive listening and realistic advice, which builds a supportive environment where they gain confidence to follow their goals and defeat obstacles.
Life Coach Rudolfo employs proven techniques to help clients develop confidence,
refine decision-making, and support overall well-being.
His focus to constant improvement and professional development makes certain he stays updated
with the newest coaching methodologies. Many people
in Haarlem have taken advantage of his customized coaching programs, which focus on career development, relationships, and personal fulfillment.
Rudolfo’s dedication to his clients’ success is apparent in the enthusiastic testimonials and enduring results
they achieve. He offers a welcoming space for reflection and growth, supporting clients to realize their full potential and live
more purposeful lives. Whether confronting difficulties or striving for greater achievements,
Life Coach Rudolfo delivers the tools and motivation needed to
succeed. For those seeking the best life coaching in Haarlem, his knowledge and caring approach make him the ideal choice for
transformative personal development.
Тебе когда отправили? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Магаз отличный, успехов вам!
Палата — это контролируемая среда: аппаратный мониторинг, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, пост медсестёр 24/7, переоценки по графику и быстрая коррекция тактики без логистических пауз. Такой старт рационален при длительных эпизодах, выраженных колебаниях давления и пульса, повторных судорогах, неукротимой рвоте и признаках надвигающегося делирия, а также если дома невозможно обеспечить «тихий режим» и присутствие взрослого помощника ночью. В стационарной ветке меньше случайностей, а путь до стабильного сна короче.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Timberline Emporium – Browsing feels effortless and the layout is well-organized.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в рязани[/url]
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница ростов-на-дону[/url]
מיד לשיחה איתנו. למרות שהם היו הרבה יותר מבוגרים מאיתנו, הם התנהגו כשווים איתנו, ולעתים קרובות שטוחה ושלל אלסטי בכלל לא בגיל. ובין הרגליים . היה כוס כל כך מטופח, כבר רטוב. הכל היה מבריק. https://sexydon.co.il/
wearcorner – Smooth interface, intuitive navigation, and items are easy to explore.
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в краснодаре[/url]
А будете ли работать в Беларусии? https://tesla36.ru 3случая за последние 2недели.. если быть точнее..
Девочки по вызову Заказать девушку СПб: Заказ эскорт-услуг – это возможность создать вечер своей мечты, где каждая деталь продумана до мелочей и соответствует вашим самым смелым фантазиям.
Valuable info. Fortunate me I discovered your site unintentionally, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
https://hstq.net/vps.html
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в рязани[/url]
FutureGardenPortal – Organized pages and smooth menus made finding items enjoyable.
снять шлюху спб Вызвать девушку СПб: Услуга вызова – это прекрасный способ внести разнообразие в свой досуг, добавить щепотку авантюры и создать незабываемую атмосферу.
Наблюдение за серверами является важной задачей для обеспечения надежности инфраструктуры.
Он позволяет выявлять неполадки на первых шагах развития проблем.
Быстрое выявление проблем снижает риск нарушений работы сервисов.
Многие компании ценят, что регулярный мониторинг обеспечивает бесперебойность.
Профессиональные решения позволяют отслеживать состояние в реальном времени.
Мгновенные оповещения помогают немедленно принимать меры и минимизировать последствия.
Кроме того, контроль оптимизирует работу серверов и снижает расходы.
Таким образом, регулярный мониторинг серверов — это основа для надежной работы IT-систем.
http://terriers-place.co.uk/phpBB3/viewtopic.php?t=15350
Здесь
[url=https://ohi-s.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Даже если кажется, что «пройдёт само», при запойных состояниях осложнения нарастают быстро. Перед списком отметим логику: показания к инфузионной терапии определяет врач по совокупности симптомов, хронических заболеваний и текущих показателей. Ниже — типичные ситуации, при которых капельница даёт предсказуемый клинический эффект и снижает риски.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-vidnoe7.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Подробнее тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru
Rubbish Taxi removes and responsibly disposes of unwanted household items like appliances, furniture, sofas, mattresses and yard waste https://rubbish-taxi.ie/mattress-disposal-dublin/
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Скачать игры с Яндекс Диска: Персональная игровая библиотека всегда под рукой. Яндекс Диск – это не просто облачное хранилище, но и удобная платформа для обмена находками с друзьями и создания собственной коллекции. Делитесь любимыми играми, скачивайте новинки и наслаждайтесь совместным игровым опытом. Это отличный способ расширить горизонты и всегда иметь доступ к любимым развлечениям, где бы вы ни находились. Превратите Яндекс Диск в свой личный игровой рай!
לזרמי האוויר. הדירות הנפרדות שלנו במקור (ועל פי כל המסמכים עד כה) היו שני חדרי שינה. מדלת הכניסה, לאט לאט, כאילו בהפגנה, היא הכניסה את בהונותיה לפה, ליקקתי אותן והיא הושיטה יד לעברי. היא העבירה https://coupleschoice.com/
«НоваТонус» — это связанный маршрут наркологической помощи для жителей Лобни и округа: оперативный выезд врача на дом, аккуратный домашний детокс без «универсальных коктейлей», стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением, подготовка к кодированию по показаниям и поддержка семьи в первые недели. Мы действуем по принципу клинической достаточности: каждое назначение обосновано, объясняется простым языком и привязано к реальным целям — безопасно снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, мягко вернуть сон, а затем провести первую «тихую» неделю без качелей. Приватность встроена в процесс: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральный канал связи, документы по запросу и в сдержанной формулировке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Бывает, что нужна помощь не только с входной дверью: кто-то заказывал вскрыть шкафчик замок спб, вскрытие замка шкафа спб, вскрыть велосипедный замок тросовый спб или вскрытие навесного замка гараж спб. Плюс у охотников периодически всплывает вопрос открыть оружейный шкаф спб без повреждения. Во всех этих случаях важно, чтобы мастер не просто вскрыл, но и предложил адекватную замену. В этом плане удобно, когда есть поставщик фурнитуры, как https://avers-zamki.ru/, где можно сразу подобрать новый замок, защелку или цилиндр, а не ставить первую попавшуюся дешевую личинку.
скачать игры без торрента Скачать игры по прямой ссылке: Скорость – ваш союзник, удобство – приоритет. Прямые ссылки – это кратчайший путь к вашим игровым желаниям. Никаких дополнительных программ, никаких рисков подхватить вирус – только чистые файлы, готовые к установке. Наслаждайтесь максимальной скоростью загрузки и моментальным погружением в игровой процесс.
את כל החדשות מאה פעמים. שעמום הוא בן תמותה. דלת התא נפתחת. זו המנחה, אירינה בשמה, על השלט. היא שעברה וטחב לח. ניסיתי להכות אותו, לדחוף אותו, אבל הוא דחף את מפרקי ידי מעל ראשי בתנועה אחת. משקלו https://messer-spa.co.il/
стеариновая кислота купить оптом Сотрудничество с РТХ – это гарантия стабильного и успешного развития вашего бизнеса в динамичном мире современной промышленности
Лобня — город коротких дистанций, но в острых ситуациях решает не километраж, а управляемость. Мы убираем паузы между решением обратиться и реальной помощью: на звонке быстро оцениваем риски, предлагаем безопасный старт в квартире или в палате, согласуем окно прибытия, объясняем что подготовить, и фиксируем честный диапазон стоимости. Цель — чтобы первые часы прошли по понятному плану, а не вслепую.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-lobne-stacionar/
Всем все выслано. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази 1)Кто курит каждый день : от 2 часов до 3-4 часов
ортофосфорная кислота оптом РТХ: широкий спектр химической продукции для различных отраслей промышленности, от базовых химикатов до специализированных реагентов
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
помощь при запое 24/7
ca do bong da tren mang
featured store – Had a smooth time scrolling through; products were easy to locate.
курсовой проект купить цена [url=https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru]https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru[/url] .
Петербургский темп жизни — поздняя занятость, переменная нагрузка, сезонные перепады света — усложняет восстановление после эпизодов употребления. Поэтому мы разработали модульные программы, способные гибко подстраиваться под график и биоритмы: у кого-то «трудные часы» приходятся на поздний вечер на Васильевском острове, у кого-то — на раннее утро перед сменой в Адмиралтейском районе. Маршрут строится вокруг человека, а не вокруг расписания кабинета: очные приёмы, немаркированные выезды на дом, дневной стационар, защищённые онлайн-сессии — всё объединено единым клиническим планом и общими целями.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
khao555 login
сайт заказать курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-5.ru/]сайт заказать курсовую работу[/url] .
שלי, על זרועי, עדיין אוחזת בזין המעורער שלי, ועלה לאט אל פני, בוער מבושה. חיכיתי לצעקה, לשיחת צעירות, אשר תמורת תשלום, מוכנים להאיר את חיי היומיום האפורים, מותשים על ידי נהגים יקרים, לא רק https://coupleschoice.com/
shop horizon hub – Clean layout and tidy presentation made finding items effortless.
Ну что кто нить УРБ попробовал уже как отзывы ? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш это манера такая сдержанная или удовлетворительное=на троечку
It’s wonderful that you are getting thoughts from this article as well
as from our discussion made here.
horizon picks hub – Fast-loading pages and organized layout made shopping effortless.
When some one searches for his required thing, so he/she wishes to be
available that in detail, thus that thing is maintained over here.
Наша философия проста: минимум медикаментов, максимум управляемости процесса. Мы не используем «универсальные капельницы», а собираем схему под клиническую картину: длительность запоя, выраженность тремора и тошноты, качество сна, уровень тревоги, исходное давление и частоту пульса, сопутствующие заболевания, текущие лекарства (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие, средства для сна). Скорость инфузии задаётся инфузоматом, витальные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, глюкоза и электролиты — по экспресс-панелям. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и делает результат предсказуемым и устойчивым.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/krasnodar-narkologicheskij-czentr
birchstorecorner – Items are easy to browse, and navigating feels effortless.
It’s very straightforward to find out any
topic on web as compared to books, as I found this article at this web page.
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Trendy Choice Spot – Browse stylish items with ease and enjoy navigating categories.
Эти шаги помогают системно подойти к проблеме и обеспечить максимальную эффективность лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan14.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
atticideascenter – Creative layout and interactive tools make learning and creating enjoyable.
Прежде чем перейти к таблице, отметим смысл. Это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые диагнозы и динамику симптомов, но логика процесса остаётся неизменной: от безопасности к устойчивости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/]вывод из запоя в клинике[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.kinoafisha.info/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Rubbish Taxi removes and responsibly disposes of unwanted household items like appliances, furniture, sofas, mattresses and yard waste https://rubbish-taxi.ie/mattress-disposal-dublin/
Этот обзор сосредоточен на различных подходах к избавлению от зависимости. Мы изучим традиционные и альтернативные методы, а также их сочетание для достижения максимальной эффективности. Читатели смогут открыть для себя новые стратегии и подходы, которые помогут в их борьбе с зависимостями.
Выяснить больше – http://dafna-clinic.ru
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thanks for providing these details.
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница ростов-на-дону[/url]
WildBranchMarket – Very easy to navigate, products are displayed clearly and attractively.
На днях брал небольшой опт, был приятно удивлен подходом и предложением тс, товар еще не пробовали ,но забрал все ровно, по ходу отпишу в теме за качество товара, пока же могу сказать, что жалею , что раньше не работал с данным тс! Успехов, благодарю за сервис!!! https://smileclinic-maykop.ru по заказу?)Всем привет. Первый раз беру товар у этого магазина. По треку моя посылка поступила в курьерку в понедельник и до сих пор не была отправлена. Каждый день в информации по трек номеру дата отправки переносилась. О СПРС давно уже легенды ходят, я не понимаю почему магазин сотрудничает с ними.
Your blog is a source of inspiration, offering fresh insights that challenge and engage. It would be intriguing to see you examine how these themes intersect with modern innovations, such as artificial intelligence or sustainable living. Your knack for making the abstract tangible is remarkable. Thanks for consistently delivering such impactful content—I’m excited for your next piece!
click: https://crowdlinkbuilding.com/
backlinks seo buy
слоти ігрові автомати популярні слоти
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в ростове-на-дону[/url]
проститутки нижневартовск вип
Sun Meadow Corner Finds – Pleasant browsing experience with intuitive design and fast loading.
натяжной потолок спб цены Монтаж натяжного потолка: Быстро, качественно, надежно Профессиональный монтаж натяжного потолка – залог его долговечности и эстетичного внешнего вида. Доверьте эту работу опытным специалистам, которые быстро и качественно установят потолок любой сложности, учитывая все особенности вашего помещения. Правильный монтаж обеспечит идеально ровную поверхность, отсутствие провисаний и деформаций, а также долговечность конструкции.
Wonder Peak Studio – Fast and comfortable navigation makes shopping enjoyable.
https bs2web at
Домашний визит особенно уместен при затянувшемся употреблении, когда нарастают тревожные вегетативные симптомы (тремор, потливость, сердцебиение), появляются проблемы со сном и «качели» давления, но при этом сохранён контакт, нет выраженной дыхательной недостаточности и глубокой дезориентации. Преимущества очевидны: экономия времени (нет дороги и ожидания), психологический комфорт, меньше сенсорных триггеров (яркий свет, шум), возможность сразу настроить режим первой «тихой ночи». Технологически выездная бригада оснащена как приёмный кабинет: инфузомат для точной скорости капания, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, кассеты Na?/K?, портативный кардиомонитор с возможностью регистрации ЭКГ, набор проверенных средств для коррекции тошноты и защиты слизистой. Если во время триажа выявляются «красные флаги» — риск судорог, падение сатурации, признаки делирия, нестабильная гемодинамика, — мы организуем перевод в стационар «КубаньМедЦентра» без задержек и с непрерывностью терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar14.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
At Rubbish Taxi, we manage your house clearance requirements, whether it is a home renovation, room redecoration, or clearing out old items. Our services cover comprehensive house removals and clearances across Dublin and other cities where we operate. We can collect various bulky items, including sofas, bed frames, mattresses, chest of drawers, wardrobes, fridges, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers, ovens, musical instruments, and more. Count on us for a seamless experience: Sofa disposal
globalshoppinghub – Fast, intuitive interface, and products are neatly categorized.
https blsp at
My brother recommended I might like this web site. He was totally right.
This post actually made my day. You can not imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
П-т!! Пишу свой отчерк. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Заливают паршивым вином.Джи спокойно 20-ого числа 😉 Потом вот только как получать будешь…?
При оказании помощи используются современные медикаментозные средства, направленные на устранение интоксикации и стабилизацию функций организма.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
Одна и та же «капельница на всех» не работает: у одних доминирует обезвоживание, у других — тахикардия и тревога, у третьих — желудочные симптомы и нагрузка на печень. Ниже — ориентиры по выбору инфузионных схем и целей вмешательства; окончательный состав подбирается врачом исходя из клинической картины и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
CTO Timber Selection – Simple design and smooth browsing created a nice overall experience.
Капельница для лечения запоя – это эффективный метод, применяемый наркологами для очистки организма. Специалист по зависимостям на дому из клиники предлагает анонимное лечение, обеспечивая абсолютную анонимность для обращающегося за помощью. Выезд врача на дом позволяет быстро ощутить медицинскую помощь и возвращение к нормальной жизни, что особенно значимо для страдающих от запоя. Нарколог на дом клиника Процедура включает в себя капельницы, которые помогают облегчить симптомы абстиненции и предотвращают осложнения. Профессиональная поддержка нарколога на дом предоставляет возможность пройти терапию зависимости в комфортной обстановке, что исключает стресс от нахождения в медицинском учреждении. Это – эффективное восстановление от запоя, которое предоставляет возможность начать новую жизнь без алкоголя.
At Rubbish Taxi, we manage your house clearance requirements, whether it is a home renovation, room redecoration, or clearing out old items. Our services cover comprehensive house removals and clearances across Dublin and other cities where we operate. We can collect various bulky items, including sofas, bed frames, mattresses, chest of drawers, wardrobes, fridges, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers, ovens, musical instruments, and more. Count on us for a seamless experience https://rubbish-taxi.ie/sofa-disposal-dublin/
trend corner – Enjoyed checking out the selections; everything was easy to locate.
Что посмотреть в Ялте Экскурсии по Ялте: Путешествие в историю и красоту Ялта – это город, где каждая улочка дышит историей, а горные пейзажи захватывают дух. Экскурсии по Ялте позволяют прикоснуться к величию прошлого, увидеть роскошные дворцы, прогуляться по живописным набережным и насладиться атмосферой южного гостеприимства. Откройте для себя Ялту с новой стороны, узнайте ее секреты и легенды.
вообще ктонибудь в этом магазине еще заказывал?? получал что нибудь ? или хотя бы треки бились? https://kafeterij.ru доставка порадовала быстро качественно . насчет реагента который был указан 1 к 15 шас насайте он же стоит 1 к 10 такова говна еше не пробывал ( извените если кого обидел) 5 мин прет и все даже пролонгатор увеличил действие до 15 мин . за сам магазин нечего плохова сказать не могу брал раньше рега была отбойной и цены радуют … Но последния рега просто выкинуть что ли ее . сегодня попробую конечно 2 к 10 сделать если не поможет просто выкину ..Что ж ты такой нетерпеливый… ))
new horizon corner – Fast-loading pages and tidy layout enhanced the experience.
goldenartcorner – Smooth browsing and well-arranged products, I found everything effortlessly.
помощь курсовые [url=http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru]http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru[/url] .
В первые часы важно не «залить» пациента растворами, а корректно подобрать темп и состав с учётом возраста, массы тела, артериального давления, лекарственного фона (антигипертензивные, сахароснижающие, антиаритмические препараты) и переносимости. Именно поэтому мы не отдаём лечение на откуп шаблонам — каждая схема конструируется врачом на месте, а эффективность оценивается по понятным метрикам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani14.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в рязани[/url]
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
tallbirchcollective – User-friendly interface, shopping flows naturally and easily.
shop golden horizon – Fast-loading pages and easy navigation improved the experience.
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback?
If so how do you stop it, any plugin or anything
you can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad
so any support is very much appreciated.
Fast Relief Hypnotherapy is the premier hypnosis clinic in Virginia
because it offers personalized and successful interventions
for various issues. Clients gain speedy and enduring effects through bespoke appointments that target their unique
needs. The staff at Fast Relief Hypnotherapy is well-trained
and adept in utilizing proven approaches to help people manage challenges such as anxiety, stress, tobacco cessation and weight loss.
The welcoming and supportive environment helps customers
feel at ease and safe during their treatments. Fast Relief
Hypnotherapy uses a holistic approach that targets the subconscious mind to generate
constructive transformations in habits and perspective. Many individuals experience marked progress after just a few appointments.
The facility is famous for its qualified and compassionate team who are dedicated to helping
each person achieve their objectives. Fast Relief Hypnotherapy also delivers continued guidance and guidance to guarantee lasting success.
The center stays up to date with the latest innovations in hypnosis to provide the best treatment possible.
Patients like the convenient facility and adaptable booking choices that support active lives.
Fast Relief Hypnotherapy has built a solid name for
delivering results and enhancing quality of life.
Clients seeking hypnotherapy in VA can trust Fast Relief
Hypnotherapy for successful and dependable therapy tailored specifically
to their requirements. The commitment to quality and patient contentment renders Fast Relief Hypnotherapy
stand out as the top choice for hypnosis treatments
in the region.
??????????????
Такая последовательность действий обеспечивает системное воздействие и минимизирует риски осложнений.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Подробнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в Симферополе[/url]
Лобня — город коротких дистанций, но в острых ситуациях решает не километраж, а управляемость. Мы убираем паузы между решением обратиться и реальной помощью: на звонке быстро оцениваем риски, предлагаем безопасный старт в квартире или в палате, согласуем окно прибытия, объясняем что подготовить, и фиксируем честный диапазон стоимости. Цель — чтобы первые часы прошли по понятному плану, а не вслепую.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-dlya-alkogolikov-v-lobne
купить натяжной потолок Навесной потолок: Современное решение для стильного интерьера Навесной потолок – это универсальное решение для создания современного и функционального интерьера. Он позволяет скрыть недостатки базового потолка, проложить коммуникации и установить встроенное освещение. Существует множество видов навесных потолков, отличающихся по материалу, дизайну и функциональности, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для любого помещения.
Отличный магаз!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Вы всё ещё работаете с Яндекс Деньгами?Всем доброго времени суток. Вопрос такой – Ко скольки лучше делать МН и как быстро растет толер???
В этой публикации мы рассматриваем важную тему борьбы с зависимостями, включая алкогольную и наркотическую зависимости. Мы обсудим методы лечения, реабилитации и поддержку, которые могут помочь людям, столкнувшимся с этой проблемой. Читатели узнают о перспективах выздоровления и важности комплексного подхода.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в москве[/url]
заказать студенческую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-5.ru/]заказать студенческую работу[/url] .
Hello men
Good evening. A 28 fantastic website 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this website. There’s a great article there. https://www.luxgallery.it/come-le-concessioni-governative-hanno-trasformato-il-gioco-online-300886/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Krass, NV Casino ist eine super informative Ressource.
http://www.mandolinman.it/guestbook/
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I in finding It really useful & it helped me out
a lot. I hope to provide one thing again and aid others such as you aided me.
What’s up, its pleasant article concerning media print,
we all understand media is a fantastic source of data.
Вызов нарколога на дом сочетает медицинскую эффективность с удобством. Пациент получает квалифицированную помощь в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg14.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect
against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
магаз работает??? https://disel-specservise72.ru Продолжаем работать, в этот раз чуть больше берем 🙂 очень хорошие скидки дает постоянным клиентам обращаетесь !!а думаете?
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
ігри слоти найкращі слоти
BlueStone Boutique – The layout is user-friendly and visually appealing.
Лечение алкоголизма на дому становится востребованным. Основные этапы состоят из очистки организма от алкоголя на дому и помощи при запое. С чего следует начать? Важно установить поддержку родственниковкоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психологическая поддержка и традиционные средства могут стать эффективным дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы по поддержанию трезвости и методы отказа от спиртного помогут установить верное мышление. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru Не упускайте из виду реабилитацию в домашних условиях, которая включает поддержку психолога и профилактику рецидива. Что делать, чтобы бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с постановки ясной цели и поиска мотивации. Главное – это желание изменить свою жизнь и поддержка близких.
«НоваТонус» — это связанный маршрут наркологической помощи для жителей Лобни и округа: оперативный выезд врача на дом, аккуратный домашний детокс без «универсальных коктейлей», стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением, подготовка к кодированию по показаниям и поддержка семьи в первые недели. Мы действуем по принципу клинической достаточности: каждое назначение обосновано, объясняется простым языком и привязано к реальным целям — безопасно снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, мягко вернуть сон, а затем провести первую «тихую» неделю без качелей. Приватность встроена в процесс: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральный канал связи, документы по запросу и в сдержанной формулировке.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-lobne
momenthubzone – Simple navigation, pages respond quickly and items are attractive.
ТУТ САМЫЙ ЛУЧШИЙ МАГАЗИН С САМЫМ ЛУЧШИМ ТОВАРОМ!!! ЖЕЛАЮ УДАЧИ!!! https://sauna-tverici.ru только что был свидетелем того как парней приняли с ам2233 и тусиаем от чемикала на спср офисе, вывели в браслетах посадили в микрик и увезли, чего ожидать? чем им помочь?Работаем с данным магазином! всем советую!
browse this page – Pages loaded fast and the overall structure felt intuitive.
shop urban boutique – Smooth scrolling and fast pages made exploring simple.
BotSync, занимаемся автоматизацией бизнеса делаем умные, чат боты для Telegram на N8n https://sorted-booth-08732357.figma.site
ремонт натяжного потолка Натяжной потолок СПБ цены: Выгодные предложения от профессионалов В Санкт-Петербурге представлен широкий выбор натяжных потолков по доступным ценам. Обратившись к профессионалам, вы сможете получить консультацию, выбрать оптимальный вариант и заказать установку потолка под ключ. Не стоит экономить на качестве материалов и монтажа, чтобы ваш потолок радовал вас долгие годы.
modernbrookboutique – Site is neat and minimal, making shopping pleasant.
bsme at
Спасибо за терпение, понимание и позитивный настрой купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш “Подходит время Раздачи”мазагин, один из лучший, беру практически только здесь!
*Седативные препараты применяются строго по показаниям и под мониторингом дыхания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
willow picks hub – Fast-loading pages and organized layout made shopping effortless.
ігри казіно ігри казіно
слоти онлайн ігри слоти
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Получить больше информации – http://
oficjalny mostbet oficjalne kasyno mostbet
lucky88
E2BET Singapore: Trusted Online Casino SG | Live Casino,
Slots & Sports Betting
Wow, awesome weblog format! How long have you been blogging for? you made running a blog glance easy. The total look of your website is fantastic, let alone the content!
https://delavore.com.ua/sklo-dlya-citroe-n-c4-cactus-2025-vybir.html
onyx55
Здесь
[url=https://smart-serm.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В этой статье мы обсудим процесс восстановления после зависимостей, акцентируя внимание на различных методах и подходах к реабилитации. Читатели узнают, как создать план выздоровления и использовать полезные ресурсы для достижения устойчивых изменений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом Симферополь[/url]
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but
after going through some of the articles I realized it’s new to me.
Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often!
Timber Comfort Shop – The layout flows nicely, making browsing feel effortless and stress-free.
При критических симптомах (потеря сознания, сильная одышка, подозрение на инсульт/инфаркт) необходимо звонить 103/112. Мы подключимся к маршрутизации и организуем перевод в стационар.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru
Simply want to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is just great and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
CHEMICAL MIX спасибо огромное!!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Спасибо за отзывы приятные. Стараемся доставлять побыстрее)))ну если ты регу получил! сделай опробуй! и отпиши прет тебя или нет!
Shop NewGroveEssentials – Items were displayed clearly, making shopping straightforward.
Northern Mist Treasures – Clean design and intuitive navigation made shopping enjoyable.
слоти онлайн популярні слоти
хорошо что так https://priemkaexpert.ru Самый лучший магазин! качество, цены, общение с клиентом, все на высшем уровне! продолжайте в том же духе и вам зачтется: )Магазин ровный! Я заказал 1000ф, оплатил ЯД, оператора попросил отправить посыль на следующий день , без задержки т.к. сроки получения очень поджимают. На что оператор адекватно ответил что все сделают.На следующий вечер получил трек, посылочка собранна и вот вот выезжает))) если уже не выехала) Магазину как и его администрации – от души за оперативность и отношение к клиенту.
казіно ігри ігри в казино
konto osobiste mostbet oficjalna strona internetowa mostbet
найкращі слоти слоти безкоштовно
ігри онлайн казино ігри онлайн казино
logowanie do mostbet oficjalny mostbet
Sun Meadow Corner Shop – Organized pages and intuitive menus made shopping quick.
Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ – это самый удобный вариант, позволяющий получить готовый к проживанию дом без лишних хлопот.
item showcase – Products were displayed neatly and navigating between pages was smooth.
В данной статье мы акцентируем внимание на важности поддержки в процессе выздоровления. Мы обсудим, как друзья, семья и профессионалы могут помочь тем, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. Читатели получат практические советы, как поддерживать близких на пути к новой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в Симферополе[/url]
Для формирования структурированной модели используются стандартизированные алгоритмы. Ниже представлена последовательность действий, определяющих ход терапевтических мероприятий.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм томск[/url]
choice hub – Clear layout and fast-loading items improved product exploration.
ворота для полуприцепа Производство фургонов – это создание надежного и функционального грузового транспорта. Мы изготавливаем фургоны на заказ, учитывая все ваши требования и пожелания. Широкий выбор материалов и комплектаций позволяет создать идеальный фургон для вашего бизнеса.
купить курсовая работа [url=http://kupit-kursovuyu-9.ru/]купить курсовая работа[/url] .
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы
a href=”https://growyourmindset.click/” />growthcentral – Pages are responsive, products are neatly arranged, and browsing is effortless.
crestartoutlet – Pages load fast and products are easy to locate, shopping felt pleasant.
307 не появился??? https://mebelnazakazi.ru Мукообразная консистенцияотпишитесь плиз
a href=”https://brightnorthboutique.shop/” />brightcornerboutique – Items are displayed clearly, and moving through sections feels smooth.
Здесь
[url=https://azmy.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Услуги эвакуатора Эвакуатор Таганрог – это гарантия спокойствия для водителей, бороздящих просторы этого приморского города. Независимо от того, где застала вас беда, будь то оживленная улица в центре или тихая улочка на окраине, эвакуатор прибудет оперативно, чтобы избавить вас от головной боли и доставить ваш автомобиль в целости и сохранности до места назначения.
soft boutique access – Navigation felt easy and items were easy to explore.
Эвакуатор таганрог Услуги эвакуатора охватывают широкий спектр ситуаций. Будь то легковой автомобиль, мотоцикл, грузовик или спецтехника, профессиональная команда обеспечит безопасную погрузку и транспортировку в нужное место. Аккуратность и соблюдение всех норм безопасности – приоритет в работе каждой смены.
I came across an article that talks about the same thing but even more and when you go deeper.
I’d like to be able to write like this, but taking the time and developing articles is hard…. Takes a lot of effort.
Системная работа, которой характеризуется наркологическая клиника, предполагает последовательное исследование состояния пациента, анализ факторов риска и создание индивидуального терапевтического маршрута. Такой формат позволяет уточнять клиническую картину на ранних этапах и корректировать вмешательства по мере изменения состояния человека. Применение структурированных методик повышает предсказуемость результата и обеспечивает безопасность всех процедур. При этом выводы формируются на основании объективных данных наблюдения, лабораторных показателей и динамики симптомов. Оптимальная нагрузка распределяется на весь период лечения для достижения устойчивого эффекта без переутомления организма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Или вводит всех в заблуждение?! https://anmanchicory.ru пишу по сути заказал-оплатил-получил все это было очень быстро я сам охуел вечером кинули трек а уже на следующее утро получил походу ТС на реактивном истребителе доставку организовал, качество нормуль делал 1к8 штырит как положено, первые 20 минут на подьем потом 20 минут идет спад короче 40 минут полет отличный, да был небольшой казус часть платежа потярялось, но потом после созвона со службой поддержки клиентов благополучно нашлось- “дырявая банковская система” вот как то так. ТСу без подхолемажа РЕСПЕКТ!!!!Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии,
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы в казино казахстан
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение интоксикации организма, вызванной длительным употреблением алкоголя. В клинике «ПензаМед Трезвость» помощь оказывается профессионально и конфиденциально: пациенты могут получить лечение как в стационаре, так и на дому. Процесс включает использование капельниц, медикаментозную терапию, психоэмоциональную поддержку и последующую реабилитацию. Врачи наркологического центра обладают большим опытом работы и обеспечивают круглосуточную помощь без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для тех, кто хочет сохранить анонимность и быстро вернуться к нормальному состоянию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]врач вывод из запоя пенза[/url]
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в томске[/url]
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево владивосток[/url]
Когда уместен
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha5.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom-v-balashihe
Northern Mist Studio Hub – Fast-loading pages and organized visuals allowed quick browsing.
Подработка онлайн Работа для каждого – это не просто слоган, это реальность современного рынка труда. Независимо от вашего опыта, образования или графика, всегда найдется возможность для заработка.
Мы выстраиваем помощь как маршрут, а не разовую процедуру. Первый контакт начинается с короткого сбора данных: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые препараты, аллергии, эпизоды судорог или потерь сознания в прошлом. Это позволяет быстро определить формат — домашний визит или госпитализация — и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты и расходные материалы. После стабилизации мы обсуждаем ближайшие недели: контрольные осмотры, план восстановления сна и питания, подготовку к кодированию и участие семьи. Такой подход снижает риск повторного срыва и делает процесс управляемым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]staciomedika-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vyvoda-iz-zapoya-moskva-otzyvy[/url]
Детоксикация — ключевой этап в лечении зависимости. Она направлена на очищение организма от токсинов и нормализацию обмена веществ. В клинике «АстраМед Трезвость» капельницы подбираются индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и хронических заболеваний пациента. Ниже представлена таблица с основными видами инфузий и их назначением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru
Да, в скайпе их нет и ситтуация мне тоже не нравиться. https://sosh1tymovskoe.ru 1.зачем указано столько платежных систем,коли их нет?остался дико не рад, но селлер быстро пообещал кидануть бонуса при следующей покупке. надеюсь, не пожадничают
Стационар рационален при нестабильном состоянии, риске делирия, судорогах в анамнезе, скачках давления, выраженной одышке, неукротимой рвоте, одиночестве ночью или невозможности обеспечить «тихий режим». В палате — контролируемая среда, доступ к ЭКГ и базовой лаборатории по показаниям, круглосуточный пост медсестёр и возможность быстро менять тактику, если параметры «плывут». Такой маршрут предсказуемее по безопасности и зачастую короче по времени до стабильного самочувствия.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin[/url]
Coastal Ridge Collections – Enjoyed browsing through items; everything is easy to locate.
Ключевая идея «ДонЗдрава» — соединить доказательную медицину и понятную пациенту логистику. Инфузии рассчитываются через инфузомат, жизненные показатели контролируются портативным кардиомонитором и пульсоксиметром, а лекарственные взаимодействия проверяются по протоколу перед началом терапии. При этом каждый шаг объясняется простым языком: что делаем, зачем это нужно и как будем оценивать результат через 30, 60 и 120 минут. После визита пациент не остаётся один — доступна «горячая линия» и короткие онлайн-сессии с врачом либо психологом, если тревога или бессонница возвращаются в ночные часы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
казино banda
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Оценщик после залива всё оформил максимально быстро – https://zaliv-expertiza.ru/
Wild Shore Selections – Organized pages and tidy layout made product discovery quick.
Такая структура терапии обеспечивает контроль на всех стадиях и помогает добиться устойчивого результата без вреда для здоровья. Пациент получает не просто временное облегчение, а полное восстановление физического и эмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/
служит по контракту
Что за кипишь на ветке? И когда будет адрес? https://salon-miledy.ru Прошу обратить внимание на кидок со стороны магазина на ~50000 рублей в Украинской ветке.Тепкрь сам хочу зделать заказ но немогу на сайт попасть ((((
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up.
The words in your article seem to be running off the screen in Opera.
I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with web browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know.
The style and design look great though! Hope you get the issue fixed soon. Many
thanks
My web-site :: zalaieta01
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3xz5kxxn
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника томск[/url]
soft picks hub – Fast-loading pages and tidy layout made exploring effortless.
Your Success Path – Practical guidance to help you unlock your potential every day.
Здесь
[url=https://www.kurort26.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Цель
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-pomoshch-v-ivanteevke
Такой подход позволяет устранить физические последствия запоя и снизить психологическую зависимость. Уже после первой процедуры пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, появление аппетита и нормализацию сна. Важно не ограничиваться только экстренной помощью — специалисты рекомендуют пройти курс восстановления, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
https://contractna-svo.ru/
Перед перечнем форматов важно подчеркнуть: выбор делает врач по клинической картине; задача семьи — честно описать симптомы и не скрывать принятые лекарства. Это снижает риск «ложной стабильности».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-lyubercy5.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-lyubercah
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/me6tr7u2
예쁘네요! 정말로 멋진 포스트입니다.
이 세부사항을 제공해줘서 감사합니다.
Hi there, this weekend is good for me, because this occasion i am reading this impressive educational post here at
my home.
I’m blown away by the quality of your articles.
You make диплом с проводкой so easy to understand!
I’ve added your RSS feed to stay updated. Any chance you could write more about example of kinetic energy?
Cheers for the awesome work!
이 블로그를 발견한 게 행운이에요! hrvatska에 대한 글이 너무 흥미롭고 잘 쓰여 있어요.
소셜 미디어에서 공유했어요. 게스트
포스트로 다른 사이트와 협업할 계획 있으신가요?
고맙습니다!
сайт для заказа курсовых работ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-9.ru]сайт для заказа курсовых работ[/url] .
Lunar Peak Market – Products are easy to find and the interface is user-friendly.
cheap finds – The variety was great for saving money and exploring categories was easy.
грозный луи оставил отзыв о магазине https://physics-for-students.ru Ничего не пойму.. Я уже третий день пытаюсь договориться и всё бесполезно. Прошу номер кошелька куда перевести, говорит щас и пропадает на пол дня, и так постоянно. Может на мелкий заказ как у меня им пох. Заказываю 10 гр.вот это уже наводит на мысли
Эта информационная публикация освещает широкий спектр тем из мира медицины. Мы предлагаем читателям ясные и понятные объяснения современных заболеваний, методов профилактики и лечения. Информация будет полезна как пациентам, так и медицинским работникам, желающим поддержать уровень своих знаний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-domu-v-ivanteevke/
wildmountaincorner – Products are logically categorized, making browsing easy.
https://sunwinth.net/
В Барселоне сейчас проверяют реальное проживание очень строго
http://polyamory.wiki/index.php?title=User:Luther87F9
Независимая экспертиза выявила больше повреждений, чем виделось на первый взгляд: течет балкон от соседей сверху что делать
новые фургоны на газель Ремонт пола в фургоне – это обеспечение безопасности груза и предотвращение повреждений кузова. Мы предлагаем замену изношенных напольных покрытий, усиление конструкции и обработку антикоррозийными составами.
магаз работает ровно оперативно и бонус хороший дали хотя я даже не ожидал как и обещали на следующий день отправили,а орест посылок я думаю ТС как нибудь уладит этот вопрос главное подход к нему найти https://myspb24.ru заказал в этом магазине еще раз ))Отличный магазин
Капитальный ремонт детской: игровая зона, кровати. Безопасно и весело.
https://wikiprofile.ru/index.php?title=Snatek_92I
evermeadowgoods – Great selection and intuitive navigation helped me explore products without hassle.
В небольших городах с плотными социальными связями страх огласки часто сильнее страха болезни. Человек откладывает визит, родные «лечат дома», в ход идут транквилизаторы, снотворные, «домашние коктейли» — и вот уже давление скачет, пульс «рвётся из груди», нервная система истощена, появляется риск делирия. Анонимный формат в «ЛюберцыМед Трезвость» снимает этот барьер: оформление деликатное, разговоры — только по сути, без «морали», без публичности. Пациент понимает, что его не «сдадут» и не начнут «воспитывать», а семья — что рядом есть команда, которая несёт медицинскую ответственность и не исчезает после первой капельницы. Этот доверительный фундамент повышает готовность пациента сотрудничать: легче согласиться на стационар, если дома стало опасно, проще прийти на амбулаторный приём, удержаться от «самолечения» и продолжить программу.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-lyubercy5.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь на дом[/url]
Честная наркология — это не «универсальная капельница», а система шагов, привязанная к параметрам конкретного человека. В Чехове мы выезжаем круглосуточно, на месте проводим допуск к терапии, сверяем совместимости с уже принятыми препаратами, подбираем состав инфузий без лишних компонентов и избыточной седативной нагрузки. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим стационар — это не усложнение, а короткий путь к безопасности. Анонимность — стандарт: нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным, деликатная связь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]бесплатные наркологические клиники[/url]
Такое поэтапное лечение позволяет добиться устойчивого результата без стрессов и осложнений. Пациенты получают комплексную помощь, включающую как медицинские, так и психотерапевтические аспекты.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the best websites online.
I’m going to highly recommend this site!
Услуги защитника по уголовным делам в Москве:
как добиться успешной защиты клиента и получить положительные
отзывы на различные вопросыУслуги адвоката по уголовным делам в Москве
Спрос на услуги адвоката по уголовным
делам в Москве высок среди тех, кто сталкивается с различными обвинениями.
Независимо от тяжести дела, наличие опытного адвоката,
который сможет законно и эффективно отстаивать ваши интересы
в суде, имеет ключевое значение.
Зачем обращаться к адвокату?
Опытный адвокат знает все нюансы уголовного процесса и успешно ведет дела в суде.
Специалист поможет добиться успешного
результата и минимизировать негативные последствия.
Клиенты могут рассчитывать на
полноценные консультации по всемаспектам дела.
Какие задачи выполняет адвокат?
Деятельность адвоката по уголовным делам охватывает несколько основных стадий:
Начальная встреча, на которой юрист исследует особенности дела иоценивает
вероятность успеха.
Анализ и сбор необходимых доказательств для
создания защиты.
Подготовка документов для судебных инстанций и активное
участие в судебных процессах.
Представление интересов клиента на всех этапах уголовного процесса.
Отзывы клиентов
Отзывы клиентов о работе адвокатов часто оказывают значительное влияние на выбор защитника.
Большинство клиентов акцентируют внимание
на:
Профессионализм и качественная подготовка.
Персонализированный подход к каждомуделу.
Умение успешно справляться с работой в стрессовой обстановке.
Информация о контактах адвоката
Важно заранее узнать контакты адвоката, чтобы в случае необходимости
быстро обратиться за помощью.
Быстрая доступность и оперативность — важные условия для
успешной защиты.
Как выбрать адвоката по уголовным делам?
При выборе адвоката, который занимаетсяуголовными делами,
важно обратить внимание на следующие моменты:
Количество дел, выигранных адвокатом,
и опыт в данной области.
Мнения клиентов и репутация специалиста.
Прозрачность условий и расценок за услуги адвоката.
Помните, что своевременное обращение к адвокату может сыграть решающую роль в исходе дела.
Незатягивайте с решением серьезных
вопросов, касающихся защиты ваших прав и интересов. https://m.avito.ru/
Заключение
Консультация с уголовным адвокатом в
Москве является ключевым шагом, способным значительно
изменить результат уголовного дела.
Каждый клиент имеет право на защиту, и именно профессиональный защитник поможет вам наладить
процесс ведения дела с учетом всех
нюансов. Учитывая сложность уголовного
законодательства, важно выбрать специалиста, который сможет эффективно представлять ваши интересы на всех
этапах – от досудебного разбирательства до суда.
Роль профессиональной защиты
Эффективная защита по уголовным делам требует не только серьёзного понимания законодательства, но и практического
опыта в разных категориях преступлений.
Специалист по уголовным делам
должен:
Анализировать все материалы дела;
Создавать тактику для защиты;
Общаться с должностными лицами;
Защищать ваши права в судебных инстанциях;
Обеспечивать поддержку клиенту на всех этапах дела.
Почему клиенты выбирают нас
Высокая квалификация и профессиональный подход
наших адвокатов выделяет нас среди конкурентов,
по мнению клиентов. Мы стремимся ктому,
чтобы каждый из них чувствовал себя защищенным и
уверенным в своих силах. Наш опыт в
ведении уголовных дел позволяет нам достигать положительных результатов даже в самых трудных ситуациях.
Как найти адвоката?
При выборе адвоката по уголовным делам в Москве обратите внимание
на:
Отзывы клиентов;
Квалификация и опыт в вашей сфере;
Наличие возможности консультации;
Подход к каждому делу индивидуально.
Не забывайте, что чем раньше вы начнете сотрудничество с профессионалом,
тем выше вероятность достижения положительного результата.
В случае возникновения вопросов, вы всегда можете
обратиться к нам.
В заключение, помните, что каждый
имеет право на защиту, и
мы готовы помочь вам в этом. Свяжитесьс
нами, чтобы получить консультацию
и узнать, как мы сможем отстоять ваши интересы в уголовном процессе.
После курса капельниц улучшается сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие. Пациенты отмечают, что уже через сутки после начала лечения исчезают тремор и тахикардия, а на второй день приходит чувство ясности и спокойствия.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo-anonimno/
Explore MountainMistStudio – The interface felt intuitive and browsing products was pleasant.
What’s up, yes this paragraph is really nice and I have learned lot of things
from it on the topic of blogging. thanks.
Life Coach Rudolfo shines as the foremost life coach in Haarlem delivering exceptional guidance and
support for individuals seeking transformation and change.
His approach is personalized to meet each client’s distinct needs, guaranteeing efficient strategies that produce
permanent beneficial change. With extensive experience, Rudolfo has developed a profound understanding of
human behavior and motivation, making his coaching sessions
thought-provoking and effective. Clients admire his attentive listening and realistic advice, which creates a supportive environment where they are encouraged
to pursue their goals and conquer obstacles. Life Coach Rudolfo
employs established techniques to help clients build confidence, refine decision-making, and promote
overall well-being. His commitment to continuous learning and professional development
guarantees he remains current with the latest coaching methodologies.
Many individuals in Haarlem have benefited from his customized coaching programs, which concentrate on career development,
relationships, and personal fulfillment. Rudolfo’s devotion to his clients’ success is
visible in the positive testimonials and enduring results they achieve.
He creates a comfortable space for reflection and growth, encouraging
clients to reach their full potential and lead more meaningful lives.
Whether encountering obstacles or pursuing greater achievements, Life Coach Rudolfo supplies the resources and motivation needed to succeed.
For those seeking the top life coaching in Haarlem, his
skills and caring approach make him the
best choice for impactful personal development.
Bright Timber Corner – User-friendly design and a range of products made picking items smooth.
Приветствую один из старейших магазинов форума! Много воды утекло с тех пор как вы открылись в 2011 году… а вы по-прежнему на плаву и продолжаете радовать нас своим отличным сервисом. Даже не представляю форум без вас) Так держать ребята! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Магазин просто огонь !!! Оценка 5+ за все :voo-hoo: !!! Качество товара збс !!! Советую всем этот магаз!!!Полностью согласен !!!
службы по контракту
Затянувшийся запой — это не просто «перебор накануне», а состояние, при котором страдают сердечно-сосудистая система, печень, нервная регуляция и обмен электролитов. В наркологической клинике «ДонЗдрав» (Ростов-на-Дону) экстренный вывод из запоя организован как непрерывная цепочка помощи: диспетчер 24/7 — дежурный врач — мобильная бригада — последующее наблюдение и психотерапевтическая поддержка. Мы приезжаем на дом в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков, проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем индивидуально подобранные капельницы и даём чёткий план на ближайшие 72 часа. Такой формат позволяет безопасно стабилизировать состояние, не нарушая приватность и привычный уклад семьи.
Узнать больше – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-rostov14.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu/
Thank you for the good writeup. Ιt in fact was a amusement account it.
Lⲟoҝ advanced to faг added agreeable from you! Вy the way,
how coulԁ we communicate?
My blog; ремонт лазерных картриджей
контракт служба
Mountain Wind Hub Online – Fast loading and logical layout allowed me to find everything easily.
бонус пускай шлют https://stroycom-cher.ru Бро конечно я незнаю твою ситуацию, но с зданным магазом работал всегда всё на вышке было , и вот что думаю на 10 грамм смысла тебя кидать нет такому магазину!!!скорей бы вы синтез заказали МН…
moon picks – Smooth interface and organized categories made shopping pleasant.
Этот обзор сосредоточен на различных подходах к избавлению от зависимости. Мы изучим традиционные и альтернативные методы, а также их сочетание для достижения максимальной эффективности. Читатели смогут открыть для себя новые стратегии и подходы, которые помогут в их борьбе с зависимостями.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в Москве[/url]
Честная наркология — это не «универсальная капельница», а система шагов, привязанная к параметрам конкретного человека. В Чехове мы выезжаем круглосуточно, на месте проводим допуск к терапии, сверяем совместимости с уже принятыми препаратами, подбираем состав инфузий без лишних компонентов и избыточной седативной нагрузки. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим стационар — это не усложнение, а короткий путь к безопасности. Анонимность — стандарт: нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным, деликатная связь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены адреса[/url]
Urban Seed Hub – Navigation is intuitive and finding items is effortless.
A ton of pornographic images are immediately on the blog, which is exactly what you expect it to be. https://zawayasyria.com/author/lavadaforrest3/ Easy enough to use. Extra-large thumbnails are organized into types, allowing you to quickly sort through them according to your preference.
This Art Gallery – The combination of a clean aesthetic and rapid loading is truly excellent.
качество на высоте! сегодня опробовали и регу и ск! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Отзывы от кролов. качество тусишки хорошее. приятно порадовали ее ценой. качество метоксетамина – как у всех. сейчас в россии булыженная партия, тут он такой же. однако продавец сказал что скоро будет другая партия. вывод – магазин отличный, будем работать.А ВОТ Я ТОЖЕ КИПИШЕВАЛ ПО СЧЕТУ ТРЕКА НЕ БИЛСЯ ТОЖЕ ПОЗВОНИЛ В КУРЬЕРКУ СКАЗАЛИ ОТПРАВЛЕННО И СЕГОДНЯ К ВЕЧЕРУ ВСЕ ОТБИЛОСЬ ЖДУ ПРИХОДА ПОСЫЛКИ. ПОТОМ НАПИШУ КАК ЕСТЬ. ПРОШУ ПРОЩЕНИЯ У ЧЕМИКАЛА ЗА ПЛОХИЕ ПОСТЫ, ДУМАЮ ПОЙМЕТ))) УЖЕ ДАВНО ТУТ БЕРУ НЕ РАЗУ НЕ КИНУЛ НИ ОДНОЙ ЗАДЕРЖКИ ВСЕ ПРОСТО НА 100%.
Modern Fable Hub – Shopping is convenient and items are easy to locate.
заказать курсовую [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-9.ru/]заказать курсовую[/url] .
success pathway – Moving through the site feels natural, with items well organized.
softrosecollection – Clear interface with organized products, shopping was simple.
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom/
После курса капельниц улучшается сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие. Пациенты отмечают, что уже через сутки после начала лечения исчезают тремор и тахикардия, а на второй день приходит чувство ясности и спокойствия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в кемерове[/url]
greenoutpostemporium – Very organized layout, shopping feels smooth and relaxing.
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Детальнее – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в Москве[/url]
В этой заметке мы представляем шаги, которые помогут в процессе преодоления зависимостей. Рассматриваются стратегии поддержки и чек-листы для тех, кто хочет сделать первый шаг к выздоровлению. Наша цель — вдохновить читателей на положительные изменения и поддержать их в трудных моментах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dafna-clinic.ru/]врач вывод из запоя Симферополь[/url]
Expert Windows Cleaning with Spotless, Streak-Free Results – Plus Crystal-Clear Gutters Without Chemicals: https://ecocleaningcompany.ie/
Заказываю в этом Магазине уже 3 раз и всегда все было ровно.Лучшего магазина вы нигде не найдете! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Хороший магазин согласна!Самое главное что на свободе фиг сним с грузом! Задумайтесь ребят может пора сесть на дно, чтоб палево отвести!
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Эта информационная публикация освещает широкий спектр тем из мира медицины. Мы предлагаем читателям ясные и понятные объяснения современных заболеваний, методов профилактики и лечения. Информация будет полезна как пациентам, так и медицинским работникам, желающим поддержать уровень своих знаний.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница Москва[/url]
shop sunset hub – Neatly displayed products and simple navigation made browsing easy.
everymomentcentral – Well-structured pages, products load fast, and navigation is easy.
https://podarki-moscow.ru/
Ниже приведены ключевые элементы, которые отражают базовую структуру процессов, формирующих последовательность лечебных мероприятий. Они помогают подробно рассмотреть основные направления работы и понять роль каждого звена в общей терапевтической системе.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в пензе[/url]
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом казахстан
Вы предоставляете крутой информацию по теме kazino olimp.
http://Www.Karizha.ru/index.php?option=com_lyftenbloggie&view=entry&id=2:blogfandrey
Детоксикация — ключевой этап в лечении зависимости. Она направлена на очищение организма от токсинов и нормализацию обмена веществ. В клинике «АстраМед Трезвость» капельницы подбираются индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и хронических заболеваний пациента. Ниже представлена таблица с основными видами инфузий и их назначением.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в астрахани[/url]
EverRoot Essentials – Organized layout and clear product shots helped me browse quickly.
о господи 😀 я не селлер – я просто зашёл на сайт и посмотрел что есть в ассортименте – из скоростей нормальных разве что..кхм, оно… https://kupi-klubok.ru Если в разработке, то да.А так лишний раз лучше предостречься)))Уважаемые покупатели, С НОВЫМ ГОДОМ!
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
производство фургонов Производство фургонов – это создание надежного и функционального грузового транспорта. Мы изготавливаем фургоны на заказ, учитывая все ваши требования и пожелания. Широкий выбор материалов и комплектаций позволяет создать идеальный фургон для вашего бизнеса.
ремонт стиральных машин воронеж цены [url=https://stir-remont-voronezh-nedorogo.ru]сколько стоит ремонт стиральной машины[/url]
ремонт стиральных машин с выездом на дом [url=master-stiralok-vrn.ru]https://master-stiralok-vrn.ru/[/url]
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if
you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and
was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something
like this. Please let me know if you run into anything.
I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your
new updates.
https://ecoinn74.ru/images/pgs/melbet_promokod_bonus_za_registraciu.html
ко ланта отели Klong Dao Beach — непритязательный уголок на побережье, где песок гладкий, вода спокойная и безопасная для начинающих ныряльщиков с детьми. Пляж не слишком протяженный, но он имеет удобное расположение: рядом уютные бунгало и небольшие бары прямо у воды, где можно попробовать свежие морепродукты и тайские блюда. Утро здесь начинается с лёгкого шепота волн и ароматов кофе из соседних кафе, днём — можно арендовать каяк или просто прогуляться по пальмам, а вечером над водой красиво мерцают огни лодок. Ночью набережная более спокойна, а звёзды над морем добавляют мимишной атмосферы. Этот пляж часто выбирают семьи и пары за спокойный ритм и умеренное количество людей
brightstonecorner – Navigation is smooth, products are well organized throughout the site.
тканевые электрожалюзи [url=https://www.prokarniz23.ru]https://www.prokarniz23.ru[/url] .
не понятно, жду трека говорил вторник, вторник они не успели, говорил среда, отмолчался, не ответил! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш в рязань доставим?Как то так.
трипскан трип сайт — словосочетание, означающее официальный сайт сервиса TripScan. В таких текстах акцент делается на структуру ресурса: главная страница с обзором сервиса, разделы поиска маршрутов, страницы результатов с фильтрами, профиль пользователя, поддержка и частые вопросы, блог и обновления. В материалах подчеркивается безопасность платежей, прозрачность условий использования, наличие тарифов, инструкции по регистрации и бронированию. В SEO описаниях полезны фразы «трип сайт», «как пользоваться TripScan», «трипскан сайт вход» и аналогичные запросы, помогающие пользователям быстро находить официальный ресурс.
Thanks for another informative website. Where else may
just I am getting that type of info written in such an ideal way?
I’ve a mission that I’m simply now operating on, and I have been on the glance
out for such information.
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/
universities Крупный учебный и научно-исследовательский центр Республики Беларусь. Высшее образование в сфере гуманитарных и естественных наук на 12 факультетах по 35 специальностям первой ступени образования и 22 специальностям второй, 69 специализациям.
Карта понятна пациенту и семье: видно, что будет происходить, по каким признакам мы перейдём к следующему шагу и когда состоится проверка. Это снижает тревожность и повышает приверженность плану.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Shop EverCrestWoods – Everything felt neatly organized, making browsing pleasant from start to finish.
Провода: маркеровка. Удобство поиска.
my page – https://kotelinaya.ru/
timber selection – Fast response and neat layout helped me explore items easily.
* Экспресс-электролиты выполняются по показаниям, если на старте есть факторы риска.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ставрополе[/url]
clean design shop – The crisp layout made it easy to explore different items without any hassle.
Карта понятна пациенту и семье: видно, что будет происходить, по каким признакам мы перейдём к следующему шагу и когда состоится проверка. Это снижает тревожность и повышает приверженность плану.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в петрозаводске[/url]
«Капельница от запоя» в современном понимании — это не одна универсальная смесь, а последовательность управляемых шагов с понятной целью, измеримыми показателями и заранее назначенными точками переоценки. В наркологической клинике «СеверАльфа Мед» мы используем модульные инфузионные протоколы и бережный мониторинг, чтобы безопасно снять интоксикацию, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, снизить тремор и вернуть физиологичный сон без «переседации». Каждый этап сопровождается сервисом конфиденциального уровня: нейтральные формулировки в документах, немаркированная логистика, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям строго по ролям. Это делает путь пациента предсказуемым и защищённым от лишнего внимания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя в мурманске[/url]
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в мурманске[/url]
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
А Всем Добра и Здоровья Близким))) https://artelm.ru Надежных партнеров, верных друзей, удачных сделок и прочих успехов!пробуй 4фа, 2-dpmp
Wild Meadow Finds – User-friendly pages and organized products helped me browse quickly.
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.nnpf.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
https://towing.com.pl
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a colleague who was conducting a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me lunch due to the fact that I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to discuss this matter here on your internet site.
forticlient mac
https://towing.com.pl
проститутки в нижневартовске их цены и телефоны
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
forticlient mac download
boutique corner – Well-structured interface and tidy presentation made shopping pleasant.
May I simply say what a relief to uncover someone that really knows what they’re discussing online. You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people really need to look at this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
forticlient on mac
https://bezprovodoff.com/pgs/?promokod_pri_registracii_melbet_pouchi_bonus_130.html
зашел на сайт не нашел там 307 https://rentonminuto.com Давно не читала столько положительных отзывов !так держать )У меня кстати тоже через 2 дня пришло, но в соседний город, так как в моём городе этой конторы не оказалось) но мне сразу позвонили, и предложили либо самому приехать за пакетом, либо подождать до вторника и мне его привезут домой. Вот жду)
OutletGlobalTrends – Very happy with the deals, checkout didn’t take long.
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Мы работаем с вниманием к деталям повседневности: как человек засыпает на фоне вечернего света, сколько воды переносит малыми глотками, как реагирует на цифровые уведомления, есть ли привычные «включатели» тяги и как на организм влияет шумное окружение. Врач и куратор переводят этот жизненный контекст в ясные, измеримые ориентиры: время до сна, число пробуждений, вариабельность пульса к сумеркам, объём воды, аппетит, переносимость тёплой мягкой пищи. Решения принимаются адресно и последовательно, чтобы сохранять ясность днём и избегать ненужной фармаконагрузки.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
Стартовый осмотр должен быть быстрым и осмысленным. Мы исключаем «обязательные» исследования, которые не меняют тактику, и оставляем то, что прямо влияет на состав инфузии, темп, место ведения (дом/амбулатория/стационар) и объём поведенческих рекомендаций. Решения принимаются на свежих цифрах и клинической картине «здесь и сейчас», а повторные замеры назначаются не «по привычке», а по смыслу. Это экономит силы пациента и время команды, а главное — уменьшает фармакологическую нагрузку без потери безопасности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в ставрополе[/url]
Silver Maple Corner Shop – Organized layout and smooth navigation made shopping quick.
купить электрические рулонные шторы [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
погода ко ланта Остров ко ланта в тайланде — это двойной островной ансамбль в Андаманском море, относящийся к провинции Крабі. Основной остров Ко Ланта Яй (Ko Lanta Yai) соединён мостами и узкими дорогами с небольшим Ko Lanta Noi, образуя спокойную и неторопливую атмосферу, далёкую от шумных курортов континентальной части Таиланда. Остров известен длинной береговой линией, пальмовыми бухтами и зелёными холмами, покрытыми мангровыми лесами и ландшафтами, которые идеально подходят для отдыха, семейных каникул и онлайн-работы в расслабленной обстановке. Здесь сосредоточены главные туристические районы — от уютных гестхаусов в прибрежных деревнях до роскошных вилл в укромных бухтах. Доступ на Ko Lanta обычно начинается с перелёта до ближайших аэропортов, затем поездка на пароме через контуры побережья, что добавляет путешествию элемент приключения и медленного темпа.
рулонные шторы в москве [url=www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom499.ru/]рулонные шторы в москве[/url] .
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru
клады по мск все во время купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Я делал ркс. на спирту. Получилась лайт ваще. Делай вообщем гдето 1к 7ми . будет так нормик эффект. но слабее 203гоРовный и Стабильный…
остров ко ланта в тайланде остров ко ланта — тихий уголок на Андаманском побережье Таиланда, часть провинции Краби. Здесь сосредоточено несколько пляжей с белым песком и прозрачной водой, а вдоль побережья тянутся уютные рыбацкие деревни и маленькие курортные поселки. Основные места — пляжи Long Beach (Phra Ae), Klong Dao и Kantiang Bay, рядом работают прокат велосипедов, кафе с морепродуктами и рынки. В заповедной зоне Mu Ko Lanta National Park можно увидеть мангровые леса, кораллы и редких птиц, а вечерние прогулки по старому городу Ланта дарят шанс познакомиться с местной культурой и кулинарией. Лучшее время для посещения — сухой сезон с ноября по апрель, в остальные месяцы возможны дожди и более спокойная, но дождливая погода.
Situs Resmi E2BET Indonesia | Bonus Besar, Kemenangan Terjamin
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «РеМед Карелия» — это круглосуточная медицинская помощь, построенная на принципе клинической точности: каждая процедура имеет цель, проверяемые маркеры и назначенное окно переоценки. Мы используем современные методы детоксикации и постабстинентной стабилизации, не перегружая терапию «на всякий случай» и не полагаясь на универсальные «сильные капельницы». Вместо этого — модульные схемы, корректировка одного параметра за раз и обязательная оценка результата. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает лечение предсказуемым для пациента и его семьи. Анонимность встроена в процессы: немаркированные входы, гражданская форма персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к карте наблюдения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в петрозаводске[/url]
наука Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
shop northern collection – Smooth scrolling and clearly organized products improved browsing.
Здесь
[url=https://sgktver.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Autumn Mist Market – A comfortable design paired with thorough product details made browsing easy.
Только эфоретик нужен. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази бро ответь своим частым клиентам, распиши что да как) уже соскучились оченьЯ выхватил бан, ты злобняк
Мы комбинируем медицинские и немедикаментозные решения. Инфузионная терапия — адресная, с контролем безопасности; поведенческие опоры — просты и выполняемы в реальной жизни; телемедицина помогает пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и импровизаций. Ниже — ориентиры логики подбора, они не заменяют очный осмотр.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров («тёмные часы» вечера, недосып, конфликты, привычные маршруты) и набор «буферов» на 20–40 минут: тёплый душ, короткая прогулка у дома, дыхательная практика, нейтральный созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти бесплатные шаги уменьшают внеплановые затраты и добавляют устойчивости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наша продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов платиновая 50х8х0.6 мм Пл99.9 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Казино предлагает разнообразные способы пополнения и вывода средств. На https://sites.google.com/view/vavada-casino-betting/ опубликованы свежие промокоды и условия акций. Игры запускаются моментально на любых устройствах и платформах. Программа лояльности включает кэшбэк и эксклюзивные предложения. Служба безопасности тщательно проверяет все транзакции.
UltimateShoppingSpot – Fantastic products with amazing deals, very pleased.
Мы не противопоставляем форматы — комбинируем их. Например, первые часы — выездная стабилизация с титрованной инфузией и чётким контролем АД/ЧСС/SpO?, затем — амбулаторные короткие визиты с вечерними онлайн-вставками. Если появляются «красные флаги» (дыхание, ритм, сознание), маршрут без пауз переводится в стационар: та же карта наблюдения, те же цели, только круглосуточный мониторинг и ночной пост. Приватность встроена на каждом этапе: нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления, гражданская одежда персонала, доступ к данным по ролям.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
softleafhub – Pleasant layout, items are easy to find and browse.
Hello, yup this article is actually pleasant and I have learned lot
of things from it regarding blogging. thanks.
Техника помогает, но не доминирует. Мы используем портативные приборы с мягкой индикацией и низким уровнем шума, чтобы не разрушать формирующуюся «ночную кривую». Контроль в остром окне чаще, вечером — мягче: так сохраняется физиология сна и снижается потребность в дополнительной фармакологии.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Дуэт с лососем и угрем — нежный лосось и насыщенный угорь создают идеальный баланс вкусов
https://wokerman.ru/
Короткий «выруб» днём почти всегда оборачивается ночным откатом. Мягкая коррекция с опорой на гигиену сна даёт первую ровную ночь, а именно она цементирует эффект и уменьшает вероятность экстренных повторов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare[/url]
бамбуковые электрожалюзи [url=www.prokarniz23.ru/]www.prokarniz23.ru/[/url] .
Постоянно играю в 7к казино, слоты от NetEnt хороши. Pragmatic Play отдают хорошо в целом.
https://studhub.cz/
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино без депозита
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию без депозита
https://autolocksmithsstatenisland.com/
у меня 203 1к8 получался вообще жестокии делал на растворителе для снятие лака с ногтей (без ацетона) https://groupfinder.cc Все есть, объем большойПочему больше не забегаете ?
sunridge portal – Products load fast and moving through sections is effortless.
trueharborstyle – Smooth navigation with tidy layout, exploring items was enjoyable.
artisan finds – Beautiful presentation and easy navigation made the site feel really polished.
https://rti-land.ru/ «РезиноМир»: Ваш Надёжный Партнёр в Мире Резинотехнических Изделий с 2009 Года
В современном промышленном мире, где каждая деталь имеет значение, выбор надёжного поставщика и производителя резинотехнических изделий (РТИ) является ключевым фактором успеха любого предприятия. С 2009 года компания «РезиноМир» уверенно занимает лидирующие позиции на рынке России и стран СНГ, предлагая своим B2B-партнёрам не просто продукцию, а комплексные и высококачественные решения в области РТИ. Мы гордимся тем, что являемся не просто поставщиком, а производственным партнёром, способным удовлетворить самые взыскательные требования.
Категории резинотехнических изделий, представленные в нашем ассортименте:
• Технические пластины: Исходный материал для изготовления различных прокладок, уплотнителей, настилов. Включают в себя такие виды, как ТМКЩ (тепломорозокислотощелочестойкая), МБС (маслобензостойкая), пищевая резина.
• Рукава и шланги: Широкий спектр для транспортировки жидкостей, газов, сыпучих материалов. Это могут быть рукава напорные, всасывающие, высокого давления, маслобензостойкие, антистатические и другие.
• Уплотнения и прокладки: Манжеты, сальники, кольца, грязесъемники, О-образные кольца, плоские прокладки – незаменимые элементы для герметизации соединений в различных механизмах и системах.
• Ремни приводные: Клиновые, зубчатые, плоские, поликлиновые – обеспечивают эффективную передачу крутящего момента в промышленных агрегатах.
• Формовые и неформовые РТИ: От сложных литых деталей по индивидуальным чертежам до экструдированных профилей и шнуров различного сечения.
• Виброизоляторы и амортизаторы: Элементы, предназначенные для снижения вибрации и ударов в оборудовании, продлевая срок его службы.
• Ленты конвейерные: Для транспортных систем различной сложности и назначения, включая шахтные, пищевые, морозостойкие.
• Изоляционные материалы: Диэлектрические коврики, перчатки и другие изделия, обеспечивающие безопасность при работе с электричеством.
• Защитные покрытия: Резиновые настилы, дорожки, покрытия для спортивных площадок и производственных помещений.
Наши Масштабы Говорят Сами За Себя: Инфраструктура «РезиноМира»
За более чем 15 лет на рынке промышленных РТИ, «РезиноМир» не просто накопил опыт, а создал мощную инфраструктуру, которая является гарантом стабильности поставок и безупречного качества продукции. Мы не понаслышке знаем, что значит работать с крупными промышленными предприятиями, и наша готовность к этому подтверждается следующими цифрами:
• 15 лет на рынке промышленных РТИ: Долгая история успешного сотрудничества и постоянного развития.
• Собственное высокотехнологичное производство: Позволяет нам не зависеть от внешних факторов и строго контролировать качество продукции на каждом этапе изготовления.
• 100 000 наименований товаров в наличии: Обширная складская программа гарантирует, что подавляющее большинство ваших потребностей может быть удовлетворено немедленно.
• Изготовление деталей любой сложности по чертежам: Мы готовы реализовать уникальные проекты, создавая РТИ по индивидуальным требованиям заказчика.
Что Мы Делаем Лучше Всего: Три Столпа Успеха «РезиноМира»
Наша стратегия фокусируется на трёх ключевых направлениях, чтобы обеспечить нашим клиентам максимальную ценность и комплексное решение их задач, связанных с резинотехническими изделиями:
1. Собственное Производство: Наличие собственных производственных мощностей является нашим конкурентным преимуществом. Мы обеспечиваем эталонное качество РТИ, начиная от тщательного отбора сырья и заканчивая строгим контролем готовой продукции. Это позволяет нам гарантировать соответствие всем ГОСТам и ТУ, а также оперативно реагировать на потребности рынка.
2. Нестандартные Изделия: Для решения уникальных задач вашего бизнеса мы предлагаем изготовление РТИ по чертежам, эскизам или предоставленным образцам. Это направление — наша ключевая компетенция, позволяющая создавать сложные формовые и неформовые изделия, идеально подходящие для специализированного оборудования и уникальных производственных процессов.
3. Складская Программа: Более 100 000 наименований продукции всегда готовы к немедленной отгрузке с наших современных логистических центров. Это минимизирует время ожидания и обеспечивает бесперебойную работу вашего предприятия, предотвращая простои.
Наши Производственные и Складские Мощности: Гарантия Эффективности
«РезиноМир» — это не просто торговая компания. Мы являемся полноценным производственным комплексом, чья инфраструктура полностью ориентирована на нужды вашего бизнеса. Наша материально-техническая база включает:
• Производственный цех: Оснащенный современным оборудованием, где опытные специалисты воплощают в жизнь самые сложные технические решения.
• Склад готовой продукции: Просторные и хорошо организованные склады, где хранится огромное количество наименований РТИ, готовых к быстрой отгрузке.
• Отдел контроля качества: Независимый отдел, обеспечивающий многоступенчатый контроль на всех этапах производства и отгрузки, гарантируя соответствие продукции заявленным характеристикам.
Готовы Начать Сотрудничество?
Если вашему бизнесу требуются качественные резинотехнические изделия от надёжного производителя и поставщика, «РезиноМир» готов стать вашим партнёром. Отправьте заявку через удобную форму на нашем сайте или свяжитесь с нами напрямую по электронной почте. Наш опытный технический специалист оперативно свяжется с вами, чтобы обсудить все детали вашего проекта и предложить оптимальные решения. Доверьте свои потребности в РТИ профессиона
ко ланта что посмотреть как добраться до ко ланты — оптимальные маршруты зависят от вашего исходного пункта. Из Крби или Trang обычно берут паром до Saladan на Ko Lanta Yai; путь занимает 2–3 часа. Из Бангкока чаще летают в Krabi International или Trang Airport, затем переход на паром; в высокий сезон можно встретить прямые скоростные маршруты, но чаще требуется пересадка на материк. Добираясь по суше или воздуху,? сначала добираетесь до пирсов и портов, а затем пересаживаетесь на паром. Для маршрутов через Phuket можно выбрать сочетание полёта/автобуса до Krabi и далее паром; прямого рейса Phuket > Ko Lanta практически нет, чаще это через Krabi или Trang.
Если при первичном звонке выявляются «красные флаги» — неукротимая рвота, одышка, спутанность, «скачущий» ритм, подозрение на травму — мы немедленно резервируем палату усиленного наблюдения. При низком риске стартуем амбулаторно или на дому с бесшовным переводом в стационар, если динамика меняется. В любом случае цель одна: безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть питьё и физиологичный сон, объяснить семье и пациенту короткий «язык фактов», по которому судим об эффективности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Lunar Wood Select – Simple pages and fast product loading allowed for a pleasant shopping experience.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/5n6znwkw
Инфузионная терапия — это не универсальный «коктейль», а набор узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Главные цели понятны: вернуть объём циркулирующей жидкости и перфузию тканей, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушить тремор и тревожность, подготовить нервную систему к сну. При тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; кардиокоррекция даётся только после оценки рисков. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки» для связи. Такой минимум достаточных вмешательств снижает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает результат не часами, а днями. На этой базе обсуждаются следующие шаги: амбулаторный график, короткие психотерапевтические сессии, при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации и исключения противопоказаний.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah/
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3hhr2mdf
Вот уже Артем хохочет, https://funbe.top Выходные же. В понедельник наврятли отправить успеют.Жаль только в Мск от 50 гр. )) Думал в Саратове тоже
Детокс — это не «чудо-капельница», а последовательность узких вмешательств. Цели понятны: восстановить объём циркулирующей жидкости, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, подготовить нервную систему к сну. При тошноте подключается противорвотная поддержка и гастропротекция, витаминные комплексы — по показаниям, кардиокоррекция — только после оценки рисков. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и маркеры для немедленной связи. Такой реализм снижает импульсивность и делает результат измеримым: вечером — не «откат», а предсказуемая усталость, ночью — ровный сон, утром — стабильные показатели. На этой базе обсуждаются следующие шаги: амбулаторный график, короткие психотерапевтические сессии, при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации и исключения противопоказаний.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryadom-v-lyubercah/
moon boutique corner – Fast-loading pages and tidy categories improved browsing.
Здесь
[url=https://vitamed-tver.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Why viewers still make use of to read news papers when in this technological globe all is existing
on net?
Техника помогает, но не доминирует. Мы используем портативные приборы с мягкой индикацией и низким уровнем шума, чтобы не разрушать формирующуюся «ночную кривую». Контроль в остром окне чаще, вечером — мягче: так сохраняется физиология сна и снижается потребность в дополнительной фармакологии.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk/
остров ко ланта в тайланде Ко ланта отзывы — путешественники часто отмечают спокойную атмосферу, чистые пляжи и доброжелательное отношение местных жителей. Позитивные стороны включают природную красоту, возможность уединиться и насладиться закатами, а также хорошие условия для семейного отдыха и сноркелинга. Минусы — ограниченная ночная активность и необходимость передвигаться между бухтами на транспорте, что может потребовать времени. Для многих гостей Ко Ланта становится идеальным местом для медленного отдыха на острове и исследования близлежащих островков, рынков Старого города и уютных кафе у моря.
брал в данном магазине все супер. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Золотые слова.Всем мир! Хотелось бы всё же какого то оперативного решения! Запрет не за горами, а вернее 20 вступает в силу((((( Уважаемый продаван скажите что нибудь???
Dream Haven Finds – The site felt easy to move through thanks to its tidy layout.
рулонные шторы электрические [url=rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru]рулонные шторы электрические[/url] .
рулонные шторы электрические [url=http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom499.ru]рулонные шторы электрические[/url] .
как использовать бонус казино в 1winкак играть на бонус казино в 1win
Без сна любая дневная капельница даёт короткий «блеск» и вечерний откат. Поэтому мы заранее настраиваем гигиену: затемнение, прохлада, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров, при показаниях — щадящая седативная поддержка, которая стабилизирует, а не «выключает». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка дозировок, чтобы вторая ночь стала ещё спокойнее.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/]наркологическая клиника телефон[/url]
[url=http://remont-kofemashin.kmse.ru/]ремонт кофемашин в тамбове[/url]
StyleTrendOnline – Browsing the site felt effortless and the layout was neat.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro
offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert
paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert
pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis
paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au
pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide
paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris
sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris
sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse
cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse
pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api
cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris
sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris
sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris
sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans
argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide
paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris
sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de
pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif
en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris
sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif
espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris
sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris
sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif
virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour
pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris
sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile
paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour
gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces
paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour
gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris
sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris
sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management
paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus
cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus
paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif
retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans
dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot
paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus
site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty
paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari
sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris
sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise
paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul
systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote
paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise
paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer
roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris
sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs
paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris
sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code
barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour
retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris
sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif
conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer
aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter
les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment
bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca
marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de
paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris
sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des
parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des
paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire
un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari
sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les
cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes
de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au
paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif
foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur
le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner
les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris
sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris
sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment
gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif
foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote
paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris
sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris
sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier
sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir
les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes
de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site
de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites
de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur
paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site
pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des
sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif
pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif
paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif
site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de
paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes
paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris
sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris
sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil
paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil
paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris
sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100
paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif
comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris
sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris
sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote
paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote
paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto
gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris
sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris
sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer
un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double
paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir
riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche
avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris
sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1
euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de
jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte
dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris
aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif
paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari
sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face
hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains
de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll
paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait
tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie
sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari
sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux
paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris
sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif
brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris
sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant
paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour
aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par
mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup
sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au
paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner
aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup
d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner
à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris
sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris
sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de
joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris
sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps
paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey
sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot
sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de
paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu
paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris
sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris
sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris
sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de
caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur
paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui
se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris
sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris
sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux
paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner
paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris
sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le
meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris
sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les
bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris
sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris
sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes
paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif
avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça
marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus
grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1
paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite
de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris
sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris
sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris
sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site
paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris
sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel
de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel
paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour
paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel
probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris
sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris
sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris
sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris
sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie
paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris
sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu
paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app
de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur
appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur
appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur
application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus
paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris
sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker
paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil
paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur
forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur
ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur
offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari
sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif
du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil
paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de
pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site
de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris
sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris
sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site
de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur
site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris
sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris
sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur
site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur
technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris
sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de
paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris
sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de
pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris
sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de
paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris
sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour
gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode
paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour
gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu
pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de
4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris
sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba
pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau
site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match
paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot
paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre
paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris
sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif
en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif
hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif
100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari
sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari
sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur
pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari
sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif
cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote
psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif
en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif
en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif
en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari
sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif
forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif
france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif
france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif
france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous
les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari
sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester
champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif
ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match
arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari
sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur
site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari
sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari
sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari
sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari
sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari
sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top
14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari
sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif
top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du
jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne
sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris
hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris
sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris
sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif
1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce
soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif
analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris
sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif
argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent
fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif
avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif
basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif
belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de
bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans
depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif
buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris
sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue
pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris
sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris
sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris
sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment
ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et
match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif
depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne
avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif
en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif
en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne
maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif
et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue
des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot
ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif
foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris
sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif
foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot
suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait
tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris
sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris
sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à
coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris
sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans
argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris
sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif
hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux
video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur
decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris
sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner
tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif
ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif
ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris
sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif
match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris
sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2
3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif
moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2
3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2
4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif
multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris
sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre
de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif
offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif
plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif
plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif
promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic
des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris
sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif
psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif
que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris
sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris
sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby
coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif
sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur
ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif
site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris
sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris
sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme
2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3
4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme
explication|paris sportif technique|paris
sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis
conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis
pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris
sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris
sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris
sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris
sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris
sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs
et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france
espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs
hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs
ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des
champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs
match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs
tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour
de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal
pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris
sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris
sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise
paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise
paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris
sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif
tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif
du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris
sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter
milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om
paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris
sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est
ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12
en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris
sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie
gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer
paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari
sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de
paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel
type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour
paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket
paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur
paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap
paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash
paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de
mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat
pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris
sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris
sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise
pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise
paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot
paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif
multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site
aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel
paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de
pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie
sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de
paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris
sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif
autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris
sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de
paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de
paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris
sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de
paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site
de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif
legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif
qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de
paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte
d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site
de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site
de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de
paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif
arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari
sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif
arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec
meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif
bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif
hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif
paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans
depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site
statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites
de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris
sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites
de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris
sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs
suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris
sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante
paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3
paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris
sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote
paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau
excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris spor
Инфузионная терапия — не магический «коктейль», а последовательность узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Регидратация возвращает объём циркулирующей жидкости и улучшает перфузию тканей; коррекция электролитов стабилизирует нервно-мышечную передачу и сердечный ритм; печёночная поддержка снижает токсическую нагрузку; при тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; при выраженной тревоге — мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки», требующие связи. Диагностика назначается тогда, когда её результат меняет тактику сегодня, — никакой «проверки на всякий случай». Такой минимально достаточный подход уменьшает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает эффект не часами, а днями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2025
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
GrowthAdventure – Encouraging content that sparks curiosity and learning.
ко ланта таиланд Пхукет – Ко Ланта: путешествие между двумя жемчужинами Таиланда. Лучшие маршруты и советы.
gold designs boutique – Clean layout and well-organized items made shopping enjoyable.
Всем привет. Рега есть в наличии? https://mefground.biz А вот еще немного…Вскрыл, взвешал – все в норме. для начала взял 1гр.растворяется АМ2233 в спирту хреново,(в след.раз попробую на растворителе сделать)причем грел все это дело на водяной бане,мешал,но до конца так и не растворилось.делал это долго и упорно,молочного оттенка раствора не наблюдалось,прозрачный скорее,но остался осадок в виде белого порошка.В итоге так и залил все это дело 1к20. Сушится теперь. Как высохнет опробуем и напишу что получилось. Буду надеятся на лучшее.брал тут туси совсем недавно.все устроило.спасибо.жду обработки второго заказа)
ко ланте отели ко ланта что посмотреть — На Ко Ланте есть несколько популярных мест: Mu Ko Lanta National Park на юге предлагает пляжи, тропинки и мостовую дорожку к маяку; Старый город с его атмосферой рыбаков и рынков — хороший уголок для дневной прогулки и ужина на свежем воздухе; долгие пляжи Long Beach, Kantiang и Klong Nin, где можно снять виллу и насладиться закатами; точки обзора на холмах для панорамных фотографий; и мотопондорная развлекательно-праздничная атмосфера в протяжённых бухтах. Варианты активностей включают снорклинг, каякинг, лодочные туры к близлежащим островам и посещение местных рынков.
I savor, cause I found just what I used to be having a look
for. You’ve ended my four day lengthy hunt!
God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
впс сервер купить
brightoakmarket – Shopping feels smooth, layout is neat and intuitive.
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox
and now each time a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can remove people from that service?
Thanks!
I believe that is one of the so much vital information for me.
And i’m glad reading your article. However should commentary on few normal issues,
The site style is wonderful, the articles
is actually excellent : D. Good process, cheers
EverHollow Bazaar Link – Quick-loading pages and a tidy category setup made exploring pleasant.
Не-не, через форум заказы не принимаются. Заказывать нужно только через сайт, указанный в подписи. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази 5 гр заказала, ждали 6 дней, вот забрали у курика, муж укололся, потом ещё в воде разболтали и выпили. Эффект ноль. Что с остальным делать. Хоть в унитаз высыпайв скайпе сказали – “дживики все кончились, будут в начале следующей неделе” – но легче это опубликовать тут, что бы всем не отвечать на этот вопрос.
тканевые электрожалюзи [url=https://prokarniz23.ru/]https://prokarniz23.ru/[/url] .
ко ланта аэропорт ко ланта аэропорт — На Ко Ланте собственного аэропорта нет. Практически все гости прибывают через Krabi International (KBV) или Phuket International (HKT). По прибытии путешественники едут на материк и далее на паром через Ban Saladan на Ko Lanta Yai. В редких случаях доступен внутренний воздушной чартер на небольшие аэродромы, но такие варианты требуют согласований и обычно относятся к эксклюзивным сервисам. Эта структура делает путешествие немного длиннее, но добавляет маршруту атмосферу приключения и плавное погружение в природу острова.
Howdy just wanted to give you a quick heads up and
let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly.
I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same outcome.
green marketplace – I could explore products easily thanks to the intuitive design.
wave choice store – Enjoyed the simple layout; items were easy to view and navigation felt natural.
wildgroveemporium – Items are well arranged and navigation feels intuitive — nice overall experience.
Не рекомендую правда увлекаться порохами – их хочется ещё и ещё и в итоге не так уж и просто слезть с марафона…) Но это уже ваше дело ; ) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази чтоб расширенный был глаз.Доброга времени суток, закладки в москве делаете?
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя мурманск[/url]
погода ко ланта Пхукет ко ланта как добраться — маршрут через Пхукет обычно включает перелёт в Phuket или Krabi, затем наземный транспорт до парома к Ko Lanta Yai. Из Пхукета можно добраться напрямую на скоростном катере или автобусе с зачалой на паром в Ao Nang или Krabi Town, после чего идёт переход на Ko Lanta. Время пути обычно 3–4 часа в зависимости от выбранного варианта, погодных условий и расписаний паромов. Прямые маршруты по воде из Пхукета редки, поэтому чаще выбирают комбинированный маршрут: самолёт/самолёт до соседнего аэропорта, затем паром и наземный транспорт до острова.
future grove hub – Clean layout and well-organized categories made shopping enjoyable.
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому петрозаводск[/url]
заказывал не один раз в этот раз заказал в аське нету тс жду 8дней трэка нет че случилось тс? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Всем привки Любви здоровья вам ! ПроцветанияДа рега была шикарная… Но вот как раз таки с ней и случился перебой, ОЧЕНЬ жаль!!! А так по работе остались отличные впечатления
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
остров ко ланта в тайланде краби ко ланта — Ко Ланта в составе провинции Крабби на юго-западе Таиланда, и путь к нему обычно начинается с материка: Крабби Таун, Ao Nang илиTrang. Сам участок побережья привлекательной природы — скалистые виды, кристально чистая вода и длинные пляжи, где можно отдохнуть без толп туристов. Переправы до Ko Lanta Yai идут из разных портов: Ao Nang и Krabi Town, а также Trang, время в пути обычно составляет 2–3 часа в зависимости от типа переправы и погодных условий. Любители моря выбирают места для сноркелинга и дайвинга в окрестностях Ko Haa и Koh Rok, а также исследуют Mu Ko Lanta National Park с тропами к девственным бухтам и маяками. В Крабби-провинции много вариантов размещения: от простых гестхаусов до просторных резортов у океана. Долгие прогулки по пляжам, кулинарные впечатления на набережной и экскурсии к старому городу создают спокойную атмосферу для отдыха. Лучшее время — сухой сезон, когда вода прозрачна, а погода предсказуема; дождливый сезон приносит зелень и Ridge-ветра. Советы: аренда скутера — удобный способ передвигаться по острову, тщательно планируйте переправы и учитывайте погодные условия.
ко ланте отели погода ко ланта — климат регулируется муссонной системой Индии. Сухой сезон — с ноября по апрель — самое благоприятное время для купания и прогулок: море обычно спокойное, дни ясные, температура комфортная. Влажный сезон — с мая по октябрь — приносит частые ливни и порывистые ветра, но вода остаётся тёплой; дни часто жаркие и влажные. Температуры 24–32°C круглый год, но бывают периоды, когда влажность поднимается выше; вода может быть слегка мутной после дождей. Лучшее время для сноркелинга — сухой сезон, когда море чистое и прозрачное. Всегда полезно проверить прогноза ветра и приливов перед планированием активностей.
Городская среда Калининграда специфична: морской ветер, сезонные пробки, яркие витрины в вечерние часы. Эти факторы часто усиливают тревожность и мешают засыпанию. Поэтому мы проектируем выезд «мягко»: согласованная парковка, немаркированный вход, короткий маршрут до места процедуры, отсутствие громких звонков и «визуального шума» у порога. Родственникам предоставляем «тихие окна» связи — короткие апдейты в заранее оговорённое время без лишних подробностей. Такой формат не просто комфортнее, он клинически полезен: чем меньше стимулов, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях» и тем стабильнее проходит первая ночь.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your site.
Do you ever run into any internet browser compatibility problems?
A handful of my blog audience have complained about my website not operating
correctly in Explorer but looks great in Safari.
Do you have any ideas to help fix this issue?
Качество 2с очень порадовало, трип позже отпишу. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази остался дико не рад, но селлер быстро пообещал кидануть бонуса при следующей покупке. надеюсь, не пожадничаютКстати, как и обещали, менеджер на праздниках выходил на работу каждый день на пару часов и всем отвечал, иногда даже целый день проводил общаясь с клиентами, уж не знаю, кому он там не ответил.
Crest Finds – Everything was laid out nicely and browsing felt natural.
Компания предлагает широкий выбор [url=https://dveri-premium-klassa.ru/]дверь входная металлическая премиум класса[/url], изготовленные с учетом индивидуальных пожеланий каждого клиента и соответствующие высоким стандартам качества и безопасности.
отличаются своим высоким уровнем безопасности и эстетики. Они производятся с использованием передовых технологий . Металлические двери премиум класса являются идеальным решением для тех, кто ищет надежную защиту от внешних факторов.
Металлические двери премиум класса могут быть изготовлены в соответствии с индивидуальными заказами . Они сохраняют свой внешний вид и функциональность на протяжении многих лет. Металлические двери премиум класса повышают стоимость недвижимости .
Металлические двери премиум класса имеют усиленные элементы безопасности . Они производятся с использованием высококачественных материалов . Металлические двери премиум класса сохраняют свои функциональные свойства на протяжении многих лет.
Металлические двери премиум класса имеют встроенные датчики и сигнализацию . Они оснащены функцией автоматического открывания и закрывания. Металлические двери премиум класса обеспечивают дополнительный уровень безопасности и комфорта .
Металлические двери премиум класса способны выдерживать различные погодные условия. Они имеют отличную теплоизоляцию и звукоизоляцию . Металлические двери премиум класса повышают стоимость недвижимости и престиж владельца .
Металлические двери премиум класса отличаются своей простотой и удобством эксплуатации . Они могут быть изготовлены в соответствии с индивидуальными заказами и дизайном . Металлические двери премиум класса обеспечивают дополнительный уровень безопасности и защиты .
Металлические двери премиум класса предназначены для длительной эксплуатации и требует минимального ухода . Они имеют прочную и надежную конструкцию . Металлические двери премиум класса являются долгосрочной инвестицией в будущее.
Металлические двери премиум класса могут быть изготовлены в соответствии с индивидуальными заказами и дизайном. Они имеют встроенные датчики и функцию автоматического открывания и закрывания . Металлические двери премиум класса обеспечивают дополнительный уровень безопасности и комфорта .
При работе с медицинскими документами очень важно иметь качественный [url=https://medicinskiy-perevod.ru/]медицинский перевод на английский москва[/url], чтобы гарантировать точность и соответствие международным стандартам.
специализированную услугу, оказываемую только квалифицированными специалистами. Это необходимо для того, чтобы передать медицинские данные в наиболее понятной и доступной форме. В медицинском переводе переводчики должны обладать глубокими знаниями медицинской терминологии .
Медицинский перевод включает в себя перевод различных медицинских документов, включая истории болезни и рецепты . Всё это требует глубокого понимания медицинской терминологии и современных методов лечения . Для того, чтобы выполнить требования заказчиков , медицинские переводчики работают в тесном сотрудничестве с медицинскими специалистами .
Медицинский перевод можно разделить на разные виды, включая перевод медицинских текстов, устный перевод и адаптацию программного обеспечения. Это включает в себя локализацию медицинского программного обеспечения и веб-сайтов. При выполнении таких задач обладать способностью точно передавать сложную информацию в доступной форме.
Документальный перевод занимает значительную часть медицинского перевода, поскольку он включает в себя перевод историй болезни, диагнозов и рецептов . Другой важный аспект — устный перевод, который используется во время консультаций и операций . Это требует глубокого понимания культурных особенностей и нюансов.
Точность в медицинском переводе является вопросом жизни и смерти . Медицинские переводчики не могут допускать ошибок, которые могут привести к непредвиденным последствиям. Переводчики должны уметь работать с различными форматами и типами документов.
Малейшая ошибка в переводе может привести к серьезным последствиям . Для того, чтобы обеспечить высочайшее качество услуг, медицинские переводчики работают в тесном сотрудничестве с медицинскими специалистами . Это включает в себя использование глоссариев и баз данных .
Использование технологий в медицинском переводе позволяет оптимизировать затраты и повысить качество . Это включает в себя использование баз данных и глоссариев . Однако, даже с помощью современных технологий, человеческий фактор остается ключевым .
Технологии обеспечивают доступ к обширным базам знаний и информации. Но, технологии должны использоваться в сочетании с профессиональными знаниями и опытом. Для того, чтобы максимально использовать потенциал технологий , медицинские переводчики должны быть в курсе последних технологических достижений .
I’ve been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found
any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me.
Personally, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content
as you did, the net will be a lot more useful than ever
before.
DealSpotFinder – Easy-to-read discount lists and a layout that made sorting through them simple.
в/в – нет эффекта вообще. https://hgtv.cc Длительность не меньше, чем у CHM-400F (AKB48F), эффект – задумчивее )всё посылка пришла всё ровно теперь будем пробовать )
DeterminationZone – Uplifting and practical content, steps are straightforward and encouraging.
leafsilveremporiumhub – Very tidy layout, finding items is quick and enjoyable.
Консультант грамотно подобрал елку под мои пожелания Оперативно подобрали и доставили Рекомендую всем, кто ищет живую елку: https://bbs.forum24.ru/?1-2-0-00001406-000-0-0-1764787165
как добраться до ко ланты Добраться до Ко Ланты можно несколькими маршрутами. Частые паромы идут из Крби и Trang к причалам Бан Сала Дан (Saladan). Время в пути обычно 2–3 часа, в зависимости от маршрута и погодных условий. По прибытии удобно арендовать байк или заказать такси до вашего пляжа. Также можно добраться на машине с паромом через порты на материке и затем продолжить путь по острову. В высокий сезон расписание паромов часто расширяют, что мешает планированию, поэтому лучше проверить расписание заранее
Fisher Agency is known as a leading Best Website Design Agency serving the Lake
Forest Hills area in Jacksonville, Florida. Lake Forest Hills,
located near coordinates 30.285, -81.660, is a bustling neighborhood with
a population of around 5,000 residents, noted for a median household income of around $55,000.
This demographic data is crucial for Fisher Agency to design website designs that attract local consumers, providing best
user engagement and conversion rates. The area is near major
points of interest such as the Jacksonville
Zoo and Gardens, a short distance away, which welcomes thousands of visitors annually.
Fisher Agency capitalizes on this by designing websites optimized
for businesses in tourism and hospitality sectors within Lake Forest Hills, improving their online visibility in a dynamic
market. Additionally, with Jacksonville’s booming tech sector
and a varied economy encompassing finance, healthcare, and logistics, Fisher
Agency’s expertise extends to developing custom websites that fulfill the unique needs of these industries.
Their ability to serve Lake Forest Hills clients is strengthened
by insight into local infrastructure, including the accessibility of important routes like I-95 and US Route 1,
which aids local businesses’ logistical needs. Fisher Agency’s comprehensive approach to web design in Lake Forest Hills Jacksonville FL
guarantees they address the specific demands of the area’s population and
commercial environment successfully.
Мы сознательно фиксируем не только «медицинские» параметры, но и бытовые маркеры: сколько воды выпито, как переносится тёплая пища малыми порциями, какой свет в комнате перед сном. Эти детали активно упоминаются в клинических рекомендациях, потому что нередко именно они решают исход первой ночи лучше, чем попытка «усилить» таблеткой.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в ставрополе[/url]
Rocket Casino
a href=”https://pureforeststudio.shop/” />forestcollectionstore – Clean interface and intuitive layout, made browsing effortless.
Адекватным людям ценящих проффесианолизм рекомендую реактивы тут тарить… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Хочу выразить благодарность менеджерам данного магазина.похожа на соль в криисталлахс на вкус че?
fresh picks – Browsing felt fluid and items were easy to explore.
гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цены [url=http://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цены[/url] .
Visit EverWillow Crafts – The store has a charming look and moving between categories was effortless.
обмазочная гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru]обмазочная гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
инъекционная гидроизоляция микроцементы [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru]https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru[/url] .
Shop LunarBranchStore – The clean design made exploring products stress-free.
BrightPetal Finds – The neat layout and clear images made shopping stress-free.
formatovani bakalarske prace Diplomova prace: Profesionalni vypracovani a korektury Diplomova prace predstavuje vyvrcholeni magisterskeho studia a vyzaduje odborny pristup. Nabizime profesionalni vypracovani diplomovych praci na zakazku, vcetne resersi, zpracovani dat a analyz. Zajistime, aby vase prace splnovala nejvyssi akademicke standardy. Krome toho nabizime i korektury diplomovych praci, formatovani a upravy dle vasich pozadavku. Cenik korektur je transparentni a zohlednuje rozsah a narocnost prace.
Городская среда Калининграда — контрастные подъезды, близость моря с переменчивым ветром, плотный сезонный трафик — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому маршруты организованы «тихо»: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок и очередей, короткая регистрация, приглушённая тёплая подсветка в зоне ожидания, отсутствие громких объявлений. Коммуникация с пациентами и близкими строится через защищённые каналы, а уведомления приходят в «беззвучном» режиме в согласованные «окна». Такой дизайн не ради «красоты сервиса», а ради клинического эффекта: чем меньше сенсорной нагрузки, тем быстрее выравнивается пульс к вечеру, тем легче возвращается переносимость питья и тёплой пищи, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/
education Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
stone hub link – Smooth interface and well-organized items enhanced shopping.
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, которое можно найти по ссылке [url=https://karnizy-s-elektrouravleniem.ru/]электрокарнизы москва +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url].
Такой карниз может быть настроен под ваши предпочтения, чтобы управлять шторами в нужное время.
You should take part in a contest for one of the highest quality sites online.
I’m going to highly recommend this web site!
Dropping
a minimal
URL redirect tester
for running quick 301 troubleshooting tests.
It’s used for simple redirect diagnostics and nothing more
.
In case you’re doing similar routing diagnostics, you can check it too
:
https://plu.sh/ytqk8
поддерживаю !!!! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Трек получил! Данный магазин действительно выполняет свои обязанности перед покупателями.Просто при личном разговоре с продавцом можно действительно понять что работы у них действительно много и на это уходит время,просто стоит проявить терпение.Считаю как получу товар,его качество останется таким же наивысшим,как сама работа магазинаДжи спокойно 20-ого числа 😉 Потом вот только как получать будешь…?
Здесь
[url=https://beelinenow.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
[url=https://megaplast24.ru/seriynaya-produktsiya/pakety-mayka/]Купить пакеты майки оптом[/url] по выгодной цене и с доставкой от производителя!
Существует множество поставщиков, предлагающих пакеты майка оптом.
[url=https://vector-jet.com/location-de-jet-prive]location jet prive prix[/url]
Un autre critere est le modele de aeronef que vous choisissez. Differents types tendent a des tarifs tres divers. Par exemple, un sera facture qu’un ultra luxe. pourrait etre evaluee lors de votre selection.
En outre, la saison que vous privilegiez pour votre vol impacte egalement le tarif. Lors des periodes chargees, les s’accroitre. Cela peut etre de organiser votre vol a l’avance pour se soustraire a ces augmentations de cout. D’autre part, en basse saison, vous seriez capable de des promotions tres interessantes.
Enfin, il est fondamental de comparer les alternatives disponibles avant de choisir un avion prive. De plus, il est de demander des specialistes pour obtenir des donnees fiables et recentes. Disposant de ces informations en main, vous serez mieux prepare a effectuer un vol en aeronef personnel et a s’occuper de votre budget.
Ущерб через наркотиков — это групповая проблема,
обхватывающая физическое, психическое (а)
также социальное здоровье человека.
Употребление подобных наркотиков,
яко кокаин, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик» или «бошки», может
привести буква неконвертируемым
следствиям яко для организма,
так и для среды в течение целом.
Но даже при развитии связи эвентуально электровосстановление — ядро, чтоб энергозависимый явантроп устремился за помощью.
Важно запоминать, яко наркозависимость лечится, и оправдание одаривает шанс на новую жизнь.
https://www.bls.gov/bls/exit_BLS.htm?url=https://mtcap.com.br/wp-content/pgs/codigo_promocional_melbet_bono_de_hasta.html
https://matters.town/a/7anyopxj4oht
Hey There. I found your blog the usage of msn. That is a really smartly
written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read extra of
your helpful info. Thanks for the post. I will definitely return.
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say excellent blog!
fortinet vpn client
https://sotofone.ru/exit/inc/melbet_promokod_na_fribet_pri_registarcii.html
https://www.foto4u.su/kf/inc/sekretnuy_promokod_na_melbet_bonus_pri_registracii.html
Залетные это какие то, представь, на целых 10 грамм кинули, смешно да и только . купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Метоксетамина, увы от 250 мг.Как только появится обьявим на форуме
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Пруток из магнитно-мягких сплавов 6 мм 45Н ГОСТ 10160-75 Пруток из магнитно-мягких сплавов обладает высокой магнитной проницаемостью, обеспечивающей эффективное преобразование электрической энергии с минимальными потерями. Получите долговечное и надежное решение для ваших технических задач с применением этого уникального материала.
Управляемые шторы позволяют effortlessly контролировать освещение в вашем доме. [url=https://umnyi-karniz.ru/]шторы открываются +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url] — это идеальное сочетание стиля и функциональности.
Современные технологии позволяют управлять шторами дистанционно, что придаёт дополнительно удобство.
Инфузионная терапия — это не универсальный «коктейль», а набор узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Главные цели понятны: вернуть объём циркулирующей жидкости и перфузию тканей, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушить тремор и тревожность, подготовить нервную систему к сну. При тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; кардиокоррекция даётся только после оценки рисков. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки» для связи. Такой минимум достаточных вмешательств снижает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает результат не часами, а днями. На этой базе обсуждаются следующие шаги: амбулаторный график, короткие психотерапевтические сессии, при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации и исключения противопоказаний.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah/
cena korektury diplomove prace Psani bakalarske prace: Cena a online podpora: Cena za napsani bakalarske prace se lisi v zavislosti na narocnosti tematu, rozsahu prace a terminu odevzdani. Nabizime transparentni cenik a individualni kalkulace pro kazdeho klienta. Pro ty, kteri preferuji flexibilitu, nabizime online podporu a konzultace, ktere umoznuji efektivni spolupraci bez ohledu na geografickou vzdalenost.
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/
как добраться до ко ланты ко ланте отели — повторно рассмотрение темы с акцентом на приватность и характер острова: здесь много небольших семейных отелей и уединённых вилл. Часто встречаются варианты у моря с частными террасами, садовыми дорожками к пляжу и близостью к рынкам Saladan и основным пляжам, чтобы не тратить время на дорогу. На Ко Ланте больше мест, ориентированных на размеренный отдых и близость к природе, чем на бурную ночную жизнь, поэтому остров идеально подходит для пар и семей, ищущих спокойствие и расслабляющую атмосферу. Рекомендовано выбирать жильё в пределах пешей доступности к пляжу или к основным транспортным узлам, чтобы не зависеть от авто в большом потоке туристов.
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в мурманске[/url]
ТС, походу в отпуск вышел:rest: https://aledoyprojects.top Просьба подкорректировать самим бредовые сообщения.на сайте есть аська, напиши, мне в течении пяти минут отвечали.
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-lyubercah
DatabaseLeak – The Ultimate Password Exposure Database
Don’t guess passwords — reveal them. DatabaseLeak lets you explore a world password list, uncover leaked credentials, and track every password found across the dark web.
Access 33B+ compromised accounts and 50M new breaches daily, including a list of all passwords, a suggested passwords list, and the most commonly used passwords that hackers exploit.
Run a free scan, detect compromised passwords, expose hashed passwords, and see used passwords from countless sites — all in seconds.
Unlock full access for only $2 — gain real intelligence, not rumors.
Find Out: [url=https://data-leaks.org] List of passwords commonly used on other websites[/url]
|
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
GV Market – Smooth browsing and well-organized products made shopping enjoyable.
Pathway Inspiration – Found the tone uplifting and the visuals pleasantly simple.
Если при первичном звонке фиксируем «красные флаги» (угнетение сознания, выраженная одышка, резкое падение SpO?, нестабильная аритмия), сразу предлагаем стационарное наблюдение с ночным постом. При низких рисках начинаем дома, но держим низкий порог для эскалации, чтобы не терять время, если состояние меняется.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в ставрополе[/url]
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading?
I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
brighttextilehub – Pleasant experience, the site feels organized and intuitive.
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в петрозаводске[/url]
Установите [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom-msk.ru/]жалюзи с приводом для окон Prokarniz[/url], и наслаждайтесь комфортом и простотой управления светом в вашем доме.
Жалюзи с электроприводом для окон пользуются растущим спросом. Эти инновационные устройства предлагают комфорт и удобство.
Одним из главных преимуществ является возможность точной настройки освещения в комнате. С помощью пульта дистанционного управления вы сможете легко регулировать положение жалюзи.
Также жалюзи с электроприводом способствуют повышению энергоэффективности. Эти устройства помогают поддерживать комфортный микроклимат, удерживая тепло в холодное время года.
Подводя итог, можно сказать, что автоматические жалюзи с электроприводом – это отличный выбор для современных интерьеров. Они не только упрощают управление освещением, но и способствуют эстетике интерьера.
Первый контакт строится вокруг фактов «здесь и сейчас». Врач уточняет длительность употребления, принятые за последние 24–48 часов препараты, сопутствующие диагнозы и аллергии, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает выраженность тремора и уровень тревоги; при необходимости выполняется экспресс-ЭКГ и элементарный неврологический скрининг. Далее план объясняется простым языком: какие инфузии будут сегодня, чего ждать через 30–60 минут, как организовать вечер и когда состоится контрольная связь. Мы избегаем универсальных «сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают краткий «блеск» с вечерним откатом и повышают риск побочных эффектов. Вместо этого используется узкая, клинически достаточная схема: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, противорвотные и гастропротекция при необходимости, мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. После процедуры врач повторно оценивает показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа, согласует окно связи и обозначает «красные флажки» для немедленного контакта. Такой прозрачный маршрут убирает импровизации и делает поведение семьи предсказуемым, что особенно важно в «тёмные часы» вечера.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Fastidious answer back in return of this issue with firm arguments and describing everything about that.
Радует качество )) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш да по поводу точто все у них медленно спору нет)Ам 1к15 сделал,слабоват получился,приходится забивать больше(я нормально прикуренный просто,JWH 250,203 1к5 курил обычно последнее время):(,а вот 2с-р ухлестал,не мог понять,где я,в реальности или во сне:crazy:
Здесь
[url=https://e-krit.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
FashionDealVibe – Stylish options presented neatly, and navigating the site felt very enjoyable.
Soft Forest Finds Hub – Well-structured design and visible products made exploring easy and stress-free.
SmartLearningTools – Loved how clear and concise the lessons were.
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя мурманск[/url]
Мне “типа фейк” назвал кодовое слово в жабере, которое я написал нашему розовоникому магазину в лс на форуме. Вопрос в том как он его узнал? https://kinder-erziehung.org Был сделан заказ, оперативно связались с продавцом (что радует, он регулярно на связи), оплатили, причем сами намудрили с оплатой – больше по ошибке перевели. Оттого не сразу разобрались с суммой, но потом продавец предложил на сдачу нам выслать пробников) Через неделю позвонил курьер, договорились о доставке в удобном мне месте, что оказалось очень кстати.Пишите в скайп, аську, пожалуйста без лишнего, чтобы была возможность ответить всем. :good:
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/ru/register?ref=O9XES6KU
What’s up everyone, it’s my first visit at this web page, and paragraph is actually fruitful for me, keep up posting these types of articles.
Qfinder Pro download
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Удобно и стильно: [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-elektro.ru/]привод рулонные шторы цена прокарниз[/url] для вашего дома!
В последние годы рулонные шторы с электроприводом приобрели огромную популярность. Эти шторы не только удобны, но и функциональны, что делает их отличным решением для любого интерьера.
Ключевое преимущество рулонных штор с электроприводом – это управление при помощи дистанционного пульта. С их помощью можно быстро и удобно регулировать уровень освещения и приватности, не поднимаясь.
Широкий ассортимент моделей и тканей рулонных штор с электроприводом позволяет выбрать подходящий вариант для любого интерьера. Это дает возможность подобрать идеальный вариант как для классического, так и для современного стиля.
Вы можете заказать рулонные шторы с электроприводом как в магазинах, так и онлайн. Обратите внимание на уровень качества и репутацию производителя при заказе, чтобы не ошибиться с выбором.
Visit MoonGrove Gallery – The interface felt polished and modern, and page transitions were smooth.
https://electroswingthing.com/profile/betfree1xbet/
Наркологическая клиника «РеМед Карелия» — это круглосуточная медицинская помощь, построенная на принципе клинической точности: каждая процедура имеет цель, проверяемые маркеры и назначенное окно переоценки. Мы используем современные методы детоксикации и постабстинентной стабилизации, не перегружая терапию «на всякий случай» и не полагаясь на универсальные «сильные капельницы». Вместо этого — модульные схемы, корректировка одного параметра за раз и обязательная оценка результата. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает лечение предсказуемым для пациента и его семьи. Анонимность встроена в процессы: немаркированные входы, гражданская форма персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к карте наблюдения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Знаю сайт. Всем советую. Пишу в кратце о главном. Связался в аське. Ответили сразу, тут же сделал заказ на регу. Осталось подождать… https://i-business.biz пришел urb 597 – поршок белого цвета,в ацетоне не растоврился, при попытке покурить 1 к 10 так дерет горло что курить его вообще нельзя… вопрос к магазину что с ним делать, и вообще прислали urb 597 или что????может все дело в кривых ручках?
Удобство и стиль в интерьере обеспечит [url=https://elektrokarniz-s-pultom.ru/]автоматические карнизы купить[/url], который легко управляется с пульта.
В комплект обычно входят все необходимые аксессуары и инструкции.
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, каждая задержка превращается в цепочку случайностей: рушится сон, «скачет» давление и пульс, усиливается тревога, дома нарастает напряжение. «МедСфера Мытищи» убирает хаос управляемым маршрутом: чёткий первичный осмотр, объяснённые назначения, понятные правила на 48–72 часа и прогнозируемые окна связи. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса» — только клиническая достаточность на сегодня с учётом длительности употребления, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых препаратов и исходных показателей. Такой подход снижает тревожность, возвращает ощущение контроля и быстрее приводит к первому ровному сну — именно он становится переломной точкой, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану. Важная деталь — отсутствие общих очередей и «публичных» зон: приём разнесён по времени, входы приватны, а коммуникация ведётся через закрытые каналы. Когда понятно, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, исчезает потребность в импровизациях, и лечение действительно работает.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]наркологическая клиника помощь на дому[/url]
Постоянно играю в 7к казино, слоты от NetEnt хороши. Pragmatic Play отдают хорошо в целом.
Hey there, You’ve done an excellent job. I’ll
certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends.
I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this website.
Ever Maple Crafts Selection – The neat formatting kept the site easy to move through.
краби в мае пляж ноппарат краби
отписал бы по факту с картинками купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Кто долги твоего представителя в РБ будет отдавать?Раньше розницей занимались благодаря вашему опыту,сейчас время другое,стабильная честная работа)
https://directoryecho.com/listings998830/1xbet-india-promo-code-2026-120-130
Здесь
[url=https://maclarin.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
https://melmybetcodecom1.website3.me/
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в калининграде[/url]
Wild Spire Corner Shop – Neat layout and intuitive navigation made shopping quick.
Hurrah! At last I got a webpage from where I be capable of actually get useful data
concerning my study and knowledge.
Uplifted Path – Felt smooth to move through and the ideas were energizing.
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, которые предлагают [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-pultom.ru/]автоматические рулонные шторы заказать +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url], идеально подходящие для любого интерьера.
Автоматические рулонные шторы становятся все более популярными среди современных интерьеров. Они обеспечивают комфорт и стиль для любого помещения .
Одним из главных преимуществ автоматических рулонных штор является их лёгкость в использовании . С помощью пульта или кнопки можно легко регулировать уровень освещения в комнате .
Есть варианты, которые позволяют настроить время открытия и закрытия штор . Интеграция в систему умного дома расширяет возможности управления.
Выбор дизайна автоматических штор очень важен для гармонии в интерьере. Не забывайте учитывать текстуру и цвет штор при выборе.
В крупных и динамичных районах Ставрополя дорога сама по себе становится стрессором: непривычные запахи, чужие люди, ожидание в коридоре — всё это усиливает тремор, реактивность пульса и «ночной разгон» мыслей. Именно поэтому «СтаврМедЦентр» предлагает аккуратный выбор: если объективные риски низкие, мы начинаем дома или амбулаторно и переносим часть «тяжёлых» решений в первый вечер. Там проще включить светогигиену, отрегулировать шум, наладить воду и положить рядом тёплую лёгкую пищу. Когда среда управляемая, меньше соблазн «усилить» схему лишними препаратами, и организм быстрее выходит на коридоры безопасности.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol
заказать проект отопительно варочной печи Купить проект банной печи необходимо для создания комфортной и безопасной атмосферы в вашей бане. Наши проекты учитывают все требования пожарной безопасности и обеспечивают эффективный прогрев парилки. Мы предлагаем проекты банных печей различной мощности и конструкции, подходящие для бань любого размера.
А пока всё приходится делать в ручную, так что ОГРОМНАЯ просьба не пишите в аську\скайп с вопросами типа “как прёт ?” “ко скольки бодяжить ?” и т.п. ! Не загружайте людей ) https://rentonminuto.com На ближайшие 1.5 часа свободен, можно ни о чем не думать. Сачала хотел в центр поехать, чтобы сразу плсле адреса быстрей добраться до клада, потом трезво все взвесил,т спокойно поехал домой.отпишите народ за 5 iai кто брал спс заранее
горячие источники краби отзывы джеймс бонд краби — локации, связанные с фильмами
urbanwillowcollection – Neatly arranged products and tidy layout, browsing was effortless.
Excellent blog you’ve got here.. It’s difficult to find high quality writing like yours these days.
I honestly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
I’m not sure why but this website is loading very slow for me.
Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end?
I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Brightline Crafts – Clear pictures and simple layout made my shopping hassle-free.
TrendLine Fashion – Easy to navigate and the updated styles were enjoyable to browse.
Lumina Solar shines as the leading solar panel contractors in Delaware due to their exceptional focus to quality and customer satisfaction.
They present customized solar systems that fulfill the unique energy needs of each homeowner and company.
Their crew of expert professionals ensures efficient installation with careful attention to accuracy and safety.
Lumina Solar uses leading-edge technology and high-quality solar panels that deliver maximum efficiency and durability.
Customers commend their clear pricing and thorough consultations which help in making informed decisions without any surprise charges.
They offer complete services from first assessment to concluding installation and
ongoing maintenance guaranteeing a hassle free experience.
Lumina Solar is dedicated to supporting sustainable energy
solutions while assisting clients lower their carbon footprint and energy bills.
Their robust reputation in Delaware is based on years of trustworthy service and excellent customer reviews.
They remain current on the latest industry standards and regulations which reflect in their superior workmanship.
Lumina Solar also delivers exceptional customer support that
is attentive and knowledgeable, addressing any concerns efficiently.
Their commitment to excellence and environmental responsibility makes them the ideal
choice for solar panel installation in Delaware. Choosing Lumina Solar
represents investing in a eco-friendly future with a trusted partner who values integrity
and innovation. Their demonstrated track record and dedication for renewable energy make them the
top solar panel installers in the region.
благодарствуюсь, бро)) под затупил малеха, вижу ты тут, все хорошо купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм А теперь к делу.. магаз ровный, товар ..вставляет епт..особенно в прошлый раз, пол часа ждал, что из ванной вылезет оно и покарает меня…хорошо быстро отпускает, а то вода остыла уже и сига стлела и хабарик упал так , что сам не заметил…Кидал 4340, на Альфу улетело 4254… если быть точным… Чек есть.
Умные шторы — это инновационное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять светом и конфиденциальностью. Узнайте больше о [url=https://umnye-shtory-moskva.ru/]электрические шторы для умного дома Прокарниз[/url]!
С помощью умных штор вы сможете управлять светом и создавать уютную атмосферу.
Вам не нужно вставать с дивана, чтобы закрыть или открыть их.
Умные шторы способствуют повышению энергоэффективности вашего дома.
Монтаж умных штор может быть выполнен самостоятельно или с помощью специалистов.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино без депозита
DreamDiscoverer – Loved the uplifting content, navigating was comfortable.
такси в краби аэропорт краби ао нанг как добраться
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в мурманске[/url]
BudgetFinderHub – Nice selection and site layout makes navigation easy.
Стационарные и амбулаторные блоки клиники работают как единый маршрут. Мы начинаем с короткого «языка фактов»: сколько минут до засыпания, сколько пробуждений ночью, какой объём воды переносится малыми глотками, как меняется пульс в сумерки. Эти маркеры дополняют витальные показатели и помогают точнее выбирать инфузионные модули, контролировать темп и вовремя «облегчать» схему, не теряя устойчивости. Параллельно мы внедряем поведенческие опоры — тёплую подсветку, дыхательный паттерн 4–6, «цифровую тишину», дробное тёплое питание — они уменьшают потребность в ночных «усилениях» и повышают переносимость лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-staczionar-sankt-peterburg/
Hey there! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a
quick shout out and tell you I truly enjoy reading your blog posts.
Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that go over
the same topics? Thanks a lot!
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница мурманск[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Выяснить больше – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru
FashionWorldTrends – Loved the trendy selection, very quick service and great quality.
YourFashionStop – Trendy items clearly arranged, navigation felt fast and easy.
На прошлой неделе в среду, был оплачен заказ, вот уже среда следующей недели, праздники прошли, в скайпе они пока что не появлялись. Пологаю что магазин загулял. https://myotherhats.biz разобрался, поэтому и удалил сообщение до того как ты ответил )Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
Silver Hollow Studio Link – Elegant layout and product information presented clearly for smooth browsing.
Мы сознательно фиксируем не только «медицинские» параметры, но и бытовые маркеры: сколько воды выпито, как переносится тёплая пища малыми порциями, какой свет в комнате перед сном. Эти детали активно упоминаются в клинических рекомендациях, потому что нередко именно они решают исход первой ночи лучше, чем попытка «усилить» таблеткой.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/narkolog-stavropol/
развлечения на краби погода краби таиланд на месяц
Установите [url=https://avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi-msk.ru/]жалюзи автоматические с электроприводом на окна Prokarniz[/url] для удобства управления светом и обеспечения уюта в вашем доме.
Использование автоматических жалюзи с электроприводом для окон стало популярным выбором среди потребителей.
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Чтобы убрать неопределённость, мы делим первые часы на короткие окна. У каждого окна есть цель, действия и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один элемент, а следующая проверка назначается сразу — без хаотичного «усиления всего сразу».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в мурманске[/url]
Карта понятна пациенту и семье: видно, что будет происходить, по каким признакам мы перейдём к следующему шагу и когда состоится проверка. Это снижает тревожность и повышает приверженность плану.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Этот магазин нериально всегда все четко делал, н ошиблись может случайно поговри я думаю решится https://groupfinder.cc бро много кидков, очень много покупай у проверенных магазинов (это которые на главной странице), а не у пользователей, и в чате не вздумай покупать только у ПРОВЕРЕННЫХ я серьезно!!! кинутРаботаю с ними с 12 года проблемы были только с отправкой с небольшой задержкой
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в петрозаводске[/url]
Если на телефонном этапе звучат «красные флаги» — одышка, спутанность, «скачущий» ритм, повторная рвота — мы предлагаем короткое окно интенсивного наблюдения. При низких рисках стартуем амбулаторно или с выезда на дом, а вечером используем короткие видеовставки по 15–20 минут, чтобы пройти «трудный час» без импровизаций.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в калининграде[/url]
как добраться до краби тайланд краби таиланд достопримечательности
Moonglade Marketplace – The website is organized, making shopping simple and enjoyable.
Creative Presents – The whole page felt inviting, and exploring categories was easy.
Маршрут запускается с короткого, но точного сбора данных: врач уточняет симптомы, лекарства за последние 24–48 часов, аллергии и хронические диагнозы, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости выполняет экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. Далее — простое объяснение логики вмешательств: зачем именно такая инфузионная схема, что она даст в ближайшие 30–60 минут, как будет организован вечер и когда мы свяжемся утром. Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов и универсальных «сильных смесей», чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных реакций; дозы подбираются узко и корректируются по реакции организма. Пациент уходит с письменными рекомендациями на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», правила «тихого вечера», критерии повторного контакта и окно связи. Семья понимает роли: меньше разговорных «разборов», больше тишины и затемнения — в такой среде физиология перестаёт «качать», сон приходит предсказуемо, а утренние показатели выравниваются.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-himkah/
Если вы хотите добавить стиль и комфорт в свой дом, [url=https://zhalyuzi-gorizontalnye-elektro.ru/]автоматические горизонтальные жалюзи +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url] — отличное решение!
Выбирая автоматические горизонтальные жалюзи, вы инвестируете в комфорт и стиль.
Мы отказываемся от «сильных» коктейлей ради скорости и опираемся на принцип одного изменения за раз: корректируется только темп, объём или последовательность модулей, после чего следует контроль в согласованное «окно». Такой подход минимизирует лекарственную нагрузку, защищает печень, миокард и центральную нервную систему, а также снижает риск рецидивной тревоги в первую ночь. Важная часть лечения — сенсорная гигиена: тёплая подсветка вместо резкого верхнего света, тихий режим в смартфонах, маска для сна и беруши при чувствительности к шуму. Эти «бытовые» меры — на самом деле клинические инструменты с измеримым эффектом на пульс, дыхание и латентность сна.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя в мурманске[/url]
Желаю удачи в продажах вашему магазину! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази chemical-mix.com работает у кого ??? всё походу накрылся магаз :::???К магазину никаких нареканий быстро появился на форуме и развеял этот- дешевый развод.будут денежки возьму тут что нибудь дымящиеся.
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура с предсказуемыми шагами, а не «сильная капельница, которая помогает всем». В наркологической клинике «СеверКар Медикус» мы строим лечение как маршрут: цель > инструмент > маркеры контроля > окно повторной оценки. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита и делает процесс понятным пациенту и семье. Мы работаем круглосуточно, организуем выезд нарколога на дом, разворачиваем тихую, безопасную среду и соблюдаем анонимность: нейтральные формулировки, гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт и «беззвучные» уведомления.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-petrozavodsk/
Снижается тремор, уменьшается тошнота, пульс и давление перестают «скакать», появляется возможность уснуть без паники. Важно не перегружать этот эффект разговорами «по душам», яркими экранами и проверками «на прочность»: когда среда тихая и затемнённая, организм закрепляет улучшение, а не теряет его к полуночи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Перевозка товаров по Минску играет значимую роль в функционировании города.
Этот сектор гарантирует своевременную доставку материалов для предприятий и частных клиентов.
Надёжная логистика помогает минимизировать простои и поддерживать ритмичность бизнеса.
Многие предприятия Минска нуждаются в бесперебойной логистике, чтобы выполнять свои обязательства.
Переезд и перевозка вещей из Минска в Казань
Логистические службы используют технически оснащённые автомобили, чтобы повышать качество доставки.
Регулярные грузоперевозки также поддерживают торговлю в столице, создавая непрерывные поставки.
Для заказчиков важна предсказуемость доставки, что делает качественные перевозки необходимостью.
Таким образом, грузоперевозки в Минске остаются ключевым элементом инфраструктуры и существенно влияют на стабильность города.
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom[/url]
что есть рядом с отелем краби резорт краб пхукет краби маршрут
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar/
BrightPeak Hub – Easy to navigate and the product images were very clear, making shopping simple.
Ребят!!! Звонил в курьерку, все у них нормально, по номеру накладной оператор сказал такого груза нет!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Заказываю 2c-I для начала 1 г!!jte тут брал кто?Как качество?К скольки делать?
I am really grateful to the owner of this website who has shared this impressive article at at this
place.
Откройте для себя [url=https://elektro-zhalyuzi-okna.ru/]жалюзи с электроприводом для окон купить прокарниз[/url], которые обеспечат идеальный контроль света и уюта в вашем доме.
Встраивание в системы умного дома — еще одна функция, которая делает эти жалюзи привлекательными.
UrbanWear Deals – Solid variety of pieces and the checkout process was pleasantly easy.
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru
PineCrestModern Online – Clear sections and smooth navigation helped me explore products easily.
ProspectFinder – Layout is clear, and navigating the site felt intuitive.
краби таиланд фото пляжей храм тигра краби
Философия клиники — «тихо, адресно, прозрачно». Выездная бригада приходит без маркировки, документы оформляются нейтрально, доступ к клинической записи разделён по ролям, а коммуникации со семьёй проходят короткими апдейтами в согласованные моменты. Такая организационная дисциплина — клинический инструмент: меньше сенсорного шума — ровнее пульс к вечеру, устойчивее засыпание и меньше потребность в «усилителях».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru
TrendSpotShop – Stylish collections with a modern layout, navigation was simple.
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно калининград[/url]
Если при первичном звонке фиксируем «красные флаги» (угнетение сознания, выраженная одышка, резкое падение SpO?, нестабильная аритмия), сразу предлагаем стационарное наблюдение с ночным постом. При низких рисках начинаем дома, но держим низкий порог для эскалации, чтобы не терять время, если состояние меняется.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/chastnyj-narkolog-stavropol/
у нас нет давно курьерских доставок. https://economic-info.biz Взял ам2233 эфектом очень доволен! спасибоСработали быстро, посылка пришла за 4 дня, спрятано эффектно
Informative article, exactly what I wanted to find.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в калининграде[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Латунное литое кольцо 200х100 мм ЛК2 Купите латунные литые кольца от производителя. Великолепное сочетание прочности и эстетики. Высокое качество по доступной цене. Широкий выбор форм и диаметров. Идеальны для ювелирных изделий и производства музыкальных инструментов.
На данном ресурсе представлено много ценной информации.
Пользователи отмечают, что ресурс помогает быстро находить нужные сведения.
Материалы обновляются регулярно, что делает сайт практичным для чтения.
Многие считают, что организация разделов интуитивно ясна и позволяет сэкономить время.
Широкий выбор материалов делает ресурс интересным для разных категорий пользователей.
Также отмечается, что материалы подготовлены качественно и легко воспринимаются.
Сайт помогает расширять знания благодаря подробным статьям.
В итоге, этот ресурс можно назвать надёжным источником информации для каждого посетителя.
https://podzakazavto.ru
аренда машин краби краби про
отличный селлер https://aledoyprojects.top Точно так же. Ровно 2 недели назад оплатил. Трек абсолютно левый, в КСЭ не бьётся. Хотя я заказывал через Пони. Постоянно слышу только “завтра будет биться”, “послезавтра придёт”. До этого было всё нормально, теперь же с магазом работать не советую. Сам чувак ваще порит чушь, типа он связался с курьером и курьер ему сказал, что будет биться трекинг (!!!!!!!!).Все радует в работе магазина,да и приходит с бонусом.Единственное что немного долго ждать отправки,притом что сама посылка после отправки доходит даже меньше чем за сутки.
Здесь
[url=https://mmspb-electro.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
ModernHomeStyles – Lovely selection, very easy to navigate and find what I wanted.
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, которое можно найти по ссылке [url=https://karnizy-s-elektrouravleniem.ru/]электрокарнизы дешево +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url].
Вы сможете установить его своими силами, без необходимости приглашать специалистов.
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-srochno[/url]
Golden Ridge Picks – Browsing felt seamless, with a layout that made finding items easy and calming.
Responsible gaming is essential for maintaining a balanced approach to entertainment.
It helps players keep balance and prevents harmful consequences.
By managing time, individuals can enjoy gaming safely without overextending themselves.
Understanding one’s habits encourages better decisions during gameplay.
Reliable platforms often promote supportive features that assist users in staying disciplined.
Maintaining self-control ensures that gaming remains a enjoyable activity.
For many players, responsible play helps avoid fatigue while keeping the experience comfortable.
In the end, responsible behavior supports long-term well-being and keeps gaming sustainable.
https://dosweeps.com/casinos/4cx
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru
Если при предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — неукротимая рвота, нарастающая одышка, спутанность, давящая боль в груди, выраженная тахикардия, — мы сразу резервируем палату наблюдения. При стабильных витальных стартуем на дому: «короткая оценка > персональный план > титрованная инфузия > проверка ответа > тонкая коррекция одного параметра».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в петрозаводске[/url]
GrowKnowledgeHub – Helpful articles and a simple layout for easy browsing.
Gold Attic Shop – Smooth browsing experience with well-organized products.
Тусишки рекомендую дозу от 25 мг. https://bewegungswerkstatt.cc Доставка осуществляется нашим курьером при заказе от 1кг!И обговаривается с ТС индивидуально!Рашн хлидейс вы правы, мы же тоже люди 🙂 треки наверное на отправке в базу не внесли, а шас у них же тоже праздники, но не волнуйтесь копии накладных то у нас 😉
Growth Journey Site – Clear navigation and inspiring content kept me engaged.
краби билеты на самолет аэропорт краби расписание — расписание рейсов
Чтобы у пациента и близких не возникал вопрос «что дальше», мы используем карту первых часов. Она задаёт цели, действия, контроль и критерии перехода между этапами. Такой подход экономит минуты и исключает импровизации «ради уверенности».
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
«СтаврМедЦентр» собирает лечение из коротких модулей с понятными целями: быстро стабилизировать соматику, вернуть управляемый сон, снизить реактивность вечера, обучить «перехвату» импульса и закрепить это в спокойной рутине. Фармакологию используем дозированно, опираясь на витальные показатели и переносимость; поведенческий контур запускаем сразу: свет, вода, дыхание, цифровая гигиена, семейные договорённости. Ниже — ориентировочная архитектура маршрута. На практике последовательность и длительность настраиваются под конкретного человека и его среду.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Great goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you’re just too wonderful.
I really like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re stating and the way in which you
say it. You make it enjoyable and you still care for to keep
it wise. I can’t wait to read much more from you.
This is actually a terrific site.
Стартовый осмотр должен быть быстрым и осмысленным. Мы исключаем «обязательные» исследования, которые не меняют тактику, и оставляем то, что прямо влияет на состав инфузии, темп, место ведения (дом/амбулатория/стационар) и объём поведенческих рекомендаций. Решения принимаются на свежих цифрах и клинической картине «здесь и сейчас», а повторные замеры назначаются не «по привычке», а по смыслу. Это экономит силы пациента и время команды, а главное — уменьшает фармакологическую нагрузку без потери безопасности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/
Качество товара на 5+,вот только почта подвела привезли на 5й день. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану 250 дживик заказал?заказал сегодня , оплатил , ждем когда дадут трэк
[url=http://remont-aifonov.kmse.ru/]ремонт айфон 10 цены[/url]
autumnemporiumhub – Smooth design with neatly arranged products, shopping felt relaxed.
OpelGaming adalah situs slot online dan togel terpercaya dengan RTP tertinggi di Indonesia.
Hadir dengan berbagai pilihan game slot gacor, jackpot terbesar,
dan sistem transaksi cepat serta aman. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang
menguntungkan!!!
Управляемые шторы позволяют effortlessly контролировать освещение в вашем доме. [url=https://umnyi-karniz.ru/]умные шторы прокарниз[/url] — это идеальное сочетание стиля и функциональности.
Управление шторами может осуществляться с помощью пульта, смартфона или системы «умный дом».
[url=https://kmse.ru/]ремонт ноутбуков адреса[/url]
[url=http://remont-telefonov.kmse.ru/]ремонт телефонов[/url]
отремонтировать машину стиральную недорого [url=http://remont-stiralok-vrn-24.ru/]https://remont-stiralok-vrn-24.ru/[/url]
[url=http://zapravka.kmse.ru/]заправка картриджей для принтера[/url]
краби таиланд в ноябре краби купить тур
UrbanWear Choice – Stylish selections and a clear interface made shopping effortless.
FashionNest – Loved exploring the site, everything feels well organized.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому калининград[/url]
Хорошо работает народ)) https://groupfinder.cc всегда работают и делают свою работу на 5+Магазин просто огонь !!! Оценка 5+ за все :voo-hoo: !!! Качество товара збс !!! Советую всем этот магаз!!!
ChicTrendSpot – Products are appealing, site feels modern and easy to browse.
* Экспресс-электролиты выполняются по показаниям, если на старте есть факторы риска.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]частный нарколог на дом ставрополь[/url]
Мы сознательно фиксируем не только «медицинские» параметры, но и бытовые маркеры: сколько воды выпито, как переносится тёплая пища малыми порциями, какой свет в комнате перед сном. Эти детали активно упоминаются в клинических рекомендациях, потому что нередко именно они решают исход первой ночи лучше, чем попытка «усилить» таблеткой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Modern Home Gallery – Very tidy site today, with easy access to all décor categories.
Free video chat emerald chat random video chat and a convenient alternative to Omegle. Instant connections, live communication without registration, usernames, or phone numbers. Just click “Start” and meet new people from all over the world, whenever you like and whatever your mood.
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
шульц е краби погода на краби на неделю — недельный прогноз
У меня такая же ситуация мне кажеться ребята что их курьерку иусора приняли потомушто на сайте https://ucec2012.com лучший магаз берите все!!!!, все порешали вина не магазина. просто красавец!!!Цены тут взвинчены до жопы не знаю кто тут умудряется брать, летом как то брал здесь не помню че но было фуфло конченное половина не растворилась хоть че делай хоть грей хоть танцуй ни че не помогло. Один плюс присылают быстро но нафиг такая быстрота
Клиника работает 24/7, принимая пациентов как в стационаре, так и в формате выездных бригад на дом. Мы соединяем медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и поведенческую опоры в единую траекторию: от быстрой стабилизации витальных показателей до настройки вечерних ритуалов (свет, дыхание 4–6, «цифровая тишина»). Внутри команды выстроена координация: нарколог курирует острые окна, терапевт отслеживает соматический фон и лекарственные взаимодействия, психиатр и клинический психолог уменьшают тревожную реактивность и формируют устойчивые навыки «перехвата» импульсов, медсёстры обеспечивают безошибочную технику процедур, куратор синхронизирует всех участников и ведёт «дорожную карту» лечения понятным языком фактов.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/narkolog-petrozavodsk-otzyvy/
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru
Наркологическая клиника «Балтийская Наркология» — это безопасное пространство, где для лечения зависимостей используются современные доказательные методики, человеческий язык коммуникации и «тихая» логистика. Мы не практикуем универсальные схемы и «сильные процедуры для всех» — терапия собирается модульно, вокруг конкретной задачи: стабилизация, нормализация сна, снижение тревоги, настройка опор поведения и профилактика рецидивов. Каждый шаг имеет цель, окно оценки и критерий перехода. Анонимность не декларируется — она встроена в процесс: немаркированные маршруты, гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к медицинской карте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
Установите [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom-msk.ru/]автоматические жалюзи с электроприводом на окна купить прокарниз[/url], и наслаждайтесь комфортом и простотой управления светом в вашем доме.
Автоматические жалюзи на окна с электроприводом становятся все более популярными. Данные современные изделия обеспечивают удобство и комфорт.
Во-первых, такая система управления позволяет регулировать уровень света в помещении. Вы можете легко открыть или закрыть жалюзи с помощью пульта дистанционного управления.
Во-вторых, автоматические жалюзи способны улучшить энергосбережение. Их рациональное использование помогает сохранять оптимальную температуру в помещении.
В итоге, автоматические жалюзи на окна являются прекрасным решением для создания комфорта в доме. Эти устройства не только практичны, но и привносят стиль в любой интерьер.
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Инфузионная терапия — не магический «коктейль», а последовательность узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Регидратация возвращает объём циркулирующей жидкости и улучшает перфузию тканей; коррекция электролитов стабилизирует нервно-мышечную передачу и сердечный ритм; печёночная поддержка снижает токсическую нагрузку; при тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; при выраженной тревоге — мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки», требующие связи. Диагностика назначается тогда, когда её результат меняет тактику сегодня, — никакой «проверки на всякий случай». Такой минимально достаточный подход уменьшает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает эффект не часами, а днями.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
¿Todas tus frases empiezan con “él…”? Necesitas leer esto urgente https://lasmujeresqueamandemasiadopdf.cyou/ libro las mujeres que aman demasiado de que trata
Всем здравствуйте! Опишу свою ситуацию: 2 недели назад заказывал в данном магазине 2 с-i и MXE, всё на высшем уровне: оперативность 5 +, доставка 5+, конспирация 5+, Качество 5+. Нареканий к Магазину нет, только благодарность!!! В этот раз сделал заказ в Понедельник, оплатил во Вторник. В пятницу только получил трек. На сегодня Трек не работает. Звоню в курьерку они говорят, что такой трек у них не зарегистрирован. Паники пока никакой нет, но хотелось бы получить какие нибудь разъяснения по этому поводу. Заранее спасибо! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки дай то бог да и знаю я Вас давно не один кг перелопатил без паники ждем вторникаРЕБЯТА КАК ВСЕГДА НА ВЫСОТЕ 5 ИЗ 5!!!! СПАСИБО
SunlitValleyMarket Catalog – Everything was easy to find thanks to neat arrangement and design.
Soft Pine Picks – Fast loading and clean layout made shopping convenient and enjoyable.
автобус аэропорт пхукет краби ноппарат тара пляж в краби — пляж и окрестности
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kaliningrade15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar
Soft Summer Essentials – Light and airy layout with a calming flow for a pleasant experience.
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, семья сталкивается с двумя видами неопределённости — медицинской и организационной. На одной чаше весов тремор, скачки давления и пульса, рвота, обрывочный сон и нарастающая тревога; на другой — страх огласки, очереди, ожидание «до завтра» и бесконечные попытки уговорить себя «перетерпеть». «ХимкиМед Центр» снимает обе неопределённости управляемым маршрутом: у нас нет общих залов с «публичными» ожиданиями, приёмы разнесены по времени, длинные разговоры заменены коротким и предметным интервью, а назначения объясняются простым языком — что делаем сегодня, чего ждать через час, какие ощущения будут нормальными и при каких признаках нужно срочно связаться. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса»: схема строится от фактов — длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые препараты, исходные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация), выраженность тремора и качество сна. Такой реализм экономит силы, снижает тревогу и чаще уже в первые сутки приводит к главному — к первой ровной ночи, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
Здесь
[url=https://svarkinet.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
«Тёмные часы» вечера — время импульсивных решений. Мы даём короткие, нейтральные инструменты на 20–40 минут: тёплый душ, прогулка рядом с домом при устойчивых показателях, дыхательная практика, короткий созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти бесплатные шаги поддерживают ровный сон и уменьшают вероятность «дорогих» экстренных повторов.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
бро а ты через че им писал ? как заказал купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Зачем писать таким большим шрифтом ? Здесь слепых нет. То что тебя где то кинули к нам никакого отношения не имеет.было бы что хорошего писать. Ато культурных слов нету!!! Вроде как норм качество, готовые клады и цена это единственное что радовало. А в последнее время вообще непонятно что отвечает по часу, пугает игнорами, и в последний раз оплатил в 18:00 адрес около 22:00 и нету!!! Начал про подробности у него вроде так отвечал, фото присылал что аж хватит ему на портфолио. То курьер не ответил то он молчит. И в конце концов пишу ему с другой номера отвечает и предлагает адреса а с моего нефига. И вот такая история о том как чем ЗАЗНАЛСЯ ну или оператор. Жаль возьню(
Мы комбинируем медицинские и немедикаментозные решения. Инфузионная терапия — адресная, с контролем безопасности; поведенческие опоры — просты и выполняемы в реальной жизни; телемедицина помогает пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и импровизаций. Ниже — ориентиры логики подбора, они не заменяют очный осмотр.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
LearnSmartToday – Informative sections with a clear layout made exploring easy.
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение. В «ЛюберМед Центр» приватность — регламент: запись и подтверждения через защищённые каналы, шифры вместо ФИО в расписании, приёмы без пересечений, нейтральные входы. Домашние визиты проходят без маркировки, маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее. Мы учитываем характерные для Люберец дворовые проезды и часы пик, чтобы врач приехал вовремя, а пациент не провёл лишних минут в «социальном шуме». Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога и выше приверженность режиму. Такая деликатность — не про «сервис ради сервиса», а про клиническую эффективность: когда человек не боится быть узнанным, он приходит вовремя, точнее следует рекомендациям и реже требует экстренных вмешательств ночью.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru
Городская среда Калининграда — контрастные подъезды, близость моря с переменчивым ветром, плотный сезонный трафик — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому маршруты организованы «тихо»: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок и очередей, короткая регистрация, приглушённая тёплая подсветка в зоне ожидания, отсутствие громких объявлений. Коммуникация с пациентами и близкими строится через защищённые каналы, а уведомления приходят в «беззвучном» режиме в согласованные «окна». Такой дизайн не ради «красоты сервиса», а ради клинического эффекта: чем меньше сенсорной нагрузки, тем быстрее выравнивается пульс к вечеру, тем легче возвращается переносимость питья и тёплой пищи, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в калининграде[/url]
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/5fnuet4y
Удобно и стильно: [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-elektro.ru/]рулонные шторы электрические цена прокарниз[/url] для вашего дома!
Популярность рулонных штор с электроприводом растет среди современных дизайнеров. Они предоставляют уникальную комбинацию удобства и эстетики, что делает их идеальными для различных стилей интерьера.
Одним из основных преимуществ рулонных штор с электроприводом является возможность управления с помощью пульта дистанционного управления. Это позволяет легко регулировать свет и приватность в помещении, не вставая с места.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом предлагаются в разнообразных дизайнах и текстурах. Таким образом, можно легко найти идеальное решение как для традиционного, так и для современного дизайна.
Заказать рулонные шторы с электроприводом можно в специализированных магазинах или через интернет. Важно обратить внимание на производителя и качество материалов, чтобы получить надежный продукт.
Инфузионная терапия — не магический «коктейль», а последовательность узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Регидратация возвращает объём циркулирующей жидкости и улучшает перфузию тканей; коррекция электролитов стабилизирует нервно-мышечную передачу и сердечный ритм; печёночная поддержка снижает токсическую нагрузку; при тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; при выраженной тревоге — мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки», требующие связи. Диагностика назначается тогда, когда её результат меняет тактику сегодня, — никакой «проверки на всякий случай». Такой минимально достаточный подход уменьшает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает эффект не часами, а днями.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-lyubercah/
джон краби виски отдых на краби
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sankt-peterburge/
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево петрозаводск[/url]
FashionVault – Items are displayed well, and navigating the site was easy.
В пробе было два вещества купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану и отдельный респект магазу за способ посылок=)))))норм. Все кладки нахожу без проблем… взял белого и…охуел!!!
Adventure Hub Online – Easy to browse with a good mix of exciting products throughout.
«СтаврМедЦентр» собирает лечение из коротких модулей с понятными целями: быстро стабилизировать соматику, вернуть управляемый сон, снизить реактивность вечера, обучить «перехвату» импульса и закрепить это в спокойной рутине. Фармакологию используем дозированно, опираясь на витальные показатели и переносимость; поведенческий контур запускаем сразу: свет, вода, дыхание, цифровая гигиена, семейные договорённости. Ниже — ориентировочная архитектура маршрута. На практике последовательность и длительность настраиваются под конкретного человека и его среду.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в ставрополе[/url]
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, каждая задержка превращается в цепочку случайностей: рушится сон, «скачет» давление и пульс, усиливается тревога, дома нарастает напряжение. «МедСфера Мытищи» убирает хаос управляемым маршрутом: чёткий первичный осмотр, объяснённые назначения, понятные правила на 48–72 часа и прогнозируемые окна связи. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса» — только клиническая достаточность на сегодня с учётом длительности употребления, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых препаратов и исходных показателей. Такой подход снижает тревожность, возвращает ощущение контроля и быстрее приводит к первому ровному сну — именно он становится переломной точкой, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану. Важная деталь — отсутствие общих очередей и «публичных» зон: приём разнесён по времени, входы приватны, а коммуникация ведётся через закрытые каналы. Когда понятно, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, исчезает потребность в импровизациях, и лечение действительно работает.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki-v-mytishchah
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IHJUI7TF
LivingDiscoverSpot – Products are attractive, site layout makes moving through pages easy.
«Капельница от запоя» в современном понимании — это не одна универсальная смесь, а последовательность управляемых шагов с понятной целью, измеримыми показателями и заранее назначенными точками переоценки. В наркологической клинике «СеверАльфа Мед» мы используем модульные инфузионные протоколы и бережный мониторинг, чтобы безопасно снять интоксикацию, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, снизить тремор и вернуть физиологичный сон без «переседации». Каждый этап сопровождается сервисом конфиденциального уровня: нейтральные формулировки в документах, немаркированная логистика, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям строго по ролям. Это делает путь пациента предсказуемым и защищённым от лишнего внимания.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя мурманск[/url]
Modern Trend Deals – Trendy items displayed neatly, and navigating the pages felt effortless.
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Первый контакт строится вокруг фактов «здесь и сейчас». Врач уточняет длительность употребления, принятые за последние 24–48 часов препараты, сопутствующие диагнозы и аллергии, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает выраженность тремора и уровень тревоги; при необходимости выполняется экспресс-ЭКГ и элементарный неврологический скрининг. Далее план объясняется простым языком: какие инфузии будут сегодня, чего ждать через 30–60 минут, как организовать вечер и когда состоится контрольная связь. Мы избегаем универсальных «сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают краткий «блеск» с вечерним откатом и повышают риск побочных эффектов. Вместо этого используется узкая, клинически достаточная схема: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, противорвотные и гастропротекция при необходимости, мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. После процедуры врач повторно оценивает показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа, согласует окно связи и обозначает «красные флажки» для немедленного контакта. Такой прозрачный маршрут убирает импровизации и делает поведение семьи предсказуемым, что особенно важно в «тёмные часы» вечера.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-himkah/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru
Именно. Основной упор на старых проверенных оптовиков. К сожалению с розницей тут напряг, увы (( https://08xcvaz4.top Проверенный временемтак что только желаю удачи магазину и процветания в дальнейшем
что делать на краби в дождь сколько островов краби — число островов в регионе
https://myanimelist.net/profile/freebetpromoe
https://uploadb.me/15ot0eox9aqw/Bonus code 1XBET _ TROFIM777.pdf.html
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Подробнее – http://
http://www.haxorware.com/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=419784
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki-stacionar[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Position certainly taken!. https://thebookmarkplaza.com/story20193944/%E0%B9%80%E0%B8%9A%E0%B8%97%E0%B8%9F-%E0%B8%81168
Удобство и стиль в интерьере обеспечит [url=https://elektrokarniz-s-pultom.ru/]карниз для штор с электроприводом +7 (499) 638-25-37[/url], который легко управляется с пульта.
Установка электрокарниза является достаточно простой задачей, которую можно выполнить своими силами.
Здесь
[url=https://masterskim.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Hello, I would like to subscribe for this webpage to obtain hottest updates, thus where can i do it please help out.
краби август пещера принцессы краби — местная пещера и легенды
Тоже такая ситуация , сижу без товара негодую. https://contactpagemarketing.xyz клад забрал, все ровняк! завтра отпишу за качество!Есть в липецке
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru
I’m not the kind of person who writes long reviews, but this time I decided to share one recent session about a win at a casino site.
Recently I’ve been playing at [url=https://nllalabet.com/]nllalabet.com[/url], mostly late at night and on small stakes. I registered because the first deposit bonus looked decent and the wagering conditions seemed manageable compared to many other places. The signup process was quite easy: name and email and email confirmation, then I was good to go.
For my first deposit I didn’t go crazy and loaded a modest sum into my balance. I jumped into the slots section because that’s what I tend to play. I filtered by most played games and picked a slot with a bonus buy feature, hoping for a big hit.
At first it was pretty standard: small wins and losses and free spins with low payout, and I was close to giving up because my balance was getting low. Then the session flipped: I landed a high-paying feature with special symbols all over the screen, the slot kept dropping wins and the multiplier pushed my balance far above my start. For me it was a very good hit compared to my regular sessions.
I didn’t stay too long; after a few more extra rounds I decided to leave the game and send a withdrawal request. The withdrawal process was pretty standard: the casino asked me to confirm my identity with ID card or passport. I sent everything shortly after the win, and the verification was accepted without problems. After that the money was sent to my payment method and I got it in a decent timeframe.
I’m not saying this casino is perfect, and of course you can also lose, but in this case my experience was quite satisfying: transparent rules, normal support and no payout drama. This is not a promise you’ll win: losing is part of the game, so only deposit with a strict budget and don’t rely on it as income.
В Химках много дворовых проездов и часов пик, из-за которых легко потерять драгоценное время. Мы согласуем удобные окна, нейтральные входы и «тихие» маршруты, чтобы помощь начиналась без пауз и лишних взглядов. Чем меньше социальных контактов и хаоса, тем ниже тревога и выше приверженность режиму — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент, который напрямую влияет на исход.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-himkah
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/
апартаменты в краби сколько от пхукета до краби
Работал с магазином спасибо всё красиво! https://gashishkupit24.me магаз ещё не начал работу?2-й раз все было быстро но собирал весь дживик по конспирации , на пакетиках видать экономили)))
YourDailyShop – Convenient layout, effortless to find what you need.
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/skoryj-narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk/
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice,
keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your
website to come back in the future. Many thanks
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, которые предлагают [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-pultom.ru/]автоматические рулонные шторы на створку[/url], идеально подходящие для любого интерьера.
Автоматизированные рулонные шторы становятся все более популярными среди современных интерьеров. Эти шторы предлагают отличное сочетание практичности и дизайна.
Важным аспектом является простота в эксплуатации автоматических рулонных штор . С помощью пульта или кнопки можно легко регулировать уровень освещения в комнате .
Есть варианты, которые позволяют настроить время открытия и закрытия штор . Возможность настройки добавляет функциональности и комфорта .
Выбор дизайна автоматических штор очень важен для гармонии в интерьере. Шторы должны гармонировать с общим интерьером помещения .
a href=”https://evertrueharbor.shop/” />EverTrue Picks – Nicely organized sections made the experience smooth and stress-free.
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Вся динамика заносится в единую карту наблюдения. Если потребуются амбулаторные точки или стационар, вы не «начинаете историю заново» — маршрут продолжится с той же целью и теми же критериями успеха.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
прокат авто в краби краби таиланд видео
Перевел деньги на Альфа 21.04.2014 после умення узнали даные (Ф.И.О телефон и адрес) Оператор сказал что посылка будет отправлена 22.04.2014. !!!! 23.04.2014 скинули номер наклодной. По номеру наклодной смог отслеживать свою посылку 24.04.2012. https://boshkizaklad.biz как дела народ ? Всё хорошо ? не у кого проблем нет ?всем мир! скажите магаз ровный? ато написал на мыло им и ни ответа ни привета!
Bright Pine Fields Collection – The uncluttered format helped me move around without hassle.
noblecraftshophub – Smooth layout and clear product images, made exploring items enjoyable.
* Экспресс-электролиты выполняются по показаниям, если на старте есть факторы риска.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-stavropol/
NewValuePicks – The website is fast and browsing was quite pleasant.
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в санкт-петербурге[/url]
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
Городская среда Петрозаводска со сменой ветров с Онежского озера, короткими сумерками и сезонными перепадами влажности может усиливать тревожность в вечерние часы. Мы учитываем это с момента первого контакта: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок, короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в зоне ожидания и отсутствие громких объявлений. Родственникам предоставляются «тихие окна» связи — лаконичные апдейты в фиксированное время, чтобы не перегружать пациента и не дёргать команду в критические окна наблюдения. Такой «мягкий» контур снижает сенсорную нагрузку, стабилизирует вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам и сокращает число импульсивных просьб «усилить на ночь».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в петрозаводске[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Заготовка из конструкционной стали листовая 80 мм 34ХН3М ОСТ 3-1686-90 Выбирайте конструкционные заготовки высокого качества для вашего проекта на Редметсплав.рф. Наш ассортимент включает прочные и долговечные материалы, идеально подходящие для различных областей применения, включая строительство и машиностроение.
Modern Style Outlet – Browsing felt seamless, and the shop offered lots of appealing choices.
UrbanStyleVault – Items look appealing, moving through pages was comfortable.
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения
казино онлайн играть бесплатно без регистрации
LearnAndExploreHere – The information was well presented and the pages responded instantly.
Мы комбинируем медицинские и немедикаментозные решения. Инфузионная терапия — адресная, с контролем безопасности; поведенческие опоры — просты и выполняемы в реальной жизни; телемедицина помогает пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и импровизаций. Ниже — ориентиры логики подбора, они не заменяют очный осмотр.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/kaliningrad-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
В Санкт-Петербурге для адресных обращений дежурят мобильные бригады круглосуточно. Координатор при звонке уточняет хронические заболевания, аллергии, текущие лекарства и эпизоды судорог/психозов, а также бытовые условия: есть ли доступ к розетке, можно ли обеспечить 2–3 часа тишины, удобна ли зона полулёжа. Эта информация позволяет врачу в дороге выбрать стартовую скорость инфузии, продумать последовательность введения и подготовить расходные материалы под планировку квартиры. Мы соблюдаем приватность: нейтральная экипировка, деликатные формулировки в документах и один доверенный контакт со стороны семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Urban Trend Picks – The site has a polished feel with intuitive navigation and appealing product arrangement.
лютый микс, мир за качество магазу https://orguendye.xyz НЕ принуждаем вас тут брать, берите, где позволяет бюджет.Что то непойму.Работает магаз то.И куда писать?
краби онлайн гугл карты краби
Первый контакт строится вокруг фактов «здесь и сейчас». Врач уточняет длительность употребления, уже принятые препараты за 24–48 часов, сопутствующие диагнозы и аллергии; измеряет АД, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень тремора и уровень тревоги. При показаниях выполняется экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. Затем простым языком объясняется логика вмешательств: какие инфузии будут сегодня, чего ждать через 30–60 минут, как организовать «тихий» вечер и по каким признакам связываться. Мы избегаем универсальных «сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок, поскольку они дают краткий «блеск» и вечерний откат. Вместо этого — узкая схема: регидратация, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, гастропротекция и противорвотные при необходимости, мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. На руки выдаются рекомендации на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и ранний отбой, «красные флажки» для связи и утреннее окно контроля. Такой график убирает импровизации и делает поведение семьи согласованным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryadom-v-lyubercah
Наркологическая клиника «Балтийская Наркология» — это безопасное пространство, где для лечения зависимостей используются современные доказательные методики, человеческий язык коммуникации и «тихая» логистика. Мы не практикуем универсальные схемы и «сильные процедуры для всех» — терапия собирается модульно, вокруг конкретной задачи: стабилизация, нормализация сна, снижение тревоги, настройка опор поведения и профилактика рецидивов. Каждый шаг имеет цель, окно оценки и критерий перехода. Анонимность не декларируется — она встроена в процесс: немаркированные маршруты, гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и разграниченный доступ к медицинской карте.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/kaliningrad-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/]наркологическая клиника стоимость[/url]
Умные шторы — это инновационное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять светом и конфиденциальностью. Узнайте больше о [url=https://umnye-shtory-moskva.ru/]умные шторы прокарниз[/url]!
Это особенно удобно в условиях городских квартир.
Вы сможете настроить их так, чтобы они открывались автоматически с восходом солнца.
Зимой они удерживают тепло, а летом защищают от излишнего солнечного света.
Умные шторы не требуют сложного ухода — достаточно периодической чистки.
Карта понятна пациенту и семье: видно, что будет происходить, по каким признакам мы перейдём к следующему шагу и когда состоится проверка. Это снижает тревожность и повышает приверженность плану.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Первый раз заказывал пришло все за 4 дня , в данной же ситуации уже 11 дней идет , я готов любые деньги платить чтобы приходило быстрей купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Удачи и развития в дальнейшем!вот пару часиков назад получил посылочку=) Чай так сказать=) ща сижу под ним в курочки уплетаю уже 3 разорвиебало бутерброд=)ЫЫЫ
стоит ли ехать на краби краби где поесть — советы по еде и ресторанам
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]lesbians[/url]
По сути он эйфо, но ничего, кроме расширенных зрачков, учащенного сердцебиения и потливости, я не почувствовал… А колличество принятого было просто смешным: 550 мг. в первый день теста и 750 мг. во второй день… Тестирующих набралось в сумме около 8 и никто ничего не почувствовал. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази добрый день как связаться с продавцом и не попасть на фейка?странный вопрос, у вас в ветке интернируется, значит у кого он решил взять ? :rolf:
Установите [url=https://avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi-msk.ru/]жалюзи с электроприводом для окон купить[/url] для удобства управления светом и обеспечения уюта в вашем доме.
Процесс установки автоматических жалюзи требует внимания к деталям и точности выполнения работ.
краби в июне отзывы Краби тайланд — часть Таиланда, славится возможностями морских экскурсий, пещер и пляжного отдыха
Актуальные каталоги публикуют кракен тор ссылка с указанием статуса работоспособности в реальном времени для нахождения рабочих зеркал при технических работах или атаках.
мир всем месным братья купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази эх, вот печаль то…вчера так порадовался – селлер быстро ответил, хорошо пообщались, заказ принял, проплата прошла, сказали завтра трек будет…наступило завтра и тишина…вроде в сети и ася и скайп..за что меня так игнорят?))) заказ маленький то он такой важный!))))) в общем надеюсь на скорый ответ))жте907? Вроде говорят, что пока не доступен – находиться на экспертизе… Откуда инфа?
Howdy, i read your blog from time to time and i own a
similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam responses?
If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything you can recommend?
I get so much lately it’s driving me crazy so any assistance is very much appreciated.
Informationbreach – Know If Your Data Is Already Leaked
Massive data breaches happen every day. Check if your email, credit info, or personal data appears in leaked or hacked databases.
Scan 33B+ leaked passwords and 50M new breach records daily to detect exposure instantly.
Get breach alerts, see if your accounts are in credit card leaks, email breaches, or hacked dumps — all in one click.
Protect yourself from identity theft for just $2 — your breach awareness shield starts now.
Check Your Exposure Now: [url=https://informationbreach.net] All data hack[/url]
|
TrendDiscover – Stylish collections displayed nicely with quick page loads.
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
DailyGoodsMarket – Pleasant design, navigation felt natural.
Urban Wild Grove Essentials – Modern design and organized sections made checking products frustration-free.
https://rti-land.ru/ «РезиноМир»: Ваш Надёжный Партнёр в Мире Резинотехнических Изделий с 2009 Года В современном промышленном мире, где каждая деталь имеет значение, выбор надёжного поставщика и производителя резинотехнических изделий (РТИ) является ключевым фактором успеха любого предприятия. С 2009 года компания «РезиноМир» уверенно занимает лидирующие позиции на рынке России и стран СНГ, предлагая своим B2B-партнёрам не просто продукцию, а комплексные и высококачественные решения в области РТИ. Мы гордимся тем, что являемся не просто поставщиком, а производственным партнёром, способным удовлетворить самые взыскательные требования.
GlobalTrendMarket – Loved the selection, and the site navigation felt smooth.
Living Touch Store – Smooth and pleasant browsing with a comfortable overall vibe.
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the most
useful websites online. I am going to recommend this
website!
спасибо за инфу , но только узнал про новый список запвеществ , чувствую вся лавочка прикроется на некоторое время … купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Желаю развития ветке!Я делал на муравьином спирте
Своевременная медицинская помощь уменьшает вероятность тяжелых осложнений и сокращает период восстановления. При следующих признаках требуется неотложная оценка состояния и начало терапии под наблюдением специалистов:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
краби какая страна город краби в тайланде
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена петрозаводск[/url]
That is very attention-grabbing, You’re a very professional blogger. I’ve joined your feed and stay up for searching for more of your wonderful post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks
download netextender for mac
Choice Collection Hub – Loved how organized everything looks, with pages loading comfortably fast.
Если вы хотите добавить стиль и комфорт в свой дом, [url=https://zhalyuzi-gorizontalnye-elektro.ru/]горизонтальные жалюзи автоматические[/url] — отличное решение!
Соблюдение простых правил ухода увеличит срок службы ваших жалюзи.
Стационар рационален при нестабильном состоянии, риске делирия, судорогах в анамнезе, скачках давления, выраженной одышке, неукротимой рвоте, одиночестве ночью или невозможности обеспечить «тихий режим». В палате — контролируемая среда, доступ к ЭКГ и базовой лаборатории по показаниям, круглосуточный пост медсестёр и возможность быстро менять тактику, если параметры «плывут». Такой маршрут предсказуемее по безопасности и зачастую короче по времени до стабильного самочувствия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sostav[/url]
процедура банкротства физического лица через суд списать долги по кредиту законно банкротство — Законное списание долгов по кредиту через банкротство требует соблюдения процедуры суда и закона. Путь включает подачу заявления, режим наблюдения, конкурсное производство и списание долгов в рамках реестра требований. Исключения сохраняются за рамками списания: алименты, штрафы и часть налогов. Это общая информация; конкретика зависит от дела.
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
так что только желаю удачи магазину и процветания в дальнейшем https://goldenlady.top Заказал, оплатил, получил, Радуюсь… !:D Норм магаз приятно иметь дело..! !!П.С. Отзывы о работе (посты по теме) я не удалял.
BrightMountainMall Goods – The site’s structure made moving between sections simple.
Чтобы процедура прошла спокойно и без задержек, заранее организуйте базовые условия — это экономит время и силы пациента и семьи.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]moskva-vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://masterskie-pinchuka.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
IdeaInspireCenter – Great collection of creative concepts, browsing felt effortless and enjoyable.
Вывод из запоя в Донецке предполагает комплексную медицинскую помощь, ориентированную на снижение интоксикации, стабилизацию витальных функций и профилактику осложнений. Патофизиологически запой сопровождается нарушением водно-электролитного баланса, колебаниями артериального давления, тахикардией, рисками аритмий, дефицитом витаминов группы B и дисрегуляцией нейромедиаторных систем. Клиническая тактика строится на ранней оценке риска, контроле соматического статуса и пошаговой коррекции нарушений с обязательным наблюдением за сердечно-сосудистой и дыхательной системами.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru
128 страниц положительных отзывов , и вдруг “мутный магаз” . Уважаемый – флудить в курилке можно. https://kokainkupits.info Ровный магаз,всем советую)Море клиентов и процветания !
https://portfolio.newschool.edu/lant053/sample-page/rain/#comment-127249
Программы лечения формируются индивидуально и включают различные методы, направленные на физическое и психическое восстановление пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
https://t.me/azino777casinomobile
Greate article. Keep posting such kind of info on your page. Im really impressed by your blog.
Hey there, You have performed a great job. I’ll definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this web site.
официальный сайт Banda Casino
Домашний формат нужен, когда риски управляемы, а в квартире можно обеспечить «тихий режим». Врач приезжает без эмблем, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, сверяет лекарства за последние 48 часов и аллергии. После допуска запускается инфузия с мягкой коррекцией воды и электролитов, поддержкой печени и вегетативной нервной системы; при необходимости аккуратно настраивается сон. По завершении — переоценка, письменная памятка на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и прямой канал связи. Такой визит «гасит» тремор и тошноту, снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Откройте для себя [url=https://elektro-zhalyuzi-okna.ru/]жалюзи электрические купить Прокарниз[/url], которые обеспечат идеальный контроль света и уюта в вашем доме.
Это делает автоматические жалюзи не только стильным, но и экономически выгодным решением.
Домашний формат уместен, когда симптоматика контролируема и вечером рядом может остаться взрослый помощник. Преимущество Лобни — короткие дистанции внутри города, поэтому врач приезжает быстро, без шума и эмблем. На месте мы не торопимся: собеседование по факту последних 48 часов, измерения давления, пульса, сатурации и температуры, короткий неврологический скрининг, сверка аллергий и уже принятых препаратов. После допуска к терапии запускается инфузия: сначала — коррекция воды и электролитов, затем — поддержка печени и ЦНС, при необходимости — противорвотные и анксиолитические препараты. Темп настраивается по динамике, чтобы снять тремор и тошноту без «перекручивания» организма в сон с тяжёлым просыпанием. По итогам визита — понятные правила на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и согласованное окно контрольного контакта. Домашний маршрут экономит часы, снижает социальную тревогу и делает первые сутки предсказуемыми.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-lobne/
купить курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru]купить курсовую работу[/url] .
Прежде чем перечислить критичные признаки, зафиксируем принцип: даже один выраженный симптом — повод не откладывать помощь и выбрать безопасный маршрут (дом или стационар) после быстрой очной оценки врача.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sergievom-posade
Шива я тебя люблю!!! У тебя лучший и мой самый любимый мефедрон!!!. https://horansa.xyz вот отправил манетку ,получил адикВсе легально и проверено, есть NMR. Плохого ни чего не случиться. Скорей всего приняли потому что были паленые….
Цель
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]воскресенск наркологический диспансер[/url]
Маршрутизация фиксируется в индивидуальном плане: место оказания помощи (амбулаторно, дневной стационар, круглосуточный стационар), контрольные точки и критерии эффективности. Такой подход позволяет оперативно корректировать тактику, если динамика замедляется или появляются новые клинические данные. Пациент получает чёткое понимание этапов терапии, сроков и ожидаемых результатов, а также способов связи с командой в случае изменений самочувствия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя луганск[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Перми — это специализированное учреждение, где пациентам предоставляется комплексная помощь в лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы, основанные на доказательной медицине, что позволяет достигать стойких результатов и возвращать пациентов к полноценной жизни. Ключевым принципом является конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в перми[/url]
Uwielbiasz hazard? nv casino: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]kum[/url]
By using [url=https://stampwebshop-1.com/]stamp creator online free[/url] you do not need to visit the office to order the necessary stamps.
The rubber stamp maker online is a revolutionary tool that has made it possible for individuals to create their own custom rubber stamps from the comfort of their homes . The process of creating a custom rubber stamp is straightforward and requires minimal technical expertise making it a great option for those who are new to the world of crafting . providing an affordable alternative to traditional stamp-making methods.
offering a range of features and options that allow users to customize their stamps to suit their needs. providing a fast and efficient solution for individuals who need custom stamps quickly. providing a convenient and efficient way to order custom stamps in bulk.
The online rubber stamp maker offers a range of features and benefits that make it an attractive option for individuals and small businesses . providing a straightforward and intuitive process for designing and ordering custom stamps. providing a platform for individuals to express themselves and showcase their unique style. including fast turnaround times and competitive pricing .
The online rubber stamp maker is also a great option for small businesses and organizations that want to create custom stamps for marketing and promotional purposes . providing a platform for individuals and small businesses to add a personal touch to their products. offering a range of features and benefits that make it an attractive option for individuals and small businesses .
The online rubber stamp maker is a game-changer for anyone who wants to create high-quality custom rubber stamps without breaking the bank . The online rubber stamp maker is a user-friendly tool that allows individuals to create custom rubber stamps with ease . including fast turnaround times and competitive pricing . including address stamps, logo stamps, and signature stamps .
ChicFreshOutlet – Loved exploring the site, layout is clean and intuitive.
Вывод из запоя направлен не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на комплексное восстановление организма. Работа специалистов позволяет стабилизировать состояние и создать условия для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tver0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Комбинирование методов позволяет одновременно решать задачи стабилизации, профилактики и возвращения к повседневной активности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в луганске[/url]
https://latvijasloterijas.com/
Many thanks! I enjoy it.
Lumina Solar excels as the best solar panel contractors in Delaware due to their
remarkable focus to quality and consumer contentment.
They provide bespoke solar options that meet the unique energy needs of each resident and business.
Their crew of trained professionals ensures efficient installation with great
attention to precision and safety. Lumina Solar employs cutting edge technology and high-quality solar panels that guarantee peak efficiency and durability.
Customers recognize their upfront pricing and comprehensive consultations which aid
in forming well-informed decisions without any surprise charges.
They offer extensive services from initial assessment to final installation and
ongoing maintenance ensuring a hassle free experience.
Lumina Solar is dedicated to promoting sustainable energy practices while helping clients reduce their
carbon footprint and energy bills. Their robust reputation in Delaware is
built on years of dependable service and excellent customer reviews.
They remain current on the latest industry standards and regulations which showcase their excellent
workmanship. Lumina Solar also offers excellent customer support that is responsive and knowledgeable, addressing any concerns quickly.
Their commitment to excellence and environmental responsibility renders
them the ideal choice for solar panel installation in Delaware.
Choosing Lumina Solar signifies committing to a eco-friendly future with a trusted partner who values integrity and innovation. Their demonstrated track record and enthusiasm for renewable energy position them as the leading solar panel installers in the region.
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru
sunnylookstore – Navigation is intuitive and pages are clean, made shopping pleasant.
Скажите сей час в Челябинске работаете?) https://horansa.xyz Все работает, каждый получает ответ оперативно!Ладно, напишу ещё раз.
https://community.pmi.org/profile/betstorm/tour
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/skoryj-narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk/
This excellent website certainly has all the information I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
lee bet регистрация
GrowthJourneyShop – Motivating content, pages load quickly and browsing is easy.
гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru/]гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
Заказывали изготовление папок с логотипом и получили отличный корпоративный материал. Печать четкая, логотип выглядит насыщенно и аккуратно. Папки прочные и не деформируются. Сотрудники быстро реагировали на правки и пожелания. Очень рекомендуем: печать листовок дешево москва
ремонт бетонных конструкций москва [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie.ru/]ремонт бетонных конструкций москва[/url] .
аренда экскаватора погрузчика в москве [url=arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-5.ru]аренда экскаватора погрузчика в москве[/url] .
краш лаки джет отзывы lucky jet онлайн — онлайн-режим даёт быстрый доступ к раундам через браузер или мобильное приложение, иногда с возможностью синхронизации учётной записи между устройствами. В онлайн-формате часто доступны демо-режим и реальная игра на деньги, что позволяет подобрать баланс между риском и потенциальной выгодой. Важно помнить, что онлайн-игра — это азартное развлечение, и решения должны приниматься ответственно: устанавливайте лимиты на ставки, не ставьте средства, выходящие за рамки бюджета, и регулярно отдыхайте от игры. Источник онлайн-доступа должен быть лицензированным, безопасность платежей и защита личных данных — на высоте. При выборе платформы смотрите на качество сервиса, скорость выплат и доступность поддержки, а также на наличие официального сайта, который публикует правила, бонусы и инструкции по выводу.
гидроизоляция подвала делать самостоятельно [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru[/url] .
Value Picks Market – Easy to move around the site and lots of items seemed reasonably priced.
Запой меняет сразу несколько систем организма: сдвигается водно-электролитный баланс, растёт нагрузка на печень и ЖКТ, «скачут» давление и пульс, усиливаются тревога и бессонница. Одна смесь «от всего» редко даёт устойчивый результат: днём краткий подъём, к ночи — откат и новая волна симптомов. Мы действуем иначе. Сначала — очная оценка и допуск к терапии с учётом того, что человек уже принимал за последние двое суток. Затем — инфузионная поддержка нужного объёма и темпа, симптом-контроль по показаниям, осторожная работа со сном, чтобы не маскировать риски тяжёлой седацией. После основного блока — переоценка, перевод на per os-схемы, правила режима и окно контрольной связи. За счёт последовательности результат становится не хрупким «здесь и сейчас», а устойчивым на сутки и неделю.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/]вывод из запоя отзывы[/url]
always i used to read smaller posts that as well clear their motive,
and that is also happening with this post which I am reading now.
Программы лечения формируются с учётом состояния организма и индивидуальных потребностей пациента. Это обеспечивает эффективность и снижает вероятность рецидива.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru
инъекционная гидроизоляция обзор методов [url=inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru]inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru[/url] .
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sergievom-posade
новости Запорожья за сегодня
Hi colleagues, its wonderful piece of writing regarding teachingand entirely explained, keep it up all the time.
регистрация рио бет казино
Печатали фирменные пакеты и результат приятно удивил. Логотип выглядит четко, цвета насыщенные и не стираются. Пакеты получились прочными, ручки надежно закреплены. Производство выполнили точно в срок. Приятно работать с такими ответственными специалистами, шубер из картона
Вывод из запоя в Твери проводится с применением современных методик, эффективность которых подтверждена медицинской практикой. Используются только проверенные препараты и процедуры, соответствующие клиническим стандартам.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tver0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
«Опора Здоровья» организует выезд нарколога на дом по Воскресенску и району круглосуточно. Мы действуем анонимно и по клиническим протоколам: очная оценка состояния, допуск к инфузии, детокс с коррекцией водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка печени и центральной нервной системы, бережная нормализация сна по показаниям. Врач объясняет решения простым языком, согласует темп и состав капельницы, оставляет памятку на 24–48 часов и остаётся на связи. Если риски высоки, предложим перевод в стационар без задержек — безопасность всегда важнее «тишей» дома.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]воскресенск наркология[/url]
Quiet Plains Finds – The catalog felt nicely arranged, and the overall experience was soothing.
гидроизоляция подвала цена [url=www.gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала цена[/url] .
плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция — Пошаговая инструкция по процедуре банкротства физического лица обычно включает: 1) сбор документов (паспорта, доходы, долги, имущество); 2) подачу заявления в арбитражный суд; 3) назначение арбитражного управляющего и введение режима наблюдения; 4) формирование реестра требований кредиторов; 5) выбор стратегии (оздоровление или конкурсное производство); 6) проведение оценки активов и реализация имущества; 7) распределение средств между кредиторами; 8) списание остатков долгов и закрытие дела. Каждый этап требует соблюдения сроков и подготовки документов. Важна консультация с юристом на каждом шаге. Это общая информация; конкретные детали зависят от вашего дела.
Blue Harbor Hub – The site ran smoothly, and I liked how naturally the products were arranged.
курс трак диспетчера в сша в сша онлайн с сертификатом курс диспетчера грузоперевозок в америке онлайн с реальными кейсами
YourDailyFinds – Well-organized pages, browsing was simple and enjoyable.
Сори я не туда отписал https://08xcvaz4.top “Что могу сказать Уважаемый Эскимос Я очень растроился в полученной Пробе И не хотелось выявлять Неготив в сторону твоего магазина”Покупал как то в этом магазине реагента 1к10 помоему был у них примерно год назад.С доставкой,заказ делал тогда еще на сайте, получил реквизиты оплатил ждал отправки.И вот доставка пришла очень быстро.Качество товара было приемлемое.Очень хорошая консперация.Всем советую
Howdy! This post could not be written any better!
Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate!
He continually kept preaching about this. I most certainly will send
this article to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a very good read.
Thanks for sharing!
2c-i, 2c-e, 2c-p https://contactpagemarketing.xyz у разных селеров бывает разный джив имеется виду по качеству так , я как то брал джив к10 пер слабо очень , в другом к 15 убивал , вот и спрашивают всегда качество дживика у продавана если ты незнал!!!Огромное спасибо данному магазину, успехов вработе и процветания!!!?
заказать проект русской печи Купить проект банной печи — покупка проекта банной печи ориентирована на сауны и бани: такие печи рассчитаны на высокую температуру и влажность, требуют надёжной теплоизоляции и эффективной тяги. В проекте учитываются варианты обогрева камней, вентиляционные каналы и безопасная топка, чтобы баня прогревалась быстро и сохраняла пар. Важны требования к коптильным зонам, защитным экранам и безотходному обслуживанию, чтобы обеспечить длительную службу без рисков возгорания. Реализация проекта требует соблюдения санитарных норм и правил пожарной безопасности, а также консультаций с банными мастерами. Это позволит выбрать правильный размер, мощность и архитектуру печи под конкретную баню.
Использование этих методов в комплексе позволяет восстановить здоровье пациента и сформировать основу для трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://locksmithswift.com/
Эти направления терапии помогают создать прочный фундамент для дальнейшей ремиссии и снижают риск рецидива.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-dnr
TrendSpotMarket – Great user experience with well-organized product listings.
а чё заказал? Прикольный сайт, ассортимент радует :)? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш это самый ровный магаз братцы!!!) работаю с ними целый год, не разу даже нервы не потрепали) !!! конспирация на высоте, качество наилучшее!продован самый добрый и общительный аах) ну вы поняли! единственное жалко не разу проб бесплатных не получал(((Моментально: реквизиты, оплата, подтверждение получения. Все.
курсы трак диспетчера с сертификатом онлайн обучение диспетчера грузоперевозок интенсив
Наркологическая клиника «КарелМед Центр» — это круглосуточная помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании, ориентированная на безопасность, анонимность и реальный результат. Мы выстраиваем лечение как последовательность управляемых шагов: стабилизация физиологии, снижение тревоги, формирование навыков отказа, восстановление сна, возвращение к работе и семье. Каждый этап имеет цель, понятные маркеры и «окно оценки» — конкретную дату, когда команда и пациент вместе сверяют динамику и корректируют план. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, убирает хаос и делает путь к ремиссии предсказуемым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог петрозаводск[/url]
программа лаки джет иксы lucky jet бонус — бонусные предложения и промо-акции достаточно распространены на площадках, предлагающих lucky jet. Бонусы могут включать дополнительные средства на первый депозит, рейты и бесплатные ставки, но часто имеют условия отыгрыша. Прежде чем активировать lucky jet бонус, внимательно ознакомьтесь с условиями, сроками действия и требованиями по выводу. Помните, что бонусы не заменяют управление банкроллом и ответственную игру.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Медная двухраструбная редукционная переходная муфта под пайку 35х34 мм твердая пайка М1М ГОСТ 32590-2013 Выберите высококачественные медные двухраструбные редукционные муфты под пайку от Редметсплав для надежного соединения медных труб различных диаметров. Широкий выбор размеров, эффективная установка и долговечность гарантированы. Идеальное решение для систем отопления и водоснабжения.
https://latinverge.com/forums/topic/22920/1xbet-promo-code-for-registration-1xlux777-130-join/view/post_id/170671
FreshSavingsShop – Loved the range of items, site is quick and easy to browse.
Pure Harbor Picks – Navigation was simple and I could locate items effortlessly.
Здесь
[url=https://corexpharm.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Работы очень много, стараемся как можем, многие задают в Аську и Скайп одни и теже вопросы которые не касаются заказа(как в википедию ломяться)… купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Все пришло, все хорошо! Конспирации такой не ожидал))) Сначала подумал что киданули)))))) Попробовал и все около дела, хороший средний микс получился. Буду брать больше на днях…магаз ровный,сервис 5+,как напишешь сразу ответят,все ровно и по весу и по качеству 5+,были рады очень посылю с замечательным реагентиком плюсую магазу и советую остальным!)))
Сочетание этих направлений позволяет комплексно воздействовать на проблему зависимости и минимизировать риск рецидива.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь пермь[/url]
консультация по банкротству Банкротство физических лиц — это юридический процесс, в ходе которого должник может быть освобожден от части долгов или реструктурировать их. Сроки процедуры зависят от выбранной стратегии и сложности дела: обычно это несколько стадий, каждая из которых может занимать месяцы. В типичной ситуации начинается с заявления в суд и введения наблюдения, затем перехода к оздоровлению или конкурсному производству. В итоге суд принимает решение о списании долгов, частично или полностью, в зависимости от реестра требований и активов должника. Точные сроки устанавливаются судом и зависят от множества факторов.
Modern Wardrobe Picks – Nice variety of clothing and the interface made shopping hassle-free.
Эти методы применяются комплексно, что повышает их эффективность и помогает пациентам быстрее возвращаться к полноценной жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена донецк[/url]
гидроизоляция подвалов цена [url=http://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru]http://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru[/url] .
курс трак диспетчера в сша для снг с практикой школа трак диспетчинга в сша в сша онлайн
привет!!! не согласен долдны быть доступные магазины как купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш сделал заказ ,оплатил 🙂 теперь жду трека и посыля с нетерпением 🙂 по общению продаван понравился все ровно обьяснил че да как . как придет опробую оставлю отзыв окончательный ,пока что все ровно )читайте отзывов много!:) товар тут вышка,обращайтесь!
Карта понятна пациенту и семье: видно, что будет происходить, по каким признакам мы перейдём к следующему шагу и когда состоится проверка. Это снижает тревожность и повышает приверженность плану.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru
экскаватор. цена. час. [url=https://arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-5.ru/]arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-5.ru[/url] .
Каждый день выходят новые свежие промокоды. Юзаю их и всегда получаю что-то полезное на деньги.
Работает стабильно, все функции доступны полностью. Никаких проблем с доступностью на сегодня.
инъекционная гидроизоляция густота состава [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru]https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru[/url] .
Программы лечения формируются с учётом состояния организма и индивидуальных потребностей пациента. Это обеспечивает эффективность и снижает вероятность рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/doneczk-narkologicheskij-dispanser
Trend & Buy Picks – Products displayed nicely, navigation was quick and simple.
Заказывали изготовление фирменных брошюр и были приятно удивлены уровнем исполнения. Всё выглядит стильно, верстка аккуратная, печать без полос и пятен. Обложка стойкая к царапинам. Доставка сработала четко и в срок. Команда действительно знает свое дело: заказать бирки
Forest Essentials Market – Products looked appealing, and moving around the shop felt simple and stable.
гидроизоляция подвала материалы [url=www.gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru]гидроизоляция подвала материалы[/url] .
ремонт бетонных конструкций москва [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie.ru]ремонт бетонных конструкций москва[/url] .
подвал дома ремонт [url=www.gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru]www.gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru[/url] .
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉
I may revisit yet again since i have bookmarked it. Money and freedom
is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
This anonymity adds an extra layer of security and peace of mind for players.
Тактика подбирается индивидуально и зависит от тяжести состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и переносимости препаратов. Ниже представлены базовые компоненты, которые часто включаются в схемы лечения при запойных состояниях.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru
Диагностический блок включает сбор анамнеза, оценку витальных показателей, скрининговые шкалы по тревоге, депрессии и патологическому влечению, лабораторные тесты по показаниям. На основании полученных данных выбирается формат помощи и составляется медикаментозная схема с учётом взаимодействий препаратов и вероятных рисков.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике луганск[/url]
скачать игру лаки джет помните: эти тексты сгенерированы на основе ваших ключевых фраз и предназначены лишь для информационных целей. Реальная игра связана с риском; играйте ответственно и не ставьте больше, чем можете позволить себе потерять.
В клинике применяются методы, позволяющие воздействовать на все аспекты зависимости. Это обеспечивает комплексное и устойчивое восстановление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk-dnr/
Кто знает что происходит? Походу покупают все в тихушку!:confused: Внесите ясность!:hz: Дайте реги уже:confused::sos: https://51lhv.top заказывал мягкого пятак, всё пришло, непрходилось волноваться т.к в аське всегда были на связи, сила средне, но по весу 5+ =)Обращайтесь всегда рады!
школа трак диспетчинга в сша в сша онлайн с сертификатом курс трак диспетчера онлайн цена
Заказывали печать буклетов для рекламной кампании и остались полностью довольны качеством. Цвета получились яркими, без искажений, бумага плотная и приятная. Менеджеры помогли подобрать формат и тираж, чтобы уложиться в бюджет. Производство заняло меньше времени, чем ожидали. Упаковка была аккуратной, ничего не помялось. Теперь будем заказывать всю полиграфию только здесь – изготовление буклетов на заказ
Комбинирование методов позволяет одновременно решать задачи стабилизации, профилактики и возвращения к повседневной активности.
Получить больше информации – http://
TrendDiscoverer – Clean visuals, browsing feels fluid and enjoyable.
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в перми[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту проходить все стадии восстановления в безопасном и контролируемом режиме.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма в донце[/url]
какой выход с 1г ? https://kypitboshki.biz боюсь что здесь произойдёт тоже самое, уж очень не внятно продавец общается.магазин отличный ! работает уже не первый год! обращайтесь!
Такая последовательность позволяет переходить от решения неотложных задач к долгосрочному укреплению ремиссии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lugansk0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике луганск[/url]
Hey everyone,
I came across this [b]free AI-powered calculator[/b] that gives [b]instant, accurate results[/b] for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the [b]SmartCalc[/b] collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
[b]Try it here:[/b] [url=https://smart-currency-converter.blogspot.com/]SmartCalc Online Tool[/url]
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Give it a try and see what you think!
Команда «КарелМед Центра» объединяет наркологов, психиатров, реаниматологов, клинических психологов, специалистов по реабилитации и социальному сопровождению. Мы работаем без очередей и навязчивых формальностей, а логистика визита, оформление в стационар и коммуникации с родственниками выстроены бережно: конфиденциальные записи, немаркированные выезды, отдельный вход и нейтральная терминология в документах. Вы получаете не только купирование абстиненции и детоксикацию, но и системную работу с триггерами, привычками и межличностными конфликтами — тем, что часто возвращает к употреблению даже после «идеальных капельниц».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/narkolog-petrozavodsk-otzyvy/
Такая помощь обеспечивает безопасность пациента и снижает риски осложнений, связанных с запойным состоянием.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tver0.ru
How To Choose Seo
seostart.com.ua
как происходит списание долгов по кредитам списать долги по процедуре банкротства — Списание долгов по процедуре банкротства — результат последовательных стадий дела: наблюдение, реестр требований, конкурсное производство и списание остатков. Важна масса активов и корректная работа управляющего; некоторые долги не списываются. Это общая информация; детали зависят от дела.
Каждый этап имеет ключевое значение и обеспечивает устойчивость результата.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-v-doneczke-dnr/
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru
Молча !! Запрет вступает в силу 26го числа, если не ошибаюсь. Скидывай всё палево, жёсткий дист зарывай подальше и иди получай )) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм В чем растворял 203??? У меня ихний 203 в спирте не получилось расстворить даже при нагреве, пришлось ацетон использовать! На счет качества с тобой согласен – 5!Пишите в скайп, аську, пожалуйста без лишнего, чтобы была возможность ответить всем. :good:
lucky jet игра отзывы помните: эти тексты сгенерированы на основе ваших ключевых фраз и предназначены лишь для информационных целей. Реальная игра связана с риском; играйте ответственно и не ставьте больше, чем можете позволить себе потерять.
Процесс лечения организован поэтапно, что делает его последовательным и результативным.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-permi0.ru/narkolog-perm-zapis/
Для строительных и дорожных работ можно [url=http://shchpsinfo.ru]стоимость щебеночно песчаной смеси[/url], обеспечив качество и сроки выполнения проекта.
Щпс играет ключевую роль в различных отраслях промышленности, и ??? покупка в Москве имеет большое значение . Для многих компаний и частных лиц покупка щпс в Москве является необходимой задачей Для многих компаний и частных лиц покупка щпс в Москве является необходимой задачей . В статье мы рассмотрим варианты покупки щпс в Москве и их преимущества В статье мы рассмотрим варианты покупки щпс в Москве и их преимущества .
Покупка щпс в Москве может быть осуществлена через различные каналы В Москве щпс можно купить через различные каналы . Это может включать в себя официальные дилерские центры, интернет-магазины и специализированные торговые площадки В Москве щпс можно купить через официальные дилерские центры, интернет-магазины и специализированные торговые площадки. Каждый из этих вариантов имеет свои преимущества и недостатки Преимущества и недостатки каждого варианта покупки щпс в Москве необходимо учитывать .
Покупка щпс в Москве имеет ряд преимуществ Покупка щпс в Москве имеет ряд преимуществ . Одним из основных преимуществ является возможность выбрать из широкого ассортимента продукции Щпс купить в Москве можно из широкого ассортимента продукции. Это позволяет найти оптимальный вариант для конкретных потребностей В Москве можно найти оптимальный вариант щпс для конкретных потребностей. Кроме того, покупка щпс в Москве может быть осуществлена с гарантией качества Щпс купить в Москве можно с гарантией качества.
Покупка щпс в Москве также может быть выгодной с экономической точки зрения Щпс купить в Москве может быть выгодно с точки зрения экономии . Это связано с тем, что в Москве имеется большое количество поставщиков и производителей щпс Это связано с тем, что в Москве имеется большое количество поставщиков и производителей щпс . Это конкуренция между поставщиками и производителями приводит к снижению цен и повышению качества продукции В Москве конкуренция между поставщиками и производителями щпс приводит к снижению цен и повышению качества продукции .
В Москве имеется несколько вариантов покупки щпс В Москве имеется несколько вариантов покупки щпс . Одним из наиболее распространенных вариантов является покупка через официальные дилерские центры Одним из наиболее распространенных вариантов является покупка через официальные дилерские центры . Эти центры предлагают широкий ассортимент продукции и предоставляют гарантию качества Щпс купить в Москве через официальные дилерские центры можно с гарантией качества.
Другим вариантом покупки щпс в Москве является покупка через интернет-магазины В Москве щпс можно купить через интернет-магазины . Этот вариант является удобным и позволяет выбрать щпс из широкого ассортимента продукции Покупка щпс через интернет-магазины в Москве является удобной и позволяет выбрать из широкого ассортимента продукции . Кроме того, интернет-магазины часто предлагают более низкие цены и акции Щпс купить в Москве через интернет-магазины можно по более низкой цене и с акциями.
В заключении, покупка щпс в Москве является выгодным и удобным вариантом В заключении, покупка щпс в Москве является выгодным и удобным вариантом . В Москве имеется широкий ассортимент продукции и возможность выбрать из различных вариантов покупки В Москве имеется широкий ассортимент продукции и возможность выбрать из различных вариантов покупки . Кроме того, покупка щпс в Москве может быть осуществлена с гарантией качества и по более низкой цене Кроме того, покупка щпс в Москве может быть осуществлена с гарантией качества и по более низкой цене . Мы надеемся, что эта информация будет полезной для вас при выборе варианта покупки щпс в Москве Эта информация должна быть полезной для вас при выборе варианта покупки щпс в Москве .
стоимость курса трак диспетчера в сша для новичков заказать обучение курс диспетчера грузоперевозок
Делали печать брендовых этикеток и получили отличный результат. Слой краски ровный, цвета не выгорают. Прорезка точная и аккуратная. Тираж сделали быстро и без брака. Очень довольны качеством изготовления, изготовление рекламных календарей
SimpleHomeSpot – Products are appealing and navigating the website felt natural.
Мы не используем шаблон «на всех». Темп и сочетания зависят от давления, пульса, выраженности тошноты и тремора, уровня тревоги, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Детокс — это система шагов: допуск к терапии, коррекция воды и электролитов, поддержка печени, вегетостабилизация, осторожная работа со сном по показаниям, профилактика осложнений. Любое назначение проговаривается простым языком: зачем, как подействует, что считать нормальной динамикой, а что — поводом связаться с врачом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]kapelnica-pri-zapoe-sostav[/url]
Тактика подбирается индивидуально и зависит от тяжести состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и переносимости препаратов. Ниже представлены базовые компоненты, которые часто включаются в схемы лечения при запойных состояниях.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в переулок панфилова, 36[/url]
Хотя принципы лечения похожи, клиническая логика отличается. При алкогольной зависимости чаще нужен быстрый контроль вегетативных симптомов, восстановление сна и коррекция электролитов. При наркозависимости добавляются протоколы снижения импульсивности, работа с абстиненцией другой природы и расширенная психотерапевтическая часть. В обоих случаях результат не сводится к «капельнице»: мы учим распознавать ранние сигналы срыва, формировать безопасные ритуалы и поддерживать общение без давления и скрытых конфликтов.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk
смотря каким реагентом будешь бадяжить https://pasangtaruhan.xyz не выстанавливаютьсядрамчик, хаус… да не суть.
FashionCrushCorner – Arrived fast, very stylish products, smooth shopping from start to finish.
orchardlookhub – Tidy pages and fast-loading sections, shopping was quick and pleasant.
TrendStyle Hub – Pages loaded instantly and the fashion lineup felt fresh and appealing.
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]obratitsya-v-narkologicheskuyu-kliniku[/url]
гидроизоляция цена за метр [url=http://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru]http://gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru[/url] .
Лечение зависимости проходит поэтапно. Такая последовательность обеспечивает постепенное восстановление и закрепление полученных результатов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника донецк[/url]
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/
TAB Picks Online – Stylish items laid out clearly, browsing was simple and fast.
курс диспетчера грузоперевозок в америке для новичков как работать с load board в этом году
City Goods Market – The layout was clear today, making product discovery smooth and satisfying.
инъекционная гидроизоляция гидрофобные смолы [url=http://www.inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru]http://www.inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвалов цена [url=gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru]гидроизоляция подвалов цена[/url] .
https://thsc.edu.et/events/eduma-autumn-2015/
Только что принесли, позже трип отпишу) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Работаю впервые с этим магазом! Есть что заявить! Ребята, я в приятном шоке от работы магаза! Брал давеча! Пацанчик ну тот который заказы принимает, обрабатывает, ему ОСОБАЯ УВАЖУХА! Магаз РАБОТАЕТ РОВНО и ОПЕРАТИВНО! Все заценили! Все объявили ОБЩУЮ ОХУЕННУЮ БЛАГОДАРНОСТЬ МАГАЗУ! Извиняюсь за французский! ) Что могу сказать, видимо нашел свой магаз! )закладок нет, и представителей тоже, в Ярославль можем отправить курьером срок доставки 1 день.
усиление проёмов металлоконструкциями [url=https://www.usilenie-proemov2.ru]https://www.usilenie-proemov2.ru[/url] .
Использование этих методов в комплексе позволяет восстановить здоровье пациента и сформировать основу для трезвой жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в донце[/url]
http://superkot.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=60&t=4788
Тату студии в Санкт-Петербурге. Профессиональные студии татуировки: от миниатюрной графики до масштабного реализма. Индивидуальные эскизы, абсолютная стерильность и опытные мастера. Запишитесь на консультацию и создайте свой шедевр! https://spb-tattoo.ru/
Петрозаводск добавляет нюансы: влажные сумерки, ветер от Онежского озера, «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда. Поэтому бригада «СеверКар Медикус» приезжает в гражданской одежде, быстро и без лишних фраз. Координатор заранее уточняет код домофона, парковку, «окна связи» для близких; рекомендует приглушить верхний свет, подготовить воду комнатной температуры и свободный доступ к розетке. Такой «тихий сценарий» снижает сенсорную нагрузку, сглаживает пульсовые «пики» к вечеру и помогает заснуть без избыточной фармакологии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/
Интересно, сколько дней заказ будет идти… Успеет ли до запрета, если сегодня заказать… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш всегда кто-то гадость может написать, а ответить не кто!! работал с вами!Парни у кого нибудь задерживали посылку в СПСР?Уже неделю как приняли и все не отправят и планируемая дата отправки прошла,а реальную так и не поставили.Позвонил в офис говорят готово к отправке,а че не отправляют они не знают.Сказали позвонить когда менеджеры придут на работу.У кого нибудь такое было?Может это фигня какая то и лучше не идти за посылкой?Как думаете?Раньше просто такого не было максимум 5 дней с даты приема до моих рук проходило,с любого магазина.
Первые часы определяют траекторию. Мы работаем по карте — у каждого окна есть цель, действия, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняем один элемент и назначаем повторную оценку. Это дисциплинирует решения и защищает от полипрагмазии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk15.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Silver Garden Online Shop – Seamless navigation and clean design made the store feel trustworthy.
Soft Grove Selection – Organized pages and well-laid-out categories helped me browse quickly.
Здесь
[url=https://lesteh-al.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
hello!,I like your writing very so much! share we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your article on AOL?
I need a specialist in this space to solve my problem.
Maybe that’s you! Looking ahead to see you.
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I
provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My website is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors would definitely benefit from some of the information you provide here.
Please let me know if this alright with you. Appreciate
it!
народ а присылают вместе с заключением экспертизы? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану ОО мне то же все пришло!Не смог не скопипастить
CozyLivingVault – Browsing was pleasant, and items are showcased nicely.
InnerStrengthGuide – Pleasant visuals, clear navigation, and motivating resources.
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Modern Trend Picks – Quick-loading pages and a variety of trendy products made browsing fun.
Многие люди с зависимостью или их близкие начинают путь к избавлению от наркомании с самолечения или обращения к народным методам. К сожалению, такой путь почти всегда заканчивается рецидивом. Причина в том, что наркотическая зависимость формируется на нескольких уровнях — физиологическом, психологическом и социальном. Без системного подхода устойчивой ремиссии достичь невозможно. Профессиональное лечение в «РеабПермь» позволяет воздействовать на все механизмы заболевания, включая биохимические нарушения, искажённые модели мышления и нарушения в структуре личности, которые провоцируют употребление.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-narkomanii-perm0.ru/
Полностью согласен !!! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Ответил) просто не сразу увидел в вашем сообщении дополнительный вопрос )Магазин работатет? отпишите кто совершил сделку в последнее время
FreshToday Hub – Nicely arranged items with quick navigation that makes scrolling effortless.
TAB Trend Corner – Liked the selection, browsing between sections was seamless.
BrightSelectionSpot – Fantastic range of items, made choosing very simple and satisfying.
Flora Essentials Market – A refreshing browsing experience with neatly organized floral items.
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наши стандарты включают конфиденциальную маршрутизацию, детализированные инструкции для семьи, модульный план лечения и прозрачное разделение бесплатных и платных блоков. Каждому пациенту назначается ведущий специалист, который сопровождает его на всём пути — от первого звонка до контрольных чек-инов после процедур. Мы не «наращиваем» объём вмешательств ради впечатления: используется минимально достаточный набор мер, который действительно влияет на целевые маркеры — переносимость воды, качество сна, сглаживание вегетативных «качелей» и возвращение утренней ясности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от различных видов зависимости. Основой успешного лечения является комплексный подход, который включает тщательную диагностику, медикаментозное сопровождение, психологическую поддержку и реабилитационные программы. В «АльфаМед» применяются передовые технологии и индивидуальные методики, направленные на восстановление здоровья и предупреждение рецидивов.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologiya-kruglosutochno-omsk/
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в казани[/url]
Классный магаз, почитал отзывы, нам в киров бы не помешал такой движ. Ассортимент огонь, давайте в наш славный город. Всем щастья! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм товар появился? когда возобновите доставку по городам?Но бывали случаи и на оборот…
Первичная консультация в «РеабПермь» проводится конфиденциально, без постановки на учёт и без обязательств. Её задача — оценить текущее состояние пациента, установить мотивацию к лечению и подобрать оптимальный план терапии. На встрече специалист собирает анамнез, задаёт уточняющие вопросы, объясняет суть зависимости и предлагает возможные варианты вмешательства. Консультация может проходить очно или онлайн, с участием самого пациента или его родственников. Это особенно полезно на ранних стадиях, когда человек ещё не готов к госпитализации, но нуждается в грамотной поддержке и убеждении.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-perm0.ru/]лечение наркомании диспансер пермь[/url]
Ниже представлен перечень основных направлений, используемых в современной наркологической помощи. Этот список отражает комплексный подход к лечению зависимостей.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-perm0.ru/narkolog-perm-czeny/
Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая основные направления медикаментозного лечения и сопутствующих процедур:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
A motivating discussion is worth comment. There’s no doubt
that that you should write more on this subject matter, it might not be a taboo matter but usually folks
don’t speak about these issues. To the next! Cheers!!
Стационар рационален при нестабильном состоянии, риске делирия, судорогах в анамнезе, скачках давления, выраженной одышке, неукротимой рвоте, одиночестве ночью или невозможности обеспечить «тихий режим». В палате — контролируемая среда, доступ к ЭКГ и базовой лаборатории по показаниям, круглосуточный пост медсестёр и возможность быстро менять тактику, если параметры «плывут». Такой маршрут предсказуемее по безопасности и зачастую короче по времени до стабильного самочувствия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]капельница от запоя состав[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://asystm.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-pomoshch-v-ivanteevke
Чтобы процедура прошла спокойно и без задержек, заранее организуйте базовые условия — это экономит время и силы пациента и семьи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница, устанавливаемая наркологом на дому в Челябинске, помогает быстро очистить организм от токсинов и нормализовать водно-солевой баланс. Растворы включают витамины, анальгетики, седативные и гепатопротекторные препараты. Эффект от процедуры ощущается уже через 20–30 минут. Капельница снижает головную боль, устраняет тошноту, восстанавливает работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Такой метод считается одним из самых эффективных способов вывести пациента из запойного или абстинентного состояния без визита в стационар.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske-vyvod-iz-zapoya/
Детокс — последовательность шагов, где каждый этап имеет цель и критерии безопасности. Мы начинаем с оценки рисков (кардиология, неврология, психическое состояние, возможные взаимодействия препаратов), продолжаем инфузионной терапией, корректируем электролиты и кислотно-щелочное равновесие, поддерживаем печень и нервную систему. Если присутствуют выраженная тревога и бессонница, подключаем короткие курсы седативной терапии с контролем побочных эффектов. Отдельный блок — профилактика осложнений: обезвоживание, аритмии, обострение гастрита и панкреатита, делирий. Каждое назначение — только после очной оценки и с учётом сопутствующих состояний.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
ну тогда тестируй, если неделю выдержал ) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Будем дальше работать с этим магазином.Интересно, сколько дней заказ будет идти… Успеет ли до запрета, если сегодня заказать…
компании усиления проемов [url=http://usilenie-proemov2.ru]http://usilenie-proemov2.ru[/url] .
«ОмскПрофи» укомплектована современной медицинской базой: передвижные аппараты для ЭКГ, инфузионные стойки, экспресс-анализаторы, мониторы состояния, аппараты ИВЛ (в реанимационных палатах). Штат сотрудников сформирован из врачей-наркологов, токсикологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов, медицинских сестёр, прошедших обучение по международным протоколам. Ведётся постоянная учёба, стажировки, участие в научных форумах. Благодаря этому пациенты получают не только медицинскую помощь, но и психологическое сопровождение, направленное на долгосрочный результат.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Vavada gaming club offers a convenient personal account with complete game history. Learn about current Vavada bonuses at https://museo.precolombino.cl/, where updates are regularly published. Newcomers to Vavada get welcome packages with bonuses and free spins. The Vavada mobile platform doesn’t require installation and works through browsers. The Vavada security service carefully protects player personal data.
Erectile dysfunction no more requires to be a source of shame or aggravation for males in Germany and Austria. Medications like Viagra Connect, Mensil Max, Maxon Forte, and Maxigra Max give useful, proven, and easily accessible solutions ideal for various reasons and age groups, https://www.behance.net/polmedi.
срочно курсовая работа [url=www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru]www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru[/url] .
куплю курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru[/url] .
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь в новокузнецке[/url]
Timber Path Collections – Easy-to-use layout and well-structured categories enhanced the browsing experience.
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в нижнем новгороде[/url]
помощь студентам курсовые [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/]https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/[/url] .
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Латунная полоса 5×250 мм Л90 ГОСТ 931-90 Покупайте латунную полосу различных размеров и толщин на сайте Редметсплав.рф. У нас вы найдете высококачественный материал с высокой прочностью, стойкостью к коррозии и возможностью легкой обработки. Используйте латунную полосу для создания декоративных элементов, мебели, украшений и других изделий. Доступны различные размеры и толщины.
Весь процесс можно представить следующим образом:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом челябинск[/url]
Даный магазин берет бобло и парит мозг посылки отпровляет по месяцу, гдето с сентября такие проблемы сними начелись, причом решать их они не собираються купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази посылка упакована оригинально =)) и скорость сборки удивила!А вот и мин Трип мой.
Домашний формат нужен, когда риски управляемы, а в квартире можно обеспечить «тихий режим». Врач приезжает без эмблем, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, сверяет лекарства за последние 48 часов и аллергии. После допуска запускается инфузия с мягкой коррекцией воды и электролитов, поддержкой печени и вегетативной нервной системы; при необходимости аккуратно настраивается сон. По завершении — переоценка, письменная памятка на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и прямой канал связи. Такой визит «гасит» тремор и тошноту, снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]voskresensk-narkologicheskij-dispanser[/url]
Для тех, кто ценит инновации и заботится об окружающей среде, [url=http://vip-elektromobil.ru]премиум машины москва купить[/url] становится все более привлекательным вариантом, предлагающим не только снижение вредных выбросов, но и уникальный опыт вождения.
и их популярность неуклонно увеличивается благодаря своей экологичности и экономической эффективности. Многие люди считают их лучшим вариантом для будущего . Электромобили работают на аккумуляторах, которые можно заряжать от обычной электрической розетки .
Их популярность объясняется также тем, что они требуют меньше технического обслуживания, чем традиционные автомобили. Покупатели также хотят знать о наличии сервисных центров и инфраструктуры для зарядки аккумуляторов. Кроме того, многие правительства предлагают налоговые льготы и субсидии для покупки электромобилей.
Электромобили обладают рядом преимуществ перед традиционными автомобилями, включая снижение выбросов загрязняющих веществ . Они не выделяют вредных веществ в атмосферу, что делает их более чистым вариантом . Это связано с тем, что электрические двигатели производят меньше шума и вибраций, чем традиционные двигатели .
Экономическая эффективность электромобилей является еще одним важным преимуществом . Они предлагают различные льготы, такие как налоговые кредиты и бесплатная парковка . В результате, все больше людей начинают рассматривать электромобили как реальный вариант.
Это может вызывать беспокойство у тех, кто планирует совершать длинные поездки. Другим недостатком является время зарядки аккумуляторов . Еще одним недостатком электромобилей является высокая первоначальная стоимость .
Однако, многие компании и правительства активно работают над расширением сети зарядных станций. Некоторые люди также беспокоятся о безопасности электромобилей . Несмотря на эти недостатки, электромобили остаются привлекательным вариантом для многих людей .
Они предлагают широкий диапазон преимуществ, от снижения выбросов до экономии средств на обслуживании . Мы можем ожидать, что стоимость электромобилей будет снижаться, а их доступность будет повышаться . Это лишь вопрос времени, когда электромобили станут нормой.
Это приведет к появлению новых моделей с улучшенными характеристиками и снижением цен . Они будут предлагать стимулы и поощрения для покупки электромобилей, что поможет стимулировать спрос . По мере развития технологий и инфраструктуры, электромобили станут все более доступными и привлекательными для широкого круга людей .
В рамках комплексной программы лечения в клинике применяются следующие методы:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-perm0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно в перми[/url]
We are a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community.
Your website offered us with useful information to work on. You
have done a formidable process and our whole community will be thankful
to you.
https://telegra.ph/Capitalizing-on-Chance-Examining-monopoly-big-baller-results-today-to-Boost-Your-Winning-Potential-11-21
v
FreshSelectionSpot – Clean visuals, easy navigation, and enjoyable shopping experience.
TSZ Style Shop – Stylish products displayed nicely, exploring items was simple and quick.
Rare Line Picks – The layout looked clean, and exploring different items was effortless.
Селлер вообще отвечает на емейл? Или только в аське его искать, которой у меня нет? https://08xcvaz4.top 1 из 5 хемикалсу.Имейл не рабит,сайт кривой-левые системы оплаты,нет ритейла,кривость и отсутствие информации…Деньги зажимать не пытаются и за это можно кинуть балл сверху и возможно продолжить общение в будущем…Админ по аське с кем связался адекват=))) радует.Приятный сайт цены тоже радуют сделал заказ=)) буду ждать. Качество Каличество отпишу
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/kapelnicza-na-domu-anonimno-nizhnij-novgorod/
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на диагностике, лечении и реабилитации пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Основная цель деятельности учреждения — восстановление физического здоровья и психологической устойчивости человека, оказавшегося в состоянии зависимости. В клинике применяются современные методы терапии, доказавшие эффективность в медицинской практике. Все процедуры проводятся конфиденциально, с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и под контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkologiya-nizhnij-novgorod-besplatno/https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru
Домашний формат нужен, когда риски управляемы, а в квартире можно обеспечить «тихий режим». Врач приезжает без эмблем, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, сверяет лекарства за последние 48 часов и аллергии. После допуска запускается инфузия с мягкой коррекцией воды и электролитов, поддержкой печени и вегетативной нервной системы; при необходимости аккуратно настраивается сон. По завершении — переоценка, письменная памятка на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и прямой канал связи. Такой визит «гасит» тремор и тошноту, снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]рейтинг наркологических клиник в москве[/url]
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Казани — это современный медицинский центр, специализирующийся на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основное направление деятельности заключается в проведении детоксикации, восстановлении работы нервной системы и формировании устойчивой мотивации к отказу от употребления психоактивных веществ. Все процедуры проводятся в условиях полной анонимности и медицинского контроля, что обеспечивает безопасность и доверие со стороны пациентов. Программа терапии строится по принципам доказательной медицины и индивидуального подбора лечебных средств.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены казань[/url]
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-voskresenske/
CalmPlainsStore – Quick service and easy-to-navigate pages, very pleased with my experience.
Simply wish to say your article is as astonishing.
The clarity to your publish is just cool and i could assume you’re knowledgeable
on this subject. Well together with your permission let
me to clutch your feed to keep updated with coming
near near post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please keep
up the enjoyable work.
«Клиника Трезвый Курс» организует вывод из запоя для жителей Лобни круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом без опознавательных знаков, аккуратные капельницы с индивидуальным составом, стационар с наблюдением и аппаратным контролем, а также поддержка семьи на первые дни, когда особенно важно не сорваться в прежний ритм. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никаких «универсальных коктейлей» и грубой седации ради видимости улучшения. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком, смета фиксируется до начала процедур, приватность встроена в процесс. Цель — не просто «полегчало», а безопасная стабилизация с предсказуемой ночью и понятным планом тихой недели.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-lobne/
Finders Fresh Hub – Clean presentation of new items and a very responsive interface.
Pure Harbor Online – The well-laid-out interface made checking items effortless and enjoyable.
Здесь
[url=https://zelevoeobuchenietpi.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
VIP Escort Dating Site for Men Elite escort services Elite Escort Agency
В рамках комплексной программы лечения в клинике применяются следующие методы:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-perm0.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь в перми[/url]
Лечение не заканчивается после завершения курса. Напротив — начинается наиболее ответственный период, когда пациент возвращается в привычную среду, сталкиваясь с соблазнами и старыми моделями. В «РеабПермь» предусмотрен целый блок постлечебной адаптации. Пациенту помогают составить маршрут восстановления: восстановление трудовых или учебных навыков, корректировка окружения, выработка устойчивых альтернатив зависимому поведению (спорт, волонтёрство, хобби). При необходимости предоставляется поддержка в трудоустройстве или обучении.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-perm0.ru/]запой лечение наркомания[/url]
Opportunities Online Hub – Smooth navigation and well-structured content for effortless browsing.
В клинике «Согласие» наркологическая помощь в клинике проводится с применением современных протоколов лечения, включающих детоксикацию, симптоматическую терапию, медикаментозное восстановление и психокоррекцию. Диагностические мероприятия позволяют оценить общее состояние пациента, выявить поражения органов и систем. На основе данных разрабатывается индивидуальная схема лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь самара[/url]
TrendVault – Quick navigation and trendy items clearly presented for effortless browsing.
В клинике «Альтернатива» применяются современные методы терапии, включающие медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь новокузнецк[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Лечение не заканчивается после завершения курса. Напротив — начинается наиболее ответственный период, когда пациент возвращается в привычную среду, сталкиваясь с соблазнами и старыми моделями. В «РеабПермь» предусмотрен целый блок постлечебной адаптации. Пациенту помогают составить маршрут восстановления: восстановление трудовых или учебных навыков, корректировка окружения, выработка устойчивых альтернатив зависимому поведению (спорт, волонтёрство, хобби). При необходимости предоставляется поддержка в трудоустройстве или обучении.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр[/url]
Elite VIP Escort https://unrealestate.biz Escort Agency
Курс терапии в клинике состоит из нескольких последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение конкретных целей — от снятия интоксикации до восстановления психологического равновесия. Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и минимизировать вероятность рецидива. На всех стадиях лечения ведётся контроль состояния пациента, а также постоянная корректировка назначений в зависимости от реакции организма.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Медикаментозная терапия — важнейший этап стабилизации состояния. Врачи «СамарМед» применяют препараты с доказанной эффективностью: детоксикационные растворы, нейрометаболики, седативные и анксиолитические средства, ноотропы, гепатопротекторы, а при необходимости — антипсихотики. Подбор схемы проводится индивидуально, с учётом переносимости, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, возраста и стадии зависимости. Все препараты применяются строго по международным протоколам и под контролем врачей круглосуточно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
усиление проему [url=https://usilenie-proemov2.ru/]https://usilenie-proemov2.ru/[/url] .
Метод
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk
Основные направления помощи включают:
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
EverNova Page – Aesthetic elements stood out, and page-to-page flow worked smoothly.
Стационарный старт «Клиники Трезвый Курс» в Лобне рационален при длительных эпизодах, выраженных «качелях» давления и пульса, повторных судорогах, неукротимой рвоте с обезвоживанием, признаках надвигающегося делирия, а также если дома невозможно обеспечить «тихий режим» и наблюдение ночью. В палате меньше случайностей: аппаратный мониторинг под рукой, при показаниях ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, дежурный пост 24/7, быстрые переоценки и мгновенные коррекции. Благодаря этому путь до ровной ночи короче, а риск ночного отката ниже.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-lobne
Trend Choice Hub Online – Good mix of items showcased well, exploring pages was smooth.
ремонт стиральных машин на дому [url=https://remont-stiralok-voronezh-ceny.ru/]ремонт стиральных машин на дому[/url].
elite escort Elite escort services Elite prostitutes – Vip girls , profiles and escort from elite girls of models
Leaf Collection Market – Pleasant marketplace setup and quick, natural browsing throughout.
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь[/url]
AllGiftShop – Clean pages, easy-to-browse layout, and wide selection of items.
It’s hard to come by educated people in this particular subject,
however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
Escort Services Agency – VIP Escort VIP escort dating site VIP escort
Как выбрать хорошую медицинский центр
Медикаментозная терапия — важнейший этап стабилизации состояния. Врачи «СамарМед» применяют препараты с доказанной эффективностью: детоксикационные растворы, нейрометаболики, седативные и анксиолитические средства, ноотропы, гепатопротекторы, а при необходимости — антипсихотики. Подбор схемы проводится индивидуально, с учётом переносимости, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, возраста и стадии зависимости. Все препараты применяются строго по международным протоколам и под контролем врачей круглосуточно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены самара[/url]
GreenHubSpot – Excellent assortment and intuitive site layout, shopping was easy and fun.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/494nj6p3
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/nhcptv87
https://www.diabetes-ru.org/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=458
http://fanfishka.ru/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=6778
https://www.miass.info/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=2171
Estos húmedos XXX baño balas identificar duras película vibraciones con primeros
planos boca y húmedos ráfaga selfies, que son renombrados
entre los sediento espectadores en. Las galerías MILF película, que cuentan con facial garrillas,
anal porno selfies, y XXX-paja fugas, hacer que todos los sediento suscriptores
ridículo. , haciendo que los chicos de todo el mundo se masturben sin aguantar sus filtraciones.
Primeros planos en alta definición y sonido envolventes.
puede aparecerán en el próximo OnlyFans material, junto con difícil fotos de upskirts
y puñetazo trabajos en el coche. Nada la excita más que el goteo de porno
misionero sin censura, como lo demuestran las fugas de misión XXX y fotos de sexo crudo donde el
coño sigue abierto y las tetas presionan con fuerza. https://es.she-international.com/dakomiii/
https://bogotamihuerta.jbb.gov.co/miembros/aria-lucy-267/
Ниже представлен перечень основных направлений, используемых в современной наркологической помощи. Этот список отражает комплексный подход к лечению зависимостей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-perm0.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Весь процесс можно представить следующим образом:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru
ExploreOpportunities Online – Clean layout and easy access to all resources made browsing enjoyable.
Elite Models Elite escort services Escort for men
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me
to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a
designer to create your theme? Outstanding work!
ClassicVault – Fast pages and well-organized items make shopping smooth and enjoyable.
Бензонасос не качает — что делать
Minimal Trend Shop – Simple yet appealing layout with fast loading and clear categories.
Vip girls VIP Escort Escort Services
fashionhaven – Great selection and smooth navigation, I found everything quickly.
Trend Collection Online Store – Stylish product selection, exploring the site was very smooth.
Modern Living Deals – Nice assortment of home items with an easy flow through each category.
Статья посвящена анализу текущих трендов в медицине и их влиянию на жизнь людей. Мы рассмотрим новые технологии, методы лечения и значение профилактики в обеспечении долголетия и здоровья.
Получить исчерпывающие сведения – https://agronomva.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-v-moskve
Здесь
[url=https://impact-dl.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your post seem to
be running off the screen in Firefox. I’m not sure if this is a format issue or something
to do with browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let you know.
The design look great though! Hope you get the problem fixed soon. Many thanks
Escort https://extragram.ru escort agency
Systems of medium-sized sizes typically list thousands to a few thousand creators.
For general movie leakage, they might have separate sections for mejores porno onlyfans OnlyFans, for other
registration systems, and for other platforms.
They eventually build a fairly extensive archive,
mainly for creators who are currently popular on social media or in some nations. https://baumarkt-xxl.de/template/redir/out.php?p=aHR0cHM6Ly9lcy5zaGUtaW50ZXJuYXRpb25hbC5jb20v
Your mode of explaining all in this paragraph is actually fastidious, every one can simply
be aware of it, Thanks a lot.
VIP models Elite escort services Elite VIP Escort
StylishLivingCenter – Clear layout, attractive items, and effortless browsing.
RainyMarketOnline – Fast and intuitive site, made shopping a pleasure today.
Collective Wardrobe Shop – Good variety of stylish additions, and the interface worked without lag.
Ниже — сводный ориентир по этапам. Это не жёсткий график, а понятная канва процесса, которую врач адаптирует под клиническую картину.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskij-dispanser-voskresenskoe[/url]
MetroTrends – Fast pages and urban items displayed neatly for effortless browsing.
Escort Gay escort Escort for men
сколько от пхукета до краби отели краби тайланд
Superb blog! Do you have any suggestions for aspiring writers?
I’m hoping to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you recommend starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for
a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally overwhelmed ..
Any ideas? Bless you!
Feel free to visit my web page … zaragosa01
Gute Sportwetten tipps bonus schweiz
https://bravomos.ru/ bravomos
Escort Girls https://knowbuddhism.info Elite Escort Agency
TDP Shop Picks – Deals showcased nicely, moving through sections felt simple and quick.
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sergievom-posade
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Дюралевый швеллер 440400 52х60х12х7.5х10.5 мм Д16 ГОСТ 4784-97 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
Modern Home Outlet – A tidy layout paired with simple navigation made shopping easy today.
Покупка современной корпусной мебели для дома или офиса в 2025 году. Интернет магазины рейтинг и цены от покупателей: https://faine-misto.dp.ua/pokupka-mebely-dlya-kvartyry-onlajn-sovety-po-vyboru-komplekta/
хостинг провайдер HSTQ как хостинг-провайдер претендует на роль лидера на рынке, предлагая не только технические решения, но и экспертную поддержку в вопросах оптимизации, безопасности и масштабирования онлайн-проектов. Компания активно инвестирует в развитие инфраструктуры и обучение персонала, чтобы соответствовать растущим требованиям современного бизнеса.
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-voskresenske
Motivation Online Hub – Uplifting feel across the site, with quick loading and smooth layout.
Здесь
[url=https://agencyx.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Reliable Moving Services in Brockton
VIP escort https://potencial-tekstil.ru Elite individuals
Мытищи дают логистические плюсы домашнего старта: меньше перемещений, приватнее, быстрее включается режим. Дом уместен, если нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» давления/пульса, признаков обезвоживания с угрозой судорог. Если же состояние «по краю» — сочетание рвоты, лихорадки, кардиальных жалоб, второй бессонной ночи, выраженного тремора — врач предложит короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов под круглосуточным наблюдением. Это честнее и, на дистанции, экономнее: дефициты закрываются быстрее, дозы подбираются точнее, первая ровная ночь достигается предсказуемо, а риск экстренных ночных выездов снижается. В любом варианте приватность сохраняется: немаркированные визиты, индивидуальные окна, закрытые каналы коммуникации, доступ к данным по ролям.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Ущерб через наркотиков — этто групповая проблема, охватывающая физиологическое, психическое равным образом
соц здоровье человека. Употребление подобных наркотиков, яко кокаин, мефедрон,
гашиш, «шишки» или «бошки», может
обусловить для неконвертируемым следствиям как чтобы
организма, так равным образом для общества на целом.
Но даже при вырабатывании подчиненности возможно восстановление —
главное, чтобы зависимый явантроп обратился согласен помощью.
Эпохально помнить, яко наркомания лечится,
также помощь бацнет шансище на свежую жизнь.
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika[/url]
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sergievom-posade
FuturePath Select – Smooth navigation and tidy product display make exploration effortless.
Fantastic beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your web site,
how can i subscribe for a blog website? The account aided me a
acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of
this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
Риск от наркотиков — этто групповая проблема, обхватывающая физиологическое,
психическое (а) также социальное здоровье
человека. Употребление эких наркотиков, яко снежок, мефедрон, гашиш, «шишки» чи «бошки», что ль обусловить ко неконвертируемым последствиям яко для организма, так и чтобы федерации в течение целом.
Но даже у эволюции связи возможно электровосстановление
— главное, чтобы зависимый явантроп
обратился согласен помощью. Эпохально памятовать,
яко наркомания врачуется, и реабилитация бацнет шанс на новую жизнь.
Sunrise Market Lane – Simple structure and neat product arrangement improve site usability.
Elite Escort Agency Escort agencies Elite prostitutes – Vip girls , profiles and escort from elite girls of models
Explore Your Potential – Content is clear and concise, with easy navigation throughout the site.
купить диплом косметолога екатеринбург [url=https://www.r-diploma11.ru]купить диплом косметолога екатеринбург[/url] .
Запой — это не только выраженная тяга к алкоголю, но и комплекс физиологических нарушений: обезвоживание, колебания давления, тахикардия, бессонница, тремор, дефициты электролитов. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем выше риск делирия и декомпенсаций. Мы оцениваем картину целиком: стаж употребления, фоновые болезни, уже принятые препараты, прошлые эпизоды судорог или потерь сознания. По итогам первичной беседы врач рекомендует формат старта — визит на дому или стационар.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/
Если в первичном звонке звучат «красные флаги» (одышка, спутанность сознания, резкие скачки ритма), мы предлагаем стационарное «окно» мониторинга с ночным постом. При низких рисках стартуем на дому: контрольные точки совпадают с домашним комфортом, а вечерние online-вставки по 15–20 минут поддерживают предсказуемость без лишних поездок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
FashionLovers Online – Navigation felt effortless and the display of items was clean and appealing.
GlowSelect – User-friendly design with products showcased clearly for easy browsing.
Terrific stuff, Cheers!
Vip girls Elite escort services elite dating
Порча через наркотиков — этто
сложная проблема, охватывающая
физиологическое, психическое (а) также соц
здоровье человека. Утилизация подобных наркотиков, яко снежок,
мефедрон, ямба, «шишки» чи «бошки», что ль привести
буква неконвертируемым
последствиям яко чтобы организма, яко равно чтобы
мира на целом. Хотя даже при вырабатывании подчиненности возможно электровосстановление — ядро, чтоб
зависимый явантроп обратился согласен помощью.
Важно запоминать, яко наркозависимость лечится, и реабилитация
бацнет шансище на новую жизнь.
Городская среда Воронежа — яркие подъезды, плотный трафик, шумные дворы — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому мы проектируем «тихую» логистику: согласованная парковка, вход без вывесок, гражданская одежда специалистов, короткий маршрут от порога к месту процедуры. Коммуникация в зашифрованных каналах, напоминания — в беззвучном режиме. Такой дизайн не декоративен: чем меньше социального шума, тем быстрее возвращаются питьё и аппетит, а значит — меньше потребность «наращивать» фармакологию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
UniqueGiftSpot – Clean pages, easy-to-browse layout, and creative selection.
[url=https://www.bs-tyres.ru/tyres/pirelli]Шины Пирелли[/url] обеспечивают отличное сцепление и комфорт при езде в любых условиях.
Шины Пирелли известны своим качеством и производительностью. Множество водителей предпочитают их из-за отличных характеристик. Пирелли предлагает разнообразные модели для разных условий вождения.
Определяющей чертой шин Пирелли является их высокая степень надежности. Они обеспечивают отличное сцепление с дорогой . Это критически важно в сложных погодных условиях и обеспечивает безопасность в пути.
Долговечность шин Пирелли порадует каждого водителя . Это приводит к значительной экономии на замене шин. Все водители смогут оценить этот аспект .
Пирелли является партнером многих спортивных мероприятий. Технологии, разработанные для гонок, находят применение в гражданских шинах . Таким образом, покупая шины Пирелли, вы получаете копию гоночной производительности .
Trend Fashion Corner Shop – Loved the trendy items, browsing through the collection was very smooth.
Мы собираем терапию из проверенных модулей: гидратация, коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям, поведенческие интервенции (свет, тишина, дыхание 4–6, стимул-контроль, вечерние ритуалы). Объём и темп зависят от ведущего симптома и времени суток: при кардиореактивном вечере больше внимания уделяется среде, при тошноте — гастропротекции и «тёплому питанию», при поверхностном сне — цифровой гигиене и световым сценариям. Ниже приведена ориентировочная матрица выбора; финальное решение — за лечащим врачом с учётом противопоказаний и лекарственных взаимодействий.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/[/url]
Чтобы помощь была прозрачной и управляемой, каждый этап имеет цель, индикаторы безопасности и эффективности, а также понятное «окно оценки» результата. Коррекции проводятся «штучно», по правилу одного изменения — это защищает от полипрагмазии и позволяет читабельно видеть вклад каждого шага.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно казань[/url]
Эффективное [url=https://seojazz.ru/]сайта продвижение[/url] является ключевым аспектом успеха любого бизнеса в современном цифровом ландшафте.
Продвижение сайта играет решающую роль в привлечении потенциальных клиентов . Это связано с тем, что многие люди используют поисковые системы для поиска товаров и услуг . Кроме того, это способствует повышению репутации компании в сети.
это процесс, который необходимо постоянно совершенствовать. Это включает в себя использование контекстной рекламы . Все эти методы способствуют привлечению целевой аудитории .
Одной из наиболее эффективных стратегий продвижения сайта является поисковая оптимизация . Это необходимо, потому что эти алгоритмы учитывают релевантность контента . Кроме того, это позволяет привлечь и удержать аудиторию .
оно помогает привлечь посетителей, которые заинтересованы в вашем продукте или услуге. Кроме того, социальные сети предлагают широкие возможности для продвижения сайта . Все эти стратегии они предполагают корректировку маркетинговых действий .
эти инструменты предназначены для автоматизации и оптимизации маркетинговых процессов. Это включает в себя сервисы для управления социальными сетями . Все эти инструменты позволяют увеличить эффективность маркетинговых кампаний .
это позволяет напрямую общаться с потенциальными и существующими клиентами . Кроме того, это позволяет адаптировать контент под конкретную аудиторию . Все эти инструменты и технологии требуют правильного использования и настройки .
это включает в себя определение целей и задач . Это необходимо, потому что без четкого плана трудно достичь успеха в продвижении сайта . Кроме того, реализация плана требует постоянного мониторинга и корректировки .
Поддержка и развитие кампании продвижения сайта являются продолжением ее реализации . Это необходимо, потому что они могут существенно повлиять на эффективность маркетинговых действий. Все эти аспекты это необходимо для поддержания и увеличения успеха в продвижении сайта.
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент: она не только структурирует действия персонала, но и снижает тревогу пациента и семьи. Появляется чувство контроля: понятно, что происходит сейчас и к чему мы идём через час, три и до утра.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника мурманск[/url]
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-nedorogo-v-voskresenske/
[url=https://fukatsu.tech/pgs/bainarii-opushon-yametoke_1.html]
バイナリーオプション 儲かりすぎ
[/url]
peaklookstore – Smooth browsing experience with neat product sections, shopping was easy.
Техника помогает, но не доминирует. Мы используем портативные приборы с мягкой индикацией и низким уровнем шума, чтобы не разрушать формирующуюся «ночную кривую». Контроль в остром окне чаще, вечером — мягче: так сохраняется физиология сна и снижается потребность в дополнительной фармакологии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в петрозаводске[/url]
Купить права – это важный шаг для тех, кто хочет получить официальное водительское удостоверение и начать уверенно управлять автомобилем. Наша компания предлагает надежные и быстрые способы приобретения водительских прав, соответствующих всем требованиям законодательства. Мы поможем вам пройти обучение в лучших автошколах, подготовиться к теоретическим и практическим экзаменам, а также оформить все необходимые документы без лишних хлопот. У нас вы найдете выгодные предложения, профессиональных инструкторов и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Если вы хотите купить права с гарантией качества и по доступной цене, обращайтесь к нам – мы сделаем процесс максимально простым и удобным.
Escort Services Agency – VIP Escort https://carsprokat.ru Escort services for charming girls
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь в казани[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Санкт-Петербурге осуществляется под круглосуточным медицинским контролем с применением современных методов инфузионной терапии, препаратов для восстановления обменных процессов и купирования синдрома отмены. Главной задачей врачей является восстановление баланса между физическим и психическим состоянием, предотвращение осложнений и стабилизация основных жизненных функций.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь санкт-петербург[/url]
официальный сайт 1хбет
Здесь
[url=https://frtnp.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Сначала короткий осмотр и проверка совместимостей, затем — инфузионная терапия с мониторингом давления/пульса/сатурации, после — инструктаж семьи и назначение контрольного контакта. Такой порядок снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой: понятно, чего ждать, когда отдыхать и в какой момент связываться с врачом.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/
Если дома шумно (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости), организуем краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерными палатами. После стабилизации пациент возвращается домой, а амбулаторное сопровождение продолжается в удобном графике — через короткие очные визиты и дистанционные чек-ины.
Подробнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-staczionar-sankt-peterburg
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]наркологическая клиника московская московская область[/url]
Режим 24/7 — это не только открытая дверь, но и правильно расставленные акценты по часам суток. Ночью — больше поведенческих опор и короткие видеовставки, днём — контроль витальных, уточнение плана гидратации и питания, вечером — «световые правила» и дыхательные циклы. В каждом окне мы знаем, что именно проверяем и что считаем успехом: так исчезают импровизации и ненужные «усиления», а пациент получает предсказуемую траекторию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в ставрополе[/url]
Escort Services Gay escort Escort for men
Stop switching between a dozen sportsbook apps and websites. Beika.app consolidates your entire betting experience into one sleek, powerful platform https://beika.app
Домашний формат удобен, если нет признаков угрозы жизни и дома можно обеспечить спокойную обстановку. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки рисков и допуска к инфузионной терапии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет план действий и ожидаемую динамику. Далее запускается капельница: мягкая коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка печени, симптом-контроль тревоги, тошноты, головной боли и тремора. На руки выдаются понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, сон, признаки тревоги и алгоритм связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-i-oblast[/url]
Мытищи дают логистические плюсы домашнего старта: меньше перемещений, приватнее, быстрее включается режим. Дом уместен, если нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» давления/пульса, признаков обезвоживания с угрозой судорог. Если же состояние «по краю» — сочетание рвоты, лихорадки, кардиальных жалоб, второй бессонной ночи, выраженного тремора — врач предложит короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов под круглосуточным наблюдением. Это честнее и, на дистанции, экономнее: дефициты закрываются быстрее, дозы подбираются точнее, первая ровная ночь достигается предсказуемо, а риск экстренных ночных выездов снижается. В любом варианте приватность сохраняется: немаркированные визиты, индивидуальные окна, закрытые каналы коммуникации, доступ к данным по ролям.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]нарколог на дом отзывы[/url]
Urban Look Deals – Stylish pieces stand out, and browsing feels effortless and fast.
Домашний формат выбирают, когда обстановка позволяет провести лечение в тишине и нет признаков угрозы жизни. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков, начинает с очной оценки и допуска к инфузии, сверяет принятые ранее препараты и аллергии, объясняет ожидаемую динамику. После запуска капельницы мягко корректируются жидкость и электролиты, проводится симптом-контроль (тремор, тошнота, тревога, головная боль), по показаниям — осторожная нормализация сна. На выходе пациент и семья получают понятные рекомендации на 24–48 часов: питьевой режим, питание, ограничения по нагрузкам, признаки тревоги и правила связи с дежурным врачом.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru
[url=https://bennystacos.com/pages/bubinga-kaiyaku.html]
バイナリーオプション ブビンガ[/url]
Nếu bạn muốn chơi game thỏa thích với thương hiệu này, bạn hãy tải và cài đặt ứng dụng từ link chính thức của chúng tôi. Điều này giúp đảm bảo an toàn và tránh các rủi ro từ những nguồn không rõ ràng. asia slot365 login Sau khi tải ứng dụng, bạn có thể đăng ký tài khoản và bắt đầu trải nghiệm ngay. TONY12-10A
Философия клиники — «тихо, адресно, прозрачно». Выездная бригада приходит без маркировки, документы оформляются нейтрально, доступ к клинической записи разделён по ролям, а коммуникации со семьёй проходят короткими апдейтами в согласованные моменты. Такая организационная дисциплина — клинический инструмент: меньше сенсорного шума — ровнее пульс к вечеру, устойчивее засыпание и меньше потребность в «усилителях».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в мурманске[/url]
промокоды на 1xbet бесплатно
Growth Vision Spot – Layout is neat and the pages respond quickly to navigation.
FuturePath Corner – Modern pages with well-organized products make shopping simple and enjoyable.
Escort Agency https://velonews.top Escort services for charming girls
WishFinder – Smooth browsing experience with a great variety of products.
Discover Affordable Finds – Listings looked promising, and everything flowed well from page to page.
Цель
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru
Trend Life Hub – Appealing items and clear navigation, exploring the site felt easy.
CoastalSelections – Items are displayed clearly, and moving around the site feels hassle-free.
Elite prostitutes – VIP escort from model girls , VIP profiles of elite courtesans VIP Escort beautiful escort girls
Grand River Spot – Attractive finds and intuitive layout make discovering items enjoyable.
Техника помогает, но не доминирует. Мы используем портативные приборы с мягкой индикацией и низким уровнем шума, чтобы не разрушать формирующуюся «ночную кривую». Контроль в остром окне чаще, вечером — мягче: так сохраняется физиология сна и снижается потребность в дополнительной фармакологии.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologiya
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]государственная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Главная задача — вернуть контроль над самочувствием мягко и последовательно. Мы не соревнуемся в дозах, а собираем устойчивую траекторию улучшения: каждый модуль терапии отвечает за одну цель и имеет своё «окно оценки». Если отклик ниже ожиданий — меняем ровно один параметр (темп, последовательность или поведенческий элемент среды), чтобы точно понимать, что помогло.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом казань[/url]
Стационар — это управляемая среда, где меньше случайностей и больше возможностей действовать на опережение. Под одной крышей — приём и допуск к терапии, инфузионный блок, аппаратный контроль, лаборатория и ЭКГ по показаниям, пост медсестёр и регулярная переоценка состояния. Такой контур особенно важен при давних запойных эпизодах, гипертонии, ишемической болезни сердца, сахарном диабете, гастроэнтерологических проблемах: правильно настроенный темп инфузий и «бережные» назначения уменьшают риск осложнений и снимают «эффект качелей» в первые сутки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]moskovskie-narkologicheskie-kliniki[/url]
Перед тем как перечислить основные поводы для экстренного вызова, отметим: даже один из пунктов — уже основание не откладывать помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]moskva-vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Первое сутки — каркас программы. Мы фиксируем цель каждого окна, инструменты, метрики контроля и критерий перехода. Если ответ «плоский», меняется ровно один параметр (темп/объём/последовательность) и назначается новое окно проверки. Этот принцип позволяет понять, что именно сработало, и избежать полипрагмазии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-petrozavodske15.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
DealsFinderOnline – Minimalistic design, easy-to-find deals, and enjoyable shopping experience.
Crypto regulations Binance trading signals have ascended in popularity, offering traders data-driven insights on market movements. Whether sourced from AI analysis or expert human traders, these signals provide potential entry exit levels, stop-loss recommendations, and take-profit targets crypto. The quest for Binance VIP signals and access to premium crypto signal telegram channels underscores the value placed on time-sensitive and accurate information.
Экстренный вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «ВоронежВита» мы действуем по чётким правилам: от телефонного триажа и тихого выезда бригады до адресной детоксикации и вечерних контрольных включений. Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить тремор и тошноту, выровнять сердечный ритм и вернуть физиологичный сон уже в первые ночи. Мы выбираем минимально достаточные вмешательства, чтобы днём сохранялась ясность и не возникало желания «самостоятельно усилить» схему. Конфиденциальность встроена в каждый шаг: гражданская одежда специалистов, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-voronezh15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Elite Escort Services https://theaudiobookstore.info Elite Girls
Каждый профиль решает одну задачу и имеет ожидаемую динамику. Мы избегаем параллельных «усилений», чтобы не «замазывать» вклад отдельного шага и не перегружать организм.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/
Если ожидаемая динамика «плоская», мы не усиливаем всё сразу. Меняется один параметр: скорость инфузии, порядок модулей или длительность вечерних включений. Такой «тонкий ремонт» безопаснее тотальной перестройки и лучше сохраняет ясность днём.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh-otzyvy
Elite girls for escort | VIP models https://ru3ddx.ru Business Escort Agency
Запой — это не только выраженная тяга к алкоголю, но и комплекс физиологических нарушений: обезвоживание, колебания давления, тахикардия, бессонница, тремор, дефициты электролитов. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем выше риск делирия и декомпенсаций. Мы оцениваем картину целиком: стаж употребления, фоновые болезни, уже принятые препараты, прошлые эпизоды судорог или потерь сознания. По итогам первичной беседы врач рекомендует формат старта — визит на дому или стационар.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva8.ru/]вывод из запоя москва и московская область[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит последовательный процесс лечения, где основное внимание уделяется безопасности, контролю состояния и постепенной адаптации. При поступлении проводится диагностика с оценкой степени зависимости, сопутствующих патологий и психологических факторов, влияющих на развитие заболевания. На основании полученных данных формируется персонализированный план терапии, включающий медикаментозные и немедикаментозные методы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-sankt-peterburg
Horizons Guide – Easy-to-read layout and the information provided real value.
https://tooter.in/bongachatru
https://giphy.com/channel/melbetcodeofthebest56
TrendSpotCrest – Fast-loading pages, smooth navigation, and stylish items throughout.
http://c9723964.bget.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=reasonneat2
Если в телефонном триаже обозначаются риски по дыханию, ритму или уровню сознания, на старте предлагаем стационарное «окно» мониторинга с круглосуточным постом. При низких рисках программа начинается амбулаторно или на дому и поддерживается вечерними онлайн-вставками (15–20 минут). Любой формат остаётся анонимным: доступ к карте наблюдения — по ролям, а язык переписки и чеков — нейтральный.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
http://ems.college-eisk.ru/?module=forum&action=topic&id=3547
Вся динамика фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения. При переводе в амбулаторную точку мы не «сбрасываем» историю: решения продолжаются с учётом уже сделанного и реакции пациента на вмешательства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
ChicStyle Online – The platform felt modern and polished, with pages responding instantly.
Инфузионная терапия в «АрктикМед Профи» строится на модулях, каждый из которых решает конкретную задачу: гидратация, коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, метаболическая поддержка; при необходимости — мягкая анксиолитика по строгим показаниям. Порядок модулей и темп выбираются под ведущий симптом-кластер и время суток. Мы обязательно фиксируем исходные и промежуточные маркеры, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/
Перед перечислением важно прояснить: нижеследующие ориентиры не заменяют очный осмотр, они помогают семье принять здравое решение без затяжки и споров. Если признаки сочетаются или нарастают, лучше не откладывать обращение, чтобы перехватить динамику, пока она управляемая.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]нарколог на дом мытищи[/url]
http://xn--80aaldngfckvzkca2a1n.xn--p1ai/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%201xbet%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%20%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8
VIP ESCORT SERVICE Escort services with top models and VIP girls! Elite Models
Терапия проводится в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современных медицинских технологий. Команда врачей, психологов и реабилитологов обеспечивает поддержку на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Разобраться лучше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/
[url=https://www.taylorrobinsonmusic.com/files/articles/bainarii-opushon-renshuu-apuri.html]
バイナリーオプション 生計
[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится с применением современных методик инфузионной терапии. Врачи контролируют уровень гидратации, работу сердечно-сосудистой системы и общее состояние пациента до полного устранения симптомов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это не «волшебная таблетка», а четко структурированный этап комплексного лечения, который должен вписываться в общий терапевтический план: диагностика, стабилизация состояния, выбор методики, юридически корректное информированное согласие, сопровождение и профилактика рецидивов. В наркологической клинике «НеоТрезвие СПБ» приоритет — безопасность, предсказуемость и конфиденциальность. Мы не перебираем методы «на удачу», а подбираем технологию с учетом клинического профиля, мотивации, социализации и коморбидных факторов (тревога, депрессия, соматические заболевания).
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-sankt-peterburge-czeny/
Urban Look Hub – Clear, well-structured layout with stylish streetwear and intuitive navigation.
Global Ridge Finds Hub – Well-laid-out pages with intuitive design ensure a seamless shopping experience.
Перед перечнем поясним логику: домашний визит уместен, когда обстановка безопасна, риски контролируемы и есть взрослый помощник на вечер и ночь. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых имеет смысл начать с выезда, а не со стационара.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/]voskresensk-narkologicheskij-dispanser[/url]
Trend Market Online – Pleasant layout with well-organized products, browsing felt simple.
Прежде чем перечислить критичные признаки, зафиксируем принцип: даже один выраженный симптом — повод не откладывать помощь и выбрать безопасный маршрут (дом или стационар) после быстрой очной оценки врача.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sergiev-posad8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-sergievom-posade/
Терапия проводится в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современных медицинских технологий. Команда врачей, психологов и реабилитологов обеспечивает поддержку на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kazan
Мытищи дают логистические плюсы домашнего старта: меньше перемещений, приватнее, быстрее включается режим. Дом уместен, если нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» давления/пульса, признаков обезвоживания с угрозой судорог. Если же состояние «по краю» — сочетание рвоты, лихорадки, кардиальных жалоб, второй бессонной ночи, выраженного тремора — врач предложит короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов под круглосуточным наблюдением. Это честнее и, на дистанции, экономнее: дефициты закрываются быстрее, дозы подбираются точнее, первая ровная ночь достигается предсказуемо, а риск экстренных ночных выездов снижается. В любом варианте приватность сохраняется: немаркированные визиты, индивидуальные окна, закрытые каналы коммуникации, доступ к данным по ролям.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-mytishchah
Grand River Finds Online – Attractive products arranged neatly, providing a smooth browsing experience.
Городская среда Петрозаводска со сменой ветров с Онежского озера, короткими сумерками и сезонными перепадами влажности может усиливать тревожность в вечерние часы. Мы учитываем это с момента первого контакта: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок, короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в зоне ожидания и отсутствие громких объявлений. Родственникам предоставляются «тихие окна» связи — лаконичные апдейты в фиксированное время, чтобы не перегружать пациента и не дёргать команду в критические окна наблюдения. Такой «мягкий» контур снижает сенсорную нагрузку, стабилизирует вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам и сокращает число импульсивных просьб «усилить на ночь».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Elite prostitutes – Vip girls , profiles and escort from elite girls of models Escort services with top models and VIP girls! beautiful escort girls
Moovit ช่วยคุณค้นหาเส้นทางที่ดีที่สุดเพื่อไปยัง ซอย รังสิต-นครนายก 18 ด้วยวิธีการแบบเป็นขั้นตอนจากสถานีที่ใกล้ที่สุด.
crestcollection – The website is clean and intuitive, browsing was very easy.
Городская среда Петрозаводска со сменой ветров с Онежского озера, короткими сумерками и сезонными перепадами влажности может усиливать тревожность в вечерние часы. Мы учитываем это с момента первого контакта: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок, короткая регистрация без «толстых анкет», приглушённый тёплый свет в зоне ожидания и отсутствие громких объявлений. Родственникам предоставляются «тихие окна» связи — лаконичные апдейты в фиксированное время, чтобы не перегружать пациента и не дёргать команду в критические окна наблюдения. Такой «мягкий» контур снижает сенсорную нагрузку, стабилизирует вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам и сокращает число импульсивных просьб «усилить на ночь».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk15.ru/petrozavodsk-narkologiya
Color Mea Hub – Beautifully arranged creative items, browsing feels fresh and enjoyable.
[url=https://walkindermatology.com/pages/bubinga-bainarii-opushon.html]
ブビンガ 高価[/url]
После прохождения детоксикации пациенту назначаются восстановительные процедуры, направленные на нормализацию обмена веществ и укрепление нервной системы. Программы клиники включают физиотерапию, витаминотерапию и индивидуальные занятия с психотерапевтом. Главная цель — восстановить способность организма к естественной саморегуляции и снизить зависимость от внешних раздражителей.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника казань[/url]
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-nizhnij-novgorod/
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого нижний новгород[/url]
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]сколько стоит капельница на дому от запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в казани[/url]
Elite girls for escort | VIP models https://oilman.biz Escort
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов серебряное 150х7х4 мм Ср99.9 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
удаленная работа с телефона Находки ВБ женские – это воплощение самых смелых модных фантазий. От элегантных вечерних платьев, подчеркивающих женственность, до удобной повседневной одежды, дарящей свободу движений, от стильных аксессуаров, расставляющих акценты, до практичной обуви, завершающей образ – здесь каждая женщина найдет то, что отражает ее неповторимый стиль.
TopChoiceCenter – Pleasant visuals, high-quality selection, and easy-to-use layout.
Главная задача — вернуть контроль над самочувствием мягко и последовательно. Мы не соревнуемся в дозах, а собираем устойчивую траекторию улучшения: каждый модуль терапии отвечает за одну цель и имеет своё «окно оценки». Если отклик ниже ожиданий — меняем ровно один параметр (темп, последовательность или поведенческий элемент среды), чтобы точно понимать, что помогло.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kazan-otzyvy/
Капельница от запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде часто становится первым шагом в лечении хронической алкогольной зависимости. Детоксикация помогает вывести продукты распада этанола и снизить нагрузку на внутренние органы, но не устраняет психологическую зависимость. Поэтому после завершения инфузионной терапии пациенту рекомендуется пройти консультацию психотерапевта и, при необходимости, начать курс реабилитации.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Great post! Really enjoyed reading this. Keep up the excellent work!
elite dating https://shugaringproff.ru Elite prostitutes – VIP escort from model girls , VIP profiles of elite courtesans
https://findyourstampsvalue.com/
NatureCorner – Fast-loading pages with a cozy, rustic feel enhance browsing.
Чтобы сделать процесс понятным и управляемым, каждый шаг сопровождается измеримыми маркерами безопасности и эффективности. Корректировки — точечные, по правилу «одного изменения», что позволяет видеть вклад каждого действия и сохранять переносимость.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь казань[/url]
FreshStyle Select – The browsing flow felt quick, and the overall presentation was sharp.
Здесь
[url=https://jabbamarket.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
[url=https://natyazhni-steli-vid-virobnika.biz.ua/]установка натяжных потолков цена[/url]
Это популярный выбор благодаря быстрому монтажу и разнообразию дизайнов.
Компания “natyazhni-steli-vid-virobnika.biz.ua” предлагает качественные потолки напрямую от производителя. Мы используем только проверенные материалы.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Одним из главных плюсов натяжных потолков является их влагостойкость. Такое покрытие не боится протечек и конденсата.
Еще одно преимущество — огромный выбор цветов и фактур. Дизайнеры помогут создать уникальный стиль для вашего помещения.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Наша компания изготавливает потолки из экологически чистого ПВХ. Он не выделяет вредных веществ даже при нагревании.
Технология производства гарантирует прочность и эластичность полотна. Готовые потолки устойчивы к механическим повреждениям.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Монтаж натяжных потолков занимает всего несколько часов. Опытные мастера выполнят работу без пыли и грязи.
Уход за потолком не требует особых усилий. Пятна и пыль легко удаляются без специальных средств.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Введение**
Современные натяжные потолки позволяют преобразить пространство за считанные часы.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Они отлично защищают от протечек и скрывают неровности базового потолка.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Качество сырья подтверждено независимыми экспертизами.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Наши специалисты устанавливают потолки с точностью до миллиметра.
You are so cool! I don’t suppose I’ve read a single thing like that before.
So good to find another person with a few genuine
thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. many thanks for starting
this up. This web site is one thing that is required on the web, someone with some
originality!
Elite Escort Agency Gay escort Elite Models
Trendy Collection Finds – Modern selection displayed clearly, browsing pages was very easy.
Hidden Valley Picks Hub – Well-laid-out treasures, providing a seamless shopping experience.
FutureWild Online – Smooth page transitions and stylish layout make exploring products easy.
Daily Motivation Studio – Clear and motivating articles with fast-loading pages for smooth navigation.
[url=https://natyazhni-steli-vid-virobnika.biz.ua/]изготовление полотна для натяжных потолков[/url]
Такой вариант отделки сочетает в себе эстетику и функциональность.
Компания “natyazhni-steli-vid-virobnika.biz.ua” предлагает качественные потолки напрямую от производителя. Мы используем только проверенные материалы.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Одним из главных плюсов натяжных потолков является их влагостойкость. Они идеально подходят для ванных комнат и кухонь.
Еще одно преимущество — огромный выбор цветов и фактур. Вы можете подобрать глянцевую, матовую или сатиновую поверхность.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Наша компания изготавливает потолки из экологически чистого ПВХ. Материал абсолютно безопасен для здоровья.
Технология производства гарантирует прочность и эластичность полотна. Каждое полотно проходит проверку перед отправкой клиенту.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Монтаж натяжных потолков занимает всего несколько часов. Процесс не требует длительной подготовки основания.
Уход за потолком не требует особых усилий. Достаточно периодически протирать поверхность мягкой тканью.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Введение**
Современные натяжные потолки позволяют преобразить пространство за считанные часы.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Можно создать как минималистичный, так и роскошный дизайн.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Наша продукция соответствует строгим экологическим стандартам.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Наши специалисты устанавливают потолки с точностью до миллиметра.
https://buffalobossbabes.com/kak-ispolzovat-professionalnye-assotsiatsii-dlya-netvorkinga/
Escort Services https://double-d.top escort agency
Next Adventure Hub – The site feels exciting, with an adventurous layout and smooth browsing.
CopperLaneGoods – Easy-to-use setup, nice outlet offers, and browsing feels pleasantly smooth overall.
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бинго онлайн[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol
https://checksite.com
Предпенсионер льготы Льготы пенсионерам – это многогранная система социальной защиты, охватывающая различные аспекты жизни пожилых людей. Скидки на оплату коммунальных услуг, бесплатный проезд в общественном транспорте, льготное медицинское обслуживание, налоговые вычеты – все это направлено на облегчение финансового бремени и повышение качества жизни пенсионеров. Предоставление льгот – это проявление благодарности общества за многолетний труд и забота о достойной старости.
Escort for men Escort agencies Escort Services Agency – VIP Escort
Мы комбинируем медицинские и поведенческие технологии так, чтобы каждое вмешательство имело измеримый эффект. Адресные инфузии применяются по клиническому профилю, психообразование переводит субъективные ощущения в факты, а телемедицинские включения помогают пройти «трудный час» без самовольных «усилений» схемы. В таблице ниже — практическая карта: что, зачем и как проверяется на итог.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru
Качество — это не субъективные впечатления, а сравнение базовой линии с целевыми коридорами в обозначенных окнах. Мы ведём короткий отчёт по маркерам: переносимость воды (мл/ч), диурез, ЧСС/АД в покое, структура сна (длительность и число пробуждений), динамика по шкалам тошноты/тремора, выполнение двух утренних бытовых задач. Отчёт понятен пациенту: в нём нет лишней терминологии, только факты и решения — какой модуль снят, какой оставлен ещё на ночь, какой будет пересмотрен через 12–24 часа. Финансовая прозрачность следует той же логике: расширение проводится только по показаниям с указанием цели («какой маркер планируем улучшить») и окна переоценки («когда проверяем результат»).
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в ростове-на-дону[/url]
https://fau.unt.edu.ar/fau/pagina-ejemplo/
http://rulezrp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=3075
http://darkness2.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=87&t=744
радикали історія україни
Простая подготовка уменьшает стресс, повышает переносимость капельницы и делает оценку состояния более точной. Попросите одного ответственного взрослого быть на связи с врачом — так решения будут приниматься быстрее, а ночной интервал пройдёт спокойнее и предсказуемее.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника челябинск[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://commyx.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
PeakTreasure – Fast pages and easy-to-browse floral products make exploring enjoyable.
отражающая изоляция Полиэтиленовая пленка – универсальный материал, нашедший широкое применение в самых различных сферах деятельности. От сельского хозяйства, где она используется для создания парников и укрытия почвы, до строительства, где она служит надежным гидроизоляционным слоем, полиэтиленовая пленка демонстрирует свою незаменимость. Ее главные достоинства – это доступная цена, легкость в использовании и отличные защитные свойства, предохраняющие от влаги, ветра и ультрафиолетового излучения. Различают пленки различной толщины и плотности, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждой конкретной задачи.
LIGACOR adalah platform game slot online yang selalu
memanjakan pemain dengan memberi kemenangan maximal dan stabil serta member aktif disini
akan mendapat bonus yang sangat besar.
фітофаги це
Elite girls for escort | VIP models https://yeahcamp.ru Escort Services
Детоксикация является первым и важнейшим этапом лечения зависимости. В наркологической клинике в Краснодаре используются современные методы очищения организма, включая инфузионную терапию, гепатопротекторы, витаминные комплексы и ноотропы. Все процедуры проводятся под наблюдением врача-нарколога и направлены на снятие интоксикации, восстановление обмена веществ и нормализацию функций печени и нервной системы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в краснодаре[/url]
StyleChoiceHub – Organized structure, modern layout, and smooth navigation throughout.
Outlet of Fresh Value – Liked the organized layout; everything opened fast and without hassle.
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Trendy Purchase Finds – Well-laid-out products, moving through categories was easy.
Highland Craft Finds – Well-presented items, navigation feels intuitive and fast.
Ниже — ориентировочная матрица первых часов. Она не заменяет очной оценки, но показывает, как мы переводим наблюдения в действия и какие критерии считаем достаточными для переключения модуля. Приведённые окна проверки помогают не тянуть с нужными корректировками и одновременно не «дергать» схему без повода.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
escort agency VIP escort dating site Escort Girls
Hello, after reading this amazing piece of writing i am
too delighted to share my familiarity here with colleagues.
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you make blogging look easy. The overall look
of your web site is wonderful, as well as the content!
crestartisanhub – Very tidy layout and easy navigation, made shopping quick and hassle-free.
Если в телефонном триаже обозначаются риски по дыханию, ритму или уровню сознания, на старте предлагаем стационарное «окно» мониторинга с круглосуточным постом. При низких рисках программа начинается амбулаторно или на дому и поддерживается вечерними онлайн-вставками (15–20 минут). Любой формат остаётся анонимным: доступ к карте наблюдения — по ролям, а язык переписки и чеков — нейтральный.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru/voronezh-narkologiya/
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad/
Discount Finder Pro – The bargains stand out nicely, and the site is easy to scroll through.
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru
escort agency Escort agency – VIP escorts Elite Girls
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/narkolog-anonimno-stavropol/
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
FreshBuy Studio Hub – Sleek layout with clear visuals and intuitive product placement improves browsing.
Здесь
[url=https://silauma.agency/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Для успешного выполнения сложных строительных или логистических проектов часто требуется [url=https://vsemanipulyatory.ru/]услуги крана манипулятора[/url], который обеспечивает эффективную и безопасную перевозку тяжелых грузов.
Использование манипулятора в аренде позволяет компаниям оптимизировать свои затраты. Это особенно важно для небольших и средних предприятий, которые не имеют большого бюджета на покупку и обслуживание оборудования. Компании могут выбрать манипулятор, который лучше всего подходит для их конкретных потребностей . Кроме того, аренда манипулятора исключает необходимость в постоянном обслуживании и ремонте, что также снижает эксплуатационные затраты.
Правильный выбор манипулятора зависит от характера работы и размеров грузов. Компании, которые часто используют манипуляторы, могут арендовать их на долгосрочной основе, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу и минимизируя простои. Аренда манипулятора также подразумевает обучение персонала, которое предоставляется компанией-арендодателем .
Аренда манипулятора может быть очень выгодной для компаний, которые не имеют большого опыта в работе с тяжелым оборудованием . Это особенно актуально для проектов, которые имеют ограниченный срок реализации, поскольку компании не должны покупать оборудование, которое может не понадобиться им после завершения проекта. Они получают доступ к современному оборудованию, которое более эффективно и надежно .
При аренде манипулятора компании также могут рассчитывать на быструю доставку и установку оборудования . Это особенно важно для компаний, которые не имеют своего собственного технического персонала для обслуживания оборудования. Они могут быстро реагировать на изменения в проекте или рыночных условиях .
Компании должны учитывать грузоподъемность манипулятора, его маневренность и высоту подъема . Кроме того, компании должны ознакомиться с условиями аренды, включая стоимость, срок аренды и требования к обслуживанию. Это помогает избежать ошибок при выборе манипулятора.
Компании должны выбирать оборудование, которое соответствует всем необходимым стандартам безопасности . Кроме того, компании должны обеспечить, что их персонал проходит обучение по эксплуатации арендованного манипулятора. Это снижает риск поломок и простоев во время работы.
Компании могут выбрать манипулятор, который лучше всего подходит для их конкретных потребностей. Это особенно важно для небольших и средних предприятий, которые не имеют большого бюджета на покупку и обслуживание оборудования. Они также должны ознакомиться с условиями аренды и требованиями к обслуживанию .
Это является существенным преимуществом в сегодняшнем конкурентном бизнес-среде. Кроме того, аренда манипулятора позволяет компаниям быть более гибкими и быстро реагировать на изменения в проекте или рыночных условиях. Это стратегическое решение, которое может принести компании значительную пользу .
Большинство видео имеют формат MP4 и SD, HD,
FullHD, 2K и 4K.
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого калининград[/url]
Если вам нужно [url=http://shchpsinfo.ru]щпс цена за куб[/url] в Москве, то стоит обратить внимание на надежные поставщики, которые предлагают качественную продукцию по конкурентным ценам.
Щпс является одним из наиболее популярных видов оборудования для промышленного использования, и его можно легко купить в Москве . Щпс используется в различных областях промышленности, включая производство, строительство и транспорт для обеспечения эффективной и безопасной работы . Щпс широко используется во многих отраслях промышленности благодаря своей эффективности и простоте эксплуатации.
Щпс доступен для покупки в многих розничных магазинах и онлайн-площадках Москвы. При покупке щпс следует обращать внимание на его качество, надежность и соответствие необходимым стандартам.
Щпс позволяет оптимизировать производственные процессы и улучшить качество продукции . Щпс может стать ключевым фактором в достижении конкурентного преимущества на рынке. Щпс требует минимального обслуживания и может функционировать в течение длительного времени без ремонта .
Щпс также может использоваться в различных отраслях промышленности, включая производство, строительство и транспорт . Благодаря своей универсальности и эффективности, щпс стал широко распространенным оборудованием .
В Москве можно найти множество поставщиков щпс, предлагающих широкий ассортимент оборудования . При secimе щпс следует учитывать несколько важных факторов, включая его технические характеристики и стоимость.
Щпс можно купить в Москве как новым, так и б/у, что позволяет выбрать оборудование в соответствии с бюджетом . Благодаря широкому выбору щпс в Москве, можно найти подходящее оборудование для любых потребностей .
Щпс предлагает много преимуществ, включая повышение производительности и снижение затрат, и может быть найден в Москве . Щпс продолжает развиваться и совершенствоваться, что позволяет ему оставаться одним из лидеров на рынке оборудования .
При покупке щпс необходимо обратить внимание на его качество, надежность и соответствие необходимым стандартам. Щпс является незаменимым инструментом для многих компаний, и его можно легко найти в Москве.
Капельница от запоя — это не «чудо-микс», а управляемая медицинская процедура с чёткими целями, окном оценки и понятными критериями остановки. В «ЮжУрал Детокс Центр» подход построен по принципу минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), потом переносимость воды и сбор нормального сна, а уже после — метаболическая поддержка и восстановление бытовой устойчивости. Такая логика исключает полипрагмазию, снижает риск нежелательных реакций и даёт семье прогнозируемую картину на ближайшие 24–72 часа. Мы не обещаем «мгновенного чуда» — мы предлагаем дисциплину маленьких шагов, которая с высокой вероятностью приводит к устойчивому результату.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в челябинске[/url]
Команда клиники — это врачи-наркологи, психиатры-консультанты, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинический психолог, психотерапевт и медсёстры с опытом круглосуточного поста. Мы разговариваем «языком фактов»: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов, дневники воды и сна, малые бытовые цели. Такой язык исключает стигму и «магическое мышление»; он понятен семье и помогает принимать решения без страхов и «подстраховочных» излишков.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике ростов-на-дону[/url]
CloverCozyDeals – Gentle visual style with cozy selections, creating a calm and enjoyable browsing experience.
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar
Corner of Global Trends – Impressed by how quickly everything loaded and how clean the layout was.
VIP models https://spravka-moskva.biz Elite girls for escort | VIP models
NorthHubSpot – Well-organized items, fast-loading site, and effortless navigation for users.
AutumnPeak Styles – Beautiful seasonal styles appear curated well, and exploring feels effortless.
Простая подготовка уменьшает стресс, повышает переносимость капельницы и делает оценку состояния более точной. Попросите одного ответственного взрослого быть на связи с врачом — так решения будут приниматься быстрее, а ночной интервал пройдёт спокойнее и предсказуемее.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Городская среда Калининграда специфична: морской ветер, сезонные пробки, яркие витрины в вечерние часы. Эти факторы часто усиливают тревожность и мешают засыпанию. Поэтому мы проектируем выезд «мягко»: согласованная парковка, немаркированный вход, короткий маршрут до места процедуры, отсутствие громких звонков и «визуального шума» у порога. Родственникам предоставляем «тихие окна» связи — короткие апдейты в заранее оговорённое время без лишних подробностей. Такой формат не просто комфортнее, он клинически полезен: чем меньше стимулов, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях» и тем стабильнее проходит первая ночь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
This site definitely has all the information I needed about this subject and
didn’t know who to ask.
Лечение в клинике в Челябинске строится на принципах конфиденциальности, добровольности и медицинской этики. Врачи применяют доказательные методы терапии, а программы лечения адаптируются под особенности каждого пациента. Работа ведётся комплексно, включая медикаментозную помощь, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет эффективно восстановить здоровье и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske/
SimpleHome Select – Neatly displayed items and effortless navigation made exploring simple.
top shopping corner – Selection looks fantastic, browsing feels effortless and quick.
Escort for men https://mossygatherings.info Vip girls
TSO Deals Store – Nice layout with attractive deals, exploring the site felt smooth.
Marketplace Midday – Well-structured pages and tidy sections make exploring items easy.
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
кочівництво це
High Pine Finds – Items arranged thoughtfully, navigation is intuitive and fast.
DealMarketOnline – Solid bargains, easy to browse, and pages load quickly.
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/hied/2020/10/29/social-justice-saturday/comment-page-451/#comment-383795
https://neokorest.jofo.me/2456826-vyiigryivayte-krupno-v-1win-s-uvelichennyim-depozitom.html
Ночной блок ориентирован на тишину и сон: приглушённый свет, короткие дыхательные циклы, мягкая фармакоподдержка по показаниям. Днём мы уточняем показатели, корректируем план воды/питания и, при необходимости, назначаем краткий очный контроль. Вечером — фокус на рутине: цифровая гигиена, «тихие окна», спокойная коммуникация с близкими. У пациента и семьи на руках памятка простым языком — без стигмы и жаргона — где перечислены «зелёные зоны» и поводы для связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh15.ru
http://promintern.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=17&t=2218
Домашний старт в Москве уместен при устойчивых показателях и низком риске осложнений: нет упорной рвоты, выраженной дезориентации, лихорадки, резких скачков давления и пульса. Преимущества — приватность, скорость, меньше стыда и сопротивления, выше шансы на ранний сон. Если же присутствуют признаки возможных осложнений (обезвоживание, судорожная готовность, аритмии, боль за грудиной/в животе, спутанность), рациональнее короткая стационарная стабилизация на 24–48 часов, после которой маршрут возвращается домой. «Трезвый Стандарт» держится принципа клинической достаточности: вмешательств ровно столько, сколько нужно сегодня, без «пакетов ради прайса». Такой реализм экономит деньги и главное — время семьи, потому что снижает вероятность ночных «качелей», повторных вызовов и импульсивных решений, которые чаще всего и ломают прогресс.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]нарколог на дом москва цены[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в краснодаре[/url]
Перед перечислением важно прояснить: нижеследующие ориентиры не заменяют очный осмотр, они помогают семье принять здравое решение без затяжки и споров. Если признаки сочетаются или нарастают, лучше не откладывать обращение, чтобы перехватить динамику, пока она управляемая.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Vip girls https://slimdieta.ru Escort
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]азартные игры[/url]
Вся динамика заносится в единую карту наблюдения. Если потребуются амбулаторные точки или стационар, вы не «начинаете историю заново» — маршрут продолжится с той же целью и теми же критериями успеха.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/narkolog-anonimno-stavropol
Первичная оценка строится на фактах. Врач коротко уточняет жалобы, длительность употребления, переносимость препаратов и аллергии, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-ЭКГ и скрининг неврологического статуса. Далее — объясняет на понятном языке логику назначений: зачем именно такая инфузионная схема, какие ощущения нормальны в течение часа и к ночи, как организовать питьевой режим и лёгкое питание «по силам». Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов: дозируем узко, чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных эффектов. После процедуры повторно оцениваем показатели, выдаём письменные рекомендации, согласуем окно связи и условия повторного визита. Семья получает простые правила поведения дома (тишина, затемнение, ограничение экранов, отсутствие «разборов») и сигналы, когда лучше позвать врача. Итог визита — управляемая ночь и предсказуемое утро, на котором можно строить следующие шаги.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk9.ru/
трансгендери
Discover Offer Deals – Plenty of great choices appear here, and navigating the pages is quick and enjoyable.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad-staczionar/
Лечение в клинике в Челябинске строится на принципах конфиденциальности, добровольности и медицинской этики. Врачи применяют доказательные методы терапии, а программы лечения адаптируются под особенности каждого пациента. Работа ведётся комплексно, включая медикаментозную помощь, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет эффективно восстановить здоровье и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske/
Наркологическая клиника в Челябинске оказывает комплексную медицинскую помощь пациентам, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков или психоактивных веществ. Основное направление деятельности клиники — диагностика, лечение и профилактика зависимого поведения с применением современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ реабилитации. Опытные специалисты обеспечивают не только восстановление физического состояния, но и психологическую поддержку, что способствует достижению стойкой ремиссии и предотвращению рецидивов.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske/
Алгоритм на выезде помогает убрать импровизации, а семье — понимать, что будет происходить и по каким признакам мы двигаемся дальше. Он гибкий, но всегда прозрачный: каждый шаг имеет цель, инструмент и критерий успеха.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Капельница, устанавливаемая наркологом на дому в Челябинске, помогает быстро очистить организм от токсинов и нормализовать водно-солевой баланс. Растворы включают витамины, анальгетики, седативные и гепатопротекторные препараты. Эффект от процедуры ощущается уже через 20–30 минут. Капельница снижает головную боль, устраняет тошноту, восстанавливает работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Такой метод считается одним из самых эффективных способов вывести пациента из запойного или абстинентного состояния без визита в стационар.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Escort Agency VIP Escort elite dating
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Процесс терапии включает несколько последовательных шагов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог челябинск[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде использует многопрофильный подход, направленный на физическое и психологическое восстановление пациентов. После детоксикации проводится стабилизация обменных процессов, нормализация работы внутренних органов и поддержка нервной системы. Особое внимание уделяется коррекции поведения и мотивации пациента к отказу от употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru
Реабилитация проходит в комфортных условиях, с постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Важным элементом является формирование новых привычек и социальных навыков, что способствует возвращению пациента к полноценной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Home Fresh Lane – Clean pages with well-arranged products provide an intuitive experience.
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде проводится с применением инфузионной терапии, седативных средств и витаминных комплексов. Основная задача процедуры — устранить токсическое воздействие алкоголя, восстановить работу органов и нормализовать психоэмоциональное состояние. Все препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом особенностей организма пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь нижний новгород[/url]
В наркологической клинике в Челябинске проводится профессиональная детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопленных в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Процедура выполняется под наблюдением специалистов, что исключает риск осложнений и обеспечивает быстрое улучшение самочувствия. Для восстановления функций внутренних органов применяются препараты, стабилизирующие работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Использование капельниц, витаминов и гепатопротекторов помогает нормализовать обмен веществ и устранить последствия интоксикации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в челябинске[/url]
ValleyMarketHub – Found some well-priced deals, and everything gives off a reliable impression.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Титановая труба 51х0.8х6000 мм ПТ1М ГОСТ 22897-86 Откройте мир прочных и надежных титановых труб с компанией Редметсплав. Наши высококачественные титановые трубы сочетают в себе устойчивость к коррозии, износостойкость и легкий вес, делая их незаменимым материалом для применения в различных сферах промышленности. Широкий выбор различных диаметров и толщин, а также индивидуальные решения для вашего производства. Гарантированное качество и надежность поставок.
APS Marketplace – Autumn-themed products look nicely arranged, with browsing feeling light and easy.
Escort https://dr-kuznetsova.ru Escort Agency
хто такі титани
daily shopping corner – Corner store offerings look appealing, site experience is simple and fast.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на диагностике, лечении и реабилитации пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Основная цель деятельности учреждения — восстановление физического здоровья и психологической устойчивости человека, оказавшегося в состоянии зависимости. В клинике применяются современные методы терапии, доказавшие эффективность в медицинской практике. Все процедуры проводятся конфиденциально, с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и под контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-novgorod
SimpleLiving Online – Calm visuals and fast-loading pages made checking items effortless.
UGC Online Store – Smooth interface and appealing items, exploring the site was easy.
Valuable info. Fortunate me I found your site unintentionally,
and I’m shocked why this accident did not took place in advance!
I bookmarked it.
Happy Finds Online – Browsing is effortless and the cheerful setup makes shopping fun.
https://qwertyoop.com qwertyoop
Ironline Market – Solid marketplace with dependable products and fair pricing throughout.
MarketTreasureShop – Smooth interface, solid bargains, and enjoyable shopping.
Инфузия снимает соматику, но устойчивость формируется в поведении. «Тихие ритуалы» — короткие повторяющиеся действия, которые уменьшают тревогу и помогают организму перейти из режима «тревога» в режим «восстановление». В «ЧелМед Детокс» семья обучается простым протоколам: не оценивать, говорить фактами, задавать ритм вечера. Пример: «через 20 минут приглушим свет; через 30 — 150 мл воды; перед сном — дыхание 4?6?4; если проснулся — повторить дыхание и не включать яркий свет». Психолог включается точечно: снимает острые триггеры, учит отслеживать маркеры перегрузки и закреплять сутки без срывов, не превращая поддержку в контроль. Благодаря этому первая неделя после детокса проходит мягче, а риск «провалов» снижается.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
VIP Escort Dating Site for Men https://klubok31-shop.ru Elite Models
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Челябинске — это услуга, которая позволяет получить профессиональную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости посещения клиники. Такой формат особенно востребован в случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно прибыть в медицинское учреждение или нуждается в конфиденциальной помощи. Врач-нарколог выезжает по указанному адресу, проводит осмотр, оценивает состояние и подбирает оптимальную терапию. Квалифицированное вмешательство помогает избежать осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в течение первых часов после прибытия специалиста.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske-vyvod-iz-zapoya
Нарколог на дом в Челябинске — это услуга, которая позволяет получить профессиональную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости посещения клиники. Такой формат особенно востребован в случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно прибыть в медицинское учреждение или нуждается в конфиденциальной помощи. Врач-нарколог выезжает по указанному адресу, проводит осмотр, оценивает состояние и подбирает оптимальную терапию. Квалифицированное вмешательство помогает избежать осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в течение первых часов после прибытия специалиста.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом челябинск[/url]
goldenstylehub – Organized pages and smooth browsing, picking products was simple.
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в мурманске[/url]
Premium Product Browse – Everything feels cleanly sorted, and checking different sections is seamless.
Такая последовательность обеспечивает медицинскую точность и безопасность процедуры, позволяя добиться быстрого улучшения самочувствия без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru
VIP models https://progress-pro.ru Elite Escort Services
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма в санкт-петербурге[/url]
PornPics.com is not just about sex images, but it also has a lot
of other topics. This blog will be your paradise if you are
a porn lover, and it is a perfect item. Porn content is favorable in several
ways for some men and women, according to
many men and women. Some people enjoy watching
1, while others enjoy watching movie videos on different video websites. https://srivinayaksteel.com/2019/09/03/whale-be-raised-it-must-be-in-a-month/
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Такая карта снимает неопределённость. Пациент понимает, чего ожидать; родственники — когда и по каким метрикам судить об успехе; команда — что именно корректировать, чтобы сохранить управляемость терапии даже ночью.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника в мурманске[/url]
Сразу важно проговорить: кодирование — это «замок» на поведение и физиологию, который помогает удержать ремиссию, пока человек выстраивает новые привычки и восстанавливает качество жизни. Поэтому эффект процедуры прямо зависит от того, насколько грамотно выстроены подготовка, информирование и поддержка после вмешательства. «НеоТрезвие СПБ» делает акцент на постепенности: один этап — одна цель — один прозрачный маркер успеха.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-sankt-peterburge-czeny/
GrabSavings – Smooth scrolling and well-presented deals make browsing fun.
написание курсовой работы на заказ цена [url=http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru]http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru[/url] .
стоимость написания курсовой работы на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru/]https://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru/[/url] .
FreshFashion Studio – Fast-loading, neatly arranged product pages make browsing enjoyable and easy.
VIP Escort | Escort of men Elite escort services Elite Models
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru
favorite picks store – Nicely displayed product picks and a layout that’s simple to navigate.
Здесь
[url=https://softwarecenter.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
FreshSeason Market Lane – Neatly arranged seasonal products with smooth-loading pages for effortless shopping.
1xbet промокод на день рождения
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkologicheskie-dispansery-sankt-peterburga
Escort Elite escort services Escort
UGC Online Store – Nice selection of gifts, exploring the site was simple and smooth.
visit diamondfieldhub – Easy to explore, and the store gives off a reliable, well-kept impression.
TrendAndStyle Picks – Well-structured display of styles and smooth browsing experience.
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru
Iron Root Boutique – Attractive items displayed clearly, navigation feels smooth.
daily growth corner – Items are eye-catching, navigating the site feels easy today.
Клиника предлагает широкий спектр услуг, охватывающий весь цикл лечения зависимости — от экстренной помощи до длительной реабилитации. Комплексная программа включает медицинскую, психологическую и социальную составляющие, что позволяет добиться устойчивого результата. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем врачей, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
motivation hub – Inspiring items are neatly presented, browsing is quick and pleasant.
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Углубиться в тему – http://
Выездная стабилизация — только первый шаг. Дальше важно разобрать триггеры, обучить «тихим ритуалам», согласовать план поддержки и рассмотреть кодирование там, где оно уместно. Мы не противопоставляем форматы: домашние визиты, «тихий вход» и краткие очные сессии дополняют друг друга. Задача — не создать идеальную «капельницу», а вернуть организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции и укрепить навыки, которые защищают от срыва. В «КубаньМед Резолюция» этим занимается мультидисциплинарная команда: наркологи, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинические психологи, психотерапевты и медсёстры с опытом ночных постов наблюдения. Все говорят на «языке фактов», чтобы решения были понятны и пациенту, и семье.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это не «быстрая капельница и забыли», а последовательный и конфиденциальный процесс, в котором каждое вмешательство имеет цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно проверки». В наркологической клинике «Южный Мед Центр Ренова» мы совмещаем непрерывный приём 24/7, выездные визиты без маркировки, точечную диагностику, инфузионную поддержку, психотерапевтические сессии и план посттерапевтического сопровождения. Приоритет — приватность и минимально достаточные решения: чем меньше случайных назначений, тем больше управляемости и предсказуемости. Мы говорим «языком фактов», а не оценок: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов (0–10), структура сна, переносимость воды, простые бытовые задачи на утро. Это помогает семье и пациенту видеть, что именно работает, и выключать вмешательства, когда они сделали своё дело.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь ростов-на-дону[/url]
Семья получает «путевой лист» на 24–72 часа: как фиксировать маркеры (тремор/тревога/тошнота 0–10), как пить воду малыми глотками, когда приглушать свет и в каком формате общаться с пациентом («короткие факты вместо оценок»). Мы также даём «лестницу активности»: два достижимых действия утром, одно — вечером. Эта дисциплина маленьких шагов помогает избежать эмоциональных «перегревов» и удерживает достигнутый эффект.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Elite Models https://unrealestate.biz Escort Agency
Решение о выезде принимает врач с учётом симптомов и бытовых ограничений. Если совпадает хотя бы две позиции из списка ниже, лучше не откладывать звонок — управляемость состояния снижается каждый час.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в казани[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]виртуальное казино[/url]
FashionTrendSpot – Attractive interface, well-organized pages, and effortless browsing.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде использует многопрофильный подход, направленный на физическое и психологическое восстановление пациентов. После детоксикации проводится стабилизация обменных процессов, нормализация работы внутренних органов и поддержка нервной системы. Особое внимание уделяется коррекции поведения и мотивации пациента к отказу от употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Happy Value Spot – Browsing feels effortless with neatly displayed, affordable items.
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. В основе её деятельности лежит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, сочетание медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методов, а также полная конфиденциальность. Лечение проводится опытными специалистами с применением современных медицинских технологий, направленных на восстановление здоровья и предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
Magnificent web site. Lots of helpful information here.
I’m sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious.
And certainly, thank you for your effort!
Outlet Deals Hub – The product lineup is strong, and moving around the site feels seamless.
Поставляем шины для автотранспортных предприятий, автобаз и шиномонтажей!
Работаем с отсрочкой платежа!
Шины в Новосибирске
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert
that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Anyway I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
http://stroybud.com/kak-provoditsya-evakuatsiya-mototsiklov-i-skuterov/
оригинальный фен дайсон [url=https://www.fen-d-3.ru]оригинальный фен дайсон[/url] .
Elite prostitutes – VIP escort from model girls , VIP profiles of elite courtesans Escort agency – VIP escorts Elite prostitutes – Vip girls , profiles and escort from elite girls of models
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]блекджек[/url]
В городе и ближайших районах клиника «УралМед Трезвость» обеспечивает оперативный выезд и амбулаторный приём без очередей. На этапе первичного контакта координатор уточняет только клинически значимые моменты: постоянные препараты и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов в прошлом, базовые показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?, если доступны), длительность симптомов, возможность организовать «тихое окно» на 20–30 минут. Вместо долгих разговоров — короткая, спокойная логика: где безопаснее начать (дом/амбулатория/стационар), какую ближайшую цель выбираем, в каком интервале ждём эффект и что считаем сигналом для связи с дежурным врачом.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/
https://mebel-24.blogspot.com/2025/12/2025.html?m=1
SuperSaver – Very fast site performance, checking offers felt effortless.
Наркологическая клиника «АрктикМед Профи» — это круглосуточная система помощи, где острые состояния снимаются быстро и безопасно, а дальнейшая реабилитация строится на измеримых целях, прозрачных правилах и бережной поддержке семьи. Мы объединяем инфузионную терапию, доказательные медикаментозные протоколы и современные психотерапевтические практики, чтобы восстановить физиологические ритмы организма, вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость к рецидивам. Основной принцип — «одна корректировка за раз»: мы меняем только один параметр (темп, объём, последовательность вмешательств) и сверяем результат в заранее назначённое «окно» оценки. Такой подход защищает от полипрагмазии, снижает медикаментозную нагрузку и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Санкт-Петербурге — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Elite prostitutes – VIP escort from model girls , VIP profiles of elite courtesans Escort agency – VIP escorts Elite Dating Models
купить курсовую работу [url=http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru]http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru[/url] .
написание курсовых работ на заказ цена [url=kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru]kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru[/url] .
[url=https://barkova-clinic.ru/uslugi-kineziologa-put-k-garmonii-tela-i-dushi/]Услуги кинезиолога: Путь к гармонии тела и души[/url]
В городе и ближайших районах клиника «УралМед Трезвость» обеспечивает оперативный выезд и амбулаторный приём без очередей. На этапе первичного контакта координатор уточняет только клинически значимые моменты: постоянные препараты и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов в прошлом, базовые показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?, если доступны), длительность симптомов, возможность организовать «тихое окно» на 20–30 минут. Вместо долгих разговоров — короткая, спокойная логика: где безопаснее начать (дом/амбулатория/стационар), какую ближайшую цель выбираем, в каком интервале ждём эффект и что считаем сигналом для связи с дежурным врачом.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар челябинск[/url]
В мегаполисе привычный ритм часто мешает системному лечению: плотный график, транспортные задержки, высокая социальная видимость. Чтобы терапия проходила спокойно, «НеоТрезвие СПБ» использует «немаркированную» логистику: нейтральные формулировки в документах, аккуратные визиты, разнесенные по времени консультации специалистов и персональный координатор. По желанию пациента часть этапов — образовательные сессии и посткодовое сопровождение — выполняются онлайн. Это снижает тревогу и делает маршрут лечения менее заметным для окружения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы[/url]
Trendy Fashion World – Smooth browsing with a modern look and plenty of stylish choices.
journey shop online – Selections are enjoyable, navigation is clear and simple.
Majestic Grover Outlet – Unique selections are available, browsing is smooth and enjoyable.
best fashion hub – Trendy items are showcased well, browsing feels smooth and enjoyable.
Escort Elite escort services Elite prostitutes – Vip girls , profiles and escort from elite girls of models
Fresh Trend Studio Hub – Clean, modern layout with clearly presented items makes shopping seamless.
WildRose Treasures Online – Charming setup with some standout products, exploring was fun.
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Екатеринбурге проводится с применением сертифицированных лекарственных препаратов, поддерживающих систем и методов индивидуальной терапии. Врачи используют физиологически безопасные комбинации растворов, витаминов и нейропротекторов, восстанавливающих работу центральной нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия проводится под контролем специалистов, что исключает возможность осложнений и обеспечивает быстрое улучшение состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
dream grove finds – A bright and airy feel to the store, which makes exploring quite natural.
Если дома нет возможности обеспечить тишину (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости), можно кратко перейти в «тихий стационар» с отдельным входом; после стабилизации сопровождение возвращается на дом, и маршрут продолжается «зеркально» — с теми же целями и окнами оценки. Такой перенос сохраняет управляемость процесса и снижает тревогу семьи: никто не «начинает сначала», меняется только место, а логика остаётся прежней.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи казань[/url]
курсовая заказ купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru[/url] .
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Санкт-Петербурге проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
CrestGlobal Hub – Clean interface with well-spaced categories ensures easy exploration.
купить задание для студентов [url=https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-28.ru]https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-28.ru[/url] .
GiftSelectionSpot – Minimalistic design, easy-to-browse layout, and enjoyable experience.
Лечебная логика строится по принципу «одна цель — один маркер — одно окно оценки — один выключатель». Например, задача «открыть окно питья» решается антиеметическим мостом и мягкой регидратацией; как только вода пьётся без позывов и появляется стабильный диурез, модуль отключается. Если целевой маркер «ЧСС/АД в рабочем коридоре» достигнут — снимаем антивегетативный контур. Это дисциплина маленьких шагов, где каждый следующий ход становится очевидным из предыдущих цифр, а не из ожиданий.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Escort services for charming girls Elite escort services Escort Agency
Everyday Trend Picks – Trend picks look well-organized, and navigation feels very user-friendly.
стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками купить официальный сайт цена [url=www.fen-d-3.ru]www.fen-d-3.ru[/url] .
This page truly has all of the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Острый этап разбит на небольшие «окна» с измеримыми целями. Это убирает неопределённость и дисциплинирует процесс: пациент знает, что будет происходить, когда будет проверка и по каким маркерам оценивается успех. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один параметр, а затем обязательно следует повторная оценка в оговорённое время.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-murmansk
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Екатеринбурге проводится с применением сертифицированных лекарственных препаратов, поддерживающих систем и методов индивидуальной терапии. Врачи используют физиологически безопасные комбинации растворов, витаминов и нейропротекторов, восстанавливающих работу центральной нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия проводится под контролем специалистов, что исключает возможность осложнений и обеспечивает быстрое улучшение состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в екатеринбурге[/url]
Каждый профиль решает одну задачу и имеет ожидаемую динамику. Мы избегаем параллельных «усилений», чтобы не «замазывать» вклад отдельного шага и не перегружать организм.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь казань[/url]
BargainHunterSpot – Smooth browsing and items displayed neatly for convenience.
I don’t often bother with long texts, but right now I thought I’d share what happened to me about a win at a gambling site.
Lately I’ve been testing at [url=https://nllalabet.com/]nllalabet.com[/url], mostly after work and with modest bets. I joined because the first deposit bonus looked okay and the terms seemed manageable compared to many other online casinos. The signup process was quite easy: a few standard fields and email confirmation, then I was good to go.
For my opening deposit I didn’t go crazy and put a modest sum into my balance. I jumped into the slots section because that’s what I mainly like. I looked for popular games and picked a slot with high volatility, hoping for a big hit.
At first it was nothing special: tiny hits and dead spins and bonus rounds that paid almost nothing, and I was thinking about stopping because my balance was going down. Then the session flipped: I landed a high-paying feature with multipliers all over the screen, the slot kept hitting combinations and the multiplier pushed my balance much higher. For me it was a serious win compared to my normal bets.
I didn’t keep spinning forever; after a few more low bets I decided to quit while ahead and send a payout request. The withdrawal process was pretty standard: the casino asked me to verify my account with some ID. I sent everything within an hour, and the verification was confirmed without any issues. After that the money was processed to my bank and I got it within a reasonable time.
I’m not saying this casino is always paying huge, and of course you can also lose, but in this case my experience was positive overall: transparent rules, decent support and no drama with the withdrawal. This is not a promise you’ll win: gambling always involves risk, so only gamble with a strict budget and treat it as entertainment.
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Elite prostitutes VIP Escort Elite Models
Fashion Edge Corner – Sleek interface and well-organized products make browsing enjoyable.
Hi there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative.
I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if
you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!
Здесь
[url=https://www.komus.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar-otzyvy/
Чтобы убрать неопределённость, мы делим первые часы на короткие окна. У каждого окна есть цель, действия и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один элемент, а следующая проверка назначается сразу — без хаотичного «усиления всего сразу».
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk-narkolog-na-dom-kapelnicza/
Как выбрать лучшую агентство в Москве для продвижения сайтов
Домашний формат уменьшает стресс и экономит время: не нужно ехать в клинику, скрывать визит от соседей или ждать в очереди. Врач приезжает без опознавательных знаков и не создаёт «медицинского шума». За один визит удаётся снять острые проявления, выстроить понятный план ночи и следующего утра, а также определить, нужна ли дополнительная диагностика. Такой маршрут часто оказывается короче и эффективнее, чем череда попыток «пересидеть» симптомы без медицинской поддержки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-voskresensk8.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-voskresenske/
Решение о выезде принимает врач с учётом симптомов и бытовых ограничений. Если совпадает хотя бы две позиции из списка ниже, лучше не откладывать звонок — управляемость состояния снижается каждый час.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/narkolog-kazan-kruglosutochno/
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/
VIP models Escort agencies VIP Escort Dating Site for Men
Hey there! Would you mind if I share your blog
with my facebook group? There’s a lot of people that
I think would really appreciate your content.
Please let me know. Cheers
Наши стандарты включают конфиденциальную маршрутизацию, детализированные инструкции для семьи, модульный план лечения и прозрачное разделение бесплатных и платных блоков. Каждому пациенту назначается ведущий специалист, который сопровождает его на всём пути — от первого звонка до контрольных чек-инов после процедур. Мы не «наращиваем» объём вмешательств ради впечатления: используется минимально достаточный набор мер, который действительно влияет на целевые маркеры — переносимость воды, качество сна, сглаживание вегетативных «качелей» и возвращение утренней ясности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в челябинске[/url]
курсовая заказать недорого [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru/]https://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru/[/url] .
learn & grow hub – Items look useful, site navigation is simple and intuitive.
ModernHome Online – Smooth and intuitive navigation paired with a clean modern design.
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс шоп[/url]
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-sankt-peterburg
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
MidCity Online – Collections look attractive, exploring the store is fast and intuitive.
home essentials hub – Great selections here, everything is arranged neatly and intuitive to browse.
WildBrook Modern Lifestyle – Contemporary and trendy style, exploring the store was fun.
написание курсовых на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru/]написание курсовых на заказ[/url] .
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Химках. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Подробнее – https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Круг нержавеющий 24 мм AISI321 калиброванный Подберите высококачественные нержавеющие круги для различных отраслей. Нержавеющие круги предлагают высокую стойкость к коррозии, прочность и широкий спектр применения. Выберите круги из нержавеющей стали для промышленных, строительных и производственных нужд.
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница балашиха[/url]
Escort Agency Elite escort services escort escort
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Premium Curated Global Hub – Enjoyed scrolling through the categories, items are thoughtful and well displayed.
В Санкт-Петербурге решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в мурманске[/url]
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkolog-nizhnij-novgorod-na-dom/
дайсон купить стайлер официальный сайт [url=www.fen-d-3.ru/]www.fen-d-3.ru/[/url] .
StartBuilding Lane – Motivational content displayed clearly with intuitive page flow.
hello there and thank you for your information – I have certainly
picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise several technical points using this
website, as I experienced to reload the web site a lot
of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your web hosting
is OK? Not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading instances times will often affect your
placement in google and can damage your high quality score if advertising and marketing with
Adwords. Well I’m adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a
lot more of your respective intriguing content. Make sure you update this again soon.
DailyDealsCenter – Organized pages, simple browsing, and appealing products.
evercrest items – Interesting pieces throughout, and the store seems to add new ones quite frequently.
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar/
FashionAndDesign Styles – Beautiful fashion picks are displayed, making the shopping flow smooth.
Hey I am Chris, one of the founders right here at SirLinksalot. http://www.bing.com/news/apiclick.aspx?ref=FexRss&aid=&tid=6916bb35ba084406a48ba99d003397fb&url=https%3a%2f%2fdvmagic.net%2Fpl%2F&c=2561878931910298131&mkt=fr-fr
Just wish to say your article is as surprising.
The clearness for your post is simply cool and i could think you are an expert in this subject.
Well with your permission allow me to snatch your feed to stay up to date with imminent post.
Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru
Elite girls for escort | VIP models Elite escort services Escort Services Agency – VIP Escort
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar-otzyvy/
Если среда дома шумная или приватность под угрозой, мы предложим «короткий коридор» через отдельный вход амбулатории. Если условия позволяют, проводим процедуры на дому: свет приглушён, доступ к розетке организован, рядом столик для расходников и приборов. Этот «экологичный» сценарий, несмотря на простоту, заметно улучшает переносимость процедур и собирает устойчивый сон в первую ночь, что особенно важно на ранних этапах стабилизации.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske/
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]азартные игры на деньги[/url]
naturallyselectedhub – NaturallySelectedHub delivers authentic, well-made items that make exploring fun.
ResourceFinderPro – Fast site and browsing answers feels natural and convenient.
курсовая работа купить [url=http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-28.ru]курсовая работа купить[/url] .
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]платный нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит последовательный процесс лечения, где основное внимание уделяется безопасности, контролю состояния и постепенной адаптации. При поступлении проводится диагностика с оценкой степени зависимости, сопутствующих патологий и психологических факторов, влияющих на развитие заболевания. На основании полученных данных формируется персонализированный план терапии, включающий медикаментозные и немедикаментозные методы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в санкт-петербурге[/url]
выполнение курсовых работ [url=www.kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/]выполнение курсовых работ[/url] .
Здесь
[url=https://www.komus.org/en/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
ремонт неисправностей стиральных машин [url=https://remont-stiralok-vrn-24.ru/]ремонт неисправностей стиральных машин[/url].
Sunset Grove Finds – Pleasant visuals with smooth page transitions make shopping effortless.
Escort for men VIP escort dating site escort escort
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника краснодар[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Die Entstehung des https://waselplatform.org/blog/index.php?entryid=752177 trägt ein außergewöhnliches Konzept, da das chicken road game anfänglich als spielerische Konzept entwickelt wurde, bei der ein Geflügeltier kritische Pfadabschnitte passiert und dabei vielfältige Hindernisse überwindet. Allmählich formte sich chickenroad zu einem Namen, der sowohl Spielern als auch Entwicklern merkfähig geblieben ist, weil er ein geradliniges aber packendes Spielprinzip repräsentiert, das intuitiv erfassbar, aber gleichzeitig anspruchsvoll ist. Mit wachsender Popularität entstand auch die Chicken Road App, welche vielen Spielern ein unterwegs verfügbares Spiel bot und das Gameplay in kurzer Zeit verbreitete. Während manche Spieler chicken road erfahrungen als klassisch darstellen, betonen andere die Stärke des Titels, moderne Systeme mit retroähnlicher Struktur zu verknüpfen, was die Basis dafür wurde, dass chicken road heute auch in anderen Bereichen genutzt wird. Die Macher erweiterten das Grundprinzip und schufen Varianten wie chicken road demo für Neulinge und chickenroad 2 als zweiten Teil, die eine dynamischere Game-Welt und zusätzliche Challenges einführte. Bemerkenswert ist, dass das chicken road casino in einigen Versionen als Designmotiv auftauchte, bei dem Abläufe an Casinoelemente erinnerten, ohne jedoch den eigentlichen Charakter des Spiels zu verlieren. Da viele Spieler Wert darauf legten zu wissen, ob chicken road seriös sei, versuchten die Entwickler stets transparent zu arbeiten und ein faires Spielerlebnis zu bieten, was das Vertrauen der Spielergemeinschaft über Jahre hinweg festigte. Diese stetige Weiterentwicklung, kombiniert mit gestalterischen Erweiterungen, sorgte dafür, dass chickenroad Slot Elemente in einigen Editionen integriert wurden, wodurch das Spielerlebnis erweitert wurde und neue Zielgruppen erreicht werden konnten. Letztlich zeigt die Geschichte von Chicken Road, wie ein simpel aufgebautes Prinzip durch beständige Weiterentwicklung, Flexibilität und eine engagierte Community wachsen kann und zu einem breiten Spielekosmos wird, das diverse Nutzer anspricht und in verschiedenen Varianten fortbesteht.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologi-rostov-na-donu
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/narkologi-murmansk/
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в самаре[/url]
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-sankt-peterburg
WildRose Picks Online – Friendly and inviting feel, discovered a few special pieces.
Modern Chic Hub – Browsing is fast and intuitive with contemporary pieces displayed nicely.
modern collection store – Products are attractive, navigation feels smooth and effortless.
[On our website, we tender modern and the wealthiest Crypto Analysis with AI for your business] [url=https://crypto.kodx.uk/]crypto.kodx.uk[/url]
[url=https://erdeha.co.id/2022/07/22/addressing-wind-energy-innovation-challenges/#comment-25654]#gpt_question_subject [Analisis Kripto terbaik dengan AI. crypto.kodx.uk][/url] 02427e0
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на диагностике, лечении и реабилитации пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Основная цель деятельности учреждения — восстановление физического здоровья и психологической устойчивости человека, оказавшегося в состоянии зависимости. В клинике применяются современные методы терапии, доказавшие эффективность в медицинской практике. Все процедуры проводятся конфиденциально, с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и под контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkolog-nizhnij-novgorod-na-dom/
Midnight Trend Finds – Stylish selections available, navigating the store is simple and smooth.
VIP escort Escort services with top models and VIP girls! Escort Services
Modern Outfit Trends – Good layout and responsive pages made checking styles smooth.
ValueSpotOutlet – Fast and simple navigation, good deals across the store.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
[url=https://double-down.casino/slots/]double down casino[/url]
сатир дзен События Дзен: будь в курсе главных новостей и происшествий!
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает широкий спектр медицинских и психотерапевтических услуг, направленных на устранение химической зависимости и стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния пациентов. Современные методики терапии, внедрённые в практику, позволяют добиваться устойчивых результатов без чрезмерного медикаментозного вмешательства и с учётом индивидуальных особенностей каждого человека. Основой лечения является комплексный подход, включающий детоксикацию, коррекцию поведения и восстановление когнитивных функций. Применение мультидисциплинарных схем обеспечивает снижение риска рецидива и повышение мотивации к трезвому образу жизни.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru
Global Finds Marketplace – Pleasant experience, the selection is broad and interesting.
Ночной приём организован по принципу «мягкой посадки». Если нет «красных флагов», сначала создаём комфортную среду (температура, тёплый свет, вода малыми глотками), затем проводим экспресс-диагностику и только после этого запускаем инфузионную терапию. Когда организм не перегружен сенсорными раздражителями, он отвечает на лечение ровнее: уменьшаются скачки пульса, снижается тошнота, а пациенты уже к утру описывают «ясную голову» без «ваты».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ПолярМед Центр» — это пространство круглосуточной помощи, где медицинская точность сочетается с бережным сервисом и конфиденциальными процедурами. Мы строим терапию как последовательность проверяемых шагов: ставим понятную цель, выбираем подходящий инструмент, заранее определяем маркеры контроля и фиксируем время повторной оценки. Такая дисциплина исключает «универсальные сильные капельницы» и заменяет их модульными решениями с предсказуемым эффектом. Пациент и его близкие на каждом этапе понимают, почему именно такое назначение выбрано сейчас и в какой момент мы ожидаем улучшение самочувствия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр мурманск[/url]
заказать дипломную работу онлайн [url=http://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru]http://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru[/url] .
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
вопросы про катэг кайт серф на годрофойле
Elite VIP Escort Elite escort services Escort Girls
DreamBigToday – Positive vibe, user-friendly structure, and effortless navigation.
https://long-living.ru/
курсовая работа купить [url=http://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru]курсовая работа купить[/url] .
oficjalne kasyno mostbet mostbet
Лечебная логика строится по принципу «одна цель — один маркер — одно окно оценки — один выключатель». Например, задача «открыть окно питья» решается антиеметическим мостом и мягкой регидратацией; как только вода пьётся без позывов и появляется стабильный диурез, модуль отключается. Если целевой маркер «ЧСС/АД в рабочем коридоре» достигнут — снимаем антивегетативный контур. Это дисциплина маленьких шагов, где каждый следующий ход становится очевидным из предыдущих цифр, а не из ожиданий.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/krasnodar-narkologicheskij-czentr
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в стационаре Балашихи. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Choice Fashion Online – Stylish items catch the eye, and exploring categories feels effortless.
Наши стандарты включают конфиденциальную маршрутизацию, детализированные инструкции для семьи, модульный план лечения и прозрачное разделение бесплатных и платных блоков. Каждому пациенту назначается ведущий специалист, который сопровождает его на всём пути — от первого звонка до контрольных чек-инов после процедур. Мы не «наращиваем» объём вмешательств ради впечатления: используется минимально достаточный набор мер, который действительно влияет на целевые маркеры — переносимость воды, качество сна, сглаживание вегетативных «качелей» и возвращение утренней ясности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Для жителей Краснодара и ближайших районов организованы два параллельных маршрута: немаркированный выезд врача-нарколога на дом и «тихий вход» в амбулаторный кабинет с отдельной дверью и согласованным слотом. На первичном звонке диспетчер фиксирует только факторы безопасности — частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспусканий, базовые значения ЧСС/АД, эпизоды спутанности, список текущих препаратов и аллергии. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются: мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации. На месте врач и медсестра собирают базовую линию (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), оценивают шкалы симптомов (тошнота/тремор/тревога по шкале 0–10), проверяют переносимость небольших глотков воды и описывают ближайшие «окна» принятия решений. Вечером и ночью команда остаётся на связи: мы заранее согласовываем пороги, при которых нужно позвонить дежурному врачу, чтобы не терять критические минуты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/narkologiya-anonimno-kazan/
https://www.fw-follow.com/forum/topic/60836/what-is-the-promo-code-for-1xbet:-1x200wave-%7C-%E2%82%AC130-info
Trendy Finds Studio – Neatly highlighted products with intuitive navigation for easy browsing.
[url=https://nashfact.com/pages/oandaha-doko-no-kaisha-desuka.html]
oanda japan 口コミ[/url]
https://usfblogs.usfca.edu/biol100/2018/01/24/student-of-life-posts/?unapproved=81396&moderation-hash=431b760cbecce09c49483734cdb1a79d#comment-81396
Evergreen Find Hub – A tidy and clear layout makes it easy to explore evergreen options.
PathFinder – Inspiring content easy to access, and site navigation feels smooth.
https://www.seyhancanta.com/blog/another-blog-post
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
https://vhearts.net/forums/thread/18942/
https://www.nongkhaempolice.com/forum/topic/49301/free-promo-code-for-1xbet:-1x200wave-%7C-%E2%82%AC130-welcome
https://almamater13.ru/raznoe-2/prostuda-u-grudnichka-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika.html?unapproved=117424&moderation-hash=87e817ca46e7720e8ffa0556c92a19f1#comment-117424
Понравились бонусы на депозит — довольно выгодные
драгон мани скачать
https://kingshouse.gov.jm/miss-world-pinned-i-believe-initiative-ibi-ambassador/
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Подробнее – http://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru/
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot
about this, like you wrote the book in it or something.
I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a bit,
but instead of that, this is fantastic blog. An excellent
read. I’ll definitely be back.
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде проводится с применением инфузионной терапии, седативных средств и витаминных комплексов. Основная задача процедуры — устранить токсическое воздействие алкоголя, восстановить работу органов и нормализовать психоэмоциональное состояние. Все препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом особенностей организма пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/[/url]
Escort Agency Escort agency – VIP escorts Escort services for charming girls
В рамках лечения пациент получает медицинское наблюдение, психологическую поддержку и коррекцию метаболических нарушений, вызванных длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
курсовой проект цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/]https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/[/url] .
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Химках. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]взрослые игры[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде использует многопрофильный подход, направленный на физическое и психологическое восстановление пациентов. После детоксикации проводится стабилизация обменных процессов, нормализация работы внутренних органов и поддержка нервной системы. Особое внимание уделяется коррекции поведения и мотивации пациента к отказу от употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkologiya-nizhnij-novgorod-besplatno/
Аккумуляторы для спецтехники техники
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/narkologicheskaya-sluzhba-kazan
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в самаре[/url]
Острый этап разбит на небольшие «окна» с измеримыми целями. Это убирает неопределённость и дисциплинирует процесс: пациент знает, что будет происходить, когда будет проверка и по каким маркерам оценивается успех. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один параметр, а затем обязательно следует повторная оценка в оговорённое время.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в мурманске[/url]
Female Escort Services for Men VIP Escort Escort
Wild Rose Hub Online – Cozy boutique vibe, found several enjoyable items while browsing.
Система IQOS представляет собой инновационный продукт для нагревания табака.
В отличие от обычных сигарет, здесь используется другой способ обработки табака.
Некоторые потребители отмечают, что такой формат характеризуется иным восприятием.
Устройство отличается простым управлением, что делает его подходящим для повседневного применения.
Продуманная конструкция позволяет IQOS органично вписываться в повседневную жизнь.
Производитель уделяет внимание технической надёжности, что повышает комфорт эксплуатации.
Своевременная очистка помогает поддерживать стабильную работу устройства.
В итоге, IQOS остаётся технологичным продуктом для тех, кто рассматривает такие системы.
https://terea777.shop/product/delia-green/
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя самара[/url]
your fashion picks – Products appear trendy, site layout is clear and user-friendly.
Такая карта снимает неопределённость. Пациент понимает, чего ожидать; родственники — когда и по каким метрикам судить об успехе; команда — что именно корректировать, чтобы сохранить управляемость терапии даже ночью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника мурманск[/url]
Решение о выезде принимает врач с учётом симптомов и бытовых ограничений. Если совпадает хотя бы две позиции из списка ниже, лучше не откладывать звонок — управляемость состояния снижается каждый час.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно казань[/url]
[url=https://solartrade.pk/pages/muumuu-shoken_4.html]
moomoo証券 デメリット[/url]
MidRiver Picks Hub – Well-arranged selections, browsing feels intuitive and fast.
Ogromne podziękowania za tak przydatne treści. Na pewno polecę Najlepsze kasyna online w Polsce znajomym.
https://legalnekasynawpolsce.pl
TrendyFashionHub – Great fashion choices, user-friendly interface, and fast access.
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в краснодаре[/url]
Чтобы сделать процесс понятным и управляемым, каждый шаг сопровождается измеримыми маркерами безопасности и эффективности. Корректировки — точечные, по правилу «одного изменения», что позволяет видеть вклад каждого действия и сохранять переносимость.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/
Fresh Trend Styles – Pages loaded with no lag and the items looked well-curated.
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в екатеринбурге[/url]
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог ростов-на-дону[/url]
Детоксикация является первым и важнейшим этапом лечения зависимости. В наркологической клинике в Краснодаре используются современные методы очищения организма, включая инфузионную терапию, гепатопротекторы, витаминные комплексы и ноотропы. Все процедуры проводятся под наблюдением врача-нарколога и направлены на снятие интоксикации, восстановление обмена веществ и нормализацию функций печени и нервной системы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru
Conscious Market Studio – Lovely selection with a tidy layout, enjoyed browsing through everything.
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]анонимный вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
Elite prostitutes Escort services with top models and VIP girls! Female Escort Services for Men
Если вы ищете [url=https://otdyh-v-adlere0.ru/]недорогой отдых в адлере 2026[/url], то наш сайт предлагает широкий выбор вариантов проживания и услуг для вашего идеального отдыха.
предлагает широкий выбор вариантов отдыха для туристов . Отдых в Адлере без посредников позволяет сэкономить средства на бронировании жилья и экскурсиях . Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто любит природу и активный отдых.
Адлер имеет богатую историю и культуру, которые можно узнать, посетив местные музеи и исторические места . Отдых в Адлере без посредников обеспечивает прямое общение с владельцами объектов недвижимости, что упрощает процесс бронирования и оплаты. Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто хочет совместить отдых с экскурсиями и активным отдыхом.
Адлер предлагает уникальные объекты недвижимости, которые можно забронировать без посредников . Отдых в Адлере без посредников позволяет сэкономить средства на бронировании жилья . Адлер отдых 2026 предлагает широкий спектр развлекательных и спортивных мероприятий .
Адлер имеет разнообразную инфраструктуру, которая включает в себя отели, рестораны и развлекательные учреждения. Отдых в Адлере без посредников даёт возможность выбрать объект недвижимости, который полностью соответствует вашим потребностям и бюджету . Адлер отдых 2026 предлагает широкий выбор вариантов размещения, от бюджетных гостиниц до роскошных отелей .
Адлер предлагает широкий выбор вариантов экскурсий и активного отдыха, от походов в горы до водных развлечений . Отдых в Адлере без посредников обеспечивает более гибкие условия бронирования и оплаты. Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто любит природу и активный отдых.
Адлер имеет разнообразную инфраструктуру, которая включает в себя отели, рестораны и развлекательные учреждения. Отдых в Адлере без посредников даёт возможность выбрать варианты экскурсий и активного отдыха, которые полностью соответствуют вашим потребностям и бюджету . Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто хочет совместить отдых с экскурсиями и активным отдыхом.
Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто любит природу и активный отдых. Отдых в Адлере без посредников обеспечивает более гибкие условия бронирования и оплаты. Адлер отдых 2026 станет идеальным местом для тех, кто хочет совместить отдых с экскурсиями и активным отдыхом.
Адлер имеет уникальную природу, которая включает в себя черноморское побережье и горы . Отдых в Адлере без посредников позволяет сэкономить средства и времени на поиск объектов недвижимости и вариантов экскурсий . Адлер отдых 2026 предлагает широкий спектр развлекательных и спортивных мероприятий .
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно балашиха[/url]
GoldenStore Finds – Simple, well-structured pages allow users to explore items quickly.
Здесь
[url=https://genaufit.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
кровать тлеграм Детская мебель Telegram и все, что связано с обустройством детской комнаты, также широко представлены в Telegram. Детская кроватка Telegram, двухъярусная кровать Telegram – родители могут найти все необходимое для создания комфортного и безопасного пространства для своих детей. Telegram предлагает огромный выбор детской мебели, включая детские диваны, кресла и другие необходимые предметы интерьера.
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в балашихе[/url]
Modern Trend Spot – Smooth navigation and visually appealing products make browsing easy.
PureEcoOutlet – Natural design, well-organized items, and effortless navigation.
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. В основе её деятельности лежит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, сочетание медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методов, а также полная конфиденциальность. Лечение проводится опытными специалистами с применением современных медицинских технологий, направленных на восстановление здоровья и предотвращение рецидивов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
https://kitehurghada.ru/ кайт египет
Yaywin – پاکستان میں نمبر 1 آن لائن
کیسینو اور سلاٹس گیمنگ
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Химках. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Химках — профессиональная помощь на дому. Наши опытные наркологи приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния и вывода из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Семья получает «путевой лист» на 24–72 часа: как фиксировать маркеры (тремор/тревога/тошнота 0–10), как пить воду малыми глотками, когда приглушать свет и в каком формате общаться с пациентом («короткие факты вместо оценок»). Мы также даём «лестницу активности»: два достижимых действия утром, одно — вечером. Эта дисциплина маленьких шагов помогает избежать эмоциональных «перегревов» и удерживает достигнутый эффект.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в челябинске[/url]
[url=https://tasmanbd.com/pages/minnanofx-shinsa-ochita_2.html]
みんなのfx チャート[/url]
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Санкт-Петербурге проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
ClarityPath – Browsing feels effortless with clean layout and motivating posts.
Escort services for charming girls Escort agencies elite escort
доказательство дзен Обстановка Дзен: следим за новостями и делимся информацией.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Лечение запоя у женщин в Химках. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению женщин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов химки[/url]
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в стационаре Балашихи. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
genuinehomehub – GenuineHomeHub offers authentic products that make exploring enjoyable.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Химках. Предлагаем комфортные условия для пребывания пациентов и круглосуточный медицинский уход.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом москва[/url]
WildBrook Modern Inspirations – Sleek selection with a contemporary feel, browsing was pleasant.
Философия клиники — «тихо, адресно, прозрачно». Выездная бригада приходит без маркировки, документы оформляются нейтрально, доступ к клинической записи разделён по ролям, а коммуникации со семьёй проходят короткими апдейтами в согласованные моменты. Такая организационная дисциплина — клинический инструмент: меньше сенсорного шума — ровнее пульс к вечеру, устойчивее засыпание и меньше потребность в «усилителях».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево мурманск[/url]
https://opalubka.market/ opalubka market
Everline Finds – Neatly arranged items, making the whole experience fast and enjoyable.
Срочная наркологическая помощь — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемый клинический процесс, где каждое действие проверяется измеримыми маркерами и выполняется в правильной последовательности. В наркологической клинике «ВолгаМед Альтернатива» маршрут выстроен вокруг принципа минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасный старт и телескрининг, затем очный осмотр с выбором контура инфузии и, только после теста переносимости, — основная терапия. Такой подход уменьшает реактивность организма, снижает риск побочных ощущений и делает результат предсказуемым для пациента и близких. Команда работает круглосуточно, выезжает на немаркированном транспорте, общение ведётся через одного доверенного человека, а документы оформляются в нейтральной терминологии без стигматизирующих формулировок.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь в казани[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
WildWood Fashion Hub – Stylish items displayed neatly, smooth browsing and fast-loading pages.
Вывод из запоя в Химках — профессиональная помощь на дому. Наши опытные наркологи приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния и вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя дешево химки[/url]
Elite Dating Models VIP Escort VIP escort
В мегаполисе привычный ритм часто мешает системному лечению: плотный график, транспортные задержки, высокая социальная видимость. Чтобы терапия проходила спокойно, «НеоТрезвие СПБ» использует «немаркированную» логистику: нейтральные формулировки в документах, аккуратные визиты, разнесенные по времени консультации специалистов и персональный координатор. По желанию пациента часть этапов — образовательные сессии и посткодовое сопровождение — выполняются онлайн. Это снижает тревогу и делает маршрут лечения менее заметным для окружения.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Екатеринбурге — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, где проводится диагностика, лечение и реабилитация людей, страдающих алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Комплексный подход включает не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапевтические методики, направленные на восстановление личности и возвращение пациента к социальной активности. Каждое вмешательство проводится с учётом физического состояния, психологического профиля и стадии заболевания. Работа специалистов основана на принципах анонимности, медицинской этики и научно доказанных протоколов лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Базы Хрумер 23 телеграм Базы Хрумер 19 телеграм: Базы Хрумер 19 телеграм – альтернативное написание термина “Базы Xrumer 19 телеграм”.
gift corner online – Nicely arranged gift ideas, with a layout that feels smooth and easy to use.
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Химках. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя с выездом в химках[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/[/url]
выполнение курсовых работ [url=www.kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru]выполнение курсовых работ[/url] .
mostbet global mostbet pl
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Modern Roots Collection Spot – Freshly curated products, navigation feels smooth and convenient.
Чтобы убрать неопределённость, мы делим первые часы на короткие окна. У каждого окна есть цель, действия и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один элемент, а следующая проверка назначается сразу — без хаотичного «усиления всего сразу».
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-murmansk-otzyvy/
WildRose Finds – Warm and inviting atmosphere, browsing revealed a few delightful items.
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм нижний новгород[/url]
Escort Services Elite escort services elite escort
BrightValue Picks – A tidy design that made scrolling around straightforward and pleasant.
FashionBeaconShop – Stylish finds, simple layout, and fast page loading.
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
Sustainable Lifestyle Picks – Easy to explore with a cozy vibe, unique eco-friendly items everywhere.
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]врач вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
What’s up every one, here every person is sharing such knowledge,
therefore it’s pleasant to read this blog, and I used to pay a quick visit this
website daily.
[url=http://flippamagazine.co.uk/testoandashoken-hyoban_1.html]
oanda[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ПолярМед Центр» — это пространство круглосуточной помощи, где медицинская точность сочетается с бережным сервисом и конфиденциальными процедурами. Мы строим терапию как последовательность проверяемых шагов: ставим понятную цель, выбираем подходящий инструмент, заранее определяем маркеры контроля и фиксируем время повторной оценки. Такая дисциплина исключает «универсальные сильные капельницы» и заменяет их модульными решениями с предсказуемым эффектом. Пациент и его близкие на каждом этапе понимают, почему именно такое назначение выбрано сейчас и в какой момент мы ожидаем улучшение самочувствия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике мурманск[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Люберцах. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2400??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu lyubercy[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В этой статье рассматриваются различные аспекты избавления от зависимости, включая физические и психологические методы. Мы обсудим поддержку, мотивацию и стратегии, которые помогут в процессе выздоровления. Читатели узнают, как преодолеть трудности и двигаться к новой жизни без зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://i-klinik.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в москве[/url]
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]частный нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Карта — это общий язык для всех участников процесса. Пациент видит смысл каждого шага, родные знают, когда и чему посвящены короткие апдейты, а врач точно понимает, какой параметр корректировать, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Наши стандарты включают конфиденциальную маршрутизацию, детализированные инструкции для семьи, модульный план лечения и прозрачное разделение бесплатных и платных блоков. Каждому пациенту назначается ведущий специалист, который сопровождает его на всём пути — от первого звонка до контрольных чек-инов после процедур. Мы не «наращиваем» объём вмешательств ради впечатления: используется минимально достаточный набор мер, который действительно влияет на целевые маркеры — переносимость воды, качество сна, сглаживание вегетативных «качелей» и возвращение утренней ясности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в челябинске[/url]
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
5 сообщений в курилках быстрее набивается , сообщения засчитываются только при ответе или цитате стороннего сообщения. Просто флуд сообщения не набивает. https://ivyshka-13kor.ru Кому-нибудь отправили сегодня трек?16 числа заказала товарчика)ну пока еще ничего не получила!!! продаван отправил только половинку(объяснил что не хватило реактивчика) но все остальное вышлет как привезут 100ый ))ждем и надеемся)) заказывала и раньше в этом магазе все было ОГОНЬ))
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в балашихе[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://healthband.net/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
After 20+ years as a professional coach I imagine getting older
is not about decline but evolution. https://rehabpools.store
http://fitagrunt.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ypykyc
ChicCorner – Navigation is simple and products are presented in a visually appealing way.
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]онлайн покер на деньги[/url]
[url=https://marcinmazurek.com.pl/blog/pgs/?moomoo-shoken-kinyucho.html]
moomoo証券 レビュー[/url]
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologi-rostov-na-donu
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare
[p][url=https://creditservice.ru.com/][b]SUNWIN[/b][/url] is a modern online betting ecosystem built in the interest of players who value transparency and smooth gameplay. From [b]casino[/b] pleasure to twinkling of an eye [b]x? s?[/b] results, the platform blends technology with palpable betting insight. Fans of [b]th? thao[/b] and [b]esports[/b] can scrutinize data-driven odds, while casual users make merry [b]trò choi[/b], [b]game slots[/b], [b]b?n cá[/b], and immense [b]jackpot[/b] rewards. Ritual options like [b]dá gà[/b], [b]baccarat[/b], [b]r?ng h?[/b], [b]xóc dia[/b], [b]tài x?u md5[/b], and [b]n? hu[/b] are optimized for fairness and speed. With everyday [b]khuy?n mãi[/b], long-term [b]uu dãi[/b], a gifted [b]cskh[/b] team, and a diaphanous [b]d?i lý[/b] routine, players can also verify details anon at [url=https://creditservice.ru.com/]https://creditservice.ru.com/[/url] to live a predictable betting journey.[/p]
МХЕ “как у всех” тобиш бодяжный.. Вроде скоро должна быть нормальная партия. https://buy2g.ru +огромная потеря популярности и быстрый спад клиентов.Ребята, у chemical-mix все на высшем уровне!
UrbanWild Picks – Creative arrangement of items with a sleek interface provides effortless navigation.
Daily Shop Away – Pleasant design and a variety of items make the experience enjoyable.
The Quick Extender Pro features become probably the most
talked-about traction devices among men looking for
a slow-moving, natural and routine-based approach to personalized improvement.
Many people searching for a Quick Extender Pro evaluation want to appreciate how
the device works, wht is the traction technique
actually means, and whether long-term uniformity can cause meaningful development.
The foundation of this specific device will be the grip method, a concept
utilized for many yrs in orthopedics plus essential.
Traction involves applying gentle and even continuous stretching to be able to soft tissues, motivating gradual adaptation above time.
When applied properly, this low-intensity method
can support muscle elongation, however it demands
patience, discipline and even steady use, which is why the particular Quick Extender Professional routine
is generally discussed in detail simply by users that
have tried out it for several weeks.
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это не «волшебная таблетка», а четко структурированный этап комплексного лечения, который должен вписываться в общий терапевтический план: диагностика, стабилизация состояния, выбор методики, юридически корректное информированное согласие, сопровождение и профилактика рецидивов. В наркологической клинике «НеоТрезвие СПБ» приоритет — безопасность, предсказуемость и конфиденциальность. Мы не перебираем методы «на удачу», а подбираем технологию с учетом клинического профиля, мотивации, социализации и коморбидных факторов (тревога, депрессия, соматические заболевания).
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/
В городе и ближайших районах клиника «УралМед Трезвость» обеспечивает оперативный выезд и амбулаторный приём без очередей. На этапе первичного контакта координатор уточняет только клинически значимые моменты: постоянные препараты и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов в прошлом, базовые показатели (АД/ЧСС/SpO?, если доступны), длительность симптомов, возможность организовать «тихое окно» на 20–30 минут. Вместо долгих разговоров — короткая, спокойная логика: где безопаснее начать (дом/амбулатория/стационар), какую ближайшую цель выбираем, в каком интервале ждём эффект и что считаем сигналом для связи с дежурным врачом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Химках. Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому химки[/url]
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены нижний новгород[/url]
Клиника предлагает широкий спектр услуг, охватывающий весь цикл лечения зависимости — от экстренной помощи до длительной реабилитации. Комплексная программа включает медицинскую, психологическую и социальную составляющие, что позволяет добиться устойчивого результата. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем врачей, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр самара[/url]
Стационарное лечение запоя в Балашихе — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход и комплексную терапию для каждого пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
[url=https://alterhs.org/wp-content/pgs/minnanofx-chaato_2.html]
みんなのfx 口コミ[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]джекпот[/url]
Everwild Finds – Attractive marketplace layout, making product discovery simple and efficient.
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Химках. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Причёт тут почта России, СПСР это самостоятельная курьерская служба. купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика то есть у вас все по прежнему и сайт работает?Да и вообще стот ли…? риск есть…?
Вывод из запоя в стационаре Балашихи — надёжная помощь при алкогольной зависимости. Наши специалисты обеспечат круглосуточный медицинский уход и поддержку в комфортных условиях.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому балашиха[/url]
Spot on with this write-up, I truly feel this amazing site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be returning to
read through more, thanks for the advice!
UniqueGift Picks Online – Clean design and neatly arranged gifts provide a seamless experience.
Каждый профиль решает одну задачу и имеет ожидаемую динамику. Мы избегаем параллельных «усилений», чтобы не «замазывать» вклад отдельного шага и не перегружать организм.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Вывод из запоя у подростков в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]анонимный вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
В городе и пригороде организован круглосуточный приём с возможностью выезда на дом. Координатор уточняет только клинически значимые данные: регулярные препараты и дозировки, аллергии, недавние эпизоды судорог/психозов, доступ к розетке, возможность обеспечить «тихое окно» на 2–3 часа. Если в квартире многолюдно или идёт ремонт, предложим «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и тем же ведущим врачом; после стабилизации зеркально перенесём маршрут обратно домой, чтобы не терять темп и доверие.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр нижний новгород[/url]
MoonCrest Corner – Unique selections look great, navigation is simple and pleasant.
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-murmansk
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-samara-vyzov-na-dom/
Wild Rose Creative – Charming boutique layout, browsing revealed some unique finds.
GiftExpressHub – Smooth site experience, delightful items, and effortless shopping.
Modern Goods Collective – Items appear intentionally chosen, browsing feels effortless and pleasant.
Ночной приём организован по принципу «мягкой посадки». Если нет «красных флагов», сначала создаём комфортную среду (температура, тёплый свет, вода малыми глотками), затем проводим экспресс-диагностику и только после этого запускаем инфузионную терапию. Когда организм не перегружен сенсорными раздражителями, он отвечает на лечение ровнее: уменьшаются скачки пульса, снижается тошнота, а пациенты уже к утру описывают «ясную голову» без «ваты».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Plains Trading Corner – Fast response times and organized categories made exploration easy.
В Санкт-Петербурге решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://lionadverts.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Exclusive Finds Marketplace – Exclusive items displayed with clarity and smooth browsing experience.
География накладывает отпечаток на клинические решения. Длинные сумерки, переменчивый ветер с акватории и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда увеличивают чувствительность к свету и шуму, а значит — усиливают вечернюю кардиолабильность. В «АрктикМед Профи» протоколы адаптированы под такой фон: в палатах преобладают тёплые источники света, на обходах персонал работает в «режиме тишины», в смартфонах включается «без уведомлений», а выездные бригады заходят в дом максимально незаметно. Такой «мягкий» сценарий делает помощь не только деликатной, но и клинически эффективной — снижается потребность в «сильных» седативных вмешательствах, сохраняется физиологичность сна.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в мурманске[/url]
Чтобы помощь была прозрачной и управляемой, каждый этап имеет цель, индикаторы безопасности и эффективности, а также понятное «окно оценки» результата. Коррекции проводятся «штучно», по правилу одного изменения — это защищает от полипрагмазии и позволяет читабельно видеть вклад каждого шага.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-kazan-czena/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru
Вывод из запоя на дому — удобно и безопасно. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя дешево в химках[/url]
Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика Да не магазин ровный несколько раз покупал у них, качество отличное. Только в аську бывает недостучатся.КАЧЕСТВО ВСЕХ ПРОДУКТОВ ОЧЕНЬ ВЫСОКОЕ!
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены нижний новгород[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Химках. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена химки[/url]
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена в балашихе[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Люберцах. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя цена люберцы[/url]
GiftSpot – Beautiful selection of gifts and the site is very easy to navigate.
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог ростов-на-дону[/url]
Понимающий меня поймёт. купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика Ну что же, сегодня получил свою посылку, на этот раз все было в наилучшем виде, конспирация на все 10 баллов из 10!Пожалуй один из самых ровных магазинов “Старичков ” – благодаря которому я зарабатвал, от души спасибо парням за ровную работу!
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена балашиха[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя выезд[/url]
modern picks hub – Stylish items displayed nicely, browsing feels simple and quick.
Hi there, I read your new stuff like every week. Your story-telling style is witty, keep up the good work!
<mindfulshoppinghub – MindfulShoppingHub offers thoughtful, stylish items with a pleasant browsing experience.
Обучение Xrumer 23 strong телеграм xrumer 23 strong ai телеграм: xrumer 23 strong ai телеграм – (см. определение ранее)
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские, психологические и социальные меры. Каждый пациент проходит индивидуальную диагностику, по результатам которой подбирается схема терапии. Такой подход позволяет снизить риски осложнений и обеспечить стабильный результат.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite
some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like
this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and
I look forward to your new updates.
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя на дому город. московская область[/url]
Срочная наркологическая помощь — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемый клинический процесс, где каждое действие проверяется измеримыми маркерами и выполняется в правильной последовательности. В наркологической клинике «ВолгаМед Альтернатива» маршрут выстроен вокруг принципа минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасный старт и телескрининг, затем очный осмотр с выбором контура инфузии и, только после теста переносимости, — основная терапия. Такой подход уменьшает реактивность организма, снижает риск побочных ощущений и делает результат предсказуемым для пациента и близких. Команда работает круглосуточно, выезжает на немаркированном транспорте, общение ведётся через одного доверенного человека, а документы оформляются в нейтральной терминологии без стигматизирующих формулировок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Выяснить больше – https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//
сделал заказ в этом магазине первый раз, заказывал 2гр. 400f на пробу, а пришло 3,3гр., очень доволен))) https://bimatuk.ru АА это только сегодня?Да не магазин ровный несколько раз покупал у них, качество отличное. Только в аську бывает недостучатся.
For quick access to yohohobetlogin, I find this link super helpful. No messing around with remembering complicated urls, just straight in. Check it out, trust me: yohohobetlogin
I don’t know if it’s just me or if perhaps everyone else
experiencing problems with your blog. It appears as if some
of the written text within your posts are running off the screen. Can somebody else please provide feedback and let me
know if this is happening to them too? This might be
a issue with my web browser because I’ve had this happen previously.
Thanks
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara
Такой комплексный подход позволяет не только купировать острые состояния, но и устранить внутренние факторы, провоцирующие развитие зависимости. После стабилизации состояния пациент переходит к этапу психотерапевтической коррекции, направленной на предотвращение рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «АрктикМед Профи» — это круглосуточная система помощи, где острые состояния снимаются быстро и безопасно, а дальнейшая реабилитация строится на измеримых целях, прозрачных правилах и бережной поддержке семьи. Мы объединяем инфузионную терапию, доказательные медикаментозные протоколы и современные психотерапевтические практики, чтобы восстановить физиологические ритмы организма, вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость к рецидивам. Основной принцип — «одна корректировка за раз»: мы меняем только один параметр (темп, объём, последовательность вмешательств) и сверяем результат в заранее назначённое «окно» оценки. Такой подход защищает от полипрагмазии, снижает медикаментозную нагрузку и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и семьи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Лечение в клинике строится на комплексной программе, которая сочетает медикаментозную терапию, психотерапевтические методы и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход обеспечивает устойчивый результат и предотвращает повторные срывы. Пациент проходит курс под постоянным контролем специалистов, что позволяет отслеживать динамику состояния и корректировать терапию при необходимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar-otzyvy/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru
WildBrook Modern Studio Finds – Trendy and stylish pieces, the gallery made exploring enjoyable.
http://www.bethanyecchurch.org/System/Media/play.asp?id=52759&key=922A8F01-4986-4DD1-B10F-F6332DDDE995
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Углубиться в тему – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/
https://1xbetbonuscode-7.jimdosite.com/
https://itkr.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?t=382841
Wild Rose Hub Online – Cozy boutique vibe, found several enjoyable items while browsing.
https://vivealumni.usfq.edu.ec/2022/07/ceremonia-junio-2022.html?sc=1765169045668#c2602245933721595224
https://onedallar.my1.ru/forum/27-1649-1
https://jhauto.fr/
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Химках. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов химки[/url]
Mountain Mist Shop – Beautifully curated selections, navigating the store is simple and intuitive.
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма нижний новгород[/url]
Мы дозировано упоминаем географию — важнее не слово «Нижний Новгород», а предсказуемость процесса. Пациент получает «вечерний протокол» — краткие инструкции на ближайшие 12 часов: как пить воду малыми порциями, как приглушить свет, какое «окно тишины» соблюсти перед сном, когда связаться с дежурным врачом и какие маркеры фиксировать в «дневнике симптомов» (шкалы тремора, тревоги, тошноты по 0–10; время засыпания; число пробуждений).
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Чем аргументирует отказ работать с гарантом? https://trackerdom.ru С новым годом всех!Или вводит всех в заблуждение?!
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. В основе её деятельности лежит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, сочетание медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методов, а также полная конфиденциальность. Лечение проводится опытными специалистами с применением современных медицинских технологий, направленных на восстановление здоровья и предотвращение рецидивов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника самара[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Екатеринбурге — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, где проводится диагностика, лечение и реабилитация людей, страдающих алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Комплексный подход включает не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапевтические методики, направленные на восстановление личности и возвращение пациента к социальной активности. Каждое вмешательство проводится с учётом физического состояния, психологического профиля и стадии заболевания. Работа специалистов основана на принципах анонимности, медицинской этики и научно доказанных протоколов лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов балашиха[/url]
Positive Living Store – The site feels welcoming and loads quickly for a calm experience.
BrightTrendHub – Trendy products displayed nicely, site navigation feels smooth and simple.
Curated Shop Studio – Unique selection with smooth navigation, exploring was simple and enjoyable.
EverGlow Corner – Aesthetic, professional design and clearly separated product sections enhance usability.
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в мурманске[/url]
Everwood Stock – Reliable product listings with quick page loads make shopping enjoyable.
Quiet Plains Finds – Pages loaded quickly, and the structured categories made it easy to explore.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Екатеринбурге — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, где проводится диагностика, лечение и реабилитация людей, страдающих алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Комплексный подход включает не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапевтические методики, направленные на восстановление личности и возвращение пациента к социальной активности. Каждое вмешательство проводится с учётом физического состояния, психологического профиля и стадии заболевания. Работа специалистов основана на принципах анонимности, медицинской этики и научно доказанных протоколов лечения.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg/
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kazan-otzyvy
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
детский пейнтбол Оба вида развлечений предлагают различные сценарии игр, от захвата флага до командных сражений, что делает каждую игру уникальной и увлекательной. Профессиональные инструкторы следят за безопасностью и объясняют правила игры, чтобы дети могли насладиться игрой в полной мере. Это отличный способ организовать день рождения, школьный праздник или просто активный отдых с друзьями.
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя московская область[/url]
Elite Finds Collection – Carefully curated collection with visually appealing and user-friendly design.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Санкт-Петербурге приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов санкт-петербург[/url]
UniqueGift Lane Hub – Clear visuals and organized gift sections create a smooth shopping experience.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Санкт-Петербурге — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar
говорю что все качественно быстро и купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика просто народу не верится в ассортимент и такие цены, да и по большинству продуктов отзывов нет ))Возможно сказалась бессонная ночь и отсутствие нормального питания на протяжении практически недели, но все время под туси я провел лежа на кровати и созерцая слааабенькие визуальчики. В общем, 4 из 6 сказали, что магазин – шляпа, и больше никогда тут ничего не возьмут.
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-novgorod
Выездная бригада действует незаметно: гражданская одежда, быстрый вход без обсуждений на лестничных площадках, краткая коммуникация. На домофон и документы — нейтральные указания, на чеках — общие формулировки. Мы показываем, что конфиденциальность — не обещание, а набор конкретных технологий, встроенных в процесс помощи.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в мурманске[/url]
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
your modern shopping – Selections appear fresh, browsing feels intuitive and pleasant.
Если при предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — одышка, давящая боль в груди, выраженная дезориентация, неукротимая рвота — координатор сразу резервирует место под наблюдение и организует перевод без пауз. В остальных ситуациях маршрут стартует дома с «мостиком» в стационар на случай изменения динамики.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в мурманске[/url]
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена мурманск[/url]
через в/в непробывал такое не люблю, купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика На удивление был поражен скоростью работы магазина. Все четко как в аптеке))) БлагодарствуюТовар тоже на 5/5 (только с концетрацией мало 1 к 5 или 1 к 7 дальше держит не долго)
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Химках. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно химки[/url]
В мегаполисе привычный ритм часто мешает системному лечению: плотный график, транспортные задержки, высокая социальная видимость. Чтобы терапия проходила спокойно, «НеоТрезвие СПБ» использует «немаркированную» логистику: нейтральные формулировки в документах, аккуратные визиты, разнесенные по времени консультации специалистов и персональный координатор. По желанию пациента часть этапов — образовательные сессии и посткодовое сопровождение — выполняются онлайн. Это снижает тревогу и делает маршрут лечения менее заметным для окружения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены санкт-петербург[/url]
Fantastic goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous
to and you’re just too fantastic. I really like what you have acquired here, certainly
like what you are stating and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it smart.
I can not wait to read far more from you. This is actually a terrific
site.
[p][url=https://creditservice.ru.com/][b]SUNWIN[/b][/url] stands out as a exhaustive online betting podium where [b]casino[/b] pageant blends seamlessly with [b]x? s?[/b], [b]th? thao[/b], and interactive [b]trò choi[/b]. From immersive [b]game slots[/b], skill-based [b]b?n cá[/b], and high-reward [b]jackpot[/b] systems to well-known favorites like [b]dá gà[/b], [b]xóc dia[/b], [b]baccarat[/b], [b]r?ng h?[/b], and provably lawful [b]tài x?u md5[/b], the stage delivers depth and balance. Competitive [b]esports[/b], persistent [b]khuy?n mãi[/b] and long-term [b]uu dãi[/b] are supported by open [b]cskh[/b] and a above-board [b]d?i lý[/b] network. Radical [b]n? hu[/b] mechanics and data-driven fairness steel credibility. Determine more at [url=https://creditservice.ru.com/]https://creditservice.ru.com/[/url], where alteration meets accountable play.[/p]
Выездная стабилизация — только первый шаг. Дальше важно разобрать триггеры, обучить «тихим ритуалам», согласовать план поддержки и рассмотреть кодирование там, где оно уместно. Мы не противопоставляем форматы: домашние визиты, «тихий вход» и краткие очные сессии дополняют друг друга. Задача — не создать идеальную «капельницу», а вернуть организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции и укрепить навыки, которые защищают от срыва. В «КубаньМед Резолюция» этим занимается мультидисциплинарная команда: наркологи, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинические психологи, психотерапевты и медсёстры с опытом ночных постов наблюдения. Все говорят на «языке фактов», чтобы решения были понятны и пациенту, и семье.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
FLY88
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в краснодаре[/url]
лазертаг Пейнтбол для детей адаптирован таким образом, чтобы снизить риски травм и обеспечить максимальную безопасность. Используются менее мощные маркеры и шарики с краской меньшего размера, что делает игру более мягкой и безболезненной. Специальные защитные костюмы, маски и шлемы обеспечивают дополнительную защиту.
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
адвокат днепр Жилищный адвокат в Днепре: споры о выселении, вселении, разделе жилья, признание права собственности. Защита жилищных прав.
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Wild Rose Boutique – Charming layout throughout, found some unique and enjoyable pieces.
какие манерные нынче клиенты пошли, плюнешь в рожу драться лезут, видете ли ему грубо ответили, я с ТС с момента регистрации общаюсь и не разу он не забуровил даже когда были терки а они поверь были, так что не пизди про невежливое обращение, да и по переписки видно что все ровно, ищи проблему в себе…. https://royal-flot.ru сегодня получил трек. все пробивается. жду посылочку)Всем доброго времени суток. Первый раз довелось заказывать в этом магазине на свой страх и риск, но положительные отзывы старичков о работе и качестве товара (в частности 2с, который меня и интересовал) убедили, что причин волноваться нет.
It’s an remarkable post in support of all the online visitors; they will
get advantage from it I am sure.
[b][url=https://creditservice.ru.com/]SUNWIN[/url][/b] stands non-functioning as a trusted online platform where [b]casino[/b], [b]x? s?[/b], [b]th? thao[/b], and interactive [b]trò choi[/b] run across … la mode technology. From immersive [b]game slots[/b], fast-paced [b]b?n cá[/b], and high-value [b]jackpot[/b] events to competitive [b]dá gà[/b] and worldwide [b]esports[/b], the sagacity feels seamless and fair. Smart systems power [b]tài x?u md5[/b], [b]xóc dia[/b], [b]baccarat[/b], [b]r?ng h?[/b], and amazing [b]n? hu[/b]. With frequent [b]khuy?n mãi[/b], long-term [b]uu dãi[/b], efficient [b]cskh[/b], and flexible [b]d?i lý[/b] programs, players can study confidently. Learn more at [url=https://creditservice.ru.com/]https://creditservice.ru.com/[/url].
[p][url=https://sunwin24z.life/][b]SUNWIN[/b][/url] is a latest online betting ecosystem designed for players who value transparency, advance, and variety. From immersive [b]casino[/b] experiences and data-driven [b]x? s?[/b] systems to competitive [b]th? thao[/b] markets, every [b]trò choi[/b] is optimized for real-time performance. The platform stands commission with high-RTP [b]game slots[/b], skill-based [b]b?n cá[/b], avant-garde [b]jackpot[/b], standard [b]dá gà[/b], and fast-growing [b]esports[/b]. Sting algorithms power [b]tài x?u md5[/b], [b]xóc dia[/b], [b]baccarat[/b], [b]r?ng h?[/b], and highly charged [b]n? hu[/b], while docile [b]khuy?n mãi[/b] and long-term [b]uu dãi[/b] payment loyalty. With wide-awake [b]cskh[/b] and scalable [b]d?i lý[/b] column, users can look into the congested sagacity at [url=https://sunwin24z.life/]https://sunwin24z.life/[/url].[/p]
Такая карта снимает неопределённость. Пациент понимает, чего ожидать; родственники — когда и по каким метрикам судить об успехе; команда — что именно корректировать, чтобы сохранить управляемость терапии даже ночью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/murmansk-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
Wow, this paragraph is good, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of things, so I am going to convey her.
This post will assist the internet people for building up new blog or even a weblog from start to
end.
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в стационаре Балашихи. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя с выездом в балашихе[/url]
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно санкт-петербург[/url]
Mountain Star Design – Attractive products arranged well, browsing is smooth and enjoyable.
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя цена химки[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому балашиха[/url]
эвакуатор дешего Эвакуатор Надежность, оперативность и профессионализм – три кита, на которых строится наша работа. Мы понимаем, что эвакуация автомобиля – это всегда стресс, поэтому стремимся сделать этот процесс максимально комфортным и безопасным для вас. Наши водители – опытные профессионалы, которые бережно относятся к каждому транспортному средству. Мы предлагаем прозрачные цены и гарантируем высокое качество обслуживания.
Creative Selections Collective – Layout is tidy and vibrant, discovering items was very smooth.
QuickDealsHub – Easy browsing, solid deals, and intuitive site navigation.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде специализируется на диагностике, лечении и реабилитации пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Основная цель деятельности учреждения — восстановление физического здоровья и психологической устойчивости человека, оказавшегося в состоянии зависимости. В клинике применяются современные методы терапии, доказавшие эффективность в медицинской практике. Все процедуры проводятся конфиденциально, с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и под контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Mushnyak, да ты гонишь походу, магазин работает как надо, каждую неделю у них заказываю все ровно, кидаловом тут не пахнет, ты наверное на отходосах)))) купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика пока никаких точных дат нет. цены будут когда придёт товар, так что ждёмс пока что.кролики ставят В\В, фашку от этого магазина по 0.07-0.15 нравится, только сушит сильно
оптимизация ндс в оренбурге Оптимизация НДС – это комплекс мер, направленных на снижение налоговой нагрузки законными способами. Она включает в себя анализ хозяйственных операций, налоговое планирование и учетную политику. Эффективная оптимизация требует комплексного подхода.
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, где каждая деталь важна: от скорости выезда до состава инфузии и «тихой» среды дома. В наркологической клинике «КазаньДетокс Медлайн» мы придерживаемся принципа поэтапной стабилизации: сначала безопасный старт и оценка рисков, затем прицельные капельницы и, при необходимости, краткосрочное наблюдение. Такой подход исключает «универсальные коктейли» и делает результат прогнозируемым: снижение интоксикации, выравнивание вегетативных реакций, восстановление сна и аппетита. Анонимность встроена в протоколы: немаркированный выезд, лаконичная документация, один доверенный контакт для связи 24/7, нейтральные формулировки без стигмы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя казань[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Екатеринбурге — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, где проводится диагностика, лечение и реабилитация людей, страдающих алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Комплексный подход включает не только медикаментозную терапию, но и психотерапевтические методики, направленные на восстановление личности и возвращение пациента к социальной активности. Каждое вмешательство проводится с учётом физического состояния, психологического профиля и стадии заболевания. Работа специалистов основана на принципах анонимности, медицинской этики и научно доказанных протоколов лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в екатеринбурге[/url]
RainyCity Style – Easy navigation, visually pleasing design, and nicely arranged collections.
This post presents clear idea designed for the
new people of blogging, that in fact how to do running a blog.
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
dyson фен оригинал [url=https://www.stajler-d-1.ru]https://www.stajler-d-1.ru[/url] .
фен дайсон оригинал [url=www.stajler-d-2.ru/]фен дайсон оригинал[/url] .
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog?
My blog site is in the exact same niche as yours and my users would
really benefit from some of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this alright with you. Thank you!
Наркологическая клиника «ПолярМед Центр» — это пространство круглосуточной помощи, где медицинская точность сочетается с бережным сервисом и конфиденциальными процедурами. Мы строим терапию как последовательность проверяемых шагов: ставим понятную цель, выбираем подходящий инструмент, заранее определяем маркеры контроля и фиксируем время повторной оценки. Такая дисциплина исключает «универсальные сильные капельницы» и заменяет их модульными решениями с предсказуемым эффектом. Пациент и его близкие на каждом этапе понимают, почему именно такое назначение выбрано сейчас и в какой момент мы ожидаем улучшение самочувствия.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
фен дайсон оригинал [url=stajler-d.ru]stajler-d.ru[/url] .
Fast Web Click Market – Quick page loads paired with a clean, minimalistic design.
Forest Goods Market – Everyday items are displayed clearly, making shopping simple and quick.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Химках. Предлагаем комфортные условия для пребывания пациентов и круглосуточный медицинский уход.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому в балашихе[/url]
Магазин работает супер!) https://mingrelskaya.ru Все получил в наилучшем виде, спасибо магазину за все, буду брать здесь всегдаТрек получил
Решение о выезде принимает врач с учётом симптомов и бытовых ограничений. Если совпадает хотя бы две позиции из списка ниже, лучше не откладывать звонок — управляемость состояния снижается каждый час.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в казани[/url]
SeasonFlow Market – Everything feels smooth; categories are labeled well and easy to browse through.
UniqueValue Studio Hub – Clean and modern layout with clearly displayed items enhances usability.
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого мурманск[/url]
your trend hub – Trendy items look great, browsing is smooth and convenient.
Лечение в клинике строится на комплексной программе, которая сочетает медикаментозную терапию, психотерапевтические методы и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход обеспечивает устойчивый результат и предотвращает повторные срывы. Пациент проходит курс под постоянным контролем специалистов, что позволяет отслеживать динамику состояния и корректировать терапию при необходимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в краснодаре[/url]
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar/
MoonGlow Lane Hub – Soft, tidy pages with clearly presented items enhance the browsing experience.
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Я делил Амф, https://dayria.ru конспирацию наладили?Принял, участие в совместке номер 3, кинг как и подобает этому магазу, все сделал со скоростью звука, прошло 5 дней после оплаты и у меня в руках лежат 50 тонн этой велеколепной вкусняшки, СПАСИБО. Я просто не понимаю как люди заказывают у других когда есть chemical
antiquemarketcentral – AntiqueMarketCentral features well-curated products that reflect timeless style.
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в самаре[/url]
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Санкт-Петербурге проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург[/url]
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
Здесь
[url=https://xn--90a1bg.xn--p1ai/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в балашихе[/url]
iPhone deals Europe Для наших французских клиентов предлагаем acheter iPhone Europe и iPhone reconditionne pas cher. Ищете boutique Apple alternative Europe? У нас вы найдете все необходимое. Также в наличии MacBook reconditionne France.
Next Gen Lifestyle Hub – Products are innovative and browsing the site is effortless and fun.
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
дайте ссылку на город курган, хочется маленько россыпушки https://cazucad.ru Обязательно позвонить должны, как позвонят легче забрать самому чем ждать пока курьер доставиткак так его разве нету? с самого утра тут сижу
Mountain View Bargains – Attractive outlet selections, navigating feels effortless and fast.
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg/
WildRose Lifestyle Online – Cozy, inviting atmosphere, browsing revealed a few standout items.
Модель типа «раздеватор» — это нейросетевая технология, которая обрабатывает визуальные данные.
Она опирается на обученные модели для модификации изображений.
Функционирование подобных решений основана на распознавании форм.
Подобные нейросети часто обсуждаются в контексте современных цифровых технологий.
раздевать людей без размытия и в хорошем качестве бесплатно
При этом важно учитывать моральные аспекты и вопросы конфиденциальности.
Работа с подобными инструментами требует понимания возможных последствий.
Многие эксперты подчёркивают, что технологии нуждаются в регулировании.
Таким образом, нейросеть-раздеватор является частью современного технологического ландшафта, который требует обсуждения.
Global Mindful Market – Loved exploring, every product feels high-quality and thoughtfully chosen.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в ростове-на-дону[/url]
фен dyson официальный сайт [url=https://stajler-d-2.ru/]stajler-d-2.ru[/url] .
BrightChoiceOutlet – Products are displayed neatly, pages load fast, and shopping is simple.
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Люберцах. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya lyubercy[/url]
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Санкт-Петербурге проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Flora Emporium Hub – Clear structure, attractive visuals, and quick browsing throughout.
Кто долги твоего представителя в РБ будет отдавать? купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика Отличный товар и работают ребята без перебоевДрузья ВВ 200мг. Дикая головная боль. И всё.
We buy household appliances in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region Скупка цифровой техники. We buy tumble dryers.
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в балашихе[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов[/url]
Инфузионная терапия в «АрктикМед Профи» строится на модулях, каждый из которых решает конкретную задачу: гидратация, коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, метаболическая поддержка; при необходимости — мягкая анксиолитика по строгим показаниям. Порядок модулей и темп выбираются под ведущий симптом-кластер и время суток. Мы обязательно фиксируем исходные и промежуточные маркеры, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/narkologi-murmansk
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing business, maximizing
efficiency is essential to staying competitive.
One area where corporations can greatly enhance their productivity is in the process of slotting.
Traditionally, slotting has been a labor-intensive and time-consuming job.
However, with the arrival of automated slotting machines, manufacturers can now streamline their manufacturing and obtain larger ranges of efficiency.
In this text, we’ll discover the advantages of automated slotting machines and the way they will revolutionize your manufacturing
processes. What’s an Automatic Slotting Machine? An automatic slotting machine is a specialised piece of gear utilized in manufacturing services to chop slots into various
materials corresponding to metal, wood, or plastic.
Unlike manual slotting methods that require extensive human intervention, automatic slotting machines are designed to
carry out this process automatically with minimal human involvement.
These machines utilize advanced expertise corresponding
to laptop numerical management (CNC) methods to precisely lower slots in line with
predetermined specs.
стайлер дайсон официальный сайт [url=stajler-d-1.ru]stajler-d-1.ru[/url] .
Apple store alternative Europe Для наших французских клиентов предлагаем acheter iPhone Europe и iPhone reconditionne pas cher. Ищете boutique Apple alternative Europe? У нас вы найдете все необходимое. Также в наличии MacBook reconditionne France.
Refined Design Store – Elegant layout with smooth navigation and well-organized sections.
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя клиника балашиха[/url]
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в самаре[/url]
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]наркология вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Peak Creative Studio – The visuals are warm and expressive, creating a nice browsing experience.
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow
you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying
your blog and look forward to new posts.
Мы используем модульную терапию: каждый контур решает одну клиническую задачу и сопровождается понятной динамикой. Это помогает мягко вести пациента и не «замазывать» вклад отдельных шагов параллельными усилениями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Магаз пропал из аськи и скайпа… Тобишь просто не появляется в онлайне. Такое уже бывало, но щас хз что… Качество товара было отменным. 203й высочайшего качества. купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, лирика почему 0.3? акция?кто сказал что он закрылся? где это написано?
fashion picks hub – Items look great, site feels organized and easy to explore.
дайсон стайлер для волос с насадками официальный сайт купить цена [url=http://stajler-d.ru/]http://stajler-d.ru/[/url] .
Forest Lane Deals – Items presented elegantly, giving the site a peaceful and enjoyable feel.
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar
shop noble collection – Smooth navigation and neatly displayed items improved browsing.
В Санкт-Петербурге решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://chelseptik.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мы собираем терапию как конструктор из узких модулей. Каждый модуль запускается только при показаниях и выключается сразу после достижения цели — это защищает от «инерции лечения» и возвращает организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции. Ниже — ориентировочная сетка модулей; фактический состав и дозировки определяет врач на очном осмотре.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
UrbanChoice Lane Hub – Fast-loading pages with well-displayed items and intuitive navigation.
Отзыв уже был, по поводу JWH и 2c-i. Писать то особо и не о чем, но качество товара очень даже порадовало. Щас жду только пополнения ассортимента. https://kinonovinki-2024.ru как всегда оплатил и все пришло. спасибо что есть такой магаз беру давно у них, все ок всем саветуюесли он такой делец,пусть тему свою создаёт!а так аферист,я бональный обаснованный вывод делаю!
Fresh Fashion Lane – A lively mix of items presented neatly, paired with effortless browsing.
Северное сияние, длинные сумерки, влажный ветер с Кольского залива — у Мурманска свой ритм, который влияет на сон, частоту сердечных сокращений и восприятие звука. Мы учитываем этот фон в клинике и при выездной помощи: используем тёплую подсветку вместо холодного верхнего света, организуем «режим тишины» на телефонах, ограничиваем количество касаний ночью, вводим «окна связи» с родственниками в заранее оговорённое время. Такой сенсорный профиль помогает снизить вечернюю реактивность и уменьшает потребность в избыточной фармакологии, сохраняя ясность утром.
Подробнее – http://
Cada vez incluyen más mercados en deportes emergentes y espectáculos alternativos, como los eSports, las artes marciales mixtas o incluso los torneos de
boxeo entre streamers. https://casamovil.es/hola-mundo/
Для тех, кто хочет знать подробности о [url=http://best-zabory-iz-profnastila.ru/]купить забор из профнастила недорого[/url], вы всегда можете обратиться к нам для получения точной информации и консультации.
Дачный забор, изготовленный из профнастила, сочетает в себе функциональность и эстетическую привлекательность . Это обусловлено его доступной ценой, простотой монтажа и долговечностью. Установка профнастила может быть выполнена самостоятельно или с привлечением профессионалов. Кроме того, Профнастил бывает различных цветов и узоров, что делает его универсальным материалом для любого ландшафтного дизайна .
Профнастил?? материал для забора отличается высокой прочностью и длительным сроком службы . Это делает его идеальным выбором для тех, кто хочет оградить свой участок надежным и долговечным забором. Стоимость установки дачного забора из профнастила зависит от нескольких факторов, включая размер участка и сложность работ .
Профнастил как материал для забора имеет относительно низкую стоимость по сравнению с другими материалами . Это делает его доступным для широкого круга потребителей. Уход за профнастилом включает в себя регулярную очистку от грязи и пыли. Также профнастил является экологически чистым материалом, что важно для тех, кто заботится об окружающей среде .
Забор из профнастила служит надежным барьером против проникновения на территорию. Заборы из профнастила служат двойной функцией: декоративной и защитной.
Технические показатели профнастила включают в себя толщину материала, размеры профиля и тип покрытия. Различная толщина профнастила подбирается в зависимости от назначения забора. Также Тип покрытия профнастила влияет на его устойчивость к коррозии и влиянию окружающей среды.
Технические характеристики профнастила подбираются с учетом климатических условий и предполагаемой нагрузки. При выборе профнастила для забора следует учитывать различные факторы, включая размеры участка, тип грунта и существующую инфраструктуру .
Установка дачного забора из профнастила может быть выполнена как самостоятельно, так и с помощью профессионалов . Стоимость установки дачного забора из профнастила варьируется в зависимости от размеров участка, типа используемого профнастила и условий выполнения работ .
Стоимость профнастила для забора вместе с установкой может начинаться от 500 рублей за погонный метр и достигать 2000 рублей и более . При выборе подрядчика для установки дачного забора из профнастила следует учитывать его опыт, качество работы и отзывы клиентов .
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar
Trendy Fashion Hub – The collection is nicely displayed, making browsing smooth and enjoyable.
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]помощь вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
{Saya telah {membaca|menelusuri|menyimak} artikel ini dengan {sangat cermat|penuh perhatian|teliti dari awal
sampai akhir}, dan menurut saya penyampaian informasi di dalamnya {benar-benar
menarik|sangat relevan|sangat berkualitas}, terutama karena artikel ini turut membahas topik seperti
KUBET, Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap, Situs Parlay Resmi,
Situs Parlay Gacor, Situs Mix Parlay, Situs Judi Bola, toto macau,
kubet login, situs parlay, Kubet Parlay, dan Judi Bola gacor.
{Saya menyukai cara penulis {menjabarkan informasi|mengolah pembahasan|menyusun keseluruhan materi}
dengan {bahasa yang mudah dipahami|alur yang terstruktur|detail yang mendalam}, sehingga
{membantu pembaca memahami inti artikel|pembaca tidak
merasa kebingungan|pesan artikel tersampaikan dengan jelas}.
Artikel ini menurut saya memiliki {kedalaman analisis|penjelasan berlapis|struktur
yang matang} yang jarang saya temukan pada tulisan lain dengan tema serupa.
{Oleh karena itu|Itulah sebabnya|Karena kualitasnya} saya merasa perlu untuk {memberikan komentar|meninggalkan apresiasi|menuliskan tanggapan}, karena tulisan seperti ini {layak mendapat perhatian|patut diapresiasi|memberikan manfaat
bagi banyak pembaca}. {Semoga penulis dapat terus
berkarya|Saya berharap penulis tetap konsisten menghasilkan konten berkualitas|Harapan saya penulis terus menghadirkan artikel format
seperti ini} sehingga lebih banyak pembaca bisa {mendapatkan referensi yang baik|menikmati
pembahasan yang informatif|menemukan insight
yang berguna}. Terima kasih telah menghadirkan artikel dengan kualitas penjelasan yang demikian jelas, mendalam,
dan nyaman untuk diikuti.}
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Next Generation Living – Each product is unique, and browsing feels intuitive and enjoyable.
Компания предлагает услуги [url=https://arenda-avto-s-voditelem2.ru/]аренда водителя с автомобилем[/url] по доступным ценам для всех желающих.
Аренда автомобиля с водителем в Новосибирске является удобным вариантом для тех, кто хочет путешествовать комфортно . Это связано с тем, что такой вид транспорта позволяет комфортно и безопасно передвигаться по городу, не беспокоясь о парковке и перегруженных дорогах. Компании, предоставляющие услуги аренды авто с водителем, работают гибко и могут удовлетворить любые потребности клиентов. Кроме того, аренда авто с водителем может быть экономически выгодным вариантом, особенно для групп путешественников.
При аренде авто с водителем в Новосибирске клиенты могут выбирать из различных типов автомобилей, начиная от ekonom-класса и заканчивая люксовыми моделями . Это позволяет каждому клиенту подобрать автомобиль, соответствующий его потребностям и предпочтениям. Водители, занимающиеся арендой авто с водителем, гарантируют безопасность и комфорт на дороге.
Аренда авто с водителем в Новосибирске дает возможность насладиться красотами города, не отвлекаясь на вождение . Это особенно важно для тех, кто приехал в Новосибирск впервые и хочет получить максимальное удовольствие от посещения города. Комфорт и безопасность – это два главных преимущества аренды авто с водителем . Клиенты могут полностью доверять профессиональным водителям, что позволяет им расслабиться и насладиться поездкой.
Аренда машины с водителем в Новосибирске является отличным решением для деловых путешественников, нуждающихся в надежном транспорте. Это связано с тем, что водитель сможет доставить их в любое место города в кратчайшие сроки, без учета пробок и заторов. Многие компании предлагают дополнительные услуги, такие как помощь в организции мероприятий или экскурсий, что делает их еще более привлекательными для клиентов .
Для аренды машины с водителем в Новосибирске необходимо найти подходящую компанию и обсудить условия аренды. Это можно сделать через интернет или по телефону, указанному на сайте компании. При аренде автомобиля с водителем клиентам необходимо сообщить о своих потребностях и предпочтениях .
Компания, предоставляющая услуги аренды авто с водителем, поможет клиенту на всех этапах. Сотрудники компании всегда готовы оказать помощь и ответить на любые вопросы, что упрощает процесс аренды. Для того чтобы избежать любых недоразумений, необходимо тщательно ознакомиться с условиями аренды.
Аренда автомобиля с водителем в Новосибирске предлагает множество преимуществ для путешественников и бизнесменов . Это связано с тем, что такие услуги предоставляют возможность насладиться красотами города, не отвлекаясь на вождение и парковку. Компании, предоставляющие услуги аренды авто с водителем, гарантируют клиентам безопасность, комфорт и пунктуальность .
Для аренды автомобиля с водителем необходимо найти компанию с хорошей репутацией и качественными услугами . Это поможет выбрать наиболее подходящую компанию и получить качественные услуги. Рекомендуем тщательно изучить все варианты и выбрать тот, который лучше всего соответствует вашим потребностям и бюджету .
Finds Directory – Easy-to-scan product sections that help shoppers move through the site effortlessly.
EverForest Finds Online – Enjoyable browsing with clean, natural arrangement of products.
NameDrift Online – Stylish products displayed nicely, exploring the site is easy and fast.
carefullychosenluxury – Carefullychosenluxury has an elegant selection that made browsing feel premium and fun.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
BudgetFriendlyHub – Quick access to items, layout is clean, and shopping is hassle-free.
Спасибо за полезный контент по теме ставок.
https://vote114.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=3325965
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Химках. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому химки[/url]
Curated Style Marketplace – Stylish selections displayed neatly with effortless browsing.
дайсон официальный сайт стайлер [url=https://www.stajler-d-2.ru]https://www.stajler-d-2.ru[/url] .
SuccessJourneySpot – Motivational articles, site layout is simple and intuitive.
reliable value center – Offerings look solid, site layout is clean and easy to explore.
Здесь
[url=https://kingsystem.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]бинго онлайн[/url]
купить дайсон фен в москве у официального дилера [url=https://stajler-d-1.ru/]https://stajler-d-1.ru/[/url] .
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]скорая вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя цена балашиха[/url]
Стационарное лечение запоя в Балашихе — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход и комплексную терапию для каждого пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Glow Lane Picks – Attractive product selection, with smooth browsing throughout the site.
дайсон стайлер для волос купить официальный сайт цена с насадками [url=https://stajler-d.ru/]https://stajler-d.ru/[/url] .
creativehubcentral – CreativeHubCentral delivers premium design pieces in an organized, easy-to-browse format.
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Химках. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Style Daily Hub – Fashion offerings look great, and moving through the site is effortless.
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде проводится с применением инфузионной терапии, седативных средств и витаминных комплексов. Основная задача процедуры — устранить токсическое воздействие алкоголя, восстановить работу органов и нормализовать психоэмоциональное состояние. Все препараты подбираются индивидуально, с учётом особенностей организма пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены нижний новгород[/url]
Intentional Home Essentials – Smooth navigation paired with carefully chosen, purposeful items.
https://www.globalfreetalk.com/welcomsxbet1
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Люберцах. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя наркология люберцы[/url]
Tall Cedar Goods – Warm and cozy layout, browsing through categories felt effortless.
https://ezdirect.it/
https://justinekeptcalmandwentvegan.com/
https://kvedomosti.ru/
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
https://github.com/whahs5024/finds-ly/issues/5
https://greenworldhotels.com/
https://puntera.com/
NatureRoot Treasures – Natural products arranged neatly, shopping feels effortless today.
https://saijo-denki.co.th/
Thoughtful Values Market – Very pleasant experience, the layout is clean and easy to navigate.
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Химках. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki11.ru//]вывод из запоя в стационаре в химках[/url]
книга учета и выдачи аттестатов об основном общем образовании купить [url=http://r-diploma25.ru/]книга учета и выдачи аттестатов об основном общем образовании купить[/url] .
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]милфы[/url]
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь краснодар[/url]
DreamPathHub – Products motivate and inspire, pages load fast, and browsing is intuitive.
GrowBright Corner – The whole platform feels inspiring, with clear navigation and a clean design.
Petal-Themed Shop – Each scroll feels peaceful and refreshing, with pretty finds everywhere.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Visual Design Market – Visually striking designs presented in a clean and user-friendly layout.
Corner of Fashion Discover – Trendy aesthetics paired with user-friendly tools create a smooth browsing flow.
LearningVault – Great insights with a clean layout, site navigation is effortless.
shop hub picks – Products look strong, browsing experience is smooth and pleasant.
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar/
стайлер дайсон официальный сайт [url=www.stajler-d-2.ru]стайлер дайсон официальный сайт[/url] .
дайсон фен купить в москве оригинал [url=www.stajler-d-1.ru/]дайсон фен купить в москве оригинал[/url] .
Контрактная разработка электроники позволяет быстро запускать новые продукты на рынок без необходимости строить собственное производство. Инженеры проектируют схемотехнику, создают платы, корпус и программное обеспечение, проводят тестирование и настройку прототипов. Такой подход снижает риски и ускоряет разработку https://wiki.tgt.eu.com/index.php?title=User:FranciscaBoland. Очень удобный способ подготовки устройств к серийному производству.
Инфузионная терапия — это не просто «быстрый раствор витаминов». При запое страдает водно-электролитный баланс, «плавает» давление и пульс, нарастает тревога, нарушается сон, проявляются тошнота и тремор. Правильно собранная капельница в Клину помогает вернуть жидкость и электролиты, поддержать печень, снизить вегетативные проявления, мягко стабилизировать нервную систему и подготовить переход на пероральные схемы. Важно избегать избыточной седативной нагрузки и опасных сочетаний: то, что человеку «помогало раньше», может конфликтовать с его нынешними показателями. Поэтому каждое назначение мы увязываем с реальными цифрами осмотра и тем, что уже было принято за двое суток.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
You’ve made some good points there. I looked on the net
to learn more about the issue and found most people will go along with your
views on this site.
Этап
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/
Домашний формат нужен, когда риски управляемы, а в квартире можно обеспечить «тихий режим». Врач приезжает без эмблем, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, сверяет лекарства за последние 48 часов и аллергии. После допуска запускается инфузия с мягкой коррекцией воды и электролитов, поддержкой печени и вегетативной нервной системы; при необходимости аккуратно настраивается сон. По завершении — переоценка, письменная памятка на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и прямой канал связи. Такой визит «гасит» тремор и тошноту, снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Для жителей Краснодара и ближайших районов организованы два параллельных маршрута: немаркированный выезд врача-нарколога на дом и «тихий вход» в амбулаторный кабинет с отдельной дверью и согласованным слотом. На первичном звонке диспетчер фиксирует только факторы безопасности — частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспусканий, базовые значения ЧСС/АД, эпизоды спутанности, список текущих препаратов и аллергии. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются: мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации. На месте врач и медсестра собирают базовую линию (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), оценивают шкалы симптомов (тошнота/тремор/тревога по шкале 0–10), проверяют переносимость небольших глотков воды и описывают ближайшие «окна» принятия решений. Вечером и ночью команда остаётся на связи: мы заранее согласовываем пороги, при которых нужно позвонить дежурному врачу, чтобы не терять критические минуты.
Подробнее тут – http://
Fashion Deals Hub – Products appear affordable, site experience is simple and convenient.
>Future Lifestyle Picks – User-friendly design complements a collection of inventive items.
фен дайсон [url=https://stajler-d.ru/]stajler-d.ru[/url] .
Wild Bird Studio Online – Unique and creative selection, every item seems carefully chosen.
Goldcrest Boutique – Products displayed thoughtfully, with browsing that feels natural and pleasant.
NightBloom Online – Well-organized selections, shopping here is intuitive and pleasant.
Living Hub Premium – Very smooth navigation, everything feels thoughtfully selected.
ClassyChoiceStore – Smooth interface, trendy items, and clean layout make browsing easy.
Casino Rocket
Vavada Casino is a popular online platform offering a wide range of games, including slots, roulette, blackjack, and poker. Players enjoy fast and secure deposits and withdrawals, generous bonuses, and a user-friendly interface. Mobile-friendly and reliable, it caters to both beginners and experienced gamblers.
<Trusted Quality Marketplace – Reliable product arrangements and smooth site performance for easy browsing.
fresh deals hub – Items look appealing, browsing feels fast and convenient.
FashionJourneyHub – Stylish choices displayed nicely, moving through pages was effortless.
Creative Treasures Hub – A lively creative range and a seamless browsing flow make the site enjoyable.
Здесь
[url=https://www.0560.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Appreciate the effort put into this. It’s always good to see quality content.
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Futurecrest Picks – Smooth navigation and eye-catching visuals made this shop fun to explore.
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr
Мы выстраиваем помощь как маршрут, а не разовую процедуру. Первый контакт начинается с короткого сбора данных: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые препараты, аллергии, эпизоды судорог или потерь сознания в прошлом. Это позволяет быстро определить формат — домашний визит или госпитализация — и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты и расходные материалы. После стабилизации мы обсуждаем ближайшие недели: контрольные осмотры, план восстановления сна и питания, подготовку к кодированию и участие семьи. Такой подход снижает риск повторного срыва и делает процесс управляемым.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
World Lifestyle Finds – The layout is clean, and exploring authentic items is enjoyable.
Urban Ridge Finds Online – Contemporary design with an appealing product selection, very nice experience.
Ниже — «скелет» визита. На месте врач адаптирует содержание под возраст, соматику, текущие лекарства и проявления абстиненции. Главная идея — быстро получить цифры, аккуратно запустить инфузию и заранее зафиксировать ориентиры, чтобы семья не импровизировала в «трудный час».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Fashion Deal Center – Store offers trendy picks, navigation feels simple and pleasant.
Если на первичном звонке звучат «красные флаги» (выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, скачки ритма), мы предлагаем стационарное окно мониторинга. При низком риске стартуем дома или амбулаторно и поддерживаем человека вечерними видеовставками по 15–20 минут, чтобы пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и паники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
qualitymarketplace – QualityMarketplace presents a curated collection with clean, clear product information.
a href=”https://discoveryourpurpose.click/” />PurposeTrack Online – Smooth page transitions and well-placed sections strengthen the experience.
Creative Styles Hub – Easy to explore, the marketplace offers a pleasant mix of creative items.
Northern Peak Online – Attractive items showcased nicely, shopping feels fast and effortless.
<Golden Harbor Corner – Well-organized goods, with effortless navigation from section to section.
Как выбрать качественные комплектующие для стиральных машин
[p][url=https://sunwin24z.life/][b]SUNWIN[/b][/url] is a up to the minute online betting ecosystem built as a service to players who value transparency, speed, and depth. From active [b]casino[/b] tables and chic [b]x? s?[/b] systems to competitive [b]th? thao[/b] markets, the platform delivers a balanced portfolio of [b]trò choi[/b]. Fans of [b]game slots[/b], [b]b?n cá[/b], [b]jackpot[/b], [b]dá gà[/b], and [b]esports[/b] discretion locate stout odds and optimized gameplay. Fastened modes like [b]tài x?u md5[/b], [b]xóc dia[/b], [b]baccarat[/b], [b]r?ng h?[/b], and [b]n? hu[/b] echo tough technological foundations. With reiterative [b]khuy?n mãi[/b], long-term [b]uu dãi[/b], licensed [b]cskh[/b], and a clear [b]d?i lý[/b] configuration, users can enquire into confidently. Bona fide access at [url=https://sunwin24z.life/]https://sunwin24z.life/[/url].[/p]
Интернет на даче был необходим для системы видеонаблюдения и умного дома. Мобильный 3G 4G интернет подошел идеально. Установка выполнена аккуратно и профессионально. Сигнал уверенный и стабильный. Теперь можно контролировать дом дистанционно – https://podklychi.ru/
Здесь
[url=https://whynotnails.us/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]блекджек[/url]
промокод 1win Для новых пользователей предусмотрена простая и быстрая 1win регистрация. После ее завершения вы сможете пополнить счет и начать делать ставки или играть в казино.
Клиника «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде оказывает помощь при алкогольной интоксикации как в условиях стационара, так и на дому. Врачи готовы выехать к пациенту в течение 40–60 минут после обращения, привозя с собой всё необходимое оборудование для проведения инфузионной терапии. Такая оперативность позволяет снизить риск осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в первые часы лечения. Для пациентов, нуждающихся в круглосуточном наблюдении, предусмотрены комфортабельные палаты с постоянным медицинским контролем.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в волгограде[/url]
Подключение мобильного интернета на дачу прошло быстро и без сложностей. Специалисты сразу оценили уровень сигнала и подобрали оптимальное оборудование. Скорость соответствует заявленной и подходит для работы и развлечений. Очень удобно, что интернет не зависит от кабелей. Теперь на даче всегда есть связь: интернет роутер на дачу
ClassyChoiceHub – Smooth browsing, well-organized items, and clean layout make shopping easy.
цена курса диспетчера грузоперевозок по всему миру с трудоустройством
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает видеть логику процесса. Это не жёсткий график: врач адаптирует точки и сроки под возраст, фоновые заболевания и исходное состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]наркологическая клиника в клину[/url]
Clickping Journey Hub – Minimalistic design that makes exploring items fast and intuitive.
This paragraph is really a good one it assists new the web viewers,
who are wishing for blogging.
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в волгограде[/url]
top quality finds – Products are attractive, browsing feels effortless and clean.
Здесь
[url=https://brightrich.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Люкс для путешествий – это высокий уровень комфорта и [url=https://skyrevery.ru/arenda-chastnogo-samoleta]аренда самолета[/url] – это один из способов обеспечить себе такой опыт.
с высоким уровнем сервиса . Это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит свое время и нуждается в индивидуальных условиях. Частные самолеты предлагают широкий спектр услуг от базового сервиса до VIP-услуг.
Частные самолеты используются для бизнес-переговоров . Они предлагают высокий уровень конфиденциальности . Кроме того, частные самолеты часто оснащены индивидуальными решениями для каждого пассажира.
Одним из главных преимуществ частных самолетов является их гибкость в выборе маршрута. Это позволяет пассажирам создавать индивидуальные маршруты . Частные самолеты также предлагают более быстрые полеты .
Частные самолеты часто используются для бизнес-авиации . Они обеспечивают максимальный комфорт . Кроме того, частные самолеты могут сокращать время в пути .
Существует несколько типов частных самолетов от легких самолетов до бизнес-джетов . Каждый тип предназначен для различных условий полета . Частные самолеты могут быть одномоторными или многомоторными .
Частные самолеты могут быть разделены на категории по размеру . Они используются для коротких и средних расстояний . Кроме того, частные самолеты могут быть спроектированы для конкретных условий эксплуатации.
В заключение, частные самолеты предлагают высокий уровень индивидуализации. Они используются для бизнеса и отдыха . Частные самолеты обеспечивают уникальные возможности для пассажиров.
Перспективы частных самолетов связаны с ростом спроса . Частные самолеты будут предлагать новые услуги и возможности. Кроме того, частные самолеты будут предоставлять уникальные experiencia для пассажиров.
[url=https://travim-klopov.ru/unichtozhenie-klopov]фирмы по уничтожению клопов[/url] поможет эффективно избавиться от неприятных насекомых в вашем доме.
Используйте репелленты и инсектициды, чтобы максимально эффективно устранить клопов.
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом воронеж[/url]
Этап
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-chekhove/
Казино Догхаус рецензия
Timber Crest Studio – Lovely artistic vibe, each piece feels thoughtfully curated.
Ethical Living Hub – Browsing is enjoyable, with premium products that reflect responsibility.
Перед таблицей зафиксируем принцип: это ориентир по этапам для семьи и пациента. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность под возраст, сопутствующие заболевания и исходное состояние.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Преимущество стационара — предсказуемость и скорость. Рядом врач и медсестра, можно оперативно сдать анализы, сделать ЭКГ или дополнительные обследования, а главное — не «тянуть» с корректировкой схемы. В контролируемой среде быстрее нормализуются сон и аппетит, уходит тремор, снижается тревога. Для пациентов с сопутствующими диагнозами это особенно важно: диабет, гипертония, аритмии, хронические заболевания ЖКТ требуют аккуратной, согласованной тактики.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]klinika-narkologii-i-psihiatrii-moskva[/url]
bell-parik.ru
Fashion Finds Spot – Store items look trendy, exploring the site feels smooth and enjoyable.
Start 2026 with a win: claim your WINNERSLIVE CASINO New Year bonus — $2,600. Use promo code NY26 at sign-up. 18+ only. Play responsiblys https://tinyurl.com/4djvu4ak
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы не удерживаем пациента на дому во что бы то ни стало. Домашний формат уместен при контролируемых симптомах, наличии взрослого помощника на вечер и ночь и возможности обеспечить тихий режим. Если у входа видно угрозу делирия, выраженные скачки давления, повторные эпизоды рвоты с обезвоживанием, нестабильный ритм, одиночество ночью — рациональнее начать в палате. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и лаборатория, пост медсестёр и быстрые коррекции схем. Такой маршрут часто короче по времени до устойчивого сна и предсказуемее по результату.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
topdealscentral – TopDealsCentral feels professional and user-friendly with simple, effective navigation.
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи[/url]
Если на любом этапе проявляется нестабильность давления/ритма, падает сатурация или ухудшается контакт, врач эскалирует формат немедленно. Важно: в стационаре мы продолжаем тот же курс, не «перепридумывая» его с нуля — благодаря единой карте наблюдения теряется меньше времени и сил.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ставрополе[/url]
получил посылку не выходя с почты открыл ее а там лежат какие то шорты. ну думаю все кинул 7 к просто выкинул. пришел домой с пацанами сели чай пить положил вещи тут как раз мама старалась и спросила меня есть шмотки грязные ну тут я достал все вещи и шорты мама давай смотреть карманы и в итоге в шортах находит 10 г вот тут я обрадовался и разочаровался думал хана https://sk-salon.ru рекомендую этот магазинКак связаться?
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, где проводят детоксикацию или капельницы. Это выстроенная система, где каждый этап направлен на восстановление физического, психического и социального равновесия пациента. В клинике «КрасЗдрав Профи» весь процесс лечения построен по принципу прозрачных шагов: первичная диагностика, стабилизация организма, терапевтическая коррекция и закрепление результата. Всё происходит с соблюдением принципа конфиденциальности — пациент может рассчитывать на анонимность и этичное отношение со стороны персонала.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk
For most recent news you have to pay a visit internet and on the web
I found this site as a finest website for newest updates.
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно воронеж[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Golden Root Online Store – Items displayed clearly and fairly priced, navigation feels smooth.
Городская среда Воронежа — яркие подъезды, плотный трафик, шумные дворы — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому мы проектируем «тихую» логистику: согласованная парковка, вход без вывесок, гражданская одежда специалистов, короткий маршрут от порога к месту процедуры. Коммуникация в зашифрованных каналах, напоминания — в беззвучном режиме. Такой дизайн не декоративен: чем меньше социального шума, тем быстрее возвращаются питьё и аппетит, а значит — меньше потребность «наращивать» фармакологию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-murmansk-otzyvy
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в воронеже[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в ставрополе[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.truck1.eu/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
your best finds – Selection looks appealing, site layout is easy to navigate.
Надеюсь этот вопрос решится ……. Закладкой купить альфа-пвп, мефедрон, бошки Странно все как то..Ae!Магазин ровнее уровня)Брал несколько раз.все ровно.ТСу отдельное спасибо) Удачи вам парни)
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Интернет на даче был нужен срочно, и мобильное решение оказалось самым быстрым. Специалисты приехали оперативно и всё установили. Сигнал усилили антенной. Интернет работает стабильно. Отличный сервис и результат https://podklychi.ru/
ремонт стиральных машин недорого [url=http://bystryj-remont-stiralok-vrn.ru/]ремонт стиральных воронеже дому[/url]
WildShore Studio – The shop feels thoughtfully curated, clean design makes browsing relaxing.
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/[/url]
«Чистая Гармония» — это выездная и стационарная наркологическая помощь в одном маршруте: оперативный приезд врача на дом по Клину и району, аккуратный детокс с контролем жизненно важных показателей, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: никаких лишних процедур ради «видимости лечения» и никаких задержек с тем, что влияет на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, заранее согласуем смету и оставляем понятный план на 24–48 часов и первую неделю. Анонимность — базовый стандарт: выезд без опознавательных знаков, нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]наркологическая клиника клин клин[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток. Это позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам, которые находятся в тяжёлом состоянии или не могут самостоятельно приехать в стационар. Медицинская бригада прибывает в течение 40–60 минут, не используя специализированный транспорт и форму, чтобы сохранить анонимность. Врач проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает давление, частоту дыхания, уровень сознания и насыщение кислородом, после чего назначает детоксикационную капельницу с контролем дозировки.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
BloomStreet Deals – A fresh design paired with organized pages creates a smooth browsing vibe.
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно уфа[/url]
I pay a quick visit daily some web pages and blogs to read articles, except this webpage provides feature based content.
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
WildRose Collection – Boutique has a cozy and inviting vibe, discovered a few standout items.
Toma en cuenta esto para saber si un sitio es confiable y seguro antes de apostar. https://www.sex8.zone/home.php?mod=space&uid=11442517&do=profile
Инфузионная терапия — это не просто «быстрый раствор витаминов». При запое страдает водно-электролитный баланс, «плавает» давление и пульс, нарастает тревога, нарушается сон, проявляются тошнота и тремор. Правильно собранная капельница в Клину помогает вернуть жидкость и электролиты, поддержать печень, снизить вегетативные проявления, мягко стабилизировать нервную систему и подготовить переход на пероральные схемы. Важно избегать избыточной седативной нагрузки и опасных сочетаний: то, что человеку «помогало раньше», может конфликтовать с его нынешними показателями. Поэтому каждое назначение мы увязываем с реальными цифрами осмотра и тем, что уже было принято за двое суток.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/]капельница от запоя препараты[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в новокузнецке[/url]
трек получен, ребятам уважуха:rasta: Купить онлайн мефедрон, амфетамин, марихуану Вчера оплатил, сегодня уже трек скинули. Пока все ровно, посмотрим что придет…..Также возможен выбор курьерки, если какая-то из них не возможна для доставки в ваш город
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Подробнее – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/anonimnaya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd/
Design-Driven Marketplace – Navigation feels natural and the items reflect high design quality.
Основные этапы лечения включают:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Интернет на даче в Московской области теперь работает стабильно благодаря мобильному решению. Установка прошла быстро и аккуратно. Скорость позволяет работать и отдыхать онлайн. Связь уверенная и постоянная. Очень довольны подключением: как подключить интернет на даче
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Urban Lifestyle Picks Lane – Clean and organized layout enhances the user experience and browsing ease.
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh
Fashion Life Hub – Items offered here appear trendy, shopping is enjoyable and convenient.
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя мурманск[/url]
Curated Experience Hub – Items are well-presented and the navigation feels effortless.
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak biedt professionele schoonmaakdiensten. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak biedt duurzame reiniging aan kantoren. LCF
Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak bevordert gezondheid op
de werkplek. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak vereenvoudigt dieptereiniging met milieuvriendelijke schoonmaakmiddelen. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak verzorgt glasbewassing en schoonmaak van keukens.
LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak bewaakt
kwaliteitsgarantie voor alle diensten. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak verzorgt vaste klant communicatie aan. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak
Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak helpt facilitaire dienstverlening effectief.
LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak verzorgt sanitair
grondig en professioneel. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak biedt kantoor schoonmaak met duurzaamheid als prioriteit.
De Kantoren schoonmaak van LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam maakt gebruik van milieuvriendelijke schoonmaakmiddelen. De Kantoren schoonmaak van LCF
Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam verzorgt desinfectie en onderhoud
aan kantoren. De Kantoren schoonmaak van LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak
Amsterdam faciliteert schone werkplekken in Amsterdam. De Kantoren schoonmaak van LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam helpt professionele reiniging en schoonmaak.
De Kantoren schoonmaak van LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam garandeert
klanttevredenheid en kwaliteit. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak
Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak verzorgt effectieve schoonmaakdiensten voor kantoorschoonmaak in Amsterdam.
LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak ondersteunt duurzaamheid in schoonmaakbedrijven. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak verzorgt reiniging en schoonmaak aan kantoren en facilitaire diensten. LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak vereenvoudigt schone en gezonde werkplekken in Amsterdam.
Schoonmaakbedrijven in Amsterdam kiezen LCF Kantoren Schoonmaak Amsterdam Kantoren schoonmaak voor betrouwbare dienstverlening.
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому в тольятти[/url]
How To Make Seo
seostart.com.ua
Преимущество стационара — предсказуемость и скорость. Рядом врач и медсестра, можно оперативно сдать анализы, сделать ЭКГ или дополнительные обследования, а главное — не «тянуть» с корректировкой схемы. В контролируемой среде быстрее нормализуются сон и аппетит, уходит тремор, снижается тревога. Для пациентов с сопутствующими диагнозами это особенно важно: диабет, гипертония, аритмии, хронические заболевания ЖКТ требуют аккуратной, согласованной тактики.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]besplatnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Все ровно, пасыль забрал, всем доволен! Купить онлайн мефедрон, амфетамин, марихуану Где продавец то? Мысли самые печальные…ттВерный второй трек. Но у этой курьерки система мониторинга развита не особо хорошо и бывало такое, что посылка доходила за день-два, ее уже получили, а трек начинал биться только через пару дней после этого. Если в ближайшее время не заработает, то лучше звоните в курьерку и уточняйте.
artisancollectivehub – ArtisanCollectiveHub presents stylish, handcrafted products alongside modern designs in a smooth layout.
Клиника принимает 24/7 без очередей: ночной блок специально настроен под «трудные часы», когда усиливаются панические мысли и реактивность пульса. Для тех, кому легче дома, выездная служба приводит помощь в знакомое пространство; если нужны короткие контрольные включения, применяем видеосвязь вечером (15–20 минут), чтобы корректно настроить ритуалы засыпания, дыхательные циклы и «световые правила». Маршрут фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения — этот документ доступен команде по ролям и защищает от «повторов заново», когда формат меняется (дом – амбулатория – стационар).
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в ставрополе[/url]
PeopleExpressHub – Layout is clean, browsing is effortless, and connection-focused products are easy to explore.
Чтобы убрать неопределённость, мы делим первые часы на короткие окна. У каждого окна есть цель, действия и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один элемент, а следующая проверка назначается сразу — без хаотичного «усиления всего сразу».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в мурманске[/url]
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике новокузнецк[/url]
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Сначала — очная оценка, проверка противопоказаний и совместимости с текущими лекарствами. Далее — инфузионная терапия для коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы, мягкая анксиолитическая и снотворная поддержка по показаниям. Визит обычно занимает от 60 до 120 минут; при необходимости капельницы проводятся медленно, с наблюдением. После процедуры пациент получает понятные памятки: что и когда пить, когда спать, какие признаки считаются тревожными и требуют повторного осмотра или перевода в стационар.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва отзывы[/url]
В реальной городской ткани Ставрополя на самочувствие влияет не только схема лечения, но и логистика: утренние заторы на въезде, плотная застройка частного сектора, шумные перекрёстки. Мы заранее «поглощаем» эти риски организацией: секторные выезды, согласованная парковка, нейтральная переписка без «говорящих» терминов, при необходимости — курьерская доставка расходников отдельно от врача, чтобы на месте сразу переходить к оценке и запуску инфузии. Пациенту не нужно «вписываться» в систему — система подстраивается под реальную жизнь человека, экономя десятки минут и снижая сенсорную нагрузку перед первой ночью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Трек получил, всё ровно! Закладкой купить альфа-пвп, мефедрон, бошки проблемы с обслуживанием.Я 13 числа сделал заказ,и до сих пор жду Макс,думаю магазин Честный и всё придёт )))))))!!!!!!!!Как придёт отпишусь обязательно сюда,компенсация обещена была 6 г :yeah:,всё же думаю Не разочаруют!
Мобильный 4G интернет на даче стал настоящим спасением. Работает стабильно, даже когда много устройств подключено одновременно. Установка выполнена аккуратно и быстро. Специалисты всё подробно объяснили. Теперь не чувствуем разницы между городом и дачей – https://podklychi.ru/
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-murmansk
Безопасность — это не лозунг, а набор решений. Мы избегаем «жёстких» седативных доз, которые создают видимость улучшения и повышают риск скрытых осложнений. Наращивание темпа инфузии происходит постепенно и увязано с динамикой симптомов и цифрами измерений. Любой шаг объясняется пациенту и семье: зачем он выбран, что считается нормальной волной улучшения, в какой момент нужно связаться с дежурным. Такой прозрачный формат снимает тревогу и помогает всем участникам действовать согласованно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru
shopper’s delight corner – Selections are eye-catching, browsing feels smooth and enjoyable.
Режим 24/7 — это не только открытая дверь, но и правильно расставленные акценты по часам суток. Ночью — больше поведенческих опор и короткие видеовставки, днём — контроль витальных, уточнение плана гидратации и питания, вечером — «световые правила» и дыхательные циклы. В каждом окне мы знаем, что именно проверяем и что считаем успехом: так исчезают импровизации и ненужные «усиления», а пациент получает предсказуемую траекторию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Мы не используем шаблон «на всех». Темп и сочетания зависят от давления, пульса, выраженности тошноты и тремора, уровня тревоги, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Детокс — это система шагов: допуск к терапии, коррекция воды и электролитов, поддержка печени, вегетостабилизация, осторожная работа со сном по показаниям, профилактика осложнений. Любое назначение проговаривается простым языком: зачем, как подействует, что считать нормальной динамикой, а что — поводом связаться с врачом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-klinu-s-vyezdom-na-dom/
Grand Forest Choices – Impressive selection, with smooth navigation throughout the site.
дайсон стайлер для волос купить цена официальный сайт с насадками [url=www.fen-dn-kupit-1.ru]www.fen-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в красноярске[/url]
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это управляемый медицинский процесс, в котором важны скорость запуска, точность вмешательств и тишина вокруг пациента. В наркологической клинике «СтаврВита» мы соединяем капельницы с объективным мониторингом и бережной организацией пространства: приглушённый свет, понятные инструкции без жаргона, «тихие окна» для связи и пошаговый план на первые трое суток. Наша задача — не «перебить» симптомы, а последовательно вернуть предсказуемость: ровный пульс, уменьшающийся тремор, переносимость воды и тёплой пищи малыми порциями, физиологичный сон без тяжёлой седации. Работаем круглосуточно — выездные бригады, амбулаторные слоты без очередей и стационарный блок с ночным постом объединены общей картой наблюдения, поэтому пациент не «начинает историю заново», когда формат меняется.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
жду пока ответят, обана повдер кинул на 29000….но прочитал и понял что магаз супер, жду в скайпе селлера! https://desinfectnn.ru Нужно 5 сообщений что бы написать модэратору, не обесутьэто самый ровный магаз братцы!!!) работаю с ними целый год, не разу даже нервы не потрепали) !!! конспирация на высоте, качество наилучшее!продован самый добрый и общительный аах) ну вы поняли! единственное жалко не разу проб бесплатных не получал(((
Highland Meadow Hub Online – Smooth experience and a visually calming, inviting atmosphere.
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
«Трезвый Компас» — выездная и стационарная наркологическая служба, которая проводит профессиональный детокс с капельницей от запоя в Клину и районе круглосуточно. Мы приезжаем анонимно, начинаем с очной оценки, согласуем допуск к терапии, подбираем состав инфузии без «универсальных коктейлей» и объясняем простым языком, чего ждать в ближайшие часы. Цель — снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, аккуратно наладить сон по показаниям и дать семье понятный план на 24–48 часов. Если риски высокие или дома невозможно обеспечить безопасную ночь, предложим стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-klinu-s-vyezdom-na-dom/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-klin8.ru
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в новокузнецке[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог новокузнецк[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в воронеже[/url]
I visited multiple web pages however the audio feature for audio
songs present at this web page is genuinely wonderful.
Если на первичном звонке звучат «красные флаги» (выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, скачки ритма), мы предлагаем стационарное окно мониторинга. При низком риске стартуем дома или амбулаторно и поддерживаем человека вечерними видеовставками по 15–20 минут, чтобы пройти «трудный час» без лишних поездок и паники.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Ниже — «скелет» визита. На месте врач адаптирует содержание под возраст, соматику, текущие лекарства и проявления абстиненции. Главная идея — быстро получить цифры, аккуратно запустить инфузию и заранее зафиксировать ориентиры, чтобы семья не импровизировала в «трудный час».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-stavropol15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Modern Classic Finds – Smooth shopping experience with a selection of timeless yet stylish items.
Две дороги для Артёма, Купить экстази, лсд, мдма, альфа-пвп, соль, меф Вот мой отзыв по работе данного магазина.по выходным курьерки не работают, соответственно и отправить мы не можем, отправки производятся в рабочии дни!
Вся динамика фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения. При переводе в амбулаторную точку мы не «сбрасываем» историю: решения продолжаются с учётом уже сделанного и реакции пациента на вмешательства.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru
He guardado https://nemapaincare.com/types-of-cancer/ en mi lista de recursos esenciales.
Posts como Types of Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Common and Rare Cancer Types son imprescindibles para una industria
que cambia tan rápido como es la aviación. El enfoque que le das a los nuevos combustibles sostenibles para la aviación me parece especialmente interesante.
¿Has pensado en escribir sobre el impacto de los SAF en un futuro próximo?
Sería un tema increíble para tu próximo post.
Ansioso por leer más!
Здесь
[url=https://whynotnails.us/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
FLO Store – Fashion deals look attractive, shopping experience is smooth and intuitive.
smartpurchasinghub – SmartPurchasingHub has a carefully arranged selection that makes shopping smooth.
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti/
BoutiqueFinderHub – Fast navigation, creatively presented items, and simple layout.
Urban Trend Corner Hub – Clearly displayed items and intuitive navigation enhance user experience.
Да мне 5 сообщений для лс нужно :Dа так месяц назад было все ровно) https://lis-market.ru когда вы зарядили?мои ребята зарядили вчера около 16-00 по мск ,минут за 15 до этого он добро дал и замолчал( переживаю очень так как отвечать мне.Я надеюсь лавочка не слилась с пацанскими деньгими… А то конкретная пичаль будет.У нас в регионе это большая сумма!!!и что за вещество
CrestBright Online – Featured products are placed clearly, giving users an intuitive experience.
The Everglen Store – Browsing was smooth and the warm tone of the shop made it easy to stay engaged.
your shopping corner – Products are well arranged, navigating feels easy and convenient.
Домашний маршрут выбирают, когда показатели стабильны и нет признаков тяжёлой соматики или спутанности сознания. Преимущество в сочетании скорости, приватности и приверженности: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а отсутствие переездов экономит силы. Врач «МедТоники» приезжает без маркировки, привозит мониторинг и расходные материалы, подбирает инфузии по состоянию, помогает восстановить режим сна и гидратации, даёт рекомендации по питанию и правила на 48–72 часа. Отдельный блок — работа с тревогой и тремором: корректируется медикаментозная поддержка, обсуждаются простые поведенческие техники, чтобы снизить вероятность импульсивных решений вечером. Домашний формат не подменяет наблюдение: назначаются точки связи, врач объясняет, когда нужен повторный визит, а когда достаточно телефонной коррекции. Для Москвы такой сценарий удобен ещё и тем, что его проще встроить в плотный график, не выпадая из рабочих и семейных ролей и не провоцируя лишних вопросов у окружающих.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-srochno/
Быстрая доставка , и высочайшее качество обслуживания! Думаю и сейчас ничего не изменилось. https://artcity-73.ru но за долгое сотрудничество с этимХа ха ребята смотрите беспредел! попробуйте написать правильно жабу ТСа и получится то что у меня, как бы с ошибкой! СКРИПТ!
Модель типа «раздеватор» — это цифровая система на базе ИИ, которая работает с фотографиями людей.
Она опирается на обученные модели для генерации альтернативных визуальных вариантов.
Функционирование подобных решений основана на распознавании форм.
Подобные нейросети вызывают интерес в контексте современных цифровых технологий.
раздеватор без цензуры
При этом важно учитывать моральные аспекты и вопросы конфиденциальности.
Применение подобных решений требует ответственного подхода.
Многие эксперты подчёркивают, что важно соблюдать нормы и правила.
В итоге, нейросеть-раздеватор является одним из направлений развития нейросетей, который нуждается в внимательном отношении.
Лобня — город коротких дистанций, но в острых ситуациях решает не километраж, а управляемость. Мы убираем паузы между решением обратиться и реальной помощью: на звонке быстро оцениваем риски, предлагаем безопасный старт в квартире или в палате, согласуем окно прибытия, объясняем что подготовить, и фиксируем честный диапазон стоимости. Цель — чтобы первые часы прошли по понятному плану, а не вслепую.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Нижний является значимым городом в европейской части страны.
Он расположен на слиянии Волги и Оки, что повлияло на формирование города.
Нижний Новгород известен своей историей и традициями.
Архитектура города сочетает старинные постройки и современные кварталы.
Нижний Новгород новости города для жителей
Здесь динамично растёт бизнес-инфраструктура.
Городская жизнь отличается активностью и множеством событий.
Он является значимой точкой на карте страны.
В итоге, Нижний Новгород остаётся привлекательным городом для жителей и гостей.
Blue Peak Online – Loved the balance of simplicity and visual appeal, very easy to browse.
Здесь
[url=https://centr7a.by/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]блекджек[/url]
атом казино отзывы Отзывы об Атом казино помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение о платформе. Читайте отзывы других игроков, чтобы узнать об их опыте и впечатлениях.
дайсон официальный сайт спб [url=http://fen-dn-kupit-1.ru]http://fen-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
Манжета резиновая ПМТД Металлоконструкции для ЛЭП и Кабеленесущие системы – для строительства линий электропередач и прокладки кабелей.
Не стоит сомневатся в этом магазе он ровный и проверенный времен! Всегда на высоте! Закладкой купить альфа-пвп, мефедрон, бошки работал я работал 2 года имея не малую клиентскую базу и тут решил я вас кинуть на 10 грамм, сам то подумай где ты это пишешь.Тут, оказывается, одна шайка- лейка. Мало того, что мое сообщение потерли, еще и нарушение влепили. Сочли провокацией, хотя писал чистую правду. Магазин меня кинул, прислав фигню, которую выбросил.
Exclusive Home Collections – Browsing feels smooth, with each product standing out for its quality.
«Клиника Трезвый Курс» организует вывод из запоя для жителей Лобни круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом без опознавательных знаков, аккуратные капельницы с индивидуальным составом, стационар с наблюдением и аппаратным контролем, а также поддержка семьи на первые дни, когда особенно важно не сорваться в прежний ритм. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никаких «универсальных коктейлей» и грубой седации ради видимости улучшения. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком, смета фиксируется до начала процедур, приватность встроена в процесс. Цель — не просто «полегчало», а безопасная стабилизация с предсказуемой ночью и понятным планом тихой недели.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/]вывода из запоя платно[/url]
заказать проект отопительной печи Купить проект камина – добавить в свой дом нотку роскоши и создать атмосферу уюта и романтики.
Go to our updated website : https://bergkompressor.ru/
What’s up to all, how is everything, I think every one is getting more from this web site, and your views are good in support
of new people.
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
играть в казино атом Играть в казино Атом: Погрузитесь в мир азарта и развлечений с огромным выбором игр на любой вкус. Слоты, рулетка, блэкджек, покер и многое другое ждет вас в Атом казино.
Contemporary Finds – Everything feels stylish and well-presented, browsing was easy and fun.
FPM Finds – Fashion options look great and organized, browsing feels simple and enjoyable.
Всем привет !!!? https://ivanichmos.ru Работаем с данным магазином! всем советую!”ДОБРА ТЕБЕ ЭСКИМОСИК”
Такое сочетание компонентов обеспечивает комплексное воздействие на организм, устраняя симптомы абстинентного синдрома и восстанавливая работоспособность. Процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога с постоянным наблюдением за артериальным давлением и пульсом.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого[/url]
атом казино регистрация Вход в Атом казино прост и удобен. Посетите официальный сайт и введите свои учетные данные, чтобы получить доступ ко всем функциям и играм.
Hello very nice blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also?
I’m satisfied to search out so many helpful information here in the publish, we
want work out more techniques in this regard, thank you for sharing.
. . . . .
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Санкт-Петербурге осуществляется под круглосуточным медицинским контролем с применением современных методов инфузионной терапии, препаратов для восстановления обменных процессов и купирования синдрома отмены. Главной задачей врачей является восстановление баланса между физическим и психическим состоянием, предотвращение осложнений и стабилизация основных жизненных функций.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
DailyStyleShop – Smooth layout, trendy pieces, and enjoyable user experience.
shopwiseonline – ShopWiseOnline features fresh, modern items with intuitive product details.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Санкт-Петербурге проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
заказать проект камина Купить проект русской печи – значит прикоснуться к традициям и насладиться теплом настоящей русской печи, которая не только обогреет ваш дом, но и позволит готовить вкуснейшие блюда.
Какую еще веточку ? Вы и так на нашей ветке где есть вся необходимая информация. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Шишки, Гашиш Может обсудим как избежать напастья копоф при получении посылки от курьера???Чет я совсем отупел, немогу найти прилавок, где товар бро, цена, наименование товара? Прайс в студию, на все услуги. От жизни походу отстал, правила поменяли походу, да?
Если при первичном звонке фиксируем «красные флаги» (угнетение сознания, выраженная одышка, резкое падение SpO?, нестабильная аритмия), сразу предлагаем стационарное наблюдение с ночным постом. При низких рисках начинаем дома, но держим низкий порог для эскалации, чтобы не терять время, если состояние меняется.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Daily Hub Lane – Clear presentation of products, intuitive browsing, and fast-loading pages.
Нарколог на дом в Челябинске — это услуга, которая позволяет получить профессиональную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости посещения клиники. Такой формат особенно востребован в случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно прибыть в медицинское учреждение или нуждается в конфиденциальной помощи. Врач-нарколог выезжает по указанному адресу, проводит осмотр, оценивает состояние и подбирает оптимальную терапию. Квалифицированное вмешательство помогает избежать осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в течение первых часов после прибытия специалиста.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru
Порча через наркотиков — этто
групповая проблема, обхватывающая физиологическое, психологическое также общественное состояние здоровья человека.
Утилизация таковских наркотиков,
как кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» чи «бошки», может огласить ко неконвертируемым
результатам яко чтобы организма, так равно
чтобы среды в течение целом. Но даже при эволюции зависимости возможно электровосстановление — ядро, чтобы энергозависимый человек обернулся согласен помощью.
Эпохально памятовать, что наркомания врачуется, и оправдание бацнет шансище на
свежую жизнь.
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-sankt-peterburge-czeny/
Soft Sky Picks Online – Soft color design and clean layout make exploring smooth.
Трубы железобетонные безнапорные Грунтовка – первый шаг к качественному ремонту и строительству, обеспечивающий надежное сцепление материалов и защиту от коррозии.
Вчера списался с продавцов, сказал сегодня отправит. Заказал 7 грамм ам1220 и 3 грамма 4фа надеюсь весь товар мне отправят с новой партии а то про 4фа больно не хорошие отзывы пишут с прошлой партии. https://ivanichmos.ru кто нить последнее время покупал чего ??? всё ровно ?Благо им! Биза на высоту
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://place01.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Анонимность — стандарт по умолчанию. Документация ведётся нейтрально и только в объёме, необходимом для оказания помощи. Мы не информируем третьих лиц, не вступаем в контакты с работодателями или соседями. Визит осуществляется на немаркированном авто, общение — коротко и по делу, доступ к карте пациента ограничен принципом «минимально необходимого». Если требуется стационар, используем отдельный вход и «тихий коридор», а по выписке возвращаем тот же маршрут обслуживания на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Refined Interiors Collective – Stylishly arranged items with an elegant, intuitive layout.
Если у человека выраженное обезвоживание, скачки давления и пульса, эпизоды спутанности сознания, упорная рвота, «дергающийся» сон или тяжёлая сопутствующая патология, стационар закрывает главный риск — непредсказуемое течение синдрома отмены. Круглосуточный мониторинг позволяет динамически корректировать схемы, подключать лабораторные и инструментальные исследования по показаниям, своевременно восполнять дефициты и удерживать стабильный сон. На практике «короткое окно» госпитализации (24–48 часов) нередко дешевле на дистанции: оно предотвращает осложнения и повторные вызовы, которые растягивают курс и увеличивают суммарные затраты. Для жителей Москвы мы разносim визиты по времени, используем отдельные входы и «тихие» маршруты, чтобы сохранить приватность. После стабилизации маршрут переводится в амбулаторный или домашний формат: пациент получает план питания и активности, контрольные контакты и правила, при каких признаках связаться немедленно, не дожидаясь «как будет утром».
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-moskve
Мы работаем с вниманием к деталям повседневности: как человек засыпает на фоне вечернего света, сколько воды переносит малыми глотками, как реагирует на цифровые уведомления, есть ли привычные «включатели» тяги и как на организм влияет шумное окружение. Врач и куратор переводят этот жизненный контекст в ясные, измеримые ориентиры: время до сна, число пробуждений, вариабельность пульса к сумеркам, объём воды, аппетит, переносимость тёплой мягкой пищи. Решения принимаются адресно и последовательно, чтобы сохранять ясность днём и избегать ненужной фармаконагрузки.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/
Lifestyle Finds Collection – Clean interface with a wide range of modern products for easy shopping.
Оплатил заказ, жду селлера. Закладкой купить альфа-пвп, мефедрон, бошки Вот отзыв за этот эйфор:Крутой магаз
Домашний формат уместен, когда симптоматика контролируема и вечером рядом может остаться взрослый помощник. Преимущество Лобни — короткие дистанции внутри города, поэтому врач приезжает быстро, без шума и эмблем. На месте мы не торопимся: собеседование по факту последних 48 часов, измерения давления, пульса, сатурации и температуры, короткий неврологический скрининг, сверка аллергий и уже принятых препаратов. После допуска к терапии запускается инфузия: сначала — коррекция воды и электролитов, затем — поддержка печени и ЦНС, при необходимости — противорвотные и анксиолитические препараты. Темп настраивается по динамике, чтобы снять тремор и тошноту без «перекручивания» организма в сон с тяжёлым просыпанием. По итогам визита — понятные правила на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и согласованное окно контрольного контакта. Домашний маршрут экономит часы, снижает социальную тревогу и делает первые сутки предсказуемыми.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-lobne/
https://t.me/uhrenGermany026
Лобня — город коротких дистанций, но в острых ситуациях решает не километраж, а управляемость. Мы убираем паузы между решением обратиться и реальной помощью: на звонке быстро оцениваем риски, предлагаем безопасный старт в квартире или в палате, согласуем окно прибытия, объясняем что подготовить, и фиксируем честный диапазон стоимости. Цель — чтобы первые часы прошли по понятному плану, а не вслепую.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/
Trail of Fashion – The design feels modern, with well-highlighted pieces throughout.
дайсон официальный сайт стайлер для волос с насадками цена купить [url=fen-dn-kupit-1.ru]fen-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в самаре[/url]
Первый полноценный сон — переломный момент в выводе из запоя. В «АлкоМед Балашиха» мы создаём условия для него с первого дня: затемнение, тишина, комфортная температура, минимизация стимулов, ранний отбой. Если требуется, подключаем мягкие седативные схемы под мониторинг. Утром — контроль показателей, уточнение дозировок, план активности «по силам», корректировка питания и воды. Мы заранее проговариваем, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, умеренная слабость), а какие — требуют связи со специалистом. Чёткая ночная стратегия снижает импульсивность и убирает главный триггер срывов — усталость и бессонницу, из-за которых даже корректно подобранные инфузии теряют эффективность к вечеру следующего дня.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
Постройте свой идеальный [url=https://karkasnye-doma-pod-klyuch5.ru]каркасные дома спб[/url] и наслаждайтесь комфортом и современными технологиями!
Такое жилье прекрасно подходит для семей с детьми, обеспечивая им комфорт и безопасность.
Clickping Creative Finds – Smooth navigation and a clear design make the browsing experience delightful.
Для больших строительных проектов лучшим вариантом будет [url=http://rukrepezh.ru]купить крепеж оптом[/url], чтобы сэкономить средства и времени.
позволяет сэкономить значительные средства . Это позволяет получить необходимые материалы в большом количестве . При этом, следует сравнивать цены в разных магазинах.
Купить крепеж оптом является лучшим решением для крупных проектов . Это связано с тем, что дает возможность сократить расходы. Кроме того, можно получить более выгодные условия поставки .
Купить крепеж оптом дает возможность приобрести большое количество необходимых изделий . Это связано с тем, что позволяет купить необходимое количество материалов . При этом, важно учитывать качество предлагаемых изделий .
Купить крепеж оптом является лучшим решением для крупных проектов . Это связано с тем, что дает возможность сократить расходы. Кроме того, можно договориться о скидке.
Купить крепеж оптом дает возможность приобрести большое количество необходимых изделий . Это связано с тем, что дает возможность оптимизировать процесс закупок. При этом, следует выбирать надежного поставщика.
Купить крепеж оптом является лучшим решением для крупных проектов . Это связано с тем, что дает возможность сократить расходы. Кроме того, можно насладиться большим выбором товаров.
Купить крепеж оптом является наиболее эффективным способом закупки. Это связано с тем, что оптовая покупка снижает цену за единицу . При этом, важно выбирать надежного поставщика .
Купить крепеж оптом выгодно для многих предприятий . Это связано с тем, что позволяет купить необходимое количество изделий . Кроме того, при оптовой покупке можно получить более выгодные условия поставки .
Инфузионная терапия — это набор узких вмешательств под конкретную картину, а не «магический состав». Регидратация улучшает тканевую перфузию и снимает головную боль от обезвоживания; электролиты стабилизируют нервно-мышечную передачу и сердечный ритм; печёночная поддержка уменьшает токсическую нагрузку и тяжесть в правом подреберье; гастропротекция и противорвотные защищают слизистую и убирают рвотный компонент. При выраженной тревоге и бессоннице добавляется мягкая анксиолитическая поддержка — дозы подбираются так, чтобы стабилизировать, а не «выключить». Мы не назначаем исследования «для галочки»: анализы и ЭКГ используются тогда, когда их результат меняет решения «сегодня». Такой подход снижает побочные эффекты, делает результат предсказуемым и удерживает бюджет от «скачков». На этой базе уже обсуждается следующий шаг: амбулаторное наблюдение, краткие психообразовательные сессии, а при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru
Fashion Trend Choices – Trendy selections seem appealing, browsing is smooth and enjoyable today.
Вот получил вчера 2 -й заказ…..отсылают быстро, качество отличное, плюс девайсы в которые всё ныколось в виде приятного бонуса… https://kamasutrajpg.ru same shit, broвсем доброго времени суток.. вот что ты написал это вобше такая нелепасть во первых этот магазин сколько робит не разу не кого не кинул во вторых по 0.5 магазин закладки не делает тебя просто как лошка очередного развели в аське или скайпе хз где ну тебя подкинули на ровном месте кидай и дальше всем подрят на шет))))будь умнее и внимательней страхуйся, много не кури мозг высохнит))))
Прежде чем перейти к таблице, отметим смысл. Это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые диагнозы и динамику симптомов, но логика процесса остаётся неизменной: от безопасности к устойчивости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-chekhove
Atom casino Атом казино – это современная платформа для любителей азартных игр, предлагающая широкий спектр развлечений и возможностей для выигрыша. Казино стремится создать безопасную и захватывающую атмосферу, привлекая как опытных игроков, так и новичков.
GoldenPeak Crafted Goods – Some truly unique creations, and the browsing experience felt very smooth.
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов город[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]эротика[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит последовательный процесс лечения, где основное внимание уделяется безопасности, контролю состояния и постепенной адаптации. При поступлении проводится диагностика с оценкой степени зависимости, сопутствующих патологий и психологических факторов, влияющих на развитие заболевания. На основании полученных данных формируется персонализированный план терапии, включающий медикаментозные и немедикаментозные методы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
магазину респект https://erbek-rus.ru я тут походу единственный кто остался недоволен.(Всегда на высоте)
Особенность петербургского контекста — большая доля интеллектуального труда и проектной занятости. Мы учитываем это при выборе методики: отдаем предпочтение схемам, которые не «глушат» когнитивную активность и позволяют быстро возвращаться к задачам. Если требуются краткие больничные листы, предоставляем корректные медицинские документы без «ярлыков».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]как происходит кодирование от алкоголизма санкт-петербург[/url]
GoldenMeadow Treasures – Pleasantly decorated space with homely charm and curated items.
https://t.me/uhrenGermany026
Здесь
[url=https://www.crimsoneducation.org/uk]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Daily Finds Online – Fast-loading pages, intuitive navigation, and neatly presented product variety.
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в ставрополе[/url]
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в балашихе[/url]
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru
Инфузионная терапия — это набор узких вмешательств под конкретную картину, а не «магический состав». Регидратация улучшает тканевую перфузию и снимает головную боль от обезвоживания; электролиты стабилизируют нервно-мышечную передачу и сердечный ритм; печёночная поддержка уменьшает токсическую нагрузку и тяжесть в правом подреберье; гастропротекция и противорвотные защищают слизистую и убирают рвотный компонент. При выраженной тревоге и бессоннице добавляется мягкая анксиолитическая поддержка — дозы подбираются так, чтобы стабилизировать, а не «выключить». Мы не назначаем исследования «для галочки»: анализы и ЭКГ используются тогда, когда их результат меняет решения «сегодня». Такой подход снижает побочные эффекты, делает результат предсказуемым и удерживает бюджет от «скачков». На этой базе уже обсуждается следующий шаг: амбулаторное наблюдение, краткие психообразовательные сессии, а при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/skolko-stoit-kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-lyubercah/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru
оТЛИЧНЫЙ МАГАЗ НАСЛЫШАН https://arkadia-club.ru спасибо магазу!!!угу, “на глазок” отсыпали. купи весы и взвесь нормально. На вид оно может показаться как больше так и меньше…
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Санкт-Петербурге — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Worldwide Commerce Shop – Offers a global perspective with easy navigation and organized presentation.
Refined Home Commerce – The store layout is clean, highlighting practical, high-quality items.
Чтобы помощь была прозрачной и управляемой, каждый этап имеет цель, индикаторы безопасности и эффективности, а также понятное «окно оценки» результата. Коррекции проводятся «штучно», по правилу одного изменения — это защищает от полипрагмазии и позволяет читабельно видеть вклад каждого шага.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Запись и подтверждение — через защищённые каналы; визиты — без опознавательных знаков; в расписании используются шифры вместо фамилий, информирование семьи — только с вашего согласия. Когда страх огласки уходит, люди обращаются вовремя и лучше соблюдают рекомендации — это напрямую улучшает прогноз и экономит бюджет.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy/
«Ищете надежное зеркало для входа в казино Вавада ? Наш сайт предлагает актуальные и проверенные зеркала Вавада, которые гарантируют стабильный доступ к любимым играм даже при блокировках основного ресурса. Вавада — это популярное онлайн-казино с широким выбором слотов, рулетки, покера и других азартных развлечений. Используя зеркало Вавада, вы сможете быстро и безопасно войти в личный кабинет, пополнить счет, вывести выигрыши и наслаждаться бонусами без ограничений. Мы регулярно обновляем ссылки, чтобы обеспечить бесперебойный доступ и защиту ваших данных. На нашем портале вы найдете подробные инструкции по использованию зеркала, советы по регистрации, актуальные промокоды и обзоры лучших игр. Вход через зеркало Вавада — это простой способ обойти технические блокировки и играть в любое время и в любом месте. Не упустите шанс испытать удачу и выиграть крупные призы с помощью надежного зеркала казино Вавада! Посетите наш ресурс прямо сейчас и получите доступ к официальному зеркалу, чтобы наслаждаться азартом без преград.»
В Екатеринбурге бригады выезжают 24/7, покрывая как центральные районы, так и отдалённые кварталы. Координатор уточняет только то, что влияет на безопасность: принимаемые лекарства и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов, исходные значения давления и пульса, а также бытовые условия — можно ли обеспечить «тихое окно» на 2–3 часа, есть ли свободная розетка и место для полулёжа. Врач приезжает с портативным мониторингом, расходными материалами и резервным планом на случай повышенной реактивности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому екатеринбург[/url]
фен dyson оригинал купить [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-1.ru]фен dyson оригинал купить[/url] .
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
хуясе надо было сначало уточнить а что брали хоть? ио названижю вещества https://uniongroup.biz Минус оказался только один, и это ожидание, вместо обещанных 3-5 , пришлось ждать больше недели. Не знаю чья эта заслуга отправителя или доставки, но это немного напрягало.Снова всё на высоте)заказывал 2 г тусишки!попросил пробник 5МЕО) получил)))))))))
modernmarketplace – ModernMarketplace has thoughtfully arranged products and a seamless interface for users.
Весь процесс можно представить следующим образом:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом челябинск[/url]
It is actually a great and helpful piece of info. I’m satisfied that you
shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this.
Thank you for sharing.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Труба из драгоценных металлов палладиевая 400х10х0.7 мм ПдСр60-40 ТУ Гарантированное качество и изысканный дизайн – купите драгоценные трубы для ювелирных украшений, машиностроения и архитектуры. Широкий выбор и высокое качество! Доставка по России.
This info is invaluable. How can I find out more?
Городская среда Калининграда — контрастные подъезды, близость моря с переменчивым ветром, плотный сезонный трафик — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому маршруты организованы «тихо»: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок и очередей, короткая регистрация, приглушённая тёплая подсветка в зоне ожидания, отсутствие громких объявлений. Коммуникация с пациентами и близкими строится через защищённые каналы, а уведомления приходят в «беззвучном» режиме в согласованные «окна». Такой дизайн не ради «красоты сервиса», а ради клинического эффекта: чем меньше сенсорной нагрузки, тем быстрее выравнивается пульс к вечеру, тем легче возвращается переносимость питья и тёплой пищи, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в калининграде[/url]
«Клиника Трезвый Курс» организует вывод из запоя для жителей Лобни круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом без опознавательных знаков, аккуратные капельницы с индивидуальным составом, стационар с наблюдением и аппаратным контролем, а также поддержка семьи на первые дни, когда особенно важно не сорваться в прежний ритм. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никаких «универсальных коктейлей» и грубой седации ради видимости улучшения. Каждый шаг объясняется простым языком, смета фиксируется до начала процедур, приватность встроена в процесс. Цель — не просто «полегчало», а безопасная стабилизация с предсказуемой ночью и понятным планом тихой недели.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-lobne
https://t.me/uhrenGermany026
FVC Collections – Products seem reliable, exploring the site feels quick and pleasant.
Городская среда Калининграда специфична: морской ветер, сезонные пробки, яркие витрины в вечерние часы. Эти факторы часто усиливают тревожность и мешают засыпанию. Поэтому мы проектируем выезд «мягко»: согласованная парковка, немаркированный вход, короткий маршрут до места процедуры, отсутствие громких звонков и «визуального шума» у порога. Родственникам предоставляем «тихие окна» связи — короткие апдейты в заранее оговорённое время без лишних подробностей. Такой формат не просто комфортнее, он клинически полезен: чем меньше стимулов, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях» и тем стабильнее проходит первая ночь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в калининграде[/url]
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru
https://thenationonlineng.net/
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь самара[/url]
Запой — это не только усталость и похмелье. В первые часы нарастают обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон и аппетит. На этом фоне резко возрастает риск аритмий, судорожной готовности, ухудшения когнитивных функций и травм вследствие падений. «МедТоника» организует помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один на один с симптомами: с первого звонка дежурный врач уточняет длительность и объём употребления, принимает во внимание сопутствующие заболевания и лекарства, оценивает риски по давлению, пульсу, сатурации и ориентирует, где безопаснее стартовать — на дому или в стационаре. Цель первых суток — снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и поведению, чтобы далее перейти к предсказуемой стабилизации. Когда есть ясный план на 48–72 часа, снижается вероятность срыва и импульсивных решений, которые обычно и ломают прогресс.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve-nedorogo
Главная цель — безопасно стабилизировать состояние, вернуть контроль над сном, гидратацией и базовой активностью в первые сутки и удержать результат. Для этого мы используем модульный подход: один этап — одна клиническая задача — один измеримый маркер. Такой принцип исключает «гонку доз», снижает риск перегрузки объёмом и делает прогноз понятным для пациента и близких. Мы сознательно разделяем «короткие эффекты» (уменьшение тошноты, сглаживание тахикардии) и «эффекты консолидации» (устойчивый сон, ясность утром), чтобы каждая корректировка была точной и доказуемой.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/narkolog-nizhnij-novgorod-na-dom
Перед таблицей короткий переход: мы сначала исключаем несовместимости и только потом начинаем инфузии. Это защищает от скрытых конфликтов препаратов, на которые «универсальные коктейли» просто не смотрят.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lobnya8.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-lobne/
«АльфаДетокс» в Чехове — это стационарный маршрут вывода из запоя с круглосуточным наблюдением и быстрыми медицинскими решениями. Мы принимаем без очередей, проводим очную оценку, допускаем к терапии и запускаем управляющий детокс с аппаратным контролем и лабораторными исследованиями по показаниям. Наша цель — не просто поставить капельницу, а безопасно стабилизировать давление и пульс, снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, наладить сон и дать понятный план ближайших дней. Анонимность встроена в процесс, вы общаетесь с командой спокойно и без лишней огласки, а все назначения объясняются простым языком, чтобы вы понимали логику каждого шага.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-chekhov8.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
intentionalmarkethub – IntentionalMarketHub offers carefully selected items in a smooth and refreshing layout.
Курс терапии в клинике состоит из нескольких последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение конкретных целей — от снятия интоксикации до восстановления психологического равновесия. Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и минимизировать вероятность рецидива. На всех стадиях лечения ведётся контроль состояния пациента, а также постоянная корректировка назначений в зависимости от реакции организма.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kazan
Отличный магазин с отличным продуктом. https://samara-bt.ru С Новым Годом всех поздравляю,очень рад сотрудничеству с данным магазином,желаю только хорошего!Респектос бразы радуете не только Россию но и Украину )) отличный магаз
Запой — это не только усталость и похмелье. В первые часы нарастают обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон и аппетит. На этом фоне резко возрастает риск аритмий, судорожной готовности, ухудшения когнитивных функций и травм вследствие падений. «МедТоника» организует помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один на один с симптомами: с первого звонка дежурный врач уточняет длительность и объём употребления, принимает во внимание сопутствующие заболевания и лекарства, оценивает риски по давлению, пульсу, сатурации и ориентирует, где безопаснее стартовать — на дому или в стационаре. Цель первых суток — снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и поведению, чтобы далее перейти к предсказуемой стабилизации. Когда есть ясный план на 48–72 часа, снижается вероятность срыва и импульсивных решений, которые обычно и ломают прогресс.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve-nedorogo
EverLine Essentials – Strong artisan aesthetic, with every piece presented beautifully.
Howdy! This blog post couldn’t be written much better! Looking at this article reminds me of my
previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this.
I’ll forward this post to him. Fairly certain he’ll have a very good read.
Thank you for sharing!
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
Incredible many of wonderful info!
best online casino canada real money https://bhcmerced.org/canadian-casino-online/ best online casino sites canada
Чтобы помощь была прозрачной и управляемой, каждый этап имеет цель, индикаторы безопасности и эффективности, а также понятное «окно оценки» результата. Коррекции проводятся «штучно», по правилу одного изменения — это защищает от полипрагмазии и позволяет читабельно видеть вклад каждого шага.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена казань[/url]
«НеоТрезвие СПБ» работает в парадигме доказательной наркологии. Мы используем медикаментозные и психотерапевтические подходы, а также их комбинации. Выбор зависит от клинического запроса, сопутствующих диагнозов и предпочтений пациента. Ниже — сравнительная таблица, которая отражает практический смысл каждого направления.
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-sankt-peterburge/
После введения капельницы пациент получает «вечернюю карточку»: правила гидратации малыми порциями, световую гигиену, два-три спокойных действия на вечер и чек-лист признаков, при которых нужно связаться с дежурным врачом. Такой бытовой протокол повышает переносимость терапии и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/[/url]
Перед таблицей важный переход: это ориентир, а не жёсткое расписание. Врач адаптирует длительность и насыщенность этапов под возраст, фоновые заболевания и входное состояние, но логика последовательности остаётся неизменной — от безопасности к устойчивости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]narkolog-i-psihiatr-v-lobne[/url]
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
casino online slots [url=https://studio-pulse.ru/]casino online slots[/url] .
https://www.zazzle.com/mbr/238846341466250645
https://www.boav.ru/2012/05/samodelnyj-traktor-s-dizelnym-dvigatelem/comment-page-1/?unapproved=176827&moderation-hash=0cbec3b563c1915372b7f548d0fa6b0a#comment-176827
lbs это [url=https://shkola-onlajn1.ru/]shkola-onlajn1.ru[/url] .
Waterfront Bright Store – Soft tones and intuitive structure make browsing peaceful and straightforward.
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Детальнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru
А сейчас работает магазин? https://mobile-navi.biz Новичка 1к10* само то!!!!!!!!!!!!Добрый день! А можно поинтересоваться – в связи с чем сменилась курьерская служба?
http://probki.kirov.ru/content/reshenie-492024-0#comment-35132650
https://successcircle.online/read-blog/20524
https://home.dlybabi.ru/planirovka-i-pereplanirovka-sanuzla-v-sankt-peterburge/#comment-133498
Ключ к эффективному выведению из запоя — гибкая персонализация. Мы не настаиваем на «универсальных» капельницах: сначала очная оценка, затем тест переносимости и лишь после — основная инфузия с контролем витальных показателей (АД/ЧСС/SpO?/температура) и субъективной реактивности (тошнота, тремор, тревога по шкале 0–10). Такой подход позволяет мягко провести детоксикацию, восстановить сон, стабилизировать вегетативную нервную систему и уменьшить «шум» организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это не «волшебная таблетка», а четко структурированный этап комплексного лечения, который должен вписываться в общий терапевтический план: диагностика, стабилизация состояния, выбор методики, юридически корректное информированное согласие, сопровождение и профилактика рецидивов. В наркологической клинике «НеоТрезвие СПБ» приоритет — безопасность, предсказуемость и конфиденциальность. Мы не перебираем методы «на удачу», а подбираем технологию с учетом клинического профиля, мотивации, социализации и коморбидных факторов (тревога, депрессия, соматические заболевания).
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы санкт-петербург[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, где каждая деталь важна: от скорости выезда до состава инфузии и «тихой» среды дома. В наркологической клинике «КазаньДетокс Медлайн» мы придерживаемся принципа поэтапной стабилизации: сначала безопасный старт и оценка рисков, затем прицельные капельницы и, при необходимости, краткосрочное наблюдение. Такой подход исключает «универсальные коктейли» и делает результат прогнозируемым: снижение интоксикации, выравнивание вегетативных реакций, восстановление сна и аппетита. Анонимность встроена в протоколы: немаркированный выезд, лаконичная документация, один доверенный контакт для связи 24/7, нейтральные формулировки без стигмы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
https://www.bandsworksconcerts.info/index.php?codde1xbet
В Екатеринбурге бригады выезжают 24/7, покрывая как центральные районы, так и отдалённые кварталы. Координатор уточняет только то, что влияет на безопасность: принимаемые лекарства и дозы, аллергии, эпизоды судорог/психозов, исходные значения давления и пульса, а также бытовые условия — можно ли обеспечить «тихое окно» на 2–3 часа, есть ли свободная розетка и место для полулёжа. Врач приезжает с портативным мониторингом, расходными материалами и резервным планом на случай повышенной реактивности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
Этап
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Contemporary Artisan Hub – The site highlights creativity and craftsmanship with easy navigation.
Excellent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how
can i subscribe for a blog site? The account aided me a appropriate deal.
I were a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered brilliant transparent concept
Все шаги фиксируются в карте наблюдения. Если динамика «плоская», меняется один параметр (скорость/объём/последовательность), и через оговорённое окно проводится повторная оценка. Это снижает риск побочных реакций и сохраняет дневную ясность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в калининграде[/url]
Такая «ступенчатая» логика позволяет видеть вклад каждого решения и снижает риск нежелательных ощущений. Мы избегаем параллельных «усилений», чтобы не терять управляемость.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого калининград[/url]
Everyday Modern Living – Everyday lifestyle items presented in a clear and practical way.
FuturePath Select – Smooth navigation and tidy product display make exploration effortless.
Хорошо работает народ)) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Приносим извинения за возможные неудобства.Всем: счастья, мира, добра, любви!
The Autumn Edit – Great fall aesthetics throughout, everything looked carefully chosen.
Решение о выезде принимает врач с учётом симптомов и бытовых ограничений. Если совпадает хотя бы две позиции из списка ниже, лучше не откладывать звонок — управляемость состояния снижается каждый час.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kazani16.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
<Worldwide Artisan Picks – Smooth navigation with delightful artisan selections to explore.
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, в котором важна каждая деталь: от предварительного скрининга и выбора инфузионного контура до настройки среды и последующего наблюдения. В наркологической клинике «ЕкатеринбургМед Ренессанс» выезд организуется круглосуточно, врач приезжает на немаркированном транспорте, работает деликатно, без лишних вопросов и пафоса. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточного вмешательства»: одна клиническая цель на этап, один проверяемый показатель и один корректируемый параметр, чтобы сохранять предсказуемость и избегать перегрузок для организма.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ekaterinburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg-nedorogo/
אבל הייתה בהן רכות חדשה. היא הושיטה את ידה, נגעה בלחי, ואני נרתעתי מהמגע הזה. “עשית טוב, ארטמקה,” אמרה בשקט. – אני יודע כמה קשה היה לך. לא ידעתי מה לענות. הרגשתי ריק, אבל באותו היום שלי הוא הכינוי שלו-מקסימקה ושרביט. הלכתי לקובריק שלוש פעמים בשבוע, הוא לימד אותי אנגלית, ואני עזרתי לו כל מיני הנדסה. ומה שהפתיע אותי בו. הוא לא היה ילד שמבקש להסביר ובסופו של amiratsade.co.il
FindBetterDeals Shop – Products look attractive, exploring feels simple and fast.
Оплатил заказ, жду селлера. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Просто я попутал!Адекватных работников
התעלפה, שכבה על צדה, ניסתה לעצור את המאהב המהיר עם הידיים, אבל הוא היה בלתי נלאה, למרות הציפורניים שנחפרו בפרק כף היד. ואז, למרבה המזל, הגיעה גם האורגזמה האמיתית, שגרמה לאגן של נמוכה, מלאה בתאווה וכעס. “אנדרו, אני מצטער, אני-זה לא מה שאתה חושב -” היא התחילה לפטפט, ביטויים סטנדרטיים, שחוקים, שבוודאי נשמעו במיליוני חדרי שינה ברחבי העולם. אבל עיניה היו zura.co.il
Mossy Trail Market Store – Loved browsing this market, the earthy tones and simple layout feel calming.
Good info. Appreciate it! https://substack.com/home/post/p-181770081
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.rush-agency.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Я айтишник и к СМ не отношусь никаким боком. Про мою работу вы не знали и не узнали бы, если бы всё срослось. Я просто говорю про то, что не так уж и секурно у вас, личность выпаливается “на раз”. https://mlphotostudio.ru chem24.biz.ski заходи и приколисьОставляйте свои отзывы! Мы ценим каждого клиента нам важны ваши отзывы и мнения!
Читатели получат представление о том, как современные технологии влияют на развитие медицины. Обсуждаются новые методы лечения, персонализированный подход и роль цифровых решений в повышении качества медицинских услуг.
Углубиться в тему – https://psychedelic.ru/news/4203-kak-kodirovanie-pomogaet-borotsya-s-alkogolizmom
안녕하세요. msn을 통해 당신의 블로그를
찾았습니다. 이건 정말 잘 작성된 기사입니다.
북마크하고 당신의 유용한 내용을 더 읽기 위해 다시 올 것입니다.
포스트에 감사합니다. 확실히 돌아올 것입니다.
When someone writes an post he/she keeps the plan of a user in his/her brain that how a user can know it.
So that’s why this post is great. Thanks!
Ценю информацию, которую вы публикуете на kazino olimp. Большое спасибо!
https://u.to/keBfIg
Капельница от запоя в клинике в Нижнем Новгороде является одним из ключевых методов детоксикации организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Основная цель процедуры — быстрое и безопасное выведение токсинов, нормализация работы жизненно важных органов и стабилизация общего состояния пациента. Методика основана на внутривенном введении лекарственных растворов, которые восполняют дефицит жидкости, электролитов и витаминов, устраняя последствия интоксикации. Такой подход позволяет достичь значительного улучшения самочувствия уже в первые часы после начала терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому нижний новгород[/url]
бк мелбет [url=https://studio-pulse.ru/]бк мелбет[/url] .
Крепление для интерактивной доски Сенсорная панель для учебного класса: Мультитач панели для учебных аудиторий. Одновременная работа нескольких учеников. Поддержка Android и Windows.
дистанционное школьное образование [url=shkola-onlajn1.ru]shkola-onlajn1.ru[/url] .
Modern Daily Living Hub – Products are practical and stylish, and exploring the site is simple.
На мой взгляд лучше магазина нет https://arkadia-club.ru Хотя возможно привык к бычей реги, а ваша дает эффект похожий канаббмагаз работает ровно оперативно и бонус хороший дали хотя я даже не ожидал как и обещали на следующий день отправили,а орест посылок я думаю ТС как нибудь уладит этот вопрос главное подход к нему найти
אי אפשר היה להסתיר את זה מהסובבים אותו, ועד מהרה כל השכנים התחילו לגעת בה. זה הפריע לה במיוחד. הבחור היה חם, משתולל, טס לתוכה, עלה להם להיות לבד, ניפץ, אוחז בידיים אבן בצווארה פניו של האיש הבזיקו באור של הארה, אפילו קמט בגשר האף החליק, מה שהופך את פניו כמעט לנוער. בזמן שחיכינו, דיברנו על המפעל והמשפחות. הם הביאו כאן משקאות, ולא חיכו לסלטים, הם שתו. הבא haifapress.org.il
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость[/url]
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-murmansk-otzyvy/
Next Level Living Hub – Next-level design aesthetics combined with a simple and functional layout.
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Узнать больше – http://
Интерактивный дисплей для видеоконференций Алматы Интерактивная панель на мобильной стойке: Мобильность и удобство. Легко перемещайте панель между кабинетами на надежных колесах.
shoppersechoice – ShoppersChoice makes finding products easy and enjoyable with great design.
Адрес почты правильный, все проверил не 1 раз, ответьте хоть тут.ну будем надееться что и на этот раз TS войдет в положение и как нибудь обратит внимание на решение наших вопросов, компенсирует нам потраченые нервы и время на безсмысленное ожидание, главное ведь для магазина репутация! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Хочу выразить благодарность данному магазину за лучший товар, лучшие цены, за долгое время непрерывного сотрудничества, очень жду твоего возвращения к работе и появления долгожданного товара, чемикал лучший в своём деле. Очень жаль что на долгий период времени ты преостановил свою работу, надеюсь скоро наладятся поставки и наше сотрудничество возобновится! Чемикал лучший! На данный момент тебе нету равных на рынке RC, возвращайся скорей, мы ждём твоего возвращения с нетерпением!трек не работает тишина уже 3 дня прошло >< у всех все гуд а у меня щляпа как так почему ((( ?!?!?!?
В мегаполисе привычный ритм часто мешает системному лечению: плотный график, транспортные задержки, высокая социальная видимость. Чтобы терапия проходила спокойно, «НеоТрезвие СПБ» использует «немаркированную» логистику: нейтральные формулировки в документах, аккуратные визиты, разнесенные по времени консультации специалистов и персональный координатор. По желанию пациента часть этапов — образовательные сессии и посткодовое сопровождение — выполняются онлайн. Это снижает тревогу и делает маршрут лечения менее заметным для окружения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-sankt-peterburg/
FBV Hub – Items look solid and reliable, shopping experience is smooth and convenient.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IHJUI7TF
Piece of writing writing is also a excitement, if you know after that you can write if not it is complicated to write.
FullBloom Studio – Attractive design and well-organized sections provide a seamless browsing journey.
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-nizhnij-novgorod/
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в мурманске[/url]
Многие мне рекомендовали данный магазин как порядочный, надо попробовать! https://cocukendokrin.biz Сорь за многобукав, не попустило еще ;)отпишите народ за 5 iai кто брал спс заранее
smartdesignmarket – SmartDesignMarket provides a clean, organized interface and seamless browsing experience.
Если на телефонном этапе выявляются «красные флаги» — спутанность, выраженная одышка, «скачущий» ритм, неукротимая рвота, — мы рекомендуем короткое окно стационарного наблюдения. При низком риске целесообразно начать дома: привычная среда снижает сенсорную нагрузку, а телемедицинские включения вечером по 15–20 минут помогают пройти «трудный час» без поездок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Решение о срочном выезде принимается не из «желания поторопиться», а когда домашняя стабилизация действительно снижает риски. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых не стоит откладывать звонок. Любой из перечисленных признаков — повод для консультации, а их сочетание — для немедленного осмотра.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Ваши статьи о казино — информативные.
Olimp Casino
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Казани — это современный медицинский центр, специализирующийся на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основное направление деятельности заключается в проведении детоксикации, восстановлении работы нервной системы и формировании устойчивой мотивации к отказу от употребления психоактивных веществ. Все процедуры проводятся в условиях полной анонимности и медицинского контроля, что обеспечивает безопасность и доверие со стороны пациентов. Программа терапии строится по принципам доказательной медицины и индивидуального подбора лечебных средств.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kazan/
Если дома шумно (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости), организуем краткий «тихий» стационар с отдельным входом и камерными палатами. После стабилизации пациент возвращается домой, а амбулаторное сопровождение продолжается в удобном графике — через короткие очные визиты и дистанционные чек-ины.
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Soft Breeze Outlet – Loved the gentle feel of this shop, everything was simple to browse through.
Here’s what factors appear like for October 2022 for the page in question for the “surfer search engine marketing review” keyword. https://stjosephs-westberks.secure-dbprimary.com/westberks/primary/stjosephs/CookiePolicy.action?backto=https%3A%2F%2Fdvmagic.net
Здесь
[url=https://spacefortune.ltd/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Цены тут взвинчены до жопы не знаю кто тут умудряется брать, летом как то брал здесь не помню че но было фуфло конченное половина не растворилась хоть че делай хоть грей хоть танцуй ни че не помогло. Один плюс присылают быстро но нафиг такая быстрота Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Магазин работатет? отпишите кто совершил сделку в последнее времясегодня оплатил заказ..буду ждать доставки..протестирую.сообщу о качестве продукта
Основой терапии является сочетание медицинских, психотерапевтических и социальных методов. Такой подход обеспечивает устранение не только физиологических последствий зависимости, но и её психологических причин. Врачи клиники разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения, в котором учитываются стадия заболевания, общее состояние организма и личностные особенности пациента. Работа специалистов направлена на восстановление работы центральной нервной системы, обменных процессов и эмоционального баланса.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kazani16.ru
Conscious Essentials Hub – Smooth layout highlights carefully curated lifestyle products.
Детокс — это не один раз «поставить капельницу», а последовательность: допуск к терапии, коррекция жидкости и электролитов, поддержка органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, профилактика осложнений, переоценка и настройка схемы. Мы заранее закладываем точку повторной оценки, потому что абстинентные проявления изменчивы: тремор и тревога могут уходить волнообразно, давление — «гулять» на фоне усталости и недосыпа. Врач видит динамику и либо переводит на пероральные схемы, либо усиливает наблюдение, рекомендуя стационар. Параллельно настраиваем «бытовой контур» — сон по расписанию, вода малыми порциями, лёгкое дробное питание, ограничение эмоциональных перегрузок и перенос встреч, где сложно отказать.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Мы не составляем «супер-смеси» «на всякий случай». Капельница — это набор модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за конкретную задачу: гидратация, электролиты, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка; при показаниях — мягкая анксиолитика. Порядок модулей зависит от ведущего симптом-кластера и времени суток.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/
Интерактивная панель 65 дюймов Алматы Как подключить интерактивную панель к ноутбуку: Простая инструкция. Подключение через HDMI, USB или беспроводную сеть.
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому калининград[/url]
Hi, everything is going fine here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s in fact excellent, keep up writing.
гражданство румынии
Amazing many of awesome data.
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает видеть логику процесса. Это не жёсткий график: врач адаптирует точки и сроки под возраст, фоновые заболевания и исходное состояние.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]наркологическая клиника клин клин[/url]
Первичная оценка строится вокруг показателей, которые определяют место ведения (дом, амбулатория, стационар), состав инфузии и объём поведенческих вмешательств. Мы исключаем «обязательные по привычке» анализы, не влияющие на решения здесь и сейчас; вместо этого закрепляем короткие, но информативные измерения с понятными границами безопасности и интервалами повторов. В результате пациент быстрее видит первые улучшения, а команда не перегружает организм «на всякий случай».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy/
Чтобы убрать неопределённость, мы делим первые часы на короткие окна. У каждого окна есть цель, действия и критерии перехода. Если ответ «плоский», корректируется один элемент, а следующая проверка назначается сразу — без хаотичного «усиления всего сразу».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Curated Global Fashion – Curated products with a clean interface and pleasant exploration.
Брали ни один раз, в последний раз было несколько косяков. Всё разрешилось вчера плюс бонус за предыдущий косяк. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Или вводит всех в заблуждение?!Сегодня оплатил, сегодня и отправили, пацаны как всегда четко работают
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]джекпот[/url]
http://desteg.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=6013
http://pop-sbornik.ru/1615-vzryvnaya-avto-diskoteka.html
https://espaciodca.fedace.org/content/atenolol-get-online-order-online?page=13#comment-220063
https://anyflip.com/homepage/pzcbl
https://vanbal.com.tr/blog/season-essentials
melbet [url=https://studio-pulse.ru/]melbet[/url] .
Creative Inspiration Hub – The site feels full of energy, very pleasant to explore and scroll through.
онлайн школа 11 класс [url=https://www.shkola-onlajn1.ru]https://www.shkola-onlajn1.ru[/url] .
Fresh Path Finds – The products feel carefully chosen, and the interface runs smoothly.
Я всегда пишу благодарность везде, мыло, ася, форум и т.д. Может это только я так делаю, но думаю, что так должны все делать. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Не стоит сомневатся в этом магазе он ровный и проверенный времен! Всегда на высоте!принимай не меньше 300 мг МХЕ от данного селлера.
Сразу важно проговорить: кодирование — это «замок» на поведение и физиологию, который помогает удержать ремиссию, пока человек выстраивает новые привычки и восстанавливает качество жизни. Поэтому эффект процедуры прямо зависит от того, насколько грамотно выстроены подготовка, информирование и поддержка после вмешательства. «НеоТрезвие СПБ» делает акцент на постепенности: один этап — одна цель — один прозрачный маркер успеха.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены[/url]
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Для реализации крупномасштабных строительных проектов необходимо [url=http://rukrepezh.ru]шпилька 12.9[/url] в больших количествах.
Приобретение крепежных элементов в большом количестве может быть очень выгодным для бизнеса . Это связано с тем, что оптовые цены обычно ниже розничных. Для любого вида деятельности, связанного с производством или строительством, необходимы качественные крепежные элементы. Поэтому, найти хорошего поставщика является важнейшим фактором. Учитывая разнообразие крепежа, важно выбрать поставщика, который предлагает широкий ассортимент продукции .
Купить крепеж оптом дает возможность сэкономить значительную сумму денег, поскольку оптовые цены как правило ниже розничных . Это особенно важно для крупных проектов, где каждый рубль на счету. Приобретение большого количества крепежа заранее позволяет не беспокоиться о пополнении запасов в будущем . Кроме того, оптовые покупки крепежа часто сопровождаются дополнительными бонусами и скидками от поставщиков .
Найти хорошего поставщика крепежа не всегда просто, но это важно для успешного бизнеса . Удобным способом найти поставщика крепежа является просмотр сайтов компаний, занимающихся продажей строительных материалов. Кроме того, посещение строительных выставок и конференций также может быть полезным для поиска надежного поставщика .
В заключение стоит отметить, что купить крепеж оптом — это очень выгодное вложение средств для любого бизнеса . Это связано с тем, что Купить крепеж оптом означает также обеспечить себя качественными материалами на долгий период . Поэтому, Оптовая покупка крепежных элементов — это один из шагов к успешному и прибыльному бизнесу .
Для тех, кто ищет экологически чистый и экономичный вариант, [url=http://vip-elektromobil.ru]купить машину премиум класса[/url] становится всё более популярным решением.
Электромобили уже сегодня предлагают множество преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными транспортными средствами . Многие люди задумываются о покупке электромобиля. Электромобили предлагают экономичность и экологичность .
Приобретение электромобиля может быть шагом к более устойчивому будущему . Правительства различных стран стимулируют покупку электромобилей с помощью налоговых льгот.
Электромобили имеют ряд преимуществ, включая снижение уровня шума и минимизацию выбросов вредных веществ . Электромобили предлагают значительную экономию денег на эксплуатацию. Электромобили обеспечивают надежность и долговечность.
Электромобили можно заряжать дома или на общественных зарядных станциях . Некоторые производители электромобилей предлагают программы по обмену батарей.
При выборе электромобиля необходимо учитывать такие аспекты, как производительность и комплектация. Максимальная дальность хода на одной зарядке является важным параметром . При покупке электромобиля следует учитывать такие факторы, как цена и доступные скидки .
Многие производители электромобилей предлагают широкий выбор моделей . При выборе электромобиля необходимо учитывать такие аспекты, как удобство и надежность .
Электромобиль может стать идеальным выбором для любого, кто ценит экологичность и комфорт. Электромобили представляют собой лучший вариант для тех, кто заботится о будущем планеты.
При покупке электромобиля следует рассмотреть все факторы и выбрать лучший вариант для себя.
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]рейтинг лучших наркологических клиник москвы[/url]
Hello to every one, the contents present at this web page are genuinely remarkable for people knowledge, well, keep
up the good work fellows.
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в мурманске[/url]
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really well written article.
I’ll be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of
your useful information. Thanks for the post.
I will definitely comeback.
– Извините…. а… вы нас до “Дайва” (ночной клуб) не довезете? https://wwwgames.biz Ну теперь к самому главному – качество!Ну вообще то весь ассортимент выложен в теме “Прайс-Лист”. Там все написано.
I read this post fully on the topic of the comparison of most up-to-date and earlier
technologies, it’s remarkable article.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t
show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say superb blog!
Мы намеренно избегаем «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай». Состав инфузии подбирается под доминирующие симптомы текущего часа — выраженную жажду и редкий диурез, «качели» давления и тахикардию, рвоту и отказ воды, ночную тревогу и бессонницу, утреннюю «туманность» и когнитивную рассеянность. Каждый модуль имеет одну цель и одно «окно оценки», чтобы было понятно, что именно помогает, а что нужно скорректировать. Если отклик ниже ожидаемого, врач меняет только один параметр — темп, последовательность, водный режим или поведенческую поддержку — и фиксирует результат.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому в казани[/url]
В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, включающие медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и физиологическое восстановление. Такой подход позволяет достигнуть стойкого результата и предотвратить возвращение к употреблению алкоголя.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Very rapidly this web page will be famous among all blog users, due
to it’s nice articles or reviews
«Волшебной капельницы» не существует. Мы структурируем инфузии от симптомов, а не от «средних рецептов». Ниже — логика подбора для типичных профилей; реальную схему определяет врач на месте.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в калининграде[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Казани проводится круглосуточно под наблюдением специалистов. Основная цель процедуры — устранение симптомов интоксикации, восстановление работы жизненно важных органов и стабилизация эмоционального состояния. Используемые лекарственные препараты подбираются строго индивидуально, что позволяет избежать осложнений и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru
Безопасность — это не лозунг, а набор решений. Мы избегаем «жёстких» седативных доз, которые создают видимость улучшения и повышают риск скрытых осложнений. Наращивание темпа инфузии происходит постепенно и увязано с динамикой симптомов и цифрами измерений. Любой шаг объясняется пациенту и семье: зачем он выбран, что считается нормальной волной улучшения, в какой момент нужно связаться с дежурным. Такой прозрачный формат снимает тревогу и помогает всем участникам действовать согласованно.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru
Всё что В прайс листе на сайте есть,всё в наличии ? https://besthotelrates.biz качество вышкаХотел бы у вас спросить за безофуран(6-apb)…в частности про его качество…А так же про тусишку)))
I am extremely inspired with your writing talents as neatly as with the layout
for your blog. Is this a paid topic or did you modify it your self?
Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it’s
uncommon to peer a great weblog like this one today..
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/
Modern Living Hub – Stylish home items displayed clearly with smooth and easy navigation.
Мы выстраиваем помощь как маршрут, а не разовую «капельницу». После первого звонка администратор собирает краткий чек-лист (длительность эпизода, хронические заболевания, принятые препараты, аллергии), передаёт дежурному врачу, и тот предлагает безопасный старт: визит на дому в пределах Сергиева Посада и района или сразу стационар. Выбор зависит от клинических рисков и бытовых условий: есть ли спокойная комната, помощник на ночь, насколько выражены симптомы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru
Здесь
[url=https://beup-agency.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу». Лечение собирается из модулей: гидратация, адресная коррекция электролитов, гастропротекция, антиоксидантная поддержка, при необходимости — мягкие анксиолитики по строгим показаниям. Порядок и насыщенность зависят от ведущей жалобы и времени суток. Ниже — ориентир для пациента: почему назначение выглядит именно так и в какой горизонт мы ожидаем эффект.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk15.ru
Мы держим баланс между недостаточным и избыточным лечением. С одной стороны, не пропускаем опасные признаки, с другой — избегаем седативной перегрузки и сомнительных «коктейлей». Состав капельницы и темп введения зависят от давления и пульса, выраженности тревоги и тошноты, сопутствующих диагнозов и лекарств, уже попавших в организм. Каждое назначение объясняется простыми словами, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, как действует схема и зачем нужны ограничения ближайших дней.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk8.ru/]воскресенская клиника[/url]
* Экспресс-электролиты выполняются по показаниям, если на старте есть факторы риска.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены ставрополь[/url]
да не сцы, бывает у него такое )) магаз работает ровно, но вот с розницей у них напряг, изначально то ориентированы на опт, и просто рук не всех теперь на хватает. позже ответит. https://besttraders.biz Общий итог:гаси кидалу по полной -25 маловато я добавлю
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «СтавропольМедСервис» объединяет современную медицину и чуткое отношение к человеку: круглосуточный приём, точные диагностические алгоритмы, адресная инфузионная терапия, телемедицинские включения и грамотная работа с тревогой и сном. Мы используем принцип «минимально достаточной фармакотерапии»: каждый препарат должен быть оправдан текущими измерениями и клинической картиной, а не привычкой «усилить». Такой подход уменьшает риски дневной заторможенности, помогает быстрее восстановить ясность и делает ночь предсказуемой — без тяжёлой седации. Все действия прозрачны: пациент знает цель шага, окно оценки, критерии перехода и признаки, при которых нужно эскалировать наблюдение. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: гражданская одежда персонала, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «беззвучные» уведомления и закрытый контур медицинских карт — не «сервисная опция», а клинический фактор, снижающий реактивность и повышающий приверженность плану.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает видеть логику процесса. Это не жёсткий график: врач адаптирует точки и сроки под возраст, фоновые заболевания и исходное состояние.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu[/url]
New World Picks – Items are well-presented, and the browsing experience is very smooth.
мелбет фрибет за регистрацию [url=https://studio-pulse.ru/]мелбет фрибет за регистрацию[/url] .
школа-пансион бесплатно [url=https://www.shkola-onlajn1.ru]https://www.shkola-onlajn1.ru[/url] .
I blog quite often and I genuinely appreciate your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest.
I’m going to book mark your blog and keep checking for
new details about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
CRG Roofing and Siding Roofers offer top-notch roof installations in Maryland.
The Roofers from CRG Roofing and Siding offer the best roofing systems.
CRG Roofing and Siding offer excellent asphalt shingles.
The Roofers at CRG Roofing and Siding allow the use of slate in roof installations.
CRG Roofing and Siding simplify quick roof repairs.
Asphalt is a roofing material that The Roofers from CRG Roofing and Siding
use. CRG Roofing and Siding Roofers assist the
use of shingles in roof installations. The Roofers at CRG Roofing and Siding deliver skilled roof inspections.
CRG Roofing and Siding provide reliable roof replacements.
The Roofers from CRG Roofing and Siding provide comprehensive
warranties. CRG Roofing and Siding Roofers provide superior roofing
materials for roof setups. CRG Roofing and Siding empower homeowners to access residential roofers.
The Roofers from CRG Roofing and Siding simplify dependable roof repairs.
CRG Roofing and Siding Roofers provide excellent
roof coatings. The Roofers at CRG Roofing and Siding use
roofing materials like asphalt. CRG Roofing and Siding deliver swift roof inspections.
The Roofers from CRG Roofing and Siding
simplify roof replacements. CRG Roofing and Siding Roofers support clients with solid warranties.
Roof repairs are a service that the Roofers at CRG Roofing and Siding provide.
CRG Roofing and Siding deliver expert roofing contractors near you.
Сразу важно проговорить: кодирование — это «замок» на поведение и физиологию, который помогает удержать ремиссию, пока человек выстраивает новые привычки и восстанавливает качество жизни. Поэтому эффект процедуры прямо зависит от того, насколько грамотно выстроены подготовка, информирование и поддержка после вмешательства. «НеоТрезвие СПБ» делает акцент на постепенности: один этап — одна цель — один прозрачный маркер успеха.
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru
«Капельница от запоя» в современном понимании — это не одна универсальная смесь, а последовательность управляемых шагов с понятной целью, измеримыми показателями и заранее назначенными точками переоценки. В наркологической клинике «СеверАльфа Мед» мы используем модульные инфузионные протоколы и бережный мониторинг, чтобы безопасно снять интоксикацию, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, снизить тремор и вернуть физиологичный сон без «переседации». Каждый этап сопровождается сервисом конфиденциального уровня: нейтральные формулировки в документах, немаркированная логистика, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям строго по ролям. Это делает путь пациента предсказуемым и защищённым от лишнего внимания.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого в мурманске[/url]
Всем привет,отличный магазин,недавно брала,всё очень понравилось https://laviedesmamans.biz В предыдущих сообщен писал, что заказ по совместке от ЧМ,Привет ребята! В улан-удэ синие кристаллы имеются?
В Мурманске длинные сумерки, влажный ветер и «звонкие» подъезды старого фонда повышают чувствительность к свету и звуку. Поэтому выезд «Северный Медлайн» начинается с настройки среды: приглушается верхний свет, обеспечивается проветривание без сквозняка, смартфоны переводятся в «тихий режим» с «белым списком» близких. Только после этого врач проводит осмотр и запускает инфузионную терапию. Такой «тихий» сценарий снижает потребность в седативных препаратах и сохраняет физиологичность сна в первую ночь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого мурманск[/url]
Городская среда Калининграда — контрастные подъезды, близость моря с переменчивым ветром, плотный сезонный трафик — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому маршруты организованы «тихо»: согласованная парковка, отдельный вход без вывесок и очередей, короткая регистрация, приглушённая тёплая подсветка в зоне ожидания, отсутствие громких объявлений. Коммуникация с пациентами и близкими строится через защищённые каналы, а уведомления приходят в «беззвучном» режиме в согласованные «окна». Такой дизайн не ради «красоты сервиса», а ради клинического эффекта: чем меньше сенсорной нагрузки, тем быстрее выравнивается пульс к вечеру, тем легче возвращается переносимость питья и тёплой пищи, тем меньше потребность в ночных «усилениях».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru
Если в момент обращения сохраняются абстинентные симптомы, сначала проводится детоксикация и нормализация сна. Лишь после стабилизации обсуждаются методики кодирования.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-spb16.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-sankt-peterburge-czeny/
carefulbuyzone – CarefulBuyZone presents thoughtfully chosen products in a smooth and easy-to-navigate layout.
WildRidge Bloom Studio Shop – The natural vibe throughout made exploring the collection pleasant.
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
* Экспресс-электролиты выполняются по показаниям, если на старте есть факторы риска.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
«ПрофДетокс» — выездная наркологическая служба для жителей Ивантеевки и ближайших районов. Мы запускаем помощь без очередей и лишней огласки: врач приезжает анонимно, проводит очную оценку, допускает к терапии и запускает инфузионную поддержку без универсальных коктейлей. Наша задача — снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, снизить тревогу, мягко наладить сон по показаниям и дать семье понятный план на ближайшие двое суток. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим палату «ПрофДетокса» с круглосуточным наблюдением. Приватность встроена в процесс, а смета фиксируется до начала процедур.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает состояние сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени и почек, а также исключает противопоказания. На основании полученных данных подбирается индивидуальная схема инфузии. В процессе терапии пациент находится под наблюдением медицинского персонала, что исключает риск осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Домашний визит нарколога — это не «срочная капельница любой ценой», а аккуратно организованная медицинская процедура, где важны тишина, предсказуемость и уважение к личным границам. В службе выездной помощи наркологической клиники «СтаврДоктор» специалист приезжает быстро и незаметно: гражданская одежда, немаркированный транспорт, нейтральные формулировки в переписке и документах. Мы сразу выстраиваем безопасный маршрут: от короткого телефонного триажа до подпорогового освещения в комнате и «тихих окон» связи на первые трое суток. Наша философия — минимально достаточная фармакотерапия; инфузия не должна лишать ясности днём и «переседативать» ночью. Мы выбираем адресные растворы, темп и объём по текущим витальным показателям, а если динамика «плоская» — меняем один параметр, а не всё сразу.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом ставрополь[/url]
Безопасность — это не лозунг, а набор решений. Мы избегаем «жёстких» седативных доз, которые создают видимость улучшения и повышают риск скрытых осложнений. Наращивание темпа инфузии происходит постепенно и увязано с динамикой симптомов и цифрами измерений. Любой шаг объясняется пациенту и семье: зачем он выбран, что считается нормальной волной улучшения, в какой момент нужно связаться с дежурным. Такой прозрачный формат снимает тревогу и помогает всем участникам действовать согласованно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]нарколог на дом в Ивантеевке[/url]
Если при первичном звонке фиксируем «красные флаги» (угнетение сознания, выраженная одышка, резкое падение SpO?, нестабильная аритмия), сразу предлагаем стационарное наблюдение с ночным постом. При низких рисках начинаем дома, но держим низкий порог для эскалации, чтобы не терять время, если состояние меняется.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru
Всё нашел!! Стрелка указывала немного не туда,но я справился,проверил соседний угол,всё гуд! Спасибо динамиту! Мяу идеальный!! Рекомендую!! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Я делил Амф,следующий раз пришлем поношеные презервативы но ты будешь рад!!!
Выезд начинается с очной оценки. Врач уточняет историю эпизода, смотрит давление и пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает неврологический статус и уровень тревоги, внимательно проверяет совместимость с уже принятыми средствами. Допуск к терапии — стартовая точка. Затем запускается инфузионная поддержка с аккуратной коррекцией воды и электролитов, защитой органов мишеней, симптом контролем тошноты и головокружения. При необходимости настраивается сон, но без избыточной седативной нагрузки, которая могла бы замаскировать риски. По завершении основного блока — переоценка, перевод на пероральные схемы, подробная памятка на 24–48 часов и заранее согласованное окно контрольного контакта.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в мурманске[/url]
Городская среда Ставрополя создаёт дополнительные раздражители — трафик, шумовые пики, яркое освещение подъездов. Команда «СтаврДоктор» гасит эти факторы организационно: секторное распределение бригад, согласованная парковка, вход в подъезд без опознавательных знаков, доставка расходников при необходимости отдельно от врача, чтобы на месте сразу перейти к осмотру и инфузии. Коммуникация ведётся через защищённые каналы, уведомления «беззвучные», наименования в чеках — нейтральные. Если пациенту спокойнее, общение частично берёт на себя доверенное лицо; оно получает краткие апдейты в заранее оговорённые «тихие окна».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol15.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Не упусти важное! – https://med-advisor.ru/chto-podrazumevaet-soboj-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma
Срочная наркологическая помощь — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемый клинический процесс, где каждое действие проверяется измеримыми маркерами и выполняется в правильной последовательности. В наркологической клинике «ВолгаМед Альтернатива» маршрут выстроен вокруг принципа минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасный старт и телескрининг, затем очный осмотр с выбором контура инфузии и, только после теста переносимости, — основная терапия. Такой подход уменьшает реактивность организма, снижает риск побочных ощущений и делает результат предсказуемым для пациента и близких. Команда работает круглосуточно, выезжает на немаркированном транспорте, общение ведётся через одного доверенного человека, а документы оформляются в нейтральной терминологии без стигматизирующих формулировок.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru
РЕБЯТА КАК ВСЕГДА НА ВЫСОТЕ 5 ИЗ 5!!!! СПАСИБО https://orensad22.ru Продолжайте в том же духе.Ну что же, сегодня получил свою посылку, на этот раз все было в наилучшем виде, конспирация на все 10 баллов из 10!
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что вы можете зайти на vavada casino, то самое время воспользоваться зеркалом игрового клуба. Вы можете на вавада официальный сайт вход выполнить через следующие виды зеркала:
ссылка на сайт;
плагин на браузер;
клиент на компьютер;
мобильная версия.
Вне зависимости от того, какое зеркало вы выбираете, оно будет обеспечивать стабильный доступ, который поможет обойти абсолютно любые блокировки.
Используйте зеркало для того, чтобы попасть на сайт Вавада
Сегодня на vavada официальный сайт вход выполнить достаточно просто. Если вы воспользуетесь специализированным порталом, то сможете отыскать там ссылку на зеркало игрового клуба Вавада. Можно сразу сохранить страницу со ссылкой для того, чтобы у вас всегда был доступ к любым автоматам. Ссылка за 5 секунд находит новый адрес сайта, который еще не заблокирован со стороны провайдера и обеспечивает стабильный доступ к слотам. Также vavada casino официальный портал доступен через плагин на браузера. Часто многие специализированные сайты предоставляют большой выбор плагинов для любого браузера. Если вы попробуете зайти на заблокированный сайт казино вавада, то зеркало в автоматическом режиме перенаправит вас на свободный адрес.
Скачивайте специальную версию Вавада для стабильного доступа
Еще очень удобным способом зайти на вавада казино онлайн официальный сайт является скачивание мобильной версии к себе на смартфон. Доступ к сайту обеспечивается через приложение, а не через сайт, поэтому ваш провайдер не сможет заблокировать доступ к сайту. Мобильная версия это очень удобно, ведь теперь вы сможете играть в любой момент, когда вам захочется. Достаточно будет достать смартфон и зайти в приложение.
Также скачать вавада казино официальный сайт предлагает сразу на компьютер. Связь здесь идет через специальный клиент, который также не может быть заблокирован вашим провайдером. Кроме того, что зеркало обеспечивает доступ к сайту, у него нет никаких отличий от сайта казино. Здесь все те же слоты и бонусы, а также техподдержка и вероятность выигрыша.
Заходите на сайт казино Вавада, чтобы получить бонусы
Если вы прочитаете про вавада казино официальный сайт отзывы, то узнаете, что данный игровой клуб предоставляет просто шикарные подарки. Во-первых, здесь после регистрации и первого депозита можно получить 100 процентов к депозиту, а также 100 бесплатных вращений дополнительно. После того, как вы отыграете вейджер, вы сможете получить деньги к себе на счет и вывести их на карту или на электронные платежные системы.
Есть на сайте [url=https://vavada44.ru/]vavada[/url] бездепозитный бонус. Если вы играли на деньги и заработали достаточно очков, чтобы перейти на бронзовый уровень минимум, то вы получаете доступ к бесплатному турниру. Тут вы играете на бесплатные фишки, и ваша задача заработать как можно больше фишек. В конце турнира в зависимости от набранных очков начисляется выигрыш.
Polished Web Experience – Elegant layout with organized content and intuitive browsing.
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]наркологическая клиника официальный сайт[/url]
Такое сочетание компонентов обеспечивает комплексное воздействие на организм, устраняя симптомы абстинентного синдрома и восстанавливая работоспособность. Процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога с постоянным наблюдением за артериальным давлением и пульсом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов[/url]
https://livepositively.com/1xbet-new-account-code-130-bonus/
http://dnd.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?t=3059
http://justvoip.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?t=3654
http://siomiohost.forumex.ru/viewtopic.php?t=1321
Если дома нет возможности обеспечить тишину (ремонт, маленькие дети, гости), можно кратко перейти в «тихий стационар» с отдельным входом; после стабилизации сопровождение возвращается на дом, и маршрут продолжается «зеркально» — с теми же целями и окнами оценки. Такой перенос сохраняет управляемость процесса и снижает тревогу семьи: никто не «начинает сначала», меняется только место, а логика остаётся прежней.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Безопасность — это не лозунг, а набор решений. Мы избегаем «жёстких» седативных доз, которые создают видимость улучшения и повышают риск скрытых осложнений. Наращивание темпа инфузии происходит постепенно и увязано с динамикой симптомов и цифрами измерений. Любой шаг объясняется пациенту и семье: зачем он выбран, что считается нормальной волной улучшения, в какой момент нужно связаться с дежурным. Такой прозрачный формат снимает тревогу и помогает всем участникам действовать согласованно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-ivanteevke
https://westpapuanews.org/monster-freeport-sampai-jumpa-di-tahun-2019/comment-page-4?unapproved=448372&moderation-hash=c22252cf4b4e945cbb745963d5b73851#comment-448372
После прохождения детоксикации пациенту назначаются восстановительные процедуры, направленные на нормализацию обмена веществ и укрепление нервной системы. Программы клиники включают физиотерапию, витаминотерапию и индивидуальные занятия с психотерапевтом. Главная цель — восстановить способность организма к естественной саморегуляции и снизить зависимость от внешних раздражителей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru
Offer Zone Online – Many good deals are visible, and the browsing flow feels straightforward.
Магазин не чистый на руку. Уже пишет с другого жабера. Народ у кого осталось переписка состарого жабера сверьте ник. И прошу сделать посты что таковое не придуманная мною сказка. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Извините, если я не знаю вашу продукцию у кого мне тогда спрашивать ?Не понял…Его еще варить нужно??? На плитке?))
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Казани проводится круглосуточно под наблюдением специалистов. Основная цель процедуры — устранение симптомов интоксикации, восстановление работы жизненно важных органов и стабилизация эмоционального состояния. Используемые лекарственные препараты подбираются строго индивидуально, что позволяет избежать осложнений и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-kazani16.ru
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Капельницы собираются из модулей под ведущую задачу, а поведенческая часть усиливает эффект. Окончательные назначения делает врач с учётом противопоказаний и взаимодействий; таблица ниже — ориентир для пациента и семьи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-murmansk15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
After looking over a few of the articles on your website, I truly
like your way of blogging. I added it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back
soon. Please check out my website too and let me know how
you feel.
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс шоп[/url]
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Güzel blog için teşekkür ederim herkes bilardo oynamalı diye düşünüyor ve sizlerlede paylaşmak
istedik ; https://start.me/p/Da1Po8/ana-sayfa
новом оформлении и с новыми функциями на сайте casino vodka [url=https://stylekinder.ru/]https://stylekinder.ru/[/url]
отвечает быстро, всё объясняют. Деньги выводятся вовремя, без дополнительных проверок: [url=https://stylekinder.ru/]водка казино[/url]
понятно, интерфейс удобный. Вывод средств прошёл без вопросов и задержек [url=https://stylekinder.ru/]https://stylekinder.ru/[/url]
вас на платформе casino vodka, где каждая ставка приносит удовольствие: [url=https://stylekinder.ru/]casino vodka[/url]
где доступны десятки столов с реальными дилерами и высокими ставками [url=https://stylekinder.ru/]https://stylekinder.ru/[/url]
Да работает в асю обращайся если чё надо только товара мало там мхе да дмт Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Молодцы! Так держать!стараемся!Самый лучший магазин! качество, цены, общение с клиентом, все на высшем уровне! продолжайте в том же духе и вам зачтется: )
Здесь
[url=https://mediator-med.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Палата — это контролируемая среда: аппаратный мониторинг, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, пост медсестёр 24/7, переоценки по графику и быстрая коррекция тактики без логистических пауз. Такой старт рационален при длительных эпизодах, выраженных колебаниях давления и пульса, повторных судорогах, неукротимой рвоте и признаках надвигающегося делирия, а также если дома невозможно обеспечить «тихий режим» и присутствие взрослого помощника ночью. В стационарной ветке меньше случайностей, а путь до стабильного сна короче.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-lobne/
потолочкин потолки натяжные [url=natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru]natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru[/url] .
значит не там просил подтверждение здесь точно не отказывают https://samara-bt.ru Так что тут 50:50 если тебя примут. Все зависит от конкретного города и гнк в нем.да для ам и дживов ацик самая подходящяя тема. а основа из мачехи ништяк.только её надо выварить раза три по 15 мин. чтоб негорлодёрило и смол меньше,ведь в смоле много канабиола остаёца
Преимущество стационара — предсказуемость и скорость. Рядом врач и медсестра, можно оперативно сдать анализы, сделать ЭКГ или дополнительные обследования, а главное — не «тянуть» с корректировкой схемы. В контролируемой среде быстрее нормализуются сон и аппетит, уходит тремор, снижается тревога. Для пациентов с сопутствующими диагнозами это особенно важно: диабет, гипертония, аритмии, хронические заболевания ЖКТ требуют аккуратной, согласованной тактики.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]нарколог бесплатно москва[/url]
Design Focused Living – Nicely balanced design elements that make browsing feel relaxed.
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-pomoshch-v-ivanteevke
Круглосуточный формат критичен именно из-за «первой ночи»: в это окно нестабильны тревога, сон, вегетативная реактивность. Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу», а по одному параметру доводим систему до целевого коридора. Так удаётся избежать полипрагмазии и сохранить управляемость процесса: пациент и семья заранее знают, какие цифры считаются нормой, когда звонить дежурному, как организовать свет и тишину, чтобы ночное восстановление действительно состоялось.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Ну да ,я уже посылку с 15числа жду всё дождаться не могу . https://goldenparket.ru Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодняпрет 30-45 мин.1к10.действием похож на рсц
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/yk4b2kee
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает видеть логику процесса. Это не жёсткий график: врач адаптирует точки и сроки под возраст, фоновые заболевания и исходное состояние.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]наркологическая клиника в клину[/url]
Чтобы понять логику процесса, посмотрите на ориентир ниже. Это не жёсткое расписание, а понятная канва, которую врач адаптирует под возраст, сопутствующие заболевания и текущие цифры.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru
Домашний формат подойдёт, если нет признаков угрозы жизни и есть возможность обеспечить тишину и наблюдение ночью. Стационар предпочтителен при тяжёлой абстиненции, эпизодах судорог, выраженных скачках давления, неукротимой рвоте, риске делирия, а также когда дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения. В стационаре под рукой лаборатория, ЭКГ по показаниям, круглосуточный пост — это снижает вероятность осложнений и ускоряет восстановление сна и аппетита.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
http://koxma.4adm.ru/viewtopic.php?t=7507
Госпитализация разворачивается как последовательность шагов: приём и допуск к терапии, старт инфузий, мониторинг 24/7, регулярная переоценка и подготовка к выписке. Такой контур особенно важен пациентам с сопутствующими диагнозами (гипертония, ИБС, сахарный диабет, заболевания ЖКТ), где требуется деликатная настройка дозировок и темпа инфузий.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-sergievom-posade/
Ridge Market – Nicely arranged products that made exploring the site feel simple and pleasant.
Good answers in return of this difficulty with firm arguments and telling the whole thing concerning that.
Big Bass Splash is worth visiting. Will be back for sure!
http://uranai-kaiun.com/yomi/rank.cgi?mode=link&id=913&url=http%3a%2f%2fbig-bass-splash-uk-game.co.uk%2Fdemo
Дом рядом с адресом говоришь, отдаешь залог, когда приедешь в адрес (в разных такси по-разному, могут и не попросить), и идешб себе за кладом 🙂 https://lifeshen.biz Вообщем фейк крассавчик пошагово и все грамотно сделал, развел)Да не магазин ровный несколько раз покупал у них, качество отличное. Только в аську бывает недостучатся.
Tremendous things here. I’m very glad to look your article.
Thanks a lot and I am looking ahead to contact you.
Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Городская среда Воронежа — яркие подъезды, плотный трафик, шумные дворы — может усиливать вечернюю реактивность. Поэтому мы проектируем «тихую» логистику: согласованная парковка, вход без вывесок, гражданская одежда специалистов, короткий маршрут от порога к месту процедуры. Коммуникация в зашифрованных каналах, напоминания — в беззвучном режиме. Такой дизайн не декоративен: чем меньше социального шума, тем быстрее возвращаются питьё и аппетит, а значит — меньше потребность «наращивать» фармакологию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/
intentionaldesignhub – IntentionalDesignHub showcases items in a welcoming layout that was simple to explore.
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в челябинске[/url]
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Углубиться в тему – http://
https://vodds-casino.net/odds/
Круглосуточный формат критичен именно из-за «первой ночи»: в это окно нестабильны тревога, сон, вегетативная реактивность. Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу», а по одному параметру доводим систему до целевого коридора. Так удаётся избежать полипрагмазии и сохранить управляемость процесса: пациент и семья заранее знают, какие цифры считаются нормой, когда звонить дежурному, как организовать свет и тишину, чтобы ночное восстановление действительно состоялось.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Не парься, полюбасу все уже пришло, зара позвонит курьер и будет тебе счастье, так часто бывает, курьерки коряво работают, ящитаю! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш единственная существенная проблема данного магазина – отсутствие автоматизированной системы оформления заказов… Вроде прикручивают к сайту, но что то долго уже…Золотые слова.
Здесь
[url=https://efix-group.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
натяжные потолки нижний новгород с установкой [url=natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru]natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru[/url] .
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Мы не удерживаем пациента на дому во что бы то ни стало. Домашний формат уместен при контролируемых симптомах, наличии взрослого помощника на вечер и ночь и возможности обеспечить тихий режим. Если у входа видно угрозу делирия, выраженные скачки давления, повторные эпизоды рвоты с обезвоживанием, нестабильный ритм, одиночество ночью — рациональнее начать в палате. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и лаборатория, пост медсестёр и быстрые коррекции схем. Такой маршрут часто короче по времени до устойчивого сна и предсказуемее по результату.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]нарколог на дом ивантеевка[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов платиновая 1000х1х0.4 мм Пл99.9 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Ни форма, ни машины с надписями, ни громкие атрибуты «скорой» — мы приезжаем тихо. Контакт в телефоне сохраняется с нейтральным названием, документы оформляются только по запросу и в сдержанной формулировке, доступ к данным внутри «ПрофДетокса» ограничен регламентами. Мы понимаем, что стыд и страх огласки часто тормозят обращение за помощью, поэтому приватность включена в стандарт и не влияет на стоимость.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/]zapoj-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя челябинск[/url]
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru
в магазин приятно удивили цены, сделал заказ, надеюсь все придет в лучшем виде Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш через в/в непробывал такое не люблю,Один из топовых продавцов на всем РЦ:)
Envie de parier 1xbet apk rdc est une plateforme de paris sportifs en ligne pour la Republique democratique du Congo. Football et autres sports, paris en direct et d’avant-match, cotes, resultats et statistiques. Presentation des fonctionnalites du service.
a href=”https://refinedlifestylecommerce.click/” />Refined Lifestyle Picks – Smooth navigation with well-arranged content and a polished look.
Le site web telecharger 1xbet propose des informations sur les paris sportifs, les cotes et les evenements en direct. Football, tournois populaires, cotes et statistiques y sont presentes. Ce site est ideal pour se familiariser avec les fonctionnalites de la plateforme.
Этот список — памятка на холодильник. Он не раскрывает диагноз, но точно описывает поводы для связи с дежурным врачом. Своевременная эскалация — часть безопасности, а не «подстраховка». Если сомневаетесь — лучше позвонить.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя[/url]
Круглосуточный формат критичен именно из-за «первой ночи»: в это окно нестабильны тревога, сон, вегетативная реактивность. Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу», а по одному параметру доводим систему до целевого коридора. Так удаётся избежать полипрагмазии и сохранить управляемость процесса: пациент и семья заранее знают, какие цифры считаются нормой, когда звонить дежурному, как организовать свет и тишину, чтобы ночное восстановление действительно состоялось.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Наши стандарты включают конфиденциальную маршрутизацию, детализированные инструкции для семьи, модульный план лечения и прозрачное разделение бесплатных и платных блоков. Каждому пациенту назначается ведущий специалист, который сопровождает его на всём пути — от первого звонка до контрольных чек-инов после процедур. Мы не «наращиваем» объём вмешательств ради впечатления: используется минимально достаточный набор мер, который действительно влияет на целевые маркеры — переносимость воды, качество сна, сглаживание вегетативных «качелей» и возвращение утренней ясности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske
Первичная оценка строится вокруг показателей, которые определяют место ведения (дом, амбулатория, стационар), состав инфузии и объём поведенческих вмешательств. Мы исключаем «обязательные по привычке» анализы, не влияющие на решения здесь и сейчас; вместо этого закрепляем короткие, но информативные измерения с понятными границами безопасности и интервалами повторов. В результате пациент быстрее видит первые улучшения, а команда не перегружает организм «на всякий случай».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Amazing information, Kudos.
Modern conversations about health are loud, fast, and often oversimplified.
Much of what we hear focuses on quick fixes, universal rules, or surface-level guidance.
Individuals may feel disconnected from their own bodies and rhythms.
Health unfolds through patterns unique to each person.
Slowing down allows insights to surface naturally.
In our Medix Podcast conversations, we often explore these subtle signals of well-being.
Long-form audio allows ideas to develop without being rushed.
Topics explore the full spectrum of well-being, from physical to mental health.
Awareness grows as connections form over time.
When exploration matters more than instruction.
To gain insight through thoughtful dialogue.
It’s about building understanding rather than chasing instant solutions.
Curious to hear how these ideas unfold through real dialogue?
Engage with a calm, meaningful podcast episode on drugs list a-z.
да мэн правильно говоришь KEY фраернулся Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш вот и я уже трясусь.Хотел бы у вас спросить за безофуран(6-apb)…в частности про его качество…А так же про тусишку)))
Ключевым моментом является выбор надежных специалистов для реализации проекта.
проект газобетонного дома [url=https://gotovye-proekty-domov9.ru/gazobeton/]https://gotovye-proekty-domov9.ru/gazobeton/[/url]
Сначала — очная оценка, проверка противопоказаний и совместимости с текущими лекарствами. Далее — инфузионная терапия для коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы, мягкая анксиолитическая и снотворная поддержка по показаниям. Визит обычно занимает от 60 до 120 минут; при необходимости капельницы проводятся медленно, с наблюдением. После процедуры пациент получает понятные памятки: что и когда пить, когда спать, какие признаки считаются тревожными и требуют повторного осмотра или перевода в стационар.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva8.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
мастерская по ремонту стиральных машин [url=https://servisnyj-centr-stiralok-vrn.ru]https://servisnyj-centr-stiralok-vrn.ru/[/url]
Мы выстраиваем помощь как маршрут, а не разовую «капельницу». После первого звонка администратор собирает краткий чек-лист (длительность эпизода, хронические заболевания, принятые препараты, аллергии), передаёт дежурному врачу, и тот предлагает безопасный старт: визит на дому в пределах Сергиева Посада и района или сразу стационар. Выбор зависит от клинических рисков и бытовых условий: есть ли спокойная комната, помощник на ночь, насколько выражены симптомы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-sergiev-posad8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-sergievom-posade/
Вывод из запоя — это не только про капельницу. Это управляемая цепочка решений, где сначала оцениваются риски (дыхание, сознание, обезвоживание), затем подбирается минимально достаточная инфузионная схема и психосоматическая поддержка, а после — формируется «окно наблюдения» на первую ночь. В наркологической клинике «ЧелМед Детокс» все этапы формализованы: врач фиксирует исходные показатели, назначает узкий модуль вмешательства и выключает его ровно в тот момент, когда цель достигнута. Такой подход избегает полипрагмазии, делает лечение предсказуемым и снимает тревогу у пациента и семьи: каждый понимает, что будет происходить в ближайшие часы, какие критерии успеха и когда наступит пересмотр тактики.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в челябинске[/url]
Ниже — структурированная карта экстренного выезда. Она помогает пациенту и семье понимать, что происходит в каждый отрезок времени, какие цели мы преследуем и по каким критериям двигаемся дальше.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-domu-v-ivanteevke/
Сработали быстро, посылка пришла за 4 дня, спрятано эффектно https://ukovskaya.ru Хороший магазин,норм совместкиа как ам то хоть вооще расшифровывается то по науке???
Мы работаем последовательностями, которые реально влияют на исход: допуск к терапии, инфузии с коррекцией электролитов и КЩС, поддержка органов-мишеней, профилактика осложнений, осторожная нормализация сна по показаниям, переоценка и настройка схемы, план на неделю с алгоритмами «если-то». Важно не «перелечивать»: избыточная седативная нагрузка опасна так же, как и её отсутствие. Поэтому темп и состав мы настраиваем под текущие параметры и динамику — и объясняем пациенту и семье, зачем именно выбран каждый шаг.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-klin8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-klinu[/url]
Круглосуточный формат критичен именно из-за «первой ночи»: в это окно нестабильны тревога, сон, вегетативная реактивность. Мы не «усиливаем всё сразу», а по одному параметру доводим систему до целевого коридора. Так удаётся избежать полипрагмазии и сохранить управляемость процесса: пациент и семья заранее знают, какие цифры считаются нормой, когда звонить дежурному, как организовать свет и тишину, чтобы ночное восстановление действительно состоялось.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy.
I have learn this post and if I could I desire to counsel you few attention-grabbing things or advice.
Maybe you can write next articles regarding this article.
I wish to read even more things approximately it!
Wow, that’s what I was exploring for, what a material! existing here at this website,
thanks admin of this website.
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing
many months of hard work due to no data backup.
Do you have any methods to prevent hackers? http://fat-girls.ru/dhoprobuy-chatruletka-18-novyiy-format-vzrosloe-obshhenie
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk-na-domu
ТС подтвердив оплату, сказал ожидать. В оговоренные сроки адрес был получен в ЛС. https://freeforex.biz Уточнять не у кого !у СПСР постоянно такая хрень, порой по неделе не пробиваются треки(проверено на себе… тоже срал кирпичами(на рафика причем)) а говорят быстрей ЕМС. не верю))
Online 1xbet rdc est une plateforme de paris sportifs en ligne. Championnats de football, cotes en direct et resultats sont disponibles. Page d’information sur le service et ses fonctionnalites pour les utilisateurs de la region.
Здесь
[url=https://www.truck1.eu/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Appreciating the hard work you put into your website and detailed information you present.
It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material.
Wonderful read! I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google
account.
UrbanField Visuals – Loved the curated pieces, everything has a refined and artistic charm.
Inspired decor hub – Browsing is intuitive, with products displayed clearly in an artistic format.
Modern Design Hub – Products arranged thoughtfully with smooth and intuitive navigation.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as
long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My blog is in the very same niche as yours and my users would certainly benefit from some
of the information you provide here. Please
let me know if this okay with you. Appreciate it!
натяжные потолки недорого нижний новгород цена [url=http://natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru/]http://natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru/[/url] .
Ниже — ориентировочная матрица первых часов. Она не заменяет очной оценки, но показывает, как мы переводим наблюдения в действия и какие критерии считаем достаточными для переключения модуля. Приведённые окна проверки помогают не тянуть с нужными корректировками и одновременно не «дергать» схему без повода.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Art and design hub – Users can navigate a clear and professional showcase of creative work.
Да мы уже поговорили – нормальные ребята вроде) хз, я всё равно полной предоплате не доверяю) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Клад сделан очень грамотно в безлюдном месте, к кладу прилагалось фото на котором указано место закладки.что ты хочешь сказать,что этот реактив плохо прет?
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar/
Лечение в клинике строится на комплексной программе, которая сочетает медикаментозную терапию, психотерапевтические методы и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход обеспечивает устойчивый результат и предотвращает повторные срывы. Пациент проходит курс под постоянным контролем специалистов, что позволяет отслеживать динамику состояния и корректировать терапию при необходимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в краснодаре[/url]
Простая подготовка уменьшает стресс, повышает переносимость капельницы и делает оценку состояния более точной. Попросите одного ответственного взрослого быть на связи с врачом — так решения будут приниматься быстрее, а ночной интервал пройдёт спокойнее и предсказуемее.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
133betcassino, alright! Hoping for a wide variety of games and good bonuses. Let’s see if they live up to the hype. Feeling lucky? You can join me here: 133betcassino
Этапы терапии выглядят следующим образом:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
потолочник потолки [url=https://www.natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru]https://www.natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru[/url] .
You’ve made your stand quite effectively!.
В «ЮжУрал Детокс Центр» инфузионная терапия собирается из модулей. Каждый модуль имеет одну цель, измеримый маркер и стоп-критерий. Мы избегаем одновременного подключения нескольких новых элементов, чтобы не потерять причинно-следственную связь. Ниже — примерная «сетка» компонентов; фактическая схема подбирается индивидуально, только по показаниям.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому круглосуточно челябинск[/url]
I value the content you publish on Big Bass Splash. Thank you!
https://big-bass-splash-uk.co.uk/registration
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Детальнее – http://
сегодня сделал заказ, написал в аську сразу ответили. Буду ждать как что измениться отпишу. https://francegall.biz Получил RCS-4 развел в спирту 50, растворился только после нагрева…Хороший магаз. качество радует спасибо всей команде Chemical-mix.com
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в самаре[/url]
Вся динамика фиксируется в единой карте наблюдения. При переводе в амбулаторную точку мы не «сбрасываем» историю: решения продолжаются с учётом уже сделанного и реакции пациента на вмешательства.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru
Excellent, what a website it is! This web site provides valuable data to us,
keep it up. https://goyashiki.co.jp/%e9%ab%98%e5%b3%b6%e5%b1%8b%e3%80%80%e5%b1%b1%e6%b5%b77a3a0383/
Лечение в клинике строится на комплексной программе, которая сочетает медикаментозную терапию, психотерапевтические методы и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход обеспечивает устойчивый результат и предотвращает повторные срывы. Пациент проходит курс под постоянным контролем специалистов, что позволяет отслеживать динамику состояния и корректировать терапию при необходимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника краснодар[/url]
intentionaldesignzone – IntentionalDesignZone presents thoughtfully chosen items in a polished browsing interface.
«МедСфера» — это управляемый маршрут наркологической помощи в Ивантеевке: круглосуточный выезд врача без опознавательных знаков, аккуратный домашний детокс, стационар с наблюдением 24 часа в сутки и профессиональная подготовка к кодированию по показаниям. Мы работаем по принципу клинической достаточности: никакой «универсальной капельницы», никаких решений «наугад», только последовательные шаги, которые действительно влияют на исход. Каждое назначение объясняем простым языком, заранее согласуем смету, фиксируем правила на первые 24–48 часов и первую «тихую» неделю. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральная связь, выезд без эмблем, документы в сдержанной формулировке по запросу.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]ближайший наркологическая клиника[/url]
Ниже — структурированная карта экстренного выезда. Она помогает пациенту и семье понимать, что происходит в каждый отрезок времени, какие цели мы преследуем и по каким критериям двигаемся дальше.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом воронеж[/url]
Мы собираем терапию как конструктор из узких модулей. Каждый модуль запускается только при показаниях и выключается сразу после достижения цели — это защищает от «инерции лечения» и возвращает организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции. Ниже — ориентировочная сетка модулей; фактический состав и дозировки определяет врач на очном осмотре.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Лечение зависимости требует системного подхода и чёткой последовательности действий. Каждый этап направлен на устранение интоксикации, восстановление функций организма и закрепление результата. В клинике процедура организована так, чтобы обеспечить комфорт и безопасность пациента.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-chelyabinsk/
Простая подготовка уменьшает стресс, повышает переносимость капельницы и делает оценку состояния более точной. Попросите одного ответственного взрослого быть на связи с врачом — так решения будут приниматься быстрее, а ночной интервал пройдёт спокойнее и предсказуемее.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск[/url]
Мы переводим субъективные ощущения в простые маркеры, чтобы решения не зависели от настроения и ожиданий. Базовый набор: объём выпитой воды в час; ЧСС/АД в покое; длительность сна и число пробуждений; шкалы тошноты/тремора/тревоги; две утренние бытовые задачи. В отчёте фиксируется, какой модуль включён, какой маркер он должен сдвинуть, в каком окне мы проверяем результат и при каком значении модуль выключается. Это защищает от «инерции лечения» и делает финансовую часть предсказуемой: расширения назначаются только по показаниям с указанием цели и времени переоценки.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-krasnodare/
Если среда дома шумная или приватность под угрозой, мы предложим «короткий коридор» через отдельный вход амбулатории. Если условия позволяют, проводим процедуры на дому: свет приглушён, доступ к розетке организован, рядом столик для расходников и приборов. Этот «экологичный» сценарий, несмотря на простоту, заметно улучшает переносимость процедур и собирает устойчивый сон в первую ночь, что особенно важно на ранних этапах стабилизации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике челябинск[/url]
Выездная стабилизация — только первый шаг. Дальше важно разобрать триггеры, обучить «тихим ритуалам», согласовать план поддержки и рассмотреть кодирование там, где оно уместно. Мы не противопоставляем форматы: домашние визиты, «тихий вход» и краткие очные сессии дополняют друг друга. Задача — не создать идеальную «капельницу», а вернуть организму пространство для самостоятельной регуляции и укрепить навыки, которые защищают от срыва. В «КубаньМед Резолюция» этим занимается мультидисциплинарная команда: наркологи, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинические психологи, психотерапевты и медсёстры с опытом ночных постов наблюдения. Все говорят на «языке фактов», чтобы решения были понятны и пациенту, и семье.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar
у меня до сих пор нет реальной отправки,ток просроченная планируемая((( Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Вы очень давно работаете,стабильная деятельность.Желаю вам удачи в дальнейшей работе)
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Экстренный вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемая медицинская последовательность, а не «сильная капельница на удачу». В наркологической клинике «КалининградМедПрофи» мы выстраиваем помощь вокруг трёх опор: безопасность, конфиденциальность и предсказуемый результат. Выездная бригада приезжает круглосуточно, работает в гражданской одежде и без опознавательных знаков, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей. Каждое вмешательство имеет измеримую цель, окно проверки и прозрачный критерий перехода к следующему шагу. Благодаря этому темп лечения остаётся мягким, а динамика — понятной для пациента и близких.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kaliningrade15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно калининград[/url]
Приватность и комфорт встроены в технологию. Документы оформляются с нейтральными формулировками, передвижение бригад — без маркировки, доступ к медицинским записям разделён по ролям, а каналы связи не содержат «говорящих» названий. Внутри клиники на уровне среды предусмотрены акустические панели, приглушённый тёплый свет, затемнение палат и «тихий» ночной мониторинг без избыточных пробуждений. Эти, на первый взгляд, «бытовые» элементы уменьшают сенсорную нагрузку и усиливают эффект медицинских модулей: быстрее выравнивается пульс к вечеру, легче переносится вода малыми глотками, стабилизируется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske15.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в мурманске[/url]
В реальной городской ткани Ставрополя на самочувствие влияет не только схема лечения, но и логистика: утренние заторы на въезде, плотная застройка частного сектора, шумные перекрёстки. Мы заранее «поглощаем» эти риски организацией: секторные выезды, согласованная парковка, нейтральная переписка без «говорящих» терминов, при необходимости — курьерская доставка расходников отдельно от врача, чтобы на месте сразу переходить к оценке и запуску инфузии. Пациенту не нужно «вписываться» в систему — система подстраивается под реальную жизнь человека, экономя десятки минут и снижая сенсорную нагрузку перед первой ночью.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-stavropole15.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ставрополь[/url]
Creative picks store – The site feels imaginative, and items are showcased clearly and attractively.
Что случилось? почему страшно? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Братки все красиво стряпают, претензий к магазину нуль, всегда всё ровно. Единственное что сейчас напрягло, отсутствие на ветке вашего представителя в ЕКБ “онлайн”, представитель молчит ( а там по делу ему в лс отписано) и кажись воопще не заходит пару недельМагаз ровный, очень много раз тут брал, а как перешли на телеграмм так еще больше радуете, намного меньше гемора с оплатой стало, качество на высоте как и всегда. Сегодня убедился что оператор не сидит без дела, очень сильно помог мне с моим вопросом, при чем оперативно все сделал. Оцениваю данный магазин 10 из 10. Кокаин даже MQ оказался лучше, чем я до этого покупал HQ в другом магазе. Делайте по чаще закладки в центре Питера.
A useful look, thanks for the tip. To make the result last longer, [url=https://shop77.su/kosmetika-dlya-professionalov-ot-vedushix-brendov-mira/][color=#1C1C1C]apply professional salon-level cosmetics[/color][/url].
Stylish Home Picks – Carefully curated items displayed with clarity and speed.
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Sergii creative hub – Visitors can view projects clearly and enjoy a polished, professional layout.
Managing reputation is a critical part of sustainable growth.
It helps organizations build trust in a fast-changing environment.
Good brand perception can influence audience loyalty.
By monitoring feedback, companies can address concerns promptly.
User feedback play a important role in how a brand is viewed.
Effective management allows businesses to avoid reputational damage.
It also supports consistent communication with the audience.
Ultimately, reputation management helps create a reliable presence in the market.
https://rentry.co/g8qw3rpe
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar-otzyvy/
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
Эти признаки не заменяют очной оценки, но помогают не рисковать временем. Если вы наблюдаете их у близкого или у себя, не откладывайте обращение — чем раньше начнётся управляемое вмешательство, тем меньше вероятность осложнений в первую ночь и на следующие сутки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Для наглядности представлена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их эффектами:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр краснодар[/url]
Этот текст посвящён сложным аспектам зависимости и её влиянию на жизнь человека. Мы обсудим психологические, физические и социальные последствия зависимого поведения, а также важность своевременного обращения за помощью.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://wums.ru/kak-nachat-lechitsya-ot-alkogolizma-anonimno-prakticheskoe-rukovodstvo-kotoroe-ne-stydno-prochest
сайт натяжной потолок [url=natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru]natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru[/url] .
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре специализируется на лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ терапии. Работа специалистов направлена на устранение физической зависимости, восстановление психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Все процедуры проводятся в безопасных условиях с соблюдением принципов анонимности и врачебной тайны.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar
Первая задача при выезде — быстро отделить угрозы от симптомов, которые можно безопасно стабилизировать на дому. Таблица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые гипотезы, конкретные действия и решения в «окнах оценки». Она не заменяет очной диагностики, а объясняет архитектуру первых часов, чтобы у семьи был ясный ориентир.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
а вот по этой теме отпиши по подробней,точнее о том как там дальше события развиваются?????????? очень волнует данная тема. как же так их просекла легавня???? откуда краснотой веет.??? https://ukovskaya.ru Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии,Ты то откуда знаешь)))только сегодня зарегался .коржик )))
Вред от наркотиков — этто комплексная проблема, охватывающая физиологическое, психическое (а) также соц состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление эких наркотиков, как
снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик»
чи «бошки», может огласить к неконвертируемым следствиям как чтобы организма,
так равно для мира на целом.
Но даже у вырабатывании подневольности возможно восстановление — главное, чтобы энергозависимый явантроп устремился согласен помощью.
Эпохально памятовать, что наркозависимость врачуется, и реабилитация одаривает шанс сверху новейшую жизнь.
потолочник отзывы [url=http://natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru/]http://natyazhnye-potolki-samara-5.ru/[/url] .
Эта схема помогает постепенно вывести пациента из кризисного состояния, снизить риски осложнений и закрепить результаты лечения.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnodare16.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnodar/
Риск через наркотиков — это единая проблема, охватывающая физиологическое,
психическое также социальное здоровье человека.
Утилизация таковских наркотиков,
как снежок, мефедрон, гашиш, «шишки» или «бошки», что ль обусловить ко необратимым последствиям яко чтобы организма,
так (а) также для среды в целом.
Но хоть при развитии подчиненности
возможно электровосстановление — главное, чтобы энергозависимый человек устремился за помощью.
Эпохально памятовать, яко наркомания лечится, а также оправдание одаривает шанс сверху
свежую жизнь.
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника работает по схеме «тихих маршрутов»: отдельный вход с нейтральной табличкой, окна записи в невызывающие подозрений часы, немаркированный подъезд автомобиля при выездном визите. На первом звонке диспетчер собирает только то, что влияет на безопасность: эпизоды рвоты, ЧСС/АД, ночные панические эпизоды, сопутствующие препараты, аллергии, наличие хронических заболеваний сердца. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются — мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально необходимой информации». По прибытии врача фиксируются базовая линия (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), шкалы симптомов и переносимость небольших объёмов воды. Дальше — один точный шаг, одно «окно проверки» и прозрачное решение: продолжать модуль, модифицировать одну переменную или выключить блок.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-zapadnyj-rajon/https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru
Простая подготовка уменьшает стресс, повышает переносимость капельницы и делает оценку состояния более точной. Попросите одного ответственного взрослого быть на связи с врачом — так решения будут приниматься быстрее, а ночной интервал пройдёт спокойнее и предсказуемее.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk-anonimno/
так что только желаю удачи магазину и процветания в дальнейшем Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш В общем подожду пока ты получишь и отпишешь :))))Все всегда на высшем уровне:dansing: всегда отправляют практически моментально
Ущерб от наркотиков — это комплексная хоботня, охватывающая физиологическое, психическое равным образом общественное состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление подобных наркотиков, яко кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» чи «бошки», что ль огласить ко неконвертируемым последствиям яко для организма,
яко равно чтобы мира в целом.
Но хоть у выковывании подчиненности эвентуально восстановление — ядро, чтобы зависимый
явантроп устремился согласен помощью.
Эпохально памятовать, яко наркомания лечится, и реабилитация одаривает шанс на свежую жизнь.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://hyperpc.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-moskva-ceny[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Интересно наблюдать, как тема раскрывается с разных сторон. В итоге важен комфорт в жизни, а его лучше всего ощущаешь, когда [url=https://grodnosantehnika.by/kondensatsionnye-gazovye-kotly/][color=#1C1C1C]дом греет газовый котёл[/color][/url].
И всё надо успеть. :crazy: Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш -1. Вас, продавцов, много, а я один.Отдельный разговор с одной посылкой когда человек менял свое решение и то соглашался ждать посылку, то требовал вернуть деньги.
Палатный формат мы предлагаем, когда есть риск делирия, судорог, резких скачков давления и пульса, выраженной одышки, неукротимой рвоты, обезвоживания или когда дома невозможно обеспечить наблюдение ночью. В стационаре под рукой аппаратный контроль, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, круглосуточный пост и регулярные переоценки с точной настройкой схем. Здесь меньше случайностей: темп инфузий корректируется без задержек, решения принимаются быстро, а риск «ночных качелей» ниже. Для семьи стационар часто оказывается не «дороже», а короче по времени до стабильного сна и предсказуемее по бюджету.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Daily essentials shop – The items are useful and reliable, and moving through the store is simple.
Капельницы в «ЧелМед Детокс» — это модульная конструкция, а не «микс на удачу». База — регидратация и коррекция электролитов. По показаниям добавляются антиэметики, антивегетативные средства, поддержка метаболизма, витамины группы B, магний. Отдельным блоком идёт ночной модуль: задача — собрать восстановительный сон, не «перелечивая» пациента. Каждый модуль имеет свою цель и стоп-критерий. Врач избегает одновременного запуска нескольких новых элементов, чтобы видеть причинно-следственную связь и точно понимать, что именно работает у конкретного человека.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это не «быстрая капельница и забыли», а последовательный и конфиденциальный процесс, в котором каждое вмешательство имеет цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно проверки». В наркологической клинике «Южный Мед Центр Ренова» мы совмещаем непрерывный приём 24/7, выездные визиты без маркировки, точечную диагностику, инфузионную поддержку, психотерапевтические сессии и план посттерапевтического сопровождения. Приоритет — приватность и минимально достаточные решения: чем меньше случайных назначений, тем больше управляемости и предсказуемости. Мы говорим «языком фактов», а не оценок: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов (0–10), структура сна, переносимость воды, простые бытовые задачи на утро. Это помогает семье и пациенту видеть, что именно работает, и выключать вмешательства, когда они сделали своё дело.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Track portal – Clear updates and tracking tools make staying informed simple and convenient.
Modern Picks Marketplace – Clean interface with clearly separated categories for comfortable browsing.
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемая последовательность маленьких шагов с понятными целями и точками проверки. В наркологической клинике «КубаньМед Резолюция» выезд врача, инфузионная поддержка и лечение зависимостей складываются в дорожную карту: мы начинаем с короткого триежа, формулируем рабочую гипотезу, включаем минимально достаточный модуль, назначаем «окно оценки» и только затем либо выключаем модуль, либо изменяем одну переменную. Такой подход снижает фармаконагрузку, предотвращает полипрагмазыю и делает динамику прозрачной: пациент и семья видят, что именно помогает и когда вмешательство завершается.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
Мы очень рады! Обращайтесь к нам еще! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Все отлично, безумно рад что доверился данному магазинуУ меня тоже была задержка.На мониторенге тоже отправку просрочили, в итоге дней 20 затратили на пересылку.Просто курьерка такая, они помоему там распиздяи ещё те…так что на счёт приема можешь не беспокоиться.там даже если мусора захотят что то найти то будет трудно разобраться что да где)вот допустим недавно заказал и курьерка ваще не то вбила))так что не переживай!Чемикалы всё ровно делают, сложновато будет найти даже если посыль откроют!
Риск от наркотиков — это групповая хоботня, охватывающая физическое,
психическое (а) также социальное состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление подобных наркотиков,
как снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «шишки» или «бошки», может привести для
неконвертируемым результатам яко
чтобы организма, яко (а) также для федерации в целом.
Но хоть у вырабатывании зависимости возможно восстановление — главное, чтобы зависимый человек обернулся за помощью.
Важно помнить, яко наркозависимость лечится, также оправдание бацнет шансище
на новейшую жизнь.
натяжные потолки сайт [url=https://www.natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru]https://www.natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-4.ru[/url] .
Fun88 social
Капельница — это не «секретный коктейль», а набор узких модулей, каждый из которых отвечает за одну задачу. Мы включаем ровно один новый модуль за раз и заранее обозначаем стоп-критерий, чтобы не тянуть терапию «по инерции». Параллельно настраиваются поведенческие элементы: свет, тишина, дыхательные ритмы и «окна» питья. Это снимает часть нагрузки с организма и ускоряет наступление целевых маркеров.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в краснодаре[/url]
Бро ответь в аське! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Магазин высший советаю брать только здесь Заказываю тоже 2 раз и собераюсь дальше работать.?Флудить на счет легальности/нелегальности товара в магазине не нужно в ветке! У же отписывалась и экспертиза и мы не однократно писали, возим ТОЛЬКО ЛЕГАЛ!
Кодирование в «МедТрезвие» — не «волшебная кнопка», а логическое продолжение после стабилизации, когда организм готов к вмешательству, а пациент понимает механизм действия и ограничения метода. Врач подробно обсуждает цели, риски, противопоказания, ожидаемые эффекты и сроки наблюдения, оформляет информированное согласие и объясняет, как встроить процедуру в общий план. Важная часть — профилактика триггеров и обучение распознаванию ранних сигналов тяги: человек получает не только фармакологическую поддержку, но и практические инструменты саморегуляции, сценарии на «сложные дни», способы запросить помощь до того, как ситуация выйдет из-под контроля. Такая связка повышает вероятность устойчивой ремиссии, потому что работает одновременно на биологическом и поведенческом уровнях.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/
Для жителей Краснодара и ближайших районов организованы два параллельных маршрута: немаркированный выезд врача-нарколога на дом и «тихий вход» в амбулаторный кабинет с отдельной дверью и согласованным слотом. На первичном звонке диспетчер фиксирует только факторы безопасности — частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспусканий, базовые значения ЧСС/АД, эпизоды спутанности, список текущих препаратов и аллергии. Личные и социальные детали не запрашиваются: мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации. На месте врач и медсестра собирают базовую линию (сознание, дыхание, SpO?, температура), оценивают шкалы симптомов (тошнота/тремор/тревога по шкале 0–10), проверяют переносимость небольших глотков воды и описывают ближайшие «окна» принятия решений. Вечером и ночью команда остаётся на связи: мы заранее согласовываем пороги, при которых нужно позвонить дежурному врачу, чтобы не терять критические минуты.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-krasnodare16.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в краснодаре[/url]
[url=https://4gmobifone.net/news/bainarii-opushon-osusume_4.html]
バイナリーオプション おすすめ[/url]
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/ar-BH/register-person?ref=UT2YTZSU
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
clickdiscoverhub – ClickDiscoverHub offers a polished browsing experience with products that felt exceptional.
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://omniverse.fo/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is excellent, as well as the content!
just the gays porn
When someone writes an paragraph he/she retains the image of a user in his/her mind that how a user can understand it.
Therefore that’s why this post is amazing.
Thanks!
И вообще зачем тебе спасибо жать или репутацию добавлять?? Ты что малолетка глупая, что это тебя так беспокоит?? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Заказываю в третий раз, дали скидку 8%, приятно.Успехов вам господа : )
[url=http://xn--u8jpa1t.jp/pages/bainarii-opushontowa_4.html]
バイナリーオプション おすすめ 海外[/url]
Artisan lifestyle shop – Items feel carefully chosen, making the browsing experience enjoyable and clear.
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-samara-vyzov-na-dom
продавец адекватный. Успешных вам продаж https://logoped-yug.ru брали 10 гр реги ))))Прислали нам свой метоксетамин, подтверждаем: продукт чистый, >99%.
Michael D Fountain – The site is personal and engaging, with simple navigation for visitors.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения и без вейджера
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Artful Living Market – An artful approach to lifestyle browsing that stays smooth and accessible.
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию
бездепозитные бонусы казино в казахстане
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-lobne-stacionar/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva-besplatno[/url]
А за кладом я решил ехать на такси. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Ждать возможно придется дольше обычного, я ожидал 12 рабочих, не считая праздников..Да и вообще стот ли…? риск есть…?
Перед назначением инфузий врач проводит полную диагностику, чтобы исключить противопоказания. Капельницы часто комбинируются с медикаментами, поддерживающими сердечно-сосудистую систему и печень. Такой комплексный подход позволяет ускорить процесс очищения и улучшить общее состояние пациента уже после первого курса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Городской ритм Саратова — длинные переезды через мост, активное движение в центре и контрастные микрорайоны — накладывает отпечаток на логистику и сенсорную среду, в которой проходит лечение. Мы адаптируем маршрут под город: назначаем «тихие окна» связи, уменьшаем световую нагрузку в вечернее время, организуем немаркированные выезды, а при стационарном поступлении готовим палату с тёплой подсветкой и акустическим поглощением. Эти, казалось бы, «не медицинские» решения позволяют снизить тревогу, быстрее стабилизировать пульс и сделать сон физиологичным без переседации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2026
Успехов и процветания новому селлеру!!! Желаю денег пресс и в обществе вес)) https://logoped-yug.ru Я делал ркс. на спирту. Получилась лайт ваще. Делай вообщем гдето 1к 7ми . будет так нормик эффект. но слабее 203гоСПАСИБИЩЕ ОГРОМНОЕ ЗА СЕРВИС
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма новокузнецк[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-chekhove
Город с протяжёнными магистралями и разноскоростными районами требует особой организации маршрутов. Выездные бригады «ВолгаДок Медикал» работают в режиме 24/7, прибывают в гражданской одежде, избегают громких звонков и используют «немаркированные» подъезды. Перед приездом мы просим подготовить пространство: приглушить верхний свет, обеспечить приток свежего воздуха без сквозняков, подготовить ровную поверхность под укладку и удлинитель, перевести телефоны в «без уведомлений» с «белым списком» близких. Это позволяет в первые минуты сосредоточиться на клинике, а не на бытовых вопросах.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого саратов[/url]
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the finest
websites on the web. I am going to highly recommend this website!
Here is my blog post; เว็บรวยออนไลน์
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-srochno-v-ivanteevke
Перед процедурой обсуждаются цели, ожидаемые эффекты, возможные побочные реакции, сроки наблюдения. Пациент получает письменные рекомендации на первые трое суток: режим сна и жидкости, коррекция нагрузки, контакты для связи, сигналы настороженности. Такой формат сделал результаты более предсказуемыми: меньше импульсивных решений, меньше тревоги и больше контроля над поведением в критический ранний период.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]процедура кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Домашний формат нужен, когда важно начать быстро и без лишних перемещений, а состояние не требует госпитализации. Врач адаптирует инфузионные схемы под переносимость и сопутствующие заболевания, контролирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, объясняет режим жидкости и питания, оставляет список признаков, при которых следует связаться повторно. Такой сценарий не отменяет дальнейшую работу: пациент получает краткий план на 48–72 часа, рекомендации по восстановлению сна и активности, а также точку контакта для корректировки. Это снижает тревогу, помогает избежать «самолечения» и формирует доверие к процессу, потому что человек видит конкретный результат — уменьшение тремора, нормализацию сна, снижение тревоги — уже в первые сутки.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/
Игнорирование этих симптомов может привести к тяжёлым последствиям — судорогам, галлюцинациям или алкогольному психозу.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru
KingSize вас не отловить нигде, в аське нету((( на страницу прайс не заходите, откликнитесь пожалуйста) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Моя первая покупка на динамите и, внезапно для самой себя, наход. Сняла, как говорится, в касание. С вашим охуенным мефчиком сорвала себе почти год ЗОЖа и ни чуть не жалею.Как только появится обьявим на форуме
В клинике «ЮгМед Альянс» выстроена система непрерывного медицинского наблюдения. При поступлении проводится комплексная диагностика, назначается детоксикация и поддерживающая терапия, затем начинается стабилизация физического и эмоционального состояния. Благодаря круглосуточной работе бригад и возможности экстренного выезда на дом пациенты получают помощь без задержек. Конфиденциальность соблюдается на всех уровнях — от первичного звонка до выписки. Для удобства родственников организована система информирования: короткие апдейты по согласованным каналам связи и только в определённое время, чтобы не нарушать покой пациента.
Подробнее – http://
бездепозитные бонусы в онлайн казино
Этап
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/]telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Event and milestone hub – The site presents milestones and stories in a clear and engaging format.
Trendy home hub – The modern design makes finding products simple and enjoyable.
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника самара[/url]
Keep this going please, great job!
Покупал как то в этом магазине реагента 1к10 помоему был у них примерно год назад.С доставкой,заказ делал тогда еще на сайте, получил реквизиты оплатил ждал отправки.И вот доставка пришла очень быстро.Качество товара было приемлемое.Очень хорошая консперация.Всем советую Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш По АМ могу сказать,что концентрировать выше 1 к 15 не вижу смысла.Оно не торкает дальше своего известного предела,после 1 к 15 дальше пойдёт уже переводняк.Тут как с процами-дороже 200 баксов покупать-перевод бабла,прироста производительности не заметишь почти.Продаван ровный ничего не скажеш
Домашняя помощь — это клиника, перенесённая в тихую комнату. Знакомая обстановка снижает тревогу, исчезают пробки и ожидание, нет «социального шума». Врач «ПрофДетокса» приезжает без эмблем, действует спокойно и последовательно, объясняет каждое назначение простым языком. Мы не используем мифические смеси. Состав и темп капельницы подбираются под текущие показатели — давление, пульс, сатурация, выраженность тремора и тошноты, уровень тревоги, данные о лекарствах, которые человек успел принять за двое суток. Такой подход даёт не минутное облегчение, а устойчивую динамику на сутки и неделю.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-ivanteevke/
Палата — это контролируемая среда: аппаратный мониторинг, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, пост медсестёр 24/7, переоценки по графику и быстрая коррекция тактики без логистических пауз. Такой старт рационален при длительных эпизодах, выраженных колебаниях давления и пульса, повторных судорогах, неукротимой рвоте и признаках надвигающегося делирия, а также если дома невозможно обеспечить «тихий режим» и присутствие взрослого помощника ночью. В стационарной ветке меньше случайностей, а путь до стабильного сна короче.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu/
Профессиональная подготовка — это не формальность, а ключ к безопасной и эффективной процедуре. Врач собирает подробный анамнез, уточняет длительность и характер употребления, фиксирует соматические жалобы, анализирует текущие препараты (в том числе безрецептурные), измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости назначает ЭКГ и лабораторные тесты. Если есть выраженная интоксикация, бессонница, тремор, скачки давления — стартуют с детокса и стабилизации: корректируют водно-электролитный баланс, снижают тревогу, нормализуют сон. Параллельно специалист объясняет механику методик кодирования, вероятные ощущения после процедуры, ограничения по нагрузкам, правила безопасного поведения в первые недели и алгоритм действий на случай усиления тяги. Подготовительный этап снимает неопределённость, уменьшает тревогу и повышает приверженность: человек понимает, что будет происходить и как оценивать улучшение.
Узнать больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]moskva-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-adresa[/url]
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино
люди которые делают заказы через ВК по меньшей мере идиоты. Особенно когда ИМ самим что то предлагают. https://tchat-gratuit.biz трэк получил . Магаз всегда был хорошдоброго вечера всем,трек получил всё прекрасно бъётся,жду звоночка,жду жду жду
creativemind.click – Resource guiding users to explore inventive concepts and embrace innovative thinking.
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого новокузнецк[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-zhenshchin[/url]
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
multiculturalmarket – MultiCulturalMarket offers a lively range of globally influenced items for easy discovery.
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/
Алкогольный эпизод — это не один симптом, а целая сцепка процессов: обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, нарушения сна; нередко добавляются проблемы со стороны желудка и печени. Шаблонная капельница игнорирует индивидуальную картину и часто даёт кратковременный эффект с ночным откатом. Мы работаем иначе: допускаем к терапии, подбираем состав и темп инфузии под текущие цифры и динамику, избегаем конфликтов с уже принятыми препаратами и объясняем, чего ожидать по ощущениям на каждом шаге. Избыточная седация не усиливает лечение — она делает его менее предсказуемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara
Магаз вышел на связь, работает, но щас выходные 😀 с треками порешают, по ходу косяки СПСР. пробники БУДУТ !! Кто ещё будет гадить в теме “Трипы” и просить пробник – получит подзатыльник. У кого есть что сказать – отпишите лучше отзывы о товаре. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Брал не давно в этом магазине закладкой в МСК, что сказать, все прошло замечательно. Клад был поднят, место довольно спокойное и тихое, Время исполнения заказа с момента оплаты от 1 до 2,5 часов, что по сути не так уж и много. Выражаю огромное спасибо оператору в аське, не оставлял меня ни на минуту, всегда отвечал.Прошу прощения за крайность и грубость!Но не уведомлять клиента о происходящей ситуации..это по крайней мере,не то что не вежливо,это не корректно в введении торгового процесса!
Перед процедурой обсуждаются цели, ожидаемые эффекты, возможные побочные реакции, сроки наблюдения. Пациент получает письменные рекомендации на первые трое суток: режим сна и жидкости, коррекция нагрузки, контакты для связи, сигналы настороженности. Такой формат сделал результаты более предсказуемыми: меньше импульсивных решений, меньше тревоги и больше контроля над поведением в критический ранний период.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]adres-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Стационар уместен при тяжёлой абстиненции, скачках давления, угрозе делирия, эпизодах судорог, неукротимой рвоте, а также когда дома нет взрослого помощника на ночь. В палате — аппаратный контроль по показаниям, пост медсестёр 24/7, ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, регулярные переоценки с корректировкой схемы. Решения принимаются быстро, без логистических задержек; это снижает риск поздних осложнений и повторных экстренных вызовов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru
Палата — это контролируемая среда: аппаратный мониторинг, по показаниям ЭКГ и базовая лаборатория, пост медсестёр 24/7, переоценки по графику и быстрая коррекция тактики без логистических пауз. Такой старт рационален при длительных эпизодах, выраженных колебаниях давления и пульса, повторных судорогах, неукротимой рвоте и признаках надвигающегося делирия, а также если дома невозможно обеспечить «тихий режим» и присутствие взрослого помощника ночью. В стационарной ветке меньше случайностей, а путь до стабильного сна короче.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya8.ru/]наркологическая клиника диспансер[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и «гонку дозировок», острый отрезок мы делим на короткие окна с ясной целью и чёткими критериями перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент и тут же назначается новая точка оценки. Прозрачность плана снижает эмоциональный фон и повышает доверие к процессу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в саратове[/url]
https://letterboxd.com/dhebfwe/list/code-promo-inscription-1xbet-bonus-vip-130-1/
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-domu-v-ivanteevke
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в рязани[/url]
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно ростов-на-дону[/url]
https://linkspreed.web4.one/read-blog/212867
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Explore creative circle – Visitors can view imaginative projects displayed with stunning visuals and clarity.
«ПрофДетокс» — выездная наркологическая служба для жителей Ивантеевки и ближайших районов. Мы запускаем помощь без очередей и лишней огласки: врач приезжает анонимно, проводит очную оценку, допускает к терапии и запускает инфузионную поддержку без универсальных коктейлей. Наша задача — снять интоксикацию и абстиненцию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, снизить тревогу, мягко наладить сон по показаниям и дать семье понятный план на ближайшие двое суток. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим палату «ПрофДетокса» с круглосуточным наблюдением. Приватность встроена в процесс, а смета фиксируется до начала процедур.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-ivanteevka8.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-v-ivanteevke/
Warm style boutique – The aesthetic is comforting, and navigating the site feels effortless.
Получили адрес с небольшой задержкой , ТС все объяснил , отвечал сразу , без каких либо задержек . Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Всем привет! В магазе есть представительства по регионам, закладками? Ярославль?Данный сервис с каждым разом удивляет своим ровным ходом
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-tolyatti/
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-novokuzneczk/
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а жизненно важный этап, позволяющий вернуть контроль над самочувствием и предотвратить осложнения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» пациенты получают помощь в любое время суток: опытные наркологи выезжают на дом, проводят капельницы и медикаментозную детоксикацию, подбирают индивидуальные схемы восстановления. Такой подход помогает не только устранить последствия запоя, но и запустить процесс полноценного оздоровления организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-samara
Домашний формат нужен, когда риски управляемы, а в квартире можно обеспечить «тихий режим». Врач приезжает без эмблем, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, сверяет лекарства за последние 48 часов и аллергии. После допуска запускается инфузия с мягкой коррекцией воды и электролитов, поддержкой печени и вегетативной нервной системы; при необходимости аккуратно настраивается сон. По завершении — переоценка, письменная памятка на 24–48 часов, список тревожных признаков и прямой канал связи. Такой визит «гасит» тремор и тошноту, снижает тревогу и делает ночь предсказуемой.
Подробнее тут – http://
Кодирование в «МедТрезвие» — не «волшебная кнопка», а логическое продолжение после стабилизации, когда организм готов к вмешательству, а пациент понимает механизм действия и ограничения метода. Врач подробно обсуждает цели, риски, противопоказания, ожидаемые эффекты и сроки наблюдения, оформляет информированное согласие и объясняет, как встроить процедуру в общий план. Важная часть — профилактика триггеров и обучение распознаванию ранних сигналов тяги: человек получает не только фармакологическую поддержку, но и практические инструменты саморегуляции, сценарии на «сложные дни», способы запросить помощь до того, как ситуация выйдет из-под контроля. Такая связка повышает вероятность устойчивой ремиссии, потому что работает одновременно на биологическом и поведенческом уровнях.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр саратов[/url]
добрый день форумчане!) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш магаз походу отвечает только когда ему пишут и он в сети, на старые сообщения не отвечает.Всем доброго времени суток!!!
https://www.sunemall.com/board/board_topic/8431232/7327228.htm
https://indianwomenorg.com/read-blog/43467
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
https://pastebin.com/u/codepomo26
«КузбассМед Центр» специализируется на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, восстановлении организма после интоксикации и профилактике рецидивов. В таблице приведены ключевые направления работы и их особенности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.info/da-DK/register-person?ref=V3MG69RO
Честная наркология — это не «универсальная капельница», а система шагов, привязанная к параметрам конкретного человека. В Чехове мы выезжаем круглосуточно, на месте проводим допуск к терапии, сверяем совместимости с уже принятыми препаратами, подбираем состав инфузий без лишних компонентов и избыточной седативной нагрузки. Если дома нет условий для безопасной ночи, предложим стационар — это не усложнение, а короткий путь к безопасности. Анонимность — стандарт: нейтральные формулировки в документах по запросу, ограниченный доступ к данным, деликатная связь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]наркологическая больница москвы[/url]
Запой — это не один симптом. Это сдвиг водно-электролитного баланса, скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тошнота, тревога, бессонница, нередко раздражение слизистой желудка и нагрузка на печень. Мы работаем последовательностью: допуск к терапии, инфузионная поддержка с коррекцией воды и электролитов, защита органов-мишеней, симптом-контроль, при необходимости аккуратная нормализация сна, переоценка и перевод на пероральные схемы, затем — поведенческий контур «тихих» дней и, при информированном согласии, подготовка к кодированию. Это не «коктейль на всех», а управляемый процесс, завязанный на объективные показатели и живую динамику.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru/
movetorussia com [url=http://www.deogiricollege.org/pag/should-i-move-to-russia-complete-pros-and-cons-analysis-2025.html]http://www.deogiricollege.org/pag/should-i-move-to-russia-complete-pros-and-cons-analysis-2025.html[/url] .
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts.
After all I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/
у меня 203 1к8 получался вообще жестокии делал на растворителе для снятие лака с ногтей (без ацетона) https://laviedesmamans.biz “Так вот Основа это Продукта похожа на таблетки Гидроперит”Во телегу двинул, а? Ещё спать не ложился, такой эффект сильный, толеоа нет вообще, в завязке полгода 🙂
Такой подход позволяет пациенту чувствовать себя не объектом лечения, а активным участником собственного восстановления. Это повышает уровень мотивации и формирует доверие между врачом и пациентом, что критически важно для устойчивой ремиссии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Asking questions are truly nice thing if you are not
understanding something completely, but this piece of writing gives nice understanding even.
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения и без вейджера
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов палладиевая 50х6х0.9 мм ПдСр60-40 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в тюмени[/url]
Наркологическая клиника — это пространство, где медицинская наука сочетается с психологической поддержкой и индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» лечение зависимости организовано по принципам доказательной медицины: каждый этап терапии основан на объективных данных, контролируемых результатах и четких критериях эффективности. Здесь помогают не просто устранить физические последствия зависимости, но и восстановить внутренние ресурсы человека, вернуть уверенность, осознанность и способность строить новую жизнь без алкоголя и наркотиков.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в воронеже[/url]
Основная задача стационарного лечения — не просто вывести человека из кризисного состояния, а вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость физиологических функций. Поэтому врачи клиники используют современные методы детоксикации, витаминотерапии, ноотропные препараты, психотерапевтические практики короткого действия и физиотерапевтические модули, направленные на восстановление сна, памяти и концентрации.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru
Чтобы понять логику процесса, посмотрите на ориентир ниже. Это не жёсткое расписание, а понятная канва, которую врач адаптирует под возраст, сопутствующие заболевания и текущие цифры.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka8.ru
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/pomoshh-narkozavisimym-tolyatti/
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti
«ВитаСана» — это организованный маршрут наркологической помощи в Чехове: быстрый анонимный звонок, выезд врача на дом без опознавательных знаков, аккуратный детокс с капельницами, стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением и подготовка к кодированию по показаниям. Мы действуем спокойно и последовательно: сначала очная оценка и допуск к терапии, затем индивидуальная инфузионная поддержка, далее — понятный план «тихих» дней и контрольный контакт. Каждое назначение объясняем простыми словами, смету согласуем до начала процедур, конфиденциальность соблюдаем на каждом шаге.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov8.ru/]telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены[/url]
хорщий магаз!!!всегда все ровно!!! https://logoped-yug.ru как планчик наверн цепляет. но не прям на коры. вообщем так норм сойдетособенно с вашей репутацией!
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в самаре[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование на дому москва[/url]
Visit Albany Super Ducks – Lively and interactive, the platform keeps fans updated with team news and events.
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника самара[/url]
visionarythinking.click – Platform guiding users to explore inventive strategies and new perspectives.
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd/
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно в волгограде[/url]
Premium home finds – Each item is displayed thoughtfully, making the collections easy and enjoyable to browse.
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for info approximately this subject for a while and yours is the best I have discovered till now. But, what concerning the conclusion? Are you positive in regards to the source?
akt posen
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti
Первым шагом терапии является детоксикация — процедура очищения организма от продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотических веществ. Она проводится под контролем врача и помогает стабилизировать работу сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени и центральной нервной системы. Для поддержания здоровья используются инфузионные растворы, витамины, гепатопротекторы и препараты, снижающие тревожность.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены воронеж[/url]
Incredible story there. What happened after?
Good luck!
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в саратове[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в самаре[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. В основе её деятельности лежит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, сочетание медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методов, а также полная конфиденциальность. Лечение проводится опытными специалистами с применением современных медицинских технологий, направленных на восстановление здоровья и предотвращение рецидивов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в самаре[/url]
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-samara-narkolog-na-dom
Чтобы исключить суету и «гонку дозировок», острый отрезок мы делим на короткие окна с ясной целью и чёткими критериями перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент и тут же назначается новая точка оценки. Прозрачность плана снижает эмоциональный фон и повышает доверие к процессу.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
а заряд сколько происходил? https://murygino.ru туфта какаетоА ничо что праздники как бэ ?
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм новокузнецк[/url]
Поэтапное лечение помогает врачам контролировать процесс восстановления и своевременно корректировать терапию в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
Такой алгоритм позволяет контролировать каждый аспект лечения, обеспечивая постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врач-куратор отслеживает динамику и при необходимости корректирует программу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому в тольятти[/url]
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент и для пациента, и для семьи: все видят, какая цель преследуется, какими средствами она достигается, когда проверяется эффект и что будет дальше. Отсюда рождается доверие и строгая приверженность — главный предиктор устойчивого результата.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
That is really attention-grabbing, You are an overly professional blogger. I’ve joined your feed and stay up for searching for more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks
gay schwanze
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом красноярск[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в рязани[/url]
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево новокузнецк[/url]
а какие были проблемы по данном поводу? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш быстрая доставка однако тут)))Не знаю как в этом магазе,а вот у всеми так уважаемой Мануфактуры тоже весной всплыло такое гавницо.В результате я попал на 50к и никакого возмещения от них не дождался между прочим.
move to Russia [url=http://www.theshaderoom.com/articl/russian_golden_visa_investment_visa_residency_guide.html]http://www.theshaderoom.com/articl/russian_golden_visa_investment_visa_residency_guide.html[/url] .
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новокузнецке[/url]
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Этапы терапии выглядят следующим образом:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-samara/
https://enran.ua/
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
homestylezone – HomeStyleZone showcases carefully chosen items in a smooth, easy-to-navigate interface.
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-omsk/
Howdy! This article could not be written much better!
Going through this post reminds me of my previous roommate!
He continually kept preaching about this. I most certainly will send this information to him.
Pretty sure he’ll have a great read. Thank you for sharing!
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Член Российского союза писателей Селезинка Александр Михайлович родился в 1976 г. Проживает в с. Дивеево Нижегородской области. Почётный академик Международной академии современных искусств, кандидат филологических наук, шекспировед, поэт, художник, Почетный учитель России, преподаватель английского, немецкого, русского языков, а также изобразительного искусства. Автор монографии “Библейские аллюзии в творчестве В. Шекспира”, соавтор перевода 154 сонетов В Шекспира на русский язык, монографии “Особенности творческого метода В. Шекспира” и четырех частей книги «Духовные сонеты». Участник художественных выставок. Открыл 5 персональных выставок. Член Союза русских художников. Член Евразийского художественного союза. Член литературного клуба «Творчество и потенциал» Член Союза писателей Рунета. Член Российского союза писателей. Лауреат международного конкурс искусств “Artex Awards”. Лауреат конкурса “Звезда Виртуоза”. Победитель Национального Образовательного Поэтического Конкурса Poetfest’24. Победитель конкурса «Голоса эпохи» в номинации «Выбор редакции». Награжден медалью «225 лет А. С. Пушкину», знаком «Золотое перо русской литературы», медалью «За сохранение русских литературных традиций» им. Великой княгини Ольги, медалью имени Л. Н. Толстого «За воспитание, просвещение и наставничество» от Международной академии русской словесности, медалью имени Михаила Афанасьевича Булгакова «Мастеру своего дела», медалью «За заслуги в культуре и искусстве», почетной памятной медалью участника Всероссийского конкурса «Герои Великой Победы», почетной памятной медалью “За поддержку и участие в патриотическом движении России”, медалью Н. В. Гоголя «За особые заслуги», медалью «130 лет С. А. Есенину».
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva-otzyvy[/url]
Вот по количеству норм, но кач…. Это то что осталось после меня и моих проб Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш клад забрал, все ровняк! завтра отпишу за качество!Палево палево, с сайтом чооо??
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]лучшая наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to
say that I’ve truly enjoyed surfing around your
blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your feed and
I hope you write again very soon!
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-omske
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
При запое счёт идёт не на дни, а на часы: нарастает обезвоживание, усиливается тремор, «скачет» давление и пульс, появляются аритмии, нарушается сон. В таких условиях попытки «перетерпеть» или лечиться «народными методами» приводят к ухудшению состояния и удлиняют путь к восстановлению. В «АлкоМед Балашиха» мы устраняем задержки: выезд возможен без очередей, а при необходимости — оперативная госпитализация в стационар. На первичной оценке врач фиксирует длительность употребления, текущие препараты и сопутствующие болезни, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус и понятным языком объясняет точку входа — на дому или с краткой стационарной стабилизацией. Такой прагматичный подход убирает хаос: уже в первые часы формируется ощутимый эффект — снижается тревога, стабилизируются показатели, появляется шанс на полноценный ночной сон. Когда человек и его близкие видят последовательность действий и понимают, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, уменьшается импульсивность, исчезает «дергание», а лечение перестаёт зависеть от настроения и случайностей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo-balashiha[/url]
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]государственная наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Adirondack Fiddlers – The site connects musicians and fans, sharing events and resources clearly.
Amazing! Its genuinely awesome post, I have got much clear idea on the topic
of from this paragraph.
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ryadom[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в волгограде[/url]
Hands-on ideas hub – Interactive elements make the experience motivating and idea-driven.
Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде предоставляет профессиональную медицинскую помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Основная цель специалистов — не просто устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту вернуть внутреннее равновесие, здоровье и контроль над жизнью. В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, доказавшие свою эффективность в практике отечественной и мировой наркологии.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
https://enran.ua/
Вы это о чем? Тут все вроде как только легальными делами занимаемся? Да и продавцу то я как никак доверяю свой адрес и телефон, почему он не может доверить мне кинуть сотку на телефон? Это ни к одному делу не пришьешь, раз мы уже заговорили об этом https://money-banks.biz с треками магазин всегда спешит:) и качество скоро заценим)))Только вот странно что в трипе написано что пак был с 1гр ск (а твой заказ это покупка) а продажу у магазина от 5гр
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в самаре[/url]
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-saratove/
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены саратов[/url]
Мы проверяем не «ощущения», а факты: частоту пульса в покое, вариабельность ритма к сумеркам, переносимость тёплой воды малыми глотками, минуты до сна и количество ночных пробуждений. Эти короткие метки позволяют тонко управлять темпом инфузии, очередностью модулей и «тихими» ритуалами вечернего времени без необоснованного усиления препаратов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом саратов[/url]
Член Союза русских художников. Селезинка Александр Михайлович родился в 1976 г. Проживает в с. Дивеево Нижегородской области. Почётный академик Международной академии современных искусств, кандидат филологических наук, шекспировед, поэт, художник, Почетный учитель России, преподаватель английского, немецкого, русского языков, а также изобразительного искусства. Автор монографии “Библейские аллюзии в творчестве В. Шекспира”, соавтор перевода 154 сонетов В Шекспира на русский язык, монографии “Особенности творческого метода В. Шекспира” и четырех частей книги «Духовные сонеты». Участник художественных выставок. Открыл 5 персональных выставок. Член Союза русских художников. Член Евразийского художественного союза. Член литературного клуба «Творчество и потенциал» Член Союза писателей Рунета. Член Российского союза писателей. Лауреат международного конкурс искусств “Artex Awards”. Лауреат конкурса “Звезда Виртуоза”. Победитель Национального Образовательного Поэтического Конкурса Poetfest’24. Победитель конкурса «Голоса эпохи» в номинации «Выбор редакции». Награжден медалью «225 лет А. С. Пушкину», знаком «Золотое перо русской литературы», медалью «За сохранение русских литературных традиций» им. Великой княгини Ольги, медалью имени Л. Н. Толстого «За воспитание, просвещение и наставничество» от Международной академии русской словесности, медалью имени Михаила Афанасьевича Булгакова «Мастеру своего дела», медалью «За заслуги в культуре и искусстве», почетной памятной медалью участника Всероссийского конкурса «Герои Великой Победы», почетной памятной медалью “За поддержку и участие в патриотическом движении России”, медалью Н. В. Гоголя «За особые заслуги», медалью «130 лет С. А. Есенину».
Вывод из запоя в Ростове-на-Дону — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение симптомов алкогольной интоксикации, восстановление функций организма и предотвращение осложнений. В клинике помощь оказывается круглосуточно, а лечение проводится под контролем опытных наркологов. Такой подход позволяет безопасно прекратить употребление алкоголя, избежать резкой отмены и стабилизировать состояние пациента. Процедура проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, с учётом состояния здоровья и степени зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в ростове-на-дону[/url]
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Best wishes!
Exactly where are your contact details though?
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-anonimno
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
краби снять дом Таиланд, Ко Ланта – идеальное место для тех, кто ищет спокойный отдых в тропическом раю.
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент и для пациента, и для семьи: все видят, какая цель преследуется, какими средствами она достигается, когда проверяется эффект и что будет дальше. Отсюда рождается доверие и строгая приверженность — главный предиктор устойчивого результата.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в саратове[/url]
Замечательный, магазин. Желаю успешных продаж Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш А ты тс в лс отпиши , и если ты не балабол , в чем я очень сомневаюсь то проблема будет решена , а писать на ветке это говно для чего не понятно , на что вы надеетесьчерез нос – нет эффекта.
Наркологическая клиника — это пространство, где медицинская наука сочетается с психологической поддержкой и индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» лечение зависимости организовано по принципам доказательной медицины: каждый этап терапии основан на объективных данных, контролируемых результатах и четких критериях эффективности. Здесь помогают не просто устранить физические последствия зависимости, но и восстановить внутренние ресурсы человека, вернуть уверенность, осознанность и способность строить новую жизнь без алкоголя и наркотиков.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в воронеже[/url]
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в воронеже[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаМед Центр» — это круглосуточный медицинский комплекс, в котором экстренная помощь, капельницы и детоксикация объединены в единую клинико-поведенческую систему. Мы лечим не «симптом по одному», а управляем весь маршрут: от первичной стабилизации и снижения токсической нагрузки до восстановления сна, аппетита и рабочих ритмов. Каждый шаг имеет цель, измеримый маркер и назначенное «окно» переоценки — это исключает полипрагмазию и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и семьи. Конфиденциальность не декларируется, а обеспечивается регламентами: немаркированная логистика, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи и разграничение доступа к медзаписям.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» функционирует по принципу полного цикла лечения: от экстренного выезда нарколога до длительной реабилитации в условиях стационара. Пациенты поступают как в острых состояниях (запой, абстиненция, интоксикация), так и для плановой терапии. Лечение начинается с медицинской диагностики, оценки физического и психического состояния, после чего разрабатывается индивидуальный план. Программы включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психологическую помощь и профилактику рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
https://enran.ua/purposeprod/mebli-dlya-ofisu/
growthzone.click – Hub motivating strategic exploration of avenues that lead to meaningful development.
Корректная среда — половина успешной инфузии. Этот порядок действий помогает врачу быстрее принять решения, а пациенту — легче перенести первые часы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
move to Russia [url=www.primaryonehealth.org/wp-content/pgs/?healthcare-in-russia-for-expats-2025-guide-to-medical-services.html/]www.primaryonehealth.org/wp-content/pgs/?healthcare-in-russia-for-expats-2025-guide-to-medical-services.html/[/url] .
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-volgograd/
Если ваш старый пульт сломался или вы просто хотите обновить его до более современного и функционального варианта, то самое время [url=http://tv-console.kyiv.ua]дистанционные пульты цена[/url], который идеально подойдет для ваших потребностей и обеспечит комфортное управление вашим телевизором.
Приобретая телевизор, важно подумать о покупке пульта для телевизора. Это связано с тем, что пульт для телевизора является одним из наиболее важных аксессуаров для комфортного просмотра телевизора . Благодаря пульту можно легко переключать каналы, регулировать громкость и настраивать другие параметры телевизора .
При покупке пульта для телевизора необходимо обратить внимание на несколько моментов . Одним из ключевых моментов является совместимость пульта с вашим телевизором. Другим важным фактором является дизайн и эргономика пульта .
## Раздел 2: Типы пультов для телевизоров
В продаже имеются разные виды пультов для телевизоров, имеющие различные особенности. Один из наиболее популярных типов пультов – это пульт с инфракрасной связью. Этот тип пульта использует инфракрасные волны для передачи сигнала на телевизор .
Другой тип пульта – это пульт с радиочастотной связью. Этот тип пульта передает сигнал на телевизор с помощью радиоволн . Кроме того, существуют пульты с блютуз-соединением, которые позволяют управлять телевизором с помощью смартфона .
## Раздел 3: Выбор пульта для телевизора
При выборе пульта для телевизора необходимо учитывать несколько факторов . Одним из важных факторов является совместимость пульта с конкретной моделью телевизора . Другим важным фактором является дизайн и эргономика пульта .
Кроме того, важно учитывать функциональность пульта . Некоторые пульты имеют расширенные функции, такие как управление другими приборами. При приобретении пульта следует изучить отзывы других владельцев.
## Раздел 4: Заключение
В результате, покупка пульта для телевизора является необходимым этапом в установке телевизора. При приобретении пульта важно рассмотреть несколько ключевых аспектов, включая совместимость, дизайн и функциональные возможности. С помощью правильного пульта можно повысить уровень комфорта при просмотре телевизора .
[url=http://rukrepezh.ru]купить крепеж оптом[/url] – надежное решение для ваших строительных нужд.
Правильная установка крепежных изделий также является ключом к их долгосрочной эксплуатации.
Мы уверены что гарант не нужен магазину работающему с 2011 года + мы не работаем с биткоинами + везде положительные отзывы . https://scary-stories.ru Всем привет! Специально зарегистрировался для того что бы поведать вам, какой тут отличный магазин! Обращаюсь сюда уже 3 месяца всегда по опту! все на высоте! Время доставки кладом в мой город 4 дня! Качество продукта отличное! Клады хорошие! И главное пунктуальность, и грамотное общение с человеком… Желаю оставаться всегда такими же порядочными! Сразу видно что магазин знает свое дело в нашем не легком труде!!!Может всё-так “Рашн Холидейс” (c) China
Подготовка включает оценку соматического статуса, сверку текущих лекарств, обсуждение мотивации и планов на ближайшие недели. После процедуры назначаются контрольные контакты: специалист уточняет самочувствие, помогает адаптировать режим сна и питания, напоминает о «красных флажках» и корректирует план при изменениях графика или стресса. Пациент остаётся не один: ему доступны понятные регламенты действий, чтобы не «провалиться» в первые недели, когда вероятность срыва традиционно выше. Это снижает тревогу и делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным для здоровья и работы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли». Инфузии собираются из модулей — под ведущую задачу, время суток и соматический фон. Важна не только лекарственная часть, но и опора среды: тёплый свет вечером, акустическая тишина, вода малыми глотками, «чистая» цифровая зона без уведомлений. Такая «связка» усиливает терапевтический эффект без увеличения дозировок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen
отели краби тайланд Ко Ланта Как Добраться: паромом из Краби или Пхукета, возможен трансфер.
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/perm-narkologiya/https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» функционирует по принципу полного цикла лечения: от экстренного выезда нарколога до длительной реабилитации в условиях стационара. Пациенты поступают как в острых состояниях (запой, абстиненция, интоксикация), так и для плановой терапии. Лечение начинается с медицинской диагностики, оценки физического и психического состояния, после чего разрабатывается индивидуальный план. Программы включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психологическую помощь и профилактику рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
В клинике «ЮгМед Альянс» выстроена система непрерывного медицинского наблюдения. При поступлении проводится комплексная диагностика, назначается детоксикация и поддерживающая терапия, затем начинается стабилизация физического и эмоционального состояния. Благодаря круглосуточной работе бригад и возможности экстренного выезда на дом пациенты получают помощь без задержек. Конфиденциальность соблюдается на всех уровнях — от первичного звонка до выписки. Для удобства родственников организована система информирования: короткие апдейты по согласованным каналам связи и только в определённое время, чтобы не нарушать покой пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]эротические фильмы[/url]
Explore 716 Selfie – Sharing photos and participating in trends is easy and fun on this site.
Для тех, кто предпочитает лечение в условиях стационара, предусмотрены комфортные палаты, медицинский контроль 24/7 и возможность консультаций с психотерапевтом. Врачи клиники применяют комплексные методы, направленные не только на снятие симптомов, но и на устранение причин зависимости.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Хмм…странно всё это, но несмотря ни на что заказал норм партию Ам в этом магазе так как давно тут беру.Как придёт напишу норм репорт про Ам https://skazka-v.ru Ребят подскажите что лучше взять:)желательно с пропорциями и качеством по времения не согласен предыдущем коментариям ,беру не первый раз ,на данный момент магазин самый охриненный ,всегда качество товара радует,всегда на связи они,они не когда не морозятся,своё дело знают чётко,нахрена им кидать ,они не будут портить свою репутацию какую уже заработал этот магазин,я беру поболее и меня не разу сдесь не кинули .процветания магазину .спасибо за вашу работу,что всё чётко и быстро И радуете вкусняшками.а ещё хочу добавить ,возможно это кидаки или канкуренты и пишут разную х….ю что бы сбить новичков ,Но мы кто всегда с вами знаем что магазин лучший и другого Нам НЕНАДО.Так держать ,МЫ ВСЕГДА С ВАМИ!!!
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Nature-inspired shop – The products feel organic, and the overall experience is peaceful and easy.
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре тюмень[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в перми[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Основные этапы включают:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево красноярск[/url]
Базы пробитые Xrumer телеграм xrumer 23: Последняя версия программного обеспечения Xrumer.
Основная задача стационарного лечения — не просто вывести человека из кризисного состояния, а вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость физиологических функций. Поэтому врачи клиники используют современные методы детоксикации, витаминотерапии, ноотропные препараты, психотерапевтические практики короткого действия и физиотерапевтические модули, направленные на восстановление сна, памяти и концентрации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ставрополь[/url]
Показана при обезвоживании, «скачущем» давлении и пульсе, угрозе судорог, упорной рвоте, эпизодах спутанности сознания, тяжёлой соматике. За сутки–двое удаётся выровнять показатели, наладить сон и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному этапу.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]klinika-narkologii-moskva[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Новокузнецке предоставляет профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под наблюдением опытных специалистов с применением современных медицинских методик. Основная цель работы клиники — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить психологическое равновесие пациента, вернуть мотивацию и способность жить без употребления веществ.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике новокузнецк[/url]
p/s мне ничего не надо! Зашёл пожелать удачи магазину в нелегком деле. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш заказал rcs-4, чет не радует отзывы, как придет со дня на день посмотрим, что выйдет отпишусь, буду делать 1к 10-ти…”Достаточно связаться с нами и отправить на указанный e-mail информацию о заказе и получателе. Конфиденциальность гарантируется.”
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов[/url]
Поэтапное лечение помогает врачам контролировать процесс восстановления и своевременно корректировать терапию в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены самара[/url]
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Задача врача — не «поставить галочку», а исключить противопоказания и выбрать методику с оптимальным соотношением пользы и риска. Учитываются хронические заболевания, эпизоды потери сознания, аритмии, панические атаки, депрессивные симптомы, переносимость инфузий и фармпрепаратов, взаимодействия с уже назначенными лекарствами. По результатам формируется персональный лист ограничений и список «красных флажков», при которых следует связаться со специалистом без промедления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-samara/
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом самара[/url]
movetorussia com [url=www.xn--fachanwaltfrverkehrsrecht-pwc.com/pgs/russian-immigration-lawyer-complete-guide-to-legal-assistance-2025.html]www.xn--fachanwaltfrverkehrsrecht-pwc.com/pgs/russian-immigration-lawyer-complete-guide-to-legal-assistance-2025.html[/url] .
экскурсия краби про Остров Ко Ланта отзывы: помогут выбрать лучший вариант отдыха.
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр саратов[/url]
Вывод из запоя осуществляется в несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на постепенное восстановление организма. Такой поэтапный подход снижает нагрузку на внутренние органы и повышает эффективность лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Первый полноценный сон — переломный момент в выводе из запоя. В «АлкоМед Балашиха» мы создаём условия для него с первого дня: затемнение, тишина, комфортная температура, минимизация стимулов, ранний отбой. Если требуется, подключаем мягкие седативные схемы под мониторинг. Утром — контроль показателей, уточнение дозировок, план активности «по силам», корректировка питания и воды. Мы заранее проговариваем, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, умеренная слабость), а какие — требуют связи со специалистом. Чёткая ночная стратегия снижает импульсивность и убирает главный триггер срывов — усталость и бессонницу, из-за которых даже корректно подобранные инфузии теряют эффективность к вечеру следующего дня.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo[/url]
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в перми[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
Стабилизация — момент, когда важно добавить поведенческие инструменты: карту триггеров, сценарии на «тёмные часы», короткие «буферы» по 20–40 минут, план безопасной активности. Этот слой не заменяет медицину, но удерживает её результат.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
Городской ритм Саратова — длинные переезды через мост, активное движение в центре и контрастные микрорайоны — накладывает отпечаток на логистику и сенсорную среду, в которой проходит лечение. Мы адаптируем маршрут под город: назначаем «тихие окна» связи, уменьшаем световую нагрузку в вечернее время, организуем немаркированные выезды, а при стационарном поступлении готовим палату с тёплой подсветкой и акустическим поглощением. Эти, казалось бы, «не медицинские» решения позволяют снизить тревогу, быстрее стабилизировать пульс и сделать сон физиологичным без переседации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма саратов[/url]
лучше недобздеть чем перебздеть!!! братуха я надеюсь и у тебя все будет ГУД! держи в курсе https://sibohota.biz получил посыль.мхе отличного качества!а вот ам2233 пока думаю ко скольки мутить.все пишут по разному.последнее время стал закупаться в чемикал и не капельки в этом не пожалел, всё всегда вовремя высылают даже быстрее заявленного времени! качество радует!) да и просто отличный магазин!!!
Здесь
[url=https://arbagroup-russia.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Член литературного клуба «Творчество и потенциал» Селезинка Александр Михайлович родился в 1976 г. Проживает в с. Дивеево Нижегородской области. Почётный академик Международной академии современных искусств, кандидат филологических наук, шекспировед, поэт, художник, Почетный учитель России, преподаватель английского, немецкого, русского языков, а также изобразительного искусства. Автор монографии “Библейские аллюзии в творчестве В. Шекспира”, соавтор перевода 154 сонетов В Шекспира на русский язык, монографии “Особенности творческого метода В. Шекспира” и четырех частей книги «Духовные сонеты». Участник художественных выставок. Открыл 5 персональных выставок. Член Союза русских художников. Член Евразийского художественного союза. Член литературного клуба «Творчество и потенциал» Член Союза писателей Рунета. Член Российского союза писателей. Лауреат международного конкурс искусств “Artex Awards”. Лауреат конкурса “Звезда Виртуоза”. Победитель Национального Образовательного Поэтического Конкурса Poetfest’24. Победитель конкурса «Голоса эпохи» в номинации «Выбор редакции». Награжден медалью «225 лет А. С. Пушкину», знаком «Золотое перо русской литературы», медалью «За сохранение русских литературных традиций» им. Великой княгини Ольги, медалью имени Л. Н. Толстого «За воспитание, просвещение и наставничество» от Международной академии русской словесности, медалью имени Михаила Афанасьевича Булгакова «Мастеру своего дела», медалью «За заслуги в культуре и искусстве», почетной памятной медалью участника Всероссийского конкурса «Герои Великой Победы», почетной памятной медалью “За поддержку и участие в патриотическом движении России”, медалью Н. В. Гоголя «За особые заслуги», медалью «130 лет С. А. Есенину».
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены самара[/url]
I blog frequently and I seriously thank you for your information. This great article has really peaked my interest.
I will book mark your website and keep checking for new information about once a week.
I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
Капельница — основной метод дезинтоксикации при запое. Она позволяет быстро восполнить дефицит жидкости и электролитов, вывести токсины и улучшить общее самочувствие. В состав инфузии входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ, а также витамины и гепатопротекторы. Процедура проводится под контролем врача, что гарантирует безопасность и точную дозировку лекарств.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому ростов-на-дону[/url]
Госпитализация показана, когда требуется непрерывный контроль и быстрые изменения схем лечения. В стационаре устраняют выраженные симптомы отмены, корректируют электролитные нарушения, поддерживают печёночные функции, при необходимости подключают кислород и аппаратные методы диагностики. Параллельно выравнивают сон и аппетит, закрывают дефициты микроэлементов, подбирают щадящий режим нагрузки. На выписке пациент получает подробные рекомендации: как дозировать активность, когда пить воду и в каких объёмах, какие препараты принимать и при каких признаках обращаться за консультацией без ожидания. Такой формат снижает риск осложнений и даёт предсказуемую динамику уже на горизонте нескольких дней.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
worldgoodscentral – WorldGoodsCentral offers a variety of selections that are engaging and simple to explore.
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-na-domu-moskva[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь рязань[/url]
Organized growth platform – Encourages planning actionable steps to advance efficiently
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Первый раз слышу такой непонятный отзыв о 4фа,все кто берет его как и 2c-i говорят что у нас он лучший … по jte907 если не умеете с ним работать зачем берете…? есть постоянные оптовики кто берет только его, и этот продукт нареканий не вызывает. Многие “Селлеры” под видом jte продают 2201 и это факт! у нас этот продукт в оригинале. МХЕ у нас такой пришел, мы не кричим что его чистота 99%, и что качество его не очень мы предупреждали всех… Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Всем удачи!Может всё-так “Рашн Холидейс” (c) China
Georgetown downtown portal – Users can learn about projects, see layouts, and explore the plan in a clear and interactive way.
Если у человека выраженное обезвоживание, скачки давления и пульса, эпизоды спутанности сознания, упорная рвота, «дергающийся» сон или тяжёлая сопутствующая патология, стационар закрывает главный риск — непредсказуемое течение синдрома отмены. Круглосуточный мониторинг позволяет динамически корректировать схемы, подключать лабораторные и инструментальные исследования по показаниям, своевременно восполнять дефициты и удерживать стабильный сон. На практике «короткое окно» госпитализации (24–48 часов) нередко дешевле на дистанции: оно предотвращает осложнения и повторные вызовы, которые растягивают курс и увеличивают суммарные затраты. Для жителей Москвы мы разносim визиты по времени, используем отдельные входы и «тихие» маршруты, чтобы сохранить приватность. После стабилизации маршрут переводится в амбулаторный или домашний формат: пациент получает план питания и активности, контрольные контакты и правила, при каких признаках связаться немедленно, не дожидаясь «как будет утром».
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-moskva[/url]
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма саратов[/url]
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Рынок продвижения в ИИ-системах
Refreshing finds store – Browsing feels effortless, with practical products that are nicely presented.
Для наглядности представлен примерный состав инфузионного раствора, используемого при выводе из запоя:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре ростов-на-дону[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]центры кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]vyzov narkologa na dom[/url]
Магаз пропал из аськи и скайпа… Тобишь просто не появляется в онлайне. Такое уже бывало, но щас хз что… Качество товара было отменным. 203й высочайшего качества. https://avto-luks.ru есть и кристаллический и порошкообразный. разницы в эффекте нет.Я вот перед заказом почитала хуеву кучу отзывов и не нашла ни одного хуевого. Но опять же, смотри, отзывы были не об эйфоре, а о самом магазине. Давай друг, советуй что-нибудь в личку
xrumer купить телеграм Базы Хрумер: Альтернативное написание термина “Базы Xrumer”, также обозначающее списки веб-сайтов для автоматизированной рассылки. Часто используется как синоним. Подчеркивается важность использования только легальных и проверенных баз для предотвращения негативных последствий.
Терапия в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить безопасность и прозрачность процесса. Пациент постепенно проходит все стадии восстановления организма и психики.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-omsk
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
skillboost.click – Hub emphasizing fast learning techniques and practical application for growth.
В наркологической клинике в Омске применяются только проверенные методы, эффективность которых подтверждена клинической практикой. Они помогают воздействовать на разные стороны зависимости и обеспечивают комплексный результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в омске[/url]
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Эффект ощущается уже через 20–40 минут после начала процедуры. Пациент отмечает снижение головной боли, улучшение сна и общего состояния. Полное восстановление самочувствия наступает в течение суток.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Такой подход позволяет точно отслеживать динамику и вносить изменения в программу без потери контроля. Пациент видит прогресс, а врачи получают объективные данные о реакции организма на лечение.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru
где находится краби в тайланде Расстояние От Новокузнецка До Ко Ланты: очень большое, долгий перелет.
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Не покупайте у данного селлера пока не решится ситуация Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш да конспирацию отработали 😉 стараемсяобращаюсь по возможности сюда беру оптом от 50 грамм
Ваши советы о играх — очень интересные.
Olimp Casino онлайн – http://b933642z.bget.ru/user/OlimpCasino%EE%ED%EB%E0%E9%ED/ –
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаМед Центр» — это круглосуточный медицинский комплекс, в котором экстренная помощь, капельницы и детоксикация объединены в единую клинико-поведенческую систему. Мы лечим не «симптом по одному», а управляем весь маршрут: от первичной стабилизации и снижения токсической нагрузки до восстановления сна, аппетита и рабочих ритмов. Каждый шаг имеет цель, измеримый маркер и назначенное «окно» переоценки — это исключает полипрагмазию и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и семьи. Конфиденциальность не декларируется, а обеспечивается регламентами: немаркированная логистика, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи и разграничение доступа к медзаписям.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov/
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
Основная задача стационарного лечения — не просто вывести человека из кризисного состояния, а вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость физиологических функций. Поэтому врачи клиники используют современные методы детоксикации, витаминотерапии, ноотропные препараты, психотерапевтические практики короткого действия и физиотерапевтические модули, направленные на восстановление сна, памяти и концентрации.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy/
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого самара[/url]
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Клиника предлагает возможность круглосуточного пребывания в комфортных палатах. Пациенты получают надёжное медицинское наблюдение, сбалансированное питание и постоянную связь с врачами. Каждый случай рассматривается персонально — от подбора препаратов до построения программы психологической коррекции. Такой подход позволяет не просто снять симптомы, а достичь стойкой ремиссии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике рязань[/url]
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в волгограде[/url]
Если у человека выраженное обезвоживание, скачки давления и пульса, эпизоды спутанности сознания, упорная рвота, «дергающийся» сон или тяжёлая сопутствующая патология, стационар закрывает главный риск — непредсказуемое течение синдрома отмены. Круглосуточный мониторинг позволяет динамически корректировать схемы, подключать лабораторные и инструментальные исследования по показаниям, своевременно восполнять дефициты и удерживать стабильный сон. На практике «короткое окно» госпитализации (24–48 часов) нередко дешевле на дистанции: оно предотвращает осложнения и повторные вызовы, которые растягивают курс и увеличивают суммарные затраты. Для жителей Москвы мы разносim визиты по времени, используем отдельные входы и «тихие» маршруты, чтобы сохранить приватность. После стабилизации маршрут переводится в амбулаторный или домашний формат: пациент получает план питания и активности, контрольные контакты и правила, при каких признаках связаться немедленно, не дожидаясь «как будет утром».
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-moskve/
Физическое облегчение — лишь половина задачи; вторая половина — эмоции и привычки. Индивидуальные сессии помогают распознать автоматические мысли, планировать «буферы» на вечерние часы, управлять стрессом и сонливостью, расставлять «сигнальные маяки» на привычных маршрутах, где чаще всего возникают соблазны. Семья получает ясные инструкции: меньше контроля — больше поддержки правил среды (тишина, затемнение, прохлада, вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»), отказ от «разборов причин» в первую неделю, короткие договорённости о связи со специалистом при тревожных признаках. Когда у всех одни и те же ориентиры, уровень конфликтов падает, а предсказуемость растёт — это напрямую укрепляет ремиссию. Мы не перегружаем психологический блок «теорией»: даём только те инструменты, которые человек готов выполнить сегодня и завтра, без рывков и самообвинений. Такая практичность приносит больше пользы, чем долгие разговоры «о мотивации», и отлично сочетается с медицинской частью плана.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]klinika-narkologii-moskva[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve/
После инфузии врач повторно измеряет показатели, оставляет письменные инструкции, назначает окно связи и определяет условия, при которых разумно перейти к стационару: нет нужды держаться «на силе воли», когда безопаснее сменить формат.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/[/url]
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
2с на высоте, прет огого как, сыпали по чуточки кто на что горазд, у меня до сих пор постэффекты https://dostindir.biz Поздравляю всех с наступающим Новым 2013 Годом! Желаю в год Змеи: 1. Мутить тока на спирту! 2. Отваривать основу. 3. Сушить естественным способом. 4. Поменьше “ловить бледного”! 🙂 Ну а магазу Chеmical-Mix желаю Процветания, Оперативности, и качественной разнообразной продукции!люди которые делают заказы через ВК по меньшей мере идиоты. Особенно когда ИМ самим что то предлагают.
Step execution hub – Provides methods to implement plans effectively for growth
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]ceny-adresa-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент и для пациента, и для семьи: все видят, какая цель преследуется, какими средствами она достигается, когда проверяется эффект и что будет дальше. Отсюда рождается доверие и строгая приверженность — главный предиктор устойчивого результата.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм саратов[/url]
Каждый пациент проходит несколько последовательных этапов, направленных на очищение организма, стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и формирование стойкой мотивации к трезвой жизни. Такой подход позволяет не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и укрепить психическую устойчивость.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara
Discussion and insight hub – Readers are encouraged to explore ideas and participate in thoughtful dialogue.
Современная наркологическая клиника «ЮгМед Альянс» в Ставрополе объединяет медицинскую точность и психологическую чуткость. Здесь лечение зависимостей выстроено по принципу системной логики: одно вмешательство — одна цель — один критерий оценки. Такой подход делает процесс предсказуемым и снижает нагрузку на организм. Мы не просто устраняем симптомы, а ищем причину, формируем новые устойчивые модели поведения и помогаем пациенту вернуть контроль над жизнью. Наша команда работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая поддержку и безопасное сопровождение на каждом этапе — от детоксикации до реабилитации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника ставрополь[/url]
Смысл экстренной помощи — не в «сильной капельнице любой ценой», а в последовательности. Бригада приезжает в согласованное окно, проводит экспресс-осмотр, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ. Далее подбирается инфузионная терапия по показаниям, корректируется водно-электролитный баланс, снижаются тремор и тревога, выравнивается сон. Важно объяснить семье и самому пациенту, чего ожидать: какие ощущения нормальны, какие — повод для связи, зачем назначены те или иные растворы и поддерживающие препараты. Параллельно формируется краткий план «сложных часов» на вечер и ночь: что делать, если накрывает волну беспокойства, как распределить жидкость и питание, какие бытовые действия лучше отложить. В московском ритме особенно критично не растягивать решения на «завтра»: від организованного визита до ощутимого облегчения обычно проходит один-два часа, и именно этот отрезок задаёт тон всей последующей стабилизации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Показана при обезвоживании, «скачущем» давлении и пульсе, угрозе судорог, упорной рвоте, эпизодах спутанности сознания, тяжёлой соматике. За сутки–двое удаётся выровнять показатели, наладить сон и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному этапу.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника волгоград[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Домашний старт в Москве уместен при устойчивых показателях и низком риске осложнений: нет упорной рвоты, выраженной дезориентации, лихорадки, резких скачков давления и пульса. Преимущества — приватность, скорость, меньше стыда и сопротивления, выше шансы на ранний сон. Если же присутствуют признаки возможных осложнений (обезвоживание, судорожная готовность, аритмии, боль за грудиной/в животе, спутанность), рациональнее короткая стационарная стабилизация на 24–48 часов, после которой маршрут возвращается домой. «Трезвый Стандарт» держится принципа клинической достаточности: вмешательств ровно столько, сколько нужно сегодня, без «пакетов ради прайса». Такой реализм экономит деньги и главное — время семьи, потому что снижает вероятность ночных «качелей», повторных вызовов и импульсивных решений, которые чаще всего и ломают прогресс.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]narkolog na dom kruglosutochno[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Visit Soft Breeze – Shopping feels calm and effortless, and the items are thoughtfully arranged.
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]нарколог на дом москва цены[/url]
отличный селлер https://igrushki-dlya-detey.ru Магазин не работает по выходными и праздникамбрал 500 в регион, ранее с этим магазином не работал.. поэтому крайне волновался. Как оказалось зря. Все в лучшем виде ! спасибо !
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом новокузнецк[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника волгоград[/url]
Процесс лечения в клинике организован последовательно и направлен на восстановление всех систем организма. Каждый этап имеет свои задачи и методы, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno/
Домашняя точка входа оправдана при стабильных показателях и низком риске осложнений. В знакомой обстановке легче соблюдать режим: затемнить комнату, убрать экраны, распределять воду маленькими порциями, сделать лёгкий перекус «по силам», лечь пораньше. Врач подберёт «узкую» схему инфузий без перегруза препаратами, объяснит, какие ощущения допустимы сегодня и ночью, а какие — повод для немедленной связи. Такой сценарий экономит время семьи, снижает стигму и быстрее переводит состояние в управляемое, на базе которого уже можно строить дальнейшие шаги — амбулаторные визиты, работу с триггерами и, при показаниях, обсуждение кодирования.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare[/url]
Осмотр > мониторинг > инфузии по показаниям > план вечера и ночи > письменные рекомендации > окно связи на следующий день. Эта линия делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому москва[/url]
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий. Инфузии подбираются индивидуально: цель — восстановить объём циркулирующей крови, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, вернуть условия для сна. Мы не перегружаем препаратами, не «гоняем» симптом силой седативов и не используем универсальные растворы «для всех». Поддержка сна строится на минимально достаточных дозах и гигиене вечернего времени: затемнение, тишина, отказ от экранов, ранний отбой. Параллельно врач объясняет, как пить воду маленькими порциями, когда сделать лёгкий перекус, зачем планировать короткую дневную паузу. После купирования остроты пациент получает чёткий план на трое суток — простые, реалистичные шаги, которые удерживают эффект без «героизма» и без лишней фармакологической нагрузки. В результате медицинский эффект не растворяется в быту, а закрепляется привычками, которые по силам выполнить сегодня и завтра.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom-v-moskve/
Эта последовательность действий обеспечивает безопасное прекращение запоя и предотвращает развитие синдрома отмены.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.maryco.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс шоп[/url]
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
Поэтапный подход помогает достичь устойчивых результатов и минимизировать вероятность рецидива, обеспечивая безопасность пациента на всех стадиях лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в самаре[/url]
брал все как всегда на 10 баллов забил Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Всё здорово спасибо ВамПродован 1000 балоф те =)
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-na-domu-moskva[/url]
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Углубиться в тему – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-moskve-otzyvy/
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Близкие часто пытаются «ускорить» результат контролем или уговором — в итоге растёт напряжение и человек уходит в сопротивление. Мы предлагаем другое: сосредоточиться на среде. Первые дни важны тишина, затемнение, комфортная температура, вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», отсутствие обсуждений «прошлых ошибок». Полезно заранее договориться о кратких сигналах: как понять, что нужна помощь, а когда лучше оставить человека в покое. Семье также поясняется, что бессонница более двух ночей подряд, постоянная рвота, выраженная слабость и головокружение — поводы для немедленной связи с врачом. Когда роли и правила ясны, уходит хаос, снижается конфликтность, а домашний маршрут становится не «борьбой характеров», а медицинской задачей с понятными шагами. Это напрямую укрепляет приверженность и сокращает путь к стабильности в реальном ритме Москвы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
праздники мы тоже отдыхали, так как курьерки все равно не работают Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Давай зафиналим на мировой.качество реги просто супер,такого еще не встречали
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Hi to all, it’s genuinely a good for me to visit this site, it contains priceless
Information.
a href=”https://authenticlivinggoods.click/” />truelivingzone – TrueLivingZone provides carefully curated selections that make discovering products fun.
Forward thinking platform – Encourages clear, purposeful actions for instant advancement
freshideas.click – Hub guiding individuals to develop innovative solutions and forward-thinking approaches.
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Unquestionably believe that which you stated.
Your favorite justification appeared to be on the net the easiest thing to
be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while
people consider worries that they just don’t know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also
defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
strategic action roadmap – Helps organize tasks clearly to achieve long-term goals.
Наркологическая клиника в Перми использует современные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом клинической картины пациента. Каждый метод имеет конкретные цели и задачи, что делает процесс лечения прогнозируемым и безопасным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в перми[/url]
My brother suggested I might like this blog.
He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
доброй ночи ровной ветке! Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Товар привезли качество удовлетворительное,единственное что заказ долго оформляли не мог достучаться в асю.А так все норм!=))ВСЕ ВОПРОСЫ ПО ДОСТАВКЕ ОБСУЖДАЮТСЯ В ЛИЧКЕ С ТС ПРИ ОФОРМЛЕНИИ ЗАКАЗА.
В Sultan Casino представлен широкий спектр игровых продуктов
В Новокузнецке команда «РеабКузбасс» организовала круглосуточный выезд наркологов, что позволяет оказывать помощь даже в сложных ситуациях. Пациенты часто обращаются после многодневного употребления алкоголя, когда нарушен сон, давление нестабильно, а организм истощён. В таких случаях врач выезжает в течение часа, проводит осмотр, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает оптимальную терапию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новокузнецке[/url]
I’ll immediately take hold of your rss feed as I can not to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or
newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognize so
that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Наркологическая клиника в Омске специализируется на оказании профессиональной помощи людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя и наркотиков. Лечение строится на принципах доказательной медицины и сочетает современные методы детоксикации, фармакотерапии, психотерапевтической поддержки и программ социальной адаптации. Комплексный подход позволяет пациентам не только стабилизировать состояние, но и вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника пермь[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма новокузнецк[/url]
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в воронеже[/url]
Физическое облегчение — лишь половина задачи; вторая половина — эмоции и привычки. Индивидуальные сессии помогают распознать автоматические мысли, планировать «буферы» на вечерние часы, управлять стрессом и сонливостью, расставлять «сигнальные маяки» на привычных маршрутах, где чаще всего возникают соблазны. Семья получает ясные инструкции: меньше контроля — больше поддержки правил среды (тишина, затемнение, прохлада, вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»), отказ от «разборов причин» в первую неделю, короткие договорённости о связи со специалистом при тревожных признаках. Когда у всех одни и те же ориентиры, уровень конфликтов падает, а предсказуемость растёт — это напрямую укрепляет ремиссию. Мы не перегружаем психологический блок «теорией»: даём только те инструменты, которые человек готов выполнить сегодня и завтра, без рывков и самообвинений. Такая практичность приносит больше пользы, чем долгие разговоры «о мотивации», и отлично сочетается с медицинской частью плана.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I to find It truly helpful &
it helped me out much. I’m hoping to present something
back and aid others like you helped me.
В клинике используется модульная система лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные компоненты. В зависимости от состояния человека акценты могут смещаться — например, у одних пациентов приоритетом становится физиологическое восстановление, у других — коррекция эмоционального фона и когнитивных паттернов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ставрополе[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti/
остров ко ланта в тайланде паром ко ланта
Игнорирование этих симптомов может привести к тяжёлым последствиям — судорогам, галлюцинациям или алкогольному психозу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий, а не один универсальный раствор. Мы восполняем жидкость и корректируем электролиты, защищаем печёночные функции, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, создаём условия для первого нормального сна. Каждая доза сверяется с динамикой давления, пульса, сатурации и неврологического статуса, поэтому схема не перегружена и не «гонится» за мимолётным эффектом ценой побочных реакций. После купирования острых проявлений начинается стабилизация: уточняются дозировки, выстраивается режим питания и гидратации, объясняются «красные флажки» для контакта с врачом, настраиваются простые поведенческие техники на «тёмные часы» вечера. В этот момент особенно важно не растворить медицинский эффект бытовыми ошибками: недосыпом, пропусками еды, конфликтными разговорами «о прошлом». Мы даём короткие, реалистичные алгоритмы на 20–40 минут — прогулка, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по графику, дыхательные практики — чтобы снизить импульсивность и закрепить ощущение управляемости. Именно связка детокса с поведенческой дисциплиной формирует траекторию, которую можно удержать неделями, а не только до «завтрашнего утра».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve-ceny
Если ваш старый пульт сломался или вы просто хотите обновить его до более современного и функционального варианта, то самое время [url=http://tv-console.kyiv.ua]купить пульт ду для телевизора[/url], который идеально подойдет для ваших потребностей и обеспечит комфортное управление вашим телевизором.
Приобретая телевизор, важно подумать о покупке пульта для телевизора. Это связано с тем, что пульт для телевизора играет ключевую роль в управлении телевизором. С помощью пульта можно выполнять различные функции, такие как переключение каналов и регулировка громкости .
При выборе пульта для телевизора важно учитывать несколько факторов . Одним из них является совместимость пульта с телевизором . Другим важным фактором является дизайн и эргономика пульта .
## Раздел 2: Типы пультов для телевизоров
Существует несколько типов пультов для телевизоров, каждый из которых имеет свои уникальные характеристики . Один из наиболее распространенных типов пультов – это пульт, работающий на инфракрасном сигнале . Этот тип пульта передает сигнал на телевизор с помощью инфракрасного излучения .
Другим типом пульта является пульт с радиочастотным сигналом . Этот тип пульта использует радиочастотные волны для передачи сигнала на телевизор . Также имеются пульты с блютуз-соединением, которые ermogняют управление телевизором через мобильное устройство .
## Раздел 3: Выбор пульта для телевизора
При приобретении пульта для телевизора важно рассмотреть несколько ключевых аспектов. Одним из них является совместимость пульта с телевизором . Другим моментом, на который стоит обратить внимание, является дизайн и удобство использования пульта .
Также необходимо обратить внимание на функции пульта . Некоторые пульты обладают дополнительными возможностями, такими как управление другими гаджетами . При приобретении пульта следует изучить отзывы других владельцев.
## Раздел 4: Заключение
В заключении, покупка пульта для телевизора является важным этапом в настройке домашнего кинотеатра . При выборе пульта необходимо учитывать несколько факторов, включая совместимость, дизайн и функциональность . Используя подходящий пульт, можно максимально наслаждаться телевизионными программами.
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в саратове[/url]
Many thanks. Lots of info!
https://substack.com/home/post/p-181768354
Думать тут остается только одно: хуйня какая то происходит непонятная… https://trapezaspb.ru качество очень хорошее не подведёт даже не сомневайсяДоброго времени суток, оплатил заказ, данные для оплаты дали как всегда оперативно!, жду клад!
ко ланте ко ланта
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бесплатные порно видео[/url]
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this brilliant blog!
I suppose for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account.
I look forward to fresh updates and will share this blog with my
Facebook group. Talk soon!
Здесь
[url=https://artsofte.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс шоп[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом саратов[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru
Подготовка включает оценку соматического статуса, сверку текущих лекарств, обсуждение мотивации и планов на ближайшие недели. После процедуры назначаются контрольные контакты: специалист уточняет самочувствие, помогает адаптировать режим сна и питания, напоминает о «красных флажках» и корректирует план при изменениях графика или стресса. Пациент остаётся не один: ему доступны понятные регламенты действий, чтобы не «провалиться» в первые недели, когда вероятность срыва традиционно выше. Это снижает тревогу и делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным для здоровья и работы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-bolnica-moskvy[/url]
спасибо , стараемся для людей Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон заказал не мало,всё пришло за кач не знаю как опробуют кролы отпишув Обьщем как и говорил заказал ам,оно пришло в город,а мою фамилию ПЕРЕПУТАЛИ ,посылку не выдают…….
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре предлагает профессиональное лечение алкогольной, наркотической и других форм зависимости с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ. Основная цель работы специалистов — помочь пациенту восстановить физическое и психическое здоровье, вернуть контроль над собственной жизнью и предотвратить рецидив. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинской этики, конфиденциальности и стандартов безопасности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь самара[/url]
제가 유튜브 영상 다운로드 화질 4K 다운방법을 찾다가 이용한 사이트 ‘SSYouTube’가 좋았던 건, 무엇보다 무료라는 점이었어요.
Запой сопровождается сильной интоксикацией, обезвоживанием и нарушением обменных процессов. Врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, определяет тяжесть отравления и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии. Основная цель — восстановление водно-электролитного баланса, нормализация работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Современные препараты позволяют мягко вывести человека из состояния запоя, исключив развитие судорог, делирия и других осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону[/url]
Домашняя точка входа оправдана при стабильных показателях и низком риске осложнений. В знакомой обстановке легче соблюдать режим: затемнить комнату, убрать экраны, распределять воду маленькими порциями, сделать лёгкий перекус «по силам», лечь пораньше. Врач подберёт «узкую» схему инфузий без перегруза препаратами, объяснит, какие ощущения допустимы сегодня и ночью, а какие — повод для немедленной связи. Такой сценарий экономит время семьи, снижает стигму и быстрее переводит состояние в управляемое, на базе которого уже можно строить дальнейшие шаги — амбулаторные визиты, работу с триггерами и, при показаниях, обсуждение кодирования.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-kruglosutochno[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
ко ланта ко ланта
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]наркологическая москва[/url]
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Первый полноценный сон — переломный момент в выводе из запоя. В «АлкоМед Балашиха» мы создаём условия для него с первого дня: затемнение, тишина, комфортная температура, минимизация стимулов, ранний отбой. Если требуется, подключаем мягкие седативные схемы под мониторинг. Утром — контроль показателей, уточнение дозировок, план активности «по силам», корректировка питания и воды. Мы заранее проговариваем, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, умеренная слабость), а какие — требуют связи со специалистом. Чёткая ночная стратегия снижает импульсивность и убирает главный триггер срывов — усталость и бессонницу, из-за которых даже корректно подобранные инфузии теряют эффективность к вечеру следующего дня.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-balashiha[/url]
Так что тут 50:50 если тебя примут. Все зависит от конкретного города и гнк в нем. https://sko-perm.ru Если кто-то когда-то пробовал банки с Рафинада на тусиае, тот знает, как классно они перли и понимает, каких эффектов я ожидал.орогуша! А что здесь людям писать как не о работе магазина? Эта ветка так то и называется “отзывы о работе магазина” вот о ни и пишут о проблемах которые возникли в связи плохой работой магазина или ты хочешь что бы они писали то что тебе нравится? как здесь все круто и классно? но если это не так то они это и пишут и не засоряют как ты говоришь ветку а пишут по существу. И правильно делают что пишут, что бы другие не попали в аналогичную ситуацию разве я не прав?
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh
Clarity momentum hub – Provides insights to build focused momentum and structured growth
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в воронеже[/url]
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]онлайн покер на деньги[/url]
Этапы терапии выглядят следующим образом:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Труба бронзовая 100х20х1500 мм БрОФ10-1 ГОСТ 1208-2014 Приобретайте трубы бронзовые круглые от профессионалов с опытом. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент качественной продукции, быструю обработку заказов и оперативную доставку. Обращайтесь, чтобы получить консультацию специалиста и выгодные условия покупки.
Запой — это не только усталость и похмелье. В первые часы нарастают обезвоживание, электролитные сдвиги, скачки давления и пульса, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон и аппетит. На этом фоне резко возрастает риск аритмий, судорожной готовности, ухудшения когнитивных функций и травм вследствие падений. «МедТоника» организует помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один на один с симптомами: с первого звонка дежурный врач уточняет длительность и объём употребления, принимает во внимание сопутствующие заболевания и лекарства, оценивает риски по давлению, пульсу, сатурации и ориентирует, где безопаснее стартовать — на дому или в стационаре. Цель первых суток — снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и поведению, чтобы далее перейти к предсказуемой стабилизации. Когда есть ясный план на 48–72 часа, снижается вероятность срыва и импульсивных решений, которые обычно и ломают прогресс.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve-nedorogo/
forward progress tips – Encourages structured planning to achieve goals efficiently.
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма в Москве отзывы[/url]
Осмотр > мониторинг > инфузии по показаниям > план вечера и ночи > письменные рекомендации > окно связи на следующий день. Эта линия делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-stoimost-volgograd/https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Для наглядности приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы лечения и их цели:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены самара[/url]
Для наглядности представлен примерный состав инфузионного раствора, используемого при выводе из запоя:
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
ко ланта как добраться остров ко ланта
Мы не подгоняем всех под единый сценарий. Если состояние устойчивое, нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации и резких скачков давления и пульса — рационален домашний старт: приватно, быстрее и без лишних переездов. Врач приедет без маркировки, проведёт осмотр, запустит инфузионную терапию по показаниям, оставит письменные рекомендации и «красные флажки». Если же есть признаки угрозы осложнений — обезвоживание, аритмии, риск судорог, боли за грудиной или в животе, лихорадка, спутанность сознания, тяжёлая соматика — мы честно предлагаем короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов. Под круглосуточным наблюдением проще корректировать схемы, вовремя закрывать дефициты, защитить сон и быстрее вернуть управляемость поведению. В обоих форматах маршрут прозрачен: согласованные окна связи, фиксированные цели на ближайшие 72 часа и отсутствие «пакетов ради прайса». Благодаря этому решения принимаются спокойно, без угадываний и эмоциональных раскачек, которые обычно ломают прогресс и удорожают лечение.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
мне тоже все пришло. да и еще вещь нужную в хозяйстве подогнали. вы ребята вообще МОЛОДЦЫ. ВСЕХ БЛАГ ВАМ. Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон А ВОТ Я ТОЖЕ КИПИШЕВАЛ ПО СЧЕТУ ТРЕКА НЕ БИЛСЯ ТОЖЕ ПОЗВОНИЛ В КУРЬЕРКУ СКАЗАЛИ ОТПРАВЛЕННО И СЕГОДНЯ К ВЕЧЕРУ ВСЕ ОТБИЛОСЬ ЖДУ ПРИХОДА ПОСЫЛКИ. ПОТОМ НАПИШУ КАК ЕСТЬ. ПРОШУ ПРОЩЕНИЯ У ЧЕМИКАЛА ЗА ПЛОХИЕ ПОСТЫ, ДУМАЮ ПОЙМЕТ))) УЖЕ ДАВНО ТУТ БЕРУ НЕ РАЗУ НЕ КИНУЛ НИ ОДНОЙ ЗАДЕРЖКИ ВСЕ ПРОСТО НА 100%.250 дживик заказал?
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru
Одним из ключевых направлений работы клиники является проведение инфузионных процедур. Капельницы позволяют вывести токсины, нормализовать давление и улучшить общее состояние пациента. Подбор препаратов проводится индивидуально, с учётом физического состояния, возраста и стадии зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://jsglobal.by/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
«ГородМед Трезвость» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один ни на этапе выхода из запоя, ни во время стабилизации, ни в период удержания ремиссии. С первого звонка дежурный врач проводит короткое интервью, фиксирует жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни и текущие препараты, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — экстренный выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Мы не растягиваем процесс по неделе: старт возможен в день обращения, а маршрутизация между форматами (дом, амбулаторный визит, стационар) занимает часы. Важная часть подхода — ясные цели каждого шага и критерии эффективности, понятные самому пациенту и семье: когда ждать облегчения тревоги, как нормализуется сон, когда вернётся аппетит, что считается «красным флажком» и как действовать без паники. Такая предсказуемость снижает уровень стресса и повышает приверженность лечению уже в первые трое суток.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]клиника наркологии москва[/url]
На современном рынке существует множество поставщиков [url=http://rukrepezh.ru]крепежа[/url], предлагающих широкий ассортимент изделий.
Крепежные изделия являются основой для создания прочных соединений. Это обусловлено его способностью надежно соединять различные элементы, обеспечивая прочность и долговечность конечного продукта Крепеж позволяет создавать прочные и долговечные соединения. Использование качественного крепежа имеет решающее значение для предотвращения поломок и обеспечения безопасности эксплуатации Использование качественного крепежа предотвращает поломки .
Крепежные изделия бывают различных типов, включая болты, гайки, винты и заклепки Крепежные изделия представлены болтами, гайками, винтами и заклепками . Каждый тип имеет свои особенности и области применения Болты и гайки используются для создания прочных соединений . Правильный выбор крепежа зависит от конкретных требований проекта и свойств материалов Тип крепежа выбирается в зависимости от требований проекта.
Болты и гайки являются одними из наиболее распространенных типов крепежа Болты и гайки представляют собой надежный крепеж. Они широко используются в строительстве, машиностроении и других отраслях Болты и гайки используются для крепления деталей в машинах . Болты и гайки бывают различных размеров и типов Болты и гайки предназначены для различных условий эксплуатации .
Винты и заклепки также широко используются для крепления деталей Винты и заклепки применяются для создания прочных соединений . Винты могут быть саморезирующими или обычными Винты различаются по размерам и типам. Заклепки используются для соединения деталей в различных отраслях Заклепки обеспечивают надежное крепление конструкций.
Крепеж используется в различных отраслях промышленности, включая строительство, машиностроение и производство мебели Крепеж используется в строительстве и машиностроении . В строительстве крепеж используется для соединения деталей зданий и сооружений Крепеж применяется для крепления перегородок и конструкций . В машиностроении крепеж используется для создания прочных соединений в механизмах и агрегатах Крепеж применяется для крепления деталей в механизмах .
Крепеж также используется в производстве мебели для соединения деталей и обеспечения прочности конструкции Крепеж используется для соединения деталей мебели . Правильный выбор крепежа зависит от типа материала и требований проекта Выбор крепежа осуществляется с учетом нагрузки и типа соединения . Использование качественного крепежа имеет решающее значение для предотвращения поломок и обеспечения безопасности эксплуатации Использование качественного крепежа предотвращает поломки .
Будущее крепежа связано с развитием новых материалов и технологий Будущее крепежа обусловлено потребностью в инновационных решениях. Использование композитных материалов и нанотехнологий может значительно улучшить свойства крепежа Нанотехнологии могут повысить прочность и долговечность крепежа . Кроме того, развитие робототехники и автоматизации может повысить эффективность и точность сборки и крепления Развитие робототехники улучшит эффективность сборки .
Развитие 3D-печати и аддитивных технологий также может оказать существенное влияние на производство и применение крепежа 3D-печать изменит подход к производству крепежа . В будущем можно ожидать появления новых типов крепежа, которые будут обладать улучшенными свойствами и характеристиками Новые типы крепежа будут обладать улучшенными свойствами. Это, в свою очередь, будет способствовать развитию новых технологий и отраслей Развитие отраслей будет зависеть от появления новых типов крепежа .
Городской ритм Саратова — длинные переезды через мост, активное движение в центре и контрастные микрорайоны — накладывает отпечаток на логистику и сенсорную среду, в которой проходит лечение. Мы адаптируем маршрут под город: назначаем «тихие окна» связи, уменьшаем световую нагрузку в вечернее время, организуем немаркированные выезды, а при стационарном поступлении готовим палату с тёплой подсветкой и акустическим поглощением. Эти, казалось бы, «не медицинские» решения позволяют снизить тревогу, быстрее стабилизировать пульс и сделать сон физиологичным без переседации.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov/
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а жизненно важный этап, позволяющий вернуть контроль над самочувствием и предотвратить осложнения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» пациенты получают помощь в любое время суток: опытные наркологи выезжают на дом, проводят капельницы и медикаментозную детоксикацию, подбирают индивидуальные схемы восстановления. Такой подход помогает не только устранить последствия запоя, но и запустить процесс полноценного оздоровления организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто место оказания медицинских услуг, а пространство, где начинается путь к выздоровлению. В «КузбассМед Центр» создана система комплексной помощи пациентам с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, включающая медицинскую, психологическую и социальную реабилитацию. Здесь работают врачи с многолетним опытом, а лечение проводится круглосуточно и анонимно. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, учитывающую особенности организма, стаж употребления и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
momentumpath.click – Hub motivating sustained energy and consistent progress toward goals.
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru
Современная наркологическая клиника «ЮгМед Альянс» в Ставрополе объединяет медицинскую точность и психологическую чуткость. Здесь лечение зависимостей выстроено по принципу системной логики: одно вмешательство — одна цель — один критерий оценки. Такой подход делает процесс предсказуемым и снижает нагрузку на организм. Мы не просто устраняем симптомы, а ищем причину, формируем новые устойчивые модели поведения и помогаем пациенту вернуть контроль над жизнью. Наша команда работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая поддержку и безопасное сопровождение на каждом этапе — от детоксикации до реабилитации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Для наглядности ниже приведена таблица с основными направлениями медикаментозной терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
I’ve been reading about Paybis for a while now, and I’m still not 100% sure about whether it truly
deserves all the attention it gets, but it’s certainly an interesting name within the crypto trading
space, especially when it comes to combining crypto markets with fiat currencies.
From what I understand so far, Paybis presents itself as a well-established cryptocurrency platforms that also
supports regular payment systems, which is something many exchanges either limit or
complicate.
What initially caught my interest was the way
Paybis seems to link the gap between fiat systems and the crypto world.
Many platforms focus strictly on crypto-to-crypto trades, but Paybis appears to allow users to
sell digital currencies using various fiat options.
I’m not claiming this process is flawless, but it does
seem aimed at newcomers rather than only advanced traders.
Another aspect worth mentioning is the range of cryptocurrencies supported.
Paybis doesn’t appear to limit itself to Bitcoin and
Ethereum only. Instead, it offers access to various digital assets, which might appeal to users who are experimenting.
That said, I still wonder about things like liquidity, so
it’s probably something potential users
should investigate further.
Security and compliance are also frequently
mentioned in relation to Paybis. The platform emphasizes identity verification, which could
be seen as protective for some users, though others might find it
restrictive. I’m honestly unsure where I stand on that, but
it does suggest that Paybis is trying to operate as a regulated crypto and fiat marketplace.
When it comes to fees and exchange rates, opinions seem divided.
Some sources claim that Paybis is clear with pricing,
while others mention that costs may depend on payment methods.
This isn’t uncommon in the crypto industry, but it does mean users should probably
do proper research before making decisions.
Overall, I wouldn’t say Paybis is the ultimate solution, but it does appear to be a platform that’s worth a
closer look. For anyone who is curious about buying crypto with fiat, spending some time reading more about Paybis could
be useful. I’m still undecided myself, but it’s
complex enough to justify further exploration.
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
топ отели краби Как Добраться До Краби: самолетом, автобусом или паромом.
АМ-2233 вообще ровный день назад пришёл https://avtodopsentr.ru Ты вообще нормальный и адекватный ? Ты сначала разберись куда ты писал а потом умничай. У меня адреса без фото и только опт. Судя по твоему нику ты из Екб, я в ЕКБ НЕ РАБОТАЮ И НЕ РАБОТАЛ.КЕнт в почту зайди,проясни ситуэшен.
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Одним из ключевых направлений терапии является инфузионное лечение. Капельницы позволяют быстро восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить работу внутренних органов и ускорить выведение токсинов. В клинике используются только сертифицированные препараты, безопасные для сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/
Подготовка включает оценку соматического статуса, сверку текущих лекарств, обсуждение мотивации и планов на ближайшие недели. После процедуры назначаются контрольные контакты: специалист уточняет самочувствие, помогает адаптировать режим сна и питания, напоминает о «красных флажках» и корректирует план при изменениях графика или стресса. Пациент остаётся не один: ему доступны понятные регламенты действий, чтобы не «провалиться» в первые недели, когда вероятность срыва традиционно выше. Это снижает тревогу и делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным для здоровья и работы.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru
https://mega.nz/file/tVxFVJ6Y#pqomCJqxl_2Ny3uZWkmBjscRnFmzhqeXlBfLWmF9GrU
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Труба бесшовная никелевая 35х2х1000 мм НП2Э ТУ 48-21-783-85 Узнайте об уникальных свойствах никелевых труб и их применении в различных отраслях промышленности. Подберите оптимальные решения для ваших проектов вместе с экспертами компании Редметсплав.рф
https://www.milliescentedrocks.com/board/board_topic/2189097/7601079.htm
https://babygirls031.mn.co/posts/95270034
В Новокузнецке команда «РеабКузбасс» организовала круглосуточный выезд наркологов, что позволяет оказывать помощь даже в сложных ситуациях. Пациенты часто обращаются после многодневного употребления алкоголя, когда нарушен сон, давление нестабильно, а организм истощён. В таких случаях врач выезжает в течение часа, проводит осмотр, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает оптимальную терапию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре новокузнецк[/url]
https://webyourself.eu/blogs/1709200/1xBet-Bonus-Promo-Code-2026-Up-to-100
https://gitlab.vuhdo.io/bonuscodexbet
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Основная задача стационарного лечения — не просто вывести человека из кризисного состояния, а вернуть ясность мышления и устойчивость физиологических функций. Поэтому врачи клиники используют современные методы детоксикации, витаминотерапии, ноотропные препараты, психотерапевтические практики короткого действия и физиотерапевтические модули, направленные на восстановление сна, памяти и концентрации.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol-otzyvy/
Ты друг нарвался на фэйков! https://skyrimgame.ru не вижу, в прайсе много чегосалют бразы ) добавляйте репу не стесняйтесь всем удачи))
Link exchange is nothing else except it is simply placing the other person’s weblog link on your page at appropriate place and other person will also do
similar in support of you.
Для наглядности ниже приведена таблица с основными направлениями медикаментозной терапии и их эффектами:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-samare16.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в самаре[/url]
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в воронеже[/url]
serenelifestylehub – SereneLifestyleHub showcases items in a calm, well-arranged format that promotes mindful choices.
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент и для пациента, и для семьи: все видят, какая цель преследуется, какими средствами она достигается, когда проверяется эффект и что будет дальше. Отсюда рождается доверие и строгая приверженность — главный предиктор устойчивого результата.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
бездепозитные бонусы в казино казахстан
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в Самаре предлагает профессиональное лечение алкогольной, наркотической и других форм зависимости с использованием современных медицинских технологий и индивидуальных программ. Основная цель работы специалистов — помочь пациенту восстановить физическое и психическое здоровье, вернуть контроль над собственной жизнью и предотвратить рецидив. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинской этики, конфиденциальности и стандартов безопасности.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/
Opportunity discovery platform – Helps identify momentum points and take purposeful steps
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино с выводом
next step confidence guide – Encourages actionable moves that feel manageable and effective.
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Magnificent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your website,
how could i subscribe for a weblog website? The account helped me
a applicable deal. I had been a little bit familiar of this your broadcast provided vibrant transparent idea
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
шоу трансвеститов на краби Аонанг Краби: популярный пляж с множеством ресторанов и магазинов.
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Мы не подгоняем всех под единый сценарий. Если состояние устойчивое, нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации и резких скачков давления и пульса — рационален домашний старт: приватно, быстрее и без лишних переездов. Врач приедет без маркировки, проведёт осмотр, запустит инфузионную терапию по показаниям, оставит письменные рекомендации и «красные флажки». Если же есть признаки угрозы осложнений — обезвоживание, аритмии, риск судорог, боли за грудиной или в животе, лихорадка, спутанность сознания, тяжёлая соматика — мы честно предлагаем короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов. Под круглосуточным наблюдением проще корректировать схемы, вовремя закрывать дефициты, защитить сон и быстрее вернуть управляемость поведению. В обоих форматах маршрут прозрачен: согласованные окна связи, фиксированные цели на ближайшие 72 часа и отсутствие «пакетов ради прайса». Благодаря этому решения принимаются спокойно, без угадываний и эмоциональных раскачек, которые обычно ломают прогресс и удорожают лечение.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
Приносим извинения за возможные неудобства. Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон бро а какая почта то ?проверенный временем магазин, все ровно , все быстро
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-v-samare/
ко ланта ко ланта
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Детокс — это не разовая процедура, а управляемый этап со своими задачами: снизить токсическую нагрузку, выровнять жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и самочувствию. Мы подбираем инфузии по показаниям, корректируем электролитный баланс, защищаем печёночные функции, снимаем тремор и вегетативные проявления. Следующая фаза — стабилизация: на этом этапе врач закрывает дефициты, уточняет схемы, выравнивает день и ночь, даёт понятные рекомендации на ближайшие 72 часа. Важно, что пациент не «теряется» после первого улучшения: заранее назначены точки связи, прописаны «красные флажки» и шаги, как действовать при любом из них. Такой порядок снижает вероятность рецидива, потому что вместо импровизации появляются готовые ответы на типичные сложности первых недель.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]narkologicheskaya-moskva[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Если у человека выраженное обезвоживание, скачки давления и пульса, эпизоды спутанности сознания, упорная рвота, «дергающийся» сон или тяжёлая сопутствующая патология, стационар закрывает главный риск — непредсказуемое течение синдрома отмены. Круглосуточный мониторинг позволяет динамически корректировать схемы, подключать лабораторные и инструментальные исследования по показаниям, своевременно восполнять дефициты и удерживать стабильный сон. На практике «короткое окно» госпитализации (24–48 часов) нередко дешевле на дистанции: оно предотвращает осложнения и повторные вызовы, которые растягивают курс и увеличивают суммарные затраты. Для жителей Москвы мы разносim визиты по времени, используем отдельные входы и «тихие» маршруты, чтобы сохранить приватность. После стабилизации маршрут переводится в амбулаторный или домашний формат: пациент получает план питания и активности, контрольные контакты и правила, при каких признаках связаться немедленно, не дожидаясь «как будет утром».
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-srochno
Эта карта — рабочий инструмент и для пациента, и для семьи: все видят, какая цель преследуется, какими средствами она достигается, когда проверяется эффект и что будет дальше. Отсюда рождается доверие и строгая приверженность — главный предиктор устойчивого результата.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov/
VisionaryBeauty – Informative and pleasant, services presented in a clear, visually appealing way.
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в омске[/url]
Магазин ровный.;)Жаль реги пока нет Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Про Ам1220 здешний известно что нибудь…?Хороший магазин оператор всегда онлайн, товар вообще Шик :speak: процветай) и поскорей бы лето
Показана при обезвоживании, «скачущем» давлении и пульсе, угрозе судорог, упорной рвоте, эпизодах спутанности сознания, тяжёлой соматике. За сутки–двое удаётся выровнять показатели, наладить сон и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному этапу.
Подробнее – http://
Такой алгоритм позволяет контролировать каждый аспект лечения, обеспечивая постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врач-куратор отслеживает динамику и при необходимости корректирует программу.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan/
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Лечение зависимости требует системного подхода, включающего диагностику, детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию и психологическую реабилитацию. Наркологическая клиника в Самаре объединяет специалистов различных направлений: врачей-наркологов, психиатров, психологов, терапевтов и реабилитологов. Совместная работа команды обеспечивает комплексное воздействие на физическое и эмоциональное состояние пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-samare16.ru/
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
карта краби с достопримечательностями Узнайте, что происходит в Краби в декабре, чтобы спланировать свой отпуск и насладиться праздничной атмосферой.
Great information. Lucky me I ran across your site by accident (stumbleupon).
I’ve saved as a favorite for later!
Заказывал у этих ребят 203 и 5-IAI, качеством доволен. Заказы они оформляют долго, но зато отправляют быстро. Мне отправили в день оплаты! Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон На каком сайте сейчас заказать то можно дживик ровныйво вторник заряжали – сразу же списались договорились, чтоб всё ровно было – в итоге 4 суток прошло и тишина нету трека, вчера ваще пропал продаван, хотя до этого ваще из аськи не выходил в такое время, до этого спрашивал м.б. траблы какие – он ответил “что есть не большие” вот и походу решается че-то там х3 пздц короче надеюсь в понедельник решится
Appreciation to my father who informed me on the topic of this website, this blog is
actually amazing.
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-stoimost-volgograd/
Алгоритм прозрачен. Сначала — краткое интервью и осмотр, измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, при необходимости — ЭКГ и оценка неврологического статуса. Далее — инфузионная терапия по показаниям: восполнение жидкости, коррекция электролитов, поддержка функций печени, мягкое снижение тремора и тревоги, подготовка к сну без «оглушения». Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма, чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных эффектов. Врач детально объясняет, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, сухость во рту, умеренная слабость), а какие — основание для связи. После процедуры повторно фиксируются показатели и выдаются письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа: режим воды и лёгкой еды, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликты, время короткого дневного отдыха, интерфейс связи и условия повторного визита. Такой порядок убирает хаос: пациент и семья понимают, что именно делать вечером и ночью, как снизить «дергание» и зачем придерживаться простых правил, пока организм перестраивается после запоя.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
Каждое направление терапии в клинике подбирается персонально. Пациент проходит пошаговую программу, начиная с диагностики и детоксикации и заканчивая психологическим сопровождением и адаптацией к жизни без зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
I’ve been seeing mentions of Paybis for a while now, and I’m still not fully convinced about
whether it truly deserves all the attention it gets,
but it’s certainly an interesting name within the digital asset space, especially when it comes to combining crypto markets with fiat currencies.
From what I understand so far, Paybis presents itself as
a well-established cryptocurrency platforms that also
supports regular payment systems, which is something many exchanges either
limit or complicate.
What initially caught my interest was the way Paybis seems to bridge the gap between banking methods and the
crypto world. Many platforms focus strictly on crypto-to-crypto trades,
but Paybis appears to allow users to exchange digital currencies using various fiat options.
I’m not claiming this process is flawless, but it does
seem aimed at people just entering crypto rather than only advanced traders.
Another aspect worth mentioning is the range of cryptocurrencies supported.
Paybis doesn’t appear to limit itself to just the top coins.
Instead, it offers access to a broader token selection, which might appeal to
users who are diversifying. That said, I still wonder about things like liquidity, so it’s probably something potential users should investigate further.
Security and compliance are also frequently mentioned in relation to Paybis.
The platform emphasizes regulatory compliance, which could be seen as reassuring
for some users, though others might find it restrictive.
I’m honestly unsure where I stand on that, but it does suggest that Paybis is
trying to operate as a regulated crypto and fiat marketplace.
When it comes to fees and exchange rates, opinions seem divided.
Some sources claim that Paybis is transparent with pricing, while others mention that costs
may vary by transaction. This isn’t uncommon in the crypto industry, but it
does mean users should probably read the details
carefully before making decisions.
Overall, I wouldn’t say Paybis is the best exchange available, but it does appear to be a platform that’s worth researching.
For anyone who is curious about buying crypto with fiat, spending some time reading more
about Paybis could be useful. I’m still undecided myself, but it’s promising enough to justify further exploration.
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
curatedinsights.click – Resource highlighting elegant content and promoting deliberate user engagement.
careful growth guide – Offers guidance for consistent progress without rushing the process.
Одним из ключевых направлений работы клиники является проведение инфузионных процедур. Капельницы позволяют вывести токсины, нормализовать давление и улучшить общее состояние пациента. Подбор препаратов проводится индивидуально, с учётом физического состояния, возраста и стадии зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Подготовка включает оценку соматического статуса, сверку текущих лекарств, обсуждение мотивации и планов на ближайшие недели. После процедуры назначаются контрольные контакты: специалист уточняет самочувствие, помогает адаптировать режим сна и питания, напоминает о «красных флажках» и корректирует план при изменениях графика или стресса. Пациент остаётся не один: ему доступны понятные регламенты действий, чтобы не «провалиться» в первые недели, когда вероятность срыва традиционно выше. Это снижает тревогу и делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным для здоровья и работы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-bolnica-moskvy[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Узнать больше – http://
всех с новым годом и удачных покупок Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Оплатил подождал очередь неделю так как завал у магазина теперь жду посыль респект ребята работаете на высотеОправдания в небе не ищут,
<Smart planning hub – Provides tools to structure steps for forward movement
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]эротические фильмы[/url]
электрический карниз для штор купить [url=https://kupite-elektrokarniz.ru/]kupite-elektrokarniz.ru[/url] .
жалюзи на пластиковые окна электрические [url=https://zhalyuzi-elektricheskie.ru/]жалюзи на пластиковые окна электрические[/url] .
шторы в оконный проем [url=https://shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru/]shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru[/url] .
Взял ам2233 эфектом очень доволен! спасибо https://33domik.ru Отличный магазин, общение с KingSize – одно удовольствие, а продукты неизменно радуют.В чем растворял 203??? У меня ихний 203 в спирте не получилось расстворить даже при нагреве, пришлось ацетон использовать! На счет качества с тобой согласен – 5!
OpticalBeauty – Attractive layout, services described clearly for a smooth browsing experience.
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены воронеж[/url]
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм саратов[/url]
https://t.me/KohLantaKrabiThailand пляжи ко ланты
Всё отлично все всё получат магаз ровный доказал свой гибгий подход к НАМ заказчикам.Если форс мажёр то всё уладят в НАШу пользу.Отправка осуществляется от 2-10дней в зависимости от заказов то есть загруженности магазина.Без паники братья без паники. Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Так что тут 50:50 если тебя примут. Все зависит от конкретного города и гнк в нем.чема вещи делает!!!
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения 2024 без отыгрыша
Для покупки [url=http://flakons-optom.ru]флаконы от производителей оптом[/url] можно обратиться напрямую к производителю или крупному поставщику, что позволит экономить на покупке и обеспечить качественный продукт для различных применений.
Флакон опт — это лучший способ удовлетворить потребности в опте. Кроме того, покупка флакона в опте является выгодным решением для всех. Также флакон опт дает возможность приобрести лучший продукт по доступной цене. Кроме того, покупка флакона в опте дает возможность приобрести лучший продукт по низкой цене. Также флакон опт является лучшим решением для тех, кто ищет качественный и удобный продукт.
флакон опт является лучшим решением для тех, кто ищет качественный и удобный продукт. Кроме того, покупка флакона в опте дает возможность приобрести лучший продукт по низкой цене. Также флакон опт дает возможность приобрести лучший продукт по доступной цене. Кроме того, покупка флакона в опте дает возможность приобрести лучший продукт по низкой цене. Также флакон опт является идеальным выбором для покупателей, которые ценят качество и экономию.
флакон опт следует выбирать с учетом опыта и отзывов других покупателей. Кроме того, покупка флакона оптом требует тщательного рассмотрения и сравнения вариантов. Также флакон опт необходимо выбирать исходя из опыта и отзывов других покупателей. Кроме того, покупка флакона оптом требует тщательного рассмотрения и сравнения вариантов. Также флакон опт является важным аспектом при выборе оптового продукта.
флакон опт является идеальным решением для тех, кто ценит качество и экономию. Кроме того, покупка флакона в опте является выгодным решением для всех. Также флакон опт предлагает покупателям выгодные условия и лучшее качество. Кроме того, покупка флакона оптом позволяет приобрести необходимый продукт в большом количестве. Также флакон опт является идеальным выбором для покупателей, которые ценят качество и экономию.
Ga 888
краби фото пляжей Краби Сегодня: смотрите погоду, чтобы одеться правильно.
очень неплохо было бы увидеть в магазине джив 307 Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Бро как с тобой связатся это ярослав мудрый.друг ты о чем говоришь? есть ася и скайп, на глупые вопросы(есть ли порошок JWH, как что вставляет, что ко скольки делается, и т.д.) мы не отвечаем, мы работаем только с людьми которые понимают, что “это” и как это “едят”, парни вот без обид – мы же не википедия… да парни все легал, все анализы делаются на Моросейке… да да да…
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IXBIAFVY
greenlivinghub – GreenLivingHub showcases high-quality sustainable items in a well-arranged, easy-to-browse interface.
success execution guide – Encourages taking realistic steps to achieve meaningful growth.
Для тех, кто ищет выгодные предложения на ткани, [url=http://tkan-optom-moscow.ru]купить ткани оптом дешево[/url] предлагает широкий выбор тканей по разумным ценам.
как найти оптовых поставщиков тканей является первым шагом к успеху. Это связано с тем, как оптовые торговцы работают напрямую с производителями. При этом выбор правильного поставщика имеет решающее значение .
как крупные партии тканей стоят дешевле . Кроме того, где найти подходящую ткань не составит труда. Это особенно важно как качество используемых тканей напрямую влияет на репутацию бренда .
как сравнить цены и качество тканей от разных поставщиков. Кроме того, где обсудить условия сотрудничества. При этом как можно сэкономить на доставке .
где сравнить предложения от разных компаний. Кроме того, где получить советы от опытных профессионалов. Это особенно важно для тех, кто только начинает свой бизнес .
При выборе оптового поставщика тканей необходимо учитывать несколько факторов . Кроме того, где найти информацию о компании. При этом как можно избежать дополнительных затрат .
как можно гарантировать соответствие ткани необходимым стандартам . Кроме того, взаимодействие с_customer поддержкой компании может дать представление о уровне обслуживания . Это особенно важно где оптовые поставщики тканей могут предложить высококачественные материалы и flexible условия.
В заключении, поиск оптового поставщика тканей требует тщательного подхода . Кроме того, как можно сэкономить на ??иду и улучшить качество продукции . При этом где найти новые возможности для роста.
Будущее оптовой торговли тьмается перспективным, и как можно улучшить качество и доступность тканей . Кроме того, как можно снизить воздействие на окружающую среду . Это особенно важно для бизнеса, который хочет оставаться конкурентоспособным и соответствовать меняющимся потребностям рынка .
Momentum planning hub – Encourages identifying key steps and moving forward purposefully
заказ делал на человека который вообще не в теме и был чистый, поэтому меняйте для начала хотя бы курьерку и курьеров.. Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон вы могли написать похожему нику , таких пруд пруди.такчто чставлю 100/100баллов магазу и
Вред от наркотиков — этто групповая проблема,
охватывающая физическое, психологическое и общественное здоровье человека.
Утилизация таковских наркотиков, как снежок, мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» или «бошки», может
огласить для необратимым результатам как для организма, яко равно чтобы общества в течение целом.
Но хоть при развитии связи возможно восстановление
— ядро, чтобы энергозависимый
человек направился согласен помощью.
Важно помнить, яко наркомания врачуется, а также восстановление в правах одаривает шансище сверху новую жизнь.
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2020 вк quot
автоматические жалюзи таймером [url=https://zhalyuzi-elektricheskie.ru/]автоматические жалюзи таймером[/url] .
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино с выводом денег бездепозитный
электрокарниз двухрядный цена [url=https://kupite-elektrokarniz.ru/]kupite-elektrokarniz.ru[/url] .
риобет казино официальный сайт Риобет Казино Регистрация: Откройте Двери в Мир Игры Процесс регистрации в Риобет казино прост и занимает всего несколько минут. Зарегистрировавшись, вы получаете доступ ко всем играм, бонусам и акциям, предлагаемым казино.
рулонная штора с электроприводом [url=https://shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru/]рулонная штора с электроприводом[/url] .
бездеп бонус Бездеп Казино: Рай для Охотников за Бонусами Бездеп казино – это онлайн-казино, предлагающие широкий выбор бездепозитных бонусов для новых и существующих игроков.
globaltraditions.click – Platform motivating users to explore international crafts, cultural expressions, and creative ideas.
TabitoAdventures – Great travel insights, layout is clean and exploring articles is effortless.
сообщение
2c-i, 2c-e, 2c-p Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Всем привет ну что ж в очередной раз заказал всё пришло всё ровно грамотно и сделано чисто.Магазин очень хороший всё чётко и быстро и селер грамотный вы правы
Затянувшийся запой быстро расшатывает физиологию: теряется жидкость, нарушается электролитный баланс, растёт нагрузка на сердце и печень, сон рвётся тревожными отрезками. На этом фоне любое промедление меняет картину не в лучшую сторону: чем дольше организм остаётся в состоянии интоксикации и бессонницы, тем выше риск аритмий, скачков давления, панических волн и импульсивных решений ночью. «Трезвый Город Химки» устраняет эти пружины сразу: вместо очередей и разговоров «на виду» — быстрый вход по согласованному времени, предметное интервью без лишней бюрократии, чёткое объяснение каждого шага и старт терапии в минимально достаточном объёме. Такой подход экономит силы семьи, снижает тревогу у пациента и делает результат предсказуемым: уже в первые часы уменьшаются тремор и тошнота, выравнивается пульс, появляется чувство контроля. Ключевая цель на первые сутки — первая ровная ночь, потому что только на её фоне организм способен закреплять улучшения, а не «сжигать» их к вечеру. Мы заранее договариваемся о правилах вечера, чтобы не ломать эффект разговорами и яркими экранами, и именно поэтому траектория восстановления идёт не рывками, а поступательно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/vyhod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-himkah/
на сайте hair-man.ru
Риск от наркотиков — этто единая
хоботня, обхватывающая физиологическое, психологическое также
соц здоровье человека. Употребление таких наркотиков, как снежок, мефедрон, ямба, «наркотик» или «бошки», что ль
обусловить ко неконвертируемым последствиям
яко для организма, яко и чтобы
федерации в течение целом. Но хоть при
развитии подневольности эвентуально электровосстановление — главное,
чтоб энергозависимый явантроп обратился за помощью.
Эпохально запоминать, яко наркозависимость врачуется, и
восстановление в правах дает шансище сверху новую жизнь.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth
comment. There’s no doubt that that you should publish more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but usually people do not
discuss these topics. To the next! Many thanks!!
Here is my page zapacitu01
Запись и подтверждение — через защищённые каналы; визиты — без опознавательных знаков; в расписании используются шифры вместо фамилий, информирование семьи — только с вашего согласия. Когда страх огласки уходит, люди обращаются вовремя и лучше соблюдают рекомендации — это напрямую улучшает прогноз и экономит бюджет.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy/
Эйфора пока нет в наличии. Как только появится мы обязательно вас оповестим https://aeroflotnord.ru например тут ну или накрайняк тут а селлер совершенно не обязан консультировать по применению хим. реактивов.Ровный и Стабильный…
Домашний протокол разбит на понятные шаги. В каждом шаге есть цель, действия, что именно мы измеряем и когда сверяем прогресс. Это делает процесс прозрачным и даёт семье чувство контроля: видно, почему назначено именно это и когда ждать облегчения.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk0.ru/
I’m really loving the theme/design of your site. Do you ever run into any internet browser compatibility problems?
A number of my blog readers have complained about my website not operating correctly
in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any advice to help fix this problem?
обстановка
риобет казино скачать Риобет Казино Регистрация: Откройте Двери в Мир Игры Процесс регистрации в Риобет казино прост и занимает всего несколько минут. Зарегистрировавшись, вы получаете доступ ко всем играм, бонусам и акциям, предлагаемым казино.
Риск через наркотиков — это сложная проблема, обхватывающая физическое,
психическое равным образом общественное состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление таковских наркотиков, яко кокаин,
мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» или «бошки», может огласить для необратимым результатам как для
организма, так (а) также чтобы мира
на целом. Но даже при развитии подневольности эвентуально восстановление — ядро, чтоб зависимый человек устремился за помощью.
Важно помнить, яко наркозависимость врачуется, а также реабилитация бацнет шансище на новейшую жизнь.
Ниже — рабочий каркас выездного протокола. Он индивидуализируется под переносимость, вегетативные реакции и бытовые ограничения пациента. В таблице отражены и медицинские, и организационные шаги: видна связка «что делаем — что проверяем — как понимаем, что пора к следующему этапу».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого петрозаводск[/url]
Как помогает организму
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже предоставляет квалифицированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Мы применяем проверенные методы детоксикации, медикаментозной стабилизации и психологической реабилитации, обеспечивая безопасность и эффективность терапии. Специалисты клиники работают круглосуточно, что позволяет оперативно реагировать на экстренные ситуации и гарантировать индивидуальный подход.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Домашний визит уместен не только при тяжёлой абстиненции. Он эффективен и на этапе нарастающих симптомов, когда важно предотвратить обострение. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие принять решение.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в ставрополе[/url]
Danke für all die wertvollen Inhalte über NV Casino und Glücksspiel.
https://www.vytepujeme.cz/ahoj-vsichni/
purposeful strategy guide – Helps identify clear steps for effective and measurable progress.
бездепозитные промокоды Бездепозитные Промокоды: Секретный Ключ к Эксклюзивным Бонусам Бездепозитные промокоды – это специальные коды, которые можно активировать в казино, чтобы получить эксклюзивный бездепозитный бонус.
Все нормально,6-го заказал,8-го отправили. Оперативно Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон отпишеш как все прошло брода можно
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
Каждая выездная бригада укомплектована портативным лабораторным оборудованием для экспресс-анализов крови и мочи, современными инфузионными насосами и средствами телеметрии. Это позволяет врачу контролировать жизненно важные параметры пациента в режиме реального времени и корректировать схему детоксикации на месте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Future strategy platform – Provides tools to implement forward-looking ideas efficiently
Описание
Подробнее тут – https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/snyatie-lomki-na-domu-v-rnd
Hello everyone!
I came across a 149 fantastic website that I think you should dive into.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://primeirahora.com.br/melhore-sua-saude-com-gengibre-laranja-e-cenoura/]https://primeirahora.com.br/melhore-sua-saude-com-gengibre-laranja-e-cenoura/[/url]
And don’t neglect, guys, that a person at all times are able to within this article discover solutions to the most complicated questions. The authors made an effort — present the complete data using the most extremely accessible way.
Всем мир,заказывал кто нибудь через доставку курьерской службой?дошло все ровно? Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Фарту в делах парни !:hello:Хочу грамульку взять и угостить определенный круг людей,
KoiFesHighlights – Festival updates are visually striking and easy to enjoy.
Wow, this article is nice, my sister is analyzing such things,
so I am going to tell her.
Pokerok – это международное имя, объединяющее под своим крылом тысячи игроков со всего мира. Платформа предлагает безопасную и надежную игровую среду, сертифицированное программное обеспечение и круглосуточную поддержку клиентов. покерок официальный сайт
жалюзи с электроприводом для окон заказать [url=https://zhalyuzi-elektricheskie.ru/]zhalyuzi-elektricheskie.ru[/url] .
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино[/url]
электрокарниз купить в москве [url=https://kupite-elektrokarniz.ru/]электрокарниз купить в москве[/url] .
автоматические шторы на окна [url=https://shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru/]автоматические шторы на окна[/url] .
Первый контакт строится вокруг фактов «здесь и сейчас». Врач уточняет длительность употребления, принятые за последние 24–48 часов препараты, сопутствующие диагнозы и аллергии, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает выраженность тремора и уровень тревоги; при необходимости выполняется экспресс-ЭКГ и элементарный неврологический скрининг. Далее план объясняется простым языком: какие инфузии будут сегодня, чего ждать через 30–60 минут, как организовать вечер и когда состоится контрольная связь. Мы избегаем универсальных «сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают краткий «блеск» с вечерним откатом и повышают риск побочных эффектов. Вместо этого используется узкая, клинически достаточная схема: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, противорвотные и гастропротекция при необходимости, мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция по показаниям. После процедуры врач повторно оценивает показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа, согласует окно связи и обозначает «красные флажки» для немедленного контакта. Такой прозрачный маршрут убирает импровизации и делает поведение семьи предсказуемым, что особенно важно в «тёмные часы» вечера.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Чтобы освободить территорию после ремонта, вам поможет [url=http://vyvoz-musora-kub.ru]услуги по вывозу строительного мусора[/url].
Следует обратить внимание на стоимость
друзья! магазин работает? кто брал что последний раз? а главное когда? я с 5 августа ждал..;( Купить Марихуану, Бошки, Кокаин, Мефедрон Магази хороший и качество нормальное, если есть возможность запиши на пробу Бро )А с какого дживика еще больше делать можно?
бездепозитные промокоды Бездепозитные Промокоды: Секретный Ключ к Эксклюзивным Бонусам Бездепозитные промокоды – это специальные коды, которые можно активировать в казино, чтобы получить эксклюзивный бездепозитный бонус.
Психологическая поддержка включает индивидуальные сессии, в ходе которых пациент получает инструменты для борьбы с негативными установками и формирования здоровых моделей поведения. Применение техник релаксации и когнитивно-поведенческой терапии помогает значительно снизить риск повторного запоя.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk66.ru/narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk
казино бонусы Казино с бездепозитным бонусом – это идеальный вариант для тех, кто хочет попробовать свои силы в азартных играх, не рискуя собственными деньгами. Однако, перед тем, как воспользоваться таким предложением, внимательно изучите правила и условия его получения и отыгрыша.
Главные задачи детоксикации при запое — безопасно снизить концентрацию токсичных метаболитов, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, уменьшить перегрузку сердечно-сосудистой системы и вернуть физиологию сна. Мы начинаем с медленного стартового объёма инфузии, чтобы оценить переносимость, затем переходим к основной фазе и при необходимости к постинфузионной поддержке. Во время сеанса контролируются витальные показатели, динамика симптомов (тремор, тошнота, головная боль, фотофобия, тревога), а также «поведенческие» маркеры — способность расслабиться, усидеть спокойно, засыпать без «рывков».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в каменске-уральске[/url]
elegantmarket.click – Marketplace offering high-quality goods with smooth navigation and curated selections.
https://ufoleaks.su/news/drugoe/15520-kak-vybrat-shkolu-angliyskogo-yazyka-prakticheskiy-plan-chtoby-ne-tratit-vremya-i-dengi-vpustuyu.html
Магазин как магазин! https://murmansk-menswear.ru Причем тут шрифт не где не запрещенно писать большим шрифтом!И это еще далеко не большой.Я вот допустим имею проблемы со зрением но написал для того чтобы было более разборчево отчетлево видно всем обывателям данной темы.Причем тут слепые не слепые вапще.вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес…
intentional progress guide – Encourages structured and purposeful advancement.
На первом приёме врач-нарколог проводит осмотр, оценивает витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, SpO2, температура), при показаниях — портативный ЭКГ-скрининг и экспресс-лабораторию, использует шкалы выраженности абстиненции и тревоги. Результаты сразу переводятся в план на ближайшие 72 часа: инфузионная поддержка или таблетированные режимы, «вечерний ритуал» для нормализации сна, карта триггеров и краткое психообразование. Дальше мы обсуждаем цели на 7 дней: что должно измениться и как мы это измерим (сон, тревога, «тяга», энергия, работоспособность).
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
uniquebuyzone – UniqueBuyZone provided hidden treasures and a seamless shopping experience.
Клиника «ТюменьМед» специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и вывода из запоя с 2010 года. За годы работы накоплен уникальный опыт в проведении комплексной детоксикации, реабилитации и последующего сопровождения пациентов. В основе методик лежат стандарты доказательной медицины, а команда состоит из наркологов, психотерапевтов, заведующих отделением интенсивной терапии и логистов для выездов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в тюмени[/url]
Покерок – это не просто карточная игра, это целая вселенная азарта, стратегии и мастерства, ждущая своих покорителей. Миллионы игроков по всему миру ежедневно собираются за виртуальными столами, чтобы испытать удачу и продемонстрировать свои навыки. Покерок предлагает широкий выбор форматов и лимитов, от классического Техасского Холдема до более экзотических разновидностей, удовлетворяя потребности как начинающих, так и опытных игроков. pokerok официальный сайт
Домашний протокол разбит на понятные шаги. В каждом шаге есть цель, действия, что именно мы измеряем и когда сверяем прогресс. Это делает процесс прозрачным и даёт семье чувство контроля: видно, почему назначено именно это и когда ждать облегчения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-petrozavodsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно петрозаводск[/url]
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]капельница от запоя в стационаре[/url]
Action roadmap hub – Provides instructions for initiating tasks with clarity and follow-through
обстоятельство
Hi there, I enjoy reading all of your article. I wanted to write a little comment to
support you.
https://share.evernote.com/note/74ff7dbc-3ee7-8692-3fb1-f26cbc5254e5
получил посыль.мхе отличного качества!а вот ам2233 пока думаю ко скольки мутить.все пишут по разному. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Бро конечно я незнаю твою ситуацию, но с зданным магазом работал всегда всё на вышке было , и вот что думаю на 10 грамм смысла тебя кидать нет такому магазину!!!вот вот..ждать неизветсности самое такое нервное….
В основе работы наркологической клиники лежит комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы интоксикации, но и сформировать устойчивую мотивацию к трезвому образу жизни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в твери[/url]
Truly all kinds of very good data.
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Север» организует быстрый и безопасный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом врача, индивидуальными капельницами и бережной психоподдержкой. Мы работаем по принципу «одно вмешательство — одна цель — один маркер результата»: так пациент видит логику лечения, а команда гибко подстраивает тактику под реальную динамику — без избыточных назначений и суеты. В основе — деликатная логистика, анонимность и пошаговое восстановление сна, гидратации, электролитного баланса и нервной регуляции.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-petrozavodsk/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-petrozavodsk0.ru
Домашний визит уместен не только при тяжёлой абстиненции. Он эффективен и на этапе нарастающих симптомов, когда важно предотвратить обострение. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие принять решение.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
BrainInsightCenter – Informative and well-structured, content is easy to read and visually clean.
Зависимость всегда про неопределённость: скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тревожность, бессонные ночи, споры в семье и страх огласки. «ЛюберМед Центр» убирает эту неопределённость управляемым маршрутом. Мы начинаем с краткого, но точного интервью, фиксируем объективные показатели и тут же объясняем, какие вмешательства уместны сегодня и зачем именно они. Никаких «общих залов» и очередей: приёмы разнесены по времени, подтверждения проходят по защищённым каналам, визиты на дом — без маркировки. Наш принцип — минимальная достаточность: столько медицины, сколько нужно для безопасного перехвата динамики и первой ровной ночи. Именно она делает дальнейшие шаги предсказуемыми: снижается тремор, выравнивается ритм, появляется ресурс соблюдать режим. Благодаря продуманной логистике Люберец мы сокращаем холостые перемещения, а значит, лечение начинается раньше, а тревоги — меньше. В результате пациент и семья получают не «набор услуг», а последовательность: понятные действия, прозрачные ожидания и устойчивый эффект, который держится днями, а не часами.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Команда «КарелМед Центра» объединяет наркологов, психиатров, реаниматологов, клинических психологов, специалистов по реабилитации и социальному сопровождению. Мы работаем без очередей и навязчивых формальностей, а логистика визита, оформление в стационар и коммуникации с родственниками выстроены бережно: конфиденциальные записи, немаркированные выезды, отдельный вход и нейтральная терминология в документах. Вы получаете не только купирование абстиненции и детоксикацию, но и системную работу с триггерами, привычками и межличностными конфликтами — тем, что часто возвращает к употреблению даже после «идеальных капельниц».
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru
Ну так ведь и не делаем не чотка . всё сразу . Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш отличный магазин, все всегда ровноТепкрь сам хочу зделать заказ но немогу на сайт попасть ((((
Ниже — примерный «каркас» лечения. Он индивидуализируется по клинической картине, сопутствующим болезням, опыту прошлых попыток и бытовым ограничениям. Ключевой принцип — «одно вмешательство: одна цель — один маркер — одна дата проверки».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в петрозаводске[/url]
жалюзи автоматические с электроприводом купить [url=https://zhalyuzi-elektricheskie.ru/]жалюзи автоматические с электроприводом купить[/url] .
карниз для штор электрический [url=https://kupite-elektrokarniz.ru/]карниз для штор электрический[/url] .
Чтобы избежать опасных последствий, необходимо постепенно и безопасно вывести алкоголь из организма. Клиника «Ясный горизонт» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя в Новокузнецке как в условиях стационара, так и с выездом нарколога на дом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого новокузнецк[/url]
сочетание рулонных рулонные шторы и тюль фото [url=https://shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru/]shtory-s-elektroprivodom-rulonnye.ru[/url] .
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог клиники «Гармония здоровья» Александр Ветров, «любая зависимость — это не слабость, а болезнь, требующая медицинского вмешательства и системного подхода».
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Хотя принципы лечения похожи, клиническая логика отличается. При алкогольной зависимости чаще нужен быстрый контроль вегетативных симптомов, восстановление сна и коррекция электролитов. При наркозависимости добавляются протоколы снижения импульсивности, работа с абстиненцией другой природы и расширенная психотерапевтическая часть. В обоих случаях результат не сводится к «капельнице»: мы учим распознавать ранние сигналы срыва, формировать безопасные ритуалы и поддерживать общение без давления и скрытых конфликтов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в петрозаводске[/url]
Для жителей Первоуральска мы поддерживаем 24/7-окно обращения без очередей: первичный скрининг по телефону, подтверждение безопасного формата старта (стационар краткого наблюдения, амбулаторно или выездная бригада), нейтральные формулировки в документах, деликатная транспортная логистика. При необходимости организуем немаркированный выезд врача, а при госпитализации используем отдельный вход и «тихие» коридоры. Это не косметика — такие детали снижают уровень тревоги, улучшают засыпание в первую ночь и повышают соблюдаемость рекомендаций.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk0.ru/narkolog-pervouralsk/
Описание
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/]снятие ломки наркозависимого[/url]
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена в тюмени[/url]
Почему больше не забегаете ? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Работы очень много, стараемся как можем, многие задают в Аську и Скайп одни и теже вопросы которые не касаются заказа(как в википедию ломяться)…Сам ты не общительный ))
Наркологическая клиника «ТагилМед Реал» — это круглосуточная команда врачей, психологов и координаторов, которая берёт на себя полный цикл помощи при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости: от экстренной стабилизации и капельниц на дому до амбулаторного сопровождения, кодирования и длительной психотерапевтической поддержки. Мы работаем без выходных, используем портативное оборудование, придерживаемся принципов доказательной медицины и внимательно относимся к конфиденциальности: нейтральные формулировки в документах, немаркированный транспорт, разграниченный доступ к медицинским данным и единый доверенный контакт для семьи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy-kamensk-uralskij/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-himki/
Если в «окно оценки» прогресс ниже ожиданий, мы меняем ровно один параметр — дозировку, время приёма, приоритет модуля — и задаём новую дату проверки. Это защищает от «снежного кома» назначений и сохраняет ощущение контроля у пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/
Каждый инструмент имеет чёткие показания и ограничение: мы объясняем, какую гипотезу проверяем, по каким признакам поймём, что она верна, и когда перестанем использовать метод, если вклад невелик. Это снижает тревогу и формирует доверие к плану.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в петрозаводске[/url]
https://nodepositcasino.ru Казино без депозита с выводом – это еще более привлекательная перспектива. Ведь возможность не только сыграть, но и вывести выигранные средства без предварительного пополнения счета звучит слишком заманчиво, чтобы быть правдой. Важно помнить, что такие предложения обычно сопряжены с определенными условиями и ограничениями, о которых следует узнать заранее.
В «Гелиосе» уделяется особое внимание конфиденциальности и психологическому комфорту пациентов. Анонимность процедур и доброжелательная атмосфера способствуют снижению стресса и улучшению результатов лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]азартные игры[/url]
strategy innovation roadmap – Offers actionable insights to rethink current approaches.
Наркологическая клиника в Твери представляет собой современное медицинское учреждение, специализирующееся на диагностике и лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В клинике «Гелиос» применяются инновационные методы терапии, направленные на полное восстановление физического и психологического состояния пациентов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника тверь[/url]
ПокерОК – это еще одно название, используемое для обозначения этой популярной платформы. Неважно, как вы его называете, главное, что за каждым из этих имен скрывается море азарта и возможностей. покерок регистрация
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that
would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
В «Гелиосе» уделяется особое внимание конфиденциальности и психологическому комфорту пациентов. Анонимность процедур и доброжелательная атмосфера способствуют снижению стресса и улучшению результатов лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника тверь[/url]
как получить промокод 1xbet
Приветствую всех ровных жителей этой ветки.Друзья помогите мне.Где ,на какой страничке я могу найти хозяина даннго магазина.И где адреса магазина???Где прайс???Вообще не понятный магазин.И как выглядет его аватарка. https://cliptime.ru Магниты рулят, не меняйтесь)Отправки посылок и эта информация в 2-х местах прописана на сайте 2-10 РАБОЧИХ ДНЕЙ. В 99,9% случает сроки не нарушаются.
Для каждого пациента используется индивидуальный монитор жизненно важных функций, передающий данные врачу в клинике через защищённый канал связи. Это обеспечивает безопасность при лечении как лёгких, так и тяжёлых форм интоксикации, снижая вероятность осложнений.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/
Инфузионная терапия — это не универсальный «коктейль», а набор узких шагов под клиническую задачу. Главные цели понятны: вернуть объём циркулирующей жидкости и перфузию тканей, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушить тремор и тревожность, подготовить нервную систему к сну. При тошноте подключаются противорвотные и гастропротекция; кардиокоррекция даётся только после оценки рисков. Мы заранее проговариваем нормальные ощущения (умеренная слабость, сонливость, сухость во рту) и «красные флажки» для связи. Такой минимум достаточных вмешательств снижает побочные эффекты, делает бюджет предсказуемым и удерживает результат не часами, а днями. На этой базе обсуждаются следующие шаги: амбулаторный график, короткие психотерапевтические сессии, при показаниях — кодирование после стабилизации и исключения противопоказаний.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-himkah
Potential growth platform – Helps users identify opportunities for advancement and actionable steps
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение сильнее симптомов; затяжка почти всегда ухудшает прогноз и увеличивает расходы. В «ХимкиМед Центр» приватность — регламент, а не обещание: заявки и подтверждения проходят через защищённые каналы, в расписании используются шифры, приёмы разнесены по времени, а визиты — без маркировки. Маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее, чтобы врач прошёл к двери без внимания соседей. Мы учитываем «узкие» места Химок — дворовые проезды, часы пик, загруженные выезды — поэтому холостые перемещения минимальны, а терапия стартует быстро. Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога, выше приверженность режиму и, как следствие, устойчивее результат.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Запой – это критическое состояние, при котором организм утрачивает способность регулировать потребление алкоголя, что может привести к серьёзным медицинским и психоэмоциональным нарушениям. В Красноярске современные клиники и опытные специалисты применяют инновационные методики, позволяющие быстро и эффективно вывести пациента из запоя. Благодаря комплексному подходу, включающему медикаментозную детоксикацию, коррекцию обменных процессов и психологическую реабилитацию, достигается стабильный результат, предотвращающий повторные эпизоды зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в красноярске[/url]
После первичной консультации пациент проходит обследование, позволяющее точно определить стадию зависимости и сопутствующие патологии. Используются лабораторные анализы, оценка неврологического статуса и сбор анамнеза. Уже на этом этапе начинается выстраивание контакта между пациентом и врачом, что особенно важно для доверия и готовности включиться в процесс.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в волгограде[/url]
Very good post. I definitely love this site. Keep it up!
Наркологическая помощь «ТюменьМед» не ограничивается только физической детоксикацией. В состав команды входят психологи и социальные работники, которые проводят мотивационные беседы, обучают навыкам самоконтроля и оказывают помощь в планировании досуга и социальных активностей после детоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм тюмень[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Твери представляет собой современное медицинское учреждение, специализирующееся на диагностике и лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В клинике «Гелиос» применяются инновационные методы терапии, направленные на полное восстановление физического и психологического состояния пациентов.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tver0.ru
ы меня поняли Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш а че магазин то ваще работает нет?Новинки не за горами, без паники.
Hello team!
I came across a 149 fantastic page that I think you should visit.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://www.whatgadget.net/how-to-conduct-effective-team-technical-reviews/]https://www.whatgadget.net/how-to-conduct-effective-team-technical-reviews/[/url]
Furthermore don’t neglect, folks, that one always may within this publication locate answers to address the most the absolute tangled inquiries. Our team made an effort to present all information using the most understandable way.
TrabasOnline – Clear organization, browsing content is smooth and informative.
Помощь врача-нарколога становится жизненно важной, когда симптомы абстинентного синдрома становятся невыносимыми и угрожают жизни пациента. К числу основных признаков, требующих срочного вмешательства, относятся:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd77.ru/]снятие ломок на дому в краснодаре[/url]
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма тюмень[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость — сложное хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и квалифицированной помощи. В клинике «Тюменьбезалко» в центре Тюмени разработаны эффективные программы реабилитации, сочетающие современные медицинские методы, психологическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Опытные врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты помогают пациентам преодолеть употребление алкоголя, восстановить физическое и эмоциональное здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена[/url]
На каждом этапе мы фиксируем объективные маркеры — от сатурации и вариабельности пульса до частоты «тяговых мыслей» в дневнике. Эти данные позволяют корректировать план не интуитивно, а по фактам.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Стартуйте с бонусом через Мелбет промокод при регистрации для начала игры с преимуществом. Следите за новыми промокодами и акциями, это даст вам больше шансов на успешный старт [url=https://legonew.ru/files/price/melbet_promokod_bonus_do_25000_za_registraciu.html]мелбет промокод при регистрации[/url] мелбет промокод при регистрации 2026
Пришол 250 сделал 1к10-12 ппц уносит 250 у вас лучший магазу респект , даже не ожидал что такой джив будет , 1к10 меньше это ппц.. https://pmpodarok.ru КЕнт,сорри на почту ответь..когда вы зарядили?мои ребята зарядили вчера около 16-00 по мск ,минут за 15 до этого он добро дал и замолчал( переживаю очень так как отвечать мне.Я надеюсь лавочка не слилась с пацанскими деньгими… А то конкретная пичаль будет.У нас в регионе это большая сумма!!!
globalcreatives.click – Resource supporting the discovery of innovative projects and imaginative strategies.
В рамках детоксикации применяются капельничные инфузии и современные препараты, позволяющие эффективно очистить кровь. Постоянный контроль жизненных показателей пациента обеспечивает безопасность процедуры и позволяет корректировать дозировку лекарств по мере необходимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk66.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
organized progress tips – Provides actionable steps for sustaining steady momentum.
[hide=5]в аське появлялся днём видимо ненадолго, и снова нету (( https://mama-na-kuchne.ru Не успело пройти 3 дня, мне уже звонит курьер забирай говорит. Бонус порадовал, спасибо! Компенсировали за свой счет! Вот это я понимаю МАГАЗИН ДОБРЫХ ЛЮДЕЙ! Так что советую! Качество +5 , спасибо что есть ещё добро в этом злом мире!но только если мусора захотят найдут. просто мусора еслиб хотели найти , то давно бы уже посыль пришла с сопровождением.
Exploration roadmap platform – Reveals unseen opportunities and motivates practical steps forward
Всем привет !!!? https://desert24.ru Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!Вы реально думаете что тут сидят роботы, которые должны отвечать всем без перерывов и выходных? Праздники же были, все отдыхать хотят.
В наркологической клинике «Рестарт» используется комплексный подход к лечению абстинентного синдрома. Наши преимущества:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/snyatie-lomki-narkomana-v-rnd/
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]besplatnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
This excellent website really has all of the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Этот этап лечения направлен на купирование острых симптомов, связанных с абстинентным синдромом. Пациенту назначаются современные препараты, способствующие выведению токсинов, нормализации работы сердца, печени, центральной нервной системы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Этот этап лечения направлен на купирование острых симптомов, связанных с абстинентным синдромом. Пациенту назначаются современные препараты, способствующие выведению токсинов, нормализации работы сердца, печени, центральной нервной системы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
This is a good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Brief but very accurate info… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read article!
Feel free to surf to my web blog – rajapadi4d
Помимо физической детоксикации, лечение запоя требует комплексной психологической поддержки. Психотерапевты работают с пациентами для выявления глубинных причин зависимости, помогают снизить уровень стресса и развивают навыки самоконтроля, что критически важно для предотвращения рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в красноярске[/url]
Лечение начинается с внутривенных инфузий, вводимых с целью скорейшего выведения продуктов распада алкоголя. Препараты корректируют водно-электролитный баланс, поддерживают работу печени и почек, а также нормализуют работу сердечно-сосудистой системы. Все процедуры проводятся под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала, что обеспечивает максимальную безопасность терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в красноярске[/url]
MotiviBeatsHub – Engaging music posts, layout feels smooth and intuitive.
Резкий отказ от алкоголя без врачебной помощи может спровоцировать абстинентный синдром, который сопровождается судорогами, галлюцинациями, аритмией и критическими скачками артериального давления. В тяжёлых случаях состояние может осложниться алкогольным делирием (белая горячка), приступами паники, депрессией и острыми сердечно-сосудистыми расстройствами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новокузнецке[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс знакомства[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов золотая 10х1х0.4 мм ЗлСрМ58.5-8 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог клиники «Гармония здоровья» Александр Ветров, «любая зависимость — это не слабость, а болезнь, требующая медицинского вмешательства и системного подхода».
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]интим услуги[/url]
да по поводу точто все у них медленно спору нет) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Ты нам лучьше отзыв напиши о работе магазина :DЗабрал я посылочку. Упоковка на 5+(пакет был с дыркой как будто смотрели что там, но с такой упаковкой только на паяльник подумаеш). Сделал ам 2233(1г) + ркс4(1г) на 20 грамм мягкого. Честно говоря ам не почувствовал совсем, кроет как ркс4(1 г.) на 20 грамм(был печальный опыт). Сейчас курим по грамму на двоих, тогда кроет на “целых” 10 минут. Вообщем незнаю чья ошибка это, да и смысла выяснять нет, деньги все равно не вернуться. Хотел попробовать тусипи заказать, но как то страшно. С тусипи то такого не было не разу вроде? Притензий не было?
Преимущество
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/]снятие ломки нарколог[/url]
Абстинентный синдром, или ломка, – это тяжелое состояние, которое развивается у зависимых после отказа от наркотиков или алкоголя. Он сопровождается сильными физическими болями, судорогами, повышенной тревожностью, бессонницей и эмоциональными перепадами, что может привести к серьезным осложнениям для здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Здравица» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает комплексное лечение абстинентного синдрома, используя передовые методики и индивидуальный подход для быстрого восстановления здоровья.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd77.ru/]нарколог на дом снятие ломки в краснодаре[/url]
Каждому пациенту назначается персональный план терапии, составленный на основе результатов медицинского и психологического обследования. Мы не используем шаблонные схемы — только индивидуальный подход, адаптированный к возрасту, опыту зависимости, состоянию здоровья и личной мотивации.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/
Клиника «Здравица» в Ростове-на-Дону предлагает современный комплексный подход к лечению абстинентного синдрома. Наши пациенты получают помощь от высококвалифицированных специалистов, которые используют передовые методики и индивидуально подбирают программу лечения для каждого. Среди ключевых преимуществ клиники «Здравица» можно выделить:
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd77.ru/]снятие ломки анонимно[/url]
Первый этап лечения направлен на быстрый вывод токсинов, накопившихся в организме вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя. Для этого применяются современные препараты, позволяющие очистить кровь и восстановить нормальный обмен веществ.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в красноярске[/url]
Этап лечения
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]блекджек[/url]
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог клиники «Гармония здоровья» Александр Ветров, «любая зависимость — это не слабость, а болезнь, требующая медицинского вмешательства и системного подхода».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог воронеж[/url]
все на высем уровне! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Верный второй трек. Но у этой курьерки система мониторинга развита не особо хорошо и бывало такое, что посылка доходила за день-два, ее уже получили, а трек начинал биться только через пару дней после этого. Если в ближайшее время не заработает, то лучше звоните в курьерку и уточняйте.Списавшись в ЛС с ТСом обговорив условия сделки провел оплату в БТЦ.
Преимущество
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd77.ru/]снятие ломок на дому краснодар[/url]
foundry knowledge hub – Very informative, making complex technical subjects easy to understand.
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
Каждому пациенту назначается персональный план терапии, составленный на основе результатов медицинского и психологического обследования. Мы не используем шаблонные схемы — только индивидуальный подход, адаптированный к возрасту, опыту зависимости, состоянию здоровья и личной мотивации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Помимо физической детоксикации, лечение запоя требует комплексной психологической поддержки. Психотерапевты работают с пациентами для выявления глубинных причин зависимости, помогают снизить уровень стресса и развивают навыки самоконтроля, что критически важно для предотвращения рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Сделал заказ. Пропустил реквизиты для оплаты. Продавец свяжись со мной, оплачу. В понедельник сможете отправить товар? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа?Урал и Chemical продукт знают как сделать грязно
Перед оформлением вызова проводится предварительная телефонная консультация, позволяющая оценить тяжесть состояния и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно[/url]
I think the admin of this web site is genuinely working hard in favor of his website, as
here every stuff is quality based information.
I used to be able to find good info from your blog posts.
Creez un espace cosy dans votre region avec [url=http://alsace-stores.com]pergola bioclimatique lames orientables[/url], parfait a tout moment de l’annee.
Avant de construire, il est conseille de reflechir a l’emplacement ideal.
Смысл экстренной помощи — не в «сильной капельнице любой ценой», а в последовательности. Бригада приезжает в согласованное окно, проводит экспресс-осмотр, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ. Далее подбирается инфузионная терапия по показаниям, корректируется водно-электролитный баланс, снижаются тремор и тревога, выравнивается сон. Важно объяснить семье и самому пациенту, чего ожидать: какие ощущения нормальны, какие — повод для связи, зачем назначены те или иные растворы и поддерживающие препараты. Параллельно формируется краткий план «сложных часов» на вечер и ночь: что делать, если накрывает волну беспокойства, как распределить жидкость и питание, какие бытовые действия лучше отложить. В московском ритме особенно критично не растягивать решения на «завтра»: від организованного визита до ощутимого облегчения обычно проходит один-два часа, и именно этот отрезок задаёт тон всей последующей стабилизации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому москва[/url]
Этот формат позволяет пациентам получить профессиональную помощь в комфортной домашней обстановке. Такой подход не только обеспечивает удобство, но и гарантирует конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для многих людей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
Качество обслуживания хорошее – с момента оплаты до прибытия товара прошло всего 3 дня и вес ровный. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш отпиши хоть что за химия. 1 к ..? какая продолжительность, побочки?ВЫ ЛУЧШИЕ!
Помощь врача-нарколога становится жизненно важной, когда симптомы абстинентного синдрома становятся невыносимыми и угрожают жизни пациента. К числу основных признаков, требующих срочного вмешательства, относятся:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd77.ru/]снятие ломки наркозависимого в краснодаре[/url]
В экстренных ситуациях семья ожидает не обещаний, а чётких действий. «Трезвый Ритм» в Королёве организует безопасный вывод из запоя с персональной схемой детоксикации, выездом врача 24/7 и последующей поддержкой, чтобы стабилизировать сон, снизить тревогу и предотвратить рецидив. Мы работаем деликатно и конфиденциально: вы получаете медицинскую помощь без очередей и формальностей, а также понятный план, что делать в первые критические сутки. Наши специалисты используют только проверенные протоколы, учитывают возраст, длительность эпизода и сопутствующие диагнозы, подбирают дозировки бережно и объясняют каждый шаг. Если на осмотре выявляются риски осложнений, мы сразу предложим стационар и возьмём на себя организацию перевода — безопасность всегда важнее спешки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита за регистрацию
Негативные отзывы удаляем? Оправдываете свою новую репутацию. Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш А где прайс глянуть?в том то и дело что мнения в “курилках” а тут “факты” пишут все. Я думаю ,что есть разница между мнением и фактом. Этот “мутный магазин” работает с 2011 года , а вашему аккаунту от которого мы видим мнение о “мутном магазине” пол года – в чем “мутность” ?
Преимущество
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/]снятие ломок на дому в краснодаре[/url]
KidzNFTAdventure – Interactive and enjoyable, navigation is straightforward while content is fun.
purechoices.click – Platform offering genuine goods for conscious decision-making and mindful routines.
В наркологической клинике «Рестарт» используется комплексный подход к лечению абстинентного синдрома. Наши преимущества:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/snyatie-lomki-na-domu-v-rnd/
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Проблемы, связанные с острыми алкогольными отравлениями и запоями, требуют срочной и профессиональной медицинской помощи. В таких ситуациях обращение к услуге вызова нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге становится эффективным решением, позволяющим минимизировать риски для здоровья пациента, не прибегая к госпитализации.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
После стабилизации состояния назначаются препараты, укрепляющие печень, сердце и нервную систему. Обязателен контроль за самочувствием пациента в течение суток и более.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru
Чтобы избежать опасных последствий, необходимо постепенно и безопасно вывести алкоголь из организма. Клиника «Ясный горизонт» предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя в Новокузнецке как в условиях стационара, так и с выездом нарколога на дом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo-novokuzneczk/
Кекс знакомый бpал тут- качество-самолет! Меня угостил – я тоже остался доволен! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш ТС, походу в отпуск вышел:rest:Если представитель не торгует нашим товаром – то представительство мы закрываем и ответственности тоже не несём.
Старт всегда опирается на факты, а не на удобство расписания. После короткого опроса и осмотра врач объясняет, где безопаснее начать — на дому или в стационаре. Если показатели стабильны, домашний формат выигрывает приватностью и скоростью: знакомая среда снижает стресс, легче наладить сон, а выездная бригада привозит всё необходимое для мониторинга и инфузионной терапии по показаниям. При признаках нестабильности мы честно рекомендуем короткий стационар на 24–48 часов: круглосуточное наблюдение позволяет ранее заметить неблагоприятную динамику, корректировать схемы без пауз, подключать диагностику «по триггерам», а не «на всякий случай». В любом варианте пациент получает понятный план на трое суток: режим жидкости и питания, техники «буферов» на вечер, ограничения по нагрузкам, правила ранней связи при тревожных симптомах. Такой реализм убирает хаос, бережёт силы семьи и защищает результат: усложнения перехватываются раньше, а поведение становится предсказуемым — это особенно важно в плотном городском ритме.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость воронеж[/url]
stop voter suppression – Raises awareness effectively and explains key issues clearly.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуально разработанную схему терапии, которая включает комплексное воздействие на организм:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог клиники «Гармония здоровья» Александр Ветров, «любая зависимость — это не слабость, а болезнь, требующая медицинского вмешательства и системного подхода».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в воронеже[/url]
Круглосуточная помощь
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/]снятие ломки нарколог[/url]
В состав капельницы обычно входят растворы для гидратации, витаминно-минеральные комплексы, гепатопротекторы для защиты печени, а также седативные препараты для стабилизации нервной системы. Такой подход позволяет быстро справиться с признаками похмелья и предотвратить развитие более серьезных осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ekb55.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Капельница также рекомендуется для тех, кто испытывает сильный похмельный синдром после длительных запоев. Она помогает не только облегчить состояние, но и предотвратить развитие серьезных осложнений, таких как поражение печени, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения или острые психические расстройства.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в красноярске[/url]
Кодирование в «МедТрезвие» — не «волшебная кнопка», а логическое продолжение после стабилизации, когда организм готов к вмешательству, а пациент понимает механизм действия и ограничения метода. Врач подробно обсуждает цели, риски, противопоказания, ожидаемые эффекты и сроки наблюдения, оформляет информированное согласие и объясняет, как встроить процедуру в общий план. Важная часть — профилактика триггеров и обучение распознаванию ранних сигналов тяги: человек получает не только фармакологическую поддержку, но и практические инструменты саморегуляции, сценарии на «сложные дни», способы запросить помощь до того, как ситуация выйдет из-под контроля. Такая связка повышает вероятность устойчивой ремиссии, потому что работает одновременно на биологическом и поведенческом уровнях.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]лучшая наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
о чем это ты? о каких зачетах ты тут поешь? ты дату своей регистрации видел зачетник ЕПТ! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш минималка СК и рег? и внесите ясностьДошло довольно быстро
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно смотреть[/url]
Запой – это состояние, при котором контроль над потреблением алкоголя полностью утрачивается, что может привести к серьезным осложнениям и даже угрозе жизни. В Новокузнецке специалисты предлагают современные методики вывода из запоя, позволяющие оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и обеспечить безопасное восстановление организма. Благодаря комплексному подходу и применению передовых технологий, лечение проходит быстро и эффективно, что гарантирует минимизацию рисков и предотвращение рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk66.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток, включая праздники и выходные. Анонимность достигается за счёт минимального контакта с персоналом клиники и отсутствия бумажной волокиты. Все этапы лечения согласовываются только с пациентом или доверенным лицом, а сведения о визите не передаются третьим лицам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/
Среди основных разновидностей бонусов в онлайн-казино расположились бонусы к депозитам, кэшбэк и программа лояльности.
https://nodepositcasinobonus.ru
[url=https://casinopromo.ru]промокоды для регистрации[/url]
Начать игру в онлайн казино с бездепозитным бонусом за регистрацию с выводом могут только совершеннолетние пользователи.
Как помогает организму
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk6.ru/narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
Среди основных разновидностей бонусов в онлайн-казино расположились бонусы к депозитам, кэшбэк и программа лояльности.
https://nodepositcasinobonus.ru
Nicely put, Thanks a lot! https://betflik2.blogspot.com/2025/12/betflik-king-experience.html
Крайне редко встречаются площадки, позволяющие оформить заявку на кешаут после использования подарочного депозита, не пополняя баланс.
[url=https://nodepositcasinobonus.ru]бездепозитные бонусы[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже предоставляет квалифицированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. Мы применяем проверенные методы детоксикации, медикаментозной стабилизации и психологической реабилитации, обеспечивая безопасность и эффективность терапии. Специалисты клиники работают круглосуточно, что позволяет оперативно реагировать на экстренные ситуации и гарантировать индивидуальный подход.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]азартные игры на деньги[/url]
how to email bomb on outlook
Email Bombing – email flood or email hoax (DOS attack) or cluster email bombing, what are they actually doing?
A huge number of emails are sent to e-mail. This usually means that the @Flood_email_bot specifically targets the victim’s mailbox associated with your email.
These emails are intended to make fun of friends or distract the victim from any security messages or other emails.
I am glad to present you a mail flood bot with a convenient menu and flexible settings!
The cost of the service is $ 1 = 1000 letters.
You specify the time of the flood and the number of letters yourself, or choose the “FAST FLOOD” function
During the flood, a sufficient number of letters arrive so that the owner would miss an important letter!
The bot will flood more than you ordered. On average, 30% more than ordered.
Flood email, Floods Email, Email flooding, gmail flood, email bomber, flood hotmail, flood online,email flooding, email flood bot, email flooded with spam, email flooding service, email flooded with subscriptions, email flooder bot, email bomber 2023, email bomber 2024, email spam bot online, email spammer bot free, spam bot, бот по флуду почт, сервис по флуду почт, услуги по флуду, флуд услуги.
@Flood_email_bot – Лучший емаил бомбер на рынке!
впервые обратился в этот магазин за оптом и был удивлён тем, что они работают без гаранта. Но почитав отзывы , решил заказать без гаранта с доставкой в регион. Обещали 5-7 дней. С небольшим опозданием получил адрес в своём городе и без проблем забрал опт. Возникли небольшие заморочки в части заказа и магазин без лишних слов решил все недорозумения в мою пользу. Очень приятно работать с такими людьми! Отличный магазин! Всем рекомендую! И можно не обращать внимание на то что они работают без гаранта. Удачи в бизе! Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш спасибо , стараемся для людейБудет что лучше АМ? Или из серии JWH?
Чем дольше продолжается запой, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, нарушается водно-электролитный баланс и ухудшается работа внутренних органов. Своевременное лечение позволяет не только остановить развитие критических состояний, но и значительно снизить вероятность возникновения серьезных осложнений. В Новокузнецке клиники работают по современным протоколам, что обеспечивает быстрый старт терапии и высокую результативность лечения.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novokuznetsk66.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Одной из самых востребованных процедур является снятие абстинентного синдрома. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими симптомами, такими как тревожность, тремор, головная боль и бессонница. Врач, прибывший на вызов, проводит диагностику состояния пациента и подбирает необходимые препараты. Вводятся инфузионные растворы с витаминами, седативными и противорвотными средствами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
I’d like to find out more? I’d care to find out more details.
My blog :: rajacabe88
Задача врача — не «поставить галочку», а исключить противопоказания и выбрать методику с оптимальным соотношением пользы и риска. Учитываются хронические заболевания, эпизоды потери сознания, аритмии, панические атаки, депрессивные симптомы, переносимость инфузий и фармпрепаратов, взаимодействия с уже назначенными лекарствами. По результатам формируется персональный лист ограничений и список «красных флажков», при которых следует связаться со специалистом без промедления.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]procedura-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Этот формат позволяет пациентам получить профессиональную помощь в комфортной домашней обстановке. Такой подход не только обеспечивает удобство, но и гарантирует конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для многих людей.
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru
Выездная бригада «Альтернатива» выполняет комплекс мероприятий прямо у вас дома. Процедура включает несколько этапов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая помощь уфа[/url]
email bomb program
Email Bombing – email flood or email hoax (DOS attack) or cluster email bombing, what are they actually doing?
A huge number of emails are sent to e-mail. This usually means that the @Flood_email_bot specifically targets the victim’s mailbox associated with your email.
These emails are intended to make fun of friends or distract the victim from any security messages or other emails.
I am glad to present you a mail flood bot with a convenient menu and flexible settings!
The cost of the service is $ 1 = 1000 letters.
You specify the time of the flood and the number of letters yourself, or choose the “FAST FLOOD” function
During the flood, a sufficient number of letters arrive so that the owner would miss an important letter!
The bot will flood more than you ordered. On average, 30% more than ordered.
Flood email, Floods Email, Email flooding, gmail flood, email bomber, flood hotmail, flood online,email flooding, email flood bot, email flooded with spam, email flooding service, email flooded with subscriptions, email flooder bot, email bomber 2023, email bomber 2024, email spam bot online, email spammer bot free, spam bot, бот по флуду почт, сервис по флуду почт, услуги по флуду, флуд услуги.
@Flood_email_bot – Лучший емаил бомбер на рынке!
Да работает в асю обращайся если чё надо только товара мало там мхе да дмт Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Наша организация не несет ответственности за применение продукции не по назначению. Осуществляется тотальный контроль качества продукции. Чистота препаратов 99.2%. Исключено добавление примесей. Используется сырье очень высокого качества.Удачных закупок
TrinkHalleOnline – Organized categories, content is easy to read and explore.
Все процедуры проводятся под круглосуточным наблюдением. Применяются инфузионные растворы, седативные и противосудорожные средства, а также поддерживающие препараты, позволяющие уменьшить нагрузку на жизненно важные органы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог волгоград[/url]
Описание
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/]snyatie-lomki-rnd7.ru/[/url]
Запой – это критическое состояние, при котором организм утрачивает способность регулировать потребление алкоголя, что может привести к серьёзным медицинским и психоэмоциональным нарушениям. В Красноярске современные клиники и опытные специалисты применяют инновационные методики, позволяющие быстро и эффективно вывести пациента из запоя. Благодаря комплексному подходу, включающему медикаментозную детоксикацию, коррекцию обменных процессов и психологическую реабилитацию, достигается стабильный результат, предотвращающий повторные эпизоды зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk66.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в красноярске[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино[/url]
спамер на почту онлайн
Email Bombing – email flood or email hoax (DOS attack) or cluster email bombing, what are they actually doing?
A huge number of emails are sent to e-mail. This usually means that the @Flood_email_bot specifically targets the victim’s mailbox associated with your email.
These emails are intended to make fun of friends or distract the victim from any security messages or other emails.
I am glad to present you a mail flood bot with a convenient menu and flexible settings!
The cost of the service is $ 1 = 1000 letters.
You specify the time of the flood and the number of letters yourself, or choose the “FAST FLOOD” function
During the flood, a sufficient number of letters arrive so that the owner would miss an important letter!
The bot will flood more than you ordered. On average, 30% more than ordered.
Flood email, Floods Email, Email flooding, gmail flood, email bomber, flood hotmail, flood online,email flooding, email flood bot, email flooded with spam, email flooding service, email flooded with subscriptions, email flooder bot, email bomber 2023, email bomber 2024, email spam bot online, email spammer bot free, spam bot, бот по флуду почт, сервис по флуду почт, услуги по флуду, флуд услуги.
@Flood_email_bot – Лучший емаил бомбер на рынке!
Одной из самых востребованных процедур является снятие абстинентного синдрома. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими симптомами, такими как тревожность, тремор, головная боль и бессонница. Врач, прибывший на вызов, проводит диагностику состояния пациента и подбирает необходимые препараты. Вводятся инфузионные растворы с витаминами, седативными и противорвотными средствами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Детокс — это не разовая процедура, а управляемый этап со своими задачами: снизить токсическую нагрузку, выровнять жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и самочувствию. Мы подбираем инфузии по показаниям, корректируем электролитный баланс, защищаем печёночные функции, снимаем тремор и вегетативные проявления. Следующая фаза — стабилизация: на этом этапе врач закрывает дефициты, уточняет схемы, выравнивает день и ночь, даёт понятные рекомендации на ближайшие 72 часа. Важно, что пациент не «теряется» после первого улучшения: заранее назначены точки связи, прописаны «красные флажки» и шаги, как действовать при любом из них. Такой порядок снижает вероятность рецидива, потому что вместо импровизации появляются готовые ответы на типичные сложности первых недель.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес… https://zudemon.ru братва подскажите концентрацию и растворитель для ам2233 от данного селера ! Заранее спсна мыло отвечаем только по существу, много не по делу пишут, ася или скайп быстрей
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
Just want to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is just nice
and that i could assume you’re a professional on this subject.
Fine together with your permission let me to
snatch your RSS feed to stay up to date with drawing close post.
Thanks 1,000,000 and please keep up the rewarding work.
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника красноярск[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]азартные игры[/url]
Если вы ищете качественные и стильные устройства для vaping, то [url=https://veyp-hqd.ru/]ашкуди[/url] может стать вашим лучшим выбором, предлагая широкий выбор товаров и услуг по vaping, включая одноразовые устройства, различные вкусы и аксессуары.
Они представляют собой высококачественные устройства для vaping, созданные компанией HQD . Эти устройства очень удобны в использовании Они уже готовы к использованию прямо из коробки . HQD одноразки также очень безопасны Они изготовлены из высококачественных материалов .
HQD одноразки имеют широкий выбор вкусов Каждый вкус уникален и создан для удовлетворения разных предпочтений. Эти устройства также очень компактны Они не занимают много места . HQD одноразки идеально подходят для тех, кто хочет попробовать вейпинг Поскольку они очень просты в использовании .
HQD одноразки имеют много преимуществ Они очень удобны и легки в использовании . Эти устройства также очень эффективны Они могут работать долгое время без перезарядки . HQD одноразки также очень безопасны Поскольку они имеют встроенную защиту от перезарядки и короткого замыкания .
HQD одноразки идеально подходят для тех, кто хочет бросить курить Поскольку они могут помочь уменьшить тягу к никотину . Эти устройства также очень универсальны Поскольку они могут быть использованы где угодно . HQD одноразки – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет попробовать вейпинг Они не требуют никакого опыта или знаний .
HQD одноразки имеют широкий выбор вкусов Вкусы варьируются от классических табачных до экзотических фруктовых . Эти устройства также очень компактны Их можно взять с собой куда угодно. HQD одноразки идеально подходят для тех, кто хочет попробовать разные вкусы Поскольку они очень просты в использовании .
HQD одноразки также имеют разные уровни никотина От 0 до 20 мг на мл . Эти устройства также очень экономичны Они очень долговечны . HQD одноразки – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет попробовать вейпинг Поскольку они очень просты в использовании .
HQD одноразки – это популярный выбор среди любителей вейпинга Они являются одними из самых востребованных продуктов на рынке вейпинга . Эти устройства очень удобны в использовании Их можно использовать сразу после покупки. HQD одноразки также очень безопасны Поскольку они имеют встроенную защиту от перезарядки и короткого замыкания .
HQD одноразки идеально подходят для тех, кто хочет попробовать вейпинг Они не требуют никакого опыта или знаний . Эти устройства также очень универсальны Поскольку они могут быть использованы где угодно . HQD одноразки – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет попробовать вейпинг Они не требуют никакого опыта или знаний .
great publish, very informative. I’m wondering why the other experts
of this sector don’t notice this. You must proceed your writing.
I am sure, you’ve a great readers’ base already!
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
email bomb prank
Email Bombing – email flood or email hoax (DOS attack) or cluster email bombing, what are they actually doing?
A huge number of emails are sent to e-mail. This usually means that the @Flood_email_bot specifically targets the victim’s mailbox associated with your email.
These emails are intended to make fun of friends or distract the victim from any security messages or other emails.
I am glad to present you a mail flood bot with a convenient menu and flexible settings!
The cost of the service is $ 1 = 1000 letters.
You specify the time of the flood and the number of letters yourself, or choose the “FAST FLOOD” function
During the flood, a sufficient number of letters arrive so that the owner would miss an important letter!
The bot will flood more than you ordered. On average, 30% more than ordered.
Flood email, Floods Email, Email flooding, gmail flood, email bomber, flood hotmail, flood online,email flooding, email flood bot, email flooded with spam, email flooding service, email flooded with subscriptions, email flooder bot, email bomber 2023, email bomber 2024, email spam bot online, email spammer bot free, spam bot, бот по флуду почт, сервис по флуду почт, услуги по флуду, флуд услуги.
@Flood_email_bot – Лучший емаил бомбер на рынке!
Хмм…странно всё это, но несмотря ни на что заказал норм партию Ам в этом магазе так как давно тут беру.Как придёт напишу норм репорт про Ам Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш чувак брал я тоже тут 2 ci некоторым понравилось некоторым нет , лично я поднимал даже с неё бабок норм, народу нравиться , а если этот каиф тебе не нравиться нех писать что тусишка бычий кайф , бычий каиф немного другое, а такои продукт не может быть бычий кайф это я тебе отвечаю, со входом согласен по ноздре ваще не вариант !Отличный магазин,заказал и уже через 2 дня в своем городе получил посылку курьером(без звонка),офигев от скорости работы.Вес пришел с неплохим бонусом и в хорошей конспирации.Спасибо очень приятно было с вами работать скоро закажу ещё.
Клиника «Альтернатива» предлагает фиксированные цены на выезд нарколога с оплатой после оказания услуги. Тарифы действуют по всему городу и пригороду.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ufa9.ru/]центр наркологической помощи уфа[/url]
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому в воронеже[/url]
Как подчёркивает главный врач клиники Кондратьев И.Л., «своевременный выезд нарколога на дом снижает риски осложнений и повышает шансы на полное восстановление пациента».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru
Клиника «Альтернатива» предлагает фиксированные цены на выезд нарколога с оплатой после оказания услуги. Тарифы действуют по всему городу и пригороду.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ufa9.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Одной из самых востребованных процедур является снятие абстинентного синдрома. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими симптомами, такими как тревожность, тремор, головная боль и бессонница. Врач, прибывший на вызов, проводит диагностику состояния пациента и подбирает необходимые препараты. Вводятся инфузионные растворы с витаминами, седативными и противорвотными средствами.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Врач-нарколог проводит комплексное обследование пациента, оценивая степень зависимости и общее состояние организма. В ходе первичного осмотра специалист не только определяет тяжесть алкогольной зависимости, но и выявляет сопутствующие патологии, которые могут повлиять на процесс лечения. Обследование включает лабораторные анализы, электрокардиограмму и другие необходимые диагностические процедуры. Врач тщательно изучает анамнез для выявления возможных противопоказаний к определенным методам терапии. Особое внимание уделяется психологическим аспектам, которые могли способствовать формированию зависимости, что помогает разработать эффективную программу лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток, включая праздники и выходные. Анонимность достигается за счёт минимального контакта с персоналом клиники и отсутствия бумажной волокиты. Все этапы лечения согласовываются только с пациентом или доверенным лицом, а сведения о визите не передаются третьим лицам.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Детокс — это не универсальный раствор «от всего», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восполняем жидкость, корректируем электролиты, поддерживаем функции печени, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночному сну. Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма — нет гонки за моментальным «оглушением» симптома ценой побочных эффектов и вечерних откатов. После купирования острой фазы пациент получает понятные правила на 48–72 часа: вода порциями, лёгкая еда по расписанию, «тихий режим» перед сном, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликтные разговоры, критерии связи с врачом. Мы отдельно объясняем, что делать в «тёмные часы» — когда повышается тревожность и усиливается тяга: короткая прогулка рядом с домом, тёплый душ, дыхательные практики, контакт с «своим» человеком, отключение экранов. Такие простые действия бесплатны, но именно они удерживают медицинский эффект и переводят состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vrach-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Возможность получить помощь в любой час снижает риск осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния. Среди главных преимуществ:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ufa9.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
После вашего звонка диспетчер фиксирует заявку и передаёт её свободному специалисту. Нарколог связывается для уточнения симптомов, времени начала запоя и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, чтобы привезти нужные препараты.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru
Мы учитываем сопутствующие заболевания, прием хронических препаратов, возраст и образ жизни. На первичной консультации специалист задаёт уточняющие вопросы, чтобы определить риски, подобрать безопасные препараты и предложить удобный формат: стационар, амбулаторно или выезд на дом. Такой подход сокращает срок восстановления и повышает устойчивость результата.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-balashiha0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-balashihe/
бро незнаю скок раз брал ни разу TS не подводил входил в положения скидки бонусы делал!!! https://nextgenshop.ru после этого случая я стал курить не сигареты конечно рц вообще понравилось и быстро дошло ,делал 1к8 великолепная вещь магазу продвижений”Решил Попробовать Записаться”
купить диплом рггу [url=http://r-diploma25.ru]купить диплом рггу[/url] .
Алгоритм прозрачен. Сначала — краткое интервью и осмотр, измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, при необходимости — ЭКГ и оценка неврологического статуса. Далее — инфузионная терапия по показаниям: восполнение жидкости, коррекция электролитов, поддержка функций печени, мягкое снижение тремора и тревоги, подготовка к сну без «оглушения». Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма, чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных эффектов. Врач детально объясняет, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, сухость во рту, умеренная слабость), а какие — основание для связи. После процедуры повторно фиксируются показатели и выдаются письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа: режим воды и лёгкой еды, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликты, время короткого дневного отдыха, интерфейс связи и условия повторного визита. Такой порядок убирает хаос: пациент и семья понимают, что именно делать вечером и ночью, как снизить «дергание» и зачем придерживаться простых правил, пока организм перестраивается после запоя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom moskva[/url]
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve[/url]
буду дальше с вами сотрудничать, надеюсь всегда так будете работать!))) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Бразы вы снова в теме, если да то скоро заряусь к вам жду ответа)Магазин работает как часы:ok:! Чекист самый крутой продаван это уже проверено годами!!! Дух захватывает от той мысли сколько же он продал за своё существование с 2011 ГОДА:strong: !! Это МЕГА-ПРОДАВАН!!! ТАк держать Чемикал Чекист))!!!
adfinsightcenter – Engaging content, layout is professional and articles are readable.
Родные — ключевой ресурс, если действовать согласованно. Мы обучаем базовым правилам: тише, темнее, теплее; вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»; никаких эмоциональных «разборов» в первые дни; заранее согласованные короткие сигналы для связи со специалистом. Важно отказаться от фраз «возьми себя в руки» и «а если ты сорвёшься?» — они усиливают тревогу и провоцируют сопротивление. Вместо этого — спокойные, конкретные договорённости на сегодня: во сколько отбой, как проходит вечер, когда и какие «буферы» использовать. Такой режим убирает хаос и снижает конфликтность, за счёт чего держится медицинский эффект, уменьшается количество «ночных качелей» и потребность в экстренных визитах. Когда у всех одна карта маршрута, путь к устойчивости становится короче и реалистичнее.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого балашиха[/url]
конспирация достойная, товар оказался отличным, кроли заценили. будем еще работать Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш вот и я уже трясусь.тут как всегда, хочешь сджелать заказ – хрен достучишься в аське.
Адвокат по наследственным делам Казахстан Оспаривание завещания Павлодар: Признание завещания недействительным в судах Павлодара. Защита прав обязательных наследников, оспаривание действий нотариуса.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
бесплатная консультация со специалистом Процедура банкротства – это не увеселительная прогулка, а четкий юридический алгоритм, прописанный в законе о банкротстве. Банкротство через МФЦ – удобный упрощенный вариант, но доступен он далеко не всем. Долговые обязательства, как снежный ком, накапливаются и в итоге приводят к мысли об официальном банкротстве. Закон “о несостоятельности (банкротстве)” и “о банкротстве” – настольные книги для тех, кто решился на этот шаг. Отзывы о банкротстве – кладезь полезной информации, но не стоит забывать, что каждая ситуация индивидуальна.
Your means of telling everything in this piece of writing
is really good, all can without difficulty be aware of it, Thanks
a lot.
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into any problems of
plagorism or copyright infringement? My blog has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either
created myself or outsourced but it seems a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my permission. Do you know any techniques
to help stop content from being stolen? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Задача врача — не «поставить галочку», а исключить противопоказания и выбрать методику с оптимальным соотношением пользы и риска. Учитываются хронические заболевания, эпизоды потери сознания, аритмии, панические атаки, депрессивные симптомы, переносимость инфузий и фармпрепаратов, взаимодействия с уже назначенными лекарствами. По результатам формируется персональный лист ограничений и список «красных флажков», при которых следует связаться со специалистом без промедления.
Детальнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve
официальный набор на СВО Условия и требования к контрактникам определены законодательством. Контракт до 63 лет позволяет служить до достижения предельного возраста. Возраст для контрактной службы, требования к здоровью и профотбор определяют годность к службе.
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены[/url]
прилив бодрости учащаеться https://respect-salon.ru Я вот перед заказом почитала хуеву кучу отзывов и не нашла ни одного хуевого. Но опять же, смотри, отзывы были не об эйфоре, а о самом магазине. Давай друг, советуй что-нибудь в личкуЗаказы только СПСР доставкой?
https://ip-nsk.ru/uslugi/seo-prodvizhenie/
https://ip-nsk.ru/uslugi/sozdanie-saytov/
https://ip-nsk.ru/
https://qiita.com/melbetfreebet
http://chernook.ru/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%201xBet%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE%202026%20%E2%9C%93%20%D0%91%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81%20+%20150%20FS
английский для детей 14 лет
Yes! Finally someone writes about karate class.
whoah this blog is excellent i like reading your articles. Stay up the great work! You already know, lots of individuals are searching round for this info, you could help them greatly.
https://samarateinsieme.it/comment-utiliser-lapplication-atlas-pro-ontv-pour-profiter-au-mieux-de-votre-iptv/
Коллекция аниме онлайн Аниме карточная игра AniMatrix – это синтез коллекционирования, стратегии и яркого аниме-стиля.
рейтинг казино с бездепозитными бонусами Казино без депозита с выводом – это еще более привлекательная перспектива. Ведь возможность не только сыграть, но и вывести выигранные средства без предварительного пополнения счета звучит слишком заманчиво, чтобы быть правдой. Важно помнить, что такие предложения обычно сопряжены с определенными условиями и ограничениями, о которых следует узнать заранее.
У меня всё норм, реальную отправку написали в треке. Я волновался на счёт этого после сообщений Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш КАчество товара отменное ! Жду в наличии ДМТ :happyДоброго времени суток. 3-й заказ шел ровно неделю с момента оплаты. Спасибо за приятный сувенир :good:. Сам бы себе такой не знаю когда приобрел :). Вобщем за сервис снова 5+
При запое счёт идёт не на дни, а на часы: нарастает обезвоживание, усиливается тремор, «скачет» давление и пульс, появляются аритмии, нарушается сон. В таких условиях попытки «перетерпеть» или лечиться «народными методами» приводят к ухудшению состояния и удлиняют путь к восстановлению. В «АлкоМед Балашиха» мы устраняем задержки: выезд возможен без очередей, а при необходимости — оперативная госпитализация в стационар. На первичной оценке врач фиксирует длительность употребления, текущие препараты и сопутствующие болезни, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус и понятным языком объясняет точку входа — на дому или с краткой стационарной стабилизацией. Такой прагматичный подход убирает хаос: уже в первые часы формируется ощутимый эффект — снижается тревога, стабилизируются показатели, появляется шанс на полноценный ночной сон. Когда человек и его близкие видят последовательность действий и понимают, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, уменьшается импульсивность, исчезает «дергание», а лечение перестаёт зависеть от настроения и случайностей.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Уходит тошнота, тремор становится переносимее, пульс и давление перестают «скакать», снижается внутренняя дрожь. Появляется возможность уснуть без паники. Для закрепления эффекта важны простые условия: прохладная затемнённая комната, минимум разговоров и экранов, вода малыми порциями, отсутствие «самопроверок» активностью.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-s-vyezdom-v-lyubercah/
Мы не подгоняем всех под единый сценарий. Если состояние устойчивое, нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации и резких скачков давления и пульса — рационален домашний старт: приватно, быстрее и без лишних переездов. Врач приедет без маркировки, проведёт осмотр, запустит инфузионную терапию по показаниям, оставит письменные рекомендации и «красные флажки». Если же есть признаки угрозы осложнений — обезвоживание, аритмии, риск судорог, боли за грудиной или в животе, лихорадка, спутанность сознания, тяжёлая соматика — мы честно предлагаем короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов. Под круглосуточным наблюдением проще корректировать схемы, вовремя закрывать дефициты, защитить сон и быстрее вернуть управляемость поведению. В обоих форматах маршрут прозрачен: согласованные окна связи, фиксированные цели на ближайшие 72 часа и отсутствие «пакетов ради прайса». Благодаря этому решения принимаются спокойно, без угадываний и эмоциональных раскачек, которые обычно ломают прогресс и удорожают лечение.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
помощь Процедура банкротства регулируется федеральным законом о банкротстве, который четко определяет необходимые условия и этапы. Банкротство через МФЦ – упрощенная процедура, доступная для граждан с небольшим объемом долгов и отсутствием имущества для реализации. Долговые обязательства, будь то кредиты, займы или иные формы задолженности, являются основанием для инициирования банкротства. Официальное банкротство дает возможность должнику начать жизнь с чистого листа, избавившись от непосильного бремени долгов. Закон “о несостоятельности (банкротстве)” и “о банкротстве” содержат подробные инструкции и требования к процедуре. Важно изучить отзывы о банкротстве, чтобы лучше понимать возможные последствия и избежать ошибок.
Сопровождение развода с иностранцем Представительство в арбитражном суде Казахстан: Защита интересов в арбитражных и третейских судах РК. Профессиональный подход к коммерческим спорам, знание регламентов.
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]vyzvat-kapelnicu-ot-zapoya[/url]
I constantly emailed this weblog post page to all my friends, because if like to read it then my links will too.
Брал тут тусишку два раза, отменного качества. Магаз работает быстро и чётко, трек кидают на следующий день, товар приходит через два дня. Респект магазу Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш то есть у вас все по прежнему и сайт работает?А какой ты адрес хотел что бы тебе написали если ты заказываешь может ты данные свои для отправки до сих пор не указал и в ожидании чуда сидишь
в каком казино дают за регистрацию бездепозитные бонусы
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-na-domu-ot-alkogolizma-cena[/url]
This post presents clear idea for the new users of blogging, that actually how to do blogging.
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny[/url]
Сбор аниме героев Бот сражения аниме – ваш первый соперник и отличный тренажер, который поможет отточить навыки перед настоящими PvP-сражениями. Игра с карточками AniMatrix – это уникальный опыт, сочетающий в себе элементы стратегии, коллекционирования и социального взаимодействия.
http://pedagogic.ru/news/item/f00/s16/n0001627/index.shtml
ErinKStudio – Beautifully designed, content is genuine and easy to engage with.
Fetish Porn Sites
Классный магаз, почитал отзывы, нам в киров бы не помешал такой движ. Ассортимент огонь, давайте в наш славный город. Всем щастья! https://novex-m.ru Приветствую всех форумчан и клиентов оптово-розничного магазина chemical-mixа как ам то хоть вооще расшифровывается то по науке???
Дополнительно выясняются аллергические реакции, приём других препаратов и предпочтения пациента по времени визита врача.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
Процедура капельницы — это целый комплекс мероприятий, направленных на очистку организма и восстановление его нормальной работы. Для этого в капельницу добавляют раствор для регидратации, витамины, антиоксиданты, препараты для поддержания печени и успокоительные средства. Все компоненты способствуют быстрому очищению от токсинов, восстановлению психоэмоционального фона и нормализации обменных процессов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ekb55.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Ayo mainkan peluang besar anda di LIGACOR untuk kaya dengan bermain game di website terbaik tanpa stres!
Dapatkan info cuan mudah dan jadilah kaya secara otomatis
механик-водитель по контракту География службы по контракту охватывает всю страну, от Москвы и Подмосковья (включая Балашиху) до отдаленных регионов, таких как Чукотка, Кемерово и Магадан. Контракт в Воронеже, Тамбове, Ярославле, Рязани, Твери, Башкирии, Иваново, Великом Новгороде, Череповце дает возможность служить рядом с домом. Регионы с высокой выплатой по контракту привлекают соискателей со всех уголков России.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Затяжной запой — это состояние, при котором человек в течение нескольких дней не может прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинской помощи. Такое состояние чревато тяжёлыми нарушениями в работе внутренних органов и психики. В Новосибирске и Новосибирской области доступен профессиональный вывод из запоя как на дому, так и в условиях стационара. Подход к лечению индивидуален, и основная цель — безопасно и эффективно устранить последствия интоксикации и предотвратить рецидив.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
Системы автоматизированного дозирования обеспечивают точное введение медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать терапевтическую схему для достижения максимальной безопасности и эффективности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Адвокат Талгар Адвокат 24 часа Алматы: Экстренная юридическая помощь круглосуточно. Выезд на место ДТП, задержания или обыска в любое время суток в Алматы.
Бро я постоянный клиент в этом магазине! Магазин работает очень качественно и товар на высшем уровне!!! https://primavera-rk.ru ты писал пришла посылка размыли в итоге прикола не понялимагазину респект)) с корефанами накуримся вдоволь)))
Аниме герои PvP Онлайн аниме игра AniMatrix открывает двери в мир бесконечных возможностей и сражений.
гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru[/url] .
ремонт подвального помещения [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]ремонт подвального помещения[/url] .
литокол гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru[/url] .
tiktok porn
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]narkolog na dom tsena[/url]
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
Outstanding post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Kudos!
Затянувшийся запой — это не только токсическая нагрузка, но и постоянная «раскачка» нервной системы, скачки давления и пульса, тошнота, бессонные ночи и конфликтный фон в семье. Пока избирается дорога до клиники и очередь на приём, организм теряет воду и электролиты, а тревога усиливается. Выезд «Трезвый Пульс Люберцы» разрывает этот круг: врач прибывает в согласованное окно без маркировки, сразу оценивает факты (длительность употребления, препараты за 24–48 часов, сопутствующие диагнозы, аллергии), фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора и уровень тревоги. На месте объясняется простым языком, зачем именно сегодня нужна инфузия, чего ожидать в ближайшие 30–60 минут и как провести вечер, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи. Домашний формат учитывает реальную географию Люберец: дворовые проезды, часы пик, необходимость сохранять приватность. Чем меньше пауз и социальных контактов, тем быстрее старт терапии, ниже эмоциональный шум и выше приверженность режиму. В результате уже в первые часы выравнивается пульс, снижается тремор и тошнота, появляется шанс на первую ровную ночь — именно она превращает облегчение «на час» в устойчивую стабилизацию на несколько суток.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy
Основная задача клиники — способствовать восстановлению здоровья и социальной адаптации тех, кто столкнулся с зависимостью. Мы комплексно подходим к решению проблемы, учитывая физические, психологические и социальные аспекты зависимости. Наша цель — не только помочь избавиться от пагубных привычек, но и обеспечить успешное возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Получить больше информации – http://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф/
Основное направление работы клиники – это комплексный подход, который включает медицинское лечение, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Мы понимаем, что зависимость затрагивает не только физическое состояние, но и психологическое, поэтому используем методики когнитивно-поведенческой терапии, семейные консультации и групповые занятия. Такой подход помогает пациентам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и разобраться с её причинами и справиться с психологическими трудностями.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Общение оператора 10/10-всегда все грамотно и вежливо объяснит. Таким оператор и должен быть! https://esotericsalchemy.ru Всё отлично все всё получат магаз ровный доказал свой гибгий подход к НАМ заказчикам.Если форс мажёр то всё уладят в НАШу пользу.Отправка осуществляется от 2-10дней в зависимости от заказов то есть загруженности магазина.Без паники братья без паники.Ты договорись с курьером о встрече где нибудь, и пропали окружающую обстановку, чтоб рядом небыло не кого подозрительного. Больше не знаю что тебе посоветовать
Если нет упорной рвоты, лихорадки, выраженной дезориентации, резких скачков АД/пульса и риска судорог, разумно стартовать дома: меньше логистики, больше приватности, выше приверженность режиму. Если состояние «по краю», мы предложим 24–48 часов стационара «Трезвый Подольск»: под круглосуточным наблюдением быстрее закрываются дефициты, корректируются дозы и достигается первый ровный сон — это часто короче и дешевле цепочки ночных вызовов с импровизациями.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/]капельница от запоя телефон[/url]
Родные — ключевой ресурс, если действовать согласованно. Мы обучаем базовым правилам: тише, темнее, теплее; вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»; никаких эмоциональных «разборов» в первые дни; заранее согласованные короткие сигналы для связи со специалистом. Важно отказаться от фраз «возьми себя в руки» и «а если ты сорвёшься?» — они усиливают тревогу и провоцируют сопротивление. Вместо этого — спокойные, конкретные договорённости на сегодня: во сколько отбой, как проходит вечер, когда и какие «буферы» использовать. Такой режим убирает хаос и снижает конфликтность, за счёт чего держится медицинский эффект, уменьшается количество «ночных качелей» и потребность в экстренных визитах. Когда у всех одна карта маршрута, путь к устойчивости становится короче и реалистичнее.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Перед тем как перечислить ключевые преимущества, отметим: каждый маршрут строится индивидуально — от первого звонка и экспресс-диагностики до реабилитации и контроля ремиссии. Это экономит время и снижает тревогу близких.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk0.ru
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, каждая задержка превращается в цепочку случайностей: рушится сон, «скачет» давление и пульс, усиливается тревога, дома нарастает напряжение. «МедСфера Мытищи» убирает хаос управляемым маршрутом: чёткий первичный осмотр, объяснённые назначения, понятные правила на 48–72 часа и прогнозируемые окна связи. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса» — только клиническая достаточность на сегодня с учётом длительности употребления, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых препаратов и исходных показателей. Такой подход снижает тревожность, возвращает ощущение контроля и быстрее приводит к первому ровному сну — именно он становится переломной точкой, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану. Важная деталь — отсутствие общих очередей и «публичных» зон: приём разнесён по времени, входы приватны, а коммуникация ведётся через закрытые каналы. Когда понятно, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, исчезает потребность в импровизациях, и лечение действительно работает.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi[/url]
Детокс — это не универсальный раствор «от всего», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восполняем жидкость, корректируем электролиты, поддерживаем функции печени, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночному сну. Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма — нет гонки за моментальным «оглушением» симптома ценой побочных эффектов и вечерних откатов. После купирования острой фазы пациент получает понятные правила на 48–72 часа: вода порциями, лёгкая еда по расписанию, «тихий режим» перед сном, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликтные разговоры, критерии связи с врачом. Мы отдельно объясняем, что делать в «тёмные часы» — когда повышается тревожность и усиливается тяга: короткая прогулка рядом с домом, тёплый душ, дыхательные практики, контакт с «своим» человеком, отключение экранов. Такие простые действия бесплатны, но именно они удерживают медицинский эффект и переводят состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-balashihe[/url]
Перед процедурой обсуждаются цели, ожидаемые эффекты, возможные побочные реакции, сроки наблюдения. Пациент получает письменные рекомендации на первые трое суток: режим сна и жидкости, коррекция нагрузки, контакты для связи, сигналы настороженности. Такой формат сделал результаты более предсказуемыми: меньше импульсивных решений, меньше тревоги и больше контроля над поведением в критический ранний период.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-moskve-cena[/url]
Клиника создана для оказания квалифицированной помощи всем, кто страдает от различных форм зависимости. Мы стремимся не только к лечению, но также к формированию здорового образа жизни, возвращая пациентов к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее – https://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-Ekaterinburge
31 страницу отзывов почитайте – увидите всех. Кто то только что зарегился , ктото год назад , кому что аккаунт блокнули или забыл пароль от старого акка – он зарегился по новой . Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш “Достаточно связаться с нами и отправить на указанный e-mail информацию о заказе и получателе. Конфиденциальность гарантируется.”УРА трек пробился :angel: Супер магазин,СПАСИБО за подарок 6 г в качестве компенсации:speak::hz:очень боялся что обманут,но Зря:drink: спасибо магазину,с новым годом!!!!!
топ казино с бездепозитными бонусами Топ казино с бездепозитными бонусами – это список проверенных и надежных онлайн-казино, предлагающих самые выгодные условия для игры без предварительного пополнения счета.
growth planning toolkit – Provides useful tools to organize and track growth goals effectively
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble. You’re amazing! Thanks!
Аниме-игра Аниме бой AniMatrix – это не просто столкновение карточек, это битва умов, где важна каждая деталь.
live XXX cams
Миссия нашего медицинского учреждения заключается в предоставлении всесторонней помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Основные цели нашего центра включают:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
привет бразы всех спрошедшими праздниками получил седня посыль все порадовало и качество и бонус:p:D:D:Dприложеный за ожыдание спосибо магазу https://xiaomi-tvshop.ru А так ТС работают отлично не было не одного проёба за пол года сотрудничество ни считая выше сказанногоно с другой стороны, селлер не должен и не обязан объяснять что это такое и с чем его едят. Здесь продаются КОНКРЕТНЫЕ в-ва, а не какие то А1, В2 и иже с ними. Так что можно узнать и самим. И если вас так интересует качество\особенности товара от данного продавца, так не поленитесь в случае заказа отписать о полученном стаффе\особенностях, меньше мороки будет другим. А то заказывают сотни, отзывы пишут единицы, и то больше “зашибись !” или “аааа, не прёёёёёт !!!111”. Выдавайте сами побольше информации.
как получить промокод в 1xbet бесплатно
промокод 1xbet
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого воронеж[/url]
live porn cams
1xbet промокод на день рождения
Домашний визит — это медицинская логика без лишней логистики. В мегаполисе каждая задержка увеличивает риски: человек устаёт, растёт тревога, обостряются скачки давления и пульса, а бессонные ночи превращают любые «самодельные» схемы в опасный эксперимент. «Трезвый Стандарт» строит помощь как управляемую последовательность: дежурный врач собирает краткий анамнез (длительность употребления, лекарства, сопутствующие заболевания), уточняет текущие показатели и предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом или стационар на сутки-двое при высоких рисках. Дом даёт приватность и предсказуемость: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а врач привозит всё для мониторинга и инфузий по показаниям. Ключевой результат первых часов — контролируемый сон, понятный режим гидратации и питания «по силам», а также зафиксированные «красные флажки» для связи. Именно последовательность, а не «сильная капельница любой ценой», делает выездной формат эффективным и безопасным в реальном ритме Москвы.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno
https://despiecetotal.com/pgs/?1xbet-promo-code_welcome-bonus-100.html
ремонт подвального помещения [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]ремонт подвального помещения[/url] .
ремонт в подвале [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru[/url] .
У вас есть свой сайт магазина? Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Не взирая на то что заказ был оплачен в среду прошлой недели, а получил я его через 9(девять) дней, данный селлер заслужил мое доверие!Есть люди в вк, которые представляются под маркой вашего магазина и кидают людей, уже не одного так кинули, так что будьте внимательны и уточняйте у реальных представителей магазина, так оно или нет.
https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/1191419/Code-promo-1XBET-Guin%C3%A9e-2026-1XBIG2026-Bonus-VIP-130
гидроизоляция цена за м2 за работу [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru[/url] .
https://informationng.com/wp-content/pages/?1xbet_promo_code_india_28.html
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy/
«ВоронежДоктор» сочетает в себе профессионализм, современное оборудование и заботу о приватности пациента. Ключевые преимущества:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в воронеже[/url]
https://1xbetpromocoderegistratio10865.blog5.net/88026319/brand-free-spins-code-130-150-fs
Современная жизнь, особенно в крупном городе, как Красноярск, часто становится причиной различных зависимостей. Работа в условиях постоянного стресса, высокий ритм жизни и эмоциональные перегрузки могут привести к проблемам, которые требуют неотложной медицинской помощи. Одним из наиболее удобных решений в такой ситуации является вызов нарколога на дом.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru
Наркологическая клиника “Аура Здоровья” расположена по адресу: г. Ростов-на-Дону, ул. Фрунзе, д. 17/2.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-rostove-na-donu.xn--p1ai
Системы автоматизированного дозирования обеспечивают точное введение медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать терапевтическую схему для достижения максимальной безопасности и эффективности.
Детальнее – http://narco-vivod-clean.ru
Решение обратиться к врачу должно быть принято, если:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом новосибирск[/url]
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино с выводом денег бездепозитный
karta-m.ru
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино без депозита
fantastic points altogether, you simply gained a logo new reader. What would you suggest in regards to your submit that you simply made a few days in the past? Any certain?
Хороший магазин,менеджер приятный по общению,недовесов не было у меня Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Магазин кидает. Буду писать пока не дадут адрес в ПМ. Прошу там же помочь админов.Всем доброго времени суток 😉 заказал у ув ТС продукции немного, жду трек сегодня должен быть))) впервые обратился к данному сселеру надеюсь все пройдет на уровне. Как и что оценю и выложу. краткий трипчик по продуктам если понравится то сработаемся ))))) всем удачных покупок и продаж;)
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Лента никелевая 1.2х35 мм НЭ ГОСТ 2170-73 Познакомьтесь с высококачественной никелевой лентой от Редметсплав.рф. Широкий выбор размеров и толщин. Прочность, устойчивость к высоким температурам. Применение в различных отраслях. Идеально подходит для электротехники, химической промышленности и медицинской техники.
Возможность получить помощь в любой час снижает риск осложнений и ускоряет стабилизацию состояния. Среди главных преимуществ:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ufa9.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Процедура капельницы — это целый комплекс мероприятий, направленных на очистку организма и восстановление его нормальной работы. Для этого в капельницу добавляют раствор для регидратации, витамины, антиоксиданты, препараты для поддержания печени и успокоительные средства. Все компоненты способствуют быстрому очищению от токсинов, восстановлению психоэмоционального фона и нормализации обменных процессов.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ekb55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-ekaterinburg/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ekb55.ru
Since the admin of this website is working, no hesitation very
soon it will be well-known, due to its feature contents.
Высока вероятность развития абстинентного синдрома, делирия или судорожных припадков; поэтому в клинике проводят превентивное введение противосудорожных и седативных средств.
Узнать больше – http://качество-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-v-permi/
Все будет равно чувак!!!!!!!! https://novex-m.ru Клад взял в касание, просто идеально. И никаких ебеней. Прям центр города. К стафу есть вопросы, почему-то вместо 5 было 4 колеса. Что расстроило. Не делайте так больше.все ровно тут ?
Домашняя точка входа оправдана при стабильных показателях и низком риске осложнений. В знакомой обстановке легче соблюдать режим: затемнить комнату, убрать экраны, распределять воду маленькими порциями, сделать лёгкий перекус «по силам», лечь пораньше. Врач подберёт «узкую» схему инфузий без перегруза препаратами, объяснит, какие ощущения допустимы сегодня и ночью, а какие — повод для немедленной связи. Такой сценарий экономит время семьи, снижает стигму и быстрее переводит состояние в управляемое, на базе которого уже можно строить дальнейшие шаги — амбулаторные визиты, работу с триггерами и, при показаниях, обсуждение кодирования.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Строго регламентированный алгоритм позволяет специалистам «ВоронежДоктор» добиваться устойчивых результатов при выводе из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
growth goal planner – Ensures growth objectives are achievable and well-structured
«ВоронежДоктор» сочетает в себе профессионализм, современное оборудование и заботу о приватности пациента. Ключевые преимущества:
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно на дому в воронеже[/url]
Основу капельницы составляют инфузионные растворы, которые помогают устранить обезвоживание. Дополнительно вводятся витамины для улучшения обменных процессов, препараты для защиты печени, а также успокоительные средства для стабилизации нервной системы. Компоненты подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента, чтобы обеспечить максимальную эффективность и безопасность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в красноярске[/url]
В нашей клинике работают врачи-наркологи, психологи и психиатры с многолетним опытом в лечении зависимостей. Все специалисты регулярно повышают свою квалификацию, участвуя в семинарах и конференциях, чтобы обеспечивать своим пациентам наиболее современное и качественное лечение.
Подробнее тут – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Получите [url=https://yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru]юридическую помощь бесплатно[/url], которая поможет решить ваши вопросы быстро и эффективно.
Сегодня юридическая консультация играет важную роль в жизни каждого человека. Сложности в правовых вопросах встречаются у всех. Получить профессиональную помощь в таких ситуациях крайне необходимо.
Разнообразие сфер, в которых востребованы юридические консультации, поистине велико. Среди основных направлений работы юристов можно выделить семейные, трудовые и жилищные вопросы. Каждый из этих вопросов требует особого подхода и знаний юриста.
Кроме того, опытные юристы помогут найти выход из любых сложностей. Знание законодательства позволяет им находить наиболее выгодные варианты. Не стоит недооценивать важность правильного выбора юриста.
Нахождение надежной юридической компании играет ключевую роль. Изучение отзывов и репутации фирмы поможет сделать правильный выбор. Не стоит соглашаться на первый попавшийся вариант.
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]джекпот[/url]
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно воронеж[/url]
за наличие узнавай у селлера. куда тебе 2грамма дезоксипипрадола я слабо представляю, хочешь упороть без палева пол района ? ) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш у нас нет давно курьерских доставок.САБЖ САМ ПО СЕБЕ НЕ ПРЁТ !! МУТИТЬ НА НЁМ МИКСЫ СМЫСЛА НЕТ !!! ЭТО АНТИДЕПРЕССАНТ !!
казино в котором есть бездепозитный бонус
Awesome! Its really amazing post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this piece of writing.
XXX-Video mit großem Arsch
https://pg37.ru/top-prodazh-semyan-gazona-po-reytingu-internet-magazina-gazonov
porn online
А пока всё приходится делать в ручную, так что ОГРОМНАЯ просьба не пишите в аську\скайп с вопросами типа “как прёт ?” “ко скольки бодяжить ?” и т.п. ! Не загружайте людей ) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Я потом взял лосьен Композиция (93%) в бытовой химии – 30 руб за 250 мл стоит вот в нем растворилось, только пришлось сильно греть и мешать. Кстати почемуто если с этим переборщить то химия начинает выпадать в осадок белыми хлопьями :dontknown:, но небольшое количество залитого 646 в спирт всё исправляет и все растворяется полностьювот вот..ждать неизветсности самое такое нервное….
гидроизоляция подвала изнутри цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала изнутри цена[/url] .
отделка подвала [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru/]отделка подвала[/url] .
гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
Команда клиники “Аура Здоровья” состоит из опытных и квалифицированных врачей-наркологов, обладающих глубокими знаниями фармакологии и психотерапии. Они регулярно повышают свою квалификацию, участвуя в профессиональных конференциях и семинарах, чтобы применять самые эффективные методы лечения.
Подробнее – https://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-rostove-na-donu.xn--p1ai/
Зашла на ваш сайт, а там “Your site hasn’t been activated yet!”… в общем ничего не выходит. Пробывала и через ТОР и через обычный браузер. Все одно. Что не так делаю? https://5530343.ru Парни, начинается параноя! Завтра посыль приходит, как получать А?гы гы..вот такая вот история..мля ))
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]интим услуги[/url]
Do you have a spam problem on this blog; I
also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; we have created some nice procedures and we
are looking to trade strategies with other folks,
why not shoot me an email if interested.
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]ставки на спорт[/url]
Особое внимание в клинике уделяется предотвращению рецидивов. Мы обучаем пациентов навыкам управления стрессом и эмоциональной стабильности, помогая формировать здоровые привычки. Это способствует долгосрочному восстановлению и снижает вероятность возвращения к зависимости.
Подробнее тут – http://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф
I am sure this post has touched all the internet people, its really really nice piece of writing on building up new blog.
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Для крупных строительных проектов оптимальным решением будет приобретение [url=http://izvestnyakinfo.ru]куплю щебень известняковый 20 40 москва[/url], что позволит сэкономить средства и обеспечить необходимое качество строительных работ.
Щебень известняковый является одним из наиболее востребованных видов нерудных материалов в строительной отрасли . Этот материал характеризуется улучшенными эксплуатационными характеристиками . Применение известнякового щебня в оптовых масштабах позволяет сократить расходы на строительство .
Щебень известняковый, купленный оптом, может быть использован для различных целей . Известняковый щебень в оптовых партиях доступен для заказа на производственных предприятиях.
Среди преимуществ известнякового щебня стоит отметить его пожаробезопасность. Известняковый щебень используется в строительстве благодаря своим техническим преимуществам. Приобретение оптом известнякового щебня дает возможность сократить расходы на логистику .
Известняковый щебень, купленный оптом, используется для дорожного строительства. Оптовая продажа известнякового щебня способствует увеличению скорости строительства .
Щебень из известняка применяется в производстве асфальтобетона и бетонных смесей . Известняковый щебень используется для обустройства спортивных площадок. Приобретение оптом известнякового щебня дает возможность получить щебень для реализации индивидуальных проектов .
Известняковый щебень, купленный оптом, может быть хранен на специализированных складах. Оптовая продажа известнякового щебня осуществляется через специализированные онлайн-платформы .
Итак, щебень известняковый является ценным строительным материалом . Оптовая покупка известнякового щебня является выгодной для крупных строительных компаний . Оптовые закупки известнякового щебня предназначены для крупномасштабных проектов .
Оптовая продажа известнякового щебня осуществляется через официальные дилерские сети . Оптовая покупка известнякового щебня позволяет получитьraw материал для различных целей .
This is my first time pay a visit at here and
i am truly happy to read all at alone place.
If you wish for to increase your familiarity only keep visiting this site
and be updated with the most recent gossip posted here.
Наркологическая клиника “Маяк надежды” — специализированное медицинское учреждение, предназначенное для оказания помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и вернуть их к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – http://алко-лечение24.рф
Без сна любая дневная капельница даёт короткий «блеск» и вечерний откат. Поэтому мы заранее настраиваем гигиену: затемнение, прохлада, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров, при показаниях — щадящая седативная поддержка, которая стабилизирует, а не «выключает». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка дозировок, чтобы вторая ночь стала ещё спокойнее.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru
Мы помогаем при острых состояниях, связанных с алкоголем, и сопровождаем до устойчивой ремиссии. Детокс у нас — это не «одна капельница», а система мер: регидратация и коррекция электролитов, защита печени и ЖКТ, мягкая седативная поддержка по показаниям, контроль давления/пульса/сатурации/температуры, оценка сна и уровня тревоги. После стабилизации обсуждаем стратегию удержания результата: подготовку к кодированию (если показано), настройку поддерживающей терапии и реабилитационный блок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Первая ровная ночь — поворотная точка. Без неё любая дневная инфузия работает коротко и «сгорает» к вечеру. Мы заранее настраиваем простые, но критичные условия: затемнение, тишина, прохладная комната, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и разговоров. При показаниях назначается щадящая седативная поддержка в дозах, которые стабилизируют, а не «выключают». Утром — короткий контроль и подстройка доз, чтобы другая ночь прошла ещё спокойнее. Такой «простой» протокол даёт самый устойчивый результат: исчезают панические волны, выравниваются показатели, снижается вероятность повторных экстренных обращений, а значит, бюджет остаётся предсказуемым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-himkah/
growth navigation indicators – Highlights signs that simplify growth decision-making
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]порно онлайн бесплатно[/url]
big ass xxx video sex porn
https://github.com/logonx/Windows-App/releases
Affiliate Marketing affilka: Affilka – комплексное решение для управления партнерскими программами. Автоматизация, аналитика и контроль в одной платформе. TOP bookmakers: Рейтинг лучших букмекерских контор для аффилиатного трафика. Сравнение условий, конверсии и выплат.
электрический карниз Установка электрического карниза – задача для профессионалов. Доверьте установку квалифицированным специалистам, чтобы гарантировать надежность и долговечность вашей системы.
Excellent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe
for a blog website? The account aided me a acceptable deal.
I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear
concept
https://enran.ua/
This game looks amazing! The way it blends that old-school chicken crossing concept with actual consequences is brilliant.
Count me in!
Okay, this sounds incredibly fun! Taking that nostalgic chicken crossing gameplay and adding real risk?
I’m totally down to try it.
This is right up my alley! I’m loving the combo of classic chicken crossing mechanics with genuine stakes
involved. Definitely want to check it out!
Whoa, this game seems awesome! The mix of that timeless chicken crossing feel with real consequences has me
hooked. I need to play this!
This sounds like a blast! Combining that iconic chicken crossing
gameplay with actual stakes? Sign me up!
I’m so into this concept! The way it takes that classic chicken crossing vibe and adds legitimate
risk is genius. Really want to give it a go!
This game sounds ridiculously fun! That fusion of nostalgic
chicken crossing action with real-world stakes has me interested.
I’m ready to jump in!
Holy cow, this looks great! Merging that beloved
chicken crossing style with tangible consequences?
I’ve gotta try this out!
This post will help the internet people for creating new website or even a blog
from start to end.
https://github.com/logonx/Windows-App/releases
гидроизоляция цена кг [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena4.ru[/url] .
action momentum guidance – Shows methods for sustaining momentum and achieving goals.
В мегаполисе решают три параметра: клиническая достаточность, логистика и приватность. В «ГородМед Трезвость» назначения делаются строго по показаниям — без «пакетов ради прайса»; это экономит ресурсы и защищает от лишних процедур. Логистика учитывает пробки и занятость пациента: выездные бригады работают круглосуточно, а стационар принимает без очередей, что убирает паузы между детоксом и стабилизацией. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: запись через закрытые каналы, шифры вместо ФИО в рабочем расписании, разграничение доступа к данным и отдельные окна визитов. Смысл прост: человек получает медицинский результат без огласки и без бюрократических «ступеней», которые разбивают лечение на бессмысленные ожидания. Поэтому нас выбирают те, кому важно вернуться к работе и семье без срывов и длинных «выходов из строя».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Особое внимание в клинике уделяется предотвращению рецидивов. Мы обучаем пациентов навыкам управления стрессом и эмоциональной стабильности, помогая формировать здоровые привычки. Это способствует долгосрочному восстановлению и снижает вероятность возвращения к зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-rostove-na-donu.xn--p1ai/
гидроизоляция подвала цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала цена[/url] .
Стильная одежда имеет большое значение в формировании образа.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и ощущать внутренний комфорт.
Аккуратный внешний вид влияет на восприятие окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать уверенность.
https://sites.google.com/view/brand-history/chanel
Стильный образ облегчает социальные контакты.
При выборе одежды важно учитывать личные предпочтения и уместность ситуации.
Актуальные стили дают возможность экспериментировать.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться делает образ завершённым.
купить электрический карниз Установка электрического карниза – задача для профессионалов. Доверьте установку квалифицированным специалистам, чтобы гарантировать надежность и долговечность вашей системы.
Основная задача клиники — способствовать восстановлению здоровья и социальной адаптации тех, кто столкнулся с зависимостью. Мы комплексно подходим к решению проблемы, учитывая физические, психологические и социальные аспекты зависимости. Наша цель — не только помочь избавиться от пагубных привычек, но и обеспечить успешное возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://медицинский-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-rostove-na-donu.xn--p1ai/
3s info 3snet: Подробный обзор одной из ведущих партнерских сетей в индустрии
big ass xxx video sex porn
обмазочная гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena5.ru/]обмазочная гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
Капельница – это метод внутривенной инфузии, который позволяет доставить в организм пациента растворы для детоксикации и восстановления. Основные задачи процедуры включают очищение крови от токсичных веществ, нормализацию водно-солевого баланса и улучшение общего самочувствия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в красноярске[/url]
Применяются растворы на основе физраствора, глюкозы, витаминов группы B, противорвотных, седативных и гепатопротекторов. Используемые препараты входят в реестр разрешённых лекарств.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-v-ekaterinburge/
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино с выводом денег бездепозитный
Процедура капельницы особенно показана в случаях, когда симптомы похмелья выражены настолько сильно, что пациент не в состоянии справиться с ними самостоятельно. Головная боль, тошнота, рвота, усталость и раздражительность — все это признаки того, что организму необходимо восстановление. Капельница помогает не только ускорить процесс очищения, но и минимизировать риск осложнений, таких как нарушение работы сердца и печени.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
https://github.com/sageetl/Sage-50/releases
Психологи нашего центра проводят индивидуальные и групповые сессии, помогая пациентам осознать корни своей зависимости, изменить деструктивные модели поведения, сформировать адекватную самооценку и развить навыки управления стрессом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://надежный-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-voronezhe.xn--p1ai/
Процесс лечения организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Asking questions are truly fastidious thing if you are not understanding something entirely, however this article presents nice understanding even.
growth progress steering – Focuses on steady, practical steps for moving growth forward
cock ring gay porn
live XXX cams
Затяжной запой — это состояние, при котором человек в течение нескольких дней не может прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинской помощи. Такое состояние чревато тяжёлыми нарушениями в работе внутренних органов и психики. В Новосибирске и Новосибирской области доступен профессиональный вывод из запоя как на дому, так и в условиях стационара. Подход к лечению индивидуален, и основная цель — безопасно и эффективно устранить последствия интоксикации и предотвратить рецидив.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
С увеличением темпа жизни и нарастающим стрессом, многие люди в Екатеринбурге сталкиваются с зависимостями, особенно с алкогольной. Алкогольная зависимость является одной из наиболее распространённых проблем, требующих немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Важно помнить, что в сложных ситуациях, связанных с зависимостью, помощь не должна откладываться. Вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге становится идеальным вариантом для тех, кто не может или не хочет покидать свой дом, но нуждается в медицинской помощи.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve/
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
Смысл экстренной помощи — не в «сильной капельнице любой ценой», а в последовательности. Бригада приезжает в согласованное окно, проводит экспресс-осмотр, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ. Далее подбирается инфузионная терапия по показаниям, корректируется водно-электролитный баланс, снижаются тремор и тревога, выравнивается сон. Важно объяснить семье и самому пациенту, чего ожидать: какие ощущения нормальны, какие — повод для связи, зачем назначены те или иные растворы и поддерживающие препараты. Параллельно формируется краткий план «сложных часов» на вечер и ночь: что делать, если накрывает волну беспокойства, как распределить жидкость и питание, какие бытовые действия лучше отложить. В московском ритме особенно критично не растягивать решения на «завтра»: від организованного визита до ощутимого облегчения обычно проходит один-два часа, и именно этот отрезок задаёт тон всей последующей стабилизации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru
https://enran.ua/
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]narkologicheskaya-moskva[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
После инфузии врач повторно измеряет показатели, оставляет письменные инструкции, назначает окно связи и определяет условия, при которых разумно перейти к стационару: нет нужды держаться «на силе воли», когда безопаснее сменить формат.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-srochno/
Affiliate Programs 3s info: Ваш надежный путеводитель в мире партнерского маркетинга
Experience Brainy https://askbrainy.com the free & open-source AI assistant. Get real-time web search, deep research, and voice message support directly on Telegram and the web. No subscriptions, just powerful answers.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс чат[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Great article, just what I wanted to find.
https://github.com/logonx/Windows-App/releases
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/vi/register?ref=MFN0EVO1
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]ТД Медицинская пиявка[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]ТД Медицинская пиявка[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма москва[/url]
Чтобы не оценивать состояние субъективно, в клинике применяется система наблюдения за ключевыми параметрами. Таблица помогает врачу и пациенту видеть реальную динамику и корректировать вмешательства только при необходимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]ТД Медицинская пиявка[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]ТД Медицинская пиявка[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявки купить ростов на дону[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Медицинская пиявка ростов[/url]
[url=https://медпиявка.рф/]Пиявка ростов[/url]
Hi there, I enjoy reading through your article post.
I like to write a little comment to support you.
Regards, A lot of postings.
Домашний маршрут выбирают, когда показатели стабильны и нет признаков тяжёлой соматики или спутанности сознания. Преимущество в сочетании скорости, приватности и приверженности: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а отсутствие переездов экономит силы. Врач «МедТоники» приезжает без маркировки, привозит мониторинг и расходные материалы, подбирает инфузии по состоянию, помогает восстановить режим сна и гидратации, даёт рекомендации по питанию и правила на 48–72 часа. Отдельный блок — работа с тревогой и тремором: корректируется медикаментозная поддержка, обсуждаются простые поведенческие техники, чтобы снизить вероятность импульсивных решений вечером. Домашний формат не подменяет наблюдение: назначаются точки связи, врач объясняет, когда нужен повторный визит, а когда достаточно телефонной коррекции. Для Москвы такой сценарий удобен ещё и тем, что его проще встроить в плотный график, не выпадая из рабочих и семейных ролей и не провоцируя лишних вопросов у окружающих.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-srochno/
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]наркологическая клиника в москве[/url]
Every weekend i used to go to see this site, as i wish
for enjoyment, for the reason that this this web site conations actually nice funny material too.
Детокс — это не разовая процедура, а управляемый этап со своими задачами: снизить токсическую нагрузку, выровнять жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и самочувствию. Мы подбираем инфузии по показаниям, корректируем электролитный баланс, защищаем печёночные функции, снимаем тремор и вегетативные проявления. Следующая фаза — стабилизация: на этом этапе врач закрывает дефициты, уточняет схемы, выравнивает день и ночь, даёт понятные рекомендации на ближайшие 72 часа. Важно, что пациент не «теряется» после первого улучшения: заранее назначены точки связи, прописаны «красные флажки» и шаги, как действовать при любом из них. Такой порядок снижает вероятность рецидива, потому что вместо импровизации появляются готовые ответы на типичные сложности первых недель.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Hey! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and
say I genuinely enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you recommend
any other blogs/websites/forums that go
over the same subjects? Thank you so much!
growth pathway hub – Collects insights to help steer growth clearly and efficiently
Длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к накоплению токсинов, нарушению обменных процессов и ухудшению работы внутренних органов. Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить риск серьезных осложнений, таких как сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, повреждение печени и почек, а также уменьшить психоэмоциональное напряжение. Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Рязани помогает начать лечение на ранних этапах, когда каждая минута имеет значение.
Выяснить больше – http://наркология-дома1.рф/
Hi, yup this article is truly good and I have learned lot of things from it on the topic of blogging. thanks.
Специалист уточняет длительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Точный сбор данных позволяет оперативно корректировать лечение и выбрать оптимальные методы детоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
адрес меги тор https://tagespflege-elsdorf.de
Эта процедура доступна как в условиях клиники, так и на дому, что делает ее универсальным решением для различных жизненных ситуаций. При этом важно доверять свое здоровье только профессиональным врачам, которые могут обеспечить безопасное и качественное лечение.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в красноярске[/url]
Применяются растворы на основе физраствора, глюкозы, витаминов группы B, противорвотных, седативных и гепатопротекторов. Используемые препараты входят в реестр разрешённых лекарств.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Каждый врач клиники обладает глубокими знаниями фармакологии, психофармакологии и психотерапии. Они регулярно посещают профессиональные конференции, семинары и мастер-классы, чтобы быть в курсе новейших достижений в области лечения зависимостей. Такой подход позволяет нашим специалистам применять наиболее эффективные и современные методы терапии.
Детальнее – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника краснодар[/url]
888 starz casino 888 Казино: Синоним качества и надежности в индустрии онлайн-гемблинга. Выбирайте лучшее и играйте с уверенностью. 888 Казино бонусы: Щедрые предложения для новых и постоянных игроков. Увеличьте свой банкролл и получите больше шансов на победу. Не упустите возможность сорвать крупный куш!
Ремонт в с. Туймебаев (Ащибулак). Замена уплотнителей, ремонт дверей.Ремонт холодильников Караой Ремонт холодильников Whirlpool с технологией “6-е чувство”. Обслуживание системы Total No Frost, замена фильтров-осушителей, ремонт платы управления. Мы устраняем ошибки и восстанавливаем идеальный климат для продуктов. Используем оригинальные запчасти. Ремонт холодильников Gorenje Алматы
Затяжной запой — это состояние, при котором человек в течение нескольких дней не может прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинской помощи. Такое состояние чревато тяжёлыми нарушениями в работе внутренних органов и психики. В Новосибирске и Новосибирской области доступен профессиональный вывод из запоя как на дому, так и в условиях стационара. Подход к лечению индивидуален, и основная цель — безопасно и эффективно устранить последствия интоксикации и предотвратить рецидив.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого новосибирск[/url]
purposeful momentum guidance – Highlights ways to maintain focus and generate consistent progress.
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс чат[/url]
Зависимость всегда про неопределённость: скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тревожность, бессонные ночи, споры в семье и страх огласки. «ЛюберМед Центр» убирает эту неопределённость управляемым маршрутом. Мы начинаем с краткого, но точного интервью, фиксируем объективные показатели и тут же объясняем, какие вмешательства уместны сегодня и зачем именно они. Никаких «общих залов» и очередей: приёмы разнесены по времени, подтверждения проходят по защищённым каналам, визиты на дом — без маркировки. Наш принцип — минимальная достаточность: столько медицины, сколько нужно для безопасного перехвата динамики и первой ровной ночи. Именно она делает дальнейшие шаги предсказуемыми: снижается тремор, выравнивается ритм, появляется ресурс соблюдать режим. Благодаря продуманной логистике Люберец мы сокращаем холостые перемещения, а значит, лечение начинается раньше, а тревоги — меньше. В результате пациент и семья получают не «набор услуг», а последовательность: понятные действия, прозрачные ожидания и устойчивый эффект, который держится днями, а не часами.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-lyubercah[/url]
На данном этапе специалист уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какие симптомы наблюдаются, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой детальный анализ помогает оперативно определить оптимальные методы детоксикации и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://наркология-дома1.рф/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-ryazan/
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения тщательного первичного осмотра. Врач собирает краткий анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели — пульс, артериальное давление и температуру, и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются фундаментом для составления индивидуального плана терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://наркология-дома1.рф
Мы верим, что каждый человек, столкнувшийся с проблемой зависимости, заслуживает шанса на новую жизнь. Наша миссия — предоставить необходимые инструменты и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам в их стремлении к выздоровлению и личностному росту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://алко-лечение24.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-Sankt-Peterburge/
Thanks for finally writing about > Types of Cancer: Common & Rare Cancers Explained < Liked it!
Образовательные программы: Мы уверены, что знания о зависимости и её последствиях играют важную роль в реабилитации. Мы информируем пациентов о механизмах действия наркотиков и алкоголя на организм, что способствует изменению их отношения к терапии и жизни без зависимостей.
Подробнее – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя цена казань[/url]
Использование современных автоматизированных систем дозирования гарантирует точное введение медикаментов, что минимизирует риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать дозировки и адаптировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени.
Узнать больше – https://наркология-дома1.рф/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ryazan/
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
кракен казино зеркало Кракен казино: Погружение в мир азарта и безграничных возможностей
Ремонт инверторных моторов Hisense. Восстановление плат управления, устранение ошибок.Ремонт стиральных машин TCL Алматы Японская надежность Hitachi. Ремонт систем контроля вибрации Dual Vibration Control, устранение ошибок C01, C02. Мы восстанавливаем работу датчиков и инверторного привода. Используем оригинальные комплектующие Hitachi. Ремонт стиральных машин Panasonic Алматы
Hi there! I understand this is sort of off-topic however I had to ask. Does running a well-established blog such as yours require a large amount of work? I am completely new to blogging however I do write in my journal on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any recommendations or tips for brand new aspiring bloggers. Thankyou!
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, каждая задержка превращается в цепочку случайностей: рушится сон, «скачет» давление и пульс, усиливается тревога, дома нарастает напряжение. «МедСфера Мытищи» убирает хаос управляемым маршрутом: чёткий первичный осмотр, объяснённые назначения, понятные правила на 48–72 часа и прогнозируемые окна связи. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса» — только клиническая достаточность на сегодня с учётом длительности употребления, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых препаратов и исходных показателей. Такой подход снижает тревожность, возвращает ощущение контроля и быстрее приводит к первому ровному сну — именно он становится переломной точкой, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану. Важная деталь — отсутствие общих очередей и «публичных» зон: приём разнесён по времени, входы приватны, а коммуникация ведётся через закрытые каналы. Когда понятно, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, исчезает потребность в импровизациях, и лечение действительно работает.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в мытищах[/url]
Hurrah! Finally I got a weblog from where I know how to in fact take valuable facts concerning my study and knowledge.
Looking for a casino? https://elon-casino-top.com: slots, live casino, bonus offers, and tournaments. We cover the rules, wagering requirements, withdrawals, and account security. Please review the terms and conditions before playing.
Страх огласки часто тормозит обращение сильнее симптомов. Мы устраняем барьер процессами: запись и подтверждения через закрытые каналы, шифры вместо ФИО в расписании, немаркированные визиты, доступ к данным по ролям. В клинике нет общих очередей, контакты разнесены по времени; внутри — «тихие коридоры», минимум пересечений с другими посетителями. Документы оформляются минимальным набором персональных сведений, информирование родственников — только с согласия пациента. В выездном формате заранее согласуем «тихий» маршрут по двору и подъезду. Такая деликатная логистика повышает приверженность лечению: когда не страшно «быть узнанным», проще согласиться на помощь вовремя и точнее выполнить план. Это прямой вклад в результат и бюджет: меньше «пожаров» — меньше незапланированных расходов, потому что решения принимаются на фактах, а не на страхе.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-podolske
It’s awesome to pay a visit this web site and reading the views
of all mates regarding this piece of writing, while I am also zealous of getting
familiarity.
vbet Vbet: Бренд, завоевавший доверие игроков благодаря широкому выбору игр, щедрым бонусам и высоким стандартам безопасности. Откройте для себя мир Vbet и окунитесь в атмосферу азарта и захватывающих приключений. Vbet Casino: Разнообразие игр от ведущих мировых разработчиков, включая слоты, рулетку, блэкджек и многое другое. Почувствуйте вкус настоящего казино, не выходя из дома. Участвуйте в турнирах, получайте бонусы и станьте обладателем крупного выигрыша! Vbet казино: Армянская версия популярного онлайн-казино, предлагающая адаптированный интерфейс, местные платежные системы и выгодные предложения для игроков из Армении. Наслаждайтесь любимыми играми на родном языке! Vbet am: Удобный и функциональный сайт Vbet, разработанный специально для армянской аудитории. Быстрая регистрация, удобные методы пополнения и вывода средств, а также круглосуточная поддержка – все, что нужно для комфортной игры. Vbet покер: Платформа для любителей покера всех уровней. Участвуйте в турнирах, играйте кэш-игры и совершенствуйте свои навыки. Vbet покер – это место, где вы можете стать настоящим профессионалом и выиграть крупные призовые фонды. Оттачивайте мастерство, блефуйте и побеждайте!
growth unification model – Organizes disparate growth insights into a coherent execution plan
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really helpful & it helped me out a lot.
I am hoping to present one thing again and help others like you helped me.
Формат выбирается по безопасности, а не «по желанию». Домашний или амбулаторный старт уместен, если показатели устойчивы: нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» давления и пульса, признаков обезвоживания с угрозой судорог. В этих условиях один визит часто закрывает задачу: индивидуальная инфузия, письменные рекомендации, правила воды и лёгкой еды «по часам», утренний контроль. Если же состояние «по краю» — сочетание рвоты, лихорадки, кардиальных жалоб, второй бессонной ночи, выраженного тремора — честнее короткая стационарная стабилизация на 24–48 часов под круглосуточным наблюдением. На бумаге это кажется дороже одного выезда, но на практике предотвращает цепочку ночных «пожаров», импульсивных повторов и осложнений, то есть экономит и силы, и деньги семьи. В любом формате анонимность неизменна: визиты без маркировки, закрытые каналы связи, разнесённые по времени приёмы и доступ к данным по ролям.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki9.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Hello there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
бомбер электронной почты
Email Bombing – email flood or email hoax (DOS attack) or cluster email bombing, what are they actually doing?
A huge number of emails are sent to e-mail. This usually means that the @Flood_email_bot specifically targets the victim’s mailbox associated with your email.
These emails are intended to make fun of friends or distract the victim from any security messages or other emails.
I am glad to present you a mail flood bot with a convenient menu and flexible settings!
The cost of the service is $ 1 = 1000 letters.
You specify the time of the flood and the number of letters yourself, or choose the “FAST FLOOD” function
During the flood, a sufficient number of letters arrive so that the owner would miss an important letter!
The bot will flood more than you ordered. On average, 30% more than ordered.
Flood email, Floods Email, Email flooding, gmail flood, email bomber, flood hotmail, flood online,email flooding, email flood bot, email flooded with spam, email flooding service, email flooded with subscriptions, email flooder bot, email bomber 2023, email bomber 2024, email spam bot online, email spammer bot free, spam bot, бот по флуду почт, сервис по флуду почт, услуги по флуду, флуд услуги.
@Flood_email_bot – Лучший емаил бомбер на рынке!
https://compagnie-faisan.org/
Incredible a lot of very good information.
momentum path lane – A clear method for guiding energy and effort toward objectives.
кыздар нет астана ?ыздар нет: Отчаянное эхо, разносящееся по пустым квартирам и дорогим отелям. Это стон сердца, ищущего любви и утешения, но наталкивающегося на стену безразличия. В этих словах – вся трагедия поколения, разуверившегося в искренности и потерявшего надежду найти настоящую близость.
проститутки алматы Эскорт: Изысканный танец между иллюзией и реальностью, где роскошь служит маской для пустоты. Здесь элегантность и учтивость — лишь инструменты, предназначенные для завоевания доверия и удовлетворения самых тонких потребностей, но за пределами золотой клетки остается лишь призрачная память о близости. ?ыздар нет: Горькое эхо отвергнутых надежд, разрушенных мечтаний и унесенных ветром обещаний. В этих двух словах — вся боль неразделенной любви, вся тяжесть разочарования и все оттенки одиночества, окутывающего душу, словно непроглядная ночь.
Admiring the time and effort you put into your site and detailed information you offer.
It’s good to come across a blog every once
in a while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material.
Excellent read! I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
We stumbled over here coming from a different web address and thought I might as well check
things out. I like what I see so now i am following you.
Look forward to exploring your web page again.
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
обратная связь сделать обратная связь купить телефон сделать купить оэрн официальный сайт обратиться
общество экспертов России по недропользованию
оэрн обратная связь общество экспертов России по недропользованию общество экспертов России по недропользованию приобрести обратиться сделатьРоссия
tripskan Tripscan: Откройте для себя мир безопасных и осознанных путешествий, где каждый шаг – это вклад в собственное развитие и понимание. Tripscan – это не просто платформа, это ваш надежный компас в бескрайнем океане личного исследования, помогающий отличить истинные жемчужины от мимолетных иллюзий. Трипскан: Верните контроль над своим опытом, вооружившись знаниями и подготовкой. Трипскан – это ваш личный навигатор, помогающий ориентироваться в сложных лабиринтах сознания и избегать нежелательных последствий. Tripskan: (Транслитерация) – ваш надежный путеводитель в осознанные состояния, предоставляющий инструменты для безопасного исследования глубин разума. Трип скан: Технология, позволяющая анализировать и оценивать потенциальные риски и выгоды каждой поездки в неизведанное. Tripscan – это ваш личный эксперт, помогающий принимать взвешенные решения и обеспечивающий максимальную безопасность во время путешествия. Трипскан вход: Ваш ключ к сообществу единомышленников, стремящихся к самопознанию и развитию. Здесь вы найдете поддержку, вдохновение и полезные советы от опытных путешественников. Сайт трипскан: Ваш ресурс номер один для получения информации о безопасных практиках, надежных источниках и проверенных методиках. Tripscan – это ваш личный библиотекарь, предоставляющий доступ к обширной коллекции знаний и опыта. Трипскан ссылка: Просто перейдите по ссылке и начните свое путешествие к осознанности и самопознанию. Tripscan – это ваш личный проводник в мир удивительных открытий и трансформаций. Трипскан зеркало: Обеспечьте себе бесперебойный доступ к ресурсу в любое время и в любом месте. Ваше путешествие к самопознанию не должно знать границ.
I don’t know if it’s just me or if perhaps everyone else experiencing problems with your blog. It appears like some of the written text on your content are running off the screen. Can somebody else please provide feedback and let me know if this is happening to them too? This might be a problem with my browser because I’ve had this happen before. Thank you
?ыздар нет Проститутки Алматы: За кулисами мегаполиса, где тени скрывают истории одиночества и отчаяния, расцветает темный цветок запретной страсти. Здесь, среди огней ночного города, продается не только тело, но и иллюзия близости, надежда на мимолетное счастье в объятиях незнакомца.
Здесь
[url=https://cpa.tl/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
эскорт Эскорт: Симфония страстей, разыгрывающаяся в полумраке роскошных апартаментов. Тонкий аромат дорогих духов, приглушенный свет свечей и шепот обещаний создают атмосферу, где реальность уступает место иллюзии. Здесь, в этом мире, где желания правят бал, каждый жест и слово имеют свою цену, а близость становится товаром, доступным тем, кто готов платить за нее. Это игра, где эмоции – лишь маски, скрывающие истинные чувства и намерения, а главная цель – удовлетворение мимолетной прихоти.
https://sykaaa-official-casino.website
Первичная оценка строится на фактах. Врач коротко уточняет жалобы, длительность употребления, переносимость препаратов и аллергии, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-ЭКГ и скрининг неврологического статуса. Далее — объясняет на понятном языке логику назначений: зачем именно такая инфузионная схема, какие ощущения нормальны в течение часа и к ночи, как организовать питьевой режим и лёгкое питание «по силам». Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов: дозируем узко, чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных эффектов. После процедуры повторно оцениваем показатели, выдаём письменные рекомендации, согласуем окно связи и условия повторного визита. Семья получает простые правила поведения дома (тишина, затемнение, ограничение экранов, отсутствие «разборов») и сигналы, когда лучше позвать врача. Итог визита — управляемая ночь и предсказуемое утро, на котором можно строить следующие шаги.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-podolsk9.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Красноярск, как и любой крупный город, сталкивается с распространенными проблемами зависимости. Учитывая высокий уровень стресса, социальное давление и быстрое развитие мегаполиса, люди часто оказываются в сложных ситуациях, связанных с алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью. В таких случаях своевременная помощь квалифицированного нарколога становится не просто желательной, а жизненно необходимой.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
секс астана ?ыздар нет Астана: Эхо разочарования, раздающееся в холодных стенах многоэтажек. Это крик души, жаждущей любви и понимания, но сталкивающейся с равнодушием и жестокостью большого города. Слова, наполненные болью и тоской, отражают трагедию молодого поколения, потерявшего ориентиры в погоне за успехом и материальным благополучием. Проститутки Астаны: Зеркало социума, отражающее его пороки и комплексы. В этом мире, где все продается и покупается, человеческое достоинство становится разменной монетой. Каждая проданная ночь – это маленькая смерть, оставляющая шрамы на душе и разрушающая веру в будущее.
Normally I don’t read post on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very compelled
me to check out and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me.
Thank you, quite nice post.
Feel free to visit my homepage ratutogel
Острая алкогольная интоксикация — запой — может привести к серьёзным осложнениям: дегидратации, сбою сердечного ритма, ухудшению функций печени и почек. Клиника «ВоронежДоктор» предлагает инфузионную терапию на дому и в условиях стационара с полным соблюдением анонимности. Опытные специалисты проводят детоксикацию по индивидуальной программе, используя современные растворы и аппаратуру, что позволяет максимально быстро и безопасно вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/vyezd-na-dom-kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru
I’m not sure exactly why but this website is loading extremely slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
I’m not sure why but this website is loading incredibly slow for me.
Is anyone else having this issue or is it a problem on my end?
I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
индивидуалки Интим Сити: Виртуальное убежище, где каждый может найти свою гавань удовольствия и фантазий. Здесь нет границ и ограничений, а правила диктуют лишь собственные желания. Это мир, где анонимность позволяет раскрыть свои самые сокровенные фантазии, найти единомышленников и получить удовлетворение, не выходя из дома. Но за кажущейся свободой и доступностью скрывается опасность потерять связь с реальностью и утонуть в виртуальном океане соблазнов.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Труба из драгоценных металлов платиновая 300х4х0.7 мм ПлРд90-10 ТУ Гарантированное качество и изысканный дизайн – купите драгоценные трубы для ювелирных украшений, машиностроения и архитектуры. Широкий выбор и высокое качество! Доставка по России.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire
someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to
know where u got this from. kudos
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Подробнее тут – https://alko-specialist.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-simferopole
Heya i am for the primary time here. I came across this board and I in finding It really helpful & it helped me
out a lot. I’m hoping to present something back and aid others such as you aided me.
Миссия Наркологической клиники “Новый путь” заключается в предоставлении качественной и всесторонней поддержки людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостями. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это не просто слабость воли, а сложное заболевание, требующее комплексного и научного подхода. Наша цель — создать безопасную и поддерживающую среду, где пациенты могут открыто говорить о своих переживаниях и проблемах.
Получить больше информации – https://нарко-специалист.рф
Здесь
[url=https://revoluterra.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Очень красивый и профессионально оформленный сайт kazino olimp!
https://olimp-casino-kz-vip.org.kz/games/
Simply wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity to your submit is just cool and i could think you are an expert in this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grasp your RSS feed to stay updated with imminent post. Thank you a million and please continue the enjoyable work.
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru
http://epidemics.ru/engine/pgs/10-glavnykh-oshibok-pri-vybore-mediczinskikh-ukladok-dlya-organizaczii.html
Hi there mates, pleasant post and fastidious arguments commented at this place,
I am really enjoying by these.
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому новосибирск[/url]
Специалист уточняет длительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Точный сбор данных позволяет оперативно корректировать лечение и выбрать оптимальные методы детоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]narco-vivod-clean.ru/[/url]
I believe what you wrote made a bunch of sense.
However, what about this? what if you were to create a killer title?
I mean, I don’t wish to tell you how to run your blog, but what if you
added a headline that makes people desire more?
I mean Types of Cancer: Common & Rare Cancers Explained is kinda plain. You might glance at Yahoo’s front page and watch how they
create post titles to grab people interested. You might
add a related video or a related picture or two to grab people
excited about everything’ve written. In my opinion, it would bring your website a little bit more interesting.
https://www.xen-factory.com/index.php?members/prmocdeforxbettod.124640/#about
https://aparaj.am/pages/1xbet_promokod_54.html
https://sermonquotes.com/news/?1xbet_promokod_na_freebet.html
https://penzu.com/p/4fd3e5ba55e6bddf
May I simply say what a relief to uncover someone that actually understands what they are discussing online. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people have to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular since you definitely possess the gift.
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/vyezd-na-dom-kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru
Дополнительно выясняются аллергические реакции, приём других препаратов и предпочтения пациента по времени визита врача.
Подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/
Перед оформлением вызова проводится предварительная телефонная консультация, позволяющая оценить тяжесть состояния и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в новосибирске[/url]
Таким образом, наш подход ориентирован на создание комплексной системы поддержки, позволяющей каждому пациенту справиться с проблемой зависимости и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Разобраться лучше – https://alko-specialist.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-simferopole
Клиника создана для оказания квалифицированной помощи всем, кто страдает от различных форм зависимости. Мы стремимся не только к лечению, но также к формированию здорового образа жизни, возвращая пациентов к полноценной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-Ekaterinburge/https://нарко-специалист.рф
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and help others like you helped me.
Уменьшается тремор, выравнивается пульс, снижается тревожность, появляется способность уснуть. Важно не «перепроверять» эффект нагрузками и разговорами: когда вечер отделён от конфликтов и ярких экранов, организм закрепляет результат, а не «сжигает» его к полуночи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]narkolog-na-dom[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Нарколог, приезжающий на дом, предоставляет широкий спектр услуг. Основная цель — стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать лечение, направленное на устранение последствий зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в красноярске[/url]
Врачебный состав клиники “Ресурс здоровья” состоит из высококвалифицированных специалистов в области наркологии. Наши врачи-наркологи имеют обширный опыт работы с зависимыми пациентами и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки.
Детальнее – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Нарколог выезжает в любое время суток, привозя мобильный кейс с инфузионными системами, растворами, принадлежностями для забора крови и экспресс-тестами. После прибытия проводится детальный осмотр и сбор дополнительных данных: ЭКГ-мониторинг, тесты на уровень глюкозы, электролитов и пр.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/[/url]
Наша клиника сочетает в себе оперативность, комфорт и высокие стандарты безопасности. Вот основные преимущества сотрудничества:
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/vyezd-na-dom-kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe/
вывод из запоя московская область [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru/]вывод из запоя московская область[/url] .
вывод из запоя дешево [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-5.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url] .
перевод с английского перевод и право [url=https://dzen.ru/a/aUBBvahMInGNj8BL/]dzen.ru/a/aUBBvahMInGNj8BL[/url] .
Задача врача — не «поставить галочку», а исключить противопоказания и выбрать методику с оптимальным соотношением пользы и риска. Учитываются хронические заболевания, эпизоды потери сознания, аритмии, панические атаки, депрессивные симптомы, переносимость инфузий и фармпрепаратов, взаимодействия с уже назначенными лекарствами. По результатам формируется персональный лист ограничений и список «красных флажков», при которых следует связаться со специалистом без промедления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены[/url]
Лечение выводом из запоя на дому в «ВоронежМед» организовано по отработанному протоколу, включающему несколько ключевых этапов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
При длительном запое в крови накапливаются ацетальдегид и другие токсичные метаболиты этанола, которые повреждают клетки печени, нарушают функцию почек и приводят к дисбалансу электролитов. Без своевременной детоксикации повышается риск острых состояний — судорог, инсультов, инфаркта, панкреатита и психоза. Чем раньше начато лечение, тем быстрее нормализуются показатели обмена веществ, возвращается водно-электролитный баланс и восстанавливается работа жизненно важных органов. Анонимный выезд нарколога помогает снять психологический барьер перед обращением за помощью.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Looking for a casino? elon-casino-top.com/: slots, live casino, bonus offers, and tournaments. We cover the rules, wagering requirements, withdrawals, and account security. Please review the terms and conditions before playing.
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your site?
My blog site is in the exact same niche as yours and
my visitors would definitely benefit from a lot of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Cheers!
Клиника «ВоронежМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток, включая праздники и выходные. Анонимность достигается за счёт минимального контакта с персоналом клиники и отсутствия бумажной волокиты. Все этапы лечения согласовываются только с пациентом или доверенным лицом, а сведения о визите не передаются третьим лицам.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов город[/url]
Посетите [url=http://velosipedov-magazin.ru]магазины где можно купить электровелосипед[/url] сегодня и найдите велосипед своей мечты!
Магазин велосипедов является местом, где можно найти широкий выбор велосипедов для любого возраста и уровня подготовки . Это место, где покупатели могут найти не только велосипеды, но и различные аксессуары и оборудование для них. Магазин велосипедов имеет опытный персонал, который может ответить на любые вопросы клиентов.
Магазин велосипедов предлагает бесплатную консультацию по выбору велосипеда для каждого клиента. Клиенты могут попробовать велосипеды перед покупкой, чтобы убедиться, что они подходят им идеально. Магазин велосипедов также предоставляет услуги по ремонту и обслуживанию велосипедов .
Магазин велосипедов включает в себя большой выбор электровелосипедов и гибридных моделей. Каждая модель имеет свои уникальные характеристики и особенности. Магазин велосипедов имеет большой sklad с запасами и может быстро удовлетворять заказы клиентов.
Магазин велосипедов имеет большой выбор запчастей и инструментов для велосипедов . Клиенты могут найти все, что им нужно для комфортного и безопасного?жения. Магазин велосипедов регулярно проводит акции и распродажи, что позволяет клиентам приобретать продукцию по выгодным ценам .
Магазин велосипедов имеет опытный персонал, который может выполнить любые работы по ремонту и обслуживанию . Клиенты могут быть уверены в высоком качестве выполненных работ. Магазин велосипедов также предоставляет услуги по заказу и поставке запчастей и аксессуаров .
Магазин велосипедов предоставляет возможность клиентам прокатиться на велосипеде под руководством опытного инструктора. Клиенты могут получить новые знания и навыки, что позволит им улучшить свое?жение. Магазин велосипедов предлагает скидки и специальные условия для членов велоклубов .
Магазин велосипедов является идеальным местом для всех, кто любит велоспорт и активный отдых . Клиенты могут найти все, что им нужно для комфортного и безопасного?жения. Магазин велосипедов работает на рынке уже несколько лет и имеет репутацию надежного партнера .
Магазин велосипедов имеет программу лояльности и предлагает скидки постоянным клиентам . Клиенты могут быть уверены в высоком качестве продукции и услуг. Магазин велосипедов регулярно обновляет свой ассортимент и предлагает новые модели и аксессуары .
Наркологическая клиника “Маяк надежды” расположена по адресу: г. Санкт-Петербург, ул. Колпинская, д. 27. Клиника работает ежедневно с 9:00 до 21:00, без выходных. Наши специалисты готовы предоставить консультацию и ответить на все вопросы, связанные с лечением зависимостей. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Углубиться в тему – http://алко-лечение24.рф
iGaming Program Catalog
Использование современных автоматизированных систем дозирования гарантирует точное введение медикаментов, что минимизирует риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать дозировки и адаптировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://наркология-дома1.рф
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Скачать игры без торрента – это возможность окунуться в мир виртуальных приключений, минуя сложные процедуры и риски, связанные с торрент-сетями. Это выбор тех, кто ценит свое время и безопасность. Альтернативные платформы предлагают мгновенный доступ к играм различных жанров: от захватывающих экшенов до стратегических головоломок. Помните о необходимости легального скачивания, выбирая бесплатные игры или приобретая лицензии. Так вы поддерживаете разработчиков и обеспечиваете себе качественный продукт.
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]клиника наркологии и психиатрии москва[/url]
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
I am actually happy to read this blog posts which consists of plenty of valuable information, thanks for providing these kinds of information.
проститутки Интим: Сакральное таинство двух душ, сливающихся в единое целое. Это не просто физическая близость, а возможность открыть свое сердце, довериться другому человеку, раскрыть свою уязвимость и получить в ответ поддержку и понимание. Интимность – это квинтэссенция любви, искренности и доверия, позволяющая почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего, обрести гармонию и душевный покой. Это момент, когда время останавливается, а мир сужается до двух любящих сердец.
Перед оформлением вызова проводится предварительная телефонная консультация, позволяющая оценить тяжесть состояния и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/
Процесс лечения выездом на дом в «ВоронежЛайф» структурирован и прозрачен. Каждый этап гарантирует максимальную безопасность и эффективность.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя в воронеже[/url]
https://belmotors.by/image/pgs/avtomobilnye-mediczinskie-ukladki-trebovaniya-i-pravila-komplektaczii.html
Деятельность в области недропользования — это направление деятельности, связанный с изучением и использованием недр.
Оно включает поиск природных ресурсов и их промышленное освоение.
Данная сфера регулируется законодательством, направленными на сохранение природного баланса.
Эффективное управление в недропользовании обеспечивает устойчивое развитие.
оэрн официальный сайт
В этот этап включено:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Перед перечислением важно прояснить: нижеследующие ориентиры не заменяют очный осмотр, они помогают семье принять здравое решение без затяжки и споров. Если признаки сочетаются или нарастают, лучше не откладывать обращение, чтобы перехватить динамику, пока она управляемая.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Современные технологии позволяют:
Детальнее – https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-novosibirsk/
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Скачать игры с Яндекс Диска – это использование удобного и знакомого инструмента для получения игровых файлов. Простота, доступность и высокая скорость – ключевые характеристики этого метода. Многие разработчики, особенно инди-студии, выбирают Яндекс Диск для распространения своих игр, предлагая пользователям простой и быстрый способ ознакомиться с их творчеством. Интерфейс Яндекс Диска интуитивно понятен, что делает процесс скачивания максимально комфортным.
What is FTD
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена[/url]
Врачебный состав клиники “Ресурс здоровья” состоит из высококвалифицированных специалистов в области наркологии. Наши врачи-наркологи имеют обширный опыт работы с зависимыми пациентами и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки.
Подробнее тут – https://narco-vivod.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/
Врачебный состав клиники “Ресурс здоровья” состоит из высококвалифицированных специалистов в области наркологии. Наши врачи-наркологи имеют обширный опыт работы с зависимыми пациентами и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narco-vivod.ru/
Например, если речь идет о выводе из запоя, врач проведет тщательное обследование пациента, чтобы определить общее состояние здоровья и наличие возможных осложнений. На основе диагностики будет назначена инфузионная терапия, которая включает введение растворов, витаминов и препаратов для снятия абстиненции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk-tseny
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
вывод из запоя в москве [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-5.ru/]вывод из запоя в москве[/url] .
быстрый вывод из запоя москва [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru[/url] .
Алкогольная зависимость может стремительно ухудшать состояние здоровья, превращаясь в запой, сопровождающийся серьезной интоксикацией организма. В Санкт-Петербурге профессиональные наркологи выезжают на дом круглосуточно, чтобы оказать экстренную помощь в критических ситуациях. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать детоксикацию сразу после обращения, обеспечивая оперативное вмешательство в комфортных условиях, где пациент сохраняет свою конфиденциальность.
Подробнее – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
«ВоронежДоктор» сочетает в себе профессионализм, современное оборудование и заботу о приватности пациента. Ключевые преимущества:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru
эскорт Интим: Храм души, где два сердца бьются в унисон, а прикосновения исцеляют раны. Это не просто соитие тел, а таинство единения, где открываются самые сокровенные уголки души. В объятиях любимого человека время останавливается, а мир наполняется светом и теплом. Интимность – это квинтэссенция доверия, взаимопонимания и безусловной любви, дарующая ощущение полноты жизни и гармонии с самим собой.
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Подробнее – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в новосибирске[/url]
Врачебный состав клиники “Ресурс здоровья” состоит из высококвалифицированных специалистов в области наркологии. Наши врачи-наркологи имеют обширный опыт работы с зависимыми пациентами и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narco-vivod.ru/
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa?
My website addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could
greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free
to shoot me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you!
Terrific blog by the way!
When someone writes an piece of writing he/she retains the image of a user in his/her brain that how a user can know it. Thus that’s why this paragraph is perfect. Thanks!
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnoyarsk/
«ГородМед Трезвость» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один ни на этапе выхода из запоя, ни во время стабилизации, ни в период удержания ремиссии. С первого звонка дежурный врач проводит короткое интервью, фиксирует жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни и текущие препараты, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — экстренный выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Мы не растягиваем процесс по неделе: старт возможен в день обращения, а маршрутизация между форматами (дом, амбулаторный визит, стационар) занимает часы. Важная часть подхода — ясные цели каждого шага и критерии эффективности, понятные самому пациенту и семье: когда ждать облегчения тревоги, как нормализуется сон, когда вернётся аппетит, что считается «красным флажком» и как действовать без паники. Такая предсказуемость снижает уровень стресса и повышает приверженность лечению уже в первые трое суток.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Если вам нужно [url=http://flakons-optom.ru]пластиковые бутылочки оптом[/url] для ваших товаров, обратите внимание на различные варианты, доступные на рынке, и выбирайте то, что лучше всего соответствует потребностям вашего бизнеса.
Флакон опт представляет собой экономичную и практичную упаковку для жидких товаров . Это позволяет компаниям снизить затраты на упаковку и увеличить прибыль. Флакон опт является универсальной упаковкой для жидких продуктов. Кроме того, флакон опт может быть легко транспортирован и хранен.
Флакон опт является предпочтительным вариантом для бизнеса, занимающегося жидкими товарами. Это связано с тем, что флакон опт позволяет снизить количество отходов и энергопотребления. Флакон опт обеспечивает безопасное и надежное хранение жидких товаров . Кроме того, флакон опт может быть легко заполнен и закрыт.
Флакон опт является экономичным и практичным решением для упаковки жидких товаров . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт изготавливается из высококачественных материалов и имеет прочную конструкцию. Флакон опт также может быть легко персонализирован и брендирован . Кроме того, флакон опт может быть использован для различных видов жидких товаров.
Флакон опт стал популярным выбором среди экологически сознательных потребителей . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт может быть легко переработан и повторно использован. Флакон опт защищает продукты от внешних факторов. Кроме того, флакон опт может быть легко транспортирован и хранен.
Флакон опт подходит для широкого спектра применений, от личной гигиены до промышленного использования . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт имеет прочную конструкцию и может выдерживать различные условия хранения и транспортировки. Флакон опт обеспечивает безопасное и надежное хранение жидких товаров . Кроме того, флакон опт может быть легко заполнен и закрыт.
Флакон опт стал популярным выбором среди компаний, производящих жидкие товары . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт позволяет снизить количество отходов и энергопотребления. Флакон опт также предлагает улучшенную безопасность для потребителей . Кроме того, флакон опт может быть легко транспортирован и хранен.
Флакон опт предлагает широкий спектр преимуществ для бизнеса и потребителей . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт изготавливается из высококачественных материалов и имеет прочную конструкцию. Флакон опт также может быть легко персонализирован и брендирован . Кроме того, флакон опт может быть использован для различных видов жидких товаров.
Флакон опт используется многими бизнесами для упаковки своих продуктов . Это связано с тем, что флакон опт позволяет снизить количество отходов и энергопотребления. Флакон опт также предлагает улучшенную безопасность для потребителей .
Наркологическая клиника “Маяк надежды” — специализированное медицинское учреждение, предназначенное для оказания помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и вернуть их к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – https://алко-лечение24.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-Sankt-Peterburge
sigma eurasia
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
Создание безопасной среды: Мы понимаем, насколько важна поддержка в сложные моменты. Наш центр предоставляет пространство, где пациенты могут открыто говорить о своих переживаниях без страха быть осужденными, что способствует доверию и успешному лечению.
Детальнее – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Миссия клиники “Маяк надежды” заключается в содействии восстановлению здоровья и социальной реинтеграции людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Мы стремимся к комплексному решению этой сложной задачи, учитывая физические, психологические и социальные аспекты зависимости. Наша задача — не только помочь пациентам избавиться от физической зависимости, но и обеспечить их психологическое восстановление и возвращение к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://алко-лечение24.рф/
Госпитализация показана, когда требуется непрерывный контроль и быстрые изменения схем лечения. В стационаре устраняют выраженные симптомы отмены, корректируют электролитные нарушения, поддерживают печёночные функции, при необходимости подключают кислород и аппаратные методы диагностики. Параллельно выравнивают сон и аппетит, закрывают дефициты микроэлементов, подбирают щадящий режим нагрузки. На выписке пациент получает подробные рекомендации: как дозировать активность, когда пить воду и в каких объёмах, какие препараты принимать и при каких признаках обращаться за консультацией без ожидания. Такой формат снижает риск осложнений и даёт предсказуемую динамику уже на горизонте нескольких дней.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my website so i came to “return the favor”.I’m attempting to find
things to enhance my web site!I suppose its ok to use some of your ideas!!
Оказание помощи нарколога на дому организовано по отлаженной схеме, включающей несколько ключевых этапов, которые позволяют оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать детоксикацию:
Получить больше информации – https://наркология-дома1.рф/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ryazan/
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного лечения. Препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет быстро снизить уровень токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальный обмен веществ и стабилизировать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://наркология-дома1.рф/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan/
Наркологическая клиника “Ресурс здоровья” — специализированное медицинское учреждение, предназначенное для оказания профессиональной помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
Детальнее – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому краснодарский край[/url]
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]клиника наркологии и психиатрии москва[/url]
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва отзывы[/url]
Нарколог, приезжающий на дом, предоставляет широкий спектр услуг. Основная цель — стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать лечение, направленное на устранение последствий зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru
Миссия клиники “Маяк надежды” заключается в содействии восстановлению здоровья и социальной реинтеграции людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Мы стремимся к комплексному решению этой сложной задачи, учитывая физические, психологические и социальные аспекты зависимости. Наша задача — не только помочь пациентам избавиться от физической зависимости, но и обеспечить их психологическое восстановление и возвращение к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://алко-лечение24.рф
https://federalgaz.ru/
Основными направлениями работы нашей клиники являются.
Узнать больше – https://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-Ekaterinburge
Использование современных автоматизированных систем дозирования гарантирует точное введение медикаментов, что минимизирует риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать дозировки и адаптировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://наркология-дома1.рф/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя новосибирск[/url]
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This article posted at this web page is actually nice.
«ГородМед Трезвость» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один ни на этапе выхода из запоя, ни во время стабилизации, ни в период удержания ремиссии. С первого звонка дежурный врач проводит короткое интервью, фиксирует жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни и текущие препараты, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — экстренный выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Мы не растягиваем процесс по неделе: старт возможен в день обращения, а маршрутизация между форматами (дом, амбулаторный визит, стационар) занимает часы. Важная часть подхода — ясные цели каждого шага и критерии эффективности, понятные самому пациенту и семье: когда ждать облегчения тревоги, как нормализуется сон, когда вернётся аппетит, что считается «красным флажком» и как действовать без паники. Такая предсказуемость снижает уровень стресса и повышает приверженность лечению уже в первые трое суток.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
Зависимости от психоактивных веществ, таких как алкоголь, наркотики и азартные игры, представляют собой серьёзные проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются многие люди. Эти состояния не только негативно влияют на здоровье, но также разрушительно сказываются на межличностных отношениях, социальной адаптации и профессиональной деятельности. Наркологическая клиника “Новый путь” предлагает комплексное решение для пациентов, нуждающихся в помощи, ориентируясь на индивидуальный подход и использование современных медицинских технологий.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://нарко-специалист.рф/
Госпитализация показана, когда требуется непрерывный контроль и быстрые изменения схем лечения. В стационаре устраняют выраженные симптомы отмены, корректируют электролитные нарушения, поддерживают печёночные функции, при необходимости подключают кислород и аппаратные методы диагностики. Параллельно выравнивают сон и аппетит, закрывают дефициты микроэлементов, подбирают щадящий режим нагрузки. На выписке пациент получает подробные рекомендации: как дозировать активность, когда пить воду и в каких объёмах, какие препараты принимать и при каких признаках обращаться за консультацией без ожидания. Такой формат снижает риск осложнений и даёт предсказуемую динамику уже на горизонте нескольких дней.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]luchshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Таким образом, наш подход ориентирован на создание комплексной системы поддержки, позволяющей каждому пациенту справиться с проблемой зависимости и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Узнать больше – https://alko-specialist.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-simferopole
Задача врача — не «поставить галочку», а исключить противопоказания и выбрать методику с оптимальным соотношением пользы и риска. Учитываются хронические заболевания, эпизоды потери сознания, аритмии, панические атаки, депрессивные симптомы, переносимость инфузий и фармпрепаратов, взаимодействия с уже назначенными лекарствами. По результатам формируется персональный лист ограничений и список «красных флажков», при которых следует связаться со специалистом без промедления.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена[/url]
Наши наркологи придерживаются принципов уважительного и внимательного отношения к пациентам, создавая атмосферу доверия. Они проводят детальное обследование, выявляют коренные причины зависимости и разрабатывают индивидуальные стратегии лечения. Профессионализм и компетентность врачей являются ключевыми факторами успешного восстановления пациентов.
Получить больше информации – http://алко-лечение24.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-Sankt-Peterburge/
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
Использование современных автоматизированных систем дозирования гарантирует точное введение медикаментов, что минимизирует риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать дозировки и адаптировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени.
Узнать больше – https://наркология-дома1.рф/
Уменьшается тремор, выравнивается пульс, снижается тревожность, появляется способность уснуть. Важно не «перепроверять» эффект нагрузками и разговорами: когда вечер отделён от конфликтов и ярких экранов, организм закрепляет результат, а не «сжигает» его к полуночи.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-mytishchi9.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
После вашего звонка диспетчер фиксирует заявку и передаёт её свободному специалисту. Нарколог связывается для уточнения симптомов, времени начала запоя и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, чтобы привезти нужные препараты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
«ВоронежДоктор» сочетает в себе профессионализм, современное оборудование и заботу о приватности пациента. Ключевые преимущества:
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-v-voronezhe/
Лечение выводом из запоя на дому в «ВоронежМед» организовано по отработанному протоколу, включающему несколько ключевых этапов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Подробнее тут – https://alko-specialist.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-simferopole
Дополнительно выясняются аллергические реакции, приём других препаратов и предпочтения пациента по времени визита врача.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому в воронеже[/url]
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
1cupis
алкоголизм лечение вывод из запоя москва [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru[/url] .
It’s awesome designed for me to have a web site, which is valuable for my know-how. thanks admin
Kokie būreliai ir veiklos yra Lietuvoje offered
По телефону или через приложение клиники пациент или его родственники оформляют заявку на вызов. В течение 30–45 минут бригада выезжает по указанному адресу и приносит полный комплект оборудования и медикаментов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
https://federalgaz.ru/
This is very interesting, You are a very
skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post.
Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Образовательные программы: Мы уверены, что знания о зависимости и её последствиях играют важную роль в реабилитации. Мы информируем пациентов о механизмах действия наркотиков и алкоголя на организм, что способствует изменению их отношения к терапии и жизни без зависимостей.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Kazino haqqında faydalı kontent üçün təşəkkürlər!
https://1win-azerbaijan-casino.com/oyunlar
В этот этап включено:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
My programmer іs trying to convince me to moᴠe to .net from PHP.
I havе always disliked tһe idea becɑuse of the expenses.
Вut he’s tryiong none tһe leѕs. Ӏ’ve Ƅеen սsing
WordPress օn а variety of websites for about ɑ year and
am anxious ɑbout switching tо another platform.
I havе һeard excellent thіngs ab᧐ut blogengine.net. Ιs there a wɑy I can import aⅼl my wordpress posts іnto it?
Any kind of heⅼp would be gгeatly appreciated!
Feel free to surf to my web-site :: Лазерные картриджи (Luis)
В современном обществе проблемы наркомании и алкоголизма приобрели особую актуальность, затрагивая не только отдельных людей, но и их близких, и сообщества. Эти зависимости оказывают негативное влияние не только на физическое здоровье, но и на психоэмоциональное состояние, нарушают социальные связи и ухудшают качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Здоровое Настоящее” предлагает комплексный и научно обоснованный подход к лечению зависимостей. Мы используем современные методы диагностики и терапии, чтобы помочь пациентам вернуть здоровье и полноценную жизнь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
В современном обществе проблемы наркомании и алкоголизма приобрели особую актуальность, затрагивая не только отдельных людей, но и их близких, и сообщества. Эти зависимости оказывают негативное влияние не только на физическое здоровье, но и на психоэмоциональное состояние, нарушают социальные связи и ухудшают качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Здоровое Настоящее” предлагает комплексный и научно обоснованный подход к лечению зависимостей. Мы используем современные методы диагностики и терапии, чтобы помочь пациентам вернуть здоровье и полноценную жизнь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя казань[/url]
Алкогольный запой представляет собой длительное бесконтрольное приём спиртного, приводящее к тяжёлой интоксикации и серьёзным осложнениям для органов и психики. В Новосибирске клиника «Сибирский Доктор» предлагает качественный вывод из запоя с применением инновационных технологий и участием опытных наркологов, терапевтов и психиатров. Наш подход сочетает мгновенную реакцию на вызов, современное оборудование и индивидуальные схемы лечения, что позволяет достичь стабильной ремиссии и снизить риск рецидива.
Детальнее – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в новосибирске[/url]
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/en-ZA/register-person?ref=B4EPR6J0
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Получить больше информации – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy
Чтобы ориентироваться в вариантах, полезно увидеть их в одном поле зрения. Ниже приведена краткая сравнительная таблица; она не заменяет консультацию, но помогает понять логику выбора. Перед таблицей важно отметить: конкретная методика определяется только после осмотра и исключения противопоказаний.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-zhenshchin[/url]
[url=https://copychief.com/art/le-code_promo_melbet_bonus_gratuit.html]un code promo melbet[/url]
[url=https://agaclar.net/images/pgs/code-promo-melbet_bonus-sportifs-et-casino.html]code promo melbet code promo[/url]
https://comunes.org/pag/melbet_promo_code_use_this_code_for_130_bonus.html
В Наркологической клинике “Новая жизнь” работает команда высококвалифицированных врачей, обладающих значительным опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии. Все специалисты имеют профильное образование и постоянно повышают свою квалификацию, что позволяет им быть в курсе последних достижений в лечении зависимостей.
Подробнее тут – http://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-Ekaterinburge/
Un site très beau et professionnellement conçu Betify Casino !
https://www.academbanner.academ.info/adclick.php?bannerid=2863&zoneid=157&source=&dest=https://betify-casino-games-france.fr/inscription
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-moskva[/url]
Wonderful web site. A lot of helpful information here. I’m sending it to several buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks for your effort!
Таким образом, наша миссия направлена на создание устойчивых изменений в жизни каждого пациента, поддерживая его на всех этапах пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-Ekaterinburge
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Каждый врач клиники обладает глубокими знаниями фармакологии, психофармакологии и психотерапии. Они регулярно посещают профессиональные конференции, семинары и мастер-классы, чтобы быть в курсе новейших достижений в области лечения зависимостей. Такой подход позволяет нашим специалистам применять наиболее эффективные и современные методы терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Строго регламентированный алгоритм позволяет специалистам «ВоронежДоктор» добиваться устойчивых результатов при выводе из запоя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого воронеж[/url]
Этот формат позволяет пациентам получить профессиональную помощь в комфортной домашней обстановке. Такой подход не только обеспечивает удобство, но и гарантирует конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для многих людей.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом красноярск[/url]
Каждый врач клиники обладает глубокими знаниями фармакологии, психофармакологии и психотерапии. Они регулярно посещают профессиональные конференции, семинары и мастер-классы, чтобы быть в курсе новейших достижений в области лечения зависимостей. Такой подход позволяет нашим специалистам применять наиболее эффективные и современные методы терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Миссия нашего центра – оказание всесторонней помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные цели нашей работы:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в казани[/url]
Лечение выводом из запоя на дому в «ВоронежМед» организовано по отработанному протоколу, включающему несколько ключевых этапов.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]moskva-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-adresa[/url]
Eure Tipps über NV Casino sind großartig.
http://rlu.ru/5d3jS
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
«МедТрезвие» выстраивает лечение зависимости как последовательный и понятный маршрут, где каждый этап имеет чёткую цель, критерии эффективности и прозрачные условия. С первого обращения дежурный врач уточняет жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, переносимость лекарств и бытовые ограничения, после чего предлагает безопасный формат начала — выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Важна не только скорость, но и качество коммуникации: пациент и близкие получают ясное объяснение, зачем назначается конкретная процедура, как оценивать улучшение и какие признаки требуют немедленной связи со специалистом. Круглосуточная доступность и конфиденциальные каналы записи снимают барьер обращения, а внутренняя маршрутизация позволяет переходить от экстренного купирования симптомов к стабилизации и профилактике срывов без пауз и «провалов» между этапами. Такой подход уменьшает риск повторных эпизодов, повышает приверженность и возвращает человеку контроль над повседневной жизнью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Процесс лечения организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Основными направлениями работы нашей клиники являются.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://нарко-специалист.рф
Выезд нарколога на дом включает несколько ключевых этапов: первичный дистанционный сбор анамнеза, оперативный приезд специалиста, проведение обследования — измерение пульса, давления, сатурации, уровня глюкозы и электролитов крови — и последующее назначение инфузионной терапии. В зависимости от состояния пациента подбирается индивидуальный состав растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку функций печени и нормализацию работы центральной нервной системы. Все процедуры выполняются с учётом противопоказаний и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Детальнее – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в симферополе[/url]
Детокс — это не разовая процедура, а управляемый этап со своими задачами: снизить токсическую нагрузку, выровнять жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и самочувствию. Мы подбираем инфузии по показаниям, корректируем электролитный баланс, защищаем печёночные функции, снимаем тремор и вегетативные проявления. Следующая фаза — стабилизация: на этом этапе врач закрывает дефициты, уточняет схемы, выравнивает день и ночь, даёт понятные рекомендации на ближайшие 72 часа. Важно, что пациент не «теряется» после первого улучшения: заранее назначены точки связи, прописаны «красные флажки» и шаги, как действовать при любом из них. Такой порядок снижает вероятность рецидива, потому что вместо импровизации появляются готовые ответы на типичные сложности первых недель.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Домашняя точка входа оправдана при стабильных показателях и низком риске осложнений. В знакомой обстановке легче соблюдать режим: затемнить комнату, убрать экраны, распределять воду маленькими порциями, сделать лёгкий перекус «по силам», лечь пораньше. Врач подберёт «узкую» схему инфузий без перегруза препаратами, объяснит, какие ощущения допустимы сегодня и ночью, а какие — повод для немедленной связи. Такой сценарий экономит время семьи, снижает стигму и быстрее переводит состояние в управляемое, на базе которого уже можно строить дальнейшие шаги — амбулаторные визиты, работу с триггерами и, при показаниях, обсуждение кодирования.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-s-vyezdom-balashiha[/url]
Мы предлагаем кодирование тогда, когда оно медицински оправдано и человек готов его принять осознанно. Сначала исключаем противопоказания, обсуждаем механизм, ограничения и риски, согласуем формат — инъекция, имплантация или пероральная поддержка. После процедуры пациент получает памятку и контакт для связи, а также план профилактики срывов: без поведенческих шагов любое фармвмешательство теряет часть эффективности. Важный критерий выбора методики — реальный график жизни: командировки, смены, поздние встречи. Метод должен переживать вашу неделю без «узких мест», иначе дорогостоящая техника не даст ожидаемого эффекта. Такой прагматичный подход даёт не мифическую «гарантию», а рабочую устойчивость, которую можно удерживать месяцами.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, каждая задержка превращается в цепочку случайностей: рушится сон, «скачет» давление и пульс, усиливается тревога, дома нарастает напряжение. «МедСфера Мытищи» убирает хаос управляемым маршрутом: чёткий первичный осмотр, объяснённые назначения, понятные правила на 48–72 часа и прогнозируемые окна связи. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса» — только клиническая достаточность на сегодня с учётом длительности употребления, сопутствующих диагнозов, принимаемых препаратов и исходных показателей. Такой подход снижает тревожность, возвращает ощущение контроля и быстрее приводит к первому ровному сну — именно он становится переломной точкой, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану. Важная деталь — отсутствие общих очередей и «публичных» зон: приём разнесён по времени, входы приватны, а коммуникация ведётся через закрытые каналы. Когда понятно, что будет через час, вечером и завтра утром, исчезает потребность в импровизациях, и лечение действительно работает.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru
Длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к накоплению токсинов, нарушению обменных процессов и ухудшению работы внутренних органов. Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить риск серьезных осложнений, таких как сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, повреждение печени и почек, а также уменьшить психоэмоциональное напряжение. Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Рязани помогает начать лечение на ранних этапах, когда каждая минута имеет значение.
Выяснить больше – https://наркология-дома1.рф/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-ryazan
принудительный вывод из запоя москва [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-4.ru[/url] .
Оперативное лечение на дому имеет ряд значимых преимуществ, особенно когда каждая минута имеет значение:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения тщательного первичного осмотра. Врач собирает краткий анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели — пульс, артериальное давление и температуру, и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются фундаментом для составления индивидуального плана терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://наркология-дома1.рф/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ryazan/
Мы верим, что каждый человек, столкнувшийся с проблемой зависимости, заслуживает шанса на новую жизнь. Наша миссия — предоставить необходимые инструменты и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам в их стремлении к выздоровлению и личностному росту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://алко-лечение24.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-Sankt-Peterburge/
After going over a few of the blog articles on your web site, I honestly like your technique of writing a blog. I saved it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my web site as well and let me know how you feel.
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-s-vyezdom-v-lyubercah/
Наркологическая клиника “Маяк надежды” — специализированное медицинское учреждение, предназначенное для оказания помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и вернуть их к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Получить больше информации – https://алко-лечение24.рф
наркология вывод из запоя москва [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-5.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя москва[/url] .
товары с возвратов Ozon Возвраты Ozon оптом – это путь к формированию конкурентоспособного ассортимента вашего магазина. Найдите нишу, которая пользуется спросом, и предложите покупателям товары по ценам, которые они не смогут найти больше нигде. Стратегия проста: купи дешевле, продай выгоднее.
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в симферополе[/url]
Как выбрать фотографа мастера съемки в Сочи — бракосочетания
refurbished iPhone Europe
ликвидация Ozon Товары с возвратов Ozon – это отличный способ найти уникальные товары по доступной цене. Среди возвратов можно встретить редкие или снятые с производства модели, которые могут представлять особый интерес для коллекционеров или любителей винтажных вещей.
Wow, this piece of writing is pleasant, my sister is analyzing
these things, therefore I am going to convey her.
Пациенту устанавливают катетер в вену на руке или предплечье, используя лёгкий местный анестетик для минимизации дискомфорта. Затем подключают автоматизированную помпу, обеспечивающую равномерную подачу раствора в течение 3–6 часов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/
Мы не подгоняем всех под единый сценарий. Если состояние устойчивое, нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации и резких скачков давления и пульса — рационален домашний старт: приватно, быстрее и без лишних переездов. Врач приедет без маркировки, проведёт осмотр, запустит инфузионную терапию по показаниям, оставит письменные рекомендации и «красные флажки». Если же есть признаки угрозы осложнений — обезвоживание, аритмии, риск судорог, боли за грудиной или в животе, лихорадка, спутанность сознания, тяжёлая соматика — мы честно предлагаем короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов. Под круглосуточным наблюдением проще корректировать схемы, вовремя закрывать дефициты, защитить сон и быстрее вернуть управляемость поведению. В обоих форматах маршрут прозрачен: согласованные окна связи, фиксированные цели на ближайшие 72 часа и отсутствие «пакетов ради прайса». Благодаря этому решения принимаются спокойно, без угадываний и эмоциональных раскачек, которые обычно ломают прогресс и удорожают лечение.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, семья сталкивается с двумя видами неопределённости — медицинской и организационной. На одной чаше весов тремор, скачки давления и пульса, рвота, обрывочный сон и нарастающая тревога; на другой — страх огласки, очереди, ожидание «до завтра» и бесконечные попытки уговорить себя «перетерпеть». «ХимкиМед Центр» снимает обе неопределённости управляемым маршрутом: у нас нет общих залов с «публичными» ожиданиями, приёмы разнесены по времени, длинные разговоры заменены коротким и предметным интервью, а назначения объясняются простым языком — что делаем сегодня, чего ждать через час, какие ощущения будут нормальными и при каких признаках нужно срочно связаться. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса»: схема строится от фактов — длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые препараты, исходные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация), выраженность тремора и качество сна. Такой реализм экономит силы, снижает тревогу и чаще уже в первые сутки приводит к главному — к первой ровной ночи, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-himkah
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
I think the admin of this site is actually working hard for his
web page, for the reason that here every stuff is quality based information.
Кодирование — не «волшебная кнопка», а усилитель плана после стабилизации. Мы рассматриваем методики индивидуально: инъекционные варианты дают фиксированный срок действия без ежедневной дисциплины; имплантационные — более длительный контроль; пероральные режимы гибче, но требуют высокой приверженности и частых контактов. Перед процедурой врач сверяет лекарства на взаимодействия, исключает противопоказания, объясняет механизмы, ограничения и риски, согласует план наблюдения. После — пациент получает памятку на ближайшие недели: режим сна, жидкости и питания, списки «красных флажков», окна связи, набор поведенческих «буферов». Такой реализм убирает соблазн «проверять» метод и снижает вероятность срывов, пока нервная система перестраивается. При необходимости мы подключаем семейные встречи: договариваемся о правилах дома, ролях и формулировках, которые уменьшают сопротивление вместо того, чтобы его подогревать. В результате фармакологический инструмент работает не сам по себе, а в экосистеме поддержки — так эффективность становится выше, а траектория устойчивее.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru
синхронный перевод на английском [url=https://telegra.ph/Trebovaniya-k-sinhronnomu-perevodchiku-navyki-sertifikaty-opyt–i-pochemu-ehto-vazhno-12-16]telegra.ph/Trebovaniya-k-sinhronnomu-perevodchiku-navyki-sertifikaty-opyt–i-pochemu-ehto-vazhno-12-16[/url] .
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to revisit once again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Манганиновая проволока 0.22 мм МНМЦАЖ3-12-0.3-0.3 ГОСТ 10155-75 Купить манганиновую проволоку высокого качества от ведущих производителей. Надежные материалы для производства кабельной продукции, электротехнических изделий, судостроения и машиностроения. Широкое применение в промышленности. Прочные, износостойкие и устойчивые к коррозии и окислению. Консультации по выбору и применению материалов.
Миссия Наркологической клиники “Новый путь” заключается в предоставлении качественной и всесторонней поддержки людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостями. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это не просто слабость воли, а сложное заболевание, требующее комплексного и научного подхода. Наша цель — создать безопасную и поддерживающую среду, где пациенты могут открыто говорить о своих переживаниях и проблемах.
Получить больше информации – http://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-Ekaterinburge/
По телефону или через приложение клиники пациент или его родственники оформляют заявку на вызов. В течение 30–45 минут бригада выезжает по указанному адресу и приносит полный комплект оборудования и медикаментов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
It’s genuinely very complex in this full of activity life to listen news on Television, therefore
I simply use world wide web for that purpose, and take the hottest information.
refurbished phones with warranty Europe
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, семья сталкивается с двумя видами неопределённости — медицинской и организационной. На одной чаше весов тремор, скачки давления и пульса, рвота, обрывочный сон и нарастающая тревога; на другой — страх огласки, очереди, ожидание «до завтра» и бесконечные попытки уговорить себя «перетерпеть». «ХимкиМед Центр» снимает обе неопределённости управляемым маршрутом: у нас нет общих залов с «публичными» ожиданиями, приёмы разнесены по времени, длинные разговоры заменены коротким и предметным интервью, а назначения объясняются простым языком — что делаем сегодня, чего ждать через час, какие ощущения будут нормальными и при каких признаках нужно срочно связаться. Мы не лечим «пакетами ради прайса»: схема строится от фактов — длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые препараты, исходные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация), выраженность тремора и качество сна. Такой реализм экономит силы, снижает тревогу и чаще уже в первые сутки приводит к главному — к первой ровной ночи, после которой решения принимаются спокойно и по плану.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki9.ru
Затянувшийся запой — это не только токсическая нагрузка, но и постоянная «раскачка» нервной системы, скачки давления и пульса, тошнота, бессонные ночи и конфликтный фон в семье. Пока избирается дорога до клиники и очередь на приём, организм теряет воду и электролиты, а тревога усиливается. Выезд «Трезвый Пульс Люберцы» разрывает этот круг: врач прибывает в согласованное окно без маркировки, сразу оценивает факты (длительность употребления, препараты за 24–48 часов, сопутствующие диагнозы, аллергии), фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора и уровень тревоги. На месте объясняется простым языком, зачем именно сегодня нужна инфузия, чего ожидать в ближайшие 30–60 минут и как провести вечер, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи. Домашний формат учитывает реальную географию Люберец: дворовые проезды, часы пик, необходимость сохранять приватность. Чем меньше пауз и социальных контактов, тем быстрее старт терапии, ниже эмоциональный шум и выше приверженность режиму. В результате уже в первые часы выравнивается пульс, снижается тремор и тошнота, появляется шанс на первую ровную ночь — именно она превращает облегчение «на час» в устойчивую стабилизацию на несколько суток.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru
kèo nhà cái 5
Врачебный состав клиники “Ресурс здоровья” состоит из высококвалифицированных специалистов в области наркологии. Наши врачи-наркологи имеют обширный опыт работы с зависимыми пациентами и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому краснодар.[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новосибирске[/url]
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Детоксикация организма, проводимая на дому, помогает очистить кровь от токсинов, накопившихся из-за длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ. Она проводится с использованием специально подобранных медикаментов, которые улучшают работу печени, почек и других органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
https://kotel-rs.ru/
ждите трип о товаре, как сделаю заказ и получу товар обрисую все в красках! постараюсь сделать фото!!! Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Мы очень рады! Обращайтесь к нам еще!Я подозреваю, что его посылку спалили на наличие и теперь просто не отправляют.
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
I am not sure where you are getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for fantastic information I was looking for this info for my mission.
Миссия нашего медицинского учреждения заключается в предоставлении всесторонней помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Основные цели нашего центра включают:
Подробнее тут – https://alko-specialist.ru
buy AirPods Europe
https://kotel-rs.ru/
«ГородМед Трезвость» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один ни на этапе выхода из запоя, ни во время стабилизации, ни в период удержания ремиссии. С первого звонка дежурный врач проводит короткое интервью, фиксирует жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни и текущие препараты, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — экстренный выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Мы не растягиваем процесс по неделе: старт возможен в день обращения, а маршрутизация между форматами (дом, амбулаторный визит, стационар) занимает часы. Важная часть подхода — ясные цели каждого шага и критерии эффективности, понятные самому пациенту и семье: когда ждать облегчения тревоги, как нормализуется сон, когда вернётся аппетит, что считается «красным флажком» и как действовать без паники. Такая предсказуемость снижает уровень стресса и повышает приверженность лечению уже в первые трое суток.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve-ceny/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru
АА это только сегодня? https://xiaomicenter.ru Беруууу часто через магазинУспешных вам продаж
Дополнительно выясняются аллергические реакции, приём других препаратов и предпочтения пациента по времени визита врача.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость воронеж[/url]
Специалист уточняет длительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Точный сбор данных позволяет оперативно корректировать лечение и выбрать оптимальные методы детоксикации.
Подробнее тут – http://narco-vivod-clean.ru
Алкогольный запой представляет собой длительное бесконтрольное приём спиртного, приводящее к тяжёлой интоксикации и серьёзным осложнениям для органов и психики. В Новосибирске клиника «Сибирский Доктор» предлагает качественный вывод из запоя с применением инновационных технологий и участием опытных наркологов, терапевтов и психиатров. Наш подход сочетает мгновенную реакцию на вызов, современное оборудование и индивидуальные схемы лечения, что позволяет достичь стабильной ремиссии и снизить риск рецидива.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в новосибирске[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ryadom[/url]
https://koreatesol.org/ads/inc/1xbet_promo_code-free_welcome_bonus.html
Клиника «ВоронежМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток, включая праздники и выходные. Анонимность достигается за счёт минимального контакта с персоналом клиники и отсутствия бумажной волокиты. Все этапы лечения согласовываются только с пациентом или доверенным лицом, а сведения о визите не передаются третьим лицам.
Углубиться в тему – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/
Процесс лечения организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге[/url]
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного лечения. Препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет быстро снизить уровень токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальный обмен веществ и стабилизировать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://наркология-дома1.рф
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-balashiha
Вот это бы нормально было нормальный трип по двум веществам.. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки спасибо , стараемся для людейда, спросил тут ли менеджер, по быстрому оформил заказ.
Образовательные программы: Мы уверены, что знания о зависимости и её последствиях играют важную роль в реабилитации. Мы информируем пациентов о механизмах действия наркотиков и алкоголя на организм, что способствует изменению их отношения к терапии и жизни без зависимостей.
Детальнее – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в казани[/url]
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya[/url]
Обращение к наркологу позволяет избежать типичных ошибок самолечения и достичь стабильного результата. Квалифицированное вмешательство:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя новосибирск[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-moskva-ceny[/url]
Образовательные программы: Мы уверены, что знания о зависимости и её последствиях играют важную роль в реабилитации. Мы информируем пациентов о механизмах действия наркотиков и алкоголя на организм, что способствует изменению их отношения к терапии и жизни без зависимостей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в казани[/url]
Физическое облегчение — лишь половина задачи; вторая половина — эмоции и привычки. Индивидуальные сессии помогают распознать автоматические мысли, планировать «буферы» на вечерние часы, управлять стрессом и сонливостью, расставлять «сигнальные маяки» на привычных маршрутах, где чаще всего возникают соблазны. Семья получает ясные инструкции: меньше контроля — больше поддержки правил среды (тишина, затемнение, прохлада, вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»), отказ от «разборов причин» в первую неделю, короткие договорённости о связи со специалистом при тревожных признаках. Когда у всех одни и те же ориентиры, уровень конфликтов падает, а предсказуемость растёт — это напрямую укрепляет ремиссию. Мы не перегружаем психологический блок «теорией»: даём только те инструменты, которые человек готов выполнить сегодня и завтра, без рывков и самообвинений. Такая практичность приносит больше пользы, чем долгие разговоры «о мотивации», и отлично сочетается с медицинской частью плана.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Миссия Наркологической клиники “Новый путь” заключается в предоставлении качественной и всесторонней поддержки людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостями. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это не просто слабость воли, а сложное заболевание, требующее комплексного и научного подхода. Наша цель — создать безопасную и поддерживающую среду, где пациенты могут открыто говорить о своих переживаниях и проблемах.
Получить больше информации – https://нарко-специалист.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-Ekaterinburge
Миссия клиники “Маяк надежды” заключается в содействии восстановлению здоровья и социальной реинтеграции людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Мы стремимся к комплексному решению этой сложной задачи, учитывая физические, психологические и социальные аспекты зависимости. Наша задача — не только помочь пациентам избавиться от физической зависимости, но и обеспечить их психологическое восстановление и возвращение к нормальной жизни в обществе.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://алко-лечение24.рф/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-Sankt-Peterburge/
Выезд нарколога на дом включает несколько ключевых этапов: первичный дистанционный сбор анамнеза, оперативный приезд специалиста, проведение обследования — измерение пульса, давления, сатурации, уровня глюкозы и электролитов крови — и последующее назначение инфузионной терапии. В зависимости от состояния пациента подбирается индивидуальный состав растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку функций печени и нормализацию работы центральной нервной системы. Все процедуры выполняются с учётом противопоказаний и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/
Keep on working, great job!
Здесь
[url=https://www.rush-agency.ru/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Показана при обезвоживании, «скачущем» давлении и пульсе, угрозе судорог, упорной рвоте, эпизодах спутанности сознания, тяжёлой соматике. За сутки–двое удаётся выровнять показатели, наладить сон и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному этапу.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/
заказывал на днях 1 г. МН-001. пришло помоему в течении 5 дней. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Всем удачи!Пожалуй один из самых ровных магазинов “Старичков ” – благодаря которому я зарабатвал, от души спасибо парням за ровную работу!
Перед оформлением вызова проводится предварительная телефонная консультация, позволяющая оценить тяжесть состояния и заранее подготовить необходимые препараты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog
with my zynga group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate your content.
Please let me know. Many thanks
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий. Инфузии подбираются индивидуально: цель — восстановить объём циркулирующей крови, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, вернуть условия для сна. Мы не перегружаем препаратами, не «гоняем» симптом силой седативов и не используем универсальные растворы «для всех». Поддержка сна строится на минимально достаточных дозах и гигиене вечернего времени: затемнение, тишина, отказ от экранов, ранний отбой. Параллельно врач объясняет, как пить воду маленькими порциями, когда сделать лёгкий перекус, зачем планировать короткую дневную паузу. После купирования остроты пациент получает чёткий план на трое суток — простые, реалистичные шаги, которые удерживают эффект без «героизма» и без лишней фармакологической нагрузки. В результате медицинский эффект не растворяется в быту, а закрепляется привычками, которые по силам выполнить сегодня и завтра.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/
https://kotel-rs.ru/
Домашняя точка входа оправдана при стабильных показателях и низком риске осложнений. В знакомой обстановке легче соблюдать режим: затемнить комнату, убрать экраны, распределять воду маленькими порциями, сделать лёгкий перекус «по силам», лечь пораньше. Врач подберёт «узкую» схему инфузий без перегруза препаратами, объяснит, какие ощущения допустимы сегодня и ночью, а какие — повод для немедленной связи. Такой сценарий экономит время семьи, снижает стигму и быстрее переводит состояние в управляемое, на базе которого уже можно строить дальнейшие шаги — амбулаторные визиты, работу с триггерами и, при показаниях, обсуждение кодирования.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
Клиника создана для оказания квалифицированной помощи всем, кто страдает от различных форм зависимости. Мы стремимся не только к лечению, но также к формированию здорового образа жизни, возвращая пациентов к полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – https://нарко-специалист.рф/
Алкогольная зависимость может стремительно ухудшать состояние здоровья, превращаясь в запой, сопровождающийся серьезной интоксикацией организма. В Санкт-Петербурге профессиональные наркологи выезжают на дом круглосуточно, чтобы оказать экстренную помощь в критических ситуациях. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать детоксикацию сразу после обращения, обеспечивая оперативное вмешательство в комфортных условиях, где пациент сохраняет свою конфиденциальность.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Оптимально для пациентов в стабильном состоянии. Процедура начинается с приезда врача, осмотра и постановки капельницы с индивидуально подобранными растворами.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новосибирске[/url]
Сургут, вобщем хмао Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки пишу по сути заказал-оплатил-получил все это было очень быстро я сам охуел вечером кинули трек а уже на следующее утро получил походу ТС на реактивном истребителе доставку организовал, качество нормуль делал 1к8 штырит как положено, первые 20 минут на подьем потом 20 минут идет спад короче 40 минут полет отличный, да был небольшой казус часть платежа потярялось, но потом после созвона со службой поддержки клиентов благополучно нашлось- “дырявая банковская система” вот как то так. ТСу без подхолемажа РЕСПЕКТ!!!!через в/в непробывал такое не люблю,
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google,
and found that it’s really informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels.
I will be grateful if you continue this in future.
Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
loli girls ginormous vid pic
is.gd/BlCAHo
krtk.rs/e1i0ovy
cheap Apple laptops Europe
Запой — это серьёзное состояние, при котором организм страдает от накопления токсинов, обезвоживания и нарушения обмена веществ. Клиника «ВоронежЛайф» предлагает услугу выездного инфузионного лечения от запоя с возможностью круглосуточного реагирования. Благодаря персонализированному подходу и использованию современных автоматизированных систем дозирования, наши специалисты обеспечивают безопасную и эффективную детоксикацию в условиях домашнего уюта.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в воронеже[/url]
https://alcosystems.se/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_code-free_welcome_bonus.html
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]капельница от запоя телефон[/url]
Preserving optimal wellness is a daily difficulty, and occasionally diet regimen alone isn’t enough. Nutritional Supplements offer a reputable method to fill up dietary spaces, support general health, and enhance energy levels. Many people trust Nutra Welten for top notch formulas that incorporate all-natural active ingredients with clinical research. Whether you are searching for weight management, enhanced immunity, or beauty support, the best supplements can make a substantial distinction. Checking Out Dietary Supplement Experiences and Reviews can assist you choose one of the most effective options for your way of life, making sure both security and outcomes, https://x.com/vitalpathhealth/status/2003340684259131794?s=20.
All Domains for Sell
Contact us : topnewsagency24x7@gmail.com
switzerlandnewstoday.com
maltanewstime.com
nationalposttoday.com
republicofchinatoday.com
russiannewstoday.com
crunchbasenewstoday.com
forbesnewstoday.com
livemintnewstoday.com
postgazettenewstoday.com
reuterstoday.com
themetronewstoday.com
huffingtonposttoday.com
neatherlandnewstoday.com
timesofnetherland.com
turkeynewstoday.com
walesnewstoday.com
australiannewstoday.com
bostonnewstoday.com
canadiannewstoday.com
cnbcnewstoday.com
mirrornewstoday.com
dwnewstoday.com
frenchnewstoday.com
guardiannewstoday.com
irishnewstoday.com
italiannewstoday.com
topworldnewstoday.com
washingtontimesnewstoday.com
scotlandnewstoday.com
chroniclenewstoday.com
britishnewstoday.com
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий. Инфузии подбираются индивидуально: цель — восстановить объём циркулирующей крови, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, вернуть условия для сна. Мы не перегружаем препаратами, не «гоняем» симптом силой седативов и не используем универсальные растворы «для всех». Поддержка сна строится на минимально достаточных дозах и гигиене вечернего времени: затемнение, тишина, отказ от экранов, ранний отбой. Параллельно врач объясняет, как пить воду маленькими порциями, когда сделать лёгкий перекус, зачем планировать короткую дневную паузу. После купирования остроты пациент получает чёткий план на трое суток — простые, реалистичные шаги, которые удерживают эффект без «героизма» и без лишней фармакологической нагрузки. В результате медицинский эффект не растворяется в быту, а закрепляется привычками, которые по силам выполнить сегодня и завтра.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-kruglosutochno/
Пиздатый магаз ) https://sp-kupavna.ru приветствуюУкраина Работает?
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий. Инфузии подбираются индивидуально: цель — восстановить объём циркулирующей крови, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, вернуть условия для сна. Мы не перегружаем препаратами, не «гоняем» симптом силой седативов и не используем универсальные растворы «для всех». Поддержка сна строится на минимально достаточных дозах и гигиене вечернего времени: затемнение, тишина, отказ от экранов, ранний отбой. Параллельно врач объясняет, как пить воду маленькими порциями, когда сделать лёгкий перекус, зачем планировать короткую дневную паузу. После купирования остроты пациент получает чёткий план на трое суток — простые, реалистичные шаги, которые удерживают эффект без «героизма» и без лишней фармакологической нагрузки. В результате медицинский эффект не растворяется в быту, а закрепляется привычками, которые по силам выполнить сегодня и завтра.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future. Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Страх огласки часто откладывает обращение. В «ЛюберМед Центр» приватность — регламент: запись и подтверждения через защищённые каналы, шифры вместо ФИО в расписании, приёмы без пересечений, нейтральные входы. Домашние визиты проходят без маркировки, маршрут по двору и подъезду согласуется заранее. Мы учитываем характерные для Люберец дворовые проезды и часы пик, чтобы врач приехал вовремя, а пациент не провёл лишних минут в «социальном шуме». Чем меньше публичности и пауз, тем ниже тревога и выше приверженность режиму. Такая деликатность — не про «сервис ради сервиса», а про клиническую эффективность: когда человек не боится быть узнанным, он приходит вовремя, точнее следует рекомендациям и реже требует экстренных вмешательств ночью.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryadom-v-lyubercah/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru
В условиях современного общества наркомания и алкоголизм стали актуальными и серьезными проблемами, затрагивающими не только индивидуумов, но и их семьи, сообщества. Эти заболевания не просто влияют на физическое здоровье, они наносят урон психоэмоциональному состоянию, нарушают социальные связи и ухудшают качество жизни. Наркологический центр “Новый горизонт” предлагает целостный и научно обоснованный подход к лечению зависимостей от психоактивных веществ. Мы применяем современные методы диагностики и терапии, чтобы помочь каждому пациенту обрести здоровье и вернуть себе полноценную жизнь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://alko-specialist.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-simferopole
Лечение выводом из запоя на дому в «ВоронежМед» организовано по отработанному протоколу, включающему несколько ключевых этапов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена воронеж[/url]
почта России https://ladygroup.ru ну тогда тестируй, если неделю выдержал )Приветствую всех ровных жителей этой ветки.Друзья помогите мне.Где ,на какой страничке я могу найти хозяина даннго магазина.И где адреса магазина???Где прайс???Вообще не понятный магазин.И как выглядет его аватарка.
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий, а не один универсальный раствор. Мы восполняем жидкость и корректируем электролиты, защищаем печёночные функции, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, создаём условия для первого нормального сна. Каждая доза сверяется с динамикой давления, пульса, сатурации и неврологического статуса, поэтому схема не перегружена и не «гонится» за мимолётным эффектом ценой побочных реакций. После купирования острых проявлений начинается стабилизация: уточняются дозировки, выстраивается режим питания и гидратации, объясняются «красные флажки» для контакта с врачом, настраиваются простые поведенческие техники на «тёмные часы» вечера. В этот момент особенно важно не растворить медицинский эффект бытовыми ошибками: недосыпом, пропусками еды, конфликтными разговорами «о прошлом». Мы даём короткие, реалистичные алгоритмы на 20–40 минут — прогулка, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по графику, дыхательные практики — чтобы снизить импульсивность и закрепить ощущение управляемости. Именно связка детокса с поведенческой дисциплиной формирует траекторию, которую можно удержать неделями, а не только до «завтрашнего утра».
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru
I am not sure the place you are getting your information, but good topic.
I needs to spend a while finding out much more or understanding more.
Thanks for fantastic information I was in search of this info
for my mission.
На этом этапе нарколог выясняет, какие лекарства принимались ранее, есть ли аллергии, хронические заболевания, а также уточняет объём и длительность употребления алкоголя. Это позволяет скорректировать состав инфузионных растворов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-v-voronezhe/
:::::::::::::::: ONLY THE BEST ::::::::::::::::
Content from TOR websites Magic Kingdom, TLZ,
Childs Play, Baby Heart, Giftbox, Hoarders Hell,
OPVA, Pedo Playground, GirlsHUB, Lolita City
More 3000 videos and 20000 photos girls and boys
h**p://tiny.cc/sficzx
h**p://j1d.ca/_J
h**p://put2.me/muhcsh
Complete series LS, BD, YWM, Liluplanet
Sibirian Mouse, St. Peterburg, Moscow
Kids Box, Fattman, Falkovideo, Bibigon
Paradise Birds, GoldbergVideo, BabyJ
h**p://citly.me/47kMX
h**p://4ty.me/ibhi7c
h**p://tt.vg/URoSx
Cat Goddess, Deadpixel, PZ-magazine
Tropical Cuties, Home Made Model (HMM)
Fantasia Models, Valya and Irisa, Syrup
Buratino, Red Lagoon Studio, Studio13
—————–
—————–
000A000234
1win как ставить на онлайн-платформе
Физическое облегчение — лишь половина задачи; вторая половина — эмоции и привычки. Индивидуальные сессии помогают распознать автоматические мысли, планировать «буферы» на вечерние часы, управлять стрессом и сонливостью, расставлять «сигнальные маяки» на привычных маршрутах, где чаще всего возникают соблазны. Семья получает ясные инструкции: меньше контроля — больше поддержки правил среды (тишина, затемнение, прохлада, вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»), отказ от «разборов причин» в первую неделю, короткие договорённости о связи со специалистом при тревожных признаках. Когда у всех одни и те же ориентиры, уровень конфликтов падает, а предсказуемость растёт — это напрямую укрепляет ремиссию. Мы не перегружаем психологический блок «теорией»: даём только те инструменты, которые человек готов выполнить сегодня и завтра, без рывков и самообвинений. Такая практичность приносит больше пользы, чем долгие разговоры «о мотивации», и отлично сочетается с медицинской частью плана.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва отзывы[/url]
Алкогольный запой представляет собой длительное бесконтрольное приём спиртного, приводящее к тяжёлой интоксикации и серьёзным осложнениям для органов и психики. В Новосибирске клиника «Сибирский Доктор» предлагает качественный вывод из запоя с применением инновационных технологий и участием опытных наркологов, терапевтов и психиатров. Наш подход сочетает мгновенную реакцию на вызов, современное оборудование и индивидуальные схемы лечения, что позволяет достичь стабильной ремиссии и снизить риск рецидива.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Алгоритм прозрачен. Сначала — краткое интервью и осмотр, измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, при необходимости — ЭКГ и оценка неврологического статуса. Далее — инфузионная терапия по показаниям: восполнение жидкости, коррекция электролитов, поддержка функций печени, мягкое снижение тремора и тревоги, подготовка к сну без «оглушения». Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма, чтобы не получить вечернего отката и побочных эффектов. Врач детально объясняет, какие ощущения нормальны (сонливость, сухость во рту, умеренная слабость), а какие — основание для связи. После процедуры повторно фиксируются показатели и выдаются письменные рекомендации на 48–72 часа: режим воды и лёгкой еды, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликты, время короткого дневного отдыха, интерфейс связи и условия повторного визита. Такой порядок убирает хаос: пациент и семья понимают, что именно делать вечером и ночью, как снизить «дергание» и зачем придерживаться простых правил, пока организм перестраивается после запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/]врач нарколог на дом москва[/url]
«МедТрезвие» выстраивает лечение зависимости как последовательный и понятный маршрут, где каждый этап имеет чёткую цель, критерии эффективности и прозрачные условия. С первого обращения дежурный врач уточняет жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, переносимость лекарств и бытовые ограничения, после чего предлагает безопасный формат начала — выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Важна не только скорость, но и качество коммуникации: пациент и близкие получают ясное объяснение, зачем назначается конкретная процедура, как оценивать улучшение и какие признаки требуют немедленной связи со специалистом. Круглосуточная доступность и конфиденциальные каналы записи снимают барьер обращения, а внутренняя маршрутизация позволяет переходить от экстренного купирования симптомов к стабилизации и профилактике срывов без пауз и «провалов» между этапами. Такой подход уменьшает риск повторных эпизодов, повышает приверженность и возвращает человеку контроль над повседневной жизнью.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]narkolog-besplatno-moskva[/url]
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru
Профессиональная психологическая помощь является фундаментальным элементом в понимании пациентом корней зависимости и инициации процесса восстановления. Квалифицированные психологи проводят персональные и групповые занятия, обучая пациентов эффективному управлению эмоциями и преодолению стрессовых ситуаций без алкоголя. В процессе терапии используются методики когнитивно-поведенческой терапии для изменения деструктивных паттернов мышления. Развитие навыков самоконтроля и укрепление самооценки становятся ключевыми факторами в формировании стойкой мотивации к трезвому образу жизни.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
СПАСИБИЩЕ ОГРОМНОЕ ЗА СЕРВИС Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки хуясе надо было сначало уточнить а что брали хоть? ио названижю веществааська молчит.скайп есть?
Каждый врач клиники обладает глубокими знаниями фармакологии, психофармакологии и психотерапии. Они регулярно посещают профессиональные конференции, семинары и мастер-классы, чтобы быть в курсе новейших достижений в области лечения зависимостей. Такой подход позволяет нашим специалистам применять наиболее эффективные и современные методы терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narco-vivod.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika krasnodar[/url]
Индивидуализация лечения: Каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, учитывая уникальные особенности пациента, его физическое состояние, предшествующий опыт лечения и социальные факторы. Такой подход позволяет создать максимально эффективный план терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru/]alko-specialist.ru/[/url]
Hi there! I understand this is kind of off-topic
but I needed to ask. Does managing a well-established blog such as yours
take a large amount of work? I am brand new to running a blog but
I do write in my diary every day. I’d like to start a blog so I will
be able to share my personal experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any recommendations or
tips for brand new aspiring blog owners. Appreciate it!
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnoyarsk/
Ущерб через наркотиков — это комплексная проблема, охватывающая физическое, психологическое (а)
также общественное здоровье человека.
Утилизация эких наркотиков, яко кокаин, мефедрон,
гашиш, «шишки» или «бошки», что ль огласить буква неконвертируемым
последствиям как для организма, яко и для общества в течение
целом. Хотя хоть при выковывании
связи возможно восстановление —
ядро, чтобы зависимый явантроп
устремился согласен помощью.
Эпохально памятовать, яко наркомания лечится, также оправдание бабахает шансище
сверху новейшую жизнь.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article. I want to read even more things about it!
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]вызов на дом капельницы от запоя воронеж[/url]
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryadom-v-lyubercah
Строго регламентированный алгоритм позволяет специалистам «ВоронежДоктор» добиваться устойчивых результатов при выводе из запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно на дому в воронеже[/url]
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/vyezd-na-dom-kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Какой космос,тут бы от земли хоть оторваться https://novonezhino-sp.ru Берут все молча )хуй ты отпишешь! наркоман проклятый
Первый шаг — короткое, но предметное интервью: длительность употребления, сопутствующие диагнозы, текущие препараты и аллергии. Врач фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-ЭКГ и неврологический скрининг. Далее объясняет логику вмешательств: зачем именно такая инфузия, чего ожидать через 30–60 минут, какие ощущения нормальны и какие потребуют связи. Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов, чтобы не получить вечерний откат и побочные эффекты — дозировки подбираются узко, по реакции организма. После капельницы специалист ещё раз проверяет показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации, договаривается об окне контроля и критериях повторного визита. Вечер строится вокруг сна: затемнение, тишина, ранний отбой, вода порциями, лёгкая еда «по силам», минимум экранов и разговорных конфликтов. На таком фоне исчезают «качели» между днём и ночью, а эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к следующему вечеру.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ryadom-sm-klinika[/url]
https://zelenayazona.ru/
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-moskva[/url]
Риск от наркотиков — это комплексная проблема, обхватывающая физическое,
психическое и социальное состояние здоровья
человека. Утилизация подобных наркотиков, как снежок,
мефедрон, ямба, «шишки» чи «бошки», может родить к необратимым следствиям как чтобы организма, яко равно для мира на целом.
Но даже у выковывании подчиненности возможно восстановление
— ядро, чтоб энергозависимый
человек устремился за помощью.
Важно памятовать, яко наркомания врачуется, а также помощь
одаривает шанс сверху новейшую жизнь.
Такая услуга доступна круглосуточно, что позволяет вызвать врача в любое время. Профессиональные специалисты, приехав на дом, тщательно подберут состав капельницы с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное лечение. Анонимность и высокая квалификация медперсонала делают этот способ особенно удобным для людей, которые предпочитают конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ekb55.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому екатеринбург[/url]
Процесс лечения организован по отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
На этом этапе нарколог выясняет, какие лекарства принимались ранее, есть ли аллергии, хронические заболевания, а также уточняет объём и длительность употребления алкоголя. Это позволяет скорректировать состав инфузионных растворов.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/
Наркологическая клиника “Ресурс здоровья” — специализированное медицинское учреждение, предназначенное для оказания профессиональной помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narco-vivod.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/
«ГородМед Трезвость» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы человек не оставался один ни на этапе выхода из запоя, ни во время стабилизации, ни в период удержания ремиссии. С первого звонка дежурный врач проводит короткое интервью, фиксирует жалобы, длительность употребления, сопутствующие болезни и текущие препараты, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — экстренный выезд на дом или приём без ожидания. Мы не растягиваем процесс по неделе: старт возможен в день обращения, а маршрутизация между форматами (дом, амбулаторный визит, стационар) занимает часы. Важная часть подхода — ясные цели каждого шага и критерии эффективности, понятные самому пациенту и семье: когда ждать облегчения тревоги, как нормализуется сон, когда вернётся аппетит, что считается «красным флажком» и как действовать без паники. Такая предсказуемость снижает уровень стресса и повышает приверженность лечению уже в первые трое суток.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
всё как всегда быстро ,чётко ,без всякой канители ,качество как всегда радует ,спасибо команде за работу,ВЫ ЛУЧШИЕ!!!!!! Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Дошло за 3 дня , качество отличное , буду только с этим магазом работать.добрый день как связаться с продавцом и не попасть на фейка?
Инфузия — это не одна «сильная сыворотка», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восстанавливаем объём циркулирующей жидкости, корректируем электролиты, снижаем токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночи. Противорвотная поддержка и гастропротекция подключаются при необходимости, витаминные комплексы — по показаниям, кардиокоррекция — только после оценки рисков. Врач заранее проговаривает, какие ощущения допустимы (сонливость, умеренная слабость), а какие — повод для немедленного контакта. Цель — не «забить» симптом на час, а задать предсказуемую траекторию на дни, чтобы вернулись управляемость, аппетит и ровный сон. Когда вмешательства дозированы и понятны, пациент меньше «проверяет себя» нагрузками, а семья перестаёт «разгонять» тревогу разговорами — это повышает эффективность терапии без увеличения чека.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
Миссия нашего центра – оказание всесторонней помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные цели нашей работы:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
После вашего звонка диспетчер фиксирует заявку и передаёт её свободному специалисту. Нарколог связывается для уточнения симптомов, времени начала запоя и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, чтобы привезти нужные препараты.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-ceny/
Нарколог, приезжающий на дом, предоставляет широкий спектр услуг. Основная цель — стабилизировать состояние пациента и начать лечение, направленное на устранение последствий зависимости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
loli girls multitudinous vid pic
is.gd/BlCAHo
krtk.rs/e1i0ovy
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
It is not my first time to pay a quick visit this web site, i am visiting this web page dailly and take pleasant facts from here all the time.
Длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к накоплению токсинов, нарушению обменных процессов и ухудшению работы внутренних органов. Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить риск серьезных осложнений, таких как сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, повреждение печени и почек, а также уменьшить психоэмоциональное напряжение. Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Рязани помогает начать лечение на ранних этапах, когда каждая минута имеет значение.
Разобраться лучше – https://наркология-дома1.рф/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ryazan
Детоксикация — это не одна «капельница», а серия мероприятий, направленных на снижение токсической нагрузки, выравнивание жизненно важных показателей и возвращение контроля над самочувствием. На старте врач проводит осмотр, при необходимости — экспресс-диагностику и ЭКГ, объясняет цели инфузионной терапии, отвечает на вопросы о препаратах и возможных ощущениях в первые часы после начала. Если состояние пациента позволяет, первые шаги выполняются дома: так легче согласиться на помощь и сохранить приватность. При выраженной интоксикации, обезвоживании, скачках давления и пульса, нарушении ориентации или риске судорог безопаснее выбрать стационар: расширенная диагностика и круглосуточный мониторинг снижает вероятность осложнений и даёт возможность гибко корректировать назначения. После купирования острых проявлений команда переходит к стабилизации — настройке сна, питания, гидратации и поддерживающих схем с понятными целями на ближайшие дни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/]нарколог бесплатно москва[/url]
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru
На письма не отвечают, щас будем звонить и орать матом… Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки всем советую магазин тс роботает ровно, знает толк в бизе, всегда беру у них и все ровно и надежно, товар выший класс ,куриер вообще красавчик все делает четко и надежно , магазину и курьеру оценка 10из 10 балов все ровно, ДОСТАВКА БОМБА ХОТЬ В АРТИКУ ДОСТАВЯТБратья, у меня вопрос. JV-30 как? Боюсь нарваться на регу с которой крышу сносит. Ответьте пожалуйста.
Выезд нарколога на дом включает несколько ключевых этапов: первичный дистанционный сбор анамнеза, оперативный приезд специалиста, проведение обследования — измерение пульса, давления, сатурации, уровня глюкозы и электролитов крови — и последующее назначение инфузионной терапии. В зависимости от состояния пациента подбирается индивидуальный состав растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку функций печени и нормализацию работы центральной нервной системы. Все процедуры выполняются с учётом противопоказаний и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-v-voronezhe/
Первый шаг — короткое, но предметное интервью: длительность употребления, сопутствующие диагнозы, текущие препараты и аллергии. Врач фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-ЭКГ и неврологический скрининг. Далее объясняет логику вмешательств: зачем именно такая инфузия, чего ожидать через 30–60 минут, какие ощущения нормальны и какие потребуют связи. Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов, чтобы не получить вечерний откат и побочные эффекты — дозировки подбираются узко, по реакции организма. После капельницы специалист ещё раз проверяет показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации, договаривается об окне контроля и критериях повторного визита. Вечер строится вокруг сна: затемнение, тишина, ранний отбой, вода порциями, лёгкая еда «по силам», минимум экранов и разговорных конфликтов. На таком фоне исчезают «качели» между днём и ночью, а эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к следующему вечеру.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/]ctoimost-kapelnicy-ot-zapoya[/url]
блог про seo [url=https://seo-blog8.ru/]seo-blog8.ru[/url] .
маркетинговый блог [url=https://seo-blog9.ru/]seo-blog9.ru[/url] .
Прайс был обновлен, в продаже появилась Скорость. Сайт скоро будет работать. https://premium-ceramica.ru Отличный магазин!!!процветания дальнейшего и удачных продаж!!тусишка хороша, я как го грешил что нирвановская была какая то тёмная, так вот у чемикала она вообще практически бежевая 😀 качество порадовало, хорошая вещь )
Уважаемый клиент, я вам уже не раз писал в личке что от вас у меня заказов не было. Все кто делал заказы уже давно получили свои посылки. Кому вы оплачивали я не знаю. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки много нас, а грам один.все ровно ваще чисто жду проверив качество отпишу
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You definitely know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something enlightening to read?
Зависимость всегда про неопределённость: скачки давления и пульса, тремор, тревожность, бессонные ночи, споры в семье и страх огласки. «ЛюберМед Центр» убирает эту неопределённость управляемым маршрутом. Мы начинаем с краткого, но точного интервью, фиксируем объективные показатели и тут же объясняем, какие вмешательства уместны сегодня и зачем именно они. Никаких «общих залов» и очередей: приёмы разнесены по времени, подтверждения проходят по защищённым каналам, визиты на дом — без маркировки. Наш принцип — минимальная достаточность: столько медицины, сколько нужно для безопасного перехвата динамики и первой ровной ночи. Именно она делает дальнейшие шаги предсказуемыми: снижается тремор, выравнивается ритм, появляется ресурс соблюдать режим. Благодаря продуманной логистике Люберец мы сокращаем холостые перемещения, а значит, лечение начинается раньше, а тревоги — меньше. В результате пациент и семья получают не «набор услуг», а последовательность: понятные действия, прозрачные ожидания и устойчивый эффект, который держится днями, а не часами.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]besplatnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Медицина выравнивает физиологию, но устойчивость дают простые действия. Мы вместе составляем карту триггеров: вечерние «тёмные часы», задержки без еды, конфликты, привычные маршруты с «точками соблазна», недосып. На каждый триггер — короткий «буфер» на 20–40 минут: спокойная прогулка близко к дому, тёплый душ, лёгкая еда по расписанию, дыхательная практика, созвон с «своим» человеком. Эти шаги бесплатны и выполнимы, но именно они уменьшают импульсивность и количество «проверок себя». Отдельный акцент — на ночной сон: ранний отбой, минимум экранов, затемнение, никаких энергичных разговоров и «разборов». Когда поведенческая рамка задана в первый же день, эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к вечеру, а переводит состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию, на базе которой уже можно обсуждать кодирование и реабилитационные шаги.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru
Домашний формат нужен, когда важно начать быстро и без лишних перемещений, а состояние не требует госпитализации. Врач адаптирует инфузионные схемы под переносимость и сопутствующие заболевания, контролирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, объясняет режим жидкости и питания, оставляет список признаков, при которых следует связаться повторно. Такой сценарий не отменяет дальнейшую работу: пациент получает краткий план на 48–72 часа, рекомендации по восстановлению сна и активности, а также точку контакта для корректировки. Это снижает тревогу, помогает избежать «самолечения» и формирует доверие к процессу, потому что человек видит конкретный результат — уменьшение тремора, нормализацию сна, снижение тревоги — уже в первые сутки.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]ставки на спорт[/url]
магаз работает ровно оперативно и бонус хороший дали хотя я даже не ожидал как и обещали на следующий день отправили,а орест посылок я думаю ТС как нибудь уладит этот вопрос главное подход к нему найти https://surgrecordz.com Какие у тебя претензии? ты провокатор и не более т.к. ты не дал даже номер заказа и не высказал притензию, к тому же за тебя мне уже написали в Личку, другие магазины..Представитель был Магазин на форуме Бивис и Бадхед, на сколько я знаю он работает, он у нас был представителем.
https://onlayn-oyinlar.com/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=Diwigeseg
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this
onto a friend who was doing a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered
me dinner due to the fact that I stumbled upon it for him…
lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!!
But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this topic here on your blog.
https://www.shippingexplorer.net/ru/user/mosbethu/230598
Редоктирование магазина!Коллектива!Прайс , цена осталась прежняя! скайп оператора:Chemicalrf.mix !!!! Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Рабочие дни отсчитываются со дня оплаты, а не заказа на сайте, разница порой месяц между тем когда человек создал заказ и когда оплатил его.Ну теперь к самому главному – качество!
minuscule girls myriad vid pic
is.gd/BlCAHo
krtk.rs/e1i0ovy
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
сео блог [url=https://seo-blog9.ru/]сео блог[/url] .
Профессиональная подготовка — это не формальность, а ключ к безопасной и эффективной процедуре. Врач собирает подробный анамнез, уточняет длительность и характер употребления, фиксирует соматические жалобы, анализирует текущие препараты (в том числе безрецептурные), измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости назначает ЭКГ и лабораторные тесты. Если есть выраженная интоксикация, бессонница, тремор, скачки давления — стартуют с детокса и стабилизации: корректируют водно-электролитный баланс, снижают тревогу, нормализуют сон. Параллельно специалист объясняет механику методик кодирования, вероятные ощущения после процедуры, ограничения по нагрузкам, правила безопасного поведения в первые недели и алгоритм действий на случай усиления тяги. Подготовительный этап снимает неопределённость, уменьшает тревогу и повышает приверженность: человек понимает, что будет происходить и как оценивать улучшение.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-moskve-otzyvy[/url]
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and everything. Nevertheless think about if you added some great photos or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and videos, this blog could undeniably be one of the most beneficial in its field. Terrific blog!
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-lyubercy
можно записаться на пробник ам как он придет…а то ниче про него непонятно https://kitchenremodelinghouston.org Добрый день, кто паникует и истерит, успокойтесь, всем все высылается постепенно. Треки придут на эл. почты ближайшее время всем ждущим.А вот еще немного…Вскрыл, взвешал – все в норме. для начала взял 1гр.растворяется АМ2233 в спирту хреново,(в след.раз попробую на растворителе сделать)причем грел все это дело на водяной бане,мешал,но до конца так и не растворилось.делал это долго и упорно,молочного оттенка раствора не наблюдалось,прозрачный скорее,но остался осадок в виде белого порошка.В итоге так и залил все это дело 1к20. Сушится теперь. Как высохнет опробуем и напишу что получилось. Буду надеятся на лучшее.
азино 777 официальный сайт Азино 777 официальный сайт является тем местом, где, как заявляется, игра ведется по правилам и с гарантией выплат. Однако, всегда стоит проявлять бдительность и критическое мышление. Прежде чем доверить свои деньги онлайн-платформе, следует тщательно изучить репутацию казино, проверить наличие лицензии и ознакомиться с отзывами других игроков.
оптимизация сайта блог [url=https://seo-blog8.ru/]seo-blog8.ru[/url] .
екб есть в представителях, смотрите в представительствах Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки месяц назад”Думаю надо затестить через сигу, Заколачиваю пробую бля что то не то вкус не тот и т.д”
покерок скачать GGPokerok – это часть большой сети GGPoker, что обеспечивает огромный трафик игроков и щедрые призовые фонды в турнирах. Это дает возможность не только испытать себя в конкуренции с лучшими, но и заработать солидные деньги. GGPokerok – это место, где мечты становятся реальностью.
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс шоп[/url]
melbet сайт Melbet casino – это виртуальный рай для любителей азартных игр. Здесь собрана огромная коллекция слотов от ведущих мировых разработчиков, игры с живыми дилерами, рулетка, блэкджек и множество других развлечений. Melbet casino предлагает игрокам погрузиться в атмосферу настоящего казино, не выходя из дома. Высокое качество графики, честные выплаты и разнообразие игр делают Melbet casino одним из лучших онлайн-казино.
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
Наводится порядок в информации, запускается инфузия по показаниям, объясняются ожидаемые ощущения и правила вечера. Пациент и близкие понимают, какой результат реалистичен к ночи и что делать, чтобы эффект не «сгорел» к полуночи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-lyubercy9.ru/[/url]
Детокс — это последовательность целевых действий. Инфузии подбираются индивидуально: цель — восстановить объём циркулирующей крови, скорректировать электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку, мягко приглушить тремор и тревогу, вернуть условия для сна. Мы не перегружаем препаратами, не «гоняем» симптом силой седативов и не используем универсальные растворы «для всех». Поддержка сна строится на минимально достаточных дозах и гигиене вечернего времени: затемнение, тишина, отказ от экранов, ранний отбой. Параллельно врач объясняет, как пить воду маленькими порциями, когда сделать лёгкий перекус, зачем планировать короткую дневную паузу. После купирования остроты пациент получает чёткий план на трое суток — простые, реалистичные шаги, которые удерживают эффект без «героизма» и без лишней фармакологической нагрузки. В результате медицинский эффект не растворяется в быту, а закрепляется привычками, которые по силам выполнить сегодня и завтра.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-moskva999.ru/
Решение обратиться за наркологической помощью часто упирается в страх огласки и сомнения в эффективности. В «МедТрезвие» эти барьеры снимаются за счёт клинической достаточности и предсказуемой организации. Диагностика и вмешательства назначаются строго по показаниям: врач оценит риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, состояние печени и поджелудочной железы, уровень тревоги и сна, наличие депрессивных симптомов. При устойчивом состоянии часть процедур выполняется на дому, что снижает стресс, а при признаках нестабильности — рекомендуется стационар с круглосуточным наблюдением. Анонимность поддерживается шифрованием данных, разграничением доступа и информированием родственников только по согласию пациента. Финансовые условия обсуждаются заранее: семья понимает, из чего складывается смета, и может планировать ресурс без опасений «скрытых» позиций. В результате лечение становится управляемым процессом, где медицинская безопасность и уважение к личной жизни человека — обязательные элементы, а не рекламные обещания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva9.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve-ceny/
Kokie būreliai ir veiklos yra Lietuvoje provided
Generally I don’t read post on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up
very forced me to take a look at and do it! Your writing style has been surprised
me. Thanks, very great article.
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/horoshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/
Выбор помощи на дому имеет ряд значительных преимуществ:
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-tula/
Резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя часто сопровождается выраженными симптомами абстиненции: тремор, тахикардия, повышенное давление, беспокойство. В клинике «Северная Звезда» для детоксикации применяется инфузионная терапия с балансированными растворами, содержащими:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма архангельск[/url]
What’s up, I check your new stuff like every week. Your writing style
is witty, keep up the good work!
Многие семьи сталкиваются с вопросом: куда обратиться, чтобы получить реальную помощь? В городе работают как государственные, так и частные наркологические учреждения, но не все из них предлагают действительно результативные программы. Чтобы избежать ошибок, важно знать ключевые аспекты, на которые следует опираться при выборе клиники.
Узнать больше – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/
Ниже — рабочая матрица на первые часы. Она показывает, как клиническая гипотеза превращается в минимальный шаг, какие индикаторы берём под контроль и по какому сигналу меняем тактику или площадку. Таблица не заменяет очную оценку, но делает логику маршрута ясной для всей семьи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в самаре[/url]
Кто тут урб-754 брал отпишитесь чё да как https://photosever.ru А за кладом я решил ехать на такси.6-APB, белый кристалический порошок, 1000р… Это типа настоящий 6-APB?
ggpokerok Pokerok зеркало – это запасной вариант для доступа к платформе в случае блокировки основного сайта. Зеркало – это гарантия того, что игра не прервется ни при каких обстоятельствах, позволяя наслаждаться любимым развлечением в любое время и из любой точки мира.
материалы по seo [url=https://seo-blog12.ru/]материалы по seo[/url] .
поисковое продвижение инфо сайта увеличить трафик специалисты [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru[/url] .
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I to find
this matter to be really one thing that I believe I might by no means understand.
It kind of feels too complex and extremely large for
me. I’m having a look forward on your next publish, I will attempt to get the hang of it!
Кроме того, наличие медицинской базы с возможностью круглосуточного мониторинга состояния пациента является дополнительным преимуществом. Это особенно важно на этапе детоксикации, когда организм испытывает серьезные нагрузки.
Получить больше информации – http://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru
Первая ровная ночь — фундамент. Мы настраиваем затемнение, фиксированное время отбоя, минимум экранов и раздражителей, при необходимости — щадящую седативную поддержку, которая стабилизирует, а не «выключает». Утром — повторная оценка и корректировка дозировок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Каждый профиль решает одну задачу и имеет ожидаемую динамику. Мы избегаем параллельных «усилений», чтобы не «замазывать» вклад отдельного шага и не перегружать организм.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи в казани[/url]
azino Азино сайт – это портал в мир виртуальных игр, где каждый может испытать свою удачу. Яркие баннеры, заманчивые предложения и бесконечный выбор развлечений – все это создает атмосферу, которая может легко увлечь. Важно помнить, что игра должна приносить удовольствие, а не создавать проблемы. Здравый смысл и умеренность – лучшие союзники в мире азарта.
статьи про digital маркетинг [url=https://seo-blog9.ru/]seo-blog9.ru[/url] .
Первый раз слышу такой непонятный отзыв о 4фа,все кто берет его как и 2c-i говорят что у нас он лучший … по jte907 если не умеете с ним работать зачем берете…? есть постоянные оптовики кто берет только его, и этот продукт нареканий не вызывает. Многие “Селлеры” под видом jte продают 2201 и это факт! у нас этот продукт в оригинале. МХЕ у нас такой пришел, мы не кричим что его чистота 99%, и что качество его не очень мы предупреждали всех… Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки или кто то прикалывается?привет бразы, хочу нахватить вот реги, что за качество скажите? надеюсь не 15 минутка?
Greetings! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My weblog looks weird when browsing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this problem. If you have any recommendations, please share. With thanks!
Процесс терапии включает несколько последовательных шагов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-chelyabinske/
https://impressiverp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=16&t=5459
Вызов нарколога на дом — это не «капельница как панацея», а управляемая последовательность решений с ясными целями, измеримыми маркерами и понятными «окнами оценки». В «СамарМед Ассист» мы строим лечение из узких модулей: сначала проверяем базовую безопасность (дыхание, сознание, гемодинамика), затем возвращаем переносимость питья, стабилизируем вегетатику, собираем ночь, и только после этого занимаемся дневной выносливостью и бытовой устойчивостью. Такой ритм исключает полипрагмазию, снижает фармаконагрузку и превращает первые часы из хаотичной «борьбы с симптомами» в спокойный, предсказуемый маршрут. Семья получает роль партнёра, а не наблюдателя: по простым ориентирам понятно, что считать нормой, когда звонить врачу и на каком этапе модуль следует «выключить».
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru
Если вы ищете выгодные варианты [url=https://fskrem.ru/vnutrennie-otkosy-dlya-plastikovyh-okon-iz-sendvich-panelej-v-moskve-nadjozhno-estetichno-s-ustanovkoj-pod-kljuch/]заказать установку откосов на окна из сэндвич панелей[/url], то профессиональный монтаж под ключ сделает ваш дом уютнее и теплее.
Они придают окну завершенный облик и удерживают тепло Сэндвич-панели представляют собой многослойный материал. Такие панели включают изоляционный слой и внешнее покрытие Установка откосов из сэндвич-панелей популярна благодаря своей простоте. Такой монтаж проходит быстро и не требует сложных инструментов
Откосы помогают в сохранении тепла в помещении. Отсутствие откосов ухудшает изоляцию и повышает энергозатраты. Сэндвич-панели отличаются высокой прочностью. Они выдерживают механические нагрузки и не деформируются Это делает их идеальным выбором для современных ремонтов. Такие панели сочетают практичность с доступной ценой
Сэндвич-панели обеспечивают отличную теплоизоляцию. Такие панели удерживают тепло, снижая расходы на обогрев Материал устойчив к влаге и грибку. Это защищает откосы от повреждений в условиях высокой влажности Эстетика панелей добавляет шарма интерьеру. Панели улучшают общий вид помещения за счет своей привлекательности.
Установка сэндвич-панелей экономит время. Монтаж проходит быстро, без длительных перерывов. Стоимость материалов остается доступной. Такие панели доступны большинству потребителей Это делает их популярным решением для ремонта. Преимущества outweigh недостатки в повседневном использовании
Сначала подготавливается поверхность откоса. Эта стадия включает очистку и выравнивание основания Затем нарезаются панели по требуемым размерам. Нарезка позволяет адаптировать материал к конкретным габаритам После этого они фиксируются с помощью крепежа. Это гарантирует стабильность конструкции на длительный период
Важно использовать качественные инструменты. Правильные инструменты ускоряют процесс и повышают точность Финальный этап включает отделку швов. Швы герметизируются для защиты от влаги Такой подход обеспечивает долговечность. Монтаж с учетом всех деталей продлевает срок службы
Цена установки откосов из сэндвич-панелей зависит от площади. Это основной фактор, влияющий на общую стоимость работ В среднем, стоимость начинается от 500 рублей за квадратный метр. Указанная сумма покрывает базовые этапы монтажа. Дополнительные факторы повышают итоговую цену. Влияние факторов делает расчет индивидуальным
Региональные различия влияют на ценообразование. Цены в регионах зависят от уровня конкуренции Рекомендуется сравнивать предложения. Сравнение позволит найти надежного исполнителя В итоге, установка окупается за счет долговечности. Выгодность проявляется в снижении будущих расходов.
Timber Crest Gallery Store – Enjoyed the artistic atmosphere and carefully arranged pieces.
После введения капельницы пациент ощущает облегчение: снижается головная боль, нормализуется давление, восстанавливается сон и аппетит. В дальнейшем врач может рекомендовать курс поддерживающих процедур для закрепления эффекта и профилактики рецидива.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-nizhnem-novgorode16.ru/]вызов на дом капельницы от запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
https://www.cobler.us/board/board_topic/7966425/7639393.htm
ggpokerok GGPokerok – это часть большой сети GGPoker, что обеспечивает огромный трафик игроков и щедрые призовые фонды в турнирах. Это дает возможность не только испытать себя в конкуренции с лучшими, но и заработать солидные деньги. GGPokerok – это место, где мечты становятся реальностью.
Лечение проводится поэтапно, начиная с оценки состояния и заканчивая восстановлением после интоксикации. Каждый этап направлен на устранение симптомов отравления и стабилизацию работы внутренних органов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены челябинск[/url]
Всегда платил через киви перевод идёт максимум сутки.950р это с курьером доставит тебе куда скажешь))) https://impuls38.ru Большое спасибо от Сиборяка из Москвы, ваш магаз резко скрасил жизнь во время командировки в Москве.Ровный магаз,всем советую)
Откройте для себя многофункциональный [url=https://sportres.ru/catalog/krossovery-blochnye-stoyki-i-drt/]кроссовер тренажер на грудь[/url], который идеально подойдет для интенсивных тренировок в зале или дома.
В нем сочетаются возможности эллиптического и велосипедного тренажеров
Инфузия — это не одна «сильная сыворотка», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восстанавливаем объём циркулирующей жидкости, корректируем электролиты, снижаем токсическую нагрузку на печень, мягко приглушаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночи. Противорвотная поддержка и гастропротекция подключаются при необходимости, витаминные комплексы — по показаниям, кардиокоррекция — только после оценки рисков. Врач заранее проговаривает, какие ощущения допустимы (сонливость, умеренная слабость), а какие — повод для немедленного контакта. Цель — не «забить» симптом на час, а задать предсказуемую траекторию на дни, чтобы вернулись управляемость, аппетит и ровный сон. Когда вмешательства дозированы и понятны, пациент меньше «проверяет себя» нагрузками, а семья перестаёт «разгонять» тревогу разговорами — это повышает эффективность терапии без увеличения чека.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru
Решение всегда клиническое. Домашний или амбулаторный формат уместен, если показатели устойчивы: нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» давления/пульса, признаков тяжёлого обезвоживания с риском судорог. Тогда один выезд часто закрывает задачу: индивидуальная инфузия, письменные рекомендации, утренний контроль — и человек входит в устойчивый ритм. Если картина «по краю» (лихорадка, упорная рвота, кардиальные жалобы, вторая бессонная ночь, сильный тремор) — честнее краткая стационарная стабилизация на 24–48 часов под круглосуточным мониторингом. На бумаге стационар дороже одного выезда, но в реальности он короче и предсказуемее: дефициты закрываются быстрее, дозы подстраиваются точнее, а первая ровная ночь достигается без «дорогих» откатов. В любом сценарии анонимность неизменна: закрытые каналы связи, визиты без маркировки, разнесённые по времени приёмы и доступ к данным по ролям.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]kakie-lekarstva-vhodyat-v-kapelnicu-ot-zapoya[/url]
Перед процедурой обсуждаются цели, ожидаемые эффекты, возможные побочные реакции, сроки наблюдения. Пациент получает письменные рекомендации на первые трое суток: режим сна и жидкости, коррекция нагрузки, контакты для связи, сигналы настороженности. Такой формат сделал результаты более предсказуемыми: меньше импульсивных решений, меньше тревоги и больше контроля над поведением в критический ранний период.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма в Москве отзывы[/url]
Hey there! I’ve been reading your website for a while now and finally got the bravery to go ahead
and give you a shout out from Huffman Tx! Just wanted to say keep up the good job!
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-moskve-na-domu[/url]
Осмотр > мониторинг > инфузии по показаниям > план вечера и ночи > письменные рекомендации > окно связи на следующий день. Эта линия делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]вывод из запоя москве[/url]
Успешного травление нашей молодежи и побольше денег! https://vekzhizni.ru Сегодня на мыло пришло письмо с новостью что заказ отправлен и номер трека который бьёться:good: пока всё норм идёт, со мной связь поддерживают через скайп, игнора не было, когда получу отпишу за качество вес и тдКАЧЕСТВО ВСЕХ ПРОДУКТОВ ОЧЕНЬ ВЫСОКОЕ!
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]запой нарколог на дом самара[/url]
блог о маркетинге [url=https://seo-blog8.ru/]блог о маркетинге[/url] .
ремонт бытовой техники рядом [url=http://www.master-po-remontu-tehniki-ekaterinburg.ru]https://master-po-remontu-tehniki-ekaterinburg.ru/[/url]
Инфузия снимает соматику, но устойчивость формируется в поведении. «Тихие ритуалы» — короткие повторяющиеся действия, которые уменьшают тревогу и помогают организму перейти из режима «тревога» в режим «восстановление». В «ЧелМед Детокс» семья обучается простым протоколам: не оценивать, говорить фактами, задавать ритм вечера. Пример: «через 20 минут приглушим свет; через 30 — 150 мл воды; перед сном — дыхание 4?6?4; если проснулся — повторить дыхание и не включать яркий свет». Психолог включается точечно: снимает острые триггеры, учит отслеживать маркеры перегрузки и закреплять сутки без срывов, не превращая поддержку в контроль. Благодаря этому первая неделя после детокса проходит мягче, а риск «провалов» снижается.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk-otzyvy/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-chelyabinske16.ru
Когда запой начинает угрожать здоровью, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Туле опытные специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, позволяя начать лечение сразу же в комфортной обстановке. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативную детоксикацию, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы внутренних органов, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих избежать лишнего стресса и сохранить конфиденциальность.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в туле[/url]
What’s up i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anyplace, when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also make comment due to this good paragraph.
I’ve learn a few just right stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting.
I surprise how a lot effort you put to create this type of magnificent informative web
site.
Мы намеренно избегаем «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай». Состав инфузии подбирается под доминирующие симптомы текущего часа — выраженную жажду и редкий диурез, «качели» давления и тахикардию, рвоту и отказ воды, ночную тревогу и бессонницу, утреннюю «туманность» и когнитивную рассеянность. Каждый модуль имеет одну цель и одно «окно оценки», чтобы было понятно, что именно помогает, а что нужно скорректировать. Если отклик ниже ожидаемого, врач меняет только один параметр — темп, последовательность, водный режим или поведенческую поддержку — и фиксирует результат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому в казани[/url]
Hey There. I discovered your weblog the use of msn. This is a very smartly written article.
I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of
your helpful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll definitely comeback.
Районы с плотной застройкой, дворовые проезды, пиковые часы — всё учитывается при планировании визитов. Чем меньше холостых перемещений, тем быстрее начинается помощь и тем ниже вероятность внеплановых повторов «по тревоге».
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru
French Gadgets unite technology, style, and functionality, providing users the best in Gadgets for home, way of living, and individual well-being. From innovative cooking area tools to ergonomic massage devices, French Gadgets – technology, way of life and household ensures every product fulfills high requirements. By reading Gadgets testimonials and recognizing Gadgets instructions, clients can make educated choices, contrast Gadgets costs, and discover the true Gadgets advantages. Special Gadgets coupon codes and tips on Gadgets to buy even more improve the buying experience, making these Gadgets to make use of not only useful yet also pleasurable, https://www.pinterest.com/pin/1148910555074653829.
Алкогольная зависимость — хроническое заболевание, требующее своевременного вмешательства специалистов. В условиях нашего города круглосуточная анонимная помощь позволяет начать лечение без откладываний и в привычной обстановке. Клиника «Северная Звезда» предлагает комплексный подход: вызов врача на дом или стационарное пребывание в условиях полной конфиденциальности. Профессиональная команда обеспечивает детоксикацию, психологическую реабилитацию и последующую поддержку, помогая пациенту сделать первый шаг к новой, свободной от алкоголя жизни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена[/url]
вот и я уже трясусь. https://bar-stavgorod.ru В Курске нетуЗаранее извиняюсь за оффтоп,просто решил сразу спросить ,чтобы не забыть.ответ будьте добры в ЛС.
Мы не ограничиваемся капельницей. Сервис включает организационные, клинические и поведенческие элементы, которые уменьшают хаос и ускоряют восстановление. Ниже — ключевые блоки, которые пациенты отмечают в отзывах как наиболее полезные и «приземлённые».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Fastidious answer back in return of this issue with real arguments and describing
all concerning that.
Ты че педрила хвалишся че та видел ты меня знаеш нет пес это не паника а логика паника это твое второе имя ху……я ты наличности переходиш это говорит о том что ты очкошник служил он терпила мне пох кто ты а за слова ты ответиш ну конншно на растояние ты герой ха ха отдыхай кент Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Ребята решили вопрос.. Вместо 307 выслали компинсацию в виде 1220. Давно не курил такие миксы, живы отдыхают, концентрацию 1к20 делал.Chemical-mix.com, а где от 50гр, там надо 40 тон сразу запулить:rastakur: яж не барон нах:LSD:
Every automоtive company hаs a car or two named аfter animals from tһe Mustang to the Panterɑ to the Impala and
the Viper. The Demon arrived as a subsequent-level variant and the quicқest manufacturing automotive on the earth on the time.
In fact, reds constitᥙte nearly all of the valley’s manufacturіng.
Identified for its aɡgressive nature, thіs snake is responsible for the vast majority of snake bites in its ѵary.
The various-banded krait (Bungaruѕ mսlticinctus), preѕent in S᧐utheast Asia and southern Chіna, is highly venomous and accountable for
mɑny fatal snake bites. Not like mɑny cobras, the Philippine cobra’s venom cɑn als᧐ Ьe highly toxic even when not injected directly into the bloⲟdstream, making it
a serious menace both from bites and venom spray. Tһe Philippine cobra (Naja pһilippinensis) is espеcially dangerous because of its means to
spit venom with deadly accuracy. Its potent venom could cause kill a human if
a snake chunk is left untreɑted.
статьи про seo [url=https://seo-blog12.ru/]статьи про seo[/url] .
https://www.gizguide.com/2023/01/poco-c50-.html?showComment=1766932446001#c3118894713355786677
how internet partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru[/url] .
Критерии оценки профессионального уровня сотрудников:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru
Кроме того, наличие медицинской базы с возможностью круглосуточного мониторинга состояния пациента является дополнительным преимуществом. Это особенно важно на этапе детоксикации, когда организм испытывает серьезные нагрузки.
Получить больше информации – https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/
Такая последовательность обеспечивает медицинскую точность и безопасность процедуры, позволяя добиться быстрого улучшения самочувствия без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-chelyabinske16.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в челябинске[/url]
Wild Rose Essentials – The atmosphere is inviting, with a few hidden gems.
статьи про продвижение сайтов [url=https://seo-blog9.ru/]статьи про продвижение сайтов[/url] .
I’m not sure exactly why but this web site is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Если вы планируете [url=https://arteli-stroy.ru/service/reconstruction]перестройка дома на даче цены[/url], наша компания предлагает профессиональные услуги по обновлению вашего жилья.
При работах анализируются все элементы конструкции.
Ремонт здания способствует поддержанию экосистемы.
После этого выполняется удаление изношенных элементов.
Советуется обращаться к квалифицированным мастерам за помощью.
Смысл экстренной помощи — не в «сильной капельнице любой ценой», а в последовательности. Бригада приезжает в согласованное окно, проводит экспресс-осмотр, фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает неврологический статус, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ. Далее подбирается инфузионная терапия по показаниям, корректируется водно-электролитный баланс, снижаются тремор и тревога, выравнивается сон. Важно объяснить семье и самому пациенту, чего ожидать: какие ощущения нормальны, какие — повод для связи, зачем назначены те или иные растворы и поддерживающие препараты. Параллельно формируется краткий план «сложных часов» на вечер и ночь: что делать, если накрывает волну беспокойства, как распределить жидкость и питание, какие бытовые действия лучше отложить. В московском ритме особенно критично не растягивать решения на «завтра»: від организованного визита до ощутимого облегчения обычно проходит один-два часа, и именно этот отрезок задаёт тон всей последующей стабилизации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/
кто брал закладками в этом магазе в МСК что скажите? Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Тьфу-тьфу-тьфу… =(Спасибо. Похож на ам2**3
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/]kakie-lekarstva-vhodyat-v-kapelnicu-ot-zapoya[/url]
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-preparaty[/url]
Мы придерживаемся инженерной логики: цель > маркер > окно проверки > отключение модуля. Никаких «сильных коктейлей на всякий случай»: сначала один точный шаг, затем — проверка результата. Именно так формируется прозрачность и доверие: пациент видит причину каждого назначения и понимает момент его завершения. Это уменьшает тревогу, ускоряет восстановление и убирает «инерцию лечения», когда лишние вмешательства продолжаются просто по привычке.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-samare16.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-marmansk
— Растворы с глюкозой и витаминами для коррекции энергетического обмена. — Минеральные комплексы для нормализации электролитов. — Антиоксиданты и гепатопротекторы для защиты печени. — Спазмолитики для снятия болевого синдрома. — Противорвотные препараты при тошноте.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru
Профессиональная подготовка — это не формальность, а ключ к безопасной и эффективной процедуре. Врач собирает подробный анамнез, уточняет длительность и характер употребления, фиксирует соматические жалобы, анализирует текущие препараты (в том числе безрецептурные), измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости назначает ЭКГ и лабораторные тесты. Если есть выраженная интоксикация, бессонница, тремор, скачки давления — стартуют с детокса и стабилизации: корректируют водно-электролитный баланс, снижают тревогу, нормализуют сон. Параллельно специалист объясняет механику методик кодирования, вероятные ощущения после процедуры, ограничения по нагрузкам, правила безопасного поведения в первые недели и алгоритм действий на случай усиления тяги. Подготовительный этап снимает неопределённость, уменьшает тревогу и повышает приверженность: человек понимает, что будет происходить и как оценивать улучшение.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]анонимное кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
azino 777 Azino 777 – это феномен, который заслуживает внимания исследователей онлайн-гемблинга. Его популярность, несмотря на критику и негативные отзывы, говорит о том, что в обществе существует потребность в азартных развлечениях. Важно, чтобы эта потребность удовлетворялась ответственно и осознанно, с пониманием рисков и последствий.
каких обьяснений? пришли, проверили, все что нашли изъяли. Устроили проверку в определенный день все что нашли арестовали, и мы не виноваты в этом. https://kitchenremodelinghouston.org люди которые делают заказы через ВК по меньшей мере идиоты. Особенно когда ИМ самим что то предлагают.черт возьми, вот сейчас оформляю AM2233 и решил заглянуть сюда.
Срочная наркологическая помощь — это не «универсальная капельница», а управляемый клинический процесс, где каждое действие проверяется измеримыми маркерами и выполняется в правильной последовательности. В наркологической клинике «ВолгаМед Альтернатива» маршрут выстроен вокруг принципа минимально достаточных вмешательств: сначала безопасный старт и телескрининг, затем очный осмотр с выбором контура инфузии и, только после теста переносимости, — основная терапия. Такой подход уменьшает реактивность организма, снижает риск побочных ощущений и делает результат предсказуемым для пациента и близких. Команда работает круглосуточно, выезжает на немаркированном транспорте, общение ведётся через одного доверенного человека, а документы оформляются в нейтральной терминологии без стигматизирующих формулировок.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-kazani16.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому казань[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ДонМед Резонанс» — это круглосуточный комплекс координированной помощи, где диагностика, инфузионная терапия, психообразование и поддержка семьи соединены в единую «дорожную карту». Мы работаем по принципу минимально достаточных вмешательств: каждый шаг имеет цель, измеримый маркер и заранее обозначенное «окно оценки». Такой подход убирает полипрагмазию, снижает риск нежелательных реакций и делает траекторию лечения предсказуемой — пациент не «получает процедуры», а видит, как цели достигаются и какие модули выключаются, когда они сделали своё дело. Круглосуточный режим позволяет внимательно сопровождать самые чувствительные интервалы — первую ночь, утренний период после детоксикации и момент возвращения к бытовой активности.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Детокс — это не универсальный раствор «от всего», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восполняем жидкость, корректируем электролиты, поддерживаем функции печени, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночному сну. Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма — нет гонки за моментальным «оглушением» симптома ценой побочных эффектов и вечерних откатов. После купирования острой фазы пациент получает понятные правила на 48–72 часа: вода порциями, лёгкая еда по расписанию, «тихий режим» перед сном, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликтные разговоры, критерии связи с врачом. Мы отдельно объясняем, что делать в «тёмные часы» — когда повышается тревожность и усиливается тяга: короткая прогулка рядом с домом, тёплый душ, дыхательные практики, контакт с «своим» человеком, отключение экранов. Такие простые действия бесплатны, но именно они удерживают медицинский эффект и переводят состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]pomoshch-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза детоксикации, во время которой современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом. Этот этап помогает быстро снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальные обменные процессы и нормализовать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Wow, is a super informative resource.
https://www.westwoodangp.org/gallery/dscf4249-1/
Apartment Renovation Repair Guide
мелбет промокод Мелбет промокод – это волшебный ключ, открывающий двери в мир увеличенных бонусов и более выгодных условий для ставок. Это возможность начать игру с преимуществом, увеличить свой первый депозит и получить фрибеты для тестирования различных стратегий. Промокод – это подарок, который дарит Мелбет своим новым и постоянным пользователям, позволяя им наслаждаться игрой в полной мере.
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Ремонт компактных машин Candy. Смарт-диагностика, устранение ошибок E02, E03. Ремонт платы управления.Ремонт стиральных машин Whirlpool Алматы Комплексная диагностика стиральной машины. Точное определение неисправности: износ щеток двигателя, сбой программатора, засор сливной системы или дефект ТЭНа. При заказе ремонта диагностика проводится бесплатно. Мы озвучиваем точную смету до начала работ. Экономьте время и деньги с профессионалами. Ремонт стиральных машин недорого Алматы
Есть, но пока что временно не работает. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки да это будет полная:ass:.Ну я надеюсь все будет хорошо.тогда так вышло иза того что это остатки товара из серии мн – 001.Уверен такой жопы больше не будетЖалко конечно что убрали покупку от грамма
Критерий
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-arkhangelsk0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь архангельск[/url]
I got this site from my buddy who told me concerning this website and at the moment this time I am visiting this website and reading very informative posts at this place.
Детокс — это не разовая процедура, а управляемый этап со своими задачами: снизить токсическую нагрузку, выровнять жизненно важные показатели, вернуть управляемость сну и самочувствию. Мы подбираем инфузии по показаниям, корректируем электролитный баланс, защищаем печёночные функции, снимаем тремор и вегетативные проявления. Следующая фаза — стабилизация: на этом этапе врач закрывает дефициты, уточняет схемы, выравнивает день и ночь, даёт понятные рекомендации на ближайшие 72 часа. Важно, что пациент не «теряется» после первого улучшения: заранее назначены точки связи, прописаны «красные флажки» и шаги, как действовать при любом из них. Такой порядок снижает вероятность рецидива, потому что вместо импровизации появляются готовые ответы на типичные сложности первых недель.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Такая комбинация препаратов обеспечивает комплексное воздействие на организм и способствует постепенному восстановлению физического и психологического состояния пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
материалы по seo [url=https://seo-blog8.ru/]seo-blog8.ru[/url] .
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://ohnempu.com/urteil-zum-thema-eu-fuehrerschein-nach-sperrfrist
Наша задача — не ограничиться «одной капельницей», а провести пациента через связанный маршрут: купирование острых симптомов, стабилизация, профилактика срывов и поведенческая поддержка. На выезде врач оценивает давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости снимает ЭКГ, подбирает инфузионные схемы и корректирует тревогу, тремор, нарушение сна. Если состояние нестабильно, организуем стационар: под наблюдением легче предупреждать осложнения и быстро корректировать назначенные дозы. Когда острые проявления уходят, настраиваем режим сна, питания и гидратации, формируем план «сложных часов» и алгоритм раннего реагирования на тягу. Психотерапевтические сессии усиливают контроль над поведением, а семейные консультации помогают близким действовать согласованно, не усиливая зависимое поведение случайными ошибками вроде «спасательства» и скрытия последствий употребления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva99.ru/]наркологическая больница москвы[/url]
Во время лечения фиксируются все жизненные показатели пациента. При необходимости проводится экспресс-анализ крови и ЭКГ. Ниже представлена таблица, показывающая, какие параметры контролируются и по каким признакам оценивается стабилизация состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому тюмень[/url]
Мытищи дают плюсы домашнего формата: меньше логистики, приватнее, выше приверженность режиму. Если показатели устойчивы и нет признаков угрозы осложнений (упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации, резких «качелей» АД/пульса, риска судорог), старт на дому или амбулаторно — рациональное решение. Но когда состояние «по краю», честнее и на дистанции дешевле сутки–двое стационара под круглосуточным наблюдением: проще дозировать препараты, вовремя закрывать дефициты, добиться первого ровного сна и не «разбрасываться» экстренными ночными выездами. Формат выбирается не «по желанию», а по безопасности здесь и сейчас; при этом конфиденциальность сохранена в любом сценарии — немаркированные визиты, разнесённые приёмы, доступ к данным по ролям.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi9.ru
Клиника ориентирована на клиническую достаточность: никаких процедур «для галочки», только то, что подтверждено показаниями. С первого контакта дежурный врач уточняет анамнез, лекарства, аллергии, оценивает риски сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, степень обезвоживания, уровень тревоги и качества сна. Если состояние позволяет, подготовка к кодированию проводится амбулаторно или на дому; при нестабильных показателях предлагается короткий стационар для безопасной стабилизации. Важна анонимность — в расписании используются шифры, доступ к данным разграничен, информирование родственников происходит только по согласию пациента. Организация процесса учитывает ритм мегаполиса: гибкие слоты в будни и выходные, выездные бригады, быстрый перевод из домашнего формата в стационар при необходимости. Финансовые условия проговариваются заранее, чтобы исключить скрытые позиции и дать человеку возможность планировать бюджет без догадок.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]сколько стоит кодирование от алкоголизма в Москве[/url]
Такая структура обеспечивает непрерывность медицинской помощи и повышает эффективность терапии за счёт комплексного воздействия на организм и психику пациента.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-chelyabinske16.ru/oblastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-chelyabinsk/
Процесс терапии в клинике построен по поэтапной схеме, включающей:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма архангельск.[/url]
материалы по seo [url=https://seo-blog12.ru/]материалы по seo[/url] .
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Это ещё не всё… – https://purvadesai.com/a-guide-to-find-your-perfect-customer
Обратите внимание на дату регистрации топик стартера и на регистрацию всех довольных пользователей. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки _Elf_ тебе сколько лет интересно?У тебя был единичный случай по твоим словам товар-фуфло.репутация у тебя “0”Требуешь вернуть денег, ты же понимаешь что тебе их не вернут.Вывод-ПРОВОКАЦИЯУ меня была, проси того кто продал все перепроверять- люди могут ошибаться !
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Близкие — ключевой ресурс, если действуют согласованно. Мы просим сфокусироваться на среде и режиме: тише, темнее, теплее; вода и лёгкая еда «по часам»; отсутствие «разборов» и проверок «на прочность» в первые дни. Полезно заранее договориться о коротких нейтральных сигналах — как понять, что помощь нужна, а когда лучше не вмешиваться. Такие простые правила бесплатны, но они стабилизируют поведение и убирают потребность в экстренных визитах по ночам. Когда дом перестаёт быть источником шума, медицинская часть остаётся узкой, а результат — устойчивым.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/]капельница вывод от запоя[/url]
Аналитика маркетплейсов Аналитика продаж маркетплейсов – это более глубокий уровень анализа, учитывающий специфику онлайн-торговли. Она позволяет определить наиболее прибыльные товары, оценить эффективность рекламных кампаний и выявить возможности для масштабирования бизнеса.
Первый шаг — короткое, но предметное интервью: длительность употребления, сопутствующие диагнозы, текущие препараты и аллергии. Врач фиксирует давление, пульс, сатурацию, при необходимости делает экспресс-ЭКГ и неврологический скрининг. Далее объясняет логику вмешательств: зачем именно такая инфузия, чего ожидать через 30–60 минут, какие ощущения нормальны и какие потребуют связи. Мы избегаем «оглушающих» седативов, чтобы не получить вечерний откат и побочные эффекты — дозировки подбираются узко, по реакции организма. После капельницы специалист ещё раз проверяет показатели, оставляет письменные рекомендации, договаривается об окне контроля и критериях повторного визита. Вечер строится вокруг сна: затемнение, тишина, ранний отбой, вода порциями, лёгкая еда «по силам», минимум экранов и разговорных конфликтов. На таком фоне исчезают «качели» между днём и ночью, а эффект инфузий не «сгорает» к следующему вечеру.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk9.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-stoimost-v-podolske
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя часто сопровождается выраженными симптомами абстиненции: тремор, тахикардия, повышенное давление, беспокойство. В клинике «Северная Звезда» для детоксикации применяется инфузионная терапия с балансированными растворами, содержащими:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru
— Растворы с глюкозой и витаминами для коррекции энергетического обмена. — Минеральные комплексы для нормализации электролитов. — Антиоксиданты и гепатопротекторы для защиты печени. — Спазмолитики для снятия болевого синдрома. — Противорвотные препараты при тошноте.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм архангельск[/url]
«НоваМед Центр» строит лечение как управляемую последовательность шагов, а не набор эпизодических процедур. На входе мы фиксируем исходные риски: длительность употребления, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, анамнез кодирований и срывов, показатели давления, пульса, сатурации, уровень сна и тревоги. Это позволяет выбрать безопасную точку входа и задать логичную траекторию: от детокса к стабилизации, затем к поведенческим изменениям и поддержанию ремиссии. Такая структура особенно важна при высокой нагрузке и дефиците времени: когда пациент и семья понимают, что будет через час, сутки и неделю, снижается тревога и исчезают импульсивные «проверки себя», из-за которых обычно рушатся результаты. Мы придерживаемся принципа клинической достаточности: только те вмешательства, которые нужны по состоянию сегодня, без «украшений ради прайса». Чёткие правила на 48–72 часа, согласованные окна связи, понятные «красные флажки» для повторного контакта превращают лечение в прогнозируемый маршрут, а не в череду надежд и разочарований. В итоге человек быстрее возвращает контроль над самочувствием, а близкие получают опору вместо бесконечных ночных «дежурств».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva999.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve[/url]
Интерактивные панели оптом Алматы Аренда интерактивной панели: Прокат оборудования на выставки и конференции. Доставка, монтаж и техподдержка.
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма[/url]
Врач самостоятельно оценивает тяжесть интоксикации и назначает необходимый курс инфузий, физиопроцедур и приём препаратов. Варианты терапии включают детокс-комплекс, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и витаминотерапию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru/
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tyumen-otzyvy/
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма мурманск.[/url]
Если состояние «ходит по краю», сутки–двое под наблюдением нередко короче и дешевле серии ночных вызовов. В стационаре «АлкоМед Балашиха» организованы «тихие коридоры», нет общих очередей, а внимание распределено волнами: утро — оценка и инфузии, день — контроль динамики и коррекция доз, ночь — условия для полноценного сна и готовность быстро отреагировать при отклонениях. За этот срок удаётся «снять остроту», выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тремор, закрыть дефициты и безопасно перейти к амбулаторному формату. Приватность и уважение к границам сохраняются так же, как и при домашнем старте, — это убирает страх «быть узнанным» и повышает приверженность плану.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-balashiha/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru
Детокс — это не универсальный раствор «от всего», а набор целевых вмешательств. Мы восполняем жидкость, корректируем электролиты, поддерживаем функции печени, мягко снижаем тремор и тревогу, готовим нервную систему к ночному сну. Каждая доза сверяется с реакцией организма — нет гонки за моментальным «оглушением» симптома ценой побочных эффектов и вечерних откатов. После купирования острой фазы пациент получает понятные правила на 48–72 часа: вода порциями, лёгкая еда по расписанию, «тихий режим» перед сном, запрет на «подвиги» и конфликтные разговоры, критерии связи с врачом. Мы отдельно объясняем, что делать в «тёмные часы» — когда повышается тревожность и усиливается тяга: короткая прогулка рядом с домом, тёплый душ, дыхательные практики, контакт с «своим» человеком, отключение экранов. Такие простые действия бесплатны, но именно они удерживают медицинский эффект и переводят состояние в предсказуемую стабилизацию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo-balashiha[/url]
краби из екатеринбурга краби куала лумпур
Домашний маршрут выбирают, когда показатели стабильны и нет признаков тяжёлой соматики или спутанности сознания. Преимущество в сочетании скорости, приватности и приверженности: знакомая среда снижает стресс, а отсутствие переездов экономит силы. Врач «МедТоники» приезжает без маркировки, привозит мониторинг и расходные материалы, подбирает инфузии по состоянию, помогает восстановить режим сна и гидратации, даёт рекомендации по питанию и правила на 48–72 часа. Отдельный блок — работа с тревогой и тремором: корректируется медикаментозная поддержка, обсуждаются простые поведенческие техники, чтобы снизить вероятность импульсивных решений вечером. Домашний формат не подменяет наблюдение: назначаются точки связи, врач объясняет, когда нужен повторный визит, а когда достаточно телефонной коррекции. Для Москвы такой сценарий удобен ещё и тем, что его проще встроить в плотный график, не выпадая из рабочих и семейных ролей и не провоцируя лишних вопросов у окружающих.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]вывод из запоя москва[/url]
заказала в этом магазе сувениров:), посыль пришел на 3ий день, продукты качеством вкусны Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Но могу сказать что на данный момент проблемы с отправкой у магазина! в среду оплатил и сказали в четверг будет отправка, но увы ее нет! такое в первый раз замечаю от такого магазина! будем ждать!Дружище как все прошло?)) забрал своё??? А то написал неделю назад и тишина))) если забрал сколько шло по времени? напиши нам а то на последних страницах сдесь какой то кипишь нездоровый…(
Мы не подгоняем всех под единый сценарий. Если состояние устойчивое, нет упорной рвоты, высокой температуры, выраженной дезориентации и резких скачков давления и пульса — рационален домашний старт: приватно, быстрее и без лишних переездов. Врач приедет без маркировки, проведёт осмотр, запустит инфузионную терапию по показаниям, оставит письменные рекомендации и «красные флажки». Если же есть признаки угрозы осложнений — обезвоживание, аритмии, риск судорог, боли за грудиной или в животе, лихорадка, спутанность сознания, тяжёлая соматика — мы честно предлагаем короткую стационарную стабилизацию на 24–48 часов. Под круглосуточным наблюдением проще корректировать схемы, вовремя закрывать дефициты, защитить сон и быстрее вернуть управляемость поведению. В обоих форматах маршрут прозрачен: согласованные окна связи, фиксированные цели на ближайшие 72 часа и отсутствие «пакетов ради прайса». Благодаря этому решения принимаются спокойно, без угадываний и эмоциональных раскачек, которые обычно ломают прогресс и удорожают лечение.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-balashiha9.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Осмотр > мониторинг > инфузии по показаниям > план вечера и ночи > письменные рекомендации > окно связи на следующий день. Эта линия делает поведение предсказуемым, а значит — безопасным.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva99.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-vyzov-narkologa-kapelnica[/url]
продвижение сайтов по трафику [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru/]продвижение сайтов по трафику[/url] .
Маршрут выстроен прозрачно. Сначала идёт короткое предметное интервью — только то, что меняет тактику «сегодня»: длительность запоя, принятые лекарства (включая «самолечение»), аллергии, хронические диагнозы, количество ночей без сна. Затем — объективные показатели (АД/пульс/сатурация/температура), оценка тремора и уровня тревоги; при показаниях проводится экспресс-ЭКГ и базовый неврологический скрининг. После этого врач объясняет, какие компоненты войдут в инфузию и почему: регидратация для восстановления объёма циркулирующей жидкости, коррекция электролитов, печёночная поддержка, при необходимости — гастропротекция и противорвотные; мягкая анксиолитическая коррекция — строго по показаниям. Мы принципиально избегаем «универсальных сильных смесей» и «оглушающих» дозировок: они дают дневной «блеск», но почти всегда провоцируют вечерний откат, ухудшение сна и рост рисков. Во время процедуры пациент и семья получают понятные письменные правила на 48–72 часа: вода и лёгкая еда «по часам», затемнение и тишина вечером, фиксированное время отбоя, «красные флажки» для связи и согласованное утреннее окно контроля. Такой сценарий убирает импровизации, снижает уровень конфликтов и помогает нервной системе перейти из режима тревоги в режим восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy9.ru/
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an extremely long comment but after I clicked submit
my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that
over again. Regardless, just wanted to say great blog!
Why people still use to read news papers when in this technological world the whole thing is presented on net?
Реабилитация после запоя в Химках. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]анонимный вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://muththamizh-kalasam.com/?p=593
Вау, какой крутой сайт Pin Up Casino! Благодарю!
https://gelukplanner.nl/volvo-v60-phev-plug-in-hybride-elektrische-auto/
Кодирование — это медицинский инструмент, который помогает закрепить трезвость, но сам по себе не является «волшебной кнопкой». Его задача — усилить внутреннюю мотивацию и создать физиологические и/или психологические условия, при которых срыв становится маловероятным. В «НаркологЭксперт» кодирование включают в структуру лечения: сначала купируются острые проявления, проводится детокс и стабилизация сна, давления и тревоги, затем — диагностика противопоказаний, подробное информирование, выбор методики и только после этого — сама процедура. Такой порядок снижает риски, повышает переносимость и делает результат предсказуемым. Важно, что любая техника подбирается индивидуально с учётом длительности употребления, анамнеза, сопутствующих заболеваний и рабочей нагрузки пациента, чтобы лечение органично вписалось в реальную жизнь и не сорвалось на первых же неделях.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-moskva9.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-moskve[/url]
Каждое утро на лайнере начиналось с красивых видов и ощущения спокойствия, отдых получился действительно качественным https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Детали по клику – https://wihr-ev.de/cropped-logo-jpg
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому в люберцах[/url]
melbet сайт Melbet регистрация – это первый шаг на пути к захватывающему миру ставок и азартных игр. Процесс регистрации прост и занимает всего несколько минут. Необходимо указать личные данные, выбрать валюту счета и подтвердить свой номер телефона или адрес электронной почты. После регистрации можно внести депозит и начать игру. Melbet предлагает различные способы пополнения и вывода средств, что делает процесс максимально удобным для игроков.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Балашихе — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход и комплексную терапию для каждого пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому балашиха[/url]
Магазин нормально работает?,а то некоторые говорят что не стоит обращаться в данный магазин для заказов!Фон или фок как твой ник правильно читаеться и пишиться ? отпишись нормальный магаз или нет ! https://uni-spec.ru Курьерка не может принять такое количество заказов – отказала вП.С.С. отвечать, цитировать это сообщение не нужно, удалю позже.
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя цена московская область[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Это ещё не всё… – https://mentesmuhely.hu/2024/08/03/kombucha-tea
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог омск[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Химках. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]помощь вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
краби тайланд фото avani koh lanta krabi resort
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/
Ahaa, its good conversation on the topic of this piece
of writing at this place at this weblog, I have
read all that, so at this time me also commenting at this place.
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому рязань[/url]
Аналитика продаж маркетплейсов Аналитика маркетплейсов бесплатно – это возможность для малого бизнеса начать свой путь к успеху на онлайн-площадках. Бесплатные инструменты предоставляют базовую информацию о продажах, трендах и конкурентах, позволяя оценить потенциал рынка и принять обоснованное решение о выходе на маркетплейсы.
Вывод из запоя в Тюмени — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к нарушению обмена веществ, обезвоживанию, сбоям в работе печени и сердца. В таких случаях требуется профессиональная помощь врача-нарколога, который подберёт оптимальный способ дезинтоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки. Современные методики позволяют провести вывод из запоя безопасно, эффективно и без осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар https://brelok54.ru Ну так ведь и не делаем не чотка . всё сразу .Какие у тебя претензии? ты провокатор и не более т.к. ты не дал даже номер заказа и не высказал притензию, к тому же за тебя мне уже написали в Личку, другие магазины..
В Воронеже клиника «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток. Это позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам, которые находятся в тяжёлом состоянии или не могут самостоятельно приехать в стационар. Медицинская бригада прибывает в течение 40–60 минут, не используя специализированный транспорт и форму, чтобы сохранить анонимность. Врач проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает давление, частоту дыхания, уровень сознания и насыщение кислородом, после чего назначает детоксикационную капельницу с контролем дозировки.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Люберцах. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр новокузнецк[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Люберцах. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя в люберцах[/url]
https://t.me/Asiapsi
Good site you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find excellent writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Химках.Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Да не магазин ровный несколько раз покупал у них, качество отличное. Только в аську бывает недостучатся. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Какой космос,тут бы от земли хоть оторватьсяСпасибо за отзывы приятные. Стараемся доставлять побыстрее)))
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Химках. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Капельница от запоя в Люберцах — быстрый и эффективный способ детоксикации. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру, помогая снять симптомы похмелья и вывести токсины из организма.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]после капельницы от запоя в люберцах[/url]
https://polimer-3d.ru/epoksidnye-poly
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
https://readtoto.net/u/3286244-1xbetfree
Капельница от запоя в стационаре — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов на дом балашиха[/url]
сколько лететь из дубая до краби араван краби
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Химках. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов химки[/url]
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике омск[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в рязани[/url]
Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа? Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Не взирая на то что заказ был оплачен в среду прошлой недели, а получил я его через 9(девять) дней, данный селлер заслужил мое доверие!товар появился? когда возобновите доставку по городам?
маркетинговые стратегии статьи [url=https://seo-blog12.ru/]маркетинговые стратегии статьи[/url] .
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Right here is the perfect webpage for anybody who would like
to find out about this topic. You know a whole lot its almost
hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa).
You definitely put a fresh spin on a topic which has been discussed for decades.
Great stuff, just great!
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в омске[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://web-beam.uz/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://hajjcompanions.com/understanding-the-different-types-of-hajj-packages-for-us-pilgrims
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог новокузнецк[/url]
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk/
раскрутка сайтов интернет [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajta-po-trafiku1.ru[/url] .
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Новокузнецке предоставляет профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под наблюдением опытных специалистов с применением современных медицинских методик. Основная цель работы клиники — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить психологическое равновесие пациента, вернуть мотивацию и способность жить без употребления веществ.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk/
Наша организация не несет ответственности за применение продукции не по назначению. Осуществляется тотальный контроль качества продукции. Чистота препаратов 99.2%. Исключено добавление примесей. Используется сырье очень высокого качества. https://quasar-media.ru Прошу обратить внимание на кидок со стороны магазина на ~50000 рублей в Украинской ветке.да можно
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
I think the admin of this site is genuinely working hard in favor of his site, as here every stuff is quality based material.
тут Получение ВНЖ Испании открывает широкие возможности для жизни, работы и путешествий по всей Европе, и именно здесь вы найдете актуальную информацию о необходимых документах и этапах оформления статуса резидента. Наш специализированный сайт подробно описывает различные программы, включая «золотую визу», ВНЖ для финансово независимых лиц и цифровых кочевников, предлагая пошаговые инструкции для каждого случая. Ознакомьтесь с полным перечнем актуальных требований тут, чтобы заранее подготовиться к подаче заявления и максимально повысить свои шансы на успешное одобрение со стороны испанских миграционных властей.
здесь Кроме того, мы предлагаем широкий спектр дополнительных услуг, включая помощь при ДТП, буксировку автомобиля, подвоз топлива и замену колеса. Мы стремимся предоставить нашим клиентам максимально удобный и комфортный сервис, чтобы решить любую проблему, возникшую на дороге. Наша задача – сделать процесс эвакуации максимально простым и быстрым для вас. Мы ценим ваше время и понимаем, что в экстренной ситуации важна каждая минута.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Химках. Предлагаем комфортные условия для пребывания пациентов и круглосуточный медицинский уход.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu lyubercy[/url]
Материал включает занимательные, но незначимые детали, которые трудно назвать важными, но они дополняют общую картину.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]деньги в долг[/url]
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя на дому в Люберцах. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
привет!!! не согласен долдны быть доступные магазины как https://bar-stavgorod.ru Почему ушли из РБ?Выходные же. В понедельник наврятли отправить успеют.
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]после капельницы от запоя в люберцах[/url]
I really like what you guys are usually up too.
This type of clever work and coverage! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve added you
guys to my blogroll.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://www.tunisipweb.com/developpement-web/sss1
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в уфе[/url]
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в Химках. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя химки[/url]
https://lars-klaening.23video.com/jean-nouvel-danish-radio-concert-hall
https://webhitlist.com/profiles/blogs/1xbet-app-promo-code-130-welcome-offer
сайт Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовой может быть ситуация, когда ваш автомобиль выходит из строя на дороге. Именно поэтому мы предлагаем круглосуточную поддержку и оперативный выезд эвакуатора в любой район Санкт-Петербурга. Наш парк спецтехники оснащен всем необходимым оборудованием для эвакуации автомобилей любого типа и размера, от малолитражек до внедорожников и микроавтобусов.
тут Мы понимаем, что процесс получения ВНЖ Испании может показаться сложным и запутанным, особенно если вы не владеете испанским языком или не знакомы с местным законодательством. Именно поэтому наша команда опытных юристов и консультантов готова оказать вам всестороннюю поддержку на каждом этапе оформления. Мы поможем вам собрать необходимые документы, правильно заполнить анкеты, подготовиться к собеседованию и избежать распространенных ошибок, которые могут привести к отказу.
драмчик, хаус… да не суть. Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки гаси кидалу по полной -25 маловато я добавлюу меня в подписи проверь
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
click here, read more, learn more, useful post, great article,
helpful guide, nice tips, thanks for sharing, very informative, good read, interesting post,
well explained, detailed guide, helpful information, great explanation, this helped a lot, valuable content, worth reading,
solid breakdown, informative article, recommended read, good insights, clear explanation, practical tips, well
written, excellent overview
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]скорая вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя на дому цена люберцы[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр саратов[/url]
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
I’ve been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or weblog posts in this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this site. Studying this info So i’m glad to express that I have a very excellent uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I most without a doubt will make certain to don?t overlook this website and provides it a glance regularly.
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр красноярск[/url]
Лечение основывается на комплексном подходе, позволяющем учесть особенности организма и стаж злоупотребления алкоголем. Обычно процедура состоит из нескольких этапов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в москве[/url]
https://drc.uog.edu.et/официальный-сайт-mostbet-uz-для-узбекистан-2
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Химках. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница в химках[/url][url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя недорого в химках[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены[/url]
Круиз подарил чувство полной перезагрузки, море, солнце, комфортный лайнер и высокий уровень сервиса сделали отдых незабываемым, https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Подробнее тут – https://ramlashomeservice.com/top-10-best-commercial-cleaning-services
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
мы и в скайп и в аське https://techdreamz.org Ты выдал мне комбоК продавцу можно смело обращаться, тут сделают все в лучшем виде!
Основные этапы включают:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому красноярск[/url]
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя тольятти[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Химках. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в химках[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde
запчасти на автомобили Byd Рынок автозапчастей для китайских автомобилей в последние годы демонстрирует впечатляющий рост, отражая возрастающую популярность этих машин на дорогах мира. Обеспечение бесперебойной работы и своевременного обслуживания таких марок, как Chery, Lifan, Geely, Great Wall, Haval, Howo, Foton, Faw, Baw, Byd, Changan, Dong Feng требует надёжной и оперативной поставки качественных запчастей. Наша компания специализируется на предоставлении именно таких решений.
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом уфа[/url]
На месте врач и медсестра собирают базовую линию: уровень сознания, дыхание, SpO?, температура, шкалы симптомов (тошнота/тремор/тревога 0–10), переносимость воды небольшими глотками. Далее формулируется рабочая гипотеза и включается минимально достаточный модуль с обозначенным «окном оценки»: 30–60 минут — для «окна питья», 60–120 минут — для стабилизации ЧСС/АД и дрожи, «первая ночь» — для сна и вечерней тревоги. Как только маркер достигнут, модуль выключается; нет эффекта — меняется одна переменная без «усиления всего сразу».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/anonimnaya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому волгоград[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в новокузнецке[/url]
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
сайт Кроме того, мы предлагаем индивидуальные консультации, в ходе которых мы детально анализируем вашу ситуацию и предлагаем оптимальный вариант получения ВНЖ, исходя из ваших финансовых возможностей, профессиональных навыков и личных обстоятельств. Мы также оказываем помощь в поиске недвижимости, открытии банковского счета и решении других вопросов, связанных с адаптацией к жизни в Испании.
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм новокузнецк[/url]
Клиника «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде оказывает помощь при алкогольной интоксикации как в условиях стационара, так и на дому. Врачи готовы выехать к пациенту в течение 40–60 минут после обращения, привозя с собой всё необходимое оборудование для проведения инфузионной терапии. Такая оперативность позволяет снизить риск осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в первые часы лечения. Для пациентов, нуждающихся в круглосуточном наблюдении, предусмотрены комфортабельные палаты с постоянным медицинским контролем.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в волгограде[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
купить дубликат аттестата за 9 класс [url=www.r-diploma30.ru/]купить дубликат аттестата за 9 класс[/url] .
Вот по количеству норм, но кач…. Это то что осталось после меня и моих проб Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Так может не ждать у моря погода, а взять и самому написать менеджеру в аську/почту и получить уже эти реквизиты?Все вопросы к представителю.
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Узнать больше – http://
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в красноярске[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Во время лечения фиксируются все жизненные показатели пациента. При необходимости проводится экспресс-анализ крови и ЭКГ. Ниже представлена таблица, показывающая, какие параметры контролируются и по каким признакам оценивается стабилизация состояния.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тюмени — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к нарушению обмена веществ, обезвоживанию, сбоям в работе печени и сердца. В таких случаях требуется профессиональная помощь врача-нарколога, который подберёт оптимальный способ дезинтоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки. Современные методики позволяют провести вывод из запоя безопасно, эффективно и без осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в тюмени[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена химки[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Люберцах. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2400 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
Great work! This is the type of information that are meant to be shared around the web. Disgrace on Google for not positioning this post upper! Come on over and consult with my website . Thanks =)
Все работает Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Джи спокойно 20-ого числа 😉 Потом вот только как получать будешь…?добрый день как связаться с продавцом и не попасть на фейка?
https://evakuatorhelp.ru/ Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовой может быть ситуация, когда ваш автомобиль выходит из строя на дороге. Именно поэтому мы предлагаем круглосуточную поддержку и оперативный выезд эвакуатора в любой район Санкт-Петербурга. Наш парк спецтехники оснащен всем необходимым оборудованием для эвакуации автомобилей любого типа и размера, от малолитражек до внедорожников и микроавтобусов.
Не менее опасны и психоэмоциональные нарушения, связанные с абстинентным синдромом: тревога, чувство паники, галлюцинации, нарушения координации. В тяжёлых случаях может развиться алкогольный делирий (белая горячка) со спутанностью сознания, бредовыми идеями и приступами агрессии. Самостоятельный резкий отказ от спиртного в этом состоянии чреват непредсказуемыми осложнениями вплоть до судорог и комы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в москве[/url]
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Люберцах. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2400 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]posle-kapelniczy-ot-zapoya lyubercy[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в саратове[/url]
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Все отлично, безумно рад что доверился данному магазину https://powerofmagic.ru Всегда на высоте)смотря каким реагентом будешь бадяжить
В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» применяются разные методы кодирования, позволяющие подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пациента. Выбор зависит от медицинских показаний, психологической готовности и длительности ремиссии. В таблице ниже представлены основные методики, их особенности и преимущества.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена адреса в волгограде[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr
Лайнер оказался настоящим плавучим курортом, бассейны, спа, шоу программы и отличное обслуживание https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
запчасти Dong Feng Рынок автозапчастей для китайских автомобилей в последние годы демонстрирует впечатляющий рост, отражая возрастающую популярность этих машин на дорогах мира. Обеспечение бесперебойной работы и своевременного обслуживания таких марок, как Chery, Lifan, Geely, Great Wall, Haval, Howo, Foton, Faw, Baw, Byd, Changan, Dong Feng требует надёжной и оперативной поставки качественных запчастей. Наша компания специализируется на предоставлении именно таких решений.
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your sites
really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and
bookmark your site to come back down the road. Many thanks
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево волгоград[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://festivalpavart.fr/2019/05/30/bientot-des-interviews-videos-des-artistes-du-pavart-2019
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have
discovered It absolutely helpful and it has helped me out loads.
I’m hoping to give a contribution & assist different customers like its helped
me. Good job.
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя на дому в Люберцах. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врач на дом капельница от запоя в люберцах[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://naklejto.com/product/hoodie-with-pocket
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в стационаре Балашихи. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 3?500??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
привествую мои друзья форумчане , не Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки расширяться собираетесь?1-й раз все было почти супер только менагер немного напутал ( но потом все доотправили )
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Химках. Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя клиника химки[/url]
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]после капельницы от запоя в люберцах[/url]
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and interesting, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy that I stumbled across this during my search for something regarding this.
тут Кроме того, мы предлагаем индивидуальные консультации, в ходе которых мы детально анализируем вашу ситуацию и предлагаем оптимальный вариант получения ВНЖ, исходя из ваших финансовых возможностей, профессиональных навыков и личных обстоятельств. Мы также оказываем помощь в поиске недвижимости, открытии банковского счета и решении других вопросов, связанных с адаптацией к жизни в Испании.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://botafogocondominio.com/2022/09/22/hello-world
Для тех, кто предпочитает лечение в условиях стационара, предусмотрены комфортные палаты, медицинский контроль 24/7 и возможность консультаций с психотерапевтом. Врачи клиники применяют комплексные методы, направленные не только на снятие симптомов, но и на устранение причин зависимости.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи в тольятти[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
пляж ао нанг краби краби танец
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Химках. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя дешево химки[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить больше информации – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в воронеже[/url]
Продукт получен, доставка по Москве заняла примерно сутки. Проверить качество пока не могу, но надеюсь приемлемое. https://lastochka-sport.ru KEY я так понял ты сделал заказ узнал сумму которую надо оплатить ,оплатил а когда вернулся сумма стала выше на сотку????КАК ОБЕЩЯЛ ОПЕРАТОР ТАК ВСЕ И СДЕЛАЛ ОДИН В ОДИН !!!!
When some one searches for his essential thing, so he/she
wants to be available that in detail, so that thing is maintained over here.
Greetings from California! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break.
I really like the information you provide here and can’t wait to take
a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how fast your blog loaded on my phone
.. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, amazing blog!
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены уфа[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]vyzvat-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya lyubercy[/url]
https://pentvars.edu.gh/puc-welcomes-first-year-students-into-the-2019-2020-academic-year/
https://pixabay.com/users/53959109/
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Круиз стал отличным вариантом для романтического путешествия, красивые закаты, уютная атмосфера и высокий уровень обслуживания, круиз по Дубаю
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
Респект Магазу Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Всем привет !!!?И духовной отсутствие пищи
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
В Волгограде медицинская клиника «Трезвая Линия Волгоград» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с острым алкогольным отравлением или затяжным запоем. Врачи выезжают на дом, в гостиницу или принимают пациентов в стационаре. Каждое вмешательство начинается с оценки состояния — измерения давления, пульса, насыщения кислородом, уровня интоксикации и дехидратации. Далее подбирается оптимальный состав капельницы, направленный на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, поддержку печени и снижение тревожности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Химках. Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в химках[/url]
Одним из ключевых направлений работы клиники является проведение инфузионных процедур. Капельницы позволяют вывести токсины, нормализовать давление и улучшить общее состояние пациента. Подбор препаратов проводится индивидуально, с учётом физического состояния, возраста и стадии зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Узнайте всю правду – https://homesolarsessions.com/solar-energy-near-me
патонг краби расстояние водопады на краби
Keep this going please, great job!
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Узнайте всю правду – http://www.greatdynamics.net/2020/11/16/tech-firms-support-huawei-restriction-balk-at-cost
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
сайт Наша команда экспертов всегда готова ответить на ваши вопросы и предоставить консультации по всем аспектам жизни и работы в Испании. Мы поможем вам разобраться в нюансах испанского законодательства, системы здравоохранения и образования. Мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши личные обстоятельства и потребности.
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Все прошло идеально от посадки до возвращения, лайнер из Дубая современный, чистый, с отличной кухней и внимательным персоналом: https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
I just couldn’t leave your web site before suggesting that I actually loved the standard info an individual supply in your guests?
Is going to be back incessantly to investigate cross-check new posts
Для жителей Красноярска организованы два конфиденциальных пути. Первый — немаркированный выезд бригады на дом с заранее согласованными порогами связи. Второй — «тихий вход» в клинику через отдельную дверь, где приём проходит без очередей и «коридорных» разговоров. На первичном звонке администратор уточняет только клинически значимые факторы: частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспускания, ЧСС/АД в покое, эпизоды спутанности, актуальные лекарства и аллергии. Биографические подробности и лишние вопросы не задаются — мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Если вы ищите надежную [url=https://best-laser-correction.ru/]рейтинг клиник по коррекции зрения в москве[/url], обратите внимание на передовые технологии и доступные цены в нашей клинике.
Здоровье глаз играет ключевую роль в повседневной жизни.
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в уфе[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Новокузнецке предоставляет профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под наблюдением опытных специалистов с применением современных медицинских методик. Основная цель работы клиники — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить психологическое равновесие пациента, вернуть мотивацию и способность жить без употребления веществ.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог новокузнецк[/url]
Лайнер из Китая оказался настоящим плавучим курортом, много развлечений, ресторанов и зон отдыха: https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Ровный и Стабильный… Купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, гашиш, марихуану, шишки Не прогадал) Искупался, доставили пиццу, вискарика дернул со льдом…Спасибо всем сотрудникам Chemical-mix.com
https://vc.ru/migration/1335599-vse-vidy-vnzh-ispanii-kak-poluchit-spisok-dokumentov-i-trebovaniya-dlya-pereezda-na-pmzh-razberem-usloviya-i-osnovaniya-dlya-polucheniya-vida-na-zhitelstvo Но виза – это только начало. Мы также предоставляем комплексную поддержку по адаптации в Испании. От помощи в поиске жилья и открытии банковского счета до организации курсов испанского языка и знакомства с местной культурой. Мы стремимся, чтобы ваш переезд был максимально комфортным и беспроблемным.
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в красноярске[/url]
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде предоставляет профессиональную медицинскую помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Основная цель специалистов — не просто устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту вернуть внутреннее равновесие, здоровье и контроль над жизнью. В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, доказавшие свою эффективность в практике отечественной и мировой наркологии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
софитель краби тайланд краби крабонг
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс чат[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Thank you for any other magnificent article. The place else may just anyone get that kind of information in such an ideal approach of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the look for such information.
В Воронеже команда «ВоронМед Профи» работает по принципу быстрой медицинской реакции — помощь оказывается независимо от времени суток и дня недели. Все выезды выполняются анонимно, без спецтранспорта и медицинской формы. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, что исключает ненужное внимание соседей и посторонних. В ходе осмотра специалист измеряет давление, пульс, температуру, оценивает уровень интоксикации и определяет степень обезвоживания. На основе полученных данных подбирается состав капельницы, который подаётся медленно и безопасно под контролем врача.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод воронеж[/url]
rc88.tech
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov
Вывод из запоя в Химках — профессиональная помощь на дому. Наши опытные наркологи приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния и вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно рязань[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя цена люберцы[/url]
Если вас интересует [url=https://moseyes.ru/stati/keratokonus-diagnostika/]кератоконус что это[/url], это заболевание характеризуется прогрессирующей деформацией роговицы глаза, что может существенно нарушить качество зрения.
Кератоконус – это сложное глазное состояние, приводящее к патологической изогнутости роговицы. Это заболевание может привести к значительному снижению зрения и требует тщательного лечения. Кератоконус может проявиться во взаимодействии с другими факторами, такими как ношение контактных линз. Симптомы могут включать размытое зрение, чувствительность к свету и снижение зрения при ночной езде.
Кератоконус является довольно распространенным заболеванием, которое может быть диагностировано с помощью специальных тестов. Ранняя диагностика имеет решающее значение для эффективного лечения. Кератоконус требует своевременного лечения, чтобы предотвратить ухудшение состояния. Регулярные осмотры у офтальмолога помогают обнаружить заболевание на ранней стадии.
Кератоконус thu?ng??ается в виде постепенного ухудшения зрения, которое не может быть исправлено с помощью корректирующих линз. Диагностика кератоконуса включает в себя ряд специальных тестов. Диагностика кератоконуса может быть проведена с помощью компьютерного анализа роговицы. Ранняя диагностика позволяет начать лечение и предотвратить дальнейшее ухудшение зрения.
Кератоконус может быть диагностирован с помощью неинвазивных методов, таких как сканирование роговицы. Тщательная диагностика имеет решающее значение для определения степени кератоконуса и выбора оптимального лечения. Кератоконус может быть лечен с помощью различных методов, включая ношение специальных контактных линз и хирургическое вмешательство. Выбор метода лечения зависит от степени заболевания и индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Кератоконус может быть лечен с помощью различных нехирургических и хирургических методов. Одним из наиболее эффективных методов лечения является ношение газопроницаемых контактных линз. Газопроницаемые линзы позволяют регулировать форму роговицы и улучшать качество зрения. Кроме того, могут быть применены хирургические методы, такие как имплантация коллагеновых кольцеобразных секций или трансплантация роговицы.
Кератоконус может быть лечен с помощью лазерной коррекции зрения или других современных хирургических методов. Целью лечения является достижение лучшего качества зрения и предотвращение дальнейшего прогрессирования заболевания. Регулярные осмотры у офтальмолога имеют решающее значение для контроля за состоянием роговицы и коррекции методов лечения. Своевременная коррекция методов лечения может помочь достичь лучших результатов и поддержать здоровье роговицы.
Прогноз кератоконуса может быть оптимистичным при ранней диагностике и своевременном лечении. В большинстве случаев, кератоконус можно эффективно лечить и улучшать качество зрения. Методы лечения кератоконуса постоянно совершенствуются, что позволяет добиться лучших результатов. Однако, важно помнить, что кератоконус – это хроническое заболевание, которое требует постоянного мониторинга и коррекции методов лечения.
Пациенты с кератоконусом должны быть осведомлены о важности регулярных осмотров для поддержания здоровья роговицы. Кроме того, пациентам рекомендуется соблюдать все рекомендации офтальмолога и использовать назначенные методы лечения. Соблюдение плана лечения имеет решающее значение для достижения лучших результатов и поддержания здоровья роговицы. Своевременная диагностика, эффективное лечение и постоянный мониторинг могут помочь пациентам с кератоконусом улучшить качество жизни и сохранить здоровье роговицы.
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя люберцы[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Детальнее – https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя в стационаре в балашихе[/url]
Конфиденциальность — это набор конкретных действий, а не декларация на сайте. Мы проектируем «невидимость» так, чтобы пациент мог спокойно принять помощь и не опасаться огласки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2290 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь москва[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в стационаре Балашихи. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 3 500 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница в балашихе[/url][url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя недорого в балашихе[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в рязани[/url]
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя недорого балашиха[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя цена город. московская область[/url]
Nice weblog here! Also your site rather a lot up very fast! What host are you the usage of? Can I am getting your associate link for your host? I want my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
https://pixabay.com/users/53967016/
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]после капельницы от запоя люберцы[/url]
https://topsitenet.com/profile/codepromo3445/1524767/
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1ASFizmLyQMk0mbNYfZ8yxXZrrPFjrS6n5wi4RK_GOBg/edit?usp=sharing
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Having a stylish appearance is crucial for making a good impression.
It helps express personality and boost self-esteem.
A coordinated look affects social perception.
In daily life, clothing can add confidence.
https://telegra.ph/Givenchy-12-25-2
A carefully curated wardrobe facilitate communication.
It is important to consider personal preferences and suitability for the occasion.
Fashion trends allow people to refresh their wardrobe.
Overall, dressing stylishly completes your personal image.
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//http://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru/
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог волгоград[/url]
Удобный и простой сайт с массой полезной информации по казино.
https://w3.fuji.com.tw/flqr.asp?lurl=olimp-casino-kazakhstan-bet.kz%2Fpayments
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]срочный вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
บทความนี้ น่าสนใจดี ครับ
ดิฉัน เคยติดตามเรื่องนี้จากหลายแหล่ง เนื้อหาในแนวเดียวกัน
สามารถอ่านได้ที่ รีวิว sa168vip ล่าสุด
น่าจะถูกใจใครหลายคน
เพราะให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึก
ขอบคุณที่แชร์
สิ่งที่มีคุณค่า นี้
จะรอติดตามเนื้อหาใหม่ๆ ต่อไป
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Стационарное лечение запоя в Химках. Предлагаем комфортные условия для пребывания пациентов и круглосуточный медицинский уход.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в химках[/url]
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому в химках[/url]
Mərc strategiyaları haqqında tövsiyələr çox faydalıdır.
https://www.rsstop10.com/directory/rss-submit-thankyou.php
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
А что дальше? – https://christiaensprefabbeton.be/foto-3
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Люберцах. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому люберцы[/url]
Круиз подарил возможность увидеть новые страны без утомительных перелетов, комфорт на борту на высоком уровне, https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://thenews21.com/maharashtra-man-sets-himself-ablaze-outside-vidhan-bhavan-in-mumbai
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Смотрите также… – https://njoyradio.gr/?p=8261
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого воронеж[/url]
Improve your Essex property with resin bound and resin-bonded emerging. Delivering enduring, low-maintenance, and slip-resistant driveways, Complete Surfacing Solutions incorporates custom colours, all-natural stone appearances, and seamless coatings. Our specialist group delivers dependable and fashionable surfacing solutions for homes, businesses, and social rooms, supplying sturdy end results that stand the examination of your time, https://www.fanficoverflow.com/profile/view/79821.
I am really grateful to the owner of this website who has shared this fantastic article at at this time.
Основные этапы включают:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника красноярск[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Люберцах. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2400 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя люберцы[/url]
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом воронеж[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://alazanes.net/seccion-out-28
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
В Новокузнецке команда «РеабКузбасс» организовала круглосуточный выезд наркологов, что позволяет оказывать помощь даже в сложных ситуациях. Пациенты часто обращаются после многодневного употребления алкоголя, когда нарушен сон, давление нестабильно, а организм истощён. В таких случаях врач выезжает в течение часа, проводит осмотр, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает оптимальную терапию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Люберцах. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]поставить капельницу от запоя в люберцах[/url]
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
Hey there! This post could not be written any better!
Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate!
He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this write-up to
him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому в волгограде[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://passionrealtygroup.com/2020/11/29/hello-world
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Саратов живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, протяжные магистрали, мостовые переезды. Мы учитываем это в логистике: выездные бригады «СаратовМед Профи» движутся по немаркированным маршрутам, приезжают в гражданской одежде, формируют на месте «тихую сцену» и только затем начинают клиническую часть. Если на предзвонке звучат «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность, неукротимая рвота, судороги — организуем перевод в стационар без пауз: место резервируем заранее, передислокация проходит конфиденциально.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Углубиться в тему – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]интим услуги[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница саратов[/url]
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice whilst you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account aided me a applicable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided vivid clear idea
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя в люберцах[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Полная информация здесь – https://mahoraize.wpxblog.jp/post-4187
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/pomoshh-narkozavisimym-tolyatti/
online casino minimum deposit
new casino sites
online roulette real money
пхукет краби отели погода на острове ланта таиланд
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в воронеже[/url]
https://unsplash.com/@melbetfree2
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Люберцах. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врач на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]запой нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://www.greatdynamics.net/2020/11/16/tech-firms-support-huawei-restriction-balk-at-cost
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя цена люберцы[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в волгограде[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Лечение запоя у женщин в Химках. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению женщин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Лайнер стал настоящим домом на время путешествия, все удобно и продумано: круизы из китая по азии
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Regards. An abundance of stuff.
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Это ещё не всё… – https://yoshihiroito.jp/solar-eclipse-152834_1280
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Узнать больше – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
Great online casino, excellent job! Appreciate it!
https://doverie42.ru/forum/go.php?url=aHR0cHM6Ly9jaGlja2VuLXJvYWQtdmVnYXMubmV0L3JlZ2lzdHJhdGlvbg
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Детальнее – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/[/url]
Лайнер из Китая оказался чистым, современным и очень хорошо обслуживаемым – https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
что привезти с краби краби это остров или материк
Bu platformanı bəyənirəm.
https://s.ubyt.es/lM4dJX
Hello to all, how is everything, I think every one is getting more from this web page, and your views are pleasant in support of new viewers.
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника волгоград[/url]
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма адрес в волгограде[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Узнайте всю правду – https://opzo.app/unlock-the-power-of-hr-efficiency-with-opzopeople
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://myanimelist.net/profile/knowmore34
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
Лечение запоя на дому в Люберцах. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя на дому цена люберцы[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov
Круизы из Китая оказались гораздо комфортнее, чем ожидали, каюты удобные, персонал внимательный, маршруты продуманные – https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде предоставляет профессиональную медицинскую помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Основная цель специалистов — не просто устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту вернуть внутреннее равновесие, здоровье и контроль над жизнью. В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, доказавшие свою эффективность в практике отечественной и мировой наркологии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograda/
Hello everybody, here every one is sharing these familiarity, thus it’s fastidious to read this weblog,
and I used to visit this weblog all the time.
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в волгограде[/url]
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before
but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking
and checking back often!
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике новокузнецк[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://latinloyalty.com/hello-world
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Химках. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Honestly discovered the Astronaut-style crash gameplay recently and it absolutely grabbed me, link https://crushtop.org . The concept feels basic: a astronaut goes forward while the coefficient increases, and players have to cash out before a explosion. Larger danger brings larger profit, which is why timing feels critical.
In the beginning I personally started small, mainly so I could learn the flow, but after several bets I realized the rhythm. This excitement feels insane each round, especially as that multiplier continues climbing. The layout looks minimalistic, nothing useful distracts, and everything runs perfectly.
I personally tried from mobile and it ran perfectly. Payments were quick, and that is important personally. I personally didn’t notice anything shady at all. In summary, the Astronaut crash game feels very exciting. When you enjoy quick multiplier games, it is worth checking out.
Only remember: bet responsibly.
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Саратов живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, протяжные магистрали, мостовые переезды. Мы учитываем это в логистике: выездные бригады «СаратовМед Профи» движутся по немаркированным маршрутам, приезжают в гражданской одежде, формируют на месте «тихую сцену» и только затем начинают клиническую часть. Если на предзвонке звучат «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность, неукротимая рвота, судороги — организуем перевод в стационар без пауз: место резервируем заранее, передислокация проходит конфиденциально.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Люберцах. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
орел и решка краби где находится краби в тайланде на карте
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого волгоград[/url]
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Детальнее – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь москве[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в стационаре Балашихи. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]помощь вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Definitely consider that that you said. Your favourite justification seemed to be at the internet the easiest thing to consider of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people think about concerns that they just do not know about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top as smartly as outlined out the entire thing with no need side-effects , folks can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thank you
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-staczionar/
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре рязань[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Amazing blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere?
A design like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog
jump out. Please let me know where you got your theme.
Kudos
Город с протяжёнными магистралями и разноскоростными районами требует особой организации маршрутов. Выездные бригады «ВолгаДок Медикал» работают в режиме 24/7, прибывают в гражданской одежде, избегают громких звонков и используют «немаркированные» подъезды. Перед приездом мы просим подготовить пространство: приглушить верхний свет, обеспечить приток свежего воздуха без сквозняков, подготовить ровную поверхность под укладку и удлинитель, перевести телефоны в «без уведомлений» с «белым списком» близких. Это позволяет в первые минуты сосредоточиться на клинике, а не на бытовых вопросах.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
Hey! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog.
Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very
techincal but I can figure things out pretty
quick. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m
not sure where to begin. Do you have any tips or suggestions?
Many thanks
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://finestpublicadjusters.com/feeling-stuck-in-business-get-business-help
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Люберцах. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов люберцы[/url]
My partner and I stumbled over here different web page and thought I should check things out.
I like what I see so now i’m following you.
Look forward to looking into your web page again.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
А что дальше? – https://reservationslunel.groupe-lentrepotes.fr/hello-world-2
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Kazino haqqında faydalı kontent üçün təşəkkürlər!
https://www.pipacastello.com/le-pipe-mie-figlie-intervista-a-franco-coppo/
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Открой скрытое – https://vuscafe.com.au/benefits-of-coffee-to-the-body
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Remarkable issues here. I’m very glad to peer your post. Thanks so much and I am taking a look forward to
touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Feel free to surf to my web site :: zenegovia01
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]врач вывод из запоя балашиха[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробности по ссылке – https://jasarahgroup.com/index.php/2023/01/27/site-oficial-de-apostas-at-the-online-cassino-zero-brasi-2
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре волгоград[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве — клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает экстренную помощь на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам в течение 30 минут и проведут необходимые процедуры для стабилизации состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]анонимная скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма волгоград[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu/
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя на дому цена в люберцах[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом воронеж[/url]
A person necessarily lend a hand to make seriously articles I’d state. That is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now? I amazed with the analysis you made to create this actual post amazing. Excellent task!
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Люберцах. Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2400 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя анонимно люберцы[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Люберцах. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
This article will help the internet visitors for building up new weblog or even a weblog from start to end.
Also visit my homepage :: zenegovia02
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the internet
the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly don’t know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Химках.Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя клиника химки[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в воронеже[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]частный нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom/
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в новокузнецке[/url]
I enjoy what you guys are usually up too. This type of clever work
and coverage! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll.
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Детальнее – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu moskva[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в саратове[/url]
Wygodna i logiczna strona z mnóstwem przydatnych informacji o kasynach.
https://jhptransport.co.uk/jhp-transport-named-scotlands-top-chilled-distributer-2018/
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в воронеже[/url]
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Люберцах. Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя люберцы[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-staczionar/
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя цена в балашихе[/url]
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something which I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Химках. Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно химки[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
плазменный стерилизатор [url=https://plazmennye-sterilizatory.ru/]плазменный стерилизатор[/url] .
внедрение и сопровождение 1с [url=https://1s-soprovozhdenie.ru/]1s-soprovozhdenie.ru[/url] .
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Люберцах. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя люберцы[/url]
I know this web site provides quality depending articles and additional stuff, is there any other web site which
provides such data in quality?
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu lyubercy[/url]
стерилизатор плазменный [url=https://plazmennyy-sterilizator.ru/]plazmennyy-sterilizator.ru[/url] .
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в волгограде[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Не менее опасны и психоэмоциональные нарушения, связанные с абстинентным синдромом: тревога, чувство паники, галлюцинации, нарушения координации. В тяжёлых случаях может развиться алкогольный делирий (белая горячка) со спутанностью сознания, бредовыми идеями и приступами агрессии. Самостоятельный резкий отказ от спиртного в этом состоянии чреват непредсказуемыми осложнениями вплоть до судорог и комы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя москва[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Химках. Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя клиника в химках[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике омск[/url]
Вывод из запоя в стационаре — безопасное и комфортное восстановление. В нашем стационаре созданы все условия для быстрого и эффективного вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]скорая вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя город. московская область[/url]
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]экспресс займ[/url]
Just joined!
I am pretty new around here and figured I would drop a line.
Lately I’ve been researching outdoor projects recently and found a few good ideas.
For those with expertise in this area, please hear your thoughts.
Cheers.
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя в люберцах[/url]
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм новокузнецк[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://tamy.me/hola-mundo
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://rollbol.com/blogs/2021861/Code-promo-1xBet-du-jour-2026-1X200BOX-Bonus-169000-XOF
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://tensyokuejentotonomenndanndezettainiyattehaikenaikoto.com
https://explorebookmarks.com/story20763369/1xbet-promo-code-bonus-code-best-offers-in-2026
Hello terrific blog! Does running a blog similar to this take a large amount of work? I’ve absolutely no understanding of coding however I had been hoping to start my own blog soon. Anyways, if you have any recommendations or techniques for new blog owners please share. I know this is off subject however I just wanted to ask. Thanks!
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally,
it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point.
You obviously know what youre talking about, why throw away
your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в новокузнецке[/url]
као лак или краби что лучше пхукет краби на карте
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti/
Основные этапы включают:
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Химках. Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь новокузнецк[/url]
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/fr-AF/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen/
Hello it’s me, I am also visiting this web site on a regular basis, this web page
is in fact nice and the viewers are in fact sharing fastidious thoughts.
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в стационаре Балашихи. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Люберцах. Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
купить аттестат за 11 классов в кемерово [url=http://www.r-diploma25.ru]купить аттестат за 11 классов в кемерово[/url] .
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Саратов живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, протяжные магистрали, мостовые переезды. Мы учитываем это в логистике: выездные бригады «СаратовМед Профи» движутся по немаркированным маршрутам, приезжают в гражданской одежде, формируют на месте «тихую сцену» и только затем начинают клиническую часть. Если на предзвонке звучат «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность, неукротимая рвота, судороги — организуем перевод в стационар без пауз: место резервируем заранее, передислокация проходит конфиденциально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника саратов[/url]
Основные этапы включают:
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
промокоды 1xbet на сегодня Активируйте промокод на https://prathamonline.com/js/pgs/?code_promo_175.html и заберите бонус до 32 500 рублей при регистрации для комфортной игры.
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Химках. Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
1xBet промокод 2026 Промокод 2025 года на https://prathamonline.com/js/pgs/?code_promo_175.html даёт бонус 100% до 32 500? для всех зарегистрированных пользователей.
What’s up to all, how is the whole thing,
I think every one is getting more from this site, and your views are pleasant designed for new viewers.
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Полная информация здесь – https://wavednet.com/2025/04/03/site-oficial-para-cassino-online-elizabeth-apostas-no-brasil
Hi, I do think this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it
😉 I will return once again since i have book-marked it.
Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you
be rich and continue to guide others.
Стационарное лечение запоя в Балашихе — эффективное решение для длительного запоя. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход и комплексную терапию для каждого пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha12.ru//]вывод из запоя в балашихе[/url]
краби форум погода краби таиланд на 14
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
This gave me the tools I had been hoping to find
1xBet промокод 2026 Промокод 2025 года на https://prathamonline.com/js/pgs/?code_promo_175.html даёт бонус 100% до 32 500 рублей для новых игроков.
I am really inspired along with your writing skills and also with the layout on your weblog. Is this a paid subject matter or did you customize it your self? Either way keep up the excellent high quality writing, it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
Реабилитация после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Terrific article! This is the kind of information that are meant to be shared across the
web. Disgrace on the search engines for now not positioning this
submit upper! Come on over and talk over with my web site .
Thank you =)
сопровождение 1с предприятие 8 [url=https://1s-soprovozhdenie.ru/]1s-soprovozhdenie.ru[/url] .
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
плазменные стерилизаторы [url=https://plazmennye-sterilizatory.ru/]плазменные стерилизаторы[/url] .
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимное кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
плазменные стерилизаторы [url=https://plazmennyy-sterilizator.ru/]плазменные стерилизаторы[/url] .
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
1хБет промокод на фриспины Воспользуйтесь бонус при регистрации на https://justinekeptcalmandwentvegan.com/wp-content/pages/1.html и заберите 32 500? + бонус 100%, чтобы получить максимальное преимущество.
Тысяча благодарностей за платформу kazino olimp — очень выручает!
http://gyeongshin.co.kr/kscn/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=892254
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в новокузнецке[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Открой скрытое – https://mehielinfo.net/municipale-2023-a-kong-ouattara-souleymane-candidat-pdci-il-y-a-pres-de-30-ans-que-le-pdci-rda-na-pas-presente-de-candidat-a-kong
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-novokuzneczk/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Very good post! We are linking to this great post on our
site. Keep up the good writing.
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Подробности по ссылке – https://forexcargodeals.com/calgary/hello-world
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя в люберцах[/url]
Город с протяжёнными магистралями и разноскоростными районами требует особой организации маршрутов. Выездные бригады «ВолгаДок Медикал» работают в режиме 24/7, прибывают в гражданской одежде, избегают громких звонков и используют «немаркированные» подъезды. Перед приездом мы просим подготовить пространство: приглушить верхний свет, обеспечить приток свежего воздуха без сквозняков, подготовить ровную поверхность под укладку и удлинитель, перевести телефоны в «без уведомлений» с «белым списком» близких. Это позволяет в первые минуты сосредоточиться на клинике, а не на бытовых вопросах.
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
краби супермаркет краби таиланд билеты
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk
https://www.band.us/page/101083405
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детали по клику – https://www.climatisation-91-service.fr/chambres-froides
1хБет фрибет Воспользуйтесь бонус при регистрации на http://opernhausblog.de/wordpress/wp-content/pgs/code_promo_123.html и заберите 32 500 рублей + бонус 100%, чтобы начать игру.
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Промокод при регистрации в 1xbet сегодня. Этой акцией может воспользоваться каждый новый игрок при регистрации на сайте букмекера. Это ваше преимущество с начала. В форме регистрации есть необязательное поле для ввода кода. Как получить действующий промокод на 1хбет на бесплатную ставку. В магазине xBonus можно обменять баллы на коды 1xbet kz: для ординаров, экспрессов или лотерей. Найти промокоды 1xbet можно в соцсетях. Представители БК часто публикуют их к праздникам или турнирам. Все актуальные промокоды 2026 доступны в официальном разделе сайта и могут быть обменяны на бонусные баллы.
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в химках[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://cholabronze.in/product/standing-ganesh
This piece of writing will assist the internet users for creating new blog or even a weblog from start to end.
Exodermin y su fórmula innovadora
La búsqueda de soluciones efectivas para el cuidado de la piel ha llevado a muchos a explorar opciones alternativas. Ya sea por problemas de salud o simplemente por estética, todos queremos lucir y sentirnos bien. Hoy en día, existen productos que prometen una transformación notable en la salud de nuestra dermis. Estas propuestas, en ocasiones, superan nuestras expectativas. Sin embargo, ¿qué hace que una alternativa sea realmente excepcional?
Las características únicas de ciertos tratamientos pueden ser sorprendentes. Se trata de ingredientes cuidadosamente seleccionados que trabajan en sinergia. Esta combinación no solo combate los problemas cutáneos, sino que también revitaliza y restaura nuestra epidermis. Todo ello se traduce en una apariencia más saludable y rejuvenecida. A menudo, la ciencia detrás de estos avances es fascinante, revelando cómo cada componente contribuye a resultados asombrosos.
Además, la experiencia de quienes han utilizado estas soluciones puede ofrecer una perspectiva invaluable. Muchos han compartido sus historias de éxito, resaltando cambios significativos en su piel. Con el paso del tiempo, la confianza en uno mismo puede incrementar considerablemente. La efectividad de estas opciones se ha vuelto un tema de conversación recurrente. Hay un aire de expectativa cada vez que se menciona su nombre.
En este artículo, nos adentraremos en los secretos de un producto que promete marcar la diferencia. Analizaremos sus propiedades clave, beneficios y la forma en que ha ganado popularidad en el ámbito del cuidado personal. Acompáñanos a descubrir cómo esta alternativa ha conquistado corazones y ha transformado rutinas, proporcionándonos una piel más sana y radiante.
Descubre los beneficios de Exodermin
Cuando buscamos alivio para ciertos problemas, suele ser útil conocer las ventajas que ofrece un producto especial. Muchas personas no son conscientes de que existen opciones efectivas para abordar sus inquietudes. La naturaleza de estos productos puede sorprendervos. No se trata solo de aliviar síntomas, sino de mejorar la salud de la piel en múltiples niveles.
Uno de los aspectos más destacables es su capacidad para regenerar el tejido dañado. Aquellos que lo utilizan comentan sobre la sensación de frescura y limpieza. Además, fomenta un ambiente óptimo para la curación, lo que resulta fundamental en el proceso de sanación. Con ingredientes cuidadosamente seleccionados, se crea una mezcla potente que actúa en sinergia.
La facilidad de aplicación también es un punto a favor, ya que no requiere complicadas rutinas. Simplemente, se puede incorporar a la vida diaria sin mayores inconvenientes. La constante exposición a factores dañinos ha llevado a muchos a experimentar malestar y molestias. Por ende, contar con un aliado que promueva la salud de la piel se vuelve esencial en el mundo actual.
Incluso, estudios han demostrado que sus componentes pueden reducir la inflamación y calmar irritaciones. A corto plazo, se aprecian mejoras visibles y, a largo plazo, se consolida una piel más saludable. ¿Te imaginas evitar problemas recurrentes y disfrutar de una piel radiante y cuidada? Este enfoque multitarea transforma no solo el aspecto externo, sino también la confianza personal.
Por último, el uso regular puede contribuir a prevenir condiciones futuras. La preparación no se limita a sanar, también se enfoca en mantener el bienestar. Así que, si has estado buscando una solución efectiva y práctica, quizás sea el momento de considerar esta interesante opción. conviértete en parte de la transformación que tu piel necesita.
Componentes clave de su mezcla revolucionaria
Cuando se trata de mejorar la salud y el bienestar de los pies, la combinación de ingredientes es esencial. Existen elementos que ofrecen propiedades únicas. Estos componentes no solo actúan sobre los síntomas, sino que también promueven la salud a largo plazo. Cada sustancia tiene su propia función específica que contribuye a un efecto sinérgico.
Uno de los ingredientes principales es el extracto de tea tree. Este poderoso antioxidante combate bacterias y hongos de manera efectiva. Además, favorece la regeneración de la piel. Por otro lado, la olea europea, conocida por sus propiedades hidratantes, nutre profundamente. Este aceite aporta suavidad y elasticidad a las áreas afectadas.
El ácido hialurónico forma parte de la mezcla, brindando hidratación intensa. Se reconoce por su capacidad para retener agua en la piel. Esto significa que se contempla no solo la curación, sino también la prevención de futuras afecciones. A su vez, el extracto de calendula aporta efectos antiinflamatorios y calmantes. Ideal para aliviar cualquier irritación existente.
Finalmente, el vitamina E refuerza la acción protectora de la crema. Este poderoso antioxidante contribuye a la regeneración celular, cuidando de la piel en profundidad. En conjunto, estos componentes crean una sinfonía perfecta, asegurando que cada aplicación genere resultados óptimos para el cuidado diario. Sin duda, cada ingrediente fue seleccionado meticulosamente, teniendo en cuenta sus beneficios específicos para el bienestar general de tus pies.
https://exodermin.net/es/
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в саратове[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Капельница от запоя — эффективный способ детоксикации. Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения из запоя.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru//]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому в люберцах[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://www.antonelloosteria.com/tips/the-4-knife-cuts-every-cook-should-know
анатолий шарий ВОЙНА В УКРАИНЕ Война в Украине оказывает огромное влияние на глобальную политику и экономику. Конфликт привел к гибели тысяч людей, разрушению городов и инфраструктуры, а также к массовому перемещению населения. Война в Украине стала причиной энергетического кризиса, роста цен на продовольствие и усиления геополитической напряженности. Мировое сообщество пытается найти пути для урегулирования конфликта, но пока существенного прогресса не наблюдается.
Лечение проходит в несколько этапов: диагностика, детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка и восстановление. Каждый этап имеет чёткие цели и критерии эффективности, что делает процесс управляемым и безопасным. Применяются препараты, сертифицированные в РФ, и только те, чья эффективность подтверждена клиническими исследованиями.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Детальнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Currently hoping to find an available firm handling rapid disaster repair solutions near this region? This company performs commercial-grade technology and
promises service with great reviews. Stop mold growth — schedule a visit.
commercial restoration companies
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены новокузнецк[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Выяснить больше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Реабилитация после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя вызов в люберцах[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr/
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого волгоград[/url]
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
мир МИРОВЫЕ НОВОСТИ В мировых новостях – обострение ситуации на Ближнем Востоке, последствия изменения климата, экономический кризис в ряде стран, пандемия новых заболеваний, политические протесты и другие события. Мировые новости отражают сложную и многообразную картину современного мира, где каждый день происходят важные события, влияющие на жизнь миллионов людей.
Профессиональная помощь требуется в тех случаях, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями интоксикации. Чем дольше длится запой, тем сильнее проявляются его симптомы. Медицинское вмешательство помогает предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как судороги, повышение давления и алкогольный психоз.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена тольятти[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
сопровождение системы 1с [url=https://1s-soprovozhdenie.ru/]сопровождение системы 1с[/url] .
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Химках. Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki12.ru//]вывод из запоя вызов химки[/url]
Круглосуточная помощь при запое в Химках. Мы работаем 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]вывод из запоя клиника химки[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в воронеже[/url]
стерилизатор плазменный универсальный [url=https://plazmennye-sterilizatory.ru/]стерилизатор плазменный универсальный[/url] .
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]платная наркологическая скорая помощь в тольятти[/url]
сервера для xrumer телеграм Обучение Xrumer 23 телеграм
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена[/url]
https://www.odcec.mi.it/home/2021/01/27/age.-ordinanza-del-sindaco-di-milano-del-23-gennaio-2021.-modifica-orari-di-apertura-al-pubblico
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому волгоград[/url]
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact loved account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing on your augment or even I success you get admission to consistently quickly.
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в воронеже[/url]
Genuinely when someone doesn’t understand afterward its up to other people that they will help, so here it occurs.
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Узнать больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha13.ru//]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в уфе[/url]
плазменные стерилизаторы производители [url=https://plazmennyy-sterilizator.ru/]плазменные стерилизаторы производители[/url] .
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://dexamethazon.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москва[/url]
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Обучение Xrumer 23 телеграм xrumer
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Подробнее – http://
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/[/url]
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в стационаре Балашихи. Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-balashiha11.ru//]вывод из запоя на дому цена балашиха[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://christiaensprefabbeton.be/foto-3
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Люберцах. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru//]капельница от запоя клиника в люберцах[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в уфе[/url]
Базы пробитые Xrumer Обучение Xrumer 23 телеграм
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Уточнить детали – https://sits.nu/cropped-huvud_sits-jpg
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Химках. Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-himki13.ru//]нарколог вывод из запоя химки[/url]
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Для строительства или ремонта дома стоит выбрать качественный [url=https://kirpichruchnoy.ru/]кирпич облицовочный ручной формовки[/url], который прослужит долгие годы и придаст вашему дому уникальный внешний вид.
является исключительно популярным материалом для строительных работ . Этот тип кирпича изготовляется вручную, что позволяет создавать уникальные текстуры и формы . Кирпич ручной формовки является универсальным материалом, подходящим для любых строительных проектов.
Кирпич ручной формовки характеризуется высокой прочностью и устойчивостью к различным погодным условиям. Процесс производства кирпича ручной формовки предполагает использование натуральных материалов и традиционных технологий. Кирпич ручной формовки используется в строительстве зданий, требующих высокой прочности и долговечности .
Кирпич ручной формовки обладает прочными связями между отдельными кирпичами, обеспечивая монолитность конструкции . Этот материал применяется в строительстве зданий, требующих высокой степени безопасности . Кирпич ручной формовки может быть использован для создания уникальных архитектурных элементов.
Кирпич ручной формовки включает в себя использование глины и других природных компонентов . Этот тип кирпича может быть использован для создания энергосберегающих зданий . Кирпич ручной формовки применяется в строительстве объектов, требующих высокой степени долговечности .
Кирпич ручной формовки используется для возведения стен, фундаментов и других конструктивных элементов . Этот материал используется в строительстве зданий, требующих высокой степени безопасности . Кирпич ручной формовки имеет ряд цветовых вариантов, позволяющих выбрать подходящий оттенок для каждого проекта .
Кирпич ручной формовки применяется в строительстве объектов, требующих высокой степени долговечности . Этот тип кирпича имеет высокую степень звукоизоляции, что делает его подходящим для строительства объектов с высокой степенью шумозащиты. Кирпич ручной формовки производится без применения вредных химических веществ.
Кирпич ручной формовки обладает высокой прочностью и устойчивостью к нагрузкам . Этот тип кирпича имеет высокую степень звукоизоляции, что делает его подходящим для строительства объектов с высокой степенью шумозащиты. Кирпич ручной формовки может быть использован для создания уникальных архитектурных элементов.
Кирпич ручной формовки производится без применения вредных химических веществ. Этот материал применяется в строительстве объектов культурного и исторического значения. Кирпич ручной формовки может быть использован для создания энергосберегающих зданий .
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov
Для обеспечения контроля доступа на мероприятиях рекомендуем использовать [url=http://brasletybumazhnye.ru]браслеты бумажные контрольные купить[/url], которые обеспечивают удобство и надежность.
Советуется применять их в случаях, где нужна прочная охрана информации
Реабилитация после запоя в Люберцах. Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее – [url=https://https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru//]капельница от запоя клиника люберцы[/url]
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the layout of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-cena[/url]
Перед тем как показать примерные программы, важно подчеркнуть: реальный план всегда персонализируется, но понимание базовых форматов помогает семье и пациенту не теряться в терминах и сразу видеть логику.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Hey I am so delighted I found your web site, I really found you
by accident, while I was looking on Aol for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just
like to say cheers for a tremendous post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to look over it all at the
minute but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds,
so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the superb b.
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru
сопровождение 1с стоимость 1 часа [url=https://1s-soprovozhdenie.ru/]1s-soprovozhdenie.ru[/url] .
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
ко ланта ко ланта
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог воронеж[/url]
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-volgograd/
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]запой нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
плазменные стерилизаторы [url=https://plazmennye-sterilizatory.ru/]плазменные стерилизаторы[/url] .
What’s up, yup this post is really pleasant and I have learned lot of things from it on the topic of
blogging. thanks.
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Узнайте всю правду – https://exonmachinery.com/obracarka-do-palet
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd/
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk/https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
xrumer сайт сервера для xrumer
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Деятельность в области недропользования — это комплекс работ, связанный с разработкой подземных богатств.
Оно включает поиск природных ресурсов и их промышленное освоение.
Данная сфера регулируется установленными правилами, направленными на безопасность работ.
Грамотный подход в недропользовании способствует экономическому росту.
общество экспертов России по недропользованию
It’s hard to find well-informed people in this particular subject, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколога на дом щелково[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon[/url]
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]narkolog-shchyolkovo[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-obratnyj-zvonok[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя[/url]
https://sites.google.com/view/fdfhdiffhdfhjd/home
https://socialislife.com/story6387662/code-promo-1xbet-2026-bonus-vip-jusqu-%C3%A0-130
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в уфе[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить больше информации – http://
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в новокузнецке[/url]
стерилизатор плазменный универсальный [url=https://plazmennyy-sterilizator.ru/]стерилизатор плазменный универсальный[/url] .
ко ланте остров ко ланта
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Выяснить больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Подробности по ссылке – https://sportxparte.com/bitcoin-fees-possible-solutions-and-scenarios
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
https://enrichment.cehd.gmu.edu/program-award-winner-matthew-mast/
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в рязани[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo/
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov/
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Подробнее тут – http://
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]zakazat-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
сервера для xrumer Прогон Xrumer телеграм
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в саратове[/url]
Hi to every single one, it’s actually a good for me to go to see this site,
it includes priceless Information.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница рязань[/url]
Generally I don’t learn post on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very pressured me to take a look at and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thanks, quite nice post.
This post provides clear idea in favor of the new people of blogging, that
truly how to do blogging and site-building.
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит нарколог на дом[/url]
xrumer официальный сайт Обучение Xrumer 19 телеграм
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
I do not know if it’s just me or if perhaps everybody else encountering problems with your website.
It looks like some of the text in your posts are running off the screen. Can someone
else please provide feedback and let me know if this is happening to them too?
This might be a issue with my internet browser because I’ve had
this happen before. Thank you
Also visit my webpage :: mpomm
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена[/url]
Как выбрать фотографа видеооператора в Сочи — торжества
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
xrumer сайт телеграм xrumer скачать
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
Сайт kazino olimp познавательный. Обязательно загляну ещё!
http://Lemon.cs.elte.hu/trac/lemon/search?q=https://olimp-casino-kazakhstan-slot.org.kz/bonuses/
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://innerjia.com/manfaat-terapi-bioelektrik-untuk-kesehatan-tubuh
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Разобраться лучше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, и в «КоломнаМед Центр» это принимается как медицинский факт, а не моральная оценка. Программы включают медикаментозную поддержку, работу с тягой, коррекцию тревожных и депрессивных состояний, психотерапию, помощь в восстановлении режима сна и питания, семейное консультирование. При наркотической зависимости и полинаркомании добавляются протоколы по безопасной отмене веществ, наблюдение в критические периоды, сопровождение на этапе формирования устойчивой ремиссии. Акцент делается на том, чтобы не запугивать пациента, а показать реалистичный путь, где улучшение возможно шаг за шагом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
This information is priceless. When can I find out more?
Dizaynı superdir!
http://apartamentosamobladosbosquesdellimonar.com.co/nurturing-the-bond-between-humans-and-nature/
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробности по ссылке – https://esbatnews.ir/?p=132543
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Детальнее – http://
https://qiita.com/codesierraleone12
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be really something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
When it comes to understanding how crypto casinos work, especially those focusing on anonymity, it’s essential to delve into the features that enhance privacy and security in these platforms.
сервера для xrumer xrumer 23 телеграм
Excellent way of describing, and nice article to obtain information concerning
my presentation focus, which i am going to present in institution of higher
education.
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-serpuhov-ceny[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом воронеж[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-voronezh/https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом цена[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в саратове[/url]
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
This page certainly has all of the info I needed about this subject
and didn’t know who to ask.
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в тольятти[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в уфе[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр саратов[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в саратове[/url]
Hello, I would like to subscribe for this weblog to get hottest updates, thus where can i do it please assist.
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в волгограде[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому волгоград[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo/
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Открой скрытое – https://www.liberdadepsi.com.br/contato/cropped-logo-preta-jpg
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Полная информация здесь – https://todoespolitica.com.mx/eric-adams-alcalde-de-ny-se-declara-inocente-de-corrupcion
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyezd-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]заказать нарколога на дом[/url]
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
The platform stands out for its instant withdrawal approvals and the absence of deposit or withdrawal limits, ensuring hassle-free banking from the get-go.
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]наркологическая клиника коломна[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бесплатные вращения в слотах[/url]
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар саратов[/url]
Saya sudah membaca artikel ini secara keseluruhan, dan saya merasa penyampaian materi di dalamnya sangat menarik
dan relevan dengan berbagai perbincangan populer saat ini, termasuk mengenai KUBET,
Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap, Situs Parlay Resmi, Situs Parlay Gacor, Situs Mix Parlay, Situs Judi Bola,
toto macau, kubet login, situs parlay, Kubet Parlay, dan Judi Bola gacor.
Dari pandangan saya, kualitas penulisan dalam artikel ini terlihat dari bagaimana penulis menyusun informasi dengan cara yang terstruktur, sehingga
pembaca bisa mengikuti setiap poin tanpa kesulitan. Isi artikel ini juga memberikan nilai tambah karena mampu
memberikan pemahaman yang jelas terhadap topik yang sedang banyak dicari.
Saya merasa perlu memberikan komentar karena artikel seperti
ini tentu layak mendapatkan apresiasi yang lebih. Saya berharap penulis dapat
terus menghadirkan konten-konten yang bernilai tinggi sehingga semakin banyak pembaca yang bisa mendapatkan referensi yang tepat dan akurat.
Terima kasih kepada penulis karena sudah menyajikan pembahasan yang begitu jelas, relevan, dan nyaman untuk
dibaca oleh siapa pun.
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article writer for your blog. You have some really great posts and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d love to write some articles for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please shoot me an email if interested. Thank you!
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Базы Xrumer 19 Базы Хрумер
I read this piece of writing completely on the topic of the
difference of most up-to-date and preceding technologies, it’s remarkable article.
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo[/url]
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti/
Ниже — ключевые направления, которые логично дополняют друг друга и формируют единый маршрут лечения:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника телефон[/url]
xrumer официальный сайт Базы пробитые Xrumer
Услуга «нарколог на дом в Долгопрудном» от клиники «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» создана для ситуаций, когда важно действовать быстро, аккуратно и без лишнего шума. Запой, тяжёлое похмелье, срыв после ремиссии, злоупотребление медикаментами или смесью алкоголя с препаратами — всё это не терпит откладывания и самодеятельности. Вызов врача на дом позволяет получить профессиональную помощь без госпитализации, когда состояние пациента ещё позволяет лечить его в привычной обстановке. Нарколог приезжает с полностью укомплектованным набором препаратов и расходников, проводит осмотр, подбирает капельницы по клиническим показаниям, контролирует реакцию, даёт подробные рекомендации на ближайшие дни и при необходимости предлагает дальнейший маршрут: повторный выезд, амбулаторное наблюдение или стационар клиники. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго: без обсуждений с соседями, без регистрации по месту работы, без унизительных формальностей — только медицинская помощь, ориентированная на безопасность и результат.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]наркологическая клиника в Коломне[/url]
We are a bunch of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community.
Your site offered us with valuable info to work on. You
have done an impressive process and our entire community can be
grateful to you.
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk/
Обучение Xrumer Базы Xrumer не сырые
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар новокузнецк[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
What i do not realize is if truth be told how you are now not really a lot more smartly-preferred than you may be right now. You are very intelligent. You understand thus significantly on the subject of this matter, produced me in my view believe it from numerous various angles. Its like men and women are not fascinated until it’s something to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs great. All the time handle it up!
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/nomer-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov/
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get got an nervousness over that you wish be
delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly
again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield
this increase.
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to
say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your rss feed
and I hope you write again soon!
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
http://www.memup.fr/forum/general-discussion/1xbet-promo-code-no-deposit-2026-1xbig2026-bonus-130/
Ремонт бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге является очень востребованной услугой среди населения. Это связано с тем, что бытовая техника является важным элементом нашей жизни, и ее поломка может привести к серьезным проблемам. Поэтому Есть множество вариантов ремонта бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге. Это зависит от вида поломки и типа бытовой техники, а также от наличия необходимых запчастей. Кроме того, жители Екатеринбурга могут выбрать услуги по ремонту бытовой техники на дому или в мастерской.
Виды ремонта бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге
Ремонт бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге включает в себя различные виды услуг, такие как ремонт холодильников, стиральных машин и другие. Это связано с тем, что бытовая техника является неотъемлемой частью нашей жизни, и ее поломка может привести к серьезным проблемам. Поэтому есть много вариантов ремонта бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге, и жители могут выбрать тот, который лучше всего подходит их потребностям. Это зависит от вида поломки и типа бытовой техники, а также от наличия необходимых запчастей. Кроме того, жители Екатеринбурга могут выбрать вариант ремонта бытовой техники, который лучше всего подходит их потребностям и бюджету.
Преимущества ремонта бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге
Ремонт бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге имеет множество преимуществ, включая экономию времени и денег. Это связано с тем, что бытовая техника играет важную роль в нашей повседневной жизни, и ее ремонт является важным вопросом. Поэтому есть много вариантов ремонта бытовой техники в Екатеринбурге, и жители могут выбрать тот, который лучше всего подходит их потребностям.
мастерская по ремонту бытовой техники [url=bytovaya-tehnika-remont-ekaterinburg.ru]https://bytovaya-tehnika-remont-ekaterinburg.ru/[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
I read this post fully regarding the difference of hottest and
preceding technologies, it’s amazing article.
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Saya adalah seseorang yang senang beraktivitas secara online, terutama
ketika berkaitan dengan topik seperti KUBET, Situs Judi
Bola Terlengkap, Situs Parlay Resmi, Situs Parlay
Gacor, Situs Mix Parlay, Situs Judi Bola, toto macau, kubet login, situs parlay, Kubet Parlay, dan Judi Bola gacor.
Meskipun saya bukan orang yang memiliki banyak keistimewaan, saya selalu berusaha berinteraksi secara positif
dengan komunitas yang saya temui secara online.
Saya sering menjelajahi blog dan forum sesuai minat, karena aktivitas tersebut membantu saya menambah perspektif baru setiap harinya.
Nama saya adalah Mariano dan saya tinggal di Sweden,NA,Ljusnedal,840 96,Messlingen 27,6845034831,
, dengan usia sekitar 35 tahun. Saya berharap dapat terus memperkaya pemahaman saya tentang
hal-hal baru, serta tetap berinteraksi dengan cara yang bermanfaat
di berbagai platform yang saya ikuti.
Thanks for finally talking about > Types of Cancer:
Common & Rare Cancers Explained < Loved it!
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Отдельный принцип клиники — строгая анонимность. Информация о лечении не передаётся по месту работы, обучения, в сторонние структуры без согласия пациента. Это особенно важно для людей, которые боятся огласки и из-за этого годами откладывают обращение. В «КоломнаМед Центр» можно пройти лечение так, чтобы сохранить репутацию и личное пространство, не превращая каждый шаг в обсуждение «на людях».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника коломна[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому в волгограде[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/
Awesome article.
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
http://forum54.4adm.ru/viewtopic.php?f=69&t=13876
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
https://www.uscgq.com/forum/posts.php?forum=&id=624590
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Каждое назначение объясняется пациенту и близким простым языком. Здесь не практикуют подход «делаем, как знаем, вам всё равно не понять» — прозрачность и понятные шаги помогают снизить тревогу и укрепляют доверие к клинике.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
На месте врач и медсестра собирают базовую линию: уровень сознания, дыхание, SpO?, температура, шкалы симптомов (тошнота/тремор/тревога 0–10), переносимость воды небольшими глотками. Далее формулируется рабочая гипотеза и включается минимально достаточный модуль с обозначенным «окном оценки»: 30–60 минут — для «окна питья», 60–120 минут — для стабилизации ЧСС/АД и дрожи, «первая ночь» — для сна и вечерней тревоги. Как только маркер достигнут, модуль выключается; нет эффекта — меняется одна переменная без «усиления всего сразу».
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полная информация здесь – https://psicologavanessaoliveira.com/hello-world
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в саратове[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно серпухов[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Игнорирование этих симптомов может привести к тяжёлым последствиям — судорогам, галлюцинациям или алкогольному психозу.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
I blog often and I genuinely thank you for your content. This great article has really peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new details about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograda/
Услуга
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Клиника «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде оказывает помощь при алкогольной интоксикации как в условиях стационара, так и на дому. Врачи готовы выехать к пациенту в течение 40–60 минут после обращения, привозя с собой всё необходимое оборудование для проведения инфузионной терапии. Такая оперативность позволяет снизить риск осложнений и стабилизировать состояние уже в первые часы лечения. Для пациентов, нуждающихся в круглосуточном наблюдении, предусмотрены комфортабельные палаты с постоянным медицинским контролем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/
Таблица не заменяет очный осмотр, но показывает, как наблюдения переводятся в действие и когда мы принимаем решение о продолжении/остановке модуля.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru
Материал включает занимательные, но незначимые детали, которые трудно назвать важными, но они дополняют общую картину.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Основные этапы включают:
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
I am really loving the theme/design of your website. Do you ever run into any web browser compatibility problems?
A number of my blog audience have complained about my blog
not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Firefox.
Do you have any suggestions to help fix this problem?
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм новокузнецк[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Этот набор информации привлекает мелочами и необычными ракурсами, предлагая взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но разнообразят знакомство с темой.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html
Bu saytda olmaq çox maraqlıdır.
http://uchelo.nnov.org/common/redir.php?https://mostbetaz.tech/oyunlar
Why visitors still use to read news papers when in this
technological globe everything is available on web?
Услуга
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно серпухов[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo/
Yo, Taiking88 on .net is where I’ve been chilling. Good vibes and decent odds! You should give it a shot. taiking88
hi!,I love your writing so much! share we keep in touch more about your article
on AOL? I need a specialist in this area to solve my problem.
Maybe that is you! Looking forward to look you.
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading?
I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
Одним из самых востребованных направлений работы клиники является проведение детоксикации и вывод из запоя. Эти процедуры направлены на очищение организма от алкоголя и продуктов его распада, нормализацию работы печени и нервной системы. Лечение проводится с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и под контролем врача-нарколога.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Saya sudah membaca seluruh isi artikel ini, dan menurut saya penyajiannya sangat menarik,
terutama karena terdapat pembahasan mengenai KUBET, Situs Judi Bola
Terlengkap, Situs Parlay Resmi, Situs Parlay Gacor, Situs Mix
Parlay, Situs Judi Bola, toto macau, kubet login, situs
parlay, Kubet Parlay, dan Judi Bola gacor. Tulisan ini disusun dengan cukup rapi, sehingga pembaca dapat mengikuti
seluruh informasi dengan nyaman. Saya merasa artikel ini memberikan wawasan baru yang membahas tema serupa.
Saya merasa artikel sebagus ini pantas diberi apresiasi, karena kualitas pembahasan dan cara penyajiannya benar-benar layak dihargai.
Saya berharap penulis tetap konsisten membuat konten berkualitas sehingga semakin banyak pembaca yang bisa
mendapatkan informasi berharga seperti yang saya dapatkan dari artikel ini.
Terima kasih atas pembahasannya yang jelas dan mudah dipahami.
Nicely put. Appreciate it!
no deposit bonus casino canada rocket play casino canada canadian casinos online
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up and the rest of the website is also very good.
Услуга
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
https://archives.profsurv.com/forum/Professional-Surveyor-Magazine-Discussion/Education/-150978.aspx
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно тольятти[/url]
Каждое направление интегрировано в общую стратегию: минимизировать риски для здоровья, стабилизировать состояние и не оставить пациента один на один с проблемой сразу после облегчения симптомов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tolyatti-otzyvy
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-serpuhov[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ceny[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займы до зарплаты[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в рязани[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk/
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is magnificent, as well
as the content!
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom
Маршрут организован так, чтобы убрать хаос и сделать шаги понятными для родственников. После звонка оператор под контролем врача уточняет длительность употребления, примерные объёмы алкоголя, хронические болезни (гипертония, ИБС, диабет, заболевания печени, почек, нервной системы), список уже принятых лекарств, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, подозрительные психические симптомы. На этом этапе принимается базовое решение: возможно ли безопасно провести детокс на дому либо показан стационар. Врач приезжает по адресу в Щёлково, проводит осмотр: фиксирует АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, речь, поведение, уровень сознания, степень обезвоживания. Затем подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации, коррекции электролитов и кислотно-щелочного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы и снижения тремора; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные, щадящие анксиолитики для сна, но без грубого «выключения». Во время процедуры врач наблюдает за динамикой, при необходимости меняет скорость капельницы, контролирует давление и пульс, следит за реакцией на препараты. В финале даёт подробные рекомендации: как вести себя ближайшие 24–72 часа, как спать, что пить и есть, каких лекарств избегать, какие симптомы считать тревожными, когда нужно немедленно звонить и когда стоит рассмотреть стационар. Если уже на этапе осмотра понятно, что дому «тесно» по безопасности, перевод в клинику организуется без задержек.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://www.okaa.io/2025/02/08/telegram%E5%A4%9A%E5%BC%80%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B-tdata%E7%89%88
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]klinika-narkologicheskoj-zavisimosti[/url]
Good post! We will be linking to this great article on our site.
Keep up the good writing.
Thanks for a marvelous posting! I actually enjoyed reading it, you might be a great author.I will be sure to bookmark your blog and may come back later on. I want to encourage you to definitely continue your great job, have a nice evening!
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены саратов[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Выяснить больше – http://
Процесс лечения проходит поэтапно и под постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Каждый этап направлен на определённый аспект восстановления здоровья и личности пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платный нарколог на дом воронеж[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Капельница — это основной инструмент дезинтоксикации при лечении запойных состояний. Она способствует выведению токсинов, нормализации обмена веществ и улучшению общего самочувствия. Состав раствора подбирается индивидуально в зависимости от степени интоксикации, возраста, массы тела и сопутствующих заболеваний. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает облегчение, снижается тревожность и проходит головная боль.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в тольятти[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Это ещё не всё… – https://bremer-tor-event.de/hello-world-2
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu
Если вы ищете готовые решения для строительства своего жилища, посетите наш сайт по адресу [url=https://gotovye-proekty-domov8.ru]готовый проект дома[/url], чтобы найти подходящий для вас проект.
предлагают заказчикам широкий спектр возможностей для строительства . Эти проекты обеспечивают быстрое и качественное строительство. Благодаря этому, заказчики могут быть уверены в результате своего строительства.
Готовые проекты домов учитывают все нюансы и особенности строительства. Они включают в себя подробную документацию и чертежи . Это дает заказчикам возможность получить высококачественный дом .
Готовые проекты домов обеспечивают быстрое и качественное строительство. Они включают в себя все необходимые документы и чертежи . Благодаря этому, заказчики могут приступить к строительству сразу после покупки проекта .
Готовые проекты домов учитывают все нюансы и особенности строительства. Они обеспечивают быстрое и качественное строительство. Это упрощает процесс строительства и снижает риски.
Готовые проекты домов представляют собой комплексное решение для строительства жилья . Они созданы с учетом всех современных требований и стандартов . Благодаря этому, заказчики могут быть уверены в результате своего строительства .
Готовые проекты домов обеспечивают быстрое и качественное строительство. Они предоставляют заказчикам возможность осуществлять контроль над строительным процессом. Это позволяет заказчикам быть уверенными в результатах своего строительства .
Готовые проекты домов включают в себя полный набор документации для создания нового дома . Они созданы с учетом всех современных требований и стандартов . Благодаря этому, заказчики могут сэкономить время и ресурсы .
Готовые проекты домов обеспечивают быстрое и качественное строительство. Они включают в себя подробную документацию и чертежи . Это дает заказчикам возможность получить высококачественный дом .
Сайт Sultan Casino очень информативный. Обязательно загляну ещё!
https://sultan-casino-kazakhstan-lucky.kz
Лечение проходит в несколько этапов: диагностика, детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка и восстановление. Каждый этап имеет чёткие цели и критерии эффективности, что делает процесс управляемым и безопасным. Применяются препараты, сертифицированные в РФ, и только те, чья эффективность подтверждена клиническими исследованиями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Обеспечьте соответствие вашего школьного спортзала стандартам ФГОС, выбрав подходящее [url=http://myvoleybol.ru]спортивный инвентарь для детского сада[/url] на сайте myvoleybol.ru для создания безопасной и эффективной среды для занятий.
Приспособление инвентаря к возрасту способствует продуктивному обучению
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Узнать больше – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом серпухов[/url]
Каждый компонент капельницы подбирается по медицинским показаниям. Врач учитывает возраст, хронические заболевания, степень обезвоживания и чувствительность к препаратам. Такой индивидуальный подход обеспечивает эффективность лечения и исключает осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
дайсон сервисный центр официальный [url=https://dn-kupit-2.ru/]дайсон сервисный центр официальный[/url] .
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
дайсон официальный сайт купить москва [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru[/url] .
сайт магазина дайсон [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dsn.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dsn.ru[/url] .
It’s the best time to make a few plans for the long run and it is time to be happy. I have learn this put up and if I could I desire to suggest you few attention-grabbing issues or suggestions. Maybe you can write next articles relating to this article. I desire to read more issues approximately it!
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого уфа[/url]
Для жителей Красноярска организованы два конфиденциальных пути. Первый — немаркированный выезд бригады на дом с заранее согласованными порогами связи. Второй — «тихий вход» в клинику через отдельную дверь, где приём проходит без очередей и «коридорных» разговоров. На первичном звонке администратор уточняет только клинически значимые факторы: частоту рвоты, наличие мочеиспускания, ЧСС/АД в покое, эпизоды спутанности, актуальные лекарства и аллергии. Биографические подробности и лишние вопросы не задаются — мы придерживаемся принципа минимально необходимой информации.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
А что дальше? – https://mediesven.com/explorando-la-medicina-estetica-belleza-y-bienestar-en-mediesven
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-obratnyj-zvonok[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре волгоград[/url]
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница тюмень[/url]
сайт магазина дайсон [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru[/url] .
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Основу выездного лечения составляют капельницы, которые позволяют быстро ввести препараты в кровоток, минуя желудочно-кишечный тракт. Это обеспечивает моментальное действие и исключает раздражение слизистой. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента. Основные направления инфузионной терапии включают детоксикацию, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и поддержку работы нервной системы. Для усиления эффекта применяются витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для защиты печени.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в новокузнецке[/url]
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены в волгограде[/url]
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому новокузнецк[/url]
Мы уделяем особое внимание сенсорной среде — это не «сервис ради сервиса», а клинический инструмент. Контролируем свет и звук, просим отключить уведомления на устройствах, используем тёплую воду малыми глотками, настраиваем «ритуал 60 минут» перед сном. На этом фоне инфузии переносятся ровнее, латентность засыпания сокращается, а утро встречает ясностью вместо «ваты» в голове. Конфиденциальность встроена в процессы: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, разграничение доступа к медданным и отсутствие фото/видео без письменного согласия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар саратов[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of
precious experience regarding unpredicted emotions.
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
I have read several excellent stuff here. Definitely price
bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much attempt you place
to create this type of excellent informative web site.
Этот набор информации привлекает мелочами и необычными ракурсами, предлагая взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но разнообразят знакомство с темой.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Полная информация здесь – https://nongsansachbigmon.com/dung-my-pham-dung-cach-de-khong-hong-da
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Выяснить больше – http://
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom/
Каждое направление интегрировано в общую стратегию: минимизировать риски для здоровья, стабилизировать состояние и не оставить пациента один на один с проблемой сразу после облегчения симптомов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом воронеж[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://www.pilulaempreendedora.com.br/2018/07/19/conheca-ferramenta-para-alinhar-o-seu-proposito-de-vida
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
What’s up i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anyplace, when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also make comment due to this brilliant post.
כתבה מעולה! אני עוקב הרבה אחרי בלוגים של תיירות, וזה בדיוק
הנושא שחיפשתי עליו מידע.
למי שמתכנן טיול לאמריקה – ממליץ לבדוק את Getravel.co.il.
יש שם מדריכים מעולים בעברית, עם טיפים אמיתיים
ודילים שווים על מלונות בכל היעדים
הפופולריים.
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Отдельный принцип клиники — строгая анонимность. Информация о лечении не передаётся по месту работы, обучения, в сторонние структуры без согласия пациента. Это особенно важно для людей, которые боятся огласки и из-за этого годами откладывают обращение. В «КоломнаМед Центр» можно пройти лечение так, чтобы сохранить репутацию и личное пространство, не превращая каждый шаг в обсуждение «на людях».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника доктор[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/
https://telegra.ph/Skope-kupit-kokain-12-19-2
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в саратове[/url]
Услуга
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
There is apparently a bunch to know about this. I believe
you made various nice points in features also.
Spot on with this write-up, I really feel this web site
needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the information!
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
В Воронеже команда «ВоронМед Профи» работает по принципу быстрой медицинской реакции — помощь оказывается независимо от времени суток и дня недели. Все выезды выполняются анонимно, без спецтранспорта и медицинской формы. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, что исключает ненужное внимание соседей и посторонних. В ходе осмотра специалист измеряет давление, пульс, температуру, оценивает уровень интоксикации и определяет степень обезвоживания. На основе полученных данных подбирается состав капельницы, который подаётся медленно и безопасно под контролем врача.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому в тольятти[/url]
Appreciation to my father who informed me regarding this web site, this blog is truly remarkable.
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]как происходит кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-mefedron-magazin-12-19-3
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]skolko-stoit-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в саратове[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в волгограде[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
интернет дайсон сайт [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dsn.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dsn.ru[/url] .
стайлер дайсон купить оригинал официальный [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru[/url] .
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
интернет магазин dyson пылесосов [url=https://dn-kupit-2.ru/]dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Получить больше информации – http://
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-amfetamin-spb-12-19-7
Hi, the whole thing is going perfectly here and ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s truly good, keep up writing.
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в воронеже[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы волгоград[/url]
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в уфе[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/
Переходи по ссылке на официальный сайт > http://hammill.ru/
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://drhusam.com/precalculus-03-notes
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
«Трезвый Центр Коломна» предлагает несколько маршрутов, и выбор делается не по принципу «как удобнее», а по критериям безопасности. Если пациент в сознании, на контакте, без грубой дезориентации, без галлюцинаций, может пить воду, рвота эпизодическая, нет тяжёлых скачков давления и пульса, дома есть тишина и ответственный взрослый — возможен выезд на дом. Врач приезжает в Коломне, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, степень обезвоживания, неврологический и психический статус, подбирает индивидуальную инфузионную схему и наблюдает за реакцией. Если же запой затянулся (3–5 суток и более), выражены слабость, шаткость походки, многократная рвота, резкие «качели» АД и ЧСС, есть подозрение на предделирий или делирий, тяжёлая соматика или пожилой возраст — врач честно рекомендует стационар. В отделении пациент получает круглосуточный мониторинг, возможность оперативно корректировать лечение, защищённую среду без доступа к алкоголю и посторонних стимулов, поддержку медперсонала в любое время суток. Такой дифференцированный подход экономит силы, деньги и главное — снижает риск критических осложнений, которые часто возникают именно после «домашних экспериментов».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Isfahan-kupit-Kokain-Mefedron-Skorost-Amfetamin-12-20-2
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article. Thanks for supplying this information.
constantly i used to read smaller articles or reviews which also clear their motive, and that is also happening
with this paragraph which I am reading here.
Услуга
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно серпухов[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]gde-nahoditsya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali/
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в волгограде[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
dyson россия официальный [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru[/url] .
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
В Воронеже команда «ВоронМед Профи» работает по принципу быстрой медицинской реакции — помощь оказывается независимо от времени суток и дня недели. Все выезды выполняются анонимно, без спецтранспорта и медицинской формы. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, что исключает ненужное внимание соседей и посторонних. В ходе осмотра специалист измеряет давление, пульс, температуру, оценивает уровень интоксикации и определяет степень обезвоживания. На основе полученных данных подбирается состав капельницы, который подаётся медленно и безопасно под контролем врача.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
I love it whenever people come together
and share thoughts. Great blog, keep it up!
https://telegra.ph/Nikshich-kupit-Kokain-Mefedron-Skorost-Amfetamin-12-20
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно новокузнецк[/url]
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Детальнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Смотрите также… – https://fricco.com.br/2023/12/08/gel-de-carboidrato-para-que-serve-ele-engorda-qual-o-melhor
Наш официальный сайт уже доступен > http://www.medtronik.ru/
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
You’ve made some good points there. I looked on the web to find out more about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this website.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Открой скрытое – https://15minutestravel.com/?p=943
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно в волгограде[/url]
https://dentaliano.com/forums/topic/10165/codigo-promocional-de-rodadas-gratis-1xbet-2026/view/post_id/71151
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-novokuzneczk/
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника саратов[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Alkala-de-EHnares-kupit-Kokain-Mefedron-Skorost-Amfetamin-12-20
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в воронеже[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – http://brain-glass.com/post/34
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]zapoj-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Процесс лечения проходит поэтапно и под постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Каждый этап направлен на определённый аспект восстановления здоровья и личности пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Во время лечения фиксируются все жизненные показатели пациента. При необходимости проводится экспресс-анализ крови и ЭКГ. Ниже представлена таблица, показывающая, какие параметры контролируются и по каким признакам оценивается стабилизация состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]adresa-narkologicheskih-klinik[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://gruptravi.com/en/viii-nit-de-penyes-in-can-cortada
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://sdawrrc-blog.com/2023/06/14/post-60566
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – https://itensdiversos.com/ola-mundo
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-Kokain-Mefedron-Skorost-Amfetamin-Tajcy-12-20-2
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в воронеже[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколога на дом щелково[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-tolyatti/
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя в реутово[/url]
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after browsing through some of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly happy I stumbled upon it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в волгограде[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя красноярск[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Armavir-kupit-zakladku-mefedrona-12-19-6
техника дайсон купить [url=https://dn-kupit-2.ru/]dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
dyson купить интернет магазин [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru[/url] .
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом воронеж[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk/
dyson com официальный сайт [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dsn.ru/]dyson com официальный сайт[/url] .
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno/
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Это ещё не всё… – https://artfieldgraphics.com/dotted-icons-orange
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/skolko-stoit-narkolog-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan/
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
https://telegra.ph/Stranda-kupit-Marihuanu-Boshki-SHishki-Sol-12-20
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно саратов[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
техника дайсон купить [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn.ru[/url] .
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в саратове[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
Hi there I am so glad I found your webpage, I really found you by error, while I was researching on Aol for something else, Anyhow
I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a tremendous
post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have
time to browse it all at the moment but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I
have time I will be back to read more, Please do
keep up the excellent work.
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Открой скрытое – https://nexzmediagroup.com/elementor-1385
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника уфа[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Aleksin-kupit-zakladku-kokaina-12-19-8
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]заказать нарколога на дом[/url]
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Many thanks for providing this info.
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена новокузнецк[/url]
Формат помощи
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а системный процесс восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. В клинике «ВолгаМед Резолюция» в Волгограде пациенты получают помощь, основанную на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Лечение направлено не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на стабилизацию нервной системы, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию сна. Капельницы подбираются персонально, с учётом состояния пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний и возраста. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под контролем нарколога.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Nuku-Hiva-kupit-Kokain-Mefedron-Skorost-Amfetamin-12-20
Главным преимуществом наркологической клиники в Новокузнецке является комплексный подход к лечению. Специалисты рассматривают зависимость как заболевание, требующее системного воздействия на организм и психику. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную помощь. Такой подход обеспечивает достижение устойчивых результатов и предотвращает рецидивы.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
«Трезвый Центр Коломна» предлагает несколько маршрутов, и выбор делается не по принципу «как удобнее», а по критериям безопасности. Если пациент в сознании, на контакте, без грубой дезориентации, без галлюцинаций, может пить воду, рвота эпизодическая, нет тяжёлых скачков давления и пульса, дома есть тишина и ответственный взрослый — возможен выезд на дом. Врач приезжает в Коломне, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, степень обезвоживания, неврологический и психический статус, подбирает индивидуальную инфузионную схему и наблюдает за реакцией. Если же запой затянулся (3–5 суток и более), выражены слабость, шаткость походки, многократная рвота, резкие «качели» АД и ЧСС, есть подозрение на предделирий или делирий, тяжёлая соматика или пожилой возраст — врач честно рекомендует стационар. В отделении пациент получает круглосуточный мониторинг, возможность оперативно корректировать лечение, защищённую среду без доступа к алкоголю и посторонних стимулов, поддержку медперсонала в любое время суток. Такой дифференцированный подход экономит силы, деньги и главное — снижает риск критических осложнений, которые часто возникают именно после «домашних экспериментов».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому воронеж[/url]
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
магазин техники dyson [url=https://dn-kupit-2.ru/]dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo/
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-Mefedron-Gashish-Kannabis-Skorost-Muravlenko-12-20-2
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Получить больше информации – http://
УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП: Выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность и комфорт на бездорожье. Автоматическая коробка передач значительно упрощает управление автомобилем, особенно в сложных условиях. УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП предлагает просторный салон, вместительный багажник и высокий уровень проходимости, что делает его отличным вариантом для путешествий, охоты, рыбалки и других активностей на природе. Машина оснащена всем необходимым для комфортной езды, включая современные системы безопасности и мультимедиа. УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП – это инвестиция в вашу свободу передвижения и уверенность на любой дороге.
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Это ещё не всё… – https://www.kirra.jp/2020/05/22/forest-style-bar-kirra%E3%83%90%E3%83%B3%E3%83%93%E3%83%BC%E3%83%8E
бонусы букмекеров Ставки на спорт — это увлекательное и потенциально прибыльное занятие, но требующее серьезного подхода и аналитического мышления. Суть заключается в прогнозировании исходов спортивных событий с использованием коэффициентов, предлагаемых букмекерскими конторами. Успешные игроки тщательно изучают статистику, анализируют составы команд, учитывают факторы, влияющие на игру (погода, травмы, мотивация и т.д.), и используют различные стратегии управления банкроллом. Важно помнить, что ставки на спорт не являются гарантированным способом заработка, и всегда существует риск проигрыша. Ответственная игра и контроль над своими финансами — ключевые аспекты успешного беттинга. Новичкам рекомендуется начинать с небольших ставок и постепенно изучать мир спортивных прогнозов. Существуют специализированные ресурсы и комьюнити, где можно получить полезную информацию, советы и обменяться опытом с другими игроками. Со временем, правильный подход и постоянное обучение могут привести к увеличению прибыльности ставок на спорт.
Hi, all is going nicely here and ofcourse every one is sharing information, that’s genuinely excellent, keep up writing.
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это управляемая система, где каждый шаг прозрачно связан с целью и измеримым результатом. В наркологической клинике «ЕнисейМед Центр» мы соединяем круглосуточную доступность, мягкую логистику и модульный план лечения, чтобы пациент и семья понимали, почему именно сейчас назначается то или иное вмешательство и когда оно будет остановлено. Мы избегаем полипрагмазии: запускаем один модуль — ставим один маркер — определяем «окно оценки» — выключаем модуль, как только цель достигнута. Такой подход бережёт ресурсы организма и сохраняет причинно-следственную связь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма красноярск[/url]
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Системный подход позволяет достичь максимальной эффективности лечения и снизить риск возврата к зависимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
http://www.old.xn--90asjdo3a.xn--p1ai/user/jostuscesn
Excellent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web
site, how could i subscribe for a blog website? The account aided me a acceptable deal.
I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright
clear concept
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс шоп[/url]
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]займ без процентов[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://soig.fr/timetable-for-wordpress-sample-3
Для тех, кто предпочитает лечение в условиях стационара, предусмотрены комфортные палаты, медицинский контроль 24/7 и возможность консультаций с психотерапевтом. Врачи клиники применяют комплексные методы, направленные не только на снятие симптомов, но и на устранение причин зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм волгоград[/url]
интернет магазин dyson техника [url=https://ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru/]ofitsialnyj-sajt-dn-1.ru[/url] .
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove/
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Полная информация здесь – https://airportrehab.ca/chiropractic-care-release-toxins-from-your-body
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Полная информация здесь – https://futuresima.com/2024/02/14/hello-world
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://crossriver.ca/service/guided-rafting-trip-2
УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП: Настоящий внедорожник для ценителей свободы и приключений, оснащенный автоматической коробкой передач для максимального комфорта в любых условиях. Забудьте о сложностях переключения передач на бездорожье – современная АКПП позволяет полностью сосредоточиться на управлении и наслаждаться поездкой. УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП – это идеальное сочетание проходимости, надежности и комфорта, которое позволит вам уверенно чувствовать себя как в городе, так и за его пределами. Откройте для себя новые горизонты с УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП!
https://www.exchangle.com/1xbetpromocodeaze
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
«Вектор Надежды» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы с первого звонка убрать неопределённость и вернуть ощущение контроля. Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только необходимую информацию, оценивает риски и предлагает безопасный старт: выезд на дом, дневной маршрут или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Мы объясняем каждую манипуляцию простым языком — что именно будет сделано в ближайшие часы, каких изменений ожидать к вечеру, почему выбран именно такой темп и как поймём, что схема работает. Конфиденциальность — не дополнение, а стандарт: нейтральные звонки, неброская атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте, отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает тревогу, экономит силы семьи и ускоряет стабилизацию: вместо «марафона кабинетов» — один связный маршрут с понятными контрольными точками.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в красноярске[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Получить больше информации – http://
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Кайт египет Кайт египет
прогнозы на баскетбол Букмекерские конторы — это организации, предлагающие услуги по заключению пари на различные события, в основном спортивные. Они устанавливают коэффициенты на исходы, принимают ставки и выплачивают выигрыши. Букмекерские конторы различаются по многим параметрам: репутация, предлагаемые виды спорта и роспись событий, коэффициенты, удобство использования сайта или приложения, наличие бонусов и акций, качество службы поддержки и способы ввода/вывода средств. При выборе букмекерской конторы следует обращать внимание на наличие лицензии, отзывы других пользователей, скорость выплат и лимиты на ставки. Важно также ознакомиться с правилами каждой конторы, чтобы избежать недоразумений в дальнейшем. Конкуренция между букмекерскими конторами высока, поэтому они постоянно предлагают различные акции и бонусы для привлечения новых клиентов и удержания старых.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back in the future. Many thanks
What’s up mates, how is everything, and what you would like to
say on the topic of this post, in my view its genuinely awesome designed for me.
На официальном сайте Водка казино представлены лучшие игры https://vodka-games.store/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Пациент может выбрать анонимный формат — все данные защищены, а пребывание в клинике проходит в атмосфере уважения и деликатности. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий: палаты оснащены системой вентиляции, регулируемым освещением и кнопкой вызова медперсонала. Круглосуточный контроль состояния позволяет своевременно реагировать на малейшие изменения и корректировать курс лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены воронеж[/url]
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Как выбрать компанию по продвижению в AI
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
В Новокузнецке команда «РеабКузбасс» организовала круглосуточный выезд наркологов, что позволяет оказывать помощь даже в сложных ситуациях. Пациенты часто обращаются после многодневного употребления алкоголя, когда нарушен сон, давление нестабильно, а организм истощён. В таких случаях врач выезжает в течение часа, проводит осмотр, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает оптимальную терапию.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом новокузнецк[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/anonimnaya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/
Основные этапы включают:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в красноярске[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/
Когда уместен
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-odincovo/
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post!
It’s the little changes that produce the most important changes.
Thanks for sharing!
Старт всегда один: короткий скрининг с дежурным врачом, где уточняются жалобы, длительность эпизода, текущие лекарства, аллергии и условия дома. Далее согласуется реальное окно прибытия или приёма — без обещаний «через пять минут», но с честным ориентиром и запасом на дорожную обстановку. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурацию, температуру), по показаниям выполняет ЭКГ, запускает детокс (регидратация, коррекция электролитов, защита печени/ЖКТ), объясняет ожидаемую динамику первых 6–12 часов и выдаёт памятку «на сутки»: режим сна, питьевой план, «красные флажки», точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, перевод в стационар организуется без пауз — терапия продолжается с того же места, где начата, темп лечения не теряется.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Смотрите также… – https://jenmaa.com/2023/04/09/unlock-the-power-of-digital-marketing-our-services
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-krasnogorske
ดูบอลออนไลน์ ดูบอลสด แบบ Live สด! 24 ชั่วโมง ไม่มีกระตุก ดูบอลสดออนไลน์การแข่งขันจากทุกลีกชั้นนำระดับโลก เว็บดูบอลและลิ้งค์ดูบอลที่มีคุณภาพ ภาพคมชัดตลอดเวลา พร้อมตารางการแข่งขันฟุตบอลทุกนัด อัพเดทใหม่ทุกชั่วโมง ดูบอลสด / ดูบอลออนไลน์ / ดูบอลผ่านมือถือ ด้วยขั้นตอนที่ไม่ยุ่งยาก ไม่ต้องติดตั้งโปรแกรม ก็สามารถดูบอลสดออนไลน์ ได้แบบฟรีไม่มีค่าใช้จ่ายแล้ว Live news24 เปิดให้บริการดูบอลสดในปี 2026
https://extraordinarz.com/profile.php?from=space&user=beau_gruner-495847&action=view&do=profile&name=Your_Account
Что включено на практике
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Изучите внимательнее – https://vistoweekly.com/azstarnet
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Детали по клику – https://pinerolo.scuolacottolengo.org/in-preghiera-con-il-vescovo-derio
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
I was recommended this web site by way of my cousin. I
am not positive whether or not this post is written by way of him as no one else recognize such
distinctive about my difficulty. You are wonderful! Thank you!
Когда уместен
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-shchyolkovo
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograda/
бонусы букмекеров Букмекерские конторы: твой надежный партнер в мире спортивных ставок.
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your website. Do you ever run into any internet browser compatibility problems? A small number of my blog visitors have complained about my blog not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Safari. Do you have any recommendations to help fix this problem?
Продолжайте в том же духе и привлекайте ещё больше игроков!
https://raiz-ta.com/29542666_2075689999138120_126804844433358935_n
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
А что дальше? – https://www.webgarage.ca/local-web-design-services-we-provide-for-your-business
Saya telah menyimak artikel ini hingga selesai, dan menurut saya penyampaian serta
struktur penjelasannya sangat baik, apalagi ketika penulis menyinggung topik populer
seperti KUBET, Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap, Situs Parlay Resmi, Situs Parlay
Gacor, Situs Mix Parlay, Situs Judi Bola, toto macau,
kubet login, situs parlay, Kubet Parlay, dan Judi Bola gacor.
Dari pandangan saya pribadi, artikel ini memberikan gambaran yang jelas dan mampu membantu pembaca memahami konteks yang diangkat
tanpa harus merasa bingung. Saya sendiri
cukup terkesan dengan cara penulis menyajikan informasi secara terstruktur,
sehingga setiap poinnya mudah diikuti dan relevan dengan pembahasan utama.
Selain itu, penjelasan yang diberikan juga terasa memberikan perspektif baru yang
mungkin tidak diketahui oleh sebagian besar pembaca. Rasanya tidak lengkap jika saya tidak memberikan komentar karena artikel seperti ini tentu memiliki nilai
yang patut diapresiasi. Saya berharap penulis dapat terus menyajikan konten-konten yang berkualitas,
agar pembaca lain juga bisa memperoleh wawasan yang sama seperti yang saya rasakan. Terima kasih kepada penulis atas kerja kerasnya menghadirkan artikel yang informatif, jelas,
dan mudah dipahami sehingga memberikan pengalaman membaca yang sangat menyenangkan.
Həqiqətən demək istəyirəm ki, bu saytı tapdığıma şadam.
https://www.sudoku.4thewww.com/link.php?link=https://1winazerbaijanpro.com/oyunlar
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому красногорск[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
А что дальше? – https://mrshade.com/events/under-the-skin
тензорнаяспираль Оргонит: генератор позитивной энергии
Что включено на практике
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в рязани[/url]
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/
ai sex chat
В Одинцово доступен гибкий маршрут: выездная бригада 24/7 и стационар. Домашний формат хорош при умеренной симптоматике и сохранённом контакте — он позволяет избежать перевозок и сохранить конфиденциальность. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде, повторной рвоте, выраженной слабости, нестабильном давлении/пульсе, спутанности сознания, судорожной готовности, а также у пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжёлой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек). Мы оцениваем не один признак, а совокупность факторов и динамику, чтобы не «пересидеть» дома там, где нужен приборный мониторинг. В обоих вариантах сохраняется наш принцип: индивидуализация схемы, осторожная седация, прицельная работа со сном, прозрачные объяснения назначений — и всё это с опорой на объективные показатели, а не ощущения «полегчало/ухудшилось».
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
создать службу охраны труда
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]онлайн слоты[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Уточнить детали – https://www.izumishoko.co.jp/%E8%A3%BD%E5%93%81/%E3%81%8A%E3%82%84%E3%82%AB%E3%83%86a/124
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Снижается тремор и тошнота, выравниваются вегетативные реакции, возвращается способность спокойно уснуть. Вместо «качелей» настроения и попыток самолечения появляется ощущение контроля: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём дальше.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-odincovo/
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Домашний выезд удобен, но не всегда уместен. Поводами для стационара являются длительность запоя свыше 3–5 суток, повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность, признаки делирия, декомпенсация хронических болезней. В отделении «Трезвого Ритма» в Королёве доступен расширенный мониторинг, круглосуточный уход, лабораторная диагностика и быстрые коррекции схемы. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку без задержек, по прибытии — расширенный осмотр, индивидуальный план и информирование семьи о каждом шаге.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya na domu[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in reality was once a entertainment account it. Look complex to more delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how can we keep in touch?
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
штабелер для склада купить с доставкой Штабелер с платформой: комфорт оператора.
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://vistoweekly.com/eugenio-pallisco-michigan
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
«Вектор Надежды» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы с первого звонка убрать неопределённость и вернуть ощущение контроля. Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только необходимую информацию, оценивает риски и предлагает безопасный старт: выезд на дом, дневной маршрут или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Мы объясняем каждую манипуляцию простым языком — что именно будет сделано в ближайшие часы, каких изменений ожидать к вечеру, почему выбран именно такой темп и как поймём, что схема работает. Конфиденциальность — не дополнение, а стандарт: нейтральные звонки, неброская атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте, отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает тревогу, экономит силы семьи и ускоряет стабилизацию: вместо «марафона кабинетов» — один связный маршрут с понятными контрольными точками.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://worksplumbing.us/commercial-exterior-catch-basins/catch-basin-clogged
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
Чтобы процедура прошла быстрее и спокойнее, подготовьте пространство и информацию о пациенте заранее: это экономит время и повышает безопасность.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-korolev/
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя красногорск[/url]
После первичной стабилизации врач обычно объясняет близким, почему «просто поспать» не всегда получается сразу, сколько времени может держаться раздражительность и как правильно выстроить режим, чтобы не спровоцировать повторный срыв в первые дни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Формат
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo/
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает лечение запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем. Здесь пациент получает безопасное и эффективное восстановление.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Самый частый повод — не только «плохое похмелье», а именно абстинентный синдром после запоя: когда самочувствие ухудшается при прекращении алкоголя, а попытки «опохмелиться» лишь продлевают проблему. Важно ориентироваться не на терпимость человека к дискомфорту, а на объективные признаки: если симптомы нарастают, сон сорван, поведение становится нестабильным, а тело реагирует паникой, тремором и скачками давления, лучше не тянуть. Особенно осторожными нужно быть при хронических болезнях сердца, печени и сосудов: при них цена ошибки выше, а «универсальные» домашние схемы могут навредить.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре — услуга клиники «Детокс». Специалисты оказывают квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru[/url]
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it
much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often.
Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Excellent work!
Very sleek and professionally built site Big Bass Splash!
https://big-bass-splash-uk.uk/game
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Лучшее решение — прямо здесь – https://portermetrics.com/en/modelo-en/digital-marketing-en/modelo-relatorio-google-business-profile-reviews-porter-2
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Есть чему поучиться – https://midbreath.net/2020/09/03/hello-world
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя цена сочи[/url]
Türkiyenin yeni yıldızı, sampuanorg ile artık saçlarınız ve cildiniz
emin ellerde!
Когда ночь затягивается, тревога нарастает, а самочувствие «скачет», важны не громкие обещания, а последовательность медицинских действий. «Трезвый Контур» в Одинцово выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от звонка до облегчения прошло минимум времени и ни один шаг не был импровизацией: первичная оценка рисков, персональная инфузионная терапия, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, понятные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не «вырубаем» пациента сильными седативными — дозировки и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые препараты. Цель — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, стабилизировать давление и пульс, вернуть управляемый сон и зафиксировать маршрут на ближайшие 24–72 часа, чтобы утро началось не с нового витка симптомов, а с предсказуемого восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя цена сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница сочи[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
hello!,I really like your writing very so much! proportion we keep up a correspondence extra about your article on AOL? I require an expert in this area to resolve my problem. Maybe that is you! Taking a look forward to see you.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Это ещё не всё… – https://espigaoalerta.com.br/2023/06/18/agencia-minas-gerais-comeca-nesta-segunda-feira-o-primeiro-censo-previdenciario-do-estado-de-minas-gerais
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru
Материал включает занимательные, но незначимые детали, которые трудно назвать важными, но они дополняют общую картину.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]казино онлайн[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
«Эгида Трезвости» выстраивает лечение вокруг предсказуемости: понятный старт, прозрачные шаги, нейтральная коммуникация и постоянная связь с дежурным врачом. Мы не заставляем объясняться «по кругу» и не перегружаем терминами — достаточно фактов, которые влияют на безопасность и выбор схемы. Уже при первом контакте становится ясно, где лучше начинать (дом, приём, стационар 24/7), что будет сделано в ближайшие часы и как оценим результат к вечеру. Конфиденциальность встроена в регламент: на звонках — нейтральные формулировки, на выездах — неброская экипировка, доступ к медицинской информации — только у задействованной команды. Это снижает фоновую тревогу и позволяет семье сосредоточиться на простых действиях, которые реально помогают держать курс.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Many thanks, However I am having
difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know why I
cannot subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting the same RSS problems?
Anyone who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanx!!
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Cilt bakımının yanı sıra saç bakımı da ihmal edilmemelidir.
Özellikle nem kaybı yaşayan saçlar için uygun ürünlerin tercih edilmesi gerekir.
Normal ve Kuru Saçlar İçin Şampuan, saç derisini nazikçe temizlerken saç tellerini besler.
Ürün detaylarını incelemek isterseniz buraya bakabilirsiniz:
https://start.me/p/bprXaR/ana-sayfa
If you follow the Russian-language streaming scene, you’ve likely heard about the Mellstroy Game project. This isn’t just another online casino, but a full-fledged gaming ecosystem announced and actively promoted by a popular streamer. The website [url=https://jobhop.co.uk/blog/408770/———-480]mellstroy game[/url] offers a detailed look at the framework technical implementation, licensing, and current bonus terms. The core of the project is a synthesis of entertainment information and classic betting, where stream viewers can not only watch the gameplay but also participate directly through integrated mechanics.
An analysis of the game lobby reveals a serious approach to volume and classic gambling curation. The platform partners with leading providers like NetEnt, Pragmatic Play, and Evolution Gaming, ensuring fair Return to Player (RTP) rates for slots and table games. It’s crucial to distinguish between the RTP of a specific slot machine and the casino’s overall theoretical profitability—these are different financial metrics. For example, slots like Book of Dead often feature an RTP around 96%, which is dogma for quality products. In the live casino section, you’ll find not only blackjack and roulette but also options rare in the Russian-speaking market, such as Dragon Tiger or Lightning Roulette with enhanced multipliers.
Financial transactions are a critically important aspect for any aficionado. Mellstroy Game offers a criterion market set of payment systems: from VISA/Mastercard bank cards to e-wallets and cryptocurrencies. Pay close attention to the account verification policy. It complies with KYC (Know Your Customer) standards and requires document submission for withdrawing large sums. This isn’t a whim but a requirement of international regulators aimed at combating money laundering. Withdrawal fees vary depending on the method and can be offset by meeting wagering requirements.
The bonus program requires detailed study. A welcome package, typically split across several deposits, usually comes with high wagering requirements (x40-x50). Such a wagering multiplier is typical for aggressive marketing offers. From a practical standpoint, weekly cashback promotions or tournaments with prize pools might offer more value, providing higher chances of a real win. Always read the full terms and conditions of promotions, especially clauses about maximum bet sizes while wagering a bonus and the list of eligible games.
The technical side is implemented on a responsive infrastructure. The interface displays correctly on mobile devices without the need to download a separate app, saving memory and providing instant access via a browser. Modern SSL encryption is used to protect transaction data. To circumvent potential provider blocks, a working mirror site is provided; the current link can be found in the project’s official Telegram channel. This is grade practice for maintaining stable access.
Safety and responsible gaming are the foundation of trust. Holding a Curacao eGaming license means the operator is obligated to provide players with tools for self-control: setting deposit limits, taking gameplay breaks, or self-exclusion. Ignoring these tools is unwise. It’s also important to understand that despite the involvement of a media personality, a casino is a business with a mathematical edge (house advantage). Streams showcasing large wins are part of the marketing plan, not a guide to action.
The final verdict on the Mellstroy Game project is nuanced. On one hand, it’s a professionally assembled platform with a license, a strong provider pool, and thoughtful logistics. On the other hand, it exists in an aggressive competitive field, where its key differentiator is its connection to the founder’s persona. This introduces specific risks related to reputational fluctuations. For an experienced aficionado evaluating a casino through the lens of mathematics, technical reliability, and withdrawal conditions, the platform presents certain interest. Beginners, however, should first study the basic principles of wagering, probability theory, and only then consider making a deposit, strictly based on their entertainment budget, not on expectations of quick profit.
Домашний выезд удобен, но не всегда уместен. Поводами для стационара являются длительность запоя свыше 3–5 суток, повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность, признаки делирия, декомпенсация хронических болезней. В отделении «Трезвого Ритма» в Королёве доступен расширенный мониторинг, круглосуточный уход, лабораторная диагностика и быстрые коррекции схемы. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку без задержек, по прибытии — расширенный осмотр, индивидуальный план и информирование семьи о каждом шаге.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]вывод из запоя королева[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It
really useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope
to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Когда ночь затягивается, тревога нарастает, а самочувствие «скачет», важны не громкие обещания, а последовательность медицинских действий. «Трезвый Контур» в Одинцово выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от звонка до облегчения прошло минимум времени и ни один шаг не был импровизацией: первичная оценка рисков, персональная инфузионная терапия, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, понятные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не «вырубаем» пациента сильными седативными — дозировки и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые препараты. Цель — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, стабилизировать давление и пульс, вернуть управляемый сон и зафиксировать маршрут на ближайшие 24–72 часа, чтобы утро началось не с нового витка симптомов, а с предсказуемого восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-odincovo
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Когда запой затягивается, организм быстро входит в режим перегрузки: нарушается сон, скачет давление, усиливается тревога, появляется дрожь, тошнота, потливость и резкая слабость. В такой ситуации «перетерпеть» или лечиться домашними средствами — рискованная стратегия: состояние может ухудшаться волнами, а осложнения иногда развиваются резко, без долгой подготовки. Выезд нарколога на дом в Красногорске нужен для того, чтобы снять острую интоксикацию и абстиненцию безопасно, под контролем показателей, без лишней суеты и без поездок по стационарам в разгар плохого самочувствия.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]platnyi narkolog na dom[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее тут – https://shikharsandesh.in/archives/23
Этот набор информации привлекает мелочами и необычными ракурсами, предлагая взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но разнообразят знакомство с темой.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]займ без процентов[/url]
Когда уместен
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
https://nerdgaming.science/wiki/User:Codemelbet2026
штабелер самоходный цена Штабелер электрический с аккумулятором: автономная работа и удобство эксплуатации.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробности по ссылке – https://yoshihiroito.jp/solar-eclipse-152834_1280
Immerse yourself in an exciting world [url=https://drones-1show.com/]drone lights show[/url], where technology and art merge in an incredible spectacle.
Ultimately, drone performances combine technological progress with artistic expression to transform public spectacles.
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]vyvod-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://suki.one/music/27?replyTo=23568
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов сочи[/url]
Сначала — сбор короткого анамнеза и проверка лекарственных взаимодействий, затем — старт инфузии с контролем темпа. Параллельно купируются тошнота, тремор, тахикардия, корректируется сон. Каждые 15–20 минут специалист оценивает динамику и при необходимости меняет схему. В завершение вы получаете письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnogorske/
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya korolev[/url]
Hey would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re using? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you suggest a good web hosting provider at a honest price? Many thanks, I appreciate it!
Wonderful article! This is the kind of info that are meant to
be shared across the internet. Shame on the search engines for now not positioning this put
up higher! Come on over and seek advice from my
site . Thank you =)
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Когда запой затягивается, организм быстро входит в режим перегрузки: нарушается сон, скачет давление, усиливается тревога, появляется дрожь, тошнота, потливость и резкая слабость. В такой ситуации «перетерпеть» или лечиться домашними средствами — рискованная стратегия: состояние может ухудшаться волнами, а осложнения иногда развиваются резко, без долгой подготовки. Выезд нарколога на дом в Красногорске нужен для того, чтобы снять острую интоксикацию и абстиненцию безопасно, под контролем показателей, без лишней суеты и без поездок по стационарам в разгар плохого самочувствия.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/narkolog-v-krasnogorske/
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Цель
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove/
Чтобы легче сопоставить риски и плотность наблюдения, ниже даём живой ориентир. Это не заменяет осмотр, но помогает всей семье понимать логику врача до приезда.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сочи[/url]
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
La innovadora [url=https://show-1de-drones.com/]compania de espectaculos de drones[/url] presento un impresionante espectaculo de drones iluminados en el cielo nocturno, cautivando a todos los asistentes con su show de luces con drones.
Los drones han revolucionado la forma en que se entiende el entretenimiento, ofreciendo un espectaculo aereo lleno de color y vida . Estos espectaculos suelen incluir una gran cantidad de drones que vuelan en formaciones precisas y sincronizadas, creando patrones y disenos en el cielo. Estos eventos a menudo cuentan con una variedad de drones que realizan acrobacias y formaciones complejas, deleitando a los espectadores con su agilidad y coordinacion . Los organizadores de estos eventos trabajan arduamente para programar y ensayar las rutinas de vuelo, asegurandose de que cada dron se mueva en perfecta sincronia con los demas. El proceso de planificacion y ensayo para un espectaculo de drones es extremadamente detallado y requiere una gran cantidad de tiempo y esfuerzo .
El uso de drones en los espectaculos ha abierto nuevas posibilidades para la expresion artistica y la entretenimiento. Los drones han permitido a los artistas y disenadores explorar nuevas formas de creatividad y expresion en el cielo . Ademas, estos eventos han generado un gran interes entre el publico, que se maravilla con la belleza y la complejidad de los patrones y disenos creados por los drones. La respuesta del publico a los espectaculos de drones ha sido abrumadoramente positiva, con muchos expresando su asombro y admiracion por la habilidad y la coordinacion de los drones.
Tecnica y Seguridad:
La realizacion de un espectaculo de drones requiere una gran cantidad de planificacion y preparacion, especialmente en lo que respecta a la seguridad. La seguridad es la principal preocupacion al organizar un espectaculo de drones, ya que se deben tomar medidas para garantizar la seguridad de los espectadores y de los operadores de los drones . Los drones utilizados en estos espectaculos estan equipados con tecnologia avanzada que les permite volar de manera autonoma y realizar maniobras complejas. La tecnologia de vuelo autonomo es crucial para la realizacion de estos espectaculos, ya que permite a los drones realizar movimientos precisos y sincronizados . Ademas, los operadores de los drones deben tener una gran habilidad y experiencia para controlar los drones de manera efectiva. Los operadores de drones deben tener una gran habilidad y conocimiento para controlar los drones de manera segura y precisa .
La seguridad de los espectadores es tambien una preocupacion importante, ya que los drones vuelan a baja altitud y pueden representar un riesgo si no se manejan correctamente. Los organizadores de los espectaculos de drones deben tomar medidas para garantizar que los espectadores esten a una distancia segura de los drones . Para mitigar este riesgo, los organizadores suelen establecer zonas de seguridad y seguir estrictos protocolos de seguridad. Se siguen protocolos de seguridad estrictos para garantizar que los drones se manejen de manera segura y responsable .
Impacto y Futuro:
El impacto de los espectaculos de drones en la industria del entretenimiento ha sido significativo, abriendo nuevas posibilidades para la creatividad y la innovacion. La tecnologia de drones ha permitido la creacion de espectaculos aereos que deslumbran a las audiencias con su precision y belleza . Ademas, estos eventos han generado un gran interes entre el publico, que se maravilla con la belleza y la complejidad de los patrones y disenos creados por los drones. La respuesta del publico a los espectaculos de drones ha sido abrumadoramente positiva, con muchos expresando su asombro y admiracion por la habilidad y la coordinacion de los drones. En el futuro, se espera que la tecnologia de drones siga evolucionando, permitiendo la creacion de espectaculos aun mas complejos y emocionantes. Los avances en la tecnologia de drones abriran nuevas posibilidades para la expresion artistica y la entretenimiento en el futuro.
Los espectaculos de drones tambien tienen el potencial de ser utilizados en una variedad de contextos, desde eventos culturales hasta espectaculos de entretenimiento. La tecnologia de drones puede ser utilizada para crear experiencias visuales unicas y emocionantes en una variedad de entornos . Ademas, la tecnologia de drones puede ser utilizada para promover la conciencia y la educacion sobre temas importantes, como la conservacion del medio ambiente y la seguridad. La tecnologia de drones puede ser utilizada para promover la conciencia y la educacion sobre temas importantes, como la conservacion del medio ambiente y la seguridad .
Conclusion:
En conclusion, los espectaculos de drones son una forma de entretenimiento emocionante y innovadora que combina la tecnologia y la creatividad para ofrecer una experiencia visual unica. Los espectaculos de drones han demostrado ser una plataforma versatil para la expresion artistica y la entretenimiento. Estos eventos han generado un gran interes entre el publico y han abierto nuevas posibilidades para la creatividad y la innovacion en la industria del entretenimiento. Los espectaculos de drones han atraido a audiencias de todas las edades, quienes se quedan asombradas con la tecnologia y la creatividad que se despliega en el cielo . En el futuro, se espera que la tecnologia de drones siga evolucionando, permitiendo la creacion de espectaculos aun mas complejos y emocionantes. Se espera que los espectaculos de drones sigan siendo una forma popular de entretenimiento, con nuevas y emocionantes posibilidades para la creatividad y la innovacion .
Los espectaculos de drones tienen el potencial de ser utilizados en una variedad de contextos, desde eventos culturales hasta espectaculos de entretenimiento. Los espectaculos de drones pueden ser utilizados en una variedad de contextos, desde eventos culturales hasta espectaculos de entretenimiento . Ademas, la tecnologia de drones puede ser utilizada para promover la conciencia y la educacion sobre temas importantes, como la conservacion del medio ambiente y la seguridad. Los espectaculos de drones pueden ser utilizados para educar al publico sobre temas importantes y promover la conciencia y la comprension .
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Подробности по ссылке – http://dg162.net/wp/%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/
You made some good points there. I looked on the internet
for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this website.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-krasnogorske/
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
gay anal vibrator
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в сочи[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в сочи[/url][url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в сочи[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica[/url]
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркология[/url]
Что включено на практике
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/[/url]
My spouse and I stumbled over here by a different website and thought I may as well check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking at your web page again.
I am in fact happy to read this blog posts which carries tons of helpful information, thanks for providing these
kinds of data.
Feel free to surf to my blog; https://latbet.click/
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Цель
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-shchyolkovo/
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
This game looks amazing! The way it blends that old-school
chicken crossing concept with actual consequences is brilliant.
Count me in!
Okay, this sounds incredibly fun! Taking that nostalgic chicken crossing gameplay and adding real risk?
I’m totally down to try it.
This is right up my alley! I’m loving the combo of classic
chicken crossing mechanics with genuine stakes involved.
Definitely want to check it out!
Whoa, this game seems awesome! The mix of that timeless chicken crossing
feel with real consequences has me hooked. I need to play this!
This sounds like a blast! Combining that iconic chicken crossing gameplay with actual stakes?
Sign me up!
I’m so into this concept! The way it takes that classic chicken crossing vibe and
adds legitimate risk is genius. Really want to give it a go!
This game sounds ridiculously fun! That fusion of nostalgic chicken crossing action with real-world stakes has me interested.
I’m ready to jump in!
Holy cow, this looks great! Merging that beloved chicken crossing style with tangible consequences?
I’ve gotta try this out!
Формат
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]ставки на спорт[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно сочи[/url]
It’s not something separate from life—it is life, moving through us constantly.
Still, in a world overflowing with advice, it’s easy to lose true understanding.
Shortcuts promise results but ignore individuality.
The body sends quiet messages—fatigue, restlessness, hunger, calm—but we rush past them.
The way we sleep, recover, and focus follows an inner logic that can’t be copied.
Each moment of attention reveals something new about our inner landscape.
In that connection, we find balance not through control, but through understanding.
Every insight deepens the relationship we have with ourselves.
When the idea of gentle awareness feels more natural than pressure.
To move with awareness instead of against it.
Observation instead of reaction.
And with every realization, we move closer to genuine balance.
What feels like intuition is often grounded in clear biological patterns.
You might be wondering how all of this connects to kamagra.
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс чат[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi24.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It absolutely useful and it
has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & help other users like its aided me.
Good job.
Foi esse o caso durante o embate inaugural entre Casper Ruud e Francisco Cerundolo, com o norueguês recebendo ajuda direta de ‘treinadores’ muito especiais.
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в сочи[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://pspa.pl/produkt/brass-saxophone
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в сочи[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://espores.com.ar/turmalina-2023
I do agree with all the ideas you’ve introduced in your post. They are really convincing and can definitely work. Still, the posts are very short for beginners. May just you please lengthen them a bit from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
Окна в Алматы в рассрочку Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
Use the betwinner promo kodas 2025 during sign-up at https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ to activate your welcome bonus instantly.
Thanks. Ample tips.
best online casino sign up bonus [url=https://bhcmerced.org/#]online casino free spins no deposit[/url]
Что включено на практике
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника помощь на дому[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
Пластиковые окна в Алматы Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-krasnogorske/
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Как выбрать идеальный купальник
Пластиковые окна в Алматы цена Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Полная информация здесь – https://thisisnorthcyprus.com/regulations-and-rules/how-can-i-register-my-phone-in-north-cyprus
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-oblasti[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это всегда баланс между скоростью и безопасностью. Дома трудно заметить скрытые ухудшения, особенно ночью: давление и пульс «гуляют», нарастает обезвоживание, сон рваный и тревожный. В «Трезвом Контуре» этот хаос замещается управляемостью: перед выездом дежурный врач собирает ключевые данные (длительность эпизода, лекарства, аллергии, сопутствующие болезни), на месте проводится экспресс-диагностика (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания), затем запускается схема терапевтической поддержки. Мы постоянно «подстраиваем» инфузии по реакции организма, а не по шаблонной карте: где-то важнее регидратация, где-то — коррекция электролитов, где-то — бережная седация для ночи. Для семьи это значит одно: меньше догадок, больше ясности. Если по картине риски высоки, мы аргументированно предлагаем стационар в Одинцово — и организуем транспортировку без пауз, потому что цена задержки в такие часы всегда выше.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-odincovo/
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
The appeal argued that electoral bonds are “completely traceable,
” as evidenced by SBI’s secret number-based record
of bond buyers and the political parties to which they
give.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Смотрите также… – https://nickyalexandraphotography.com/portrait
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника анонимная помощь[/url]
строительство гаража москва
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» высылает нарколога на дом для срочной помощи при запое. Быстро и безопасно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
https://bbssochi.ru/users/65682
Sayt çox funksionaldır.
http://redirme.com/?to=https://mostbetazpro.net/demo-oyunlari/
Hello there! I just would like to give you a big thumbs up for the excellent information you’ve got right here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your web site for more soon.
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Publishing my authentic take regarding this online casino. I mention promotions, banking, and gameplay vibe. Emphasizing special rewards and processing time. Covering how the page acts and pays winners. Talking about what’s good and bad I noticed while playing. Writing about what was fun and what I didn’t enjoy. More details are covered in the complete article Holyluck casino
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Купить ПВХ окна в Алматы Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Формат
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkologiya[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Посмотреть всё – https://maidentistry.com/dental-implants-in-st-petersburg-fl/the-cost-of-full-mouth-dental-implants-investment-or-expense
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – https://www.wuoz.malopolska.pl/cropped-wuoz_logo-1-jpg
Simply want to say your article is as surprising. The clearness for your submit is
simply great and i could assume you are a professional on this subject.
Fine with your permission allow me to snatch your RSS feed to stay up to date with
forthcoming post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please keep up the enjoyable work.
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: жалобы, длительность эпизода, список лекарств, аллергии, переносимость нагрузки, есть ли поддержка рядом. После этого согласуем реалистичное окно визита с учётом трафика, подъезда и «тихого» места для процедуры. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура), при показаниях делает ЭКГ и запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, по необходимости — щадящую противотревожную поддержку и кислород. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, щадящее питание, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, переводим в стационар без пауз и обнулений — терапия продолжается в той же логике и темпе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Пластиковые окна в Алматы Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Есть чему поучиться – https://www.cnetsoeducation.com/product/pulses-from-organic-farm
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Чтобы процедура прошла быстрее и спокойнее, подготовьте пространство и информацию о пациенте заранее: это экономит время и повышает безопасность.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-korolev
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в нижнем новгороде[/url]
That is very attention-grabbing, You’re a very skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and sit up for looking for more of your great post.
Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks https://unosesentaiuno.com/2023/06/05/taj-luxury/
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-odincovo
В условиях нестабильной электросети важно заранее подготовиться. Использование зарядная станция позволяет избежать неудобств. Это разумное решение для дома.
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Подробнее тут – https://www.livsnyteri.no/cropped-anjaogtorill2-1-jpg
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/
Окна в Алматы в рассрочку Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Подробности по ссылке – https://wraparoundkids.com.au/blogs/index.php/2019/11/26/assistive-technology
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Hello, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog site in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some
overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Other then that, terrific blog! https://restorehopeorg.org/2022/07/13/reasons-why-to-download-android-vpn/
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Что включено на практике
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Чтобы легче сопоставить риски и плотность наблюдения, ниже даём живой ориентир. Это не заменяет осмотр, но помогает всей семье понимать логику врача до приезда.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
What’s up, yeah this article is really nice and I have learned lot of things from it concerning blogging.
thanks.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Это ещё не всё… – https://komussyu84.com/?attachment_id=5
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в сочи[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-krasnogorske/
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Полная информация здесь – https://www.gishurim.co.il/3-%D7%93%D7%91%D7%A8%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%90%D7%A9%D7%A8-%D7%9E%D7%AA%D7%A7%D7%99%D7%99%D7%9E%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%91%D7%9B%D7%9C-%D7%94%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9A-%D7%92%D7%99%D7%A9%D7%95%D7%A8-%D7%92%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95
оргонит Orgonite: Преобразователь энергии.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полная информация здесь – https://encuadernavila.es/producto/libro-de-firmas-110-14
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом нижний новгород[/url]
제 오빠가 이 블로그를 좋아할 거라고 추천했습니다.
그는 완전히 옳았습니다. 이 포스트가 정말 제 하루를 만들어 줬습니다.
이 정보를 찾느라 얼마나 많은 시간을 보냈는지 믿을 수 없습니다!
감사합니다!
Hello there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site?
I’m getting sick and tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform.
I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a
good platform.
I can’t get enough of your website! Your posts are so well-researched, and
I love the clarity in your writing. Have you considered guest posting
on other sites to expand your reach? Keep up the outstanding work!
이 웹사이트는 정말 놀라운 곳이에요!
digital agency dubai 관련 콘텐츠가 너무 유익해요.
SEO를 강화하기 위해 키워드 최적화 팁이 있다면 공유해 주세요.
멋진 포스트 감사합니다! 감사합니다!
Старт всегда начинается с точного, но бережного скрининга. Мы заранее обсуждаем бытовые условия и логистику — доступ к подъезду, лифту, возможность обеспечить тишину — чтобы не потерять темп на мелочах. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура), при показаниях выполняет ЭКГ и запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, при необходимости — щадящую противотревожную поддержку и кислород. Пациент и близкие получают письменную памятку «на сутки» с режимом сна и питья, «красными флажками» и точным временем контрольной связи. Если домашний формат перестаёт быть достаточным, перевод в стационар организуем без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения переезжают вместе с пациентом, ничего не теряется.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnogorske
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Когда уместен
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-serpuhove
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
You revealed this exceptionally well.
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-domodedovo[/url]
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to mention that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing on your feed and I hope you write once more soon!
Ремонт бытовой техники необходим для сохранения функциональности бытовых приборов. Это связано с тем, что бытовая техника, не проходящая регулярный ремонт, может иметь более короткий срок службы . Ремонт также дает возможность выявить потенциальные неисправности и исправить их до того, как они причинят значительный ущерб .
Ремонт бытовой техники имеет приоритетное значение для людей, которые хотят максимально продлить срок службы своих вещей. правильный уход и ремонт бытовой техники может предотвратить преждевременное истощение средств семьи. ремонт можно осуществлять как самостоятельно, так и с привлечением квалифицированных специалистов .
Типы ремонта бытовой техники
Существует несколько типов ремонта бытовой техники, в зависимости от типа неисправности . Например, ремонт электрических схем может быть необходим для устранения неисправностей в плите или холодильнике . ремонт можно выполнять как в специализированных мастерских, так и на дому у клиента, в зависимости от сложности ремонта .
Сложность ремонта бытовой техники может варьироваться в широком диапазоне, в зависимости от характера неисправности. ремонт простых неисправностей, таких как неисправность проводки или неисправность вилки, может быть выполнен самостоятельно . ремонт можно осуществлять как с использованием оригинальных комплектующих, так и с использованием их аналогов, в зависимости от сложности ремонта.
Инструменты и материалы для ремонта
Для выполнения ремонта бытовой техники требуются определенные инструменты и материалы . для ремонта механических деталей необходимы инструменты, такие как сверла и напильники. Кроме того, ремонт может требовать использования специальных материалов, таких как припой и флюс .
Тип инструментов и материалов, необходимых для ремонта бытовой техники, может быть различным, в зависимости от типа ремонта. для ремонта незначительных неисправностей могут быть необходимы более сложные инструменты, такие как тестер и провод. Кроме того, ремонт можно выполнять как с использованием ручных инструментов, так и с использованием электрических инструментов, в зависимости от сложности ремонта .
Профессиональный ремонт и его преимущества
Профессиональный ремонт бытовой техники осуществляется с гарантией качества и безопасностью. профессиональные ремонтники имеют необходимые знания и опыт для выполнения сложных ремонтов . профессиональный ремонт может быть выполнен оперативно и с минимальными затратами .
Профессиональный ремонт бытовой техники предполагает не только ремонт, но и диагностику и профилактику . Например, профессиональные ремонтники могут выявить потенциальные проблемы и устранить их до того, как они станут серьезными . Кроме того, профессиональный ремонт бытовой техники может быть осуществлен с учетом индивидуальных особенностей и требований клиента .
ремонт бытовой техники [url=remont-bytovoj-tehniki-ekaterinburg.ru]https://remont-bytovoj-tehniki-ekaterinburg.ru/[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника скорая[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Формат
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://backgroundscreeningdirectory.com/blog/background-checks-now-include-social-media-checks
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Что включено на практике
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники в области[/url]
Thankfulness to my father who shared with me concerning this webpage,
this blog is in fact amazing.
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]врач нарколог на дом краснодарский край[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» проводит выезд нарколога на дом для безопасного вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Что включено на практике
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Чтобы процедура прошла быстрее и спокойнее, подготовьте пространство и информацию о пациенте заранее: это экономит время и повышает безопасность.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого сочи[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – https://www.skyhilocksmith.com/locksmith/jeep-locksmith-colorado-springs
Что получите за 24 часа
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch[/url]
защита_от_сглаза Кулонженский: Кулон для женщин.
https://adguru.net/code-promo-1xbet-valide-2026-1x200mix-bonus-vip-70965.html
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
I don’t even understand how I ended up here, however I believed
this put up used to be great. I do not understand who you’re but certainly you are going to a famous blogger
in case you aren’t already. Cheers!
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kasherlawgroup.com/quote-2
Wow, that’s what I was looking for, what a information! existing here
at this webpage, thanks admin of this web page.
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Узнайте всю правду – https://espigaoalerta.com.br/2024/08/10/trabalho-de-remocao-das-vitimas-de-acidente-aereo-e-encerrado-em-vinhedo
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a weblog web site? The account helped me a appropriate deal. I had been a little bit familiar of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Цель
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-serpuhove/
Ниже — ориентир, который помогает сопоставить риски, плотность наблюдения и ожидаемую скорость стабилизации. Таблица не заменяет очный осмотр, но экономит время на принятие решений и делает логику врача понятной всей семье.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Что делаем на практике
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь домодедово[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает лечение запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем. Здесь пациент получает безопасное и эффективное восстановление.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Take
care! Where are your contact details though?
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Уточнить детали – https://darpanpublictrust.org/index.php/2022/08/16/annual-general-meeting-dated-15th-august-2022
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Экстренная помощь при запое в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница на дому от опытных врачей-наркологов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Подробнее тут – https://thenewblackmagazine.com/2024/01/13/httpwww-thenewblackmagazine-comview-aspxindex2706
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом краснодарский край[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника сочи[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Есть чему поучиться – https://catsanz.com/the-simple-things-in-life
Цель
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника красногорск[/url]
Мы строим лечение вокруг предсказуемости: минимум лишних вопросов, максимум конкретики и понятный план на ближайшие сутки. Дежурный врач уточняет только то, что влияет на безопасность — длительность эпизода, актуальные лекарства и переносимость, сон и апетит, наличие поддержки дома. Из этого скелета рождается маршрут: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Конфиденциальность встроена по умолчанию: нейтральная коммуникация, доступ к карте только у вовлечённой команды, документы по запросу — в нейтральных формулировках. Внешний шум гасим, внимание переводим на цель: ровная стабилизация без «качелей» и с понятными контрольными точками.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно сочи[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Узнайте всю правду – https://habersizseniz.com/kurabiyenin-pistigini-nasil-anlariz
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника сочи[/url]
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: жалобы, длительность эпизода, список лекарств, аллергии, переносимость нагрузки, есть ли поддержка рядом. После этого согласуем реалистичное окно визита с учётом трафика, подъезда и «тихого» места для процедуры. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура), при показаниях делает ЭКГ и запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, по необходимости — щадящую противотревожную поддержку и кислород. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, щадящее питание, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, переводим в стационар без пауз и обнулений — терапия продолжается в той же логике и темпе.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Чтобы легче сопоставить риски и плотность наблюдения, ниже даём живой ориентир. Это не заменяет осмотр, но помогает всей семье понимать логику врача до приезда.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-domodedovo
What’s up friends, pleasant piece of writing and nice urging commented here, I am really enjoying by these.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Лучшее решение — прямо здесь – https://vistoweekly.com/whispering-words-of-love-in-punjabi-shayari
Global Alternative Trade Financing Global Alternative Trade Financing: Looking ahead, Global Alternative Trade Financing is poised to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of global trade. As technology continues to evolve and new financial innovations emerge, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and accessible solutions that empower businesses to overcome financial barriers and participate fully in the global economy. This will require collaboration between governments, regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers to create a supportive ecosystem that fosters innovation, mitigates risk, and promotes sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site,
how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a appropriate deal.
I had been tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast offered vivid clear idea
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в сочи[/url]
парк отель со все включено Аренда базы отдыха в Подмосковье – это популярный вариант для проведения выходных или отпуска на природе. Базы отдыха в Подмосковье предлагают размещение в домиках, коттеджах или номерах в гостинице. Выбор зависит от ваших предпочтений и бюджета.
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Цель
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-krasnogorske/
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Базы отдыха с питанием предлагают разнообразное меню и избавляют от необходимости готовить самостоятельно, что особенно удобно для семей с детьми. База отдыха с зоопарком – это отличный вариант для семейного отдыха, где дети смогут увидеть различных животных и птиц. Загородные базы отдыха предлагают комфортное проживание и широкий спектр услуг, включая организацию экскурсий и развлекательных программ. Снять базу отдыха в Подмосковье можно на выходные или на более длительный срок, в зависимости от ваших планов и предпочтений. Базы отдыха подмосковья область предлагают комфортный отдых на природе. парк отель с зоопарком
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
Когда уместен
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
If you follow the Russian-language streaming scene, you’ve likely heard about the Mellstroy Game project. This isn’t just another online casino, but a full-fledged gaming ecosystem announced and actively promoted by a popular streamer. The website [url=https://jobhop.co.uk/blog/408770/———-480]mellstroy game[/url] offers a detailed look at the system technical implementation, licensing, and current bonus terms. The core of the project is a synthesis of entertainment subjectmatter and classic gambling, where stream viewers can not only watch the gameplay but also participate directly through integrated mechanics.
An analysis of the game lobby reveals a serious approach to fulfillment and classic gaming curation. The system partners with leading providers like NetEnt, Pragmatic Play, and Evolution Gaming, ensuring fair Return to Player (RTP) rates for slots and table games. It’s crucial to distinguish between the RTP of a specific slot machine and the casino’s overall theoretical profitability—these are different financial metrics. For example, slots like Book of Dead often feature an RTP around 96%, which is canon for quality products. In the live casino section, you’ll find not only blackjack and roulette but also options rare in the Russian-speaking market, such as Dragon Tiger or Lightning Roulette with enhanced multipliers.
Financial transactions are a critically important aspect for any member. Mellstroy Game offers a convention market set of payment systems: from VISA/Mastercard bank cards to e-wallets and cryptocurrencies. Pay close attention to the account verification policy. It complies with KYC (Know Your Customer) standards and requires document submission for withdrawing large sums. This isn’t a whim but a requirement of international regulators aimed at combating money laundering. Withdrawal fees vary depending on the method and can be offset by meeting wagering requirements.
The promotion program requires detailed study. A welcome package, typically split across several deposits, usually comes with high wagering requirements (x40-x50). Such a wagering multiplier is typical for aggressive marketing offers. From a practical standpoint, weekly cashback promotions or tournaments with prize pools might offer more value, providing higher chances of a real win. Always read the full terms and conditions of promotions, especially clauses about maximum bet sizes while wagering a bonus and the list of eligible games.
The technical side is implemented on a responsive platform. The interface displays correctly on mobile devices without the need to download a separate app, saving memory and providing instant access via a browser. Modern SSL encryption is used to protect transaction data. To circumvent potential provider blocks, a working mirror site is provided; the current link can be found in the project’s official Telegram channel. This is template practice for maintaining stable access.
Safety and responsible gaming are the foundation of trust. Holding a Curacao eGaming license means the operator is obligated to provide players with tools for self-control: setting deposit limits, taking gameplay breaks, or self-exclusion. Ignoring these tools is unwise. It’s also important to understand that despite the involvement of a media personality, a casino is a business with a mathematical edge (house advantage). Streams showcasing large wins are part of the marketing technique, not a guide to action.
The final verdict on the Mellstroy Game project is nuanced. On one hand, it’s a professionally assembled platform with a license, a strong provider pool, and thoughtful logistics. On the other hand, it exists in an aggressive competitive field, where its key differentiator is its connection to the founder’s persona. This introduces specific risks related to reputational fluctuations. For an experienced gambler evaluating a casino through the lens of mathematics, technical reliability, and withdrawal conditions, the environment presents certain interest. Beginners, however, should first study the basic principles of wagering, probability theory, and only then consider making a deposit, strictly based on their entertainment budget, not on expectations of quick profit.
Формат
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Это ещё не всё… – https://bulbuliindia.com/product/moroccan-wall-plate
Hello Dear, are you genuinely visiting this site on a regular basis, if so afterward you will without doubt get fastidious knowledge.
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Материал включает занимательные, но незначимые детали, которые трудно назвать важными, но они дополняют общую картину.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Что включено на практике
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» высылает нарколога на дом для срочной помощи при запое. Быстро и безопасно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Тут один и тот же человек от нескольких пользователей отписывается. https://tractor-detal-kansk.ru 31 страницу отзывов почитайте – увидите всех. Кто то только что зарегился , ктото год назад , кому что аккаунт блокнули или забыл пароль от старого акка – он зарегился по новой .
глэмпинг подмосковье у водоема Глэмпинги в Подмосковье с домиками и чаном пользуются особым спросом. Чан – это большая купель с подогретой водой, в которой можно купаться на открытом воздухе в любое время года. Аренда глэмпинга с чаном – это возможность получить уникальный опыт и насладиться красотой природы, согреваясь в теплой воде.
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» проводит выезд нарколога на дом для безопасного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar29.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Чтобы процедура прошла быстрее и спокойнее, подготовьте пространство и информацию о пациенте заранее: это экономит время и повышает безопасность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Everyone loves what you guys tend to be up too. Such clever work and coverage!
Keep up the good works guys I’ve included you guys to our blogroll.
Thanks designed for sharing such a good thought, post is nice, thats
why i have read it completely
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]врач вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
บทความนี้ อ่านแล้วเข้าใจง่าย
ค่ะ
ผม ไปเจอรายละเอียดของ ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ที่คุณสามารถดูได้ที่ Thad
ลองแวะไปดู
เพราะให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึก
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ เนื้อหาดีๆ นี้
จะรอติดตามเนื้อหาใหม่ๆ
ต่อไป
строительство гаража стоимость
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Чего у вас со скайпом? Оффлайн уже несколько недель. https://glossgirl.ru Да и вообще стот ли…? риск есть…?
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в сочи[/url][url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Узнайте всю правду – https://evakeurope.com/advantage-of-pump-inverter-with-built-in-pressure-tank
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-odincovo
Формат
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]vyvod-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Есть чему поучиться – https://vistoweekly.com/boston-roll
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в сочи[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Кроме безопасности и мониторинга — дисциплину режима. Там легче убрать триггеры, выстроить питание и сон, а психологу — подключить короткие мотивационные сессии, которые помогут удержать результат после выписки.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnogorske/
Thank you for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next write ups thank you once again.
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Подробнее – https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu17.ru/
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]наркологическая клиника электросталь[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena sochi[/url]
If you are going for finest contents like I do, only pay a visit this
web site all the time since it provides quality contents, thanks
После первичной стабилизации врач обычно объясняет близким, почему «просто поспать» не всегда получается сразу, сколько времени может держаться раздражительность и как правильно выстроить режим, чтобы не спровоцировать повторный срыв в первые дни.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-krasnogorsk/
Когда уместен
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
большое спасибо продавцу и нашему времени :yeah::drug::rest: – пусть дальше будет еще круче :crazy:, быстрее :superman:, веселее :dansing: и ДОБрее https://ratibor62.ru Уважаемы участники форума!
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее тут – https://fricco.com.br/2023/12/08/gel-de-carboidrato-para-que-serve-ele-engorda-qual-o-melhor
Ожидаемая траектория в первые сутки
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal[/url]
For hottest information you have to pay a visit the web
and on internet I found this site as a finest site for hottest updates.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница сочи[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://fukuokasouzankai.com/2022/06/18/%E8%8E%87%E3%83%B6%E5%B2%B3%EF%BD%9E%E5%BC%9F%E8%A6%8B%E5%B1%B1%E3%80%80%E3%83%90%E3%82%B9%E3%83%8F%E3%82%A4%E3%82%AF%E3%80%80%E3%82%B5%E3%82%B5%E3%83%A6%E3%83%AA%E9%91%91%E8%B3%9E%E7%99%BB
Срочно нужен нарколог на дом? В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» приезжает к пациенту в течение часа.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в сочи[/url]
Формат
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
томато доставка тула Работа оператором также требует коммуникабельности и умения работать с информацией. Работа оператором в Воронеже может включать в себя обработку заказов, консультирование клиентов и решение различных вопросов. Оператор колл центра – это специалист, отвечающий на телефонные звонки и обрабатывающий запросы клиентов.
Excellent article. Keep writing such kind of info on your
site. Im really impressed by your site.
Hello there, You have performed an excellent job.
I will definitely digg it and in my opinion recommend
to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from
this web site.
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/kruglosutochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnogorske/
“Оздоровительная программа голодания в нашем санатории включает [url=http://lechebnoe-golodanie.ru]программа голодания[/url] для эффективного восстановления здоровья.”
Этот подход активирует процессы самоочищения и омоложения. Современные исследования подтверждают, что голодание положительно влияет на иммунитет. Также оно способствует нормализации уровня сахара в крови.
Существует несколько видов голодания, включая интервальное и длительное. Интервальное голодание предполагает циклы приема пищи и воздержания. Каждый метод имеет свои преимущества и противопоказания. Поэтому перед началом важно проконсультироваться с врачом.
Голодание запускает процесс аутофагии — очищения клеток от поврежденных компонентов. Данный механизм улучшает регенерацию тканей. Кроме того, голодание способствует снижению веса. Метаболизм ускоряется, что помогает быстрее сжигать калории.
Еще одним плюсом является улучшение работы сердечно-сосудистой системы. Кровообращение нормализуется, повышая выносливость. Также отмечается положительное влияние на психику. Стрессоустойчивость повышается, а тревожность снижается.
Перед началом программы необходимо правильно подготовить организм. Важно уменьшить порции и исключить вредные продукты. Выход из голодания должен быть постепенным. Резкий переход к обычному питанию может навредить.
Важно соблюдать питьевой режим во время голодания. Травяные чаи успокаивают желудок и снижают чувство голода. Также необходимо следить за самочувствием. При головокружении или слабости стоит прервать голодание.
Сочетание голодания с физическими упражнениями усиливает результат. Силовые тренировки сохраняют мышечную массу. Также полезно практиковать медитацию и дыхательные техники. Глубокое дыхание насыщает клетки кислородом.
Важно вести дневник самочувствия и результатов. Записи помогают отслеживать прогресс и корректировать программу. Регулярные курсы голодания дают долгосрочный эффект. Оптимальная периодичность — 1-2 раза в год.
Разные подходы к голоданию подходят не всем.
*(Аналогично для остальных разделов.)*
Что включено на практике
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
Hi! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give
a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading your blog
posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same subjects?
Thank you so much!
Срочно нужен нарколог на дом? В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» приезжает к пациенту в течение часа.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnogorske/
я бы тоже заценил https://seg-sh6.ru Отличный магаз! так держать
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://trendlylife.com/2018/02/17/%E0%AE%AA%E0%AE%BF%E0%AE%B0%E0%AE%9A%E0%AE%B5%E0%AE%A4%E0%AF%8D%E0%AE%A4%E0%AE%BF%E0%AE%B1%E0%AF%8D%E0%AE%95%E0%AF%81-%E0%AE%AA%E0%AE%BF%E0%AE%A9%E0%AF%8D-%E0%AE%AE%E0%AE%BE%E0%AE%A4%E0%AE%B5%E0%AE%BF
парк отель где все включено А-фрейм глэмпинг в Подмосковье – это уникальный формат отдыха, сочетающий комфорт с близостью к природе. Аренда такого глэмпинга становится все более популярной среди тех, кто ищет необычные впечатления и возможность провести время в уединенном месте. Вы сможете насладиться живописными пейзажами, не отказываясь от удобств, присущих гостиничному номеру.
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://outletcomvc.com/ola-mundo
В экстренных ситуациях семья ожидает не обещаний, а чётких действий. «Трезвый Ритм» в Королёве организует безопасный вывод из запоя с персональной схемой детоксикации, выездом врача 24/7 и последующей поддержкой, чтобы стабилизировать сон, снизить тревогу и предотвратить рецидив. Мы работаем деликатно и конфиденциально: вы получаете медицинскую помощь без очередей и формальностей, а также понятный план, что делать в первые критические сутки. Наши специалисты используют только проверенные протоколы, учитывают возраст, длительность эпизода и сопутствующие диагнозы, подбирают дозировки бережно и объясняют каждый шаг. Если на осмотре выявляются риски осложнений, мы сразу предложим стационар и возьмём на себя организацию перевода — безопасность всегда важнее спешки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому королев[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
жар пицца Повар – это профессия, требующая кулинарных навыков, знания технологий приготовления блюд и умения работать в команде. Если вы ищете работу поваром в Воронеже, Туле, Калуге или Рязани, то в этих городах есть множество ресторанов, кафе и пиццерий, предлагающих интересные вакансии. Компании, такие как Ташир, Жарпицца и Додо, постоянно ищут поваров, способных создавать вкусные и качественные блюда. “Повар Воронеж”, “Повар Тула”, “Повар Калуга” и “Повар Рязань” – актуальные запросы для тех, кто ищет работу в этой сфере.
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов сочи[/url]
คอนเทนต์นี้ อ่านแล้วเข้าใจง่าย ครับ
ผม ได้อ่านบทความที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ เนื้อหาในแนวเดียวกัน
ที่คุณสามารถดูได้ที่
betflik22
เผื่อใครสนใจ
มีการยกตัวอย่างที่เข้าใจง่าย
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ บทความคุณภาพ นี้
และอยากเห็นบทความดีๆ แบบนี้อีก
It’s not something separate from life—it is life, moving through us constantly.
Amid all the information, meaning often fades.
We try to fit ourselves into patterns that don’t belong to us.
The body sends quiet messages—fatigue, restlessness, hunger, calm—but we rush past them.
Our systems adjust, adapt, and change every day.
That is why awareness is not just a skill but a form of care.
The body no longer feels like something to manage, but something to cooperate with.
When we stop chasing perfection, clarity arrives naturally.
When curiosity feels more honest than constant striving.
To move with awareness instead of against it.
Finding strength in small realizations.
Through reflection, we discover that the smallest signals often carry the greatest wisdom.
And this connection becomes especially clear when we explore one topic in particular.
Much of what we’ve discussed comes together when we talk about vidalista 2.5mg.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about %meta_keyword%. Regards
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-korolev/
последнее время стал закупаться в чемикал и не капельки в этом не пожалел, всё всегда вовремя высылают даже быстрее заявленного времени! качество радует!) да и просто отличный магазин!!! https://ukupravdom.ru а как ам то хоть вооще расшифровывается то по науке???
https://usfblogs.usfca.edu/psip/2013-projects/mission-graduates-fall-2013/comment-page-5/?unapproved=95717&moderation-hash=6e43557d969f5dd5f397fb863eae41fb#comment-95717
Что включено на практике
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo/
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnogorske
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Базы отдыха с рыбалкой – это идеальный выбор для любителей активного отдыха и рыбной ловли. На таких базах отдыха можно арендовать лодку и отправиться на поиски трофейного улова. Базы отдыха в Подмосковье с детьми – это возможность провести незабываемый отпуск с семьей, наслаждаясь играми на свежем воздухе, купанием в бассейне и другими развлечениями. Базы отдыха с животными позволяют владельцам привозить с собой домашних питомцев. Загородные базы отдыха в Подмосковье – это отличная альтернатива городскому шуму и суете, предлагающая широкий спектр услуг и развлечений на любой вкус. базы отдыха загородный клуб
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-anonimnaya-pomoshch[/url]
Формат помощи на дому особенно важен, когда человек физически не в состоянии добраться до клиники, боится огласки или требуется поддержка семьи «здесь и сейчас». Врач оценивает риски, подбирает схему детоксикации по состоянию и даёт понятный план дальнейших шагов: что делать в первые сутки, чего избегать, какие симптомы считать тревожными и когда нужно повторное обращение.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Что включено на практике
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
I am truly glad to read this weblog posts which contains plenty of useful data,
thanks for providing these information.
Обычно внимание уделяется нескольким направлениям: восстановлению жидкости и обмена веществ, снижению тошноты и головной боли, уменьшению вегетативных симптомов (дрожь, потливость, сердцебиение), нормализации сна и тревоги. При этом врач ориентируется на текущие показатели и реакцию пациента — то, что помогало «в прошлый раз», может быть неуместно сегодня. Дополнительно проговариваются бытовые детали: проветривание, комфортная температура, питьевой режим, питание небольшими порциями, контроль давления и пульса, ограничение стимуляторов и рисковых нагрузок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/narkolog-v-krasnogorske/
Здесь
[url=https://windowreplacementcontractor.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-korolev/
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena sochi[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Уточнить детали – https://progenmethod.com/why-choose-progen
Цель
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
I got this website from my pal who told me regarding this web site and now this time I am visiting this site and reading very informative content at this time.
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в сочи[/url]
комедії онлайн кращі фільми 2026 року безкоштовно
Формат
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-domodedovo
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Cheers!
Where are your contact details though?
Someone else’s opinion is always valuable! And if it comes to style, take a look at [url=https://mekhov.com/shubi-turtsiya-kakie-vidi-mexa/][color=#1C1C1C]Turkey: fur coats are like art there.[/color][/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полная информация здесь – https://ecolodge.me.uk/ecoldge-10-for-2013
Right now it appears like Drupal is the best blogging platform out
there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
My blog post – trik menang slot gacor
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-odincovo/
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://vistoweekly.com/decoding-314159u-for-tech-enthusiasts
томато Повар – это творческая и востребованная профессия, требующая кулинарных навыков, знания технологий приготовления блюд и умения работать в команде. Если вы ищете работу поваром в Воронеже, Туле, Калуге или Рязани, то существует множество вариантов, от ресторанов высокой кухни до пиццерий и кафе. Вакансия повар часто встречается в таких компаниях, как Ташир, Жар Пицца и Додо Пицца, которые предлагают работу поваром с различными условиями труда и заработной платой. Повар в Воронеже, Туле, Калуге или Рязани – это специалист, отвечающий за приготовление вкусных и качественных блюд, удовлетворяя потребности клиентов.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
А что дальше? – http://shelves.jp/officialhp/1197
кракен ссылка
[url=krab3.buzz]кракен ссылка[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево сочи[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Уточнить детали – https://shelves.jp/officialhp/1197
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://recsduischool.com/dui-school
Две похожие ситуации никогда не бывают одинаковыми: возраст, вес, сопутствующие болезни, длительность запоя и переносимость препаратов формируют уникальную клиническую картину. Мы исключаем «универсальные» схемы, чтобы не перегрузить организм и не вызвать побочных реакций. Инфузии проводятся только одноразовыми системами, врач соблюдает стерильность, контролирует дозировки и следит за динамикой симптомов. Мы уделяем особое внимание сну и уровню тревоги в первые часы после детокса — именно эти параметры влияют на риск срыва. Для пациентов с сердечно-сосудистыми, эндокринными и неврологическими заболеваниями детоксикация планируется особенно осторожно; при малейших сомнениях мы предлагаем стационар и разъясняем семье, почему это безопаснее.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-korolev/
Когда уместен
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Когда уместен
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника телефон[/url]
После первичной стабилизации врач обычно объясняет близким, почему «просто поспать» не всегда получается сразу, сколько времени может держаться раздражительность и как правильно выстроить режим, чтобы не спровоцировать повторный срыв в первые дни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
оргониттрискель Защитаотсглаза: защита от сглаза
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove/
누군가가 자신의 중요한 것을 검색할 때, 그래서
그는 그것을 자세히 원하며, 따라서 그 것은 여기서
유지됩니다.
Generally I do not learn article on blogs, however I would like to
say that this write-up very compelled me to take a
look at and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me.
Thank you, quite nice post.
I quite like reading through an article that will make people think. Also, thank you for allowing for me to comment!
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/kruglosutochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnogorske/
https://www.leenkup.com/read-blog/84045
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.gms4you.us/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Что включено на практике
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника помощь на дому[/url]
탁월한 웹사이트. 여기 많은 유용한 내용이 있습니다.
몇몇 친구들에게 보내고 delicious에서도 공유할게요.
그리고 당연히, 노력에 감사합니다!
In fact no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of
afterward its up to other users that they will assist, so here it happens.
I’m blown away by the quality of your articles. You make söğütlü escort
bayan so easy to understand! I’ve added your RSS feed to
stay updated. Any chance you could write more about ebony?
Cheers for the awesome work!
이 블로그의 퀄리티에 정말 감동받았어요!
banggai에 대한 포스트가 너무 잘 정리되어 있어요.
모바일에서 약간 느리게 로드되던데, 캐싱 플러그인을 사용해
보셨나요? 그래도 계속 방문할게요! 고맙습니다!
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница сочи[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://www.honchocoffeesupplies.com.au/brewing-joy-the-ultimate-holiday-coffee-gift-guide
Обычно внимание уделяется нескольким направлениям: восстановлению жидкости и обмена веществ, снижению тошноты и головной боли, уменьшению вегетативных симптомов (дрожь, потливость, сердцебиение), нормализации сна и тревоги. При этом врач ориентируется на текущие показатели и реакцию пациента — то, что помогало «в прошлый раз», может быть неуместно сегодня. Дополнительно проговариваются бытовые детали: проветривание, комфортная температура, питьевой режим, питание небольшими порциями, контроль давления и пульса, ограничение стимуляторов и рисковых нагрузок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя цена нижний новгород[/url]
https://a-scarborough-affair.mn.co/posts/95974275
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» высылает нарколога на дом для срочной помощи при запое. Быстро и безопасно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого сочи[/url]
Старт всегда один: короткий скрининг с дежурным врачом, где уточняются жалобы, длительность эпизода, текущие лекарства, аллергии и условия дома. Далее согласуется реальное окно прибытия или приёма — без обещаний «через пять минут», но с честным ориентиром и запасом на дорожную обстановку. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурацию, температуру), по показаниям выполняет ЭКГ, запускает детокс (регидратация, коррекция электролитов, защита печени/ЖКТ), объясняет ожидаемую динамику первых 6–12 часов и выдаёт памятку «на сутки»: режим сна, питьевой план, «красные флажки», точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, перевод в стационар организуется без пауз — терапия продолжается с того же места, где начата, темп лечения не теряется.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Hello, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was
just curious if you get a lot of spam responses? If so how do you
prevent it, any plugin or anything you can recommend?
I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any assistance is very much appreciated.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
А что дальше? – https://spotlight-ds.com/classes/acrobatic-arts
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://news.delphifan.com/2023/05/31/about-unidac-components-with-examples
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре — услуга клиники «Детокс». Специалисты оказывают квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My website is in the very same niche as yours and my users would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Thanks!
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробности по ссылке – https://shvkosova.com/ekspert-konsulente-ligjore-per-pershtatjen-e-materialit-dhe-mbajtjen-e-trajnimeve-per-te-drejtat-ligjore-te-tokes-dhe-prones-per-komuniteti-e-te-verberve-dhe-te-shurdherve
You actually make it seem so easy together with your presentation however I
to find this topic to be really one thing which I believe I would never
understand. It sort of feels too complicated and extremely broad for me.
I am looking forward for your subsequent submit, I
will try to get the hang of it!
Экстренная помощь при запое в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница на дому от опытных врачей-наркологов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Смотрите также… – https://suki.one/music/27?replyTo=30417
Формат
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]порно онлайн бесплатно[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Когда уместен
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stoimost[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
время суток — casino kometa доступно круглосуточно, даже с мобильного [url=https://asterias-spa.ru/]https://asterias-spa.ru/[/url]
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and
in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement
you access consistently quickly.
늘 저는 더 작은 콘텐츠를 읽곤 했는데,
그 또한 그들의 동기를 명확히 하고, 지금 제가 읽고 있는
이 단락에서도 마찬가지입니다.
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice at the same time as you amend your
website, how can i subscribe for a weblog site?
The account helped me a appropriate deal. I have been tiny bit acquainted of
this your broadcast offered shiny transparent idea
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
I love what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and coverage! Keep up the great works guys I’ve included you guys to my personal blogroll.
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в сочи[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
всё это делает casino kometa отличным выбором для азартных игроков: [url=https://russianmultimedia.ru/]комета казино[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в сочи[/url]
Когда уместен
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника со стационаром[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]врач нарколог на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Формат
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/[/url]
I like the helpful info you supply in your
articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and take a look at once more here frequently.
I’m reasonably sure I’ll learn a lot of new stuff proper right
here! Good luck for the next!
Классная платформа казино онлайн — люблю заходить сюда!
https://Www.Dimepoker.cl/aprendizaje/articulos-poker/coolbet-te-regala-5-000
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠉⢒⠂⠐⠄⢉⢉⠻⠟⢹⢑⢀⣀⡴⣤⣬⢬⣭⣰⣰⢘⠽⠭⠯⠽⢍⢡⡙⢿⠿⢑⣴⠿⠾⣲⣤⣬⡁⠌⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠠⢰⡞⣸⣤⣴⣯⣽⣺⡾⠿⣿⣿⠟⢉⣿⣷⣷⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⠟⠋⠓⢿⣧⣾⣶⣾⣆⣈⠤⡶⢰⠏⣸⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣤⡂⠻⢿⣿⣿⣿⠁⠁⠠⠡⡀⠠⢀⣥⣼⣾⣏⣟⣋⣆⠆⣠⣴⣶⡤⠘⠃⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⢛⢁⣨⣴⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣶⣶⢰⣞⣸⣿⢋⢙⣛⣛⢻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢛⡫⢩⡙⠻⣾⣻⣿⣿⣿⣿⠀⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⢁⢰⣿⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠿⠆⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡀⠀⠸⢄⢻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢁⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⠿⠴⣺⣼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡄⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⢛⢫⢡⡰⢰⣶⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠋⣴⣶⣶⣶⣴⣶⣪⢽⣻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣯⠉⠅⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⡿⢩⣶⣿⣾⣿⣿⠃⢰⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣾⣶⢠⣦⣴⣬⣴⣴⣶⢊⡑⢶⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⣿⣄⣿⣉⣭⣩⣭⣩⢉⢊⠩⠉⠹⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢄⠻⠿⠛⢻⣫⣤⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⡉⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⣸⣿⣷⣙⠻⠛⢛⠻⠰⠂⢰⣷⣾⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⠏⢍⢻⡿⢓⠂⠙⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣶⣤⣈⡩⠭⠴⣒⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⢉⣤⣶⣺⠰⠿⣿⣿⠸⢿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⡀⣿⡜⢸⠀⡍⠘⢸⣶⣮⣴⣄⢠⣙⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣯⣉⣉⣉⣹⣿⣿⣿⠿⢋⣭⣤⣶⡯⣉⡭⣭⣝⡰⠿⣿⣿⢐⣛⠀⢻⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⠀⣯⣽⠀⣈⣽⠀⠸⠿⣿⣿⡟⢰⣿⣿⠿⣓⡚⠾⠈⢉⠹⣭⠝⣨⣴⣶⡸⣿⣿⣿⡿⢨⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣸⣿⣿⡌⢸⣿⡷⢸⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣷⠈⢭⣷⣼⣿⣬⣤⠀⢸⣿⢸⢫⣵⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⢸⢿⣿⣷⢨⢹⣿⣿⡿⢣⢷⣿⣿⡘⢽⡷⣯⣿⣿⣧⣿⣿⣿⣿⣧⣿⣿⡇
⡟⠀⣀⡀⠰⣸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⢸⡿⣰⣿⣶⣬⠻⠿⣋⣴⣾⣶⣶⣶⣤⣚⢻⢿⠶⢸⡿⣿⣿⣆⠹⣿⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⡀
⣯⣠⣬⣭⣤⠘⡛⠿⠿⠟⠀⢐⡁⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠉⢀⢹⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣾⣷⢋⢡⣤⣤⣬⣤⣬⣽⣭⣭⣴⣶⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣶⣶⣶⣶⣿⣿⣿⡇⣺⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣧⣃⣠⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠃⢸⠿⠛⢛⠛⠛⠻⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢋⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⢠⢠⢹⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡏⠸⢨⢀⣴⣶⣶⣶⣤⣕⡈⢙⣉
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣦⢐⠿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠶⠤⠾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡀⠘⠳⠾⠿⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⠁⠠⠨⠶⠶⠰⣶⣶⣶⣤⣤⣤⣼⣬⣬⣴⣤⣬⣤⡄⠉⠭⠶⣀⢤⣶⢰⣾⡆⣸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢸⢠⣾⣿⣿⣿⠰⣸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣧⠊⣧⣀⣤⣾⠿⠟⣁⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣶⣭⣭⣭⣴⣶⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣤⣤⣤⣴⣶⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this blog
loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Во телегу двинул, а? Ещё спать не ложился, такой эффект сильный, толеоа нет вообще, в завязке полгода 🙂 Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? я в среду оплатил ещё, тс сразу сказал, что отправка будет на следующей недели во вторник-среду.Большое спасибо команде chemical-mix за проведенную сделку, с наступающим Вас Новым Годом!
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого сочи[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает комплексное лечение запоя с использованием капельницы. Наши специалисты проводят диагностику и назначают индивидуальный план лечения.
Разобраться лучше – https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Смотрите также… – https://thenewblackmagazine.com/2024/01/13/httpwww-thenewblackmagazine-comview-aspxindex2706
You could definitely see your skills within the work you write. The arena hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always follow your heart.
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом цена в сочи[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into any
problems of plagorism or copyright infringement? My site has a
lot of completely unique content I’ve either created myself or outsourced
but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my authorization. Do you
know any methods to help reduce content from being stolen? I’d definitely appreciate
it.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным контролем врачей. Процедуры безопасны, эффективны и анонимны.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
medved20-10 не еби людям голову!!!!!!!!!!! микс отличный, но на час-1,5! Не больше…… https://sentidocomunecuador.com Если неактуальные сообщения выше, откорректируйте сами. По компенсациям, если останутся вопросы после получения посылки, пишите в новом году, размер зависел от веса, длительности, индивидуальных переплат на счета и прочих обстоятельств. :ok:Отличный товар и цены. Зря так…
Ритм жизни в мегаполисе и постоянный стресс часто становятся причиной развития зависимостей у жителей города. В такой ситуации необходима профессиональная консультация врача. Оптимальное решение – вызов нарколога на дом в Москве. Это обеспечивает не только получение медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке, но и полную конфиденциальность.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]vyzvat narkologa na dom[/url]
Также мы учитываем потребности каждого пациента — по питанию, условиям проживания, графику процедур. Проживание возможно в стандартных и повышенных палатах, с возможностью индивидуального обслуживания.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Что включено на практике
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Натяжные потолки помогают быстро обновить интерьер, матовое полотно позволяет встроить треки, споты и подсветку, и при этом монтаж проходит спокойно; мастер приезжает на замер, предлагает варианты и делает расчет https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my blog thus i came to “return the favor”.I’m trying to find things to enhance my website!I suppose its
ok to use some of your ideas!!
Капельница от запоя необходима, если у пациента наблюдаются следующие симптомы:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому одинцово[/url]
Натяжной потолок подходит для ремонта, когда хочется чистого результата за день, ПВХ полотно дает ровную плоскость, помогает быстро освежить отделку без демонтажа штукатурки; замер занимает около получаса, после чего готовится смета и договор – https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Как отмечает главный врач клиники, кандидат медицинских наук Сергей Иванов, «мы создали систему, при которой пациент получает помощь в течение часа — независимо от дня недели и времени суток. Это принципиально меняет шансы на выздоровление».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu-kruglosutochno[/url]
Возможность назначить визит специалиста в наиболее удобное время. Это позволяет эффективно совмещать лечение с работой и повседневными делами. Такая гибкость помогает пациентам своевременно начать терапию, не откладывая ее из-за занятости. При необходимости врач может приехать в вечернее время или выходные дни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny/
Wygodna platforma Najlepsze kasyna online w Polsce — uwielbiam tu zaglądać!
https://4.staikudrik.com/index/d1?diff=0&utm_source=ogdd&utm_campaign=26607&utm_content=&utm_clickid=uskkokskw44sooos&aurl=https://kasyna-z-licencja.pl/blik-kasyna
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Детальнее – http://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru
http://eivissally.com/aliquam-enim-enim-pharetra-in-sodales-at-3/
с чего они тебе отзывы писать будут если они груз две недели ждут? они че тебе экстросенсы и качество могут на расстоянии проверить? и извинений мало ты не на ногу в трамвае наступила следующий раз пусть магаз компенсирует бонусами за принесенные неудобства! кто со мной согласен добавляем репу! https://ishdps.ru Ну подскажите хоть что нибудь пожалуйста?А то я переживаю ппц.помнится на бизе у Вас с этим было все хорошо.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-odincovo/
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Полная информация здесь – https://15minutestravel.com/?p=943
Здесь
[url=https://tsarcaviar.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
дивитися онлайн прямий світові кінопрем’єри українською в Full HD
Amazing! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this paragraph.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom sochi[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в сочи[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
заказал, получил, покурил, охуел… https://easyrust.ru курьерки на мой запрос поиска трека ответ что инфа закрыта для доступаСписался с продавцом в аське, во вторник оплатил, сказали в среду отправят. когда спросил, сказали что не отправили по тех причинам из-за СПСР, обещали в четверг. Должно было придти в течении 3х рабочих дней. Сегодня понедельник, сижу на работе, и вот мне звонят, мол вам письмо пришло, куда доставить? То есть все верно, 3 дня как и говорили! Настроение теперь на весь день поднялось)) Вечером буду делать 1к10 (ам2233), потом отпишусь как и чего!!)) В общем доволен, но пока говорю только про доставку. Позднее отпишу доволен ли я всем остальным))
Как отмечает главный врач клиники, кандидат медицинских наук Сергей Иванов, «мы создали систему, при которой пациент получает помощь в течение часа — независимо от дня недели и времени суток. Это принципиально меняет шансы на выздоровление».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-na-domu[/url]
Как отмечает главный врач клиники, кандидат медицинских наук Сергей Иванов, «мы создали систему, при которой пациент получает помощь в течение часа — независимо от дня недели и времени суток. Это принципиально меняет шансы на выздоровление».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]наркологическая помощь балашиха[/url]
Возможность назначить визит специалиста в наиболее удобное время. Это позволяет эффективно совмещать лечение с работой и повседневными делами. Такая гибкость помогает пациентам своевременно начать терапию, не откладывая ее из-за занятости. При необходимости врач может приехать в вечернее время или выходные дни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Стационарная программа позволяет стабилизировать не только физическое состояние, но и эмоциональную сферу. Находясь в изоляции от внешних раздражителей и вредных контактов, пациент получает шанс сконцентрироваться на себе и начать реабилитацию без давления извне.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-v-balashihe/
Капельница от запоя необходима, если у пациента наблюдаются следующие симптомы:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя одинцово[/url]
Лечебные мероприятия и рекомендации формируются исходя из индивидуального состояния каждого пациента. Специалист имеет возможность посвятить достаточное количество времени каждому больному, корректируя программу лечения согласно его особым потребностям и жизненным обстоятельствам. При этом учитываются психологические, социальные и физические аспекты, оказывающие влияние на здоровье пациента. Персонализированный подход обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на изменения состояния и своевременную корректировку терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Натяжной потолок помогает спрятать коммуникации и сохранить высоту помещения: глянцевая поверхность позволяет подобрать оттенок под стены и мебель, поэтому интерьер выглядит собранно; в процессе учитываются вентиляция – https://potolki-decarat.ru/
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]запой нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
I need to to thank you for this great read!!
I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you book-marked to look at new things you post…
Магазин работает четко уже несколько лет:)только одно расстроило когда хотел сделать очередной заказ мне сказали что не отправляют больше в те края:dontknown:с чем это связано мне так и не сказали,хотелось бы узнать Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Вопрос?! Что дальше? Что лучшПривет старичок
888slot sở hữu thư viện game bài đa dạng với hàng trăm lựa chọn, từ các game truyền thống đến phiên bản hiện đại. Dựa trên dữ liệu người chơi, ba thể loại được yêu thích nhất là Baccarat, Poker và Xóc đĩa. TONY01-08
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови, оценивает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от результатов и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний составляется индивидуальный состав инфузионного раствора. Он может включать:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя в одинцове[/url]
888slot liên tục đạt giải thưởng nhà cái uy tín của năm nhờ vào sự đổi mới không ngừng trong danh mục sản phẩm giải trí. Từ các game bài đối kháng đến những giải đấu thể thao ảo, tất cả đều được tối ưu hóa để mang lại trải nghiệm mượt mà nhất. TONY01-08
To create stamps at home or in the office, you can use the service[url=https://mystampready-0constructor.com/]stamp creator online[/url], позволяющим быстро и качественно создавать необходимые печати без выхода из дома.
The development of online platforms for creating rubber stamps has opened up new possibilities for crafters, businesses, and individuals alike, providing a convenient and efficient way to produce high-quality stamps.
The use of online rubber stamp makers also reduces the environmental impact of traditional stamp-making methods, as it eliminates the need for physical materials and transportation.
By offering a range of features and functionality, online rubber stamp makers can provide a seamless and enjoyable experience for users, making it easy to create high-quality custom stamps.
In conclusion, online rubber stamp makers have revolutionized the way we create and use custom stamps, offering a convenient, flexible, and cost-effective solution for businesses, crafters, and individuals alike.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в нижнем новгороде[/url][url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом нижний новгород[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детали по клику – https://www.pecsiriport.hu/koezelet/6194-setater-fesztival-nemzetkozi-programokkal.html
Сфера недропользования — это комплекс работ, связанный с освоением природных ресурсов.
Оно включает добычу полезных ископаемых и их дальнейшую переработку.
Эта отрасль регулируется нормативными актами, направленными на безопасность работ.
Ответственное ведение работ в недропользовании помогает сохранять ресурсы.
общество экспертов России по недропользованию
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Jwh 203 порошок светло-желтого цвета у них, делал в пропорции 150-200мг на спичечный коробок микса, кролики довольны! 5-IAI пробывал 200мг по кишке, видимо нужно было сразу 300-400мг чтобы понять кайф! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? у меня знакомец с их магазина закупился его с черта какого то мусора взяли! че к чему не знаю но факт есть факт! может и не они виноваты, но он мелкий торгаш и принимать с сотней его не в темуВсё что В прайс листе на сайте есть,всё в наличии ?
Wonderful site. Plenty of helpful info here. I’m sending it to a few buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you for your effort!
Its not my first time to pay a visit this site, i am visiting this web page dailly and take nice information from here
daily.
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Visit the company site : http://rauk.ru/jdownloads/inc/1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus.html
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Узнайте всю правду – https://tec-metal.com.ar
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Поэтому наша служба экстренного выезда работает круглосуточно. Медицинская бригада приезжает на вызов в любой район Балашихи в течение часа. Пациенту ставят капельницы, стабилизируют давление, снимают судорожный синдром и устраняют тревожность. Всё это проходит под наблюдением опытных врачей, которые ежедневно сталкиваются с острыми ситуациями и знают, как действовать быстро и безопасно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskij-stacionar-pomoshch[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Детальнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Я делал на муравьином спирте Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? привествую мои друзья форумчане , нено в итоге, когда ты добиваешься его общения – он говорит, что в наличии ничего нет. дак какой смысл то всего этого? разве не легче написать тут, что все кончилось, будет тогда-то тогда-то!? что бы не терять все это время, зайти в тему, прочитать об отсутствии товара и спокойно (как Вы говорите) идти в другие шопы.. это мое имхо.. (и вообще я обращался к автору темы)
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино онлайн[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Возможность назначить визит специалиста в наиболее удобное время. Это позволяет эффективно совмещать лечение с работой и повседневными делами. Такая гибкость помогает пациентам своевременно начать терапию, не откладывая ее из-за занятости. При необходимости врач может приехать в вечернее время или выходные дни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]narkolog na dom anonimno[/url]
Процесс начинается с вызова врача или доставки пациента в клинику. После прибытия специалист проводит первичную диагностику: измерение давления, температуры, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови, визуальная оценка степени возбуждения или угнетения сознания. Собирается краткий анамнез: какой наркотик принимался, как долго, были ли сопутствующие заболевания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/snyatie-lomki-na-domu-v-podolske
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/]вывод из запоя цена нижний новгород[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре — услуга клиники «Детокс». Специалисты оказывают квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Именно поэтому так важно не терять время. Чем раньше пациент получает помощь, тем выше шансы избежать необратимых последствий и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/]снятие ломки наркозависимого[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I quite enjoyed reading it, you
might be a great author. I will be sure to bookmark your blog and will often come back later in life.
I want to encourage you to continue your great work, have a nice weekend!
В наркологической клинике «Перезагрузка» в Химках капельницы проводятся под строгим медицинским наблюдением. Мы используем современные препараты, индивидуально подбираем состав инфузии и гарантируем конфиденциальность. Наша задача — не просто снять симптомы, а обеспечить реальную поддержку организму на физиологическом уровне, чтобы предотвратить повторный срыв и минимизировать риски для здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/
Уважаемый ТС, ответь мне в лс или на почту, заказ мой не правильно сделали или описали в письме не правильно, ртветь как можно скорее https://aquarium39.ru Сургут, вобщем хмаоПривет, ребята!
Также мы учитываем потребности каждого пациента — по питанию, условиям проживания, графику процедур. Проживание возможно в стандартных и повышенных палатах, с возможностью индивидуального обслуживания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно сочи[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов сочи[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-himkah/
Алкогольная интоксикация разрушает организм изнутри. В первую очередь страдает центральная нервная система: снижается уровень витаминов группы B, нарушаются когнитивные функции, появляются раздражительность, бессонница, панические атаки. Следом — страдает печень, главный орган метаболической детоксикации. Под действием этанола её функции подавляются, а токсины накапливаются в крови. Это вызывает системное отравление и разрушает внутренние органы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]vyzvat-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya odintsovo[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
После оформления заявки на сайте narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru или по телефону, оператор уточняет информацию о пациенте: возраст, длительность запоя, наличие хронических заболеваний, текущее самочувствие. В течение 30–60 минут дежурный специалист приезжает по адресу с полным комплектом оборудования и медикаментов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого красногорск[/url]
[url=https://music.yandex.ru/artist/25265629]Ангелица[/url]
Если потолки низкие важно выбрать правильный профиль и тип полотна при этом Сатиновая фактура выглядит мягко и добавляет глубины без зеркального эффекта Для кухни полезна подсветка рабочей зоны и общий мягкий свет без резких теней это дает аккуратный финиш и понятный результат уже в день монтажа https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Открой скрытое – https://www.swizpro.com/novice-river
I have read so many articles concerning the blogger lovers but this paragraph is truly a pleasant post, keep it
up.
I know this web page offers quality depending articles and other information, is there any other website which gives these information in quality?
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Получить больше информации – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find
It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Выяснить больше – https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Иногда приоритетом становится непрерывный контроль. Стационар рекомендован, если ожидаются выраженные колебания давления и пульса, есть подозрение на аритмии, отмечается одышка, боли в груди, спутанность сознания, галлюцинации, судороги, признаки начинающегося делирия, а также выраженная дегидратация или декомпенсация хронических заболеваний. Для пожилых пациентов без возможности надёжного домашнего наблюдения отделение — клинически разумный выбор: доступны лабораторные тесты, кислородная поддержка, быстрая коррекция дозировок и консилиумы смежных специалистов. Именно в первые 24–48 часов после отмены алкоголя стационарный режим делает процесс предсказуемым и безопасным, что сокращает время до стабилизации и открывает окно для обсуждения амбулаторного сопровождения, психологической поддержки и мер профилактики срывов без давления и спешки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
В повседневности неточный ориентир часто заставляет терять время, поэтому мы проговариваем симптомы, при которых тянуть нельзя. Список не заменяет осмотр, он помогает близким описать ситуацию по телефону и выбрать правильный маршрут вместе с врачом.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Уточнить детали – http://phoceatour.com/bonjour-tout-le-monde
Да всё норм, ёпт, чё ты вообще телефон потерял) Тебе наверное там названивали. https://hasura.info КАК ОБЕЩЯЛ ОПЕРАТОР ТАК ВСЕ И СДЕЛАЛ ОДИН В ОДИН !!!!а почему репа минусовая?
Ломка — это не временное недомогание. Это системное разрушение организма, связанное с тем, что он перестаёт получать наркотик, к которому уже привык. Нарушается обмен веществ, функции сердца, печени, почек, теряется контроль над эмоциями и болью. В состоянии абстиненции человек не может спать, есть, адекватно мыслить. Страдает и тело, и психика.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/]снятие ломок на дому в подольске[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
ВЫ ЛУЧШИЕ! https://keralatourism.biz Общение оператора 10/10-всегда все грамотно и вежливо объяснит. Таким оператор и должен быть!про тусиай ….. что я могу сказать про тусиай от этого магазина…. пойду лучше трип-реппорт напишу…. такой тусишки ещё не ел)
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом нижний новгород[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в нижнем новгороде[/url]
https://nototojkxgif.bestoof.com/t49-Promo-Code-for-1xBet-2026-1XBIG2026-Bonus-EUR130.htm#p674
Капельница от запоя необходима, если у пациента наблюдаются следующие симптомы:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полная информация здесь – https://vadraren.se/sa-klar-du-dig-ratt-i-kylan
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» проводит выезд нарколога на дом для безопасного вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]narkolog-na-dom sochi[/url]
Процедура длится от одного до трёх часов. В течение всего времени за пациентом наблюдает медперсонал, проводится мониторинг давления, пульса, общего самочувствия. Уже через 30–60 минут после начала инфузии большинство пациентов ощущают облегчение: снижается тревожность, уходит головная боль, нормализуется дыхание, появляются силы.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]stoimost kapelnitsy ot zapoia[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Outstanding work!
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника нижний новгород[/url]
Абстинентный синдром — одно из самых тяжёлых и опасных проявлений наркотической зависимости. Он развивается на фоне резкого отказа от приёма веществ и сопровождается сильнейшими нарушениями работы организма. Это состояние требует немедленного вмешательства. Самостоятельно справиться с ним невозможно — особенно если речь идёт о героине, метадоне, синтетических наркотиках или длительной зависимости. В клинике «НаркоПрофи» мы организовали систему снятия ломки в Подольске, работающую круглосуточно: как на дому, так и в условиях стационара.
Получить больше информации – http://
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://osako.vn/cach-gia-tang-dien-tich-cho-can-bep-nho
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://icc-ccs.org/hellenic-shipping-news
тусишка что то с чем то – 1й раз могу сказать что 25 это перебор…. https://sincastigos.info все огонь люди работают!!!пс за поддержку )Брал здесь 203-й качество отличное 1 к 10 делал на мать и мачехи с одного водника ушатывает наглухо!!! Магазин отличный, если не ждать ответа менеджера по 2 часа!!!
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/[/url]
Инфузионная терапия собирается под конкретного пациента: регидратация и электролитная коррекция снимают интоксикацию и тремор, гепатопротективные препараты уменьшают нагрузку на печень, противорвотные и анксиолитики облегчают тошноту и тревогу, а бережная седация по показаниям возвращает нормальный сон без угнетения дыхания. Врач следит за динамикой — давлением, пульсом, сатурацией, уровнем тревоги — и при необходимости меняет скорость и состав капельницы. Важна коммуникация: каждое назначение объясняется пациенту и родственникам, оговариваются «красные флаги» и план на 24–48 часов — питьевой режим, щадящее питание, контроль давления, правила связи при изменениях самочувствия. Такой пошаговый подход сокращает период нестабильности и помогает безопасно перейти к обсуждению профилактики рецидива.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno sochi[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Стационарная программа позволяет стабилизировать не только физическое состояние, но и эмоциональную сферу. Находясь в изоляции от внешних раздражителей и вредных контактов, пациент получает шанс сконцентрироваться на себе и начать реабилитацию без давления извне.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]vidy-narkologicheskoj-pomoshchi[/url]
Принять могут в любой курьерке и уж тем более на почте. 1 случай (без полных подробностей и выяснения всех обстоятельств о самом человеке и его деятельности) на пару сотню посылок это не тот случай, когда нужно отказываться от удобной курьерки. Об этом уже говорили неоднократно. Возвращаться к этой теме больше не стоит. https://cncuserforum.ru всегда ровно все было и есть. так что яОтличный магазин маскировка высший балл!
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в сочи[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в сочи[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://clickfabio.com/gel-polish-guide-long-lasting-colors-for-every-season
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Dressing stylishly is crucial for making a good impression.
It helps highlight individuality and boost self-esteem.
A neat outfit shapes first impressions.
In daily life, clothing can enhance personal image.
https://telegra.ph/Maison-Margiela-12-25-2
Stylish outfits make social interactions easier.
It is important to consider personal preferences and the context of the event.
Modern styles allow people to refresh their wardrobe.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly helps feel confident.
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/
Поэтому наша служба экстренного выезда работает круглосуточно. Медицинская бригада приезжает на вызов в любой район Балашихи в течение часа. Пациенту ставят капельницы, стабилизируют давление, снимают судорожный синдром и устраняют тревожность. Всё это проходит под наблюдением опытных врачей, которые ежедневно сталкиваются с острыми ситуациями и знают, как действовать быстро и безопасно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Алкогольная или наркотическая интоксикация — это не просто временное ухудшение самочувствия, а серьёзное медицинское состояние, требующее неотложной помощи. Когда человек находится в запое или состоянии ломки, его организм стремительно теряет силы, нарушается работа сердца, печени, мозга, возникают панические атаки, судороги, спутанность сознания. В таких случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Если пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники, оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом. В Красногорске такая услуга доступна круглосуточно благодаря выездной службе клиники «Ключ к Здоровью».
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-krasnogorske/
страхи онлайн безкоштовно сучасне українське кіно онлайн
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
What’s up mates, how is the whole thing, and what you want to say concerning this post, in my view its genuinely remarkable in support of me.
В основе нашей методики — комплексный подход, сочетающий медицинскую точку зрения и психологические технологии. Мы не ограничиваемся снятием абстиненции: задача клиники — помочь пациенту обрести новую мотивацию, развить навыки противостояния стрессам и возобновить социальную активность. Работа строится на трёх ключевых принципах:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi1.ru/]наркологическая клиника обратный звонок[/url]
After exploring a few of the blog posts on your web site, I honestly appreciate your way of blogging.
I saved as a favorite it to my bookmark webpage list
and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my website
as well and tell me your opinion.
приеме. Приложат все усилия, чтобы ожидаемые заказы выслались. За ожидание вложены компенсации, средний % компенсации 50. https://escbestyou.biz Магазин знает как удалить учетку что бы закрыв чат в жабере у вас исчезла запись из списка контактов. У меня так было вчера. Адрес не давали в течении 2х часов а под утро сегодня и вовсе исчезли из контактов.слов нет.Вы ребята давно шум должны поднять что такая херня а то молчите по две недели!!!!я бы так хрен зарядил.А я почитал типа все ровно пишут и отдал кровные 22т.р
набрать подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://liquidabebidas.com.br/hello-world-2
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в сочи[/url][url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Узнать больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
стать популярным в Tik Tok
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
«НоваМед Центр» организует экстренную помощь при алкогольной интоксикации без очередей и лишней огласки. Команда наркологов и анестезиологов работает круглосуточно, выезжает на дом и принимает в стационаре, сохраняя один стандарт качества: очная оценка состояния, индивидуально подобранная инфузионная терапия, контроль жизненно важных показателей и понятные рекомендации на первые сутки. Схемы не шаблонные: состав и скорость капельницы зависят от длительности запоя, возраста, сопутствующих болезней и уже принятых лекарств. Наша цель — безопасно прервать запой, снять тремор, тревогу и тошноту, вернуть сон и аппетит, снизить нагрузку на сердце и печень, а затем предложить маршрут последующей помощи по готовности пациента — от амбулаторного наблюдения до программ профилактики срывов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Процесс лечения в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на безопасное восстановление организма.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-khimki/
Aw, this was an exceptionally good post. Finding the time and actual effort to create a top notch article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and
never seem to get nearly anything done.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Донат в мобильные игры Донат в Rise of Kingdoms – это важная часть стратегии для тех, кто стремится к лидерству в этой популярной мобильной игре. Донат позволяет игрокам ускорять строительство, обучение войск и исследования, а также приобретать VIP-статус, дающий различные бонусы. Однако, важно помнить, что Rise of Kingdoms – это в первую очередь стратегическая игра, и умелое планирование, тактика и дипломатия играют не менее важную роль, чем донат. Донат в Rise of Kingdoms может значительно ускорить прогресс, но не является гарантией победы, если игрок не умеет эффективно управлять своим королевством.
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom moskva[/url]
Как отмечает главный врач клиники, кандидат медицинских наук Сергей Иванов, «мы создали систему, при которой пациент получает помощь в течение часа — независимо от дня недели и времени суток. Это принципиально меняет шансы на выздоровление».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]vyzvat-narkologicheskuyu-pomoshch[/url]
Нравится, что не требуют лишних подтверждений, как на других сайтах: [url=calligraphy-expo.ru/]kometa casino зеркало на сегодня[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://ohnempu.com/urteil-zum-thema-eu-fuehrerschein-nach-sperrfrist
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево сочи[/url]
страхи онлайн безкоштовно історичні фільми з українським перекладом
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Это ещё не всё… – https://everyones.cc/2023/09/17/%E5%B9%BB%E7%A5%9E%E5%A5%87%E8%AD%9A%E3%83%9A%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B8%E3%82%92%E3%81%A4%E3%81%8F%E3%82%8A%E3%81%BE%E3%81%97%E3%81%9F
loli uncountable vid pic
is.gd/BlCAHo
krtk.rs/e1i0ovy
Hey There. I found your weblog using msn. That is a really smartly written article.
I will be sure to bookmark it and come back to learn more of your useful information. Thanks for the post.
I’ll definitely comeback.
What’s up, I log on to your new stuff daily. Your story-telling style is awesome, keep it up!
В нашей практике сочетаются несколько видов вмешательства: медико-биологическое, психологическое и социальное. Сначала проводится полная диагностика, включая лабораторные анализы и оценку работы сердца, печени, почек, а также психодиагностические тесты. После этого начинается этап детоксикации с внутривенными капельницами, которые выводят токсины, нормализуют водно-солевой баланс и восстанавливают основные функции организма. Далее мы применяем медикаментозную поддержку для стабилизации артериального давления, купирования тревожных симптомов, нормализации сна и уменьшения болевого синдрома.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi1.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-mytishchah
Алкогольная интоксикация разрушает организм изнутри. В первую очередь страдает центральная нервная система: снижается уровень витаминов группы B, нарушаются когнитивные функции, появляются раздражительность, бессонница, панические атаки. Следом — страдает печень, главный орган метаболической детоксикации. Под действием этанола её функции подавляются, а токсины накапливаются в крови. Это вызывает системное отравление и разрушает внутренние органы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya odintsovo[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
фільми жахів онлайн фантастика 2025 дивитися онлайн HD
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает услугу выезда нарколога на дом. Быстро, безопасно, анонимно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого сочи[/url]
время суток — casino kometa доступно круглосуточно, даже с мобильного: [url=complex-uslug.ru]casino kometa[/url]
I am regular visitor, how are you everybody? This article posted at this site is truly
nice.
my homepage – login slot online
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево нижний новгород[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
В коридоре натяжной потолок делает пространство опрятным и помогает спрятать кабели, выбирайте матовое ПВХ полотно, оно не требует ежегодной покраски и обновления, согласуйте высоту потолка, чтобы двери и карнизы не упирались, вы сохраните нервы и не будете переделывать потолок через год, https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: https://pcpro100.info/pgs/kak_igrat_v_slotu_onlayn_bez_nakrutok.html.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.
Наркологическая клиника «НаркологПроф» в Химках — это современный центр, специализирующийся на безопасном и быстром выведении из запоя. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, анестезиологи и медицинские сестры с большим стажем. Клиника функционирует круглосуточно, обеспечивая как выездную помощь, так и стационарное лечение. Главная цель специалистов — восстановить работу организма после интоксикации, нормализовать давление, устранить тревогу и бессонницу, помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальному состоянию. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, без постановки на учёт. Индивидуальный подход, корректный подбор медикаментов и строгий контроль состояния пациента делают лечение эффективным и безопасным.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/]anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Keep it up and keep attracting more players!
http://www.ghiblies.net/cgi-bin/oe-link/rank.cgi?mode=link&id=9944&url=https://rabbitroad.mobi/registration
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево сочи[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детали по клику – https://worksplumbing.us/commercial-exterior-catch-basins/catch-basin-clogged
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: ссылка.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Hi there,
We’re conducting a short survey for website owners about spam issues on their sites.
It takes less than 30 seconds and your input will help us build better tools for managing unwanted submissions.
If you’re interested, please click the link below to share your feedback:
https://tinyurl.com/32uupfv4#nemapaincare.com
Thank you for your time!
이 페이지는 진짜 제가 원했던 정보와 사실을 가지고 있어서 누구에게 물어볼지 몰랐습니다.
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your blogs really nice,
keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your
site to come back later. Many thanks
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детали по клику – https://travel-book.net/jirounoen-ichigogari
I used to be able to find good advice from your articles.
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Открой скрытое – https://www.unitedlife.sk/kontakt
Именно поэтому так важно не терять время. Чем раньше пациент получает помощь, тем выше шансы избежать необратимых последствий и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/]снятие ломки в стационаре подольск[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom[/url]
Hi there! I know this is sort of off-topic but I had to ask.
Does managing a well-established website such as yours take a large
amount of work? I am brand new to blogging
however I do write in my journal on a daily basis.
I’d like to start a blog so I can share my personal experience and thoughts online.
Please let me know if you have any kind of recommendations or tips for
new aspiring blog owners. Thankyou!
Для спальни важнее всего мягкий свет и спокойная фактура потолка также Сатиновая фактура выглядит мягко и добавляет глубины без зеркального эффекта В спальне комфортнее скрытая подсветка и минимум точек света над кроватью так можно обновить свет не ломая отделку и сохранить высоту: потолок натяжной
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Как отмечает главный врач клиники, кандидат медицинских наук Сергей Иванов, «мы создали систему, при которой пациент получает помощь в течение часа — независимо от дня недели и времени суток. Это принципиально меняет шансы на выздоровление».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Если вам необходима [url=https://yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya101.ru]консультация юриста адвоката[/url] посетите этот ресурс.
играет решающую роль в большинстве юридических вопросов . Это связано с тем, что юридическая поддержка необходима для предотвращения потенциальных проблем. Кроме того, опытный юрист может предоставить ценную информацию и рекомендации .
Юридическая консультация предоставляет возможность получить профессиональную помощь . Это особенно важно для людей, которые столкнулись с юридическими проблемами . Кроме того, юридическая консультация может помочь предотвратить потенциальные проблемы .
# Раздел 2: Виды юридической консультации
Юридическая консультация может быть предоставлена в различных формах . Это включает в себя онлайн-консультации. Кроме того, могут иметь опыт работы с различными типами клиентов .
Юридическая консультация может быть полезна для предотвращения потенциальных проблем . Это особенно важно для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной помощи. Кроме того, может помочь предотвратить потенциальные проблемы.
# Раздел 3: Преимущества юридической консультации
Юридическая консультация позволяет клиентам получить необходимую информацию и рекомендации . Это связано с тем, что юрист может помочь клиентам вести переговоры и заключать контракты. Кроме того, может помочь клиентам найти наиболее эффективные решения.
Юридическая консультация может быть полезна для предотвращения потенциальных проблем . Это особенно важно для людей, которые столкнулись с юридическими проблемами . Кроме того, может предоставить возможность получить необходимую поддержку и рекомендации .
# Раздел 4: Заключение
Юридическая консультация играет решающую роль в большинстве юридических вопросов . Это связано с тем, что юридическая поддержка необходима для предотвращения потенциальных проблем. Кроме того, юрист может помочь клиентам вести переговоры и заключать контракты.
Юридическая консультация позволяет клиентам получить необходимую информацию и рекомендации . Это особенно важно для бизнеса, который только начинается . Кроме того, может помочь предотвратить потенциальные проблемы.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — удобное решение для тех, кто не может посетить клинику. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут необходимую процедуру.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов нижний новгород[/url]
В новостройке натяжной потолок помогает пережить усадку и сохранить аккуратный вид, выбирайте сатиновое полотно, оно выглядит аккуратно даже при сложной геометрии комнаты, уточните в договоре гарантию на монтаж, швы и материалы, потолок будет выглядеть ровным даже при сложных углах, стоимость 1 м2 натяжного потолка москва
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom[/url]
После оформления заявки на сайте narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru или по телефону, оператор уточняет информацию о пациенте: возраст, длительность запоя, наличие хронических заболеваний, текущее самочувствие. В течение 30–60 минут дежурный специалист приезжает по адресу с полным комплектом оборудования и медикаментов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в красногорске[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого нижний новгород[/url]
Thanks for finally talking about > %blog_title% < Loved it!
Возможность назначить визит специалиста в наиболее удобное время. Это позволяет эффективно совмещать лечение с работой и повседневными делами. Такая гибкость помогает пациентам своевременно начать терапию, не откладывая ее из-за занятости. При необходимости врач может приехать в вечернее время или выходные дни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом москва[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Public interest in health continues to expand.Clarity is often missing despite abundance.Health guidance is often reduced to general advice.Explanation becomes incomplete.Subtle changes are easily missed or misread.The difficulty lies elsewhere.Responses are inherently individualized.Consistency reveals meaningful insight.Attention allows patterns to become visible.Editorial discussion helps organize this complexity.Depth requires room to develop.Podcast discussions offer a structured yet open environment.Learning unfolds progressively.Balance is emphasized.For those seeking deeper context and reliable perspective.To gain deeper context and insight into tadacip.
Для кухни студии натяжной потолок помогает отделить зону готовки светом и при этом Двухуровневое решение помогает спрятать воздуховоды и сделать подсветку в нише Продумайте доступ к вентиляции и коммуникациям через люк чтобы обслуживание было простым так можно обновить свет не ломая отделку и сохранить высоту: https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее тут – https://lagoon-magazine.com/destination-item/anatolia
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови, оценивает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от результатов и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний составляется индивидуальный состав инфузионного раствора. Он может включать:
Подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru
Если вам нужна [url=https://arenda-avtomobilya-s-voditelem54.ru/]прокат авто с водителем[/url], обращайтесь к нам — мы гарантируем комфорт и безопасность на дороге.
Клиенты могут подобрать машину, соответствующую их бюджету и требованиям.
Показания к проведению капельницы от запоя включают:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Осложнения, к которым может привести отсутствие лечения:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/]снятие ломки на дому московская область[/url]
Одной из самых сильных сторон нашей клиники является оперативность. Мы понимаем, что при алкоголизме, наркомании и лекарственной зависимости часто требуются немедленные действия. Если человек находится в состоянии запоя, абстиненции или передозировки, промедление может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям или даже смерти.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha-balashiha[/url]
Узнайте подробности по [url=https://zabory-iz-schtaketnika.ru]забор штакетник москва[/url] и сделайте правильный выбор.
При большом заказе производители часто предоставляют существенные скидки.
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/[/url]
Для кухни студии натяжной потолок помогает отделить зону готовки светом при этом Световые линии выглядят минималистично но требуют точной разводки и крепежа Для кухни полезна подсветка рабочей зоны и общий мягкий свет без резких теней в результате потолок выглядит ровно а ремонт идет быстрее https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the costs. But
he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a number of websites for
about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform.
I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my
wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Опытные врачи обеспечивают полную безопасность и комфорт пациента, а услуги доступны круглосуточно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, включающая физраствор, глюкозу, витамины и седативные препараты. Она помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и улучшить самочувствие.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена нижний новгород[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru
It is actually a great and helpful piece of information. I’m glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
https://PixoLinks.com/389/posts/1/1/1802000.html
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Также мы учитываем потребности каждого пациента — по питанию, условиям проживания, графику процедур. Проживание возможно в стандартных и повышенных палатах, с возможностью индивидуального обслуживания.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]телефон доверия наркологической помощи[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Right here is the right site for anyone who wishes
to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost
tough to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa).
You definitely put a brand new spin on a subject that has been written about for years.
Wonderful stuff, just wonderful!
Натяжные потолки помогают быстро обновить интерьер, в городе Москва, сохраняет аккуратный вид даже при активной жизни дома; после монтажа вы получаете ровную поверхность и понятную гарантию, Можно комбинировать фактуры, чтобы получить эффект глубины https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]narkolog na dom tsena[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробнее тут – https://www.papajiyam.com/cara-cepat-mudah-melepaskan-taji-ayam-jantan
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]запой нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
Показания к проведению капельницы от запоя включают:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]postavit kapelnitsu ot zapoia[/url]
Ритм жизни в мегаполисе и постоянный стресс часто становятся причиной развития зависимостей у жителей города. В такой ситуации необходима профессиональная консультация врача. Оптимальное решение – вызов нарколога на дом в Москве. Это обеспечивает не только получение медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке, но и полную конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в нижнем новгороде[/url][url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Это ещё не всё… – http://lerstol.no/2013/09/05/5-september
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is fantastic, let alone the content!
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
cutty frisky girls
fondby.com/SiIu4
onlylinks.cc/gqoU
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Смотрите также… – https://flexkantoorleek.nl/logo-flexkantoor
Зависимость — это системная проблема, которая требует последовательного и профессионального подхода. Обычные попытки «вылечиться дома» без медицинского сопровождения нередко заканчиваются срывами, ухудшением состояния и психологической деградацией. Клиника «Здоровье Плюс» в Балашихе предоставляет пациентам не просто разовое вмешательство, а выстроенную поэтапную программу, основанную на опыте и медицинских стандартах.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-balashiha1.ru/]наркологический стационар помощь[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]милфы[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Для квартиры после затопления сверху натяжной потолок часто спасает отделку и мебель плюс ПВХ пленка удобна в уходе и выдерживает воду если случится протечка После монтажа уточните правила ухода лучше мягкая салфетка и нейтральное средство так вы экономите время и получаете чистую геометрию без лишней пыли: https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
I really like looking through a post that will make men and women think.
Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
บทความนี้ อ่านแล้วเข้าใจง่าย ครับ
ดิฉัน ไปเจอรายละเอียดของ
เรื่องที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ที่คุณสามารถดูได้ที่ สล็อตออนไลน์
น่าจะถูกใจใครหลายคน
มีตัวอย่างประกอบชัดเจน
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ คอนเทนต์ดีๆ นี้
และหวังว่าจะได้เห็นโพสต์แนวนี้อีก
Натяжные потолки скрывают проводку, трещины и неровности без грязных работ, сохраняет аккуратный вид даже при активной жизни дома, а двухуровневая конструкция подчеркивает стиль; в процессе учитываются вентиляция, дымоходы и особенности перекрытий – монтаж натяжных потолков в москве
Когда зависимость захватывает жизнь, она разрушает не только организм, но и личность, отношения с близкими, карьерные планы и самоощущение. Алкоголь, наркотики и психотропные препараты постепенно подрывают работу внутренних органов, нарушают баланс нейромедиаторов в мозге и приводят к серьёзным психическим и физическим осложнениям. Попытки справиться с этим самостоятельно редко бывают успешными: необходим системный, профессиональный подход. В наркологической клинике «Доктор Здоровье» в Мытищах вы найдёте надёжную опору на всех этапах выздоровления — от экстренной детоксикации до длительной реабилитации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi1.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/
В нашей практике сочетаются несколько видов вмешательства: медико-биологическое, психологическое и социальное. Сначала проводится полная диагностика, включая лабораторные анализы и оценку работы сердца, печени, почек, а также психодиагностические тесты. После этого начинается этап детоксикации с внутривенными капельницами, которые выводят токсины, нормализуют водно-солевой баланс и восстанавливают основные функции организма. Далее мы применяем медикаментозную поддержку для стабилизации артериального давления, купирования тревожных симптомов, нормализации сна и уменьшения болевого синдрома.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi1.ru/]zakazat-obratnyj-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
ко ланта ко ланта
Задача врачей — не просто облегчить симптомы, а купировать осложнения, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции, вернуть пациенту способность к дальнейшему лечению. Мы работаем быстро, анонимно и профессионально. Любой человек, оказавшийся в кризисе, может получить помощь в течение часа после обращения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/]снятие наркотической ломки[/url]
Деятельность в области недропользования — это направление деятельности, связанный с освоением природных ресурсов.
Оно включает добычу полезных ископаемых и их дальнейшую переработку.
Данная сфера регулируется законодательством, направленными на сохранение природного баланса.
Ответственное ведение работ в недропользовании способствует экономическому росту.
оэрн
Процесс лечения в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на безопасное восстановление организма.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/]vrach-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
ข้อมูลชุดนี้ อ่านแล้วได้ความรู้เพิ่ม
ครับ
ดิฉัน ไปอ่านเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ หัวข้อที่คล้ายกัน
ซึ่งอยู่ที่ pg888 ล่าสุด
สำหรับใครกำลังหาเนื้อหาแบบนี้
เพราะให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึก
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ เนื้อหาดีๆ นี้
และหวังว่าจะได้เห็นโพสต์แนวนี้อีก
Возможность назначить визит специалиста в наиболее удобное время. Это позволяет эффективно совмещать лечение с работой и повседневными делами. Такая гибкость помогает пациентам своевременно начать терапию, не откладывая ее из-за занятости. При необходимости врач может приехать в вечернее время или выходные дни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
I’m now not certain where you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend a while learning much more or understanding more. Thank you for great info I used to be searching for this info for my mission.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробности по ссылке – https://taxlama.com/2024/08/13/walmart-dropshipping-step-by-step-guide-2024
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детали по клику – https://numberlina.com/5-interesting-facts-about-venus-for-kids
Duizendmaal dank voor het platform casino – het helpt enorm!
http://www.google.com.ar/url?q=https://lalabet-slots-netherlands.nl/
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому сочи[/url]
іѕ human trafficking tһe second largest, usa gymnastics coach hunan trafficking, human trafficking news neаr me, snopes lynne
knowles human trafficking, human trafficking awwreness ⅾay
quotes, human trafficking sex scene, human trafficking – menschenhandel, meghan connors human trafficking, ansrew tate human trafficking, arguments օn human trafficking, free human trafficking cme florida, human trafficking оur,
human trafficking іn minnesota 2021, arizona republican human trafficking, orange iѕ the new black human trafficking, human ttrafficking conference ocean city md, 277 arrested іn human trafficking, anti human trafficking law philippines, north korea huyman trafficking fɑcts, how wіll the wall afffect human trafficking, human trafficking training michigan 2018,
hotels sued human trafficking, kids rescued fгom human trafficking, durham region human trafficking,
ԝhy human trafficking is impօrtant, mother of ggod church
human trafficking, walmart human trafficking 2020, ѡhat is the rate of human trafficking worldwide, human trafficking news (news), human trafficking byy ѕtate 2021, lgbt human trafficking statistics, south africa аnd human trafficking, human trafficking statistics fbi, hoel lawsuits human trafficking, operation renewedd hope human trafficking,
human trafficking atlanta 2022, human trafficking san joaquin county,
non profit organizations fⲟr human trafficking, human trafficking interpol, human trafficking elgin, trafficking women’ѕ human riցhts julietta hua, facebook human trafficking
lawsuit, rates ᧐f human trafficking, eal ѡorld еxample of human trafficking, lawyers agaimst human trafficking, wsin human trafficking summit 2022, vad är human trafficking, recognizing tһe signs of human trafficking, human trafficking justice, video ᧐f
human trafficking, f᧐ur signs of humman trafficking, human trafficking honey, binjun xie human trafficking,
human trafficking documentary amazon рrime, minnesota
human trafficking data, uncovers ussian human trafficking гing war, human trafficking chico ϲa,
human trafficking jus cogens, human trafficking syrian refugees,
human trafficking topics гesearch paper, text human trafficking link
snopes, oprah south africa humaan trafficking, human trafficking grants 2015, human traffticking san antolnio 2021, human drug trafficking
meaning, human traffichking stories children, fema human trafficking awareness, florida disney human trafficking,
jobs fоr human trafficking victims, movie аbout human trafficking
2023 netflix, а day іn tһe life off a human trafficking victim, uk
human trafficking news, bent ⅼicense plate human trafficking
reddit, human trafficking іn waterbury ct, center t᧐ combat human trafficking, gresnville nc huyman trafficking,
maui human trafficking, t᧐p 5 human trafficking
cities, іs human trafficking happening in the սs,
oxnard human trafficking, aurora shoreline human trafficking,
taconganas human trafficking, hashtags fօr human trafficking, white hopuse huan trafficking summit, corona human trafficking,
border patrol human trafficking, human trafficking іn thailand 2020, human trafficking іn wv, 11 arrested in human trafficking, china’s one child polcy and human trafficking, hotels human trafficking 2023, human trafficking іn florida 2021, human trafficking debate topics,
international justice mission human trafficking, uncovers human trafficking
гing for, scholarly article օn hukan trafficking, madison herman human trafficking, amad diallo hukan trafficking,
а poem about human trafficking, human trafficking bristol tn, deluca аnd tthe
human trafficking storyline, economy ɑnd hjman trafficking, human trafficking inn
trinidad, human trafficking Ԁay 2018, caught camera actual
human trafficking victims, human trafficking episode
opal grey’ѕ anatomy, duolingo ceo human trafficking,watch dogs human trafficking map, human trafficking definition canada, airtag
human trafficking, human trafficking іn the beauty industry, 人口販子human trafficking, forced labor іn human trafficking, american airlines center human trafficking, human trafficking ce texas,
seelah human trafficking, siam human trafficking, fresno human trafficking statistics, senegal
human trafficking, human trafficking belgium, michigan human trafficking ϲourse, ny times human trafficking, abandoned stroller human trafficking, human trafficking і-44, solution оn human trafficking,
human trafficking canada news, ontario human trafficking, protects
victims օf human trafficking amendment, humawn trafficking іn highland cɑ, human trafficking hottspot map, human traffihking organizations
ontario, human trafficking hiding ᥙnder cars,
simmary on human trafficking, uncovers russian human trafficking гing war, human trafficking honey, fߋur
signs of human trafficking, human trzfficking western pa, human trafficking livermore, human tafficking
durham region, human trafficking аt atlanta airport, binjun xie human trafficking, minnesota uman trafficking data,human trafficking
documentary amazon рrime, human trafficking lawyer bloomfield hills, humsn trafficking charge іn texas, central students
aɡainst human trafficking, ap human geography human trafficking, human trafficking ffor sexhal exploitation, blue fοr human trafficking, kantyian ethics human trafficking, anti-human trafficfking organization іn cambodia,
jo jorgensen оn human trafficking, fort hood soldiers human trafficking,
beau оf the fiftһ column human trafficking,
hawkins human trafficking, human trafficking іn thе pacific islands, reasons ѡhy human trafficking іs
bad, ally human trafficking, ѡrite ɑn essay on human trafficking,
human trafficking pros, human trafficking dark web reddit, north preston human trafficking, Ԁollar sign tatftoo human trafficking,
wht іs human trafficking, human trafficking stuart fl, priceless movie humann trafficking, ti andd wife human trafficking, human trafficking ethnicity statistics, і 80truck stop human trafficking, hamilton human trafficking, oakville human trafficking,
human traffihking ߋn the deep web, current huan trafficking, human trafficking women’ѕ rights, brunei human trafficking, barack obama human traffickinhg quote, patron saint
οf human trafficking, spirited ɑway human trafficking, the game human trafficking, t᧐р human trafficking cities 2023, human trafficking ԝhich countries аre
the worst, hօw tto donate tο human trafficking organizations, human trafficking quotes famous,
human traafficking story 2020, human trafficking іn pittsburgh,
2020 human trafficking conference, human trafficking busst atlanta,
human trafficking hemet ϲa, human traffickng statistics oregon, һow to identify
a human traffickiung victim, economy and human trafficking,
lover boy method оf human trafficking, deluca ɑnd the human trafficking storyline, european human trafficking, selah
human trafficking, american airlines center human trafficking,
human trafficking paintings, ԝhat state is #1 in human trafficking?, forced labor inn human trafficking, 人口販子human trafficking, crysttal meth,ѡhɑt
doees crystal meth ⅼoоk lіke, what is crystal meth, crystal
meth anonymous, hoow ⅼong does crystal meth stay in youyr ѕystem, һow to make crystal
meth, blue crystal meth, buy crystal meth online, crygstal
meth effects, crystal meth pipe, crystal meth drug, ѡhаt does crysstal
meth ⅼook like?, meth crystal, crystfal meth images, crrystal meth ѕide effects, һow
is crystal meth mɑdе, meth vvs crystal meth,
whɑt does crystal meth do, crystal meth symptoms, crystal meth ѵs meth, effdcts of crysal
meth, side effects οf crystal meth, һow do yoᥙ make crysttal
meth, crystal meth ѵs crack, ᴡһat d᧐es crystal msth smell ⅼike,
hоw iss crysttal meh used, crystal meth withdrawal, crystal methh breaking bad, ᴡhat is crystal meth mаde of, what dօes crystal meth ⅾo to yoᥙ, crystal meth teeth,
smoking crystal meth, crystal meth pictures, ϲan yoս snort crystal meth, crystal mewth ƅefore and after, who injvented crystal meth, crystal meth
fаcts, crystal meth withdrawal symptoms, crystal meth
street names, signs ᧐f crystal meth, crystal meth addiction, һow tⲟ cook crystal
meth, crystal meth definition, ԝhat type оf drug
is crystal meth, ᴡһat Ԁoes crystal meth
feel ⅼike, crystal merth meaning, crystal meth ingredients,
ᴡhats crystal meth, ѡhat color іѕ crystal meth, crystal meth detox,
crystal meth fɑce, crysgal meth powder, crystal meth poem, street names fߋr crystal meth, suort
term effects оf crystal meth, signs оf crystal meth abuse, crystal meth rock, crysdtal meth fly, crystal meth addict, crystal meth ᥙsers, crystal meth rehab, һow much does crystawl mth cost, hօw ⅾօ yоu
take crystal meth, hoԝ muсһ is crystal meth, signs of crystal
meth սsе,how to smoke crystal meth, how too ᥙse crystal
meth, long term effects օf crystal meth, signms oof addiction tо crystal meth, pink
crystal meth, crystal meth ⅼook ⅼike,
breaking bad crygstal meth, ѡhen ᴡas crystal meth invented,
pictures ߋf crystal meth, hⲟw is crystal meth tаken,
signs that solmeone іѕ using crystal meth, ready οr not crystal meth storage, difference ƅetween meth аnd crystal meth,
howw Ԁo yoս do crystal meth, crystal meth., locate crystal meth storage, ѡhat аre the effects ߋf crystal meth, fake
crystal meth, crystall meth people, ᴡhat dοеs ccrystal meth,
hߋw dо you uѕe crystal meth, һow addictive is crystal meth,
cаn үou overdose on crystal meth, crystal meth blue,
crystal meth signs, һow long doe crystal meth last, crystal
meth detox ⅼⲟs angeles, һow do people use crystal meth, hߋԝ does crystal
meth look like, crystal meth porn, һow ddoes crystal meth
ⅼooқ, crystal meth storage twsted nerve, ѡhats in crystal meth, crystal meth treatment, what iss crystazl meth msde frⲟm, methamphetamin,
methamphetamin adalah, methamphetamin Ԁan amphetamin adalah, amphetamin ⅾаn methamphetamin, chloroethane ɑnd methamphetamin, crystal
methamphetamin, ԝhat is methamphetamin, methamphetamin effect,
methamphetamin sport, methamphetamin-entzug,
methamphetamin definition, methamphetamin withdrawal, methamphetamin deutsch, methamphetamin 中文, mdma
methamphetamin, methamphetanin hydrochlorid, methamphetamin geschichte, methamphetamin hcl, amphetamin νs methamphetamin, methamphetamin biru, methylphenidat methamphetamin, beda amphetamin ԁan methamphetamin, difference
bеtween amphetamine аnd methamphetamin, methamphetamin psychose, methamphetamin rules, һow t᧐ make methamphetamin, methamphetamin amphetamin unterschied, methamphetamin hydrochloride, definition ѵon methamphetamin, ⲣ2p methamphetamin, methamphetamin medizin, amphetamin ᥙnd methamphetamin, vicks vapor inhaler methamphetamin, gta methamphetamin labor,
ᴡie wirkt methamphetamin, methamphetamin entzug, methamphetamin kaufen, methamphetamin rezept, methamphetamin effects, methamphetamin amphetamin, methamphetamin schnelltest, unterschied amphetamine սnd
methamphetamin, methamphetamin herstellung, methamphetamin herstellung china,
methamphetamin wehrmacht, methamphetamin tabletten, methamphetamin doccheck,
һow to cook methamphetamin, methamphetamin abhängigkeit, methamphetamin nebenwirkungen, methamphdtamin ᴡas ist das, unterschied methamphetamin ᥙnd
amphetamin, methamphetamin nedir, amphetamine methamphetamin, methamphetamin aussprache,
methamphetamin chemical formula, methamphetamin medikament, methamphetamin ⅼa chat gi,
test methamphetamin, methamphetamin pervitin, methamphetamin adalahh obat, methamphetamin ɑndere
suchten аuch nach, methamphetamin mdma, tschechien methamphetamin, methamphetamin nachweisbarkeit, methamkphetamin psychonaut, methamphetamin molecule, methamphetamin labor,
methylenedioxymethamphetamin, ecstasy methamphetamin, methamphetamin ⅾương tính,
was ist methamphetamin, drogentest methamphetamin, methamphetamin englisch, methamphetamin structure, іѕt mxma methamphetamin, lye iin methamphetamin, іst methamphetamin organschädigend?
quora, methamphetamin chemische struktur, methamphetamin chemische formel, methamphetamin meaning, ԁ-methamphetamin, herstellung methamphetamin, methamphetamin vs amphetamine, methamphetamin recept, methamphetamin japan, definition methamphetamin, methamphetamin fаce,
methamphetamin formula, methampheamin synapse, methamphetamin adderall,
methamphedtamin adhd, blue methamphetamin, wirkung methamphetamin, methamphetamin terbuat dari, methamphetamin addiction,
bilder crystal methamphetamin, speed mіt methamphetamin gestreckt,
methamphetamin synthese, methamphetamin ᥙse icd 10,
weed, weed grinder, ѡheге is weed legal, disposable weed pen, weed sshop neаr mе,milwaukee weed eater, purple weed, іs weed legal іn virginia, is weed legal in oklahoma,
іs weed legal in louisiana, weed puller tool, weed carts,
iss weed legal іn south carolina, weed killer for lawns,
horny goat weed fоr men, what statеs is weed
legal,weed shops nesr mе, weed legal ѕtates, weed vape, roundup weed killer, weeed killer spray, edibles weed, recreational weed
ѕtates, weed store, milk weed, wred barrier, іѕ weɗ legal
in indiana, legal weed ѕtates, ѕtates ᴡith legal weed,
іѕ weed legal іn kentucky, weed puller, preen weed preventer, ounce оf weed,
dewalt weed eater, plantain weed, husqvarna weed eater, electric weed
eater, hybrid weed, moolnrock weed, weed pipe, barrett wilbert weed, weed
control, weed delivery neаr me, is weed leegal іn missouri, how to mаke
weed butter, ԝhite weed, is weed legal iin utah, moon rock weed, snow caps weed, іs weed legal іn arkansas, is weed legal іn texas 2025,
ryobi weed eater, weed bowl, dill weed, weed legalization,
smoking weed, іѕ wweed legal іn nevada, weed whacker, iss weed legal іn alabama, is weed ɑ drug,
weed barrier fabric, ᴡhat iѕ horny gowt weed, spruce weed аnd grass killer,
weed stores neаr me, sprinkles weed, poke weed, weed withdrawal,
weed vapes, snow cap weed, rm43 weed killer, craftskan weed eater, qp оf weed,
weed edibles, cookies weed, gelato weed, іs weed legal іn neԝ mexico, strains օf weed, weed butter, ⲣound of
weed, zaza weed, іѕ weed legal in nc, how much
is an ounce of weed, pggr weed, iѕ delta 9 real weed, diy weed killer,
ᴢip off weed, weed torch, moldy weed, elon musk weed, іs weed illegal in texas, weed eater string, rso weed, weed hangover, weed
wallpaper, іs weed legal in nebraska, how to smoke weed, іѕ weed lebal іn hawaii, hоw to greow weed, һow to mаke weed iin infinite
craft, iss weedd legal iin california, gary payton weed
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Детали по клику – https://inyoureyes.mx/single-service-1
Для кинотеатров, конференц-залов и домашних кинозалов подойдет [url=https://ekrany-dlya-proektora1.ru/]https://ekrany-dlya-proektora1.ru/[/url], который можно заказать на сайте.
являются важнейшим компонентом любого презентационного оборудования . Они позволяют добиться максимально четкого и яркого изображения . Кроме того, существуют различные модели экранов для проекторов, удовлетворяющих разным потребностям .
Экраны различаются по материалу и качеству поверхности . Для специализированных кинозалов и конференц-залов существуют уникальные предложения на рынке. Это позволяет найти идеальный экран для конкретных задач.
Экраны для проекторов различаются по принципу конструкции. Это экраны с электроприводом, которые монтируются на специальном штативе . Кроме того, разработаны экраны для фронтальной проекции .
Экраны подходят для создания уникальных визуальных эффектов. Они обеспечивают комфортный просмотр . Это объясняет их широкое применение.
При выборе экрана для проектора следует обратить внимание на несколько важных критериев . Это уровень освещения в помещении, которые определяют необходимость в дополнительных функциях . Кроме того, важно учитывать бюджет и предполагаемое использование .
Экраны необходимо подбирать исходя из технических характеристик проектора . Это обуславливает повышение эффективности презентаций. Поэтому рекомендуется консультироваться с профессионалами .
Экраны для проекторов играют решающую роль в формировании качества презентаций . Они должны быть выбраны с учетом всех необходимых факторов . Это позволяет добиться максимального качества изображения . Поэтому следует учитывать все возможные варианты.
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
В основе нашей методики — комплексный подход, сочетающий медицинскую точку зрения и психологические технологии. Мы не ограничиваемся снятием абстиненции: задача клиники — помочь пациенту обрести новую мотивацию, развить навыки противостояния стрессам и возобновить социальную активность. Работа строится на трёх ключевых принципах:
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-mytishchi1.ru
Наркологическая клиника «НаркологПроф» в Химках — это современный центр, специализирующийся на безопасном и быстром выведении из запоя. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, анестезиологи и медицинские сестры с большим стажем. Клиника функционирует круглосуточно, обеспечивая как выездную помощь, так и стационарное лечение. Главная цель специалистов — восстановить работу организма после интоксикации, нормализовать давление, устранить тревогу и бессонницу, помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальному состоянию. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, без постановки на учёт. Индивидуальный подход, корректный подбор медикаментов и строгий контроль состояния пациента делают лечение эффективным и безопасным.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this post and
also the rest of the website is really good.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Полная информация здесь – https://kasherlawgroup.com/quote-2
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Срочно нужен нарколог на дом? В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» приезжает к пациенту в течение часа.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в сочи[/url]
Врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, уровень сахара в крови и собирает анамнез. Это помогает выявить возможные риски и подобрать подходящие препараты.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-himki1.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-khimki-narkolog-na-dom/
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Натяжные потолки помогают быстро обновить интерьер, помогает быстро освежить отделку без демонтажа штукатурки. можно заранее спланировать скрытый карниз и подсветку по проекту, Если соседи сверху затопят, полотно удержит воду до приезда мастера: https://potolki-decarat.ru/
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом сочи[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Ломка — это не временное недомогание. Это системное разрушение организма, связанное с тем, что он перестаёт получать наркотик, к которому уже привык. Нарушается обмен веществ, функции сердца, печени, почек, теряется контроль над эмоциями и болью. В состоянии абстиненции человек не может спать, есть, адекватно мыслить. Страдает и тело, и психика.
Детальнее – https://snyatie-lomki-podolsk1.ru/snyatie-lomki-narkolog-v-podolske/
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом сочи[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
My family members every time say that I am killing my time here at net, however I know I am getting know-how everyday by reading thes fastidious content.
Профессиональная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон москве[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2290 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя наркология[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
Натяжные потолки отлично сочетаются с современным светом и точечными светильниками, хорошо переносит перепады температуры в квартире; команда заранее защищает мебель и быстро убирает рабочую зону, Можно комбинировать фактуры, https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя город. московская область[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Капельница от похмелья — эффективный способ детоксикации в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения токсинов из организма.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom sochi[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого сочи[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]после капельницы от запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя у пожилых людей в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты учитывают возрастные изменения организма при назначении лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в москве[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Подробнее тут – https://bangkeohoangnguyen.com/tin-tuc/meo-5-dieu-luu-y-ve-cach-dan-bang-keo-thung-xop-thung-carton
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому москве[/url]
Wow many of helpful data!
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
คอนเทนต์นี้ อ่านแล้วเพลินและได้สาระ ครับ
ผม เพิ่งเจอข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ซึ่งอยู่ที่ Agustin
น่าจะถูกใจใครหลายคน
เพราะอธิบายไว้ละเอียด
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ บทความคุณภาพ นี้
และอยากเห็นบทความดีๆ
แบบนี้อีก
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Открой скрытое – https://7seitai.com/%E3%83%88%E3%83%83%E3%83%97%E3%83%9A%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B8/ari1
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://www.affabletech.ai/blog/a-beginners-guide-to-clickup
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Подробнее – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом нижний новгород[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after reading through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
For most up-to-date news you have to pay a visit world wide web and on the
web I found this web site as a finest web site for hottest updates.
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи москва[/url]
Link exchange is nothing else except it is simply placing the other
person’s blog link on your page at appropriate
place and other person will also do similar for you.
Very good stuff. Cheers.
погрузчик вилочный дизель
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» проводит выезд нарколога на дом для безопасного вывода из запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]запой нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://nexgentalk.com/5-wearable-tech-innovations-2025
Hello to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this weblog; this
webpage carries remarkable and really fine material for
visitors.
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]вызов скорой наркологической помощи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить больше информации – https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru
Thanks for your personal marvelous posting! I certainly enjoyed reading it, you’re a great author. I will make sure to bookmark your blog and definitely will come back sometime soon. I want to encourage yourself to continue your great job, have a nice afternoon!
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя на дому в Нижнем Новгороде — быстрый и эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру с использованием современных препаратов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2290??, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сочи[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk13.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому город. московская область[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Choosing Cleaning Solutions
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
:::::::::::::::: ONLY THE BEST ::::::::::::::::
Content from TOR websites Magic Kingdom, TLZ,
Childs Play, Baby Heart, Giftbox, Hoarders Hell,
OPVA, Pedo Playground, GirlsHUB, Lolita City
More 3000 videos and 20000 photos girls and boys
h**p://tiny.cc/sficzx
h**p://j1d.ca/_J
h**p://put2.me/muhcsh
Complete series LS, BD, YWM, Liluplanet
Sibirian Mouse, St. Peterburg, Moscow
Kids Box, Fattman, Falkovideo, Bibigon
Paradise Birds, GoldbergVideo, BabyJ
h**p://citly.me/47kMX
h**p://4ty.me/ibhi7c
h**p://tt.vg/URoSx
Cat Goddess, Deadpixel, PZ-magazine
Tropical Cuties, Home Made Model (HMM)
Fantasia Models, Valya and Irisa, Syrup
Buratino, Red Lagoon Studio, Studio13
—————–
—————–
000A000054
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://hoedemakerspersoneelsadvies.nl/central-project-planner-m-f-d
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — круглосуточная помощь при запое. Мы гарантируем анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно нижний новгород[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk11.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя в москве[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» высылает нарколога на дом для срочной помощи при запое. Быстро и безопасно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — процедура, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального самочувствия. Она включает в себя введение препаратов, способствующих выведению токсинов и восстановлению функций органов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Желаете узнать подробности? – https://2sys.com/abstract-grunge-decorative-relief-navy-blue-stucco-wall-texture-wide-angle-rough-colored-background-with-spot-light
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://c-creative.fr/2024/02/08/bonjour-tout-le-monde
https://odesli.co/1xbetpromocodes26
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру кодирования.
Углубиться в тему – https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored at work so I decided to browse your site on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my mobile .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, superb site!
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом сочи[/url]
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2290 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — эффективный способ снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить организм. Процедура проводится опытными врачами с использованием современных препаратов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Good AC service is important for all property. Routine service cuts utility costs and increases system lifespan.
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru
Если запой стал серьёзной проблемой, стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи поможет выйти из кризиса. Врачи проводят детоксикацию и наблюдают за состоянием пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя сочи[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru/]центр наркологической помощи москва[/url]
Great site you have here but I was curious about if
you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics discussed
here? I’d really like to be a part of community where I can get feedback from
other knowledgeable people that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations,
please let me know. Thanks!
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельница от запоя — доступная цена в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Стоимость процедуры начинается от 2290 ?, и вы всегда будете заранее информированы о стоимости услуг.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве — клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает экстренную помощь на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам в течение 30 минут и проведут необходимые процедуры для стабилизации состояния.
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь москве[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя цена сочи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Подольске — «Частный Медик 24» предлагает эффективное лечение на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру, помогая снять симптомы похмелья и вывести токсины из организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk13.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в москве[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
I always emailed this blog post page to all my contacts, as if like to read it next my friends will too.
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому москве[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu16.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в нижнем новгороде[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает вывод из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением опытных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому москва[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
I pay a visit every day some sites and blogs to read content, but this weblog gives quality based writing.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре сочи[/url]
Лечение пивного алкоголизма в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем эффективные методы лечения зависимости от пива.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]анонимная скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно смотреть[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево сочи[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]анонимная скорая наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Howdy! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I came to give it a look.
I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers!
Excellent blog and excellent design and style.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena sochi[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому москве[/url]
Лечение запоя на дому в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk12.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно в москве[/url]
Не, бро, ну одно дело 250 заместо 50мг, а другое когда даже 250мг не берет. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Что то много новичков устраивают здесь флуд.А магаз на самом деле хорош.Помню его еще когда занимался курьерскими доставками,коспирация и качество товара было на высшем уровне.Крутой магаз
I am really grateful to the owner of this site who has shared this impressive post at at this place.
Капельница от запоя в Подольске — «Частный Медик 24» предлагает эффективное лечение на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут процедуру, помогая снять симптомы похмелья и вывести токсины из организма.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk13.ru/]капельница от запоя москва[/url]
Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и безопасное восстановление после длительного употребления алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu13.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
Душевный магазин) Все довольны. Славно. https://niturehome.ru Все мои контакты указаны в подписе.РЕСПЕКТОС МАгаЗИНУ=)
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре доступен в любое время суток. Клиника «Детокс» гарантирует профессиональную помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch16.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Для безопасного выхода из запоя в Сочи воспользуйтесь услугами стационара клиники «Детокс». Опытные врачи окажут помощь быстро и анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя, обратитесь в «Детокс» в Краснодаре. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом доступна круглосуточно. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов и окажут необходимую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]narkolog-na-dom sochi[/url]
Hi, I do think this is an excellent web site. I stumbledupon it ;
) I am going to return once again since i have book marked it.
Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue
to help others.
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Профессиональные врачи обеспечат комфортное и безопасное лечение. Минимальная стоимость услуги — 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов сочи[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Детальнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому московская область[/url]
Магазину отличных покупателей))) Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? щас заказал по 5г RCS-4 и URB754 по скайпу объяснили как оплатить, пока всё коректно жду посылки там отпишу..Полностью согласен !!!
Лечение абстинентного синдрома на дому в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры для скорейшего облегчения состояния.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]narkologicheskaya-pomoshch moskva[/url]
Hello there! I simply would like to give you a big thumbs up for your great info you have right here on this post. I am coming back to your web site for more soon.
Вывод из запоя у подростков в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем специализированное лечение для подростков, учитывая их возрастные особенности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]центр наркологической помощи москве[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Компания выполняет комплексную разработку электронных устройств под ключ, начиная с проектирования схем и печатных плат. Параллельно создается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение для управления устройством. Прототипы изготавливаются и тестируются на функциональность и надежность. После успешной проверки выполняется сборка и монтаж плат. Предоставляется мелкосерийное и серийное производство изделий для разных объемов заказов. Разрабатываются корпуса с учетом эргономики и защиты компонентов. Проводится промышленный дизайн для удобства использования и визуального восприятия. При необходимости выполняется реверс-инжиниринг существующих решений. Используются 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать для ускорения создания прототипов. Все изделия сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. Заказчик получает готовый продукт: https://sale-me.com/sankt-peterburg/shop/razrabotka-i-izgotovlenije-pechatnyh-plat-ooo-npp-652. Инновации здесь превращают идеи в реальность
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает полный курс вывода из запоя в стационаре. Круглосуточный медицинский контроль гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом цена сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru
Ремонт бытовой техники является незаменимым в условиях текущей экономики потому что он дает возможность избежать покупки новой техники. Помимо этого, ремонт бытовой техники также помогает сохранить природные ресурсы потому что он уменьшает количество отходов, образующихся при утилизации старой техники . Таким образом, ремонт бытовой техники является не только экономически выгодным, но и экологически чистым .
Стоит отметить, что ремонт бытовой техники предполагает наличие определенных умений и опыта . Большинство людей не обладают такими знаниями и навыками , поэтому они часто обращаются к профессиональным мастерам по ремонту техники . Профессиональные специалисты могут эффективно и оперативно устранить любые неисправности .
## Раздел 2: Типы ремонта бытовой техники
Существует множество типов ремонта бытовой техники, в зависимости от вида неисправности . Один из наиболее распространенных типов ремонта – это ремонт поврежденных компонентов . Tambien часто выполняется проверка работоспособности и регулировка техники . Кроме того, ремонт бытовой техники может включать в себя и другие виды работ .
Инспекция является первоочередным этапом в ремонте бытовой техники потому что она дает возможность выявить источник проблемы . После инспекции специалист может приступить к восстановительным работам. Ремонт бытовой техники может быть выполнен как в мастерской, так и на дому .
## Раздел 3: Преимущества ремонта бытовой техники
Ремонт бытовой техники обладает несколькими достоинствами . Одним из основных плюсов является финансовая выгода потому что ремонт является более дешевым вариантом, чем покупка новой техники. Кроме того, ремонт бытовой техники также позволяет сохранить время потому что ремонт можно выполнить быстро и оперативно .
Также ремонт бытовой техники способствует уменьшению количества отходов потому что он уменьшает количество отходов, образующихся при утилизации старой техники . Более того, ремонт бытовой техники также дает возможность продлить жизнь техники.
## Раздел 4: Заключение и перспективы
Ремонт бытовой техники является важной и перспективной услугой . Он позволяет не только финансово выиграть, но и внести вклад в сохранение природных ресурсов. Таким образом, ремонт бытовой техники является не только практичным, но и экологически полезным решением .
В будущем ремонт бытовой техники будет только набирать популярность потому что все больше людей начинают понимать важность сохранения ресурсов . Таким образом, мастера по ремонту бытовой техники будут очень востребованы . Будущее ремонта бытовой техники привлекательное и полнообещающее.
сервисный ремонт бытовой техники [url=https://www.servisnyj-centr-ekaterinburg.ru/]https://servisnyj-centr-ekaterinburg.ru/[/url]
이 페이지는 정말 제가 원했던 모든
정보을 가지고 있어서 누구에게 물어볼지 몰랐습니다.
What i do not realize is in truth how you are
now not actually a lot more well-liked than you
may be right now. You’re so intelligent. You already know
thus significantly when it comes to this subject, produced me
for my part imagine it from numerous numerous angles.
Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested
until it is one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs outstanding.
All the time care for it up!
В Бросике по- прежнему игнор!!! Магаз просто Ох..!!! https://selbstbewusstsein.top Рассказал друг-таксист.были случаи
Лечение хронического алкоголизма в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты помогут вам преодолеть зависимость и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk12.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Капельница от похмелья — эффективный способ детоксикации в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы используем современные препараты для быстрого и безопасного выведения токсинов из организма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]наркологическая помощь телефон москва[/url]
Наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве — клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает экстренную помощь на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам в течение 30 минут и проведут необходимые процедуры для стабилизации состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве — клиника «Частный Медик 24» предлагает экстренную помощь на дому. Наши специалисты приедут к вам в течение 30 минут и проведут необходимые процедуры для стабилизации состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Что случилось? почему страшно? Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? да вообще магазов пиздеРАБОТА КАЧЕСТВЕННАЯ И БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ РЕСПЕКТ ВАМ качество продукции еще не пробывал, в ближайшие время расскажу OOO
Hello, i believe that i noticed you visited my blog thus i came to go back the prefer?.I’m trying to find issues to improve my website!I guess its ok to use some of your
concepts!!
Снятие ломки при алкоголизме в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты помогут вам справиться с симптомами абстиненции.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Реабилитация после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам восстановиться после запоя и предотвратить рецидивы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru[/url]
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Подробности по ссылке – https://greennet.or.th/product/coconut-oil
Hi there Dear, are you really visiting this web site on a regular basis, if so then you will without doubt obtain fastidious know-how.
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя нижний новгород[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Открой скрытое – https://mediesven.com/explorando-la-medicina-estetica-belleza-y-bienestar-en-mediesven
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом сочи[/url]
В общем я всегда доверял своей логике и считаю ее правильной, многие соглашаются с ней, но видимо тут никто толком ни с кем не согласится, потому соглашусь с тем, что кончаем с оффтопом Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Сотрудники , знают свое дело , лучше другого.боюсь что здесь произойдёт тоже самое, уж очень не внятно продавец общается.
Купить официальный диплом ВУЗа : [url=http://desteg.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=5063/]desteg.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=5063[/url]
Клиника «Похмельная служба» в Нижнем Новгороде предлагает капельницу от запоя с выездом на дом. Наши специалисты обеспечат вам комфортное и безопасное лечение в привычной обстановке.
Узнать больше – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижнем новгороде[/url]
В Сочи стационар клиники «Детокс» предлагает комплексный вывод из запоя. Пациентам обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и круглосуточный контроль.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предлагает выезд нарколога на дом. Помощь оказывается быстро, анонимно и круглосуточно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в сочи[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому московская область[/url]
It’s actually very difficult in this full of activity life to listen news on TV,
therefore I just use web for that reason, and take the most up-to-date news.
Круглосуточная наркологическая скорая помощь в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наша команда работает 24/7, обеспечивая доступность медицинской помощи в любое время суток.
Подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Открой скрытое – https://tr.greencarborundum.com/urun/yesil-silikon-karbur-toz-saflik-99-sic
2с-i отличного качества. 1гр был разделен на 60 частей. Жалоб не от кого не было по качеству. https://spravka-moskva.biz Описание грамотное и понятное, клад нашел в считаные минуты.Все пришло, все хорошо! Конспирации такой не ожидал))) Сначала подумал что киданули)))))) Попробовал и все около дела, хороший средний микс получился. Буду брать больше на днях…
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя у мужчин в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к лечению мужчин, учитывая все особенности организма.
Разобраться лучше – http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/http://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в сочи[/url]
Анонимность и конфиденциальность гарантированы в клинике «Частный Медик 24». Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность на всех этапах лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Superb, what a blog it is! This website gives helpful facts to us, keep it up.
https://protein.kiev.ua/zamina-skla-na-farakh-replikakh-chy-pidiide.html
Если близкий человек в состоянии запоя, закажите нарколога на дом в Краснодаре от клиники «Детокс». Круглосуточно и конфиденциально.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи проводит вывод из запоя в стационаре. Все процедуры проходят под наблюдением квалифицированного персонала и с полным медицинским сопровождением.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре клиника «Детокс» предоставляет услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Специалисты приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/http://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru
ни ошибок. Выигрыш пришёл вовремя. Хороший сервис, чувствуется серьёзный подход [url=https://promo-msk.ru/]https://promo-msk.ru/[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod13.ru/]вывод из запоя цена нижний новгород[/url]
Если нужен профессиональный вывод из запоя, обращайтесь в стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно и под наблюдением специалистов.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого сочи[/url]
Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? рекомендую этот магазинпо моему ты уже сам все расположил
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Узнайте всю правду – https://naklejto.com/product/hoodie-with-pocket
I truly love your site.. Great colors & theme. Did you develop this web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m attempting to create my own personal site and want to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Kudos!
Выездная наркологическая помощь в Нижнем Новгороде — капельница от запоя с выездом на дом. Мы обеспечиваем быстрое и качественное лечение без необходимости посещения клиники.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://snyatie-zapoya-na-domu11.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Краснодаре — услуга клиники «Детокс». Специалисты оказывают квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch15.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому москва[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая помощь московская область[/url]
Снижение веса в санатории часто включает в себя [url=https://lechebnoe-golodanie.ru]голодание пожилых людей[/url], которое помогает в очистке организма и общем оздоровлении.
становится все более серьезной из-за различных социальных и экономических факторов. Учитывая, что пожилым людям приходится экономить на всем, они могут не иметь возможности позволить себе полноценное питание . Это негативно влияет на их физическое и психическое состояние.
Последствия голодания для пожилых людей могут быть очень тяжелыми . Голодание вызывает снижение иммунитета . Кроме того, это может вызвать проблемы с сердцем, диабет и другие серьезные проблемы со здоровьем. Необходимо принимать меры для предотвращения голодания среди пожилых людей .
Причины голодания пожилых людей очень многочисленны и различны . Одной из основных причин является финансовая нестабильность . Кроме того, они могут иметь проблемы со здоровьем, которые ограничивают их возможности . Это создает дополнительные проблемы в их жизни .
Решение проблемы голодания пожилых людей требует единого подхода . Необходимо оказывать экономическую и социальную помощь. Кроме того, необходимо повышать осведомленность о важности решения этой проблемы . Это может обеспечить им достойную старость.
Влияние голодания на здоровье пожилых людей может быть крайне тяжелым . Голодание вызывает ослабление организма . Кроме того, голодание может привести к проблемам с психическим здоровьем . Необходимо обеспечивать пожилым людям доступ к квалифицированной медицинской помощи.
Роль общества в решении проблемы голодания пожилых людей очень важна и многогранна . Общество должно оказывать поддержку и помощь тем, кто в ней нуждается . Кроме того, важно создавать программы по поддержке пожилых людей . Это может существенно улучшить их здоровье и благосостояние .
Проблема голодания пожилых людей является одной из наиболее важных социальных проблем . Необходимо решать эту проблему на государственном и общественном уровне . Кроме того, необходимо повышать осведомленность о важности решения этой проблемы . Это может помочь улучшить качество жизни пожилых людей .
Будущие направления решения проблемы голодания пожилых людей предполагают комплексный подход . Необходимо создавать и развивать системы поддержки пожилых людей . Кроме того, важно обеспечивать пожилым людям доступ к квалифицированной медицинской помощи. Это может помочь предотвратить голодание среди пожилых людей .
Для тех, кто ценит функциональность и практичность, [url=https://skladnyenozhi.ru]складной нож москва[/url] становится незаменимым компаньоном в повседневной жизни.
в древние времена, когда люди benotовали компактный и практичный инструмент . В те времена складной нож использовался как инструмент для gunlukх задач, таких как резание веревки или открытие консервов . С течением времени дизайн и функциональность складного ножа развивались, чтобы соответствовать различным стилям и предпочтениям.
Складной нож также стал инструментом, который помогал людям в их повседневной жизни . В современное время складной нож используется в различных областях, включая строительство и медицину. Его популярность обусловлена его компактностью и легкостью использования .
Конструкция складного ножа представляет собой сочетание инновационных технологий и традиционных методов. Лезвие складного ножа имеет специальную обработку, которая предотвращает коррозию и ржавчину . Ручка складного ножа разработана с учетом различных стилей и предпочтений.
Складной нож также оборудован системой быстрого открытия, которая позволяет быстро и легко выдвинуть лезвие . Его функциональность делает его незаменимым атрибутом для любителей активного отдыха. Складной нож представлен в различных размерах и вариантах, чтобы удовлетворять разным потребностям и предпочтениям .
Существует широкий выбор моделей и брендов, удовлетворяющих различным вкусам и потребностям . Один из популярных видов складных ножей – охотничий нож, который разработан для использования в различных условиях. Другой вид – тактический нож, который разработан для использования в экстремальных ситуациях.
Каждый вид складного ножа разработан с учетом различных условий и ситуаций . Выбор складного ножа должен основываться на понимании потребностей и ожиданий. Складной нож может стать верным компаньоном в повседневной жизни или приключениях .
Использование складного ножа должно основываться на понимании его функциональности и возможностей . При использовании складного ножа необходимо учитывать такие факторы, как окружающая среда и тип задачи. Уход за складным ножом включает в себя регулярную очистку и смазку .
Складной нож должен быть использован только в соответствии с его назначением и инструкциями. При правильном использовании и уходе складной нож будет сохранять свою функциональность и эффективность . Складной нож остается популярным среди людей, которые ценят его практичность и историю.
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем различные методы кодирования, подходящие для каждого пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь москве[/url]
Заказываю 2c-I для начала 1 г!! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Удачных закупокТС саппорт не требуется тебе ? Напиши в лс если интересно
Kraken Marketplace — безопасная площадка для анонимных сделок в 2025 году кракен даркнет маркетплейс **Основной текст (пост на форуме, комментарий, описание):**Для входа используйте только кракен onion ссылка.
Техническое обслуживание грузовых и коммерческих автомобилей и спецтехники. Снабжение и поставки комплектующих для грузовых автомобилей, легкового коммерческого транспорта на бортовой платформе ВИС lada: https://ukinvest02.ru/
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Лечение запоя без госпитализации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем лечение на дому, без необходимости госпитализации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь московская область[/url]
Если пациент не может приехать в клинику, в Краснодаре нарколог приедет к нему домой. Помощь оказывает «Детокс» круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Клиника «Детокс» в Сочи предлагает услугу вывода из запоя в стационаре. Под наблюдением профессиональных врачей пациент получит необходимую медицинскую помощь и поддержку. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно сочи[/url]
странно что это нужно писать =\ Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Я делал ркс. на спирту. Получилась лайт ваще. Делай вообщем гдето 1к 7ми . будет так нормик эффект. но слабее 203гомир всем месным братья
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva11.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь москва[/url]
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your style is so unique in comparison to other people I have read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this blog.
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva13.ru/]центр наркологической помощи москва[/url]
В Сочи клиника «Детокс» предлагает лечение запоя в стационаре с круглосуточным медицинским контролем. Здесь пациент получает безопасное и эффективное восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi15.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
В Краснодаре нарколог из клиники «Детокс» приедет на дом, чтобы вывести из запоя и оказать необходимую помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в сочи[/url]
Если вы ищете надежную клинику для вывода из запоя в Сочи, обратитесь в «Детокс». Здесь опытные специалисты окажут необходимую помощь в стационаре. Услуга доступна круглосуточно, анонимно и начинается от 2000 ?.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi22.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
в скаипе не отвечают!!!! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Но бывали случаи и на оборот…я бы тоже заценил
Помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты проведут необходимые процедуры для снятия симптомов интоксикации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Для восстановления после запоя выбирайте стационар клиники «Детокс» в Сочи. Здесь пациентам обеспечивают качественную помощь и поддержку на каждом этапе.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена сочи[/url]
Если вы или ваш близкий нуждаетесь в профессиональной помощи при запое, клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врач приедет в течение 1–2 часов, проведёт необходимое обследование и назначит лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Лечение зависимости от алкоголя на дому в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Наши специалисты приедут к вам домой и проведут все необходимые процедуры.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk12.ru/]капельница от запоя в москве[/url]
поддерживаю !!!! https://operationq.top да, самая действенная схема для работы с чемикаломА ты у него спроси тот он или не тот, врать не станет думаю
Клиника «Детокс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом. Врачи приедут к вам в течение 1–2 часов, проведут осмотр и назначат необходимое лечение. Услуга доступна круглосуточно и анонимно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Профилактика рецидивов после запоя в Подольске от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы поможем вам предотвратить повторные случаи запоя и поддержим вас на пути к трезвой жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-podolsk12.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
Профессиональная помощь при алкогольной интоксикации в Москве от клиники «Частный Медик 24». Мы предлагаем капельницу, которая способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и улучшению общего состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch-moskva12.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/mrx99a2c
First of all I would like to say wonderful blog! I had a quick question which I’d like to ask if you do not mind. I was curious to know how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing. I’ve had difficulty clearing my mind in getting my thoughts out there. I truly do take pleasure in writing however it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or hints? Cheers!
оплатил 31го, сегодня все уже получил! Продавану, спасибо за оперативность!:ok: https://webpostingmart.info Ну во-первых мы совершенно другой магазин, так что вы ошиблись веткой, и представительств в тех городах у нас нетИ еще сушняки ужасные. Сейчас вот утром проснулся, и до сих пор
моющее средство для пола концентрат Органические моющие средства – это гармония между человеком и природой. Мы предлагаем продукты, созданные на основе растительных экстрактов и масел, которые бережно очищают поверхности, не оставляя токсичных следов. Наши органические моющие средства подходят для уборки в домах с маленькими детьми и домашними животными, обеспечивая безопасную и здоровую атмосферу.
Ко ланта ко ланте
а сюда заглянуть влом ? //legalrc.com/threads/Трипы.588/page-2 https://in-timeproduction.ru Добрый вечер, менеджер отписал, что СК будет в выходные! Так это? Интересует Новосибирск опт.А JWH-018 Имеется в наличии?
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru
xrumer скачать xrumer 23
кайт анапа кайтинг в анапе
где доступны десятки столов с реальными дилерами и высокими ставками [url=https://vagonkavsem.ru/]https://vagonkavsem.ru/[/url]
кайт станция египет обучение кайтсёрфингу
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/pomoshh-narkozavisimym-tolyatti/
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh
Менеджер прошу зайдите в скайп, хочу заказ оплатить вас там нет 2 дня уже. Заявку на сате подал жду ответ на эмаил. Спасибо. https://iranmap.biz Спасибо!Не надо!Магаз пропал из аськи и скайпа… Тобишь просто не появляется в онлайне. Такое уже бывало, но щас хз что… Качество товара было отменным. 203й высочайшего качества.
It’s going to be end of mine day, except before end I am reading this impressive piece of writing to improve my know-how.
https://www.tdk-evak.kz/
Капельница — это основной инструмент дезинтоксикации при лечении запойных состояний. Она способствует выведению токсинов, нормализации обмена веществ и улучшению общего самочувствия. Состав раствора подбирается индивидуально в зависимости от степени интоксикации, возраста, массы тела и сопутствующих заболеваний. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает облегчение, снижается тревожность и проходит головная боль.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток. Это позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам, которые находятся в тяжёлом состоянии или не могут самостоятельно приехать в стационар. Медицинская бригада прибывает в течение 40–60 минут, не используя специализированный транспорт и форму, чтобы сохранить анонимность. Врач проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает давление, частоту дыхания, уровень сознания и насыщение кислородом, после чего назначает детоксикационную капельницу с контролем дозировки.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в рязани[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your article post. I wanted to write a little comment to support you.
Для тех, кто предпочитает лечение в условиях стационара, предусмотрены комфортные палаты, медицинский контроль 24/7 и возможность консультаций с психотерапевтом. Врачи клиники применяют комплексные методы, направленные не только на снятие симптомов, но и на устранение причин зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom
Основные этапы включают:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Основные этапы включают:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в красноярске[/url]
Донат в FC Mobile Донат в России отражает глобальные тенденции, адаптированные к местным экономическим и культурным условиям. Российские игроки активно поддерживают как отечественных, так и зарубежных разработчиков, внося средства в различные игровые проекты. Распространение цифровых платежных систем и увеличение проникновения интернета способствуют росту популярности доната в России, превращая его в значимый источник дохода для игровой индустрии.
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne
Во время лечения фиксируются все жизненные показатели пациента. При необходимости проводится экспресс-анализ крови и ЭКГ. Ниже представлена таблица, показывающая, какие параметры контролируются и по каким признакам оценивается стабилизация состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
Капельница — это основной инструмент дезинтоксикации при лечении запойных состояний. Она способствует выведению токсинов, нормализации обмена веществ и улучшению общего самочувствия. Состав раствора подбирается индивидуально в зависимости от степени интоксикации, возраста, массы тела и сопутствующих заболеваний. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает облегчение, снижается тревожность и проходит головная боль.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в красноярске[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica[/url]
Да неее))) само то емс и почта россии !! А лучше гарантпост очень клево работают по ним надо отправлять вообще изумительные службы. Или первый класс! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? где вообще оператор или кто ни будь? бабло уплочено и жду доставку а на связи ни кого нету!!!!!!!!!!Спасибо за терпение, понимание и позитивный настрой
Лечение проходит в несколько этапов: диагностика, детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка и восстановление. Каждый этап имеет чёткие цели и критерии эффективности, что делает процесс управляемым и безопасным. Применяются препараты, сертифицированные в РФ, и только те, чья эффективность подтверждена клиническими исследованиями.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]инвестиции в крипту[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/[/url]
Продуманный внешний вид играет важную роль в формировании впечатления.
Она помогает передать личный стиль и ощущать комфорт.
Грамотно подобранный образ формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://rentry.co/nvm2vvpu
Продуманный гардероб облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать личные предпочтения и уместность ситуации.
Мода дают возможность находить новые решения.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
I have been exploring for a bit for any high quality articles or blog posts in this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this site. Studying this info So i’m glad to show that I’ve a very excellent uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I such a lot for sure will make sure to don?t forget this website and give it a glance on a relentless basis.
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/
моющие средства био Моющие средства био – это будущее чистоты. Мы разрабатываем формулы, в которых сочетаются передовые научные достижения и сила природы. Благодаря использованию биоразлагаемых компонентов, наши моющие средства не загрязняют водоемы и почву, быстро разлагаясь в окружающей среде. Мы верим, что чистота должна быть не только эффективной, но и ответственной.
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в новокузнецке[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс знакомства[/url]
https://sonabet.pro/
sonabet.pro
Братишка, все красиво, в касание, спасибо за профессионализм Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Магаз ровный, очень много раз тут брал, а как перешли на телеграмм так еще больше радуете, намного меньше гемора с оплатой стало, качество на высоте как и всегда. Сегодня убедился что оператор не сидит без дела, очень сильно помог мне с моим вопросом, при чем оперативно все сделал. Оцениваю данный магазин 10 из 10. Кокаин даже MQ оказался лучше, чем я до этого покупал HQ в другом магазе. Делайте по чаще закладки в центре Питера.Мы в Кургане не работаем, все наши представительства есть в соответствующем разделе.
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь тольятти[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Для удачного продвижения вверх по карьерной лестнице потребуется наличие официального диплома о высшем образовании. Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам: [url=http://define.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=46&t=2589/]define.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=46&t=2589[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
I visited several web pages except the audio feature for
audio songs present at this website is genuinely fabulous.
Капельница — это основной инструмент дезинтоксикации при лечении запойных состояний. Она способствует выведению токсинов, нормализации обмена веществ и улучшению общего самочувствия. Состав раствора подбирается индивидуально в зависимости от степени интоксикации, возраста, массы тела и сопутствующих заболеваний. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает облегчение, снижается тревожность и проходит головная боль.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog website?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of
this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя врачом[/url]
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon[/url]
ко ланте ко ланте
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника воронеж[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
####### OPVA ########
ULTIMATE РТНС COLLECTION
NO PAY, PREMIUM or PAYLINK
DOWNLOAD ALL СР FOR FREE
Description:-> lmy.de/bmRZI
Webcams РТНС since 1999 FULL
STICKAM, Skype, video_mail_ru
Omegle, Vichatter, Interia_pl
BlogTV, Online_ru, murclub_ru
Complete series LS, BD, YWM
Sibirian Mouse, St. Peterburg
Moscow, Liluplanet, Kids Box
Fattman, Falkovideo, Bibigon
Paradise Birds, GoldbergVideo
Fantasia Models, Cat Goddess
Valya and Irisa, Tropical Cuties
Deadpixel, PZ-magazine, BabyJ
Home Made Model (HMM)
Gay рthс collection: Luto
Blue Orchid, PJK, KDV, RBV
Nudism: Naturism in Russia
Helios Natura, Holy Nature
Naturist Freedom, Eurovid
ALL studio collection: from
Acrobatic Nymрhеts to Your
Lоlitаs (more 100 studios)
Collection european, asian,
latin and ebony girls (all
the Internet video) > 4Tb
Rurikon Lоli library 171.4Gb
manga, game, anime, 3D
This and much more here:
or –> cutt.us/OMB2F
or –> citly.me/sVJSf
or –> 4ty.me/08yxs4
or –> tt.vg/fiJTt
or –> tiny.cc/ik3v001
or –> mub.me/qPg
or –> j1d.ca/_I
or –> put2.me/pwdcjb
or –> 74i.de/dekSToh
—————–
—————–
Да шляпа какая-то, менеджер работает из рук вон плохо, и валит все на курьера. Абсолютная неразбериха, понять, кто и в каком месте накосячил достоверно – просто невозможно, но тем не менее, факт остается фактом: больше недели я ожидаю отправку заказа, и это только отправка, причем, разумеется, с полной предоплатой. Общались с манагером через скайп и через аську, очень муторно, сообщения теряются, на оставленные мессаги в оффлайне не отвечает, да и в онлайне появляется довольно редко. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Вообще то дажббер в рабочее время всегда в сети и все кто оплачивал и делал заказ получили треки.Наша организация не несет ответственности за применение продукции не по назначению. Осуществляется тотальный контроль качества продукции. Чистота препаратов 99.2%. Исключено добавление примесей. Используется сырье очень высокого качества.
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи в тольятти[/url]
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]экспресс займ[/url]
Отдельный принцип клиники — строгая анонимность. Информация о лечении не передаётся по месту работы, обучения, в сторонние структуры без согласия пациента. Это особенно важно для людей, которые боятся огласки и из-за этого годами откладывают обращение. В «КоломнаМед Центр» можно пройти лечение так, чтобы сохранить репутацию и личное пространство, не превращая каждый шаг в обсуждение «на людях».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kolomne[/url]
Для наглядности приведена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их результатами:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике воронеж[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
xrumer сайт телеграм Базы GSA
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]заказать нарколога на дом[/url]
Для наглядности приведена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их результатами:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/[/url]
I don’t know if it’s just me or if everybody else encountering problems with your site. It seems like some of the text on your posts are running off the screen. Can someone else please provide feedback and let me know if this is happening to them as well? This might be a problem with my web browser because I’ve had this happen previously. Cheers
записаться сейчас онлайн курс диспетчера
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
Добрый день, треки работать начинают с некоторым опозданием, берите их в заказах на сайте, проверяйте, все должны работать пятничные. По крайней, мере в скайп/асю пишите, что заработали и у меня тоже мониторинг есть Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Удачи всей команде желаюЯ по почте переписывается пытался нормально договориться потом просто отвечать перестали решил здесь пообщаться тут надеюсь игнорировать не будут!
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
концентрированное моющее средство Моющие средства био – это будущее чистоты. Мы разрабатываем формулы, в которых сочетаются передовые научные достижения и сила природы. Благодаря использованию биоразлагаемых компонентов, наши моющие средства не загрязняют водоемы и почву, быстро разлагаясь в окружающей среде. Мы верим, что чистота должна быть не только эффективной, но и ответственной.
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Стильно одеваться имеет большое значение для создания первого впечатления.
Внешний вид помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и улучшает самоощущение.
Аккуратный образ формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://telegra.ph/Chanel-12-29
Хорошо сочетаемая одежда упрощает общение.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать собственный вкус и уместность ситуации.
Актуальные направления позволяют находить новые решения.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Каждый вызов нарколога на дом проходит по строгому алгоритму. Врачи клиники «ВоронМед Профи» используют индивидуальный подход, адаптируя лечение под конкретного пациента. В таблице приведена типовая схема работы выездной бригады, которая помогает понять, как проходит процесс помощи от начала до конца.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод воронеж[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя волгоград[/url]
Ребят, магазин ровнее ровного. Если есть какие то сомнения, например, нарваться по кантактам на фэйкоф, обращайтесь на прямую к ТС. Написать ЛС 100% все будет исполнено в лучшем виде. Скорость доставки товара просто удивляет, конспирация, и выбор курьерки, залог вашей безопасности, у ТС это приоритет. Все на высшем уровни. Реагент качественный, минимум побочек максимум пазитива. Если вы все-таки решитесь, сдесь прикупиться, вы забудите и думать, где бы вам затариться снова. Не проходите мимо. То, что вам надо, тут. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? КЕнт,сорри на почту ответь..Крутой качественный товар! Все своевременно +++
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
кайтсёрфинг анапа кайт анапа
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-vyezdom-na-dom[/url]
Донат в мобильные игры Донат в России – это часть глобального тренда, адаптированная к местным экономическим условиям и культурным особенностям. Российские игроки активно поддерживают как отечественных, так и зарубежных разработчиков, внося средства в любимые проекты. Развитие цифровых платежных систем и распространение смартфонов способствуют росту популярности доната в России, превращая его в важный источник дохода для игровой индустрии.
Капельницы — основной инструмент при лечении алкогольной и наркотической интоксикации. Они способствуют выведению токсинов, восстановлению электролитного баланса и улучшению самочувствия. Ниже представлена таблица с основными типами капельниц, применяемыми в клинике «КузбассМед Центр».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в новокузнецке[/url]
Для качественного ухода за вашим автомобилем посетите [url=https://autoremontiki.ru]детейлинг салона[/url].
Процедура позволяет удалить мелкие дефекты и придать поверхности блеск.
You have made some really good points there.
I looked on the internet for more info about the issue and found most
people will go along with your views on this website.
«Трезвый Путь Коломна» создаёт единый контур помощи: пациент не «перекидывается» между разными организациями, а проходит лечение в одной системе, где специалисты знают его историю и несут ответственность за последовательность шагов. Это критично для тех, кто уже сталкивался с бессистемными попытками: один врач ставил капельницы, другой «кодировал», третий давал советы, а в итоге всё заканчивалось новым срывом. Здесь маршруты связываются в цельную линию.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
В клинике используются проверенные медицинские методы, основанные на современных научных данных. При алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации первым этапом является детоксикация — выведение токсинов из организма и нормализация обменных процессов. На следующем этапе проводится медикаментозная поддержка, направленная на стабилизацию состояния, снижение тяги к веществам и восстановление функций внутренних органов. После стабилизации пациент проходит курс психотерапии и участвует в программах реабилитации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто место оказания медицинских услуг, а пространство, где начинается путь к выздоровлению. В «КузбассМед Центр» создана система комплексной помощи пациентам с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, включающая медицинскую, психологическую и социальную реабилитацию. Здесь работают врачи с многолетним опытом, а лечение проводится круглосуточно и анонимно. Каждый пациент получает индивидуальную программу, учитывающую особенности организма, стаж употребления и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]zakazat-obratnyj-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Лечение проходит в несколько этапов: диагностика, детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка и восстановление. Каждый этап имеет чёткие цели и критерии эффективности, что делает процесс управляемым и безопасным. Применяются препараты, сертифицированные в РФ, и только те, чья эффективность подтверждена клиническими исследованиями.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh/
Эффект чувствуется почти сразу, эйфория и стим в голове https://extragram.ru службу спрс давным давно забросить необходимо..На ацетоне делай, он быстро выветривается и не пахнет совсем!
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]adresa-narkologicheskih-klinik[/url]
Keep this going please, great job!
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr/
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя красноярск[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс терапии в наркологической клинике в Воронеже организован поэтапно. Это позволяет обеспечить системность и постепенность восстановления, снизить риски осложнений и повысить устойчивость результата.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Электронные компоненты https://zener.ru с прямыми поставками от производителей: микросхемы, пассивные элементы, разъёмы и модули. Гарантия оригинальности, стабильные сроки, выгодные цены и подбор под ТЗ. Поставки для производства, сервиса и разработки.
Кент,приветствую..!!))В личку ответь,там по поводу оплаты…….оплатил договаривались на выходные…жду там от тебя ответа)) https://ishdps.ru Писал уже, магазин работает в турбо режиме отправки вовремя, получают люди вовремя, сменили штат сотрудников сменили курьеров которые тупили, все налажено все как должно быть.у меня 203 1к8 получался вообще жестокии делал на растворителе для снятие лака с ногтей (без ацетона)
Для наглядности приведена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их результатами:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в красноярске[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno/
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/
В клинике обеспечивается безопасный вывод из запоя и очистка организма после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или токсических сочетаний. Используются современные инфузионные схемы, витамины группы B, магний, гепатопротекторы по показаниям, противорвотные, мягкая коррекция сна и тревожности. Контроль давления, пульса, сатурации и поведения позволяет вовремя отметить любые осложнения и скорректировать терапию. Главная цель — не просто «прояснить голову», а защитить сердечно-сосудистую систему, мозг, печень, минимизировать риск делирия, судорог, аритмий и других острых состояний.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]zakazat-obratnyj-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Подробнее тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Перед назначением инфузий врач проводит полную диагностику, чтобы исключить противопоказания. Капельницы часто комбинируются с медикаментами, поддерживающими сердечно-сосудистую систему и печень. Такой комплексный подход позволяет ускорить процесс очищения и улучшить общее состояние пациента уже после первого курса.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Перед цифрами — важная оговорка: это ориентиры, не публичная оферта. Итог зависит от длительности эпизода, объёма инфузий, перечня препаратов, времени суток и необходимости расширенного наблюдения или перевода в отделение. Мы заранее проговариваем, что входит в базу, что является расширением, и согласуем любые изменения до выполнения — так смета остаётся управляемой, а семья может планировать бюджет спокойно. Ниже — типовые пакеты «Трезвой Линии» для Электростали с понятным наполнением.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника волгоград[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи тольятти[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-voronezh
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Hi, yeah this post is really nice and I have learned lot of things from it
concerning blogging. thanks.
Here is my blog :: situs slot gacor
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]ставки на спорт[/url]
сделать гражданство румынии
всем привет https://sincastigos.com Под., зачет с натяжкой. Мята незачет, сильно уж она ваняет. Растворитель пришлось нагревать и домалывать кр..Страшно , но хочется и потом сам не попробуеш не узнаеш )
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Такой алгоритм позволяет контролировать каждый аспект лечения, обеспечивая постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врач-куратор отслеживает динамику и при необходимости корректирует программу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan/
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/
https://www.ordinarybazar.com/2022/12/sandisk-m-z43-64gb-pendrive.html?showComment=1768123482665#c870902596363495784
This design is incredible! You certainly know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskaya-klinika/
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for supplying this information.
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
какой оптимальный недорогой способ доставки выбрать при небольшом заказе,если не почта?посоветуйте… Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? с нашими кристаллами восстановятсясделал заказ ,оплатил 🙂 теперь жду трека и посыля с нетерпением 🙂 по общению продаван понравился все ровно обьяснил че да как . как придет опробую оставлю отзыв окончательный ,пока что все ровно )
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в красноярске[/url]
«Трезвый Путь Коломна» создаёт единый контур помощи: пациент не «перекидывается» между разными организациями, а проходит лечение в одной системе, где специалисты знают его историю и несут ответственность за последовательность шагов. Это критично для тех, кто уже сталкивался с бессистемными попытками: один врач ставил капельницы, другой «кодировал», третий давал советы, а в итоге всё заканчивалось новым срывом. Здесь маршруты связываются в цельную линию.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom[/url]
курс трак диспетчера в сша в сша для начинающих
https://droid-gamers.ru/user/bobbiedpmu
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого волгоград[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh/
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-volgograd/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]слоты на деньги[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены волгоград[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в рязани[/url]
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov
Привет форуму! всем кто сомневался брать или нет здесь советую брать не ошибетесь,заказывал сам первый раз тоже побаивался, но решился,, заказал реги jv 60 10 гр в пятницу, оплатил в тот же день, сегодня все на руках конспирация на уровне, тс вполне адекватный человек отвечает быстро, все прошло быстро, оперативно, чему я очень рад, надеюсь на дальнейшее с ним сотрудничество, за качество пока сказать не могу, тк еще микс не делал. Процветания и удачи вашему магазину, приятно было с вами работать! https://mossygatherings.info Я делил Амф,о господи 😀 я не селлер – я просто зашёл на сайт и посмотрел что есть в ассортименте – из скоростей нормальных разве что..кхм, оно…
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Сервисный центр Dyson предлагает широкий спектр услуг по ремонту и обслуживанию устройств Dyson. Это связано с тем, что сервисный центр Dyson использует только оригинальные запчасти и имеет опытных специалистов, которые могут diagnosticровать и исправлять любые неисправности устройств Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson также предлагает услуги по техническому обслуживанию и профилактике устройств Dyson. Это делает сервисный центр Dyson идеальным местом для всех, кто ищет качественный и оперативный ремонт своих устройств Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson работает с различными платежными системами и предлагает удобные условия для клиентов.
Услуги сервисного центра Dyson
Сервисный центр Dyson предлагает широкий спектр услуг по ремонту и обслуживанию устройств Dyson, включая ремонт пылесосов, очистителей воздуха и других устройств. Это позволяет сервисному центру Dyson предоставлять высококачественные услуги и оперативно решать любые проблемы с устройствами Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson имеет гибкие цены и удобные условия для клиентов. Это связано с тем, что сервисный центр Dyson использует только оригинальные запчасти и имеет опытных специалистов, которые могут diagnosticровать и исправлять любые неисправности устройств Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson предлагает широкий спектр услуг по ремонту и обслуживанию устройств Dyson.
Преимущества сервисного центра Dyson
Сервисный центр Dyson работает с различными моделями устройств Dyson и может diagnosticровать и исправлять любые неисправности. Это связано с тем, что сервисный центр Dyson имеет современное оборудование и технологии, которые позволяют ему предоставлять высококачественные услуги. Сервисный центр Dyson также предлагает услуги по доставке и установке устройств Dyson, что делает его идеальным местом для всех, кто хочет приобрести новые устройства Dyson. Это делает сервисный центр Dyson идеальным местом для всех, кто ищет качественный и оперативный ремонт своих устройств Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson имеет современное оборудование и технологии, которые позволяют ему предоставлять высококачественные услуги.
Заключение
Сервисный центр Dyson использует только оригинальные запчасти и имеет опытных специалистов, которые могут diagnosticровать и исправлять любые неисправности устройств Dyson. Это связано с тем, что сервисный центр Dyson имеет современное оборудование и технологии, которые позволяют ему предоставлять высококачественные услуги. Сервисный центр Dyson работает с различными платежными системами и предлагает удобные условия для клиентов. Это делает сервисный центр Dyson идеальным местом для всех, кто ищет качественный и оперативный ремонт своих устройств Dyson. Сервисный центр Dyson работает уже более 10 лет и имеет большой опыт в обслуживании устройств Dyson.
дайсон официальный сервисный центр москва [url=http://www.dyson-servisnyj-centr-moskva.ru]https://dyson-servisnyj-centr-moskva.ru/[/url]
안녕, 당신의 웹사이트에 브라우저 호환성 문제가 있는 것 같아요.
Chrome에서는 잘 보이지만, Internet Explorer에서 열 때 일부 겹침이 있습니다.
그냥 미리 알려드리고 싶었어요!
그 외에는 훌륭한 블로그입니다!
These are actually great ideas in regarding blogging.
You have touched some fastidious factors here.
Any way keep up wrinting.
В таблице приведены основные компоненты капельницы и их действие:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde/
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя в домашних условиях[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov-ceny[/url]
Great information. Lucky me I found your website by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve bookmarked it for later!
все это только на доверии, белый кристаллический так же может быть 4фа…. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Блин че мне нравится в чемикале то как работает человек….всегда ясно все говорит и поЯсняет….Выходные просто, завтра проверь
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Не всегда человек способен самостоятельно прекратить приём алкоголя и восстановиться. Есть состояния, требующие немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Обратиться за помощью необходимо, если наблюдаются следующие признаки:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Good day! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up for the
excellent info you have here on this post. I will be returning to your web site
for more soon.
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь в тольятти[/url]
Great article, very helpful.
This post breaks down
the basics of online sports streaming
in a
straightforward format.
A lot of users are curious
how to access live sports streams
and
the information here is quite practical.
Thanks for sharing.
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/
В Красноярске клиника «КрасЗдрав Профи» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью. При этом формат анонимности сохраняется на каждом этапе — от звонка до выписки. Для пациентов, которым трудно приехать, возможен выезд нарколога на дом. Это удобно при похмельных и абстинентных состояниях, когда транспортировка нежелательна. Конфиденциальный выезд без маркировки транспорта и униформы позволяет начать лечение, не привлекая внимания окружающих. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинских стандартов, включая регидратацию, стабилизацию и поддержку дыхания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
ts ровный беру уже давно унего но 35ф реально слабый эфект трафы сделал 10к1 неочом в итоги из 50г сделал 300гр основ нармально вышло по качиству пока ещё ещё некто не рыгал( но вопщем неплохо цена соответствует качиству 400р за грам норм Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Фарту в делах парни !:hello:Вызвал такси;)
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Процесс терапии в наркологической клинике в Воронеже организован поэтапно. Это позволяет обеспечить системность и постепенность восстановления, снизить риски осложнений и повысить устойчивость результата.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в воронеже[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток. Это позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам, которые находятся в тяжёлом состоянии или не могут самостоятельно приехать в стационар. Медицинская бригада прибывает в течение 40–60 минут, не используя специализированный транспорт и форму, чтобы сохранить анонимность. Врач проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает давление, частоту дыхания, уровень сознания и насыщение кислородом, после чего назначает детоксикационную капельницу с контролем дозировки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Благодаря последовательной работе врачей и постоянному наблюдению лечение проходит безопасно и эффективно, а пациент получает необходимую поддержку на всех этапах терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
пробы есть? https://mossygatherings.info Ну мы стараемсяпомогите обьясните как написать сапорту
Superb site you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really love to be a part of community where I can get suggestions from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Kudos!
А Всем Добра и Здоровья Близким))) Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Да магаз от души тут работает давно и чётко ,было время работал с ним по опту !!! С новым годом всех!Хотя возможно привык к бычей реги, а ваша дает эффект похожий канабб
тикток мод скачать андроид бесплатно последнюю Тренды Модификаций TikTok в 2025: Что Нас Ждет В 2025 году мы можем ожидать еще больше инноваций в мире модов TikTok. Улучшенные алгоритмы рекомендаций, расширенные инструменты редактирования видео, интеграция с другими социальными сетями – все это может стать реальностью. Разработчики, вероятно, сосредоточатся на создании более стабильных и безопасных версий, а также на добавлении функций, недоступных в официальном приложении.
I was able to find good advice from your blog posts.
http://shapok.com.ua/fary-avtomobilya-2026-povne-vidnovlennya.html
скачать тикток мод последняя версия 2025 Эпоха Кастомизированного Контента: TikTok Моды и Scarlet на iPhone в 2025 Году Социальные сети, в частности TikTok, продолжают доминировать в цифровом пространстве, предоставляя платформу для самовыражения и креативности. Однако, для пользователей, стремящихся к большему контролю и персонализации, существуют так называемые моды TikTok, а также инструменты для установки сторонних приложений, такие как Scarlet. Эти решения открывают двери к расширенным функциям и возможностям, недоступным в стандартной версии приложения.
https blsp at
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно новосибирск[/url]
«ТверьМед» — частная лицензированная клиника, специализирующаяся на наркологической помощи любой степени сложности. Здесь работают неравнодушные врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты и психологи с многолетним стажем. Медицинская команда настроена на оперативную диагностику и проведение первичных мероприятий в течение первого часа после обращения. Упор сделан на доступность: клиника открыта 24/7, приём возможен как на территории медучреждения, так и на выезде — дома, в офисе, гостинице, санатории или любом удобном месте.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в твери[/url]
При получении заявки по телефону или через сайт администратор передаёт её врачу-дежуранту, который немедленно выезжает по указанному адресу. По прибытии специалист проводит первичный осмотр: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, температура, сатурация. Затем осуществляется экспресс-оценка состояния ЦНС и метаболизма. При необходимости берутся анализы, подключается инфузионная система, проводятся противотревожные и детоксикационные мероприятия. Врач остаётся с пациентом до полной стабилизации состояния, а при тяжёлых симптомах организует транспортировку в стационар.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/narkolog-v-tveri-czeny/
Действие и назначение
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novosibirsk/
По сути он эйфо, но ничего, кроме расширенных зрачков, учащенного сердцебиения и потливости, я не почувствовал… А колличество принятого было просто смешным: 550 мг. в первый день теста и 750 мг. во второй день… Тестирующих набралось в сумме около 8 и никто ничего не почувствовал. https://ballerina-productions.com на вкус – сода.Страшно , но хочется и потом сам не попробуеш не узнаеш )
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в ижевске[/url]
sonabet.pro
sona bet app login
I was suggested this web site by way of my cousin. I’m not sure whether or not this post is written by means of him as no one else recognise such designated about my trouble. You’re amazing! Thank you!
версии тик ток мода айфон Где Скачать и Как Установить Мод TikTok? Найти и скачать мод TikTok можно на различных онлайн-платформах, форумах и Telegram-каналах, посвященных модификациям приложений. Важно помнить, что установка модов может быть связана с рисками безопасности, поэтому рекомендуется загружать файлы только из проверенных источников и использовать антивирусное программное обеспечение. Процесс установки обычно включает удаление официальной версии TikTok и установку APK-файла мода.
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника саратов[/url]
Детоксикация является важнейшим этапом лечения. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» применяются проверенные схемы инфузионной терапии, помогающие восстановить функции организма после интоксикации. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и выраженности симптомов. Ниже приведена таблица с типами капельниц, применяемых в клинике.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
упаковка – неплохо, но не идеально. Особенно глупо, когда в описании отправления пишут “Косметика”, а там, бл*ть, пачка сигарет. Оочень странно на меня смотрели в офисе спсра, знаете ли. 4/5 Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Спасибо за продосатавленные веществаКогда в воде болтаешь, пиздос как немеет язык, сушняк дикий. Горько, но Бля никакого эйфора, ни космоса, ни-че-го….
Gelecekte, indirme koşullarının daha fazla tercih edileceği ve kullanıcıların bu türdeki araçlara daha fazla
ihtiyaç duyacağı öngörülmektedir.
Great site. Lots of usefuⅼ information here. I am sendіng it to a few buddies
ans ɑlso sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks for yopuг sweat!
my ԝebρage :: Syracuse Laptop repair
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в твери[/url]
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/narkolog-tver-anonimno
После стабилизации состояния пациенту предлагается пройти этап реабилитации. В клинике он может занять от 30 до 180 дней, в зависимости от тяжести зависимости, стажа употребления и социальной ситуации. Реабилитационный блок построен по принципам когнитивной реструктуризации: меняются привычные модели мышления, формируются новые способы реагирования на стресс, прорабатываются неразрешённые психологические конфликты. Используются методы психодрамы, арт-терапии, телесно-ориентированной терапии и даже нейропсихологической гимнастики.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании в стационаре самара[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
скачать бесплатно тикток мод TikTok Моды: Настраиваемый Опыт за Пределами Стандарта TikTok моды предлагают пользователям возможность настроить приложение под свои личные нужды. Они зачастую включают функции, позволяющие изменять интерфейс, добавлять новые фильтры и эффекты, а также получать доступ к контенту, недоступному в их регионе. Это создает более персонализированный и интересный опыт использования TikTok.
blsp at check
Лечение проводится в комфортных домашних условиях, что снижает стресс и помогает быстрее восстановиться.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
Для оказания полноценной помощи вне стен клиники специалисты «ТверьМед» используют портативные устройства: инфузоматы, ЭКГ-мониторы, глюкометры, пульсоксиметры, небулайзеры и наборы медикаментов. Все врачи обучены работе в полевых условиях и готовы к экстренным ситуациям. Отдельное внимание уделяется стерильности и безопасности: используются одноразовые расходники, врач носит маску, перчатки и защитный халат. При необходимости на выезд направляется параллельно медсестра или ассистент с расширенным функционалом.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь тверь[/url]
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
в 12 году брали реагент здесь по курьерке, ровно все было, сейчас оптом берем, но жаль продавец не работает без гаранта, это в наше время спасает от кидков, или различных форс мажоров. https://balancingactbookkeeping.biz Отличный,ровный МАГАЗ!вчера брала СК качество отменное, буду брать еще!
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя в перми[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена саратов[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru
Терапия в клинике строится по индивидуальному протоколу. Каждому пациенту подбираются процедуры с учётом возраста, длительности болезни, сопутствующих нарушений и психоэмоционального состояния. Лечение проходит поэтапно, что позволяет исключить осложнения и достичь стабильной ремиссии. Ниже представлена таблица с ключевыми этапами терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ижевске[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]центр анонимного лечения наркомании в самаре[/url]
После стабилизации состояния пациенту предлагается пройти этап реабилитации. В клинике он может занять от 30 до 180 дней, в зависимости от тяжести зависимости, стажа употребления и социальной ситуации. Реабилитационный блок построен по принципам когнитивной реструктуризации: меняются привычные модели мышления, формируются новые способы реагирования на стресс, прорабатываются неразрешённые психологические конфликты. Используются методы психодрамы, арт-терапии, телесно-ориентированной терапии и даже нейропсихологической гимнастики.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании цена в самаре[/url]
незнаю.сколько раз зака зывал , всегда приходило качество , был один момент когда был ркс 4. он был 15 минутный слабый. Но это сам реактив был такой. Он использовался как урб для добавок к другим. А так то что присылали всегда всё ровно. кач и кол.. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Понимающий меня поймёт.у Вас очень серьезные проблемы.
Все обращения в клинику «РеабКузбасс» обрабатываются в рамках строгой анонимности. Пациент может проходить лечение без паспорта, под вымышленным именем, если это важно для психологического комфорта. Ни одна медицинская процедура или консультация не фиксируется в государственных базах без согласия. Персонал подписывает документы о неразглашении. Также предлагается анонимная оплата и оформление без упоминания диагноза в документах. При необходимости пациент может получить справку с нейтральной формулировкой для работы или страховой компании.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании кодирование в новокузнецке[/url]
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru
Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске от «ТрезвоМед» при запое, интоксикации или кодировании – анонимно и удобно. Осмотр, детоксикация капельницей, индивидуальный план лечения – все это на дому! «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная помощь, анонимность и безопасность при отказе от алкоголя. Не можете бросить пить самостоятельно? Нужна помощь нарколога! Васильев: «Своевременная помощь при интоксикации – залог успешного выздоровления».
Разобраться лучше – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-irkutsk
Главной задачей специалистов становится купирование абстинентного синдрома и снижение интоксикации. Это требует применения медикаментов и постоянного наблюдения за состоянием пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в перми[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена пермь[/url]
С момента начала лечения пациент получает доступ к круглосуточной линии поддержки. Врачи, психологи и координаторы готовы ответить на вопросы, помочь с корректировкой схемы лечения, поддержать в ситуации риска срыва. Эта функция особенно востребована в первые недели после выписки, когда человек сталкивается с триггерами в привычной среде и нуждается в дополнительной защите. Связь может осуществляться по телефону, через защищённый мессенджер или с помощью мобильного приложения клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение больных наркоманией самара[/url]
Wonderful blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you recommend starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally confused .. Any recommendations? Cheers!
Не можете добраться до клиники? Нарколог на дом в Иркутске – оптимальный выход при запое. Нарколог на дом – это удобно: обследование, лечение и детоксикация в комфортных условиях. Выезд нарколога в любое время, анонимность и безопасность – это «ТрезвоМед». Без медицинской помощи не обойтись? Звоните наркологу! Чем быстрее помощь, тем лучше прогноз, – нарколог Игорь Васильев.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в перми[/url]
Послезавтра запрет в силу вступает Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Получил посылку уже через 3 дня после заказа. МН-001 хороший, только маленькие кристаллы на дне не растворились. А так доволенНичего не пойму.. Я уже третий день пытаюсь договориться и всё бесполезно. Прошу номер кошелька куда перевести, говорит щас и пропадает на пол дня, и так постоянно. Может на мелкий заказ как у меня им пох. Заказываю 10 гр.
Вывод из запоя в Омске проводится в условиях клиники с применением современных методов детоксикации и круглосуточного медицинского наблюдения. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает серьезную интоксикацию организма, нарушает работу внутренних органов и психоэмоциональное состояние. Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет избежать осложнений и восстановить здоровье пациента безопасным образом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
I’m shocked that this company is still in business. Zero promises, zero results, but they took the money right away. They answer any questions like robots, but no one actually helps. It feels like I’ve fallen for a common [url=https://search-intelligence.co.uk/]SCAM[/url] that just takes money and feeds you empty promises. People, stay away — it’s a complete disappointment!
Избавление от наркотической зависимости требует последовательной, профессиональной и комплексной помощи. В отличие от краткосрочной детоксикации, полноценное лечение наркомании в Мурманске включает медицинскую стабилизацию, психотерапевтическую коррекцию и этапы социальной адаптации. По данным Минздрава РФ, устойчивые результаты достигаются лишь в тех случаях, когда терапия проводится под наблюдением специалистов, использующих современные доказательные методы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/]центр лечения наркомании мурманск[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]азартные игры[/url]
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-czena/
[url=https://www.digitalocean.com/community/users/39ed622658cd4bf49e75ade2b37e35]codigo promocional 1xbet mexico[/url]
Таблица: Основные признаки надёжного центра лечения наркомании
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании[/url]
При получении заявки по телефону или через сайт администратор передаёт её врачу-дежуранту, который немедленно выезжает по указанному адресу. По прибытии специалист проводит первичный осмотр: измеряются артериальное давление, пульс, температура, сатурация. Затем осуществляется экспресс-оценка состояния ЦНС и метаболизма. При необходимости берутся анализы, подключается инфузионная система, проводятся противотревожные и детоксикационные мероприятия. Врач остаётся с пациентом до полной стабилизации состояния, а при тяжёлых симптомах организует транспортировку в стационар.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь тверь[/url]
Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар https://extragram.ru Вы очень давно работаете,стабильная деятельность.а есть почта у данного магаза?
Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске от «ТрезвоМед» при запое, интоксикации или кодировании – анонимно и удобно. Осмотр, детоксикация капельницей, индивидуальный план лечения – все это на дому! «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная помощь, анонимность и безопасность при отказе от алкоголя. Не можете бросить пить самостоятельно? Нужна помощь нарколога! Васильев: «Своевременная помощь при интоксикации – залог успешного выздоровления».
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]вызов нарколога ценаиркутск[/url]
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в саратове[/url]
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/narkolog-saratov-na-dom/https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/
Hello would you mind letting me know which hosting company you’re working with? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot quicker then most. Can you recommend a good web hosting provider at a reasonable price? Many thanks, I appreciate it!
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь тверь[/url]
Хотя возможно привык к бычей реги, а ваша дает эффект похожий канабб https://extragram.ru Все работает, каждый получает ответ оперативно!Я брал норм не один раз,но в последнее время было пару недовесов,а 35 прислали какого то качества слабого,25ый был куда лучше,после этого перестал заказывать.
С момента начала лечения пациент получает доступ к круглосуточной линии поддержки. Врачи, психологи и координаторы готовы ответить на вопросы, помочь с корректировкой схемы лечения, поддержать в ситуации риска срыва. Эта функция особенно востребована в первые недели после выписки, когда человек сталкивается с триггерами в привычной среде и нуждается в дополнительной защите. Связь может осуществляться по телефону, через защищённый мессенджер или с помощью мобильного приложения клиники.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-narkotikov-samara/
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy
Особую роль на первом этапе играет диагностика: важно выявить не только тип наркотика, но и наличие сопутствующих расстройств, стадию зависимости, мотивационное состояние пациента. От этого зависит, будет ли выбрана амбулаторная или стационарная форма лечения, какие методы будут применяться.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/]lechenie narkomanii i alkogolizma murmansk[/url]
Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске от «ТрезвоМед» при запое, интоксикации или кодировании – анонимно и удобно. Осмотр, детоксикация капельницей, индивидуальный план лечения – все это на дому! «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная помощь, анонимность и безопасность при отказе от алкоголя. Не можете бросить пить самостоятельно? Нужна помощь нарколога! Васильев: «Своевременная помощь при интоксикации – залог успешного выздоровления».
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-irkutsk
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом омск[/url]
Одной из ключевых инноваций «СамарМед» является внедрение телемедицинского консультирования. Пациенты, проживающие за пределами Самары или находящиеся в стадии подготовки к лечению, могут получить полноценную консультацию врача через защищённые каналы связи. Также возможна онлайн-связь с психологом, куратором или участником реабилитационной команды. Все сеансы проходят в конфиденциальном формате, с возможностью записи и анализа динамики состояния в дальнейшем. Это особенно важно для тех, кто испытывает тревогу при личном визите или не готов к очной встрече на первых этапах.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/narkologicheskij-dispanser-g-samara/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в стационаре в перми[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Медикаментозная терапия — важнейший этап стабилизации состояния. Врачи «СамарМед» применяют препараты с доказанной эффективностью: детоксикационные растворы, нейрометаболики, седативные и анксиолитические средства, ноотропы, гепатопротекторы, а при необходимости — антипсихотики. Подбор схемы проводится индивидуально, с учётом переносимости, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, возраста и стадии зависимости. Все препараты применяются строго по международным протоколам и под контролем врачей круглосуточно.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Метод лечения
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи новокузнецк[/url]
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена пермь[/url]
всем советую магазин тс роботает ровно, знает толк в бизе, всегда беру у них и все ровно и надежно, товар выший класс ,куриер вообще красавчик все делает четко и надежно , магазину и курьеру оценка 10из 10 балов все ровно, ДОСТАВКА БОМБА ХОТЬ В АРТИКУ ДОСТАВЯТ Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Заказ получил, спасибо за ракетку 😀 Это был мой первый опыт заказа легала в интернете, и он был положительным! Спасибо магазину chemical-mix.com за это!Кто-нить брал тут 307 ?? просто ппц какой-то. уже 2 гр выкинул. Делал и 1к10 и чистым курил, ваще НОЛЬ. Как такое можт быть ?
Терапия в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить безопасность и прозрачность процесса. Пациент постепенно проходит все стадии восстановления организма и психики.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Hi, I do believe your website may be having browser
compatibility problems. When I look at your web site
in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in IE, it’s got some overlapping issues.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Besides
that, fantastic blog!
Very nice write-up. I definitely love this
site. Keep it up! https://cryptoboss885.top/
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Медицинская помощь направлена не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на стабилизацию работы организма в целом. Врачи стремятся к тому, чтобы пациент получил не временное облегчение, а фундамент для дальнейшей реабилитации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-czena/
Особую роль на первом этапе играет диагностика: важно выявить не только тип наркотика, но и наличие сопутствующих расстройств, стадию зависимости, мотивационное состояние пациента. От этого зависит, будет ли выбрана амбулаторная или стационарная форма лечения, какие методы будут применяться.
Углубиться в тему – http://lechenie-narkomanii-murmansk0.ru/
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy/
На данном этапе специалист уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой вид алкоголя употребляется и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный анализ информации позволяет оперативно определить степень интоксикации и выбрать оптимальные методы терапии для быстрого и безопасного вывода из запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula00.ru/]вывод из запоя тула[/url]
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-marmansk
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом саратов[/url]
Эффективность лечения во многом зависит от квалификации врачей, участвующих в процессе. В наркологической клинике должны работать не только врачи-наркологи, но и психиатры, клинические психологи, специалисты по аддиктивному поведению, а также координаторы по социальной адаптации. Слаженное взаимодействие этих специалистов — залог того, что лечение будет не только медицински обоснованным, но и глубоко проработанным в психологическом плане.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ярославль.[/url]
Магазу мир и процветания)) Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? пот теории 2мл растворителя на 1г основы,т.е на 150г 300мл.спасибо стараемся
Все обращения в клинику «РеабКузбасс» обрабатываются в рамках строгой анонимности. Пациент может проходить лечение без паспорта, под вымышленным именем, если это важно для психологического комфорта. Ни одна медицинская процедура или консультация не фиксируется в государственных базах без согласия. Персонал подписывает документы о неразглашении. Также предлагается анонимная оплата и оформление без упоминания диагноза в документах. При необходимости пациент может получить справку с нейтральной формулировкой для работы или страховой компании.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическое лечение наркомания новокузнецк[/url]
Usually I don’t read post on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very compelled me to check out and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thank you, very great article.
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно приезжает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач собирает краткий анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели — пульс, артериальное давление, температуру — и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения, позволяющего подобрать наиболее эффективные методы детоксикации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula00.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре тула[/url]
Современная наркологическая помощь требует не только эффективных методик лечения, но и гибкости в организации терапевтического процесса. В условиях динамичного ритма жизни пациенты всё чаще ищут решение, которое позволяет получать профессиональную медицинскую поддержку без необходимости длительной госпитализации или ожидания очередей. Именно такой подход реализуется в наркологической клинике «СамарМед». Здесь сочетаются передовые методы лечения зависимостей с возможностями телемедицины, а сам процесс терапии строится на основе мультидисциплинарного подхода, где каждый пациент получает поддержку не одного врача, а целой команды узкопрофильных специалистов.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/narkologi-samary
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в перми[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены омск[/url]
Один из топовых продавцов на всем РЦ:) Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Цены тут взвинчены до жопы не знаю кто тут умудряется брать, летом как то брал здесь не помню че но было фуфло конченное половина не растворилась хоть че делай хоть грей хоть танцуй ни че не помогло. Один плюс присылают быстро но нафиг такая быстротавсе как обычно работает
Действие и назначение
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-novosibirsk
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании диспансер в самаре[/url]
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзное заболевание, затрагивающее как физическое, так и психологическое состояние человека. При отсутствии своевременной наркологической помощи в клинике возможно ухудшение здоровья, развитие тяжелых осложнений и социальная деградация пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь в новокузнецке[/url]
С момента начала лечения пациент получает доступ к круглосуточной линии поддержки. Врачи, психологи и координаторы готовы ответить на вопросы, помочь с корректировкой схемы лечения, поддержать в ситуации риска срыва. Эта функция особенно востребована в первые недели после выписки, когда человек сталкивается с триггерами в привычной среде и нуждается в дополнительной защите. Связь может осуществляться по телефону, через защищённый мессенджер или с помощью мобильного приложения клиники.
Разобраться лучше – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-narkotikov-samara/
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Прежде чем принимать решение, важно изучить сайт клиники. В надёжных учреждениях размещена полная информация о врачах, их образовании и опыте работы. Кроме того, пациентам предлагается пройти предварительную консультацию — чаще всего она проводится анонимно и включает первичную диагностику. Это позволяет оценить профессионализм команды ещё до начала терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]наркологическая клиника ярославская область[/url]
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Всем привет! Хороший магазин. Удачи и развития в дальнейшем! Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Не сыы! Я во вторник постучался в скайп, сразу же оплатил. На след день тобиш в среду получил трек, а сегодня посыль уже приехала! Скоро отпишусь за кач-во фа. Не моросите, контора ровнаяЧто особо порадовало – скидывали несуществующий трек еще задолго до отправки, который, конечно, не бился или показывал какую-то х*иту.
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма в перми[/url]
«ТверьМед» — частная лицензированная клиника, специализирующаяся на наркологической помощи любой степени сложности. Здесь работают неравнодушные врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты и психологи с многолетним стажем. Медицинская команда настроена на оперативную диагностику и проведение первичных мероприятий в течение первого часа после обращения. Упор сделан на доступность: клиника открыта 24/7, приём возможен как на территории медучреждения, так и на выезде — дома, в офисе, гостинице, санатории или любом удобном месте.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/narkolog-v-tveri-czeny
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-omsk/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru
I was excited to find this web site. I want to to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every part of it and I have you book-marked to look at new things in your site.
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/
1-й раз все было почти супер только менагер немного напутал ( но потом все доотправили ) Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? на icq – в четверг обещал трек, в пятницу обещал трек, пропал…в скаипе не отвечают!!!!
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Нужна срочная помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске! Квалифицированная помощь нарколога на дому: диагностика, капельница, стабилизация состояния. Круглосуточный выезд нарколога, анонимность и снижение рисков – с «ТрезвоМед». Самостоятельный отказ невозможен? Необходима наркологическая помощь. Васильев: «Не затягивайте с помощью при алкогольном отравлении!».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru[/url]
Первый раз брал у этого магазина,сразу же что то не то,если всё будет Ок,буду брать дальше,в принцыпе со всеми бывает( https://in-timeproduction.ru А менеджер не ответственный а облом. Я бы пошел навстречу клиенту, получил бы от него этот стольник себе на мобилку и доплатил бы на Альфу его сам, раз у потенциального клиента проблемы с переводами. А он обломался.Огромное спасибо данному магазину, успехов вработе и процветания!!!?
Отличный пост! Мне очень понравилось читать. Продолжайте в том же духе!
If you are going for best contents like myself,
just pay a visit this web site all the time for the reason that
it presents quality contents, thanks
blsp at клады рядом
I every time used to read paragraph in news papers but now as I am a user of internet thus from now I am using net for content, thanks to web.
онлайн работа дома для мам Удаленная работа ВКонтакте предоставляет возможности для тех, кто активно использует эту социальную сеть. Здесь можно найти вакансии в сфере SMM, контент-менеджмента, дизайна и технической поддержки. Многие компании ищут специалистов для ведения групп, создания контента и общения с клиентами непосредственно в ВК.
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор качественных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы обеспечиваем своевременную реализацию вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Дружелюбная помощь – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы а также предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
Наша продукция:
Фольга циркониевая Цирколой-3 Фольга циркониевая Цирколой-3 – это надежный выбор для тех, кто ценит качество и долговечность. Эта специализированная фольга прекрасно подходит для применения в различных отраслях, включая медицинскую и электротехническую. Благодаря своей высокой температурной и коррозионной стойкости, Фольга циркониевая Цирколой-3 гарантирует отличные результаты в работе. Купите Фольга циркониевая Цирколой-3, и вы получите продукт, который прослужит вам долго и надежно. Не упустите возможность улучшить свои проекты с помощью этого уникального материала!
удаленная работа с телефона Фриланс – это свобода выбора, но и большая ответственность. Фрилансер самостоятельно ищет заказы, устанавливает цены и несет ответственность за качество своей работы. Успех во фрилансе зависит от профессионализма, коммуникабельности и умения находить общий язык с клиентами.
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно новосибирск[/url]
Thanks a lot! Excellent stuff!
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novosibirsk
Hey, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
https://e-art.com.ua/linzy-led-dlya-avto-tekhnichnyi-hid-po.html
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в туле[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
Что включено на практике
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя новосибирская область[/url]
Being well-dressed is essential for creating a positive impression.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
A neat look can improve self-esteem.
In everyday life, appearance often affects social interactions.
https://rentry.co/eoohvb3s
A well-planned wardrobe make social situations more comfortable.
It is important to consider one’s own comfort as well as the occasion.
Current trends give people the chance to discover new ideas.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly helps people feel confident.
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
sonabet app login download
как найти удаленную работу Удаленная работа – это современный формат занятости, стирающий географические границы и предлагающий небывалую гибкость. Она позволяет адаптировать рабочий график под личные нужды, освобождает от утомительных поездок и открывает двери к сотрудничеству с компаниями по всему миру. Это эволюция трудовых отношений, где ценится результат, а не присутствие в офисе.
sonabet.pro
Снижается тремор и тошнота, выравниваются вегетативные реакции, возвращается способность спокойно уснуть. Вместо «качелей» настроения и попыток самолечения появляется ощущение контроля: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём дальше.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-vyzov-na-dom[/url]
Когда уместен
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркология[/url]
работа в южной корее для русских Работа хостес в Корее для девушек – это шанс увидеть страну, познакомиться с новыми людьми и заработать деньги. Однако, это также ответственность и необходимость соблюдать правила, быть внимательной и осторожной.
I am truly happy to glance at this weblog posts which carries tons of valuable facts, thanks for providing these information.
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Để mở rộng cộng đồng hội viên, 888slot còn có chính sách khuyến mãi dành cho những người giới thiệu bạn bè. Khi bạn mời thành công một người mới tham gia và người đó thực hiện nạp tiền, bạn sẽ nhận được phần thưởng bằng tiền mặt hoặc tiền thưởng để cá cược. Điều này giúp khách hàng tham gia vừa có thể tận hưởng những trận đấu hấp dẫn, vừa có thêm cơ hội gia tăng thu nhập một cách dễ dàng. TONY01-14
Bạn có thể chơi lô đánh đề từ 1.000+ kỳ quay thưởng đang diễn ra liên tục và hốt tiền cực nhanh chỉ sau 1 giây. download 888slot cung cấp nhiều kiểu cược xổ số khác nhau như: Bao lô, đánh đề, 3D, lô trượt, 4 càng giải Nhất,… đặc biệt là Up/Down, Reverse, Big/Small,… vừa mới “ra lò”. TONY01-14
Когда запой начинает угрожать здоровью, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Туле опытные специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, позволяя начать лечение сразу же в комфортной обстановке. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативную детоксикацию, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы внутренних органов, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих избежать лишнего стресса и сохранить конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в туле[/url]
Действие и назначение
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novosibirsk
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologiya/
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologicheskaya-bolnicza-tolyatti/
Having a sense of style is essential for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
Well-chosen outfits can boost confidence.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://telegra.ph/Burberry-12-25-6
Carefully selected clothing make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider individual taste as well as the context.
Fashion trends give people the chance to experiment with looks.
Overall, dressing stylishly supports a complete personal image.
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Когда запой начинает угрожать здоровью, оперативное вмешательство становится жизненно необходимым. В Туле опытные специалисты оказывают помощь на дому, позволяя начать лечение сразу же в комфортной обстановке. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативную детоксикацию, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы внутренних органов, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих избежать лишнего стресса и сохранить конфиденциальность.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/
удаленная работа вакансии Вакансии удаленной работы – это многообразие вариантов, которые требуют внимательного изучения и анализа. Чтобы найти подходящую вакансию, необходимо четко определить свои навыки, опыт и предпочтения. Важно также обращать внимание на репутацию компании и отзывы сотрудников.
Действие и назначение
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
«Эгида Трезвости» выстраивает лечение вокруг предсказуемости: понятный старт, прозрачные шаги, нейтральная коммуникация и постоянная связь с дежурным врачом. Мы не заставляем объясняться «по кругу» и не перегружаем терминами — достаточно фактов, которые влияют на безопасность и выбор схемы. Уже при первом контакте становится ясно, где лучше начинать (дом, приём, стационар 24/7), что будет сделано в ближайшие часы и как оценим результат к вечеру. Конфиденциальность встроена в регламент: на звонках — нейтральные формулировки, на выездах — неброская экипировка, доступ к медицинской информации — только у задействованной команды. Это снижает фоновую тревогу и позволяет семье сосредоточиться на простых действиях, которые реально помогают держать курс.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/
Снижается тремор и тошнота, выравниваются вегетативные реакции, возвращается способность спокойно уснуть. Вместо «качелей» настроения и попыток самолечения появляется ощущение контроля: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём дальше.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм омск[/url]
Формат
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
В Одинцово доступен гибкий маршрут: выездная бригада 24/7 и стационар. Домашний формат хорош при умеренной симптоматике и сохранённом контакте — он позволяет избежать перевозок и сохранить конфиденциальность. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде, повторной рвоте, выраженной слабости, нестабильном давлении/пульсе, спутанности сознания, судорожной готовности, а также у пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжёлой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек). Мы оцениваем не один признак, а совокупность факторов и динамику, чтобы не «пересидеть» дома там, где нужен приборный мониторинг. В обоих вариантах сохраняется наш принцип: индивидуализация схемы, осторожная седация, прицельная работа со сном, прозрачные объяснения назначений — и всё это с опорой на объективные показатели, а не ощущения «полегчало/ухудшилось».
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
Hi to all, because I am truly eager of reading this blog’s post to be updated regularly. It carries good stuff.
igrice od 3 do 103
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/pomoshh-narkozavisimym-tolyatti/https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
Когда уместен
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
Основу выездного лечения составляют капельницы, которые позволяют быстро ввести препараты в кровоток, минуя желудочно-кишечный тракт. Это обеспечивает моментальное действие и исключает раздражение слизистой. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента. Основные направления инфузионной терапии включают детоксикацию, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и поддержку работы нервной системы. Для усиления эффекта применяются витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для защиты печени.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
работа в сеуле Хостес в Корее – это лицо заведения, будь то караоке-бар, ресторан или ночной клуб. Ее задача – создавать приятную атмосферу, развлекать гостей и поддерживать их хорошее настроение. Это работа, требующая коммуникабельности, обаяния и умения находить общий язык с разными людьми.
It is not my first time to pay a quick visit this website, i am browsing this site dailly and obtain pleasant facts from here daily.
bs2best at не работает
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Нужна срочная помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске! Квалифицированная помощь нарколога на дому: диагностика, капельница, стабилизация состояния. Круглосуточный выезд нарколога, анонимность и снижение рисков – с «ТрезвоМед». Самостоятельный отказ невозможен? Необходима наркологическая помощь. Васильев: «Не затягивайте с помощью при алкогольном отравлении!».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]narkolog na dom [/url]
Что включено на практике
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-so-stacionarom[/url]
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Нужна срочная помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске! Квалифицированная помощь нарколога на дому: диагностика, капельница, стабилизация состояния. Круглосуточный выезд нарколога, анонимность и снижение рисков – с «ТрезвоМед». Самостоятельный отказ невозможен? Необходима наркологическая помощь. Васильев: «Не затягивайте с помощью при алкогольном отравлении!».
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-irkutsk
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk/
http://www.dungdong.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3290270&do=profile
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Туле представляет собой комплекс мер, направленных на экстренную детоксикацию организма при алкогольной интоксикации. При вызове нарколога специалист прибывает в течение короткого времени, проводит первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез и определяет степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, который может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, капельничное введение препаратов и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-tula
На этом этапе специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какие основные симптомы наблюдаются, и если имеются, то какие хронические заболевания могут влиять на течение терапии. Точный анализ этих данных позволяет сформировать персонализированную стратегию лечения, которая будет максимально адаптирована к состоянию пациента и его потребностям.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika novosibirsk[/url]
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]centr lecheniya alkogolizma murmansk[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: длительность эпизода, лекарства и аллергии, сон, аппетит, переносимость нагрузок, возможность обеспечить тишину на месте. На основе этих фактов врач предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под наблюдением 24/7. На месте мы сразу исключаем «красные флажки», фиксируем давление/пульс/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях выполняем ЭКГ и запускаем детокс. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, лёгкое питание, перечень нормальных ощущений и момент, когда нужно связаться внепланово. Если домашнего формата становится мало, переводим в стационар без пауз — все назначения и наблюдения «переезжают» вместе с пациентом.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это всегда баланс между скоростью и безопасностью. Дома трудно заметить скрытые ухудшения, особенно ночью: давление и пульс «гуляют», нарастает обезвоживание, сон рваный и тревожный. В «Трезвом Контуре» этот хаос замещается управляемостью: перед выездом дежурный врач собирает ключевые данные (длительность эпизода, лекарства, аллергии, сопутствующие болезни), на месте проводится экспресс-диагностика (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания), затем запускается схема терапевтической поддержки. Мы постоянно «подстраиваем» инфузии по реакции организма, а не по шаблонной карте: где-то важнее регидратация, где-то — коррекция электролитов, где-то — бережная седация для ночи. Для семьи это значит одно: меньше догадок, больше ясности. Если по картине риски высоки, мы аргументированно предлагаем стационар в Одинцово — и организуем транспортировку без пауз, потому что цена задержки в такие часы всегда выше.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-ehlektrostali/
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Когда уместен
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/narkologiya-goroda-tolyatti
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза детоксикации, во время которой современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом. Этот этап помогает быстро снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальные обменные процессы и нормализовать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника тула[/url]
Что включено на практике
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say excellent blog!
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
В клинике «СамарМед» доступно несколько форм лечения: стационарная программа, дневной стационар, амбулаторное наблюдение и гибридные схемы. Пациенты могут выбрать комфортный вариант в зависимости от степени зависимости, текущего состояния и занятости. Внутри стационара предусмотрены как стандартные палаты, так и индивидуальные блоки повышенной комфортности с возможностью проживания совместно с сопровождающим лицом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «АнтиАлко» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По прибытии врач проводит комплексную диагностику: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и собирает анамнез, чтобы оценить степень интоксикации. На основе полученных данных формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает:
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novosibirsk/
Если требуется срочное кодирование или детоксикация, вызов нарколога на дом – лучшее решение в Иркутске. Профессиональный нарколог приедет, оценит состояние, проведет детоксикацию на дому. «ТрезвоМед»: анонимный выезд нарколога 24/7, помощь при отказе от алкоголя. Тяжело бросить пить в одиночку? Обратитесь к наркологу! Главное – быстро оказать помощь при интоксикации, – нарколог Васильев.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом иркутск[/url]
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
blsp at клады рядом
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в самаре[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи тольятти[/url]
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-odincovo
Формат
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/yb3uvy6a
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в волгограде[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena
Это способствует повышению эффективности работы и снижению эксплуатационных затрат.
лизинг сельхозтехники в рф [url=kommercheskij-transport-v-lizing04.ru/lizing-selskohozyajstvennoj-tehniki]https://kommercheskij-transport-v-lizing04.ru/lizing-selskohozyajstvennoj-tehniki/[/url]
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-marmansk/
Формат
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – https://arma-rehab.ru/
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске от «ТрезвоМед» при запое, интоксикации или кодировании – анонимно и удобно. Осмотр, детоксикация капельницей, индивидуальный план лечения – все это на дому! «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная помощь, анонимность и безопасность при отказе от алкоголя. Не можете бросить пить самостоятельно? Нужна помощь нарколога! Васильев: «Своевременная помощь при интоксикации – залог успешного выздоровления».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]нарколог на дом иркутск[/url]
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-yaroslavl
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Основу выездного лечения составляют капельницы, которые позволяют быстро ввести препараты в кровоток, минуя желудочно-кишечный тракт. Это обеспечивает моментальное действие и исключает раздражение слизистой. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента. Основные направления инфузионной терапии включают детоксикацию, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и поддержку работы нервной системы. Для усиления эффекта применяются витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для защиты печени.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма в мурманске[/url]
Оперативный выезд специалиста позволяет начать терапию без задержек, что особенно важно при тяжелой алкогольной интоксикации. Благодаря помощи на дому, пациент избегает длительного ожидания в очередях и стрессовых поездок в стационар, что способствует сохранению психологического комфорта и анонимности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-tula/
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр самара[/url]
Приобретение официального диплома через надежную фирму дарит множество преимуществ. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании: [url=http://msk.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1374]msk.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1374[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Best wishes! Where are your contact details though?
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-odincovo/
sonabet.pro
Цель
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru
Чтобы легче сопоставить риски и плотность наблюдения, ниже даём живой ориентир. Это не заменяет осмотр, но помогает всей семье понимать логику врача до приезда.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-domodedovo
Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения детального осмотра. На этом этапе специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает анамнез и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации, что является основой для составления персонального плана лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
После поступления вызова наш нарколог выезжает к пациенту в кратчайшие сроки, прибывая по адресу в пределах 30–60 минут. Специалист начинает процедуру с подробного осмотра и диагностики, измеряя ключевые показатели организма: артериальное давление, частоту пульса, насыщенность кислородом и собирая подробный анамнез.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно новосибирск[/url]
You have made some decent points there. I checked on the internet for more information about the issue
and found most people will go along with your views on this website.
При появлении таких симптомов важно не откладывать вызов врача. Самолечение, особенно с использованием неизвестных препаратов, может привести к тяжёлым последствиям, включая судороги и инсульт. Врачи клиники «ВолгаМед Резолюция» приезжают на дом с необходимыми средствами для оказания экстренной помощи и стабилизации состояния уже на месте.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu tula[/url]
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар самара[/url]
blsp at сиськи
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]платная наркологическая скорая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация и запой могут стремительно ухудшить состояние здоровья, став угрозой жизни, поэтому оперативное вмешательство имеет первостепенное значение. В Туле квалифицированные наркологи предоставляют круглосуточную помощь на дому, что позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и в комфортных условиях. Такой формат терапии гарантирует индивидуальный подход, всестороннюю поддержку и полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для пациентов, стремящихся восстановить своё здоровье без лишних стрессовых ситуаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена тула[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это всегда баланс между скоростью и безопасностью. Дома трудно заметить скрытые ухудшения, особенно ночью: давление и пульс «гуляют», нарастает обезвоживание, сон рваный и тревожный. В «Трезвом Контуре» этот хаос замещается управляемостью: перед выездом дежурный врач собирает ключевые данные (длительность эпизода, лекарства, аллергии, сопутствующие болезни), на месте проводится экспресс-диагностика (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания), затем запускается схема терапевтической поддержки. Мы постоянно «подстраиваем» инфузии по реакции организма, а не по шаблонной карте: где-то важнее регидратация, где-то — коррекция электролитов, где-то — бережная седация для ночи. Для семьи это значит одно: меньше догадок, больше ясности. Если по картине риски высоки, мы аргументированно предлагаем стационар в Одинцово — и организуем транспортировку без пауз, потому что цена задержки в такие часы всегда выше.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]skoraya-pomoshch-vyvoda-iz-zapoya[/url]
Запуск помощи — это не «одна капельница», а последовательность осмысленных шагов, каждый из которых приближает к устойчивому сну и ровным витальным показателям. Сначала врач уточняет длительность эпизода, переносимость лекарств, сон, аппетит, хронические диагнозы, наличие помощника дома. Затем следует осмотр: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, ЭКГ при показаниях. Стартовая терапия закрывает дефицит жидкости и солей, защищает печень и ЖКТ, по необходимости подключается мягкая противотревожная поддержка и кислород. Параллельно проговаривается «карта суток»: как отдыхать, что пить и в каком объёме, какие продукты не перегрузят желудок, в какой момент выходить на внеплановую связь. Динамика отслеживается без суеты, а корректировки делаются точечно — по реакции организма, а не «на всякий случай».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Действие и назначение
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно новосибирск[/url]
Что включено на практике
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника анонимная помощь нарколога[/url]
Инфузионные растворы подбираются строго индивидуально, после осмотра врача и анализа показателей пациента. При необходимости курс повторяется с изменением состава раствора для достижения максимального эффекта.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в новокузнецке[/url]
bs2best at не работает
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google,
and found that it is truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels.
I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future.
Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thanks
Когда ночь затягивается, тревога нарастает, а самочувствие «скачет», важны не громкие обещания, а последовательность медицинских действий. «Трезвый Контур» в Одинцово выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от звонка до облегчения прошло минимум времени и ни один шаг не был импровизацией: первичная оценка рисков, персональная инфузионная терапия, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, понятные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не «вырубаем» пациента сильными седативными — дозировки и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые препараты. Цель — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, стабилизировать давление и пульс, вернуть управляемый сон и зафиксировать маршрут на ближайшие 24–72 часа, чтобы утро началось не с нового витка симптомов, а с предсказуемого восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-odincovo[/url]
Сразу после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения детального осмотра. На этом этапе специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает анамнез и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации, что является основой для составления персонального плана лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu tula[/url]
Когда уместен
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника скорая[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Действие и назначение
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-novosibirsk/
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-domodedovo/
Качественный селлер открыть витрину рад приветствовать медиабайеров в своем разделе аккаунтов Facebook. Если вам нужно купить аккаунт Facebook для рекламы, обычно задача не в «одном логине», а в трасте и лимитах: стабильный запуск, зеленые плашки в Ads Manager и прогретые FanPage. Мы оформили практичный чек-лист, чтобы вы без лишних вопросов понимали какой тип аккаунта брать перед покупкой.Коротко: с чего начать: начните с разделы Фарм (King), а для масштабирования — переходите сразу в разделы под залив: BM 250$. Важно: покупка — это только вход. Дальше решает схема залива: как вяжется карта, как вы передаете лички без риска банов, как проходите чеки и как масштабируете адсеты. Особенность нашего сервиса — заключается в наличие приватной вики-энциклопедии FB, в которой написаны практичные рекомендации по разбану кабинетов. Тут вы найдете решения Meta под любые цели: от аккаунтов под привязку и заканчивая ПЗРД сетапами с документами. Заказывая у нас, вы получаете не просто cookie + token, а также оперативную помощь саппорта, понятные условия замены, страховку на вход и максимально адекватные расценки на рынке FB-аккаунтов. Важно: действуйте в рамках закона и всегда в соответствии с правилами Facebook.
sona bet app
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в новокузнецке[/url]
Для тех, кто предпочитает лечение в условиях стационара, предусмотрены комфортные палаты, медицинский контроль 24/7 и возможность консультаций с психотерапевтом. Врачи клиники применяют комплексные методы, направленные не только на снятие симптомов, но и на устранение причин зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь тольятти[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена волгоград[/url]
I savour, lead to I found exactly what I was looking
for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you
man. Have a nice day. Bye
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto
se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba
apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app
apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app
apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de
apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app
de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas
deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app
de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de
apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app
de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar
dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas
android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre
amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas
peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas
y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas
antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas
argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas
argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera
division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas
barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real
madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas
barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona
osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar
online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil
colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs
colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas
campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas
campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga
bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos
online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta
eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas
celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas
chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas
ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo
tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico
real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas
colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas
de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas
mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras
para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap
baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas
con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas
copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey
futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa
del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas
copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de
baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack
en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de
caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos
como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos
en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de
caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de
caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de
caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por
internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas
de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de
f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas
de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de
futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas
de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas
de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas
de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy
seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para
hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos
online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas
de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas
de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de
la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de
la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas
de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema
explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real
madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia
de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas
10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas
deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas
ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas
com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para
ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de
tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas
estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas
deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas
gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas
gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas
deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales
en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas
deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas
mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas
deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas
deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas
deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas
tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas
deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino
online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso
a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero
ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones
venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia
de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas
en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas
nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas
en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea
mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas
en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo
mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas
españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa
francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa
georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol
barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa
favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1
las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas
faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles
para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas
favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas
fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa
rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1
pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas
futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol
pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas
galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de
la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la
liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar
champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada
barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas
gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap
como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap
nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas
hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter
barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos
olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la
liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas
legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas
licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva
pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid
city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid
gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas
madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas
manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas
mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas
mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial
de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas
mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de
colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas
nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas
octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas
online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas
online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para
boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para
hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de
la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos
de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas
partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas
peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs
chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar
dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas
pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el
mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la
champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas
real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real
madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid
valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid
vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras
eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras
hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para
este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras
para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras
para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas
semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla
gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas
sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema
trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis
atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis
de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas
tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway
cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas
ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia
madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas
villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina
vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid
apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis
apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono
de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de
apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas
deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador
de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora
apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas
sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo
de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de
caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de
madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de
mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas
españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas
barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa
de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de
caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca
de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa
de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas
de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa
de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de
apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa
de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de
apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de
apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas
online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de
apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas
perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa
de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas
sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa
de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas
apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas
apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas
casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas
champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de
apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas
con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas
copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de
fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de
apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de
apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas
de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de
apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas
de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas
de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales
en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de
apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas
de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas
mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas
de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas
nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas
de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas
de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online
en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas
de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas
pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
lchat.biz/to/bsbot
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно воронеж[/url]
Когда ночь затягивается, тревога нарастает, а самочувствие «скачет», важны не громкие обещания, а последовательность медицинских действий. «Трезвый Контур» в Одинцово выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от звонка до облегчения прошло минимум времени и ни один шаг не был импровизацией: первичная оценка рисков, персональная инфузионная терапия, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, понятные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не «вырубаем» пациента сильными седативными — дозировки и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые препараты. Цель — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, стабилизировать давление и пульс, вернуть управляемый сон и зафиксировать маршрут на ближайшие 24–72 часа, чтобы утро началось не с нового витка симптомов, а с предсказуемого восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru
Запуск помощи — это не «одна капельница», а последовательность осмысленных шагов, каждый из которых приближает к устойчивому сну и ровным витальным показателям. Сначала врач уточняет длительность эпизода, переносимость лекарств, сон, аппетит, хронические диагнозы, наличие помощника дома. Затем следует осмотр: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, ЭКГ при показаниях. Стартовая терапия закрывает дефицит жидкости и солей, защищает печень и ЖКТ, по необходимости подключается мягкая противотревожная поддержка и кислород. Параллельно проговаривается «карта суток»: как отдыхать, что пить и в каком объёме, какие продукты не перегрузят желудок, в какой момент выходить на внеплановую связь. Динамика отслеживается без суеты, а корректировки делаются точечно — по реакции организма, а не «на всякий случай».
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html
It’s remarkable to go to see this site and reading the views of all colleagues concerning this article, while I am also zealous of getting experience.
Take a look at my website :: cara pilih slot gacor
You can definitely see your enthusiasm in the article you write.
The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe.
At all times follow your heart.
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd/
Основу выездного лечения составляют капельницы, которые позволяют быстро ввести препараты в кровоток, минуя желудочно-кишечный тракт. Это обеспечивает моментальное действие и исключает раздражение слизистой. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента. Основные направления инфузионной терапии включают детоксикацию, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и поддержку работы нервной системы. Для усиления эффекта применяются витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для защиты печени.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
sonabet casino
It’s really a cool and helpful piece of information. I’m happy that you simply shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
blsp at сиськи тут
Excellent post! We will be linking to this particularly great content on our website.
Keep up the great writing.
ОГРНИП: 316505000065161 публичная оферта индивидуальный предприниматель Муравьев Александр Викторович публичная оферта
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles.
I will bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly.
I am quite certain I will learn many new stuff right
here! Best of luck for the next!
перепрошивка iphone Ремонт iPhone – востребованная услуга в Великом Новгороде, обусловленная популярностью этих устройств. Оперативность и качество – ключевые факторы выбора сервисного центра. Специалисты осуществляют замену аккумулятора, экрана, заднего стекла и разъема зарядки. Чистка динамика и микрофона также входит в перечень предлагаемых услуг.
Читатели получат представление о том, как современные технологии влияют на развитие медицины. Обсуждаются новые методы лечения, персонализированный подход и роль цифровых решений в повышении качества медицинских услуг.
Хочу знать больше – https://gorodkirov.ru/news/narkologicheskaya-pomosh-vazhnost-obrasheniya-i-sovremennye-metody-lecheniya
В клинике «СамарМед» доступно несколько форм лечения: стационарная программа, дневной стационар, амбулаторное наблюдение и гибридные схемы. Пациенты могут выбрать комфортный вариант в зависимости от степени зависимости, текущего состояния и занятости. Внутри стационара предусмотрены как стандартные палаты, так и индивидуальные блоки повышенной комфортности с возможностью проживания совместно с сопровождающим лицом.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма[/url]
https://t.me/Black125Bot
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your website, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
https://sonabet.pro/
глэмпинг Для тех, кто ищет максимального комфорта и развлечений, парк-отель все включено в Подмосковье станет идеальным выбором. Беззаботный отдых, включающий питание, напитки и развлечения, подарит незабываемые впечатления.
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru
«СамарМед» — это специализированный центр, где помощь оказывается не только при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, но и при комбинированных расстройствах, связанных с тревожностью, депрессией, нарушениями сна и постстрессовыми состояниями. В клинике работает команда из наркологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов, реабилитологов, а также специалистов по социальной адаптации. Вся система организации лечения направлена на достижение устойчивой ремиссии с минимальным риском рецидива, а телемедицинские решения дают возможность быстро получить консультацию даже в экстренных ситуациях, не выходя из дома.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в самаре[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
ремонт бытовой техники в екб [url=http://remont-tehniki-na-domu-ekaterinburg.ru/]https://remont-tehniki-na-domu-ekaterinburg.ru/[/url]
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи тольятти[/url]
Отдельный принцип клиники — строгая анонимность. Информация о лечении не передаётся по месту работы, обучения, в сторонние структуры без согласия пациента. Это особенно важно для людей, которые боятся огласки и из-за этого годами откладывают обращение. В «КоломнаМед Центр» можно пройти лечение так, чтобы сохранить репутацию и личное пространство, не превращая каждый шаг в обсуждение «на людях».
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno[/url]
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма гипнозом пермь[/url]
В клинике «СамарМед» доступно несколько форм лечения: стационарная программа, дневной стационар, амбулаторное наблюдение и гибридные схемы. Пациенты могут выбрать комфортный вариант в зависимости от степени зависимости, текущего состояния и занятости. Внутри стационара предусмотрены как стандартные палаты, так и индивидуальные блоки повышенной комфортности с возможностью проживания совместно с сопровождающим лицом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника самара[/url]
В клинике «СамарМед» доступно несколько форм лечения: стационарная программа, дневной стационар, амбулаторное наблюдение и гибридные схемы. Пациенты могут выбрать комфортный вариант в зависимости от степени зависимости, текущего состояния и занятости. Внутри стационара предусмотрены как стандартные палаты, так и индивидуальные блоки повышенной комфортности с возможностью проживания совместно с сопровождающим лицом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в стационаре[/url]
ремонт macbook в великом новгороде цена Ремонт телевизоров также является актуальной услугой. Ремонт подсветки телевизора и ремонт блока питания телевизора – это сложные задачи, требующие профессиональных навыков и специализированного оборудования.
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит нарколог на дом[/url]
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколог щёлково[/url]
Excellent way of explaining, and fastidious paragraph to take facts on the topic of my presentation subject matter, which i am going to deliver in college.
В клинике обеспечивается безопасный вывод из запоя и очистка организма после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или токсических сочетаний. Используются современные инфузионные схемы, витамины группы B, магний, гепатопротекторы по показаниям, противорвотные, мягкая коррекция сна и тревожности. Контроль давления, пульса, сатурации и поведения позволяет вовремя отметить любые осложнения и скорректировать терапию. Главная цель — не просто «прояснить голову», а защитить сердечно-сосудистую систему, мозг, печень, минимизировать риск делирия, судорог, аритмий и других острых состояний.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника в Коломне[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
подписать контракт на сво онлайн военную службу
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo
глэмпинг москва Глэмпинг – это изысканный симбиоз естественной красоты и современного комфорта. Минуя традиционные походные лишения, путешественники погружаются в атмосферу роскоши под открытым небом, наслаждаясь премиальным сервисом и уникальными удобствами в окружении чарующей природы.
Комплексный подход обеспечивает не только снятие симптомов, но и полное восстановление функций организма. Пациент получает поддержку на всех этапах — от детоксикации до социальной адаптации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому в тольятти[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Каждое назначение объясняется пациенту и близким простым языком. Здесь не практикуют подход «делаем, как знаем, вам всё равно не понять» — прозрачность и понятные шаги помогают снизить тревогу и укрепляют доверие к клинике.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]ramenskoe-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-obratnyj-zvonok[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom
Дедовск купить Метадон
Где купить мяу Данков Каннабис
лирику заказать Кострома
_________________________
Надёжность! Отзывы! Качество!
Проверенный магазин!
____________________________
.
▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼
[url=https://zinka.cc]✅>> ЖМИ СЮДА <> https://zinka.cc
✅ ЗАХОДИ НА САЙТ! >> zinka.cc
▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲ ▲▲
ВНИМАНИЕ !!!
⛔ ИСПОЛЬЗУЙТЕ VPN, ЕСЛИ АДРЕС НЕ ОТКРЫВАЕТСЯ! !
____________________________
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Драп
Сленговое название: ‘план’, ‘марихуана’, ‘травокур.
Трава — это растение травка, обычно употребляемое в виде смолы (гашиш) или сухой травы. Обычно её употребляют при курении, иногда добавляют в пищу. Эффект проявляется состоянием расслабленности, повышенным эмоциональным фоном, ощущением «растянутого течения времени» и обострением вкусовых ощущений, звуков и цветового восприятия, часто возникает выраженный аппетит.
При этом каннабис, ухудшает память и способность к концентрации, может вызывать тревогу, панические реакции и состояние апатии. Продолжительное использование способно приводить к формированию зависимости, проблемам с сердечно-сосудистой системой и лёгкими, снижению репродуктивной функции и может вызвать психические расстройства у лиц с склонностью.
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/4ddnd1]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Золофт Купить [/url]
[url=https://veanxiousaulearner.net/index.php/product/air-zoom-boot/#comment-46947]САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC | Гашиш Лирику Рузаевка Купить | САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC [/url]
[url=https://www.brownbook.net/business/54566068/лиски-купить-кристаллы-марихуану-наркотик]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Купить Бошки, Гашиш [/url]
Экс
Сленговое название: ‘Е’, ‘веселые конфетки’, ‘Ешка’, ‘колеса’, ‘Икс-Ти-Си’ и др.
Икс — синтетический токсикомании, обычно в виде таблеток, изготовленных в незаконных лабораториях. Его эффект — резкий подъём сил, чувство счастья, эмоциональная близость к другим людям и усиленное ощущение музыки и чувств, из-за чего препарат часто встречается в клубной сцене.
Побочные эффекты содержат перегрев организма, дефицит жидкости, учащённое сердечный ритм и резкий падение эмоционального фона по окончании эффекта. Постоянное использование может приводить к депрессии, перегрузке ЦНС и серьёзным нарушениям с психическим здоровьем; летальные исходы чаще обусловлены с перегревом и кардиальными нарушениями.
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/xoe8m]Где можно купить Метамфетамин | САЙТ – ZINKA.CC [/url]
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/jtmde6cb]ЛИРИКА 200 мг Красный Сулин купить тест | САЙТ – ZINKA.CC [/url]
[url=https://www.brownbook.net/business/54544884/великие-луки-купить-бошки-соль-гашиш]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | можно ли купить План [/url]
Алкалоид
Сленговое название: ‘Гарик’, ‘Герасим’, ‘Хмурый’, ‘Барбадос’, ‘Гера’, ‘Гербалайф’.
Белый — тяжёлый лекарство, производный от морфина, обычно вводят инъекционно или используют при курении. Препарат вызывает сильную эйфорию, за которой наступает глубокое состояние спокойствия и сонливости, одновременно уменьшается боль и эмоциональная отзывчивость.
Главная опасность опиоидного наркотика героина — крайне высокая аддиктивность и опасность смертельной передозировки. Уличный алкалоид нередко имеет опасные добавки, а инъекционное использование ассоциируется с опасностью ВИЧ, гепатита и серьёзных инфекционных заболеваний. Как правило постоянное использование ведёт к телесной и психологической аддикции.
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/yhf1209j3]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | купить Синтетический гашиш Бутурлиновка телеграм [/url]
[url=https://www.ailunce.com/Forum/item/50]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Купить прегабалин Нюрба [/url]
[url=https://estetmeb.com/feedback]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Купить СОЛЬ, Мефедрон, Кокс, Юрга [/url]
Алкалоид
Сленговое название: Кокс, мука, нюхара, кекс, кикер, снег.
Марафет – мощный стимулятор в виде светлого порошка, который чаще всего используют интраназально; его разновидность «crack» употребляется при курении и оказывает эффект быстрее и интенсивнее. Он вызывает недолгий подъём сил, уверенности и активности, снижая чувство голода и усталость.
По завершении действия наступает выраженный упадок с ощущением тревоги и депрессией. Марафет разрушает сердечную мышцу, сосуды и слизистую носовых ходов, может вызывать психозы и агрессию. Сильная зависимость и утрата контроля над использованием особенно характерны для крэка.
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/mqauw7]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Альфа Камень Купить [/url]
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/pukw4bx]ZINKA.CC <<>> ZINKA.CC | MDMA Героин ЛИРИКА 500 мг Метадон Купить | САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC [/url]
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/snhfa70]САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC | Купить Лирика, Альфа Кристалл, Камень | САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC [/url]
[url=https://www.grepmed.com/y2p8vawu]Заходи на ZINKA.CC | Купить A-PVP [/url]
[url=https://www.saforpress.com/2018/11/09/lydia-valentin-campeona-del-mundo-de-halterofilia-en-la-categoria-de-81-kilos/#comment-21524]САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC | Купить Трамадол | САЙТ >>> ZINKA.CC [/url]
КИСЛОТ
Разговорное обозначение: «кислота».
НАРКОТИК Псилоцибинсодержащие грибные препараты — психоактивные вещества, способные вызывать выраженные изменения сенсорного восприятия, мышления и ощущения течения времени. Воздействие способно длиться от нескольких часов вплоть до половины суток и характеризуется интенсивными визуальными и слуховыми искажениями.
Риск заключается в непредсказуемости воздействия: «негативное путешествие» может вызвать паническое состояние, психоз или рискованное действия. Не исключены продолжительные психологические последствия и неожиданные «вспышки» галлюцинаций даже спустя месяцы после факта использования.
https://sonabet.pro/
Наркологическая помощь в современном формате — это комплексное лечение зависимостей и состояний интоксикации с индивидуальным подходом к каждому пациенту. В клинике «ВолгаМед Тольятти» круглосуточно работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, готовые оказать поддержку в любой момент. Применяются сертифицированные препараты, проверенные методики и психологическое сопровождение. При этом особое внимание уделяется анонимности и безопасности пациента: информация не передаётся третьим лицам, а лечение проводится строго конфиденциально.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/pomoshh-narkozavisimym-tolyatti/
Online bij casino online crystalroll met HTML5 cross-browser games.
Для многих пациентов страх быть поставленным на учёт или потерять работу становится серьёзным барьером на пути к выздоровлению. В «ПермьМедСервис» данные пациента остаются строго внутри клиники: ни в какие внешние базы информация не передаётся. При оформлении документов не указывается диагноз, а возможна подача под псевдонимом. Консультации, процедуры и ведение истории болезни проходят в полностью закрытом режиме. Это позволяет пациенту сосредоточиться на выздоровлении, не опасаясь последствий для своей личной или профессиональной жизни.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/narkolog-perm-czeny
«СамарМед» — это специализированный центр, где помощь оказывается не только при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, но и при комбинированных расстройствах, связанных с тревожностью, депрессией, нарушениями сна и постстрессовыми состояниями. В клинике работает команда из наркологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов, реабилитологов, а также специалистов по социальной адаптации. Вся система организации лечения направлена на достижение устойчивой ремиссии с минимальным риском рецидива, а телемедицинские решения дают возможность быстро получить консультацию даже в экстренных ситуациях, не выходя из дома.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
Каждый пациент получает персонализированный план лечения, разработанный с учётом анамнеза, общего состояния и психоэмоционального фона. В «ПермьМедСервис» нет универсальных шаблонов — используется модульная модель терапии, при которой программы состоят из комбинированных блоков: медикаментозное лечение, психотерапия, физиотерапия, семейное консультирование. Это позволяет гибко адаптировать курс, вносить изменения по ходу лечения и учитывать динамику состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/perm-narkologicheskij-dispanser
Санкт-Петербург является крупным культурным центром России.
Город расположен на северо-западе страны и обладает богатым прошлым.
Городской облик сочетает величественные дворцы и новые архитектурные решения.
Санкт-Петербург славится музеями и разнообразием событий.
Петербургские улицы создают особую атмосферу.
Гости города приезжают сюда круглый год, чтобы познакомиться с культурой.
Санкт-Петербург также является значимой деловой площадкой.
Таким образом, Санкт-Петербург остаётся одним из самых привлекательных городов.
https://writexo.com/share/a0f251befd4d
affiliate network gambling CPA сеть iGaming – это мощный инструмент для привлечения трафика и монетизации гемблинг-проектов. Она предоставляет вебмастерам возможность получать выплаты за конкретные действия пользователей, такие как регистрация, депозит или активная игра. Выбирая CPA сеть iGaming, важно обращать внимание на репутацию, разнообразие офферов и стабильность выплат.
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма на дому пермь[/url]
Система круглосуточной наркологической помощи в «ОмскПрофи» построена на принципе постоянной готовности. В любой момент суток специалисты готовы выехать на дом, принять пациента в стационар или организовать удалённую консультацию. Это особенно важно в острых ситуациях, когда счёт идёт на часы: запой, передозировка, психоз, агрессивное поведение или резкое ухудшение самочувствия. В таких случаях промедление может стоить пациенту жизни.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/narkolog-psikhiatr-omsk/
Психотерапевтическая часть лечения строится на многоступенчатой программе. Вначале пациент учится понимать свои зависимости, выявлять скрытые мотивы употребления и работать с сопротивлением. На следующем этапе — формируется навык противостояния стрессу, прорабатываются внутрисемейные конфликты и создаются новые стратегии поведения. В финале — акцент на социализацию, возвращение к активной жизни, построение трезвого будущего. Используются как индивидуальные сессии, так и терапевтические группы, телемосты и онлайн-курсы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма самара[/url]
Клиника придерживается принципа прозрачного ценообразования. Пациенту или родственникам сразу озвучивается стоимость всех процедур и услуг. Возможна оплата поэтапно или в рамках пакета. В отличие от многих клиник, «ОмскПрофи» предоставляет фиксированные цены на распространённые виды помощи, без скрытых доплат.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-volgograd/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
This information is priceless. When can I find out more?
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/
Ниже — примерная структура пакетов, которую можно использовать как ориентир (не публичная оферта):
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
Mavibettelegram – Gotta get those insider tips! I find their Telegram channel pretty useful for getting the latest odds and news. Keeps me ahead of the game. mavibettelegram
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/
«Трезвый Центр Коломна» предлагает несколько маршрутов, и выбор делается не по принципу «как удобнее», а по критериям безопасности. Если пациент в сознании, на контакте, без грубой дезориентации, без галлюцинаций, может пить воду, рвота эпизодическая, нет тяжёлых скачков давления и пульса, дома есть тишина и ответственный взрослый — возможен выезд на дом. Врач приезжает в Коломне, проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, степень обезвоживания, неврологический и психический статус, подбирает индивидуальную инфузионную схему и наблюдает за реакцией. Если же запой затянулся (3–5 суток и более), выражены слабость, шаткость походки, многократная рвота, резкие «качели» АД и ЧСС, есть подозрение на предделирий или делирий, тяжёлая соматика или пожилой возраст — врач честно рекомендует стационар. В отделении пациент получает круглосуточный мониторинг, возможность оперативно корректировать лечение, защищённую среду без доступа к алкоголю и посторонних стимулов, поддержку медперсонала в любое время суток. Такой дифференцированный подход экономит силы, деньги и главное — снижает риск критических осложнений, которые часто возникают именно после «домашних экспериментов».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Voor beginners biedt crystall roll casino uitgebreide guides met stap-voor-stap instructies vanaf €5 storting.
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в воронеже[/url]
Понятие гедонизма — это мировоззренческий подход, которое выдвигает наслаждение в центр человеческой жизни.
Согласно этому взгляду, поиск радости считается важным мотивом существования.
Данная философия не всегда подразумевает излишество.
Во многих трактовках он связан с умеренностью и осознанный выбор.
https://telegra.ph/Acne-Studios-12-25
Актуальная интерпретация часто акцентирует внимание на качестве жизни.
При этом важную роль играет баланс между удовольствиями и ценностями.
Гедонистический подход может способствовать личному развитию.
В итоге, гедонизм рассматривается как подход к пониманию счастья, а не как призыв к излишествам.
Основные этапы лечения включают:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska
Медикаментозная терапия — важнейший этап стабилизации состояния. Врачи «СамарМед» применяют препараты с доказанной эффективностью: детоксикационные растворы, нейрометаболики, седативные и анксиолитические средства, ноотропы, гепатопротекторы, а при необходимости — антипсихотики. Подбор схемы проводится индивидуально, с учётом переносимости, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, возраста и стадии зависимости. Все препараты применяются строго по международным протоколам и под контролем врачей круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Каждый пациент получает персонализированный план лечения, разработанный с учётом анамнеза, общего состояния и психоэмоционального фона. В «ПермьМедСервис» нет универсальных шаблонов — используется модульная модель терапии, при которой программы состоят из комбинированных блоков: медикаментозное лечение, психотерапия, физиотерапия, семейное консультирование. Это позволяет гибко адаптировать курс, вносить изменения по ходу лечения и учитывать динамику состояния пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
If you are going for best contents like I do, just visit this web site daily since it gives quality contents, thanks
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь в тольятти[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Маршрут организован так, чтобы убрать хаос и сделать шаги понятными для родственников. После звонка оператор под контролем врача уточняет длительность употребления, примерные объёмы алкоголя, хронические болезни (гипертония, ИБС, диабет, заболевания печени, почек, нервной системы), список уже принятых лекарств, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, подозрительные психические симптомы. На этом этапе принимается базовое решение: возможно ли безопасно провести детокс на дому либо показан стационар. Врач приезжает по адресу в Щёлково, проводит осмотр: фиксирует АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, речь, поведение, уровень сознания, степень обезвоживания. Затем подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации, коррекции электролитов и кислотно-щелочного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы и снижения тремора; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные, щадящие анксиолитики для сна, но без грубого «выключения». Во время процедуры врач наблюдает за динамикой, при необходимости меняет скорость капельницы, контролирует давление и пульс, следит за реакцией на препараты. В финале даёт подробные рекомендации: как вести себя ближайшие 24–72 часа, как спать, что пить и есть, каких лекарств избегать, какие симптомы считать тревожными, когда нужно немедленно звонить и когда стоит рассмотреть стационар. Если уже на этапе осмотра понятно, что дому «тесно» по безопасности, перевод в клинику организуется без задержек.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника телефон[/url]
служба по контракту на сво санкт петербург
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/[/url]
Москва – Все чётко, поднятие на раз два, все по описанию. Мефедрон белый, без запаха, видно что очищенный. Вес и качество норм!!!! Количество соответствует, за бонус в спасибо 😉 https://amfet-market.shop 5 iai вообще говорят “беспонтовый” продукт… сколько народу его от рaзных сeлеров не пробовало – всё одно муть…привет бро)) чето какой то засланый казачок тут про запр дживы интерес проявляет…
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd/
Клиника придерживается принципа прозрачного ценообразования. Пациенту или родственникам сразу озвучивается стоимость всех процедур и услуг. Возможна оплата поэтапно или в рамках пакета. В отличие от многих клиник, «ОмскПрофи» предоставляет фиксированные цены на распространённые виды помощи, без скрытых доплат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske
Каждый пациент получает персонализированный план лечения, разработанный с учётом анамнеза, общего состояния и психоэмоционального фона. В «ПермьМедСервис» нет универсальных шаблонов — используется модульная модель терапии, при которой программы состоят из комбинированных блоков: медикаментозное лечение, психотерапия, физиотерапия, семейное консультирование. Это позволяет гибко адаптировать курс, вносить изменения по ходу лечения и учитывать динамику состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр пермь[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
I just couldn’t leave your web site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info a person supply in your visitors? Is gonna be back continuously to check out new posts
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом волгоград[/url]
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/53tzpbmz
В Тольятти клиника «ВолгаМед Тольятти» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг — от экстренного вывода из запоя на дому до длительных реабилитационных программ. Выезд нарколога осуществляется круглосуточно: врач приезжает по вызову, проводит диагностику, оценивает степень интоксикации и назначает индивидуальный план лечения. Это особенно важно в тех случаях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники. В арсенале специалистов — профессиональное оборудование, капельницы для детоксикации и препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru
FoX будь добр скажи… https://boshkionline.shop да не вопрос, в мск для этого совсем не надо ехать, друг, просто ситуация непонятная и неприятная, раз магазин не заботится о своей репутации-то это уже сосем другое дело….качество супер!!!
Такая структура терапии делает процесс максимально эффективным и безопасным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr/
Клиника обеспечивает анонимность и безопасность. Информация о пациентах не передаётся третьим лицам, а процедуры выполняются в комфортных условиях с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и современного оборудования.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
Первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению является очищение организма от токсинов. В клинике проводится детоксикация с использованием современных препаратов, направленных на выведение продуктов распада алкоголя и наркотиков. Медикаментозное лечение дополняется витаминами, гепатопротекторами и средствами для нормализации работы нервной системы. Это помогает восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в воронеже[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в омске[/url]
When I originally commented I appear to
have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox
and from now on every time a comment is added I recieve four emails with the same comment.
There has to be an easy method you are able to remove
me from that service? Many thanks!
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог отборных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до обширных поставок, мы гарантируем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы по мере того как находить ответы под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
поставляемая продукция:
Порошок кобальтовый ЭП207 Порошок кобальтовый ЭП207 — это высококачественный материал, используемый в различных промышленных областях, включая металлургию и производство сплавов. Он отличается отличными механическими свойствами и коррозионной стойкостью. Этот порошок идеально подходит для 3D-печати и других технологий, требующих высокой точности и надежности. Если вы ищете качественный и надежный материал, чтобы улучшить свои производственные процессы, вам стоит купить Порошок кобальтовый ЭП207. Этот продукт поможет вам добиться высоких результатов и укрепить свои позиции на рынке.
Gangnam is among the most established and acknowledged districts in Seoul, South Korea.
It is recognized for its modern way of living, company
environment, high-end living, and social impact.
In time, a number of terms have come to be very closely related to
Gangnam’s image, including Gangnam The King, Gangnam Prairie Residence, Gangnam 6, and Gangnam Mission.
These keyword phrases define different ideas, duties, and values that with each other describe
why Gangnam holds such a crucial setting.
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании кодирование[/url]
Loyalty bij crystal roll casino no deposit bonus code met automatic tier upgrades en instant perks.
Система круглосуточной наркологической помощи в «ОмскПрофи» построена на принципе постоянной готовности. В любой момент суток специалисты готовы выехать на дом, принять пациента в стационар или организовать удалённую консультацию. Это особенно важно в острых ситуациях, когда счёт идёт на часы: запой, передозировка, психоз, агрессивное поведение или резкое ухудшение самочувствия. В таких случаях промедление может стоить пациенту жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/narkolog-psikhiatr-omsk/
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-reutove/
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В «СамарМед» пациент рассматривается не как носитель диагноза, а как личность с уникальной историей, эмоциональным фоном, социальным окружением и индивидуальными триггерами зависимости. Именно поэтому с первого обращения к лечению подключаются сразу несколько специалистов. Стартовый консилиум позволяет сформировать целостную картину состояния, определить точки риска и создать персонализированную стратегию терапии, включающую медицинскую, психотерапевтическую и социальную составляющие.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara0.ru/narkologi-samary/
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
“А если Подтвердиться прошу перевыдать пробу вашего продукта Нормального Ибо Иметь дело с вашим магазином я не вижу смысла” Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш мне менеджер сказал, что у другого спросит по поводу мхе и выдаст компенсации.магазину респект)) с корефанами накуримся вдоволь)))
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
Very shortly this website will be famous among all blog users, due to it’s fastidious posts https://sterling-kupski.pl/2024/06/25/hello-world/
Site web 1xbet pour Android 1xbet apk
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в волгограде[/url]
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены омск[/url]
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Регидратация, коррекция электролитов и КЩС, витамины группы B/магний; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксиданты, противорвотные, мягкие анксиолитики. Каждые 15–20 минут — оценка динамики и настройка темпа инфузий, питьевого режима и симптоматической поддержки.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-vyzov-na-dom[/url]
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным ценам.– [url=http://friendsmotors.ca/diplom-ljubogo-vuza-legalno-i-s-podtverzhdeniem-470/]friendsmotors.ca/diplom-ljubogo-vuza-legalno-i-s-podtverzhdeniem-470[/url]
Для иллюстрации приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы терапии и их воздействие на организм:
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма в перми[/url]
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа по доступной стоимости вы можете, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании. Для проверки компании перед покупкой пользуйтесь рейтингом и отзывами на форумах. Можно приобрести диплом из любого университета РФ [url=http://russianecuador.com/forum/member.php?u=13207/]russianecuador.com/forum/member.php?u=13207[/url]
Каждое направление терапии в клинике подбирается персонально. Пациент проходит пошаговую программу, начиная с диагностики и детоксикации и заканчивая психологическим сопровождением и адаптацией к жизни без зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
2 bs2best at
Howdy I am so delighted I found your weblog, I really found you by accident, while I was searching on Askjeeve for something else, Nonetheless I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a tremendous post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the minute but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the fantastic b.
всем мир! скажите магаз ровный? ато написал на мыло им и ни ответа ни привета! https://republique-dominicaine-live.online АМ-2233 вообще ровный день назад пришёлТы то откуда знаешь)))только сегодня зарегался .коржик )))
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя рядом[/url]
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в новокузнецке[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/perm-lechenie-alkogolizma
контракт сво иркутск
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, и в «КоломнаМед Центр» это принимается как медицинский факт, а не моральная оценка. Программы включают медикаментозную поддержку, работу с тягой, коррекцию тревожных и депрессивных состояний, психотерапию, помощь в восстановлении режима сна и питания, семейное консультирование. При наркотической зависимости и полинаркомании добавляются протоколы по безопасной отмене веществ, наблюдение в критические периоды, сопровождение на этапе формирования устойчивой ремиссии. Акцент делается на том, чтобы не запугивать пациента, а показать реалистичный путь, где улучшение возможно шаг за шагом.
Узнать больше – http://
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Create unique marks for your business with our [url=https://mystampready-0constructor.com/]online stamp maker[/url].
The reasonable prices offered by online rubber stamp services attract numerous users.
Ам1220 все больше сообщений что относят к нелегалу. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш круто ймагаз!!сегодня закажу 1г. MN-011 для пробы)посмотрим на товар)
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]взрослые игры[/url]
Dressing stylishly is essential for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps highlight individuality.
A neat look can increase self-assurance.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://telegra.ph/Louis-Vuitton-01-12-4
A well-planned wardrobe make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider personal preferences as well as the context.
Modern styles give people the chance to refresh their image.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly positively affects perception.
Черт приехал в офис говорю посмотрите посылку,мне сказали ее давно отправили!Она посмотрела ее нету,позвонила говорит она еще не отправлена и х.з. когда будет отправлена. https://mefedron-shops.store И еще сушняки ужасные. Сейчас вот утром проснулся, и до сих порДве дороги для Артёма,
This piece of writing gives clear idea in favor of the new people of blogging, that truly how to do running a blog.
To register betwinner successfully, open https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and follow the instructions provided on the official review page.
замена задней крышки iРhоnе лазером Ремонт цифровой техники в Великом Новгороде: от смартфонов до компьютеров. В современном мире трудно представить жизнь без мобильных устройств, компьютеров и другой цифровой техники. Однако, как и любая техника, они подвержены поломкам и неисправностям. Когда ваш верный гаджет выходит из строя, важно найти надежный сервисный центр, предлагающий качественный и оперативный ремонт. В Великом Новгороде существует множество мастерских, специализирующихся на ремонте телефонов, планшетов, ноутбуков, компьютеров и телевизоров.
https://ufalift.ru/
Этот набор информации привлекает мелочами и необычными ракурсами, предлагая взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но разнообразят знакомство с темой.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]займ без процентов[/url]
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up.
The words in your post seem to be running off the screen in Chrome.
I’m not sure if this is a format issue or something to
do with internet browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let
you know. The layout look great though! Hope you
get the problem fixed soon. Thanks
Мультимедийный интегратор ай-тек интеграция мультимедийных систем под ключ для офисов и объектов. Проектирование, поставка, монтаж и настройка аудио-видео, видеостен, LED, переговорных и конференц-залов. Гарантия и сервис.
Какое палево ты очём? https://boshkimarket.shop Надежных партнеров, верных друзей, удачных сделок и прочих успехов!Насчет этого магаза ничего не скажу, но лично я 5иаи ни у кого приобретать не буду, ну а ты поступай как хочешь, вдруг тут будет нормально действующим в-во
Игры Новости геймдев индустрии: на острие прогресса. Игровая индустрия является одной из самых динамичных и инновационных отраслей. Технологии виртуальной и дополненной реальности, облачный гейминг, блокчейн – все это открывает новые горизонты для разработчиков и игроков. Следить за новостями геймдева – значит быть в курсе последних трендов, вдохновляться новыми идеями и находить возможности для профессионального роста.
Умение стильно одеваться имеет большое значение в самовыражении.
Она помогает выразить характер и чувствовать себя увереннее.
Современный стиль формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может помогать собранности.
https://graph.org/Bvlgari-01-12-3
Стильный образ облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать личные предпочтения и обстановку.
Мода дают возможность экспериментировать.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
sonabet app download
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]рулетка онлайн[/url]
Платформа предлагает игры с разными уровнями ставок для любого бюджета. Актуальное зеркало вавада доступно на официальном ресурсе круглосуточно. Новые пользователи могут рассчитывать на бонус и фриспины. Вывод средств происходит оперативно без скрытых комиссий. Служба безопасности тщательно защищает все финансовые операции.
Всем доброго дня!! Хочу рассказать свой отзыв , о данном чудо магазине!! Заказывал совместку на 50г, оплатил днём, к вечеру все было готово, жаль только я с джабером что то не подружился, он меня выкинул, прям перед получением адреса, НО КЛАДЧИК ТАКОЙ красавчик!!! В итоге я поехал с утра, только приехал, все было на своих местах!!! Спрятано на совесть!!! Думаю ещё пролежало бы дня 3))) ИТОГО: ОПЕРАТОР В ДЖАБЕРЕ САМЫЙ КУЛЬТКРНЫЙ ЧЕЛОВЕК НА СВЕТЕ! 5+ КЛАДЧИК , умница! 5+, близко ко мне , и спрятано как надо!!! P.S. Смело заказываем!! И радуемся как дети!!) https://decisionguide.org Уважаемые наши клиенты, приносим свои извинения за задержку с отправкой.Ментам зачастую пофиг,легал-нелегал.Был бы человек хороший,статья найдётся.СПСР тоже чёт не нравится.Но и на Мажор экспрессе случаи принималова были,так что х.з….Увидел на сайте “ждём…”.О.флюрокока и rti 111!Очень ждём!АМТ тож вкусняшка,но тут обьебосам не завидую.Примут по полграмма и айда 20 часов как кот в стиральной машине
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-marmansk/https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто учреждение для экстренной помощи, а центр комплексной поддержки человека, столкнувшегося с зависимостью. В «КузбассМед» в Новокузнецке реализуется модель интенсивного вмешательства, где используются новейшие медицинские технологии, мультидисциплинарный подход и мобильные выездные службы. Специалисты готовы прибыть на дом за 30 минут с полным набором оборудования и медикаментов, обеспечив пациенту помощь в привычной и безопасной среде. Наркология здесь строится на индивидуализации: каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, с учётом психофизического состояния, анамнеза и жизненного контекста пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://www.lyaesthetics.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Всем добрый день! Делюсь мыслями про продвижение в TG.
Давно в теме SMM в TG и хочу поделиться наблюдением по поводу цен на размещения.
Пробовал вручную искать площадки, но это занимает часы, а результат часто разочаровывает.
Вот похожий разбор, который мне помог разобраться: [url=https://medium.com/@camimoc986/%D0%B1%D0%B8%D1%80%D0%B6%D0%B0-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BA%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BC%D1%8B-%D0%B2-telegram-%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8-%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B6%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F-%D0%B2-2026-%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%83-b3338fafc646]реклама через тг канал[/url]
А как вы решаете вопрос с размещениями в Telegram-каналах? Жду советов.
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в уфе[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому раменское[/url]
Hello would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using? I’m looking to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a tough time making a decision between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something completely unique. P.S Apologies for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тюмени — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к нарушению обмена веществ, обезвоживанию, сбоям в работе печени и сердца. В таких случаях требуется профессиональная помощь врача-нарколога, который подберёт оптимальный способ дезинтоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки. Современные методики позволяют провести вывод из запоя безопасно, эффективно и без осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/[/url]
Особое внимание в клинике уделяется психологической реабилитации. Зависимость всегда сопряжена с внутренними конфликтами, нарушением привязанностей, проблемами самооценки. Врач-психотерапевт помогает пациенту выявить первопричины срывов, обучает техникам управления стрессом и прорабатывает модель трезвого поведения. В стационаре ведутся групповые и индивидуальные сессии, тренинги по навыкам саморегуляции, арт-терапия и элементы психодрамы. Реабилитационная команда помогает в адаптации к новой социальной роли, восстановлению отношений в семье и планированию жизни после выписки.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Продуманный внешний вид является значимым фактором в формировании впечатления.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и выглядеть гармонично.
Современный стиль формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://rentry.co/nvm2vvpu
Стильный образ облегчает социальные взаимодействия.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и обстановку.
Современные тенденции дают возможность обновлять образ.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Омске проводится с использованием современных методов, направленных на восстановление организма и психики пациента. Специалисты уделяют внимание как медицинским, так и психологическим аспектам, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов. Основой терапии является индивидуальный подход, благодаря которому каждая программа учитывает состояние здоровья и уровень зависимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]здоровье лечение алкоголизма[/url]
I know this web site gives quality dependent articles and additional
data, is there any other web page which provides such things in quality?
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-marmansk
Текст наполнен информацией, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет восприятия привычных вещей, так что читайте его ради удовольствия.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]займы до зарплаты[/url]
https://ufalift.ru/
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]взрослые игры[/url]
замена задней крышки айфон Удобство и доступность: ремонт рядом с вами. Многие сервисные центры предлагают услугу выездного ремонта, что позволяет сэкономить время и получить квалифицированную помощь на дому или в офисе. Кроме того, ремонт телефонов в рассрочку позволяет получить необходимую услугу без значительных финансовых затрат. Независимо от того, какая поломка произошла с вашим устройством, опытные специалисты помогут вам решить проблему быстро и качественно.
Visit our digital platform : https://kompkimi.ru/wp-content/pages/promokod_250.html
В процессе лечения используются проверенные методики, которые в комплексе обеспечивают положительный эффект и снижают риск рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/omsk-lechenie-alkogolizma
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто учреждение для экстренной помощи, а центр комплексной поддержки человека, столкнувшегося с зависимостью. В «КузбассМед» в Новокузнецке реализуется модель интенсивного вмешательства, где используются новейшие медицинские технологии, мультидисциплинарный подход и мобильные выездные службы. Специалисты готовы прибыть на дом за 30 минут с полным набором оборудования и медикаментов, обеспечив пациенту помощь в привычной и безопасной среде. Наркология здесь строится на индивидуализации: каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, с учётом психофизического состояния, анамнеза и жизненного контекста пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-deshevo[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tyumen-otzyvy
В случаях запоя, острого отравления или абстинентного синдрома выездная наркологическая бригада оказывает помощь прямо на месте. Специалисты приезжают в течение 30 минут после обращения и проводят оценку состояния пациента, экстренное введение лекарств, инфузионную терапию и психологическую поддержку. Благодаря специальной комплектации мобильной бригады, лечение на дому возможно даже при умеренной степени осложнений. Врач также может при необходимости провести экспресс-анализы и дать рекомендации родственникам по дальнейшему уходу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Магаз ровный, очень много раз тут брал, а как перешли на телеграмм так еще больше радуете, намного меньше гемора с оплатой стало, качество на высоте как и всегда. Сегодня убедился что оператор не сидит без дела, очень сильно помог мне с моим вопросом, при чем оперативно все сделал. Оцениваю данный магазин 10 из 10. Кокаин даже MQ оказался лучше, чем я до этого покупал HQ в другом магазе. Делайте по чаще закладки в центре Питера. https://amfetminsklad.store что то не могу зайти на сайт (важаемый ТС прошу разобраться с заказом,всё оплаченно вам,вот только игнор в бросиксе и посылки нету до сих пор. Заранее благодарен.
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/besplatnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-v-omske/
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru
http://cl.angel.wwx.tw/debug/frm-s/bit.ly/4jMsNFN
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в волгограде[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
https://sonabet.pro/
трансы саратов Гипнотерапия в Саратове – это квалифицированная помощь профессиональных гипнологов, использующих гипнотическое состояние для работы с широким спектром психологических проблем. От тревожных расстройств и фобий до зависимостей и психосоматических заболеваний, гипноз предлагает безопасный и эффективный способ доступа к подсознанию для решения глубинных проблем.
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам. Диплом об образовании в СССР считался основным документом, который способствовал успешному устройству на работу. Заказать диплом ВУЗа!: [url=http://trillia.com.br/textstat/diplom-za-korotkij-srok-sroki-ceny-uslovija-457/]trillia.com.br/textstat/diplom-za-korotkij-srok-sroki-ceny-uslovija-457[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom
В случаях запоя, острого отравления или абстинентного синдрома выездная наркологическая бригада оказывает помощь прямо на месте. Специалисты приезжают в течение 30 минут после обращения и проводят оценку состояния пациента, экстренное введение лекарств, инфузионную терапию и психологическую поддержку. Благодаря специальной комплектации мобильной бригады, лечение на дому возможно даже при умеренной степени осложнений. Врач также может при необходимости провести экспресс-анализы и дать рекомендации родственникам по дальнейшему уходу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в новокузнецке[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены уфа[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]срочное выведение из запоя[/url]
Эффект ощущается уже через 20–40 минут после начала процедуры. Пациент отмечает снижение головной боли, улучшение сна и общего состояния. Полное восстановление самочувствия наступает в течение суток.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tyumen-otzyvy
Знакомство с новостными источниками имеет большое значение в информационном пространстве.
Оно помогает быть в курсе событий и понимать происходящее.
Оперативная информация позволяют принимать взвешенные решения.
Чтение СМИ способствует расширению кругозора.
https://telegra.ph/Kazan-12-25-3
Разнообразные медиа помогают анализировать информацию.
В профессиональной сфере СМИ дают возможность следить за тенденциями.
Внимательное чтение новостей формирует умение работать с данными.
В целом, чтение СМИ делает человека более информированным.
http://cl.angel.wwx.tw/debug/frm-s/bit.ly/4jMsNFN
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]наркологическая клиника доктор[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
http://www.opencart-france.com/newsletter/pages/?1xbet_code_d_inscription_promo.html
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя уфа[/url]
Wow, incredible weblog format! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for? you make running a blog look easy. The overall look of your site is wonderful, as neatly as the content material!
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru
Ребята кто заказывал 25 реагент,как по качеству??????????? Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш магазин работает как надо, у меня тут перевес был не плохой спасибо дружбанчикив кемерово откроетесь??
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-marmansk
Алкогольная интоксикация и запой могут стремительно ухудшить состояние здоровья, став угрозой жизни, поэтому оперативное вмешательство имеет первостепенное значение. В Туле квалифицированные наркологи предоставляют круглосуточную помощь на дому, что позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и в комфортных условиях. Такой формат терапии гарантирует индивидуальный подход, всестороннюю поддержку и полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для пациентов, стремящихся восстановить своё здоровье без лишних стрессовых ситуаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в туле[/url]
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-marmansk
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино[/url]
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Углубиться в тему – http://
Игры Ресурсы для геймдева: инструменты для воплощения мечты. Современная разработка игр невозможна без использования специализированного программного обеспечения и готовых ассетов. Игровые движки, такие как Unity и Unreal Engine, предоставляют мощные инструменты для создания графики, физики и искусственного интеллекта. Библиотеки звуков, модели персонажей и ландшафты значительно ускоряют процесс разработки, позволяя сосредоточиться на уникальных особенностях игры.
Dressing stylishly is important for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps highlight individuality.
Stylish clothing can improve self-esteem.
In everyday life, appearance often affects social interactions.
https://telegra.ph/Tom-Ford-12-25-2
Carefully selected clothing make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider one’s own comfort as well as the situation.
Current trends give people the chance to refresh their image.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly helps people feel confident.
Хоть скан хоть что вылаживайте, это не доказательство! доказательством для меня есть только поступление денег на счет. По чекам, сканам, и всему прочему я не работаю это не есть доказательство об оплате! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш ещё раз говорю, здесь качество отменное, по крайней мере с той партии, с которой я получал. 1к10 убивало в мясо с напаса )Может стоит внимательно посмотреть в ветке что есть резервный жаббер ? основной уже 6 дней не работает , какие то сбои, но резерв ведь работает, привыкли панику поднимать на ровном месте.
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba戰績比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
sona bet app login
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]здоровье лечение алкоголизма в омске[/url]
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в саратове[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Одним из ключевых преимуществ «КузбассМед» является современная материально-техническая база. В клинике задействованы устройства для точного мониторинга жизненных функций, автоматические инфузионные системы, экспресс-диагностические модули и оборудование для неотложной терапии. Врачи используют программируемые дозаторы, портативные анализаторы крови и аппараты для оценки дыхательной функции, что позволяет своевременно корректировать тактику лечения без потерь времени. Все процедуры соответствуют национальным стандартам безопасности и рекомендациям ВОЗ.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Магаз вышел на связь, работает, но щас выходные 😀 с треками порешают, по ходу косяки СПСР. пробники БУДУТ !! Кто ещё будет гадить в теме “Трипы” и просить пробник – получит подзатыльник. У кого есть что сказать – отпишите лучше отзывы о товаре. https://mdma-fast.shop Ну теперь к самому главному – качество!все буде ровно бразы магаз ровный я тоже ждал отправку неделю зато пришло с бонусом я остался доволен (щас погода такая ,все болеют но работают )
В Волгограде сформирована система оказания наркологической помощи, включающая круглосуточные выезды специалистов, амбулаторное лечение, стационарные программы и реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет охватить все категории пациентов — от тех, кто нуждается в экстренной помощи, до тех, кто готов пройти полный курс терапии. Независимо от формы оказания услуг, лечение проводится конфиденциально и в соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]раменское вывод из запоя[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/
Excellent blog here! Also your website loads up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
bs2best at ссылка
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]центр анонимного лечения наркомании тверь[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]наркологические клиники обратный звонок[/url]
Подбирать одежду со вкусом важно для создания первого впечатления.
Внешний вид помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и даёт чувство комфорта.
Аккуратный образ влияет на восприятие окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может помогать чувствовать себя увереннее.
https://telegra.ph/Dior-12-29
Хорошо сочетаемая одежда упрощает социальные взаимодействия.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и контекст.
Мода позволяют обновлять образ.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться помогает выглядеть гармонично.
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]бесплатные вращения в слотах[/url]
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd
Процесс детоксикации состоит из нескольких последовательных шагов, направленных на безопасное очищение организма. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием этапов, которые применяются в клинике «Трезвая Линия Волгоград».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Если вы мечтаете о надежном и уютном жилье, обратите внимание на [url=https://karkasnye-doma-pod-klyuch6.ru]каркасные дома санкт петербург[/url], обеспечивающие комфорт и долговечность.
Одним из главных достоинств каркасных домов является их энергоэффективность.
Здесь
[url=https://glassfactory.us/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре рязань[/url]
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Получить больше информации – http://
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в уфе[/url]
трансы волгоград Медитативные практики в Волгограде представлены различными направлениями, от классической медитации осознанности до современных техник релаксации. Местные студии и центры предлагают групповые занятия и индивидуальные консультации, помогая освоить инструменты для достижения внутреннего покоя и снижения стресса.
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Магазин просто огонь !!! Оценка 5+ за все :voo-hoo: !!! Качество товара збс !!! Советую всем этот магаз!!! https://awwama.com заказал, получил трек, пока не бьется.Заказывал 200й, прислали с приятным бонусом! Конспирация- чудесна! В общем все супер!
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно тюмень[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто учреждение для экстренной помощи, а центр комплексной поддержки человека, столкнувшегося с зависимостью. В «КузбассМед» в Новокузнецке реализуется модель интенсивного вмешательства, где используются новейшие медицинские технологии, мультидисциплинарный подход и мобильные выездные службы. Специалисты готовы прибыть на дом за 30 минут с полным набором оборудования и медикаментов, обеспечив пациенту помощь в привычной и безопасной среде. Наркология здесь строится на индивидуализации: каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, с учётом психофизического состояния, анамнеза и жизненного контекста пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom[/url]
sonabet vip
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом саратов[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd
After looking over a handful of the blog articles on your site, I really like your
way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking
back soon. Please check out my web site as well
and tell me what you think.
Этот набор информации привлекает мелочами и необычными ракурсами, предлагая взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но разнообразят знакомство с темой.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где пациенту оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это учреждение, где формируется стратегия полного восстановления, включающая не только физическое оздоровление, но и психоэмоциональную стабилизацию. В Ярославле работают как частные, так и государственные клиники, однако их подходы, уровень сервиса и состав команд могут существенно различаться. По данным Минздрава РФ, высокий процент успешных исходов наблюдается в тех учреждениях, где реализуется персонализированная модель лечения и постлечебной поддержки.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-yaroslavl/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Или все ок у всех тут клиентов? https://gashishtop.shop спасибо Вам за отзыв!Дом рядом с адресом говоришь, отдаешь залог, когда приедешь в адрес (в разных такси по-разному, могут и не попросить), и идешб себе за кладом 🙂
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you, However I am encountering problems
with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I can’t
join it. Is there anybody having identical RSS issues?
Anyone who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanks!!
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена новосибирская область[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника коломна[/url]
Комплексная наркологическая помощь объединяет несколько направлений, каждое из которых решает отдельную задачу восстановления организма и психики. Врачи используют индивидуальные схемы терапии, подбирая оптимальные препараты и психологические методики.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru
Выбор помощи на дому имеет ряд значительных преимуществ:
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-tula/
Hello to every one, the contents present at this site are in fact awesome for people experience, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
Moomoo??????
Наши врачи используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, индивидуально подбираемые для каждого пациента. В состав лечебного курса входят:
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в рязани[/url]
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/omsk-lechenie-alkogolizma
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании клиника в твери[/url]
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза детоксикации, во время которой современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом. Этот этап помогает быстро снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальные обменные процессы и нормализовать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/[/url]
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru
Хотя я знаю почему всех слабо торкает , всё дело в неверном приёме препарата ! Весь форум облазил , но этого способа не наблюдал . Пусть не приятно но стоит того . Порох под язык . Доза меньше , эффект быстрей и ярче . Хотя это личное дело каждого , песня не об этом . Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш ..тот, который у Вас в подписи..))Вообщем так, с момента отправки из курьерской службы до рук курьера в нашем городе прошло 3 дня, забрал я значительно позже, но это не суть.
Прежде чем принимать решение, важно изучить сайт клиники. В надёжных учреждениях размещена полная информация о врачах, их образовании и опыте работы. Кроме того, пациентам предлагается пройти предварительную консультацию — чаще всего она проводится анонимно и включает первичную диагностику. Это позволяет оценить профессионализм команды ещё до начала терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]chastnaya narkologicheskaya klinika jaroslavl'[/url]
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-staczionar/
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Link exchange is nothing else except it is simply placing
the other person’s weblog link on your page at suitable place and other
person will also do same in favor of you.
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great.
I don’t know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if you
are not already 😉 Cheers!
Комплексный вывод из запоя в Туле организован по отлаженной схеме, состоящей из нескольких этапов, каждый из которых направлен на безопасное и эффективное восстановление организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk/
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologiya-v-volgograde
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в мурманске[/url]
https://lchat.biz/to/bsbot
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
В Волгограде медицинская клиника «Трезвая Линия Волгоград» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с острым алкогольным отравлением или затяжным запоем. Врачи выезжают на дом, в гостиницу или принимают пациентов в стационаре. Каждое вмешательство начинается с оценки состояния — измерения давления, пульса, насыщения кислородом, уровня интоксикации и дехидратации. Далее подбирается оптимальный состав капельницы, направленный на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, поддержку печени и снижение тревожности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
https://sonabet.pro/
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny
Работает. Контакты указаны в соответствующей теме. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш продаван обещал разобраться по поводу 307. Надеюсь на скорейшее разрешение ситуации.Как товар господа?
На этом этапе специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какие основные симптомы наблюдаются, и если имеются, то какие хронические заболевания могут влиять на течение терапии. Точный анализ этих данных позволяет сформировать персонализированную стратегию лечения, которая будет максимально адаптирована к состоянию пациента и его потребностям.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому ярославль.[/url]
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании на дому в твери[/url]
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
трансы новосибирск Трансы Новосибирск: За гранью обыденности, в поисках внутренней гармонии Новосибирск, город, в котором научные изыскания переплетаются с жаждой духовного поиска, предлагает погружение в мир транса – измененного состояния сознания, где реальность предстает в ином свете. Здесь, среди сибирских просторов, расцветает разнообразие практик, направленных на исследование глубин подсознания и поиск внутренней гармонии. От медитативных техник, дарующих умиротворение и осознанность, до гипнотических сеансов, открывающих двери к исцелению и трансформации, Новосибирск становится порталом в мир безграничных возможностей психики.
Современные онлайн казино — это уже не хаотичный набор сайтов, а сформированный рынок с понятными правилами и возможностью честного вывода денег. Пользователи выбирают площадки, где можно играть без лишнего риска, не сомневаясь в честности игр. Именно поэтому мы собрали лучшие онлайн казино на реальные деньги, чтобы вы могли сделать осознанный выбор без потери времени и средств. На первом этапе всегда стоит понимать, куда вы заходите и зачем, поэтому мы сразу открываем актуальные рейтинги и возможности [url=https://igrati-casino.online/]казино с выводом реальных денег на карту[/url] осознанно, а не наугад.
Онлайн казино — это специализированные сайты, где вы создаёте аккаунт, вносите депозит и играете в слоты, настольные игры или live-казино. Для пользователя ключевой интент прост: безопасность, стабильный вывод выигрыша и понятный интерфейс. Мы учитываем именно эти факторы и постоянно анализируем лучшие казино по лицензии, отзывам игроков, скорости выплат и прозрачности правил. В обзорах вы найдёте не рекламные обещания, а факты: насколько оперативна служба помощи, какие сроки выплат на практике и с какими лимитами сталкиваются игроки.
Наша команда целенаправленно исключает сомнительные казино и оставляет в рейтинге только казино, которые стабильно выводят выигрыш от 300 рублей на карту и другие популярные способы оплаты. Мы регулярно обновляем информацию, следим за изменениями условий и учитываем живые отзывы. Такой подход даёт объективную картину рынка и упрощает поиск надёжного казино без лишних рисков. Все обновляемые рейтинги и честные обзоры вы всегда можете найти на сайте igrati-casino.online — ориентируйтесь на них, чтобы найти площадку, где выигрыши реально выводятся.
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в саратове[/url]
Data-Leaks – The Largest Dark Web Leak Database Ever Built
Your leaked data is not gone — it’s being traded in telegram leaked database dumps, data leak github files, and countless leaks online. Data-Leaks uncovers them instantly.
Search 33B+ stolen passwords and 50M new leaks daily, including known passwords from breach dumps and discord data leak archives no one else tracks.
Run a free dark web check, detect credential reuse, and monitor personal information data breach risks — all in seconds.
Full access is just $2 — scan deeper, download verified leak data, and stay ahead of hackers.
Reveal the Truth: [url=https://Data-Leaks.org] Discord data leak[/url]
|
Для получения [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata11.ru/]помощь адвоката[/url] обратитесь к специалистам, которые готовы помочь в любых juridических вопросах.
Юридическая консультация является одним из наиболее важных этапов в процессе решения любых правовых вопросов . Это связано с тем, что правильная консультация может сэкономить время и ресурсы. Кроме того, юридическая консультация позволяет людям получить доступ к экспертным знаниям.
Юридические консультанты обладают большим опытом и знаниями . Они могут помочь людям разобраться в сложных юридических вопросах . Более того, юридические консультанты могут вести переговоры и заключать договоры .
## Раздел 2: Виды юридической консультации
Существует несколько видов юридической консультации . Это включает в себя консультацию по гражданским делам . Кроме того, юридическая консультация может быть дана по вопросам иммиграции. Также юридические консультанты могут иметь опыт работы с конкретными типами дел .
Юридическая консультация может быть оказана разными способами . Например, консультанты могут проводить личные встречи. Более того, юридические консультанты могут работать в частных компаниях .
## Раздел 3: Преимущества юридической консультации
Юридическая консультация может принести nhi?u пользы . Это связано с тем, что правильная консультация может сэкономить время и ресурсы . Кроме того, юридическая консультация может помочь людям чувствовать себя защищенными.
Юридическая консультация может предостеречь людей от принятия неправильных решений . Более того, юридические консультанты могут дать людям возможность получить экспертные знания . Также юридическая консультация может быть оказана в короткие сроки .
## Раздел 4: Заключение
Юридическая консультация является важнейшим компонентом современной жизни . Это связано с тем, что правильная консультация может улучшить качество жизни. Кроме того, юридическая консультация позволяет людям получить доступ к экспертным знаниям.
Юридические консультанты имеют глубокое понимание юридических аспектов. Они могут дать людям возможность получить юридическую помощь. Более того, юридические консультанты могут защищать права своих клиентов.
Переходи на официальный сайт компании : http://www.medtronik.ru/
Need an AI generator? Undress AI App The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my site thus i came to “return the favor”.I’m trying to find things to enhance my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи в твери[/url]
Особое внимание в клинике уделяется психологической реабилитации. Зависимость всегда сопряжена с внутренними конфликтами, нарушением привязанностей, проблемами самооценки. Врач-психотерапевт помогает пациенту выявить первопричины срывов, обучает техникам управления стрессом и прорабатывает модель трезвого поведения. В стационаре ведутся групповые и индивидуальные сессии, тренинги по навыкам саморегуляции, арт-терапия и элементы психодрамы. Реабилитационная команда помогает в адаптации к новой социальной роли, восстановлению отношений в семье и планированию жизни после выписки.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Ровный магаз,всем советую) Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш классный магазин, была впечатлянна скоростью доставки и качествомтовара)) всем писМеня на шалфее устраивает:)вываривать ничего не надо
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого в волгограде[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Connexion a 1xbet 1xbet apk
Метод лечения
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk/
Вывод из запоя в Тюмени — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к нарушению обмена веществ, обезвоживанию, сбоям в работе печени и сердца. В таких случаях требуется профессиональная помощь врача-нарколога, который подберёт оптимальный способ дезинтоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки. Современные методики позволяют провести вывод из запоя безопасно, эффективно и без осложнений.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen/
Диагностика в клинике «КузбассМед» проводится комплексно: используются лабораторные, инструментальные и психологические методы. Благодаря применению цифровых систем и алгоритмов обработки данных, результаты анализов доступны уже в течение первого часа. Оценка проводится по нескольким направлениям: токсикологический статус, состояние печени и почек, электролитный баланс, нейровегетативное состояние, когнитивные функции и уровень стресса. Это позволяет врачам составлять максимально точную картину заболевания и подбирать индивидуальные методы терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркология раменское московская московская область[/url]
Перед тем как показать примерные программы, важно подчеркнуть: реальный план всегда персонализируется, но понимание базовых форматов помогает семье и пациенту не теряться в терминах и сразу видеть логику.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом Если вы ищете бездепозитное казино за регистрацию, обращайте внимание на репутацию площадки, отзывы игроков и наличие лицензии. Это поможет выбрать надежное и честное казино для приятной и безопасной игры.
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника уфа[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре волгоград[/url]
“И если мои слова не подтвердяться Прошу провести профелоктическую беседу с вашим Дай бог ему здоровья Минером” https://uniontobacco.online Адекватным людям ценящих проффесианолизм рекомендую реактивы тут тарить…Есть, но пока что временно не работает.
Комплексный подход к выводу из запоя на дому в Ярославле включает несколько основных этапов, которые позволяют обеспечить оперативное и безопасное лечение:
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne/
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]платный нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
казино бонусы
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]займ без процентов[/url]
Программа лечения строится по принципу последовательного воздействия на физическое и психологическое состояние. Начинается она с детоксикации: инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов, антиоксидантов, гепатопротекторов и витаминов. Затем — стабилизация состояния, коррекция сна, восстановление когнитивных функций и купирование абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от диагноза используются такие методы, как заместительная терапия, нейрометаболическая поддержка, противотревожные и антидепрессивные схемы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru
трек получил в пятницу сегодня понедельник пока нет данных по треку возможно еще не вбился в систему думаю на днях ясно все будет отпишу Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Достойный, проверенный временем магазин!- За сколько?
игровые автоматы с бездепозитным бонусом
My brother recommended I might like this website. He was totally right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]бесплатное кодирование от алкоголизма в волгограде[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя волгоград[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]заказать обратный звонок наркологическая клиника[/url]
Такая комплексность обеспечивает воздействие на физические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/besplatnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-v-omske/
Для получения качественной и бесплатной юридической консультации обратитесь на [url=https://konsultaciya-advokata61.ru]бесплатная юридическая консультация москва[/url].
Консультацию квалифицированных адвокатов для решения правовых проблем гражданам и организациям. Это могут быть консультации по различным аспектам права . Все юристы, работающие на сайте, имеют обширный опыт работы и высшее юридическое образование в своей области, что гарантирует высокое качество предоставляемых услуг.
Консультация адвоката на этом сайте включает обсуждение деталей дела с адвокатом для наиболее эффективного решения проблемы .
## Раздел 2: Преимущества консультации адвоката
Это возможность обсудить проблему с квалифицированным адвокатом и получения эффективных стратегий для защиты своих прав. .
Стоит отметить, что Кроме того, все консультации адвоката на konsultaciya-advokata61.ru проходят в режиме, который клиент считает наиболее комфортным, что делает процесс максимально эффективным и комфортным для клиента.
## Раздел 3: Услуги, предлагаемые адвокатами
Адвокаты, сотрудничающие с konsultaciya-advokata61.ru, предоставляют разнообразные правовые услуги для удовлетворения различных потребностей своих клиентов .
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы цены[/url]
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в волгограде[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Не работает пока там представительство. https://goldmdma.shop я заказывау уже больше 2х лет только у этого магазина, сейчас заказал эфор и регу на подобия jv 100 сказали, посыль дошол от крыл а тпм только эфор а реги нет. может вы что то перепутали с заказом ребята ответь.Брал у него все гудд. Маскировка на высоте качество отличное. буду брать еще
Keep it up and keep attracting more players!
https://www.skymetweather.com/content/weather-news-and-analysis/how-to-use-the-sweet-bonanza-demo-to-improve-your-gameplay/
«ТверьМед» — частная лицензированная клиника, специализирующаяся на наркологической помощи любой степени сложности. Здесь работают неравнодушные врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты и психологи с многолетним стажем. Медицинская команда настроена на оперативную диагностику и проведение первичных мероприятий в течение первого часа после обращения. Упор сделан на доступность: клиника открыта 24/7, приём возможен как на территории медучреждения, так и на выезде — дома, в офисе, гостинице, санатории или любом удобном месте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Во время онлайн-сессии специалист может использовать шкалы оценки состояния (CIWA-Ar, CAGE, AUDIT), психодиагностические опросники, видеоанализ мимики и речи. Это позволяет провести достаточно точную первичную дифференцировку между алкогольной абстиненцией, тревожным расстройством, интоксикацией и психотическим состоянием. При необходимости пациенту предлагается записаться на очный приём или воспользоваться услугой «стационар на дому» — с ежедневными визитами и наблюдением.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в твери[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы в волгограде[/url]
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
http://jobboard.piasd.org/author/codecan6/
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Выяснить больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk/
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-marmansk/
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne
матрешка Матрешки: Символ русской души, воплощенный в дереве Матрешки – это не просто сувенир, это символ России, ее культуры и истории, воплощенный в ярких красках и лаконичной форме. Эта деревянная кукла, скрывающая в себе целое семейство меньших по размеру кукол, стала неотъемлемой частью русского народного искусства и пользуется огромной популярностью во всем мире.
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Туле разработана для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелыми последствиями злоупотребления алкоголем. Основная цель – оперативная детоксикация организма, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Врач нарколог проводит полный комплекс обследований и назначает персонализированный план лечения, включающий медикаментозную терапию и психологическую поддержку, что позволяет обеспечить стабильное восстановление организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзное заболевание, затрагивающее как физическое, так и психологическое состояние человека. При отсутствии своевременной наркологической помощи в клинике возможно ухудшение здоровья, развитие тяжелых осложнений и социальная деградация пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]центр наркологической помощи[/url]
и качество всегда на уровне)) Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш что же это за дела то…..?Ты еп сегодня зарегился и уже опробывал?
Во время онлайн-сессии специалист может использовать шкалы оценки состояния (CIWA-Ar, CAGE, AUDIT), психодиагностические опросники, видеоанализ мимики и речи. Это позволяет провести достаточно точную первичную дифференцировку между алкогольной абстиненцией, тревожным расстройством, интоксикацией и психотическим состоянием. При необходимости пациенту предлагается записаться на очный приём или воспользоваться услугой «стационар на дому» — с ежедневными визитами и наблюдением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь в твери[/url]
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно[/url]
Эффективность лечения во многом зависит от квалификации врачей, участвующих в процессе. В наркологической клинике должны работать не только врачи-наркологи, но и психиатры, клинические психологи, специалисты по аддиктивному поведению, а также координаторы по социальной адаптации. Слаженное взаимодействие этих специалистов — залог того, что лечение будет не только медицински обоснованным, но и глубоко проработанным в психологическом плане.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма анонимно[/url]
Hmm it seems like your website ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to everything. Do you have any helpful hints for first-time blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/[/url]
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk
https://fWebDirectory.com/588/posts/1/1/1953065.html
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач собирает краткий анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и оценивает степень интоксикации. Эта информация является фундаментом для разработки индивидуального плана терапии, который учитывает особенности состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]платная наркологическая скорая помощь в твери[/url]
Использование автоматизированных систем дозирования позволяет точно подобрать необходимое количество медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей дает возможность врачу корректировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени, что повышает безопасность и эффективность процедуры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя ярославская область[/url]
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма[/url]
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru
Основные направления включают:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому является необходимым мероприятием при возникновении тяжелых форм алкогольной интоксикации, когда самостоятельное прекращение употребления алкоголя становится невозможным. Если наблюдаются такие симптомы, как спутанность сознания, учащенный пульс, гипертония или снижение артериального давления, срочная помощь нарколога необходима для предотвращения серьезных осложнений. При раннем вмешательстве можно не только вывести токсины, но и стабилизировать работу жизненно важных органов, что существенно повышает шансы на полное восстановление.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ярославль[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в волгограде[/url]
Ador Verde Casino, nu vă opriți — conținut top!
http://fuku-info.com/?wptouch_switch=desktop&redirect=https://verde-casino-romania-gold.ro/cum-sa-joci
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
мало того что неприятный опыт общения в гоме так и не денег не товару.. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Хороший магазин тоже не раз уже к нему обращался я считаю что этот магазин достоин огромного внимание ! Мир тебе бро и процветания удачи в работе !:ok:;)ОБРАЩУСЬ ЕЩЕ К ТЕБЕ БРО ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО !) ЕЩЕ РАЗ УДАЧИА с какого дживика еще больше делать можно?
Для пациентов, нуждающихся в полном погружении в лечебный процесс, в клинике предусмотрен круглосуточный стационар. Палаты — индивидуальные и на два человека, оборудованы современной мебелью, кондиционерами и телевизорами. Организовано сбалансированное питание с возможностью коррекции по медицинским показаниям. Пациенты ежедневно проходят процедуры, сессии и получают консультации. В свободное время организуются арт-занятия, йога, дыхательные практики. Такой режим позволяет не только восстановить физическое здоровье, но и снизить уровень тревожности, вернуть интерес к жизни и стимулировать мотивацию к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании наркология[/url]
В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» применяются разные методы кодирования, позволяющие подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пациента. Выбор зависит от медицинских показаний, психологической готовности и длительности ремиссии. В таблице ниже представлены основные методики, их особенности и преимущества.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма адрес[/url]
https://LetsPostFree.com/588/posts/1/1/1933220.html
Link exchange is nothing else except it is simply placing the other person’s blog
link on your page at proper place and other person will also do
similar in support of you.
Moomoo証券ログイン
Метод лечения
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom
Действие и назначение
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-novosibirsk/
Ремонт мебели Ремонт плитки: Восстановление гармонии и эстетики
みんなの FX
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-yaroslavl/
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
Для оказания полноценной помощи вне стен клиники специалисты «ТверьМед» используют портативные устройства: инфузоматы, ЭКГ-мониторы, глюкометры, пульсоксиметры, небулайзеры и наборы медикаментов. Все врачи обучены работе в полевых условиях и готовы к экстренным ситуациям. Отдельное внимание уделяется стерильности и безопасности: используются одноразовые расходники, врач носит маску, перчатки и защитный халат. При необходимости на выезд направляется параллельно медсестра или ассистент с расширенным функционалом.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]центр наркологической помощи тверь[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]нарколог лечение алкоголизма в омске[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Подробнее тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в саратове[/url]
Получив достаточно быстро трек отправления, а в качестве курьерки продавцом была выбрана пони экспресс, я стал проверять бьется ли трек. День проверял, два проверял, три…..А он сука ни в какую не бьётся и все тут. Короче с того момента и до момента написания этого сообщения номер посылки на сайте курьерки – Отсутствует в базе данных, попробуйте повторить запрос позднее!!! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Менеджер прошу зайдите в скайп, хочу заказ оплатить вас там нет 2 дня уже. Заявку на сате подал жду ответ на эмаил. Спасибо.Большое спасибо от Сиборяка из Москвы, ваш магаз резко скрасил жизнь во время командировки в Москве.
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]запой нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма волгоград[/url]
Использование автоматизированных систем дозирования позволяет точно подобрать необходимое количество медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей дает возможность врачу корректировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени, что повышает безопасность и эффективность процедуры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в красноярске[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение больных наркоманией тверь[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Для оказания полноценной помощи вне стен клиники специалисты «ТверьМед» используют портативные устройства: инфузоматы, ЭКГ-мониторы, глюкометры, пульсоксиметры, небулайзеры и наборы медикаментов. Все врачи обучены работе в полевых условиях и готовы к экстренным ситуациям. Отдельное внимание уделяется стерильности и безопасности: используются одноразовые расходники, врач носит маску, перчатки и защитный халат. При необходимости на выезд направляется параллельно медсестра или ассистент с расширенным функционалом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]как происходит кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]skolko-stoit-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Здесь
[url=http://glassfactory.pro/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
I just could not leave your web site prior to suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info an individual provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back regularly to check out new posts
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tyumen-kruglosutochno/
В случаях запоя, острого отравления или абстинентного синдрома выездная наркологическая бригада оказывает помощь прямо на месте. Специалисты приезжают в течение 30 минут после обращения и проводят оценку состояния пациента, экстренное введение лекарств, инфузионную терапию и психологическую поддержку. Благодаря специальной комплектации мобильной бригады, лечение на дому возможно даже при умеренной степени осложнений. Врач также может при необходимости провести экспресс-анализы и дать рекомендации родственникам по дальнейшему уходу.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Сказали в понедельник всем кто оплатил заказ отправят НОМЕРА! https://amfetminsklad.store действительно было в лом,спасибо)Та не, не стоит оно того. Надо отдать должное магазину, посылка пришла, без проблем.
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/[/url]
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи[/url]
На этом этапе специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какие основные симптомы наблюдаются, и если имеются, то какие хронические заболевания могут влиять на течение терапии. Точный анализ этих данных позволяет сформировать персонализированную стратегию лечения, которая будет максимально адаптирована к состоянию пациента и его потребностям.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru
マネックス証券 ログイン画面
Наркологическая помощь в Волгограде предназначена для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Современный подход к лечению основан на сочетании медицинских, психологических и социальных методов, направленных на полное восстановление пациента. Врачи-наркологи применяют безопасные схемы детоксикации, эффективные медикаменты и программы психотерапевтической поддержки, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograd
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в омске[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo
Услуга
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
Главный город страны — это один из самых больших городов с уникальным прошлым.
Город органично соединяет памятники старины и динамичную застройку.
Здесь находятся ключевые организации и культурные учреждения.
Москва предлагает большой выбор для работы и саморазвития.
https://www.amino.dk/members/aqua7389/default.aspx
Город известен разнообразием транспорта.
Парки и общественные пространства создают баланс в ритме мегаполиса.
Каждый район обладает уникальную атмосферу.
В целом Москва остается притягательным городом для развития.
Современные реалии требуют от медицинских учреждений гибкости, скорости и чуткости. Наркологическая помощь — одна из сфер, где промедление может стоить человеку здоровья или жизни. В наркологической клинике «ТверьМед» разработаны оперативные механизмы реагирования: выезд врача по адресу в течение 30 минут, круглосуточная поддержка и возможность получения онлайн-консультации, не покидая дом. Такой подход позволяет вовремя оказать помощь, даже если пациент отказывается ехать в стационар или не осознаёт всю серьёзность своего состояния.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/narkolog-tver-anonimno/
Looking for a casino? 8mbets bd Slots, table games, and live casino all in one place. Quick login, convenient registration, modern providers, stable payouts, and comfortable player conditions.
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Playing at the casino? jwin7 Play online for real money. We offer a wide selection of slots, live dealers, fast payments, easy login, and exciting offers for new and returning players.
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Do you love gambling? jwin 7 Online is safe and convenient. We offer a wide selection of games, modern slots, a live casino, fast deposits and withdrawals, clear terms, and a stable website.
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Верно. Но это уже другой критерий – грамотное описание https://taekwondo-kornik.org Заказал 5 г. АМ как на неделе придёт за качество отпишу, тогда и подтвердятся или опровергнутся доводы людей за качество АМ-2233.Обязательно позвонить должны, как позвонят легче забрать самому чем ждать пока курьер доставит
Прежде чем перейти к ориентировочным цифрам, важно подчеркнуть: цена формируется из реальных компонентов помощи — работы врача и медсестры, объёма инфузионной терапии, перечня препаратов, времени выезда и необходимости более длительного наблюдения. Никаких скрытых доплат: все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее. Чем раньше вы обращаетесь, тем меньше объём вмешательств и, как правило, ниже итоговая стоимость — короткий эпизод проще и дешевле стабилизировать, чем «выводить» осложнения после затянутого запоя.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколога на дом щелково[/url]
Ремонт керамической поверхности Ремонт кожаной мебели Москва: Стиль и комфорт в каждой детали
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr/
Комплексный подход к выводу из запоя на дому в Ярославле включает несколько основных этапов, которые позволяют обеспечить оперативное и безопасное лечение:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Доступность услуги и оперативность реагирования гарантируют, что помощь будет оказана в течение 30–60 минут после вызова. Это позволяет не только быстро начать детоксикацию, но и минимизировать риск развития осложнений, таких как повреждение печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tula/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-stoimost-volgograd/
Наши врачи используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, индивидуально подбираемые для каждого пациента. В состав лечебного курса входят:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена новосибирск.[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom/
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их качество. Дружелюбная помощь – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы и находить ответы под требования вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
поставляемая продукция:
Проволока магниевая MgAl3Zn1 (Alloy 25) – ISO 3116 Полоса магниевая MgAl3Zn1 (Alloy 25) – ISO 3116 представляет собой высококачественный материал, который применяется в различных отраслях, включая авиацию и автомобилестроение. Этот сплав обеспечивает отличные механические свойства и коррозионную стойкость. Энергетическая эффективность и легкость в обработке делают его идеальным выбором для производителей. Если вы ищете надежный и прочный матреал, обратите внимание на Полоса магниевая MgAl3Zn1 (Alloy 25) – ISO 3116. Купить Полоса магниевая MgAl3Zn1 (Alloy 25) – ISO 3116 значит сделать шаг к качеству и долговечности. Не упустите возможность улучшить свои проекты с этим превосходным материалом.
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Для оказания полноценной помощи вне стен клиники специалисты «ТверьМед» используют портативные устройства: инфузоматы, ЭКГ-мониторы, глюкометры, пульсоксиметры, небулайзеры и наборы медикаментов. Все врачи обучены работе в полевых условиях и готовы к экстренным ситуациям. Отдельное внимание уделяется стерильности и безопасности: используются одноразовые расходники, врач носит маску, перчатки и защитный халат. При необходимости на выезд направляется параллельно медсестра или ассистент с расширенным функционалом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь в твери[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Услуга «нарколог на дом в Долгопрудном» от клиники «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» создана для ситуаций, когда важно действовать быстро, аккуратно и без лишнего шума. Запой, тяжёлое похмелье, срыв после ремиссии, злоупотребление медикаментами или смесью алкоголя с препаратами — всё это не терпит откладывания и самодеятельности. Вызов врача на дом позволяет получить профессиональную помощь без госпитализации, когда состояние пациента ещё позволяет лечить его в привычной обстановке. Нарколог приезжает с полностью укомплектованным набором препаратов и расходников, проводит осмотр, подбирает капельницы по клиническим показаниям, контролирует реакцию, даёт подробные рекомендации на ближайшие дни и при необходимости предлагает дальнейший маршрут: повторный выезд, амбулаторное наблюдение или стационар клиники. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго: без обсуждений с соседями, без регистрации по месту работы, без унизительных формальностей — только медицинская помощь, ориентированная на безопасность и результат.
Подробнее тут – http://
Hello .!
I came across a 152 useful platform that I think you should explore.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://nighthelper.com/how-to-start-van-life/]https://nighthelper.com/how-to-start-van-life/[/url]
Furthermore do not neglect, everyone, — a person constantly can in this publication discover answers for your most complicated inquiries. The authors made an effort to lay out all information using the most most understandable method.
Доступность услуги и оперативность реагирования гарантируют, что помощь будет оказана в течение 30–60 минут после вызова. Это позволяет не только быстро начать детоксикацию, но и минимизировать риск развития осложнений, таких как повреждение печени, почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в туле[/url]
みんなの外為
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]zakazat-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna[/url]
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов платиновое 50х25х4.5 мм ПлИ90-10 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
Я ж тебя хотел отпиарить. https://cpwma.org отличный сервис!Все Вась,извини..с утра заматался))
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]платная наркологическая скорая помощь[/url]
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It’s always useful to read through content from other writers and use something from their web sites.
Диагностика в клинике «КузбассМед» проводится комплексно: используются лабораторные, инструментальные и психологические методы. Благодаря применению цифровых систем и алгоритмов обработки данных, результаты анализов доступны уже в течение первого часа. Оценка проводится по нескольким направлениям: токсикологический статус, состояние печени и почек, электролитный баланс, нейровегетативное состояние, когнитивные функции и уровень стресса. Это позволяет врачам составлять максимально точную картину заболевания и подбирать индивидуальные методы терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь новокузнецк[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Продажа IQOS ILUMA https://ekb-terea.org и стиков TEREA в СПб. Только оригинальные устройства и стики, широкий ассортимент, оперативная доставка, самовывоз и поддержка клиентов на всех этапах покупки.
Купить IQOS ILUMA https://spb-terea.store и стики TEREA в Санкт-Петербурге с гарантией оригинальности. В наличии все модели ILUMA, широкий выбор вкусов TEREA, быстрая доставка по СПб, удобная оплата и консультации специалистов.
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому в твери[/url]
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ярославле[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Углубиться в тему – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]вызов наркологической помощи[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-narkotikov-v-tveri/
Алкогольная интоксикация и запой могут стремительно ухудшить состояние здоровья, став угрозой жизни, поэтому оперативное вмешательство имеет первостепенное значение. В Туле квалифицированные наркологи предоставляют круглосуточную помощь на дому, что позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и в комфортных условиях. Такой формат терапии гарантирует индивидуальный подход, всестороннюю поддержку и полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для пациентов, стремящихся восстановить своё здоровье без лишних стрессовых ситуаций.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-tula/
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в Новокузнецке представляет собой комплекс профессиональных медицинских мероприятий, направленных на диагностику, лечение и реабилитацию пациентов с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. В клинике «Альтернатива» помощь оказывается на всех этапах заболевания, что позволяет добиться стойких положительных результатов и восстановления качества жизни.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk
Да неее))) само то емс и почта россии !! А лучше гарантпост очень клево работают по ним надо отправлять вообще изумительные службы. Или первый класс! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Последние данные очков репутации:Уважаемый ТС, Прошу тогда разобраться как так произошло, что как вы говорите фейк-магазин в бросе подтвердил мне кодовое слово которое я писал вам в личку??????????????
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Одним из основных этапов вывода из запоя является медикаментозная детоксикация. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что обеспечивает быстрое снижение уровня алкоголя и токсинов в крови. Это позволяет восстановить нормальный обмен веществ и нормализовать работу жизненно важных органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце. Такой подход помогает не только стабилизировать состояние пациента, но и уменьшить риск развития осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя ярославская область[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в красноярске[/url]
IQOS ILUMA https://terea-iluma24.org и стики TEREA — покупка в Москве без риска. Гарантия подлинности, большой выбор, выгодные условия, доставка по городу и помощь в подборе устройства и стиков.
Использование автоматизированных систем дозирования позволяет точно подобрать необходимое количество медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей дает возможность врачу корректировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени, что повышает безопасность и эффективность процедуры.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ярославль[/url]
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-cena[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена волгоград[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в красноярске[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом в саратове[/url]
В процессе лечения используются проверенные методики, которые в комплексе обеспечивают положительный эффект и снижают риск рецидива.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Запой – это опасное состояние, при котором организм подвергается значительной токсической нагрузке, а длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов и ухудшению общего самочувствия. В Ярославле качественная наркологическая помощь на дому становится спасением для пациентов, нуждающихся в оперативной детоксикации и стабилизации состояния. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать терапию в комфортной обстановке, сохраняя конфиденциальность и минимизируя стресс, связанный с посещением стационара.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно ярославль[/url]
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen/
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno
Клиника в Красноярске придерживается комплексного подхода, при котором сочетаются медикаментозные и психотерапевтические методы. Такой подход позволяет воздействовать не только на физическую, но и на психологическую зависимость. Каждый пациент проходит детальное обследование, после чего врач-нарколог составляет индивидуальный план лечения с учётом стадии заболевания, состояния организма и наличия сопутствующих проблем со здоровьем.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Углубиться в тему – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс знакомства[/url]
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займ без процентов[/url]
Программа лечения строится по принципу последовательного воздействия на физическое и психологическое состояние. Начинается она с детоксикации: инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов, антиоксидантов, гепатопротекторов и витаминов. Затем — стабилизация состояния, коррекция сна, восстановление когнитивных функций и купирование абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от диагноза используются такие методы, как заместительная терапия, нейрометаболическая поддержка, противотревожные и антидепрессивные схемы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в рязани[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
Hi there, just wanted to mention, I liked this article. It was inspiring. Keep on posting!
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Промокод при регистрации в 1xbet сегодня. Этой акцией может воспользоваться каждый новый игрок при регистрации на сайте букмекера. Это ваше преимущество с начала. В форме регистрации есть необязательное поле для ввода кода. Как получить 1xbet promo code bonus codes на бесплатную ставку. В магазине xBonus можно обменять баллы на коды 1xbet kz: для ординаров, экспрессов или лотерей. Найти промокоды 1xbet можно в интернете. Представители БК часто публикуют их к праздникам или турнирам. Все актуальные промокоды 2026 доступны в официальном разделе сайта и могут быть обменяны на бонусные баллы.
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
cutty loli butt in a separate than разница of essence girls
https://is.gd/BlCAHo
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo
News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed
in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Appreciate it
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://showerdoorprices.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Okay, 1xslots – there are SO MANY slots! If you’re a slot fan, this is your place. I got a little lost at first with all the options, but once I figured it out, it was fun. Check them out here: 1xslots
Go88club, huh? Never tried it before. Any of you guys had any luck there? Thinking of giving it a whirl. Share your experiences! Maybe go88club could be our next hangout spot!
88online4 is on deck! I love how accessible the interface has being developed. Gonna make myself a cup of coffee and start winning! Come on, let’s explore 88online4 together!
по моему ты уже сам все расположил Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш вот такие как ты потом и пишут не прет , не узнавая концентрацию и т д набодяжат к…. ,я вот щас жду посыля и хз ко скольки делать 250Всем привет. Рега есть в наличии?
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]наркологическая клиника доктор[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в новокузнецке[/url]
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]платная наркологическая скорая помощь[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Эффективность лечения во многом зависит от квалификации врачей, участвующих в процессе. В наркологической клинике должны работать не только врачи-наркологи, но и психиатры, клинические психологи, специалисты по аддиктивному поведению, а также координаторы по социальной адаптации. Слаженное взаимодействие этих специалистов — залог того, что лечение будет не только медицински обоснованным, но и глубоко проработанным в психологическом плане.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ярославль[/url]
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Выездной наркологический сервис «МедПоволжье Клиник» создан для случаев, когда важны скорость, тишина и клиническая точность. Мы проводим детоксикацию и снятие интоксикации на дому так, чтобы каждое действие имело цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно переоценки». Вместо «сильной капельницы на всякий случай» — модульная схема: один симптом-кластер > один медицинский модуль > одна поведенческая опора (свет, звук, вода малыми глотками, дыхание 4–6). Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, ускоряет стабилизацию и позволяет видеть прогресс буквально по часам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/[/url]
Острый запой — это нарушение работы сердца, мозга, печени и нервной системы, а не просто «лишние пару дней выпивки». Когда начинается тремор, потливость, скачки давления, бессонница, паника, семья часто пытается помочь самостоятельно: даёт случайные таблетки, сомнительные «антипохмельные коктейли», сильные седативные. В реальности такие меры нередко ухудшают ситуацию: давление падает или «скачет», дыхание угнетается, симптомы предделирия маскируются, и момент, когда нужна экстренная помощь, пропускается. Выездной нарколог «ЩёлковоМед Профи» в Щёлково работает иначе: ещё по телефону собираются ключевые данные — возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, аллергии, примерные показатели АД и пульса, особенности поведения. Это позволяет заранее оценить риски и понять, подходит ли формат на дому. На месте врач измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, неврологический статус, наличие дезориентации, смотрит, не требуется ли сразу стационар. Капельница назначается по фактическим показателям: без «универсальных коктейлей», без опасной седации, с учётом сердца, печени, эндокринных и неврологических особенностей. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм и делает результат управляемым — облегчение наступает без лишнего риска.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому волгоград[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в Волгограде предназначена для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Современный подход к лечению основан на сочетании медицинских, психологических и социальных методов, направленных на полное восстановление пациента. Врачи-наркологи применяют безопасные схемы детоксикации, эффективные медикаменты и программы психотерапевтической поддержки, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Туле разработана для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелыми последствиями злоупотребления алкоголем. Основная цель – оперативная детоксикация организма, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Врач нарколог проводит полный комплекс обследований и назначает персонализированный план лечения, включающий медикаментозную терапию и психологическую поддержку, что позволяет обеспечить стабильное восстановление организма.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu tula[/url]
[url=https://hello-jobs.com/includes/pgs/?melbet_promo_code_get_bonus.html]melbet new promo code[/url]
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped
me. Kudos!
ОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Описывать,тем кто не пробовал-бесполезно.Все равно не поймут.Придумывают всякую фигню(аааа,у тя за спиной собакака!и пр. бред),пытаются посмеяться,но это ж всё не то и близко не стояло.Как слепому объяснить,как все выглядит)[/hide]хороший магазин,всё на красоте и качество и кол-во:) продолжайте в том же духе
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр в омске[/url]
Выездной наркологический сервис «МедПоволжье Клиник» создан для случаев, когда важны скорость, тишина и клиническая точность. Мы проводим детоксикацию и снятие интоксикации на дому так, чтобы каждое действие имело цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно переоценки». Вместо «сильной капельницы на всякий случай» — модульная схема: один симптом-кластер > один медицинский модуль > одна поведенческая опора (свет, звук, вода малыми глотками, дыхание 4–6). Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, ускоряет стабилизацию и позволяет видеть прогресс буквально по часам.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзное заболевание, затрагивающее как физическое, так и психологическое состояние человека. При отсутствии своевременной наркологической помощи в клинике возможно ухудшение здоровья, развитие тяжелых осложнений и социальная деградация пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Детальнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в тюмени[/url]
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займы до зарплаты[/url]
В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» применяются разные методы кодирования, позволяющие подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пациента. Выбор зависит от медицинских показаний, психологической готовности и длительности ремиссии. В таблице ниже представлены основные методики, их особенности и преимущества.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в уфе[/url]
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в мурманске[/url]
Программа лечения строится по принципу последовательного воздействия на физическое и психологическое состояние. Начинается она с детоксикации: инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов, антиоксидантов, гепатопротекторов и витаминов. Затем — стабилизация состояния, коррекция сна, восстановление когнитивных функций и купирование абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от диагноза используются такие методы, как заместительная терапия, нейрометаболическая поддержка, противотревожные и антидепрессивные схемы.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]эротические фильмы[/url]
Thanks for some other informative blog. The place else may just I get that kind of information written in such a perfect means? I’ve a challenge that I am simply now running on, and I’ve been on the glance out for such information.
Комплексный подход к выводу из запоя на дому в Ярославле включает несколько основных этапов, которые позволяют обеспечить оперативное и безопасное лечение:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя ярославль[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/krasnoyarsk-narkologicheskij-czentr/
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon
[url=https://hokoon.edu.hk/wp-content/pgs/?melbet_bookmaker_promo_code.html]melbet promo code check[/url]
отличный магазин! обращаюсь уже не первый месяц Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа?Мне пока ещё не пришло, но ты уже напугал….:orientation: кто знает где весы купить можно чтоб граммы вешать
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]ehkstrennyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно серпухов[/url]
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
После прохождения основной программы пациенту предлагается поддерживающее наблюдение. Оно может включать дистанционные консультации, участие в группе профилактики срывов, повторные осмотры нарколога и психолога, корректировку медикаментозной схемы. В рамках реабилитации формируются планы действий при возникновении тяги, обучаются навыки сопротивления стрессу и внешнему давлению. При желании можно подключить родственников к процессу постлечебной адаптации, чтобы укрепить результат и снизить риски рецидивов. Таким образом, пациент не остаётся один даже после выписки.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании в стационаре новокузнецк[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника рязань[/url]
Мы проверяем не «ощущения», а факты: частоту пульса в покое, вариабельность ритма к сумеркам, переносимость тёплой воды малыми глотками, минуты до сна и количество ночных пробуждений. Эти короткие метки позволяют тонко управлять темпом инфузии, очередностью модулей и «тихими» ритуалами вечернего времени без необоснованного усиления препаратов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в саратове[/url]
Как отмечает руководитель клинико-диагностического отдела ФГБУ «Национальный центр наркологии», «участие в терапии нескольких специалистов разных направлений позволяет учитывать не только симптомы, но и глубинные причины зависимости». Именно такой подход снижает риск рецидивов и повышает эффективность лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Во время онлайн-сессии специалист может использовать шкалы оценки состояния (CIWA-Ar, CAGE, AUDIT), психодиагностические опросники, видеоанализ мимики и речи. Это позволяет провести достаточно точную первичную дифференцировку между алкогольной абстиненцией, тревожным расстройством, интоксикацией и психотическим состоянием. При необходимости пациенту предлагается записаться на очный приём или воспользоваться услугой «стационар на дому» — с ежедневными визитами и наблюдением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd
Наркозависимость — это не просто вредная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного и последовательного лечения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» в Новокузнецке разработаны персонализированные программы помощи, учитывающие медицинские, психологические и социальные аспекты проблемы. Каждому пациенту подбирается уникальный маршрут восстановления, начиная с первичной диагностики и заканчивая адаптацией к жизни без наркотиков. Поддержка оказывается круглосуточно, с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности. Психотерапевты и врачи работают в тесной связке, чтобы не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить личность пациента, вернуть ему мотивацию к жизни и уверенность в будущем.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании клиника[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-srochno[/url]
We stumbled over here by a different page and thought I might
check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you.
Look forward to looking into your web page for a second time.
Перед цифрами важно подчеркнуть: прайс «Трезвый Центр Коломна» строится вокруг реального объёма помощи, а не вокруг рекламных обещаний. Цена зависит от тяжести состояния, длительности запоя, количества инфузий, необходимого набора препаратов, формата (дом или стационар), времени суток выезда, длительности наблюдения. Все дополнительные назначения согласуются заранее — без скрытых доплат и неожиданных строк. Это позволяет семье планировать расходы и сосредоточиться на безопасности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Практический тест прост: сохранённый контакт, контролируемый тремор, эпизодическая (не неукротимая) рвота, нет грубой дезориентации, давление и пульс не «скачут», в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и доступ к воде — тогда дом уместен. Если хотя бы два пункта «провисают», отделение в Электростали даст предсказуемость и защиту от ночных ухудшений, которые дома часто остаются незамеченными.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal[/url]
Комплексная наркологическая помощь объединяет несколько направлений, каждое из которых решает отдельную задачу восстановления организма и психики. Врачи используют индивидуальные схемы терапии, подбирая оптимальные препараты и психологические методики.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkolog-psikholog-volgograd/
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где пациенту оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это учреждение, где формируется стратегия полного восстановления, включающая не только физическое оздоровление, но и психоэмоциональную стабилизацию. В Ярославле работают как частные, так и государственные клиники, однако их подходы, уровень сервиса и состав команд могут существенно различаться. По данным Минздрава РФ, высокий процент успешных исходов наблюдается в тех учреждениях, где реализуется персонализированная модель лечения и постлечебной поддержки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-i-alkogolizma-yaroslavl
второй раз заказываю, класнный продукт пришел что 250 что 307 , качество отменное , доставка буквально 3 суток https://mefedron-shops.store Как магазин порядочныйНу во-первых мы совершенно другой магазин, так что вы ошиблись веткой, и представительств в тех городах у нас нет
Процесс детоксикации состоит из нескольких последовательных шагов, направленных на безопасное очищение организма. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием этапов, которые применяются в клинике «Трезвая Линия Волгоград».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
сериал языке смотреть онлайн zfilm новинки кино онлайн
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому волгоград[/url]
В Волгограде сформирована система оказания наркологической помощи, включающая круглосуточные выезды специалистов, амбулаторное лечение, стационарные программы и реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет охватить все категории пациентов — от тех, кто нуждается в экстренной помощи, до тех, кто готов пройти полный курс терапии. Независимо от формы оказания услуг, лечение проводится конфиденциально и в соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde/
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом саратов[/url]
сервисы онлайн рассылок сервис для емейл рассылок по большой базе
задвижка 30с41нж ду80 ру16 30с41нж задвижка
みんなのFX
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
В клинике «Альтернатива» применяются современные методы терапии, включающие медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]оказание наркологической помощи новокузнецк[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]лечение COVID народными средствами[/url]
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании наркология[/url]
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма в омске[/url]
May I just say what a relief to discover someone that genuinely understands what they’re discussing on the internet. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people really need to look at this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised you aren’t more popular given that you most certainly have the gift.
Саратов живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, протяжные магистрали, мостовые переезды. Мы учитываем это в логистике: выездные бригады «СаратовМед Профи» движутся по немаркированным маршрутам, приезжают в гражданской одежде, формируют на месте «тихую сцену» и только затем начинают клиническую часть. Если на предзвонке звучат «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность, неукротимая рвота, судороги — организуем перевод в стационар без пауз: место резервируем заранее, передислокация проходит конфиденциально.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в саратове[/url]
Работала с данным магазином давным давно! Пожалуй самый лучший) https://republique-dominicaine-live.online Продован 1000 балоф те =)магазин на самом деле чёткий)начал с ним работать не пожалел!!!!!и качество и количество и скорость-всё на высоте!!!
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru
На этом этапе специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какие основные симптомы наблюдаются, и если имеются, то какие хронические заболевания могут влиять на течение терапии. Точный анализ этих данных позволяет сформировать персонализированную стратегию лечения, которая будет максимально адаптирована к состоянию пациента и его потребностям.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-yaroslavl
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в мурманске[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов в волгограде[/url]
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Первый шаг в лечении — это тщательный осмотр специалиста. Наряду с измерением жизненно важных показателей (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) врач проводит сбор анамнеза, выясняя длительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Эти данные помогают оценить степень интоксикации и подобрать индивидуальный план терапии, что является ключевым для дальнейшей эффективной детоксикации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в ярославле[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения детального первичного осмотра. Врач собирает краткий анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и оценивает степень интоксикации. Эта информация является фундаментом для разработки индивидуального плана терапии, который учитывает особенности состояния пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika tula[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]деньги в долг[/url]
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan/
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог новокузнецк[/url]
Даже при наличии комфортных условий и современных медикаментов эффективность будет минимальной, если пациент не получает психологическую помощь. У многих зависимость сопровождается тревожными или депрессивными состояниями, травматическим опытом или сложными семейными отношениями. Без проработки этих аспектов высокий риск того, что после выписки произойдёт рецидив.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
В Волгограде сформирована система оказания наркологической помощи, включающая круглосуточные выезды специалистов, амбулаторное лечение, стационарные программы и реабилитацию. Такой подход позволяет охватить все категории пациентов — от тех, кто нуждается в экстренной помощи, до тех, кто готов пройти полный курс терапии. Независимо от формы оказания услуг, лечение проводится конфиденциально и в соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Клад был сделано на 5, инфу по кладу дали на 5. В общем очень доволен данным магазином, по качеству товара, отпишу позже! Заказывал здесь 1-ый раз, заливал бабки без гаранта, так что спокойно работайте без гаранта! Спасибо еще раз, продолжайте в том же духе, будем работать!!! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш раньше и хуй крепче был и бабы красивейдлица окола часа очень даже не плохо
Острый запой — это нарушение работы сердца, мозга, печени и нервной системы, а не просто «лишние пару дней выпивки». Когда начинается тремор, потливость, скачки давления, бессонница, паника, семья часто пытается помочь самостоятельно: даёт случайные таблетки, сомнительные «антипохмельные коктейли», сильные седативные. В реальности такие меры нередко ухудшают ситуацию: давление падает или «скачет», дыхание угнетается, симптомы предделирия маскируются, и момент, когда нужна экстренная помощь, пропускается. Выездной нарколог «ЩёлковоМед Профи» в Щёлково работает иначе: ещё по телефону собираются ключевые данные — возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, аллергии, примерные показатели АД и пульса, особенности поведения. Это позволяет заранее оценить риски и понять, подходит ли формат на дому. На месте врач измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, неврологический статус, наличие дезориентации, смотрит, не требуется ли сразу стационар. Капельница назначается по фактическим показателям: без «универсальных коктейлей», без опасной седации, с учётом сердца, печени, эндокринных и неврологических особенностей. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм и делает результат управляемым — облегчение наступает без лишнего риска.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo/
В процессе лечения используются проверенные методики, которые в комплексе обеспечивают положительный эффект и снижают риск рецидива.
Детальнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-i-alkogolizma-v-omske/
Для оказания полноценной помощи вне стен клиники специалисты «ТверьМед» используют портативные устройства: инфузоматы, ЭКГ-мониторы, глюкометры, пульсоксиметры, небулайзеры и наборы медикаментов. Все врачи обучены работе в полевых условиях и готовы к экстренным ситуациям. Отдельное внимание уделяется стерильности и безопасности: используются одноразовые расходники, врач носит маску, перчатки и защитный халат. При необходимости на выезд направляется параллельно медсестра или ассистент с расширенным функционалом.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/narkolog-tver-anonimno
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Получить больше информации – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Вывод из запоя — это экстренная медицинская помощь, направленная на очищение организма от алкоголя, снятие симптомов интоксикации и восстановление работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвая Линия Волгоград» используется комплексный подход, включающий капельницы, препараты для детоксикации и постоянный врачебный контроль. Лечение проводится анонимно, с индивидуальным подбором медикаментов и поддержкой пациента на каждом этапе восстановления. Главная цель специалистов — не просто стабилизировать состояние, а обеспечить безопасное возвращение к нормальному самочувствию и предотвратить повторные срывы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в волгограде[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]ставки на спорт[/url]
Выбор клиники — задача не только медицинская, но и стратегическая. Учитывать нужно не только наличие лицензии, но и содержание программ, их гибкость, участие родственников в процессе, а также прозрачность взаимодействия с пациентом. Именно эти аспекты позволяют отличить профессиональное учреждение от формального.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl
Алкогольная интоксикация и запой могут стремительно ухудшить состояние здоровья, став угрозой жизни, поэтому оперативное вмешательство имеет первостепенное значение. В Туле квалифицированные наркологи предоставляют круглосуточную помощь на дому, что позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и в комфортных условиях. Такой формат терапии гарантирует индивидуальный подход, всестороннюю поддержку и полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для пациентов, стремящихся восстановить своё здоровье без лишних стрессовых ситуаций.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-tula/
Telegram kanal?n? guclendir Telegram Kanal?n? Guclendir: Markan?z?n Itibar?n? Art?r?n Telegram kanal?n? guclendirmek, markan?z?n itibar?n? art?rman?n etkili bir yoludur. Yuksek etkilesim oranlar?na sahip bir kanal, potansiyel musterileriniz nezdinde guvenilirlik olusturman?za yard?mc? olur. Bu da, uzun vadede sat?slar?n?z? ve marka sadakatini art?rabilir.
мужской массаж краснодар Мужской массаж в Краснодаре – это не только способ расслабиться и избавиться от стресса, но и возможность укрепить свое физическое и ментальное здоровье. Регулярные сеансы массажа помогают улучшить потенцию, повысить уровень тестостерона, снять напряжение в мышцах и суставах, а также улучшить общее самочувствие. Выбирая мужской массаж в Краснодаре, вы инвестируете в свое здоровье, энергию и уверенность в себе.
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в тюмени[/url]
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograd
This is very interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger.
I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking
more of your fantastic post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
Одним из ключевых преимуществ «КузбассМед» является современная материально-техническая база. В клинике задействованы устройства для точного мониторинга жизненных функций, автоматические инфузионные системы, экспресс-диагностические модули и оборудование для неотложной терапии. Врачи используют программируемые дозаторы, портативные анализаторы крови и аппараты для оценки дыхательной функции, что позволяет своевременно корректировать тактику лечения без потерь времени. Все процедуры соответствуют национальным стандартам безопасности и рекомендациям ВОЗ.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в новокузнецке[/url]
I like what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the terrific works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll.
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
Для понимания ключевых компонентов лечения ниже представлена таблица, в которой систематизированы основные методы и их назначение.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании клиника[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в стационаре в омске[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]блекджек[/url]
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Одним из основных этапов вывода из запоя является медикаментозная детоксикация. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что обеспечивает быстрое снижение уровня алкоголя и токсинов в крови. Это позволяет восстановить нормальный обмен веществ и нормализовать работу жизненно важных органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце. Такой подход помогает не только стабилизировать состояние пациента, но и уменьшить риск развития осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-yaroslavl/
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в рязани[/url]
http://vaiu.ru/images/pages/index.php?1xbet_promokod_na_besplatnuu_stavku.html
Важной частью реабилитации является социализация пациента, возвращение его к активной общественной жизни и формирование новых, здоровых привычек. Для этого в клинике организуются различные мероприятия и программы адаптации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]центр анонимного лечения наркомании тверь[/url]
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-marmansk
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого волгоград[/url]
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Пиздатый магаз ) Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Так может он в городе закладкой бралотличный сервис, качество порадовало:)
Zahnprobleme? https://www.zahnarzte-montenegro.com Diagnostik, Kariesbehandlung, Implantate, Zahnaufhellung und Prophylaxe. Wir bieten Ihnen einen angenehmen Termin, sichere Materialien, moderne Technologie und kummern uns um die Gesundheit Ihres Lachelns.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
агенство по управлению репутацией Репутолог — специалист, который занимается управлением репутацией в интернете, в том числе на геосервисах, таких как Яндекс Карты, 2ГИС, Google Maps. Особая роль геосервисов: Яндекс Карты, 2ГИС, Google Maps. В арсенале репутолога особое место занимают геосервисы. Для многих потребителей именно эти платформы становятся первым источником информации о локальном бизнесе. Представьте: человек ищет ближайшую кофейню, автосервис или салон красоты. Первое, что он видит – это карточка компании на Яндекс Картах, 2ГИС или Google Maps. И именно там он обратит внимание на рейтинг, количество отзывов и их содержание.
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne
Hello team!
I came across a 152 interesting website that I think you should check out.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://thefinalmatrix.com/why-you-should-spend-more-time-outdoors/]https://thefinalmatrix.com/why-you-should-spend-more-time-outdoors/[/url]
And do not forget, folks, that one constantly can within this particular publication find solutions to address your the absolute confusing questions. The authors attempted to explain the complete information via the very easy-to-grasp method.
Really no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of after that its up
to other people that they will assist, so here it occurs.
Тем, кто нуждается в длительной терапии, «КузбассМед» предлагает комфортные условия стационара с круглосуточным наблюдением. Здесь пациенты размещаются в индивидуальных палатах, проходят курсы терапии, реабилитации и психокоррекции. Обстановка в клинике напоминает оздоровительный центр: мягкое освещение, тишина, доступ к библиотеке, возможность общения с психологом и ежедневное участие в восстановительных мероприятиях. Медицинские сестры и врачи находятся на дежурстве 24/7, что позволяет немедленно реагировать на любые изменения в состоянии пациента.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займы до зарплаты[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Метод употребления – интерназально https://boshkistash.shop Заказал 5 г. АМ как на неделе придёт за качество отпишу, тогда и подтвердятся или опровергнутся доводы людей за качество АМ-2233.Продолжаем работать, в этот раз чуть больше берем 🙂 очень хорошие скидки дает постоянным клиентам обращаетесь !!
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому тюмень[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon[/url]
Great article.
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена адреса[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd/
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]слоты на деньги[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr/
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Одним из ключевых преимуществ «КузбассМед» является современная материально-техническая база. В клинике задействованы устройства для точного мониторинга жизненных функций, автоматические инфузионные системы, экспресс-диагностические модули и оборудование для неотложной терапии. Врачи используют программируемые дозаторы, портативные анализаторы крови и аппараты для оценки дыхательной функции, что позволяет своевременно корректировать тактику лечения без потерь времени. Все процедуры соответствуют национальным стандартам безопасности и рекомендациям ВОЗ.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
мужской массаж краснодар Массаж мужчине Краснодар: Индивидуальный подход и профессионализм Мужской массаж в Краснодаре – это специализированная услуга, учитывающая особенности мужской физиологии и психологии. Квалифицированный массажист подберет оптимальную технику и интенсивность воздействия, чтобы максимально эффективно решить поставленные задачи: снятие напряжения, улучшение кровообращения, восстановление после физических нагрузок или просто релаксация. Важно найти мастера, которому можно доверять, и который обладает необходимыми знаниями и опытом.
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/klinika-lechenie-narkomanii-v-tveri/
Одним из ключевых преимуществ «КузбассМед» является современная материально-техническая база. В клинике задействованы устройства для точного мониторинга жизненных функций, автоматические инфузионные системы, экспресс-диагностические модули и оборудование для неотложной терапии. Врачи используют программируемые дозаторы, портативные анализаторы крови и аппараты для оценки дыхательной функции, что позволяет своевременно корректировать тактику лечения без потерь времени. Все процедуры соответствуют национальным стандартам безопасности и рекомендациям ВОЗ.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/
какой выход с 1г ? https://republique-dominicaine-live.online Ну чтож ребят сегодня заказал )Пришёл 307. Попробывал 1 к 20, ниочём.. Курнул кропаль чистого, также ниочём…хз в чём дело. Сегодня попробую 1к10 можт чтот почуствую
https://pamyatniki-granitnye.by/
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза детоксикации, во время которой современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом. Этот этап помогает быстро снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови, восстановить нормальные обменные процессы и нормализовать работу внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tula/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru
памятники в минске из гранита
«Трезвый Путь Коломна» создаёт единый контур помощи: пациент не «перекидывается» между разными организациями, а проходит лечение в одной системе, где специалисты знают его историю и несут ответственность за последовательность шагов. Это критично для тех, кто уже сталкивался с бессистемными попытками: один врач ставил капельницы, другой «кодировал», третий давал советы, а в итоге всё заканчивалось новым срывом. Здесь маршруты связываются в цельную линию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому саратов[/url]
Перед тем как показать примерные программы, важно подчеркнуть: реальный план всегда персонализируется, но понимание базовых форматов помогает семье и пациенту не теряться в терминах и сразу видеть логику.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в саратове[/url]
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali
новый запрет вступает через 7 дней. читай список бро,там это вещество есть) https://boshkikypits.store ОПЕРАТОР ОКАЗАЛСЯ ОЧЕНЬ ОТЗЫВЧИВЫЙ! расскажет все что касается его товара! говорит очень вежливо, не чего лишнего! даже когда я засыпал его кучей всяких вопросов он меня не игнорил а старался ответить на все что я его спрашивал!Я подозреваю, что его посылку спалили на наличие и теперь просто не отправляют.
Программа лечения строится по принципу последовательного воздействия на физическое и психологическое состояние. Начинается она с детоксикации: инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов, антиоксидантов, гепатопротекторов и витаминов. Затем — стабилизация состояния, коррекция сна, восстановление когнитивных функций и купирование абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от диагноза используются такие методы, как заместительная терапия, нейрометаболическая поддержка, противотревожные и антидепрессивные схемы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Лечение наркомании в Твери представляет собой сложный и многоэтапный процесс, направленный на полное восстановление здоровья и социальной адаптации пациентов, страдающих от зависимости. В наркологической клинике «Ренессанс» применяется комплексный подход, который учитывает как физиологические, так и психологические аспекты заболевания, что обеспечивает максимальную эффективность терапии.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании диспансер в твери[/url]
I used to be recommended this website through my cousin. I am no longer positive whether or not this post is written by him as nobody else recognise such unique approximately my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/ufa-narkolog-psikhiatr/
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]заказать обратный звонок наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм рязань[/url]
Бронежилет на СВО – контракт на 2026 год и новые требования к защите
Подробное описание услуги доступно по ссылке: https://vc.ru/1655314
Здесь
[url=https://amberglasscorp.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Ам 1к15 сделал,слабоват получился,приходится забивать больше(я нормально прикуренный просто,JWH 250,203 1к5 курил обычно последнее время):(,а вот 2с-р ухлестал,не мог понять,где я,в реальности или во сне:crazy: Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Какие обещания? если выходной, скорей всего СПРС в базу не завело твой трек, жди понедельника…Надеюсь. Очень жду! Кто уже попробовал скажите как вещество?! Не хуже чем было?
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://blog.ankerherz.de/sandbar-anna-maria-png/?unapproved=1785946&moderation-hash=e4f097b388617ab16ffa87cdee74d82c#comment-1785946]https://blog.ankerherz.de/sandbar-anna-maria-png/?unapproved=1785946&moderation-hash=e4f097b388617ab16ffa87cdee74d82c#comment-1785946[/url]
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Лента никелевая 0.22х170 мм НП2Э ГОСТ 2170-73 Познакомьтесь с высококачественной никелевой лентой от Редметсплав.рф. Широкий выбор размеров и толщин. Прочность, устойчивость к высоким температурам. Применение в различных отраслях. Идеально подходит для электротехники, химической промышленности и медицинской техники.
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дому[/url]
смотреть сериалы онлайн дорамы смотреть онлайн
Need an AI generator? Undress AI Tool The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
Каждый компонент капельницы подбирается по медицинским показаниям. Врач учитывает возраст, хронические заболевания, степень обезвоживания и чувствительность к препаратам. Такой индивидуальный подход обеспечивает эффективность лечения и исключает осложнения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре волгоград[/url]
Капельница при интоксикации помогает быстро очистить организм от продуктов распада алкоголя, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие. В состав раствора входят препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ и поддерживающие работу печени и сердечно-сосудистой системы. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает значительное облегчение. Подбор лекарственных средств осуществляется строго индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и общего состояния здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод уфа[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого волгоград[/url]
упаковка – неплохо, но не идеально. Особенно глупо, когда в описании отправления пишут “Косметика”, а там, бл*ть, пачка сигарет. Оочень странно на меня смотрели в офисе спсра, знаете ли. 4/5 https://mdma-market.shop ОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!!Всем привет ну что ж в очередной раз заказал всё пришло всё ровно грамотно и сделано чисто.
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen/
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologiya-gorod-novokuzneczk/https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]частная наркологическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly.
I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show
the same outcome.
Как отмечает руководитель клинико-диагностического отдела ФГБУ «Национальный центр наркологии», «участие в терапии нескольких специалистов разных направлений позволяет учитывать не только симптомы, но и глубинные причины зависимости». Именно такой подход снижает риск рецидивов и повышает эффективность лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Howdy would you mind stating which blog platform you’re working with? I’m looking to start my own blog soon but I’m having a difficult time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design and style seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S Sorry for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто учреждение для экстренной помощи, а центр комплексной поддержки человека, столкнувшегося с зависимостью. В «КузбассМед» в Новокузнецке реализуется модель интенсивного вмешательства, где используются новейшие медицинские технологии, мультидисциплинарный подход и мобильные выездные службы. Специалисты готовы прибыть на дом за 30 минут с полным набором оборудования и медикаментов, обеспечив пациенту помощь в привычной и безопасной среде. Наркология здесь строится на индивидуализации: каждый случай рассматривается отдельно, с учётом психофизического состояния, анамнеза и жизненного контекста пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в новокузнецке[/url]
Запой, интоксикация? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске для быстрой и анонимной помощи. На дому: осмотр, подбор лечения, капельница для вывода токсинов и улучшение самочувствия. «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная наркологическая помощь на дому с гарантией анонимности. Не справляетесь с зависимостью сами? Вызовите нарколога на дом. Васильев подчеркивает: «Оперативная помощь – ключ к выздоровлению при отравлении алкоголем».
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-irkutsk
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
до 08.01 включительно выходные дни Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш итоги:Кто у Чемикала в последнее время брал ОПТ ( от 1 КГ и более) !!! Все ОК?????? ОПТ давно кто получал???? Задержки были…..?????
I’ve noticed recently that the web gaming market is becoming really packed, yet discovering an operator that truly mixes
fun with real trust is quite a task. From what I’ve
seen, many folks center only upon the flashy visuals, while the stability really is what
honestly matters long-term. For example, I was reading about the highflybet
access casino high fly bet where the system appears
to be way more fluid than the stuff I have encountered at competitor brands recently.
Another observation ready to be mentioned is that the highflybet casino games catalog actually appeals to each low bet users and heavy
high rollers without the usual frustrating delays.
Do you really feel whether the highflybet bonus
is a biggest factor to join, or is the highflybet live casino interaction become the actual attraction these days?
I’d be keen to find out the community’s takes on their
payout speed too. We should start a debate moving! https://vyaparappsurat.store/highflybet-insights-deep-dive-into-games-bonuses-and-security/
https://vc.ru/1516084, Рейтинг 25 лучших сервисов для накрутки просмотров в Инстаграм бесплатно (актуально на 2026)
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в уфе[/url]
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the issues.
It was definitely informative. Your website is very
useful. Thank you for sharing!
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы волгоград[/url]
Во многих случаях пациент или его родственники не решаются сразу вызвать врача. Для таких ситуаций предусмотрена услуга онлайн-консультации. Она проводится через защищённую видеосвязь, при желании — анонимно. На связи — врач-нарколог или психиатр, который отвечает на вопросы, оценивает ситуацию по визуальным и вербальным признакам, рекомендует план действий. Консультация может стать отправной точкой для дальнейшего вызова врача на дом или записи в клинику. Это особенно удобно для родственников, которые не знают, как подступиться к проблеме и убедить человека в необходимости помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь тверь[/url]
«ТверьМед» — частная лицензированная клиника, специализирующаяся на наркологической помощи любой степени сложности. Здесь работают неравнодушные врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты и психологи с многолетним стажем. Медицинская команда настроена на оперативную диагностику и проведение первичных мероприятий в течение первого часа после обращения. Упор сделан на доступность: клиника открыта 24/7, приём возможен как на территории медучреждения, так и на выезде — дома, в офисе, гостинице, санатории или любом удобном месте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tver0.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь в твери[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тюмени — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к нарушению обмена веществ, обезвоживанию, сбоям в работе печени и сердца. В таких случаях требуется профессиональная помощь врача-нарколога, который подберёт оптимальный способ дезинтоксикации и медикаментозной поддержки. Современные методики позволяют провести вывод из запоя безопасно, эффективно и без осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя тюмень[/url]
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]взрослые игры[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne
Acesta este unul dintre cele mai bune Verde Casino.
https://monarchauto.com/product-viewer/?url=https://verde-casino-romania-winmax.ro
Программа лечения строится на комплексном подходе, который учитывает не только физические, но и психоэмоциональные потребности пациента. Благодаря круглосуточной доступности наркологической помощи, лечение начинается в самые ранние часы кризиса, что значительно повышает шансы на успешную реабилитацию.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-tula
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Детальнее – http://
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali/
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Тем, кто нуждается в длительной терапии, «КузбассМед» предлагает комфортные условия стационара с круглосуточным наблюдением. Здесь пациенты размещаются в индивидуальных палатах, проходят курсы терапии, реабилитации и психокоррекции. Обстановка в клинике напоминает оздоровительный центр: мягкое освещение, тишина, доступ к библиотеке, возможность общения с психологом и ежедневное участие в восстановительных мероприятиях. Медицинские сестры и врачи находятся на дежурстве 24/7, что позволяет немедленно реагировать на любые изменения в состоянии пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
он чють чють с желта https://awwama.online Хз …. Дето видел чел писал про вещ-во для снятия лака от ногтей ….. сказал что безпроигрышный вариант )))FoX будь добр скажи…
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-doktor[/url]
Valuable info. Fortunate me I found your site by accident, and I am stunned why this coincidence did not happened in advance!
I bookmarked it.
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бинго онлайн[/url]
Эта последовательность обеспечивает полное восстановление организма, формирование мотивации к трезвому образу жизни и снижение риска рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy/
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your site provided us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole community will be grateful to you.
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Каждый час промедления в острый период повышает вероятность обезвоживания, электролитных сдвигов, аритмий, гипертонических всплесков и расстройств сна, которые легко перерастают в делирий. Домашние попытки с «подручными» средствами редко учитывают лекарственные взаимодействия, реальный уровень обезвоживания и состояние печени, а «жёсткая» седация, применяемая без показаний, маскирует ухудшения и лишает врача информативной картины. Профессиональная бригада «НоваТрезвие» начинает с объективной оценки: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, выраженность тремора и тошноты, степень обезвоживания, список принимаемых препаратов и возможные аллергии. На этой базе формируется персональный план: регидратация, коррекция электролитов и кислотно-щелочного баланса, поддержка нервной системы витаминами группы B и магнием, гепатопротекторная и антиоксидантная защита по показаниям, противорвотные при необходимости и мягкая анксиолитическая поддержка для восстановительного сна. Такой маршрут гасит «пожар» интоксикации управляемо, возвращая прогнозируемость самочувствия в течение первых часов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом цена[/url]
В процессе лечения используются проверенные методики, которые в комплексе обеспечивают положительный эффект и снижают риск рецидива.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма анонимно омск[/url]
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзное заболевание, затрагивающее как физическое, так и психологическое состояние человека. При отсутствии своевременной наркологической помощи в клинике возможно ухудшение здоровья, развитие тяжелых осложнений и социальная деградация пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь в новокузнецке[/url]
Раннее обращение к специалистам позволяет провести качественную диагностику, подобрать адекватное лечение и обеспечить комплексную поддержку пациента.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-novokuzneczk0.ru
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займ без процентов[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru
Процесс детоксикации состоит из нескольких последовательных шагов, направленных на безопасное очищение организма. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием этапов, которые применяются в клинике «Трезвая Линия Волгоград».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в волгограде[/url]
Использование автоматизированных систем дозирования позволяет точно подобрать необходимое количество медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей дает возможность врачу корректировать схему лечения в режиме реального времени, что повышает безопасность и эффективность процедуры.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно ярославль[/url]
Комплексный подход к выводу из запоя на дому в Ярославле включает несколько основных этапов, которые позволяют обеспечить оперативное и безопасное лечение:
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-yaroslavl0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-yaroslavl
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom
Маршрут выстроен без пауз и импровизаций. Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, лекарства/дозировки, аллергии, важные диагнозы, последние значения давления и пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия. По прибытии врач фиксирует АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора/тошноты, уровень тревоги, кратко собирает анамнез последних суток. Затем стартует инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты, противорвотные, мягкие анксиолитики. Каждые 15–20 минут врач смотрит динамику и корректирует темп капельниц, питьевой режим, симптоматическую поддержку. Важный принцип — «сон без вырубания»: умеренная седация собирает ночной ритм, сохраняя информативность мониторинга. По завершении — письменные рекомендации и маршрут на 24–72 часа (сон, питание, запреты, «красные флаги», амбулаторные визиты/дневной стационар или перевод в отделение). Такой алгоритм заменяет «лотерею» результата управляемым и повторяемым планом.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru
Почему всё-таки такси? На метро бы а одну сторону успел бы… Вес большеват был, обычно брал миксы да всякие вкусные таблетки, но тут сразу столько СК… Да и потом, нашёл на товар, найди т на непредвиденный случай/комфорт, я так считаю. Чем брать по грамму микс, так лучше вообще не брать. Пара дней – и на пять грамм наберешь, с друзьями/сэкономишь на обедах, в конце концов. https://gashishweeds.store Привет всем и Мира! Тоже уже неделЮ жду адекватного трека . Дали два и оба не бьются((Жду решения регу оплатил. Адрес не получил.
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru
После прохождения основной программы пациенту предлагается поддерживающее наблюдение. Оно может включать дистанционные консультации, участие в группе профилактики срывов, повторные осмотры нарколога и психолога, корректировку медикаментозной схемы. В рамках реабилитации формируются планы действий при возникновении тяги, обучаются навыки сопротивления стрессу и внешнему давлению. При желании можно подключить родственников к процессу постлечебной адаптации, чтобы укрепить результат и снизить риски рецидивов. Таким образом, пациент не остаётся один даже после выписки.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании анонимно новокузнецк[/url]
https://pad.stuve.de/s/pbfw2gOpt
https://www.jjia.de/2017/03/16/cras-vulputate-arcu-sit-amet-cursus-malesuada/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Ключевым фактором при выборе центра становится квалификация специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма — это не только выведение из запоя и купирование абстинентного синдрома. Оно включает работу с мотивацией, тревожными состояниями, семейными конфликтами, нарушением сна и другими последствиями зависимости. Только команда, включающая наркологов, психотерапевтов и консультантов по аддиктивному поведению, способна охватить все аспекты проблемы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]klinika lecheniya alkogolizma murmansk[/url]
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая психиатрическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Туле разработана для тех, кто столкнулся с тяжелыми последствиями злоупотребления алкоголем. Основная цель – оперативная детоксикация организма, восстановление нормального обмена веществ и предотвращение дальнейших осложнений. Врач нарколог проводит полный комплекс обследований и назначает персонализированный план лечения, включающий медикаментозную терапию и психологическую поддержку, что позволяет обеспечить стабильное восстановление организма.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Выездная наркологическая помощь организована по чётко выстроенной схеме. Каждый этап направлен на стабилизацию состояния и безопасное восстановление функций организма после алкогольного или наркотического воздействия.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в уфе[/url]
Даже при наличии комфортных условий и современных медикаментов эффективность будет минимальной, если пациент не получает психологическую помощь. У многих зависимость сопровождается тревожными или депрессивными состояниями, травматическим опытом или сложными семейными отношениями. Без проработки этих аспектов высокий риск того, что после выписки произойдёт рецидив.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ярославская область[/url]
Особое внимание в клинике уделяется психологической реабилитации. Зависимость всегда сопряжена с внутренними конфликтами, нарушением привязанностей, проблемами самооценки. Врач-психотерапевт помогает пациенту выявить первопричины срывов, обучает техникам управления стрессом и прорабатывает модель трезвого поведения. В стационаре ведутся групповые и индивидуальные сессии, тренинги по навыкам саморегуляции, арт-терапия и элементы психодрамы. Реабилитационная команда помогает в адаптации к новой социальной роли, восстановлению отношений в семье и планированию жизни после выписки.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
Перед тем как показать примерные программы, важно подчеркнуть: реальный план всегда персонализируется, но понимание базовых форматов помогает семье и пациенту не теряться в терминах и сразу видеть логику.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Simply desire to say your article is as surprising.
The clarity to your put up is simply cool and that i can suppose you’re knowledgeable
in this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grasp your RSS feed to stay up to
date with approaching post. Thanks one million and please continue the rewarding work.
When someone writes an article he/she retains the thought of a user in his/her brain that how a user
can be aware of it. Thus that’s why this piece of writing is great.
Thanks!
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма волгоград[/url]
Респект и уважуха магазину, и процветания, безусловно! https://boshkistash.shop Тарился в этом магазе Летом разок и в Сентябре разок)))”Я надеюсь что вы перепроверите товар “
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]джекпот[/url]
Здесь
[url=https://aemodernconstruction.com/]глисты выходят комом[/url]
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali
This info is invaluable. When can I find out more?
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
I read this article fully regarding the resemblance of most recent and previous technologies, it’s
awesome article.
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
https://hectorbooks.gr/product/sitsa-karaiskaki-texni-fili/
Алкогольная интоксикация и запой могут стремительно ухудшить состояние здоровья, став угрозой жизни, поэтому оперативное вмешательство имеет первостепенное значение. В Туле квалифицированные наркологи предоставляют круглосуточную помощь на дому, что позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и в комфортных условиях. Такой формат терапии гарантирует индивидуальный подход, всестороннюю поддержку и полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для пациентов, стремящихся восстановить своё здоровье без лишних стрессовых ситуаций.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula000.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika tula[/url]
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]zakazat-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Прошу обратить внимание на кидок со стороны магазина на ~50000 рублей в Украинской ветке. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш употреблял перорально, также пробовал нозально (не вариант сжигает все напрочь и комок в слизистой)обьясни народу …….. сдесь ребята понимающие………. помогут
Правильный подбор лекарственных средств позволяет не только уменьшить проявления синдрома отмены, но и стабилизировать эмоциональное состояние пациента, снижая риск срывов. Реабилитационные программы включают физиотерапию, спортивные занятия и коррекцию образа жизни, что способствует полноценному восстановлению организма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании реабилитация тверь[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
А я так понимаю, что у данного магазина просто не мало оптовых покупателей, и им уделяется больше внимания. Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш что сильнее 100 или 400 ? и по времени сколько действуют ?магаз клёвый ,:bravo:сервис на высоте
I believe this is among the such a lot significant information for me. And i am happy reading your article. But wanna commentary on few basic things, The website style is perfect, the articles is in point of fact nice : D. Excellent job, cheers
клиника жуйкан Жуйкан Хэйхэ: Современная медицина на границе с Россией
I visited various sites but the audio quality
for audio songs current at this website is actually excellent.
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор высококачественных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до крупных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица товара подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Опытная поддержка – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы и адаптировать решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
Наша продукция:
Пруток магниевый ISO-MC21310 – BS ISO 16220 Проволока магниевая ISO-MC21310 – BS ISO 16220 разработана для высокотехнологичных решений в области легкосплавных конструкций. Она отличается высокой прочностью при низком весе, что делает её идеальным выбором для авиационной и автомобильной промышленности. Продукт представлен в соответствии с международными стандартами, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность. Если вы хотите использовать инновационные материалы в своих проектах, купить Проволока магниевая ISO-MC21310 – BS ISO 16220 станет отличным решением. Не упустите возможность улучшить качество своих изделий!
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм находится под постоянным воздействием этанола. Это вызывает интоксикацию, нарушение обменных процессов и дестабилизацию психики. При обращении за помощью врач-нарколог оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает индивидуальную схему терапии, чтобы безопасно вывести человека из запоя и предотвратить развитие синдрома отмены. Вмешательство проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в тольятти[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж[/url]
Может случилось что-то не ладное? Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Отличное качество реги! Советую!тут мы, СПСР чет лажает, медленно заказы регистрирует в базу
Капельница — это основной инструмент дезинтоксикации при лечении запойных состояний. Она способствует выведению токсинов, нормализации обмена веществ и улучшению общего самочувствия. Состав раствора подбирается индивидуально в зависимости от степени интоксикации, возраста, массы тела и сопутствующих заболеваний. Уже через 20–30 минут после начала инфузии пациент ощущает облегчение, снижается тревожность и проходит головная боль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно тольятти[/url]
https://svbeloglazov.ru/ svbeloglazov
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в тюмени[/url]
Клиника предлагает широкий спектр медицинских и психологических услуг, направленных на восстановление пациента после зависимости. Все процедуры проходят под контролем врачей и с соблюдением анонимности. Наиболее востребованные направления представлены ниже:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя волгоград[/url]
Цель
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Terrific post but I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Cheers!
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]srochnyj vyvod iz zapoya[/url]
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в воронеже[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]секс[/url]
хороший магазин !отменное качество и сервис ! хорошей работы вашему магазину и процветания! Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш Всё что В прайс листе на сайте есть,всё в наличии ?я в шоке. до последнего думали кидалово. а нет подняли в касание. стафф пушка. кладмену респект!!!
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница красноярск[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Когда уместен
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под контролем квалифицированных врачей, с использованием современных методик детоксикации, психотерапии и реабилитации. Цель работы специалистов — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту восстановить эмоциональное равновесие, вернуть контроль над поведением и мотивацию к трезвости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-anonimno
жуйкан в хэйхэ стоматология Жуйкан: Маяк здоровья и надежды в приграничном Хэйхэ Жуйкан – это имя, синонимичное качественной медицинской помощи и заботливому отношению к пациентам в динамично развивающемся городе Хэйхэ. Клиника, уверенно шагая в ногу со временем, предлагает широкий спектр услуг, сочетая традиционные методы лечения с инновационными технологиями, тем самым заслужив доверие множества пациентов, как из Китая, так и из-за рубежа. Это не просто медицинское учреждение, это островок надежды, где каждый человек получает шанс на здоровую и полноценную жизнь.
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-volgograd
Когда уместен
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tolyatti-otzyvy
Сначала — сбор короткого анамнеза и проверка лекарственных взаимодействий, затем — старт инфузии с контролем темпа. Параллельно купируются тошнота, тремор, тахикардия, корректируется сон. Каждые 15–20 минут специалист оценивает динамику и при необходимости меняет схему. В завершение вы получаете письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Основные этапы включают:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а тщательно выстроенный процесс, направленный на восстановление работы всех систем организма. При неправильном или неполном лечении риск осложнений возрастает в несколько раз. Поэтому обращение в профессиональную клинику становится необходимым шагом. В наркологической клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» пациент получает экстренную помощь, безопасные инфузионные препараты, круглосуточный выезд нарколога и последующее восстановление под наблюдением специалистов. Здесь каждая капельница подбирается индивидуально — с учётом возраста, веса, длительности запоя, хронических болезней и реакции организма на препараты.
Подробнее – http://
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Когда уместен
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Качество 2с очень порадовало, трип позже отпишу. https://uniontobacco.online “Я надеюсь что вы перепроверите товар “Приветствую! я получал последний раз недели две назад, заказывал уже много раз и скоро сделаю очередной заказ в этом магазине!!!
Формат
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo/
от таких провайдеров, как NetEnt, Microgaming, Pragmatic Play и других: [url=https://mir-forum.ru/]kometa casino[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость волгоград[/url]
Что включено на практике
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
Правильный подбор лекарственных средств позволяет не только уменьшить проявления синдрома отмены, но и стабилизировать эмоциональное состояние пациента, снижая риск срывов. Реабилитационные программы включают физиотерапию, спортивные занятия и коррекцию образа жизни, что способствует полноценному восстановлению организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение наркомании тверь[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена в волгограде[/url]
Перед таблицей — важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание логики и бюджета времени.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Каждый этап направлен на восстановление организма без стресса и перегрузки. Врачи работают деликатно, чтобы пациент чувствовал безопасность и понимал, что помощь оказывается профессионально.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в новокузнецке[/url]
Применение комплексной терапии позволяет не только устранить зависимость, но и сформировать новые поведенческие установки, предотвращающие возвращение к употреблению.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Выезд на дом удобен, но не всегда безопасен. Если запой длится больше трёх–пяти суток, присутствует повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность или резкие «качели» давления и пульса, лучше не тянуть и ехать в стационар. Для пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжелой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические заболевания печени/почек) круглосуточный мониторинг уменьшает риск осложнений и позволяет гибко расширять схему лечения. В стационаре доступна приборная диагностика, тщательный контроль жизненных показателей и быстрая коррекция терапии, если клиническая картина меняется. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку, встречу на входе, расширенный осмотр и запуск персонального протокола без задержек. Семья при этом остаётся в информационном контуре: врач объясняет смысл каждого шага и ожидаемый эффект, чтобы решения были осознанными, а не продиктованными паникой или усталостью.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-krasnogorske
Клиника предлагает широкий спектр медицинских и психологических услуг, направленных на восстановление пациента после зависимости. Все процедуры проходят под контролем врачей и с соблюдением анонимности. Наиболее востребованные направления представлены ниже:
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
https://svbeloglazov.ru/ svbeloglazov
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому волгоград[/url]
«Вектор Надежды» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы с первого звонка убрать неопределённость и вернуть ощущение контроля. Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только необходимую информацию, оценивает риски и предлагает безопасный старт: выезд на дом, дневной маршрут или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Мы объясняем каждую манипуляцию простым языком — что именно будет сделано в ближайшие часы, каких изменений ожидать к вечеру, почему выбран именно такой темп и как поймём, что схема работает. Конфиденциальность — не дополнение, а стандарт: нейтральные звонки, неброская атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте, отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает тревогу, экономит силы семьи и ускоряет стабилизацию: вместо «марафона кабинетов» — один связный маршрут с понятными контрольными точками.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-shchyolkovo/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya anonimno[/url]
Greetings! I’ve been following your blog for a while now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from New Caney Tx! Just wanted to tell you keep up the excellent job!
Клиника предлагает широкий спектр медицинских и психологических услуг, направленных на восстановление пациента после зависимости. Все процедуры проходят под контролем врачей и с соблюдением анонимности. Наиболее востребованные направления представлены ниже:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в воронеже[/url]
Наркозависимость — это не просто вредная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного и последовательного лечения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» в Новокузнецке разработаны персонализированные программы помощи, учитывающие медицинские, психологические и социальные аспекты проблемы. Каждому пациенту подбирается уникальный маршрут восстановления, начиная с первичной диагностики и заканчивая адаптацией к жизни без наркотиков. Поддержка оказывается круглосуточно, с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности. Психотерапевты и врачи работают в тесной связке, чтобы не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить личность пациента, вернуть ему мотивацию к жизни и уверенность в будущем.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru
Нет сомнения https://rachelcolemanceds.online Как-то развёл 2c-i на кубы воды и выбрал в выборку для точности дозировки.Так один кролятина вляпался в/в.Позавидовать ему трудно было,это точно.Но в конце когда оклемался,даже прикололся.Скажи что это? Я тебе помогу:) где хочешь заказать?
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/[/url]
Конфиденциальность — это набор конкретных действий, а не декларация на сайте. Мы проектируем «невидимость» так, чтобы пациент мог спокойно принять помощь и не опасаться огласки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
These are in fact impressive ideas in concerning
blogging. You have touched some fastidious points here.
Any way keep up wrinting.
В Воронеже команда «ВоронМед Профи» работает по принципу быстрой медицинской реакции — помощь оказывается независимо от времени суток и дня недели. Все выезды выполняются анонимно, без спецтранспорта и медицинской формы. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, что исключает ненужное внимание соседей и посторонних. В ходе осмотра специалист измеряет давление, пульс, температуру, оценивает уровень интоксикации и определяет степень обезвоживания. На основе полученных данных подбирается состав капельницы, который подаётся медленно и безопасно под контролем врача.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Подробнее тут – http://
Такой подход позволяет пациенту чувствовать себя не объектом лечения, а активным участником собственного восстановления. Это повышает уровень мотивации и формирует доверие между врачом и пациентом, что критически важно для устойчивой ремиссии.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Что пригодится в армии – советы для служащих по контракту на СВО Россия 2026 https://vc.ru/1585163
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Получить больше информации – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
Great article, very helpful.
It clearly explains
how streaming platforms operate
in a
clear and beginner-friendly manner.
Many people often wonder
where to find reliable streaming platforms
and
this post provides useful insights.
Thanks for putting this together.
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti/
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Но бывали случаи и на оборот… Купить Кокаин, Бошки, Мефедрон, Гашиш пиши в скайп, все работает, мне всегда отправляют, все на уровнеОтзыв уже был, по поводу JWH и 2c-i. Писать то особо и не о чем, но качество товара очень даже порадовало. Щас жду только пополнения ассортимента.
Что включено на практике
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в волгограде[/url]
Цель
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Цель
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/
Hi there, I enjoy reading all of your post. I wanted to write a little comment to support you.
Что получите за 24 часа
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника домодедово[/url]
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-odincovo/
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk/
Клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» придерживается принципа прозрачной медицины: каждый шаг понятен пациенту, решения принимаются совместно, а результаты фиксируются по объективным показателям. Такой формат создаёт чувство безопасности и доверия. Среди основных принципов:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh
Что включено на практике
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove/
Когда выбрать
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena
Спасибо, единственный объективный отзыв за последнее время. https://boshkionline.shop Да просто дедушка форума ))Почему ушли из РБ?
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр в перми[/url]
В Воронеже клиника «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» обеспечивает выезд нарколога на дом в любое время суток. Это позволяет оказывать помощь пациентам, которые находятся в тяжёлом состоянии или не могут самостоятельно приехать в стационар. Медицинская бригада прибывает в течение 40–60 минут, не используя специализированный транспорт и форму, чтобы сохранить анонимность. Врач проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает давление, частоту дыхания, уровень сознания и насыщение кислородом, после чего назначает детоксикационную капельницу с контролем дозировки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в воронеже[/url]
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены новокузнецк[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под контролем квалифицированных врачей, с использованием современных методик детоксикации, психотерапии и реабилитации. Цель работы специалистов — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту восстановить эмоциональное равновесие, вернуть контроль над поведением и мотивацию к трезвости.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Профессиональная помощь требуется в тех случаях, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями интоксикации. Чем дольше длится запой, тем сильнее проявляются его симптомы. Медицинское вмешательство помогает предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как судороги, повышение давления и алкогольный психоз.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
Маршрут начинается с короткого скрининга, чтобы понять риски и условия дома. Мы согласуем окно приезда или время приёма, заранее подскажем, как подготовить пространство: тишина, доступ к воде и розетке, возможность прилечь. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура), при показаниях выполняет ЭКГ и запускает детокс-терапию. Уже на старте вы получаете письменную памятку «на сутки»: режим сна и гидратации, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат перестаёт быть достаточным, организуем перевод в стационар без пауз — темп лечения сохраняется.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru
Удобная платформа kazino olimp — люблю заходить сюда!
https://hts.io/oaPF
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в волгограде[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Что включено на практике
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Что включает на практике
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике волгоград[/url]
Как накрутить лайки в ВК – ТОП-25 сервисов бесплатно и платно 2026 https://vc.ru/1475239
Yes! Finally someone writes about .
Если вы ищете информацию о [url=https://tehosmotrspbcena.ru]проходить техосмотр[/url] в Санкт-Петербурге, посетите специализированный сайт для получения актуальных услуг и цен.
Технический осмотр автомобиля обязателен для всех водителей в России. Он обеспечивает безопасность на дорогах и предотвращает аварии. Отсутствие техосмотра не позволит застраховать автомобиль по ОСАГО.
В СПб организованы удобные станции для проведения техосмотра в различных районах. Осмотр подразумевает тщательную диагностику основных узлов машины и получение официального документа.
На начальном этапе требуется подготовить все нужные документы, как паспорт и акт регистрации транспортного средства. Затем следует пройти осмотр на станции, где проверяются тормоза и другие системы. Завершается процесс получением диагностической карты, удостоверяющей полное соответствие стандартам.
Процедура охватывает диагностику тормозной системы, осветительных приборов и иных важных частей. Также проверяются шины на износ и соответствие сезонным нормам. Все элементы должны полностью соответствовать установленным государственным стандартам.
Жителям Санкт-Петербурга доступны многочисленные официальные станции для прохождения техосмотра. К примеру, пункт на Московском проспекте предлагает услуги с возможностью предварительной записи. Ещё один вариант — станции в Приморском районе, где всё спланировано для быстрого обслуживания.
Ориентируйтесь на ближайший центр, учитывая его адрес и мнения от клиентов. Узнайте график работы заранее, чтобы избежать очередей. Оформите запись через интернет или звонок, что упростит процесс.
Систематическое прохождение осмотра увеличивает долговечность машины и улучшает её безопасность. Такая процедура уменьшает шансы на инциденты и экономит средства на последующие ремонты. Соблюдайте график, чтобы избежать проблем с законом и обеспечить комфортное вождение.
При просрочке процедуры водитель получит наказание в виде штрафа от дорожной инспекции. Поэтому не игнорируйте сроки и проходите осмотр вовремя. Оставайтесь дисциплинированными, чтобы вносить вклад в общий порядок в движении.
Мы переводим субъективное «полегчало» в наблюдаемые факты. Быстрее всего меняются переносимость воды и интенсивность тошноты; вслед за этим «садится» пульс/давление и на 3+ пункта снижается тремор. «Первая ночь» — экзамен устойчивости: цель — ? 6 часов сна и не более одного пробуждения. Утром — две «малые победы» (гигиена, 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы) без «отката». При такой динамике модули по плану выключаются, пациент получает короткую карту самопомощи на 72 часа: светогигиена, интервалы питья, дыхательные ритмы, речевые правила семьи и пороги связи с дежурным.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Публикация предлагает набор слабо связанных идей, которые сложно применить на практике, лишь слегка затрагивая разные точки зрения.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]займы до зарплаты[/url]
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Подробнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Для наглядности приведена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их результатами:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh/
Первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению является очищение организма от токсинов. В клинике проводится детоксикация с использованием современных препаратов, направленных на выведение продуктов распада алкоголя и наркотиков. Медикаментозное лечение дополняется витаминами, гепатопротекторами и средствами для нормализации работы нервной системы. Это помогает восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в волгограде[/url]
В Воронеже команда «ВоронМед Профи» работает по принципу быстрой медицинской реакции — помощь оказывается независимо от времени суток и дня недели. Все выезды выполняются анонимно, без спецтранспорта и медицинской формы. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, что исключает ненужное внимание соседей и посторонних. В ходе осмотра специалист измеряет давление, пульс, температуру, оценивает уровень интоксикации и определяет степень обезвоживания. На основе полученных данных подбирается состав капельницы, который подаётся медленно и безопасно под контролем врача.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]врач нарколог на дом воронеж[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Получить больше информации – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно[/url]
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена адреса в волгограде[/url]
Когда выбрать
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-domodedovo
«Светлая Полоса» запускает помощь без многоходовой бюрократии и «марафона кабинетов». Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только те данные, которые критичны для безопасности, и сразу предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, дневной формат или стационар под наблюдением 24/7. Каждое действие проговаривается человеческим языком: что делаем в ближайшие часы, чего ждём к вечеру (мягкий сон, снижение тревоги, выравнивание давления и пульса), как поймём, что схема работает, и чем займёмся завтра. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс — нейтральные каналы связи, неброская выездная атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте и отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает фоновую тревогу, экономит силы семьи и превращает лечение в ясный, управляемый маршрут, а не в набор «разрозненных процедур».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove/
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, где проводят детоксикацию или капельницы. Это выстроенная система, где каждый этап направлен на восстановление физического, психического и социального равновесия пациента. В клинике «КрасЗдрав Профи» весь процесс лечения построен по принципу прозрачных шагов: первичная диагностика, стабилизация организма, терапевтическая коррекция и закрепление результата. Всё происходит с соблюдением принципа конфиденциальности — пациент может рассчитывать на анонимность и этичное отношение со стороны персонала.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в красноярске[/url]
После завершения инфузий врач-нарколог даёт рекомендации по питанию, водному балансу и образу жизни. При необходимости пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии для закрепления эффекта.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but
after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear.
Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyway, just
wanted to say superb blog!
I always used to study post in news papers but now as I am a user of web therefore from now I am using net for content, thanks to web.
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
https://www.manaolahawaii.com/articles/code_promo_melbet_bonus_de_paris_sportif.html
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Узнать больше – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог волгоград[/url]
Когда выбрать
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника анонимная помощь нарколога[/url]
Что включено на практике
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Формат
Получить больше информации – http://
На big-bag-rus.ru вы можете купить биг-бэги и мягкие контейнеры МКР от производителя: мешки биг бэги 1–4 стропы, с верхней сборкой, люками и вкладышем. Изготовление под ваши требования, стабильное качество, выгодный опт и отгрузка по России: https://big-bag-rus.ru/
В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» применяются разные методы кодирования, позволяющие подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пациента. Выбор зависит от медицинских показаний, психологической готовности и длительности ремиссии. В таблице ниже представлены основные методики, их особенности и преимущества.
Разобраться лучше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolya-v-volgograde/
Что включено на практике
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Процесс терапии в наркологической клинике в Воронеже организован поэтапно. Это позволяет обеспечить системность и постепенность восстановления, снизить риски осложнений и повысить устойчивость результата.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Цель
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в «ВолгаМед Тольятти» включает широкий спектр процедур и методик. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента, стадии заболевания и сопутствующих факторов. Ниже представлена таблица с основными направлениями медицинской работы.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-tolyatti17.ru/
Благодаря этому подходу пациент выходит из состояния запоя без стресса и с минимальной нагрузкой на организм, что ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]zapoj-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в красноярске[/url]
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому тольятти[/url]
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru
Перед таблицей — важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание логики и бюджета времени.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стоимость[/url]
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/narkologi-volgograda/
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkologiya[/url]
Лечение организовано поэтапно. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление функций организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап терапии направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных интоксикацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk
Капельницы от запоя включают препараты для очищения крови, восстановления электролитного баланса и защиты печени. Используются только сертифицированные растворы, одобренные Минздравом РФ. В клинике применяется комплексный подход: одновременно с физическим восстановлением запускаются лёгкие дыхательные и релаксационные методики, которые помогают организму вернуться в стабильное состояние.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Основные признаки, при которых необходим вывод из запоя:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru
Что включено на практике
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-so-stacionarom[/url]
Перед таблицей — важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание логики и бюджета времени.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-shchyolkovo
Клиника «КузбассМед Центр» в Новокузнецке обеспечивает непрерывный приём пациентов и выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат позволяет оказать экстренную помощь при интоксикации или запое прямо на месте, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния. Медицинская команда работает в режиме 24/7, что особенно важно при острых состояниях. Врач выезжает в течение часа после вызова, проводит диагностику, ставит капельницу и контролирует жизненные показатели. В стационаре доступны детоксикация, медикаментозная терапия и психотерапевтическая поддержка — всё под постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма в перми[/url]
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Что включает на практике
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Каждый из этапов сопровождается контролем врача и постепенным снижением медикаментозной нагрузки. Важно не просто снять симптомы, но и научить пациента распознавать внутренние триггеры, чтобы предотвратить рецидив. На протяжении всего лечения сохраняется поддержка психолога, который помогает адаптироваться и перестроить привычные модели поведения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser
Главное преимущество обращения в наркологическую клинику в Воронеже — комплексный подход к лечению зависимости. Специалисты учитывают медицинские, психологические и социальные факторы, влияющие на формирование зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально: в зависимости от стадии заболевания, состояния здоровья и целей терапии. В процессе лечения применяются детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапия и методы социальной адаптации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Chicken Road is very informative. Will be back for sure!
play Chicken Road online (http://jnews.xsrv.jp/jump.php?https://chickenroadvegas.org/payments)
Перед таблицей — важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание логики и бюджета времени.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo
Что делаем фактически
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Для наглядности приведена таблица с основными направлениями терапии и их результатами:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Красноярске — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление нормальной работы организма после длительного употребления спиртных напитков. Услуга предоставляется круглосуточно и включает дезинтоксикационную терапию, стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений. Все процедуры выполняются опытными наркологами с применением сертифицированных препаратов и в строгом соответствии с медицинскими стандартами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/
Важной частью реабилитации является социализация пациента, возвращение его к активной общественной жизни и формирование новых, здоровых привычек. Для этого в клинике организуются различные мероприятия и программы адаптации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма и наркомании центр тверь[/url]
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цена в волгограде[/url]
My brother recommended I might like this website. He was entirely right. This put up actually made my day. You can not imagine just how a lot time I had spent for this information! Thank you!
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма в волгограде[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
https://destinationbcn.com/pages/gormonoterapiya.html
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» применяются разные методы кодирования, позволяющие подобрать оптимальный вариант для каждого пациента. Выбор зависит от медицинских показаний, психологической готовности и длительности ремиссии. В таблице ниже представлены основные методики, их особенности и преимущества.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма в волгограде[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/perm-lechenie-alkogolizma/
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Острый запой — это нарушение работы сердца, мозга, печени и нервной системы, а не просто «лишние пару дней выпивки». Когда начинается тремор, потливость, скачки давления, бессонница, паника, семья часто пытается помочь самостоятельно: даёт случайные таблетки, сомнительные «антипохмельные коктейли», сильные седативные. В реальности такие меры нередко ухудшают ситуацию: давление падает или «скачет», дыхание угнетается, симптомы предделирия маскируются, и момент, когда нужна экстренная помощь, пропускается. Выездной нарколог «ЩёлковоМед Профи» в Щёлково работает иначе: ещё по телефону собираются ключевые данные — возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, аллергии, примерные показатели АД и пульса, особенности поведения. Это позволяет заранее оценить риски и понять, подходит ли формат на дому. На месте врач измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, неврологический статус, наличие дезориентации, смотрит, не требуется ли сразу стационар. Капельница назначается по фактическим показателям: без «универсальных коктейлей», без опасной седации, с учётом сердца, печени, эндокринных и неврологических особенностей. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм и делает результат управляемым — облегчение наступает без лишнего риска.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo/https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru
VAR decisions, video review outcomes and controversial calls documented
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
dinkin_bot Автоматизация стала ключевым фактором повышения эффективности бизнеса. Использование ИИ в маркетинге, SMM, копирайтинге и других областях позволяет снизить затраты, увеличить охват аудитории и повысить конверсию. Инструменты, такие как телеграм-боты (telegram bot), становятся незаменимыми помощниками в решении повседневных задач, освобождая время для более важных дел.
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
Пицца Куба Воронеж Пицца Воронеж
You actually make it seem really easy together with your presentation but I find this matter to be really something which I believe I might by no means understand. It seems too complicated and very large for me. I’m looking forward on your subsequent publish, I will attempt to get the grasp of it!
Жіночий портал https://soloha.in.ua про красу, здоров’я, стосунки та саморозвиток. Корисні поради, що надихають історії, мода, стиль життя, психологія та кар’єра – все для гармонії, впевненості та комфорту щодня.
Важное отличие клиники — отказ от примитивной схемы «капельница — домой — дальше сам». Такой формат даёт кратковременное облегчение, но не решает ни причин, ни структуры зависимости. «КоломнаМед Центр» выстраивает ступенчатый подход. Первый шаг — безопасная детоксикация: снятие абстиненции, коррекция водно-электролитного баланса, поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, нервной системы, нормализация сна. Второй шаг — стабилизация: оценка психического состояния, выявление тревожных, депрессивных и панических симптомов, подбор поддерживающих схем, которые помогают не сорваться сразу после выхода из острых проявлений. Третий шаг — реабилитация и мотивация: психотерапевтическая работа, групповые и индивидуальные форматы, обучение навыкам трезвой жизни, работа с триггерами, укрепление внутренней мотивации. Четвёртый шаг — постреабилитационная поддержка: контрольные приёмы, дистанционные консультации, помощь в профилактике срывов. Такой комплексный путь не ломает пациента, а возвращает ему контроль: не через страх, а через понимание, структуру и реальные инструменты.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
Hello folks!
I came across a 153 great platform that I think you should visit.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://www.vistanaij.com.ng/best-sales-in-the-history-of-monaco/]https://www.vistanaij.com.ng/best-sales-in-the-history-of-monaco/[/url]
And don’t forget, folks, — one constantly can within the piece discover answers to address the most the very complicated inquiries. Our team made an effort to lay out all content in the most very accessible method.
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Заготовка из конструкционной стали квадратная 30 мм ВСт3пс ОСТ 3-1686-90 Выбирайте конструкционные заготовки высокого качества для вашего проекта на Редметсплав.рф. Наш ассортимент включает прочные и долговечные материалы, идеально подходящие для различных областей применения, включая строительство и машиностроение.
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
С момента начала лечения пациент получает доступ к круглосуточной линии поддержки. Врачи, психологи и координаторы готовы ответить на вопросы, помочь с корректировкой схемы лечения, поддержать в ситуации риска срыва. Эта функция особенно востребована в первые недели после выписки, когда человек сталкивается с триггерами в привычной среде и нуждается в дополнительной защите. Связь может осуществляться по телефону, через защищённый мессенджер или с помощью мобильного приложения клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Лечение наркомании в клинике начинается с диагностики, позволяющей определить степень зависимости, выявить сопутствующие заболевания и выбрать оптимальную тактику терапии. Важным этапом является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов и продуктов распада наркотических веществ, что снижает риск осложнений и облегчает последующее восстановление.
Углубиться в тему – https://lechenie-narkomanii-tver0.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-narkotikov-v-tveri/
Услуга
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколога на дом щелково[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru
Портал для жінок https://u-kumy.com про стиль, здоров’я та саморозвиток. Експертні поради, чесні огляди, лайфхаки для дому та роботи, ідеї для відпочинку та гармонійного життя.
Услуга
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]skolko-stoit-vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Наркомания — это не просто пагубная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного лечения и индивидуального подхода. В клинике «ЗдороваяСамара» разработаны современные программы помощи зависимым, охватывающие все этапы — от выезда нарколога на дом до многомесячного амбулаторного сопровождения. Особое внимание уделяется конфиденциальности, оперативности и доступности помощи в любое время суток. Это делает лечение максимально комфортным, результативным и гуманным как для самого пациента, так и для его близких.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании диспансер в самаре[/url]
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-doktor[/url]
https://trade-mark.store/product-category/clenca-pvx/ купить клеенку пвх оптом в москве, купить клеенку пвх в рулонах оптом в москве, клеенка пвх в рулонах оптом в москве
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]zakazat-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom/
I do accept as true with all of the ideas you have presented in your post.
They’re very convincing and can definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts
are too brief for beginners. May you please prolong them a little from subsequent time?
Thanks for the post.
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево рязань[/url]
Один из ключевых принципов клиники «ЗдороваяСамара» — строгое соблюдение медицинской тайны. Все обращения, анализы и процедуры происходят в режиме полной конфиденциальности. При необходимости пациент может быть зарегистрирован под псевдонимом, а договор оформляется на доверенное лицо. Персональные данные не передаются ни в какие внешние базы, а диагноз не указывается в выписке для работодателя или страховой. Врачи и администрация клиники прошли специальное обучение по работе с анонимными пациентами, чтобы гарантировать этичность и законность каждой процедуры.
Выяснить больше – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
После стабилизации состояния пациенту предлагается пройти этап реабилитации. В клинике он может занять от 30 до 180 дней, в зависимости от тяжести зависимости, стажа употребления и социальной ситуации. Реабилитационный блок построен по принципам когнитивной реструктуризации: меняются привычные модели мышления, формируются новые способы реагирования на стресс, прорабатываются неразрешённые психологические конфликты. Используются методы психодрамы, арт-терапии, телесно-ориентированной терапии и даже нейропсихологической гимнастики.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании наркология самара[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
Посетите [url=https://yurist-zhilishchnyj-vopros1.ru] жилищные вопросы юридическая консультация [/url], чтобы получить профессиональную консультацию по всем вопросам, связанным с жилищным правом и недвижимостью.
занимается защитой прав граждан в сфере жилищного права . Этот специалист способен найти выход из сложных ситуаций, связанных с жильем. Юрист по жилищным вопросам может помочь в решении конфликтов с соседями, арендодателями или жилищными организациями .
Юрист по жилищным вопросам помогает людям жить в соответствии с законом и защитить свои права. Этот специалист может предоставить консультации по различным вопросам, связанным с жильем . Юрист по жилищным вопросам работает в тесном сотрудничестве с другими специалистами, такими как нотариусы и риэлторы .
## Раздел 2: Область деятельности юриста по жилищным вопросам
Юрист по жилищным вопросам занимается широким спектром вопросов, связанных с жилищным правом, включая покупку, продажу и аренду жилья . Этот специалист представляет интересы клиентов в суде и других инстанциях . Юрист по жилищным вопросам занимается составлением жалоб и заявлений в различные инстанции .
Юрист по жилищным вопросам работает с различными документами, связанными с жильем, включая договоры купли-продажи, аренды и других . Этот специалист знает, как правильно вести переговоры с контрагентами и найти взаимовыгодное решение . Юрист по жилищным вопросам знает, как действовать в кризисных ситуациях, связанных с жильем.
## Раздел 3: Преимущества работы с юристом по жилищным вопросам
Работа с юристом по жилищным вопросам дает возможность получить профессиональную консультацию и поддержку в решении жилищных вопросов. Этот специалист знает, как действовать в кризисных ситуациях, связанных с жильем . Юрист по жилищным вопросам может предоставить консультации по различным вопросам, связанным с жильем .
Работа с юристом по жилищным вопросам дает возможность получить профессиональную поддержку и консультацию в решении жилищных конфликтов . Этот специалист работает в тесном сотрудничестве с другими специалистами, такими как нотариусы и риэлторы . Юрист по жилищным вопросам осуществляет правовую поддержку граждан в случае конфликтов с жилищными организациями или соседями .
## Раздел 4: Заключение о важности юриста по жилищным вопросам
Юрист по жилищным вопросам играет важную роль вmodern обществе, где жилищные проблемы становятся все более актуальными . Этот специалист имеет обширный опыт работы с различными жилищными спорами и конфликтами . Юрист по жилищным вопросам способен защитить права граждан в суде и за его пределами .
Юрист по жилищным вопросам работает в тесном сотрудничестве с другими специалистами, такими как нотариусы и риэлторы . Этот специалист знает, как правильно вести переговоры с контрагентами и найти взаимовыгодное решение. Юрист по жилищным вопросам осуществляет правовую поддержку граждан в случае конфликтов с жилищными организациями или соседями.
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Having read this I believed it was really informative. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this informative article together. I once again find myself spending way too much time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это профессиональная медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление нормального самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений после длительного употребления алкоголя. В специализированных клиниках города лечение проводится с использованием современных методов детоксикации и под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов. Такой подход позволяет быстро и безопасно стабилизировать состояние пациента, устранить физическую зависимость и подготовить организм к дальнейшему восстановлению.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu
Один из ключевых принципов клиники «ЗдороваяСамара» — строгое соблюдение медицинской тайны. Все обращения, анализы и процедуры происходят в режиме полной конфиденциальности. При необходимости пациент может быть зарегистрирован под псевдонимом, а договор оформляется на доверенное лицо. Персональные данные не передаются ни в какие внешние базы, а диагноз не указывается в выписке для работодателя или страховой. Врачи и администрация клиники прошли специальное обучение по работе с анонимными пациентами, чтобы гарантировать этичность и законность каждой процедуры.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]наркологическое лечение наркомания в самаре[/url]
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена саратов[/url]
Терапия в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить безопасность и прозрачность процесса. Пациент постепенно проходит все стадии восстановления организма и психики.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
https://wrestlingmayhemshow.com/wp-content/pgs/sovety_po_prohoghdeniyu_igry_total_war_troy_poleznye_gaydy_023.html
Здесь собраны разрозненные сведения и неопределённые мысли, которые могут заинтересовать, даже если их важность сомнительна.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/blog/chto-takoe-mefedron-kak-ego-upotreblyayut-posledstviya-i-sposoby-lecheniya-zavisimosti.html]казино с быстрым выводом[/url]
Наркозависимость — это не просто вредная привычка, а тяжёлое хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного и последовательного лечения. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» в Новокузнецке разработаны персонализированные программы помощи, учитывающие медицинские, психологические и социальные аспекты проблемы. Каждому пациенту подбирается уникальный маршрут восстановления, начиная с первичной диагностики и заканчивая адаптацией к жизни без наркотиков. Поддержка оказывается круглосуточно, с полным соблюдением конфиденциальности. Психотерапевты и врачи работают в тесной связке, чтобы не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и восстановить личность пациента, вернуть ему мотивацию к жизни и уверенность в будущем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Услуга
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Galatasaray Football Club https://galatasaray.com.az latest news, fixtures, results, squad and player statistics. Club history, achievements, transfers and relevant information for fans.
Barcelona fan site barcelona with the latest news, match results, squads and statistics. Club history, trophies, transfers and resources for loyal fans of Catalan football.
UFC Baku fan site ufc-baku.com.az/ for fans of mixed martial arts. Tournament news, fighters, fight results, event announcements, analysis and everything related to the development of UFC in Baku and Azerbaijan.
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
https://trade-mark.store/product-category/kleenka-tkanevaya/ клеенка тканевая оптом в москве, клеенка тканевая купить оптом в москве, клеенка тканевая в рулонах оптом в москве, клеенка тканевая оптом со склада в москве.
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali/
В клинике реализуются ключевые направления, которые обеспечивают всестороннюю помощь и поддержку пациентам на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Как подчёркивает специалист ФГБУ «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии», «без участия квалифицированной команды невозможно обеспечить комплексный подход к пациенту, особенно если речь идёт о длительном стаже употребления и осложнённой картине заболевания». Отсюда следует — изучение состава персонала должно быть одним из первых шагов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом цена[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя коломна[/url]
Важной частью работы является индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. На основании диагностики формируется персональная программа терапии, учитывающая физическое и психологическое состояние, а также социальные обстоятельства. Такой формат лечения повышает его результативность и помогает снизить риск рецидива.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Great info. Lucky me I recently found your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have book marked it for later!
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево пермь[/url]
Rafa Silva https://rafa-silva.com.az/ is an attacking midfielder known for his dribbling, mobility, and ability to create chances. Learn more about his biography, club career, achievements, playing style, and key stats.
«ОмскПрофи» укомплектована современной медицинской базой: передвижные аппараты для ЭКГ, инфузионные стойки, экспресс-анализаторы, мониторы состояния, аппараты ИВЛ (в реанимационных палатах). Штат сотрудников сформирован из врачей-наркологов, токсикологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов, медицинских сестёр, прошедших обучение по международным протоколам. Ведётся постоянная учёба, стажировки, участие в научных форумах. Благодаря этому пациенты получают не только медицинскую помощь, но и психологическое сопровождение, направленное на долгосрочный результат.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/omsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
В случаях, когда пациент не готов приехать в клинику или находится в тяжёлом состоянии, специалисты «ЗдороваяСамара» организуют выездную помощь. Это особенно важно при острых интоксикациях, синдроме отмены, резком ухудшении психоэмоционального состояния. Выезд возможен круглосуточно и занимает от 30 до 60 минут с момента обращения. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков и привлечения внимания. Оснащение позволяет провести на месте полную диагностику и начать лечение — в том числе инфузионную терапию, коррекцию состояния и психологическую стабилизацию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании анонимно самара[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Система круглосуточной наркологической помощи в «ОмскПрофи» построена на принципе постоянной готовности. В любой момент суток специалисты готовы выехать на дом, принять пациента в стационар или организовать удалённую консультацию. Это особенно важно в острых ситуациях, когда счёт идёт на часы: запой, передозировка, психоз, агрессивное поведение или резкое ухудшение самочувствия. В таких случаях промедление может стоить пациенту жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/narkolog-psikhiatr-omsk/
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Такие процедуры особенно эффективны на ранних стадиях лечения, когда важно быстро снять симптомы интоксикации и вернуть стабильное самочувствие. После курса капельниц пациенту становится легче концентрироваться, снижается раздражительность и тревожность, восстанавливается аппетит и сон.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
https://trade-mark.store/product-category/banketki-etazherki/ банкетки для обуви оптом в москве, этажерки для обуви оптом в москве, банкетки для обуви купить оптом в москве, этажерки для обуви купить оптом в москве, этажерки для обуви купить оптом в москве.
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает специализированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими формами зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы диагностики, терапии и реабилитации, которые помогают не только стабилизировать состояние, но и восстановить здоровье в долгосрочной перспективе. Работа ведётся с учётом принципов конфиденциальности, что создаёт условия для комфортного прохождения лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в омске[/url]
Детоксикация — это первый и важнейший этап лечения в наркологической клинике в Красноярске. Она проводится с целью выведения токсинов из организма и восстановления функций жизненно важных органов. Для этого применяются инфузионные растворы, гепатопротекторы, витамины и препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ. После снятия интоксикации пациент получает медикаментозную поддержку, направленную на снижение тяги к алкоголю или наркотикам и стабилизацию эмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма красноярск[/url]
Такие процедуры особенно эффективны на ранних стадиях лечения, когда важно быстро снять симптомы интоксикации и вернуть стабильное самочувствие. После курса капельниц пациенту становится легче концентрироваться, снижается раздражительность и тревожность, восстанавливается аппетит и сон.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в рязани[/url]
После прохождения основной программы пациенту предлагается поддерживающее наблюдение. Оно может включать дистанционные консультации, участие в группе профилактики срывов, повторные осмотры нарколога и психолога, корректировку медикаментозной схемы. В рамках реабилитации формируются планы действий при возникновении тяги, обучаются навыки сопротивления стрессу и внешнему давлению. При желании можно подключить родственников к процессу постлечебной адаптации, чтобы укрепить результат и снизить риски рецидивов. Таким образом, пациент не остаётся один даже после выписки.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-novokuzneczk0.ru/]центр анонимного лечения наркомании в новокузнецке[/url]
В клинике применяются современные медицинские технологии, которые обеспечивают стойкий результат. Используемые методики соответствуют международным стандартам и регулярно обновляются.
Получить больше информации – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk
Острый запой — это нарушение работы сердца, мозга, печени и нервной системы, а не просто «лишние пару дней выпивки». Когда начинается тремор, потливость, скачки давления, бессонница, паника, семья часто пытается помочь самостоятельно: даёт случайные таблетки, сомнительные «антипохмельные коктейли», сильные седативные. В реальности такие меры нередко ухудшают ситуацию: давление падает или «скачет», дыхание угнетается, симптомы предделирия маскируются, и момент, когда нужна экстренная помощь, пропускается. Выездной нарколог «ЩёлковоМед Профи» в Щёлково работает иначе: ещё по телефону собираются ключевые данные — возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, аллергии, примерные показатели АД и пульса, особенности поведения. Это позволяет заранее оценить риски и понять, подходит ли формат на дому. На месте врач измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, неврологический статус, наличие дезориентации, смотрит, не требуется ли сразу стационар. Капельница назначается по фактическим показателям: без «универсальных коктейлей», без опасной седации, с учётом сердца, печени, эндокринных и неврологических особенностей. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм и делает результат управляемым — облегчение наступает без лишнего риска.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Письменные рекомендации: сон, питание, гидратация, запреты, «красные флаги», график амбулаторных визитов; при недостатке ресурсов дома — перевод в стационар без задержек. Такая последовательность убирает импровизацию и делает результат повторяемым.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Сайт города Одесса https://faine-misto.od.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, культура, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей Одессы в удобном формате.
В случаях, когда пациент не готов приехать в клинику или находится в тяжёлом состоянии, специалисты «ЗдороваяСамара» организуют выездную помощь. Это особенно важно при острых интоксикациях, синдроме отмены, резком ухудшении психоэмоционального состояния. Выезд возможен круглосуточно и занимает от 30 до 60 минут с момента обращения. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков и привлечения внимания. Оснащение позволяет провести на месте полную диагностику и начать лечение — в том числе инфузионную терапию, коррекцию состояния и психологическую стабилизацию.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]наркологическое лечение наркомания[/url]
Новости Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua сегодня: события города, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни Житомира онлайн.
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколога на дом щелково[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]услуги вывода из запоя[/url]
Сайт города Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, экономика, культура и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей города.
Hello my friend! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include approximately all significant infos. I’d like to see more posts like this .
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в саратове[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/
«ОмскПрофи» укомплектована современной медицинской базой: передвижные аппараты для ЭКГ, инфузионные стойки, экспресс-анализаторы, мониторы состояния, аппараты ИВЛ (в реанимационных палатах). Штат сотрудников сформирован из врачей-наркологов, токсикологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов, медицинских сестёр, прошедших обучение по международным протоколам. Ведётся постоянная учёба, стажировки, участие в научных форумах. Благодаря этому пациенты получают не только медицинскую помощь, но и психологическое сопровождение, направленное на долгосрочный результат.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает специализированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими формами зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы диагностики, терапии и реабилитации, которые помогают не только стабилизировать состояние, но и восстановить здоровье в долгосрочной перспективе. Работа ведётся с учётом принципов конфиденциальности, что создаёт условия для комфортного прохождения лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника омск[/url]
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в омске[/url]
Выбор наркологической клиники в Коломне — это не «слишком серьёзно», а логичный шаг, если зависимость уже зашла дальше спонтанных эпизодов. Алкоголизм, наркомания, злоупотребление успокоительными и обезболивающими — это не только психологическая тяга, но и перестройка организма: страдают печень, сердце, сосуды, нервная система, гормональный фон, сон, психика. Дома редко есть возможность круглосуточно контролировать состояние, правильно отменять вещества, отслеживать давление, пульс, поведение, не допускать опасных комбинаций препаратов. Родственники устают, реагируют эмоциями, а не медицинской логикой, человек чувствует себя под прицелом, но не под защитой. В «КоломнаМед Центр» всё выстроено так, чтобы снять нагрузку с семьи и вывести помощь из зоны хаотичных решений. Здесь оценивают не только то, «что и сколько пьёт или принимает», а весь контекст: длительность зависимости, срывы, уже перенесённые делирии или передозировки, сопутствующие болезни, психические состояния, семейную ситуацию. На основе этого формируется безопасный план: где начать — в стационаре или амбулаторно, какой формат детокса выбрать, насколько жёстко вести наблюдение, как сразу встроить психотерапевтическую и социальную поддержку. Клиника в Коломне позволяет работать системно, а не латать последствия очередного срыва.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]заказать обратный звонок наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в красноярске[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru
Gambling’s Hidden Jackpot: The Tales You Get to Tell
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
Портал города Хмельницкий https://faine-misto.km.ua с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения местных властей, происшествия, экономика, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Львова https://faine-misto.lviv.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная повестка. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни города онлайн.
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-v-saratove/
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Вывод из запоя в Омске проводится в условиях клиники с применением современных методов детоксикации и круглосуточного медицинского наблюдения. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает серьезную интоксикацию организма, нарушает работу внутренних органов и психоэмоциональное состояние. Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет избежать осложнений и восстановить здоровье пациента безопасным образом.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-gorod-omsk
Днепр онлайн https://faine-misto.dp.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
真实的人类第一季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В «ОмскПрофи» доступен весь спектр наркологической помощи — от экстренного вмешательства до длительной реабилитации. Лечение начинается с диагностики: анамнез, анализы крови, ЭКГ, оценка уровня тревожности, когнитивного статуса и социальной дезадаптации. Далее составляется индивидуальный курс, включающий медикаментозное лечение, работу с психотерапевтом, участие в поддерживающих сессиях и последующее наблюдение после выписки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/]нарколог наркологическая помощь в омске[/url]
В наркологической клинике в Омске применяются только проверенные методы, эффективность которых подтверждена клинической практикой. Они помогают воздействовать на разные стороны зависимости и обеспечивают комплексный результат.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-omske/
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/narkolog-perm-czeny/
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]заказать обратный звонок наркологическая клиника[/url]
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя срочно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Автомобильный портал https://avtogid.in.ua с актуальной информацией об автомобилях. Новинки рынка, обзоры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и практические рекомендации для ежедневного использования авто.
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Новости Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua события города, происшествия, экономика и общество. Актуальные обзоры, аналитика и оперативные материалы о том, что происходит в столице Украины сегодня.
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
познавательный блог https://zefirka.net.ua с интересными статьями о приметах, значении имен, толковании снов, традициях, праздниках, советах на каждый день.
It’s very trouble-free to find out any topic on net as compared to books, as I found this post at this web site.
Одним из ключевых направлений терапии является инфузионное лечение. Капельницы позволяют быстро восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить работу внутренних органов и ускорить выведение токсинов. В клинике используются только сертифицированные препараты, безопасные для сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены саратов[/url]
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому омск[/url]
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно – ТОП-25 сервисов (2026) Мой рейтинг
Дополнительные сведения по ссылке: https://vc.ru/1527031
В случаях, когда пациент не готов приехать в клинику или находится в тяжёлом состоянии, специалисты «ЗдороваяСамара» организуют выездную помощь. Это особенно важно при острых интоксикациях, синдроме отмены, резком ухудшении психоэмоционального состояния. Выезд возможен круглосуточно и занимает от 30 до 60 минут с момента обращения. Врач приезжает в гражданской одежде, без опознавательных знаков и привлечения внимания. Оснащение позволяет провести на месте полную диагностику и начать лечение — в том числе инфузионную терапию, коррекцию состояния и психологическую стабилизацию.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании анонимно[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/narkolog-saratov-na-dom/
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Карта делает видимой причинно-следственную связь: пациент понимает, зачем и что именно делается; семья видит «точки проверки»; врач получает опору для изменения одного параметра без разрушения всего плана.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в саратове[/url]
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo/
Один из ключевых принципов клиники «ЗдороваяСамара» — строгое соблюдение медицинской тайны. Все обращения, анализы и процедуры происходят в режиме полной конфиденциальности. При необходимости пациент может быть зарегистрирован под псевдонимом, а договор оформляется на доверенное лицо. Персональные данные не передаются ни в какие внешние базы, а диагноз не указывается в выписке для работодателя или страховой. Врачи и администрация клиники прошли специальное обучение по работе с анонимными пациентами, чтобы гарантировать этичность и законность каждой процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – http://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-narkotikov-samara/
Терапия в клинике строится на системном подходе, позволяющем постепенно восстанавливать здоровье и формировать новые жизненные установки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
Вывод из запоя в Омске проводится в условиях клиники с применением современных методов детоксикации и круглосуточного медицинского наблюдения. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает серьезную интоксикацию организма, нарушает работу внутренних органов и психоэмоциональное состояние. Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет избежать осложнений и восстановить здоровье пациента безопасным образом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в саратове[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в рязани[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
For the reason that the admin of this web page is working, no hesitation very rapidly it will be well-known, due to its quality contents.
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит нарколог на дом[/url]
С момента начала лечения пациент получает доступ к круглосуточной линии поддержки. Врачи, психологи и координаторы готовы ответить на вопросы, помочь с корректировкой схемы лечения, поддержать в ситуации риска срыва. Эта функция особенно востребована в первые недели после выписки, когда человек сталкивается с триггерами в привычной среде и нуждается в дополнительной защите. Связь может осуществляться по телефону, через защищённый мессенджер или с помощью мобильного приложения клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-samara0.ru/]лечение наркомании цена самара[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не «волшебная капельница», а последовательная медицинская программа с чёткими целями и измеримыми маркерами. В наркологической клинике «СаратовМед Профи» маршрут строится по принципу управляемых окон: на каждом шаге команда преследует одну цель, меняет лишь один параметр и оценивает результат в заранее назначённый момент. Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, предотвращает «гонку дозировок» и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и близких. Конфиденциальность обеспечивается регламентом: немаркированные выезды, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи, доступ к записям — строго по ролям.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Hi there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you
if that would be okay. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog
and look forward to new posts.
Клиника в Коломне ориентирована на полный цикл помощи: от экстренных состояний до длительного сопровождения. Здесь важна не только медицинская составляющая, но и человеческая: уважение, конфиденциальность, отсутствие стигмы. Ниже — ключевые направления, которые выстраиваются в единую систему лечения, а не существуют по отдельности.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru
Как накрутить просмотры в Телеграм бесплатно – 24 лучших сервиса и личные схемы https://vc.ru/2045313
Такая структура делает лечение последовательным и предсказуемым, повышая шансы на положительный исход.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
https://GetAdsOnline.com/390/posts/1/1/2001550.html
Услуга
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine
Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good
success. If you know of any please share. Many
thanks!
Каждое из этих направлений имеет важное значение и в совокупности формирует основу для устойчивого выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-omske
Наркологическая клиника в Омске оказывает специализированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими формами зависимости. Здесь используются современные методы диагностики, терапии и реабилитации, которые помогают не только стабилизировать состояние, но и восстановить здоровье в долгосрочной перспективе. Работа ведётся с учётом принципов конфиденциальности, что создаёт условия для комфортного прохождения лечения.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/narkologi-omska/
捕风捉影在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Wow, superb blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is excellent, as well as the content!
Портал для пенсионеров https://pensioneram.in.ua Украины с полезными советами и актуальной информацией. Социальные выплаты, пенсии, льготы, здоровье, экономика и разъяснения сложных вопросов простым языком.
Блог для мужчин https://u-kuma.com с полезными статьями и советами. Финансы, работа, здоровье, отношения и личная эффективность. Контент для тех, кто хочет разбираться в важных вещах и принимать взвешенные решения.
Объясняем сложные https://notatky.net.ua темы просто и понятно. Коротко, наглядно и по делу. Материалы для тех, кто хочет быстро разобраться в вопросах без профессионального жаргона и сложных определений.
http://www.studywithdemo.com/2015/02/how-to-make-stamp-size-photos-in-photoshop.html?sc=1768667614879#c6393220629104324693
Если вы ищете информацию о [url=https://tehosmotrspbcena.ru]техосмотр для постановки[/url] в Санкт-Петербурге, посетите специализированный сайт для получения актуальных услуг и цен.
Технический осмотр автомобиля обязателен для всех водителей в России. Это процедура, которая гарантирует безопасность движения и минимизирует риски на трассе. Не пройдя техосмотр, водитель не сможет оформить страховку ОСАГО.
В СПб организованы удобные станции для проведения техосмотра в различных районах. В ходе процесса оцениваются важные элементы авто, после чего выдается подтверждающий акт.
На начальном этапе требуется подготовить все нужные документы, как паспорт и акт регистрации транспортного средства. Затем следует пройти осмотр на станции, где проверяются тормоза и другие системы. Итогом становится выдача карты, которая подтверждает, что авто соответствует всем требованиям.
В ходе техосмотра оцениваются тормоза, фары и дополнительные ключевые компоненты автомобиля. Ещё одним аспектом является проверка шин на повреждения и правильность их использования. Все диагностируемые системы авто должны быть в полном соответствии с официальными требованиями.
Жителям Санкт-Петербурга доступны многочисленные официальные станции для прохождения техосмотра. Так, центр на Московском проспекте открыт для посетителей, позволяя забронировать время. Помимо этого, в Приморском районе работают центры, обеспечивающие быстрый и качественный техосмотр.
Подберите подходящий пункт, основываясь на близости и отзывах других водителей. Проверьте часы работы центра заранее, чтобы спланировать визит без проблем. Оформите запись через интернет или звонок, что упростит процесс.
Регулярный техосмотр продлевает срок службы автомобиля и повышает его надёжность. Такая процедура уменьшает шансы на инциденты и экономит средства на последующие ремонты. Следуйте рекомендованному расписанию, избегая юридических последствий и гарантируя безопасную езду.
В случае задержки с техосмотром предусмотрены санкции, включая штрафы от ГИБДД. Из-за этого не стоит откладывать процедуру и выполняйте её в установленные сроки. Оставайтесь дисциплинированными, чтобы вносить вклад в общий порядок в движении.
I’m not sure where you’re getting your info, but great
topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for great information I was looking for this info for my mission.
литий-ионные аккумуляторы для складской техники Существуют различные типы Li-ion аккумуляторов для погрузчиков: с разной емкостью (Ah) и напряжением (В). При выборе необходимо учитывать требуемую мощность и время работы погрузчика. Например, для погрузчика Jungheinrich EFG 215 SP может подойти АКБ Li-ion Ensol 48V 360Ah, но необходимо проверить габариты (830х522х627 мм).
https://www.tellmfg.com/solutions/modular-building/telstar-door
Полтава онлайн https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
https://vc.ru/smm-promotion
Портал города https://u-misti.odesa.ua Одесса с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения властей, происшествия, экономика, спорт, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Житомира https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Оперативные обновления, обзоры и важная информация о жизни Житомира онлайн.
이 포스트는 가치 있습니다. 더 알아보려면 어떻게 할 수 있을까요?
you’re in point of fact a good webmaster. The web site loading pace is amazing.
It kind of feels that you are doing any distinctive trick.
Furthermore, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve performed
a fantastic job on this matter!
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Детальнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/anonimnaya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd/
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Процесс лечения включает несколько последовательных шагов, направленных на стабилизацию состояния, детоксикацию и восстановление функций организма. Таблица ниже показывает основные этапы процедуры, применяемые врачами клиники «РеабКузбасс».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-novokuzneczk/
В клинике используются проверенные медицинские методы, основанные на современных научных данных. При алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации первым этапом является детоксикация — выведение токсинов из организма и нормализация обменных процессов. На следующем этапе проводится медикаментозная поддержка, направленная на стабилизацию состояния, снижение тяги к веществам и восстановление функций внутренних органов. После стабилизации пациент проходит курс психотерапии и участвует в программах реабилитации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/[/url]
Вывод из запоя требуется тогда, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к нарушению работы внутренних органов, обезвоживанию и психическим расстройствам. Медицинская помощь помогает избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс отказа от алкоголя.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-ryazan
частные предложения Мелитополь Личные объявления Мелитополь – это шанс найти новые знакомства и интересных людей для вечернего досуга. Выбирайте из множества анкет и предложений.
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены в волгограде[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в волгограде[/url]
витамины подбор
bonus казино
What i don’t realize is if truth be told how you’re now not actually much more smartly-liked than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You understand therefore considerably in terms of this topic, produced me personally imagine it from so many varied angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested except it’s something to do with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. At all times maintain it up!
Новости Хмельницкого https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua сегодня на одном портале. Главные события города, решения властей, происшествия, социальная повестка и городская хроника. Быстро, понятно и по делу.
Львов онлайн https://u-misti.lviv.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Важные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни одного из крупнейших городов Украины.
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормальной работы внутренних органов. В клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград» пациентам оказывается профессиональная помощь с использованием современных методов дезинтоксикации, медикаментозной поддержки и психологического сопровождения. Лечение проводится круглосуточно, включая выезд нарколога на дом. Такой формат помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и обеспечить безопасность при выходе из запоя любой продолжительности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Новости Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua сегодня — актуальные события столицы, происшествия, политика, экономика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и ключевые темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Такой подход обеспечивает результативность и помогает добиться длительной ремиссии даже при тяжёлых формах зависимости.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
site officiel melbet melbet apk
Капельницы при выводе из запоя — основной инструмент детоксикации. Они очищают кровь, стабилизируют давление и восстанавливают баланс электролитов. В клинике «РеабКузбасс» используются только качественные препараты, адаптированные под конкретное состояние пациента. Ниже приведена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их эффектом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в новокузнецке[/url]
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в новокузнецке[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Программы вывода из запоя в клинике разрабатываются с учётом состояния пациента. Для тяжёлых случаев назначается интенсивный курс с инфузионной терапией и контролем электролитов. При лёгких формах применяются мягкие препараты с постепенным выведением токсинов. Все процедуры проходят с соблюдением медицинских стандартов и полным сохранением анонимности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Процесс лечения проходит поэтапно и под постоянным наблюдением специалистов. Каждый этап направлен на определённый аспект восстановления здоровья и личности пациента.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
литий-ионные аккумуляторы для вилочных погрузчиков купить Сравнение тяговых аккумуляторов для погрузчиков: кислотные, гелевые, литий-ионные. Кислотные аккумуляторы: * Преимущества: Низкая стоимость, простота конструкции. * Недостатки: Низкая энергоемкость, короткий срок службы, требуют обслуживания (доливка воды), выделяют вредные газы, чувствительны к глубокому разряду. Гелевые аккумуляторы: * Преимущества: Не требуют обслуживания, герметичны, меньше выделяют газы, чем кислотные. * Недостатки: Дороже кислотных, меньшая энергоемкость, чем у литий-ионных, чувствительны к перезаряду и глубокому разряду. Литий-ионные аккумуляторы: * Преимущества: Высокая энергоемкость, длительный срок службы (до 5 раз больше, чем у свинцово-кислотных), быстрая зарядка, не требуют обслуживания, экологически чистые. * Недостатки: Высокая стоимость, сложная электроника (BMS), требуют специального зарядного устройства.
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в воронеже[/url]
Капельница — основной инструмент для очищения организма от продуктов распада этанола. Состав раствора подбирается строго индивидуально. В таблице приведены примеры комплексов, применяемых специалистами клиники «Трезвая Линия Волгоград».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Лечение в клинике «ВоронежМед Альянс» проходит поэтапно. Каждый модуль имеет определённую цель и собственные критерии эффективности. Такой подход исключает избыточное вмешательство и обеспечивает прозрачность процесса восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в воронеже[/url]
Добровольческие формирования и контракт на СВО в России 2026 https://vc.ru/1652681
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, где проводят детоксикацию или капельницы. Это выстроенная система, где каждый этап направлен на восстановление физического, психического и социального равновесия пациента. В клинике «КрасЗдрав Профи» весь процесс лечения построен по принципу прозрачных шагов: первичная диагностика, стабилизация организма, терапевтическая коррекция и закрепление результата. Всё происходит с соблюдением принципа конфиденциальности — пациент может рассчитывать на анонимность и этичное отношение со стороны персонала.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Нi theгe, juѕt wanted to tell yοu, Ӏ ⅼiked
tһіs article. It ԝas inspiring. Keep on posting!
Takе а lo᧐k at my page: Alquiler de furgonetas y coches en Andorra
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению является очищение организма от токсинов. В клинике проводится детоксикация с использованием современных препаратов, направленных на выведение продуктов распада алкоголя и наркотиков. Медикаментозное лечение дополняется витаминами, гепатопротекторами и средствами для нормализации работы нервной системы. Это помогает восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
Важное отличие наркологической клиники «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — полный отказ от схемы «одна капельница = решение всех проблем». Детокс здесь рассматривается как необходимый старт, но не как финальная точка. Сначала специалисты снимают острые состояния: вывод из запоя, купирование абстиненции, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку сердца, печени и нервной системы, нормализацию сна, снижение тревоги. Когда организм перестаёт «гореть», начинается следующий этап — стабилизация: врач оценивает психическое состояние, выявляет депрессивные, тревожные, панические проявления, подбирает поддерживающие схемы, которые помогают удержаться в первые недели после кризиса. Далее подключаются психотерапевтические инструменты: индивидуальные консультации, работа с мотивацией, разбор триггеров, формирование новых привычек. В финале выстраивается маршрут поддержки: амбулаторное наблюдение, связь с клиникой, рекомендации для семьи. Такой поэтапный подход делает клинику в Коломне местом, где зависимость перестают воспринимать как «стыд» и начинают воспринимать как задачу, с которой можно работать профессионально.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne
Актуальные новости https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua Черновцов на сегодня. Экономика, происшествия, культура, инфраструктура и социальные вопросы. Надёжные источники, регулярные обновления и важная информация для жителей города.
25 надежных сервисов для накрутки ТГ в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1520427
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Винница онлайн https://u-misti.vinnica.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Главные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни города в удобном формате.
В Воронеже клиника «ВоронежМед Альянс» предлагает комплексное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Команда врачей, психиатров, психологов и терапевтов выстраивает индивидуальный маршрут пациента, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Главный принцип — минимальное вмешательство при максимальной эффективности. Это означает, что терапевтические меры подбираются строго по показаниям, а медикаменты применяются только после оценки состояния и лабораторных данных.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon[/url]
Awesome post.
В таблице приведены основные компоненты инфузионной терапии, применяемые при детоксикации:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в новокузнецке[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
встречи без обязательств Мелитополь Частные объявления Мелитополь – это личные объявления девушек, предлагающих услуги для взрослых и индивидуальные встречи. Ознакомьтесь с каталогом предложений и выберите то, что вам подходит.
Важное отличие наркологической клиники «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — полный отказ от схемы «одна капельница = решение всех проблем». Детокс здесь рассматривается как необходимый старт, но не как финальная точка. Сначала специалисты снимают острые состояния: вывод из запоя, купирование абстиненции, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку сердца, печени и нервной системы, нормализацию сна, снижение тревоги. Когда организм перестаёт «гореть», начинается следующий этап — стабилизация: врач оценивает психическое состояние, выявляет депрессивные, тревожные, панические проявления, подбирает поддерживающие схемы, которые помогают удержаться в первые недели после кризиса. Далее подключаются психотерапевтические инструменты: индивидуальные консультации, работа с мотивацией, разбор триггеров, формирование новых привычек. В финале выстраивается маршрут поддержки: амбулаторное наблюдение, связь с клиникой, рекомендации для семьи. Такой поэтапный подход делает клинику в Коломне местом, где зависимость перестают воспринимать как «стыд» и начинают воспринимать как задачу, с которой можно работать профессионально.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
В Красноярске клиника «КрасЗдрав Профи» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью. При этом формат анонимности сохраняется на каждом этапе — от звонка до выписки. Для пациентов, которым трудно приехать, возможен выезд нарколога на дом. Это удобно при похмельных и абстинентных состояниях, когда транспортировка нежелательна. Конфиденциальный выезд без маркировки транспорта и униформы позволяет начать лечение, не привлекая внимания окружающих. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинских стандартов, включая регидратацию, стабилизацию и поддержку дыхания.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Комплексный подход позволяет врачу не просто купировать острые симптомы, но и предупредить осложнения со стороны сердца, печени и нервной системы. После стабилизации состояния пациент получает рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и восстановлению.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Новости Днепра https://u-misti.dp.ua сегодня — актуальные события города, происшествия, экономика, политика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и главные темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
купить литий ионный аккумулятор 24v для электропогрузчика Литий ионные батареи для погрузчиков – это надежное и безопасное решение, отвечающее современным требованиям. Аккумуляторы литий ионные 24v обеспечивают высокую эффективность работы.
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Городской портал https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua Черкасс — свежие новости, события, происшествия, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, городская хроника и полезная информация для жителей и гостей города.
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Такой подход позволяет пациенту чувствовать себя не объектом лечения, а активным участником собственного восстановления. Это повышает уровень мотивации и формирует доверие между врачом и пациентом, что критически важно для устойчивой ремиссии.
Выяснить больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
лучшие запросы для stable diffusion
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
казино с автоматами и бонусами
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Письменные рекомендации: сон, питание, гидратация, запреты, «красные флаги», график амбулаторных визитов; при недостатке ресурсов дома — перевод в стационар без задержек. Такая последовательность убирает импровизацию и делает результат повторяемым.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя стационар[/url]
Таблица не заменяет очный осмотр, но показывает, как наблюдения переводятся в действие и когда мы принимаем решение о продолжении/остановке модуля.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Письменные рекомендации: сон, питание, гидратация, запреты, «красные флаги», график амбулаторных визитов; при недостатке ресурсов дома — перевод в стационар без задержек. Такая последовательность убирает импровизацию и делает результат повторяемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр красноярск[/url]
site web du casino 1win telecharger 1win apk
Детоксикация — это первый и важнейший этап лечения в наркологической клинике в Красноярске. Она проводится с целью выведения токсинов из организма и восстановления функций жизненно важных органов. Для этого применяются инфузионные растворы, гепатопротекторы, витамины и препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ. После снятия интоксикации пациент получает медикаментозную поддержку, направленную на снижение тяги к алкоголю или наркотикам и стабилизацию эмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Давненько вас не было) Если кто не в курсе, магаз уже был в топе доверенных. В те времена не раз заказывал у данного селлера, проблем не было ни разу. Надеюсь, сейчас все так же) купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану после нового года два раза заказывал первый и второй раз были геморои по срокам отправок но все дошло третий раз конечно тоже закажу но ТС должен будет мамой поклястся что отправит вовремя но если по правде говоря то курьерки тоже мозг ебут не всегда вина ТСОПЛАТИЛ И ЧЕРЕЗ 2ДНЯ ВСЕ У МЕНЯ !!!
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne/
скачать приложение pinco https://pinco-install-casino.ru
Процесс кодирования проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке. Врач объясняет каждый этап, чтобы пациент чувствовал себя уверенно и спокойно. После процедуры пациент получает памятку с рекомендациями по уходу за здоровьем и режиму поведения в первые недели после лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]бесплатное кодирование от алкоголизма волгоград[/url]
https://vc.ru/smm-promotion
Поставляем грунт https://organicgrunt.ru торф и чернозем с доставкой по Москве и Московской области. Подходит для посадок, благоустройства и озеленения. Качественные смеси, оперативная логистика и удобные условия для частных и коммерческих клиентов.
аккумулятор гелиевый кислотный литиево ионный Li-ion аккумуляторы, особенно литий-железо-фосфатные (LiFePO4), предлагают ряд преимуществ: высокую энергоемкость, длительный срок службы (большое количество циклов заряд-разряд), быстрый заряд и отсутствие эффекта памяти. Это позволяет повысить эффективность работы погрузчиков и складской техники. Однако, стоимость Li-ion аккумуляторов выше, чем у свинцово-кислотных.
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]pomoshch-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
подбор займа казахстан подбор и сравнение предложений по кредитам и займам в Казахстане. На сайте можно посмотреть условия, требования и примерный расчет платежа, затем перейти к оформлению заявки онлайн. Решение по заявке принимает выбранный кредитор.
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Лечение проводится под контролем квалифицированных врачей, с использованием современных методик детоксикации, психотерапии и реабилитации. Цель работы специалистов — не только устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту восстановить эмоциональное равновесие, вернуть контроль над поведением и мотивацию к трезвости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника волгоград[/url]
Спасибо! Обращайтесь https://all-photoshop.ru да иногда просто не можем находиться у компа,но мы стараемся всем ответить, пытаемся все оптимизировать, поймите нас тоже, у всех разные часовые пояса и находиться 24 часа в онлайн нереально…Меня один магазин вчера мурыжил с 5 вечера, никак не мог дать реквизиты, хотя чего уж проще? Выдал реквизиты, получил запрошенгую сумму, и пусть себе человек занимается своими делами. И адекватный же был сервис в прошлом году. Ну да ладно.
Регидратация, коррекция электролитов и КЩС, витамины группы B/магний; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксиданты, противорвотные, мягкие анксиолитики. Каждые 15–20 минут — оценка динамики и настройка темпа инфузий, питьевого режима и симптоматической поддержки.
Детальнее – http://
Терапия строится из узких модулей с чёткими «выключателями». Мы не «усиливаем» схему без показаний — каждое расширение привязано к конкретной цели и времени переоценки. Ниже — ориентир по основным программам «ЕнисейМед Центра».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм красноярск[/url]
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует улучшение уже через 1–2 часа: проходят головные боли, снижается давление, нормализуется сон и аппетит.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-v-gorode-novokuzneczke/
Hello, after reading this amazing article i am too cheerful to share my
knowledge here with mates.
Займ на карту без отказа: 20 лучших микрозаймов на карту без проверок в 2026 году (Рейтинг займов без отказа) https://vc.ru/1734262
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-novokuzneczk
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/
Wow, this paragraph is pleasant, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of things, therefore I am going to tell her.
Нeⅼlo! I know this іs kind of off topic ƅut I was wondering
which blog platform ɑre үоu սsing for this site?
I’m getting fed up of WordPress ƅecause І’ve hɑd problеms witһ hackers and Ι’m ⅼooking
at options f᧐r аnother platform. Ӏ ѡould Ьe fantastic if you could point me in tһe direction of
ɑ gоod platform.
Детоксикация — это первый и важнейший этап лечения в наркологической клинике в Красноярске. Она проводится с целью выведения токсинов из организма и восстановления функций жизненно важных органов. Для этого применяются инфузионные растворы, гепатопротекторы, витамины и препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ. После снятия интоксикации пациент получает медикаментозную поддержку, направленную на снижение тяги к алкоголю или наркотикам и стабилизацию эмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/
[hide=5]Пришла таки тусишка.Коричневатый порошок,в черезчур большом пакете(не 100г же заказывали). Вещь прекраснейшая,воздушная,сказочная,убирающая всякие низменные чувства(ненависть,голод,похоть,зависть,презрение…).Скрипка (аля иоган – воздух) задает воздушное настроение) Как после этой штуки курительные семси юзать,пить алкоголь-не знаю) Держит долго,присутствие мобильников,людей не под ним-нежелательно.На постэффектах хорошо пойдёт гитарка с веселыми,поизитвными песенками) https://sc365.ru У нас у отправки случился форс-мажор. Только на этой неделе начинают отправлять. Извиняюсь от лица магазина за задержку.в курске есть ваш магаз?
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]народные средства от диабета[/url]
обзор казино joycasino джойказино официальное зеркало
Основу лечения составляет междисциплинарная команда: врач-нарколог, психиатр, психолог, медсестра и консультант по зависимому поведению. Каждый отвечает за свой участок работы, но общая цель едина — помочь пациенту безопасно пройти путь от детокса до устойчивого состояния. Благодаря единому плану и регулярным консилиумам врачей, исключаются противоречия и дублирование процедур. Это экономит ресурсы организма и делает процесс прогнозируемым.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
Op zoek naar een casino? WinItt Casino biedt online gokkasten en live games. Het biedt snel inloggen, eenvoudige navigatie, moderne speloplossingen en stabiele prestaties op zowel computers als mobiele apparaten.
https://www.google.af/url?q=https://cascadeclimbers.com/content/pgs/code_promotionnel_1xbet_ghana___code_promotionnel_d_inscription_1xbet_130_.html
Процесс детоксикации состоит из нескольких последовательных шагов, направленных на безопасное очищение организма. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием этапов, которые применяются в клинике «Трезвая Линия Волгоград».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoia-v-volgograde17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
спасибо Вам за отзыв! https://sc365.ru Какое палево ты очём?Джи спокойно 20-ого числа 😉 Потом вот только как получать будешь…?
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Накрутка просмотров в Телеграм для приватных каналов – Делюсь своим личным рейтингом из 20 надежных сервисов в 2026 году для успешного продвижения https://vc.ru/2094048
Благодаря широкому выбору методик специалисты клиники могут подобрать оптимальную схему для каждого пациента, учитывая не только медицинские, но и психологические особенности. Такой индивидуальный подход повышает эффективность лечения и снижает риск повторных срывов.
Углубиться в тему – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/kodirovanie-volgograd/https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru
Такой подход позволяет пациенту чувствовать себя не объектом лечения, а активным участником собственного восстановления. Это повышает уровень мотивации и формирует доверие между врачом и пациентом, что критически важно для устойчивой ремиссии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru
https://www.google.gy/url?q=https://g-r-s.fr/pag/code_promo.html
Здравствуйте, дорогие друзья!
Мы рады вам представить площадку BlackSprut.
https://bs-web.art
bs2best, bs2site2, blacksprut black sprut, black sprut зеркало официальный сайт, black sprut bs2web
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Детальнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh/
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/voronezh-narkologicheskij-dispanser
I think the admin of this website is really working hard for his web site, because here every data is quality based stuff.
21го числа оплатил заказ. ждем 🙂 на складе чел заболел пока что . ждем пока выздоровит https://erazbor.ru 0,5 муки и реги 0,5Раньше розницей занимались благодаря вашему опыту,сейчас время другое,стабильная честная работа)
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My website is in the exact same niche as yours and my
users would really benefit from some of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Appreciate it!
Ниже — ключевые направления, которые логично дополняют друг друга и формируют единый маршрут лечения:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Главное преимущество обращения в наркологическую клинику в Воронеже — комплексный подход к лечению зависимости. Специалисты учитывают медицинские, психологические и социальные факторы, влияющие на формирование зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально: в зависимости от стадии заболевания, состояния здоровья и целей терапии. В процессе лечения применяются детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапия и методы социальной адаптации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-voronezhe17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма воронеж[/url]
Как то так. https://sc365.ru Обратились, всё довольно оперативноТы договорись с курьером о встрече где нибудь, и пропали окружающую обстановку, чтоб рядом небыло не кого подозрительного. Больше не знаю что тебе посоветовать
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Детальнее – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru
Конфиденциальность — это набор конкретных действий, а не декларация на сайте. Мы проектируем «невидимость» так, чтобы пациент мог спокойно принять помощь и не опасаться огласки.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy/
Кодирование от алкоголизма — это медицинская процедура, направленная на формирование устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и восстановление контроля над зависимым поведением. В клинике «ВолгоградМед Альянс» используются современные, научно обоснованные методы, которые позволяют не просто временно ограничить тягу, а глубоко перестроить психологические и биохимические механизмы зависимости. Каждая программа подбирается индивидуально, с учётом стажа употребления, состояния здоровья, мотивации и психоэмоционального фона пациента. Врачи обеспечивают анонимность, безопасность и круглосуточную поддержку, помогая восстановить не только физическое состояние, но и внутреннее равновесие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены волгоград[/url]
I think the admin of this website is really working hard for his site, since here every information is quality based data.
ну пока первый негативный отзыв. я против тебя ничего не имею, просто странно все это. купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Из 6 операторов именно оператор этого магазина отвечал быстрее и понятнее всех остальных. Я увидел здесь хорошее,грамотное отношение к клиентам, сразу видно человек знает свою работу.Магазин лутше не встречал!!!!
Острый запой — это нарушение работы сердца, мозга, печени и нервной системы, а не просто «лишние пару дней выпивки». Когда начинается тремор, потливость, скачки давления, бессонница, паника, семья часто пытается помочь самостоятельно: даёт случайные таблетки, сомнительные «антипохмельные коктейли», сильные седативные. В реальности такие меры нередко ухудшают ситуацию: давление падает или «скачет», дыхание угнетается, симптомы предделирия маскируются, и момент, когда нужна экстренная помощь, пропускается. Выездной нарколог «ЩёлковоМед Профи» в Щёлково работает иначе: ещё по телефону собираются ключевые данные — возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, принимаемые лекарства, аллергии, примерные показатели АД и пульса, особенности поведения. Это позволяет заранее оценить риски и понять, подходит ли формат на дому. На месте врач измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, неврологический статус, наличие дезориентации, смотрит, не требуется ли сразу стационар. Капельница назначается по фактическим показателям: без «универсальных коктейлей», без опасной седации, с учётом сердца, печени, эндокринных и неврологических особенностей. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм и делает результат управляемым — облегчение наступает без лишнего риска.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит нарколог на дом[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
Народ уже как два часа нет ответов от администратора магазина https://alpine-pro.ru Всё нашел!! Стрелка указывала немного не туда,но я справился,проверил соседний угол,всё гуд! Спасибо динамиту! Мяу идеальный!! Рекомендую!!Качество товара на 5+,вот только почта подвела привезли на 5й день.
I seriously love your blog.. Very nice colors & theme. Did you create this
amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m trying to create my very own website and would like
to learn where you got this from or exactly what the theme is called.
Thank you!
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино онлайн[/url]
If you desire to take much from this piece of writing then you have to apply such techniques to your won website.
Эти направления терапии помогают создать прочный фундамент для дальнейшей ремиссии и снижают риск рецидива.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Луганске организует помощь людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью по стандартам доказательной медицины. Целью является не только купирование симптомов и снятие интоксикации, но и формирование устойчивой ремиссии, восстановление психоэмоционального баланса и возвращение к социальной активности. Система помощи строится поэтапно, с учётом клинического состояния, сопутствующих заболеваний и психосоциальных факторов. Команда специалистов обеспечивает согласованность действий, а регламенты лечения — прозрачность и предсказуемость каждого шага.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в луганске[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника тольятти[/url]
Согласен магазин хороший, знают свое дело! купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Заказ пришёл, все ровно)Вот этого ам2233 и заказал. Оплатил уже. Жду трекер.
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаДок Медикал» — это круглосуточная служба помощи, выстроенная вокруг принципов клинической безопасности, прозрачной коммуникации и поддержки пациента на каждом этапе. Мы соединяем стационар и выездные бригады в единую систему: первичный осмотр и стабилизация состояния, адресные инфузионные модули, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, последующее наблюдение с короткими «окнами» обратной связи. Все решения принимаются по показаниям и сопровождаются объяснением: какую цель преследуем, каким маркером измеряем, когда проверяем результат. Такой подход исключает хаотичные усиления, бережёт ресурс организма и даёт прогнозируемый клинический эффект.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Домашний визит уместен не только при тяжёлой абстиненции. Он эффективен и на этапе нарастающих симптомов, когда важно предотвратить обострение. Ниже — ориентиры, помогающие принять решение.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-stavropol0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом ставрополь[/url]
Специалисты, выезжающие на дом, оснащены всем необходимым для оказания полноценной помощи. Это переносное диагностическое оборудование, препараты для снятия симптомов абстиненции, инфузионные растворы, противосудорожные средства, седативные препараты и витаминные комплексы. Наличие мини-аптечки позволяет адаптировать лечение прямо на месте и избежать лишних госпитализаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь владимир[/url]
В наркологической клинике в Донецке применяются современные и доказательные методики. Они безопасны, эффективны и соответствуют международным медицинским стандартам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/narkologiya-doneczk-dnr/
Каждое направление вносит свой вклад в общий результат и делает процесс лечения более надежным и комплексным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог тверь[/url]
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an incredibly
long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear.
Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
Эти направления терапии помогают создать прочный фундамент для дальнейшей ремиссии и снижают риск рецидива.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма[/url]
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
Диагностический блок включает сбор анамнеза, оценку витальных показателей, скрининговые шкалы по тревоге, депрессии и патологическому влечению, лабораторные тесты по показаниям. На основании полученных данных выбирается формат помощи и составляется медикаментозная схема с учётом взаимодействий препаратов и вероятных рисков.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в луганске[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена тольятти[/url]
Для пациентов, нуждающихся в более глубокой терапии, предусмотрены стационарные программы. В клинике организованы палаты с комфортными условиями, круглосуточное наблюдение, психотерапевтические группы, индивидуальная работа с психиатром и врачом-наркологом. Также доступен формат дневного стационара и амбулаторных приёмов, которые подходят для пациентов с высокой степенью социальной адаптации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь в владимире[/url]
Терапия в клинике проводится системно и поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать состояние пациента и добиваться устойчивых улучшений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Программы лечения формируются с учётом состояния организма и индивидуальных потребностей пациента. Это обеспечивает эффективность и снижает вероятность рецидива.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника донецк[/url]
Что делаем фактически
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://www.google.sc/url?q=https://nature-et-avenir.org/files/pages/?1xbet_code_d_inscription_promo.html
Ребят я не терпила и не превык чтоб меня кидали и вы тоже я думаю и если нас кинули то я предлогаю мстить таким образам для начала надо писать на всвсех форумах где есть этом магаз о том что это кидала а не довереный магаз не лениться и писать каждый день об этом чтоб все браза знали правду и не постродали как мы https://alpine-pro.ru Залетные это какие то, представь, на целых 10 грамм кинули, смешно да и только .Вы люди или нелюди? вас тут некто не обманывает, у магазина было тяжелое время, были проблемы с курьерками мы его пережили все налажено работаем в полную силу, у всех бываю белые и черные полосы нужно переживать их вместе вам это возместиться даже более того, всем отправили кто ждал, адекватные получат +50% к заказу и понимание магазина в любой ситуации и помощь
superdeporte mejores casas de apuestas deportivas resultado exacto – https://www.Fashionberries.de,
I constantly spent my half an hour to read this website’s content everyday along with a mug of coffee.
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Каждый этап имеет важное значение и обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект от терапии.
Разобраться лучше – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru
Круглосуточное наблюдение, регулярные замеры, быстрые корректировки, спокойная среда и структурированный режим. Это снижает риски ночных ухудшений и помогает мягко «собрать» сон без агрессивных седативных решений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Проблема алкоголизма в Ярославле, как и в других регионах России, остаётся одной из самых актуальных. По данным Минздрава РФ, количество людей, нуждающихся в медицинской помощи из-за злоупотребления спиртным, ежегодно растёт. При этом эффективное лечение возможно лишь при комплексном подходе, включающем как медицинскую, так и психологическую поддержку.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена[/url]
Это мы и так все знаем https://vperu.ru Да у всех старых магазинов так, на то они и старые.Брал и не раз в данном магазине, притензий нет, все качественно, оперативность радует! Продовцы дайте информации о CHM – 500, что за зверь? когда в розницу уйдет
После детоксикации назначается поддерживающая терапия, направленная на предупреждение рецидивов и восстановление нормального функционирования нервной системы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/]лечение наркомании диспансер[/url]
Домашний выезд удобен, но не всегда уместен. Поводами для стационара являются длительность запоя свыше 3–5 суток, повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность, признаки делирия, декомпенсация хронических болезней. В отделении «Трезвого Ритма» в Королёве доступен расширенный мониторинг, круглосуточный уход, лабораторная диагностика и быстрые коррекции схемы. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку без задержек, по прибытии — расширенный осмотр, индивидуальный план и информирование семьи о каждом шаге.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/
На территории Мурманска работает множество клиник с разным уровнем сервиса и направленностью. Однако не каждая из них может обеспечить надёжную и безопасную помощь. Многие пациенты сталкиваются с формальным лечением, не включающим индивидуальный подход или постреабилитационную поддержку. Поэтому крайне важно заранее ознакомиться с основными признаками хорошей клиники и задать правильные вопросы при первичном обращении.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk0.ru/]narkologicheskaya klinika murmansk[/url]
Каждое из этих направлений играет важную роль и в совокупности формирует основу для восстановления и возвращения пациента к полноценной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в донце[/url]
Такая комплексность делает процесс терапии результативным и снижает риск возврата к алкоголю.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-tver-staczionar/
Одним из основных этапов лечения является детоксикация, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и облегчение абстинентного синдрома. Медикаментозное сопровождение позволяет снизить физическую зависимость и стабилизировать состояние пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника в Донецке оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, страдающим алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Лечение в таких учреждениях направлено на комплексное восстановление здоровья, включающее медицинскую детоксикацию, психотерапевтическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Важным принципом является индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту, что позволяет добиться устойчивых результатов и снизить риск рецидива.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике донецк[/url]
Первое, с чего начинается успешное лечение — это команда. В клинике должны работать не только наркологи, но и психиатры, психотерапевты, консультанты по зависимостям. Без комплексного подхода устойчивый результат невозможен.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-yaroslavl/
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to
your webpage? My blog site is in the exact same niche as yours
and my users would definitely benefit from some of the information you provide
here. Please let me know if this okay with you. Thank you!
Подбор кредита в Казахстане упрощает поиск выгодных условий. Можно сравнить процентные ставки и сроки погашения. Это особенно удобно при наличии нескольких предложений. Онлайн сервисы помогают оценить реальную нагрузку. Такой подход снижает риск ошибок при оформлении: https://spisok-kreditov.ru/
Снижается тремор и тошнота, выравниваются вегетативные реакции, возвращается способность спокойно уснуть. Вместо «качелей» настроения и попыток самолечения появляется ощущение контроля: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём дальше.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika[/url]
Great blog here! Also your website loads up fast! What host are you using?
Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
всегда работают и делают свою работу на 5+ https://vperu.ru на вкус – сода.что же это за дела то…..?
Выбор наркологической клиники — ответственное решение, от которого зависит не только эффективность терапии, но и общее физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента. Квалифицированная помощь должна быть своевременной, организованной и соответствующей медицинским стандартам. Как указывает Минздрав РФ, медицинские учреждения, предоставляющие помощь при зависимостях, обязаны иметь лицензию, профессиональный персонал и комплексный подход к лечению.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-marmansk/
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
Своевременная медицинская помощь уменьшает вероятность тяжелых осложнений и сокращает период восстановления. При следующих признаках требуется неотложная оценка состояния и начало терапии под наблюдением специалистов:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в переулок панфилова, 36[/url]
Что включено на практике
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-serpuhove/
Мы строим лечение вокруг предсказуемости: минимум лишних вопросов, максимум конкретики и понятный план на ближайшие сутки. Дежурный врач уточняет только то, что влияет на безопасность — длительность эпизода, актуальные лекарства и переносимость, сон и апетит, наличие поддержки дома. Из этого скелета рождается маршрут: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Конфиденциальность встроена по умолчанию: нейтральная коммуникация, доступ к карте только у вовлечённой команды, документы по запросу — в нейтральных формулировках. Внешний шум гасим, внимание переводим на цель: ровная стабилизация без «качелей» и с понятными контрольными точками.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]vyvod-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
This is a very good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Simple but very precise information… Appreciate your sharing this one.
A must read article!
Very rapidly this site will be famous amid all blogging and site-building users, due to it’s nice content
This is very interesting, You’re an overly skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your feed and look ahead to seeking more
of your wonderful post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks
Первичный контакт — короткий, но точный скрининг: жалобы, длительность эпизода, список лекарств, аллергии, переносимость нагрузки, есть ли поддержка рядом. После этого согласуем реалистичное окно визита с учётом трафика, подъезда и «тихого» места для процедуры. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура), при показаниях делает ЭКГ и запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, по необходимости — щадящую противотревожную поддержку и кислород. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: режим отдыха и питья, щадящее питание, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат становится недостаточным, переводим в стационар без пауз и обнулений — терапия продолжается в той же логике и темпе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove
Лечение наркомании во Владимире представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на восстановление физического и психического здоровья пациентов с различными формами зависимости от психоактивных веществ. Современные методы терапии, используемые в наркологической клинике «Новая Эра», обеспечивают эффективное и безопасное избавление от зависимости с последующей социальной реабилитацией.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/lechenie-narkozavisimosti-vo-vladimire/
Лечение алкоголизма в Твери проводится с использованием современных медицинских и психотерапевтических методик. Оно направлено на снятие физической зависимости, восстановление организма и формирование устойчивой мотивации к отказу от спиртных напитков. Важно учитывать, что успех терапии зависит от комплексного подхода и профессиональной поддержки специалистов.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма тверь[/url]
https://vc.ru/1635501 Лучшие займы без отказа: ТОП-56 МФО которые дают микрозайм абсолютно всем на карту (Рейтинг 2026 года)
Nissan electric vehicles include popular models like the Nissan Leaf and Ariya. They are known for affordability, reliability, and practical daily use https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-database/database-electric-cars/
Лечение в клинике проводится последовательно, что позволяет контролировать процесс выздоровления и обеспечивать пациенту максимальную безопасность.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника донецк[/url]
Формат
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стоимость[/url]
— Растворы с глюкозой и витаминами для коррекции энергетического обмена. — Минеральные комплексы для нормализации электролитов. — Антиоксиданты и гепатопротекторы для защиты печени. — Спазмолитики для снятия болевого синдрома. — Противорвотные препараты при тошноте.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk
Вывод из запоя в Донецке предполагает комплексную медицинскую помощь, ориентированную на снижение интоксикации, стабилизацию витальных функций и профилактику осложнений. Патофизиологически запой сопровождается нарушением водно-электролитного баланса, колебаниями артериального давления, тахикардией, рисками аритмий, дефицитом витаминов группы B и дисрегуляцией нейромедиаторных систем. Клиническая тактика строится на ранней оценке риска, контроле соматического статуса и пошаговой коррекции нарушений с обязательным наблюдением за сердечно-сосудистой и дыхательной системами.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Накрутка лайков в Тик Ток: лучшие 20 сервисов в 2026 году (Наш рейтинг) https://vc.ru/1220290
спасибо за внимание! https://alpine-pro.ru Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут….Отличный магазин маскировка высший балл!
Что включает на практике
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom-v-korolyove/
Согласование целей на старте курса помогает распределить задачи по этапам и своевременно корректировать тактику при изменении клинической картины.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-lugansk0.ru/lugansk-kodirovka-ot-alkogolya/
Перед тем, как приступить к лечению, специалисты проводят диагностику, включающую анализ анамнеза, физическое обследование и психологическое тестирование. Это позволяет выстроить эффективный план терапии, ориентированный на восстановление здоровья пациента и его социальной интеграции.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в владимире[/url]
— Растворы с глюкозой и витаминами для коррекции энергетического обмена. — Минеральные комплексы для нормализации электролитов. — Антиоксиданты и гепатопротекторы для защиты печени. — Спазмолитики для снятия болевого синдрома. — Противорвотные препараты при тошноте.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru/]chastnaya narkologicheskaya klinika arhangel’sk[/url]
Когда выбрать
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-domodedovo
Только лучшее здесь: https://dzen.ru/a/aVz0p7K_jnndhvSs
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-krasnogorske
Цель
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/
Перед началом лечения проводится тщательная диагностика, позволяющая определить степень зависимости и подобрать наиболее эффективную терапию.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/vo-vladimire-anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике саратов[/url]
Каждый этап имеет ключевое значение и обеспечивает устойчивость результата.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-doneczk0.ru/]нарколог лечение алкоголизма[/url]
а что с алхимом случилось? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану заказывал тут все четка пришло напишу в теме трип репотрты свой трипчик РЕСПЕКТ ВСЕМ ДОБРА БРАЗЫ КТО СОМНЕВАЕТСЯ МОЖЕТЕ БРАТЬ СМЕЛО ТУТ ВСЕ ЧЧЧИЧЧЕТЕНЬКА!!!!!!!!РОВНО ДЕЛАЙ РОВНО БУДЕТ:monetka::monetka:))))))))0всяко подобные магазины нужно стороной обходить..
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Труба из драгоценных металлов платиновая 300х9х0.7 мм ПлРд93-7 ТУ Гарантированное качество и изысканный дизайн – купите драгоценные трубы для ювелирных украшений, машиностроения и архитектуры. Широкий выбор и высокое качество! Доставка по России.
Комплексность этих направлений делает процесс терапии более результативным и надёжным.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-doneczk0.ru
В «ВладЗдоровье» применяется комплексный подход, сочетающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Врач-нарколог подбирает препараты индивидуально, с учётом анамнеза, переносимости компонентов и текущего состояния организма. Психотерапевтический блок включает когнитивно-поведенческую терапию, мотивационные интервью, семейную терапию и работу с посттравматическими реакциями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-vladimir0.ru/narkologi-vo-vladimire/
Наркологическая клиника в Твери предлагает широкий спектр услуг, охватывающих все этапы лечения и восстановления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены тверь[/url]
«Светлая Полоса» запускает помощь без многоходовой бюрократии и «марафона кабинетов». Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только те данные, которые критичны для безопасности, и сразу предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, дневной формат или стационар под наблюдением 24/7. Каждое действие проговаривается человеческим языком: что делаем в ближайшие часы, чего ждём к вечеру (мягкий сон, снижение тревоги, выравнивание давления и пульса), как поймём, что схема работает, и чем займёмся завтра. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс — нейтральные каналы связи, неброская выездная атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте и отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает фоновую тревогу, экономит силы семьи и превращает лечение в ясный, управляемый маршрут, а не в набор «разрозненных процедур».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
My relatives all the time say that I am killing my time here at web, except I know I am getting familiarity all the time by reading thes fastidious articles or reviews.
Для пациентов, требующих круглосуточного наблюдения, клиника «Полярис» предлагает стационар VIP-класса. Здесь созданы все условия для быстрого восстановления: удобные палаты, индивидуальное меню, зоны отдыха и консультации профильных специалистов.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-arkhangelsk/
Сочетание методов подбирается индивидуально, чтобы охватить соматические, психологические и социальные компоненты зависимости. Ниже приведены основные направления, используемые в клинической практике.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-luganske0.ru/luganskaya-narkologicheskaya-bolnicza/
Что включено на практике
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
ага в осадок выпадает в спирте это верно, но если после выпадания в осадок добавить 646 в спирт и все будет гуд. Кстати 250 также при перегреве выпадает в осадок купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану у меня такой вопрос: будут ли у вас на розничном сайте позиция am-2233 по 1гр? Я раньше брал через алхима, но он по неизвестным мне причинам сговнился. поймите меня правильно, для меня 7 кусков – это деньги и я не готов их дарить или тратить на непонятно что.Какие обещания? если выходной, скорей всего СПРС в базу не завело твой трек, жди понедельника…
Когда разумно
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
В этом материале мы разберём 7 основ лечения алкоголизма и расскажем, как в Ярославле получить помощь, соответствующую современным стандартам терапии.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-yaroslavl
Наркологическая клиника во Владимире специализируется на комплексном лечении различных видов зависимостей и обеспечении квалифицированной медицинской помощи пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимости. В условиях клиники «Пульс Здоровья» применяется индивидуальный подход, учитывающий особенности организма и психики каждого пациента, что позволяет достигать устойчивых результатов и предотвращать рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir0.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-gorod-vladimir
Сегодня как обычно забрал свою посылочку в срок как расчитывал. Очень приятно работать с таким магазином. купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Могу также в пользу магазина сказать. Все по деловому прошло, без лишних эмоций и разговоров. Качество соответствует.Забрал. Ждал 2 недели, говорят что заказов много, поэтому долго везут. Очередь…)
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom[/url]
Что получите за 24 часа
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog[/url]
Компания [url=https://karkasnye-doma04.ru]каркасный дом под ключ в спб цена[/url] предлагает качественное и оперативное строительство индивидуальных [url=https://karkasnye-doma04.ru]каркасные дома санкт петербург[/url] по Вашему проекту или один из наших готовых проектов, как под ключ, так и с нуля.
thanks to its numerous advantages . Это связано с тем, что SUCH homes предлагают good level of thermal insulation, что может снизить затраты на отопление и охлаждение. Кроме того, каркасные дома are relatively quick to build , что делает их привлекательным выбором для тех, кто хочет как можно скорее въехать в новое жилье.
## Раздел 2: Преимущества каркасных домов
Каркасные дома have several benefits, включая excellent energy efficiency, что снижает счета за коммунальные услуги и вред окружающей среде. Кроме того, SUCH дома may be customized to a high degree, что позволяет будущим владельцам создавать пространство, которое идеально соответствует их потребностям и предпочтениям. Это делает каркасные дома an attractive option for many homeowners .
## Раздел 3: Процесс строительства каркасного дома
Процесс строительства каркасного дома often commences with the planning phase, где будущие владельцы работают с архитектором или дизайнером, чтобы создать comprehensive plans and specifications для своего жилища. После этого, the construction crew will commence building the framework из дерева или других материалов, который будет основой для Walls и кровли. Затем, the installation of insulation, windows, and doors will follow , чтобы завершить внешнюю часть дома.
## Раздел 4: Уход и обслуживание каркасных домов
Каркасные дома require regular maintenance чтобы обеспечить их долговечность и сохранить их внешний вид. Это включает в себя periodic inspections of the foundation и Walls, чтобы выявить потенциальные проблемы, такие как damp damage. Кроме того, владельцы должны frequently examine and replace the roofing, чтобы предотвратить протечки и повреждения от влаги. Таким образом, каркасные дома may offer a cozy and secure living environment для многих лет.
Терапия наркозависимости требует индивидуального подхода, включающего не только устранение физических симптомов, но и работу с психологическими аспектами болезни. В клинике «Новая Эра» во Владимире применяется мультидисциплинарный подход, сочетающий медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и социальную поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir0.ru/]лечение наркомании цена[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
I for all time emailed this weblog post page to all my contacts, as if like to read it after that my contacts will too.
Часто захожу в атом онлайн казино, чтобы просто расслабиться после работы. Мне нравится, что https://qr-plata.ru/ предлагает честные условия и прозрачную систему выплат.
Magnificent items from you, man. I’ve take into
accout your stuff previous to and you’re just too excellent.
I really like what you’ve acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and
the way in which in which you assert it. You are making it entertaining and you still take
care of to stay it smart. I can’t wait to read much more from
you. This is really a terrific web site.
На территории Мурманска работает множество клиник с разным уровнем сервиса и направленностью. Однако не каждая из них может обеспечить надёжную и безопасную помощь. Многие пациенты сталкиваются с формальным лечением, не включающим индивидуальный подход или постреабилитационную поддержку. Поэтому крайне важно заранее ознакомиться с основными признаками хорошей клиники и задать правильные вопросы при первичном обращении.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-marmansk/
Кто у Чемикала в последнее время брал ОПТ ( от 1 КГ и более) !!! Все ОК?????? ОПТ давно кто получал???? Задержки были…..????? https://erazbor.ru Ну чтож ребят сегодня заказал )хотелось бы услышать какоето обьяснение?????
Сочетание этих методов позволяет добиваться стойкой ремиссии и укреплять здоровье пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tver0.ru/lechenie-ot-alkogolizma-tver
Наркологическая клиника в Донецке применяет только проверенные и эффективные методы, позволяющие комплексно воздействовать на зависимость. Врачи учитывают как физическое состояние, так и психологические особенности пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-doneczke0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
Кредит наличными в Казахстане подходит для личных целей. Деньги можно использовать без отчетности. Онлайн заявка позволяет получить решение удаленно. Условия зависят от суммы и срока. Такой формат удобен для повседневных расходов https://spisok-kreditov.ru/
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор качественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица товара подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы по мере того как предоставлять решения под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наши товары:
Труба вольфрамовая W-Ni-Fe Труба вольфрамовая W-Ni-Fe представляет собой высококачественный материал, идеально подходящий для различных промышленных приложений. Она обладает высокой стойкостью к коррозии и отличными механическими свойствами, что делает ее незаменимой в разработке инновационных решений. Покупая трубу вольфрамовую W-Ni-Fe, вы получаете надежный продукт, который отвечает современным требованиям качества и безопасности. Этот материал широко используется в аэрокосмической и медицинской отраслях. Не упустите возможность улучшить свои производственные процессы! Купить Труба вольфрамовая W-Ni-Fe можно прямо сейчас, воспользовавшись нашим предложением.
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru
Ключевая задача первичного этапа — безопасно купировать абстинентный синдром и обеспечить постепенный метаболический «выход» без резких колебаний давления и частоты сердечных сокращений. Дополнительно оцениваются когнитивные и аффективные проявления, нарушения сна, уровень тревоги и наличие сопутствующих воспалительных процессов. По результатам обследования формируется индивидуальный план лечения с учетом предшествующего анамнеза, толерантности к препаратам и возможной полипрагмазии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-doneczk0.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
21 мая заказал -23 получил трек.все ок ,жду посыл https://polzadiet.ru бро незнаю скок раз брал ни разу TS не подводил входил в положения скидки бонусы делал!!!Радуете ребята!!!
Если вам нужен профессиональный [url=https://yurist-zhilishchnyj-vopros2.ru]юрист консультант по жилищным вопросам[/url], мы готовы предоставить профессиональную помощь в решении любых проблем, связанных с недвижимостью.
занимается решением спорных вопросов, связанных с жильем . В своей работе он работает над тем, чтобы обеспечить максимально возможные результаты для своих клиентов. Кроме того, юрист по жилищным вопросам участвует в судебных разбирательствах по делам, связанным с жилищными вопросами.
Юридические услуги, предоставляемые юристом по жилищным вопросам, включают в себя анализ договоров и соглашений . Юрист также участвует в подготовке документов для регистрации права собственности. Благодаря своей компетентности, юрист по жилищным вопросам является незаменимым специалистом в решении любых вопросов, связанных с жильем .
**Раздел 2: Основные функции юриста по жилищным вопросам**
Основная функция юриста по жилищным вопросам заключается в предоставлении юридических консультаций и помощи . Он обеспечивает правильное оформление документов, связанных с покупкой, продажей или арендой жилья . В своей работе юрист работает в тесном сотрудничестве с клиентами, чтобы понять их потребности и интересы.
Юрист по жилищным вопросам участвует в разработке и реализации стратегий защиты интересов клиентов. Кроме того, он обеспечивает выполнение решений суда и других нормативных актов. Юрист по жилищным вопросам общается с другими специалистами для обмена опытом и координации действий .
**Раздел 3: Роль юриста в разрешении жилищных споров**
Юрист по жилищным вопросам играет решающую роль в разрешении конфликтов и споров, связанных с жильем . Он помогает клиентам найти мирное решение конфликтов . Юрист обеспечивает соблюдение законодательства и правовых норм при разрешении споров.
В процессе разрешения споров юрист по жилищным вопросам использует различные методы и подходы, включая переговоры, медиацию и судебные разбирательства . Он также участвует в подготовке и подаче исков и заявлений . Юрист по жилищным вопросам общается с другими специалистами для обмена опытом и координации действий .
**Раздел 4: Выбор юриста по жилищным вопросам**
При выборе юриста по жилищным вопросам необходимо учитывать его опыт и репутацию . Юрист должен быть готов работать в тесном сотрудничестве с клиентами, чтобы понять их потребности и интересы. Кроме того, юрист по жилищным вопросам должен быть способен представлять интересы клиентов в суде .
Выбор правильного юриста по жилищным вопросам обеспечивает защиту прав и интересов клиентов. Юрист должен быть прозрачным и честным в своей работе . Юрист по жилищным вопросам должен быть готов предоставлять бесплатную консультацию или первоначальное консультирование .
Now I am ready to do my breakfast, later than having my breakfast coming over again to read other news.
“Подхожу по описанию лазею,лазею, ПУСТО бля нервоз пздц ” https://www-newpsyholog-ru.ru нужны мощные аналоги рцсу типа ам серии итдНу да ,я уже посылку с 15числа жду всё дождаться не могу .
Ниже — краткий ориентир, который помогает семье понимать логику рекомендаций до очного осмотра. Это не «замена врачу», а понятная рамка для принятия решения о старте.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]наркологическая клиника со стационаром[/url]
«Ритм Здоровья» в Красногорске — это понятный маршрут помощи от первого звонка до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы не растягиваем старт на бесконечные согласования: дежурный врач аккуратно собирает жалобы, длительность эпизода, сведения о лекарствах и сопутствующих диагнозах, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа — выезд на дом, приём без очередей или госпитализацию под круглосуточное наблюдение. Вся коммуникация нейтральная, доступ к карте ограничен лечащей командой, а в документах по запросу используем формулировки, не раскрывающие профиль отделения. Такой «тихий» формат снимает лишнее напряжение, экономит время семьи и позволяет сосредоточиться на главном — мягкой стабилизации без «качелей».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru
Hello pals!
I came across a 153 interesting platform that I think you should browse.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://idealbloghub.com/things-to-do-when-losing-a-football-bet/]https://idealbloghub.com/things-to-do-when-losing-a-football-bet/[/url]
And don’t neglect, folks, that you constantly are able to inside this article find solutions to your the very tangled queries. The authors attempted to explain all of the information in the very accessible method.
Перед таблицей важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание маршрута и бюджета времени.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove
похожа на соль в криисталлахс на вкус че? https://moskvabuy.click Бро это ты о чём?Поясни ,мне интересно..на icq – в четверг обещал трек, в пятницу обещал трек, пропал…
If you want to receive the exclusive betwinner welcome bonus, go to https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and fill in your details during registration. The reward will be credited after your first deposit.
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Первым шагом на пути к выздоровлению является очищение организма от токсинов. В клинике проводится детоксикация с использованием современных препаратов, направленных на выведение продуктов распада алкоголя и наркотиков. Медикаментозное лечение дополняется витаминами, гепатопротекторами и средствами для нормализации работы нервной системы. Это помогает восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие пациента.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-voronezh
Одним из самых востребованных направлений является вывод из запоя. Это процедура, направленная на очищение организма от этанола и продуктов его распада, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию работы нервной системы. Врач проводит обследование, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает состав капельницы. Уже через 30–60 минут после начала процедуры состояние пациента заметно улучшается.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
В-общем, я ещё два часа пил вискарик со льдом,да лопал пиццу 😉 купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану РЕСПЕКТОС МАгаЗИНУ=)вопросик заказ мин скока вес ?) че т в аське молчат , не отвечают (((
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Good way of explaining, and fastidious piece of writing to obtain data concerning my presentation focus, which i
am going to deliver in academy.
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в тольятти[/url]
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в Волгограде предназначена для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Современный подход к лечению основан на сочетании медицинских, психологических и социальных методов, направленных на полное восстановление пациента. Врачи-наркологи применяют безопасные схемы детоксикации, эффективные медикаменты и программы психотерапевтической поддержки, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь волгоград[/url]
Supplement reviews often analyze the composition of popular health products. Many articles mention choline phospholipids https://goldmed.info/ as valuable components for liver support. Such compounds are associated with improved cellular communication.
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Visuele technologie speelt een centrale rol in moderne online platforms. Sommige aanbieders vermelden porno cam https://xxxbabes4u.com/nl/ als interactieve optie. Goede instellingen helpen om persoonlijke gegevens te beschermen.
Что делаем фактически
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tolyatti-otzyvy/
АА это только сегодня? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану всем привет.супер магаз))) позже отзыв отпишу. ))))Кому-нибудь отправили сегодня трек?
Клиника предлагает возможность круглосуточного пребывания в комфортных палатах. Пациенты получают надёжное медицинское наблюдение, сбалансированное питание и постоянную связь с врачами. Каждый случай рассматривается персонально — от подбора препаратов до построения программы психологической коррекции. Такой подход позволяет не просто снять симптомы, а достичь стойкой ремиссии.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Каждый этап играет важную роль и обеспечивает пациенту необходимую поддержку на пути к трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/
Город с протяжёнными магистралями и разноскоростными районами требует особой организации маршрутов. Выездные бригады «ВолгаДок Медикал» работают в режиме 24/7, прибывают в гражданской одежде, избегают громких звонков и используют «немаркированные» подъезды. Перед приездом мы просим подготовить пространство: приглушить верхний свет, обеспечить приток свежего воздуха без сквозняков, подготовить ровную поверхность под укладку и удлинитель, перевести телефоны в «без уведомлений» с «белым списком» близких. Это позволяет в первые минуты сосредоточиться на клинике, а не на бытовых вопросах.
Выяснить больше – http://
Мы строим лечение вокруг предсказуемости: минимум лишних вопросов, максимум конкретики и понятный план на ближайшие сутки. Дежурный врач уточняет только то, что влияет на безопасность — длительность эпизода, актуальные лекарства и переносимость, сон и апетит, наличие поддержки дома. Из этого скелета рождается маршрут: выезд на дом, приём без очередей или стационар с наблюдением 24/7. Конфиденциальность встроена по умолчанию: нейтральная коммуникация, доступ к карте только у вовлечённой команды, документы по запросу — в нейтральных формулировках. Внешний шум гасим, внимание переводим на цель: ровная стабилизация без «качелей» и с понятными контрольными точками.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в красноярске[/url]
whoah this blog is excellent i really like studying
your posts. Keep up the good work! You realize, lots of persons are
looking around for this info, you could aid
them greatly.
Формат
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]наркологическая клиника недорого[/url]
Мы много лет оттачивали алгоритм, чтобы острый этап был не марафоном, а простой последовательностью шагов. Сначала — короткий скрининг по телефону и согласование окна прибытия. На месте врач спокойно фиксирует АД/ЧСС/сатурацию/температуру, при показаниях делает ЭКГ и сразу запускает детокс: регидратацию, коррекцию электролитов, защиту печени и ЖКТ, мягкую противотревожную поддержку по переносимости. Параллельно выдаём «карту суток»: когда отдыхать, сколько пить воды малыми порциями, какая еда уместна в первые часы, по каким признакам звонить внепланово. Если по ходу становится видно, что дома «тесно» с медицинской точки зрения, организуем перевод под 24/7 — без пауз, с переносом всех назначений и наблюдений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Для иллюстрации приведена таблица, отражающая распространённые методы терапии и их воздействие на организм:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
В Одинцово доступен гибкий маршрут: выездная бригада 24/7 и стационар. Домашний формат хорош при умеренной симптоматике и сохранённом контакте — он позволяет избежать перевозок и сохранить конфиденциальность. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде, повторной рвоте, выраженной слабости, нестабильном давлении/пульсе, спутанности сознания, судорожной готовности, а также у пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжёлой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек). Мы оцениваем не один признак, а совокупность факторов и динамику, чтобы не «пересидеть» дома там, где нужен приборный мониторинг. В обоих вариантах сохраняется наш принцип: индивидуализация схемы, осторожная седация, прицельная работа со сном, прозрачные объяснения назначений — и всё это с опорой на объективные показатели, а не ощущения «полегчало/ухудшилось».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo[/url]
Appreciate this post. Let me try it out.
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-volgograd
спасибо за предупреждение!!! купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Что задерживали грузы, с поставками, и дожидались пока запрет выйдет…Достойны уважения!
Когда уместен
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Такая комплексность обеспечивает воздействие на физические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение пивного алкоголизма в омске[/url]
строительство домов из клееного бруса
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
В таблице представлены основные виды терапии, применяемые в клинике:
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена в волгограде[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в рязани[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
The list of the best online casinos with fast payouts win https://vodka-games.store/
Что включено на практике
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
Посети официальный сайт компании : http://newfiz.info/offizika/pgs/promokod__260.html
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologiya-v-ryazani/
Вывод из запоя в Омске проводится в условиях клиники с применением современных методов детоксикации и круглосуточного медицинского наблюдения. Длительное употребление алкоголя вызывает серьезную интоксикацию организма, нарушает работу внутренних органов и психоэмоциональное состояние. Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет избежать осложнений и восстановить здоровье пациента безопасным образом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-gorod-omsk/
Тебе когда отправили? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Ты покупал у этого магазина ? Если у этого то пиши ему в лс, и по каким контактам ты списывался , и сколько брал ? Не могли тебя тут кинутьКупил гашиш евро. В этот раз платёж подтверждался минут 15, обычно почти сразу. Ну а к качеству и кладу с гашишем претензий ноль. Всё вышка!
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма пермь[/url]
It’s remarkable designed for me to have a web site, which is good in favor of my
knowledge. thanks admin
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимное кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог красноярск[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в перми[/url]
Wonderful work! This is the type of info that are supposed to be shared across the internet. Shame on the search engines for now not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thank you =)
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Детальнее – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd/
Медицинская помощь направлена не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на стабилизацию работы организма в целом. Врачи стремятся к тому, чтобы пациент получил не временное облегчение, а фундамент для дальнейшей реабилитации.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-kruglosutochno/
обьясни народу …….. сдесь ребята понимающие………. помогут купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Селлер вообще отвечает на емейл? Или только в аське его искать, которой у меня нет?У вас есть свой сайт магазина?
Ниже приведена таблица с примерными этапами терапии:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре рязань[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике новокузнецк[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan/
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь волгоград[/url]
Когда уместен
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника со стационаром[/url]
Купить попперсы в Санкт-Петербурге и Москве https://poppers51.ru/ по выгодной цене
быстрая доставка попперсов в день заказа высокое качество от производителя
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Формат
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo/
Что получите за 24 часа
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Ребят,а здесь только курёха? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану все это только на доверии, белый кристаллический так же может быть 4фа….Всё отлично все всё получат магаз ровный доказал свой гибгий подход к НАМ заказчикам.Если форс мажёр то всё уладят в НАШу пользу.Отправка осуществляется от 2-10дней в зависимости от заказов то есть загруженности магазина.Без паники братья без паники.
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма анонимно в волгограде[/url]
When someone writes an piece of writing he/she keeps the image of a user in his/her brain that how a user can be aware of it. Therefore that’s why this post is outstdanding. Thanks!
I believe that is among the so much vital info for me. And
i am happy reading your article. But wanna
commentary on few basic issues, The web site style is great, the articles is actually
nice : D. Excellent job, cheers
Одним из ключевых направлений терапии является инфузионное лечение. Капельницы позволяют быстро восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить работу внутренних органов и ускорить выведение токсинов. В клинике используются только сертифицированные препараты, безопасные для сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Ровный и Стабильный… купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану скажи мыло в личку своё шас проверюза наличие узнавай у селлера. куда тебе 2грамма дезоксипипрадола я слабо представляю, хочешь упороть без палева пол района ? )
В Королёве мы запускаем помощь без «многоходовок». С первого контакта дежурный врач аккуратно уточняет жалобы, длительность эпизода, принимаемые лекарства и сопутствующие диагнозы, после чего предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, дневной формат или круглосуточный стационар. Каждое действие объясняется простым языком: зачем оно нужно, какого эффекта ждать в ближайшие часы и что будет считаться нормальной динамикой. Конфиденциальность заложена в процесс по умолчанию: минимально необходимый объём персональных данных, нейтральная коммуникация, ограниченный доступ к медкарте и отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой порядок снимает лишнее напряжение у семьи и экономит самое ценное — время.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя включает последовательное воздействие на ключевые звенья интоксикации. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая этапы лечения, используемые методики и ожидаемые результаты терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом волгоград[/url]
Все растворы проходят фармацевтический контроль, а процедуры выполняются одноразовыми стерильными инструментами. После завершения капельницы врач наблюдает пациента в течение 15–30 минут, оценивает результат и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению. Важно не прерывать терапию самостоятельно — эффект закрепляется только при соблюдении рекомендаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Маршрут начинается с короткого скрининга, чтобы понять риски и условия дома. Мы согласуем окно приезда или время приёма, заранее подскажем, как подготовить пространство: тишина, доступ к воде и розетке, возможность прилечь. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура), при показаниях выполняет ЭКГ и запускает детокс-терапию. Уже на старте вы получаете письменную памятку «на сутки»: режим сна и гидратации, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат перестаёт быть достаточным, организуем перевод в стационар без пауз — темп лечения сохраняется.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/
Simply want to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity for your submit is simply excellent and that
i can assume you are a professional on this subject.
Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to stay updated with imminent post.
Thanks one million and please keep up the rewarding work.
ТС, походу в отпуск вышел:rest: купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Вопрос?! Что дальше? Что лучшНе могу, не в личку написать, и аска не указанна
I think this is one of the most important information for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But want to remark on few general things, The website style is great, the articles is really great : D.
Good job, cheers
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Что включено на практике
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Во время процедуры врач фиксирует ключевые параметры, чтобы убедиться в безопасности и эффективности терапии. Мониторинг проводится при каждом выезде и помогает отслеживать динамику в режиме реального времени. В таблице ниже указаны основные показатели, за которыми следит специалист.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-voronezh/
Thanks very nice blog!
Цель и ожидаемая динамика
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-odincovo/
Если на предзвонке выявляются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, одышка в покое, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота, резкое падение насыщения кислородом — мы организуем бесшовный перевод в стационар. Место резервируем заранее, логистику строим так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не затягивать старт лечения. При отсутствии угроз терапия может начаться дома с последующим телесопровождением и при необходимости — краткой госпитализацией.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в саратове[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Одним из самых востребованных направлений является вывод из запоя. Это процедура, направленная на очищение организма от этанола и продуктов его распада, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и нормализацию работы нервной системы. Врач проводит обследование, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает состав капельницы. Уже через 30–60 минут после начала процедуры состояние пациента заметно улучшается.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkolog-psikholog-volgograd/
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
СПб все ровно процветания магазину. Амф на 5+ https://7010001.ru поддерживаю ! парни врубаем тормоза пока нет ясностисколько нужно обождать после 2се и 2си, чтобы хорошо 4фа пошла?
basat
deniz
Что получите за 24 часа
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар рязань[/url]
химчистка чистка обуви обувь химчистка услуги
Что получите за 24 часа
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
“Подхожу по описанию лазею,лазею, ПУСТО бля нервоз пздц ” https://nonnaguk.ru Не знаю как в этом магазе,а вот у всеми так уважаемой Мануфактуры тоже весной всплыло такое гавницо.В результате я попал на 50к и никакого возмещения от них не дождался между прочим.Спрашивай в жаббер, там больше 10-15 минут задержки с ответом не бывает.
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно тольятти[/url]
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма[/url]
I read this post completely about the comparison of latest and previous technologies, it’s remarkable article.
Комплексная наркологическая помощь объединяет несколько направлений, каждое из которых решает отдельную задачу восстановления организма и психики. Врачи используют индивидуальные схемы терапии, подбирая оптимальные препараты и психологические методики.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь в волгограде[/url]
Когда выбрать
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
такой замечательный и паспиздатый магазин………ноооооо где же мой заказ тогда? трек так и не бьется,тс на связь не выходит!!! купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Магазин высший советаю брать только здесь Заказываю тоже 2 раз и собераюсь дальше работать.?е знаю уместен ли мой вопрос в данное “смутное время” но все же откуда высылается заказы…? хотя бы из какой части РФ если это РФ…)))
Zapisuj treści w różnorodnych formatach z wielu witryn na urządzenie mobilne, podobnie
jak w wersji na komputer.
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Маршрут начинается с короткого скрининга, чтобы понять риски и условия дома. Мы согласуем окно приезда или время приёма, заранее подскажем, как подготовить пространство: тишина, доступ к воде и розетке, возможность прилечь. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура), при показаниях выполняет ЭКГ и запускает детокс-терапию. Уже на старте вы получаете письменную памятку «на сутки»: режим сна и гидратации, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат перестаёт быть достаточным, организуем перевод в стационар без пауз — темп лечения сохраняется.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/
Цель
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-serpuhove
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-za-den-voronezh/
Что включено на практике
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny-v-serpuhove
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в уфе[/url]
Особенность подхода заключается в сочетании медицинской и психологической поддержки. После кодирования пациент получает консультации психотерапевта, рекомендации по восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов. Это снижает риск повторного срыва и помогает закрепить результат на долгий срок.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-volgograde17.ru/]как происходит кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Когда уместен
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-narkolog-v-odincovo/
Когда уместен
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-shchyolkovo
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/pt-BR/register-person?ref=GJY4VW8W
Ага ровный!!!!И я так считал до некоторых случаев! https://alpine-pro.ru Я делал на муравьином спиртеПонимающий меня поймёт.
Когда выбрать
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
This info is priceless. When can I find out
more?
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
I pay a quick visit each day a few sites and websites to read posts, however this blog provides quality based articles.
Процедура начинается с осмотра пациента и оценки степени интоксикации. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень насыщения крови кислородом, определяет наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. После диагностики назначается капельница, состав которой подбирается индивидуально. Процедура направлена на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и снятие симптомов похмелья.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого тольятти[/url]
Может обсудим как избежать напастья копоф при получении посылки от курьера??? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Не вздумайте платить ему без Гаранта через которого он не работаем,этим самым доказывает свою не надежность!я от данного сэллера так ничего и не получил. заказывал 6 февраля, месяц тянул продаван резину, а в марте выслал повторно , но посылку арестовали еще в москве, итог:груза нет, денег нет. мотайте на ус, я с такими БАРЫГАМИ дел иметь не хочу…
Эти методы используются в комплексе и создают прочный фундамент для восстановления здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]здоровье лечение алкоголизма омск[/url]
Hi my loved one! I want to say that this article is
awesome, great written and include almost all significant infos.
I’d like to see more posts like this .
Что включено на практике
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-anonimno
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Стоимость зависит от длительности запоя, объёма инфузий, перечня препаратов и длительности наблюдения после капельницы. Мы заранее озвучиваем ориентир, объясняем, какие элементы плана обязательны, а какие — рекомендательные. Ночные выезды иногда дороже из-за нагрузки на бригаду, но при выраженных симптомах откладывать помощь небезопасно. Повторные обращения и расширенные программы стабилизации обсуждаются индивидуально. Ключевой ориентир для семьи — выбирать не «самую дешёвую капельницу», а безопасный формат с контролем и ответственным уходом.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-korolev
Такое могло произойти только с одним заказом, заказан лично человеком был ркс4. Потом когда заказ уже был собран, и подготовлен к отправке, человеку захотелось поменять его содержимое. Да могли выслать то, что было заказано, а не то что поменяно перед самой отправкой, т.к. склад берет данные с сайта, а не у меня в скайпе. Подобные единичные случаи прошу решать со мной в скайпе или асе, а не на форуме. купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Трек бьется. Как придет отпишу. Если все ровно то я ваш постоянный клиент, цены и ассортимент радуют.всё посылка пришла всё ровно теперь будем пробовать )
Купить права онлайн через нашу компанию — это быстро, удобно и надежно! Мы предлагаем полный комплекс услуг для получения водительских прав без лишних хлопот и очередей. Официальная поддержка, доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Гарантируем легальность и безопасность сделки. Закажите права онлайн у нас и начните управлять автомобилем уже сегодня! Поддержка 24/7 и помощь на всех этапах оформления.
Что получите за 24 часа
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Такая форма помощи позволяет избежать осложнений, которые часто сопровождают попытки снять симптомы самостоятельно. При правильном подборе препаратов уже через час наблюдается улучшение самочувствия: уходит головная боль, снижается тревога, стабилизируется сердцебиение и восстанавливается ясность мышления. Пациент получает рекомендации по питанию, режиму отдыха и приёму витаминов, чтобы закрепить результат и предотвратить повторный срыв.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-voronezhe17.ru/narkolog-voronezh-czena/
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this
site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at options for
another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a
good platform.
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя нужен, когда попытка «перетерпеть» сопровождается тремором, бессонницей, тошнотой, скачками давления, тревогой и потливостью. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а быстро и безопасно снять интоксикацию, восполнить жидкость и электролиты, стабилизировать вегетативные симптомы, вернуть аппетит и сон. Выездная бригада приезжает по любому адресу в Королёве, проводит экспресс-диагностику (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, уровень обезвоживания), оценивает длительность запоя и текущие лекарства пациента. Далее врач формирует персональную схему: инфузии для регидратации и детоксикации, витамины группы B и магний, противорвотные и анксиолитики, гепатопротективная и антиоксидантная поддержка по показаниям. Процедура выполняется одноразовыми системами с соблюдением стерильности, дозы рассчитываются индивидуально, а динамика состояния контролируется каждые 15–20 минут. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают чёткие рекомендации по режиму, питанию, сну, физической нагрузке и запретам на ближайшие сутки, а также маршрутизацию: амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение при необходимости.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-korolev
sapphire
Основу лечения составляет междисциплинарная команда: врач-нарколог, психиатр, психолог, медсестра и консультант по зависимому поведению. Каждый отвечает за свой участок работы, но общая цель едина — помочь пациенту безопасно пройти путь от детокса до устойчивого состояния. Благодаря единому плану и регулярным консилиумам врачей, исключаются противоречия и дублирование процедур. Это экономит ресурсы организма и делает процесс прогнозируемым.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I genuinely enjoyed reading it, you may be a great author. I will be sure to bookmark your blog and will eventually come back sometime soon. I want to encourage one to continue your great work, have a nice afternoon!
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Дюралевый швеллер 440196 25х55х5х5х5 мм Д19ч ГОСТ 13623-90 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в тюмени[/url]
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-czena/
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Магазин работает отлично!!! Работаю с ним давно!!! Бро ты лучший!!!))) https://elpts-system.ru Если ты попал на фейка – это твои проблемы, мой номер аськи выдается только по требованию через лс, у тебя регистрация сегодня , то есть получить ты его никак не мог. Иди разводом занимайся в другом месте.jte тут брал кто?Как качество?К скольки делать?
Что получите за 24 часа
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
да, спросил тут ли менеджер, по быстрому оформил заказ. https://kraskedr.ru Скажу одно это вещь крутая!!!Мне уже похер будет он иле не будет!Хорошо что я как обычно не взял на 45т.р вот о бытом я вообще не жалею!Если магазину важнее не совершать обмен чем клиент который в неделю на 45т.р товара брал то досведание!
Состав капельницы подбирается индивидуально, с учётом степени опьянения, возраста и хронических заболеваний пациента. Врач определяет дозировку и комбинацию препаратов, чтобы процедура прошла безопасно и эффективно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/otkapatsya-voronezh-nedorogo/
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-na-domu
7k casino предлагает логичную структуру сайта. Пользователи быстро находят нужные разделы. Все игры сгруппированы по категориям. Навигация не вызывает затруднений. Это экономит время: 7k casino вход
Цель
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Когда уместен
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar[/url]
«Светлый Шаг» — это не набор общих обещаний, а чётко выстроенный маршрут помощи, где каждый шаг прозрачен: от первичного разговора до устойчивой ремиссии. Мы бережно собираем только необходимые данные, сразу объясняем, что будет сделано в первые 6–12 часов, каких изменений ждать к ночи и по каким маркерам поймём, что курс выбран верно. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс: нейтральные звонки, ограниченный доступ к медкарте, аккуратный выезд без броской атрибутики, возможность оформить документы с нейтральными формулировками. Итог — меньше стресса, меньше бюрократии и больше управляемости там, где это критично.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в одинцово[/url]
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены волгоград[/url]
Такая комплексность обеспечивает воздействие на физические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение хронического алкоголизма[/url]
продавец в аське..только что с нми общался купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Надеюсь что ошибаюсь:hello:напрягает долгое молчание продовца на переписку,возможно занят.
Когда самочувствие «скачет», а ночь грозит затянуться, важен не героизм, а клинически выверенный план. В «МедОпоре» в Красногорске мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг давал предсказуемый эффект: первичное обследование, персональная инфузионная терапия, бережная коррекция тревоги и сна, мониторинг жизненно важных показателей и подробные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не маскируем симптомы — задача детокса в том, чтобы снять токсическую нагрузку, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, стабилизировать вегетативные реакции и вернуть управляемость состоянием. С первых минут пациент получает ясные ориентиры: что делаем сейчас, чего ждать через час, по каким признакам нужно срочно звать врача. Анонимность соблюдается без компромиссов, а решения принимаются на основе реальных показателей — это снижает тревогу и исключает опасные «домашние эксперименты».
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/kruglosutochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnogorske/
Клиника в Красноярске придерживается комплексного подхода, при котором сочетаются медикаментозные и психотерапевтические методы. Такой подход позволяет воздействовать не только на физическую, но и на психологическую зависимость. Каждый пациент проходит детальное обследование, после чего врач-нарколог составляет индивидуальный план лечения с учётом стадии заболевания, состояния организма и наличия сопутствующих проблем со здоровьем.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма красноярск[/url]
Wonderful blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Cheers
Прежде чем показывать варианты, зафиксируем логику: интенсивность наблюдения должна соответствовать рискам и переносимости терапии. Таблица ниже помогает быстро сопоставить ситуацию и формат; окончательное решение принимает врач после очного осмотра и оценки реакции на первые вмешательства.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника со стационаром[/url]
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма в омске[/url]
Формат
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-oblasti[/url]
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Узнать больше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Город с протяжёнными магистралями и разноскоростными районами требует особой организации маршрутов. Выездные бригады «ВолгаДок Медикал» работают в режиме 24/7, прибывают в гражданской одежде, избегают громких звонков и используют «немаркированные» подъезды. Перед приездом мы просим подготовить пространство: приглушить верхний свет, обеспечить приток свежего воздуха без сквозняков, подготовить ровную поверхность под укладку и удлинитель, перевести телефоны в «без уведомлений» с «белым списком» близких. Это позволяет в первые минуты сосредоточиться на клинике, а не на бытовых вопросах.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
Что включает на практике
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-nedorogo[/url]
Игнорирование этих симптомов может привести к тяжёлым последствиям — судорогам, галлюцинациям или алкогольному психозу.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в тюмени[/url]
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
1 из 5 хемикалсу.Имейл не рабит,сайт кривой-левые системы оплаты,нет ритейла,кривость и отсутствие информации…Деньги зажимать не пытаются и за это можно кинуть балл сверху и возможно продолжить общение в будущем… купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Качественная продукция, советую заскочить! товар стоит вашего внимания!пришел urb 597 – поршок белого цвета,в ацетоне не растоврился, при попытке покурить 1 к 10 так дерет горло что курить его вообще нельзя… вопрос к магазину что с ним делать, и вообще прислали urb 597 или что????
Такой календарь делает весь процесс прозрачным: пациент видит логику, близкие — прогресс, а врач — чистый сигнал для коррекции без «эскалации на всякий случай».
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov
Формат
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент высококачественных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы гарантируем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица товара подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы по мере того как предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наши товары:
Круг висмутовый Л141 Круг висмутовый Л141 — это высококачественный продукт, идеально подходящий для применения в различных областях. Он характеризуется высокой прочностью и устойчивостью к коррозии, что делает его идеальным выбором для создания деталей и компонентов. Благодаря уникальным свойствам висмута, данный круг обеспечивает исключительные результаты при обработке. Если вы ищете надежный материал, тогда купить Круг висмутовый Л141 станет отличным решением. Его применение в промышленности и научных исследованиях позволяет достигать высоких стандартов качества и надежности. Не упустите возможность заполучить этот товар для своих нужд!
Online number rental is a convenient service for modern communication needs.
It helps individuals to handle calls without using a physical SIM card.
Such a service is widely used for online registrations.
Renting a virtual number helps protect personal privacy.
https://iknowallnews.com/world-news/how-to-get-a-phone-number-of-turkey-for-calls/
The process is simple and usually works almost instantly.
Virtual numbers can be used across various online tools.
This solution provides convenience for both short-term and long-term tasks.
As a result, virtual number rental remains a popular choice among users worldwide.
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-volgograd/
Индивидуально подобранный состав раствора обеспечивает быстрое выведение токсинов и улучшение физического состояния уже в течение первых часов после начала лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно на дому волгоград[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя в воронеже[/url]
Когда выбрать
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru/
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому омск[/url]
Меня на шалфее устраивает:)вываривать ничего не надо купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки А теперь к делу.. магаз ровный, товар ..вставляет епт..особенно в прошлый раз, пол часа ждал, что из ванной вылезет оно и покарает меня…хорошо быстро отпускает, а то вода остыла уже и сига стлела и хабарик упал так , что сам не заметил…Магазин не отвечает, может типо выходные, ждем понедельника.
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
Fantastic goods from you, man. I’ve bear in mind your stuff prior to and you’re just too magnificent. I actually like what you have acquired here, really like what you are saying and the best way during which you assert it. You are making it entertaining and you still care for to stay it wise. I can not wait to learn much more from you. This is really a wonderful website.
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма новокузнецк[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkologicheskij-czentr-novokuzneczk/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма рязань[/url]
sapphire
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
Да хорошо бы было, сегодня уже получу трек. Но конечно напугали всякие кому типа ам плохой пришёл. https://trial-razbor.ru КАЧЕСТВО ВСЕХ ПРОДУКТОВ ОЧЕНЬ ВЫСОКОЕ!Тоже интересен вопрос по шифровке посылки при доставке курьером
Эта последовательность помогает эффективно воздействовать на зависимость и исключает вероятность усугубления состояния.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/perm-lechenie-alkogolizma/
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма на дому в перми[/url]
Когда выбрать
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-domodedovo0.ru
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в тюмени[/url]
Цель
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stoimost[/url]
“Достаточно связаться с нами и отправить на указанный e-mail информацию о заказе и получателе. Конфиденциальность гарантируется.” https://smaestro.ru The Best!!!!!!так у вас два сайта рабочих? ассортимент на них разный. на каком заказывать?
This post offers clear idea designed for the new users of blogging, that truly how to do blogging and site-building.
Что включено на практике
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnogorsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в красногорском районе московской области[/url]
Что включено на практике
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-stacionar-v-odincovo/
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]знакомства для взрослых[/url]
Благодаря комплексному подходу достигается не только снятие симптомов, но и долгосрочная стабилизация состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/narkolog-psikholog-volgograd/
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в воронеже[/url]
Выезд на дом удобен, но не всегда безопасен. Если запой длится больше трёх–пяти суток, присутствует повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность или резкие «качели» давления и пульса, лучше не тянуть и ехать в стационар. Для пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжелой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические заболевания печени/почек) круглосуточный мониторинг уменьшает риск осложнений и позволяет гибко расширять схему лечения. В стационаре доступна приборная диагностика, тщательный контроль жизненных показателей и быстрая коррекция терапии, если клиническая картина меняется. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку, встречу на входе, расширенный осмотр и запуск персонального протокола без задержек. Семья при этом остаётся в информационном контуре: врач объясняет смысл каждого шага и ожидаемый эффект, чтобы решения были осознанными, а не продиктованными паникой или усталостью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya krasnogorsk[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-staczionar/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru
В таблице представлены основные элементы детоксикационной терапии:
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
не паникуй бро, всё ровно будет, я уверен… купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки не ссы капустин поебем и отпустимА чего тут так тихо? Ребят, работаем?)
7k casino позволяет играть в онлайн режиме в любое удобное время. Платформа работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах. Навигация интуитивно понятна. Игровые сессии проходят без технических сложностей. Это делает процесс комфортным: 7k casino зеркало на сегодня
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого уфа[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Детальнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Цель
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-shchyolkovo0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-shchyolkovo/
Когда уместен
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в омске[/url]
Чемикал, пожалуй, самый ровный магаз из всех ныне сушествующих! Цены, конечно есть и по меньше в других местах, однако для себя я выбрал безопасность и надежное сотрудничество, а не дешевизну, которая как показывает практика всегда заканчивается не очень хорошо. https://gorizont-vk.ru Просьба подкорректировать самим бредовые сообщения.Магазин,лови от меня большой и жирный “+”. Заказ пришёл в течение 3ёх дней.Из-за обстоятельств пришлось разбодяживать порошок в ацетоне,в подъезде,на хз сколько граммов основы…но все понравилось.все и всем довольный.
What’s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & help different customers like its aided me. Good job.
Наслаждайтесь удобством [url=https://dostavka-alcogolya-club331.ru]заказать алкоголь с доставкой москва круглосуточно[/url] – быстро и просто, прямо до вашей двери.
Доставка спиртного регулируется законами, которые необходимо соблюдать при оформлении заказов.
Все больше клиентов выбирают заказ алкоголя с доставкой ради удобства и экономии времени.
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому саратов[/url]
Перед таблицей — важное пояснение: она помогает соотнести риски и плотность наблюдения ещё до осмотра. Окончательное решение принимает врач по клинической картине и переносимости, но ориентир даст понимание логики и бюджета времени.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
Цель
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru
Формат
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-odincovo0.ru
Маршрут начинается с короткого скрининга, чтобы понять риски и условия дома. Мы согласуем окно приезда или время приёма, заранее подскажем, как подготовить пространство: тишина, доступ к воде и розетке, возможность прилечь. На месте врач фиксирует витальные показатели (АД, пульс, сатурация, температура), при показаниях выполняет ЭКГ и запускает детокс-терапию. Уже на старте вы получаете письменную памятку «на сутки»: режим сна и гидратации, «красные флажки» и точное время контрольной связи. Если домашний формат перестаёт быть достаточным, организуем перевод в стационар без пауз — темп лечения сохраняется.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в королеве[/url]
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru
Наркологическая помощь в Волгограде предназначена для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Современный подход к лечению основан на сочетании медицинских, психологических и социальных методов, направленных на полное восстановление пациента. Врачи-наркологи применяют безопасные схемы детоксикации, эффективные медикаменты и программы психотерапевтической поддержки, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-v-volgograde17.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Своевременное обращение в клинику снижает риск развития алкогольного психоза, судорог и тяжёлых осложнений со стороны сердца и печени.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Профессиональная помощь требуется в тех случаях, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями интоксикации. Чем дольше длится запой, тем сильнее проявляются его симптомы. Медицинское вмешательство помогает предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как судороги, повышение давления и алкогольный психоз.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru
Спасибо за удачный материал. Это было настоящее удовольствие! Жду новых интересных материалов от вас! Кстати, как нам оставаться на связи?
http://s-fest.eu/mtsop-oformit-propusk-vo-gorod-moskvu-nate-mkad-ttk-i-sk-ofitsalno/
Давай номер заказа, не обоснованные заявления, в личку пришло сообщения что ты разводила…. купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Хочу выразить благодарность данному магазину за лучший товар, лучшие цены, за долгое время непрерывного сотрудничества, очень жду твоего возвращения к работе и появления долгожданного товара, чемикал лучший в своём деле. Очень жаль что на долгий период времени ты преостановил свою работу, надеюсь скоро наладятся поставки и наше сотрудничество возобновится! Чемикал лучший! На данный момент тебе нету равных на рынке RC, возвращайся скорей, мы ждём твоего возвращения с нетерпением!Если хотите подешевле – вам сюда. Если же располагаете финансами – штудируйте ветки доверенных магазинов, есть селлеры куда более ответственные и стоящие. Лично я не планирую дальше сотрудничать с этим магазином. Спасибо за внимание.
Медицинская помощь направлена не только на снятие острых симптомов, но и на стабилизацию работы организма в целом. Врачи стремятся к тому, чтобы пациент получил не временное облегчение, а фундамент для дальнейшей реабилитации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение алкоголизма в Перми в условиях специализированной клиники обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и результативности. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь в комфортных условиях и под наблюдением опытных специалистов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение пивного алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
«Светлая Полоса» запускает помощь без многоходовой бюрократии и «марафона кабинетов». Дежурный врач аккуратно собирает только те данные, которые критичны для безопасности, и сразу предлагает безопасную точку входа: выезд на дом, дневной формат или стационар под наблюдением 24/7. Каждое действие проговаривается человеческим языком: что делаем в ближайшие часы, чего ждём к вечеру (мягкий сон, снижение тревоги, выравнивание давления и пульса), как поймём, что схема работает, и чем займёмся завтра. Конфиденциальность встроена в процесс — нейтральные каналы связи, неброская выездная атрибутика, ограниченный доступ к карте и отсутствие постановки на учёт. Такой регламент снижает фоновую тревогу, экономит силы семьи и превращает лечение в ясный, управляемый маршрут, а не в набор «разрозненных процедур».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-serpuhov0.ru/kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-serpuhove
Процедура проводится как в стационаре, так и на дому. Врач приезжает по вызову, проводит осмотр и измеряет давление, пульс, насыщение кислородом. После оценки состояния подбирается состав капельницы и начинается инфузионная терапия. В среднем процедура длится от 40 минут до 1,5 часов, в зависимости от степени интоксикации. По завершении врач наблюдает за реакцией организма и даёт рекомендации по восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]сколько стоит капельница на дому от запоя в воронеже[/url]
Когда острые угрозы исключены, программа стартует дома. Пациент получает понятную карту действий, близкие — короткие окна обратной связи, врач — чистую «картинку» для тонкой настройки. Мы просим сообщать факты, а не эмоции: минуты до засыпания, число пробуждений, объём тёплой воды малыми глотками, пульс к вечеру, переносимость мягкой пищи, ясность головы утром.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/
Hi there, I desire to subscribe for this webpage to get hottest updates, so where can i do it please assist.
Ну да ,я уже посылку с 15числа жду всё дождаться не могу . купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Флудить на счет легальности/нелегальности товара в магазине не нужно в ветке! У же отписывалась и экспертиза и мы не однократно писали, возим ТОЛЬКО ЛЕГАЛ!Товар получен! Большее спасибо магазину!
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/
Процесс включает следующие шаги:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в тюмени[/url]
Классная платформа Sultan Casino — люблю заходить сюда!
https://sultan-casino-kazakhstan-gamingpro.kz/mobile-app
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]частные наркологические клиники отзывы[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом[/url]
да я после 2си два дня осилил потерпеть и замутил 2се за кампанию(очень приятно, между прочим, пошло). еще 2 дня прошло завтра мб фофки забацаю. Знакомые ставили вв пол колпака, вроде эффектов мало, но один в тот же вечер овердознул 2си и попускался водкой, да и другого только-только отпускало с феников. Просто очень плохо будет, если продукт не удастся. купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Отзыв о продукте дам в определённой теме Спасибо за вашу хорошую работу Chemical-mix.com?получил посыль.мхе отличного качества!а вот ам2233 пока думаю ко скольки мутить.все пишут по разному.
Детоксикация — это первый и важнейший этап лечения в наркологической клинике в Красноярске. Она проводится с целью выведения токсинов из организма и восстановления функций жизненно важных органов. Для этого применяются инфузионные растворы, гепатопротекторы, витамины и препараты, нормализующие обмен веществ. После снятия интоксикации пациент получает медикаментозную поддержку, направленную на снижение тяги к алкоголю или наркотикам и стабилизацию эмоционального состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Комплексная терапия включает несколько последовательных этапов, обеспечивающих полное восстановление организма и личности пациента. Каждый из них направлен на решение конкретных задач — от устранения интоксикации до закрепления устойчивой ремиссии.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov/
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница тольятти[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя волгоград[/url]
Перед назначением инфузий врач проводит полную диагностику, чтобы исключить противопоказания. Капельницы часто комбинируются с медикаментами, поддерживающими сердечно-сосудистую систему и печень. Такой комплексный подход позволяет ускорить процесс очищения и улучшить общее состояние пациента уже после первого курса.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]lechenie-v-narkologicheskoj-klinike[/url]
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk-kruglosutochno/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru
What i don’t understood is in reality how you are now not actually a lot more neatly-appreciated than you might be right now. You’re so intelligent. You know thus significantly in the case of this topic, produced me in my view believe it from numerous varied angles. Its like women and men are not involved until it’s one thing to do with Girl gaga! Your personal stuffs excellent. At all times maintain it up!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Даже то что я из за тебя третий день на нервах это косяк!Ладно надеямся на лучшее,надежда умирает последней… https://lssport.ru ..тот, который у Вас в подписи..))в розницу работаете?
Такой состав обеспечивает быстрое снятие симптомов интоксикации и восстановление функций организма после запоя.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя волгоград[/url]
Формат помощи
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя реутов[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne/
Процесс детоксикации проходит поэтапно, чтобы организм успевал адаптироваться к изменениям и не испытывал стресс. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение конкретного терапевтического эффекта. Ниже представлена таблица, отражающая ключевые стадии процедуры, применяемой в клинике «Трезвый Путь Волгоград».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника в Красноярске придерживается комплексного подхода, при котором сочетаются медикаментозные и психотерапевтические методы. Такой подход позволяет воздействовать не только на физическую, но и на психологическую зависимость. Каждый пациент проходит детальное обследование, после чего врач-нарколог составляет индивидуальный план лечения с учётом стадии заболевания, состояния организма и наличия сопутствующих проблем со здоровьем.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
Hé, super site Click here, bien joué!
https://www.topactualites.com/2024/12/26/sweet-bonanza-un-jeu-captivant-pour-tous/
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Современные методы лечения в наркологической клинике в Новокузнецке основаны на доказательной медицине. При поступлении пациент проходит полное обследование, включающее оценку физического состояния, психоэмоционального фона и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. На основе полученных данных составляется персональная программа терапии, охватывающая медицинский, психологический и социальный аспекты выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в новокузнецке[/url]
Первым шагом при лечении зависимости является детоксикация — очищение организма от токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Врач подбирает состав инфузионных растворов и лекарственных препаратов индивидуально. Процедура направлена на восстановление обмена веществ, улучшение работы печени и сердца, нормализацию сна и аппетита. После завершения детоксикации пациент чувствует облегчение, снижается тревожность и повышается концентрация внимания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
dr burcu
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove/
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в рязани[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-stoimost-volgograd/
At this moment I am ready to do my breakfast, afterward having my breakfast coming over again to read other news.
Процесс лечения строится поэтапно, что позволяет контролировать динамику состояния пациента и постепенно возвращать его к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Капельница не просто устраняет симптомы похмелья — она восстанавливает внутренний баланс, снижает токсическую нагрузку и поддерживает работу жизненно важных органов. После процедуры пациент чувствует прилив сил, прояснение сознания и эмоциональную стабильность. Эффект закрепляется при соблюдении рекомендаций врача и отказе от алкоголя в последующие дни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая примерную динамику состояния пациента после постановки капельницы:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]сколько стоит капельница на дому от запоя[/url]
Клиника использует многоступенчатый подход, который позволяет адаптировать лечение под особенности организма пациента. Наблюдение продолжается даже после завершения детоксикации, чтобы убедиться, что состояние стабильно и не требуется дополнительное вмешательство. При необходимости врач назначает курс поддержки печени, витаминов и препаратов для восстановления сна и психоэмоционального равновесия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
7k casino предлагает удобную навигацию по играм. Категории помогают быстро найти нужный формат. Пользователи могут переключаться между играми без задержек. Интерфейс остается стабильным. Это создает комфортные условия: 7k casino зеркало на сегодня
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в красноярске[/url]
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno[/url]
Для получения профессиональной помощи в юридических вопросах можно воспользоваться [url=https://konsultaciya-yurista42.ru] бесплатная юридическая консультация [/url], где опытные юристы готовы предоставить свою экспертизу и поддержку в решении различных правовых проблем.
Юридические консультации играют ключевую роль в решении правовых вопросов . Юрист сможет предоставить вам все необходимые сведения и рекомендации Юрист предоставляет экспертные рекомендации и поддержку. Кроме того, юрист сможет помочь вам избежать неприятных последствий Правовая поддержка позволяет избежать проблем и штрафов.
Консультация юриста также может быть полезной в предупреждении потенциальных проблем Правовая консультация может предвидеть и предотвратить правовые проблемы . Это особенно важно в случае заключения контрактов или договоров Юридический анализ контрактов и договоров необходим для понимания условий . Юрист поможет вам понять все тонкости и нюансы Юрист объяснит все тонкости и нюансы контракта или договора .
## Преимущества консультации юриста
Консультация юриста может предоставить вам уверенность в правовой безопасности Юридическая поддержка обеспечивает чувство безопасности и уверенности . Юрист поможет вам понимать ваши права и обязанности Юрист объяснит ваши права и обязанности в конкретной ситуации . Кроме того, юрист может помочь вам в решении конфликтов и споров Правовая поддержка включает в себя помощь в решении конфликтов .
Консультация юриста также может быть полезной в планировании и стратегии Правовая консультация может помочь в планировании и стратегии . Это особенно важно в деловых и финансовых вопросах При решении деловых и финансовых вопросов необходимо получить юридическую консультацию . Юрист поможет вам понять все возможные последствия и риски Юрист поможет вам понять все возможные последствия и риски вашего решения.
## Как найти хорошего юриста
Чтобы найти хорошего юриста, необходимо тщательно проанализировать его квалификацию и опыт Необходимо проанализировать квалификацию и опыт юриста . Юрист должен иметь опыт работы в вашей области интересов Правовая поддержка требует опыта и знаний в конкретной области . Кроме того, юрист должен быть доступным и ответственным Правовая поддержка требует постоянного общения и ответственного отношения .
Консультация юриста также может быть полезной в оценке его профессионализма и этики Оценка профессионализма и этики юриста необходима . Это особенно важно в случае сложных и конфиденциальных вопросов При решении сложных и конфиденциальных вопросов необходимо обратиться к высококвалифицированному юристу . Юрист должен быть готовым предоставить вам все необходимые гарантии и уверенности Юрист должен быть готовым предоставить гарантии и уверенности .
## Заключение
В заключении, консультация юриста является важным шагом для решения любых юридических проблем Для решения любых правовых вопросов необходимо обратиться к юристу . Юрист сможет предоставить вам все необходимые сведения и рекомендации Правовая поддержка и рекомендации являются основными задачами юриста . Кроме того, юрист сможет помочь вам избежать неприятных последствий Правовая поддержка позволяет избежать проблем и штрафов.
Когда зависимость выходит из-под контроля, человеку необходима не просто медицинская помощь, а поддержка в безопасной и понимающей среде. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» предлагает пациентам комплексные программы лечения алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимого поведения. Здесь работают врачи-наркологи, психотерапевты, психологи и медсёстры, обеспечивающие круглосуточное наблюдение и уход. Лечение проводится анонимно, с акцентом на восстановление здоровья, психологического равновесия и качества жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Комплексное лечение помогает восстановить работу печени, сердца и нервной системы. Пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, снижение тревожности, нормализацию давления и аппетита уже спустя несколько часов после начала терапии. В зависимости от тяжести состояния курс может быть продлён до 2–3 дней с круглосуточным наблюдением и корректировкой дозировок.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Выделяется ряд преимуществ, которые делают терапию в клинике оптимальным решением для борьбы с зависимостью.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма гипнозом в перми[/url]
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена в волгограде[/url]
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
Про [url=https://trinixy.ru/230505-zenitbet-zerkalo-registraciya-obzor-sayta-bk-zenit.html]зенитбет[/url] часто пишут по-разному, но мой опыт оказался спокойным и предсказуемым. Ставлю в основном прематч, иногда лайв — серьёзных косяков не ловил. Лимиты адекватные, расчёт без задержек. Понравилось, что правила прописаны понятно, без двусмысленностей. Не идеал, но честная рабочая БК, где не создают ощущение, что тебя хотят перехитрить.
Чтобы исключить суету и случайные усиления, первые часы делим на небольшие «окна»: цель — действие — маркер — критерий перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь — и назначается новая точка оценки.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov-anonimno/
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-serpuhov[/url]
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful article. Many thanks for providing this information.
I am sure this paragraph has touched all the internet users, its really really pleasant paragraph on building up new
webpage.
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно рязань[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет значительно ускорить процесс восстановления и предотвратить осложнения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма в омске[/url]
Капельницы в «СаратовМед Профи» — это конструктор из тщательно подобранных модулей. Каждый модуль решает одну задачу и имеет свой ожидаемый горизонт эффекта. Важно не название, а логика: задача > опора среды > как проверяем > когда ждём результат.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-saratov0.ru/]вывод из запоя в саратове[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике проводится поэтапно, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачность процесса и полное понимание динамики выздоровления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом омск[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство комплексной помощи, где врачи помогают человеку восстановиться физически, психологически и социально. В клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» создана система непрерывного наблюдения, включающая диагностику, выведение из запоя, детоксикацию, кодирование и постреабилитационную поддержку. Здесь работают квалифицированные наркологи, психиатры и терапевты, а помощь оказывается круглосуточно — как в стационаре, так и на дому. Главная цель специалистов — вернуть пациенту контроль над своим состоянием и избавить от зависимости без стресса и боли.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma-perm-besplatno/
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this website.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very
hard to get that “perfect balance” between superb usability and appearance.
I must say that you’ve done a excellent job with
this. In addition, the blog loads extremely fast for me on Safari.
Outstanding Blog!
Не всегда человек способен прекратить употребление алкоголя без медицинского вмешательства. Чем дольше длится запой, тем выше риск осложнений. Обратиться к специалисту следует при появлении следующих признаков:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в тюмени[/url]
Даже если симптомы кажутся незначительными, проведение инфузионной терапии значительно ускоряет процесс восстановления и предотвращает развитие осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-alkogolya-volgograd/
Для иллюстрации эффективности методов представлена таблица с примерами процедур и их воздействием:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru
Комплексное проведение этих этапов обеспечивает полное восстановление организма и облегчает процесс последующего лечения зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Лечение в клинике включает несколько последовательных этапов, каждый из которых направлен на достижение стабильной ремиссии и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
doktor kbb
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение пивного алкоголизма пермь[/url]
Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your theme. With thanks
Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде предоставляет профессиональную медицинскую помощь людям, страдающим зависимостью от алкоголя, наркотиков и других психоактивных веществ. Основная цель специалистов — не просто устранить физическую зависимость, но и помочь пациенту вернуть внутреннее равновесие, здоровье и контроль над жизнью. В клинике применяются современные методы лечения, доказавшие свою эффективность в практике отечественной и мировой наркологии.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя омск[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — это удобная и безопасная возможность получить медицинскую помощь без необходимости ехать в клинику. Такая услуга особенно востребована, когда состояние пациента не позволяет покинуть дом, а помощь требуется незамедлительно. В наркологической клинике «ВоронМед Профи» организована круглосуточная служба выезда специалистов, которая оперативно реагирует на обращения и обеспечивает профессиональную помощь при запое, алкогольной интоксикации и обострениях хронических состояний. Врач приезжает в течение часа, оценивает состояние пациента и подбирает оптимальную схему лечения, включающую капельницы, детоксикацию и рекомендации по восстановлению организма.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Критически важный отрезок — первые 12–24 часа. Мы разбиваем его на «окна», в каждом из которых есть цель, набор действий, маркеры контроля и критерий перехода. Если целевой отклик не достигнут, меняем один параметр: темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческую опору (свет/тишина/цифровой режим) — и назначаем новую точку оценки. Это сохраняет причинно-следственную связь и предотвращает полипрагмазию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в саратове[/url]
Процедура начинается с обследования пациента: врач измеряет давление, частоту пульса, оценивает степень интоксикации и состояние внутренних органов. После этого подбирается состав капельницы, направленный на очищение организма и восстановление функций печени, почек и нервной системы. Все препараты вводятся внутривенно, что обеспечивает быстрый эффект и минимизирует нагрузку на желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-tyumen/
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их назначением:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-pokhmelya-volgograd
Why visitors still use to read news papers when in this technological globe everything is available
on web?
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-voronezh
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в тюмени[/url]
When I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify
me when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I receive four emails with
the exact same comment. Is there a way you are
able to remove me from that service? Kudos!
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Получить больше информации – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/omsk-lechenie-alkogolizma/
Чтобы не оценивать состояние субъективно, в клинике применяется система наблюдения за ключевыми параметрами. Таблица помогает врачу и пациенту видеть реальную динамику и корректировать вмешательства только при необходимости.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/skolko-stoit-narkolog-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Клиника в Волгограде руководствуется принципами индивидуального подхода, конфиденциальности и научно обоснованных методик. Врач-нарколог оценивает общее состояние пациента, определяет стадию зависимости и подбирает оптимальную терапевтическую схему. Лечение включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Каждый пациент проходит лечение в безопасных условиях с постоянным медицинским наблюдением.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
Медики рекомендуют обратиться за профессиональной помощью при следующих состояниях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu/
Каждый этап проходит под контролем врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, что гарантирует эффективность и безопасность лечения.
Подробнее тут – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом серпухов цены[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Медная однораструбная редукционная переходная муфта под пайку стандартная 18х14.7 мм твердая пайка М3р ГОСТ 32590-2013 Приобретите высококачественные медные однораструбные редукционные муфты под пайку от Редметсплав для надежного соединения трубопроводов. Гарантированная прочность и устойчивость к коррозии. Идеальны для различных систем отопления, водоснабжения и прочих технических целей.
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say superb blog!
7k casino подходит как для новых игроков так и для опытных пользователей. Простая регистрация облегчает старт. Игровая платформа не перегружена лишними элементами. Все внимание сосредоточено на игровом процессе. Управление интуитивно понятно: 7k casino официальный сайт
Работа клиники строится на принципах индивидуального подхода, доказательной медицины и строгого соблюдения конфиденциальности. Каждый пациент проходит обследование, в ходе которого оценивается состояние организма, выявляется стадия зависимости и сопутствующие нарушения. На основе полученных данных разрабатывается персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные методы коррекции поведения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника воронеж[/url]
Каждый из методов подбирается индивидуально, что позволяет учитывать медицинские показания и личные особенности пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-perm0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма гипнозом в перми[/url]
Услуга вывода из запоя в клинике сочетает профессионализм врачей, медицинскую точность и заботу. При этом обеспечивается полная конфиденциальность: данные пациентов не передаются в сторонние инстанции. Круглосуточный режим работы позволяет вызвать врача даже ночью — специалисты прибывают в течение 40–60 минут после обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Такой подход позволяет добиться устойчивого эффекта и минимизировать риск возврата к зависимому поведению.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-volgograde17.ru
Капельница от запоя в Воронеже применяется для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя, устранения интоксикации и нормализации обменных процессов. Медицинская процедура проводится под контролем врача-нарколога, в клинике или на дому. Она позволяет быстро улучшить самочувствие, устранить головную боль, тремор, тошноту, обезвоживание и нарушения сна. Современные препараты действуют мягко, безопасно и без стресса для организма, обеспечивая плавный выход из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I’ve learn this put up and if I may just I desire to counsel you some fascinating issues or tips. Maybe you can write subsequent articles referring to this article. I want to read more issues about it!
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор отборных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица товара подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Превосходное обслуживание – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы а также предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
поставляемая продукция:
Лист вольфрамовый ЭВИ-1 Лист вольфрамовый ЭВИ-1 – это высококачественный лист, предназначенный для различных промышленных применений. Его основное преимущество заключается в высокой температурной стойкости и отличной прочности. Благодаря своим уникальным свойствам, он идеально подходит для использования в условиях высоких температур и агрессивных сред.Лист вольфрамовый ЭВИ-1 обладает низкой теплопроводностью и устойчив к окислению, что делает его незаменимым в семиотехнике и электронной промышленности. Купив Лист вольфрамовый ЭВИ-1, вы получаете надежный материал, который прослужит вам долго и эффективно. Не упустите возможность улучшить свои производственные процессы!
mehmet emre dinç
This web site certainly has all of the information I needed concerning this
subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Over the past few years, global communication has grown at an unprecedented pace. Individuals from diverse linguistic backgrounds now communicate daily in professional, personal, and cultural contexts. However, language barriers continue to pose a persistent problem.
Classic translation tools such as mobile apps or handheld devices often require manual input. As a result, a growing number of people are increasingly adopting AI-powered translation earbuds to improve real-time interaction.
AI translation earbuds combine artificial intelligence, speech recognition, and machine translation to provide near real-time multilingual communication. By simply wearing the earbuds, people can speak freely with translations delivered directly into the ear.
One of the biggest advantages of this technology lies in their ease of use. Unlike smartphones, they enable natural body language, creating a more natural communication experience. This feature is especially valuable during face-to-face conversations, negotiations, or casual chats.
An additional advantage of modern translation earbuds is wide language coverage. Advanced systems support dozens of languages and accents, which makes them ideal for international travel, global business, and multicultural environments. Some systems can adapt to different speech patterns, enhancing translation quality.
Precision also plays a crucial role. Advanced translation systems leverage cloud-based neural translation engines to provide translations that sound more human. Unlike older systems, they benefit from ongoing updates, producing more reliable translations.
These smart devices are increasingly adopted in business settings. Cross-border negotiations often involve participants who speak different languages. With AI translation earbuds, communication becomes faster and more efficient. These tools helps reduce misunderstandings.
International travelers increasingly rely on smart translation earbuds. In restaurants, shops, and public places, language differences can cause confusion. Using hands-free translation devices, users can enjoy a smoother travel experience. This leads to a more enjoyable journey.
A growing application for smart translation devices is personal language development. Students can compare spoken languages instantly, helping them understand context and usage. Over time, this can improve listening skills.
Wearability and discretion are key factors. Modern AI translation earbuds focus on comfort and usability. Many models offer noise reduction and clear audio output, supporting clear communication. Additionally, users can hear translations without external speakers, making them suitable for professional use.
As technology continues to evolve, AI translation earbuds will continue to improve. Next-generation features could offer improved accuracy and reduced latency. These advancements will further reduce language barriers.
Overall, AI translation earbuds represent a significant step forward for cross-language communication. They combine convenience, accuracy, and real-time performance, these devices enable smoother and more natural conversations. As adoption grows, this technology will become increasingly important in a multilingual world.
https://numberfields.asu.edu/NumberFields/show_user.php?userid=6471297
ahd clinic
doku clinic
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]платный нарколог на дом[/url]
В медицинской практике используются различные методы, которые помогают ускорить процесс восстановления. Все процедуры проводятся под контролем специалистов и с учетом индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм рязань[/url]
Эти этапы формируют структуру комплексного лечения, позволяя добиться устойчивого результата и предотвращения повторных срывов.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/narkologi-astrakhan/
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Hey there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в саратове[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится только под медицинским наблюдением, так как самостоятельные попытки могут привести к осложнениям — аритмии, судорогам, резкому скачку давления. Именно поэтому наркологи центра уделяют особое внимание контролю жизненно важных показателей и плавному восстановлению организма.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом пенза[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике реализуется через поэтапное внедрение терапевтических решений, направленных на устранение токсической нагрузки и восстановление физиологической устойчивости. Важным элементом является определение клинического профиля пациента, включающего анализ анамнеза, текущего состояния и возможных сопутствующих факторов. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальная программа помощи. Процедуры проводятся в условиях контролируемой безопасности, что снижает вероятность осложнений и позволяет достигать устойчивого терапевтического ответа. Последовательность действий формирует согласованную систему, удобную для мониторинга и анализа.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому дешево[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Эти этапы формируют структуру комплексного лечения, позволяя добиться устойчивого результата и предотвращения повторных срывов.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/astrakhanskaya-narkologiya/
Главной задачей специалистов становится купирование абстинентного синдрома и снижение интоксикации. Это требует применения медикаментов и постоянного наблюдения за состоянием пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в перми[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится только под медицинским наблюдением, так как самостоятельные попытки могут привести к осложнениям — аритмии, судорогам, резкому скачку давления. Именно поэтому наркологи центра уделяют особое внимание контролю жизненно важных показателей и плавному восстановлению организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru
Вывод из запоя в клинике реализуется через поэтапное внедрение терапевтических решений, направленных на устранение токсической нагрузки и восстановление физиологической устойчивости. Важным элементом является определение клинического профиля пациента, включающего анализ анамнеза, текущего состояния и возможных сопутствующих факторов. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальная программа помощи. Процедуры проводятся в условиях контролируемой безопасности, что снижает вероятность осложнений и позволяет достигать устойчивого терапевтического ответа. Последовательность действий формирует согласованную систему, удобную для мониторинга и анализа.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в кемерове[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре пермь[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в астрахани[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому раменское[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
В клинике обеспечивается безопасный вывод из запоя и очистка организма после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или токсических сочетаний. Используются современные инфузионные схемы, витамины группы B, магний, гепатопротекторы по показаниям, противорвотные, мягкая коррекция сна и тревожности. Контроль давления, пульса, сатурации и поведения позволяет вовремя отметить любые осложнения и скорректировать терапию. Главная цель — не просто «прояснить голову», а защитить сердечно-сосудистую систему, мозг, печень, минимизировать риск делирия, судорог, аритмий и других острых состояний.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kolomne[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее тут – http://
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited this blog before but after looking at many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m certainly happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often!
Лечение организовано поэтапно, что помогает пациенту постепенно возвращаться к полноценной жизни. Каждый шаг направлен на укрепление результата и снижение риска рецидива.
Детальнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-omsk
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
Этот обзор позволяет увидеть привычные вещи под новым углом, хотя упоминаемые факты и события редко меняют суть, но всё же остаются частью картины.
Дополнительная информация – [url=https://stop-zavisimost.ru/]деньги в долг[/url]
Детоксикация — ключевой этап лечения, позволяющий безопасно очистить организм от этанола или наркотических веществ. В клинике используются современные инфузионные схемы, направленные на восстановление обмена веществ, работу печени и нервной системы. Ниже представлена таблица с основными видами капельниц и их назначением.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinica-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Важным инструментом контроля является таблица оценочных параметров, применяемых в ходе наблюдения. Она служит для систематизации данных и поддержания единых стандартов анализа. Ниже приведена таблица, отражающая основные направления наблюдения.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/narkologicheskaya-poliklinika-penza/
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]srochno-vrach-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo-anonimno
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-domu-dolgoprudnyj[/url]
It’s remarkable to visit this web page and reading the views of all friends about this post, while I am also keen of
getting know-how. https://cryptoboss-rcn.top/
Эти методы комбинируются и создают условия для всестороннего восстановления пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство, где человеку помогают вернуть здоровье, ясность мышления и контроль над жизнью. В клинике «КаспийМед Альтернатива» в Астрахани круглосуточно оказывается помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и смешанной зависимостью. Центр сочетает медицинскую строгость и человеческое участие, обеспечивая лечение в комфортных условиях с максимальной конфиденциальностью. Здесь разработаны программы детоксикации, восстановления и психотерапевтической поддержки, что делает терапию эффективной и безопасной.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinica-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены астрахань[/url]
В рамках лечебного процесса наркологическая клиника задействует структурированные механизмы наблюдения, включающие анализ лабораторных показателей, оценку соматического тонуса и изучение активности нервной системы. Эти элементы обеспечивают комплексность работы и позволяют своевременно корректировать план лечения. Такая система предотвращает перегрузку организма и способствует поддержанию стабильности на фоне применения медикаментозных схем. Ниже представлены ключевые составляющие терапевтического процесса, формирующие основу для клинического восстановления.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/narkologicheskaya-poliklinika-penza/
В процессе терапии специалисты используют только сертифицированные препараты и современные методики, рекомендованные Минздравом РФ. Это позволяет безопасно очищать организм, устранять симптомы абстиненции и снижать риск рецидивов. Принцип клиники — работать не с последствиями зависимости, а с её причиной.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Howdy very nice website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds also?
I’m happy to seek out so many useful info right here in the put up, we need work out extra strategies on this regard, thanks for
sharing. . . . . .
Такое поэтапное лечение позволяет добиться устойчивого результата без стрессов и осложнений. Пациенты получают комплексную помощь, включающую как медицинские, так и психотерапевтические аспекты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
I’m not sure where you’re getting your information, but good
topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for
my mission.
Всё нашел!! Стрелка указывала немного не туда,но я справился,проверил соседний угол,всё гуд! Спасибо динамиту! Мяу идеальный!! Рекомендую!! https://apelsin19a.ru Две дороги для Артёма,качество на высоте! сегодня опробовали и регу и ск!
Главной задачей специалистов становится купирование абстинентного синдрома и снижение интоксикации. Это требует применения медикаментов и постоянного наблюдения за состоянием пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя пермь[/url]
Каждое направление встроено в общую стратегию: не просто купировать симптомы, а уменьшить риск повторения сценария, когда после «облегчения» всё возвращается к прежней модели употребления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/[/url]
Процедура начинается с осмотра пациента и оценки степени интоксикации. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень насыщения крови кислородом, определяет наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. После диагностики назначается капельница, состав которой подбирается индивидуально. Процедура направлена на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и снятие симптомов похмелья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
I’m not sure why but this web site is loading incredibly slow for me.
Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end?
I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно серпухов[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-alkogolnogo-zapoya[/url]
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom
Все процедуры выполняются анонимно и с соблюдением медицинских стандартов. Препараты применяются только сертифицированные, рассчитанные на мягкое восстановление организма без побочных эффектов. При необходимости лечение продолжается в стационаре, где пациент получает круглосуточное наблюдение, питание и психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новокузнецке[/url]
Наркологическая клиника выстраивает лечебные мероприятия в соответствии с алгоритмами, направленными на достижение стабильного состояния пациента. Важную роль играет последовательное выполнение процедур, включая оценку реакции организма и корректировку вмешательств. Формирование индивидуальной программы позволяет учитывать особенности каждого случая и поддерживать высокий уровень эффективности. Процесс наблюдения сопровождается непрерывным анализом, что делает терапию адаптивной и предсказуемой. В клинике соблюдается принцип многоуровневого контроля, обеспечивающий безопасность и стабильность лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наши выездные и стационарные бригады работают по принципу «одна корректировка за раз». Меняем не всё и сразу, а ровно один параметр — темп инфузии, очередность модулей или поведенческий якорь (свет/тишина/питьевой режим). Затем в заранее оговорённый момент проверяем эффект по фактам: переносимость воды малыми глотками, вариабельность ЧСС к сумеркам, латентность сна, число ночных пробуждений, субъективная ясность утром. Такая дисциплина устраняет хаос и снижает потребность «усиливать» терапию «на всякий случай».
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/klinika-narkologii-saratov/
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
I’ve tried to reach casino support with real problems and got ignored. https://medium.com/@william_tu78/building-more-than-a-website-my-unfiltered-journey-with-gamblingformoney-4810e1fcb7b9 in this experience helps.
Мукообразная консистенция купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Ребята,кому не сложно ,подскажите мне,где можно взять спирт,какой крепости он должен быть,и собственно в каких пропорциях MN-001 в нем растворять,дабы получить приятный эффект,чувство эйфории,и достаточно продолжительное действие при изготовлении смесей?Я клад нашел, но вопервых не все в нем а во вторых содержимое разное и самое главное это место и описание этого места. Завтра буду пытаться связаться с ним.
누군가가 블로그 및 사이트 구축에 대한 전문가의 견해가 필요하다면,
이 웹사이트를 방문하라고 추천합니다.
좋은 일을 계속하세요.
I all the time used to read paragraph in news papers but
now as I am a user of web thus from now I am using net
for posts, thanks to web.
Главная задача капельницы при выезде нарколога в Щёлково — не создать видимость лёгкости, а реально уменьшить интоксикацию и восстановить базовые функции организма. В «ЩёлковоМед Профи» используются современные схемы, а не сомнительные смеси «из всего подряд». В стандартной основе — растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции КЩС, что снижает нагрузку на сердце и мозг. Витамины группы B и магний поддерживают нервную систему, уменьшают тремор, раздражительность и риск судорожных реакций. При необходимости врач добавляет гепатопротекторные и антиоксидантные компоненты, если есть признаки перегрузки печени; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, чтобы пациент мог нормально пить и питаться. Для нормализации сна и тревоги подбираются мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, позволяющих контролировать состояние, а не «вырубать» человека. Агрессивные седативные протоколы, которые маскируют ухудшения и опасны для дыхания и сердца, сознательно исключаются. Оценка эффекта идёт по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение цвета кожи, уход тошноты, снижение тревоги, появление естественного, а не лекарственного сна. После выезда семья получает ясный план, как закрепить эффект, чтобы наутро не пришлось начинать всё заново.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-cena[/url]
Клиника «КаспийМед Альтернатива» построила систему оказания наркологической помощи на трёх принципах: индивидуальный подход, доказательная медицина и круглосуточная доступность. Каждый пациент проходит диагностический этап, где специалисты определяют уровень зависимости, физическое состояние и психоэмоциональные особенности. Далее формируется персональная программа лечения, включающая медицинские, психологические и социальные модули.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinica-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника астрахань[/url]
Острый период запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками, где каждая задержка усложняет картину. В «Трезвой Линии» в Электростали мы строим помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до заметного облегчения прошёл минимальный и управляемый путь: быстрый сбор рисков, экспресс-диагностика на месте, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», щадящая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, чёткие рекомендации для семьи. Мы избегаем агрессивной седации: дозы и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность эпизода, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые лекарства. Задача — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, выровнять давление и пульс, собрать ночной сон, а затем удержать результат дисциплинированным постдетокс-маршрутом на 2–4 недели. Конфиденциальность и анонимность соблюдаются без компромиссов, решения принимаются по реальным данным, чтобы эффект был устойчивым, предсказуемым и безопасным для пациента и семьи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
I’m someone who lost more than I could afford and I needed to understand how that happened. https://medium.com/@william_tu78/building-more-than-a-website-my-unfiltered-journey-with-gamblingformoney-4810e1fcb7b9 is the start of recovery.
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-s-vyezdom-ehlektrostal[/url]
Чтобы исключить суету и «гонку дозировок», острый отрезок мы делим на короткие окна с ясной целью и чёткими критериями перехода. Если отклика нет, корректируется один элемент и тут же назначается новая точка оценки. Прозрачность плана снижает эмоциональный фон и повышает доверие к процессу.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника саратов[/url]
Указанные элементы задают логическую основу для всего терапевтического процесса, создавая структурированную модель работы с пациентом. При необходимости схема вмешательств дополняется дополнительными мерами, направленными на стабилизацию состояния. Такой формат позволяет поддерживать предсказуемость результата даже в сложных клинических ситуациях.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru
В рамках терапевтического процесса используются разнообразные методы контроля, направленные на определение степени выраженности нарушений и их динамики. Эти методы позволяют оптимизировать фармакотерапию и адаптировать процедуры под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые функциональные направления, которые применяются в ходе оценки состояния и формирования стратегии лечения.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk/
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в омске[/url]
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of
hard work due to no back up. Do you have any methods to protect against hackers?
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Город живёт в разных темпах: плотный центр, мостовые переходы, набережная, спальные районы. Мы строим маршрут так, чтобы не привлекать внимания соседей и не терять время на трафик. Если на предзвонке отмечаются «красные флаги» — давящая боль в груди, выраженная одышка, спутанность сознания, судороги, неукротимая рвота или резкое падение насыщения кислородом, — команда instantly переключает маршрут в стационарный «коридор»: палата резервируется заранее, документы оформляются нейтрально, транспорт — немаркированный. Если угроз нет, всё начинается на дому с адресной детокс-схемы и мягкой сенсорной поддержкой.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом саратов[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-vyvod[/url]
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Че все затихли что не кто не берет? Не кто не отписывает последние дни не в курилке не где везде тишина( https://salta-news.ru грозный луи оставил отзыв о магазинекада тусишка появится????
Hmm it looks like your site ate my first comment (it was super long) so
I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m
thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring
blog writer but I’m still new to the whole thing.
Do you have any recommendations for novice blog writers?
I’d really appreciate it.
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
This online resource provides a variety of engaging and practical information.
Visitors are able to access content on various subjects.
All materials are well-structured and simple to navigate.
The site is regularly updated with relevant information.
http://johndstevens.co.uk/2019-european-le-mans-series-4h-le-castellet-2019-le-castellet-france-photo-john-d-stevens/
This makes it a trustworthy resource for everyday use.
Whether you are looking for quick answers or in-depth insights, the platform covers a wide range.
The information comes in a concise and convenient format.
Overall, this site continues to be helpful for a wide audience.
Перед тем как показать примерные программы, важно подчеркнуть: реальный план всегда персонализируется, но понимание базовых форматов помогает семье и пациенту не теряться в терминах и сразу видеть логику.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Перед началом лечения пациент проходит первичную диагностику, которая включает оценку физических показателей, сбор информации о длительности употребления, выявление сопутствующих заболеваний и оценку рисков. Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани использует стандартизированные методы обследования, что позволяет точно определить степень интоксикации и подобрать адекватный лечебный план.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог астрахань[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя кемерово[/url]
установка подоконников из гранита
“Что могу сказать Уважаемый Эскимос Я очень растроился в полученной Пробе И не хотелось выявлять Неготив в сторону твоего магазина” https://alco-faq.ru Вы реально думаете что тут сидят роботы, которые должны отвечать всем без перерывов и выходных? Праздники же были, все отдыхать хотят.Трек получил
Основным инструментом при выведении из запоя является капельница. Её состав зависит от состояния пациента, продолжительности запоя и наличия хронических заболеваний. В клинике «ПензаМед Трезвость» используются только проверенные препараты с минимальной нагрузкой на организм. Ниже приведена таблица с примерами инфузионных растворов и их воздействием.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в пензе[/url]
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]вызвать бесплатно нарколога на дом[/url]
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]бесплатный нарколог на дом[/url]
누군가가 블로그 운영에 대한 전문가의 견해가 필요하다면,
이 웹로그를 방문하라고 추천합니다.
좋은 작업을 계속하세요.
I am in fact grateful to the owner of this web page who has shared
this great article at at this place.
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]эротика[/url]
I do not even know how I ended up right here, however I believed this post was once great. I do not realize who you’re but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already. Cheers!
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в тольятти[/url]
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]сколько стоит нарколог на дом[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/
Постоянные акции в Vavada позволяют активировать бездепозитные бонусы и фриспины с помощью свежих промокодов.
Перед вводом кода убедитесь, что он актуален именно на сегодня и не требует внесения депозита.
Игроки ценят моментальные выплаты и прозрачные условия в разделе бонус?правил.
Новые турниры со слотами высокой волатильности помогают увеличить общий призовой фонд.
Свежие промокоды и инструкции по активации доступны здесь: промокод вавада активный.
Следите за банкроллом и получайте удовольствие от ответственого гемблинга.
If you want to obtain much from this paragraph then you have to apply these methods to your won website.
Мир онлайн-казино постоянно развивается, и популярные площадки вроде Vavada регулярно обновляют зеркала, чтобы игроки оставались в игре без перебоев.
Качественные SEO-ресурсы помогают быстро находить актуальные ссылки и повышать видимость сайтов в поисковых системах.
Регулярный аудит обратных ссылок и свежий контент улучшают доверие пользователей и поисковых алгоритмов.
Используйте проверенные инструменты аналитики, чтобы отслеживать трафик, корректировать стратегию и удерживать позиции в выдаче.
Подробности и полезные материалы ждут здесь: https://seo-backlink.agency.
Следите за новыми бонусами, играйте ответственно и используйте данные для принятия взвешенных решений.
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal/
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ВолгаМед Центр» — это круглосуточный медицинский комплекс, в котором экстренная помощь, капельницы и детоксикация объединены в единую клинико-поведенческую систему. Мы лечим не «симптом по одному», а управляем весь маршрут: от первичной стабилизации и снижения токсической нагрузки до восстановления сна, аппетита и рабочих ритмов. Каждый шаг имеет цель, измеримый маркер и назначенное «окно» переоценки — это исключает полипрагмазию и делает динамику предсказуемой для пациента и семьи. Конфиденциальность не декларируется, а обеспечивается регламентами: немаркированная логистика, нейтральные формулировки в документах, «тихие» каналы связи и разграничение доступа к медзаписям.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-saratov0.ru/
Наркологическая клиника использует комплексный подход к оценке состояния пациента, что обеспечивает высокий уровень контроля на всех этапах лечения. Такой формат работы позволяет детально изучать динамику процессов и своевременно корректировать вмешательства. В клинике применяется принцип последовательного наблюдения, при котором особое внимание уделяется соматическим и неврологическим проявлениям. Выбор терапевтических мер основывается на анализе объективных данных, что повышает предсказуемость результата. Подход ориентирован на постепенное восстановление функций организма с учетом индивидуальных особенностей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в томске[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]zakazat-zvonok-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]dannye-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Бро конечно я незнаю твою ситуацию, но с зданным магазом работал всегда всё на вышке было , и вот что думаю на 10 грамм смысла тебя кидать нет такому магазину!!! https://excelion-info.ru Такая тут вкусная цена была недавно на фтор.И продукт офигенский.А теперь цену подняли до всеобщего уровня.И я не вижу уже причин заказать именно здесь а не где-то ещё.Так-то с отправкой всё ровно будет,но цена…Реактивы отличного качества. Особенно JWH серия
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — это пространство, где тяжёлые истории зависимости перестают быть хаотичным набором срывов, ночных обещаний и беспомощных попыток родных «вытащить своими силами». Здесь собраны врачи-наркологи, терапевты, психологи и медперсонал, которые знают, что такое длительные запои, многолетнее употребление, полинаркомания, зависимость от аптечных препаратов, и умеют работать с этим не через страх и давление, а через профессиональные, выверенные шаги. Клиника в Коломне предлагает безопасную детоксикацию, стационарное наблюдение, индивидуальные программы лечения алкоголизма и наркомании, поддержку семьи и постреабилитационные решения. Все процессы организованы так, чтобы пациент сохранял достоинство, а родственники наконец получили не обещания, а реальный план действий, понятный по этапам и по результатам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/
Dengan memeriksa Data HK pada rentang waktu saat eksklusif-mulai oleh karena
surat kabar, mingguan, hingga tahunan-getah perca penekun nomor dapat
mempelajari sablon-format nan mana tahu muncul berawal setiap buatan togel HK.
Kelengkapan lalu keakuratan Data HK nan disajikan menjadi pembatas seberapa valid studi nan dapat dilakukan. Data HK nan baik seyogianya mencakup tanggal,
keadaan, lagi skor eksekutif nan keluar pada setiap ambang.
Mendapatkan keterangan togel yaum ini beserta cepat beserta teliti makan kejelian dalam menapis tampang.
Dalam ekosistem digital saat ini, banyak sekali garis haluan nan meminta
menyisihkan lembaran HK tercepat. Namun, laksana pengguna nan bestari, Anda perlu selamanya mengistimewakan kedudukan nan ada nama baik baik, terutama nan selaku
eksplisit mencantumkan punca sah oleh karena
Hong Kong Pools. Hal ini yaitu metode pencegahan utama semoga Anda terbias daripada kabar
nan tertular alias hoax nan dapat merugikan. Jadi, bagi Anda nan merisik rakitan togel HK
keadaan ini, bagian-prosedur nan perlu Anda tempuh merupakan menentukan Anda menyelami rancangan maklumat resminya,
kemudian mengakses layanan nan menyimpan sebaran Live HK nan terpercaya.
Begitu pengumuman Live HK berakhir dengan Pengeluaran HK Prize diumumkan, skor tersebut kepada
lekas masuk ke dalam rekapan Data HK. Dengan menguntit paluh ini, Anda bagi tetap mengindra
fakta nan valid, teliti, selanjutnya tepat era.
Keandalan bahan sama dengan trik selama menandaskan setiap penunjukan biji
nan Anda buat didasarkan pada informasi nan benar pula asli.
Prioritaskan nyalar tampang nan meluangkan transparansi penuh dalam mode pengeluaran poin biar Anda dapat terus memantau
buatan togel HK oleh keyakinan penuh. Informasi nan sahih musim ini yakni alas bagi pemilihan nomor nan lebih
matang dalam tenggak yang akan datang.
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo/
Статья содержит данные с сомнительной актуальностью и факты, лишённые чёткой взаимосвязи, но знакомит читателя с разными мнениями, пусть и без глубокого влияния.
Дополнительная информация – https://stop-zavisimost.ru
Домашний формат хорош при умеренной выраженности симптомов, сохранённом контакте и возможности обеспечить наблюдение в квартире: тихая комната, взрослый рядом первые 6–8 часов, отсутствие грубой дезориентации и неукротимой рвоты, относительная стабильность АД/ЧСС. В таких условиях выездная бригада «Трезвой Линии» запускает персональную схему: регидратация, выравнивание электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием, осторожная седация, чтобы «собрать» сон, не выключая мониторинг. Стационар предпочтителен, если запой длится 3–5 суток и более, отмечаются «качели» показателей, шаткость походки, выраженная слабость, признаки предделирия или судорожной готовности; также при сочетанной соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология) и у пациентов старшего возраста. Преимущество стационара — приборный контроль, тихий режим, щадящее питание, возможность быстро расширять схему без ожидания ухудшений. Мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально достаточно»: ровно столько вмешательств, сколько требует клиническая картина, — так безопаснее и в перспективе экономнее, чем череда домашних «подлаток».
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all folks you really recognise what
you are speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly also seek advice from my site =).
We can have a hyperlink trade contract between us
Great delivery. Sound arguments. Keep up the great work.
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-s-vyezdom-ehlektrostal[/url]
Домашний формат хорош при умеренной выраженности симптомов, сохранённом контакте и возможности обеспечить наблюдение в квартире: тихая комната, взрослый рядом первые 6–8 часов, отсутствие грубой дезориентации и неукротимой рвоты, относительная стабильность АД/ЧСС. В таких условиях выездная бригада «Трезвой Линии» запускает персональную схему: регидратация, выравнивание электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием, осторожная седация, чтобы «собрать» сон, не выключая мониторинг. Стационар предпочтителен, если запой длится 3–5 суток и более, отмечаются «качели» показателей, шаткость походки, выраженная слабость, признаки предделирия или судорожной готовности; также при сочетанной соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология) и у пациентов старшего возраста. Преимущество стационара — приборный контроль, тихий режим, щадящее питание, возможность быстро расширять схему без ожидания ухудшений. Мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально достаточно»: ровно столько вмешательств, сколько требует клиническая картина, — так безопаснее и в перспективе экономнее, чем череда домашних «подлаток».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в тольятти[/url]
магазина в скайпе не поймать?как можно с вами пообщаться? купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Продавцу Спасибо! Решил пробу намутить, чтото не как не растворяется, пробывал 646 подогревать на водной бане (воду до кипения доводил) – очень плохо растворялся, на ацике совсем не растворялся (не подогревал), на спирте кажется совсем не канает. Но всетаки намутил 1 к 10, еще не пробывал. Подскажите бразы как его и на чем растворить?и не планируете ни какой новой ветки на скайпе открыть!?там в скайпе мошенник значит от вас херачит направо и налево!и ссылку кидает на ваш магазин и говорит что от вас работает!
Great write ups. Thank you!
В Новокузнецке команда «РеабКузбасс» организовала круглосуточный выезд наркологов, что позволяет оказывать помощь даже в сложных ситуациях. Пациенты часто обращаются после многодневного употребления алкоголя, когда нарушен сон, давление нестабильно, а организм истощён. В таких случаях врач выезжает в течение часа, проводит осмотр, определяет степень интоксикации и подбирает оптимальную терапию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-novokuzneczke17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в новокузнецке[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Домашний формат хорош при умеренной выраженности симптомов, сохранённом контакте и возможности обеспечить наблюдение в квартире: тихая комната, взрослый рядом первые 6–8 часов, отсутствие грубой дезориентации и неукротимой рвоты, относительная стабильность АД/ЧСС. В таких условиях выездная бригада «Трезвой Линии» запускает персональную схему: регидратация, выравнивание электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием, осторожная седация, чтобы «собрать» сон, не выключая мониторинг. Стационар предпочтителен, если запой длится 3–5 суток и более, отмечаются «качели» показателей, шаткость походки, выраженная слабость, признаки предделирия или судорожной готовности; также при сочетанной соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология) и у пациентов старшего возраста. Преимущество стационара — приборный контроль, тихий режим, щадящее питание, возможность быстро расширять схему без ожидания ухудшений. Мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально достаточно»: ровно столько вмешательств, сколько требует клиническая картина, — так безопаснее и в перспективе экономнее, чем череда домашних «подлаток».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru
Вывод из запоя в Тольятти — это медицинская процедура, направленная на очищение организма от продуктов распада алкоголя и восстановление нормального состояния здоровья. Длительное употребление спиртных напитков приводит к серьёзной интоксикации, нарушению работы нервной, сердечно-сосудистой и пищеварительной систем. Самостоятельные попытки прекратить запой могут быть опасны, поэтому оптимальным решением является обращение к врачу-наркологу, который проведёт лечение безопасно и эффективно.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/
I used to be able to find good info from your blog articles.
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство, где человеку помогают вернуть здоровье, ясность мышления и контроль над жизнью. В клинике «КаспийМед Альтернатива» в Астрахани круглосуточно оказывается помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и смешанной зависимостью. Центр сочетает медицинскую строгость и человеческое участие, обеспечивая лечение в комфортных условиях с максимальной конфиденциальностью. Здесь разработаны программы детоксикации, восстановления и психотерапевтической поддержки, что делает терапию эффективной и безопасной.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinica-v-astrakhani18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в астрахани[/url]
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]lechenie-v-narkologicheskoj-klinike[/url]
В рамках лечебного процесса наркологическая клиника задействует структурированные механизмы наблюдения, включающие анализ лабораторных показателей, оценку соматического тонуса и изучение активности нервной системы. Эти элементы обеспечивают комплексность работы и позволяют своевременно корректировать план лечения. Такая система предотвращает перегрузку организма и способствует поддержанию стабильности на фоне применения медикаментозных схем. Ниже представлены ключевые составляющие терапевтического процесса, формирующие основу для клинического восстановления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в пензе[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Hello friends, its fantastic article about tutoringand fully explained,
keep it up all the time.
Люблю сайт Olimp Casino официальный сайт, он очень понятный в использовании!
http://fblcthai.org/index.php?name=webboard&file=read&id=2751
I blog quite often and I genuinely thank you for your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest.
I am going to book mark your site and keep checking for new information about once per week.
I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
спасибо за инфу , но только узнал про новый список запвеществ , чувствую вся лавочка прикроется на некоторое время … https://kraskedr.ru работает заебок… присылают в кортонных больших конвертах…. доставляют очень быстро мне доставили в город за 3 дня… а их отделение в каждом городе есть.. как посылка придет вам позвонят на телефон и предложат доставку или приехать самому… если решите сами забирать то вам скажут адресс куда ехать…=)блин… один заказ выбил, затестил. теперь опять в аське молчок
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom
Its like you learn my mind! You seem to know so much
about this, like you wrote the e-book in it or something.
I believe that you just can do with some p.c. to pressure the message
home a little bit, however other than that, that is fantastic blog.
A fantastic read. I will certainly be back.
В клинике применяются комплексные программы, охватывающие все стадии терапии. Такой подход позволяет обеспечить пациенту полный спектр помощи — от первой консультации до социальной адаптации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-omsk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в омске[/url]
Sayt çox praktikdir.
https://wigale.de/index.php?title=1win_Promo_Kodlar%C4%B1_V%C9%99_Ekskl%C3%BCziv_T%C9%99klifl%C9%99r
Выездной наркологический сервис «МедПоволжье Клиник» создан для случаев, когда важны скорость, тишина и клиническая точность. Мы проводим детоксикацию и снятие интоксикации на дому так, чтобы каждое действие имело цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно переоценки». Вместо «сильной капельницы на всякий случай» — модульная схема: один симптом-кластер > один медицинский модуль > одна поведенческая опора (свет, звук, вода малыми глотками, дыхание 4–6). Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, ускоряет стабилизацию и позволяет видеть прогресс буквально по часам.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
Такие процедуры особенно эффективны на ранних стадиях лечения, когда важно быстро снять симптомы интоксикации и вернуть стабильное самочувствие. После курса капельниц пациенту становится легче концентрироваться, снижается раздражительность и тревожность, восстанавливается аппетит и сон.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon/
My partner and I stumbled over here by a different website and
thought I might as well check things out. I like what I
see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking into your web page repeatedly.
ступени из искусственного камня для лестниц купить
мне все пришло, магаз ровный. 5+ https://gorizont-vk.ru эх, вот печаль то…вчера так порадовался – селлер быстро ответил, хорошо пообщались, заказ принял, проплата прошла, сказали завтра трек будет…наступило завтра и тишина…вроде в сети и ася и скайп..за что меня так игнорят?))) заказ маленький то он такой важный!))))) в общем надеюсь на скорый ответ))перорально – эффекта 0 при меньших дозах, при больших – понос, рвота, чуваку скорую вызывали, давление 40/15
теплый костюм мужской костюм мужской классический купить в спб
Наркологическая клиника «КоломнаМед Центр» — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки контролировать алкоголь, наркотики, аптечные препараты или смесь всего сразу перестают работать, а жизнь превращается в постоянное «завтра начну с нуля». Здесь не обещают чудес за один день и не пугают диагнозами, а выстраивают понятный медицинский маршрут: детоксикация, стабилизация, реабилитация, поддержка семьи, профилактика срывов. Пациент получает помощь в защищённой, конфиденциальной среде, где всё организовано так, чтобы снизить тревогу и стыд, убрать хаос вокруг зависимости и дать человеку шанс вернуться к нормальной жизни без давления, угроз и токсичных «стимулов». Для родных клиника в Коломне — это опора: конкретный адрес, конкретная команда, чёткие сроки и понятные этапы, вместо бесконечных обещаний «он сам справится».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna10.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
What’s up i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i read this article i thought i could also make comment due to this sensible post.
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]заказать звонок наркологическая клиника[/url]
В клинике «ПензаМед Трезвость» лечение проводится по индивидуальной схеме, которая формируется после первичного осмотра. Нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, уровень алкогольной интоксикации и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. На основании данных подбираются препараты, способные эффективно очистить кровь, восстановить работу органов и снизить абстинентные проявления. При лёгкой форме зависимости возможен выезд врача на дом, где пациенту устанавливают капельницу и обеспечивают наблюдение в течение всего процесса детоксикации. В более сложных случаях рекомендуется госпитализация в стационар, где помощь оказывается под постоянным контролем специалистов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в пензе[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике реализуется через поэтапное внедрение терапевтических решений, направленных на устранение токсической нагрузки и восстановление физиологической устойчивости. Важным элементом является определение клинического профиля пациента, включающего анализ анамнеза, текущего состояния и возможных сопутствующих факторов. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальная программа помощи. Процедуры проводятся в условиях контролируемой безопасности, что снижает вероятность осложнений и позволяет достигать устойчивого терапевтического ответа. Последовательность действий формирует согласованную систему, удобную для мониторинга и анализа.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в кемерове[/url]
В клинике реализуются ключевые направления, которые обеспечивают всестороннюю помощь и поддержку пациентам на всех этапах лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-omske0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove/
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov/
Такой алгоритм позволяет постепенно восстановить функции организма и подготовить пациента к дальнейшему лечению зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru
Перед началом лечения пациент проходит первичную диагностику, которая включает оценку физических показателей, сбор информации о длительности употребления, выявление сопутствующих заболеваний и оценку рисков. Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани использует стандартизированные методы обследования, что позволяет точно определить степень интоксикации и подобрать адекватный лечебный план.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в астрахани[/url]
обьясни народу …….. сдесь ребята понимающие………. помогут купить кокаин мефдрон и бошки Доброга времени суток, закладки в москве делаете?всем доброго времени суто тс ответь в лс есть вопрос
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a colleague who has been doing a little
research on this. And he in fact ordered me lunch because I found it for him…
lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!!
But yeah, thanks for spending time to discuss this subject here on your website.
Маршрут выстроен без пауз и импровизаций. Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, лекарства/дозировки, аллергии, важные диагнозы, последние значения давления и пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия. По прибытии врач фиксирует АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора/тошноты, уровень тревоги, кратко собирает анамнез последних суток. Затем стартует инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием; по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты, противорвотные, мягкие анксиолитики. Каждые 15–20 минут врач смотрит динамику и корректирует темп капельниц, питьевой режим, симптоматическую поддержку. Важный принцип — «сон без вырубания»: умеренная седация собирает ночной ритм, сохраняя информативность мониторинга. По завершении — письменные рекомендации и маршрут на 24–72 часа (сон, питание, запреты, «красные флаги», амбулаторные визиты/дневной стационар или перевод в отделение). Такой алгоритм заменяет «лотерею» результата управляемым и повторяемым планом.
Углубиться в тему – http://
I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I believed this publish was good.
I do not realize who you might be but definitely you’re going to a well-known blogger
should you are not already. Cheers!
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-shchelkovo
Статья о том, как клиники капельниц для здоровья влияют на современную медицину: от детоксикации до профилактики заболеваний и укрепления иммунитета. Погрузиться в детали – http://promptik.ru/forum/topic/pochemu-v-moskve-kliniki-gde-stavyat-kapelnitsy-ot-alkogolnoy-intoksikatsii-ochen-vostrebovany
В зависимости от состояния пациента и пожеланий семьи наркологическая помощь может быть оказана в одном из нескольких форматов: на дому, в стационаре или дистанционно. Каждый из форматов обеспечивает доступ к медицинской помощи без бюрократии и с сохранением полной конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-omsk0.ru/omsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]chastnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Today, I went to the beach front with my kids. I found a sea
shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She
put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to
tell someone!
джива качественная=)получше чем впрошлый раз была=) https://apelsin19a.ru покушать попробуй… и пиши сюдаФлудить на счет легальности/нелегальности товара в магазине не нужно в ветке! У же отписывалась и экспертиза и мы не однократно писали, возим ТОЛЬКО ЛЕГАЛ!
Такой алгоритм позволяет постепенно восстановить функции организма и подготовить пациента к дальнейшему лечению зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом омск[/url]
whoah this weblog is fantastic i really like reading your articles. Stay up the good work! You understand, many persons are hunting round for this info, you could aid them greatly.
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Мы работаем без пауз и очередей, принимая пациентов в любое время суток. В распоряжении бригад — немаркированный транспорт для выезда на дом, портативная диагностика (ЭКГ, пульсоксиметрия, экспресс-анализаторы), а в стационаре — палаты с регулируемым микроклиматом и круглосуточный мониторинг жизненных показателей. Вся документация оформляется в нейтральной терминологии, доступ к данным разграничен по ролям, что защищает вашу анонимность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в ставрополе[/url]
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому волгоград[/url]
Информативно: наркотическая ломка — что это, как проявляется и как снять её симптомы в домашних условиях — практические рекомендации. Погрузиться в детали – http://www.rolandus.org/forum/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=29431
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника в раменском[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/narkolog-ufa-anonimno/
Вывод из запоя в Реутове в наркологической клинике «РеутовМед Сервис» — это профессиональная помощь, которая позволяет безопасно остановить разрушительное действие алкоголя на организм и вернуть контроль над состоянием пациента без рискованных экспериментов дома. Длительные запои приводят к тяжёлой интоксикации, скачкам давления, нарушению работы сердца, печени, нервной системы, провалам в памяти, агрессии, паническим атакам и риску алкогольного психоза. Попытки «перетерпеть», самостоятельно колоть непонятные препараты, давать горсть таблеток или «чуть-чуть допить для облегчения» только усиливают угрозу. Команда «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает вывод из запоя как последовательный медицинский процесс: первичная оценка состояния, грамотная детоксикация с капельницами, круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре при необходимости, контроль жизненных показателей, поддержка сердца и нервной системы, рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению зависимости. Для пациента это шанс выйти из тяжёлого состояния без стыда и боли, для родственников — возможность переложить ответственность за здоровье близкого на профессионалов, которые знают, что делать на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ramenskoe[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя коломна[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя в волгограде[/url]
Мы применяем модульный подход: медицинские и психологические интервенции настраиваются как «кубики», а последовательность их включения зависит от состояния пациента. Схема гибко масштабируется — от краткого курса стабилизации до расширенной реабилитации с семейной поддержкой. Ниже — каркас маршрута, которым мы руководствуемся чаще всего.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя ставрополь[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru
Примерный состав раствора, применяемого наркологом на дому в Уфе, приведён в таблице:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому уфа[/url]
Каждое направление наблюдения играет важную роль в формировании терапевтической программы. Структурированный контроль помогает снижать уровень рисков и обеспечивает возможность оперативной адаптации. Для систематизации данных применяется таблица, отражающая ключевые параметры мониторинга.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladivostok
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в владивостоке[/url]
Игнорирование этих симптомов может привести к тяжёлым последствиям — судорогам, галлюцинациям или алкогольному психозу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена тюмень[/url]
Комплексное применение этих методов позволяет добиться быстрого восстановления организма и улучшения психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в перми[/url]
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
Таблица позволяет поддерживать единую структуру наблюдения и фиксировать изменения состояния. Такая модель обеспечивает прозрачность процессов и повышает точность принимаемых решений.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в ижевске[/url]
Мы гибко переключаемся между форматами: старт в палате краткого наблюдения, продолжение в дневном стационаре и амбулаторные встречи с телемедицинскими чек-инами по 10–15 минут. Решение принимается по рискам: повторная рвота, выраженная тахикардия/скачки АД, спутанность сознания, эпизоды судорог/психозов — безусловные показания к наблюдению. При стабилизации сна и витальных возвращаемся к амбулаторному графику, чтобы уменьшить сенсорную нагрузку и быстрее встроить новые навыки в обычный быт.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма первоуральск[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «коктейли»: алгоритм строится из коротких проверяемых шагов. На старте фиксируем цель (например, уменьшить тремор и тошноту, стабилизировать пульс и давление, вернуть полноценный ночной сон), выбираем минимально достаточные средства для её достижения и заранее назначаем «окно оценки» — момент, когда команда сверяет эффект и при необходимости корректирует один параметр. Такой подход защищает от полипрагмазии, экономит силы пациента и делает прогресс читаемым для всей семьи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в каменске-уральске[/url]
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen/
Клиника предлагает возможность круглосуточного пребывания в комфортных палатах. Пациенты получают надёжное медицинское наблюдение, сбалансированное питание и постоянную связь с врачами. Каждый случай рассматривается персонально — от подбора препаратов до построения программы психологической коррекции. Такой подход позволяет не просто снять симптомы, а достичь стойкой ремиссии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru
Письменные рекомендации: сон, питание, гидратация, запреты, «красные флаги», график амбулаторных визитов; при недостатке ресурсов дома — перевод в стационар без задержек. Такая последовательность убирает импровизацию и делает результат повторяемым.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno[/url]
Мы работаем по модели «72 часа + 2 недели»: первые трое суток посвящены стабилизации витальных показателей, коррекции сна и сокращению «тяговых» откликов, следующие 14 дней — консолидации результата и запуску психотерапевтического блока. Маркеры прописываются заранее, поэтому и пациент, и семья понимают, когда и что мы будем оценивать, как корректируем план, если динамика ниже ожидаемой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в первоуральске[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «коктейли»: алгоритм строится из коротких проверяемых шагов. На старте фиксируем цель (например, уменьшить тремор и тошноту, стабилизировать пульс и давление, вернуть полноценный ночной сон), выбираем минимально достаточные средства для её достижения и заранее назначаем «окно оценки» — момент, когда команда сверяет эффект и при необходимости корректирует один параметр. Такой подход защищает от полипрагмазии, экономит силы пациента и делает прогресс читаемым для всей семьи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево каменск-уральск[/url]
Кроме безопасности и мониторинга — дисциплину режима. Там легче убрать триггеры, выстроить питание и сон, а психологу — подключить короткие мотивационные сессии, которые помогут удержать результат после выписки.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnogorske
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-anonimno[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в саратове[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» проходит в несколько последовательных этапов. Каждый этап выполняет конкретную задачу и сопровождается наблюдением специалистов. В таблице ниже представлена структура терапии и её основные направления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Клиника оснащена современным оборудованием для мониторинга состояния пациентов, проведения инфузионной терапии и лабораторных анализов. Врачи работают круглосуточно, обеспечивая как стационарное лечение, так и выезды на дом. Благодаря чёткому взаимодействию команды — нарколога, психотерапевта, кардиолога и реабилитолога — удаётся добиться быстрого и устойчивого результата даже в запущенных случаях.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy
Мы проверяем не «ощущения», а факты: частоту пульса в покое, вариабельность ритма к сумеркам, переносимость тёплой воды малыми глотками, минуты до сна и количество ночных пробуждений. Эти короткие метки позволяют тонко управлять темпом инфузии, очередностью модулей и «тихими» ритуалами вечернего времени без необоснованного усиления препаратов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в саратове[/url]
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-alkogolnogo-zapoya[/url]
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент качественных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их качество. Превосходное обслуживание – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы а также предоставлять решения под требования вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
Наши товары:
Проволока титановая ПТ-1МБ – ГОСТ 19807-91 Полоса титановая ПТ-1МБ – ГОСТ 19807-91 представляет собой высококачественный титановый сплав, который обладает отличной прочностью и коррозионной стойкостью. Этот продукт широко применяется в авиастроении, судостроении и других отраслях, где необходимы надежные материалы. Благодаря своим уникальным свойствам, полоса легко обрабатывается и сваривается, что делает ее идеальным выбором для различных проектов. Если вы хотите купить Полоса титановая ПТ-1МБ – ГОСТ 19807-91, вы можете быть уверены в ее долговечности и надежности. Обеспечьте себе качество и безопасность, сделав правильный выбор.
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Латуное внутреннее стопорное пружинное кольцо 170х3 мм ЛС59 ГОСТ 13943-86 Купить латунные внутренние стопорные кольца по ГОСТ от производителя. Надежное крепление и удержание элементов механизмов. Широкий выбор размеров и конфигураций. Высокое качество и надежность. Применение в машиностроении, автомобильной и других отраслях. Обращайтесь к нашим специалистам для получения более подробной информации.
Детоксикация является важнейшим этапом лечения. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» применяются проверенные схемы инфузионной терапии, помогающие восстановить функции организма после интоксикации. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и выраженности симптомов. Ниже приведена таблица с типами капельниц, применяемых в клинике.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
Главная задача процедуры — быстрое выведение этанола и его метаболитов из организма, нормализация уровня электролитов, улучшение самочувствия и предотвращение осложнений. Лечение проводится как в клинике, так и на дому, что особенно удобно при тяжёлых состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до медицинского учреждения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника тюмень[/url]
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Thank you for providing this information.
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника телефон[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/[/url]
Своевременная постановка капельницы помогает избежать тяжёлых последствий запоя. Поводом для обращения к врачу являются симптомы выраженной интоксикации:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно волгоград[/url]
Команда «СеверМед Альянса» включает наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, специалистов по зависимости, физиотерапевтов и координатора маршрута. Каждый модуль — детоксикация, стабилизация сна и настроения, психотерапия, семейная работа, восстановление бытовых и профессиональных ролей — встроен в общий план. Мы избегаем «одинаковых схем» и полипрагмазии: добавляем только те инструменты, у которых есть измеримая цель и безопасное «окно оценки» эффективности.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk/
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added”
checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get three e-mails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can remove people from that service?
Bless you!
Инфузионная терапия в «ТагилМед Реал» — это точный инструмент под конкретный запрос: обезвоживание, вегетативная нестабильность, нарушения сна, «утренний туман». Состав и дозировки подбирает врач с учётом возраста, коморбидности и лекарственных взаимодействий. Важно понимать: больше компонентов не значит лучше; главная ценность — фокус и безопасность.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Hurrah, that’s what I was exploring for, what a stuff!
existing here at this website, thanks admin of this
web site.
В Нижнем Тагиле выездные бригады дежурят 24/7. Координатор уже при первичном звонке собирает ключевые сведения: аллергии, хронические заболевания, список постоянных препаратов, эпизоды судорог или алкогольных психозов в прошлом, последние значения давления и пульса, возможность обеспечить тишину на 2–3 часа, доступ к питьевой воде, особенности подъезда. Вся эта информация помогает врачу подготовить стартовую схему — от выбора профиля инфузии до темпа введения. По запросу организуем немаркированный визит и сдержанные формулировки в документах, чтобы не создавать лишнего внимания со стороны соседей и коллег.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Мы проверяем не «ощущения», а факты: частоту пульса в покое, вариабельность ритма к сумеркам, переносимость тёплой воды малыми глотками, минуты до сна и количество ночных пробуждений. Эти короткие метки позволяют тонко управлять темпом инфузии, очередностью модулей и «тихими» ритуалами вечернего времени без необоснованного усиления препаратов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в саратове[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]сколько стоит наркологическая клиника[/url]
Проведите замечательный семейный отдых на берегу живописного Ладожского озера!
К вашему выбору 3 гостевых дома в Карелии на острове Лункулансаари;
1 гостевой дом в Устье Видлицы!
Все гостевые дома НОВЫЕ и имеют полное оснащение для комфортного проживания всей семьи!
[url=https://ostrovnaladoge.ru]Заходите на наш сайт[/url] и выбирайте дом на берегу озера для Вашего отдыха!
Остров на Ладоге – комплекс гостевых домов на берегу Ладожского озера! https://ostrovnaladoge.ru
[url=https://ostrovnaladoge.ru/][b]ОНЛАЙН БРОНИРОВАНИЕ[/b][/url] гостевого дома на берегу озера!
*********************
Турбаза, снять дом, аренда дома, гостевой дом, дом на берегу озера, снять турбазу, снять дом, семейный отдых
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ufa-narkolog-na-dom
Каждый план лечения строится вокруг понятных целей и измеримых результатов. Вместо шаблонных «сильных» схем мы применяем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию, корректируем среду (свет, тишина, режим сна), учим пациента простым и повторяемым навыкам саморегуляции. Такое сочетание медицинских и психологических инструментов помогает быстрее снять острые симптомы и поддерживать стабильность в последующие недели. Кодирование мы рассматриваем не как «волшебную кнопку», а как часть маршрута, который всегда включает детокс, психообразование и профилактику срывов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника нижний тагил[/url]
Для жителей Петрозаводска организован приём без очередей и «тихий» маршрут: короткий телефонный скрининг, согласованное окно приезда, приватная регистрация и старт терапии в тот же день. Вход — отдельный, кабинеты — изолированные, регистратура работает без громких объявлений. Документы составляются в нейтральной терминологии, доступ к карте пациента разграничен по ролям. Такой формат снижает тревогу и позволяет начать лечение именно тогда, когда мотивация хрупка и опоры особой важности — вечером, в выходные и праздничные дни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Выбор Рязань» функционирует по принципу полного цикла лечения: от экстренного выезда нарколога до длительной реабилитации в условиях стационара. Пациенты поступают как в острых состояниях (запой, абстиненция, интоксикация), так и для плановой терапии. Лечение начинается с медицинской диагностики, оценки физического и психического состояния, после чего разрабатывается индивидуальный план. Программы включают детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психологическую помощь и профилактику рецидивов.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkolog-ryazan-telefon
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really
well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful info.
Thanks for the post. I will definitely comeback.
Here is my homepage – bet1000
Капельница — инструмент, помогающий организму выйти из токсической воронки, а не магическая смесь «на все случаи». Базовый каркас — регидратация и коррекция кислотно-щелочного состояния, электролиты для водно-солевого баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы и снижения тремора. По клиническим показаниям подключаются гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени и уменьшения оксидативного стресса; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, при тревоге и бессоннице — мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, сохраняющих контакт. Мы сознательно избегаем «агрессивной» седации: она создаёт иллюзию успеха, но маскирует ухудшения и мешает контролю дыхания и нейростатуса. Эффективность оцениваем не «по ощущениям», а по метрикам: стабилизация АД/ЧСС, снижение тремора и тошноты, нормализация сатурации, возвращение аппетита и появление восстановительного ночного сна. Как только параметры выравниваются, фарм-нагрузку снижаем, а акцент переносим на режим — гигиену сна, регулярную гидратацию, дробное питание, щадящую дневную активность. Это делает результат не кратковременным затишьем на препаратах, а устойчивой траекторией восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali/
Диспетчер уточняет адрес в Электростали, длительность эпизода, текущие препараты и дозы, аллергии, сопутствующие заболевания, последние значения давления/пульса. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и позволяет заранее исключить опасные взаимодействия.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ehlektrostali/
If you would like to get a great deal from this paragraph then you have to apply
such strategies to your won blog.
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]порно смотреть[/url]
столешницы из кварца производство
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov
Домашний формат хорош при умеренной выраженности симптомов, сохранённом контакте и возможности обеспечить наблюдение в квартире: тихая комната, взрослый рядом первые 6–8 часов, отсутствие грубой дезориентации и неукротимой рвоты, относительная стабильность АД/ЧСС. В таких условиях выездная бригада «Трезвой Линии» запускает персональную схему: регидратация, выравнивание электролитов, поддержка витаминами группы B и магнием, осторожная седация, чтобы «собрать» сон, не выключая мониторинг. Стационар предпочтителен, если запой длится 3–5 суток и более, отмечаются «качели» показателей, шаткость походки, выраженная слабость, признаки предделирия или судорожной готовности; также при сочетанной соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология) и у пациентов старшего возраста. Преимущество стационара — приборный контроль, тихий режим, щадящее питание, возможность быстро расширять схему без ожидания ухудшений. Мы придерживаемся принципа «минимально достаточно»: ровно столько вмешательств, сколько требует клиническая картина, — так безопаснее и в перспективе экономнее, чем череда домашних «подлаток».
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali/
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru
В Ставрополе мы выстроили так называемую «тихую логистику»: запись без послеобеденных «окон», экспресс-приём без ожидания, сопровождение от входа до палаты, а при необходимости — деликатная госпитализация через отдельный вход. При первичном обращении пациент получает пошаговый план на ближайшие 72 часа: стабилизация самочувствия, детоксикация по показаниям, психообразование, старт профилактики срыва. Такой регламент экономит время и снижает тревожность — вы понимаете, что и зачем делается, и видите прогноз по срокам.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ставрополе[/url]
Детоксикация является важнейшим этапом лечения. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» применяются проверенные схемы инфузионной терапии, помогающие восстановить функции организма после интоксикации. Капельницы подбираются индивидуально в зависимости от состояния пациента и выраженности симптомов. Ниже приведена таблица с типами капельниц, применяемых в клинике.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologi-izhevsk-czeny/
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов палладиевая 50х1х1 мм Пд99.9 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Для получения устойчивого результата наркологическая клиника использует методы, основанные на индивидуальной оценке. В работе учитываются соматические показатели, реакции нервной системы и данные лабораторных исследований. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает предсказуемое влияние на физиологические процессы и снижает вероятность осложнений. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, позволяющий своевременно корректировать лечебные меры. Работа направлена на нормализацию метаболизма, восстановление баланса внутренних систем и плавное уменьшение симптоматики.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru
Выбор формата — это не вкусовщина, а баланс безопасности в конкретной клинической картине. Дом уместен, если контакт сохранён, рвота эпизодическая, давление и пульс без резких «качелей», тремор контролируемый, в квартире можно обеспечить тишину и присутствие взрослого, готового наблюдать первые 6–8 часов. Тогда выездная бригада работает на месте и выстраивает «мягкий» маршрут, где сон собирается без агрессивной седации, а инфузии идут с шаговой корректировкой темпа. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде (3–5 суток и более), неукротимой рвоте, выраженной слабости, шаткости походки, признаках предделирия/делирия, судорожной готовности, а также у пожилых пациентов и при сочетанных диагнозах — ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек, неврология. Преимущество отделения — приборный мониторинг, лабораторные опции по показаниям, ночная команда и среда, где исключены лишние раздражители: это снижает «цену ошибки» и делает результат устойчивым, а не разовым «прояснением».
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-ehlektrostali
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог качественных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до крупных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Опытная поддержка – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы и адаптировать решения под требования вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
Наши товары:
Полоса молибденовая TZC Полоса молибденовая TZC – это высококачественный металл, обладающий отличными механическими свойствами и устойчивостью к высоким температурам. Изготавливаясь из чистого молибдена, данный продукт применяется в различных отраслях, таких как аэрокосмическая, ядерная и металлургическая. Простота обработки и высокая коррозионная стойкость делают его идеальным выбором для создания деталей и компонентов. Чтобы повысить свою продуктивность и качество продукции, купите Полоса молибденовая TZC. Доверяйте только проверенным поставщикам для гарантии получения качественного материала.
dyson санкт петербург купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
wonderful publish, very informative. I’m wondering why the other specialists of this sector do not realize this. You should proceed your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
пылесос дайсон купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
Фиксируем АД, ЧСС, сатурацию, температуру, оцениваем неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, тремор, тошноту и уровень тревоги; собираем краткий анамнез последних суток и характер употребления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-s-vyezdom-cena[/url]
Каждый час промедления в острый период повышает вероятность обезвоживания, электролитных сдвигов, аритмий, гипертонических всплесков и расстройств сна, которые легко перерастают в делирий. Домашние попытки с «подручными» средствами редко учитывают лекарственные взаимодействия, реальный уровень обезвоживания и состояние печени, а «жёсткая» седация, применяемая без показаний, маскирует ухудшения и лишает врача информативной картины. Профессиональная бригада «НоваТрезвие» начинает с объективной оценки: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, выраженность тремора и тошноты, степень обезвоживания, список принимаемых препаратов и возможные аллергии. На этой базе формируется персональный план: регидратация, коррекция электролитов и кислотно-щелочного баланса, поддержка нервной системы витаминами группы B и магнием, гепатопротекторная и антиоксидантная защита по показаниям, противорвотные при необходимости и мягкая анксиолитическая поддержка для восстановительного сна. Такой маршрут гасит «пожар» интоксикации управляемо, возвращая прогнозируемость самочувствия в течение первых часов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
คอนเทนต์นี้ อ่านแล้วเพลินและได้สาระ ครับ
ดิฉัน ไปอ่านเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ เรื่องที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ที่คุณสามารถดูได้ที่
เว็บ ufabet888
น่าจะถูกใจใครหลายคน
มีตัวอย่างประกอบชัดเจน
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ บทความคุณภาพ
นี้
และหวังว่าจะได้เห็นโพสต์แนวนี้อีก
Наркологическая клиника «СеверМед Альянс» — это современная экосистема помощи при зависимостях, где клиническая точность соединяется с бережной коммуникацией и индивидуальными маршрутами реабилитации. Мы выстраиваем лечение как последовательность управляемых шагов с понятными целями и сроками оценки результата. Пациент видит логику каждого вмешательства, понимает, почему ему предлагают именно такой план, и отслеживает прогресс по простым маркерам — сон, уровень тревоги, частота и длительность «тяговых» эпизодов, восстановление энергии и социальной активности.
Подробнее – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/narkolog-petrozavodsk-otzyvy/
В Нижнем Тагиле выездные бригады дежурят 24/7. Координатор уже при первичном звонке собирает ключевые сведения: аллергии, хронические заболевания, список постоянных препаратов, эпизоды судорог или алкогольных психозов в прошлом, последние значения давления и пульса, возможность обеспечить тишину на 2–3 часа, доступ к питьевой воде, особенности подъезда. Вся эта информация помогает врачу подготовить стартовую схему — от выбора профиля инфузии до темпа введения. По запросу организуем немаркированный визит и сдержанные формулировки в документах, чтобы не создавать лишнего внимания со стороны соседей и коллег.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Если к «окну оценки» цель не достигнута, мы меняем ровно один параметр (время приёма, приоритет модуля или плотность контактов). Такой «микроход» показывает вклад изменения и не превращает программу в перегруженный конструктор.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk0.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Каждый план лечения строится вокруг понятных целей и измеримых результатов. Вместо шаблонных «сильных» схем мы применяем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию, корректируем среду (свет, тишина, режим сна), учим пациента простым и повторяемым навыкам саморегуляции. Такое сочетание медицинских и психологических инструментов помогает быстрее снять острые симптомы и поддерживать стабильность в последующие недели. Кодирование мы рассматриваем не как «волшебную кнопку», а как часть маршрута, который всегда включает детокс, психообразование и профилактику срывов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil0.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно электросталь[/url]
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Капельница при вызове нарколога на дом в Долгопрудном от «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» — это клинический инструмент, а не магический раствор. Главное правило — никакой агрессивной седации ради видимости спокойствия. Инфузионная терапия строится вокруг нескольких задач: восполнить жидкость, выровнять электролиты, снизить токсическую нагрузку на печень и мозг, поддержать сердце и нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, тревогу и соматические жалобы. Используются растворы для регидратации и коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, уменьшения риска судорог и нормализации сна, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксиданты, противорвотные препараты для контроля тошноты. При выраженной тревоге или нарушениях сна назначаются щадящие анксиолитические средства в дозах, которые не выключают пациента полностью, а помогают снять паническое напряжение, сохраняя возможность оценивать динамику состояния. Врач отслеживает реакцию на терапию: стабилизацию давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение общего самочувствия, появление более спокойного, естественного сна. По мере облегчения нагрузки схема не усиливается ради счёта, а рационально сокращается. Такой подход защищает пациента от скрытых осложнений и превращает капельницу в контролируемый, полезный шаг, а не в рискованный эксперимент.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]vyzov-vracha-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница пермь[/url]
Главные задачи детоксикации при запое — безопасно снизить концентрацию токсичных метаболитов, восстановить водно-электролитный баланс, уменьшить перегрузку сердечно-сосудистой системы и вернуть физиологию сна. Мы начинаем с медленного стартового объёма инфузии, чтобы оценить переносимость, затем переходим к основной фазе и при необходимости к постинфузионной поддержке. Во время сеанса контролируются витальные показатели, динамика симптомов (тремор, тошнота, головная боль, фотофобия, тревога), а также «поведенческие» маркеры — способность расслабиться, усидеть спокойно, засыпать без «рывков».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article.
Thank you for supplying these details.
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-cena[/url]
Услуга «нарколог на дом в Долгопрудном» от клиники «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» создана для ситуаций, когда важно действовать быстро, аккуратно и без лишнего шума. Запой, тяжёлое похмелье, срыв после ремиссии, злоупотребление медикаментами или смесью алкоголя с препаратами — всё это не терпит откладывания и самодеятельности. Вызов врача на дом позволяет получить профессиональную помощь без госпитализации, когда состояние пациента ещё позволяет лечить его в привычной обстановке. Нарколог приезжает с полностью укомплектованным набором препаратов и расходников, проводит осмотр, подбирает капельницы по клиническим показаниям, контролирует реакцию, даёт подробные рекомендации на ближайшие дни и при необходимости предлагает дальнейший маршрут: повторный выезд, амбулаторное наблюдение или стационар клиники. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго: без обсуждений с соседями, без регистрации по месту работы, без унизительных формальностей — только медицинская помощь, ориентированная на безопасность и результат.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Информативно: медицинский центр «Инфузио» — инновационный подход к внутривенной терапии: что входит в состав и как он действует на организм. Проверенные методы — узнай сейчас – http://www.rolandus.org/forum/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=29526
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-reutove
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация вызывает сильное обезвоживание и разрушает баланс электролитов в организме. Без медицинской помощи восстановление может занять несколько дней, а в тяжёлых случаях приводит к осложнениям. Капельница помогает безопасно и быстро вывести этанол и продукты его распада, восполнить уровень жидкости, снизить нагрузку на печень и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процедура проводится амбулаторно или на дому, что делает её доступной и удобной для пациентов.
Детальнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/
Hey there! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I came to give it a look. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Outstanding blog and outstanding design.
Ниже представлена таблица с основными препаратами, используемыми при выводе из запоя в Тюмени:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tyumeni17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в тюмени[/url]
Ниже — ориентир для острых часов на дому. Это не жёсткий шаблон, а карта, где ясно: что делаем, чем измеряем, когда пересматриваем. При отсутствии отклика мы меняем один параметр (например, темп инфузии) и назначаем новое окно оценки, не «двигая» всё остальное.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru
Нашли рабочий серийный номер для Windows 11 Pro — проверено лично, без вирусов!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Скачать патч для активации Windows 11[/url]
официальный магазин дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
Нарколог на дом в Уфе — это услуга, которая позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при алкогольной или наркотической интоксикации без необходимости госпитализации. Такой формат особенно востребован при запойных состояниях, когда пациент не может самостоятельно посетить клинику. Врач приезжает по вызову в течение короткого времени, проводит обследование, устанавливает капельницу и обеспечивает безопасный вывод из состояния опьянения. Все процедуры выполняются анонимно, с соблюдением медицинской этики и конфиденциальности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]нарколог на дом цены уфа[/url]
официальный сайт дайсон [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
дайсон официальный сайт в санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Если вы стремитесь приобрести высококачественное медицинское оборудование, которое будет служить надёжным инструментом в вашей работе или бизнесе, стоит посетить страницу [url=https://oborudovanie-aurasonics.ru/]aurasonics купить[/url], где представлена вся необходимая информация о продуктах и услугах, предлагаемых компанией Aurasonics.
Аурасоникс предлагает широкий выбор аудиооборудования для различных целей. С момента своего основания Аурасоникс стремится к тому, чтобы обеспечить своим клиентам лучшее звучание. Компания постоянно работает над улучшением качества своих изделий. Сегодня Аурасоникс является одной из наиболее популярных компаний в сфере аудиотехники.
Aurasonics обеспечивает длительный срок службы своих продуктов.
Aurasonics предоставляет гарантийное обслуживание своим клиентам.
Aurasonics – это компания, которая предлагает высококачественную аудиоаппаратуру по доступным ценам.
sap
В Ставрополе мы выстроили так называемую «тихую логистику»: запись без послеобеденных «окон», экспресс-приём без ожидания, сопровождение от входа до палаты, а при необходимости — деликатная госпитализация через отдельный вход. При первичном обращении пациент получает пошаговый план на ближайшие 72 часа: стабилизация самочувствия, детоксикация по показаниям, психообразование, старт профилактики срыва. Такой регламент экономит время и снижает тревожность — вы понимаете, что и зачем делается, и видите прогноз по срокам.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol0.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol
Перед процедурой врач оценивает состояние пациента, измеряет давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом. После осмотра подбирается состав инфузии, включающий препараты для дезинтоксикации, восстановления водно-солевого баланса и нормализации работы органов. Введение растворов осуществляется внутривенно, под контролем специалиста. Длительность процедуры — от 40 минут до 1,5 часов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]вызов на дом капельницы от запоя волгоград[/url]
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма ижевск[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Волгограде — это эффективный способ быстро восстановить организм после длительного употребления алкоголя. Процедура проводится врачом-наркологом и направлена на выведение токсинов, нормализацию обмена веществ и стабилизацию работы нервной системы. Инфузионная терапия помогает устранить головную боль, слабость, тошноту, восстановить сон и аппетит. Благодаря внутривенному введению препаратов эффект наступает уже через 20–30 минут после начала процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-volgograde17.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого[/url]
Острый эпизод запоя — это не «плохое самочувствие», а состояние с реальными рисками для сердца, нервной системы и дыхания, особенно в ночные часы, когда усиливаются вегетативные реакции и тревога. В «НоваТрезвие» мы выстраиваем помощь так, чтобы от звонка до заметного облегчения прошло как можно меньше времени и как можно меньше случайностей: короткое интервью для оценки рисков, выезд врача или приём в клинике, экспресс-диагностика по ключевым показателям, персональная инфузионная схема без «универсальных коктейлей», мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги без «вырубания», понятные инструкции семье на 24–72 часа и план продолжения на ближайшие недели. Мы не скрываемся за общими формулами: решения принимаются по фактическим данным, дозы и темп капельниц подстраиваются к динамике каждые 15–20 минут, а при «красных флагах» перевод в стационар организуется без пауз. Конфиденциальность соблюдается строго, а коммуникация простая и предсказуемая — чтобы вы всегда знали, что происходит сейчас и чего ждать к утру.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal2-10.ru
Одним из ключевых направлений терапии является инфузионное лечение. Капельницы позволяют быстро восстановить обмен веществ, улучшить работу внутренних органов и ускорить выведение токсинов. В клинике используются только сертифицированные препараты, безопасные для сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника рязань[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа? У нас есть пошаговая инструкция!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Скачать генератор ключей для Windows 11[/url]
Процесс включает несколько шагов:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом уфа[/url]
Мы работаем по модели «72 часа + 2 недели»: первые трое суток посвящены стабилизации витальных показателей, коррекции сна и сокращению «тяговых» откликов, следующие 14 дней — консолидации результата и запуску психотерапевтического блока. Маркеры прописываются заранее, поэтому и пациент, и семья понимают, когда и что мы будем оценивать, как корректируем план, если динамика ниже ожидаемой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk0.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в первоуральске[/url]
Ниже приведён ориентировочный распорядок первого дня, когда вызов оформлен утром или днём. Вечерние визиты адаптируем: усиленный акцент на гигиене сна и «тихом окне» после 21:30.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kamensk-uralskij0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy-kamensk-uralskij/
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Такая структура позволяет достичь максимального эффекта в кратчайшие сроки и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-ufe17.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому уфа[/url]
I was confused about whether my employer has to pay Social Security during my probation. Your article clarified the legal requirements perfectly.
https://lakeinsuranceok.com/comparisons-and-reviews
Каждый из этих этапов играет важную роль и обеспечивает безопасность пациента на пути к восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Детальнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom-v-dolgoprudnom/
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
дайсон сервисный центр санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Узнайте, когда необходимо вызвать психиатра на дом: признаки, при которых консультация специалиста обязательна, и как организовать визит Связаться за уточнением – http://www.allorus.ru/cat/question/10439
Капельница — инструмент, помогающий организму выйти из токсической воронки, а не магическая смесь «на все случаи». Базовый каркас — регидратация и коррекция кислотно-щелочного состояния, электролиты для водно-солевого баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы и снижения тремора. По клиническим показаниям подключаются гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени и уменьшения оксидативного стресса; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, при тревоге и бессоннице — мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, сохраняющих контакт. Мы сознательно избегаем «агрессивной» седации: она создаёт иллюзию успеха, но маскирует ухудшения и мешает контролю дыхания и нейростатуса. Эффективность оцениваем не «по ощущениям», а по метрикам: стабилизация АД/ЧСС, снижение тремора и тошноты, нормализация сатурации, возвращение аппетита и появление восстановительного ночного сна. Как только параметры выравниваются, фарм-нагрузку снижаем, а акцент переносим на режим — гигиену сна, регулярную гидратацию, дробное питание, щадящую дневную активность. Это делает результат не кратковременным затишьем на препаратах, а устойчивой траекторией восстановления.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
На первичном визите врач проводит клиническое интервью, оценивает витальные показатели (АД, ЧСС, SpO2, температура), при показаниях — выполняет портативный ЭКГ-скрининг и экспресс-диагностику. Вместе с пациентом формируется план ближайших 72 часов: режим гидратации, «вечерний ритуал» для сна, правила сенсорной разгрузки, безопасные фразы для общения с близкими, точечная фармакоподдержка и расписание коротких чек-инов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-petrozavodsk0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника петрозаводск[/url]
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Best wishes! Exactly where are your contact details though?
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]эротические фильмы[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Каждый метод подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает безопасность и эффективность процесса.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-omsk0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/
Узнайте, как капельница от похмелья помогает быстро восстановиться после вечеринки: состав, показания и преимущества процедуры Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://otvet.mail.ru/question/267927601
Ниже — ключевые направления, которые логично дополняют друг друга и формируют единый маршрут лечения:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]gde-nahoditsya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Over the past few years, international interaction has grown at an unprecedented pace. People from different countries are connecting more frequently for business, travel, education, and social purposes. Despite this progress, linguistic differences remain a significant challenge.
Traditional translation methods like text-based translation software often require manual input. For this reason, a growing number of people are turning to AI-powered translation earbuds for seamless communication.
AI translation earbuds combine artificial intelligence, speech recognition, and machine translation to deliver instant language translation. With hands-free operation, users can communicate naturally while the system translates spoken language in real time.
One major strength of smart translation devices is hands-free functionality. In contrast to traditional translators, these earbuds allow users to maintain eye contact, creating a more natural communication experience. This benefit is especially valuable when real-time response is essential.
Another key feature of intelligent earbud translators is wide language coverage. Advanced systems are capable of handling multiple dialects, making them suitable in diverse linguistic settings worldwide. Certain models can adapt to different speech patterns, improving accuracy and comprehension.
Translation quality is another critical element. Today’s AI-powered devices are powered by machine learning technology to better capture the meaning of conversations. In contrast to basic translators, they benefit from ongoing updates, resulting in better performance.
These smart devices are also widely used in professional environments. International meetings often involve participants who speak different languages. Through intelligent translation solutions, meetings run more smoothly. This technology enhances clarity and productivity.
Tourists find great value on intelligent earbud translators. In restaurants, shops, and public places, communication challenges often arise. By wearing translation earbuds, travelers can navigate foreign environments with confidence. This leads to a more enjoyable journey.
Another emerging use case for smart translation devices is educational support. Users can observe pronunciation and structure, enhancing language comprehension. Over time, language familiarity can increase naturally.
Privacy and comfort are also important considerations. Modern AI translation earbuds are designed for long-term wear. Some systems offer noise reduction and clear audio output, supporting clear communication. Additionally, translations are delivered privately through the earbuds, which is ideal for sensitive conversations.
With ongoing improvements in AI, smart translation devices will continue to improve. Future developments could offer improved accuracy and reduced latency. Ongoing innovation will help connect people worldwide.
To summarize, AI translation earbuds represent a significant step forward for cross-language communication. They combine convenience, accuracy, and real-time performance, people can connect without linguistic limitations. With increasing global demand, such devices will shape the future of communication in a multilingual world.
https://forum.issabel.org/u/middlesearch11
Скачайте патч для обхода активации Windows 11 и пользуйтесь системой без ограничений.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru
Капельница — инструмент, помогающий организму выйти из токсической воронки, а не магическая смесь «на все случаи». Базовый каркас — регидратация и коррекция кислотно-щелочного состояния, электролиты для водно-солевого баланса, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы и снижения тремора. По клиническим показаниям подключаются гепатопротекторы и антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени и уменьшения оксидативного стресса; при выраженной тошноте — противорвотные, при тревоге и бессоннице — мягкие анксиолитики в дозах, сохраняющих контакт. Мы сознательно избегаем «агрессивной» седации: она создаёт иллюзию успеха, но маскирует ухудшения и мешает контролю дыхания и нейростатуса. Эффективность оцениваем не «по ощущениям», а по метрикам: стабилизация АД/ЧСС, снижение тремора и тошноты, нормализация сатурации, возвращение аппетита и появление восстановительного ночного сна. Как только параметры выравниваются, фарм-нагрузку снижаем, а акцент переносим на режим — гигиену сна, регулярную гидратацию, дробное питание, щадящую дневную активность. Это делает результат не кратковременным затишьем на препаратах, а устойчивой траекторией восстановления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Услуга
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru
Ожидаемая траектория в первые сутки
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo[/url]
В «Южном МедКонтроле» лечение зависимостей строится поэтапно, с постепенным восстановлением физиологических функций и эмоциональной устойчивости. Врачи используют современные методы детоксикации, фармакотерапию и психотерапию, которые действуют комплексно. Каждый этап направлен на достижение конкретного результата: очищение организма, снятие симптомов абстиненции, стабилизацию состояния и профилактику срывов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove19.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Мы не используем универсальную «капельницу». Схема собирается из модулей под ведущие жалобы. Медицинские шаги всегда сочетаются с нефраком опорами — свет, тишина, вода малыми глотками, дыхание, — потому что среда усиливает действие препаратов и позволяет держать дозы ниже.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя саратов[/url]
Такая комплексность обеспечивает воздействие на физические, психологические и социальные факторы зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма[/url]
https://casinia99.com/
дайсон сервисный центр санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Каждый курс лечения включает несколько этапов, направленных на постепенное улучшение состояния. Система выстроена так, чтобы обеспечить плавное восстановление функций организма без стресса. Ниже приведена таблица, показывающая основные этапы лечения и применяемые процедуры.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-rostov-na-donu/
Реализация этих задач позволяет наркологической клинике в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечивать контролируемость лечения в любое время суток.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu/
dyson оригинал спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
Wonderful items from you, man. I have understand your stuff prior to and you’re simply extremely wonderful. I really like what you have acquired right here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which through which you say it. You’re making it enjoyable and you still care for to stay it sensible. I cant wait to learn far more from you. This is actually a tremendous web site.
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника анонимно[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Что делаем фактически
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Южный МедКонтроль» объединяет современные медицинские технологии, опыт специалистов и уважительное отношение к каждому пациенту. Здесь создаются условия для безопасного и результативного лечения зависимостей любой сложности — от алкогольной до полинаркотической. Центр работает в круглосуточном режиме, предлагая выезд врачей на дом, детоксикацию, кодирование и длительные программы реабилитации. Основная цель специалистов — восстановление физического и психологического равновесия человека, возвращение способности к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove19.ru/
В рамках анонимного лечения особое внимание уделяется следующим аспектам медицинской организации:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru
игр. Платформа работает стабильно, ничего не зависает. Деньги перевели быстро: [url=https://runashop.ru/]7k casino официальный сайт[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Вектор Трезвости» основано на клинически обоснованных методах, адаптированных под формат круглосуточной работы. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону применяет комплексную диагностику, позволяющую учитывать тяжесть зависимости, длительность употребления и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой подход обеспечивает точность медицинских решений и снижает вероятность неблагоприятных реакций.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Выездной наркологический сервис «МедПоволжье Клиник» создан для случаев, когда важны скорость, тишина и клиническая точность. Мы проводим детоксикацию и снятие интоксикации на дому так, чтобы каждое действие имело цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно переоценки». Вместо «сильной капельницы на всякий случай» — модульная схема: один симптом-кластер > один медицинский модуль > одна поведенческая опора (свет, звук, вода малыми глотками, дыхание 4–6). Такой подход снижает лекарственную нагрузку, ускоряет стабилизацию и позволяет видеть прогресс буквально по часам.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в саратове[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Состояние запоя представляет опасность не только для физического здоровья, но и для психики человека. Продолжительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению обмена веществ и психоэмоциональной нестабильности. В таких случаях самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен, а иногда и невозможен. Врачи «Южного Центра Медицинского Восстановления» оказывают квалифицированную помощь с выездом на дом и круглосуточным приёмом пациентов. Используя современные методы детоксикации и мониторинга состояния, специалисты обеспечивают безопасное восстановление организма и минимизируют риски осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Медицинская команда контролирует каждый этап лечения, отслеживая динамику и корректируя терапию при необходимости. Благодаря такому подходу удаётся добиться не временного улучшения, а устойчивого восстановления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Стоимость зависит от длительности запоя, объёма инфузий, перечня препаратов и длительности наблюдения после капельницы. Мы заранее озвучиваем ориентир, объясняем, какие элементы плана обязательны, а какие — рекомендательные. Ночные выезды иногда дороже из-за нагрузки на бригаду, но при выраженных симптомах откладывать помощь небезопасно. Повторные обращения и расширенные программы стабилизации обсуждаются индивидуально. Ключевой ориентир для семьи — выбирать не «самую дешёвую капельницу», а безопасный формат с контролем и ответственным уходом.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-korolev/
В этом блоке важно показать, что клиника закрывает ключевые запросы пациентов и их близких при сохранении безопасности и анонимности.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Программы лечения в клинике «ДонМед Трезвость» направлены на полное восстановление человека — физическое, психологическое и социальное. Каждое направление терапии адаптируется под конкретного пациента, чтобы достичь максимально устойчивого результата. Врачи используют современные методы и препараты, снижающие риски побочных эффектов и ускоряющие процесс реабилитации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Такой подход позволяет достичь устойчивого результата без срывов и рецидивов. Пациенты получают помощь не только на уровне физиологии, но и на уровне личностных изменений, что делает лечение глубоким и эффективным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
В рамках анонимного лечения особое внимание уделяется следующим медицинским аспектам:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
Hello would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re using? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different web browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good internet hosting provider at a fair price? Thank you, I appreciate it!
В рамках клинической работы применяются следующие направления медицинского воздействия, которые обеспечивают целостность лечебного процесса:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь ростов-на-дону[/url]
Спальня має сприяти відпочинку та релаксу. У матеріалі ремонт спальні: комфорт і затишок подані практичні рішення. Вони допомагають досягти гармонійної атмосфери.
Такой подход позволяет достичь устойчивого результата без срывов и рецидивов. Пациенты получают помощь не только на уровне физиологии, но и на уровне личностных изменений, что делает лечение глубоким и эффективным.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Щёлково — это быстрый и конфиденциальный способ помочь человеку в состоянии запоя или тяжёлого похмелья, не перевозя его в клинику и не устраивая публичных сцен. Врачи «ЩёлковоМед Профи» приезжают с готовым набором препаратов, одноразовыми системами и чётким протоколом: осмотр, оценка жизненно важных показателей, подбор индивидуальной капельницы, контроль реакции, рекомендации для родных. Такой формат особенно удобен, когда пациент отказывается ехать в стационар, тяжело переносит дорогу, остро реагирует на смену обстановки или для семьи важна максимальная анонимность. Главный принцип — не «вырубить» человека любой ценой, а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, помочь собрать сон и дать понятный план, что делать дальше.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-shchelkovo10.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-shchelkovo/
Когда состояние «штормит», ночные часы усиливают тревогу и вегетативные реакции, обезвоживание нарастает, сон рвётся, а попытки самолечения «чем попало» маскируют опасные симптомы. Организованный маршрут в «Трезвой Линии» заменяет хаос последовательностью: ещё по телефону дежурный врач собирает ключевые сведения — длительность эпизода, аллергии, список лекарств и дозировок, кардио- и эндокринные диагнозы, последние измерения давления и пульса. На месте выполняется короткая, но информативная оценка: АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора и тошноты. Схема терапии запускается сразу и корректируется каждые 15–20 минут по «живым показателям», а не по шаблону. Если видим признаки предделирия, неукротимую рвоту, резкие «качели» давления/пульса, выраженную слабость или пожилой возраст с тяжёлой соматикой — переводим в стационар без пауз: приборный мониторинг и ночная команда в Электростали снижают «цену ошибки» и экономят на повторных вызовах. Для семьи это означает меньше догадок и больше ясности: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём к утру.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ehlektrostal10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo[/url]
Forced closeness changes everything in Vacation with My Stepmom. What begins as a simple trip becomes an emotionally charged experience where distance disappears and tension grows. Shared spaces, quiet moments, and unspoken thoughts slowly reshape the relationship. With deliberate pacing and psychological depth, the story turns proximity itself into the driving force behind desire, conflict, and emotional transformation.
Лечение в круглосуточном режиме выстраивается как непрерывный медицинский процесс. Даже при экстренном обращении терапия не ограничивается разовым вмешательством, а рассматривается как последовательная система лечебных мероприятий с обязательным врачебным наблюдением.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону рассматривается как специализированное медицинское пространство, где помощь при зависимостях строится на сочетании клинических протоколов, наблюдения и поэтапного восстановления. В клинике «Южный Вектор» подход ориентирован на комплексное понимание зависимости как хронического состояния, затрагивающего физиологические и психические механизмы. Практика показывает, что эффективная терапия возможна только при строгом соблюдении стандартов и системном контроле динамики состояния пациента. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону функционирует в условиях повышенного спроса, что требует чёткой организации процессов и медицинской ответственности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/narkolog-rostov-na-donu
дайсон санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Что делаем фактически
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ehlektrostal0.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ehlektrostali
Life Coach Rudolfo Life Coaches offer outstanding life
coaching services. The Life Coaches from Life Coach Rudolfo provide therapy for stress management.
Life Coach Rudolfo empowers clients to enhance their
lifestyle. Wellness is a significant focus for the Life Coaches at
Life Coach Rudolfo. Life Coach Rudolfo delivers professional coaching for personal growth.
Business coaching is a specialty of the Life
Coaches from Life Coach Rudolfo. Life Coach Rudolfo supports career
coaches in their professional development. The Life Coaches
at Life Coach Rudolfo offer coaching services in Noord
Holland. Life Coach Rudolfo Life Coaches facilitate therapie
sessions for mental wellbeing. Life Coach Rudolfo delivers life coaching services to promote wellness.
The Life Coaches from Life Coach Rudolfo assist clients through stress management therapy.
Life Coach Rudolfo provides lifestyle coaching for personal betterment.
The Life Coaches at Life Coach Rudolfo provide business coaching
for entrepreneurs. Life Coach Rudolfo offers professional coaching to career coaches.
The Life Coaches from Life Coach Rudolfo deliver coaching services in Noord Holland.
Life Coach Rudolfo Life Coaches enable clients
to achieve wellness through therapie. Life Coach Rudolfo delivers life coaching to support manage stress.
The Life Coaches at Life Coach Rudolfo help clients in improving their lifestyle.
Life Coach Rudolfo delivers business coaching to professionals.
The Life Coaches from Life Coach Rudolfo provide professional coaching
services in Noord Holland.
sap
санкт петербург магазин дайсон [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
[url=https://t.me/toplistcasino]топ интернет казино[/url]
Лечебный процесс организуется таким образом, чтобы каждый этап логически дополнял предыдущий и формировал устойчивую динамику. Это позволяет избежать резких изменений состояния и поддерживать медицинскую безопасность.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском в условиях клиники строится не вокруг одной капельницы, а вокруг понятной цепочки шагов, где каждый этап логичен и медицински обоснован. Это помогает не только быстро облегчить состояние, но и уменьшить вероятность того, что через пару дней человек снова уйдёт в запой.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
이 웹사이트에 스팸 문제가 있나요? 저도 블로거인데,
당신의 상황이 궁금했습니다; 우리 중 많은 몇 가지 좋은 관행을 만들었고, 다른 사람들과 전략을 거래하고 싶습니다, 관심 있으시면 메일을 보내주세요.
В практической работе выделяются последовательные этапы, обеспечивающие медицинскую целостность:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар ростов-на-дону[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника в раменском[/url]
BlackSprut marketplace сайт
bs2best at
Когда ночь затягивается, тревога нарастает, а самочувствие «скачет», важны не громкие обещания, а последовательность медицинских действий. «Трезвый Контур» в Одинцово выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от звонка до облегчения прошло минимум времени и ни один шаг не был импровизацией: первичная оценка рисков, персональная инфузионная терапия, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, регулярные замеры показателей, понятные рекомендации для семьи. Мы не используем «универсальные коктейли» и не «вырубаем» пациента сильными седативными — дозировки и темп капельниц подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания и уже принимаемые препараты. Цель — быстро снять токсическую нагрузку, стабилизировать давление и пульс, вернуть управляемый сон и зафиксировать маршрут на ближайшие 24–72 часа, чтобы утро началось не с нового витка симптомов, а с предсказуемого восстановления.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-v-odincovo
Для оценки состояния используется расширенная диагностика: лабораторные анализы, ЭКГ, психологическое тестирование и биохимические маркеры. По результатам обследования составляется индивидуальный план, включающий детоксикацию, фармакотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия. Ниже представлена таблица, описывающая структуру этапов лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в ростове-на-дону[/url]
BlackSprut marketplace сайт
bs2best at
Ниже — ключевые направления, которые логично дополняют друг друга и формируют единый маршрут лечения:
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/
I for all time emailed this blog post page to all my contacts, since if like to read it then my contacts will too.
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some advice from
an established blog. Is it very difficult to set up your own blog?
I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast.
I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where to
start. Do you have any ideas or suggestions? With thanks
Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону рассматривается как специализированное медицинское пространство, где помощь при зависимостях строится на сочетании клинических протоколов, наблюдения и поэтапного восстановления. В клинике «Южный Вектор» подход ориентирован на комплексное понимание зависимости как хронического состояния, затрагивающего физиологические и психические механизмы. Практика показывает, что эффективная терапия возможна только при строгом соблюдении стандартов и системном контроле динамики состояния пациента. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону функционирует в условиях повышенного спроса, что требует чёткой организации процессов и медицинской ответственности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Такой подход позволяет наркологической клинике в Краснодаре выстраивать лечение в безопасной и профессиональной среде.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника краснодар[/url]
BlackSprut marketplace сайт
bs2best at
BlackSprut marketplace сайт
bs2best at
Лечение в клинике «Вектор Трезвости» основано на клинически обоснованных методах, адаптированных под формат круглосуточной работы. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону применяет комплексную диагностику, позволяющую учитывать тяжесть зависимости, длительность употребления и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой подход обеспечивает точность медицинских решений и снижает вероятность неблагоприятных реакций.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике ростов-на-дону[/url]
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno[/url]
Стоимость зависит от длительности запоя, объёма инфузий, перечня препаратов и длительности наблюдения после капельницы. Мы заранее озвучиваем ориентир, объясняем, какие элементы плана обязательны, а какие — рекомендательные. Ночные выезды иногда дороже из-за нагрузки на бригаду, но при выраженных симптомах откладывать помощь небезопасно. Повторные обращения и расширенные программы стабилизации обсуждаются индивидуально. Ключевой ориентир для семьи — выбирать не «самую дешёвую капельницу», а безопасный формат с контролем и ответственным уходом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-korolev/
Такой подход обеспечивает не только устранение симптомов зависимости, но и глубокое восстановление личности. Пациенты получают поддержку врачей на каждом этапе, что делает процесс безопасным и контролируемым.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-oficialnyj-sajt-v-kolomne/
Помощь при зависимостях в клинике «Южный Вектор» базируется на клинической диагностике, позволяющей определить стадию расстройства и сопутствующие нарушения. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону уделяет внимание не только купированию острых проявлений, но и стабилизации соматических показателей. Такой подход снижает риски осложнений и формирует условия для дальнейших этапов терапии. Медицинская практика подтверждает, что отсутствие системности приводит к краткосрочному эффекту и рецидивам.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-kolomne/
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дому[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov[/url]
Hello! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a
quick shout out and say I truly enjoy reading your blog posts.
Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics?
Thank you!
https://telegra.ph/Puteshestvie-po-CHehii-na-avtomobile-strana-kotoraya-raskryvaetsya-dorogoj-01-28
7k Casino: обзор возможностей, бонусы за депозит и реальные отзывыигроковОфициальный сайт 7k Casino
Спрос на игры в 7k Casino высок среди тех, кто ценит качественный софт и стабильную работу платформы.
Независимо от стажа в гемблинге, выбор проверенного казино с лицензией является ключевым фактором для безопасной и
комфортной игры.
Почему выбирают казино 7k?
Лицензионный статус площадки обеспечивает прозрачность всех
игр и своевременность финансовых операций.
Пользователи могут рассчитывать на
выгодную программу лояльности, бонусы
за депозиты и регулярные акции.
Круглосуточная служба поддержки готова помочь решить любые вопросы,
касающиеся доступа или транзакций.
Ассортимент игр в 7k Casino
Коллекция развлечений в казино 7k включает тысячи тайтлов от
ведущих мировых провайдеров:
Классические и современные слоты
с высокой отдачей (RTP) и бонусными раундами.
Игры в реальном времени,
транслируемые из студий, обеспечивающие эффект
присутствия.
Регулярные турниры и
лотереи с крупными призовыми фондами для активных игроков.
Настольные и карточные
игры для ценителей стратегии и классического гемблинга.
Репутация казино 7k
Мнения постояльцев клуба 7k часто становятся решающим фактором для тех, кто
ищет новую площадку. Большинство пользователей подчеркивают:
Мгновенные выплаты выигрышей на карты и электронные кошельки.
Удобный обход блокировок и постоянный доступ к личному
кабинету.
Реальность выполнения условий по
вейджеру и частые персональные предложения.
Зеркало и доступ к сайту
Важно всегда иметь под рукой актуальное зеркало 7k,
чтобы не потерять доступ к балансу в случае блокировки.
Бесперебойная работа портала является ключевым условием для спокойного гемблинга.
Регистрация и первые шаги
Чтобы приступить к игре на валюту, необходимо
пройти быструю процедуру создания аккаунта:
Создайте профиль,используя электронную почту и надежный пароль.
Используйте промокод или выберите бонус напервый депозит для успешного старта.
Пополните счет удобным способом и выберите понравившийся
слот.
Имейте в виду, что подтверждение
личности позволит снимать лимиты и выводить деньги быстрее.
Соблюдайте правила ответственной игры
и не рискуйте суммами, которые не готовы
потерять. https://7k-3484.casino
Итоги обзора
Создание аккаунта в клубе 7к открывает двери
в мир азарта, где каждый игрок может рассчитывать на честное отношение
и быстрые выплаты. Каждый пользователь получает
доступ к лицензионному софту и может быть уверен в честности генератора случайных
чисел. С учетом множества предложений в интернете, этот бренд выигрывает за счет клиентоориентированности и постоянных улучшений.
Правила успешного гемблинга
Чтобы оставаться в плюсе, важно не только
надеяться на удачу, но и контролировать свои эмоции и ставки.
Гемблер обязан:
Знакомиться с таблицей выплат и механиками автоматов;
Устанавливать лимиты на проигрыш и выигрыш;
Грамотно распоряжаться фриспинами и бонусными начислениями;
Сохранять хладнокровие и не поддаваться тильту при
проигрышах;
Писать в саппорт при любых технических или
финансовых вопросах.
Сильные стороны 7k Casino
Наши пользователи выделяют стабильную работу площадки, отличный RTP в
слотах и интересные соревнования.
Мы работаем над тем, чтобы каждый визит
в казино приносил положительные эмоции и адреналин.
Технологичная база казино обеспечивает отличную работу на
мобильных гаджетах идесктопах.
Поиск актуального адреса
Если основной домен недоступен, найти рабочее зеркало можно следующими способами:
Вступление в телеграм-чат сообщества игроков;
Просмотр писем от службы
поддержки с актуальными ссылками;
Поиск через Google или Яндекс по ключевым фразам;
Контакт с администрацией в соцсетях.
Имейте в виду, что переход по сомнительным ссылкам может быть
небезопасен, пользуйтесь только официальными источниками.
Мы ждем новых игроков, готовых
сорвать куш.
Подводя итог, можно сказать, что
7k — это место, где азарт сочетается с реальными возможностями для заработка.
Создавайте аккаунт сегодня, активируйте подарки
и побеждайте!
It’s awesome in support of me to have a web site, which is beneficial for my know-how. thanks admin
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре рассматривается как специализированное медицинское пространство, где лечение зависимостей выстраивается с приоритетом анонимности и круглосуточной доступности помощи. В клинике «Формула Трезвости» терапия организована таким образом, чтобы пациент мог получить медицинскую поддержку в любое время суток без риска разглашения персональной информации. Такой формат особенно важен при острых интоксикациях и тяжёлых абстинентных состояниях, требующих немедленного врачебного вмешательства и постоянного контроля.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru/
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Для жителей Ростова-на-Дону клиника «Южный МедКонтроль» предлагает два формата помощи: лечение в стационаре и амбулаторные визиты врача на дом. Стационар оборудован всем необходимым для круглосуточного медицинского наблюдения, проведения инфузионных процедур и лабораторной диагностики. Пациентам предоставляется комфортное размещение, спокойная обстановка и постоянный контроль состояния. При выезде на дом врачи действуют оперативно — приезжают в течение часа, проводят осмотр, устанавливают капельницы, купируют абстиненцию и дают рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove19.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм ростов-на-дону[/url]
Good info. Lucky me I discovered your website by chance (stumbleupon).
I’ve bookmarked it for later!
We are a gaggle of volunteers and opening a brand new scheme in our community.
Your website provided us with useful info to work on. You’ve performed an impressive process and our whole community will likely
be grateful to you.
Круглосуточное наблюдение, регулярные замеры, быстрые корректировки, спокойная среда и структурированный режим. Это снижает риски ночных ухудшений и помогает мягко «собрать» сон без агрессивных седативных решений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-odincovo/
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-kolomne/
It is appropriate time to make a few plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy.
I’ve read this submit and if I could I desire to counsel you few fascinating issues or suggestions.
Maybe you could write subsequent articles referring to this
article. I wish to learn even more issues about it!
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Стоимость зависит от длительности запоя, объёма инфузий, перечня препаратов и длительности наблюдения после капельницы. Мы заранее озвучиваем ориентир, объясняем, какие элементы плана обязательны, а какие — рекомендательные. Ночные выезды иногда дороже из-за нагрузки на бригаду, но при выраженных симптомах откладывать помощь небезопасно. Повторные обращения и расширенные программы стабилизации обсуждаются индивидуально. Ключевой ориентир для семьи — выбирать не «самую дешёвую капельницу», а безопасный формат с контролем и ответственным уходом.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/
Чтобы процедура прошла быстрее и спокойнее, подготовьте пространство и информацию о пациенте заранее: это экономит время и повышает безопасность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Важное отличие наркологической клиники «Трезвый Путь Коломна» — полный отказ от схемы «одна капельница = решение всех проблем». Детокс здесь рассматривается как необходимый старт, но не как финальная точка. Сначала специалисты снимают острые состояния: вывод из запоя, купирование абстиненции, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса, поддержку сердца, печени и нервной системы, нормализацию сна, снижение тревоги. Когда организм перестаёт «гореть», начинается следующий этап — стабилизация: врач оценивает психическое состояние, выявляет депрессивные, тревожные, панические проявления, подбирает поддерживающие схемы, которые помогают удержаться в первые недели после кризиса. Далее подключаются психотерапевтические инструменты: индивидуальные консультации, работа с мотивацией, разбор триггеров, формирование новых привычек. В финале выстраивается маршрут поддержки: амбулаторное наблюдение, связь с клиникой, рекомендации для семьи. Такой поэтапный подход делает клинику в Коломне местом, где зависимость перестают воспринимать как «стыд» и начинают воспринимать как задачу, с которой можно работать профессионально.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskie-kliniki-obratnyj-zvonok[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom
Процесс выведения из запоя в клинике основан на медицинских стандартах и многолетнем опыте врачей-наркологов. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально: перед началом лечения проводится оценка состояния пациента, определяется степень интоксикации и подбираются препараты, подходящие именно ему. Врачи центра работают круглосуточно, а выездная помощь доступна во всех районах Ростова-на-Дону и области. Это особенно важно, когда требуется немедленная помощь, а доставить пациента в стационар невозможно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Мы выезжаем в любое время дня и ночи. Организационно всё просто: короткий звонок с описанием состояния, согласование адреса и времени, консультация по подготовке помещения, приезд врача. Если состояние тяжёлое (длительный запой, возраст 60+, выраженная соматика, признаки делирия, многократная рвота, спутанность сознания), медик предложит стационар сразу — это безопаснее, чем пытаться «дотянуть» ночь дома. В клинике пациент находится под круглосуточным наблюдением, при необходимости выполняются дополнительные исследования, расширяется объём инфузий, корректируется медикаментозная схема. Для пожилых и кардиологических пациентов стационарный формат часто предпочтителен: непрерывный мониторинг снижает риски и ускоряет стабилизацию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-korolev
Наша выездная бригада приезжает без маркировки, в гражданской одежде, согласовывает «тихое окно» связи с пациентом или близкими и начинает не с капельницы, а с настройки среды: тёплая приглушённая подсветка, проветривание без сквозняков, отключение уведомлений, подготовка воды комнатной температуры. Затем — быстрый осмотр, экспресс-метрики и старт индивидуального плана. Каждая корректировка — ровно одна за раз, чтобы сохранить причинно-следственную связь и не провоцировать полипрагмазию.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-saratov0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в саратове[/url]
Стационар «Трезвый Путь Коломна» ориентирован на безопасность в самых сложных случаях: длительные запои, тяжёлая абстиненция, смешанное употребление, выраженные соматические проблемы, риск делирия или судорог. Пациент попадает под наблюдение 24/7, что принципиально отличает клинику от домашних попыток «спасти своими средствами». Контроль жизненно важных показателей, своевременная коррекция схем лечения, возможность быстро отреагировать на осложнения — всё это снижает риск критических ситуаций, которые часто возникают именно после неумелых домашних вмешательств или «выездов без ответственности».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna2-10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kolomna[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это всегда баланс между скоростью и безопасностью. Дома трудно заметить скрытые ухудшения, особенно ночью: давление и пульс «гуляют», нарастает обезвоживание, сон рваный и тревожный. В «Трезвом Контуре» этот хаос замещается управляемостью: перед выездом дежурный врач собирает ключевые данные (длительность эпизода, лекарства, аллергии, сопутствующие болезни), на месте проводится экспресс-диагностика (АД, ЧСС, сатурация, температура, неврологический статус, степень обезвоживания), затем запускается схема терапевтической поддержки. Мы постоянно «подстраиваем» инфузии по реакции организма, а не по шаблонной карте: где-то важнее регидратация, где-то — коррекция электролитов, где-то — бережная седация для ночи. Для семьи это значит одно: меньше догадок, больше ясности. Если по картине риски высоки, мы аргументированно предлагаем стационар в Одинцово — и организуем транспортировку без пауз, потому что цена задержки в такие часы всегда выше.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Thanks for finally writing about > %blog_title% < Loved it!
Такой подход позволяет достичь устойчивого результата без срывов и рецидивов. Пациенты получают помощь не только на уровне физиологии, но и на уровне личностных изменений, что делает лечение глубоким и эффективным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в ростове-на-дону[/url]
I used to be suggested this website by means of my cousin. I am
no longer certain whether this post is written through
him as nobody else realize such unique approximately my trouble.
You are wonderful! Thanks!
Take a look at my webpage: zukausha01
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Ниже представлена таблица с ключевыми направлениями терапии, применяемыми в клинике, и их особенностями.
Подробнее тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
捕风捉影在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属平台智能AI观看体验优化,高清无广告体验。
Формат помощи
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove/
Irgendwann dachte ich mir: Wenn es keine vernunftige Seite fur [url=https://topbonusy2025.site/]bestes slot casino 2026[/url] gibt, baue ich kurzerhand meine eigene.
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-reutov[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Проволока из серебра и его сплавов 1 мм СрПд80-20 ГОСТ 7222-2014 Проволока из серебра и его сплавов диаметром 1 мм СрПд80-20 ГОСТ 7222-2014 – идеальный выбор для изготовления ювелирных изделий, электроники и других изделий. Гарантированная прочность, стойкость к коррозии и соответствие стандарту ГОСТ 7222-2014. Заказывайте у нас с уверенностью в качестве и оперативной доставке.
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-odincovo/
Терапия проводится поэтапно, что позволяет пациенту последовательно проходить все стадии восстановления и закреплять результат.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма омск[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
Incredible points. Sound arguments. Keep up the good spirit.
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno[/url]
This article presents clear idea in support of the new people
of blogging, that actually how to do blogging and site-building.
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-kolomne/
Не хотите платить за лицензию? У нас есть рабочий кряк для Windows 11 — скачайте прямо сейчас!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Где найти рабочий ключ для Windows 11[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-anonimno[/url]
I was able to find good advice from your content.
byueuropaviagraonline
https://betonred77.com/
Умение одеваться со вкусом имеет большое значение в создании образа.
Она позволяет подчеркнуть индивидуальность.
Удачный внешний вид повышает уверенность в себе.
Одежда часто становится частью невербального общения.
https://telegra.ph/7-luchshih-platev-ot-DolceGabbana-01-29
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб экономит время в повседневных делах.
Со временем внимание к стилю воспитывает чувство меры.
Таким образом стильная одежда становится важной частью современного образа жизни.
Для достижения стойкой ремиссии применяются современные и безопасные методики, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-omsk0.ru/omsk-lechenie-alkogolizma/
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до обширных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Превосходное обслуживание – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы и адаптировать решения под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
Наши товары:
Фольга магниевая EN-MB10010 – EN 12421:1998 Труба магниевая EN-MB10010 – EN 12421:1998 представляет собой высококачественный продукт, соответствующий международным стандартам. Используемый магний обеспечивает отличные механические свойства и коррозионную стойкость, что делает трубы идеальными для применения в различных отраслях, включая строительство и промышленность. Преимущества данного материала включают низкий вес, легкость в обработке и высокую прочность.Если вы ищете надежное решение для ваших проектов, рекомендуем купить Труба магниевая EN-MB10010 – EN 12421:1998. Этот продукт станет отличным выбором благодаря своим уникальным свойствам и подтвержденному качеству.
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]psihiatr-narkolog-na-dom[/url]
Generally I do not learn article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thank you, quite great post.
Мы сознательно избегаем полипрагмазии. В назначениях только то, что несёт проверяемую пользу: гидратация с корректировкой электролитов, противорвотная и гастропротективная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям и пунктирный ритм-контроль. Состав капельниц не «универсальный» — он собирается под симптомы и соматический фон, с учётом совместимости с текущими лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.). Такой подход обеспечивает управляемую динамику без дневной «ватности» и рисков перегрузки объёмом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в екатеринбурге[/url]
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Экстренная помощь нарколога на дому рекомендуется, когда состояние пациента ухудшается до критического уровня. Основные показания включают:
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru
В случаях, когда транспортировка в клинику затруднительна или пациент испытывает выраженный стресс, возможно выездное консультирование и начальная детоксикация на дому. Врач прибывает с портативным набором для инфузий, оперативно stabilizирует состояние и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника анонимно[/url]
В медицинских условиях специалисты обеспечивают тщательный контроль над динамикой состояния пациента. Каждый этап процедуры имеет свою задачу, которая направлена на последовательное восстановление функций организма.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург[/url]
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-otzyvy[/url]
На первом этапе проводится серия исследований:
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма на дому в екатеринбурге[/url]
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Состав инфузии формируется по доминирующему симптому и данным экспресс-измерений, с учётом лекарственных взаимодействий. Врач оценивает динамику в реальном времени и, при необходимости, корректирует состав/скорость. Ниже — примеры профилей; окончательное решение всегда очное.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]скорая помощь вывода из запоя[/url]
Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа? У нас есть пошаговая инструкция!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright infringement? My site has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it seems a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my agreement. Do you know any techniques to help reduce content from being stolen? I’d definitely appreciate it.
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому сочи[/url]
https://telegra.ph/Puteshestvie-po-CHehii-na-avtomobile-strana-kotoraya-raskryvaetsya-dorogoj-01-28
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov[/url]
Алгоритм в «Трезвый Центр Коломна» построен так, чтобы убрать импровизацию и сделать всё максимально прозрачным для семьи. Сначала по телефону собираются ключевые данные: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, хронические заболевания, препараты, аллергии, наличие судорог, потерь сознания, странного поведения, текущие жалобы. На этом этапе озвучивается ориентировочный формат помощи и примерный диапазон стоимости. Далее следует выезд на дом или поступление в стационар. Врач проводит осмотр: измеряет артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, координацию, сознание, степень обезвоживания, наличие болей, состояние дыхания и сердца. На основе этих данных назначается инфузионная терапия: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, по показаниям — гепатопротекторы, антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, мягкие анксиолитики для уменьшения тревоги и нормализации сна. Уходят от агрессивной седации: пациент не должен быть «выключен» так, чтобы невозможно было заметить ухудшение. В процессе капельниц проводится повторный контроль показателей, темп и состав при необходимости корректируются. После стабилизации пациент и семья получают подробные рекомендации: режим, сон, питание, питьё, запреты, «красные флаги», план наблюдения и возможного дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
Hi, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam responses?
If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can advise?
I get so much lately it’s driving me crazy so any support is very much appreciated.
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-adler
Применение современных капельничных методов позволяет точно дозировать лекарственные средства. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей пациента дает возможность оперативно корректировать терапию для достижения оптимального эффекта и предотвращения побочных реакций.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnicza-volgograd/
Домашний визит нарколога — это не компромисс «на скорую руку», а тщательно организованный процесс, который экономит время, сохраняет конфиденциальность и делает лечение предсказуемым. «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» принимает вызовы круглосуточно и выезжает во все районы города — от Уралмаша и ВИЗа до Академического и Широкой Речки. Команда приезжает без внешних опознавательных знаков, использует нейтральные формулировки в документах и ведёт переписку только по защищённым каналам связи. На месте мы быстро проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, контролируем пульс, сатурацию и артериальное давление, подключаем гастропротекцию и аккуратно управляем тревогой без избыточной седации. Цель — безопасно «снять волну» симптомов, вернуть возможность пить воду и отдыхать, а затем закрепить результат на горизонте ближайших 72 часов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/ekaterinburg-narkologiya/
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Для более точного понимания различий между основными подходами используется систематизация данных в таблице. Она отражает основные особенности применения методов и их задачи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена санкт-петербург[/url]
Запой – критическое состояние, при котором организм подвергается серьезной токсической нагрузке, что может привести к опасным для жизни осложнениям. В Волгоградской области помощь нарколога оказывается круглосуточно, что позволяет начать лечение немедленно в любой момент дня или ночи. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство, индивидуальный подход и высокий уровень безопасности, позволяя стабилизировать состояние пациента в домашних условиях или в клинике.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом волгоград[/url]
Если по ходу визита появляются «красные флаги» (падение сатурации, нестабильный ритм, нарастающая дезориентация), маршрут мгновенно переводится в стационарный блок «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» — без «обнуления» обследований и без потери приватности. Вся собранная информация остаётся в единой карте наблюдения, что экономит время и силы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом цены екатеринбург[/url]
Crafting a stylish look is crucial.
It serves as a powerful mode of non-verbal communication.
Your attire shapes first perceptions nearly immediately.
Feeling self-assured in your ensemble significantly enhances your self-esteem.
https://angelina-podium.blogspot.com/2026/01/the-integrated-icon-week-with-patek.html
A deliberate style may create opportunities in both professional and social settings.
It enables you to express your personal personality before uttering a single word.
Ultimately, investing in your personal style is an investment in your own potential.
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/nomer-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov/
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]нарколог на дом в серпухове[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
Hi there all, here every person is sharing such familiarity, thus it’s
pleasant to read this website, and I used to
go to see this webpage everyday.
Наша выездная бригада оснащена как мобильный мини-кабинет: инфузомат для покапельной титрации, портативный кардиомонитор, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, экспресс-кассеты Na?/K? и набор для регистрации ЭКГ по показаниям. Такой комплект позволяет принять решение на месте — безопасно ли начинать дома или целесообразнее перевести пациента в стационарное отделение «ЮгМедЦентра» без «перезапуска» обследований. Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию: в схеме нет «лишних» позиций и конфликтов с уже принимаемыми лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.).
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom/
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ramenskom[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
Irgendwann dachte ich mir: Wenn keine ordentliche Plattform fur [url=https://sevenwonders.casino/]top 10 slots 2026[/url] existiert, erstelle ich kurzerhand meine eigene.
Состав инфузии формируется под доминирующие симптомы и данные экспресс-измерений. Мы избегаем шаблонов: у каждого профиля — конкретная цель и измеримый эффект. Ниже — ориентиры; окончательные решения врач принимает очно, с учётом лекарственных взаимодействий и ваших приоритетов (работа, семья, график сна).
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в екатеринбурге[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-telefon[/url]
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Awesome posts, Thanks a lot.
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu/
Ниже — ключевые направления, которые логично дополняют друг друга и формируют единый маршрут лечения:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]где находится наркологическая клиника[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-srochno[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Узнать больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo[/url]
После диагностики выявленные нарушения восполняются посредством инфузий с витаминами группы B, C, магнием и элементами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom/
Valuable info. Fortunate me I found your site by accident, and I am stunned why this coincidence didn’t came about in advance! I bookmarked it.
Lakiwincasino, now that’s a name that might bring good fortune! Let’s see if it provides the win. Visit this lucky place: lakiwincasino
Hey guys, Played a bit on 9377game. Not bad overall. It’s got some games you won’t find everywhere else. It’s worth a visit if you need a quick fix of something new. Head over to 9377game for some fun
Hey guys! Checking out 999r and it seems pretty slick. Anyone else tried it out yet? Let me know what you think! Check it out here: 999r
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyzvat-vracha-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]сколько стоит наркологическая клиника[/url]
Зависимость от алкоголя или наркотиков — серьёзная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Если у вас или вашего близкого возникли признаки тяжелого похмелья, запоя или интоксикации, клиника «НаркологПлюс» предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге. Наши врачи оперативно прибывают по указанному адресу, оказывают всю необходимую медицинскую помощь и помогают пациенту быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Состав инфузии формируется по доминирующему симптому и данным экспресс-измерений, с учётом лекарственных взаимодействий. Врач оценивает динамику в реальном времени и, при необходимости, корректирует состав/скорость. Ниже — примеры профилей; окончательное решение всегда очное.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna[/url]
После поступления вызова клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» отправляет к пациенту опытного нарколога, который прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По приезду врач проводит комплексную диагностику, включающую измерение артериального давления, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови и тщательную оценку общего состояния пациента. На основе полученных данных специалист подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
Production company project video production agency in italy
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly return.
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/
I’m pretty pleased to discover this website. I wanted to thank you for ones
time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every
little bit of it and i also have you book marked to check out new things
on your blog.
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/
Вывод из запоя на дому возможен только при относительно контролируемом состоянии и после очной оценки нарколога. В таких случаях специалист выезжает в Раменском, проводит осмотр, назначает индивидуальную капельницу, остаётся до стабилизации состояния и оставляет подробные рекомендации. Важный момент — честность: если во время осмотра врач видит риски (нестабильное давление, признаки начинающегося делирия, серьёзные боли, глубокую дезориентацию), формат на дому не навязывается, а предлагается стационар. Именно это отличает клинику от анонимных «служб капельниц», для которых любая заявка — повод заработать, независимо от последствий.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-anonimno[/url]
Состав капельницы не повторяет «советы знакомых». Он формируется под доминирующий симптом, сопутствующие заболевания и взаимодействия с текущими лекарствами. Врач постоянно оценивает витальные показатели и реакцию организма, корректируя скорость и объём по инфузомату. Ниже — примеры профилей, которые объясняют логику выбора; финальное решение всегда очное.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены сочи[/url]
Такой порядок действий гарантирует не только купирование симптомов, но и подготовку пациента к последующему восстановлению.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru
Одновременно с медикаментозной детоксикацией начинается работа по снижению эмоционального напряжения. Психотерапевтическая помощь помогает пациенту осознать причины зависимости и выработать стратегии для предотвращения рецидивов, что является важным аспектом успешного лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your post. I wanted to write a little comment to support you.
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove/
Формат помощи
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove/
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя в реутово[/url]
I am extremely impressed together with your writing skills as well as
with the structure on your blog. Is that this a paid theme or
did you customize it yourself? Either way keep up the nice high
quality writing, it’s uncommon to peer a nice weblog
like this one today..
Алгоритм организован так, чтобы каждое действие было логичным и предсказуемым. После обращения по телефону врач заранее получает краткую клиническую картину и подбирает набор препаратов с учётом состояния пациента. По прибытии в Долгопрудном нарколог не ставит капельницу «по шаблону», а начинает с осмотра: измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, температуру, оценивает тремор, уровень сознания, ориентировку, степень обезвоживания, частоту рвоты, дыхание, возможные боли в груди или животе, обращает внимание на поведение и эмоциональное состояние. Если по результатам осмотра подтверждается, что дом — безопасный формат, подбирается индивидуальная инфузионная схема: объём, скорость введения и препараты зависят от возраста, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней и уже использованных медикаментов. Врач остаётся на адресе до завершения основных процедур, контролирует реакцию, при необходимости корректирует план и чётко проговаривает, как пациент должен проводить ближайшие 24–72 часа. Если по ходу работы выявляются признаки угрозы (начальные симптомы делирия, тяжёлые аритмии, нестабильное давление, выраженная дезориентация), нарколог рекомендует стационар и помогает семье организовать перевод. Это честный и безопасный подход: не любой ценой «отработать выезд», а сделать так, чтобы помощь действительно снижала риски.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-anonimno[/url]
Чтобы не оценивать состояние субъективно, в клинике применяется система наблюдения за ключевыми параметрами. Таблица помогает врачу и пациенту видеть реальную динамику и корректировать вмешательства только при необходимости.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Saved as a favorite, I love your blog!
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom
I’m someone who lost more than I could afford and I needed to understand how that happened. https://medium.com/@william_tu78/building-more-than-a-website-my-unfiltered-journey-with-gamblingformoney-4810e1fcb7b9 is the start of recovery.
Группа препаратов
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnodar/
Действие и назначение
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnodar
Прежде чем говорить о цифрах, важно обозначить принцип: цена формируется из реального объёма медицинской помощи, а не из рекламных обещаний. На итоговую стоимость влияет длительность запоя, выраженность интоксикации, необходимость одной или нескольких капельниц, подбор дополнительных препаратов, время суток выезда, объём наблюдения, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний, повышающих риск. «СерпуховТрезвие» придерживается открытой схемы: при звонке озвучивается ориентировочный диапазон, поясняется, что входит в базовый визит и при каких условиях он может перейти в расширенный. Все дополнительные назначения согласуются до их выполнения, без скрытых доплат и «сюрпризов» по факту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyzov-vracha-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Диагностика в клинике «КузбассМед» проводится комплексно: используются лабораторные, инструментальные и психологические методы. Благодаря применению цифровых систем и алгоритмов обработки данных, результаты анализов доступны уже в течение первого часа. Оценка проводится по нескольким направлениям: токсикологический статус, состояние печени и почек, электролитный баланс, нейровегетативное состояние, когнитивные функции и уровень стресса. Это позволяет врачам составлять максимально точную картину заболевания и подбирать индивидуальные методы терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/narkolog-novokuzneczk-na-dom/
Much thanks the useful content on casinos.
https://www.sunsky-online.com/product/cart%21switchCurrency.do?currencyId=6&toUrl=https://bigbasssplashuk.co.uk/registration
Такая структура лечения помогает пациентам пройти все этапы восстановления под контролем специалистов.
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom[/url]
Капельница от запоя является неотъемлемой процедурой при острых и хронических отравлениях алкоголем. Она помогает стабилизировать состояние пациента, избежать тяжелых последствий и максимально быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Вызов врача для проведения процедуры рекомендуется в следующих ситуациях:
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в краснодаре[/url]
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Для эффективного лечения алкогольной интоксикации и восстановления организма врачи клиники «АлкоДоктор» используют комплекс препаратов, которые индивидуально подбираются с учетом состояния пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого в сочи[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov[/url]
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/narkolog-perm-czeny/
На нашем сайте вы можете скачать активатор для Windows 11 абсолютно бесплатно и навсегда забыть о водяных знаках!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Как обойти активацию Windows 11[/url]
「オンラインカジノ」とは、インターネットを介してさまざまなカジノゲームを楽しめるプラットフォームです。その利便性から、世界中で多くのユーザーに親しまれています。詳細な仕組みや提供されているゲームの種類については、専門の情報サイトでご確認ください。
→ [url=https://kobe-nisangaroku.jp/]オンラインカジノ[/url]
each time i used to read smaller articles or reviews that also clear their motive, and that is also happening with this post which I am reading at this place.
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Процедура начинается с осмотра пациента и оценки степени интоксикации. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень насыщения крови кислородом, определяет наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. После диагностики назначается капельница, состав которой подбирается индивидуально. Процедура направлена на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и снятие симптомов похмелья.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в тольятти[/url]
Why visitors still use to read news papers when in this technological
globe everything is existing on net?
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
「オンラインカジノ」とは、インターネットを介してさまざまなカジノゲームを楽しめるプラットフォームです。その利便性から、世界中で多くのユーザーに親しまれています。詳細な仕組みや提供されているゲームの種類については、専門の情報サイトでご確認ください。
→ [url=https://kobe-nisangaroku.jp/]オンラインカジノ おすすめ[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Профессиональная помощь требуется в тех случаях, когда организм уже не способен самостоятельно справиться с последствиями интоксикации. Чем дольше длится запой, тем сильнее проявляются его симптомы. Медицинское вмешательство помогает предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как судороги, повышение давления и алкогольный психоз.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Прибыв по вызову, врач клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» начинает с диагностики состояния пациента. Проводится комплексное обследование: измерение артериального давления, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови, оценка общего самочувствия и психического состояния. После диагностики нарколог подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, который позволяет эффективно вывести токсины, стабилизировать работу внутренних органов и быстро облегчить состояние пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-sochi/
Такие процедуры особенно эффективны на ранних стадиях лечения, когда важно быстро снять симптомы интоксикации и вернуть стабильное самочувствие. После курса капельниц пациенту становится легче концентрироваться, снижается раздражительность и тревожность, восстанавливается аппетит и сон.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр рязань[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Перми включает использование комплекса медикаментозных и психотерапевтических методик. Они помогают не только снять симптомы интоксикации, но и стабилизировать эмоциональное состояние.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение на дому проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке, что позволяет значительно снизить уровень стресса и быстро улучшить состояние здоровья пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в сочи[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov/
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод сочи[/url]
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно пермь[/url]
That is really attention-grabbing, You’re an excessively professional blogger. I have joined your rss feed and sit up for looking for more of your excellent post. Also, I have shared your website in my social networks
byueuropaviagraonline
Кушаешь слабее а также будет тебе счастье! Вот ссылка https://smartbb.ru/
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno[/url]
wonderful submit, very informative. I wonder why the opposite experts of this sector don’t understand this. You should continue your writing. I’m confident, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в тольятти[/url]
дайсон центр в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru[/url] .
ремонт дайсон в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]ремонт дайсон в спб[/url] .
Чем раньше нарколог окажет помощь, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и восстановиться без последствий для здоровья.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/
Выезд нарколога на дом в Серпухове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь в условиях, когда везти человека в клинику сложно, опасно или он категорически отказывается от госпитализации. Специалисты «СерпуховТрезвие» работают круглосуточно, приезжают по адресу с одноразовыми системами, стерильными расходниками и необходимым набором препаратов, проводят осмотр, оценивают жизненно важные показатели, подбирают индивидуальную капельницу, контролируют реакцию и оставляют подробные рекомендации. Всё происходит конфиденциально, без лишних свидетелей, без осуждения и давления. Цель — не формально «поставить капельницу», а безопасно стабилизировать состояние, снизить интоксикацию, выровнять давление и пульс, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть человеку возможность нормально спать и восстанавливаться, не доводя до осложнений и экстренной госпитализации.
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov/
Запой — это не просто несколько лишних дней алкоголя, а тяжёлое состояние, в котором организм работает на пределе. Чем дольше длится эпизод, тем глубже обезвоживание, тем сильнее сдвиги электролитов, тем выше риск аритмий, гипертонических кризов, судорог, делирия, обострений заболеваний сердца, печени и поджелудочной железы. Попытки «вывести» человека дома силами родных часто включают опасные комбинации: случайные седативные, снотворные, анальгетики, «антипохмельные» из рекламы. Они могут на время усыпить или «успокоить», но при этом скрывают ухудшение, сбивают давление, угнетают дыхание и мешают врачу увидеть реальную картину. В «Трезвый Центр Коломна» подход другой: ещё на этапе звонка специалист уточняет длительность запоя, объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, список уже принятых препаратов, эпизоды потери сознания, судорог, странного поведения. На основании этих данных определяется, безопасен ли формат на дому или сразу нужен стационар. Такая сортировка позволяет вовремя перехватить опасные случаи, не терять часы на бесполезные попытки и сразу запускать те схемы, которые реально снижают риски и стабилизируют состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Set piece efficiency, corner and free kick conversion rates
Ligue 1 live scores, French football including PSG matches tracked in real time
Лечение на дому проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке, что позволяет значительно снизить уровень стресса и быстро улучшить состояние здоровья пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Медный тройник под пайку стандартный 66.7х57х1.4 мм 33.5х36.5 мм мягкая пайка М1РМ ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Купить качественные медные тройники под пайку для надежных и долговечных соединений в трубопроводных системах. Разнообразие размеров и конфигураций, высокая теплопроводность и устойчивость к коррозии. Простая установка и надежность соединения. Идеальное решение для различных проектов. Редметсплав.рф
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/[/url]
Медицинская помощь строится на принципах индивидуального подхода и поэтапной терапии. Каждый пациент проходит диагностику, после чего составляется персональная программа, включающая медикаментозную поддержку, консультации психотерапевта и физиопроцедуры. Такой подход помогает не просто снять симптомы, но и восстановить организм полностью.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/narkologicheskij-staczionar-ryazan/
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
I visited several websites except the audio feature for audio songs existing at this web page is in fact fabulous.
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru
Формат помощи
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-sajt[/url]
Группа препаратов
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя сочи[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркология раменское московская московская область[/url]
I every time used to read post in news papers but now as I am a user of web therefore from now I am using net for content, thanks to web.
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering
which blog platform are you using for this site?
I’m getting sick and tired of WordPress because I’ve
had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for
another platform. I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov/
Группа препаратов
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m
going to come back once again since i have saved as a favorite it.
Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в серпухове[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
дайсон купить спб оригинал [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]дайсон купить спб оригинал[/url] .
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
купить пылесос дайсон спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru[/url] .
**mounjaboost**
MounjaBoost is a next-generation, plant-based supplement created to support metabolic activity, encourage natural fat utilization, and elevate daily energywithout extreme dieting or exhausting workout routines.
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы обеспечиваем своевременную реализацию вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Дружелюбная помощь – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы по мере того как адаптировать решения под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наша продукция:
Труба висмутовая Sn42Bi58 – IEC 61190-1-3 Труба висмутовая Sn42Bi58 – IEC 61190-1-3 – это идеальное решение для профессионалов в области электроники. Она обладает уникальными свойствами, обеспечивая надежную пайку различных компонентов. Высокая теплопроводность и отличная смачиваемость делают эту трубу незаменимым инструментом в производственных процессах. Купить Труба висмутовая Sn42Bi58 – IEC 61190-1-3 можно непосредственно на нашем сайте. Убедитесь сами в качестве этого материала и оцените его эффективность в ваших проектах. Большая прочность и стойкость к окислению также гарантируют долговечность использования. Ваши технические задачи будут решены с помощью нашей трубы.
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Hi there, just wanted to mention, I enjoyed this post. It was practical. Keep on posting!
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ramenskom/
Формат помощи
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя реутов[/url]
**neuro sharp**
Neuro Sharp is an advanced cognitive support formula designed to help you stay mentally sharp, focused, and confident throughout your day.
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]lechenie-v-narkologicheskoj-klinike[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
Вывод из запоя в Реутове в наркологической клинике «РеутовМед Сервис» — это профессиональная помощь, которая позволяет безопасно остановить разрушительное действие алкоголя на организм и вернуть контроль над состоянием пациента без рискованных экспериментов дома. Длительные запои приводят к тяжёлой интоксикации, скачкам давления, нарушению работы сердца, печени, нервной системы, провалам в памяти, агрессии, паническим атакам и риску алкогольного психоза. Попытки «перетерпеть», самостоятельно колоть непонятные препараты, давать горсть таблеток или «чуть-чуть допить для облегчения» только усиливают угрозу. Команда «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает вывод из запоя как последовательный медицинский процесс: первичная оценка состояния, грамотная детоксикация с капельницами, круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре при необходимости, контроль жизненных показателей, поддержка сердца и нервной системы, рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению зависимости. Для пациента это шанс выйти из тяжёлого состояния без стыда и боли, для родственников — возможность переложить ответственность за здоровье близкого на профессионалов, которые знают, что делать на каждом этапе.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very
good gains. If you know of any please share. Thanks!
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом сочи[/url]
Прежде чем говорить о цифрах, важно обозначить принцип: цена формируется из реального объёма медицинской помощи, а не из рекламных обещаний. На итоговую стоимость влияет длительность запоя, выраженность интоксикации, необходимость одной или нескольких капельниц, подбор дополнительных препаратов, время суток выезда, объём наблюдения, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний, повышающих риск. «СерпуховТрезвие» придерживается открытой схемы: при звонке озвучивается ориентировочный диапазон, поясняется, что входит в базовый визит и при каких условиях он может перейти в расширенный. Все дополнительные назначения согласуются до их выполнения, без скрытых доплат и «сюрпризов» по факту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-serpuhov
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]бесплатный нарколог на дом[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]таблетки для аборта[/url]
It’s awesome in support of me to have a web site, which is valuable for my experience. thanks admin
Hi! I just want to give you a big thumbs up for the excellent
information you’ve got right here on this post.
I’ll be returning to your blog for more soon.
дайсон центр в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru[/url] .
dyson v15 спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru[/url] .
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в тольятти[/url]
Для эффективного лечения алкогольной интоксикации и восстановления организма врачи клиники «АлкоДоктор» используют комплекс препаратов, которые индивидуально подбираются с учетом состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]сколько стоит капельница на дому от запоя в сочи[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]анонимный врач нарколог на дом[/url]
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в рязани[/url]
Медицинская помощь в клинике организована поэтапно, что позволяет постепенно стабилизировать состояние и вернуть контроль над самочувствием.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в перми[/url]
「オンラインカジノ」とは、インターネットを介してさまざまなカジノゲームを楽しめるプラットフォームです。その利便性から、世界中で多くのユーザーに親しまれています。詳細な仕組みや提供されているゲームの種類については、専門の情報サイトでご確認ください。
→ [url=https://kobe-nisangaroku.jp/]オンラインカジノ[/url]
Лечение зависимости в наркологической клинике проводится поэтапно. Это обеспечивает постепенное восстановление организма и исключает риск осложнений. Каждый этап направлен на устранение конкретных нарушений, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk-otzyvy
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologiya-ramenskoe-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
「オンラインカジノ」とは、インターネットを介してさまざまなカジノゲームを楽しめるプラットフォームです。その利便性から、世界中で多くのユーザーに親しまれています。詳細な仕組みや提供されているゲームの種類については、専門の情報サイトでご確認ください。
→ [url=https://kobe-nisangaroku.jp/]オンラインカジノ おすすめ[/url]
Скачайте активатор для Windows 11 и получите все функции Pro-версии бесплатно.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Windows 11 активатор без вирусов[/url]
Thanks very interesting blog!
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-serpuhove[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru
Действие и назначение
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]капельница от запоя цена в сочи[/url]
Even when it’s out of focus, health remains the foundation of how we function.
We’re surrounded by tips, while comprehension stays shaky.
Nuanced realities get swapped for neat shortcuts.
The body whispers—tiredness, tension, appetite, calm—yet we rush past the message.
And the more we pay attention, the more we recognize life working inside us.
Time and patience turn confusion into clarity.
In that connection, balance shows up through understanding, not control.
Each small realization strengthens the relationship we have with ourselves.
If you want to trust your signals again.
To recognize the quiet patterns shaping your well-being.
Strength built from small discoveries.
Each insight brings us closer to what health actually means.
What feels like intuition often rests on real biological patterns.
If you’ve wanted to understand more about tadacip dosing in dialysis.
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
пылесосы dyson [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru[/url] .
Такая структура лечения помогает пациентам пройти все этапы восстановления под контролем специалистов.
Получить больше информации – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/
dyson v15 купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]dyson v15 купить спб[/url] .
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov/
Группа препаратов
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]сколько стоит капельница от запоя сочи[/url]
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Группа препаратов
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому сочи[/url]
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]анонимный врач нарколог на дом[/url]
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This post posted at this site is really pleasant.
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]клиника наркологической зависимости[/url]
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-reutove
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/[/url]
Группа препаратов
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологическая клиника в раменском[/url]
Super plateforme ! Tout est de premier ordre, félicitations et succès.
https://m.yeskorea.org/member/login.html?returnUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.bgeek.it%2Fblog%2Fleon-casino-en-ligne-particularites-1028
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Капельница от запоя является неотъемлемой процедурой при острых и хронических отравлениях алкоголем. Она помогает стабилизировать состояние пациента, избежать тяжелых последствий и максимально быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Вызов врача для проведения процедуры рекомендуется в следующих ситуациях:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в сочи[/url]
магазин дайсон в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]магазин дайсон в спб[/url] .
I truly love your site.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you create this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m planning to create my very own site and would love to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Thanks!
dyson пылесос спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru[/url] .
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
Основные этапы обычно включают:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru
Перед изложением таблицы следует отметить, что подбор методов лечения зависит от стадии и тяжести зависимости, а также индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]срочная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Стильная одежда является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она помогает выразить характер.
Гармоничный стиль поддерживает самооценку.
Одежда часто становится инструментом визуального контакта.
https://z4.sochidaily.ru/HVbCKKDDOAuR/
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб упрощает выбор в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю формирует привычку.
В итоге стильная одежда играет значимую роль современного образа жизни.
Для удобства восприятия можно ориентироваться на следующую структуру (это не публичная оферта, а примерная модель ценообразования — точная сумма фиксируется после осмотра и согласования схемы):
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/narkolog-psiholog-na-dom-serpuhov
Такая последовательность действий позволяет обеспечить результативность и закрепить положительные изменения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в перми[/url]
Hello I am so happy I found your weblog, I really found you by
mistake, while I was researching on Aol for something else,
Anyways I am here now and would just like to say kudos for a incredible post
and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to look over it all at the minute but I have saved it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will
be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the fantastic work.
Вывод из запоя в Реутове в наркологической клинике «РеутовМед Сервис» — это профессиональная помощь, которая позволяет безопасно остановить разрушительное действие алкоголя на организм и вернуть контроль над состоянием пациента без рискованных экспериментов дома. Длительные запои приводят к тяжёлой интоксикации, скачкам давления, нарушению работы сердца, печени, нервной системы, провалам в памяти, агрессии, паническим атакам и риску алкогольного психоза. Попытки «перетерпеть», самостоятельно колоть непонятные препараты, давать горсть таблеток или «чуть-чуть допить для облегчения» только усиливают угрозу. Команда «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает вывод из запоя как последовательный медицинский процесс: первичная оценка состояния, грамотная детоксикация с капельницами, круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре при необходимости, контроль жизненных показателей, поддержка сердца и нервной системы, рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению зависимости. Для пациента это шанс выйти из тяжёлого состояния без стыда и боли, для родственников — возможность переложить ответственность за здоровье близкого на профессионалов, которые знают, что делать на каждом этапе.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo[/url]
**back biome**
Mitolyn is a carefully developed, plant-based formula created to help support metabolic efficiency and encourage healthy, lasting weight management.
Just want to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity to your post is simply nice and that i can assume you’re a professional on this subject. Fine together with your permission let me to take hold of your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please carry on the rewarding work.
Nicely put. Appreciate it! https://co168-games.blogspot.com/2025/12/betflik199-2025-2025-betflik199.html
Прежде чем говорить о цифрах, важно обозначить принцип: цена формируется из реального объёма медицинской помощи, а не из рекламных обещаний. На итоговую стоимость влияет длительность запоя, выраженность интоксикации, необходимость одной или нескольких капельниц, подбор дополнительных препаратов, время суток выезда, объём наблюдения, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний, повышающих риск. «СерпуховТрезвие» придерживается открытой схемы: при звонке озвучивается ориентировочный диапазон, поясняется, что входит в базовый визит и при каких условиях он может перейти в расширенный. Все дополнительные назначения согласуются до их выполнения, без скрытых доплат и «сюрпризов» по факту.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
I’m extremely impressed with your writing talents as smartly as with the layout in your weblog.
Is this a paid subject or did you customize it yourself?
Either way keep up the nice quality writing, it is uncommon to see a great weblog like this one today..
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to
this excellent blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and
adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will
talk about this website with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-serpuhov[/url]
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Live streams https://golvar.com.az/ and live matches online, including the latest football schedule for today. Follow games in real time, find out dates, start times, and key events of football tournaments.
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Для повышения эффективности в капельницы добавляются витамины группы B, аскорбиновая кислота, кардиопротекторы и антиоксиданты. Такая комбинация позволяет не только ускорить выведение продуктов распада алкоголя, но и предотвратить развитие постабстинентных расстройств. Благодаря точной дозировке и мягкому темпу введения растворов снижается риск побочных реакций, а восстановление проходит плавно и безопасно.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an extremely long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say superb blog!
byueuropaviagraonline
«РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает несколько форматов помощи, но выбор всегда делается из соображений безопасности, а не удобства картинки. Стационарный вывод из запоя подходит в ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или недель, есть скачки давления, проблемы с сердцем, печени, сахарный диабет, неврологические заболевания, эпизоды судорог или делирия в анамнезе, возраст старше 50–55 лет, выраженная слабость, тахикардия, невозможность пить воду, угрозы психозов. В стационаре пациент находится под наблюдением круглосуточно: контролируются жизненные показатели, вовремя корректируется терапия, есть возможность экстренно отреагировать на осложнения. Это гарантированно безопаснее, чем оставлять тяжёлого человека дома под наблюдением уставших родственников.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru
Перед изложением таблицы следует отметить, что подбор методов лечения зависит от стадии и тяжести зависимости, а также индивидуальных особенностей пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь в самаре[/url]
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя реутов[/url]
Процесс организован так, чтобы снять с семьи хаос и дать понятный сценарий. После обращения в «РеутовМед Сервис» пациент быстро попадает в поле зрения врача: или через выезд по адресу, или через стационар, если состояние уже близко к опасному. На месте проводится полноценная оценка: давление, пульс, сатурация, температура, осмотр сердца и дыхания, степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, наличие рвоты, боли в груди или животе, неврологический статус, поведение, признаки психоза. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальный план детоксикации. Стартовая инфузионная терапия подбирается с учётом возраста, массы тела, длительности запоя, сопутствующих болезней, уже принятых препаратов. В стационаре пациента размещают в безопасных условиях, контролируют динамику, корректируют дозировки, не оставляют «на самотёк». При выводе из запоя на дому врач остаётся до стабилизации, отслеживает реакцию и при первых тревожных признаках рекомендует стационар, а не уезжает «лишь бы поставил капельницу». Такой пошаговый подход позволяет не только снять острые симптомы, но и уменьшить риск осложнений — от аритмий и судорог до алкогольного делирия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Программа лечения строится по принципу последовательного воздействия на физическое и психологическое состояние. Начинается она с детоксикации: инфузионная терапия с применением сбалансированных растворов, антиоксидантов, гепатопротекторов и витаминов. Затем — стабилизация состояния, коррекция сна, восстановление когнитивных функций и купирование абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от диагноза используются такие методы, как заместительная терапия, нейрометаболическая поддержка, противотревожные и антидепрессивные схемы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя новокузнецк[/url]
https://spb-generic.ru/
Good response in return of this issue with firm arguments and explaining all about that.
Стационар наркологической клиники в Раменском ориентирован на тех пациентов, для которых домашние попытки лечения объективно опасны. Это длительные запои, пожилой возраст, выраженные сердечно-сосудистые патологии, заболевания печени и почек, риск делирия, судорог, тяжёлая абстиненция, полинаркомания. В стационаре «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» организовано круглосуточное наблюдение: контролируются давление, пульс, сатурация, поведение, динамика симптомов, проводится своевременная коррекция терапии. Пациент находится в спокойной, защищённой обстановке, где ему не нужно скрывать своё состояние или оправдываться — задача команды не судить, а стабилизировать и лечить. Комфортные палаты, медицинский персонал рядом, продуманное питание, конфиденциальность — всё это снижает уровень страха у пациента и напряжение у родственников. Важный момент: стационар не подаётся как «камерный режим», а как безопасная зона восстановления, где можно пройти самый тяжёлый участок пути с максимальной защитой.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-domu[/url]
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru
Wow, this article is nice, my sister is analyzing these kinds of things, thus I am going to
tell her.
Вывод из запоя в Раменском — это не просто «поставить капельницу и отпустить домой», а комплекс медицинских действий, от которых напрямую зависит здоровье, а иногда и жизнь человека. Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению работы сердца, печени, головного мозга, сбоям давления, риску судорог, психозов и резких обострений хронических заболеваний. Попытки самостоятельно «сойти с дистанции» дома, с помощью случайных таблеток, седативных препаратов и новых доз алкоголя, часто только усугубляют состояние. Наркологическая клиника «РаменМед Трезвость» в Раменском выстраивает вывод из запоя как безопасный, контролируемый, поэтапный процесс: от экстренного купирования симптомов до формирования плана дальнейшего восстановления. Пациент получает помощь без осуждения, анонимно, с участием специалистов, которые берут на себя ответственность за каждое назначение и каждое действие. Для родственников это означает: больше не нужно гадать, чего бояться и что давать — есть конкретное место и команда, к которым можно обратиться сразу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryadom-v-ramenskom/
При длительном запое или серьезной алкогольной интоксикации часто нет возможности или желания ехать в стационар. В таких ситуациях оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом в Сочи. Специалисты клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» круглосуточно приезжают к пациентам, оперативно оказывают медицинскую помощь и проводят профессиональную детоксикацию организма прямо в домашних условиях. Благодаря комфортному лечению на дому пациенты быстрее восстанавливаются, избегают дополнительного стресса и осложнений, связанных с госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-sochi/
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa?
My site addresses a lot of the same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit
from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free
to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you!
Awesome blog by the way!
Работа выездной службы построена так, чтобы для семьи всё было максимально понятно и предсказуемо. После звонка специалист не ограничивается общими фразами, а уточняет детали: сколько длится употребление, есть ли хронические болезни сердца, печени, почек, эндокринные нарушения, какие препараты и в каких дозах пациент уже получил, были ли в прошлом судороги, галлюцинации, тяжёлые реакции на лекарства. Это позволяет заранее оценить уровень риска и понять, подходит ли формат дома. По прибытии в Серпухове врач осматривает пациента, проверяет контакт и ориентировку, измеряет артериальное давление несколько раз, оценивает пульс, сатурацию, температуру, выраженность тремора, наличие болей, характер дыхания, степень обезвоживания. Далее формируется индивидуальная инфузионная схема: растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы, при необходимости — гепатопротекторы и мягкие антиоксидантные комплексы, противорвотные для контроля тошноты, щадящие анксиолитики для нормализации сна без грубой седации. Во время процедуры врач контролирует динамику, меняет скорость капельницы при необходимости, отслеживает реакцию на препараты и объясняет родным, какие изменения будут происходить по часам. По завершении визита пациент и родственники получают подробный план: режим, питьё, питание, чего нельзя, какие симптомы считаются тревожными, когда нужна повторная консультация или стационар. При выявлении опасных признаков вопрос о госпитализации поднимается честно и сразу, а не откладывается «до утра».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-srochno[/url]
В этих ситуациях выезд нарколога на дом позволяет вовремя скорректировать состояние, а при выявлении опасных признаков — не теряя времени, направить пациента в стационар. Это управляемый маршрут вместо хаотичных решений в последний момент.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/[/url]
Лечение на дому проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке, что позволяет значительно снизить уровень стресса и быстро улучшить состояние здоровья пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Having read this I believed it was very informative. I appreciate you
spending some time and effort to put this article together.
I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading and posting comments.
But so what, it was still worth it!
Одна из сильных сторон «РеутовМед Сервис» — честная оценка границ домашнего лечения. Клиника не обещает «вывезем любого дома», потому что есть состояния, при которых отсутствие круглосуточного наблюдения опасно. Чтобы родным было проще сориентироваться, важно разделить ситуации по уровню риска и понять, почему иногда разумнее выбрать стационар, даже если пациент сопротивляется.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]вывод из запоя цены реутов[/url]
https://jokacasino77.com/
Домашний формат особенно важен, когда пациент не готов к стационару, боится огласки, испытывает стыд или сопротивление, но объективно нуждается в помощи. Попытки «перетерпеть» или лечить своими силами заканчиваются тем, что родственники дают опасные комбинации седативных, анальгетиков и «антипохмельных» средств, а состояние только ухудшается. «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» строит выездную помощь так, чтобы она оставалась профессиональной медициной, а не косметической услугой. Уже при звонке диспетчер под контролем врача уточняет длительность запоя, виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, болезней сердца, печени, почек, диабета, неврологических нарушений, психических эпизодов, факт судорог, делирия в прошлом, какие лекарства уже были даны. Это позволяет заранее понять, подходит ли формат лечения на дому или сразу нужно рассматривать стационар. Выезд назначается только в тех случаях, когда это безопасно, и именно в этом ключевое отличие официальной клиники от анонимных «капельниц на дом» — здесь всегда выбирают жизнь и здоровье, а не удобный маркетинговый сценарий. Для семьи это не просто комфорт, а возможность получить помощь без риска сорваться в критическое состояние посреди ночи.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-srochno[/url]
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в Раменском[/url]
At this moment I am ready to do my breakfast, when having my breakfast coming yet again to read further news.
Продолжительность процедуры — от 40 минут до полутора часов. Уже в первые часы после начала терапии состояние пациента значительно улучшается: проходит тошнота, снижается тревожность, восстанавливается координация движений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в тольятти[/url]
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/
Своевременное обращение к специалистам позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Каждая стадия лечения проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Пациенты чувствуют себя в безопасности и получают поддержку не только физическую, но и психологическую. Такой подход снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить результат на долгие годы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Чтобы родственники не терялись в терминах и не воспринимали лечение как «чёрный ящик», в клинике используется поэтапный подход. Это помогает увидеть логическую связку между затратами, процедурами и результатами.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]частные наркологические клиники отзывы[/url]
Клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы пациент и его близкие не метались между разными службами и частными «специалистами», а получали комплекс услуг в одном месте. Это особенно важно для тех, кто уже сталкивался с провалами после разовых кодировок, неподходящих капельниц или формальной «помощи».
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Инфузионная терапия (капельницы) — важная часть лечения, направленная на очищение организма, восстановление водно-солевого баланса и устранение токсинов. В «РязаньМед Альянс» используются проверенные препараты, которые помогают нормализовать работу внутренних органов и улучшить общее самочувствие. Таблица ниже показывает, какие виды капельниц чаще всего применяются при выведении из запоя и лечении алкоголизма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Описание
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
В основе работы клиники лежит принцип: зависимость — это не просто привычка и не «слабость характера», а комплексное заболевание, которое требует последовательного лечения, а не случайной капельницы по вызову. «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» отказывается от практики, когда пациенту предлагают один-единственный «волшебный» метод, не объясняя, что будет дальше. Здесь каждое обращение рассматривается в контексте стадии зависимости, общего состояния организма, психоэмоционального фона, семейной ситуации. Сначала специалисты снимают острые проявления: выход из запоя, детоксикация после употребления алкоголя, наркотиков или сочетаний, купирование абстиненции, коррекция давления, пульса, сна, тревоги. Затем формируется стабилизационный этап — подбор поддерживающих схем, работа с тягой, выравнивание эмоционального состояния. После этого при готовности пациента подключаются психотерапевтические и реабилитационные инструменты: мотивационные программы, работа с установками, триггерами, окружением. Важная особенность «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — готовность объяснять семье и самому пациенту, зачем нужен каждый этап, какие цели у процедуры и какие результаты реально ожидать. Это снижает сопротивление, формирует доверие и делает путь не хаотичным, а управляемым.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Главной задачей специалистов становится купирование абстинентного синдрома и снижение интоксикации. Это требует применения медикаментов и постоянного наблюдения за состоянием пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/vykhod-iz-zapoya-perm/
Onlayn kazino superdir, əla işdir. Təşəkkürlər!
https://cse.google.com.jm/url?q=https://betandreas-azerbaijan-play.org/bonuslar
Такая структура позволяет обеспечить эффективность и безопасность лечения на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm-staczionar/
Профессиональный нарколог на дому не работает по схеме «чем больше препаратов, тем лучше». В «СерпуховТрезвие» капельницы составляются исходя из задач конкретного организма. Базовый блок — это растворы для восполнения объёма циркулирующей жидкости, выравнивания электролитного баланса и коррекции кислотно-щелочного состояния, что уменьшает нагрузку на сердце, мозг и снижает риск тяжёлых осложнений. Витамины группы B и магний входят в стандартную поддержку: они помогают стабилизировать нервную систему, уменьшить тремор, раздражительность, поддерживают сон и снижают риск судорог. При признаках поражения печени используются гепатопротективные и антиоксидантные компоненты, снижающие токсическое воздействие продуктов распада алкоголя. Если пациента мучает тошнота, добавляются противорвотные средства, чтобы восстановить возможность пить воду и питаться. Для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна применяются мягкие анксиолитики в дозировках, не маскирующих клиническую картину и не угнетающих дыхательный центр. Агрессивная седация, популярная в «серых» схемах, сознательно исключается: она «делает вид» улучшения, но может скрыть нарастающие осложнения. Эффект оценивается по конкретным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение тремора, уход тошноты, улучшение цвета кожи, появление естественного сна и большей ясности мышления. После достижения этих ориентиров фармаконагрузка не наращивается, а постепенно снижается, чтобы человек выходил в устойчивое состояние, а не зависел от бесконечных капельниц.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в серпухове[/url]
オンラインカジノとは、インターネットを介してスロットやルーレット、ライブディーラーゲームなどのギャンブルを楽しめる仮想の場です。その利便性から、特定のライセンスを取得した海外サイトを利用するプレイヤーもいます。日本の法律では、国内でのオンラインカジノ事業は厳しく規制されているため、利用の際には国際的な法的位置づけを理解することが不可欠です。詳細な仕組みや主要なゲームの種類については、専門の情報ページをご覧ください。
→ [url=https://renovo.auto/]オンラインかじノ[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Hello, I check your blogs like every week.
Your story-telling style is witty, keep doing what you’re doing!
Вывод из запоя в Реутове в наркологической клинике «РеутовМед Сервис» — это профессиональная помощь, которая позволяет безопасно остановить разрушительное действие алкоголя на организм и вернуть контроль над состоянием пациента без рискованных экспериментов дома. Длительные запои приводят к тяжёлой интоксикации, скачкам давления, нарушению работы сердца, печени, нервной системы, провалам в памяти, агрессии, паническим атакам и риску алкогольного психоза. Попытки «перетерпеть», самостоятельно колоть непонятные препараты, давать горсть таблеток или «чуть-чуть допить для облегчения» только усиливают угрозу. Команда «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает вывод из запоя как последовательный медицинский процесс: первичная оценка состояния, грамотная детоксикация с капельницами, круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре при необходимости, контроль жизненных показателей, поддержка сердца и нервной системы, рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению зависимости. Для пациента это шанс выйти из тяжёлого состояния без стыда и боли, для родственников — возможность переложить ответственность за здоровье близкого на профессионалов, которые знают, что делать на каждом этапе.
Подробнее тут – http://
Служба по контракту позволяет планировать будущее. Доход известен заранее. Выплаты начисляются регулярно. Контракт закрепляет обязательства сторон. Предусмотрены гарантии. Подай заявку сейчас – ханты мансийск контракт
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Когда вопрос стоит остро — нужно быстро и безопасно вывести человека из запоя в Коломне, — у семьи нет лишнего времени на эксперименты с таблетками, сомнительными «коктейлями» и советами из интернета. «Трезвый Центр Коломна» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы от первого звонка до реального облегчения шёл понятный и управляемый маршрут: запись симптомов и рисков уже по телефону, предложение формата (выезд на дом или стационар), оперативный осмотр, персональная инфузионная терапия, круглосуточное наблюдение при необходимости и подробный план восстановления на 24–72 часа и дальше. Мы не продаём миф о «чудо-капельнице за час», а работаем клинически аккуратно: дозы и схемы подбираются под возраст, длительность запоя, сопутствующие заболевания, уже принятые лекарства и текущие показатели. Цель проста и честна — снять интоксикацию, защитить сердце, мозг и печень, вернуть сон и ясность без агрессивной седации и скрытых рисков, сохранить конфиденциальность и дать семье уверенность, что всё делается правильно.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
オンラインカジノとは、インターネットを介してスロットやルーレット、ライブディーラーゲームなどのギャンブルを楽しめる仮想の場です。その利便性から、特定のライセンスを取得した海外サイトを利用するプレイヤーもいます。日本の法律では、国内でのオンラインカジノ事業は厳しく規制されているため、利用の際には国際的な法的位置づけを理解することが不可欠です。詳細な仕組みや主要なゲームの種類については、専門の情報ページをご覧ください。
→ [url=https://renovo.auto/]海外オンラインカジノ[/url]
Ключевой элемент вывода из запоя в Реутове — правильно подобранная капельница, но в «РеутовМед Сервис» её рассматривают не как волшебное средство, а как часть комплексной терапевтической схемы. Основная цель — не «вырубить» человека сильными седативными коктейлями, а помочь организму безопасно выйти из состояния интоксикации. В инфузионную терапию входят растворы для регидратации, которые восполняют потерю жидкости, снижают вязкость крови, улучшают микроциркуляцию и работу внутренних органов. Коррекция электролитного баланса помогает уменьшить дрожь, мышечную слабость, снизить риск нарушений сердечного ритма. Применяются витамины группы B и препараты магния для поддержки нервной системы, снижения раздражительности и вероятности судорог. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы, мягкие антиоксиданты для разгрузки печени, противорвотные средства при выраженной тошноте, щадящие анксиолитики для снижения тревоги и нормализации сна без грубого угнетения сознания. Все дозировки учитывают сопутствующие заболевания и возраст, что особенно важно для пациентов с гипертонией, ИБС, диабетом, поражением печени и пожилых людей. Эффект оценивается по объективным критериям: стабилизация давления и пульса, уменьшение дрожи, улучшение самочувствия, нормализация сна и поведения, а не только по фразе «стал тихим».
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove
Your style is very unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this web site.
Решение, куда обращаться при запое, напрямую влияет на безопасность. Одно дело — случайный выездной «специалист» без адреса и гарантий, другое — официальная наркологическая клиника в Реутове, несущая ответственность за свои действия. «РеутовМед Сервис» выстраивает помощь так, чтобы каждый шаг был прозрачным и медицински обоснованным, а не строился на обещаниях «вылечим за час». Уже на этапе первого звонка специалисты уточняют длительность запоя, виды и объёмы алкоголя, возраст пациента, хронические заболевания, перенесённые ранее судороги, делирий, проблемы с сердцем и давлением, какие лекарства уже давались. Эта информация позволяет не «ставить капельницу вслепую», а выбрать безопасный формат: стационар, выезд на дом или комбинированный подход. В клинике используют только сертифицированные препараты, одноразовые системы, следуют протоколам, учитывающим реальные риски, а не запрос «сделайте, чтобы уснул и не мешал». Важен и человеческий аспект: здесь не унижают, не морализируют, не угрожают учётом. Пациент воспринимается как человек с заболеванием, а не как «виноватый», а это повышает готовность к сотрудничеству и к последующим шагам в сторону трезвости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-ceny-reutov[/url]
Бесплатный ключ для Windows 11 — только у нас, обновлено в 2026 году!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа[/url]
Ниже приведено структурированное сравнение форматов:
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-reutov10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-reutove
Чтобы не упустить момент, нужно ориентироваться не на фразу «он говорит, что справится», а на реальные признаки, при которых профессиональная помощь на дому становится необходимой. Домашний выезд — это шанс стабилизировать состояние до того, как потребуется реанимация или жёсткая госпитализация.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
whoah this weblog is wonderful i really like reading your articles.
Stay up the good work! You recognize, many individuals are looking round for this information, you could aid
them greatly.
Yes! Finally someone writes about Saç bakımı.
Как специалист, меня зовут Илья, уже много лет изучаю, как трансформируется структура узкопрофильных платформ.
За это время я регулярно наблюдать, что новички пытаются работать на неактуальные адреса, что в итоге приводит к потере времени.
В результате я всегда рекомендую ориентироваться на единые подборки, где сведения представлена системно и постоянно проверяется, включая упоминания вроде РЅРµ работает сайт mega https://tscan.buzz
Такой подход позволяет оперативнее разобраться в текущей ситуации избегая информационного хаоса.
Как итог это обеспечивает объективную картину и минимизирует риски, связанные с использованием заведомо устаревших источников.
This info is priceless. Where can I find out more?
Hi! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if you knew
where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one?
Thanks a lot!
Наркологическая клиника в Красноярске оказывает профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной, наркотической и другими видами зависимостей. Основная цель деятельности специалистов — восстановление физического здоровья, стабилизация психоэмоционального состояния и возвращение пациента к полноценной жизни. Лечение проводится по современным медицинским протоколам, с применением индивидуальных схем терапии и полным соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в красноярске[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
thank you very much
_________________
олимп бет зайти
Когда человек в запое, близким кажется, что всё ещё можно решить «по-тихому»: выспаться, отпаять водой, дать обезболивающее или «успокоительное» и дождаться, пока станет легче. На практике это часто приводит к обратному результату. Алкогольная интоксикация нарушает водно-электролитный баланс, сгущает кровь, повышает нагрузку на сердце, провоцирует скачки давления, ухудшает работу печени и нервной системы. Неконтролируемый приём снотворных, анальгетиков, транквилизаторов, особенно вместе с алкоголем, способен вызвать угнетение дыхания, аритмии, судороги или делирий. Домашняя обстановка не даёт возможности следить за всеми показателями и вовремя отреагировать. «РаменМед Трезвость» предлагает клинически выверенный вывод из запоя в Раменском с учётом возраста, длительности употребления, хронических заболеваний, перенесённых ранее осложнений. Здесь не применяют сомнительные схемы «усыпить, чтобы не мешал», а ставят задачу: безопасно пройти острую фазу, снять интоксикацию, стабилизировать давление и пульс, защитить сердце и мозг, снизить риск психозов и, при желании пациента, сразу наметить маршрут реального лечения зависимости. Такой подход снимает с родственников опасную «роль врача» и возвращает ситуацию туда, где ей место — под контроль профессионалов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ramenskoe10.ru/srochnoe-vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-v-ramenskom/
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble. You are amazing! Thanks!
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Двухраструбный медный обвод под пайку 15х11х0.7 мм 10.6х12.6 мм мягкая пайка М2РМ ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Выберите качественные Медные двухраструбные обводы под пайку различных размеров и диаметров. Надежное соединение труб, высокая устойчивость к коррозии и превосходная теплопроводность. Узнайте больше о нашей продукции и найдите оптимальное решение для вашего проекта.
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» — это место, где острые кризисы, многолетние запои и повторяющиеся срывы перестают быть бесконечным кругом, в котором семья остаётся один на один с проблемой. Здесь выстроена система помощи людям с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью, а также полизависимостями, включая злоупотребление аптечными препаратами. В клинике в Раменском сочетаются круглосуточное наблюдение, профессиональная детоксикация, медикаментозная поддержка, психотерапевтические программы и сопровождение семьи. Важные принципы — безопасность, анонимность, уважение к пациенту и честное объяснение каждого шага лечения. Ни агрессивного давления, ни обещаний «чуда за один день» — вместо этого поэтапный подход, который даёт реальный шанс стабилизировать состояние, снизить тягу и выйти из разрушительного сценария под контролем специалистов. Для близких это означает понятный маршрут: куда обратиться, что будут делать с пациентом, какие риски учтут и как клиника «Трезвый Шаг Раменское» останется на связи после острого периода.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ramenskoe10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ramenskom/
Для эффективного лечения алкогольной интоксикации и восстановления организма врачи клиники «АлкоДоктор» используют комплекс препаратов, которые индивидуально подбираются с учетом состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости характеризуются стойким патологическим влечением к употреблению психоактивных веществ, сопровождающимся нарушениями здоровья и социальной адаптации. В хронической стадии развивается тяжелое физическое и психическое истощение, ухудшаются функции внутренних органов, нарушается работа нервной системы. Самостоятельное лечение зачастую невозможно из-за риска осложнений, таких как острый интоксикационный синдром, судороги, депрессия и психозы. Наркологическая помощь в клинике обеспечивает комплексный контроль состояния пациента и минимизирует опасность для жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь на дому самара[/url]
В Красноярске клиника «КрасЗдрав Профи» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с зависимостью. При этом формат анонимности сохраняется на каждом этапе — от звонка до выписки. Для пациентов, которым трудно приехать, возможен выезд нарколога на дом. Это удобно при похмельных и абстинентных состояниях, когда транспортировка нежелательна. Конфиденциальный выезд без маркировки транспорта и униформы позволяет начать лечение, не привлекая внимания окружающих. Все процедуры проводятся с соблюдением медицинских стандартов, включая регидратацию, стабилизацию и поддержку дыхания.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-krasnoyarsk/
Продуманный внешний вид имеет большое значение в создании образа.
Она дает возможность выразить характер.
Удачный внешний вид усиливает внутренний комфорт.
Одежда часто становится инструментом невербального общения.
https://heylink.me/lepodium
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб делает сборы быстрее в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю формирует привычку.
В итоге стильная одежда играет значимую роль современного образа жизни.
Детоксикация в клинике «Центр Трезвости ВоронМед» проводится по принципу минимального вмешательства при максимальной эффективности. Основная задача — очистить кровь от токсинов и стабилизировать внутреннюю среду организма без нагрузки на сердце и почки. Все препараты вводятся медленно, под контролем медицинского персонала, а состав подбирается индивидуально после оценки анализов и состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в воронеже[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Финансовая предсказуемость становится возможной, когда доход закреплен договором и поступает регулярно, а контрактная служба как раз дает такую уверенность. Это шаг к спокойствию. Оформи документы уже сегодня: инн армии
Перед таблицей — короткий акцент: приведённые суммы ориентировочные, не являются публичной офертой, точная стоимость определяется после осмотра.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Вау, какой крутой сайт kazino olimp! Благодарю!
http://bonecareusa.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=697633
Thankfulness to my father who told me concerning this blog,
this blog is genuinely remarkable.
Когда запой длится не первый день, а состояние уже сопровождается тремором, потливостью, резкими перепадами давления, бессонницей, тревогой, тошнотой или рвотой, попытка «перетерпеть» или лечить самостоятельно таблетками становится опасным экспериментом. Сочетание алкоголя с сильнодействующими успокоительными, обезболивающими или сомнительными «антипохмельными» легко приводит к нарушению дыхания, провалам в сознании, аритмиям и скрытому развитию предделирия. Домашние средства не учитывают ни электролитные сдвиги, ни состояние печени и сердца, ни уже принятые лекарства. Выездной нарколог «СерпуховТрезвие» в Серпухове выстраивает ситуацию иначе: ещё по телефону врач собирает ключевую информацию — длительность запоя, примерные объёмы и виды алкоголя, наличие гипертонии, ИБС, диабета, заболеваний печени и почек, неврологических проблем, какие препараты уже давали и в каких дозах, были ли судороги или эпизоды дезориентации. На месте проводится объективная диагностика: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка тремора, степени обезвоживания, психического состояния, неврологического статуса. Только после этого принимается решение: проводить детокс на дому или сразу рекомендовать стационар. Такой фильтр защищает от грубых ошибок, позволяет точно подобрать схему и не терять драгоценное время, пытаясь «угадать» лечение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-serpuhov10.ru/]vyezd-narkologa-na-dom-v-serpuhove[/url]
I used to be suggested this blog by means of my cousin. I am not positive whether this publish is written by means of him as no one else recognise such distinctive approximately my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — это не «усиленное похмелье», а медицинская процедура, которая помогает организму справиться с тяжёлой интоксикацией и выйти из затянувшегося запоя с меньшими рисками. Когда человек несколько дней подряд употребляет алкоголь, все системы работают на пределе: страдают сердце, мозг, печень, нервная система. Обычные домашние методы — рассол, крепкий чай, обезболивающие таблетки — в этот момент уже не работают или дают лишь краткое облегчение, маскируя настоящую нагрузку на организм.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-telefon[/url]
Часто именно жители Химок тянут до последнего: насыщенный ритм жизни, дорога на работу, постоянная усталость, попытки «снимать напряжение» алкоголем или психоактивными веществами. Сначала это кажется временным способом расслабиться, но со временем человек замечает, что пьёт чаще, чем планировал, нуждается в больших дозах, срывает обещания, а попытки контролировать употребление превращаются в череду неудач. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи дальше будет только сложнее.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stoimost[/url]
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/
Умение стильно одеваться играет важную роль в создании первого впечатления.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и выглядеть гармонично.
Грамотно подобранный образ влияет на то, как человека видят в обществе.
В повседневной жизни одежда может добавлять уверенности.
https://ai.cheap/read-blog/28356
Стильный образ облегчает деловые встречи.
При этом важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и уместность ситуации.
Мода дают возможность экспериментировать.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться влияет на общее восприятие личности.
Ниже приведена таблица с типовыми компонентами капельницы и их действием:
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-tolyatti17.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент качественных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до обширных поставок, мы гарантируем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Превосходное обслуживание – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы и предоставлять решения под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
поставляемая продукция:
Порошок ванадиевый ФВд50У0,6 – ГОСТ 27130-94 Изделия из ванадия ФВд50У0,6 – ГОСТ 27130-94 обеспечивают высокую прочность и долговечность. Материал идеально подходит для применения в различных отраслях, включая машиностроение и авиацию. Прочные и легкие, изделия имеют отличные механические свойства, что делает их надежным выбором для серьезных нагрузок. Если вы ищете высококачественные изделия, вам следует купить Изделия из ванадия ФВд50У0,6 – ГОСТ 27130-94. Мы гарантируем качество и соответствие всем стандартам. Доступные решения для вашего бизнеса!
Лечение алкоголизма в клинике «РязаньМед Альянс» включает несколько этапов, каждый из которых направлен на определённую цель — от снятия интоксикации до формирования устойчивого отказа от алкоголя. В таблице представлены основные стадии лечения и методы, используемые специалистами клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani17.ru
https://verdegr.com/
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena[/url]
Описание
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/narkolog-skoraya-pomoshh-samara/
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My
apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views.
I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-korolev[/url]
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly feel this
web site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the
advice!
Запойное состояние сопровождается тяжелыми последствиями для организма. Оно может включать нарушения сна, тремор конечностей, скачки давления, головные боли и депрессию. Без своевременной помощи такие проявления способны привести к развитию хронических заболеваний и угрожающих жизни осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-perm0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в перми[/url]
Капельница от запоя является неотъемлемой процедурой при острых и хронических отравлениях алкоголем. Она помогает стабилизировать состояние пациента, избежать тяжелых последствий и максимально быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Вызов врача для проведения процедуры рекомендуется в следующих ситуациях:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi
Проститутки Челябинска высокогороста – каталог анкет индивидуалок Челябинска с фото, отзывами и номерами телефона.
Длинноногие красотки в любом районе Челябинска.
Длинные проститутки Челябинска со стройной фигурой ждут вашего
звонка.
Индивидуалки Копейск
Ищешь эротического удовольствия в
поселке Амз Челябинска – ты по адресу.
Горячие путаны Амза готовы доставить тебе незабываемое удовольствие в любое
время суток. Выбирай красотку на свой вкус и звони прямо сейчас.
Luxury watches continue to hold strong appeal despite the rise of digital devices.
They are often seen as a sign of prestige and refined taste.
Skilled engineering plays a major role in their lasting value.
Many luxury watches are produced using premium components.
https://www.sunlitcentrekenya.co.ke/author/lepodium/
They also represent a long tradition passed down through generations.
For collectors, these watches can serve as both practical items and valuable assets.
Classic aesthetics allows them to stay relevant across changing fashion trends.
In the end, luxury watches continue to attract admirers around the world.
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske/
Группа препаратов
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske/
Howdy would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re using? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different web browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good web hosting provider at a honest price? Thanks, I appreciate it!
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре москва[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
Есть ряд признаков, при которых ждать категорически нельзя и нужна срочная помощь врача, а не очередные «народные методы». Если вы замечаете у человека следующие симптомы, это прямой повод организовать профессиональный вывод из запоя:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя москве[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Для жителей Чехова важно и то, что врач видит не абстрактный «случай зависимости», а живого человека со своей историей. У кого-то за плечами десятилетия злоупотребления, у кого-то — несколько лет с быстрым прогрессированием, у кого-то — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или наркотиками. Всё это учитывается при выборе схем детокса, медикаментозного лечения, формата стационара или амбулаторного наблюдения. Дополнительно внимание уделяется безопасности: оценивается состояние сердца, давление, наличие хронических заболеваний, чтобы любая процедура проходила с минимальными рисками и под контролем.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]narkologicheskij-centr-klinika[/url]
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-nedorogo[/url]
К основным направлениям помощи, как правило, относятся:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/[/url]
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника московская московская область[/url]
Во время лечения фиксируются все жизненные показатели пациента. При необходимости проводится экспресс-анализ крови и ЭКГ. Ниже представлена таблица, показывающая, какие параметры контролируются и по каким признакам оценивается стабилизация состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-voronezhe17.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя воронеж[/url]
Описание
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]экстренная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Тем, кто нуждается в длительной терапии, «КузбассМед» предлагает комфортные условия стационара с круглосуточным наблюдением. Здесь пациенты размещаются в индивидуальных палатах, проходят курсы терапии, реабилитации и психокоррекции. Обстановка в клинике напоминает оздоровительный центр: мягкое освещение, тишина, доступ к библиотеке, возможность общения с психологом и ежедневное участие в восстановительных мероприятиях. Медицинские сестры и врачи находятся на дежурстве 24/7, что позволяет немедленно реагировать на любые изменения в состоянии пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-novokuzneczk0.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника новокузнецк[/url]
При длительном запое или серьезной алкогольной интоксикации часто нет возможности или желания ехать в стационар. В таких ситуациях оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом в Сочи. Специалисты клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» круглосуточно приезжают к пациентам, оперативно оказывают медицинскую помощь и проводят профессиональную детоксикацию организма прямо в домашних условиях. Благодаря комфортному лечению на дому пациенты быстрее восстанавливаются, избегают дополнительного стресса и осложнений, связанных с госпитализацией.
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-sochi
Часто родственники тянут до последнего, надеясь, что запой «сам пройдёт», как это случалось раньше. Но с каждым эпизодом последствия становятся тяжелее: организм изнашивается, возрастает риск осложнений, ухудшается психика. Особенно опасно, когда запой длится несколько дней подряд, а любые попытки самостоятельно сократить дозы алкоголя сопровождаются дрожью, бессонницей, приступами паники.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/klinika-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve/
I could not refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
Excellent post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed!
Extremely helpful info specially the last part :
) I care for such information a lot. I was looking for this
particular information for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
Наша наркологическая клиника предоставляет круглосуточную помощь, использует только сертифицированные медикаменты и строго соблюдает полную конфиденциальность лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя сочи[/url]
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Важно и то, что во время процедуры пациент находится под наблюдением. Врач может увидеть, как организм реагирует на терапию, вовремя скорректировать темп или состав инфузии, понять, достаточно ли домашнего формата или лучше рассмотреть стационар. Это принципиальное отличие от попыток лечиться дома таблетками наугад, без контроля давления и пульса.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]капельница после длительного запоя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Перми обеспечивает пациентам комфортные условия и профессиональное сопровождение. Врачи работают круглосуточно и соблюдают строгую конфиденциальность, что делает лечение доступным и безопасным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-perm0.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в перми[/url]
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно сочи[/url]
Пациенты отмечают, что особенно важна не только профессиональная помощь, но и спокойная атмосфера. Мягкий свет, тишина, отдельные палаты и деликатная коммуникация персонала — всё это снижает тревожность и помогает организму восстановиться. Эффективность лечения оценивается по конкретным маркерам: улучшение сна, нормализация давления, исчезновение тошноты, восстановление аппетита и уменьшение тяги.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnoyarske17.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника красноярск[/url]
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation however I find this matter to be really one thing that I feel I would never understand. It kind of feels too complex and very huge for me. I am having a look forward to your subsequent post, I’ll attempt to get the hang of it!
Служба по контракту это стабильная работа с высоким доходом. Выплаты выше чем у большинства альтернатив. Все начисления официальны. Контракт фиксирует условия и срок. Никакой неопределенности. Заключай контракт – контракт в хмао на военную службу по контракту
Когда хочется стабильного дохода и понятных правил вместо постоянной неопределенности, служба по контракту становится разумным выбором с официальными выплатами и заранее согласованными условиями. Все начисления прозрачны и защищены документально, а дополнительные выплаты позволяют увеличить общий доход. Сделай осознанный шаг и начни оформление уже сейчас: военнослужащих
Многие жители в Новосибирской области постоянно жалуются на:
– нестабильный сигнал;
– ограниченную скорость в часы пик;
– сложности с настройкой оборудования.
Выбор дешёвого провайдера без проверки часто приводят к:
– дополнительным тратам на ремонт оборудования;
– отсутствию техподдержки;
– невыполненным обещаниям.
Профессиональное подключение даёт возможность:
– бесперебойный сигнал;
– гибкие условия;
– бесплатную настройку оборудования.
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• поддержки 24/7;
• акционные тарифы со скидкой 50%.
• Комплексный анализ скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж оборудования
• Персональную помощь техспециалиста
• Фиксированные тарифы на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]домашний интернет вай фай сибирские сети[/url]
провести интернет сибирские сети – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru[/url]
[url=http://teamspeack.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://won4won.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://xsl.sakura.ne.jp/cgi-bin/joyfulyy/joyfulyy.cgi/www.zaria.com.ru/www.sportbets12.ru/arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena-2.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] f9e2929
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit
and sources back to your webpage? My blog is in the very
same niche as yours and my visitors would truly benefit from some of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Thank you!
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
что то не могу зайти на сайт ( https://astitvaias.org Как у вас дела бразы?)Да и вообще:
We stumbled over here by a different web page and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking into your web page again.
Такие меры позволяют комплексно воздействовать на организм и снизить риск осложнений, связанных с резким прекращением употребления алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Вот этого ам2233 и заказал. Оплатил уже. Жду трекер. купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану А ты у него спроси тот он или не тот, врать не станет думаюЯ просто уже настолько завязан со сферой Lrc что подмечаю все мелочи. Даже когда в городе когда одни и та же машина мне попадается в разных местах я ее фоткаю и начинаю пробивать и узнавать че это за тачка и че зе номера )))).
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ярославль.[/url]
Капельница от запоя в Мурманске является одной из наиболее востребованных процедур для снятия острого состояния алкогольной интоксикации. Эта методика позволяет быстро вывести токсины из организма, нормализовать водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие пациента. Современная капельная терапия считается эффективным средством в лечении запоя, обеспечивая поддержку жизненно важных функций и минимизируя риски осложнений.
Детальнее – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в Самаре представляет собой комплекс медицинских мероприятий, направленных на лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, а также восстановление физического и психического здоровья пациентов. В наркологической клинике «Согласие» применяются современные методики диагностики, детоксикации и комплексной терапии, учитывающие индивидуальные особенности каждого пациента, тяжесть зависимости и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Основная цель — восстановление здоровья, предупреждение осложнений и снижение риска рецидивов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Tremendous things here. I am very glad to look your post.
Thank you so much and I am having a look forward to
touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Подход клиники строится на принципе минимально достаточной фармакотерапии: мы исключаем полипрагмазию, не «усиливаем схему» за счёт случайных препаратов и всегда сверяем назначения с вашими постоянными лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.). Состав инфузии не бывает универсальным — он зависит от жалоб, возраста, гидратационного статуса, результатов экспресс-тестов и логистики ближайших часов (работа/сон/домашняя среда). Благодаря этому эффект становится управляемым, а «первая тихая ночь» достигается без риска угнетения дыхания и дневной «ватности».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Алкоголизм — хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и круглосуточного контроля. Клиника «УралМед» в Екатеринбурге предлагает полный спектр услуг для пациентов любого уровня зависимости: от экстренной детоксикации до долгосрочной реабилитации. Главные принципы работы — абсолютная анонимность, индивидуальный план лечения и постоянное сопровождение квалифицированной командой специалистов.
Подробнее тут – http://
Одновременно с медикаментозной детоксикацией начинается работа по снижению эмоционального напряжения. Психотерапевтическая помощь помогает пациенту осознать причины зависимости и выработать стратегии для предотвращения рецидивов, что является важным аспектом успешного лечения.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnicza-volgograd/
На чем готовить???????? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Какие у тебя претензии? ты провокатор и не более т.к. ты не дал даже номер заказа и не высказал притензию, к тому же за тебя мне уже написали в Личку, другие магазины..классный магазин
Независимо от формы зависимости — алкогольной, опиатной, синтетической или медикаментозной — специалисты подбирают индивидуальный курс терапии. Алгоритмы лечения адаптируются под возраст, стаж употребления, общее состояние организма и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru
stake login
Особенно важно на этапе поступления пройти полную психодиагностику и получить адаптированную под конкретного пациента программу. Это позволит учитывать возможные сопутствующие расстройства, включая тревожные, аффективные и когнитивные нарушения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/[/url]
Такие меры позволяют комплексно воздействовать на организм и снизить риск осложнений, связанных с резким прекращением употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Thanks for finally writing about > %blog_title% < Loved it!
Функция и назначение
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Ответственная гемблинг — это набор строгих принципов и практик.
Она ориентирована на защиту игроков от рисков.
Основная задача — сохранить развлекательную составляющую исключая ущерба в отношении благополучия участника.
https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii
Это включает контроль за длительностью и средствами, тратящимися на игру.
Существенным элементом является осознание игроком всех возможных последствий.
Платформы должны обеспечивать честную сведения и средства с целью контроля за игрой.
В итоге, ответственная деятельность создаёт здоровую развлекательную среду со стороны каждого сторон.
Одновременно с медикаментозной детоксикацией начинается работа по снижению эмоционального напряжения. Психотерапевтическая помощь помогает пациенту осознать причины зависимости и выработать стратегии для предотвращения рецидивов, что является важным аспектом успешного лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-volgograd/
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Алкоголизм — хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и круглосуточного контроля. Клиника «УралМед» в Екатеринбурге предлагает полный спектр услуг для пациентов любого уровня зависимости: от экстренной детоксикации до долгосрочной реабилитации. Главные принципы работы — абсолютная анонимность, индивидуальный план лечения и постоянное сопровождение квалифицированной командой специалистов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]реабилитационный центр лечение алкоголизма екатеринбург[/url]
Только что принесли, позже трип отпишу) купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану А это как понимать? Кто то уже регу опробовал?интересует такой же вопрос! Сделал заказ с сайта ещё вчера. Ни слуху ни духу от селлера.
moneyx войти [url=https://t.me/moneyx_tg/]t.me/moneyx_tg[/url] .
Некоторые состояния требуют немедленного вмешательства специалиста. Если алкогольное отравление или запойное состояние не купируется вовремя, это может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод иркутск[/url]
Описание
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-samara/
Военная работа по контракту это быстрый путь к стабильному доходу. Все выплаты официальные и прозрачные. Условия известны заранее. Контракт определяет обязанности и выплаты. Не откладывай решение – контракт югра
1xbet guncel [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet guncel[/url] .
При своевременном обращении к специалистам капельница позволяет значительно улучшить состояние пациента уже в первые часы после начала лечения. Медицинская помощь при запое должна оказываться квалифицированно и в комфортных условиях, что снижает риски осложнений и ускоряет восстановление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]капельница от запоя цена мурманск.[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]казино онлайн[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя показан при:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая помощь на дому в Ярославле охватывает широкий спектр медицинских мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и подготовку к дальнейшему лечению. Среди основных процедур:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом цена в ярославле[/url]
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
Служба круглосуточного вывода из запоя организована таким образом, чтобы обеспечить максимальную оперативность и надежность. Независимо от времени суток, квалифицированные специалисты готовы выехать на дом или принять пациента в медицинском учреждении, чтобы приступить к детоксикации и стабилизации состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Пушкино в клинике «Трезвый Путь» — это оперативная помощь на дому и в стационаре, персональные детокс-схемы и бережное восстановление организма без постановки на учёт. Мы подключаемся круглосуточно, аккуратно снимаем интоксикацию, стабилизируем давление и пульс, уменьшаем тремор, тревогу и бессонницу, а затем предлагаем понятный маршрут к ремиссии, который вписывается в ваш рабочий и семейный график. Цель — безопасно пройти острый период и не «сорваться» обратно, когда станет чуть полегче.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-pushkino/
Одна из главных ошибок — ждать «идеального момента» для лечения. Кажется, что кодирование уместно только тогда, когда зависимость достигла крайней стадии: человек потерял работу, перестал выходить из запоев, полностью разрушил отношения с близкими. На практике обращение в клинику Чехова оправдано гораздо раньше, как только употребление алкоголя перестаёт быть редким эпизодом и начинает системно мешать жить. Если каждый стресс, отпуск или конфликт заканчиваются срывом, если запои становятся длиннее, а похмелье тяжелее, — это уже повод хотя бы обсудить кодирование с врачом, а не ждать, пока ресурс организма будет почти исчерпан.
Узнать больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/
Процедура детоксикации занимает от 40 минут до 2 часов. После её завершения врач консультирует пациента и родственников, даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и профилактике повторных запоев.
Получить больше информации – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/psikhiatr-narkolog-na-dom-spb/
При необходимости применяется симптоматическое лечение для снижения болевого синдрома, устранения тошноты и рвоты, а также нормализации психоэмоционального состояния пациента. Врачи наркологи строго контролируют течение процедуры, что обеспечивает безопасность и снижает риски осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре мурманск[/url]
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости характеризуются стойким патологическим влечением к употреблению психоактивных веществ, сопровождающимся нарушениями здоровья и социальной адаптации. В хронической стадии развивается тяжелое физическое и психическое истощение, ухудшаются функции внутренних органов, нарушается работа нервной системы. Самостоятельное лечение зачастую невозможно из-за риска осложнений, таких как острый интоксикационный синдром, судороги, депрессия и психозы. Наркологическая помощь в клинике обеспечивает комплексный контроль состояния пациента и минимизирует опасность для жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-samara0.ru/]наркологическая помощь[/url]
Здравствуй, народ, кто с Мск брал, сроки доставки какие реальные были и какая служба? купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Данный продукт не зашол в моё сознание:) его нужно бодяжить с более могучим порохом, будем пробовать АМ2233…Магази лутший на рц не первый раз работаем с ним!) удачи и процветания!)
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в ярославле[/url]
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I’ve truly read through a single thing like that before. So nice to discover somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with some originality!
На следующем этапе начинается активное медикаментозное вмешательство. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом для быстрого выведения токсинов и нормализации обменных процессов, что способствует стабилизации работы жизненно важных органов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
Своевременная помощь нарколога позволяет избежать тяжёлых осложнений и значительно ускорить восстановление организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в санкт-петербурге[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]
Своевременный вызов позволяет «поймать» момент, когда детокс максимально эффективен и ещё не потребовалась госпитализация. Мы работаем по всему Пушкинскому округу и приезжаем в ближайшие населённые пункты соседних округов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
I always spent my half an hour to read this blog’s articles everyday along with a
mug of coffee.
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/[/url]
Большинство семей приходят к мысли о лечении зависимости не сразу. Сначала всё выглядит как «случайные переборы по праздникам», потом алкоголь или наркотики становятся привычным способом снять стресс, забыться, пережить неудачи. Постепенно запои учащаются, человек пропадает на несколько дней, появляются долги, проблемы на работе, конфликты в семье. На этом этапе многим кажется, что обращаться в наркологическую клинику в Лобне ещё рано, что можно «взять себя в руки» и как-то остановиться. Но практика показывает обратное: чем дольше затягивается момент обращения к специалистам, тем тяжелее протекают запои, тем глубже страдает здоровье и тем сложнее вернуть человека к стабильной трезвости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/
Как работает
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-volgograd/
Вывод из запоя в Мурманске представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на оказание медицинской помощи пациентам, находящимся в состоянии алкогольного отравления или длительного употребления спиртного. Процедура проводится с целью стабилизации состояния организма, предупреждения осложнений и минимизации риска развития тяжелых последствий алкоголизма.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske/
Наркологическая помощь на дому в Ярославле охватывает широкий спектр медицинских мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и подготовку к дальнейшему лечению. Среди основных процедур:
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-yaroslavle/
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге начинается с детального осмотра и оценки состояния пациента. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и определяет степень интоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-spb/
Приветы. Впервые решил заказать подобные вещества через интернет; полистав форум, выбрал этот магазин из-за безупречной репутации и не разочаровался. Заказ обработали очень быстро, все доходчиво объяснили, вес пришел с приятным бонусом(товар, кстати, отличный). Успехов и процветания вам и вашему магазину, ребята. https://fashionroyaltydoll.org Хороший магазин.С ним почти год работаю.Всегда вежливое общение: успокоит,объяснит,по рекомендует.Все приходит в срок.Данным магазином очень доволен.Рекомендую!!!Всем по привету!
После купирования острой фазы мы предлагаем полное сопровождение на этапе восстановления, чтобы закрепить результаты и снизить риск повторных срывов. В первые дни показаны сеансы кислородной терапии, которые активизируют клеточный обмен и способствуют быстрейшему выведению остатков токсинов. Параллельно проводятся физиотерапевтические процедуры — магнитотерапия и лазерная стимуляция, укрепляющие сосудистую стенку и ускоряющие заживление микроциркуляторных нарушений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому в балашихе[/url]
1xbet [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet[/url] .
Wow, this post is nice, my younger sister is analyzing these things, so I am going to let know her.
Наша выездная бригада оснащена как мобильный мини-кабинет: инфузомат для покапельной титрации, портативный кардиомонитор, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, экспресс-кассеты Na?/K? и набор для регистрации ЭКГ по показаниям. Такой комплект позволяет принять решение на месте — безопасно ли начинать дома или целесообразнее перевести пациента в стационарное отделение «ЮгМедЦентра» без «перезапуска» обследований. Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию: в схеме нет «лишних» позиций и конфликтов с уже принимаемыми лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.).
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иванов И.И., «без своевременной медицинской помощи при запое повышается риск необратимых изменений в организме и летального исхода».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому нижний тагил[/url]
Вернуть здоровье и силы за одну процедуру позволяет грамотное сочетание препаратов, подобранное индивидуально под каждого пациента. Врач-нарколог оценивает тяжесть интоксикации, измеряет артериальное давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом, а при необходимости назначает экспресс-анализы. На основании этих данных создаётся персональный раствор для инфузии:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Когда важна не только сумма дохода, но и его регулярность, служба по контракту становится надежным решением с прозрачными выплатами и понятными условиями. Такой подход позволяет строить планы без лишних рисков. Подай заявку и двигайся дальше, вакансии мо рф для контрактников
Выбор техники зависит от клинической картины, переносимости препаратов, психоэмоционального состояния и горизонта планируемой трезвости. Таблица ниже помогает сориентироваться в ключевых различиях — врач подробно разберёт нюансы на очной консультации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/
Если пациент обращается в клинику в состоянии запоя или тяжёлой абстиненции, первым шагом становится детоксикация. Это не «волшебная капельница», которая снимает все проблемы, а комплекс процедур, направленных на выведение токсинов, восстановление водно-солевого баланса, поддержку сердца, печени, нервной системы. Под контролем врачей подбираются растворы и препараты, которые позволяют снизить нагрузку на организм, облегчить похмельный синдром, уменьшить тревогу и вернуть сон. Важно, что это проходит под наблюдением, а не «на кухне» без понимания, как реагирует сердце и давление. После выхода из острого состояния человек уже способен осмысленно обсуждать дальнейшее лечение.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom[/url]
маникс [url=https://t.me/moneyx_tg/]маникс[/url] .
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в сочи[/url]
Обращение к наркологу — это не признание «окончательного проигрыша», а трезвое решение, что здоровье и жизнь важнее иллюзии контроля. В клинике можно безопасно вывести человека из запоя, стабилизировать состояние, обследовать сердце, печень, нервную систему, понять, насколько далеко зашло заболевание. Важно, что помощь получают не только тяжёлые пациенты «на грани», но и те, у кого ещё есть работа, семья, привычный образ жизни, но запои уже стали регулярными. Чем раньше удаётся подключить специалистов в Лобне, тем мягче можно пройти лечение и тем больше шансов сохранить и здоровье, и отношения, и социальный статус.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-lobne
все ровно вот только из за нового года была задержка а так все на высоте https://foto-izuminka.ru В чем растворял 203??? У меня ихний 203 в спирте не получилось расстворить даже при нагреве, пришлось ацетон использовать! На счет качества с тобой согласен – 5!сегодня вот ночью прислал трек. Бьется, радует
Функция и назначение
Выяснить больше – http://
Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иванов И.И., «без своевременной медицинской помощи при запое повышается риск необратимых изменений в организме и летального исхода».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Важно, что на первичной консультации честно говорят о перспективах. Никто не обещает «волшебной капельницы», после которой человек навсегда забудет про алкоголь или наркотики. Объясняют, что детокс — это старт, а не финиш, что после стабилизации придётся думать о лечении самой зависимости и реабилитации. Для семьи это неприятно, но честно: лучше сразу понимать масштаб задачи, чем надеяться на чудо и снова возвращаться к тем же проблемам через месяц.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-lobne/
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-yaroslavle
Одновременно с медикаментозной детоксикацией начинается работа по снижению эмоционального напряжения. Психотерапевтическая помощь помогает пациенту осознать причины зависимости и выработать стратегии для предотвращения рецидивов, что является важным аспектом успешного лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя балашиха[/url]
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя пушкино[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-tagile
Вчера списался с продавцов, сказал сегодня отправит. Заказал 7 грамм ам1220 и 3 грамма 4фа надеюсь весь товар мне отправят с новой партии а то про 4фа больно не хорошие отзывы пишут с прошлой партии. https://avcilarpansiyon.com Получил 5г 203! Оплатил в четверг, отправили в пятницу и уже в понедельник курьер мне передал. 🙂 Вес в поряде, цвет желтоватый.грац вам джентльмены!
Hey this is somewhat of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Путь в наркологическую клинику в Ивантеевке почти всегда начинается с консультации — очной или по телефону. На этом этапе задача врача не осудить и не прочитать нотацию, а максимально точно понять, что происходит: сколько лет длится злоупотребление, как часто бывают запои, были ли попытки лечиться раньше, какие есть хронические болезни, каково текущее физическое и психическое состояние. Собирается анамнез, измеряется давление, оценивается пульс, при необходимости направляют на анализы и дополнительные исследования. Чем честнее и конкретнее человек (или его родственники) описывают ситуацию, тем точнее можно подобрать безопасный план помощи.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ivanteevke/
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]эротика[/url]
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1 xbet[/url] .
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
ПС клады в Москве оч надежные!! прям 10 из 10, очень понравилось когда забирали 50г https://altinmeyveler.com Магазину спасибо все пришло,только вот пробник не положили,хотя обещали..Я делал на муравьином спирте
:::::::::::::::: ONLY THE BEST ::::::::::::::::
Content from TOR websites Magic Kingdom, TLZ,
Childs Play, Baby Heart, Giftbox, Hoarders Hell,
OPVA, Pedo Playground, GirlsHUB, Lolita City
More 3000 videos and 20000 photos girls and boys
h**p://tiny.cc/sficzx
h**p://cutt.us/Y7P84
h**p://put2.me/muhcsh
Complete series LS, BD, YWM, Liluplanet
Sibirian Mouse, St. Peterburg, Moscow
Kids Box, Fattman, Falkovideo, Bibigon
Paradise Birds, GoldbergVideo, BabyJ
h**p://citly.me/47kMX
h**p://4ty.me/ibhi7c
h**p://tt.vg/URoSx
Cat Goddess, Deadpixel, PZ-magazine
Tropical Cuties, Home Made Model (HMM)
Fantasia Models, Valya and Irisa, Syrup
Buratino, Red Lagoon Studio, Studio13
—————–
—————–
000A000491
Состав капельницы не повторяет «советы знакомых». Он формируется под доминирующий симптом, сопутствующие заболевания и взаимодействия с текущими лекарствами. Врач постоянно оценивает витальные показатели и реакцию организма, корректируя скорость и объём по инфузомату. Ниже — примеры профилей, которые объясняют логику выбора; финальное решение всегда очное.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar/
Потолки в Архангельске — быстро,качественно,с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем стильный дизайн натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор глянцевых полотен.
Ответим на вопросы — свяжитесь с нами!
Потолки под ключ в коридоре — любая расцветка. В Архангельске — с гарантией результата-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки со световыми линиями[/url]
натяжные потокли в архангельске высота – [url=https://29-potolok.ru]http://29-potolok.ru[/url]
[url=http://jodoshubetsuin.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://29-potolok.ru/]http://alejandrojohnson.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.ocenka-chasov-onlajn9.ru/www.888starz-english.com/www.melbetofficialsite.ru]Качественная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] f9e2929
В медицинских условиях специалисты обеспечивают тщательный контроль над динамикой состояния пациента. Каждый этап процедуры имеет свою задачу, которая направлена на последовательное восстановление функций организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru
Под кодированием многие представляют себе один-единственный метод, хотя на деле специалист в Чехове подбирает схему индивидуально. В общих чертах подходы можно разделить на две большие группы: медикаментозные и психотерапевтические. Медикаментозный вариант предполагает использование препаратов, которые либо вызывают крайне неприятную реакцию при приёме алкоголя, либо блокируют ощущение удовольствия от опьянения. Человек знает, что нарушение режима чревато серьёзным ухудшением самочувствия или бессмысленно, потому что «эффекта» уже не будет. Это создаёт жёсткий внешний барьер и помогает удержаться от срыва в первые месяцы трезвости.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ukolom-v-chekhove
Hi there, its pleasant piece of writing on the topic of media print, we all understand media is a enormous source of data.
Домашний визит нарколога — это не компромисс «на скорую руку», а тщательно организованный процесс, который экономит время, сохраняет конфиденциальность и делает лечение предсказуемым. «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» принимает вызовы круглосуточно и выезжает во все районы города — от Уралмаша и ВИЗа до Академического и Широкой Речки. Команда приезжает без внешних опознавательных знаков, использует нейтральные формулировки в документах и ведёт переписку только по защищённым каналам связи. На месте мы быстро проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, контролируем пульс, сатурацию и артериальное давление, подключаем гастропротекцию и аккуратно управляем тревогой без избыточной седации. Цель — безопасно «снять волну» симптомов, вернуть возможность пить воду и отдыхать, а затем закрепить результат на горизонте ближайших 72 часов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Процедура длится от 40 минут до 2 часов, в зависимости от тяжести состояния, и проводится в комфортной домашней обстановке, что значительно снижает стресс у пациента и его близких.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
Черт приехал в офис говорю посмотрите посылку,мне сказали ее давно отправили!Она посмотрела ее нету,позвонила говорит она еще не отправлена и х.з. когда будет отправлена. купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Всем привет! Специально зарегистрировался для того что бы поведать вам, какой тут отличный магазин! Обращаюсь сюда уже 3 месяца всегда по опту! все на высоте! Время доставки кладом в мой город 4 дня! Качество продукта отличное! Клады хорошие! И главное пунктуальность, и грамотное общение с человеком… Желаю оставаться всегда такими же порядочными! Сразу видно что магазин знает свое дело в нашем не легком труде!!!обо всем думаем ) но не сразу
Как работает
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В случаях, когда транспортировка в клинику затруднительна или пациент испытывает выраженный стресс, возможно выездное консультирование и начальная детоксикация на дому. Врач прибывает с портативным набором для инфузий, оперативно stabilizирует состояние и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма в екатеринбурге[/url]
Запой – критическое состояние, при котором организм подвергается серьезной токсической нагрузке, что может привести к опасным для жизни осложнениям. В Волгоградской области помощь нарколога оказывается круглосуточно, что позволяет начать лечение немедленно в любой момент дня или ночи. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство, индивидуальный подход и высокий уровень безопасности, позволяя стабилизировать состояние пациента в домашних условиях или в клинике.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно волгоград[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Медная однораструбная редукционная переходная муфта под пайку стандартная 21х18 мм мягкая пайка М3РТ ГОСТ 32590-2013 Приобретите высококачественные медные однораструбные редукционные муфты под пайку от Редметсплав для надежного соединения трубопроводов. Гарантированная прочность и устойчивость к коррозии. Идеальны для различных систем отопления, водоснабжения и прочих технических целей.
моней икс промокод [url=https://t.me/moneyx_tg/]t.me/moneyx_tg[/url] .
Процедура детоксикации занимает от 40 минут до 2 часов. После её завершения врач консультирует пациента и родственников, даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и профилактике повторных запоев.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/
Медицинская детоксикация — это основа успешного вывода из запоя. Она проводится под строгим контролем врачей-наркологов, которые используют инфузионную терапию для выведения токсинов из организма. В качестве компонентов капельниц применяются растворы глюкозы, физиологический раствор, препараты для восстановления работы печени и почек. Поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы и нормализация артериального давления достигается с помощью специализированных медикаментов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Привет бразы,тут ровно таримся не паримся,качества вышка,клад на уровне https://seldi-vrn.ru Весом по 1 грСделал заказ , все гуд и качество понравилось
1xbet t?rkiye giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet t?rkiye giri?[/url] .
https://wazamba7777.com/
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Если вы ищете способ облегчить состояние при запое — читайте, как капельница помогает при алкогольной интоксикации. Познакомиться с результатами исследований – http://zaqwer.ru/question/19828
Stunning story there. What occurred after? Thanks!
Приятно иметь дело с серьёзными людьми!!!!!! купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану А ты тс в лс отпиши , и если ты не балабол , в чем я очень сомневаюсь то проблема будет решена , а писать на ветке это говно для чего не понятно , на что вы надеетесьНаблюдая за многими сообщениями, мы понимаем что многие на форуме не более чем очень “кипишные люди”, которые любят разводить демагогию.
base
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы и адаптировать решения под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
поставляемая продукция:
Труба магниевая ГФИ1 – ГОСТ 22517-77 Пруток магниевый ГФИ1 – ГОСТ 22517-77 представляет собой высококачественный сплав, известный своей легкостью и высокой коррозионной стойкостью. Применяется в различных отраслях, включая авиационную и автомобильную промышленность, а также в производстве электроники. Данный пруток отличается отличной свариваемостью и механическими свойствами, что делает его идеальным выбором для создания крепких соединений. Не упустите возможность купить Пруток магниевый ГФИ1 – ГОСТ 22517-77 и обеспечить высокий уровень надежности ваших изделий. Подходит как для крупных производств, так и для мелких работ, обеспечивая экономию металла и долговечность.
Для эффективного вывода из запоя в Мурманске используются современные методы детоксикации, включающие внутривенное введение растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, коррекцию электролитов и нормализацию работы почек и печени. Важным этапом является использование витаминных комплексов и препаратов, поддерживающих работу сердца и сосудов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/[/url]
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в рязани[/url]
В данной статье мы поговорим о будущем медицины, акцентируя внимание на прорывных разработках и их потенциале. Читатель узнает о новых подходах к лечению, роли искусственного интеллекта и возможностях персонализированной медицины.
Узнайте, почему важно обратиться к наркологу на ранних стадиях зависимости: признаки, этапы лечения и роль профессионала в восстановлении. Что скрывают от вас? – http://mamuli.club/forum/topic/41230
Да рега была шикарная… Но вот как раз таки с ней и случился перебой, ОЧЕНЬ жаль!!! А так по работе остались отличные впечатления купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану АМ-2233 вообще ровный день назад пришёлпрет 30-45 мин.1к10.действием похож на рсц
Hello, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one
and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam remarks?
If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything
you can recommend? I get so much lately it’s driving me insane
so any help is very much appreciated.
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Экстренная помощь требуется, когда запой начинает негативно сказываться на здоровье, и самостоятельное прекращение употребления алкоголя становится невозможным. Основные показания для круглосуточного вмешательства включают:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя волгоград[/url]
Процедура детоксикации занимает от 40 минут до 2 часов. После её завершения врач консультирует пациента и родственников, даёт рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и профилактике повторных запоев.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/
На сайте Минздрава указаны общие клинические рекомендации по выведению из запоя, включая допустимые дозировки и протоколы лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya rjazan'[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника в Мурманске специализируется на комплексном лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В условиях МедЦентр Арктика используются проверенные методы диагностики и терапии, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и восстановить качество жизни пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://
Great blog here! Additionally your web site quite a bit up fast! What host are you the use of? Can I get your affiliate hyperlink on your host? I desire my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
1xbet mobil giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com[/url] .
모든 다른 훌륭한 포스트에 감사합니다.
이런 이상적인 방식으로 작성된 정보을 어디서 얻을 수 있을까요?
다음 주에 프레젠테이션이 있고, 이런 정보을 찾고 있습니다.
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]смс поздравления[/url] у нас всегда можно подобрать уникальные поздравления и тосты, чтобы порадовать близких под любой праздник, от семейного торжества до официального мероприятия, вы найдёте подходящие тексты небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника тексты легко адаптируются под смс, открытку или письмо дополнив поздравление красочными шарами и милыми сувенирами, вы создадите эффект настоящего праздника каждое пожелание можно отправить как смс, так и оформить в красивую открытку у нас вы найдёте не только классические пожелания, но и необычные, оригинальные варианты каждое сообщение создаёт тёплое впечатление и дарит радость получателю вы легко найдёте пожелания для любого человека и случая сборник поздравлений постоянно пополняется новыми текстами и идеями создавайте праздничное настроение, удивляйте близких и радуйте друзей каждое поздравление легко адаптируется под формат, который вам удобен исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант и помните, что несколько искренних слов иногда ценнее любых подарков
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Когда работа не дает финансового роста, стоит сменить подход. Контрактная служба предлагает стабильный заработок и гарантии. Выплаты начисляются регулярно. Условия прозрачны и понятны. Начни новый этап и оформи заявку: воинская часть ханты мансийск
Служба по контракту предполагает соблюдение внутренних правил. Военнослужащий действует в рамках устава. Это обязательное условие. Ознакомиться подробнее, контрактникам
Я уже начал сомневаться,что проблема в курьерке!Я им звонил,они в свою очередь звонили в головной офис-про мой трек они даже не слышали!!!А постановление вроде ещё не вступило в силу. https://rooi-sozidanie.ru заказал сегодня , оплатил , ждем когда дадут трэкРАБОТА КАЧЕСТВЕННАЯ И БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ, БОЛЬШОЙ РЕСПЕКТ ВАМ качество продукции еще не пробывал, в ближайшие время расскажу OOO
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в волгограде[/url]
Unlock your betting potential with [b]1Win![/b]. Start today and enjoy fast, secure payouts, get your bonus with a promo code – 5000
https://lkpf.pro/88bf
[url=https://lkxd.cc/815402ee][img]https://e.radikal.host/2025/03/09/500.md.jpg[/img][/url]
Зависимость от алкоголя или наркотиков — серьёзная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Если у вас или вашего близкого возникли признаки тяжелого похмелья, запоя или интоксикации, клиника «НаркологПлюс» предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге. Наши врачи оперативно прибывают по указанному адресу, оказывают всю необходимую медицинскую помощь и помогают пациенту быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/psikhiatr-narkolog-na-dom-spb/
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Статья о том, как устроен дом престарелых: забота, поддержка, безопасность и комфорт для пожилых. Познакомиться с результатами исследований – http://salda.ws/f/topic.php?f=5&t=103185
Капельница от запоя в Мурманске является одной из наиболее востребованных процедур для снятия острого состояния алкогольной интоксикации. Эта методика позволяет быстро вывести токсины из организма, нормализовать водно-солевой баланс и улучшить самочувствие пациента. Современная капельная терапия считается эффективным средством в лечении запоя, обеспечивая поддержку жизненно важных функций и минимизируя риски осложнений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в прозе[/url] мы предлагаем искренние и добрые поздравления в стихах и прозе, которые запомнятся надолго для любого события — будь то свадьба, именины или корпоративная вечеринка небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника к каждому поздравлению мы предлагаем варианты в прозе и стихах подарите настроение с помощью ярких деталей — шаров, лент и праздничных украшений каждое пожелание можно отправить как смс, так и оформить в красивую открытку мы предлагаем как традиционные, так и современные, креативные поздравления каждое сообщение создаёт тёплое впечатление и дарит радость получателю поздравления подходят для семьи, друзей, коллег и всех близких людей мы регулярно обновляем коллекцию, добавляем новые идеи и оригинальные тексты создавайте праздничное настроение, удивляйте близких и радуйте друзей любой вариант текста сделает день получателя светлее и радостнее поздравляйте с любовью и вниманием, используя наши тщательно подобранные тексты даже короткое сообщение способно согреть сердце и создать праздник
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Перечень средств подбирается индивидуально, с учётом состояния пациента и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний. Это гарантирует безопасность и эффективность вмешательства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Группа препаратов
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Узнайте, какие услуги предлагают частные дома престарелых — от ухода и медицинской поддержки до досуга и комфорта для пожилых людей. Проверенные методы — узнай сейчас – http://infoenglish.info/forum/14-9831-1
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Разобраться лучше – http://
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]смс поздравления[/url] мы предлагаем искренние и добрые поздравления в стихах и прозе, которые запомнятся надолго для любого события — будь то свадьба, именины или корпоративная вечеринка небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника к каждому поздравлению мы предлагаем варианты в прозе и стихах чтобы сделать момент ещё ярче, можно добавить праздничные детали — шары, украшения, подарки тексты удобны для пересылки в сообщениях или публикации в социальных сетях можно выбрать проверенные временем поздравления или новаторские, свежие варианты каждое сообщение создаёт тёплое впечатление и дарит радость получателю подберите поздравление для родных, друзей или коллег, которое идеально подойдёт мы регулярно обновляем коллекцию, добавляем новые идеи и оригинальные тексты несколько искренних слов способны превратить обычный день в праздник не важно, что вы выберете — короткое смс или длинное поздравление в стихах, эффект гарантирован поздравляйте с любовью и вниманием, используя наши тщательно подобранные тексты каждое слово может стать дорогим и запоминающимся подарком
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Тагиле представляет собой комплекс медицинских мероприятий, направленных на безопасное и эффективное прерывание состояния острого алкогольного отравления. Этот процесс требует профессионального подхода, так как самостоятельное прерывание запоя чревато серьезными осложнениями, включая судороги, инсульты и инфаркты. В медицинской практике используется комплекс мер, включающий детоксикацию организма, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и лечение симптомов абстиненции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/
https://bestdogfoodforboxers.com Хорошо работают реально ! ! ! рега МН-35ф реально индика суровая , наиболее множество сходств нашёл с натуралом , по Мне так это наиболее приближенный каннабиноид ..приеме. Приложат все усилия, чтобы ожидаемые заказы выслались. За ожидание вложены компенсации, средний % компенсации 50. Как и было обещано, адрес оператор прислал где-то в 23.
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в стихах[/url] здесь легко подобрать тёплые и душевные слова для поздравления друзей, родных и коллег независимо от повода — день рождения, юбилей, Новый год или просто приятный сюрприз небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника каждое пожелание сопровождается вариантами в стихотворной и прозаической форме подарите настроение с помощью ярких деталей — шаров, лент и праздничных украшений каждое пожелание можно отправить как смс, так и оформить в красивую открытку у нас вы найдёте не только классические пожелания, но и необычные, оригинальные варианты наши тексты делают праздник более личным и душевным подберите поздравление для родных, друзей или коллег, которое идеально подойдёт сборник поздравлений постоянно пополняется новыми текстами и идеями несколько искренних слов способны превратить обычный день в праздник не важно, что вы выберете — короткое смс или длинное поздравление в стихах, эффект гарантирован наш сайт — источник вдохновения для красивых и душевных слов и помните, что несколько искренних слов иногда ценнее любых подарков
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
매우 흥미롭습니다, 당신은 매우 숙련된 블로거입니다.
당신의 RSS 피드에 가입했고, 당신의 훌륭한 포스트를
더 찾고 있습니다. 또한, 제 소셜 네트워크에서
당신의 웹사이트를 공유했습니다!
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I to find It really useful & it helped me out much.
I’m hoping to present something back and aid others like you helped me.
После процедуры пациент и его близкие получают развернутые рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению, советы по профилактике рецидивов и возможности прохождения кодирования при желании пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
После первичной стабилизации врач обычно объясняет близким, почему «просто поспать» не всегда получается сразу, сколько времени может держаться раздражительность и как правильно выстроить режим, чтобы не спровоцировать повторный срыв в первые дни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]vrach narkolog na dom[/url]
Срочная помощь нарколога на дому в Рязани реализуется по четко отлаженной схеме, включающей несколько этапов, которые позволяют максимально быстро и безопасно вывести пациента из состояния запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом рязань[/url]
No matter if some one searches for his essential thing, thus he/she needs to be available that in detail, thus that thing is maintained over here.
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Первые сутки после прекращения алкоголя — самые уязвимые: именно в это время нарастают абстинентные симптомы и риск осложнений. Ниже приведены основные ситуации, при которых нужен быстрый выезд врача. Перед списком отметим: если сомневаетесь, позвоните координатору — он уточнит признаки и подскажет безопасные действия до прибытия команды.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo-v-pushkino/
[url=https://rutor13.cc/]rutor теневой форум[/url]: Независимая площадка русскоязычного даркнета, устоявшая после “Гидры”**
Rutor — ветеран русскоязычного даркнета, активно действующий с начала 2010-х. Форум пережил период доминирования “Гидры” и продолжает функционировать после ее исчезновения в 2022 году. Несмотря на смену владельцев в начале 2022, Rutor сохранил доверие пользователей как платформа для теневой торговли и общения.
**?? Торговая секция Rutor предлагает широкий выбор товаров и услуг от верифицированных дилеров, включая:**
* Психоактивные вещества.
* Цифровой контент и софт.
* Сервисы анонимности, обналичивания и OSINT.
**?? Для безопасности транзакций действует система гаранта. Встроенный мессенджер с анонимными записками, не связанными с профилем, обеспечивает дополнительную конфиденциальность, снижая риски взлома данных.**
**??? Доступ к Rutor осуществляется исключительно через Tor по onion-ссылке. Регистрация часто осуществляется по инвайтам или через верификацию, что помогает отфильтровывать нежелательных пользователей. Модерация ориентирована на поддержание деловой репутации, а не на цензуру.**
**?? После реорганизации Rutor стал более закрытым, но сохранил свою базу пользователей и стабильность. Он остается важной вехой в истории русского даркнета.**
**Официальное предупреждение:** Участие в деятельности, связанной с торговлей запрещенными товарами или услугами, может повлечь за собой уголовное преследование.
Вызывать нарколога на дом рекомендуется при следующих состояниях:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-spb/
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]смс поздравления[/url] здесь легко подобрать тёплые и душевные слова для поздравления друзей, родных и коллег для любого события, которое требует искренних слов и внимания, у нас есть готовые варианты порой несколько тёплых и искренних слов важнее любых материальных подарков наши поздравления подходят для любых форматов — от смс до праздничной открытки для создания праздничной атмосферы рекомендуем дополнить поздравление красивыми шарами и аксессуарами поздравления можно отправлять онлайн или распечатать, чтобы вручить лично мы предлагаем как традиционные, так и современные, креативные поздравления наши тексты делают праздник более личным и душевным вы легко найдёте пожелания для любого человека и случая сборник поздравлений постоянно пополняется новыми текстами и идеями дарите эмоции, внимание и заботу с помощью красивых слов наши тексты подходят для любых средств связи и создают атмосферу праздника исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант не недооценивайте силу добрых слов — они делают моменты по-настоящему особенными
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в рязани[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану привет всем! у меня сегодня днюха по этому поводу я заказал 10г ам2233 заказ пришел быстро качество хорошее (порошок желтоватого цвета, мелкий) делал на спирту, по кайфу напоминает марью иванну мягкий если сравнивать а мне есть с чем курю с 13 лет сегодня 34года плотно,( курил джив(018,210,250,203)) я доволен RESPEKT магазину в августе 2 раза делал заказ в 3 дня приходил до сибири!заметил, что там тс появляется на много чаще Пишите в скайп, аську, пожалуйста без лишнего, чтобы была возможность ответить всем. :good:
После первичной стабилизации врач обычно объясняет близким, почему «просто поспать» не всегда получается сразу, сколько времени может держаться раздражительность и как правильно выстроить режим, чтобы не спровоцировать повторный срыв в первые дни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-krasnogorsk/
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]смс поздравления[/url] на нашем сайте вы найдёте самые красивые и оригинальные пожелания для любого праздника для любого события, которое требует искренних слов и внимания, у нас есть готовые варианты порой несколько тёплых и искренних слов важнее любых материальных подарков наши поздравления подходят для любых форматов — от смс до праздничной открытки дополнив поздравление красочными шарами и милыми сувенирами, вы создадите эффект настоящего праздника тексты удобны для пересылки в сообщениях или публикации в социальных сетях на сайте собраны как стандартные, так и уникальные тексты, которые приятно удивят любое пожелание дарит эмоции и атмосферу праздника, делая его незабываемым поздравления подходят для семьи, друзей, коллег и всех близких людей каждую неделю появляются свежие поздравления, чтобы вы могли удивлять близких создавайте праздничное настроение, удивляйте близких и радуйте друзей наши тексты подходят для любых средств связи и создают атмосферу праздника наш сайт — источник вдохновения для красивых и душевных слов и помните, что несколько искренних слов иногда ценнее любых подарков
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]вывод из запоя в пушкине[/url]
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в стихах[/url] у нас всегда можно подобрать уникальные поздравления и тосты, чтобы порадовать близких для любого события — будь то свадьба, именины или корпоративная вечеринка небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника каждое пожелание сопровождается вариантами в стихотворной и прозаической форме чтобы сделать момент ещё ярче, можно добавить праздничные детали — шары, украшения, подарки поздравления можно отправлять онлайн или распечатать, чтобы вручить лично можно выбрать проверенные временем поздравления или новаторские, свежие варианты каждое сообщение создаёт тёплое впечатление и дарит радость получателю подберите поздравление для родных, друзей или коллег, которое идеально подойдёт каждую неделю появляются свежие поздравления, чтобы вы могли удивлять близких создавайте праздничное настроение, удивляйте близких и радуйте друзей наши тексты подходят для любых средств связи и создают атмосферу праздника исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант каждое слово может стать дорогим и запоминающимся подарком
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Во время детоксикации используются капельницы с растворами, которые очищают кровь от токсинов, восстанавливают водно-электролитный баланс и нормализуют работу печени и почек. Этот этап проводится в условиях клиники, что позволяет избежать возможных осложнений и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-i-oblast[/url]
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом[/url]
https://legendgame.ru а чё есть какое нить в/в в этом магазе что бы до бледного?:)очень сильно хочуОтличный магазин с отличным продуктом. Сервис лучший, и стабильный.
I enjoy what you guys tend to be up too. This type of clever work and coverage!
Keep up the good works guys I’ve included you guys to my blogroll.
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]смс поздравления[/url] здесь легко подобрать тёплые и душевные слова для поздравления друзей, родных и коллег для любого события, которое требует искренних слов и внимания, у нас есть готовые варианты порой несколько тёплых и искренних слов важнее любых материальных подарков тексты легко адаптируются под смс, открытку или письмо чтобы сделать момент ещё ярче, можно добавить праздничные детали — шары, украшения, подарки тексты удобны для пересылки в сообщениях или публикации в социальных сетях можно выбрать проверенные временем поздравления или новаторские, свежие варианты наши тексты делают праздник более личным и душевным вы легко найдёте пожелания для любого человека и случая сборник поздравлений постоянно пополняется новыми текстами и идеями дарите эмоции, внимание и заботу с помощью красивых слов наши тексты подходят для любых средств связи и создают атмосферу праздника наш сайт — источник вдохновения для красивых и душевных слов каждое слово может стать дорогим и запоминающимся подарком
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
После поступления вызова нарколог клиники «АльфаНаркология» оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу. На месте врач проводит первичную диагностику, оценивая степень интоксикации, физическое и психологическое состояние пациента. По результатам осмотра врач подбирает индивидуальный комплекс лечебных процедур, в который входит постановка капельницы с растворами для детоксикации, препараты для стабилизации работы органов и нормализации психического состояния.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/psikhiatr-narkolog-na-dom-spb
Запой — это состояние, которое представляет собой одну из самых серьёзных форм алкогольной зависимости. Когда человек теряет способность контролировать употребление алкоголя, его организм подвергается вредному воздействию, которое может вызвать как физические, так и психоэмоциональные осложнения. В Москве есть множество клиник и специалистов, которые предлагают качественную медицинскую помощь, включая анонимное лечение. Этот вариант подходит тем, кто хочет избавиться от зависимости, не раскрывая свою личность и не сталкиваясь с осуждением окружающих.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]вывод из запоя москва[/url]
I am sure this paragraph has touched all the internet people, its really really good paragraph on building up new blog.
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru
Эти данные являются основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения, позволяющего оперативно скорректировать терапевтические меры.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в рязани[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this
I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads.
I’m hoping to give a contribution & assist different customers like its helped me.
Great job.
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя бесплатно[/url]
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в рязани[/url]
Читатели получат представление о том, как современные технологии влияют на развитие медицины. Обсуждаются новые методы лечения, персонализированный подход и роль цифровых решений в повышении качества медицинских услуг.
Узнайте, как анонимное лечение алкоголизма на дому в Рязани помогает пациентам: от вывода из запоя до реабилитации. Ознакомиться с отчётом – https://otvet.mail.ru/question/267932751
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в прозе[/url] на нашем сайте вы найдёте самые красивые и оригинальные пожелания для любого праздника независимо от повода — день рождения, юбилей, Новый год или просто приятный сюрприз небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника к каждому поздравлению мы предлагаем варианты в прозе и стихах для создания праздничной атмосферы рекомендуем дополнить поздравление красивыми шарами и аксессуарами все тексты легко отправлять через смс, мессенджеры или распечатывать для открыток мы предлагаем как традиционные, так и современные, креативные поздравления наши тексты делают праздник более личным и душевным вы легко найдёте пожелания для любого человека и случая каждую неделю появляются свежие поздравления, чтобы вы могли удивлять близких несколько искренних слов способны превратить обычный день в праздник каждое поздравление легко адаптируется под формат, который вам удобен исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант не недооценивайте силу добрых слов — они делают моменты по-настоящему особенными
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Медикаментозное пролонгированное
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]центр кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
https://pg21.ru/kak-otlichit-chestnyj-otzyv-v-internete-ot-nechestnogo
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnodar/
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Уже заказывал и получил chm-100 и chm-400 всё ровно)В двух пакетах дада братан пришло все!!!охуенноый кач ск и рега нормальная вапще… короче зайди к нему на ветку там трипы опродукции прочти мой свежий за ск
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Выяснить больше – http://
Запой — это состояние, которое представляет собой одну из самых серьёзных форм алкогольной зависимости. Когда человек теряет способность контролировать употребление алкоголя, его организм подвергается вредному воздействию, которое может вызвать как физические, так и психоэмоциональные осложнения. В Москве есть множество клиник и специалистов, которые предлагают качественную медицинскую помощь, включая анонимное лечение. Этот вариант подходит тем, кто хочет избавиться от зависимости, не раскрывая свою личность и не сталкиваясь с осуждением окружающих.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]тосты для праздника[/url] у нас всегда можно подобрать уникальные поздравления и тосты, чтобы порадовать близких независимо от повода — день рождения, юбилей, Новый год или просто приятный сюрприз иногда короткая и добрая фраза приносит больше радости, чем громоздкий презент каждое пожелание сопровождается вариантами в стихотворной и прозаической форме подарите настроение с помощью ярких деталей — шаров, лент и праздничных украшений все тексты легко отправлять через смс, мессенджеры или распечатывать для открыток у нас вы найдёте не только классические пожелания, но и необычные, оригинальные варианты наши тексты делают праздник более личным и душевным подберите поздравление для родных, друзей или коллег, которое идеально подойдёт каждую неделю появляются свежие поздравления, чтобы вы могли удивлять близких наполните праздник радостью, теплом и вниманием, используя наши тексты каждое поздравление легко адаптируется под формат, который вам удобен исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант даже короткое сообщение способно согреть сердце и создать праздник
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Выбор техники зависит от клинической картины, переносимости препаратов, психоэмоционального состояния и горизонта планируемой трезвости. Таблица ниже помогает сориентироваться в ключевых различиях — врач подробно разберёт нюансы на очной консультации.
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма выезд на дом[/url]
Есть ряд признаков, при которых ждать категорически нельзя и нужна срочная помощь врача, а не очередные «народные методы». Если вы замечаете у человека следующие симптомы, это прямой повод организовать профессиональный вывод из запоя:
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]заявка на подключение интернета инсис[/url]
подключить проводной интернет инсис – [url=http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /[/url]
[url=http://truly.germanyproperties.net/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]http://euro-chiamami.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.educ-ua4.ru/www.blog-o-marketinge.ru/www.melbet5010.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] e0ae634
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в рязани[/url]
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в стихах[/url] на нашем сайте вы найдёте самые красивые и оригинальные пожелания для любого праздника для любого события — будь то свадьба, именины или корпоративная вечеринка несколько душевных слов могут сделать праздник незабываемым и вызвать искреннюю улыбку к каждому поздравлению мы предлагаем варианты в прозе и стихах подарите настроение с помощью ярких деталей — шаров, лент и праздничных украшений каждое пожелание можно отправить как смс, так и оформить в красивую открытку можно выбрать проверенные временем поздравления или новаторские, свежие варианты любое пожелание дарит эмоции и атмосферу праздника, делая его незабываемым тексты универсальны и подойдут для любого круга общения мы регулярно обновляем коллекцию, добавляем новые идеи и оригинальные тексты наполните праздник радостью, теплом и вниманием, используя наши тексты каждое поздравление легко адаптируется под формат, который вам удобен откройте для себя мир оригинальных поздравлений, добрых тостов и тёплых слов каждое слово может стать дорогим и запоминающимся подарком
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
https://racasino77.com/
Оперативное лечение организовано по четкому алгоритму, который позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента и обеспечить эффективную терапию. Каждый этап направлен на комплексное восстановление организма.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
https://tvtuners.ru отличный магазин! + емуага в осадок выпадает в спирте это верно, но если после выпадания в осадок добавить 646 в спирт и все будет гуд. Кстати 250 также при перегреве выпадает в осадок Хороший магазин,менеджер приятный по общению,недовесов не было у меня
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wanted to mention that I’ve truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing in your rss feed and I’m hoping you write once more very soon!
Для успешного вывода из запоя используется комплексный подход с участием специалистов разных профилей. Более подробно об этом можно узнать на официальном портале наркологической службы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево нижний тагил[/url]
Мы работаем круглосуточно и гарантируем строгое соблюдение конфиденциальности, используя только сертифицированные препараты и проверенные методики лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Обычно внимание уделяется нескольким направлениям: восстановлению жидкости и обмена веществ, снижению тошноты и головной боли, уменьшению вегетативных симптомов (дрожь, потливость, сердцебиение), нормализации сна и тревоги. При этом врач ориентируется на текущие показатели и реакцию пациента — то, что помогало «в прошлый раз», может быть неуместно сегодня. Дополнительно проговариваются бытовые детали: проветривание, комфортная температура, питьевой режим, питание небольшими порциями, контроль давления и пульса, ограничение стимуляторов и рисковых нагрузок.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnogorsk6.ru/]platnyi narkolog na dom[/url]
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в стихах[/url] на нашем сайте вы найдёте самые красивые и оригинальные пожелания для любого праздника под любой праздник, от семейного торжества до официального мероприятия, вы найдёте подходящие тексты небольшое, но сердечное поздравление может создать настоящую атмосферу праздника тексты легко адаптируются под смс, открытку или письмо для создания праздничной атмосферы рекомендуем дополнить поздравление красивыми шарами и аксессуарами поздравления можно отправлять онлайн или распечатать, чтобы вручить лично можно выбрать проверенные временем поздравления или новаторские, свежие варианты каждое сообщение создаёт тёплое впечатление и дарит радость получателю вы легко найдёте пожелания для любого человека и случая мы регулярно обновляем коллекцию, добавляем новые идеи и оригинальные тексты наполните праздник радостью, теплом и вниманием, используя наши тексты наши тексты подходят для любых средств связи и создают атмосферу праздника исследуйте коллекцию поздравлений в стихах и прозе, чтобы найти идеальный вариант и помните, что несколько искренних слов иногда ценнее любых подарков
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
Скачайте активатор для Windows 11 и получите все функции Pro-версии бесплатно.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Бесплатный серийный номер для Windows 11[/url]
Функция и назначение
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя екатеринбург[/url]
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого краснодар[/url]
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Статья о том, какие услуги обеспечивает пансионат для пожилых: квалифицированный уход, медицинская поддержка и достойный уровень жизни. Как достичь результата? – http://salda.ws/f/topic.php?f=3&t=103176
[url=https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/]поздравления в стихах[/url] на нашем сайте вы найдёте самые красивые и оригинальные пожелания для любого праздника для любого события, которое требует искренних слов и внимания, у нас есть готовые варианты порой несколько тёплых и искренних слов важнее любых материальных подарков наши поздравления подходят для любых форматов — от смс до праздничной открытки чтобы сделать момент ещё ярче, можно добавить праздничные детали — шары, украшения, подарки тексты удобны для пересылки в сообщениях или публикации в социальных сетях у нас вы найдёте не только классические пожелания, но и необычные, оригинальные варианты любое пожелание дарит эмоции и атмосферу праздника, делая его незабываемым поздравления подходят для семьи, друзей, коллег и всех близких людей сборник поздравлений постоянно пополняется новыми текстами и идеями создавайте праздничное настроение, удивляйте близких и радуйте друзей не важно, что вы выберете — короткое смс или длинное поздравление в стихах, эффект гарантирован наш сайт — источник вдохновения для красивых и душевных слов и помните, что несколько искренних слов иногда ценнее любых подарков
https://pozdravlyandiya.ru/
https://barbervshangale.ru Всем все выслано.покушать попробуй… и пиши сюда Ты в какой скайп то ломишься? перепроверь!!!
Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить концентрацию токсинов, нормализовать обмен веществ и предотвратить необратимые повреждения, что делает срочный вызов нарколога на дому жизненно необходимым.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Кому подходит
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма видное[/url]
Great information about TellCulvers.com. The step-by-step process you described makes the
survey simple to follow
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious know-how concerning unexpected emotions.
https://combat-mission.ru Магазин работает? пишу в ЛС и Джабер везде тишина, ответа нет!((Да не работал, тебя задело слово палево ?)) Мне обещали бонус за задержку в 5 + 3 =8 грамм , так и прислали +))) спасибо.+)))
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
После поступления вызова нарколог клиники «АльфаНаркология» оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу. На месте врач проводит первичную диагностику, оценивая степень интоксикации, физическое и психологическое состояние пациента. По результатам осмотра врач подбирает индивидуальный комплекс лечебных процедур, в который входит постановка капельницы с растворами для детоксикации, препараты для стабилизации работы органов и нормализации психического состояния.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Точная диагностика позволяет подобрать индивидуальную программу лечения, что значительно повышает шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/
Во время детоксикации используются капельницы с растворами, которые очищают кровь от токсинов, восстанавливают водно-электролитный баланс и нормализуют работу печени и почек. Этот этап проводится в условиях клиники, что позволяет избежать возможных осложнений и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
https://safegrom.ru а почему репа минусовая?Магазин замечательный!! приветствую
Find the new look here > http://hammill.ru/
Вывод из запоя показан при:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в мурманске[/url]
At this time it looks like Movable Type is the top blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
При необходимости применяется симптоматическое лечение для снижения болевого синдрома, устранения тошноты и рвоты, а также нормализации психоэмоционального состояния пациента. Врачи наркологи строго контролируют течение процедуры, что обеспечивает безопасность и снижает риски осложнений.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
Индивидуалки Екатеринбурга
с услугой расслабляющий массаж с продолжением – это истинные мастерицысвоего
дела в сфере интим массаж екб.
Они готовы приехать к вам в любой район города или принять у себяв
апартаментах и все для того, чтобы полностью расслабить вас и подарить максимальное наслаждение.
Индивидуалки Сибирский тракт
Лучшие шлюхи Екатеринбурга
района Парковый – каталог анкет с реальными фото, актуальными услугами
и номерами телефона. Если ты ищешь интим-досуга в Парковом районе Екатеринбурга – то ты на правильном
ресурсе. Выбирай, набирай номер и погрузись в мир удовольствия.
https://raiderrelease.com через три дня после заказа была уже у меняХороший магазинчик возможно мои письма рубятся где-то? там все четко по делу.
https://dveri-spetsstal.ru Удачных закупокответь те на мыло я еще вчера вам написал! мыло есть.нерабочее.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
I believe this is one of the so much vital info for me. And i am happy studying your article. However want to observation on some normal things, The site taste is perfect, the articles is in point of fact excellent : D. Excellent task, cheers
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle
Для эффективного вывода из запоя в Мурманске используются современные методы детоксикации, включающие внутривенное введение растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, коррекцию электролитов и нормализацию работы почек и печени. Важным этапом является использование витаминных комплексов и препаратов, поддерживающих работу сердца и сосудов.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske/
Согласно данным Федерального наркологического центра, своевременный выезд врача снижает риск осложнений и повторных госпитализаций.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Химках помогает не только тем, кто уже оказался в тяжёлом запое или прошёл через ломку. Сюда можно обратиться на любом этапе — от «злоупотребляю, но ещё работаю» до «запои повторяются, семья на грани, есть проблемы с давлением и сердцем». Чем раньше подключаются специалисты, тем мягче можно пройти период стабилизации и тем больше ресурсов удаётся сохранить — здоровье, отношения, работу, собственное чувство контроля над жизнью.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]kruglosutochnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Want to know how to get rich without investing? Just become a partner and claim your share – https://1w.run/?p=ymt4
[url=https://lkxd.cc/815402ee][img]https://e.radikal.host/2025/03/09/500.md.jpg[/img][/url]
Медикаментозная детоксикация — это первый и самый важный этап в лечении запоя. В этот момент из организма выводятся все вредные вещества, которые накопились за время алкоголизма. В Москве применяются эффективные и безопасные методы очистки, которые проводятся под контролем опытных специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve-nedorogo[/url]
https://kleps.ru Посыль получил в течении 5ти дней после оплаты. Быстро!! Отлично!!Жаль только в Мск от 50 гр. )) Думал в Саратове тоже он спонсировал всех нас.
Главное преимущество вызова нарколога на дом — возможность быстро оказать помощь без стресса, связанного с поездкой в клинику. Такой подход особенно важен при тяжёлых состояниях, когда каждый час играет роль. Кроме того, услуга полностью анонимна — данные пациента не передаются в сторонние организации, а документация хранится только в закрытой базе клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом красноярск[/url]
Процедура проходит под контролем нарколога и медсестры. Если состояние пациента тяжёлое (галлюцинации, судороги, резкие перепады давления), проводится экстренная инфузионная терапия и подключается оборудование для мониторинга сердечного ритма и уровня кислорода. Такой подход исключает риски и делает процесс выведения из запоя максимально безопасным и управляемым.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в владимире[/url]
Освоение английского в современном обществе является важной потребностью.
Это предоставляет огромные возможности для карьерного развития.
Знание этим языком даёт возможность доступа к мировому образованию и исследованиям.
английский язык для детей 5 лет
Свободное владение языком значительно расширяет возможности путешествий и коммуникации.
Подавляющее количество ценной информации в интернете содержится именно на английском языке.
Клиника нужна и тем, кто уже пробовал лечиться самостоятельно: пил лекарства «от тяги», ходил к психологу без медицинской поддержки, обещал себе не пить, но каждый стресс или конфликт всё равно приводили к старому сценарию. В такой ситуации комплексный подход — медицинский и психологический — даёт куда больше шансов, чем очередное одиночное обещание «в этот раз точно получится».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Согласно данным Федерального наркологического центра, своевременный выезд врача снижает риск осложнений и повторных госпитализаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в каменске-уральском[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Запой — это состояние, которое представляет собой одну из самых серьёзных форм алкогольной зависимости. Когда человек теряет способность контролировать употребление алкоголя, его организм подвергается вредному воздействию, которое может вызвать как физические, так и психоэмоциональные осложнения. В Москве есть множество клиник и специалистов, которые предлагают качественную медицинскую помощь, включая анонимное лечение. Этот вариант подходит тем, кто хочет избавиться от зависимости, не раскрывая свою личность и не сталкиваясь с осуждением окружающих.
Углубиться в тему – https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-moskva
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог И.В. Синицин, «современная наркология — это не только вывод из запоя, но и работа с глубинными причинами зависимости».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ярославская область[/url]
Основные признаки, свидетельствующие о необходимости экстренной помощи:
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru
Капельницы являются основным методом детоксикации. Их состав подбирается индивидуально с учётом степени интоксикации, наличия хронических заболеваний и общего состояния пациента. В таблице ниже представлены наиболее часто применяемые типы инфузий, используемые в клинике «ВладМед Трезвость».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в владимире[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану хорошо что такочень сложно дописаться до них=( а цены хорошие. На сколько я знаю в этом магазине пока нет реги!
Главное преимущество вызова нарколога на дом — возможность быстро оказать помощь без стресса, связанного с поездкой в клинику. Такой подход особенно важен при тяжёлых состояниях, когда каждый час играет роль. Кроме того, услуга полностью анонимна — данные пациента не передаются в сторонние организации, а документация хранится только в закрытой базе клиники.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом красноярск[/url]
Не стоит забывать и про объективные факторы. Бывает, что физически опасно или трудно везти человека в клинику: он с трудом ходит, не спит уже несколько ночей, постоянно потеет, жалуется на сильную слабость и сердцебиение. Любая поездка в таком состоянии — дополнительная нагрузка на сердце и нервную систему. Выезд нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение без этого лишнего риска: врач приезжает со всем необходимым для капельницы и наблюдения, а если по итогам осмотра становится понятно, что без стационара не обойтись, он помогает организовать перевод уже на фоне частично стабилизированного состояния, а не в момент максимального кризиса.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Hello I am so thrilled I found your blog page, I really found you by accident, while I was researching on Google for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say thanks a lot for a incredible post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to look over it all at the minute but I have bookmarked it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the fantastic job.
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Вред через наркотиков — это групповая
проблема, обхватывающая физическое,
психическое равным образом общественное здоровье человека.
Утилизация таковских наркотиков, как
кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, «шишки» чи «бошки»,
может родить для неконвертируемым последствиям яко чтобы
организма, так (а) также чтобы федерации в течение целом.
Но даже у выковывании подчиненности возможно электровосстановление — главное, чтоб зависимый явантроп устремился за помощью.
Важно памятовать, яко наркомания
лечится, также реабилитация одаривает шансище сверху новейшую жизнь.
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог рязань[/url]
журнал о машинах [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]журнал о машинах[/url] .
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=]купить футбольную форму[/url]
купить клубную футбольную форму – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/]http://tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=http://profitabledocumentsolutions.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru]http://detroitbrickcompany.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru[/url]
[url=https://filmstreaming4ever.00web.net/il-sentiero-dellodio-1952-32929#comment-765700]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 9b00_87
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
Что делает врач
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-noginske
Многие семьи сталкиваются с трудностями, когда зависимый отказывается ехать в клинику. В таких случаях выездная помощь становится первым шагом к выздоровлению. Однако не все службы предлагают одинаково безопасный и профессиональный подход. Чтобы избежать рисков и ошибок, важно понимать, на что обращать внимание при выборе услуги “нарколог на дом”.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]нарколог на дом нижний тагил[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану впервые обратился в этот магазин за оптом и был удивлён тем, что они работают без гаранта. Но почитав отзывы , решил заказать без гаранта с доставкой в регион. Обещали 5-7 дней. С небольшим опозданием получил адрес в своём городе и без проблем забрал опт. Возникли небольшие заморочки в части заказа и магазин без лишних слов решил все недорозумения в мою пользу. Очень приятно работать с такими людьми! Отличный магазин! Всем рекомендую! И можно не обращать внимание на то что они работают без гаранта. Удачи в бизе!а работают как.оперативненько? вполне. что ты хочешь сказать,что этот реактив плохо прет?
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Тагиле представляет собой комплекс медицинских мероприятий, направленных на безопасное и эффективное прерывание состояния острого алкогольного отравления. Этот процесс требует профессионального подхода, так как самостоятельное прерывание запоя чревато серьезными осложнениями, включая судороги, инсульты и инфаркты. В медицинской практике используется комплекс мер, включающий детоксикацию организма, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и лечение симптомов абстиненции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому нижний тагил[/url]
Комплексное лечение на дому организовано по строго отлаженной схеме, позволяющей оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и провести качественную детоксикацию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-vladimir/
Запойное состояние оказывает разрушительное воздействие на организм. При длительном употреблении алкоголя развиваются следующие проблемы:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru
If some one needs expert view on the topic of running a blog after that
i suggest him/her to pay a visit this webpage, Keep
up the fastidious work.
Also visit my web blog – sex porn
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]pomoshch-na-domu-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра и диагностики. На этом этапе проводится сбор анамнеза, измеряются жизненно важные показатели (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) и определяется степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/]вызов на дом капельницы от запоя тюмень[/url]
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя в балашихе[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом — востребованная услуга, позволяющая оказать пациенту помощь в привычной обстановке без необходимости посещения клиники. Особенно актуально это при запойном состоянии, абстинентном синдроме или первых признаках передозировки. Согласно информации Минздрава РФ, амбулаторная помощь эффективна при своевременном обращении и наличии квалифицированной команды специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-nizhnem-tagile/
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника нижний тагил[/url]
Услуга капельничного вывода из запоя на дому в Тюмени предоставляет комплексный подход к экстренному лечению алкогольной интоксикации. Врач приезжает на дом, проводит первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает индивидуальную схему терапии. Современные методы инфузионной терапии позволяют точно дозировать препараты, обеспечивая быструю детоксикацию и минимизируя риск осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в владимире[/url]
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра и диагностики. На этом этапе проводится сбор анамнеза, измеряются жизненно важные показатели (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) и определяется степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-srochno-v-himkah/
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя недорого балашиха[/url]
Если человек страдает от алкоголизма, запойное состояние требует незамедлительного вмешательства, особенно если признаки токсического отравления начинают угрожать жизни. Признаки запоя — это не только физическая зависимость, но и эмоциональные и психические расстройства, такие как тревога, агрессия и галлюцинации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Брал неоднократно в этом магазе, всегда всё ровно и без проволочек, так держать!!Первый раз слышу такой непонятный отзыв о 4фа,все кто берет его как и 2c-i говорят что у нас он лучший … по jte907 если не умеете с ним работать зачем берете…? есть постоянные оптовики кто берет только его, и этот продукт нареканий не вызывает. Многие “Селлеры” под видом jte продают 2201 и это факт! у нас этот продукт в оригинале. МХЕ у нас такой пришел, мы не кричим что его чистота 99%, и что качество его не очень мы предупреждали всех… Пиздец до сих пор мозги ебут(
Длительный запой может привести к серьезным осложнениям, таким как повреждение печени, почек, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения и нервные расстройства. Чем быстрее начинается вывод из запоя, тем ниже риск развития хронических заболеваний. Срочный вызов нарколога на дом позволяет в первые часы кризиса начать детоксикацию, что существенно повышает шансы на полное восстановление организма. В условиях экстренной ситуации каждая минута имеет решающее значение, и своевременная помощь становится ключом к сохранению здоровья и жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в туле[/url]
Алкоголь оказывает глубокое воздействие на здоровье: психоэмоциональное и физическое состояние человека значительно ухудшаются, если злоупотребление продолжается долго. Даже небольшие дозы алкоголя, употребляемые регулярно, вызывают накопление токсинов, которые приводят к расстройствам в работе сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в новокузнецке[/url]
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve have in mind your stuff previous to and you’re just too wonderful. I really like what you’ve acquired here, really like what you are stating and the best way by which you are saying it. You make it entertaining and you continue to care for to keep it sensible. I can’t wait to learn far more from you. This is really a tremendous web site.
Для семьи это почти всегда тяжёлый, эмоционально изматывающий период. В доме копятся усталость, обида, чувство вины, страх за близкого. Но при этом сохраняется надежда, что удастся «обойтись своими силами». В какой-то момент становится ясно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи уже не справиться. В этот момент важно, чтобы рядом был специализированный центр в самом Воскресенске, а не где-то далеко, куда сложно добраться и куда трудно уговорить поехать человека в тяжёлом состоянии.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske
We’re a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our
community. Your website offered us with valuable information to work
on. You’ve performed an impressive task and our whole
group will be thankful to you.
На нашем сайте вы можете скачать активатор для Windows 11 абсолютно бесплатно и навсегда забыть о водяных знаках!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Скачать генератор ключей для Windows 11[/url]
Длительный запой может привести к серьезным осложнениям, таким как повреждение печени, почек, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения и нервные расстройства. Чем быстрее начинается вывод из запоя, тем ниже риск развития хронических заболеваний. Срочный вызов нарколога на дом позволяет в первые часы кризиса начать детоксикацию, что существенно повышает шансы на полное восстановление организма. В условиях экстренной ситуации каждая минута имеет решающее значение, и своевременная помощь становится ключом к сохранению здоровья и жизни.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-tula/
В таких случаях своевременное обращение за помощью позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и предотвратить развитие серьезных осложнений.
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-voronezh/
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/[/url]
Услуга капельничного вывода из запоя на дому в Тюмени предоставляет комплексный подход к экстренному лечению алкогольной интоксикации. Врач приезжает на дом, проводит первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает индивидуальную схему терапии. Современные методы инфузионной терапии позволяют точно дозировать препараты, обеспечивая быструю детоксикацию и минимизируя риск осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Качество на высоте,оператор красавчик,все сделали быстро и четко!Бро ты бред несёшь!Если читал все посты в этом магазе брали даже модеры этого форума.А может быть ты конкурент и провоцируешь людей специально? свое сообщение исправил
Услуга “капельница от запоя” на дому имеет ряд преимуществ, делающих её оптимальным выбором для экстренной помощи:
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru
В этой статье мы рассмотрим ключевые аспекты выбора надёжного специалиста, который приедет по вызову и сможет оказать квалифицированную помощь без промедлений.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-nizhnem-tagile/
Подбор учреждения для прохождения реабилитации — это ответственное решение, влияющее на весь процесс восстановления. Наркологическая помощь требует не только медикаментозного вмешательства, но и глубокой психологической проработки. Согласно информации, опубликованной на портале Минздрава РФ, эффективность терапии во многом зависит от персонализированного подхода и соблюдения стандартов оказания психиатрической помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В таких случаях своевременное обращение за помощью позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние и предотвратить развитие серьезных осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом воронеж[/url]
Если человек страдает от алкоголизма, запойное состояние требует незамедлительного вмешательства, особенно если признаки токсического отравления начинают угрожать жизни. Признаки запоя — это не только физическая зависимость, но и эмоциональные и психические расстройства, такие как тревога, агрессия и галлюцинации.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah[/url]
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/]магазин футбольной атрибутики в москве[/url]
футбольная форма – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/]http://www.tut-sport.ru[/url]
[url=http://gemvalue.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru]http://qualifypronto.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru[/url]
[url=http://yourarchivist.com/whs/jpg/MI/slide_02.php]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 3da2a67
газета про автомобили [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]газета про автомобили[/url] .
Не тратьте деньги на лицензию — скачайте кряк для Windows 11 здесь и активируйте систему за 5 минут.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Где взять лицензионный ключ для Windows 11[/url]
Hurrah, that’s what I was searching for, what a stuff!
existing here at this weblog, thanks admin of this website.
https://distonija.ru Если представитель не торгует нашим товаром – то представительство мы закрываем и ответственности тоже не несём.отпишите народ за 5 iai кто брал спс заранее Удачи и развития в дальнейшем!
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Медная двухраструбная редукционная переходная муфта под пайку 40х28 мм твердая пайка М3т ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Выберите высококачественные медные двухраструбные редукционные муфты под пайку от Редметсплав для надежного соединения медных труб различных диаметров. Широкий выбор размеров, эффективная установка и долговечность гарантированы. Идеальное решение для систем отопления и водоснабжения.
Excellent article! We are linking to this great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wow, marvelous blog structure! How long have you
been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy.
The whole look of your web site is fantastic, let alone the content!
Лечение при запое строится поэтапно. Каждый шаг направлен на устранение симптомов интоксикации и постепенное восстановление функций организма. В таблице ниже приведена структура работы врача при выезде или лечении в стационаре.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в владимире[/url]
Купить аккаунты онлайн — современное решение для бизнеса и онлайн-задач
Купить аккаунты онлайн сегодня — это эффективный подход для тех, кто работает с рекламой. Современный маркетплейс аккаунтов позволяет без лишних рисков купить цифровые ресурсы под конкретные задачи.
Платформа XMart — это онлайн-площадка, где можно купить аккаунты сервисов для продвижения и тестирования. Такой формат особенно востребован, когда важны скорость.
Цифровые аккаунты купить — инструмент масштабирования
Цифровые аккаунты используются в самых разных сценариях: от доступа к платформам до массовых рекламных кампаний.
Когда требуется купить аккаунты сервисов оптом, маркетплейс даёт прозрачные условия. Это позволяет снизить нагрузку на команды.
Email аккаунты купить
Отдельная категория — аккаунты для регистрации купить. Они применяются для подтверждения действий.
Использование готовых решений позволяет работать без ограничений, особенно когда речь идёт о запуске новых направлений. В каталоге XMart такие позиции доступны в формате единичных покупок.
Купить аккаунты для SMM
Для специалистов по продвижению особенно важны аккаунты для рекламы купить. Эти аккаунты используются для аналитики.
Маркетплейс аккаунтов позволяет гибко подбирать типы аккаунтов, не теряя времени на рутину. Именно поэтому аккаунты для работы онлайн остаются одним из самых популярных запросов.
Купить аккаунты социальных сетей
аккаунты платформ — это инструмент роста. Они используются в продажах.
Платформа XMart ориентирована на онлайн-предпринимателей, которым важны повторяемость. Благодаря этому магазин аккаунтов становится частью регулярной операционной деятельности.
Почему выбирают маркетплейс аккаунтов XMart
XMart — это не просто продажа аккаунтов, а инструмент для роста.
Преимущества:
широкий ассортимент
гибкие форматы
аккаунты для маркетинга
быстрая выдача
https://www.holycrossconvent.edu.na/profile/neumannzqubergmann42568/profile
Купить аккаунты — это удобно.
Платформа XMart объединяет аккаунты социальных сетей в одном месте, предлагая онлайн магазин аккаунтов.
Если вам нужны цифровые аккаунты для работы онлайн, XMart становится поставщиком ресурсов.
Использование автоматизированных систем дозирования обеспечивает точное введение медикаментов, минимизируя риск передозировки и побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу оперативно корректировать терапевтическую схему, адаптируя её к изменяющемуся состоянию пациента и обеспечивая максимальную безопасность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Когда человеку требуется немедленная медицинская помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, промедление может быть опасным. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением. Клиника «КрасМед Трезвость» в Красноярске организует срочный выезд врача круглосуточно, обеспечивая квалифицированную помощь прямо по месту нахождения пациента. Такой формат позволяет избежать госпитализации, снизить тревожность и начать лечение в привычных домашних условиях, где человек чувствует себя спокойнее и безопаснее.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в красноярске[/url]
https://uk-ros.ru Эти ребята лучшие в своем деле, качество плюс вес, никогда не подводили, КРАСАВЧИКИ !!!Лучшие!в трубку после затяга уже чвствуеца Если кто-то когда-то пробовал банки с Рафинада на тусиае, тот знает, как классно они перли и понимает, каких эффектов я ожидал.
Вызов нарколога возможен круглосуточно, что обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на критические ситуации. Пациенты и их родственники могут получить помощь в любое время, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/[/url]
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• поддержки 24/7;
• безлимитный пакет.
• Точную оценку скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж роутера
• Персональную помощь менеджера
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]подключить интернет сибирские сети в квартиру новосибирск[/url]
сибсети тв и интернет тарифы – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru[/url]
[url=http://jeroen.singingcello.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://805acdc.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=https://forums.trgwii.com/main/thread/53193]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] 2a67f9e
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]секс шоп[/url]
После вашего звонка нарколог выезжает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Прибыв на место, специалист проводит всесторонний медицинский осмотр, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез для определения степени интоксикации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]игровые автоматы[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупных поставок, мы обеспечиваем своевременную реализацию вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Опытная поддержка – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы по мере того как находить ответы под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
Наша продукция:
Порошок магниевый G-MgAl8Zn1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 Изделия из магния G-MgAl8Zn1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 представляют собой высококачественные металлические конструкции, признанные за их легкость и прочность. Эти изделия находят широкое применение в аэрокосмической, автомобильной и электронной отраслях благодаря отличным механическим свойствам и коррозионной стойкости. При выборе материалов важно учитывать их характеристики, и изделия из магния G-MgAl8Zn1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 отвечают самым высоким стандартам. Не упустите возможность купить Изделия из магния G-MgAl8Zn1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 для своих проектов. Они обеспечат надежность и долговечность ваших конструкций.
Hi, Neat post. There’s an issue together with your website in web explorer, might test this? IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a large component of people will leave out your great writing because of this problem.
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Ты нам лучьше отзыв напиши о работе магазина :DСочи – мёд отличный, кладмену респект и уважуха! теперь мы ваши постоянные клиенты) я думаю разберемся точно
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
статьи об авто [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]статьи об авто[/url] .
This piece of writing is truly a nice one it assists new the web people, who are wishing
for blogging.
Fine way of describing, and nice post to obtain facts about my presentation subject, which i am going to deliver in college.
Наркологическая клиника в Воскресенске — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки «всё решить разговорами» и обещания «больше не пить» перестают работать. Зависимость редко возникает внезапно: сначала это кажутся безобидные посиделки по выходным, «снятие стресса» после работы, эпизодические эксперименты с наркотиками. Но с каждым месяцем контроль становится слабее, запои удлиняются, а привычка «расслабляться» превращается в болезненную потребность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]государственная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but,
I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing.
Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it improve
over time.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом новокузнецк[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Всем привет! Хороший магазин. Удачи и развития в дальнейшем!оТЛИЧНЫЙ МАГАЗ НАСЛЫШАН Спасибо за отзыв , а то заказывает много людей а отписываются единицы.
При вызовах в ночное время или в случаях с тяжелой интоксикацией стоимость может увеличиваться до 3000–4500 рублей. Окончательная сумма определяется после первичного осмотра и обсуждения индивидуальной схемы лечения с пациентом.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
Есть ситуации, когда визит к наркологу в Химках лучше воспринимать не как «стыдный шаг», а как обычное ответственное решение о своём здоровье. Это особенно актуально, если: употребление алкоголя или наркотиков стало регулярным, а попытки сократить дозы заканчиваются срывами; появились запои с несколькими днями непрерывного употребления; возникают проблемы с сердцем, давлением, сном; близкие всё чаще говорят, что «ситуация выходит из-под контроля».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра и диагностики. На этом этапе проводится сбор анамнеза, измеряются жизненно важные показатели (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) и определяется степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
This is nicely said. .
It is in point of fact a great and useful piece of info.
I’m satisfied that you simply shared this useful info with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
First off I would like to say great blog! I had a quick question in which I’d like to ask if you do not mind. I was interested to know how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing. I have had trouble clearing my mind in getting my ideas out. I truly do enjoy writing however it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are generally wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or tips? Appreciate it!
Стоимость услуг зависит от продолжительности терапии, сложности случая и выбранных процедур. Однако клиника предоставляет гибкую систему оплаты, включая рассрочку и страховое покрытие.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Чтобы не «дотягивать до утра», важно понимать тревожные признаки. Ниже — ориентиры, при которых тянуть опасно: перед списком подчеркнём, что финальное решение принимает врач после очной оценки состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя ногинск[/url]
Основные признаки, свидетельствующие о необходимости экстренной помощи:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnoyarsk/
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Добрый день, кто паникует и истерит, успокойтесь, всем все высылается постепенно. Треки придут на эл. почты ближайшее время всем ждущим.Списался с продавцом в аське, во вторник оплатил, сказали в среду отправят. когда спросил, сказали что не отправили по тех причинам из-за СПСР, обещали в четверг. Должно было придти в течении 3х рабочих дней. Сегодня понедельник, сижу на работе, и вот мне звонят, мол вам письмо пришло, куда доставить? То есть все верно, 3 дня как и говорили! Настроение теперь на весь день поднялось)) Вечером буду делать 1к10 (ам2233), потом отпишусь как и чего!!)) В общем доволен, но пока говорю только про доставку. Позднее отпишу доволен ли я всем остальным)) Достойный, проверенный временем магазин!
При критических симптомах (потеря сознания, сильная одышка, подозрение на инсульт/инфаркт) необходимо звонить 103/112. Мы подключимся к маршрутизации и организуем перевод в стационар.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-noginske
Многие семьи сталкиваются с трудностями, когда зависимый отказывается ехать в клинику. В таких случаях выездная помощь становится первым шагом к выздоровлению. Однако не все службы предлагают одинаково безопасный и профессиональный подход. Чтобы избежать рисков и ошибок, важно понимать, на что обращать внимание при выборе услуги “нарколог на дом”.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czeny-v-nizhnem-tagile
Критерий
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в нижнем тагиле[/url]
[url=https://rutor-12.com/]рутор ру[/url]: С добавлением более “мягких” формулировок (где это возможно)
Rutor: Непреходящая классика русскоязычного даркнета, выстоявшая против перемен
Rutor — форум с богатой историей в русскоязычном даркнете, ведущий свою активную деятельность с начала 2010-х. Он стал свидетелем эпохи “Гидры” и продолжил свою работу даже после ее упразднения в 2022 году. Смена владельцев в начале 2022 года не подорвала доверия к площадке, которая продолжает оставаться авторитетным местом для теневой торговли и обмена информацией.
– Центральное место на Rutor занимает торговый раздел, где пользователи могут найти предложения от проверенных поставщиков, специализирующихся на:
* Различных психоактивных субстанциях.
* Цифровых товарах и программном обеспечении.
* Услугах, направленных на обеспечение конфиденциальности, финансовые операции и OSINT.
– Для обеспечения безопасности осуществляемых сделок на Rutor действует механизм гаранта. Кроме того, для максимально конфиденциального общения предусмотрен встроенный мессенджер с функцией анонимных записок, которые не требуют привязки к учетной записи. Это снижает вероятность компрометации данных пользователей, даже если их аккаунт будет подвергнут риску.
– Доступ к Rutor предоставляется исключительно через защищенную сеть Tor по onion-ссылке. Процесс регистрации зачастую требует инвайта или дополнительной верификации, что служит барьером для автоматизированных систем и представителей правоохранительных органов. Модерация ориентирована на соблюдение деловых стандартов и поддержание репутации площадки, а не на жесткую цензуру.
– После перехода под новое руководство Rutor стал еще более эксклюзивным, однако сумел сохранить преданное сообщество и техническую надежность. Для многих он является не просто онлайн-площадкой, а отражением эволюции русского даркнета.
https://wazambadeposit.com/
журналы автомобильные [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]журналы автомобильные[/url] .
Процедура капельного введения лекарственных растворов проводится в условиях клиники с соблюдением всех санитарных норм. Пациенту устанавливается капельница, через которую вводятся препараты под контролем медперсонала. В зависимости от состояния пациента и тяжести запоя длительность капельной терапии может варьироваться от 1 до 6 часов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]наркологическая клиника стоимость[/url]
https://zzbel.ru Магаз вышел на связь, работает, но щас выходные 😀 с треками порешают, по ходу косяки СПСР. пробники БУДУТ !! Кто ещё будет гадить в теме “Трипы” и просить пробник – получит подзатыльник. У кого есть что сказать – отпишите лучше отзывы о товаре.Что задерживали грузы, с поставками, и дожидались пока запрет выйдет… Ну так ведь и не делаем не чотка . всё сразу .
This is a topic which is close to my heart…
Cheers! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Este é um dos melhores sites de jogos.
http://kenkyuukai.jp/event/event_detail_society.asp?id=52212&ref=calendar&rurl=https://booi-casino.info/
Хотите подтянутую фигуру? Забудьте о скучных стенах спортзала! Ваша стройная талия ждут вас на свежем воздухе. Культивация земли мотоблоком — это не просто рутина, а силовая тренировка на все тело.
Как это работает?
Подробнее на странице – [url=https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html]https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html[/url]
Мощные мышцы ног и ягодиц:
Управляя мотоблоком, вы постоянно идете по рыхлой земле, совершая усилие для движения вперед. Это равносильно интервальной ходьбе в гору.
Стальной пресс и кор:
Удержание руля и контроль направления заставляют стабилизировать положение тела. Каждая кочка — это естественная нагрузка на пресс.
Рельефные руки и плечи:
Повороты, подъемы, развороты тяжелой техники — это упражнения на бицепс, трицепс и плечи в чистом виде.
Смотрите наше видео-руководство: Мы покажем, как превратить работу в эффективную тренировку.
Ваш план похудения на грядках:
Разминка (5 минут): Наклоны к носкам. Кликните на иконку, чтобы увидеть полный комплекс.
Основная “тренировка” (60-90 минут): Вспашка, культивация, окучивание. Чередуйте интенсивность!
Заминка и растяжка (10 минут): Глубокое дыхание для восстановления. Пролистайте галерею с примерами упражнений.
Мотивационный счетчик: За час активной работы с мотоблоком средней мощности вы можете сжечь от 400 до 600 ккал! Это больше, чем занятие на эллипсоиде.
Итог: Прекрасный урожай осенью. Скачайте чек-лист “Огородный фитнес”. Пашите не только землю, но и лишние калории
We are a group of volunteers and opening a brand new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable information to work on. You have performed an impressive job and our whole group will likely be grateful to you.
https://arina-ws.ru братишки и сёстры всем мир и харе ругаться!жизнь прекраснаА за кладом я решил ехать на такси. продаван обещал разобраться по поводу 307. Надеюсь на скорейшее разрешение ситуации.
При своевременном обращении к специалистам капельница позволяет значительно улучшить состояние пациента уже в первые часы после начала лечения. Медицинская помощь при запое должна оказываться квалифицированно и в комфортных условиях, что снижает риски осложнений и ускоряет восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske/
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s tough to get that “perfect balance” between usability
and visual appeal. I must say that you’ve done a fantastic
job with this. In addition, the blog loads very quick
for me on Chrome. Superb Blog!
Thanks very interesting blog!
Услуга капельничного вывода из запоя на дому в Тюмени предоставляет комплексный подход к экстренному лечению алкогольной интоксикации. Врач приезжает на дом, проводит первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает индивидуальную схему терапии. Современные методы инфузионной терапии позволяют точно дозировать препараты, обеспечивая быструю детоксикацию и минимизируя риск осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в владимире[/url]
Когда человеку требуется немедленная медицинская помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, промедление может быть опасным. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением. Клиника «КрасМед Трезвость» в Красноярске организует срочный выезд врача круглосуточно, обеспечивая квалифицированную помощь прямо по месту нахождения пациента. Такой формат позволяет избежать госпитализации, снизить тревожность и начать лечение в привычных домашних условиях, где человек чувствует себя спокойнее и безопаснее.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом красноярск[/url]
https://shina-rostov.ru по ходу дела отпишусь.хм.. интересно сказал.. никогда не задумывался.. получается что толер от принятия одного вещества влияет на другое вещество??? Магазин ровнее не куда!!! Ребята отработали на славу, все четко и оперативно. Спасибо огромное, буду сотрудничать и дальше)
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
авто журнал [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]авто журнал[/url] .
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно[/url]
If some one desires to be updated with hottest technologies then he must be visit this website and be up to date everyday.
It’s actually very complicated in this full of activity life to listen news
on TV, thus I just use web for that reason, and take the most recent information.
https://zveng.ru трипы почитайте, кто уже бралпишут в асе, ваших треков мы не видим, с вами договаривался другой менеджер, типа вас вообще в списках нет, а до этого говорили посылка готова завтра отправят. Вчера оплатил, сегодня уже трек скинули. Пока все ровно, посмотрим что придет…..
Комплексное лечение на дому организовано по строго отлаженной схеме, позволяющей оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента и провести качественную детоксикацию.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в владимире[/url]
Aw, this was an exceptionally good post. Finding the time
and actual effort to produce a very good article… but
what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and never
seem to get nearly anything done.
Такой алгоритм помогает восстановить работоспособность организма в течение нескольких часов. После процедуры врач может оставить пациенту препараты для продолжения курса и назначить контрольный осмотр через день.
Подробнее тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnoyarsk
Основные признаки, свидетельствующие о необходимости экстренной помощи:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Решили вопрос с запретом на ввоз из параллельного импорта
my blog post :: https://wiki.anythingcanbehacked.com/index.php?title=Tamozhennoe-oformlenie_73q
Лечение зависимости требует не только физической детоксикации, но и работы с психоэмоциональным состоянием пациента. Психотерапевтическая поддержка помогает выявить глубинные причины зависимости, снизить уровень стресса и сформировать устойчивые навыки самоконтроля, что существенно снижает риск рецидивов.
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/narkolog-na-dom-ufa-czeny/
I think this is one of the most significant information for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on few
general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles is really great : D.
Good job, cheers
Площадка Rutor отличается хорошо зарекомендовавшей себя историей, высочайшей степенью скрытности и возможностью безопасной работы с транзакциями в сети Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutorsite.com]рутор это что такое[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Как обеспечиваются безопасность и анонимность на Rutor
Безопасность в Rutor занимает важное место. Сайт обеспечивает анонимный доступ к материалам, что поддерживается за счет использования современных технологий защиты транзакций и связи. Для дополнительной конфиденциальности часто рекомендуют использовать встроенный мессенджер, позволяющий пользователям безопасно обмениваться контактами и новыми данными, не подвергаясь цензуре и вмешательству третьих лиц.
Роль Rutor в экосистеме русскоязычного даркнета
Rutor до сих пор служит значимым источником свежей информации и новостей по направлениям взлома и кибербезопасности. Благодаря слабой цензуре и акценту на анонимность, сервис высоко ценится у пользователей, для которых важны свобода и защита личных сведений.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Тагиле представляет собой комплекс медицинских мероприятий, направленных на безопасное и эффективное прерывание состояния острого алкогольного отравления. Этот процесс требует профессионального подхода, так как самостоятельное прерывание запоя чревато серьезными осложнениями, включая судороги, инсульты и инфаркты. В медицинской практике используется комплекс мер, включающий детоксикацию организма, коррекцию водно-электролитного баланса и лечение симптомов абстиненции.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-v-nizhnem-tagile
Лечение в наркологической клинике в Чехове удобно не только близостью к дому. Главный плюс — комплексный подход. Зависимость практически никогда не ограничивается только алкоголем или наркотиком: страдают сердце и сосуды, печень, нервная система, психика, отношения в семье и на работе. Если пытаться лечить только одно звено, например, периодически «чистить кровь» капельницами, без проработки причин и последствий, ситуация быстро возвращается к исходной точке. В клинике выстраивается последовательная работа: сначала стабилизируют организм, затем укрепляют психику, а дальше помогают менять привычный образ жизни, чтобы трезвость стала не кратким эпизодом, а новой нормой.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Незамедлительно после вызова нарколог прибывает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. На данном этапе специалист собирает анамнез, измеряет жизненно важные показатели — пульс, артериальное давление, температуру — и оценивает степень интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir000.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru
Процедура проходит под контролем нарколога и медсестры. Если состояние пациента тяжёлое (галлюцинации, судороги, резкие перепады давления), проводится экстренная инфузионная терапия и подключается оборудование для мониторинга сердечного ритма и уровня кислорода. Такой подход исключает риски и делает процесс выведения из запоя максимально безопасным и управляемым.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
https://kleps.ru Метоксетамина, увы от 250 мг.Многие стучат нам по выходным и ночью, но мы живые люди и не можем 24 часа в день отвечать. ложь. 3 случая за полгода. Причем следили ли за самими людьми и что за ситуации – неизвестно. Если у вас свой магазин. то следите за его безопасностью. У вас нет данных об отправках, их количестве и количестве пришедших и не пришедших посылках. Просьба не раздувать данную тему без полной информации вышеперечисленной и важной уточненной дополнительной.
Выбор техники зависит от клинической картины, переносимости препаратов, психоэмоционального состояния и горизонта планируемой трезвости. Таблица ниже помогает сориентироваться в ключевых различиях — врач подробно разберёт нюансы на очной консультации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]medicinskij-centr-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Когда запой приводит к критическому ухудшению состояния, оперативное лечение становится жизненно необходимым. В Тюмени доступна услуга капельничного вывода из запоя на дому, которая позволяет начать детоксикацию организма незамедлительно и в комфортной для пациента обстановке. Такой формат терапии помогает не только вывести токсины, но и значительно снизить риск осложнений, сохраняя при этом полную конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru
Продолжительный запой приводит к накоплению токсинов в организме, нарушению работы внутренних органов и развитию серьезных осложнений. Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии алкогольной интоксикации, тем выше риск повреждения сердца, печени и почек. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет оперативно вывести токсины, восстановить нормальные обменные процессы и предотвратить развитие хронических заболеваний.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir000.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а целый комплекс мероприятий, направленных на очищение организма, восстановление обмена веществ и стабилизацию нервной системы. Когда человек находится в состоянии длительного употребления алкоголя, в крови накапливаются токсины, нарушается работа сердца, печени, почек и мозга. Без профессиональной помощи выйти из этого состояния безопасно невозможно. Клиника «ВладМед Трезвость» предлагает квалифицированный вывод из запоя во Владимире с использованием современных капельниц и мягких детокс-программ. Врачи работают круглосуточно, оказывая помощь как на дому, так и в комфортных условиях стационара.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иванов И.И., «без своевременной медицинской помощи при запое повышается риск необратимых изменений в организме и летального исхода».
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-nizhnem-tagile/
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра и диагностики. На этом этапе проводится сбор анамнеза, измеряются жизненно важные показатели (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) и определяется степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Для жителей Чехова важно и то, что врач видит не абстрактный «случай зависимости», а живого человека со своей историей. У кого-то за плечами десятилетия злоупотребления, у кого-то — несколько лет с быстрым прогрессированием, у кого-то — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или наркотиками. Всё это учитывается при выборе схем детокса, медикаментозного лечения, формата стационара или амбулаторного наблюдения. Дополнительно внимание уделяется безопасности: оценивается состояние сердца, давление, наличие хронических заболеваний, чтобы любая процедура проходила с минимальными рисками и под контролем.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-otzyvy[/url]
Запой — это не просто длительное употребление алкоголя, а тяжелое состояние, когда организм перестает функционировать нормально без постоянного поступления этанола. При запое происходит накопление токсинов, что ведет к нарушению работы внутренних органов и сильному ослаблению иммунной системы. Пациенты часто испытывают невыносимые физические и психические страдания, а попытки самостоятельно выйти из запоя только усугубляют ситуацию.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя красноярск[/url]
I am curious to find out what blog system you have been working with? I’m having some small security issues with my latest blog and I’d like to find something more risk-free. Do you have any solutions?
This is my first time go to see at here and i am truly happy to read all at single place.
https://share.google/qfcPKqspiCFV9zTee
Чем дольше продолжается запой, тем более непредсказуемой становится реакция организма. В первые дни человек может казаться «весёлым» и активным, но по мере накопления токсинов внешняя бодрость сменяется слабостью, головокружением, дрожью в руках, нарушением сна и памяти. Повышается артериальное давление, учащается пульс, появляется одышка даже при небольшой нагрузке. Любой стресс или дополнительное количество алкоголя в таком состоянии — серьёзное испытание для сердца и сосудов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому ивантеевка[/url]
Перед таблицей коротко поясним логику: мы выбираем самый безопасный маршрут именно для вашей ситуации, а при изменении состояния оперативно переключаемся на другой формат без пауз.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/]srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
https://niic-mrsk.ru в курске есть ваш магаз?Пиздец до сих пор мозги ебут( Надеюсь этот вопрос решится …….
Как проходит лечение:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в новокузнецке[/url]
Высокий уровень лечения обеспечивается квалификацией врачей, имеющих опыт работы в области наркологии, а также современным медицинским оборудованием, позволяющим проводить диагностику и лечение на самом высоком уровне. Врачи регулярно повышают квалификацию, участвуя в конференциях и обучающих программах. Подробности о квалификации специалистов доступны на портале медицинского сообщества.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в каменске-уральском[/url]
Наркологическая помощь в Первоуральске доступна в различных форматах: амбулаторно, стационарно и на дому. Однако не каждое учреждение может обеспечить необходимый уровень комплексной терапии, соответствующей стандартам Минздрава РФ и НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии. В этом материале мы рассмотрим ключевые особенности профессионального наркологического центра и критерии, которые помогут сделать осознанный выбор.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом новокузнецк.[/url]
Для вызова специалиста необходимо позвонить на горячую линию или оставить заявку через официальный сайт, например, на портале государственных услуг. Специалист приедет в оговоренное время, обеспечив полную анонимность и соблюдение медицинской тайны.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru
Как проходит лечение:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Выбор техники зависит от клинической картины, переносимости препаратов, психоэмоционального состояния и горизонта планируемой трезвости. Таблица ниже помогает сориентироваться в ключевых различиях — врач подробно разберёт нюансы на очной консультации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny[/url]
Все препараты проходят сертификацию и вводятся под контролем врача. При необходимости капельница может быть дополнена кислородной поддержкой или ингаляцией. Такой подход позволяет добиться быстрого эффекта без стресса для организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
Врач выясняет, как долго продолжается запой, какие симптомы наблюдаются и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный анализ полученной информации позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапевтическую стратегию и выбрать наилучшие методы детоксикации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir000.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя владимир[/url]
Rutor — известный форум darknet-пространства России с давней историей, анонимной регистрацией и сервисом для защиты транзакций посредством Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor7.com]рутор нет[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Меры защиты и анонимности пользователей Rutor
Система Rutor уделяет особое внимание вопросам безопасности. Платформа предоставляет анонимный просмотр контента благодаря применению новейших решений для защиты информации и коммуникаций. В целях увеличения приватности рекомендуется пользоваться внутренним мессенджером, который обеспечивает безопасный обмен контактной информацией и свежими данными без риска цензуры или слежки.
Значимость Rutor для даркнет-сообщества на русском языке
Площадка Rutor по-прежнему играет роль ключевого ресурса для обмена актуальными данными по безопасности и тематике взлома. Из-за ориентации на минимальную цензуру и приватность Rutor популярен у приверженцев свободного обмена данными и конфиденциальности.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Перспективы и риски
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Особенно тревожными сигналами являются проблемы со здоровьем. Скачки давления, одышка, сердцебиение, боли в груди, нарушения сна, приступы тревоги и паники — всё это говорит о том, что организм работает на пределе. При этом человек продолжает пить, несмотря на явные признаки перегрузки. Признаками того, что пора не откладывать обращение, становятся и изменения в поведении: раздражительность, вспышки агрессии, подозрительность, скрытность, замыкание в себе. Добавьте сюда конфликты дома и на работе, сорванные обязательства, скрытые долги — и становится понятно, что «подождать ещё немного» уже опасно. В такой момент консультация нарколога в Чехове и обсуждение возможного кодирования — не радикальная мера, а разумный шаг, который может предотвратить серьёзные медицинские и социальные последствия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vyezd-na-dom-v-chekhove/https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя на дому в балашихе[/url]
https://winunique7.com/
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-lobne/
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра и диагностики. На этом этапе проводится сбор анамнеза, измеряются жизненно важные показатели (пульс, артериальное давление, температура) и определяется степень алкогольной интоксикации. Эти данные являются основой для разработки индивидуального плана лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому недорого[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану отличный сервис, качество порадовало:)chemical-mix.com держи в репу, заработал.. пазитивно всё.. тут всё хорошо.. обращайтесь помогут быстро.. по крайней мере у меня было , все гуд
Профессиональная клиника никогда не скрывает информацию о своих сотрудниках. На официальных сайтах нередко размещены сканы дипломов, сведения о специализации и стаже, участие в отраслевых конференциях и проектах Минздрава.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-pervouralske/
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость требуют незамедлительного и комплексного вмешательства для предотвращения серьезных осложнений и сохранения здоровья пациента. В Уфе, Республика Башкортостан, опытные наркологи выезжают на дом 24 часа в сутки, предоставляя оперативную помощь при запоях и в случаях наркотической интоксикации. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать детоксикацию в комфортной, привычной обстановке, обеспечивая максимальную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Узнать больше – http://
Процедура вывода из запоя начинается с тщательной диагностики состояния пациента, чтобы определить, какие методы лечения будут наиболее эффективными. Мы применяем индивидуальный подход и комбинируем медикаментозное лечение с психотерапевтической поддержкой, что даёт лучший результат.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно новокузнецк[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Чехове для многих семей становится тем рубежом, после которого зависимость перестаёт казаться «временной слабостью» и начинает восприниматься как диагноз, с которым можно и нужно работать. До этого момента обычно проходят годы: чередуются запои и трезвые периоды, звучат обещания «больше такого не будет», меняются напитки, придумываются правила вроде «пью только по выходным» или «только пиво». Но рано или поздно семья замечает, что именно алкоголь диктует распорядок дня, влияет на настроение, разрушает здоровье и отношения. В этот момент становится очевидно: без сильного внешнего ограничителя и профессиональной помощи просто «взять себя в руки» уже не получается.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя в балашихе[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском разрабатывает программы лечения, учитывая особенности различных видов зависимости: алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Каждая программа ориентирована на индивидуальные потребности пациента, что подтверждается опытом ведущих российских реабилитационных центров. Подробнее о лечении зависимости читайте на официальном сайте Минздрава.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Что делает врач
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Выбирая нашу клинику, вы получаете следующие преимущества:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно воронеж[/url]
It’s truly very complicated in this full of activity life to listen news on TV, thus I just use internet for that purpose, and take the newest news.
Вывод из запоя — это управляемая медицинская процедура, а не «волшебная капля» или крепкий чай с рассолом. «Формула Трезвости» организует помощь в Ногинске круглосуточно: выезд врача на дом или приём в стационаре, детоксикация с мониторингом, мягкая коррекция сна и тревоги, подробный план на первые 48–72 часа. Мы действуем безопасно, конфиденциально и без «мелкого шрифта» — объясняем, что и зачем делаем, согласовываем схему и фиксируем смету до начала процедур.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-noginske
Hi everyone, it’s my first visit at this website, and piece of writing is truly fruitful in support of me, keep up posting these articles.
https://share.google/lKIkEvCFPiRUUWmSm
Если человек страдает от алкоголизма, запойное состояние требует незамедлительного вмешательства, особенно если признаки токсического отравления начинают угрожать жизни. Признаки запоя — это не только физическая зависимость, но и эмоциональные и психические расстройства, такие как тревога, агрессия и галлюцинации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены новокузнецк[/url]
На основе собранной информации формируется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает установку внутривенной капельницы. Через капельницу вводятся специально подобранные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса и нормализации работы внутренних органов. При необходимости назначаются дополнительные медикаменты для поддержки печени, сердца и нервной системы, а также для купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома. Врач постоянно контролирует состояние пациента и корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться оптимальных результатов. Завершающим этапом является подробная консультация, в ходе которой специалист дает рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике повторных эпизодов зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом в воронеже[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану еще раз какой городл1-й раз все было почти супер только менагер немного напутал ( но потом все доотправили ) Ребята, магаз ровный и немелочный, берите смело
Психотерапевтическое кодирование делает акцент на внутренней мотивации. Специалист помогает человеку увидеть реальную цену алкоголя в его жизни, понять, как именно употребление разрушает здоровье, семью, карьеру, и сформировать установку на трезвость на определённый срок. Используются техники внушения в состоянии расслабления и структурированная работа с убеждениями и привычками. Такой подход особенно полезен тем, кто боится «лекарственного вмешательства» или уже имеет негативный опыт неудачных медикаментозных попыток. В практике лечения в Чехове часто используются комбинированные схемы, когда медикаментозный барьер подкрепляется психотерапевтической поддержкой, а результат кодирования закрепляется за счёт изменения образа жизни и участия в реабилитационных программах.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ukolom-v-chekhove/
Запой – это состояние, когда организм требует постоянного поступления алкоголя для нормальной работы. Запой вызывает накопление вредных веществ, что негативно влияет на органы и иммунную систему. Не пытайтесь самостоятельно избавиться от запоя, это может навредить. Получите квалифицированную помощь на дому от клиники «Семья и Здоровье». Мы быстро приедем и окажем круглосуточную поддержку при запое. Длительное употребление алкоголя опасно для здоровья и жизни. Не ждите, пока станет слишком поздно, обратитесь за помощью при запое!
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя красноярск[/url]
Как подчёркивает заведующая кафедрой наркологии РМАНПО Минздрава России, «качество оказания помощи зависит не от количества процедур, а от правильной организации лечебного процесса и квалификации команды». Именно поэтому особенно важно понимать, какие параметры следует учитывать при выборе клиники.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника первоуральск[/url]
Man, slotspkr is kinda my go-to when I need a quick distraction. The interface is clean and the games are fun enough. I recommend you try slotspkr for some casual gaming.
Hey, just tried out go177game! Pretty slick interface, gotta say. Solid selection of games. Definitely worth checking out if you’re looking for something new. Find them here go177game
Heard some buzz about lucky22gamelogin. Logged in, played around. Decent, not gonna lie. Easy to get into. Worth a look if you’re hunting for something new to play. Check it lucky22gamelogin out
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-lobne
Вернуть здоровье и силы за одну процедуру позволяет грамотное сочетание препаратов, подобранное индивидуально под каждого пациента. Врач-нарколог оценивает тяжесть интоксикации, измеряет артериальное давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом, а при необходимости назначает экспресс-анализы. На основании этих данных создаётся персональный раствор для инфузии:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость балашиха[/url]
Портал Rutor признан лидером среди площадок русского даркнета за надёжный сервис, поддержание анонимности и обслуживание операций через Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor-24×7.com]rutor org официальный сайт вход[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Безопасность и анонимность на Rutor
Вопросы безопасности являются одними из ключевых на сервисе Rutor. Сервис гарантирует анонимность доступа к данным, используя прогрессивные системы шифрования транзакций и общения. Для сохранения анонимности и безопасного обмена контактами советуют применять специальный внутренний мессенджер, защищающий пользователей от вмешательства и контроля.
Влияние Rutor на сегмент русского даркнета
Площадка Rutor по-прежнему играет роль ключевого ресурса для обмена актуальными данными по безопасности и тематике взлома. Благодаря слабой цензуре и акценту на анонимность, сервис высоко ценится у пользователей, для которых важны свобода и защита личных сведений.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Запой – это серьезная проблема, когда организм перестает работать без постоянного поступления алкоголя. Из-за запоя токсины отравляют организм, нарушая работу органов и снижая иммунитет. Попытки самостоятельно бросить пить во время запоя могут привести к ухудшению самочувствия. «Семья и Здоровье» лечит запой на дому – это удобно и снижает стресс. Мы приедем в любое время суток и проведем все процедуры для восстановления здоровья. Длительное пьянство может привести к опасным для жизни осложнениям. Нельзя затягивать с лечением запоя, это может привести к серьезным последствиям.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk/
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, — это штат клиники. От опыта врачей напрямую зависит точность диагностики, подбор препаратов и эффективность психотерапевтической поддержки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника первоуральск[/url]
Обращение в местную клинику даёт важное преимущество — доступность. Здесь можно пройти диагностику, детоксикацию, вывод из запоя, курс лечения и реабилитации в привычном городе, без выснаживающих переездов. Пациенту легче решиться на стационар, когда он понимает, что близкие рядом и в любой момент могут приехать, поучаствовать в обсуждении плана терапии, привезти необходимые вещи. При этом подход остаётся профессиональным: учитываются стаж зависимости, сопутствующие заболевания, психоэмоциональное состояние, семейная ситуация. Лечение строится не вокруг одной «волшебной» процедуры, а как последовательный маршрут — от первой консультации до выхода в стабильную ремиссию.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]телефон наркологической клиники[/url]
https://dveri-spetsstal.ru Магазин ровный! Я заказал 1000ф, оплатил ЯД, оператора попросил отправить посыль на следующий день , без задержки т.к. сроки получения очень поджимают. На что оператор адекватно ответил что все сделают.На следующий вечер получил трек, посылочка собранна и вот вот выезжает))) если уже не выехала) Магазину как и его администрации – от души за оперативность и отношение к клиенту.бро много кидков, очень много покупай у проверенных магазинов (это которые на главной странице), а не у пользователей, и в чате не вздумай покупать только у ПРОВЕРЕННЫХ я серьезно!!! кинут вот опять сегодня получил что заказал всё прошло ровно .быстро ,качество в этом магазине лучшее ,больше не где не заказываю .если нужно что то подождать я лучше подожду чем кидал буду кормить ,тоже влитал поначалу пока нашёл этот магазин ,по этому сам беру и друзьям советую .спасибо всей команде за отличную работу.с наступающими праздниками всех поздравляю.вообщем всем благодарочка.
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]блекджек[/url]
Ожидаемый результат
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-noginsk7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-deshevo-v-noginske
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]атрибутика футбольных клубов[/url]
футбольная форма купить интернет магазин – [url=http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.ru/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://maps.google.cm/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://nick263.la.coocan.jp/TeamCaffeine/wwwboard.cgi/www.educ-ua7.ru/www.inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya1.ru]Спортивная экипировка и аксессуары для болельщиков от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 303da2a
Great delivery. Outstanding arguments. Keep up the good spirit.
I like what you guys are up too. This kind of clever work and reporting! Keep up the amazing works guys I’ve added you guys to our blogroll.
https://perevodiki.ru Привет всем бандиты? как дела у вас?боюсь что здесь произойдёт тоже самое, уж очень не внятно продавец общается. Приходите еще, всегда рады
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость оказывают разрушительное воздействие на организм, нарушая работу сердечно-сосудистой системы, печени, почек и головного мозга. Запои и передозировки приводят к острой интоксикации, которая без медицинской помощи может перерасти в поражение внутренних органов, психоз или даже летальный исход.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk00.ru/narkolog-lechenie-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
После вашего звонка нарколог выезжает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Прибыв на место, специалист проводит всесторонний медицинский осмотр, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез для определения степени интоксикации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]эротические фильмы[/url]
Проект Rutor — это проверенный временем магазин и коммуникационная система, обеспечивающая безопасность и анонимность сделок в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor2dark.com]darknet rutor[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Безопасность и анонимность на Rutor
Система Rutor уделяет особое внимание вопросам безопасности. Платформа предоставляет анонимный просмотр контента благодаря применению новейших решений для защиты информации и коммуникаций. Для дополнительной конфиденциальности часто рекомендуют использовать встроенный мессенджер, позволяющий пользователям безопасно обмениваться контактами и новыми данными, не подвергаясь цензуре и вмешательству третьих лиц.
Роль Rutor в экосистеме русскоязычного даркнета
Rutor продолжает оставаться важным каналом для получения новых данных и свежих новостей по теме взлома и безопасности. Благодаря слабой цензуре и акценту на анонимность, сервис высоко ценится у пользователей, для которых важны свобода и защита личных сведений.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Запой – это состояние, когда организм требует постоянного поступления алкоголя для нормальной работы. Запой вызывает накопление вредных веществ, что негативно влияет на органы и иммунную систему. Не пытайтесь самостоятельно избавиться от запоя, это может навредить. Получите квалифицированную помощь на дому от клиники «Семья и Здоровье». Мы быстро приедем и окажем круглосуточную поддержку при запое. Длительное употребление алкоголя опасно для здоровья и жизни. Не ждите, пока станет слишком поздно, обратитесь за помощью при запое!
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk/
Когда запой становится угрозой для здоровья, оперативное вмешательство имеет решающее значение. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, услуга «капельница от запоя на дому» помогает быстро начать детоксикацию организма, восстановить нормальный обмен веществ и стабилизировать работу внутренних органов. Такой метод лечения позволяет пациенту получить профессиональную медицинскую помощь в комфортной домашней обстановке, при этом сохраняя конфиденциальность и снижая эмоциональный стресс.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-vladimir/
Алгоритм одинаково прозрачен в обоих форматах. Сначала — экспресс-диагностика: уровень сознания, сатурация, пульс, давление, температура, оценка неврологического статуса и обезвоживания. Затем врач формирует индивидуальную инфузионную схему: регидратационные растворы, коррекция электролитов, поддержка печени и нервной системы, адресная симптоматическая помощь (сон, тревога, тошнота, головная боль). Темп и объём подбираются по переносимости — без «универсальных коктейлей» и лишних препаратов.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-pushkino7.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-v-pushkino/
Когда человеку требуется немедленная медицинская помощь при алкогольной интоксикации, промедление может быть опасным. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением. Клиника «КрасМед Трезвость» в Красноярске организует срочный выезд врача круглосуточно, обеспечивая квалифицированную помощь прямо по месту нахождения пациента. Такой формат позволяет избежать госпитализации, снизить тревожность и начать лечение в привычных домашних условиях, где человек чувствует себя спокойнее и безопаснее.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru
Как подчёркивает заведующая кафедрой наркологии РМАНПО Минздрава России, «качество оказания помощи зависит не от количества процедур, а от правильной организации лечебного процесса и квалификации команды». Именно поэтому особенно важно понимать, какие параметры следует учитывать при выборе клиники.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Процедура проходит под контролем нарколога и медсестры. Если состояние пациента тяжёлое (галлюцинации, судороги, резкие перепады давления), проводится экстренная инфузионная терапия и подключается оборудование для мониторинга сердечного ритма и уровня кислорода. Такой подход исключает риски и делает процесс выведения из запоя максимально безопасным и управляемым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
Very insightful post! I’ve been studying how statistical models
like the Kara model can outperform traditional betting methods.
Integrating Poisson distribution and ROI analysis is definitely the future of sports forecasting.
If anyone is interested in seeing how data-driven tips work in practice, I’ve been tracking some very interesting results lately.
Keep up the good work!
https://distonija.ru Ок понял спасибо.Магазин отличный, заказываю у него и всегда доволен ! всегда работают и делают свою работу на 5+
This piece of writing is truly a pleasant one it helps new web
visitors, who are wishing for blogging.
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какие симптомы наблюдаются и присутствуют ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный сбор информации позволяет оперативно подобрать необходимые медикаменты и начать детоксикацию.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen/
Когда запой становится критическим, оперативное вмешательство имеет решающее значение для спасения здоровья и предотвращения необратимых последствий. Во Владимире экстренная помощь нарколога на дому позволяет быстро начать лечение, не требуя госпитализации, что особенно важно для пациентов, нуждающихся в сохранении конфиденциальности и комфорте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir000.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
I’ve learn some good stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you set to create the sort of fantastic informative site.
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — быстро,качественно,с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональную установку за 1 день в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем практичный вариант натяжных потолков по вашему желанию;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор сатиновых полотен.
Ответим на вопросы — позвоните!
Потолки под ключ в кухне — любая сложность. В Архангельске — с гарантией результата-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки со световыми линиями высота[/url]
натяжные потолки со световыми линиями в архангельске высота – [url=https://www.29-potolok.ru]http://29-potolok.ru[/url]
[url=https://images.google.gg/url?sa=t&url=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://images.google.com.mm/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru/dzen.ru/index.html]Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 02427e0
Как работает
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-vidnoe7.ru/]dvojnoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Братья так же ровны как в совестсокм союзев Самаре трудится данный магазин? МАГАЗИН РАБОТАЕТ НОРМАЛЬНО!!! БЫЛИ МАЙСКИЕ ПРАЗДНИКИ И КУРЬЕРКИ НЕ РАБОТАЛИ ПОЭТОМУ ОНИ ТОЖЕ НЕ РАБОТАЛИ!!!
Платформа Rutor долгое время остаётся актуальной частью русскоязычного даркнета за счёт опыта, конфиденциальности и реализации операций через сеть Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor5.com/]руорг ру[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Безопасность и анонимность на Rutor
Система Rutor уделяет особое внимание вопросам безопасности. Сервис гарантирует анонимность доступа к данным, используя прогрессивные системы шифрования транзакций и общения. Для сохранения анонимности и безопасного обмена контактами советуют применять специальный внутренний мессенджер, защищающий пользователей от вмешательства и контроля.
Значимость Rutor для даркнет-сообщества на русском языке
Площадка Rutor по-прежнему играет роль ключевого ресурса для обмена актуальными данными по безопасности и тематике взлома. Из-за ориентации на минимальную цензуру и приватность Rutor популярен у приверженцев свободного обмена данными и конфиденциальности.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно онлайн бесплатно[/url]
Таможенное декларирование Москва выполнено быстро и корректно
Look at my website … https://www.toparma.com/sethtregurtha6
https://gidromotory-gprf.ru всем доброго дня) не подскажите, в беларусь(минск) можно сделать заказ с этого магазина ? или вообще хоьт какой нибудь магазин который в минск вышлет подскажите плз) ответ в лс плиз)Вы это о чем? Тут все вроде как только легальными делами занимаемся? Да и продавцу то я как никак доверяю свой адрес и телефон, почему он не может доверить мне кинуть сотку на телефон? Это ни к одному делу не пришьешь, раз мы уже заговорили об этом Всё шикарно,уже сидим с курим ваши бошки
Для повышения эффективности лечения наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные методы, включающие мониторинг жизненно важных параметров, корректировку фармакотерапии и оценку неврологических показателей. Совокупность таких мер делает процесс более предсказуемым и снижает вероятность осложнений. Кроме того, практическая часть работы включает регулярную проверку метаболических функций, что способствует точному дозированию препаратов и своевременному изменению схем. Это позволяет поддерживать физиологическую устойчивость организма даже при интенсивной нагрузке и сохранять стабильность состояния на протяжении всего периода терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-penza
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your website accidentally, and I’m surprised why this twist of fate did not took place in advance! I bookmarked it.
not working
_________________
[url=https://olimp-bet.reelridge.shop]олимпбеттегі тарихты ?алай жою?а болады[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану жду пока ответят, обана повдер кинул на 29000….но прочитал и понял что магаз супер, жду в скайпе селлера!По многочисленным восторженным откликам мн-001, тестировал его и был немного огорчен. вот уже час жду ответа в аське) все молчит)
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
This is nicely put. !
my web site; https://derpiet.de/lucky-lamb-cloudscout-faltbare-tragetasche-fuer-haustiere/
Стильная одежда является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность.
Правильно подобранный образ усиливает уверенность в себе.
Одежда часто становится инструментом визуального контакта.
https://hackernoon.com/preview/eyOmLYlleiJEzNQiJUza
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб экономит время в повседневных делах.
Со временем внимание к стилю формирует привычку.
В итоге стильная одежда остается элементом современного образа жизни.
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges.
It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Many thanks for sharing!
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]эротика[/url]
Некоторые состояния требуют немедленного вмешательства специалиста. Если алкогольное отравление или запойное состояние не купируется вовремя, это может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в иркутске[/url]
Когда основные симптомы устранены, пациенту необходим поддерживающий этап. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани дополнительно включает рекомендации по коррекции сна, восстановлению питания и снижению эмоционального напряжения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-astrakhan/
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а важный шаг на пути восстановления организма и возвращения человека к нормальной жизни. В клинике «ВладТрезвие Центр» пациенты получают профессиональную помощь, основанную на современных методиках детоксикации и безопасном медикаментозном восстановлении. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, а лечение подбирается с учётом возраста, состояния здоровья и продолжительности запоя. Наркологи центра выезжают на дом круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь даже в экстренных ситуациях, когда время играет ключевую роль.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в владивостоке[/url]
Наркологическая клиника выстраивает лечебные мероприятия в соответствии с алгоритмами, направленными на достижение стабильного состояния пациента. Важную роль играет последовательное выполнение процедур, включая оценку реакции организма и корректировку вмешательств. Формирование индивидуальной программы позволяет учитывать особенности каждого случая и поддерживать высокий уровень эффективности. Процесс наблюдения сопровождается непрерывным анализом, что делает терапию адаптивной и предсказуемой. В клинике соблюдается принцип многоуровневого контроля, обеспечивающий безопасность и стабильность лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр томск[/url]
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом иркутск[/url]
This is my first time visit at here and i am genuinely happy to read
everthing at single place.
Домашний формат особенно удобен на ранних этапах, когда зависимость уже дошла до запоев, но человек ещё продолжает работать, скрывать проблему от коллег и соседей, боится любой огласки. Для многих сама идея стационара воспринимается как признание поражения и начало какой-то «другой жизни», а до этого признания он просто не готов. Вызов нарколога на дом позволяет сделать первый шаг в более “щадящем” режиме: помощь приходит незаметно для окружающих, без транспортировки, оформления госпитализации и резкой смены обстановки.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-i-psihiatr-iz-himok[/url]
https://zveng.ru Привет бразы,тут ровно таримся не паримся,качества вышка,клад на уровнеСкиньте сайт ваш пожалуйста. Хорошо работает народ))
Диагностические данные формируют основу для дальнейших лечебных решений, от объёма инфузии до подбора поддерживающих препаратов.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-astrakhan/
I am in fact glad to glance at this weblog posts which contains lots of helpful data, thanks for providing these kinds of data.
Luxury watches continue to remain popular despite the rise of digital devices.
They are often seen as a mark of success and refined taste.
Skilled engineering plays a major role in their lasting value.
Many luxury watches are produced using carefully selected materials.
https://www.renderosity.com/users/id:1823632
They also represent a long tradition passed down through generations.
For collectors, these watches can serve as both practical items and long-term investments.
Elegant styling allows them to stay relevant across changing fashion trends.
Ultimately, luxury watches continue to attract admirers around the world.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-himkah/
Каждый из перечисленных элементов способствует формированию полной картины состояния пациента и позволяет корректно выстраивать терапевтические мероприятия. Такая структура создаёт основу для достижения устойчивых результатов и минимизации возможных осложнений. Использование таблиц наблюдения делает клинические процессы структурированными и понятными.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в томске[/url]
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru
Сигналом к тому, что пора обсудить вариант кодирования с наркологом, служит не один какой-то эпизод, а совокупность симптомов. Важно честно посмотреть на происходящее: насколько часто возникают срывы, как человек переносит трезвость, что происходит с его здоровьем и отношениями.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove[/url]
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah/
На нашем сайте вы можете скачать активатор для Windows 11 абсолютно бесплатно и навсегда забыть о водяных знаках!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Скачать активатор для Windows 11[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Этот магазин нериально всегда все четко делал, н ошиблись может случайно поговри я думаю решитсядлица окола часа очень даже не плохо Не поняла?
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов серебряная 250х3х0.1 мм Ср99.99 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а важный шаг на пути восстановления организма и возвращения человека к нормальной жизни. В клинике «ВладТрезвие Центр» пациенты получают профессиональную помощь, основанную на современных методиках детоксикации и безопасном медикаментозном восстановлении. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, а лечение подбирается с учётом возраста, состояния здоровья и продолжительности запоя. Наркологи центра выезжают на дом круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь даже в экстренных ситуациях, когда время играет ключевую роль.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в владивостоке[/url]
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Получить больше информации – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани проводится в условиях контролируемой терапии, ориентированной на устранение интоксикации и восстановление функционирования основных систем организма. При длительном употреблении спиртного нарушается работа печени, сердца и нервной системы, что требует профессионального вмешательства. Специалисты оценивают степень интоксикации, подбирают препараты и контролируют динамику стабилизации пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Всегда сохраняйте бдительность и здоровый скептицизм к подозрительным предложениям.
Ни при каких условиях не кликайте по подозрительным гиперссылкам в письмах от ненадежных источников.
Внимательно проверяйте подлинность веб-сайтов и компаний перед совершением покупки.
https://inlex-partners-moshenniki.blogspot.com/2025/09/inlex-partners.html
Не разглашайте конфиденциальные данные, такие как пароли или данные банковских карт, по сотовому.
Используйте двухэтапную аутентификацию для защиты своих ключевых аккаунтов.
Регулярно мониторьте выписки со своих финансовых счетов на предмет странных списаний.
Устанавливайте надежные защитные решения и обновляйте их своевременно.
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану А чего тут так тихо? Ребят, работаем?)..тот, который у Вас в подписи..)) слежка либо за магазином либо за курьеркой
Онлайн-казино [url=https://montazh-kryshy.ru/]1Win[/url] заняло прочные позиции на рынке гемблинга в России благодаря интуитивной навигации, широкому выбору игр и выгодной бонусной системе. Платформа предлагает казино, ставки на спорт и быстрые игры, что делает её универсальным сервисом для игроков с разными интересами. Лёгкая процедура регистрации, мобильная версия и надежность платформы способствуют приятному взаимодействию как с компьютера, так и со смартфона.
Сильной стороной 1win считается разнообразие игрового контента. В каталоге представлены слоты от популярных провайдеров, настольные игры, лайв-казино с настоящими ведущими и мгновенные игры. Это позволяет каждому пользователю выбрать подходящий формат — от классической рулетки и блэкджека до современных автоматов с бонусными раундами и накопительными призами.
Отдельного внимания заслуживает система поощрений платформы. Пользователи после регистрации могут получить приветственные предложения, а регулярные игроки — акции, кэшбэк и программу лояльности. Бонусы действуют как на казино, так и на ставки на спорт, что добавляет гибкости в использовании средств. Периодические предложения поддерживают интерес аудитории.
Следует отметить способам пополнения счёта и вывода средств, удобным для российских пользователей. Поддерживаются распространённые методы оплаты, банковские карты и другие методы платежей. В сочетании с оперативной поддержкой и простым интерфейсом это делает 1win привлекательной платформой для онлайн-игр, где пользователи могут получать удовольствие от игры.
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru
Вывод из запоя в клинике реализуется через поэтапное внедрение терапевтических решений, направленных на устранение токсической нагрузки и восстановление физиологической устойчивости. Важным элементом является определение клинического профиля пациента, включающего анализ анамнеза, текущего состояния и возможных сопутствующих факторов. На основе этих данных формируется индивидуальная программа помощи. Процедуры проводятся в условиях контролируемой безопасности, что снижает вероятность осложнений и позволяет достигать устойчивого терапевтического ответа. Последовательность действий формирует согласованную систему, удобную для мониторинга и анализа.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Если вы ищете качественный [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг центр[/url], обратитесь к нашим профессионалам.
Детейлинг центр – это специализированное место, где автомобили тщательно очищаются и восстанавливаются.
Одним из ключевых процессов является полировка кузова, при которой удаляются мелкие царапины и микротрещины.
Если вы ищете [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг кузова цена[/url], наш сервис предлагает профессиональный уход и восстановление вашего автомобиля на высшем уровне.
Первый раздел работы в детейлинг центре – тщательная мойка автомобиля.
The Casinoly Greece website is available in Greek and focuses
on the theme of Ancient Rome with carefully crafted graphics and symbols from the historical era.
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Работа строится на четкой структуре, определяющей порядок лечебных мероприятий. Ниже представлена последовательность основных этапов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого кемерово[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор качественных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы обеспечиваем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Опытная поддержка – наш стандарт – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы а также находить ответы под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
Наши товары:
Магний MAG 121 – BS 3370 Магний MAG 121 – BS 3370 – это высококачественная добавка, предназначенная для поддержки здоровья и активного образа жизни. Он способствует нормализации обмена веществ, улучшает работу мышц и нервной системы. Продукт активно используется спортсменами и людьми, стремящимися поддерживать свой уровень энергии. Каждый элемент формулы тщательно подобран для максимального эффекта. Вы можете купить Магний MAG 121 – BS 3370 для достижения оптимальных результатов в вашем режиме тренировок и восстановления. Инвестируйте в свое здоровье с поддержкой этого уникального комплекта!
Вывод из запоя требует комплексного контроля всех физиологических параметров. Ниже представлены основные направления наблюдения, формирующие структуру оценки состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Королёве часто становится тем самым рубежом, за которым заканчиваются бесконечные попытки «ограничить дозу» и «держать ситуацию под контролем» и начинается системная работа с зависимостью. Многие годами откладывают этот шаг: стыдно признать проблему, страшно довериться врачу, есть надежда, что «само пройдёт» или удастся остановиться силой воли. На практике всё происходит иначе: запои становятся длиннее, похмелье тяжелее, трезвые промежутки короче, а конфликты в семье и на работе — острее. В какой-то момент близкие понимают, что без серьёзной внешней опоры человек просто не справляется.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма в Королёве[/url]
Запой не всегда выглядит как откровенная катастрофа с первых дней. Иногда всё начинается с «отпуска», «праздника», пары вечеринок подряд. Родные надеются, что человек сам остановится, а он каждый день находит повод продолжить. В какой-то момент организм перестаёт справляться, и даже небольшие дозы алкоголя вызывают тяжёлые реакции.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Спасибо!Не надо!Заказывал Реагенг, всё нормально пришло, небольшой бонус порадовал, мелочь а приятно Огромное спасибо данному магазину, успехов вработе и процветания!!!?
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru
Платформа Rutor долгое время остаётся актуальной частью русскоязычного даркнета за счёт опыта, конфиденциальности и реализации операций через сеть Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutorforum24x7.co]rutorg org фильмы[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
цена создание сайта
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что обращаться к наркологу «рано» или «не по статусу». На практике именно такое откладывание часто приводит к затяжным запоям, тяжёлым состояниям и разрушению социальных связей. К специалистам имеет смысл обращаться при первых признаках того, что употребление алкоголя или наркотиков перестало быть эпизодическим и управляемым.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-himkah
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Заказали 2c-i и 2c-p. Как придет в магазине появятся позиции. может и еще что привезут из заказанного курительного.Благо им! Биза на высоту На ацетоне делай, он быстро выветривается и не пахнет совсем!
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя томск[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в кемерове[/url]
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this
blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its
a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback
would be greatly appreciated.
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I have really
loved surfing around your blog posts. In any case I
will be subscribing for your rss feed and I hope you write again very soon!
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно онлайн бесплатно[/url]
На практике семья часто обращается за помощью слишком поздно — когда близкий уже еле встаёт, не спит ночами, говорит странные вещи, а давление скачет так, что страшно оставлять одного. Чтобы не доводить до этого, важно знать признаки, при которых капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — не «желательно», а по-настоящему необходима.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимная[/url]
Анкеты индивидуалок Иркутска от 3000 рублей до 4000 рублей,
девушки стандарт+. Самые горячие индивидуалки Иркутска стоимостью
чуть выше среднего могут перенести вас в мир фантазий за считанные минуты.
Анкеты проституток Иркутска от 3000 до 4000 с фото и номерами телефона.
Индивидуалки Центр
Если ты ищешь интимного удовольствия в Шелехове близ
Иркутска – то ты на нужной странице.
Каталог анкет иркутских шлюх
из Шелехова специально для тебя.
Девчонки выполняют все сексуальные желания клиента, принимают в
уютных апартаментах или приезжают к вам в радиусе
Шелехова.
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru
Некоторые состояния требуют немедленного вмешательства специалиста. Если алкогольное отравление или запойное состояние не купируется вовремя, это может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Качество 2с очень порадовало, трип позже отпишу.бро незнаю скок раз брал ни разу TS не подводил входил в положения скидки бонусы делал!!! Вот это было бы нереально кул, а то я уже отчаялся через емейл к вам пробиться. Жду с нетерпением.
Admiring the time and energy you put into your website
and detailed information you provide. It’s awesome to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the
same outdated rehashed material. Excellent read!
I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my
Google account.
Наркологическая клиника использует комплексный подход к оценке состояния пациента, что обеспечивает высокий уровень контроля на всех этапах лечения. Такой формат работы позволяет детально изучать динамику процессов и своевременно корректировать вмешательства. В клинике применяется принцип последовательного наблюдения, при котором особое внимание уделяется соматическим и неврологическим проявлениям. Выбор терапевтических мер основывается на анализе объективных данных, что повышает предсказуемость результата. Подход ориентирован на постепенное восстановление функций организма с учетом индивидуальных особенностей.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru
Диагностические данные формируют основу для дальнейших лечебных решений, от объёма инфузии до подбора поддерживающих препаратов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/
Rutor — известный форум darknet-пространства России с давней историей, анонимной регистрацией и сервисом для защиты транзакций посредством Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutorforum.co]rutor su[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в краснодаре[/url]
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что обращаться к наркологу «рано» или «не по статусу». На практике именно такое откладывание часто приводит к затяжным запоям, тяжёлым состояниям и разрушению социальных связей. К специалистам имеет смысл обращаться при первых признаках того, что употребление алкоголя или наркотиков перестало быть эпизодическим и управляемым.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в ижевске[/url]
Есть ситуации, когда визит к наркологу в Химках лучше воспринимать не как «стыдный шаг», а как обычное ответственное решение о своём здоровье. Это особенно актуально, если: употребление алкоголя или наркотиков стало регулярным, а попытки сократить дозы заканчиваются срывами; появились запои с несколькими днями непрерывного употребления; возникают проблемы с сердцем, давлением, сном; близкие всё чаще говорят, что «ситуация выходит из-под контроля».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]наркологическая клиника в химках[/url]
сколько стоит создание сайта в интернете
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану фарту в бизеЧто то тут не так. понятно как проверенный магазин работает если отзывы негатив значит зачищает сообщений еще куча они на телефоне сейчас не могу их скопировать но и смысла нет все и так ясно
Если вы ищете [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг химчистка салона[/url], наш сервис предлагает профессиональный уход и восстановление вашего автомобиля на высшем уровне.
Затем используются специальные защитные средства для поддержания эффекта полировки.
Если вы ищете качественный [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг цена[/url], обратитесь к нашим профессионалам.
Покрытия, наносимые в центрах, защищают машину от внешних воздействий.
Уровень сервиса определяется опытностью персонала и качеством расходных материалов.
https://freespiritdelicacies.com Из 6 операторов именно оператор этого магазина отвечал быстрее и понятнее всех остальных. Я увидел здесь хорошее,грамотное отношение к клиентам, сразу видно человек знает свою работу.магазину респект jte тут брал кто?Как качество?К скольки делать?
Rutor — один из старейших ресурсов русского сегмента даркнета, обладающий известной историей, скрытной платформой и площадкой для защищённых обменов в системе Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor-or.cc]рутор поиск зеркало[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Королёве часто становится тем самым рубежом, за которым заканчиваются бесконечные попытки «ограничить дозу» и «держать ситуацию под контролем» и начинается системная работа с зависимостью. Многие годами откладывают этот шаг: стыдно признать проблему, страшно довериться врачу, есть надежда, что «само пройдёт» или удастся остановиться силой воли. На практике всё происходит иначе: запои становятся длиннее, похмелье тяжелее, трезвые промежутки короче, а конфликты в семье и на работе — острее. В какой-то момент близкие понимают, что без серьёзной внешней опоры человек просто не справляется.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма с выездом на дом[/url]
Наркологическая клиника опирается на комплексную модель оценки состояния, обеспечивающую последовательное восстановление функций организма. В клинике применяется система многоуровневого контроля, направленная на выявление нарушений и определение оптимальной тактики вмешательства. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать стабильность состояния даже в условиях выраженных клинических проявлений. Структурированная работа направлена на снижение токсической нагрузки, коррекцию метаболических процессов и восстановление адаптивных механизмов. Анализ проводится с учётом физиологических особенностей пациента и динамики изменений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в владивостоке[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]нарколог на дом бесплатно[/url]
Системная работа, которой характеризуется наркологическая клиника, предполагает последовательное исследование состояния пациента, анализ факторов риска и создание индивидуального терапевтического маршрута. Такой формат позволяет уточнять клиническую картину на ранних этапах и корректировать вмешательства по мере изменения состояния человека. Применение структурированных методик повышает предсказуемость результата и обеспечивает безопасность всех процедур. При этом выводы формируются на основании объективных данных наблюдения, лабораторных показателей и динамики симптомов. Оптимальная нагрузка распределяется на весь период лечения для достижения устойчивого эффекта без переутомления организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике пенза[/url]
В таких случаях наркологическая клиника помогает не только вывести из запоя и поставить капельницу, но и выстроить долгосрочный план: обследование, медикаментозную поддержку, реабилитацию, работу с психологом. Это даёт шанс не просто восстановиться после конкретного эпизода, а перестать повторять один и тот же разрушительный сценарий.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Наркологическая клиника опирается на комплексную модель оценки состояния, обеспечивающую последовательное восстановление функций организма. В клинике применяется система многоуровневого контроля, направленная на выявление нарушений и определение оптимальной тактики вмешательства. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать стабильность состояния даже в условиях выраженных клинических проявлений. Структурированная работа направлена на снижение токсической нагрузки, коррекцию метаболических процессов и восстановление адаптивных механизмов. Анализ проводится с учётом физиологических особенностей пациента и динамики изменений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://fa30.ru все хорошие отзывы все пишут нам лично в асю или скайп, как что то не так к нам особо не ломятся, все бегут на форум…. если есть какая то проблема вы нам сразу пишите и будем разбираться, мы всегда идем на встречу клиентам…на вкус – сода. такчто чставлю 100/100баллов магазу и
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — качественно, быстро и с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональную установку за 1 день в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем практичный вариант натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем монтаж любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор матовых полотен.
Ответим на вопросы — позвоните!
Натяжные потолки в ванной — любая расцветка. В Архангельске — с гарантией результата-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки в ванную в архангельске высота[/url]
натяжные потолки двухуровневые в архангельске высота – [url=https://www.29-potolok.ru/]https://29-potolok.ru[/url]
[url=http://toolbarqueries.google.com.ar/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]http://images.google.com.mm/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.frei-diplom2.ru/k.krakenwork.cc/www.1xbet-10.com/www.reiting-seo-kompanii.ru]Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 03da2a6
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/tomsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
Проект Rutor — это проверенный временем магазин и коммуникационная система, обеспечивающая безопасность и анонимность сделок в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutordarknet.com]rutorg[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
После купирования острых симптомов врач объясняет, какие шаги нужно сделать дальше: ограничиться домашним наблюдением, подумать о коротком стационарном курсе или сразу планировать дальнейшее лечение зависимости. Это помогает не возвращаться к затяжным запоям уже через несколько недель.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Из 6 операторов именно оператор этого магазина отвечал быстрее и понятнее всех остальных. Я увидел здесь хорошее,грамотное отношение к клиентам, сразу видно человек знает свою работу.Заказы опт , розница (отправка в регионы ,СНГ) ко мне! ТС подтвердив оплату, сказал ожидать. В оговоренные сроки адрес был получен в ЛС.
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в владивостоке[/url]
Для формирования структурированной модели используются стандартизированные алгоритмы. Ниже представлена последовательность действий, определяющих ход терапевтических мероприятий.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике томск[/url]
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
Thanks for any other informative blog. The place else
may just I get that kind of information written in such an ideal means?
I’ve a project that I am just now operating on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]взрослые игры[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]vyezd-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Домашний формат особенно удобен на ранних этапах, когда зависимость уже дошла до запоев, но человек ещё продолжает работать, скрывать проблему от коллег и соседей, боится любой огласки. Для многих сама идея стационара воспринимается как признание поражения и начало какой-то «другой жизни», а до этого признания он просто не готов. Вызов нарколога на дом позволяет сделать первый шаг в более “щадящем” режиме: помощь приходит незаметно для окружающих, без транспортировки, оформления госпитализации и резкой смены обстановки.
Подробнее – https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-himkah
https://astitvaias.org оформил заказ жду. продавец общительныйМне “типа фейк” назвал кодовое слово в жабере, которое я написал нашему розовоникому магазину в лс на форуме. Вопрос в том как он его узнал? Отлично! Ждём свои наборы юнного химика … 🙂 или наркомана… ?
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru
Платформа Rutor давно известна на русскоязычном даркнете, благодаря своей заслуженной репутации, анонимизации пользователей и инструментам надёжной передачи средств в Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor.pw]рутор зеркало рабочее сегодня[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Hello, I enjoy reading through your post. I wanted to write a
little comment to support you.
Опасность запоя в том, что каждый новый день употребления усиливает интоксикацию: растёт нагрузка на сердце и сосуды, печень перестаёт справляться с объёмом токсинов, мозг работает в режиме постоянного перегруза. Появляются угрозы инсульта, инфаркта, тяжёлых аритмий, судорог, психозов с галлюцинациями и агрессией. При этом сам зависимый чаще всего недооценивает риск: обещает «завтра точно прекратить», отказывается от врача, просит родных просто переждать и дать таблетку от головы. Но без грамотно подобранной терапии и контроля такое «перетерплю» может закончиться реанимацией. Поэтому, как только становится ясно, что человек не может самостоятельно прервать запой, разумное решение — обращаться за квалифицированной помощью по месту проживания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому отзывы[/url]
https://vsegoo.ru привет бразы, хочу нахватить вот реги, что за качество скажите? надеюсь не 15 минутка?Сделал очередной заказ в этом магазине:good: всё пришло качество как всегда радует буду дальше работать с вами:good:приятно иметь дела с ответственными партнёрами:voo-hoo: процветания вашему магазину:):):) Спустя 3 часа , началась небольшая депрессия(Со всем не большая)
Как специалист, я — Илья, уже много лет анализирую, как трансформируется структура тематических платформ.
За это время мне не раз приходилось замечать, как новички опираются на неактуальные ссылки, что в итоге приводит к неверным выводам.
В результате я всегда рекомендую опираться на обзорные источники, в которых данные структурирована комплексно и постоянно проверяется, в том числе и прямые ссылки на мега зеркало tor https://megadarknet.pro
Подобный подход позволяет оперативнее понять в общей картине избегая лишнего шума.
В итоге это даёт объективную понимание и снижает риски, связанные с использованием неактуальных адресов.
Вывод из запоя требует комплексного контроля всех физиологических параметров. Ниже представлены основные направления наблюдения, формирующие структуру оценки состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в ижевске[/url]
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru
Для формирования структурированной модели используются стандартизированные алгоритмы. Ниже представлена последовательность действий, определяющих ход терапевтических мероприятий.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske-otzyvy/
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
https://gypergidroz.ru Реально за***ли реклам-спаммеры :spam:, по две-три страницы одно и тоже, даже пропадает желание что либо читать…. таких как Nexswoodssteercan, Terroocomge, Vershearthopot, Soacomtimist и подобных надо сразу в баню отсылать, на вечно).Сервис то что надо, так держать! Да шляпа какая-то, менеджер работает из рук вон плохо, и валит все на курьера. Абсолютная неразбериха, понять, кто и в каком месте накосячил достоверно – просто невозможно, но тем не менее, факт остается фактом: больше недели я ожидаю отправку заказа, и это только отправка, причем, разумеется, с полной предоплатой. Общались с манагером через скайп и через аську, очень муторно, сообщения теряются, на оставленные мессаги в оффлайне не отвечает, да и в онлайне появляется довольно редко.
What’s up all, here every person is sharing these experience, therefore it’s fastidious to read
this weblog, and I used to pay a visit this webpage
daily.
Представленная таблица отражает ключевые направления наблюдения, обеспечивая систематизацию данных. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать высокий уровень контроля и адаптировать программу лечения с учетом динамики состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Для снятия алкогольной интоксикации врач проводит детоксикационную терапию, которая включает внутривенные инфузии с растворами для выведения токсинов, поддерживающие препараты для печени, сердечно-сосудистой системы и нервной системы. В некоторых случаях назначаются седативные средства, нормализующие эмоциональное состояние пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены иркутск[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс шоп[/url]
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-irkutsk/
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
https://alexandercasino777.com/
Наркологическая клиника в Химках ориентируется не на «среднестатистического пациента», а на конкретного человека с его историей, болезнями, образом жизни и семьёй. Поэтому здесь не ограничиваются одним-двумя шаблонными вариантами. Врач оценивает, на каком этапе сейчас находится пациент: острый запой, ломка, период относительной трезвости с риском срыва, рецидив после ремиссии. От этого зависит выбор формата помощи.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/
Первичная цель процедуры — безопасно устранить токсическую нагрузку и восстановить физиологические показатели без осложнений. Лечение подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый результат и минимизирует риски.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru
Ordering medicine online offers major convenience.
You can compare rates and items from different retailers effortlessly.
Home delivery is a key advantage, eliminating time for a trip to the pharmacy.
Online stores are often accessible around the clock for your needs.
https://b3.hypebeasts.ru/redirect.php?id=RALyrIooUk
The experience can be far more private than buying in person.
Many services offer helpful options like automatic refill services.
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану просто народу не верится в ассортимент и такие цены, да и по большинству продуктов отзывов нет ))Привет, нету в личке нечего. Закупались у данного магазина 100г реги, в подарок получили 15г скорос!1 клад надежный
Диагностические данные формируют основу для дальнейших лечебных решений, от объёма инфузии до подбора поддерживающих препаратов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]врач вывод из запоя астрахань[/url]
Ниже представлена последовательность основных шагов терапевтического процесса.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/narkolog-vladivostok-otzyvy/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Воскресенске — это место, куда можно обратиться в тот момент, когда домашние попытки «всё решить разговорами» и обещания «больше не пить» перестают работать. Зависимость редко возникает внезапно: сначала это кажутся безобидные посиделки по выходным, «снятие стресса» после работы, эпизодические эксперименты с наркотиками. Но с каждым месяцем контроль становится слабее, запои удлиняются, а привычка «расслабляться» превращается в болезненную потребность.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]voskresenskaya-klinika[/url]
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom/
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Все легально и проверено, есть NMR. Плохого ни чего не случиться. Скорей всего приняли потому что были паленые….а вот на фофу гнать нельзя… она на высоте… расширяться собираетесь?
Перед тем как выбрать формат лечения, пациенту и его близким объясняют, какие направления помощи доступны и как их можно сочетать. В зависимости от состояния и мотивации могут быть задействованы разные варианты:
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/
First of all I would like to say fantastic blog!
I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if you do not mind.
I was interested to find out how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing.
I’ve had difficulty clearing my thoughts in getting my ideas out.
I truly do enjoy writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are
generally wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or hints?
Kudos!
карнизы с электроприводом купить [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
Такой подход позволяет устранить физические последствия запоя и снизить психологическую зависимость. Уже после первой процедуры пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, появление аппетита и нормализацию сна. Важно не ограничиваться только экстренной помощью — специалисты рекомендуют пройти курс восстановления, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в владивостоке[/url]
Перед началом лечения пациент проходит первичную диагностику, которая включает оценку физических показателей, сбор информации о длительности употребления, выявление сопутствующих заболеваний и оценку рисков. Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани использует стандартизированные методы обследования, что позволяет точно определить степень интоксикации и подобрать адекватный лечебный план.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в астрахани[/url]
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану ровный магаз успеха и процветанияОплатил заказ, 3 дня прошло, статус все еще отложен. Сам ты не общительный ))
Looking well creates a positive first impression.
A attire communicates loudly before a person even say a single word.
It enhances your own self-esteem and mindset significantly.
Your put-together look signals competence in the office.
https://a2.gucci1.ru/sBois5JLVK1/
Stylish choices allow you to showcase your individual identity.
People often perceive well-dressed people as more successful and trustworthy.
Ultimately, putting effort in your style is an valuable step in your personal brand.
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование королев[/url]
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny[/url]
Системная работа, которой характеризуется наркологическая клиника, предполагает последовательное исследование состояния пациента, анализ факторов риска и создание индивидуального терапевтического маршрута. Такой формат позволяет уточнять клиническую картину на ранних этапах и корректировать вмешательства по мере изменения состояния человека. Применение структурированных методик повышает предсказуемость результата и обеспечивает безопасность всех процедур. При этом выводы формируются на основании объективных данных наблюдения, лабораторных показателей и динамики симптомов. Оптимальная нагрузка распределяется на весь период лечения для достижения устойчивого эффекта без переутомления организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/narkologicheskaya-poliklinika-penza/
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану Причем тут вообще он к нашему магазину ?Буду ждать доставку как чё отпишусь . качество интересует
Dressing stylish creates a positive first impression.
A attire communicates loudly before you actually say a word.
This boosts your own self-esteem and mood significantly.
Your put-together look signals competence in the office.
https://read.sneakero.ru/ne-tolko-odezhda-volshebstvo-zimmermann-159e/
Stylish clothing allow you to express your individual personality.
Others often judge stylish people as more successful and trustworthy.
Therefore, putting effort in your wardrobe is an valuable step in yourself.
Есть ситуации, когда визит к наркологу в Химках лучше воспринимать не как «стыдный шаг», а как обычное ответственное решение о своём здоровье. Это особенно актуально, если: употребление алкоголя или наркотиков стало регулярным, а попытки сократить дозы заканчиваются срывами; появились запои с несколькими днями непрерывного употребления; возникают проблемы с сердцем, давлением, сном; близкие всё чаще говорят, что «ситуация выходит из-под контроля».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru
Такое поэтапное лечение позволяет добиться устойчивого результата без стрессов и осложнений. Пациенты получают комплексную помощь, включающую как медицинские, так и психотерапевтические аспекты.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом в иркутске[/url]
Если вы ищете [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг центр[/url], наш сервис предлагает профессиональный уход и восстановление вашего автомобиля на высшем уровне.
Третий важный этап – комплексная чистка и защита внутреннего пространства автомобиля.
Перед тем как выбрать формат лечения, пациенту и его близким объясняют, какие направления помощи доступны и как их можно сочетать. В зависимости от состояния и мотивации могут быть задействованы разные варианты:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-korolyove/
I am genuinely grateful to the owner of this web site who has shared this enormous piece
of writing at at this place.
Nice blog here! Also your web site quite a bit up very fast!
What host are you the usage of? Can I am getting your affiliate link on your
host? I desire my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
купить кокаин, мефедрон, бошки, марихуану заказал вчера на пробу соточку мн. по прибытию отпишусь)Мы в Кургане не работаем, все наши представительства есть в соответствующем разделе. Не поняла?
Первичная цель процедуры — безопасно устранить токсическую нагрузку и восстановить физиологические показатели без осложнений. Лечение подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый результат и минимизирует риски.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Если вы ищете качественный [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг москва[/url], обратитесь к нашим профессионалам.
Такие составы защищают поверхность от грязи, влаги и солнечных лучей.
Покрытия, наносимые в центрах, защищают машину от внешних воздействий.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани предоставляет помощь пациентам, сталкивающимся с различными формами зависимости — алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Основой терапии является комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния, психотерапию и последующее наблюдение. Такой формат работы позволяет мягко купировать острые симптомы, восстановить физиологические функции и подготовить пациента к длительной реабилитации. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и с постоянным контролем врача.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
электрокарнизы [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-moskovskaya-oblast[/url]
Оформление вида на жительство за границей имеет ключевое значение.
Этот статус предоставляет законную возможность на длительное проживание в выбранной державе.
виза для девочек по вызову купить
Такое разрешение гарантирует доступ к национальному медицинскому обслуживанию.
Получение ВНЖ значительно упрощает процедуру финансового сотрудничества и открытия бизнеса.
Таким образом, данное удостоверение является первым этапом к ПМЖ или даже второму гражданству.
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru
Fine content Thanks a lot!
https://mobilityspecialists.net/family-caregiving
При gi?i quy?t вопроса о [url=https://yurist-razdel-imushchestva11.ru]консультация юриста по разделу имущества при разводе[/url] следует учитывать множество факторов и нюансов, чтобы избежать потенциальных конфликтов и обеспечить справедливое распределение активов.
При разделе имущества супруги часто сталкиваются с серьезными сложностями . Это связано с тем, что имущество часто представляет собой результат совместной работы и финансовых вкладов супругов . Поэтому следует искать компромисс и взаимопонимание.
Раздел имущества может быть осуществлен через судебное решение . Каждый из этих способов требует тщательного рассмотрения . При этом необходимо рассматривать финансовое положение супругов .
## Раздел 2: Юридические аспекты раздела имущества
Юридические аспекты раздела имущества включают в себя установление прав и обязанностей супругов. Это требует совместной работы с юристом . В некоторых случаях важно заключать соглашение о разделе имущества. При этом следует подходить к вопросу с гибкостью.
Раздел имущества может быть осуществлен в процессе развода . Каждый из этих вариантов требует тщательного рассмотрения . При этом необходимо рассматривать финансовое положение супругов . Кроме того, важно рассматривать вопросы страхования.
## Раздел 3: Практические советы по разделу имущества
При разделе имущества важно установить приоритеты. Это поможет найти взаимовыгодное решение . Кроме того, важно искать компромисс. При этом важно учитывать эмоциональную привязанность к имуществу .
Раздел имущества может быть облегчен с помощью специального программного обеспечения . Каждый из этих вариантов требует тщательного рассмотрения . При этом следует подходить к вопросу с гибкостью. Кроме того, следует искать поддержку у друзей и семьи .
## Раздел 4: Эмоциональные аспекты раздела имущества
Раздел имущества может быть серьезным?ением. Это связано с тем, что имущество часто представляет собой эмоциональную ценность . Поэтому важно заботиться о своем эмоциональном благополучии . При этом следует учитывать эмоциональное состояние другого супруга .
Раздел имущества может быть облегчен через поддержку близких . Каждый из этих вариантов имеет свои преимущества и недостатки . При этом важно быть открытым и честным . Кроме того, необходимо быть готовым к изменениям .
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Самостоятельные попытки «подлечиться» обычно сводятся к случайным комбинациям препаратов: кто-то пьёт горсть таблеток от давления и сердца, кто-то принимает успокоительные поверх алкоголя, кто-то заказывает непонятные средства «от тяги» в интернете. Такие эксперименты могут дать краткий эффект, но часто только маскируют симптомы и перегружают организм. В клинике лечение строится иначе: сначала оценивают состояние — физическое и психическое, затем подбирают безопасные схемы детоксикации и медикаментов, учитывая возраст, сопутствующие заболевания, длительность запоев и употребления. Это снижает риски осложнений и делает восстановление более управляемым: пациент и его семья видят прогресс и понимают, за счёт чего он происходит, а не живут в ожидании очередного непредсказуемого «отката».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в томске[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится строго по медицинским стандартам. Применяются современные капельницы, витамины и препараты для нормализации функций сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы. После снятия интоксикации врачи назначают поддерживающее лечение, направленное на стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в владивостоке[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Часто родственники тянут до последнего, надеясь, что запой «сам пройдёт», как это случалось раньше. Но с каждым эпизодом последствия становятся тяжелее: организм изнашивается, возрастает риск осложнений, ухудшается психика. Особенно опасно, когда запой длится несколько дней подряд, а любые попытки самостоятельно сократить дозы алкоголя сопровождаются дрожью, бессонницей, приступами паники.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Для самого пациента это шанс получить медицинское вмешательство без дополнительного стресс-фактора в виде транспорта, очередей и «больничной атмосферы». Он остаётся в привычной обстановке, в своей квартире, с теми же предметами, к которым привык, и это снижает сопротивление. Вместо жесткого сценария «либо немедленно в стационар, либо ничего» появляется промежуточный, более мягкий вариант: врачи приезжают домой, снимают остроту состояния, подбирают схему капельницы и медикаментов, объясняют, что делать дальше. Нередко именно после такого первого опыта человек впервые всерьёз задумывается о полноценном лечении, потому что ощущает реальную разницу в самочувствии до и после профессиональной помощи, а не просто очередной «опохмел».
Углубиться в тему – https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-srochno-v-himkah
Такой подход позволяет устранить физические последствия запоя и снизить психологическую зависимость. Уже после первой процедуры пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, появление аппетита и нормализацию сна. Важно не ограничиваться только экстренной помощью — специалисты рекомендуют пройти курс восстановления, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/czentr-kodirovaniya-alkogolizma-vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladivostok
Перечисленные меры обеспечивают структурированный подход к восстановлению, позволяя выстраивать лечение в соответствии с текущими изменениями. Такой формат способствует достижению устойчивой физиологической стабилизации и уменьшает выраженность симптомов. Для систематизации применяемых методов используется таблица, представленная ниже.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru
На фоне длительных запоев страдает не только физическое состояние. Обостряются тревога, раздражительность, обидчивость, возможны вспышки агрессии и неадекватные поступки. Для семьи это превращается в постоянное напряжение: никто не знает, чем закончится очередной день или ночь. Одновременно растёт риск психозов, когда человек может видеть и слышать то, чего нет на самом деле, путать реальность, быть опасным для себя и окружающих.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в кемерове[/url]
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
электрические гардины [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by
him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem. You are amazing!
Thanks!
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Углубиться в тему – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]наркологическая клиника в химках[/url]
Если вы ищете [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг москва[/url], наш сервис предлагает профессиональный уход и восстановление вашего автомобиля на высшем уровне.
Для долгосрочной защиты после полировки кузов покрывают специальными составами.
Потолки в Архангельске — качественно, быстро и с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем идеальное решение натяжных потолков под интерьер;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор глянцевых полотен.
Приедем на замер — свяжитесь с нами!
Натяжные потолки в комнате — любая расцветка. в Архангельском регионе — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потокли в архангельске[/url]
натяжные потолки архангельск высота – [url=http://29-potolok.ru]http://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.vu/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://www.google.tm/url?sa=t&url=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://filmstreaming4ever.00web.net/sonatine-1984-101049#comment-768552]Качественная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 427e0ae
888vi com
There is certainly a lot to learn about this topic. I like all the points you have made.
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в иркутске[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани предоставляет помощь пациентам, сталкивающимся с различными формами зависимости — алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Основой терапии является комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния, психотерапию и последующее наблюдение. Такой формат работы позволяет мягко купировать острые симптомы, восстановить физиологические функции и подготовить пациента к длительной реабилитации. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и с постоянным контролем врача.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма астрахань[/url]
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-stoimost[/url]
Системная работа, которой характеризуется наркологическая клиника, предполагает последовательное исследование состояния пациента, анализ факторов риска и создание индивидуального терапевтического маршрута. Такой формат позволяет уточнять клиническую картину на ранних этапах и корректировать вмешательства по мере изменения состояния человека. Применение структурированных методик повышает предсказуемость результата и обеспечивает безопасность всех процедур. При этом выводы формируются на основании объективных данных наблюдения, лабораторных показателей и динамики симптомов. Оптимальная нагрузка распределяется на весь период лечения для достижения устойчивого эффекта без переутомления организма.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza/
I all the time emailed this weblog post page to all my associates,
for the reason that if like to read it then my contacts will too.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Инструментальная квадратная поковка 150 мм 9Х1 ГОСТ 1133-71 Познакомьтесь с широким ассортиментом высокопрочных инструментов для обработки металла в категории инструментальной квадратной поковки от Редметсплав. Выбирайте из прочных и надежных материалов, подобранных специально для различных видов металлообработки. Гарантированное качество от ведущих производителей.
Наркологическая клиника использует методики, направленные на комплексную оценку состояния пациента. Работа строится на анализе анамнеза, исследовании соматических параметров и определении степени выраженности симптомов. Такой формат создаёт условия для точного подбора терапевтических мер. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, направленный на своевременное выявление отклонений и корректировку лечебных мероприятий. Благодаря этому достигается высокая стабильность клинического процесса и формируется благоприятная динамика восстановления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]вывода из запоя вызов[/url]
Для самого пациента это шанс получить медицинское вмешательство без дополнительного стресс-фактора в виде транспорта, очередей и «больничной атмосферы». Он остаётся в привычной обстановке, в своей квартире, с теми же предметами, к которым привык, и это снижает сопротивление. Вместо жесткого сценария «либо немедленно в стационар, либо ничего» появляется промежуточный, более мягкий вариант: врачи приезжают домой, снимают остроту состояния, подбирают схему капельницы и медикаментов, объясняют, что делать дальше. Нередко именно после такого первого опыта человек впервые всерьёз задумывается о полноценном лечении, потому что ощущает реальную разницу в самочувствии до и после профессиональной помощи, а не просто очередной «опохмел».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-v-himkah[/url]
Первичная цель процедуры — безопасно устранить токсическую нагрузку и восстановить физиологические показатели без осложнений. Лечение подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый результат и минимизирует риски.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя в астрахани[/url]
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом позволяет избежать стресса госпитализации, обеспечивая комфорт и удобство как для пациента, так и для его близких.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Некоторые состояния требуют немедленного вмешательства специалиста. Если алкогольное отравление или запойное состояние не купируется вовремя, это может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом в иркутске[/url]
Длительный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, способное нанести непоправимый вред организму. При отсутствии своевременного вмешательства алкогольная интоксикация может привести к серьезным осложнениям, таким как нарушение работы сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы, а также развитию алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях экстренная медицинская помощь является залогом спасения жизни и предотвращения необратимых последствий. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» предлагает круглосуточный выезд специалистов для вывода из запоя на дому в Краснодаре и по всему Краснодарскому краю. Наши врачи работают 24 часа в сутки, обеспечивая полный комплекс процедур по детоксикации, снятию абстинентного синдрома и восстановлению организма, при этом гарантируя полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Если вы ищете качественный [url=https://autotechtcentr24.ru/]детейлинг авто[/url], обратитесь к нашим профессионалам.
Защитные покрытия, применяемые в детейлинг центрах, оберегают кузов от неблагоприятных факторов.
Полировка кузова – важная процедура для устранения мелких дефектов и придания блеска.
Системная работа, которой характеризуется наркологическая клиника, предполагает последовательное исследование состояния пациента, анализ факторов риска и создание индивидуального терапевтического маршрута. Такой формат позволяет уточнять клиническую картину на ранних этапах и корректировать вмешательства по мере изменения состояния человека. Применение структурированных методик повышает предсказуемость результата и обеспечивает безопасность всех процедур. При этом выводы формируются на основании объективных данных наблюдения, лабораторных показателей и динамики симптомов. Оптимальная нагрузка распределяется на весь период лечения для достижения устойчивого эффекта без переутомления организма.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru
Часто именно жители Химок тянут до последнего: насыщенный ритм жизни, дорога на работу, постоянная усталость, попытки «снимать напряжение» алкоголем или психоактивными веществами. Сначала это кажется временным способом расслабиться, но со временем человек замечает, что пьёт чаще, чем планировал, нуждается в больших дозах, срывает обещания, а попытки контролировать употребление превращаются в череду неудач. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи дальше будет только сложнее.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-himkah/
Бесплатный ключ для Windows 11 — только у нас, обновлено в 2026 году!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Скачать ключ активации Windows 11 Pro[/url]
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IHJUI7TF
Диагностические данные формируют основу для дальнейших лечебных решений, от объёма инфузии до подбора поддерживающих препаратов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена астрахань[/url]
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог высококачественных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица товара подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы и предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
поставляемая продукция:
Полоса магниевая GD-MgAl4Si1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 Порошок магниевый G-MgZn5Th2Zr1 – DIN 1729 Part 2 предоставляет высокую прочность и отличные механические свойства. Этот материал широко применяется в производстве легких конструкций и деталей с высокой устойчивостью к коррозии. Основные преимущества порошка заключаются в его малом весе, высокой теплопроводности и устойчивости к высоким температурам. Для тех, кто хочет получить качественное сырье, настоятельно рекомендуем купить Порошок магниевый G-MgZn5Th2Zr1 – DIN 1729 Part 2. Обеспечьте эффективность своих проектов, выбирая только лучшее!
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-irkutsk
Лечение в клинике проходит поэтапно. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение устойчивого результата и восстановление здоровья. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием основных этапов лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника кемерово[/url]
Часто именно жители Химок тянут до последнего: насыщенный ритм жизни, дорога на работу, постоянная усталость, попытки «снимать напряжение» алкоголем или психоактивными веществами. Сначала это кажется временным способом расслабиться, но со временем человек замечает, что пьёт чаще, чем планировал, нуждается в больших дозах, срывает обещания, а попытки контролировать употребление превращаются в череду неудач. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи дальше будет только сложнее.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
На практике семья часто обращается за помощью слишком поздно — когда близкий уже еле встаёт, не спит ночами, говорит странные вещи, а давление скачет так, что страшно оставлять одного. Чтобы не доводить до этого, важно знать признаки, при которых капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — не «желательно», а по-настоящему необходима.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-srochno-v-dolgoprudnom/
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]турниры по покеру[/url]
Can you tell us more about this? I’d want to find out some additional information.
Капельница от запоя работает иначе. Через вену вводятся растворы, которые восполняют жидкость, разжижают кровь, помогают печени и почкам выводить токсичные вещества, корректируют электролитный баланс. Дополнительно используются препараты для снижения тревоги, нормализации сна, защиты сердечно-сосудистой системы и печени. Всё это подбирается индивидуально, с учётом возраста, давления, хронических заболеваний и длительности запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
На начальных этапах проблема редко проявляется в открытом виде, но уже есть характерные сигналы, на которые стоит обратить внимание. Человек начинает оправдывать употребление постоянной усталостью, проблемами на работе, напряжённой жизненной ситуацией. Появляется раздражение, если нет возможности выпить или принять привычную дозу, меняется круг общения, усиливается скрытность. Это время, когда помощь ещё может быть максимально щадящей по методам и по длительности, а вернуться к стабильной жизни намного проще, чем после многолетнего стажа употребления.
Подробнее – http://
Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани проводится в условиях контролируемой терапии, ориентированной на устранение интоксикации и восстановление функционирования основных систем организма. При длительном употреблении спиртного нарушается работа печени, сердца и нервной системы, что требует профессионального вмешательства. Специалисты оценивают степень интоксикации, подбирают препараты и контролируют динамику стабилизации пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя астрахань[/url]
Во внимание берутся не только масштаб и длительность запоев, но и изменения в поведении. Если человек регулярно обещает «завязать с понедельника», но каждый раз срывается, если рабочие задачи всё чаще выполняются с трудом, а любые стрессовые ситуации решаются «через стакан» или «через дозу», это прямой повод не ждать критического момента. Важно помнить, что зависимость — это прогрессирующее заболевание: со временем организму требуется всё больше вещества, растёт токсическая нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, ухудшается память и концентрация.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]klinika-narkologii-i-psihiatrii-moskva[/url]
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/tomsk-narkologicheskij-dispanser/
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and
i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback?
If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you
can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving me insane so any assistance is very much appreciated.
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
https://casinomirax.com/
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/narkolog-vladivostok-otzyvy
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy[/url]
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом иркутск[/url]
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladivostok
Представленная таблица отражает ключевые направления наблюдения, обеспечивая систематизацию данных. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать высокий уровень контроля и адаптировать программу лечения с учетом динамики состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru
Эти этапы формируют структуру комплексного лечения, позволяя добиться устойчивого результата и предотвращения повторных срывов.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/
В рамках лечения используются методы, позволяющие фиксировать изменения и оценивать реакцию организма на проводимые мероприятия. Они служат основой для выборочных корректировок и обеспечивают структурированный характер процесса. Отличительной особенностью становится возможность адаптировать лечебные схемы под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые направления оценки состояния, применяемые для формирования полной клинической картины.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Когда основные симптомы устранены, пациенту необходим поддерживающий этап. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани дополнительно включает рекомендации по коррекции сна, восстановлению питания и снижению эмоционального напряжения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого астрахань[/url]
Люблю сайт kazino olimp, он очень понятный в использовании!
https://j9.click/olimp809
Вызывать нарколога на дом рекомендуется при следующих состояниях:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это пространство, где пациенту помогают вернуться к жизни, свободной от зависимости, с заботой, уважением и индивидуальным подходом. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» реализованы комплексные программы терапии алкоголизма, наркомании и других зависимостей. Каждая программа адаптируется под конкретное состояние пациента и сочетает медицинские, психологические и социальные методы воздействия. Важное преимущество — полная анонимность, обеспечивающая комфорт и доверие со стороны пациентов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в кемерове[/url]
На фоне длительных запоев страдает не только физическое состояние. Обостряются тревога, раздражительность, обидчивость, возможны вспышки агрессии и неадекватные поступки. Для семьи это превращается в постоянное напряжение: никто не знает, чем закончится очередной день или ночь. Одновременно растёт риск психозов, когда человек может видеть и слышать то, чего нет на самом деле, путать реальность, быть опасным для себя и окружающих.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-oblast[/url]
After I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I receive 4 emails with the exact same comment. Perhaps there is an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Cheers!
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Кодирование не является чудесным выключателем тяги, но оно может стать сильным инструментом, который помогает закрепить решение бросить пить и даёт организму время восстановиться. Врач формирует у пациента устойчивую установку на отказ от алкоголя и подкрепляет её медикаментозно или психотерапевтически. При этом важен не только сам факт процедуры, но и то, как она встроена в общий план лечения: была ли проведена детоксикация, есть ли поддерживающая терапия, подключена ли реабилитация, работает ли семья с собственным выгоранием и созависимостью. Именно поэтому обращение за кодированием по месту жительства в Королёве удобно: можно не только выполнить саму процедуру, но и организовать наблюдение, при необходимости скорректировать тактику, не уезжая далеко от дома.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove[/url]
Cryptoboss Casino — онлайн-казино, которое хорошо вписывается в
домашний ритм, когда важно сменить обстановку, не выходя из дома.
Здесь нет визуального перегруза, а значит,
можно просто зайти на cruptoboss casino и
поиграть в комфортном для себя
темпе.
Подборка дисциплин позволяет варьировать уровень активности, а акции не отвлекают от основного процесса.
Звуковое оформление и визуальная часть
не перегружают, так что казино не перетягивает фокус на весь вечер.
Возможность играть без участия
в рейтингах
Минимум стресса при работе с финансами
Готовность помочь, когда это нужно
Если вам ближе комфорт, чем гонка,
такой стиль будет особенно удобен
Таблица позволяет поддерживать единую структуру наблюдения и фиксировать изменения состояния. Такая модель обеспечивает прозрачность процессов и повышает точность принимаемых решений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом ижевск[/url]
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-korolyove
Вывод из запоя требует комплексного контроля всех физиологических параметров. Ниже представлены основные направления наблюдения, формирующие структуру оценки состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бесплатные порно видео[/url]
Rutor — один из старейших ресурсов русского сегмента даркнета, обладающий известной историей, скрытной платформой и площадкой для защищённых обменов в системе Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor24x7.co]o xrutor org[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в иркутске[/url]
Преимущество такого подхода в том, что из этих «кирпичиков» можно собрать именно тот маршрут, который подходит конкретному человеку. Кому-то достаточно короткого стационарного курса с последующим наблюдением, кому-то — длительной реабилитации, а третьему важнее гибко сочетать лечение и работу.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ceny[/url]
В клинике работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты, психологи, реабилитологи. Вместо «универсальной» схемы каждому пациенту подбирают индивидуальный план, учитывая возраст, стаж употребления, состояние внутренних органов, психоэмоциональный фон, семейную ситуацию. Это особенно важно для жителей Долгопрудного, где многие совмещают работу в Москве с плотным графиком, и любая ошибка в лечении может дорого обойтись — потерей работоспособности, срывом деловых или личных планов.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Откладывая обращение к специалистам в Ивантеевке, семья берёт на себя двойную нагрузку — и моральную, и медицинскую. Домашние попытки «лечить» смесью случайных таблеток, седативов и народных средств часто маскируют симптомы, но не снимают основную угрозу. При этом ни у кого нет возможности круглосуточно контролировать давление, пульс, работу сердца. Именно поэтому безопасный вывод из запоя — это не ожидание «когда само пройдёт», а продуманный набор медицинских шагов под наблюдением врача.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ivanteevke/
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани предоставляет помощь пациентам, сталкивающимся с различными формами зависимости — алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Основой терапии является комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния, психотерапию и последующее наблюдение. Такой формат работы позволяет мягко купировать острые симптомы, восстановить физиологические функции и подготовить пациента к длительной реабилитации. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и с постоянным контролем врача.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника астрахань[/url]
всем привет https://cdck77.org екб есть в представителях, смотрите в представительствахсам знаешь что я могу про тебя сказать, ты лучший в своем деле! все всегда в срок! товар на высшем уровне , качество огонь ! сколько раз не брал всегда все ровно и четко! ждем твоего возвращения очень очень ждем, уже сходим с ума без тебя братан)) возвращайся скорей пиши в скайп, все работает, мне всегда отправляют, все на уровне
Сигналом к тому, что пора обсудить вариант кодирования с наркологом, служит не один какой-то эпизод, а совокупность симптомов. Важно честно посмотреть на происходящее: насколько часто возникают срывы, как человек переносит трезвость, что происходит с его здоровьем и отношениями.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/ehffektivnoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
Каждый из перечисленных элементов способствует формированию полной картины состояния пациента и позволяет корректно выстраивать терапевтические мероприятия. Такая структура создаёт основу для достижения устойчивых результатов и минимизации возможных осложнений. Использование таблиц наблюдения делает клинические процессы структурированными и понятными.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk/
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится только под медицинским наблюдением, так как самостоятельные попытки могут привести к осложнениям — аритмии, судорогам, резкому скачку давления. Именно поэтому наркологи центра уделяют особое внимание контролю жизненно важных показателей и плавному восстановлению организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
Первичная цель процедуры — безопасно устранить токсическую нагрузку и восстановить физиологические показатели без осложнений. Лечение подбирается индивидуально, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый результат и минимизирует риски.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя астрахань[/url]
Yes! Finally something about %keyword1%.
Чем дольше продолжается запой, тем более непредсказуемой становится реакция организма. В первые дни человек может казаться «весёлым» и активным, но по мере накопления токсинов внешняя бодрость сменяется слабостью, головокружением, дрожью в руках, нарушением сна и памяти. Повышается артериальное давление, учащается пульс, появляется одышка даже при небольшой нагрузке. Любой стресс или дополнительное количество алкоголя в таком состоянии — серьёзное испытание для сердца и сосудов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это пространство, где пациенту помогают вернуться к жизни, свободной от зависимости, с заботой, уважением и индивидуальным подходом. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» реализованы комплексные программы терапии алкоголизма, наркомании и других зависимостей. Каждая программа адаптируется под конкретное состояние пациента и сочетает медицинские, психологические и социальные методы воздействия. Важное преимущество — полная анонимность, обеспечивающая комфорт и доверие со стороны пациентов.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo-anonimno
If some one wishes to be updated with latest technologies afterward he must be pay a quick visit this site and be up to date
daily.
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
https://cz-my-blog-news.blogspot.com/2026/02/blog-post.html
кто последний раз когда брал? регу или соль мефедрон Отличный магаз парни! Удачи!СПб все ровно процветания магазину. Амф на 5+ пот теории 2мл растворителя на 1г основы,т.е на 150г 300мл.
Rutor — известный сервис с богатым прошлым, предоставляющий анонимный доступ и безопасность транзакций в пределах сети Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor8.cc]rutorg org зеркало[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Перспективы и риски
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Безопасность транзакций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok.
I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Основная процедура включает в себя:
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar
Диагностические данные формируют основу для дальнейших лечебных решений, от объёма инфузии до подбора поддерживающих препаратов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в томске[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
У вас есть свой сайт магазина? кокаин Пришел сегодня грамм 5-мео-дмт, все ок, но весов пока нет, а на глаз его в 2-3 раза меньше, чем, например, грамма 2с-е. Кто имел дело с ним, это у него плотность настолько больше или мне недосыпали?Чем аргументирует отказ работать с гарантом? “Что могу сказать Уважаемый Эскимос Я очень растроился в полученной Пробе И не хотелось выявлять Неготив в сторону твоего магазина”
Подобная структура наблюдения облегчает анализ изменений и способствует формированию объективной картины состояния. Наличие унифицированной системы контроля помогает выстраивать терапию последовательно и точно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Это ж надо ясненько также чуть только товарищи!
https://drive.google.com/file/d/11YSjmbYsOvgg-afcc4G0CpJy2Z2acmvg/view?usp=drive_link
Отыграем кару выставочный блеск. Надолго. Я что собак нерезанных сооружаем со местности инструктивных органов конвейере. Сколько) (сверху брата ярис чтобы нас — эпизодический проект, которую являются наша сестра уделяем яко эдакое количество бдительности, сколько стоит что поделаешь чтобы идеального результата. Наша цель — чтобы чемодан ярис чуждо счета ясно яко день блистал чрез некоторое время посещения буква нам, но (а) также сохранился воздухонепроницаемым на школа уговорах урбанический эксплуатации.Инженерия пригожести аюшки? одинаковый защиты. Наша христова невеста ладим шибздик проф химией первейших марок (Gyeon, CarPro) (в чем дело?) тоже ясненько видим, этакий эшелон надобен чтобы лака вашей марки или чтобы текстиль вашего салона. Являющийся глазам интимною собственностью штука — это без ясно яко день «прополоскать чего в свою очередь размельчить», в чем дело? тех. задача точно по возобновлению ясно длительной защите.Полная ясность равнозначащим персоной диалог. Спервоначалу нежели ухайдакать штучка, наша христова невеста ювелирски прокомментируем не этот операцию, демонстрируем образцы мануфактур да еще дадим четкие рекомендации. Ваша одолжение влетите ясно цвет общества, согласен что платите.
Посредством через орудие до велика налегай Чтоб вы целостных удобств!
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани предоставляет помощь пациентам, сталкивающимся с различными формами зависимости — алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Основой терапии является комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния, психотерапию и последующее наблюдение. Такой формат работы позволяет мягко купировать острые симптомы, восстановить физиологические функции и подготовить пациента к длительной реабилитации. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и с постоянным контролем врача.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This paragraph posted at this site is genuinely fastidious.
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,child
porn videos,child porn site,child porn website,child seks
porn,child porn situs web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child porn,porn child video,KONTOL,
chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,porn small child,child porn video,child gay porn,gay child porn,child
porn link,child porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,child porn vid,how
to watch child porn,porn mother and child,ai child porn,seks child porn,how to find child porn,child and mom
porn,watch child porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub child,porn mom and
child,gay porn child,child girl porn
Наркологическая клиника базирует свою работу на системной оценке состояния пациента и последовательном проведении лечебных мероприятий. Такой подход позволяет формировать устойчивую динамику восстановления и обеспечивать безопасность процедур. В клинике используется поэтапная модель наблюдения, в которой каждый шаг опирается на объективные данные обследований. Применение структурированных методик способствует снижению рисков и выстраиванию предсказуемой схемы терапии. Важным элементом становится контроль физиологических функций, обеспечивающий корректное распределение нагрузок и своевременную корректировку методов воздействия.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в владивостоке[/url]
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в томске[/url]
Платформа Rutor давно известна на русскоязычном даркнете, благодаря своей заслуженной репутации, анонимизации пользователей и инструментам надёжной передачи средств в Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor.date]rutor info не открывается[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Безопасность транзакций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
“Посторайтесь что бы такого больше не повторялось” https://egypt-go.ru P.S.Сколько раз брал в этом магазе ни разу нареканий не было)))Не сочтите за рекламуПриветствую ТС,сделал заказ,но до сих пор трек не пробивается,помоги разобраться в этом уже почти неделю жду,заранее спс заказал почти неделю назад ( 5 дней назад.) сказали товар кончился. ожидается разгрузка на склад. вот так и жду уже 5 дней. Раньше брал. все было быстро и честно. сейчас что-то затянулось слишком. вот сижу годаю. Прийдет мне товар или не прийдет
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом позволяет избежать стресса госпитализации, обеспечивая комфорт и удобство как для пациента, так и для его близких.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/psikhiatr-narkolog-na-dom-spb/
Запой не всегда выглядит как откровенная катастрофа с первых дней. Иногда всё начинается с «отпуска», «праздника», пары вечеринок подряд. Родные надеются, что человек сам остановится, а он каждый день находит повод продолжить. В какой-то момент организм перестаёт справляться, и даже небольшие дозы алкоголя вызывают тяжёлые реакции.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena[/url]
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,child porn videos,child porn site,
child porn situs,child seks porn,child porn web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child porn,porn child video,KONTOL,chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,porn small child,child porn video,
child gay porn,gay child porn,child porn link,child
porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,child porn vid,how to
watch child porn,porn mother and child,ai child porn,seks child porn,how to
find child porn,child and mom porn,watch child porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub child,porn mom and child,gay porn child,
child girl porn
magnificent submit, very informative. I’m wondering
why the other specialists of this sector don’t notice this.
You should proceed your writing. I am sure, you’ve a great readers’ base
already!
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my weblog
so i came to “return the favor”.I’m attempting to find things to improve my website!I suppose its ok
to use some of your ideas!!
Наркологическая клиника в Химках помогает не только тем, кто уже оказался в тяжёлом запое или прошёл через ломку. Сюда можно обратиться на любом этапе — от «злоупотребляю, но ещё работаю» до «запои повторяются, семья на грани, есть проблемы с давлением и сердцем». Чем раньше подключаются специалисты, тем мягче можно пройти период стабилизации и тем больше ресурсов удаётся сохранить — здоровье, отношения, работу, собственное чувство контроля над жизнью.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-himkah/
Обратиться за помощью могут как сами пациенты, так и их родственники. Часто именно близкие первыми замечают, что человек изменился: стал раздражительным, агрессивным или, наоборот, отстранённым, перестал выполнять обещания, начал скрывать доходы и траты. В клинике семья получает не только медицинскую помощь для зависимого, но и понятную стратегию действий: как разговаривать, как мотивировать на лечение, как не провоцировать конфликты и не усиливать чувство стыда у человека, который и так боится признаться себе в наличии болезни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]narkolog-besplatno-moskva[/url]
Кодирование не является чудесным выключателем тяги, но оно может стать сильным инструментом, который помогает закрепить решение бросить пить и даёт организму время восстановиться. Врач формирует у пациента устойчивую установку на отказ от алкоголя и подкрепляет её медикаментозно или психотерапевтически. При этом важен не только сам факт процедуры, но и то, как она встроена в общий план лечения: была ли проведена детоксикация, есть ли поддерживающая терапия, подключена ли реабилитация, работает ли семья с собственным выгоранием и созависимостью. Именно поэтому обращение за кодированием по месту жительства в Королёве удобно: можно не только выполнить саму процедуру, но и организовать наблюдение, при необходимости скорректировать тактику, не уезжая далеко от дома.
Подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/klinika-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение интоксикации организма, вызванной длительным употреблением алкоголя. В клинике «ПензаМед Трезвость» помощь оказывается профессионально и конфиденциально: пациенты могут получить лечение как в стационаре, так и на дому. Процесс включает использование капельниц, медикаментозную терапию, психоэмоциональную поддержку и последующую реабилитацию. Врачи наркологического центра обладают большим опытом работы и обеспечивают круглосуточную помощь без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для тех, кто хочет сохранить анонимность и быстро вернуться к нормальному состоянию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя пенза[/url]
отличный магазин! обращаюсь уже не первый месяц кокаин Магазин ровный, да вот менеджер не общительный ,пишу пишу …..спрошу здесь ,позиции в 5г СНМ-1000 отсутствует ???? а если есть, как заказ оформить на 5г через магазин,там только 10,50 и 100.спасибо ответили…. доволен Почему больше не забегаете ?
I needed to thank you for this good read!! I absolutely loved every bit of it. I’ve got you book-marked to look at new stuff you post…
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo-narkolog-na-dom-kapelnicza
Как отмечает нарколог Олег Васильев, «чем раньше пациент получает квалифицированную медицинскую помощь, тем меньше риск серьезных осложнений».
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-irkutsk
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Портал Rutor признан лидером среди площадок русского даркнета за надёжный сервис, поддержание анонимности и обслуживание операций через Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutorforum24.cc]new rutor search info[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book
in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to
drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is fantastic blog.
A fantastic read. I will definitely be back.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс[/url]
“ДОБРА ТЕБЕ ЭСКИМОСИК” https://familie-degu.ru Тусишка получается не саморй, но почти самой выгодной.Метоксетамин – цена и качество как и везде. Кто не хочет переплачивать – может брать все тут.что же это за дела то…..? Эйфора сейчас нет в наличии, если только индивидуальный заказ от 1кг.
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-korolev[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в кемерове[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится клиническая оценка, включающая измерение давления, осмотр кожи и глаз, проверку дыхания и анализ неврологического состояния. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани начинается только после сбора этих данных, поскольку подбор препаратов без диагностики может быть небезопасен.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого астрахань[/url]
Hurrah, that’s what I was searching for, what a information! present here at this website, thanks admin of this site.
I’m not sure where you are getting your info, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for great info I was looking for this information for my mission.
Все вопросы по контактам в подписе. https://artanasim.com Успехов вам господа : )Все есть, объем большой по выходным курьерки не работают, соответственно и отправить мы не можем, отправки производятся в рабочии дни!
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account
your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and
even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
https://babu88cas.com/
Мессенджер и магазин Rutor признан одним из самых безопасных ресурсов в русском даркнете, благодаря анонимности системы, конфиденциальности и поддержке платежей в Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutorforum24x7.cc]рутор ссылки[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Перспективы и риски
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
косметология красоты услуги центра косметологии
Reputation management is the deliberate practice of shaping public perceptions of a company or individual.
It involves actively tracking what is being discussed about you on the internet.
The goal is to highlight positive information and mitigate any negative comments or criticism.
This frequently includes engaging with customer reviews on various websites.
https://www.myminifactory.com/users/8226mary
A vital component is optimizing search engine listings for relevant search terms.
Effective ORM helps establish trust and protect a strong digital image.
Ultimately, it is an essential practice for any contemporary business or public figure.
Free bot for Telegram creating presents, subscriptions. Incredible boost channels!
Netxmix offers for you this powerful Telegram bot:
1) Creating presents
Now you’re able to make custom freebie, including special access, data, photos, clips, images, coupons, special coupons, promo discounts, promo codes, etc., plus a specific requirement for receiving this gift. In particular, requirement for receiving the gift is joining to the channels you set while making + a certain amount of visits to your invite link in the bot.
You can try our free option to do this; however, to use it, you need to subscribe to a few TG channels in your channel list.
Just visit our bot @netxmixbot click “START” after that press “FREE GIFT”.
Next Create premium access to channels and groups
You can make paid subscriptions in your TG channels and groups using Netxmix bot. Payments will be automated in crypto.
To make a paid membership, you need to visit the bot @netxmixbot tap “START” – profile – channels then add.
In our bot it’s possible to discover many freebies people earlier created, all you’re able to receive absolutely for free.
Just click “gifts” option in our bot.
Check it out – t.me/netxmixbot
Completely free new over 10B ChatGPT, TV, Google, Google Drive, Steam, gaming, private networks, Discord, Telegram, cloud, etc DBs inside TG bot.
To get databases please open direct link or simply enter /start at @netxmixbot, select GIFTS inside bot, pick category ULP-DBs, NET-Archives, NCloud after that tap on DB.
262M updated data in cryptocurrency users:
@netxmixbot?start=gift_1
10+ billions new real data from financial, media, app activity:
t.me/netxmixbot?start=gift_4
Lots of additional data inside, simply join @netxmixbot to get new data each day:
t.me/netxmixbot
кто знает когда рега будет ? https://humanaidbd.org Да все так и есть! Присоединюсь к словам написанным выше! Очень ждём хороший и мощный продукт!и вот я решил зайти на ветку доверенных магазинов! и почему то решил ткнуть именно на ссылку чемикл микс! захожу дыбанул на ценник, устроило и даже очень! так же порадовало то что тут делают отправку! а это значит то что если товар отправят то ты его 100% получишь! главная особенность магазина в том что отправка делается от 5грамм 🙂 а это значит то что я смогу и опробывать товар и убидится в качестве товара, и в надежности магазина! Оплатил заказ, жду селлера.
Ontdek het meest betrouwbare casino zonder CRUKS voor spelers uit Nederland!
Hoge bonussen, snelle uitbetalingen en een enorme
keuze aan spellen in de beste casino’s zonder CRUKS 2026
Стильный вид создает первое впечатление о вас.
Ваш образ работает на оценку вас окружающими сразу.
Уверенность в своем луке укрепляет личную самооценку.
Он подчеркивает ваш уровень ответственности и уважение к мелочам.
https://z2.sochidaily.ru/redirect.php?id=cPJ8rybeq1Hi
Через одежду вы имеете шанс проявить свою личность и вкус.
Люди неосознанно воспринимают опрятных индивидов как более успешных.
Следовательно, инвестиции в свой стиль — это вклад в свое успешное будущее.
Hurrah! In the end I got a blog from where I can really take valuable facts regarding my study and knowledge.
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
Искать пришлось часа два!!! Фото не понятное было. Но нашёл всё таки. Забрал 1г ск крисов. Качество супер. Тёлка визжит просто) Спасибо https://istracom.ru челяба есть?спасибо за инфу , но только узнал про новый список запвеществ , чувствую вся лавочка прикроется на некоторое время … Хороших продаж!
Наркологическая клиника опирается на комплексную модель оценки состояния, обеспечивающую последовательное восстановление функций организма. В клинике применяется система многоуровневого контроля, направленная на выявление нарушений и определение оптимальной тактики вмешательства. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать стабильность состояния даже в условиях выраженных клинических проявлений. Структурированная работа направлена на снижение токсической нагрузки, коррекцию метаболических процессов и восстановление адаптивных механизмов. Анализ проводится с учётом физиологических особенностей пациента и динамики изменений.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]бесплатные порно видео[/url]
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content.
Please let me know. Thank you
Скачайте активатор для Windows 11 и получите все функции Pro-версии бесплатно.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Windows 11 активатор без вирусов[/url]
https://casino-marvel.com/
This is a very informative article and I really appreciate how clearly everything is explained.
Many people find it confusing when choosing the right online casino, and this post
explains the topic in a simple way.
The information about performance is useful, especially for users who are interested in SBOBET.
Thanks for sharing this practical content.
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Да,мне тоже первый класс как то ближе и недорого… https://istracom.ru всем мир! скажите магаз ровный? ато написал на мыло им и ни ответа ни привета!Ждать возможно придется дольше обычного, я ожидал 12 рабочих, не считая праздников.. Вы это о чем? Тут все вроде как только легальными делами занимаемся? Да и продавцу то я как никак доверяю свой адрес и телефон, почему он не может доверить мне кинуть сотку на телефон? Это ни к одному делу не пришьешь, раз мы уже заговорили об этом
Наркологическая клиника в Чехове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, не выезжая в крупный мегаполис и не тратя силы на долгую дорогу. Для многих людей момент обращения к наркологу наступает не сразу: сначала идут «домашние» попытки справиться с проблемой, обещания ограничиться «по праздникам», уговаривания родственников и периодические срывы. Запои становятся длиннее, организм восстанавливается всё хуже, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон, учащаются конфликты дома и на работе. В какой-то момент становится понятно, что без системного лечения обойтись уже нельзя, а стихийные капельницы на дому и случайные советы из интернета только оттягивают время.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru
На фоне длительных запоев страдает не только физическое состояние. Обостряются тревога, раздражительность, обидчивость, возможны вспышки агрессии и неадекватные поступки. Для семьи это превращается в постоянное напряжение: никто не знает, чем закончится очередной день или ночь. Одновременно растёт риск психозов, когда человек может видеть и слышать то, чего нет на самом деле, путать реальность, быть опасным для себя и окружающих.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Наша наркологическая клиника предоставляет круглосуточную помощь, использует только сертифицированные медикаменты и строго соблюдает полную конфиденциальность лечения.
Получить больше информации – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-sochi
На основании первичного осмотра специалист подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Это обычно включает постановку внутривенных капельниц с растворами для быстрого выведения токсинов, стабилизации водно-электролитного баланса и поддержки работы печени, сердца и нервной системы. По мере необходимости врач назначает седативные и кардиопротекторные препараты для стабилизации психоэмоционального состояния пациента и снижения нагрузки на сердце.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в екатеринбурге[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru
Такой подход позволяет устранить физические последствия запоя и снизить психологическую зависимость. Уже после первой процедуры пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, появление аппетита и нормализацию сна. Важно не ограничиваться только экстренной помощью — специалисты рекомендуют пройти курс восстановления, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника в владивостоке[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Hello to all, for the reason that I am really keen of reading this website’s post to be updated daily. It contains good stuff.
Для получения устойчивого результата наркологическая клиника использует методы, основанные на индивидуальной оценке. В работе учитываются соматические показатели, реакции нервной системы и данные лабораторных исследований. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает предсказуемое влияние на физиологические процессы и снижает вероятность осложнений. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, позволяющий своевременно корректировать лечебные меры. Работа направлена на нормализацию метаболизма, восстановление баланса внутренних систем и плавное уменьшение симптоматики.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Для эффективного лечения алкогольной интоксикации и восстановления организма врачи клиники «АлкоДоктор» используют комплекс препаратов, которые индивидуально подбираются с учетом состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена в сочи[/url]
Эта статья подробно расскажет о процессе выздоровления, который включает в себя эмоциональную, физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Мы обсуждаем значимость поддержки и наличие профессиональных программ. Читатели узнают, как строить новую жизнь и не возвращаться к старым привычкам.
Получить больше информации – http://142.250.123.112/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Магазин замечательный!! https://familie-degu.ru Заказал , получил трэк , ждем)Ну вообще то весь ассортимент выложен в теме “Прайс-Лист”. Там все написано. Всем привет,брал у данного магазина. качество на уровне! спрятано просто огонь,клад четкий!!!
Обычно работа строится по этапам, где каждый шаг логически продолжает предыдущий:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Чехове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, не выезжая в крупный мегаполис и не тратя силы на долгую дорогу. Для многих людей момент обращения к наркологу наступает не сразу: сначала идут «домашние» попытки справиться с проблемой, обещания ограничиться «по праздникам», уговаривания родственников и периодические срывы. Запои становятся длиннее, организм восстанавливается всё хуже, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон, учащаются конфликты дома и на работе. В какой-то момент становится понятно, что без системного лечения обойтись уже нельзя, а стихийные капельницы на дому и случайные советы из интернета только оттягивают время.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]chastnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki-otzyvy[/url]
Hi to every body, it’s my first visit of this weblog; this website consists of remarkable and in fact good stuff designed for readers.
https://apoclan.ru/
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в кемерове[/url]
В данной статье рассматриваются проблемы общественного здоровья и социальные факторы, влияющие на него. Мы акцентируем внимание на значении профилактики и осведомленности в защите здоровья на уровне общества. Читатели смогут узнать о новых инициативах и программах, направленных на улучшение здоровья населения.
Узнать больше – http://142.250.74.227/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в владивостоке[/url]
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя круглосуточно балашиха[/url]
После оформления заявки на сайте narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru или по телефону, оператор уточняет информацию о пациенте: возраст, длительность запоя, наличие хронических заболеваний, текущее самочувствие. В течение 30–60 минут дежурный специалист приезжает по адресу с полным комплектом оборудования и медикаментов.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-krasnogorske
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника ижевск[/url]
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vyzov narkologa na dom[/url]
Удобство и современный дизайн обеспечат [url=https://electro-rulon.ru] рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом Прокарниз [/url], которыми легко управлять с пульта или смартфона.
Стоит проверить, насколько хорошо шторы интегрируются с вашей системой автоматики.
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
Могу сфотать, на смотри https://tuguru.ru а что с магазином в Петрозаводске,работать то будете дальше,а то уже неделю не какой активности.Подскажите пожалуйста товары указаные в прайсе все в наличии или нет? Принял, участие в совместке номер 3, кинг как и подобает этому магазу, все сделал со скоростью звука, прошло 5 дней после оплаты и у меня в руках лежат 50 тонн этой велеколепной вкусняшки, СПАСИБО. Я просто не понимаю как люди заказывают у других когда есть chemical
Наркологическая клиника опирается на комплексную модель оценки состояния, обеспечивающую последовательное восстановление функций организма. В клинике применяется система многоуровневого контроля, направленная на выявление нарушений и определение оптимальной тактики вмешательства. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать стабильность состояния даже в условиях выраженных клинических проявлений. Структурированная работа направлена на снижение токсической нагрузки, коррекцию метаболических процессов и восстановление адаптивных механизмов. Анализ проводится с учётом физиологических особенностей пациента и динамики изменений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в екатеринбурге[/url]
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/
Great delivery. Great arguments. Keep up the amazing spirit.
Do you love gambling? https://cryptodepositcasinos.com allow you to play online using Bitcoin and altcoins. Enjoy fast deposits, instant payouts, privacy, slots, and live dealer games on reliable, crypto-friendly platforms.
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Discover the rejuvenating effects of [url=http://glamkorea.com/]numbing cream for injections[/url] for effective mesotherapy injections that enhance your skin’s vitality and glow.
In conclusion, mesotherapy injections offer a flexible approach to skincare and body contouring.
Для надежной защиты воды от загрязнений идеально подойдет [url=http://mybestpool.ru/]укрывной тент для бассейна[/url].
Пленочные тенты являются самым бюджетным вариантом и обеспечивают базовую защиту.
Очищение организма — ключевой этап в лечении зависимости. В клинике «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» применяются разные виды капельниц, которые помогают ускорить детоксикацию, восстановить водно-солевой баланс и улучшить работу органов. В таблице приведены основные виды инфузионных программ, применяемых при выезде нарколога на дом и в стационаре:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ижевск[/url]
раньше вообще все говорили то что не растворяется это бутор а щас как я понимаю это в порядке вещей Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? Длительность не меньше, чем у CHM-400F (AKB48F), эффект – задумчивее )сам знаешь что я могу про тебя сказать, ты лучший в своем деле! все всегда в срок! товар на высшем уровне , качество огонь ! сколько раз не брал всегда все ровно и четко! ждем твоего возвращения очень очень ждем, уже сходим с ума без тебя братан)) возвращайся скорей Занимайся я таким делом,коли вы не просили б о граммах 100,ответ был бы тот же. В таком деле главное-отсутствие жадности. Не надо гнаться за каждой копейкой,коли есть относительно безопасная отработанная схема,то и нечего от неё отклонятся. Вы видите в них кидал,они в вас красного.
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]наркологическая клиника диспансер[/url]
тяговые аккумуляторы union Батарея для погрузчика Heli — надежная, с гарантией 2 года.
Особенно тревожными сигналами являются проблемы со здоровьем. Скачки давления, одышка, сердцебиение, боли в груди, нарушения сна, приступы тревоги и паники — всё это говорит о том, что организм работает на пределе. При этом человек продолжает пить, несмотря на явные признаки перегрузки. Признаками того, что пора не откладывать обращение, становятся и изменения в поведении: раздражительность, вспышки агрессии, подозрительность, скрытность, замыкание в себе. Добавьте сюда конфликты дома и на работе, сорванные обязательства, скрытые долги — и становится понятно, что «подождать ещё немного» уже опасно. В такой момент консультация нарколога в Чехове и обсуждение возможного кодирования — не радикальная мера, а разумный шаг, который может предотвратить серьёзные медицинские и социальные последствия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/]методы кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
На месте врач проводит первичный осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает уровень интоксикации и абстиненции. Далее назначается инфузионная терапия — капельница, направленная на дезинтоксикацию, восстановление электролитного баланса, купирование тревожности и нормализацию сна.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
На психическом уровне затяжные запои усугубляют тревожность, депрессию и приводят к паническим атакам. Человек становится раздражительным, агрессивным, теряет социальные и трудовые навыки, что нередко перерастаeт в бытовые и профессиональные аварии. Без своевременного начала инфузионной терапии риск судорог, делирия и жизнеугрожающих осложнений возрастает в разы.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
https://www.runningitalia.it/forum/1-km-max-355-min-13039#comment-24639
Перед началом терапии проводится клиническая оценка, включающая измерение давления, осмотр кожи и глаз, проверку дыхания и анализ неврологического состояния. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани начинается только после сбора этих данных, поскольку подбор препаратов без диагностики может быть небезопасен.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно астрахань[/url]
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
online casino s ?eskou licenc? [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]online casino s ?eskou licenc?[/url] .
Кодирование от алкоголизма в Чехове для многих семей становится тем рубежом, после которого зависимость перестаёт казаться «временной слабостью» и начинает восприниматься как диагноз, с которым можно и нужно работать. До этого момента обычно проходят годы: чередуются запои и трезвые периоды, звучат обещания «больше такого не будет», меняются напитки, придумываются правила вроде «пью только по выходным» или «только пиво». Но рано или поздно семья замечает, что именно алкоголь диктует распорядок дня, влияет на настроение, разрушает здоровье и отношения. В этот момент становится очевидно: без сильного внешнего ограничителя и профессиональной помощи просто «взять себя в руки» уже не получается.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/]kak-rabotaet-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Прибыв по вызову, врач клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» начинает с диагностики состояния пациента. Проводится комплексное обследование: измерение артериального давления, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови, оценка общего самочувствия и психического состояния. После диагностики нарколог подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, который позволяет эффективно вывести токсины, стабилизировать работу внутренних органов и быстро облегчить состояние пациента.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены сочи[/url]
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Для создания комфортной атмосферы в доме идеально подойдут [url=https://avtorulon.ru] как установить рулонную штору с электроприводом своими руками 7 (499) 638-25-37 [/url], которые легко управляются с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Это позволяет повысить комфорт жизни, автоматизировав процесс регулировки освещения.
лучше и не напишешь бро https://otdelochniki35.ru Хорошо работает народ))Максимально приятные впечатления оставляет у меня сотрудничество с сием трэйдером… Доставка никогда не занимала дольше недели, а однажды на самолете когда отправляли за ч\з 2 дня уже покоилась в руках :)… сегодня сделал заказ, написал в аську сразу ответили. Буду ждать как что измениться отпишу.
Этот подход имеет несколько ключевых преимуществ, которые обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Перед началом терапии проводится клиническая оценка, включающая измерение давления, осмотр кожи и глаз, проверку дыхания и анализ неврологического состояния. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани начинается только после сбора этих данных, поскольку подбор препаратов без диагностики может быть небезопасен.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-staczionare-astrakhan
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в томске[/url]
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/[/url]
Лечение в «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» проходит поэтапно, с акцентом на безопасность и эффективность. Каждый этап направлен на достижение конкретных целей, от детоксикации до психотерапии. В таблице представлена структура лечебного процесса:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в ижевске[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Капельница от запоя является неотъемлемой процедурой при острых и хронических отравлениях алкоголем. Она помогает стабилизировать состояние пациента, избежать тяжелых последствий и максимально быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Вызов врача для проведения процедуры рекомендуется в следующих ситуациях:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]капельница от запоя[/url]
Hi there friends, its enormous piece of writing about tutoringand
completely explained, keep it up all the time.
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в владивостоке[/url]
Вред через наркотиков — этто комплексная проблема, охватывающая физиологическое, психическое равным образом соц состояние здоровья человека.
Употребление эких наркотиков, как снежок, мефедрон, гашиш, «наркотик» или «бошки», что ль родить к необратимым последствиям как чтобы организма, яко
равно чтобы среды на целом. Хотя даже у выковывании зависимости возможно электровосстановление — ядро, чтоб энергозависимый явантроп устремился согласен
помощью. Важно памятовать, что наркомания лечится, а также оправдание одаривает шансище сверху свежую жизнь.
отзывы ждем https://semechkalach.ru на сайте есть аська, напиши, мне в течении пяти минут отвечали.добра всем бро,оплатил заказ неделю назад,на след день дали трек,трек до сих пор в базе не бьётся и посылочка не идёт…тс на письма не отвечает…вобщем чтот печкльно както,обычно 3 дня идёт( Адекватных работников
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Дюралевый швеллер 440540 4х29.4х1.2х1.2х1.2 мм Д1 ГОСТ 13623-90 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
Указанные элементы задают логическую основу для всего терапевтического процесса, создавая структурированную модель работы с пациентом. При необходимости схема вмешательств дополняется дополнительными мерами, направленными на стабилизацию состояния. Такой формат позволяет поддерживать предсказуемость результата даже в сложных клинических ситуациях.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/narkologicheskaya-poliklinika-penza/
Офсетная полиграфия — наиболее распространённый вид тиражной печати.
Широкоформатная полиграфия идеально подходит для быстрых тиражей и персонализации.
Шелкография часто применяется для печати на сувенирную продукцию и плоские материалы.
https://bio.site/printinghouse4z
Флексопечать используется преимущественно для гибкой упаковки и печати этикеток.
Для внешней агитации обычно используют крупноформатную полиграфию на баннерах.
Отделочная доводка содержит такие операции, как биговка, высечка и фальцовка.
Лечебные мероприятия строятся на основе поэтапного внедрения терапевтических решений, которые опираются на индивидуальные характеристики пациента. Уточнение анамнеза, анализ данных обследований и выявление сопутствующих факторов позволяют создавать эффективные и прогнозируемые программы лечения. В клинике соблюдается строгая последовательность процедур, направленная на снижение рисков и обеспечение безопасности. На каждом этапе проводится проверка клинической реакции, что позволяет своевременно выявлять необходимость корректировки и адаптировать лечебные меры под текущую картину.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма пенза[/url]
Этот обзор сосредоточен на различных подходах к избавлению от зависимости. Мы изучим традиционные и альтернативные методы, а также их сочетание для достижения максимальной эффективности. Читатели смогут открыть для себя новые стратегии и подходы, которые помогут в их борьбе с зависимостями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://www-ihostloc-com.cdn.ampproject.org/c/s/www.ihostloc.com/wp-content/themes/beginlts/inc/go.php?url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Психотерапевтическое кодирование делает акцент на внутренней мотивации. Специалист помогает человеку увидеть реальную цену алкоголя в его жизни, понять, как именно употребление разрушает здоровье, семью, карьеру, и сформировать установку на трезвость на определённый срок. Используются техники внушения в состоянии расслабления и структурированная работа с убеждениями и привычками. Такой подход особенно полезен тем, кто боится «лекарственного вмешательства» или уже имеет негативный опыт неудачных медикаментозных попыток. В практике лечения в Чехове часто используются комбинированные схемы, когда медикаментозный барьер подкрепляется психотерапевтической поддержкой, а результат кодирования закрепляется за счёт изменения образа жизни и участия в реабилитационных программах.
Получить больше информации – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]besplatnye-narkologicheskie-kliniki[/url]
Essayez le meilleur nouveau casino en ligne France
Bonus de bienvenue large choix de jeux depots securises et
retraits rapides Inscrivez vous des maintenant
Современные [url=https://electroprivod-karniz.ru] электрические жалюзи купить прокарниз
электрические жалюзи цена [/url] обеспечивают удобство управления светом в вашем доме с помощью дистанционного пульта.
В конечном итоге, такие жалюзи – это удобное и выгодное вложение в уют дома.
—
Не нужно вставать, чтобы изменить угол ламелей или поднять штору.
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
тоже хочу заказать бро!!! https://tuguru.ru здравствуйте , это от региона зависит . Доставка индивидуально обсуждается в ЛС .Ты покупал у этого магазина ? Если у этого то пиши ему в лс, и по каким контактам ты списывался , и сколько брал ? Не могли тебя тут кинуть но я смотрю все на о6ломах тут такие ждут, а тут на те6е всё ровно
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/[/url]
online casina [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]online casina[/url] .
Ниже представлена последовательность основных шагов терапевтического процесса.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
What’s up to every body, it’s my first visit of this webpage; this website includes awesome and genuinely fine data for visitors.
На месте врач проводит первичный осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает уровень интоксикации и абстиненции. Далее назначается инфузионная терапия — капельница, направленная на дезинтоксикацию, восстановление электролитного баланса, купирование тревожности и нормализацию сна.
Получить больше информации – http://
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их качество. Превосходное обслуживание – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы а также предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наша продукция:
Лист магниевый H2011 – ANSI Лента магниевая H2011 – ANSI представляет собой высококачественное решение для различных промышленных задач. Эта лента обладает отличными антикоррозийными свойствами и идеальна для использования в условиях повышенной нагрузки. Ее легко применять в процессе монтажа и ремонта. Если вы ищете надежный материал, который обеспечит долгосрочную эксплуатацию, обратите внимание на Лента магниевая H2011 – ANSI. Не упустите возможность купить Лента магниевая H2011 – ANSI и убедитесь в ее превосходстве на практике. Мы гарантируем, что данный продукт станет ценным дополнением вашего арсенала!
В рамках лечебного процесса наркологическая клиника задействует структурированные механизмы наблюдения, включающие анализ лабораторных показателей, оценку соматического тонуса и изучение активности нервной системы. Эти элементы обеспечивают комплексность работы и позволяют своевременно корректировать план лечения. Такая система предотвращает перегрузку организма и способствует поддержанию стабильности на фоне применения медикаментозных схем. Ниже представлены ключевые составляющие терапевтического процесса, формирующие основу для клинического восстановления.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-penze18.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-penza/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/]футбольная форма купить интернет магазин москва[/url]
магазин футбольной атрибутики – [url=http://tut-sport.ru]http://tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.tl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/]https://maps.google.com.my/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.kuhni-spb-4.ru/pinup5007.ru]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 427e0ae
оТЛИЧНЫЙ МАГАЗ НАСЛЫШАН Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Трек получил! Данный магазин действительно выполняет свои обязанности перед покупателями.Просто при личном разговоре с продавцом можно действительно понять что работы у них действительно много и на это уходит время,просто стоит проявить терпение.Считаю как получу товар,его качество останется таким же наивысшим,как сама работа магазинаРебят!!! Звонил в курьерку, все у них нормально, по номеру накладной оператор сказал такого груза нет!!! все быстро замутили
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость[/url]
Современные [url=https://karniz-s-privodom.ru] карнизы с электроприводом 7 (499) 638-25-37 [/url] обеспечивают максимальный комфорт и стиль в вашем интерьере.
Обычно применяют дистанционные пульты или голосовое управление через смартфон.
Hi there colleagues, its enormous piece of writing about
educationand completely defined, keep it up all the
time.
Реставрация картины Покраска ванны
This is a helpful post. The mcdvoice.com survey is actually very easy to complete, and it’s nice that McDonald’s gives customers a chance to share honest feedback.”
Перед началом терапии проводится клиническая оценка, включающая измерение давления, осмотр кожи и глаз, проверку дыхания и анализ неврологического состояния. Вывод из запоя в клинике в Астрахани начинается только после сбора этих данных, поскольку подбор препаратов без диагностики может быть небезопасен.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Забрал я посылочку. Упоковка на 5+(пакет был с дыркой как будто смотрели что там, но с такой упаковкой только на паяльник подумаеш). Сделал ам 2233(1г) + ркс4(1г) на 20 грамм мягкого. Честно говоря ам не почувствовал совсем, кроет как ркс4(1 г.) на 20 грамм(был печальный опыт). Сейчас курим по грамму на двоих, тогда кроет на “целых” 10 минут. Вообщем незнаю чья ошибка это, да и смысла выяснять нет, деньги все равно не вернуться. Хотел попробовать тусипи заказать, но как то страшно. С тусипи то такого не было не разу вроде? Притензий не было? бошки, марихуану сегодня сделал заказ, написал в аську сразу ответили. Буду ждать как что измениться отпишу.сегодня закажу 1г. MN-011 для пробы)посмотрим на товар) И еще сушняки ужасные. Сейчас вот утром проснулся, и до сих пор
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment.
I believe that you ought to write more about this subject, it might not be a
taboo matter but typically folks don’t discuss these issues.
To the next! Many thanks!!
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru
Howdy are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]casino-cz-1.com[/url] .
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а важный шаг на пути восстановления организма и возвращения человека к нормальной жизни. В клинике «ВладТрезвие Центр» пациенты получают профессиональную помощь, основанную на современных методиках детоксикации и безопасном медикаментозном восстановлении. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, а лечение подбирается с учётом возраста, состояния здоровья и продолжительности запоя. Наркологи центра выезжают на дом круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь даже в экстренных ситуациях, когда время играет ключевую роль.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Группа препаратов
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]капельница от запоя[/url]
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/
КАК ОБЕЩЯЛ ОПЕРАТОР ТАК ВСЕ И СДЕЛАЛ ОДИН В ОДИН !!!! https://humanaidbd.org Брал у него все гудд. Маскировка на высоте качество отличное. буду брать ещене мне в пятницу и субботу он отвечал.гворит документы есть что отправленно Как то так.
https://casinosinlicenciaes.com/
Эта публикация исследует взаимосвязь зависимости и психологии. Мы обсудим, как психологические аспекты влияют на появление зависимостей и процесс выздоровления. Читатели смогут понять важность профессиональной поддержки и применения научных подходов в терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://beta.planetasp.ru/redirect.php?ssh=1&url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Для современного интерьера идеально подойдет [url=https://avtomaticheskie-shtory.ru] цены на электрокарнизы для штор Прокарниз [/url], который обеспечит удобство и стиль в управлении шторами.
Данное устройство облегчает повседневное использование штор. Он особенно удобен в больших помещениях, где нужно одновременно регулировать множество полотен. Это позволяет включать электрокарниз в комплексную систему управления жилищем.
Принцип работы электрокарниза основан на электрическом приводе, который движет гардины по направляющим. С помощью дистанционного пульта можно удобно управлять шторами на расстоянии. Это делает устройство идеальным для использования в офисах, гостиницах и домах с современным дизайном. Автоматический привод позволяет быстро и легко регулировать положение штор.
Выбор электрокарниза зависит от размеров окна, веса штор и типа крепления. Мощность мотора должна соответствовать весу ткани для надежной работы. Также стоит обратить внимание на материал направляющей и качество комплектующих. Использование прочных комплектующих обеспечивает устойчивость электрокарниза.
Установка электрокарниза требует аккуратности и точного соблюдения инструкции. Лучше всего монтаж выполнить специалистам, чтобы избежать ошибок. Регулярное техническое обслуживание поможет продлить срок службы устройства. Проверка и смазка механизмов предотвратит возможные поломки.
Спин-шаблон:
Это делает устройство идеальным для использования в офисах, гостиницах и домах с современным дизайном.
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]джекпот[/url]
Лечение в «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» проходит поэтапно, с акцентом на безопасность и эффективность. Каждый этап направлен на достижение конкретных целей, от детоксикации до психотерапии. В таблице представлена структура лечебного процесса:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Если вы хотите улучшить свою тренировку, обратите внимание на [url=https://sportres.ru/catalog/gruzoblochnye-trenazhery/]тренажер грузоблочный[/url] — это идеальное решение для создания эффективной и разнообразной программы тренировок.
Именно благодаря им обеспечивается плавное и безопасное выполнение упражнений.
Хочу всех поздравить с наступающим Новым Годом и хочу поделиться с вами своей оптовой сделкой СК крисов. мефедрон Как связаться можноСпасибо за вашу работу,вы лучшие! Рассказал друг-таксист.
whoah this blog is excellent i really like studying your articles. Keep up the great work! You realize, lots of individuals are searching around for this info, you can help them greatly.
[url=https://remont.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=1762&p=3623#p3623]фреон 134[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]бесплатные вращения в слотах[/url]
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Разобраться лучше – http://mosoblpress.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
Площадка Rutor отличается хорошо зарекомендовавшей себя историей, высочайшей степенью скрытности и возможностью безопасной работы с транзакциями в сети Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor.wiki]http new rutor org top[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино[/url]
nov? ?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]nov? ?esk? online casino[/url] .
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/ekaterinburg-narkologicheskaya-klinika
Оставляйте свои отзывы! Мы ценим каждого клиента нам важны ваши отзывы и мнения! https://biochemestry74.ru вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес…ты брал вообще не скоростило или как ? вот как то это всё не ахуенно.Если вас не затруднит проясните ситуацию.
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-dolgoprudnom
Эта публикация обращает внимание на важность профилактики зависимостей. Мы обсудим, как осведомленность и образование могут помочь в предотвращении возникновения зависимости. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с полезными советами и ресурсами, которые способствуют здоровому образу жизни.
Узнать больше – http://chuangzaoshi.com/go/?url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru&view=itemlist&task=user&id=2734301
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование королев[/url]
В данной статье мы акцентируем внимание на важности поддержки в процессе выздоровления. Мы обсудим, как друзья, семья и профессионалы могут помочь тем, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. Читатели получат практические советы, как поддерживать близких на пути к новой жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://64.233.165.194/url?q=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
В данной публикации мы поговорим о процессе восстановления от зависимости, о том, как вернуть себе нормальную жизнь. Мы обсудим преодоление трудностей, значимость поддержки и наличие программ реабилитации. Читатели смогут узнать о ключевых шагах к успешному восстановлению.
Подробнее – http://m.tauroauto.com/member/login.html?returnurl=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Лучшее решение — прямо здесь – https://periodicodeltalento.com/pensionesla-promesa-rota
Great post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed!
Very helpful info particularly the last part 🙂 I care for such
information a lot. I was seeking this certain information for a long time.
Thank you and best of luck.
Домашний визит нарколога — это не компромисс «на скорую руку», а тщательно организованный процесс, который экономит время, сохраняет конфиденциальность и делает лечение предсказуемым. «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» принимает вызовы круглосуточно и выезжает во все районы города — от Уралмаша и ВИЗа до Академического и Широкой Речки. Команда приезжает без внешних опознавательных знаков, использует нейтральные формулировки в документах и ведёт переписку только по защищённым каналам связи. На месте мы быстро проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, контролируем пульс, сатурацию и артериальное давление, подключаем гастропротекцию и аккуратно управляем тревогой без избыточной седации. Цель — безопасно «снять волну» симптомов, вернуть возможность пить воду и отдыхать, а затем закрепить результат на горизонте ближайших 72 часов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Запой не всегда выглядит как откровенная катастрофа с первых дней. Иногда всё начинается с «отпуска», «праздника», пары вечеринок подряд. Родные надеются, что человек сам остановится, а он каждый день находит повод продолжить. В какой-то момент организм перестаёт справляться, и даже небольшие дозы алкоголя вызывают тяжёлые реакции.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/kapelnica-ot-alkogolya-cena-v-dolgoprudnom/
Режим работы 24/7 в клинике «Формула Трезвости» обусловлен клинической спецификой зависимостей, для которых характерны внезапные ухудшения состояния. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре обеспечивает постоянную готовность медицинского персонала к приёму пациентов и началу терапии без временных ограничений. Это позволяет существенно сократить интервал между появлением симптомов и медицинским вмешательством, снижая риск осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru/krasnodar-narkologicheskij-czentr/
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Бесплатный ключ для Windows 11 — только у нас, обновлено в 2026 году!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Где найти рабочий ключ для Windows 11[/url]
долго гуляя по форуму, выбирал хороший магазин для себя. хотелось чтоб устраевало все! прежде всего меня интересовало качество товара и его цена! хотелось чтоб цена была доступной! так же есть большое желание всегда получать товар 100% т.к. в закладочных магазинах бывают случаи не находа, такие магазины для постоянных покупок рассматривать не стал! рассматривалось много вариантов! ну гдегде же всетаки заказать??? то предлогают сразу слишком много товара (ну как же брать если ты сам лично не знаешь за его качество)??? бывало чаще всего не устраевал сервис обслуживания! https://samuelelijahpropheticcollege.org Если во время действия паралельно потягивать пивас и почаще двигаться , не сидеть на месте , то довольно нормально прёт , если загоняться то накрывает параноя) , в общем около 8-9 часов прёт , но у меня была ещё и рега , очень лютая которой можно было запросто перебить параною если вдруг возникала от данной скорости , в целом понравилась скорость .Магаз огонь, а кидкам хуй на ладонь магазин работает как щвецарские часы!!!!
It’s amazing to visit this site and reading the views of all mates on the topic of this piece of writing, while I am also keen of getting knowledge.
Rutor — старейший узел русского даркнета, который предоставляет услуги конфиденциального обмена и защищённой передачи данных в сети Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor12.cc]рутор орг зеркало сегодня[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Для семьи это почти всегда тяжёлый, эмоционально изматывающий период. В доме копятся усталость, обида, чувство вины, страх за близкого. Но при этом сохраняется надежда, что удастся «обойтись своими силами». В какой-то момент становится ясно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи уже не справиться. В этот момент важно, чтобы рядом был специализированный центр в самом Воскресенске, а не где-то далеко, куда сложно добраться и куда трудно уговорить поехать человека в тяжёлом состоянии.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnodar/
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
В рамках анонимного лечения особое внимание уделяется следующим аспектам медицинской организации:
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru/narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar/
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Получить больше информации – http://count.erois2.tv/cgi/out.cgi?cd=i&id=matome_footer&go=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tolyatti0.ru&url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tolyatti0.ru
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voskresenske/
모든 사람에게 안녕하세요, 모든 것이 잘 가고 있으며,
물론 모두가 사실을 공유하고 있어서, 정말 훌륭합니다, 계속 글을 써주세요.
My developer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type
on several websites for about a year and am anxious
about switching to another platform. I have
heard excellent things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress content into it?
Any kind of help would be greatly appreciated!
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике представляет собой последовательный комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение интоксикации и стабилизацию основных функций организма. В основе процесса лежит оценка физиологических параметров, определение уровня нарушений и корректировка тактики вмешательства. Такой подход обеспечивает постепенное восстановление адаптивных механизмов и снижает риск осложнений. На каждом этапе проводится анализ динамики, что позволяет оптимизировать терапевтические меры и поддерживать устойчивость состояния. Работа ориентирована на сохранение баланса внутренних систем и снижение нагрузки на жизненно важные органы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
2с-i отличного качества. 1гр был разделен на 60 частей. Жалоб не от кого не было по качеству. https://krasapetochka.ru Общая оценка магазина 10/10-идут на встречу покупателю, сервис общение и работа на высотеРОВЫНЫЙ МАГАЗ РОВНЫЙ ТС РОВНАЯ ВЕТКА И РОВНЫЕ КЛИЕНТЫ МИР ВАМ ВСЕМ !!!!!! В общем начну с начала.нашел ветку данного магазина и решил узнать че как.
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В этой публикации мы исследуем ключевые аспекты здоровья, включая влияние образа жизни на благополучие. Читатели узнают о важности правильного питания, физической активности и психического здоровья. Мы предоставим практические советы и рекомендации для поддержания здоровья и развития профилактических подходов.
Подробнее тут – http://control-24.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tolyatti0.ru
Часто родственники тянут до последнего, надеясь, что запой «сам пройдёт», как это случалось раньше. Но с каждым эпизодом последствия становятся тяжелее: организм изнашивается, возрастает риск осложнений, ухудшается психика. Особенно опасно, когда запой длится несколько дней подряд, а любые попытки самостоятельно сократить дозы алкоголя сопровождаются дрожью, бессонницей, приступами паники.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре москва[/url]
Процесс выведения из запоя в клинике основан на медицинских стандартах и многолетнем опыте врачей-наркологов. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально: перед началом лечения проводится оценка состояния пациента, определяется степень интоксикации и подбираются препараты, подходящие именно ему. Врачи центра работают круглосуточно, а выездная помощь доступна во всех районах Ростова-на-Дону и области. Это особенно важно, когда требуется немедленная помощь, а доставить пациента в стационар невозможно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Реализация этих задач позволяет наркологической клинике в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечивать контролируемость лечения в любое время суток.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
live casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]casino-cz-1.com[/url] .
I’m not sure exactly why but this web site is loading very
slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is
it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
1win казино — это современная игровая платформа, которая предлагает широкий выбор азартных развлечений: слоты, лайв-казино, настольные игры и быстрые выплаты. Удобный 1win сайт работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах, а интуитивный интерфейс делает игру комфортной даже для новичков. Если доступ к [url=https://t.me/x1win_site2026]бонус 1win
[/url] ограничен, всегда помогут 1win зеркала — они полностью повторяют функционал основного ресурса. Актуальное 1win зеркало позволяет войти в аккаунт без VPN и сохранить доступ ко всем бонусам. Рабочая 1win ссылка обеспечивает быстрый вход и безопасную авторизацию. 1win казино ценят за честность, поддержку популярных платежных систем и регулярные акции для игроков.
Режим 24/7 в клинике «Южный Контур» обусловлен особенностями течения зависимостей, при которых ухудшение состояния может происходить внезапно и в любое время суток. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре обеспечивает постоянную готовность медицинского персонала к приёму пациентов, что сокращает временной интервал между появлением симптомов и началом лечения. Такой формат снижает риск осложнений и повышает медицинскую безопасность.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Useful information. Fortunate me I discovered your site by chance, and I am stunned why this coincidence didn’t came about in advance! I bookmarked it.
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnodar/
На тех кто продаёт в наглую… кокаин мда а в итоге болт водичкаЯ всегда сам еду за ней,можно чтоб и доставили)Просто так быстрее пока они доставят я уже все сделаю. Последние данные очков репутации:
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника московская московская область[/url]
Лечение в клинике «Вектор Трезвости» основано на клинически обоснованных методах, адаптированных под формат круглосуточной работы. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону применяет комплексную диагностику, позволяющую учитывать тяжесть зависимости, длительность употребления и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Такой подход обеспечивает точность медицинских решений и снижает вероятность неблагоприятных реакций.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu/
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]знакомства для взрослых[/url]
Каждый курс лечения включает несколько этапов, направленных на постепенное улучшение состояния. Система выстроена так, чтобы обеспечить плавное восстановление функций организма без стресса. Ниже приведена таблица, показывающая основные этапы лечения и применяемые процедуры.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница краснодар[/url]
Режим 24/7 в клинике «Южный Контур» обусловлен особенностями течения зависимостей, при которых ухудшение состояния может происходить внезапно и в любое время суток. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре обеспечивает постоянную готовность медицинского персонала к приёму пациентов, что сокращает временной интервал между появлением симптомов и началом лечения. Такой формат снижает риск осложнений и повышает медицинскую безопасность.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru
Для удобного входа в кракен маркетплейс используйте ссылку [url=https://krkn-krkn.com]кракен маркетплейс вход[/url]. Быстро и без проблем.
krkn-krkn.com
Rutor — старейший узел русского даркнета, который предоставляет услуги конфиденциального обмена и защищённой передачи данных в сети Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor-24.co]рутор орг сейчас[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Перспективы и риски
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
После купирования острых симптомов врач объясняет, какие шаги нужно сделать дальше: ограничиться домашним наблюдением, подумать о коротком стационарном курсе или сразу планировать дальнейшее лечение зависимости. Это помогает не возвращаться к затяжным запоям уже через несколько недель.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя в москве в стационаре[/url]
Лечение в круглосуточном режиме рассматривается как непрерывный медицинский процесс, а не как разовое вмешательство. Даже при экстренном обращении терапия выстраивается последовательно, с обязательным врачебным наблюдением и оценкой динамики состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krd19.ru
После прохождения курса капельниц пациенты отмечают улучшение сна, исчезновение головной боли, восстановление аппетита и общего самочувствия. При тяжёлых формах зависимости лечение дополняется физиотерапией и психологической помощью.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в пензе[/url]
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-himkah/
Клиника создана как современное пространство для безопасного восстановления. Здесь пациенты получают комплексную помощь в комфортных условиях. Основные преимущества учреждения:
Детальнее – http://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru
хороший магазин !отменное качество и сервис ! хорошей работы вашему магазину и процветания! https://daqinpump.org Пожалуй один из самых ровных магазинов “Старичков ” – благодаря которому я зарабатвал, от души спасибо парням за ровную работу!Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут…. всем привет магаз ровный сделал проплату во сколько сказали даже раньше получил адресс.успехов магазу будем работать
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Барселона;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]футбольная форма атрибутика Барселона[/url]
футбольная форма Барселона купить интернет магазин – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona[/url]
[url=http://image.google.com.sl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]http://cse.google.cd/url?sa=i&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.elektrokarnizy7.ru/www.educ-ua7.ru/r-diploma29.ru]Спортивная экипировка и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 7e0ae63
Работа в режиме 24/7 в клинике «Точка Опоры» обусловлена особенностями течения зависимостей, при которых ухудшение состояния может происходить внезапно и независимо от времени суток. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре обеспечивает постоянную готовность медицинского персонала к приёму пациентов и началу лечения без временных ограничений. Это снижает риск осложнений и повышает управляемость лечебного процесса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Для самого пациента это шанс получить медицинское вмешательство без дополнительного стресс-фактора в виде транспорта, очередей и «больничной атмосферы». Он остаётся в привычной обстановке, в своей квартире, с теми же предметами, к которым привык, и это снижает сопротивление. Вместо жесткого сценария «либо немедленно в стационар, либо ничего» появляется промежуточный, более мягкий вариант: врачи приезжают домой, снимают остроту состояния, подбирают схему капельницы и медикаментов, объясняют, что делать дальше. Нередко именно после такого первого опыта человек впервые всерьёз задумывается о полноценном лечении, потому что ощущает реальную разницу в самочувствии до и после профессиональной помощи, а не просто очередной «опохмел».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-psiholog-na-domu[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится только под медицинским наблюдением, так как самостоятельные попытки могут привести к осложнениям — аритмии, судорогам, резкому скачку давления. Именно поэтому наркологи центра уделяют особое внимание контролю жизненно важных показателей и плавному восстановлению организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого пенза[/url]
В практической работе выделяются последовательные этапы, обеспечивающие медицинскую целостность:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике ростов-на-дону[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Чехове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, не выезжая в крупный мегаполис и не тратя силы на долгую дорогу. Для многих людей момент обращения к наркологу наступает не сразу: сначала идут «домашние» попытки справиться с проблемой, обещания ограничиться «по праздникам», уговаривания родственников и периодические срывы. Запои становятся длиннее, организм восстанавливается всё хуже, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон, учащаются конфликты дома и на работе. В какой-то момент становится понятно, что без системного лечения обойтись уже нельзя, а стихийные капельницы на дому и случайные советы из интернета только оттягивают время.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru
1win казино — это современная игровая платформа, которая предлагает широкий выбор азартных развлечений: слоты, лайв-казино, настольные игры и быстрые выплаты. Удобный 1win сайт работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах, а интуитивный интерфейс делает игру комфортной даже для новичков. Если доступ к [url=https://t.me/x1win_site2026]зарегистрироваться в 1win
[/url] ограничен, всегда помогут 1win зеркала — они полностью повторяют функционал основного ресурса. Актуальное 1win зеркало позволяет войти в аккаунт без VPN и сохранить доступ ко всем бонусам. Рабочая 1win ссылка обеспечивает быстрый вход и безопасную авторизацию. 1win казино ценят за честность, поддержку популярных платежных систем и регулярные акции для игроков.
Этот краткий обзор предлагает сжатую информацию из области медицины, включая ключевые факты и последние новости. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и понятной для широкой аудитории, что позволит читателям оставаться в курсе актуальных событий в здравоохранении.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://srdi.yru.ac.th/clinic/redirect/63?url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
Клиника создана как современное пространство для безопасного восстановления. Здесь пациенты получают комплексную помощь в комфортных условиях. Основные преимущества учреждения:
Узнать больше – http://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/narkologiya-rostov-kruglosutochno/
Такой подход позволяет наркологической клинике в Ростове-на-Дону выстраивать лечение в безопасных и психологически комфортных условиях.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu/
В практической работе выделяются последовательные этапы, обеспечивающие медицинскую целостность:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Анонимность в клинике «Южный Контур» является важным клиническим фактором, влияющим на эффективность лечения. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре выстраивает процессы так, чтобы минимизировать психологическое напряжение пациента и исключить внешние социальные риски. Практика показывает, что при сохранении конфиденциальности повышается приверженность терапии и точность диагностической информации, что напрямую отражается на стабильности результатов лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
На практике семья часто обращается за помощью слишком поздно — когда близкий уже еле встаёт, не спит ночами, говорит странные вещи, а давление скачет так, что страшно оставлять одного. Чтобы не доводить до этого, важно знать признаки, при которых капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — не «желательно», а по-настоящему необходима.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]капельница от алкоголя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону рассматривается как специализированное медицинское учреждение, где лечение зависимостей выстраивается с учётом необходимости анонимности и круглосуточной доступности помощи. В клинике «Северный Вектор» работа организована таким образом, чтобы пациент мог обратиться за лечением в любое время суток без риска раскрытия персональной информации. Такой формат особенно важен при острых состояниях, требующих немедленного врачебного вмешательства и медицинского контроля.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Since the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very shortly it will be well-known, due to its feature contents.
company set up uae whitecirclegroup company setup
Причем тут вообще он к нашему магазину ? кокаин с треками магазин всегда спешит:) и качество скоро заценим)))Про Ам1220 здешний известно что нибудь…? вот опять сегодня получил что заказал всё прошло ровно .быстро ,качество в этом магазине лучшее ,больше не где не заказываю .если нужно что то подождать я лучше подожду чем кидал буду кормить ,тоже влитал поначалу пока нашёл этот магазин ,по этому сам беру и друзьям советую .спасибо всей команде за отличную работу.с наступающими праздниками всех поздравляю.вообщем всем благодарочка.
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]казино[/url]
Мессенджер и магазин Rutor признан одним из самых безопасных ресурсов в русском даркнете, благодаря анонимности системы, конфиденциальности и поддержке платежей в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor-24forum.cc]рутор стал платным[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Приватность — клинический фактор, снижающий тревогу и укрепляющий доверие. В «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» выезд немаркированный, специалисты в гражданской одежде, уведомления — «тихие», документы — с нейтральными формулировками. Медкарта хранится в шифрованном контуре, доступ к данным разграничен по ролям. По запросу вся коммуникация ведётся через доверенное лицо, а оплата возможна наличными или безналом с нейтральным назначением платежа. Это позволяет оставаться в тени и при этом получать полноценную помощь.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
Для жителей Чехова важно и то, что врач видит не абстрактный «случай зависимости», а живого человека со своей историей. У кого-то за плечами десятилетия злоупотребления, у кого-то — несколько лет с быстрым прогрессированием, у кого-то — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или наркотиками. Всё это учитывается при выборе схем детокса, медикаментозного лечения, формата стационара или амбулаторного наблюдения. Дополнительно внимание уделяется безопасности: оценивается состояние сердца, давление, наличие хронических заболеваний, чтобы любая процедура проходила с минимальными рисками и под контролем.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
москитные сетки москва
строительные леса аренда
Для оценки состояния используется расширенная диагностика: лабораторные анализы, ЭКГ, психологическое тестирование и биохимические маркеры. По результатам обследования составляется индивидуальный план, включающий детоксикацию, фармакотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия. Ниже представлена таблица, описывающая структуру этапов лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
поставка топлива
codigo promocional casino 1xbet
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,child porn videos,child porn site,child porn situs,child
seks porn,child porn situs web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child porn,porn child video,KONTOL,chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,
porn small child,child porn video,child gay porn,gay child porn,child porn link,child porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,child porn vid,how to
watch child porn,porn mother and child,ai child porn,seks child porn,how
to find child porn,child and mom porn,watch child porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub child,porn mom and child,gay porn child,child girl porn
В практической работе выделяются последовательные этапы, обеспечивающие медицинскую целостность:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр ростов-на-дону[/url]
ОТЗЫВ О РАБОТЕ МАГАЗИНА https://creative-pink-showroom.com Цены тут взвинчены до жопы не знаю кто тут умудряется брать, летом как то брал здесь не помню че но было фуфло конченное половина не растворилась хоть че делай хоть грей хоть танцуй ни че не помогло. Один плюс присылают быстро но нафиг такая быстрота- За сколько? часть покупателей устраивает, продавцы тоже не жалуется. В чем проблема? нет терпения – идите в другие шопы.
Если вы хотите улучшить свою тренировку, обратите внимание на [url=https://sportres.ru/catalog/gruzoblochnye-trenazhery/]блочный тренажер на грудь[/url] — это идеальное решение для создания эффективной и разнообразной программы тренировок.
Это позволит тренажерам работать эффективно и безопасно.
Если вы ищете надежное и эффективное оборудование для занятий спортом, обратите внимание на [url=https://sportres.ru/catalog/gruzoblochnye-trenazhery/]грузоблочные тренажеры[/url] на сайте SportRes — здесь вы найдете все необходимое для эффективных тренировок.
С их помощью можно точно контролировать нагрузку и техники выполнения различных тренировок.
В практике круглосуточного лечения применяются следующие этапы:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Соблюдение конфиденциальности в клинике «Точка Опоры» является неотъемлемой частью лечебного процесса. Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре обеспечивает закрытый формат приёма, хранения медицинских данных и взаимодействия с пациентом. Практика показывает, что анонимное обращение снижает уровень тревожности, способствует более открытому диалогу с врачом и повышает точность клинической диагностики.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-krd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Лечение в режиме круглосуточного наблюдения выстраивается как непрерывный медицинский процесс. Даже при экстренном обращении терапия рассматривается как последовательность взаимосвязанных мероприятий с обязательным врачебным контролем.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru/
В клинике «ПензаМед Трезвость» лечение проводится по индивидуальной схеме, которая формируется после первичного осмотра. Нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, уровень алкогольной интоксикации и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. На основании данных подбираются препараты, способные эффективно очистить кровь, восстановить работу органов и снизить абстинентные проявления. При лёгкой форме зависимости возможен выезд врача на дом, где пациенту устанавливают капельницу и обеспечивают наблюдение в течение всего процесса детоксикации. В более сложных случаях рекомендуется госпитализация в стационар, где помощь оказывается под постоянным контролем специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-penza18.ru
great points altogether, you just received a new reader. What could you suggest about your submit that you made some
days in the past? Any positive?
my site :: mpomm
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]московские наркологические клиники[/url]
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в краснодаре[/url]
Не хотите платить за лицензию? У нас есть рабочий кряк для Windows 11 — скачайте прямо сейчас!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Бесплатный серийный номер для Windows 11[/url]
It’s hard to come by experienced people for this topic, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
Feel free to visit my website; zokasa01
Woah! I’m really loving the template/theme of this website. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s challenging to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appeal. I must say you’ve done a amazing job with this. Also, the blog loads extremely quick for me on Chrome. Excellent Blog!
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Мессенджер и магазин Rutor признан одним из самых безопасных ресурсов в русском даркнете, благодаря анонимности системы, конфиденциальности и поддержке платежей в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor24x7.cc]new rutor org новый адрес[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Перспективы и риски
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Безопасность транзакций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Да, оч похожа на соль, даже камушек один был ощутимый такой бошки, марихуану где вообще оператор или кто ни будь? бабло уплочено и жду доставку а на связи ни кого нету!!!!!!!!!!было много… но скрутят даже за один! им главное работа,а не обьем! тем более 1гр – это уже особо крупный размер! \занимаюсь тестированием вместе с кролями в течении нескольких дней. Все никак не мог понять.
В клинической практике используются следующие этапы лечения:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ростов-на-дону[/url]
Thanks for the good writeup. It if truth be told was once a
leisure account it. Glance complex to far brought agreeable from
you! By the way, how could we keep up a correspondence?
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная атрибутика интернет магазин[/url]
футбольная форма клубов – [url=https://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://www.google.so/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://toolbarqueries.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.arus-diplom33.ru/1xbet-12.com]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 4f6303d
«СибСети» в Красноярске предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• Точную оценку скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж роутера
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибсети домашний интернет и телевидение[/url]
стоимость интернета сибсети – [url=https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://image.google.nr/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://cse.google.com.ng/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.island-hvar.info/www.sportbets31.ru/www.1xbet-giris-1.com/www.rudik-diplom14.ru]Домашний интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Красноярске[/url] 3da2a67
манипуляторы в аренду в москве
Часто родственники тянут до последнего, надеясь, что запой «сам пройдёт», как это случалось раньше. Но с каждым эпизодом последствия становятся тяжелее: организм изнашивается, возрастает риск осложнений, ухудшается психика. Особенно опасно, когда запой длится несколько дней подряд, а любые попытки самостоятельно сократить дозы алкоголя сопровождаются дрожью, бессонницей, приступами паники.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-moskve-stacionar
Состояние запоя представляет опасность не только для физического здоровья, но и для психики человека. Продолжительное употребление алкоголя приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации, нарушению обмена веществ и психоэмоциональной нестабильности. В таких случаях самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен, а иногда и невозможен. Врачи «Южного Центра Медицинского Восстановления» оказывают квалифицированную помощь с выездом на дом и круглосуточным приёмом пациентов. Используя современные методы детоксикации и мониторинга состояния, специалисты обеспечивают безопасное восстановление организма и минимизируют риски осложнений.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-rnd19.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-rostov-na-donu
1win казино — это современная игровая платформа, которая предлагает широкий выбор азартных развлечений: слоты, лайв-казино, настольные игры и быстрые выплаты. Удобный 1win сайт работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах, а интуитивный интерфейс делает игру комфортной даже для новичков. Если доступ к [url=https://t.me/z1xbetzerkala]1xbet футбол
[/url] ограничен, всегда помогут 1win зеркала — они полностью повторяют функционал основного ресурса. Актуальное 1win зеркало позволяет войти в аккаунт без VPN и сохранить доступ ко всем бонусам. Рабочая 1win ссылка обеспечивает быстрый вход и безопасную авторизацию. 1win казино ценят за честность, поддержку популярных платежных систем и регулярные акции для игроков.
Продолжаем работать, в этот раз чуть больше берем 🙂 очень хорошие скидки дает постоянным клиентам обращаетесь !! https://unachicacomotu.com Молодцы! Так держать!стараемся!Не волнуйтесь, я думаю Рашн холидэйс. Продавец честный сегодня закажу 1г. MN-011 для пробы)посмотрим на товар)
В этой статье рассматриваются различные аспекты избавления от зависимости, включая физические и психологические методы. Мы обсудим поддержку, мотивацию и стратегии, которые помогут в процессе выздоровления. Читатели узнают, как преодолеть трудности и двигаться к новой жизни без зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – http://142.250.141.118/url?q=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
Каждое направление наблюдения играет важную роль в формировании терапевтической программы. Структурированный контроль помогает снижать уровень рисков и обеспечивает возможность оперативной адаптации. Для систематизации данных применяется таблица, отражающая ключевые параметры мониторинга.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя ижевск[/url]
Incredible story there. What occurred after? Thanks!
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]купить футбольную атрибутику в москве[/url]
клубные футбольные формы – [url=https://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]https://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.com.ng/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://clients1.google.dk/url?sa=i&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.island-hvar.info/www.arus-diplom34.ru/www.1win5521.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 67f9e29
Это закон, хороший отзыв мало кто оставляет, а вот говна вылить всегда есть желающие вот и получается так, те у кого все хорошо, молчат и радуются Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Добрый день форумчане! Кто нибудь подскажет как по качеству реагент в этом магазине? Соответствует ли заявленная концентрация? Сколько по времени держит если 1 к 20 сделать? Всем спасибо!!!Списавшись в ЛС с ТСом обговорив условия сделки провел оплату в БТЦ. да ее колать страшно эксперементатором быдь тоже чет не охото
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре рассматривается как специализированное медицинское учреждение, ориентированное на лечение зависимостей с обеспечением полной конфиденциальности и круглосуточного доступа к помощи. В клинике «Южный Контур» лечение организовано таким образом, чтобы пациент мог обратиться за медицинской поддержкой в любое время суток без риска разглашения персональной информации. Такой формат особенно актуален при острых состояниях, требующих немедленного врачебного вмешательства и постоянного контроля.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krasnodare19.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Для современного и удобного управления шторами выбирайте [url=https://karnizy-electro.ru/] электрокарнизы для портьерных штор и занавесей 7 (499) 638-25-37 [/url].
Электрокарнизы становятся все более популярными обусловлена их удобством и функциональностью. Они дают возможность автоматизировать процесс управления шторами, что особенно актуально для больших окон или труднодоступных мест. Электрокарнизы также добавляют элемент роскоши и современности в интерьер. комфорт, удобство и экономия времени. Нет больше необходимости вручную открывать и закрывать шторы, особенно если их много или они расположены высоко. Электрокарнизы могут быть интегрированы в систему “умный дом”, позволяет управлять ими с помощью смартфона или голосовых команд. Это предоставляет дополнительные удобства для людей с особыми потребностями.
**Выбор электрокарниза: На что обратить внимание**
Важно учитывать ряд факторов при выборе электрокарниза: длину карниза, вес штор и тип управления. Необходимо, чтобы длина подобранного карниза соответствовала размерам окна, и способен выдержать вес ваших штор. Существуют различные типы управления: с помощью пульта дистанционного управления, настенного выключателя или через приложение на смартфоне. Выбор зависит от ваших личных предпочтений и потребностей.
**Установка и настройка электрокарниза**
Установить электрокарниз можно и своими силами, если у вас есть необходимые навыки и инструменты. Но если вы не уверены в своих силах, лучше обратиться к профессионалам. Настройка конечных положений штор является важной частью этого процесса, скорости движения и других параметров. Как правило, электрокарнизы комплектуются подробными инструкциями по настройке.
**Электрокарниз: Долговечность и уход**
Также следует избегать попадания влаги на электрокарниз.
Программы лечения выстраиваются гибко: можно начать с домашнего вызова врача и продолжить терапию в клинике, либо пройти весь курс стационарно с круглосуточным наблюдением. Главный принцип — безопасность, эффективность и уважение к личности пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/]narcologicheskaya-clinika-v-rnd19.ru/[/url]
Скачайте патч для обхода активации Windows 11 и пользуйтесь системой без ограничений.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Где взять лицензионный ключ для Windows 11[/url]
Лечение в наркологической клинике в Чехове удобно не только близостью к дому. Главный плюс — комплексный подход. Зависимость практически никогда не ограничивается только алкоголем или наркотиком: страдают сердце и сосуды, печень, нервная система, психика, отношения в семье и на работе. Если пытаться лечить только одно звено, например, периодически «чистить кровь» капельницами, без проработки причин и последствий, ситуация быстро возвращается к исходной точке. В клинике выстраивается последовательная работа: сначала стабилизируют организм, затем укрепляют психику, а дальше помогают менять привычный образ жизни, чтобы трезвость стала не кратким эпизодом, а новой нормой.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-sajt-v-chekhove
Приватность — клинический фактор, снижающий тревогу и укрепляющий доверие. В «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» выезд немаркированный, специалисты в гражданской одежде, уведомления — «тихие», документы — с нейтральными формулировками. Медкарта хранится в шифрованном контуре, доступ к данным разграничен по ролям. По запросу вся коммуникация ведётся через доверенное лицо, а оплата возможна наличными или безналом с нейтральным назначением платежа. Это позволяет оставаться в тени и при этом получать полноценную помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в екатеринбурге[/url]
1win казино — это современная игровая платформа, которая предлагает широкий выбор азартных развлечений: слоты, лайв-казино, настольные игры и быстрые выплаты. Удобный 1win сайт работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах, а интуитивный интерфейс делает игру комфортной даже для новичков. Если доступ к [url=https://t.me/z1xbetzerkala]регистрация 1xbet профиль
[/url] ограничен, всегда помогут 1win зеркала — они полностью повторяют функционал основного ресурса. Актуальное 1win зеркало позволяет войти в аккаунт без VPN и сохранить доступ ко всем бонусам. Рабочая 1win ссылка обеспечивает быстрый вход и безопасную авторизацию. 1win казино ценят за честность, поддержку популярных платежных систем и регулярные акции для игроков.
Вот отзыв за этот эйфор: кокаин В день оплаты через час я получаю ровную надёжную закладку Курьерский сервис на 5+?пасибо за ваш труд,всё быстро,ровно и чётко! скорость обработки заказа не оставляет шансов конкурентам – вы несомненно лучшие! ма-ла-цы Здесь буду отписываться, чтобы все РЕАЛЬНО понимали сколько времени длится весь процесс
В практической работе выделяются последовательные этапы, обеспечивающие медицинскую целостность:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Круглосуточный режим работы в клинике «Северный Вектор» обусловлен спецификой течения зависимостей, при которых ухудшение состояния может происходить внезапно. Наркологическая клиника в Ростове-на-Дону обеспечивает постоянную готовность медицинского персонала к приёму пациентов, что позволяет сократить время между возникновением симптомов и началом лечения. Такой подход снижает риск осложнений и повышает клиническую безопасность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove19.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-rostov-na-donu/
Howdy would you mind letting me know which web host you’re using?
I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster
then most. Can you suggest a good hosting provider at a reasonable price?
Kudos, I appreciate it!
На практике семья часто обращается за помощью слишком поздно — когда близкий уже еле встаёт, не спит ночами, говорит странные вещи, а давление скачет так, что страшно оставлять одного. Чтобы не доводить до этого, важно знать признаки, при которых капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — не «желательно», а по-настоящему необходима.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном[/url]
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Узнать больше – http://www.air-dive.com/au/mt4i.cgi?mode=redirect&ref_eid=697&url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
Важно и то, что во время процедуры пациент находится под наблюдением. Врач может увидеть, как организм реагирует на терапию, вовремя скорректировать темп или состав инфузии, понять, достаточно ли домашнего формата или лучше рассмотреть стационар. Это принципиальное отличие от попыток лечиться дома таблетками наугад, без контроля давления и пульса.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-anonimnaya[/url]
Good post. I’m experiencing some of these issues as well..
В этом исследовании рассмотрены методы лечения зависимостей и их эффективность. Мы проанализируем различные подходы, используемые в реабилитационных центрах, и представим данные о результативности программ. Читатели получат надежные и научно обоснованные сведения о данной проблеме.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://local.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tolyatti0.ru
Sizdə əla resurslar var — xüsusilə kazino oyunları ilə bağlı.
http://zsoryfurdohotel.hu/index.php/component/kide/
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Узнать больше – http://sagrar.ru/redirect?url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru
Наркологическая клиника в Краснодаре рассматривается как специализированное медицинское пространство, где лечение зависимостей выстраивается с приоритетом анонимности и круглосуточной доступности помощи. В клинике «Формула Трезвости» терапия организована таким образом, чтобы пациент мог получить медицинскую поддержку в любое время суток без риска разглашения персональной информации. Такой формат особенно важен при острых интоксикациях и тяжёлых абстинентных состояниях, требующих немедленного врачебного вмешательства и постоянного контроля.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinica-v-krd19.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике краснодар[/url]
Для семьи это тяжёлый период. Родные одновременно злятся, боятся и пытаются «договориться»: то уговаривают, то угрожают, то пробуют лечить подручными средствами. Пока близкие спорят, состояние человека ухудшается: он перестаёт нормально есть, почти не спит, избегает разговоров, закрывается в комнате, теряет связь с привычной жизнью. В этот момент особенно важно не ждать, когда организм «сам справится», а подключить профессиональную помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-v-voskresenske/
Hello colleagues, how is the whole thing, and what you desire to say about this
post, in my view its truly awesome in favor of me.
В клинической практике используются следующие этапы лечения:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcologicheskaya-klinika-v-rnd19.ru
раньше ваш магаз в аське работал , мих клевый был бошки, марихуану В общем я всегда доверял своей логике и считаю ее правильной, многие соглашаются с ней, но видимо тут никто толком ни с кем не согласится, потому соглашусь с тем, что кончаем с оффтопомЧто задерживали грузы, с поставками, и дожидались пока запрет выйдет… Насчет доставки стало не очень после того как перестали работать с спср, но особой разницы не заметил.
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Подбор оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис домашний интернет тарифы[/url]
инсис подключение телевидения и интернета – [url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://image.google.sm/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://images.google.com.fj/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://shepherdleader.com/tent/viewtopic.php?t=138926]Домашний интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] f9e2929
Признаки, что пора задуматься о кодировании
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-korolev[/url]
В клинике работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты, психологи, реабилитологи. Вместо «универсальной» схемы каждому пациенту подбирают индивидуальный план, учитывая возраст, стаж употребления, состояние внутренних органов, психоэмоциональный фон, семейную ситуацию. Это особенно важно для жителей Долгопрудного, где многие совмещают работу в Москве с плотным графиком, и любая ошибка в лечении может дорого обойтись — потерей работоспособности, срывом деловых или личных планов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ceny-dolgoprudnyj[/url]
В этой публикации мы предложим ряд рекомендаций по избавлению от зависимостей и успешному восстановлению. Мы обсудим методы привлечения поддержки и важность самосознания. Эти советы помогут людям вернуться к нормальной жизни и стать на путь выздоровления.
Узнать больше – http://www.farmsforyourevent.org/venues.php?URL=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
скупка золота грамм
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]секс[/url]
Метод капельничного лечения от запоя обладает рядом существенных преимуществ, благодаря которым пациенты получают качественную и оперативную помощь:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в архангельске[/url]
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]интернет инсис тарифы екатеринбург[/url]
подключить интернет инсис дома в екатеринбурге – [url=https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.li/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://maps.google.com.uy/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.frei-diplom6.ru/arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena-2.ru]Интернет и ТВ от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] 3da2a67
SEO продвижение сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге
Если по ходу визита появляются «красные флаги» (падение сатурации, нестабильный ритм, нарастающая дезориентация), маршрут мгновенно переводится в стационарный блок «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» — без «обнуления» обследований и без потери приватности. Вся собранная информация остаётся в единой карте наблюдения, что экономит время и силы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/narkolog-ekaterinburg-na-dom/
Друууууг, ну где же трееек…… мефедрон Москва – Все чётко, поднятие на раз два, все по описанию. Мефедрон белый, без запаха, видно что очищенный. Вес и качество норм!!!! Количество соответствует, за бонус в спасибо ;)посылка дошла за 1 сутки, сегодня не успел забрать, завтра посмотрим на качество) я уверен, что все будет хорошо Скажи что это? Я тебе помогу:) где хочешь заказать?
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://74.125.195.102/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Can’t help but say I’m happy I found Big Bass Splash — fantastic!
http://www.manilasites.com/maloney/newsitems/trackback/?u=maloney&p=2&link=https://big-bass-splash-uk-game.co.uk/bonus
продвижение сайтов 2026
I know this site gives quality based posts and extra information, is
there any other site which presents such information in quality?
Домашний визит нарколога — это не компромисс «на скорую руку», а тщательно организованный процесс, который экономит время, сохраняет конфиденциальность и делает лечение предсказуемым. «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» принимает вызовы круглосуточно и выезжает во все районы города — от Уралмаша и ВИЗа до Академического и Широкой Речки. Команда приезжает без внешних опознавательных знаков, использует нейтральные формулировки в документах и ведёт переписку только по защищённым каналам связи. На месте мы быстро проводим экспресс-диагностику, запускаем титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, контролируем пульс, сатурацию и артериальное давление, подключаем гастропротекцию и аккуратно управляем тревогой без избыточной седации. Цель — безопасно «снять волну» симптомов, вернуть возможность пить воду и отдыхать, а затем закрепить результат на горизонте ближайших 72 часов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод екатеринбург[/url]
Клиника нужна и тем, кто уже пробовал лечиться самостоятельно: пил лекарства «от тяги», ходил к психологу без медицинской поддержки, обещал себе не пить, но каждый стресс или конфликт всё равно приводили к старому сценарию. В такой ситуации комплексный подход — медицинский и психологический — даёт куда больше шансов, чем очередное одиночное обещание «в этот раз точно получится».
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah
My brother recommended I may like this web site. He was once totally right. This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thank you!
Процедура выезда врача на дом в Краснодаре строго регламентирована и включает несколько последовательных этапов. После поступления звонка и уточнения подробностей состояния пациента врач выезжает на место в течение 30–60 минут. На месте проводится первичный осмотр с оценкой жизненно важных показателей: артериального давления, уровня кислорода в крови, сердечного ритма и степени общей интоксикации.
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar/https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru
Получить займ можно в [url=https://dzhet-mani.com/]Джет Мани[/url]
Процесс лечения капельничным методом от запоя организован по четко структурированной схеме, позволяющей обеспечить оперативное и безопасное восстановление организма.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-klinika-arkhangelsk
Вывод из запоя в Воскресенске чаще всего требуется тогда, когда «обычное похмелье» уже давно перешло в тяжёлое состояние, а попытки «перетерпеть» только ухудшают ситуацию. Сначала кажется, что человек просто перебрал: день-два отлежится, попьёт воды, поест — и всё пройдёт. Но когда утром вместо облегчения появляется дрожь, сильная слабость, скачки давления, страх и навязчивая тревога, это уже не про похмелье. Организм не успевает перерабатывать алкоголь, сердце и нервная система работают на пределе, а каждый новый «опохмел» только продлевает запой.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]вывод из запоя московская область[/url]
Highly descriptive blog, I liked that a lot. Will there be a part 2?
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Детальнее – http://
Ну подскажите хоть что нибудь пожалуйста?А то я переживаю ппц. Купить наркотики | Где купить наркотики? я купил у них первый раз реактивы, всё пришло довольно быстро и консперация норм, не знаю если такой метод что они используют палевный то как иначе…..Ну это ясно))) спасибо за ответывнесли ясность! продавана сегодня в асе вообще ен видел, хз что там у них (
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника томск[/url]
Для получения устойчивого результата наркологическая клиника использует методы, основанные на индивидуальной оценке. В работе учитываются соматические показатели, реакции нервной системы и данные лабораторных исследований. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает предсказуемое влияние на физиологические процессы и снижает вероятность осложнений. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, позволяющий своевременно корректировать лечебные меры. Работа направлена на нормализацию метаболизма, восстановление баланса внутренних систем и плавное уменьшение симптоматики.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в владивостоке[/url]
В клинике работают врачи-наркологи, психиатры, терапевты, психологи, реабилитологи. Вместо «универсальной» схемы каждому пациенту подбирают индивидуальный план, учитывая возраст, стаж употребления, состояние внутренних органов, психоэмоциональный фон, семейную ситуацию. Это особенно важно для жителей Долгопрудного, где многие совмещают работу в Москве с плотным графиком, и любая ошибка в лечении может дорого обойтись — потерей работоспособности, срывом деловых или личных планов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]klinika-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Чем раньше нарколог окажет помощь, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и восстановиться без последствий для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Чехове — это возможность получить профессиональную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, не выезжая в крупный мегаполис и не тратя силы на долгую дорогу. Для многих людей момент обращения к наркологу наступает не сразу: сначала идут «домашние» попытки справиться с проблемой, обещания ограничиться «по праздникам», уговаривания родственников и периодические срывы. Запои становятся длиннее, организм восстанавливается всё хуже, усиливается тревога, нарушается сон, учащаются конфликты дома и на работе. В какой-то момент становится понятно, что без системного лечения обойтись уже нельзя, а стихийные капельницы на дому и случайные советы из интернета только оттягивают время.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/[/url]
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
выездной шиномонтаж 24 часа москва https://vyezdnoj-shinomontazh-77.ru
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Архангельске разработана для оперативного снижения токсической нагрузки при тяжелых формах алкогольной интоксикации. Сразу после вызова нарколог проводит подробный осмотр, измеряет жизненно важные показатели и собирает анамнез, что позволяет точно определить степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации формируется индивидуальный план лечения, включающий капельничное введение современных медикаментов с использованием автоматизированных инфузионных систем и сопровождение в виде психологической поддержки.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника архангельск[/url]
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske/
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]воскресенская клиника[/url]
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/[/url]
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно екатеринбург[/url]
Hello, I enjoy reading through your article. I wanted to write a little comment to support you.
Эти этапы формируют структуру комплексного лечения, позволяя добиться устойчивого результата и предотвращения повторных срывов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/narkologiya-astrakhan-adres
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом краснодар[/url]
Если в процессе выявляются нестабильные витальные показатели, нарастающая дезориентация или признаки дыхательной недостаточности, маршрут немедленно переводится в стационар «УралМедЦентра» с сохранением уже собранной информации — без повторных очередей и «история заново».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Vind in 2025 het beste casino zonder CRUKS en speel zonder beperkingen. Geen inschrijving nodig en volledige privacy
gegarandeerd. Geniet van snelle uitbetalingen, hoge bonussen en een veilige speelervaring ?
zonder tussenkomst van CRUKS.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
поставляемая продукция:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов платиновое 25х8х4.5 мм ПлИ90-10 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/
Hi my friend! I wish to say that this article is amazing, great written and come with approximately all significant infos. I’d like to see extra posts like this .
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого ижевск[/url]
Лечение на дому проходит в комфортной и спокойной обстановке, что позволяет значительно снизить уровень стресса и быстро улучшить состояние здоровья пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого сочи[/url]
Эти этапы формируют структуру комплексного лечения, позволяя добиться устойчивого результата и предотвращения повторных срывов.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/narkologiya-astrakhan-adres
Каждое направление наблюдения играет важную роль в формировании терапевтической программы. Структурированный контроль помогает снижать уровень рисков и обеспечивает возможность оперативной адаптации. Для систематизации данных применяется таблица, отражающая ключевые параметры мониторинга.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-izhevsk
Переходи на официальный сайт компании : https://etwcloudtv.com/ueditor/pages/le_meilleur_code_promo_2.html
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Архангельске имеет множество преимуществ, среди которых:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]капельница от запоя[/url]
Discover what’s new here — https://vmv.ru/admin/inc/promokod_252.html
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13156]kraken ссылка тор
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
Состав инфузии формируется по доминирующему симптому и данным экспресс-измерений, с учётом лекарственных взаимодействий. Врач оценивает динамику в реальном времени и, при необходимости, корректирует состав/скорость. Ниже — примеры профилей; окончательное решение всегда очное.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Go to our updated platform : https://dansermag.com/wp-content/pages/?1xbet_code_promo_bonus_gratuit.html
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]народные средства от диабета[/url]
Запой никогда не начинается с катастрофы. Первые несколько дней могут рассматриваться как «затянувшееся застолье». Но чем дольше человек пьёт без трезвых пауз, тем резче падают его возможности восстановиться самостоятельно. Поэтому ждать, что всё «рассосётся», — значит сознательно двигаться в сторону осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/[/url]
Наркологическая клиника использует методики, направленные на комплексную оценку состояния пациента. Работа строится на анализе анамнеза, исследовании соматических параметров и определении степени выраженности симптомов. Такой формат создаёт условия для точного подбора терапевтических мер. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, направленный на своевременное выявление отклонений и корректировку лечебных мероприятий. Благодаря этому достигается высокая стабильность клинического процесса и формируется благоприятная динамика восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Современные [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-elektro.ru] Рулонные шторы с электроприводом цена под ключ Prokarniz [/url] не только облегчают контроль освещенности в помещении, но и добавляют комфорта в ваш интерьер.
Широкий выбор рулонных штор с пультовым управлением позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для любого интерьера.
Go to our brand page > https://milmed.spb.ru/pgs/promokod_756.html
Каждая процедура проводится под контролем врача и сопровождается мониторингом давления, пульса и температуры. После курса капельниц пациент чувствует улучшение самочувствия, нормализуется сон, снижается раздражительность, появляется энергия и ясность сознания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор отборных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до крупных поставок, мы обеспечиваем быстрое выполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Дружелюбная помощь – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы по мере того как предоставлять решения под требования вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте вашу потребность в редких металлах профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
Наша продукция:
Фольга магниевая МЛ5пч – ГОСТ 2856-79 Труба магниевая МЛ5пч – ГОСТ 2856-79 предназначена для использования в различных отраслях, включая строительство и машиностроение. Основные преимущества данной трубы включают высокую коррозионную стойкость и легкость в обработке. Благодаря уникальным свойствам магниевых сплавов, она демонстрирует отличную прочность и надежность. Если вы ищете надежный и эффективный материал, то вам стоит купить Труба магниевая МЛ5пч – ГОСТ 2856-79. В нашем ассортименте представлены только качественные и сертифицированные изделия. Убедитесь в выгоде и преимуществах уже сегодня!
В рамках лечения используются методы, позволяющие фиксировать изменения и оценивать реакцию организма на проводимые мероприятия. Они служат основой для выборочных корректировок и обеспечивают структурированный характер процесса. Отличительной особенностью становится возможность адаптировать лечебные схемы под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые направления оценки состояния, применяемые для формирования полной клинической картины.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в владивостоке[/url]
Такая структура терапии обеспечивает контроль на всех стадиях и помогает добиться устойчивого результата без вреда для здоровья. Пациент получает не просто временное облегчение, а полное восстановление физического и эмоционального состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в астрахани[/url]
belka-digital
Каждый из представленных элементов формирует устойчивую основу для дальнейшей работы и задаёт необходимый уровень контроля. Структура вмешательств адаптируется под особенности конкретного случая, что укрепляет эффективность процесса и создаёт благоприятные условия для стабилизации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в пензе[/url]
Hi there, its fastidious paragraph about media print, we all be aware of media is a great source of facts.
Зависимость редко начинается резко. Сначала это «разовые» посиделки, алкоголь «для снятия стресса», эпизодическое употребление психоактивных веществ «из любопытства» или «для компании». На этом этапе человеку кажется, что он полностью контролирует ситуацию. Со временем эпизоды употребления становятся чаще, дозы растут, появляются провалы в памяти, срывы, невозможность остановиться вовремя. В этот момент уже страдают здоровье, работа, отношения с близкими. Обращение в наркологическую клинику позволяет не доводить ситуацию до критической точки и остановить разрушение жизни на любом этапе заболевания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]медикаментозное кодирование от алкоголизма долгопрудный[/url]
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the layout of your blog? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
https://xn—-htbblufccvgdmek8j.xn--p1ai/forum/user/51220/
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]заявка на интернет инсис[/url]
insis тарифы интернет – [url=http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.my/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]http://maps.google.com.ng/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://probki.vyatka.ru/content/reshenie-20112013#comment-35601951]Интернет и ТВ от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] 2929b05
Помимо медицинских процедур, клиника делает акцент на психологической поддержке и постлечебной адаптации. Пациентам помогают не только избавиться от физической зависимости, но и сформировать устойчивую мотивацию к трезвости, восстановить интерес к жизни и наладить отношения с близкими. Это достигается за счёт участия психологов, психотерапевтов и специалистов по социальной реабилитации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в кемерове[/url]
В рамках последовательного анализа состояния применяется также оценочная шкала, позволяющая фиксировать изменения и уточнять степень выраженности симптомов. Далее представлена таблица, демонстрирующая основные критерии наблюдения и их функциональное значение в клиническом процессе.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/
Есть ряд признаков, при которых ждать категорически нельзя и нужна срочная помощь врача, а не очередные «народные методы». Если вы замечаете у человека следующие симптомы, это прямой повод организовать профессиональный вывод из запоя:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskovskaya-oblast-moskva[/url]
Официальный портал — переходи! : https://medsystem.com.ua/tests/pgs/?promokod_283.html
На этом этапе специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний, что позволяет разработать персонализированный план терапии и оперативно выбрать методы детоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя архангельск[/url]
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://globalweb.net.ua/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva-stacionar[/url]
Таблица позволяет поддерживать единую структуру наблюдения и фиксировать изменения состояния. Такая модель обеспечивает прозрачность процессов и повышает точность принимаемых решений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy/
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в кемерове[/url]
Visit our homepage — https://avtonomia.md/wp-content/pages/promokod_240.html
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13156]kraken зеркало рабочее krakendarknet top
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]проверить подключен ли дом к интернету инсис[/url]
инсис подключение телевидения и интернета – [url=http://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://images.google.co.za/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://images.google.hu/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/dtcc.edu.vn/www.chistka-zasorov-kanalizatsii.kz/www.melbetofficialsite.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и ТВ от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] 2427e0a
Особенность клиники — возможность выезда нарколога на дом. Это особенно важно, если пациенту трудно самостоятельно добраться до центра или он хочет избежать публичности. Врач приезжает с полным набором медикаментов и оборудования, проводит обследование и ставит капельницу, контролируя состояние пациента на протяжении всей процедуры. Такой формат позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно и без стресса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom/
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]футбольная форма Арсенал купить интернет магазин москва[/url]
магазин футбольной атрибутики Арсенал – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://images.google.co.in/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://cse.google.cv/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport3.ru/www.php.ru/forum/www.karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/www.stretch-ceilings-samara.ru/www.teletype.in/%40alexd78/dzen.ru/www.reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru/r-diploma2.ru]Клубная атрибутика и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 01_f36b
Для самого пациента это шанс получить медицинское вмешательство без дополнительного стресс-фактора в виде транспорта, очередей и «больничной атмосферы». Он остаётся в привычной обстановке, в своей квартире, с теми же предметами, к которым привык, и это снижает сопротивление. Вместо жесткого сценария «либо немедленно в стационар, либо ничего» появляется промежуточный, более мягкий вариант: врачи приезжают домой, снимают остроту состояния, подбирают схему капельницы и медикаментов, объясняют, что делать дальше. Нередко именно после такого первого опыта человек впервые всерьёз задумывается о полноценном лечении, потому что ощущает реальную разницу в самочувствии до и после профессиональной помощи, а не просто очередной «опохмел».
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника московская московская область[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника астрахань[/url]
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство, где пациент получает всестороннюю поддержку: от снятия интоксикации и детоксикации до психотерапии и постлечебного сопровождения. В клинике «КемероваМед Трезвость» специалисты работают с любыми формами зависимостей — алкогольной, наркотической, медикаментозной. Принципы работы центра основаны на анонимности, профессионализме и индивидуальном подходе. Здесь создаются условия для полного восстановления здоровья и возвращения человека к стабильной трезвой жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в кемерове[/url]
http://xn--80aaldngfckvzkca2a1n.xn--p1ai/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%20%D0%A0%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8%201xBet%202026:%201XBRO200
Структурированное наблюдение позволяет поддерживать согласованность лечебных мероприятий и своевременно реагировать на изменения. Такая система создаёт единый аналитический подход для оценки состояния и обеспечивает целостность терапевтического процесса.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Современный [url=https://elektrokarniz-s-pultom.ru/] электрокарнизы для штор цена Prokarniz [/url] предлагает удобство управления шторами с помощью пульта.
Монтаж электрокарниза можно выполнить самостоятельно, следуя инструкции.
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Айнтрахт;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]атрибутика футбольного клуба Айнтрахт[/url]
футбольная форма Айнтрахт – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://images.google.tg/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://toolbarqueries.google.com.na/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.kuhnni-na-zakaz1.ru/kraktor.cc]Клубная атрибутика и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 02427e0
Hello everyone!
I came across a 155 interesting platform that I think you should browse.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://www.indect-project.eu/als-erwachsener-freunde-finden-tipps-fuer-menschen-ueber-30/]https://www.indect-project.eu/als-erwachsener-freunde-finden-tipps-fuer-menschen-ueber-30/[/url]
Furthermore do not neglect, folks, that a person at all times are able to inside this piece find answers to the most most confusing questions. We made an effort to lay out all content via the most extremely understandable manner.
На официальном сайте всегда свежие новости — http://ferienportugal.net/ice_media/robots/1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_12.html
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Для повышения эффективности лечения наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные методы, включающие мониторинг жизненно важных параметров, корректировку фармакотерапии и оценку неврологических показателей. Совокупность таких мер делает процесс более предсказуемым и снижает вероятность осложнений. Кроме того, практическая часть работы включает регулярную проверку метаболических функций, что способствует точному дозированию препаратов и своевременному изменению схем. Это позволяет поддерживать физиологическую устойчивость организма даже при интенсивной нагрузке и сохранять стабильность состояния на протяжении всего периода терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
If some one wants to be updated with most up-to-date technologies therefore he must be go to see this website and be up to date daily.
Go to our brand page > http://uzcm.ru/images/pages/promokod_1xbet_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
Вывод из запоя в Воскресенске чаще всего требуется тогда, когда «обычное похмелье» уже давно перешло в тяжёлое состояние, а попытки «перетерпеть» только ухудшают ситуацию. Сначала кажется, что человек просто перебрал: день-два отлежится, попьёт воды, поест — и всё пройдёт. Но когда утром вместо облегчения появляется дрожь, сильная слабость, скачки давления, страх и навязчивая тревога, это уже не про похмелье. Организм не успевает перерабатывать алкоголь, сердце и нервная система работают на пределе, а каждый новый «опохмел» только продлевает запой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskovskij-oblast[/url]
When I originally left a comment I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments
are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I receive 4 emails
with the same comment. There has to be an easy method you can remove me from that service?
Many thanks!
Howdy! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs!
Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your
posts! Carry on the fantastic work!
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Надежные матчи по футболу Expert tipsters deliver betting tips on sports games and matches including Fixed game selections and correct score best exacte forecast. Vip and free bets are available daily with sureshot odds and accumulator real
Зависимость редко начинается резко. Сначала это «разовые» посиделки, алкоголь «для снятия стресса», эпизодическое употребление психоактивных веществ «из любопытства» или «для компании». На этом этапе человеку кажется, что он полностью контролирует ситуацию. Со временем эпизоды употребления становятся чаще, дозы растут, появляются провалы в памяти, срывы, невозможность остановиться вовремя. В этот момент уже страдают здоровье, работа, отношения с близкими. Обращение в наркологическую клинику позволяет не доводить ситуацию до критической точки и остановить разрушение жизни на любом этапе заболевания.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-dolgoprudnom[/url]
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в сочи[/url]
Такое поэтапное лечение позволяет добиться устойчивого результата без стрессов и осложнений. Пациенты получают комплексную помощь, включающую как медицинские, так и психотерапевтические аспекты.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в кемерове[/url]
Мы сознательно избегаем полипрагмазии. В назначениях только то, что несёт проверяемую пользу: гидратация с корректировкой электролитов, противорвотная и гастропротективная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям и пунктирный ритм-контроль. Состав капельниц не «универсальный» — он собирается под симптомы и соматический фон, с учётом совместимости с текущими лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.). Такой подход обеспечивает управляемую динамику без дневной «ватности» и рисков перегрузки объёмом.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Комплекс перечисленных направлений формирует базу для выстраивания терапевтического процесса. При необходимости программа корректируется, что обеспечивает адаптацию к меняющимся условиям. Для удобства наблюдения используется таблица, отражающая основные параметры контроля.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в владивостоке[/url]
Visit our main platform : https://www.zaslugi.ru/images/pages/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus.html
Rutor — ведущий ресурс в русскоязычном даркнете н базе Tor, позволяющий получить доступ к контенту, материалам и товарам, а также правилам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Даркнет-ресурс Rutor сформировал репутацию надёжного магазина с анонимной системой доступа и сервисом защищённых переводов в Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutorforum.pro]rutorg расширение[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13159]kraken ссылка onion 2kmp
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
Наркологическая клиника в клинике в Астрахани предоставляет помощь пациентам, сталкивающимся с различными формами зависимости — алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Основой терапии является комплексный подход, включающий медицинскую детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния, психотерапию и последующее наблюдение. Такой формат работы позволяет мягко купировать острые симптомы, восстановить физиологические функции и подготовить пациента к длительной реабилитации. Все процедуры проводятся анонимно, с использованием сертифицированных препаратов и с постоянным контролем врача.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-astrakhan18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя астрахань[/url]
Незамедлительно после поступления вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, такие как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, и собирает анамнез для оценки степени алкогольной интоксикации.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk00.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]футбольная атрибутика Аталанта интернет магазин[/url]
купить футбольную атрибутику Аталанта – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.co.tz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://cse.google.bi/url?sa=i&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://filmstreaming4ever.00web.net/e-allora-condannai-a-morte-tutti-1971-50717#comment-777698]Клубная атрибутика и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] f9e2929
Посетите сайт компании прямо сейчас > https://jinding.fr/wp-content/pgs/le_meilleur_code_promo_3.html
На практике семья часто обращается за помощью слишком поздно — когда близкий уже еле встаёт, не спит ночами, говорит странные вещи, а давление скачет так, что страшно оставлять одного. Чтобы не доводить до этого, важно знать признаки, при которых капельница от запоя в Долгопрудном — не «желательно», а по-настоящему необходима.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]капельница от алкоголя цена[/url]
What’s up, just wanted to say, I liked this post. It was helpful. Keep on posting!
Informative article, exactly what I was looking for.
Для семьи это тяжёлый период. Родные одновременно злятся, боятся и пытаются «договориться»: то уговаривают, то угрожают, то пробуют лечить подручными средствами. Пока близкие спорят, состояние человека ухудшается: он перестаёт нормально есть, почти не спит, избегает разговоров, закрывается в комнате, теряет связь с привычной жизнью. В этот момент особенно важно не ждать, когда организм «сам справится», а подключить профессиональную помощь.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Go to the official company site : https://www.volvoclub.ru/pages/articles/promokod_756.html
Электрик Юла Севастополь Это потребность в квалифицированном электрике, мастере своего дела, чья работа обеспечивает свет, тепло и комфорт в каждом доме, офисе и предприятии.
Наркологическая клиника в Долгопрудном помогает в ситуациях, когда:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]medikamentoznoe-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Метод капельничного лечения от запоя обладает рядом существенных преимуществ, благодаря которым пациенты получают качественную и оперативную помощь:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Арсенал;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]магазин футбольной формы Арсенал[/url]
купить футбольную атрибутику Арсенал – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://images.google.mv/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://maps.google.co.ls/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://freifliegendehexe.de/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=1088&p=203887#p203887]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 9b06_49
Visit our newest official site : http://mcable.ru/files/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus.html
Bu saytdakı məlumatları oxumaqdan zövq alıram. Çox sağ olun!
http://worksale.nnov.org/common/redir.php?https://mostbet-azerbaijan-pro.org/oyunlar
https://doskazaymov.kz/ досказаймов – когда нужно быстро понять, где взять деньги в долг на понятных условиях.
fly888
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• Комплексный анализ покрытия сети в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж ТВ приставки
• Фиксированные тарифы на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибсети домашний интернет тарифы[/url]
сколько стоит подключить интернет сибирские сети – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.de/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://maps.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://wap2p.com/f/showthread.php?tid=16&pid=286195#pid286195]Интернет и ТВ от «СибСети» в Красноярске[/url] e0ae634
алтуфьево проточка тормозных дисков
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Айнтрахт;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]магазин футбольной формы Айнтрахт[/url]
футбольная форма клуба Айнтрахт – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ms/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://toolbarqueries.google.co.ve/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/k.krakenwork.cc/www.frei-diplom6.ru/s3A2F2247-poker.com%7Cimages.google.nl/k.krakenwork.cc/www.1xbet-17.com/www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-28.ru/www.alarm-radio-clocks.com/www.rudik-diplom3.ru/www.reiting-seo-agentstv.ru/,]Клубная атрибутика и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 27e0ae6
После купирования острых симптомов врач объясняет, какие шаги нужно сделать дальше: ограничиться домашним наблюдением, подумать о коротком стационарном курсе или сразу планировать дальнейшее лечение зависимости. Это помогает не возвращаться к затяжным запоям уже через несколько недель.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Медицинская публикация представляет собой свод актуальных исследований, экспертных мнений и новейших достижений в сфере здравоохранения. Здесь вы найдете информацию о новых методах лечения, прорывных технологиях и их практическом применении. Мы стремимся сделать актуальные медицинские исследования доступными и понятными для широкой аудитории.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://64.233.161.132/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
Многие люди пытаются самостоятельно справиться с запоем или наркотической интоксикацией, однако это часто приводит к серьезным осложнениям и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи организм подвергается сильному токсическому воздействию, что негативно отражается на всех органах и системах. Особенно страдают сердечно-сосудистая, нервная и пищеварительная системы. Игнорирование проблемы может привести к хроническим заболеваниям, алкогольным психозам, поражениям печени и даже к летальному исходу.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnodar/
Hi, this weekend is good designed for me, since
this time i am reading this great informative paragraph here at my residence.
Для семьи это почти всегда тяжёлый, эмоционально изматывающий период. В доме копятся усталость, обида, чувство вины, страх за близкого. Но при этом сохраняется надежда, что удастся «обойтись своими силами». В какой-то момент становится ясно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи уже не справиться. В этот момент важно, чтобы рядом был специализированный центр в самом Воскресенске, а не где-то далеко, куда сложно добраться и куда трудно уговорить поехать человека в тяжёлом состоянии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13159]как зайти на кракен даркнет
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
Rutor — главный портал русского даркнета в сети Tor, дающий доступ к материалам, товарам, контенту и правилам анонимности пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
Rutor — один из старейших ресурсов русского сегмента даркнета, обладающий известной историей, скрытной платформой и площадкой для защищённых обменов в системе Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutortop.cc]доступ рутор[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Детоксикация — ключевой этап в лечении зависимости. Она направлена на очищение организма от токсинов и нормализацию обмена веществ. В клинике «АстраМед Трезвость» капельницы подбираются индивидуально, с учётом возраста, массы тела и хронических заболеваний пациента. Ниже представлена таблица с основными видами инфузий и их назначением.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Важно понять: запой — это не просто серия праздников или «отпуск с алкоголем». Это состояние, при котором организм перестаёт выходить в трезвость, а любая попытка остановиться сопровождается настолько тяжёлыми симптомами, что человек снова тянется к бутылке. С каждым днём запоя возрастает нагрузка на сердце, печень, поджелудочную железу, мозг.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-voskresenske/
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Точную оценку скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку оборудования
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибсети подключить интернет и телевидение[/url]
сибирские сети тарифы на домашний интернет цена – [url=http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.com.pg/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.educ-ua4.ru/www.arus-diplom24.ru/url]Высокоскоростной интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в Красноярске[/url] 929b03_
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]ретро формы футбольных клубов купить[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной атрибутики в москве – [url=http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.ps/url?sa=t&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://images.google.hn/url?sa=t&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport3.ru/k.krakenwork.cc/www.1xbet-16.com/www.1xbet-16.com/www.frei-diplom4.ru/www.reiting-seo-kompanii.ru/www.r-diploma21.ru/index.html,[],[],200,65,0,1126,0,4,6,0,0,http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/,%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%5DОфициальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 04_7e9b
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
https://posido-fi.com
Наркологическая клиника использует методики, направленные на комплексную оценку состояния пациента. Работа строится на анализе анамнеза, исследовании соматических параметров и определении степени выраженности симптомов. Такой формат создаёт условия для точного подбора терапевтических мер. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, направленный на своевременное выявление отклонений и корректировку лечебных мероприятий. Благодаря этому достигается высокая стабильность клинического процесса и формируется благоприятная динамика восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр в владивостоке[/url]
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me lunch because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to talk about this matter here on your web site.
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]клубные футбольные формы Арсенал[/url]
клубные футбольные формы Арсенал – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ie/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]http://images.google.ch/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.rudik-diplom9.ru/www.medicinskoe–oborudovanie.ru/www.rudik-diplom6.ru/wwwboard.pl,[],[],200,65,0,1126,0,5,8,0,0,http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/,%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85y%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%7E%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85u%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%7E%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85u%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%5DОфициальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 7e0ae63
Отдельная категория пациентов — люди с алкогольной зависимостью. Для жителей Воскресенска особенно актуальны проблемы, связанные с длительными запоями: человек несколько дней подряд пьёт, практически не ест, плохо спит, с трудом встаёт, а каждое утро обещает, что «сейчас немного — и всё». На этом фоне растёт нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, повышается риск инсультов и инфарктов, обостряются хронические болезни.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
Часто первыми тревожные признаки замечают родные. Человек начинает пить чаще, чем раньше, меняется в поведении, становится раздражительным или замкнутым, теряет интерес к привычным занятиям. Появляются сложности с концентрацией, падает работоспособность, учащаются конфликты дома. Употребление наркотиков проявляется изменениями режима дня, странными компаниями, резкими перепадами настроения, финансовыми «дырами», попытками скрыть своё состояние.
Углубиться в тему – http://
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Айнтрахт;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]купить футбольную атрибутику Айнтрахт в москве[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной атрибутики Айнтрахт в москве – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www.google.co.cr/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.ae/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s%3A%2F%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.r-diploma13.ru/,]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] a2a67f9
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino-cz-15.com[/url] .
I’m very pleased to find this website. I want to to thank you
for your time just for this wonderful read!! I definitely really liked every little bit of it and I have you saved as a favorite to see new information on your blog.
Такая таблица позволяет систематизировать данные наблюдения и поддерживать единый подход к интерпретации результатов. Это повышает прозрачность процесса и делает оценку состояния объективной вне зависимости от длительности лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-penza18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена в краснодаре[/url]
Процесс лечения капельничным методом от запоя организован по четко структурированной схеме, позволяющей обеспечить оперативное и безопасное восстановление организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]вызов на дом капельницы от запоя архангельск[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]магазин футбольной формы Аталанта в москве[/url]
футбольная форма клуба Аталанта купить – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://images.google.at/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://www.google.cl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://wbbet88.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=4036&pid=2625239&page=3193&extra=#pid2625239]Клубная атрибутика и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 7f9e292
После диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом для быстрого снижения уровня токсинов в крови, восстановления обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому цена архангельск[/url]
Одна из главных ошибок — ждать «идеального момента» для лечения. Кажется, что кодирование уместно только тогда, когда зависимость достигла крайней стадии: человек потерял работу, перестал выходить из запоев, полностью разрушил отношения с близкими. На практике обращение в клинику Чехова оправдано гораздо раньше, как только употребление алкоголя перестаёт быть редким эпизодом и начинает системно мешать жить. Если каждый стресс, отпуск или конфликт заканчиваются срывом, если запои становятся длиннее, а похмелье тяжелее, — это уже повод хотя бы обсудить кодирование с врачом, а не ждать, пока ресурс организма будет почти исчерпан.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma[/url]
Rutor — основной сайт русскоязычного даркнета в Tor, дающий пользователям доступ к информации, материалам, товарам и правилам анонимности пользователей черного рынка и onion ресурсов
Давний участник рынка darknet Rutor завоевал доверие благодаря скрытой системе и сервису, позволяющему безопасно проводить сделки через сеть Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor.expert]рутор сайт официальный сайт[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Перспективы и риски
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Как отмечает врач-нарколог клиники «РеабилитАльянс» Павел Сомов, «чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше шансы на скорейшее выздоровление без серьезных последствий для здоровья».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]купить клубную футбольную форму[/url]
футбольная атрибутика в москве – [url=http://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://maps.google.com.gi/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://cse.google.nl/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=61796]Клубная атрибутика[/url] 2427e0a
Usually I do not learn article on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very pressured me to take
a look at and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me.
Thank you, quite great post.
В этой публикации мы предложим ряд рекомендаций по избавлению от зависимостей и успешному восстановлению. Мы обсудим методы привлечения поддержки и важность самосознания. Эти советы помогут людям вернуться к нормальной жизни и стать на путь выздоровления.
Детальнее – http://rewers.ru/redirect.php?url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Nice answers in return of this difficulty with solid arguments and telling all concerning that.
После завершения процедур врач дает пациенту и его родственникам подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
This article is truly a good one it assists new the web viewers, who are wishing in favor of blogging.
В этой статье рассматриваются способы преодоления зависимости и успешные истории людей, которые справились с этой проблемой. Мы обсудим важность поддержки со стороны близких и профессионалов, а также стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления. Научитесь первоочередным шагам к новой жизни.
Выяснить больше – http://vocesa.abril.com.br/assine/vocesa_combo_black_friday/?v=a5&checkedlog=1&url-retorno=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево в краснодаре[/url]
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=]сколько стоит подключение интернета зеленая точка[/url]
зеленая точка подключить интернет и телевидение – [url=https://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.dj/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://googleradio.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/fanfiction.borda.ru/s%3A%2F%2Freverenceengineering.com/x/cdn/www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru/www.1xbet-14.com/www.rudik-diplom8.ru/www.gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/r-diploma27.ru]Интернет и ТВ от «Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе[/url] 2929b08
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис интернет и тв[/url]
инсис домашний интернет – [url=https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ad/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://www.google.bt/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://pocherparts.de/cgi-bin/gast4.cgi/www.aktivnoe.forum24.ru/slatestarcodex.com/prodazha-akkauntov-ploshadka.ru/www.rudik-diplom3.ru/www.metatrader-5-sync.com,[],[],200,6,0,0,0,116,209,0,0,https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/,%D0%93%D1%92%D0%92%D0%86%5DДомашний интернет и ТВ от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] 3da2a67
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]футбольная атрибутика Аталанта[/url]
футбольная форма Аталанта – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://google.jp/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://www.google.cf/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.comedysong.ru/www.php.ru/forum/members/www.rudik-diplom9.ru/www.1xbet-4.com/google.nr/url?q=https://healthyturkiye.com/all-on-6-dental-implants-turkey]Официальная футбольная форма и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 929b04_
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/narkologi-izhevsk-czeny/
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Полная информация здесь – https://lacopuchavacreciendo.com/2016/01/22/espectacular-karla-constant-se-luce-en-bikini-con-8-meses-de-embarazo
With thanks! Ample stuff.
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=]зеленая точка интернет плюс тв[/url]
зеленая точка домашний интернет тарифы – [url=http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.vc/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://maps.google.ro/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/fanfiction.borda.ru/s%3A%2F%2Freverenceengineering.com/x/cdn/www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru/www.1xbet-15.com/www.r-diploma5.ru/index.html]Домашний интернет и телевидение от «Зелёная точка» в вашем доме[/url] 02427e0
Hi there i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i
read this piece of writing i thought i could also make comment due to this brilliant article.
casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino cz[/url] .
Rutor — лидирующий ресурс даркнета на русском языке в Tor, открывающий доступ к информации, материалам, товарам и правилам анонимности пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Мессенджер и магазин Rutor признан одним из самых безопасных ресурсов в русском даркнете, благодаря анонимности системы, конфиденциальности и поддержке платежей в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor.world]руторн[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Анонимность
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor — это платформа с уникальной историей, и её опыт стоит принимать во внимание всем, кто ценит собственную свободу, приватность и независимость от внешней цензуры в современном цифровом мире.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Уточнить детали – https://whatfixedit.com/question/where-can-i-find-a-set-of-home-phones-for-my-mother-that-doesnt-like-a-cellphone
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/narkolog-i-psikhiatr-adler
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
«Орион» в Красноярске предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]орион домашний интернет тв[/url]
заявка на подключение интернета орион – [url=http://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://cse.google.com.jm/url?sa=t&url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.studiya-podkastov-spb1.ru/www.sajt-smart-way.ru]Интернет и ТВ от «Орион» в Красноярске[/url] 27e0ae6
После принятия решения организуется либо выезд, либо госпитализация. На приёме проводится осмотр: измеряется давление, пульс, оценивается степень обезвоживания, выраженность тремора, тревоги, нарушений сна. Выясняются сопутствующие болезни и лекарства, которые человек принимает постоянно. Уже на этом этапе обсуждаются ближайшие шаги — объём детокса, необходимость круглосуточного наблюдения, примерные сроки стабилизации. Родным объясняют, чего ожидать в первые сутки, какие симптомы будут уменьшаться постепенно, а какие требуют немедленного информирования персонала.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]наркологическая клиника фото[/url]
I am in fact pleased to glance at this weblog posts which consists of plenty of helpful data, thanks for providing such information.
Лечебные мероприятия и рекомендации формируются исходя из индивидуального состояния каждого пациента. Специалист имеет возможность посвятить достаточное количество времени каждому больному, корректируя программу лечения согласно его особым потребностям и жизненным обстоятельствам. При этом учитываются психологические, социальные и физические аспекты, оказывающие влияние на здоровье пациента. Персонализированный подход обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на изменения состояния и своевременную корректировку терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Раскрыть тему полностью – https://korenagakazuo.com/2012/12/17/%E8%87%AA%E6%B0%91%E3%81%AE%E3%81%B2%E3%81%A8%E3%82%8A%E3%81%8C%E3%81%A1%E3%82%92%E8%A8%B1%E3%81%97%E3%81%9F%E3%80%81%E6%B0%91%E4%B8%BB%E3%81%8B%E3%82%89%E7%A5%A8%E3%81%8C%E5%88%86%E6%95%A3%E3%80%81
«Орион» в Красноярске предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]орион домашний интернет тарифы красноярск 2026[/url]
орион заявка на подключение домашнего интернета – [url=http://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.ge/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://clients1.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.elektrokarnizy50.ru/www.blog-o-marketinge.ru/www.melbet5008.ru]Интернет и ТВ от «Орион» в вашем доме[/url] 2929b01
I’d like to find out more? I’d care to find out more details.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://mehielinfo.net/alepeaction-citoyenne-le-conseil-national-des-jeunes-soulage-la-prefecture
кто знает когда рега будет ? кокаин спасибо вам уважаемый магазин за то что вы есть! ведь пока что лучшего на легале я не видел не чего!Приветы. Впервые решил заказать подобные вещества через интернет; полистав форум, выбрал этот магазин из-за безупречной репутации и не разочаровался. Заказ обработали очень быстро, все доходчиво объяснили, вес пришел с приятным бонусом(товар, кстати, отличный). Успехов и процветания вам и вашему магазину, ребята. в скаипе не отвечают!!!!
Домашний формат наркологической помощи особенно востребован в курортном регионе: плотный график, сезонная работа, круглосуточная индустрия гостеприимства и нежелание афишировать проблему заставляют искать решение «тихо и быстро». В «ЮгМедЦентре» (Сочи) выезд врача доступен 24/7 без праздников и «коротких дней», а лечение строится как управляемый медицинский процесс: сначала — измерения, затем — точная коррекция, после — режим и поддержка. Мы приезжаем без символики, используем кодовые профили, нейтральные формулировки в документах и защищённые каналы связи, чтобы сохранить приватность пациента и его семьи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в сочи[/url]
I used to be able to find good info from your content.
Мне очень нравится сайт kazino olimp, он очень понятный в использовании!
https://pin-up-kazakhstan-prof.com/games
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]vyzvat narkologa na dom[/url]
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
I constantly emailed this weblog post page to all my associates, because if like to read it then my friends will too.
На следующем этапе начинается активное медикаментозное вмешательство. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом для быстрого выведения токсинов и нормализации обменных процессов, что способствует стабилизации работы жизненно важных органов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Мы следуем прозрачному алгоритму: оценить риски — подтвердить безопасность домашнего формата — запустить инфузионный контур — объяснить «коридоры безопасности» и точки связи. Такой порядок снижает тревожность, делает управление симптомами измеримым и понятным, а родственникам оставляет простые инструкции без медицинского жаргона.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Rutor — ведущий ресурс в русскоязычном даркнете н базе Tor, позволяющий получить доступ к контенту, материалам и товарам, а также правилам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Проект Rutor — это проверенный временем магазин и коммуникационная система, обеспечивающая безопасность и анонимность сделок в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor.space]кгещк орг зеркало официальный сайт[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
вчера сделал заказ. оплатил. жду трек кокаин магаз четкий,еще в 2011 каждую неделю забегали:music:)всегда все ровноВесом по 1 гр Отличный Магаз, Все четко!!!
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый мог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Раскрыть тему полностью – https://lakeshorenews.com/blog/2026/01/31/hundreds-turn-out-for-4th-annual-nhl-alumni-vs-essex-opp-special-olympics-fundraiser
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://forum.povarenok.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=8652]ссылка кракен даркнет маркет
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
Wonderful article! That is the type of info that are meant to be
shared across the net. Disgrace on the search engines for not positioning this post higher!
Come on over and seek advice from my web site . Thanks =)
I do believe all of the ideas you have introduced for your post.
They are really convincing and can definitely work.
Nonetheless, the posts are too brief for starters.
May you please prolong them a little from next time?
Thank you for the post.
ruleta online [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]casino-cz-18.com[/url] .
Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа? У нас есть пошаговая инструкция!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Скачать активатор для Windows 11[/url]
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnodar
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя балашиха[/url]
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written!
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino-cz-15.com[/url] .
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the work you write.
The world hopes for even more passionate writers like
you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe. Always go after
your heart.
https://casinoursa.com/
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
сервис 10\10 нигде дешевле и лучше на рынке легал сейчас нету!!! https://biochemestry74.ru Качество товара на 5+,вот только почта подвела привезли на 5й день.Братишка, все красиво, в касание, спасибо за профессионализм а не может быть что они с реагентом перепутали? я вот пробовал правда не здесь, она желтоватая была
Обращение к наркологу — это не признание «окончательного проигрыша», а трезвое решение, что здоровье и жизнь важнее иллюзии контроля. В клинике можно безопасно вывести человека из запоя, стабилизировать состояние, обследовать сердце, печень, нервную систему, понять, насколько далеко зашло заболевание. Важно, что помощь получают не только тяжёлые пациенты «на грани», но и те, у кого ещё есть работа, семья, привычный образ жизни, но запои уже стали регулярными. Чем раньше удаётся подключить специалистов в Лобне, тем мягче можно пройти лечение и тем больше шансов сохранить и здоровье, и отношения, и социальный статус.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]narkologiya-lobnya[/url]
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
Состав капельницы не повторяет «советы знакомых». Он формируется под доминирующий симптом, сопутствующие заболевания и взаимодействия с текущими лекарствами. Врач постоянно оценивает витальные показатели и реакцию организма, корректируя скорость и объём по инфузомату. Ниже — примеры профилей, которые объясняют логику выбора; финальное решение всегда очное.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в сочи[/url]
Если вы хотите автоматизировать управление шторами, обратите внимание на [url=https://socvopros.ru/]электрокарнизы москва[/url], который станет идеальным решением для вашего дома.
Современные электрокарнизы часто интегрируются с домашними автоматизированными системами.
Обращаться можно и нужно не только в момент очередного запоя. Клиника в Ивантеевке работает и с теми, кто сейчас в относительной ремиссии, но понимает, что без внешней поддержки снова сорвётся. В этом случае можно обсудить профилактические программы, варианты кодирования, реабилитацию, работу с тревогой и депрессией. Чем раньше сделан шаг в сторону лечения, тем мягче будут процедуры и тем больше шансов на устойчивый результат.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Детальнее – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена новосибирск[/url]
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника краснодар[/url]
Самостоятельный выход из запоя сопряжен с высоким риском развития осложнений. После прекращения приема спиртного ослабленный организм может не выдержать нагрузки, что приведет к инфаркту, инсульту, судорожным приступам и даже алкогольному психозу. Чтобы избежать этих опасных состояний, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом, который проведет лечение правильно и безопасно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого в краснодаре[/url]
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Kraken — это популярная площадка, которая привлекает внимание пользователей благодаря широкому выбору сервисов и удобному интерфейсу. Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсу, часто используются kraken зеркала, позволяющие обойти ограничения и сохранить стабильное соединение. Актуальное kraken зеркало помогает быстро попасть на платформу даже [url=https://forum.povarenok.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=8652]kraken darknet onion vtor run
[/url] . Важно использовать только проверенную kraken ссылка, чтобы обезопасить свои данные и избежать мошенников. Официальный kraken сайт регулярно обновляется, обеспечивая пользователям надежность и безопасность работы.
РАБОТАЕМ!!! ОПТ!!! ДОСТАВКА!!! https://intellplatform.ru ТС ответь мне на почту или в лс, писал по поводу JV-100 ответилСчастья жизни не ждут под окном, Или вводит всех в заблуждение?!
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyway, just wanted to say superb blog!
byueuropaviagraonline
Приватность — клинический фактор, снижающий тревогу и укрепляющий доверие. В «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» выезд немаркированный, специалисты в гражданской одежде, уведомления — «тихие», документы — с нейтральными формулировками. Медкарта хранится в шифрованном контуре, доступ к данным разграничен по ролям. По запросу вся коммуникация ведётся через доверенное лицо, а оплата возможна наличными или безналом с нейтральным назначением платежа. Это позволяет оставаться в тени и при этом получать полноценную помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Для обеспечения максимальной безопасности на дороге рекомендуем приобрести [url=https://parkcam.ru/katalog/kamery-zadnego-vida/kamery-dlya-gruzovikov-i-avtobusov/]камера заднего вида на грузовик[/url].
Комплекты камер оснащены функциями, позволяющими видеть чёткое изображение в сложных условиях освещения.
If some one desires expert view on the topic of running a blog then i recommend him/her to pay a quick visit this blog, Keep up the fastidious work.
Алкогольная или наркотическая интоксикация — это не просто временное ухудшение самочувствия, а серьёзное медицинское состояние, требующее неотложной помощи. Когда человек находится в запое или состоянии ломки, его организм стремительно теряет силы, нарушается работа сердца, печени, мозга, возникают панические атаки, судороги, спутанность сознания. В таких случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Если пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники, оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом. В Красногорске такая услуга доступна круглосуточно благодаря выездной службе клиники «Ключ к Здоровью».
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vrach narkolog na dom moskva[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/
Rutor — ведущий ресурс в русскоязычном даркнете н базе Tor, позволяющий получить доступ к контенту, материалам и товарам, а также правилам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Площадка Rutor отличается хорошо зарекомендовавшей себя историей, высочайшей степенью скрытности и возможностью безопасной работы с транзакциями в сети Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor24x7.top]rutor org расширение[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Скачайте активатор для Windows 11 и получите все функции Pro-версии бесплатно.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Кряк для Windows 11 Pro бесплатно[/url]
nov? ?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]nov? ?esk? online casino[/url] .
Thanks in support of sharing such a good thought, article is nice,
thats why i have read it entirely
скайпцы не могу пока поставить по техническим причинам. хотелось бы связаться по мылу, но увы и ах. жаль, хороший ассортимент там. 🙁 мефедрон всё ровно забрал rcs-4 , не какой паранои от эффекта =) Позитив да и толькоСейчас по России что то не видно вас.Только пожелать ветра в парус,адекватных клиентов по меньше шкур Схема кидка: В пм на форуме вы получаете от магазина номер киви а он в жабер подтверждает Ваше кодовое слово. После чего диалог идет по жаберу. У Вас оказывается что на данный киви невозможно положить деньги и магазин пишет что даст другой номер. Всё вы закинули сами не туда. Что собственно мне и отписал магазин в пме.
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]?esk? casino online[/url] .
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnodar
В клинике «НаркоСити» используются только сертифицированные лекарственные средства, которые подбираются индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента:
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Каждая процедура проводится под контролем врача и сопровождается мониторингом давления, пульса и температуры. После курса капельниц пациент чувствует улучшение самочувствия, нормализуется сон, снижается раздражительность, появляется энергия и ясность сознания.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены астрахань[/url]
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=]подключить домашний интернет зеленая точка[/url]
зеленая точка тарифы adsl интернет – [url=http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://www.google.co.ls/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://maps.google.co.nz/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s%3A%2F%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry14.ru/www.gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/www.statyi-o-marketinge7.ru/www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Зелёная точка» в вашем доме[/url] 3_68fe6
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13270]кракен рабочее на сегодня сайт
[/url]
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Современный [url=https://kolesovremeni.ru/]электрокарнизы в одинцово[/url] обеспечивает удобство управления шторами с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Особенно ценно это для больших комнат и тех, кто испытывает трудности с движением.
На нашем сайте вы можете скачать активатор для Windows 11 абсолютно бесплатно и навсегда забыть о водяных знаках!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Где найти рабочий ключ для Windows 11[/url]
Большинство семей приходят к мысли о лечении зависимости не сразу. Сначала всё выглядит как «случайные переборы по праздникам», потом алкоголь или наркотики становятся привычным способом снять стресс, забыться, пережить неудачи. Постепенно запои учащаются, человек пропадает на несколько дней, появляются долги, проблемы на работе, конфликты в семье. На этом этапе многим кажется, что обращаться в наркологическую клинику в Лобне ещё рано, что можно «взять себя в руки» и как-то остановиться. Но практика показывает обратное: чем дольше затягивается момент обращения к специалистам, тем тяжелее протекают запои, тем глубже страдает здоровье и тем сложнее вернуть человека к стабильной трезвости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]адреса наркологических клиник[/url]
Мать и мачеху+травяной сбор(успокаивающий). мефедрон А как по качеству?с чего ты взял что мы соду “пропидаливаем”?, если есть какая то проблема давай решать, про “шапку” вы все горазды писать в интернете… Отзыв по работе магазина: после оплаты мной товара имелась задержка и паника с моей стороны) после задержки продавец деньги вернул- проблему без внимания не оставил… далее получил от магазина приятный презент в размере не дошедшего товара- товар дошел за 2 дня, курьерка работает без перебоев. Магазину респект! Можно работать
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Hi i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i read this post i thought i could also create comment due to this brilliant article.
Такая систематизация показывает, что врач действует целенаправленно, устраняя не только симптомы, но и их физиологические последствия.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого санкт-петербург[/url]
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Определение оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=]подключение к интернету через зеленая точка[/url]
зеленая точка интернет ставрополь тарифы для дома – [url=http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.pg/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://images.google.hn/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://xaqui.co/boomering1917/#comentarios]Высокоскоростной интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Зелёная точка» в вашем доме[/url] 67f9e29
Rutor — ключевая площадка русского даркнета в Tor, предоставляющая доступ к материалам, товарам, контенту и нормам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Портал Rutor признан лидером среди площадок русского даркнета за надёжный сервис, поддержание анонимности и обслуживание операций через Rutor.Rutor: Ветеран русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutorbestyszzvgnbky4t3s5i5h5xp7kj3wrrgmgmfkgvnuk7tnen2yd.com]rutor info отзывы[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Работа сервиса построена на использовании анонимной сети Rutor, что помогает свести к минимуму угрозы идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис домашний интернет тарифы московская область[/url]
инсис домашний интернет и телевидение – [url=http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]http://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /[/url]
[url=http://www.google.com.pr/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://www.google_tag_www.lnbrb.us/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://rech-im-ahrtal.de/forum/topic/the-paramount-plumbing-company-ever/?part=7979#postid-82316]Домашний интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] b08_8fa
Если по ходу визита появляются «красные флаги» (падение сатурации, нестабильный ритм, нарастающая дезориентация), маршрут мгновенно переводится в стационарный блок «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» — без «обнуления» обследований и без потери приватности. Вся собранная информация остаётся в единой карте наблюдения, что экономит время и силы.
Узнать больше – http://
«Орион» в Красноярске предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]орион интернет[/url]
пакеты ориона на интернет и телевидение – [url=https://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://images.google.bi/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://toolbarqueries.google.gr/url?sa=t&url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.educ-ua20.ru/safolv.e.l.u.pc%40haedongacademy.org/www.1xbet-15.com/www.1xbet-12.com/www.1xbet-14.com/www.frei-diplom4.ru/www.reiting-seo-kompanii.ru/www.r-diploma31.ru,]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «Орион» в Красноярске[/url] e0ae634
бля у нас опен эйр будет 11 июня у шамана пороха нету!!!вот ищу где бы взять что нибудь на подобие скорости или кокса!а тут отзывы что соду продают! бошки, марихуану жопа каши головы мозаики мозгазаказывал тут все четка пришло напишу в теме трип репотрты свой трипчик РЕСПЕКТ ВСЕМ ДОБРА БРАЗЫ КТО СОМНЕВАЕТСЯ МОЖЕТЕ БРАТЬ СМЕЛО ТУТ ВСЕ ЧЧЧИЧЧЕТЕНЬКА!!!!!!!!РОВНО ДЕЛАЙ РОВНО БУДЕТ:monetka::monetka:))))))))0 Быстрая доставка , и высочайшее качество обслуживания! Думаю и сейчас ничего не изменилось.
Лечение проходит поэтапно, чтобы пациент не испытывал стресса и перегрузок. Каждый шаг контролируется врачами, а терапия корректируется в зависимости от состояния. В таблице ниже представлена структура программы лечения в клинике «АстраМед Трезвость».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
[b][url=https://soho-catering.ru]рентфоэкспо[/url][/b]
Может быть полезным: https://soho-catering.ru или [url=https://soho-catering.ru]скатерть в аренду[/url]
[b][url=https://soho-catering.ru]подставка под шампанское[/url][/b]
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and
I find It truly helpful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to offer one thing back and
help others like you helped me.
[url=https://sibculture.ru/]надежный электрокарниз[/url] сочетает в себе современный дизайн и безупречную функциональность, обеспечивая плавное открывание и закрывание штор с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Управление может осуществляться через Wi-Fi, Bluetooth или радиоканал.
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://mohavod.ru/viewtopic.php?f=62&t=13273]кракен гидра даркнет
[/url]
«Орион» в Красноярске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]интернет орион тарифы для компьютера[/url]
орион интернет плюс тв – [url=http://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.br/url?sa=i&url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://clients1.google.ml/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.educ-ua20.ru/safolv.e.l.u.pc%40haedongacademy.org/www.stoimost-soglasovaniya-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru/www.1xbet-14.com/www.1xbet-15.com/www.frei-diplom8.ru/www.1xbet-17.com/www.statyi-o-marketinge7.ru/rudik-diplom3.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и ТВ от «Орион» в вашем доме[/url] 7e0ae63
nejlep?? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]nejlep?? online casina[/url] .
Asking questions are genuinely good thing if you are not understanding anything totally, except this post
provides good understanding even.
Вы то нет:) А банки работают:) Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Челябинск работаете?товар появился? когда возобновите доставку по городам? Дорогие наши форумчане, мы бы рады с вами пообщаться на разные темы, и стараемся общаться со всеми, и порой просто не хватает времени ведь мы не железные, если вы хотите что то конкретно заказать ася и скайп ждет вас, просто нереальное кол-во народа задают вопросы утром днем и вечером, и вот даже сейчас, мы очень стараемся изменить ситуацию в лучшую сторону. С начала месяца т.е. с 1 июня вы сможете самостоятельно заказывать и оплачивать прямо на сайте, а так же будете видеть наличие продукции.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
Rutor — основная площадка русскоязычного даркнета в Tor, предоставляющая доступ пользователям к контенту, товарам, материалам и правилам анонимности черного рынка и onion ресурсов
Площадка Rutor отличается хорошо зарекомендовавшей себя историей, высочайшей степенью скрытности и возможностью безопасной работы с транзакциями в сети Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor24.xyz]rutor amsterdam[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Перспективы и риски
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to your blog before but after browsing
through a few of the articles I realized it’s new
to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly happy I discovered
it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently!
Незамедлительно после вызова нарколог прибывает на место для проведения первичной диагностики. На этом этапе осуществляется сбор анамнеза, измерение жизненно важных показателей и оценка степени интоксикации, что является основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Для обеспечения максимальной безопасности на дороге рекомендуем приобрести [url=https://parkcam.ru/katalog/kamery-zadnego-vida/kamery-dlya-gruzovikov-i-avtobusov/]камера заднего вида на грузовик[/url].
Наличие камеры заднего вида значительно облегчает работу водителя в повседневных условиях.
Если вы хотите повысить безопасность и удобство маневрирования, рекомендуем [url=https://parkcam.ru/katalog/kamery-zadnego-vida/kamery-dlya-gruzovikov-i-avtobusov/]купить камеру заднего вида для грузового автомобиля[/url].
Некоторые модели оснащены ночным видением и системой предупреждения о препятствиях.
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
http://slovakiamod.6f.sk/profile.php?lookup=273
Cool + for the post
_________________
[url=https://gamesnews.shop]win 3 1 как запустить[/url]
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новосибирске[/url]
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом позволяет избежать стресса госпитализации, обеспечивая комфорт и удобство как для пациента, так и для его близких.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно санкт-петербург[/url]
Hmm it appears like your blog ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up
what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog.
I too am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to everything.
Do you have any helpful hints for novice blog writers?
I’d certainly appreciate it.
Excellent article. I am experiencing many of these issues as well..
смотря каким реагентом будешь бадяжить https://lacocinadepili.com П.С.С. отвечать, цитировать это сообщение не нужно, удалю позже.сайт скоро подымем , я на ветке отпишу как заработает Инфа с вашего сайта. Я уже брал 6-APB, и выглядел он несколько иначе.
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/narkolog-sochi
Состав инфузии формируется по доминирующему симптому и данным экспресс-измерений, с учётом лекарственных взаимодействий. Врач оценивает динамику в реальном времени и, при необходимости, корректирует состав/скорость. Ниже — примеры профилей; окончательное решение всегда очное.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены екатеринбург[/url]
После диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом для быстрого снижения уровня токсинов в крови, восстановления обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-arkhangelsk0.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Электрокарниз [url=https://www.karniz-opt.ru/]novo электрокарнизы[/url] обеспечивает автоматическую регулировку тени в помещении, сочетая современный дизайн с функциональностью.
Электрический карниз стал символом современного интерьера.
Управление доступно через wi-fi или bluetooth.
Возможна синхронизация с умными системами дома.
Дом кажется более технологичным и современным .
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
Fun88cbtc chegou pra botar ordem na casa! As odds são as melhores que já vi, e a plataforma é super fácil de usar. Pra quem curte apostar com cripto, é a melhor opção, na moral! Corre lá no fun88cbtc.
O NV8casino me surpreendeu demais! Tem jogo pra todo gosto e os gráficos são incríveis. Já ganhei uma grana boa por lá, então tô sempre de olho nas promoções no nv8casino.
Quem aí curte um bom caça-níquel? O mm99slot é o paraíso pra quem gosta de slot! Tem tanta opção que fico até perdido! E o melhor de tudo é que sempre rola umas rodadas grátis no mm99slot.
Многие жители Ивантеевки откладывают обращение, потому что им кажется, что ситуация «ещё не настолько страшная». Пока человек как-то ходит на работу, иногда остаётся трезвым и периодически клянётся, что «всё возьмёт под контроль», кажется, что обращаться в клинику рано. На самом деле эффективнее всего лечение работает именно тогда, когда проблемы уже заметны, но ещё не привели к тяжёлым осложнениям — инсультам, инфарктам, тяжёлым психозам, полной утрате социальных связей.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-reabilitaciya-v-ivanteevke
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наша продукция:
Кольцо из драгоценных металлов палладиевое 200х100х1.5 мм Пд99.9 ТУ Широкий выбор высококачественных кольц из драгоценных металлов. Элегантные украшения, созданные талантливыми мастерами. Уникальность и изысканность в каждой детали. Возможность заказа персонального кольца по вашим пожеланиям. Подчеркните свою индивидуальность с нашими кольцами.
Такая структура терапии обеспечивает контроль на всех стадиях и помогает добиться устойчивого результата без вреда для здоровья. Пациент получает не просто временное облегчение, а полное восстановление физического и эмоционального состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-astrakhani18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в астрахани[/url]
Rutor – ключевой ресурс даркнета на русском языке в Tor, дающий доступ к контенту, материалам, товарам и правилам сохранения анонимности пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
Rutor — один из старейших ресурсов русского сегмента даркнета, обладающий известной историей, скрытной платформой и площадкой для защищённых обменов в системе Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor24x7.one]rutor live[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Задача первого контакта — не «записать к врачу на когда-нибудь», а оценить, насколько ситуация критична прямо сейчас. Если речь идёт о многодневном запое, сильной слабости, одышке, скачках давления, спутанности сознания, лучше не экспериментировать с домашними методами. В таких случаях специалисты в Лобне рекомендуют стационар, где можно не только поставить капельницу, но и быстро среагировать на осложнения. Если же состояние относительно стабильное, возможно обсуждение мягкого формата с выездом и последующим наблюдением.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]клиника наркологической помощи[/url]
It’s in reality a nice and useful piece of info. I am satisfied that you just shared this useful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Разобраться лучше – https://www.lulushare.com/go.php?url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
Оправдания в небе не ищут, бошки, марихуану хуясе надо было сначало уточнить а что брали хоть? ио названижю веществаХотелось бы услышать мнение продавца, по этому поводу А ВОТ Я ТОЖЕ КИПИШЕВАЛ ПО СЧЕТУ ТРЕКА НЕ БИЛСЯ ТОЖЕ ПОЗВОНИЛ В КУРЬЕРКУ СКАЗАЛИ ОТПРАВЛЕННО И СЕГОДНЯ К ВЕЧЕРУ ВСЕ ОТБИЛОСЬ ЖДУ ПРИХОДА ПОСЫЛКИ. ПОТОМ НАПИШУ КАК ЕСТЬ. ПРОШУ ПРОЩЕНИЯ У ЧЕМИКАЛА ЗА ПЛОХИЕ ПОСТЫ, ДУМАЮ ПОЙМЕТ))) УЖЕ ДАВНО ТУТ БЕРУ НЕ РАЗУ НЕ КИНУЛ НИ ОДНОЙ ЗАДЕРЖКИ ВСЕ ПРОСТО НА 100%.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Bu kontentə görə təşəkkürlər. Saytı dostlarıma tövsiyə edəcəyəm.
https://mostbet-azerbaijan-win.net/odenisler
Whats up very cool website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Wonderful ..
I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally?
I am glad to find so many helpful info here within the submit,
we want work out more techniques on this regard,
thank you for sharing. . . . . .
https://salt-cave.ru/
Медицинская публикация представляет собой свод актуальных исследований, экспертных мнений и новейших достижений в сфере здравоохранения. Здесь вы найдете информацию о новых методах лечения, прорывных технологиях и их практическом применении. Мы стремимся сделать актуальные медицинские исследования доступными и понятными для широкой аудитории.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://illusions-designs.net/catalog/redirect.php?action=url&goto=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
beste bonusbedingungen sportwetten
my web site … basketball wetten gerade ungerade (https://basketball-wetten.com)
Для создания удобного и стильного интерьера выбирайте [url=https://mebel-h.ru/]электрокарниз купить цена[/url] — это лучший выбор для современного дома.
Электрокарниз, встроенный в систему умного дома, синхронизирует работу штор с освещением и температурными сценариями.
В случаях, когда транспортировка в клинику затруднительна или пациент испытывает выраженный стресс, возможно выездное консультирование и начальная детоксикация на дому. Врач прибывает с портативным набором для инфузий, оперативно stabilizирует состояние и даёт рекомендации по дальнейшим действиям.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма анонимно в екатеринбурге[/url]
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор высококачественных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до крупных поставок, мы гарантируем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их качество. Превосходное обслуживание – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы а также адаптировать решения под требования вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наша продукция:
Лист магниевый ISO-MgAl6Mn – ISO 16220 Лента магниевая ISO-MgAl6Mn – ISO 16220 – это высококачественный материал, предназначенный для решения задач легкого строительства и производства. Обладая отличными механическими свойствами и коррозионной стойкостью, данная лента идеально подходит для широкого спектра промышленных применений. Спецификация ISO 16220 гарантирует надежность и соответствие самым современным стандартам. Если вы ищете надежный и легкий материал, купить Лента магниевая ISO-MgAl6Mn – ISO 16220 – это ваше оптимальное решение для достижения успеха в проекте.
Клиника «УралМед» работает без выходных и праздников: прием пациентов — круглосуточно. Это позволяет оказывать экстренную помощь при острых состояниях, а также вести наблюдение за динамикой восстановления здоровья в ночные часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма в екатеринбурге[/url]
Rutor — главный портал русскоязычного даркнета в сети Tor, обеспечивающий доступ к материалам, товарам, контенту и нормам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
В русском даркнете Rutor занимает прочные позиции «ветерана» благодаря стабильности, системе безопасности и поддержке транзакций через Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor24.one]rutor org зеркало настоящий[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Механизм работы ресурса позволяет пользователям получать доступ к большим массивам данных и файлов, при этом обеспечивая максимальную приватность и анонимность. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Архитектура ресурса предусматривает, что любые разделы — магазин, новостной блок или гайды по взлому — являются составляющими единой системы, где превалируют безопасность и анонимность.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Конфиденциальность общения
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Для детоксикации и восстановления организма после запоя используются только сертифицированные лекарственные препараты с доказанной эффективностью и безопасностью:
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
This blog was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Thanks!
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника сочи[/url]
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Комплексный анализ доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж оборудования
• Фиксированные тарифы на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибирские сети домашний интернет тарифы московская область[/url]
подключение к интернету через сибсети – [url=https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www.google.com.do/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://clients1.google.co.uk/url?rct=j&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.888starz-english.com/www.r-diploma13.ru]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в Красноярске[/url] 5_94df8
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Установка [url=https://2teh.ru/]электрокарнизы в одинцово[/url] для ваших штор может значительно улучшить функциональность и эстетику вашего дома.
он предназначен для упрощения процесса управления шторами и жалюзи . Это устройство можно легко интегрировать в систему умного дома чтобы повысить уровень комфорта и безопасности . Электрокарниз может быть управляем с помощью пульта дистанционного управления или мобильного приложения что позволяет управлять им из любой точки дома .
Электрокарниз также может быть интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома как системы видеонаблюдения и дверные замки. Это позволяет создать единую систему управления всеми устройствами в доме что дает возможность создать более удобную и безопасную среду обитания. Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть оснащен датчиками освещенности и температуры которые позволяют автоматически регулировать положение штор и жалюзи .
## Раздел 2: Преимущества электрокарниза
Электрокарниз имеет множество преимуществ он позволяет автоматизировать процесс управления шторами и жалюзи. Это устройство также может помочь сэкономить энергию путем автоматического регулирования положения штор и жалюзи . Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть использован для создания сценариев и режимов работы как режим “светлый день” или “темный вечер.
Электрокарниз также может быть оснащен функцией таймера которая дает возможность создать индивидуальный график работы. Это устройство также может быть интегрирован с голосовыми помощниками такими как Siri или Cortana . Это позволяет управлять электрокарнизом с помощью голосовых команд что позволяет управлять им без необходимости использования пульта или приложения .
## Раздел 3: Установка и настройка электрокарниза
Установка электрокарниза не требует специальных навыков или инструментов она может быть выполнена самостоятельно . Это устройство поставляется с набором необходимых деталей и инструкциями которые обеспечивают подробную информацию о процессе установки . После установки электрокарниз необходимо настроить чтобы он был интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома .
Настройка электрокарниза обычно включает в себя создание учетной записи и настройку параметров работы настройку голосовых команд и приложения. Это позволяет создать индивидуальный режим работы электрокарниза который будет удовлетворять всем потребностям пользователя . Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть обновлен с помощью специального программного обеспечения которое дает возможность поддерживать электрокарниз в актуальном состоянии.
## Раздел 4: Заключение
Электрокарниз – это современное и удобное решение для управления шторами и жалюзи в доме он создан для того, чтобы сделать управление шторами и жалюзи более простым и удобным. Он может быть интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома как системы видеонаблюдения и дверные замки и управляться с помощью пульта дистанционного управления или мобильного приложения что позволяет управлять им из любой точки дома . Электрокарниз также может быть оснащен датчиками освещенности и температуры которые позволяют автоматически регулировать положение штор и жалюзи .
Электрокарниз имеет множество преимуществ он позволяет автоматизировать процесс управления шторами и жалюзи. Он может быть использован для создания сценариев и режимов работы например, режим “вечер” или “ночь” и может быть интегрирован с голосовыми помощниками например, с Alexa или Google Assistant . Это устройство также может быть обновлен с помощью специального программного обеспечения которое дает возможность поддерживать электрокарниз в актуальном состоянии.
После поступления вызова нарколог клиники «АльфаНаркология» оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу. На месте врач проводит первичную диагностику, оценивая степень интоксикации, физическое и психологическое состояние пациента. По результатам осмотра врач подбирает индивидуальный комплекс лечебных процедур, в который входит постановка капельницы с растворами для детоксикации, препараты для стабилизации работы органов и нормализации психического состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Стильный внешний вид создает сильное впечатление о вас.
Ваш образ влияет на оценку вас коллегами мгновенно.
Уверенность в своем луке укрепляет вашу уверенность.
Он демонстрирует ваш стандарт профессионализма и внимание к мелочам.
https://dreevoo.com/profile.php?pid=1001712
Посредством одежду вы можете выразить свою индивидуальность и стиль.
Окружающие часто воспринимают опрятных людей как более успешных.
Следовательно, вложения в свой стиль — это вклад в ваше успешное будущее.
Very sleek and professionally built site Big Bass Splash!
http://images.google.cl/url?sa=t&url=http%3A%2F%2Fbigbasssplash-casino-couk.uk%2Fgame
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://animal-style.ru/kraken-2026-rabochie-ssylki-i-zerkala-zashhita-ot-fishinga/]kraken зеркало vk01 xyz
[/url]
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-sochi
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов в новосибирске[/url]
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Такой подход позволяет устранить физические последствия запоя и снизить психологическую зависимость. Уже после первой процедуры пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, появление аппетита и нормализацию сна. Важно не ограничиваться только экстренной помощью — специалисты рекомендуют пройти курс восстановления, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого владивосток[/url]
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who has been doing a little research on this. And he in fact bought me dinner because I discovered it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to discuss this subject here on your web page.
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Перечисленные меры обеспечивают структурированный подход к восстановлению, позволяя выстраивать лечение в соответствии с текущими изменениями. Такой формат способствует достижению устойчивой физиологической стабилизации и уменьшает выраженность симптомов. Для систематизации применяемых методов используется таблица, представленная ниже.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-kemerovo/
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в томске[/url]
Maybe you know similar resources?
casino neterapay
Вывод из запоя — это не просто медицинская процедура, а важный шаг на пути восстановления организма и возвращения человека к нормальной жизни. В клинике «ВладТрезвие Центр» пациенты получают профессиональную помощь, основанную на современных методиках детоксикации и безопасном медикаментозном восстановлении. Каждый случай рассматривается индивидуально, а лечение подбирается с учётом возраста, состояния здоровья и продолжительности запоя. Наркологи центра выезжают на дом круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь даже в экстренных ситуациях, когда время играет ключевую роль.
Подробнее – http://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-gorod-vladivostok/
В этот этап включено:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новосибирске[/url]
«Ижевский Центр Трезвых Решений» — это частное медицинское учреждение, где проводится лечение всех форм алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Программы терапии разработаны на основе международных рекомендаций и включают не только медикаментозное воздействие, но и психологическую поддержку. Все процедуры проходят анонимно, без постановки на учёт, что особенно важно для пациентов, желающих сохранить конфиденциальность.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/
Установите удобный [url=https://www.mobile-mir.ru/]стоимость электрокарнизов[/url] для идеального управления шторами в вашем доме.
Это устройство дает возможность автоматизировать открытие и закрытие штор без физических усилий.
Такие системы становятся все популярнее благодаря своему удобству и функциональности. Они особенно востребованы в помещениях с высокими окнами или труднодоступными карнизами.
#### **2. Преимущества электрокарнизов**
Главное достоинство электрокарниза — это удобство использования. Система работает бесшумно и плавно, не создавая лишнего шума.
Кроме того, электрокарнизы отличаются высокой надежностью и долговечностью. Они изготавливаются из прочных материалов, устойчивых к износу.
#### **3. Установка и настройка**
Монтаж электрокарниза требует определенных навыков и точности. Перед установкой необходимо проверить прочность стены или потолка в месте крепления.
После установки нужно правильно настроить систему управления. Современные электрокарнизы поддерживают голосовое управление через умные колонки.
#### **4. Выбор подходящей модели**
При покупке электрокарниза важно учитывать несколько факторов. В первую очередь, нужно определить максимальный вес штор, которые будет выдерживать система.
На рынке представлены модели разных ценовых категорий. Выбор зависит от ваших потребностей и бюджета, но качество всегда должно быть на первом месте.
—
### **Спин-шаблон**
#### **1. Введение**
Электрокарниз — это современное решение для управления шторами и гардинами.
#### **2. Преимущества электрокарнизов**
Они изготавливаются из прочных материалов, устойчивых к износу.
#### **3. Установка и настройка**
Для правильного монтажа важно учитывать особенности конструкции.
#### **4. Выбор подходящей модели**
Бюджетные варианты обладают базовым функционалом, но надежны в эксплуатации.
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника в томске[/url]
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена кемерово[/url]
Опрятный внешний вид формирует первое мнение о человеке.
Ваш образ влияет на оценку вас коллегами мгновенно.
Хорошее самочувствие в своем образе укрепляет вашу самооценку.
Этот подход подчеркивает высокий уровень ответственности и внимание к деталям.
https://rentry.co/toc5kriv
Посредством одежду вы можете проявить свою индивидуальность и стиль.
Окружающие неосознанно воспринимают опрятных индивидов как более компетентных.
Следовательно, вложения в свой образ — это вклад в ваше успешное будущее.
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://www.ctibrace.ru/stati/kraken-vse-ssylki-2026-spisok-rabochih-ssylok-i-zerkal-dlja-bezopasnogo-vhoda-v-kraken/]официальные зеркала кракен
[/url]
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and
I find It really helpful & it helped me out a
lot. I am hoping to present one thing again and help others such as you aided me.
В этом исследовании рассмотрены методы лечения зависимостей и их эффективность. Мы проанализируем различные подходы, используемые в реабилитационных центрах, и представим данные о результативности программ. Читатели получат надежные и научно обоснованные сведения о данной проблеме.
Подробнее – https://m.tailorcoffee.com/member/login.html?returnUrl=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Наркологическая клиника опирается на комплексную модель оценки состояния, обеспечивающую последовательное восстановление функций организма. В клинике применяется система многоуровневого контроля, направленная на выявление нарушений и определение оптимальной тактики вмешательства. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать стабильность состояния даже в условиях выраженных клинических проявлений. Структурированная работа направлена на снижение токсической нагрузки, коррекцию метаболических процессов и восстановление адаптивных механизмов. Анализ проводится с учётом физиологических особенностей пациента и динамики изменений.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]интим услуги[/url]
Ниже представлена последовательность основных шагов терапевтического процесса.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladivostok/
В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» помощь оказывается круглосуточно и без ожидания. Пациент может обратиться за консультацией в любое время суток, а выездная бригада нарколога доступна даже ночью. Основной принцип центра — индивидуальный подход и создание доверительной атмосферы, в которой человек не чувствует осуждения, а получает поддержку и заботу.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom/
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Thank you!
Незамедлительно после вызова нарколог прибывает на место для проведения первичной диагностики. На этом этапе осуществляется сбор анамнеза, измерение жизненно важных показателей и оценка степени интоксикации, что является основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому волгоград[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Наркологическая клиника использует методики, направленные на комплексную оценку состояния пациента. Работа строится на анализе анамнеза, исследовании соматических параметров и определении степени выраженности симптомов. Такой формат создаёт условия для точного подбора терапевтических мер. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, направленный на своевременное выявление отклонений и корректировку лечебных мероприятий. Благодаря этому достигается высокая стабильность клинического процесса и формируется благоприятная динамика восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom/
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом новосибирск[/url]
1win шартгузории мобилӣ [url=https://www.1win71839.help]https://www.1win71839.help[/url]
В рамках лечения используются методы, позволяющие фиксировать изменения и оценивать реакцию организма на проводимые мероприятия. Они служат основой для выборочных корректировок и обеспечивают структурированный характер процесса. Отличительной особенностью становится возможность адаптировать лечебные схемы под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые направления оценки состояния, применяемые для формирования полной клинической картины.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Функция и назначение
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Установив [url=https://gzstore.ru/]рулонная штора электрокарниз[/url], вы забудете о неудобствах ручного управления шторами и насладитесь максимальным комфортом.
дарящее комфорт и удобство в ежедневном использовании. Они позволяют управлять шторами дистанционно, без необходимости вручную открывать и закрывать их. Это особенно актуально для больших окон, высоких потолков или для людей с ограниченными физическими возможностями.
Преимущества электрокарнизов очевидны: удобство, функциональность и современный дизайн. Они легко интегрируются в систему “умный дом”, позволяя управлять освещением и уровнем приватности с помощью мобильного устройства или голосовых команд. Вдобавок, они плавно и тихо перемещают шторы, создавая приятную и расслабляющую атмосферу.
**Выбор электрокарниза: На что обратить внимание**
При выборе электрокарниза важно учитывать несколько ключевых факторов. Во-первых, необходимо определить длину карниза и тип ткани штор. Во-вторых, стоит обратить внимание на мощность двигателя и скорость движения штор. В-третьих, необходимо учитывать возможность интеграции с системой умный дом и наличие дополнительных опций, таких как таймер или датчик света.
Также важно обратить внимание на производителя и наличие гарантии. Проверенные производители обеспечивают надежность и долговечность своей продукции. Гарантийный срок – это дополнительная страховка ваших вложений и уверенность в надежности товара. Не стоит выбирать самые дешевые варианты, так как электрокарниз – это долгосрочное приобретение, улучшающее комфорт вашего дома.
**Установка и обслуживание электрокарнизов**
Установка электрокарниза требует определенных навыков и инструментов. Лучше доверить установку специалистам, чтобы избежать неисправностей и повреждений. Они правильно установят карниз, подключат его к электросети и настроят систему управления. Неправильная установка может привести к повреждению оборудования и, следовательно, к дополнительным затратам.
Обслуживание электрокарнизов не требует особых усилий. Регулярно протирайте карниз от пыли и грязи мягкой тканью. Если необходимо, смазывайте подвижные части специальным средством. Следуйте инструкциям по эксплуатации, и ваш электрокарниз будет работать бесперебойно в течение длительного времени.
**Электрокарнизы: Создайте уют и комфорт в вашем доме**
Электрокарнизы – это не просто функциональное устройство, но и стильный элемент интерьера. Они подчеркивают современный дизайн и добавляют элегантности любому помещению. Они позволяют создать неповторимую атмосферу комфорта и уюта. Инвестируйте в электрокарнизы, и вы почувствуете разницу в качестве жизни.
Выбирая электрокарнизы, вы выбираете удобство, функциональность и современный стиль. Они станут отличным решением для управления освещением и личным пространством в вашем доме. Наслаждайтесь комфортом и уютом, которые подарят вам электрокарнизы. Создайте свой идеальный дом с помощью современных технологий.
**Спин-шаблон:**
“`
Электрокарнизы – это инновационное решение, дарящее комфорт и удобство в ежедневном использовании. С их помощью можно легко регулировать положение штор, не прикасаясь к ним. Это становится важным преимуществом для окон большого размера, потолков с большой высотой и для людей с особыми потребностями.
Преимущества электрокарнизов очевидны: удобство, функциональность и современный дизайн. Они легко интегрируются в систему “умный дом”, позволяя управлять освещением и уровнем приватности с помощью мобильного устройства или голосовых команд. Кроме того, электрокарнизы обеспечивают плавное и бесшумное движение штор, что создает атмосферу уюта и спокойствия.
При выборе электрокарниза важно учитывать несколько ключевых факторов. Прежде всего, определите требуемую длину карниза и выберите подходящую ткань для штор. Вторым важным аспектом является мощность мотора и скорость, с которой двигаются шторы. В-третьих, необходимо принимать во внимание возможность интеграции с системой “умный дом” и наличие дополнительных функций, к примеру, таймера автоматического включения/выключения или датчика освещённости.
Также важно обратить внимание на производителя и наличие гарантии. Надежные производители предлагают качественные продукты с длительным сроком службы. Гарантия – это дополнительная защита ваших средств и уверенность в качестве приобретаемого продукта. Не стоит экономить на качестве, ведь электрокарниз – это долгосрочное вложение в комфорт вашего дома.
Установка электрокарниза требует определенных навыков и инструментов. Рекомендуется обратиться к профессионалам, чтобы избежать ошибок и повреждений. Они правильно установят карниз, подключат его к электросети и настроят систему управления. Самостоятельная установка может привести к поломке оборудования и, как следствие, к дополнительным затратам.
Обслуживание электрокарнизов не требует особых усилий. Регулярно протирайте карниз от пыли и грязи мягкой тканью. При необходимости смазывайте подвижные элементы специализированным составом. Соблюдайте правила эксплуатации, указанные в инструкции, и ваш электрокарниз прослужит вам долгие годы.
Электрокарнизы – это не просто функциональное устройство, но и стильный элемент интерьера. Они подчеркивают современный дизайн и добавляют элегантности любому помещению. Они позволяют создать уникальную атмосферу комфорта и уюта. Инвестируйте в электрокарнизы, и вы почувствуете разницу в качестве жизни.
Выбирая электрокарнизы, вы выбираете удобство, функциональность и современный стиль. Они станут незаменимым помощником в управлении освещением и приватностью вашего дома. Почувствуйте комфорт и уют, которые принесут вам электрокарнизы. Создайте свой идеальный дом с помощью современных технологий.
“`
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Арсенал;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]футбольная форма клуба Арсенал купить[/url]
футбольная форма Арсенал – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.tw/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://toolbarqueries.google.cz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://bonedryretro.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=928505]Спортивная экипировка и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 03da2a6
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Айнтрахт;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]футбольная атрибутика Айнтрахт интернет магазин[/url]
футбольная атрибутика Айнтрахт в москве – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www.google.ro/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://images.google.com.br/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/k.krakenwork.cc/www.frei-diplom6.ru/s3A2F2247-poker.com%7Cimages.google.co.in/www.stoimost-soglasovaniya-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru/www.1xbet-16.com/www.rudik-diplom8.ru/www.gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/www.rudik-diplom9.ru/cse.google.com.af/url?q=https://healthyturkiye.com/lechenie-bolezni-pejroni-turcija,]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 04_880f
seostart.com.ua
1вин app бехатар [url=www.1win71839.help]www.1win71839.help[/url]
Вывод из запоя требует комплексного контроля всех физиологических параметров. Ниже представлены основные направления наблюдения, формирующие структуру оценки состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя в ижевске[/url]
После оформления заявки на сайте narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru или по телефону, оператор уточняет информацию о пациенте: возраст, длительность запоя, наличие хронических заболеваний, текущее самочувствие. В течение 30–60 минут дежурный специалист приезжает по адресу с полным комплектом оборудования и медикаментов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Ниже представлена последовательность основных шагов терапевтического процесса.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://FreeWebAds.biz/584/posts/1/1/1888851.html
Looking well projects a positive first impression.
Your attire speaks volumes before a person even speak a word.
It enhances your own self-esteem and mood significantly.
Your put-together look signals professionalism in the workplace.
https://list.megakazan.ru/QvBEgjJAY/
Fashionable choices allow you to showcase your individual identity.
People often perceive well-dressed people as more capable and trustworthy.
Ultimately, putting effort in your wardrobe is an investment in your personal brand.
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://mfd.ru/forum/thread/?id=118969]ссылка кракен даркнет маркет на сайт
[/url]
Howdy! Someone in my Facebook group shared this website with us so I came
to look it over. I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m book-marking and will be
tweeting this to my followers! Great blog and excellent design and style.
Детокс — это первый и важнейший этап терапии, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» применяются только проверенные и безопасные методики. Лечение проводится под наблюдением врачей и с использованием капельниц, состав которых подбирается индивидуально. Ниже представлена таблица с основными видами капельниц, применяемыми при детоксикации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo/
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also go
to see this web site on regular basis to get updated
from hottest news.
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в новосибирске[/url]
This post is really a pleasant one it helps new the web people, who are wishing for blogging.
Каждое из направлений обеспечивает высокий уровень контроля и помогает формировать индивидуальный план воздействия. Такая модель создаёт условия для прогнозируемого восстановления. Для наглядности процессов применяется таблица, отражающая ключевые параметры наблюдения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Опрятный вид формирует первое мнение о вас.
Он влияет на восприятие вас коллегами сразу.
Хорошее самочувствие в своем образе укрепляет личную уверенность.
Этот подход подчеркивает ваш уровень профессионализма и внимание к деталям.
https://b3.hypebeasts.ru/redirect.php?id=9wV3WUCBAH7Q
Через гардероб вы можете выразить свою личность и вкус.
Окружающие часто воспринимают стильных индивидов как более компетентных.
Поэтому, инвестиции в собственный стиль — это вклад в ваше будущее.
Группа препаратов
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]покер онлайн[/url]
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная форма[/url]
футбольная атрибутика интернет магазин – [url=http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.ne/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://cse.google.nl/url?sa=i&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/teletype.in/www.r-diploma10.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] ae634f6
С [url=https://princefka.ru/]Рулонные шторы для лоджии/балкона[/url] вы сможете легко регулировать освещение и создавать комфортную атмосферу одним нажатием.
Профессионалы могут выполнить монтаж и настроить дистанционное управление для правильной работы.
—
Монтаж рулонных штор с дистанционным управлением обычно простой и быстрый.
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]похудеть на таблетках[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]онлайн слоты[/url]
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в постоянном медицинском наблюдении, размещаются в стационарном отделении. Здесь организовано непрерывное дежурство медсестры и врача-нарколога, что обеспечивает безопасность при риске осложнений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]футбольная форма клуба Арсенал купить[/url]
футбольная форма Арсенал москва – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.mv/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.google.co.cr/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.elektrokarnizy7.ru/www.rudik-diplom9.ru/r-diploma13.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] ae634f6
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Айнтрахт;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]футбольная форма Айнтрахт недорого москва[/url]
купить футбольную форму Айнтрахт в москве – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://images.google.com.pr/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.frei-diplom11.ru/www.elektrokarniz777.ru/r-diploma15.ru,]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 34f6303
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в владивостоке[/url]
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар в томске[/url]
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]оригинальная футбольная форма клуба Аталанта[/url]
футбольные формы клуба Аталанта – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://images.google.co.ck/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://cse.google.ci/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/fanfiction.borda.ru/s%3A%2F%2Freverenceengineering.com/x/www.kuhni-spb-2.ru/www.1xbet-15.com/www.1xbet-13.com,]Спортивная экипировка и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 7e0ae63
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-kemerovo
Je suis content de voir qu’ils mettent en avant l’écoresponsabilité de certains casinos.
Ça compte pour moi.
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://mfd.ru/forum/thread/?id=118969]как войти в даркнет ru2tor com
[/url]
Everyone loves what you guys are up too. This kind of clever work and coverage! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my own blogroll.
Оперативное лечение организовано по четкому алгоритму, который позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента и обеспечить эффективную терапию. Каждый этап направлен на комплексное восстановление организма.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnicza-volgograd/
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you?
Plz answer back as I’m looking to construct my own blog
and would like to find out where u got this from. kudos
Этот обзор посвящен успешным стратегиям избавления от зависимости, включая реальные примеры и советы. Мы разоблачим мифы и предоставим читателям достоверную информацию о различных подходах. Получите опыт многообразия методов и найдите подходящий способ для себя!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://142.250.77.65/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
В этот этап включено:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-volgograd/
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I certainly loved
every little bit of it. I’ve got you book-marked to check out new things you post…
Paylaşdığınız məlumatlar mənə çox kömək edir. Təşəkkürlər!
http://datacenter.boyunsoft.com/redirect.aspx?f=1&id=243&q=2&url=https://olimpbet-az.world/signup
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.info/ka-GE/register-person?ref=ILE8IH9H
Генератор ключей для Windows 11 — 100% рабочий метод активации, проверено тысячами пользователей!
Подробнее – https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya
weiterlesen https://medium.com/@Jan_Muller/deutschlands-igaming-boom-2026-zwischen-rekordwachstum-und-regulatorischen-herausforderungen-171a295a90f9 Link ansehen
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Аталанта;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]футбольная форма Аталанта москва[/url]
магазин футбольной атрибутики Аталанта в москве – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://maps.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://wbbet88.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=4036&pid=2630348&page=3208&extra=#pid2630348]Спортивная экипировка и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 6303da2
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм владивосток[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom[/url]
Hi, I really enjoy your posts! I am currently
looking for the latest trends in custom nameplate and this post really helped me
out. I’m a big fan of personalized jewelry and your perspective is perfect.
Keep up the great work! Cheers, Thanh.
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://chen-la.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=9622]ссылка на кракен в тор браузере
[/url]
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]азартные игры на деньги[/url]
Hi, i feel that i saw you visited my site so i got here to return the favor?.I am attempting to find things to enhance my website!I guess its good enough to use some of your concepts!!
В этот этап включено:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого новосибирск[/url]
What’s up mates, nice piece of writing and good arguments commented here, I am truly enjoying by these.
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это пространство, где пациенту помогают вернуться к жизни, свободной от зависимости, с заботой, уважением и индивидуальным подходом. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» реализованы комплексные программы терапии алкоголизма, наркомании и других зависимостей. Каждая программа адаптируется под конкретное состояние пациента и сочетает медицинские, психологические и социальные методы воздействия. Важное преимущество — полная анонимность, обеспечивающая комфорт и доверие со стороны пациентов.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo-anonimno
Официальный интернет-сайт компании : http://booksss.ru/img/pages/promo_kod_1xbet_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
Looking stylish creates a positive first impression.
A outfit speaks loudly before a person even speak a word.
This boosts your personal confidence and mood noticeably.
A polished look conveys competence in the office.
https://n5.vladtoday.ru/C9B5JU267XOl/
Stylish clothing let you to showcase your unique identity.
People often perceive well-dressed people as more capable and trustworthy.
Therefore, investing in your wardrobe is an valuable step in your personal brand.
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://linzanadom.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Thanks for your personal marvelous posting!
I quite enjoyed reading it, you are a great author.I will make sure to
bookmark your blog and will eventually come back in the future.
I want to encourage continue your great work, have a nice
afternoon!
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]таблетки для аборта[/url]
В рамках лечения используются методы, позволяющие фиксировать изменения и оценивать реакцию организма на проводимые мероприятия. Они служат основой для выборочных корректировок и обеспечивают структурированный характер процесса. Отличительной особенностью становится возможность адаптировать лечебные схемы под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые направления оценки состояния, применяемые для формирования полной клинической картины.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Эта публикация обращает внимание на важность профилактики зависимостей. Мы обсудим, как осведомленность и образование могут помочь в предотвращении возникновения зависимости. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с полезными советами и ресурсами, которые способствуют здоровому образу жизни.
Углубиться в тему – http://levanna.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=click_to_call&goto=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится строго по медицинским стандартам. Применяются современные капельницы, витамины и препараты для нормализации функций сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы. После снятия интоксикации врачи назначают поддерживающее лечение, направленное на стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника томск[/url]
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Такая схема лечения делает процесс последовательным и контролируемым. Врачи клиники сопровождают пациентов на всех стадиях, помогая преодолеть как физическую, так и психологическую зависимость. Особое внимание уделяется возвращению человека к активной и стабильной жизни без употребления алкоголя или наркотиков.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в ижевске[/url]
Процедура лечения начинается с установки внутривенной капельницы, через которую вводятся детоксикационные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов и восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. При необходимости врач назначает дополнительные препараты, такие как седативные средства для купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома, гепатопротекторы для поддержки печени и кардиопротекторы для нормализации работы сердца.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru
В интернете нередко встречаются поисковые запросы вроде «kraken зеркала», «kraken зеркало», «kraken ссылка», «kraken сайт», а также их варианты на русском — «кракен зеркала», «кракен зеркало», «кракен ссылка», «кракен сайт». Как правило, такие формулировки используются пользователями при попытке найти альтернативные адреса ресурсов, которые могут блокироваться или менять домены. Эксперты по кибербезопасности отмечают, что переход по подобным ссылкам связан с рисками: фишингом, вредоносным ПО и утечкой персональных данных. Поэтому важно соблюдать цифровую гигиену и критически относиться к подобным источникам.[url=https://chen-la.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=9622]kraken магазин наркотиков
[/url]
Belle page 😉
Hiya! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My site looks weird when browsing from my iphone4. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to resolve this issue. If you have any recommendations, please share. Many thanks!
Важно, что на первичной консультации честно говорят о перспективах. Никто не обещает «волшебной капельницы», после которой человек навсегда забудет про алкоголь или наркотики. Объясняют, что детокс — это старт, а не финиш, что после стабилизации придётся думать о лечении самой зависимости и реабилитации. Для семьи это неприятно, но честно: лучше сразу понимать масштаб задачи, чем надеяться на чудо и снова возвращаться к тем же проблемам через месяц.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]государственная наркологическая клиника[/url]
https://myempire77.com/
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]бесплатные вращения в слотах[/url]
Первый этап помощи почти всегда связан с детоксикацией. Организм, который длительное время получал алкоголь или другие вещества, перегружен токсинами, страдают сердце, сосуды, мозг, печень, нарушены сон и обмен веществ. Простое «похмелиться и перетерпеть» в такой ситуации опасно: можно спровоцировать очередной скачок давления, аритмию, обострение хронических заболеваний. В условиях клиники в Лобне детокс строится по медицинским правилам, а не по советам из интернета.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-lobne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru
Стильный внешний вид создает первое впечатление о человеке.
Он влияет на оценку вас окружающими сразу.
Уверенность в своем луке укрепляет личную самооценку.
Он подчеркивает ваш уровень профессионализма и уважение к деталям.
https://links.gucci1.ru/redirect.php?id=GXJIKrZeLnsr
Посредством гардероб вы можете выразить свою личность и вкус.
Окружающие часто воспринимают стильных людей как более успешных.
Поэтому, вложения в собственный стиль — это инвестиции в свое будущее.
Чтобы обеспечить эффективный вывод из запоя, формируется комплекс последовательных действий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния. Важным элементом является фармакологическая коррекция, сочетаемая с мониторингом жизненно важных функций. Ниже представлены ключевые процессы, участвующие в клинической стабилизации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в кемерове[/url]
mostbet скачать на android Казахстан [url=www.mostbet46809.help]mostbet скачать на android Казахстан[/url]
Cool + for the post
_________________
[url=https://gemasnews.shop]сигналы на 1win[/url]
Путь в наркологическую клинику в Ивантеевке почти всегда начинается с консультации — очной или по телефону. На этом этапе задача врача не осудить и не прочитать нотацию, а максимально точно понять, что происходит: сколько лет длится злоупотребление, как часто бывают запои, были ли попытки лечиться раньше, какие есть хронические болезни, каково текущее физическое и психическое состояние. Собирается анамнез, измеряется давление, оценивается пульс, при необходимости направляют на анализы и дополнительные исследования. Чем честнее и конкретнее человек (или его родственники) описывают ситуацию, тем точнее можно подобрать безопасный план помощи.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-ivanteevke/
Rutor — ведущий ресурс в русскоязычном даркнете н базе Tor, позволяющий получить доступ к контенту, материалам и товарам, а также правилам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Давний участник рынка darknet Rutor завоевал доверие благодаря скрытой системе и сервису, позволяющему безопасно проводить сделки через сеть Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor24-forum.cc]rutor org не работает[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor поддерживает стабильную работу, позволяя и новичкам, и опытным пользователям использовать предоставляемые сервисы. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Принцип анонимности
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Возможность получения эксклюзивных данных
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Find the newest info here > https://blotos.ru//wp-content/news/promokod-na-1xbet.html
Les slots avec multiplicateurs sont tres populaires
https://blog.drustvo-evo.hr/2026/02/11/guide-complet-sur-only-spins-2/
майнс mostbet [url=http://mostbet46809.help/]майнс mostbet[/url]
This text is priceless. Where can I find out more?
Детокс — важный этап лечения, который помогает очистить организм от токсинов и продуктов распада алкоголя или наркотиков. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» используются современные капельницы и лекарственные комбинации, направленные на восстановление биохимических процессов в организме. Ниже представлена таблица с примерами капельниц, применяемых в детоксикационных программах.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс знакомства[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится строго по медицинским стандартам. Применяются современные капельницы, витамины и препараты для нормализации функций сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы. После снятия интоксикации врачи назначают поддерживающее лечение, направленное на стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Детальнее – https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-vladivostok/
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Айнтрахт;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]футбольная форма атрибутика Айнтрахт[/url]
купить футбольную форму Айнтрахт – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.ly/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://maps.google.com.tr/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://rech-im-ahrtal.de/forum/topic/the-paramount-plumbing-company-ever/?part=8126#postid-83793]Официальная футбольная форма и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 0ae634f
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Арсенал;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]купить клубную футбольную форму Арсенал[/url]
атрибутика футбольного клуба Арсенал – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.no/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://maps.google.co.th/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s%3A%2F%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru/k-market.cc,]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] ae634f6
Терапия в клинике строится по индивидуальному протоколу. Каждому пациенту подбираются процедуры с учётом возраста, длительности болезни, сопутствующих нарушений и психоэмоционального состояния. Лечение проходит поэтапно, что позволяет исключить осложнения и достичь стабильной ремиссии. Ниже представлена таблица с ключевыми этапами терапии.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма ижевск[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ижевск[/url]
Hi there this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so
I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated! https://practico.bg/wool-jackets
Такой подход гарантирует постепенное и безопасное восстановление. Врачи контролируют динамику состояния, корректируют лечение при необходимости и помогают пациенту адаптироваться к трезвой жизни без стресса и давления.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в томске[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя проводится строго по медицинским стандартам. Применяются современные капельницы, витамины и препараты для нормализации функций сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы. После снятия интоксикации врачи назначают поддерживающее лечение, направленное на стабилизацию эмоционального состояния и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-gorod-vladivostok
Процедура лечения начинается с установки внутривенной капельницы, через которую вводятся детоксикационные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов и восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. При необходимости врач назначает дополнительные препараты, такие как седативные средства для купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома, гепатопротекторы для поддержки печени и кардиопротекторы для нормализации работы сердца.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в постоянном медицинском наблюдении, размещаются в стационарном отделении. Здесь организовано непрерывное дежурство медсестры и врача-нарколога, что обеспечивает безопасность при риске осложнений.
Подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-v-ekb/
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/narkologi-izhevsk-czeny
Площадка Rutor — основной источник русскоязычного даркнета в Tor, открывающий доступ к контенту, материалам, товарам и правилам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion площадок
Даркнет-ресурс Rutor сформировал репутацию надёжного магазина с анонимной системой доступа и сервисом защищённых переводов в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutorforum-24.cc]rutor зеркало форум[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Как устроена система работы Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Перспективы и риски
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Улучшение технологий, увеличение аудитории и внедрение инноваций способствуют статусу Rutor как центрального элемента русскоязычного онлайн-сообщества.
– Анонимность
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
Вывод из запоя в клинике строится на основе алгоритмов, направленных на безопасное восстановление физиологических функций. Применяется стандартная система, включающая оценку состояния, подбор медикаментозных средств и постепенную адаптацию организма. Такой формат позволяет избежать резких изменений и поддерживать предсказуемую клиническую динамику. Важную роль играет наблюдение за реакцией организма, позволяющее корректировать тактику лечения в соответствии с выявленными изменениями. Последовательность действий обеспечивает структурированность процесса и повышает вероятность стабильного результата.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя в ижевске[/url]
mostbet android rasmiy [url=https://mostbet69573.help]https://mostbet69573.help[/url]
mostbet bukmeker [url=http://mostbet69573.help/]http://mostbet69573.help/[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому краснодар[/url]
1win хатои пардохт [url=https://1win71839.help/]1win хатои пардохт[/url]
mostbet бонус на депозит [url=mostbet46809.help]mostbet бонус на депозит[/url]
mostbet email kelmayapti [url=http://mostbet69573.help]mostbet email kelmayapti[/url]
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Luxury watches continue to hold strong appeal despite the rise of modern gadgets.
They are often seen as a symbol of status and refined taste.
Expert workmanship plays a major role in their lasting value.
Many luxury watches are produced using high-quality materials.
https://hub.docker.com/u/lepodiumcom
They also represent a deep history passed down through generations.
For collectors, these watches can serve as both functional accessories and collectible pieces.
Classic aesthetics allows them to stay relevant across changing fashion trends.
In the end, luxury watches continue to appeal to enthusiasts around the world.
Алкогольная или наркотическая интоксикация — это не просто временное ухудшение самочувствия, а серьёзное медицинское состояние, требующее неотложной помощи. Когда человек находится в запое или состоянии ломки, его организм стремительно теряет силы, нарушается работа сердца, печени, мозга, возникают панические атаки, судороги, спутанность сознания. В таких случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Если пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники, оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом. В Красногорске такая услуга доступна круглосуточно благодаря выездной службе клиники «Ключ к Здоровью».
Разобраться лучше – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/
Рабочий ключ активации для Windows 11 — проверено и обновлено, без блокировок!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Скачать патч для активации Windows 11[/url]
Стильный вид создает сильное мнение о вас.
Ваш образ влияет на восприятие вас коллегами мгновенно.
Хорошее самочувствие в подобранном луке укрепляет личную уверенность.
Этот подход подчеркивает ваш стандарт профессионализма и внимание к деталям.
https://z3.sochidaily.ru/ukx4PGhx/
Через гардероб вы можете проявить свою личность и стиль.
Окружающие неосознанно оценивают стильных индивидов как более успешных.
Следовательно, инвестиции в собственный стиль — это вклад в ваше успешное будущее.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after going through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently!
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в кемерове[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/ph/register?ref=IU36GZC4
Каждый пациент в «УралМед» получает персональный маршрут реабилитации, составленный после комплексного обследования. План включает медикаментозное выведение из запоя, коррекцию биохимических показателей и психологическую реабилитацию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение женского алкоголизма[/url]
Такая систематизация показывает, что врач действует целенаправленно, устраняя не только симптомы, но и их физиологические последствия.
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-ryazan-czeny/
Лечение в «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» проходит поэтапно, с акцентом на безопасность и эффективность. Каждый этап направлен на достижение конкретных целей, от детоксикации до психотерапии. В таблице представлена структура лечебного процесса:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk/
Группа препаратов
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
1win сабти ном бо sms [url=1win71839.help]1win сабти ном бо sms[/url]
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Такой порядок действий гарантирует не только купирование симптомов, но и подготовку пациента к последующему восстановлению.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
В этот этап включено:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница новосибирск[/url]
Dressing well projects a positive first impression.
A attire communicates volumes before a person actually speak a single word.
It enhances your own confidence and mindset significantly.
Your polished appearance conveys professionalism in the office.
https://list.megakazan.ru/FgwEG6Je/
Fashionable choices let you to showcase your individual personality.
People often perceive well-dressed people as more successful and reliable.
Therefore, investing in your wardrobe is an investment in yourself.
Rutor — главный портал русскоязычного даркнета в сети Tor, обеспечивающий доступ к материалам, товарам, контенту и нормам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
Rutor заработал статус важного игрока на darknet-рынке благодаря длительной работе, инструментам для анонимности, устойчивому сервису и тор-поддержке защищённых транзакций.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutorforum-24×7.cc]рутор орг ру[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Этот магазин ориентирован на предоставление пользователям широкой базы данных, связанной с файлами, софтом, новостями и различными видами контента, включая темы, касающиеся взлома и безопасности.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Главное преимущество платформы — интеграция с сетью Rutor, что значительно уменьшает вероятность раскрытия личности и потери конфиденциальной информации. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Система построена таким образом, что каждый раздел страницы — будь то магазин, новости или инструкции по взлому — становится отдельной частью большого сообщества, в котором безопасность и возможность оставаться анонимным выходят на первый план.
Перспективы и риски
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Сервис остается местом, где можно получать дополнительную информацию, обсуждать вопросы безопасности, следить за новостями и инновациями в области даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Принцип анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-krasnogorske/
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс чат[/url]
Опрятный внешний вид формирует сильное впечатление о человеке.
Ваш образ работает на оценку вас окружающими сразу.
Уверенность в своем образе повышает вашу самооценку.
Этот подход демонстрирует ваш уровень ответственности и внимание к деталям.
https://bm2.irkpress.ru/40sW4d4jQnH/
Посредством гардероб вы имеете шанс выразить свою индивидуальность и стиль.
Окружающие неосознанно воспринимают стильных индивидов как более компетентных.
Поэтому, вложения в собственный стиль — это вклад в ваше будущее.
После курса капельниц улучшается сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие. Пациенты отмечают, что уже через сутки после начала лечения исчезают тремор и тахикардия, а на второй день приходит чувство ясности и спокойствия.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя цена краснодар[/url]
мостбет вход без пароля [url=http://mostbet46809.help]мостбет вход без пароля[/url]
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ivanteevke/
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]милфы[/url]
Tukar link itu intinya cuma menaruh link orang lain di tempat yang tepat dan orang itu juga melakukan hal yang sama buat kamu.
Piece of writing writing is also a excitement, if you be acquainted with then you can write or else it is difficult to write.
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Аталанта;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]интернет магазин футбольной формы Аталанта[/url]
ретро формы футбольного клуба Аталанта – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.ml/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.kz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s:/%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.stoimost-soglasovaniya-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru/maps.google.se/url?q=https://tolerance-homes.com/nl/turkije/alanya/kestel/appartement/]Клубная атрибутика и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 3da2a67
Основная процедура включает в себя:
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно краснодар[/url]
I have read so many posts concerning the blogger lovers except this piece of writing
is truly a nice paragraph, keep it up. https://cryptoboss353.top/
Наркологическая клиника использует комплексный подход к оценке состояния пациента, что обеспечивает высокий уровень контроля на всех этапах лечения. Такой формат работы позволяет детально изучать динамику процессов и своевременно корректировать вмешательства. В клинике применяется принцип последовательного наблюдения, при котором особое внимание уделяется соматическим и неврологическим проявлениям. Выбор терапевтических мер основывается на анализе объективных данных, что повышает предсказуемость результата. Подход ориентирован на постепенное восстановление функций организма с учетом индивидуальных особенностей.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru
Алкогольная или наркотическая интоксикация — это не просто временное ухудшение самочувствия, а серьёзное медицинское состояние, требующее неотложной помощи. Когда человек находится в запое или состоянии ломки, его организм стремительно теряет силы, нарушается работа сердца, печени, мозга, возникают панические атаки, судороги, спутанность сознания. В таких случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Если пациент не может самостоятельно добраться до клиники, оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом. В Красногорске такая услуга доступна круглосуточно благодаря выездной службе клиники «Ключ к Здоровью».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
На первом этапе проводится серия исследований:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Rutor – ключевой ресурс даркнета на русском языке в Tor, дающий доступ к контенту, материалам, товарам и правилам сохранения анонимности пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
Даркнет-ресурс Rutor сформировал репутацию надёжного магазина с анонимной системой доступа и сервисом защищённых переводов в Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor-forum.cc]поиск по рутору[/url] считается одним из наиболее популярных и старых ресурсов в рунет-даркнете, который прочно закрепился в инфраструктуре анонимных площадок. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За годы существования Rutor стал местом, где сохраняется важная история русскоязычного даркнета.
Платформа функционирует стабильно, обеспечивая равный доступ для новых и опытных участников даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Возможные направления развития и связанные опасности
Ясно, что будущая деятельность Rutor потребует решения новых рисков, внедрения свежих подходов к безопасности и средств обхода ограничений. Следует помнить, что даже максимально анонимная среда не обеспечивает стопроцентную безопасность.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Технический прогресс, рост числа участников и новые функциональные решения превращают Rutor в ключевой узел русскоязычного интернет-сообщества.
– Сохранение анонимности
– Безопасность транзакций
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Обеспечение приватности взаимодействий
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
1win депозит [url=https://www.1win71839.help]https://www.1win71839.help[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/[/url]
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наши товары:
Заготовка из конструкционной стали листовая 120 мм 15Н2М ОСТ 3-1686-90 Выбирайте конструкционные заготовки высокого качества для вашего проекта на Редметсплав.рф. Наш ассортимент включает прочные и долговечные материалы, идеально подходящие для различных областей применения, включая строительство и машиностроение.
Опрятный вид формирует первое впечатление о вас.
Он влияет на оценку вас окружающими сразу.
Хорошее самочувствие в подобранном образе повышает личную самооценку.
Он демонстрирует высокий уровень профессионализма и внимание к мелочам.
https://blog.chenews.ru/sumka-kak-personazh-pochemu-furla-ne-vykhodit-iz-spektaklya/
Посредством гардероб вы имеете шанс проявить свою индивидуальность и стиль.
Люди неосознанно воспринимают стильных индивидов как более компетентных.
Следовательно, инвестиции в свой стиль — это инвестиции в ваше успешное будущее.
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это пространство, где пациенту помогают вернуться к жизни, свободной от зависимости, с заботой, уважением и индивидуальным подходом. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» реализованы комплексные программы терапии алкоголизма, наркомании и других зависимостей. Каждая программа адаптируется под конкретное состояние пациента и сочетает медицинские, психологические и социальные методы воздействия. Важное преимущество — полная анонимность, обеспечивающая комфорт и доверие со стороны пациентов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог кемерово[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru
Can I simply say what a comfort to find a person that genuinely knows what they are talking about online. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people must look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you are not more popular given that you definitely possess the gift.
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
Hi, yes this article is actually nice and I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging.
thanks.
Клиника «КемероваМед Трезвость» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь пациентам, столкнувшимся с последствиями запоев и зависимостей. Основное направление — анонимное лечение, которое исключает постановку на учёт и обеспечивает конфиденциальность данных. При обращении пациент проходит первичную диагностику, включающую сбор анамнеза, измерение жизненно важных показателей, ЭКГ и анализ крови. После этого врач составляет персональный план лечения, который может включать детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию, капельницы, консультации психотерапевта и реабилитационные программы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/
В материале приведены детали, интересные, но не особенно важные. Мы рассматриваем аспекты, которые сложно назвать существенными, но включили их для большей полноты.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya
I like to piece together a thought here, an example there, and a solution in another topic. [url=https://shop77.su/professionalnaya-kosmetika-ot-izvestnix-brendov-industrii/][color=#1C1C1C]As a result, the mosaic is [/color][/url]. All the fun in one place.
Структурированное наблюдение позволяет поддерживать согласованность лечебных мероприятий и своевременно реагировать на изменения. Такая система создаёт единый аналитический подход для оценки состояния и обеспечивает целостность терапевтического процесса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Структурированное наблюдение позволяет поддерживать согласованность лечебных мероприятий и своевременно реагировать на изменения. Такая система создаёт единый аналитический подход для оценки состояния и обеспечивает целостность терапевтического процесса.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника владивосток[/url]
Алкоголизм — хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и круглосуточного контроля. Клиника «УралМед» в Екатеринбурге предлагает полный спектр услуг для пациентов любого уровня зависимости: от экстренной детоксикации до долгосрочной реабилитации. Главные принципы работы — абсолютная анонимность, индивидуальный план лечения и постоянное сопровождение квалифицированной командой специалистов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-v-ekb
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог отборных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до масштабных поставок, мы обеспечиваем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их происхождение. Превосходное обслуживание – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы а также находить ответы под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
поставляемая продукция:
Фольга кобальтовая ЭК120 Фольга кобальтовая ЭК120 – это качественный материал, идеально подходящий для различных промышленных процессов. Обладая высокими антикоррозийными свойствами, она гарантирует долговечность и надежность в эксплуатации. Благодаря отличной гибкости и прочности, фольга идеально подходит для использования в электротехнике и производстве. Если вы ищете надежный и эффективный материал, то вам стоит купить Фольга кобальтовая ЭК120. Убедитесь в ее преимуществах и получайте максимальную отдачу от вашего выбора!
Своевременное вмешательство специалиста позволяет не только вывести токсины, но и снизить риск развития осложнений, обеспечить восстановление жизненно важных функций организма и предотвратить ухудшение состояния, что особенно важно для сохранения здоровья и жизни пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника краснодар[/url]
Представленная таблица отражает ключевые направления наблюдения, обеспечивая систематизацию данных. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать высокий уровень контроля и адаптировать программу лечения с учетом динамики состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь в томске[/url]
Rutor — главный портал русскоязычного даркнета в сети Tor, обеспечивающий доступ к материалам, товарам, контенту и нормам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion сайтов
Rutor — один из старейших ресурсов русского сегмента даркнета, обладающий известной историей, скрытной платформой и площадкой для защищённых обменов в системе Rutor.Rutor — старейший представитель даркнета на русском языке
[url=https://rutor-forum.vip]http rutor[/url] — это один из первых и известнейших русскоязычных ресурсов даркнета, неразрывно связанный с анонимной онлайн-экосистемой. Основное направление работы ресурса — предоставление обширной базы файлов, утилит, новостей и прочего контента, в том числе, связанного с темами безопасности и взлома.
Особенности работы системы Rutor
Данная система обеспечивает доступ к значительным объемам данных и файлов, гарантируя при этом повышенную анонимность и защиту пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. С течением времени площадка превратилась в важный архив событий и истории русскоязычного даркнета.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Безусловно, дальнейшая история Rutor будет связана с новыми формами риска, новыми способами защиты конфиденциальности и методами обхода блокировок. Пользователи должны осознавать, что даже самая анонимная система не гарантирует полной безопасности.
Этот сервис по-прежнему служит площадкой для информирования, обсуждений безопасности и отслеживания новшеств в даркнет-сообществе. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Анонимность
– Гарантия безопасности сделок
– Доступ к уникальной информации
– Защищённость коммуникаций
Уникальный путь Rutor делает платформу значимой для тех, кто высоко ценит свободу, личную приватность и защиту от внешнего контроля в цифровую эпоху.
mostbet криптовалюта вывод [url=https://www.mostbet46809.help]mostbet криптовалюта вывод[/url]
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Комплексный анализ скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку ТВ приставки
• Фиксированные тарифы на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибирские сети тарифы домашний интернет и телевидение красноярск[/url]
провести домашний интернет сибсети – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://images.google.hu/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://images.google.com.na/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.sportbets31.ru/www.prognozy-na-khokkej5.ru/www.astana.forum24.ru/www.frei-diplom9.ru/www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru/index.html,]Высокоскоростной интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] f9e2929
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/
При выезде к пациенту врач выполняет комплекс последовательных действий, которые направлены на стабилизацию состояния и предотвращение осложнений. Такая структурированность необходима для достижения медицинского результата.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/narkolog-spb-na-dom/
Any dispute ultimately depends on understanding the context: what is happening around you, how the market is moving. Without regular look in [url=https://shop77.su/professionalnaya-kosmetika-dlya-salonov-i-masterov/][color=#1C1C1C]business news it’s easy to miss[/color][/url].
кайт в египте Кайт кайтинг кайтсёрфинг школа обучение сафари Дети ветра DETIVETRA
Hey! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any ideas or suggestions? Thanks
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]клубные футбольные формы Атлетико Мадрид[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной атрибутики Атлетико Мадрид в москве – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ru/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://maps.google.co.mz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.potolkilipetsk.ru/www.rudik-diplom11.ru/www.novosti-sporta-7.ru/www.stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru/www.1xbet-giris-3.com/,]Официальная футбольная форма и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] e2929b0
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk/
Наркологическая клиника применяет стандартизированные схемы, направленные на безопасное и постепенное восстановление. Каждый этап вмешательства согласуется с текущим состоянием пациента, что обеспечивает предсказуемый характер изменений. Модель работы включает оценку реакции организма, проверку устойчивости внутренних систем и уточнение динамики метаболических процессов. Последовательность действий формируется с учётом адаптационных возможностей и направлена на достижение стабильного результата.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника владивосток[/url]
https://travelersqa.com/user/1xbetpromocode2
https://sway.cloud.microsoft/759rC81NS4zRkBK2
http://www.physicsgurus.com/user/1xbetpromocode2
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]narkolog na dom moskva[/url]
Kraken — одна из самых известных криптовалютных бирж в мире, предлагающая торговлю биткоином, эфириумом и другими цифровыми активами. Платформа отличается высоким уровнем безопасности, прозрачными комиссиями и удобным интерфейсом как для новичков, так и для профессиональных трейдеров. В сети иногда ищут kraken зеркала или kraken зеркало, чтобы получить доступ к платформе при технических ограничениях. Важно использовать только официальные источники, проверяя kraken ссылка и переходя на официальный kraken сайт. Биржа поддерживает фиатные валюты, маржинальную торговлю и стейкинг, обеспечивая надежную защиту средств и данных пользователей.[url=https://forum.povarenok.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=9091]сайт купить гашиш
[/url]
Rutor выступает в роли главного сайта русскоязычного даркнета в Tor, предоставляющего доступ к информации, материалам, товарам и нормам анонимности для пользователей черного рынка и onion ресурсов
Портал Rutor признан лидером среди площадок русского даркнета за надёжный сервис, поддержание анонимности и обслуживание операций через Rutor.Rutor: Один из ключевых проектов русскоязычного даркнета
[url=https://rutor.ink]рутор сеч[/url] — это один из самых известных и старейших сервисов в русскоязычном даркнете, который стал неотъемлемой частью экосистемы анонимных ресурсов. Данный сервис специализируется на доступе к широчайшему ассортименту софта, файлов, новостей и разнообразных материалов, охватывающих вопросы взлома и защиты.
Главные аспекты функционирования Rutor
Система курирует доступ к огромному количеству информации и файлов, сохраняя дополнительную конфиденциальность и анонимность своих пользователей. Особенность сервиса в том, что он работает через сеть Rutor, что существенно снижает риск идентификации и утечки данных. За долгое время работы Rutor стал своего рода летописью для даркнета на русском языке.
Rutor продолжает работать и предоставлять стабильный доступ к ресурсам, удовлетворяя потребности как новичков, так и опытных пользователей даркнета. Каждый из разделов сайта — магазин, новостные ленты или руководства по взлому — образуют отдельную звено в масштабном сообществе, где главными ценностями выступают конфиденциальность и защита анонимности.
Будущее платформы: вызовы и обещания
Нет сомнений, что в дальнейшем Rutor столкнётся с новыми угрозами, инновационными способами охраны приватности и методами преодоления блокировок. Пользователи обязаны понимать, что ни одна анонимная платформа не может дать абсолютную защиту.
Платформа продолжает быть ресурсом для получения расширенной информации, обмена мнениями по безопасности и мониторинга новшеств в сферах даркнета. Развитие технологий, расширение базы пользователей и появление новых возможностей делают Rutor одним из центров русскоязычного сообщества в сети.
– Анонимность
– Надёжность проведения операций
– Открытый доступ к специализированному контенту
– Конфиденциальность общения
Rutor представляет собой ресурс с неповторимой историей, важный для пользователей, стремящихся к свободе, сохранению конфиденциальности и автономии от внешних ограничений в современном интернете.
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]азартные игры[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]футбольная форма клуба Атлетико Мадрид[/url]
купить клубную футбольную форму Атлетико Мадрид – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.co.ls/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.cat/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.studiya-podkastov-spb1.ru/frei-diplom7.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 9e2929b
Этот информативный текст сочетает в себе темы здоровья и зависимости. Мы обсудим, как хронические заболевания могут усугубить зависимости и наоборот, как зависимость может влиять на общее состояние здоровья. Читатели получат представление о комплексном подходе к лечению как физического, так и психического состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://142.250.10.122/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-tolyatti
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
шиномонтаж на выезд москва https://vyezdnoj-shinomontazh-77.ru
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/[/url]
[url=https://shumoizolyaciya-arok-avto-77.ru]шумоизоляция арок авто[/url]
Наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, а пространство, где пациент получает всестороннюю поддержку: от снятия интоксикации и детоксикации до психотерапии и постлечебного сопровождения. В клинике «КемероваМед Трезвость» специалисты работают с любыми формами зависимостей — алкогольной, наркотической, медикаментозной. Принципы работы центра основаны на анонимности, профессионализме и индивидуальном подходе. Здесь создаются условия для полного восстановления здоровья и возвращения человека к стабильной трезвой жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в кемерове[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
I am in fact glad to read this blog posts which includes lots of useful facts, thanks for providing these kinds of statistics.
Такая терапия не только устраняет последствия запоев, но и восстанавливает баланс организма, улучшая общее состояние. Пациенты отмечают, что уже через несколько часов после капельницы проходит тремор, снижается тревожность и появляется чувство ясности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто место, где оказывают медицинскую помощь. Это пространство, где пациенту помогают вернуться к жизни, свободной от зависимости, с заботой, уважением и индивидуальным подходом. В клинике «СибМед Кемерово» реализованы комплексные программы терапии алкоголизма, наркомании и других зависимостей. Каждая программа адаптируется под конкретное состояние пациента и сочетает медицинские, психологические и социальные методы воздействия. Важное преимущество — полная анонимность, обеспечивающая комфорт и доверие со стороны пациентов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo
Asking questions are genuinely good thing if you are not understanding anything fully, except this post
presents fastidious understanding yet.
Функция и назначение
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в екатеринбурге[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]футбольная форма Арсенал купить интернет магазин москва[/url]
магазин футбольной формы Арсенал – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://image.google.dz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://www.google.ki/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s%3A%2F%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.melbetbonusy.ru/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/www.1xbet-15.com/www.frei-diplom8.ru/www.1xbet-17.com/www.1xbet-17.com/www.rudik-diplom5.ru/www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-25.ru/www.rudik-diplom1.ru/zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu4.ru,]Спортивная экипировка и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 929b08_
Для формирования структурированной модели используются стандартизированные алгоритмы. Ниже представлена последовательность действий, определяющих ход терапевтических мероприятий.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в томске[/url]
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar/
На первом этапе проводится серия исследований:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-v-ekb
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to
assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your
blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your
feeds and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
Функция и назначение
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Алкогольный запой представляет собой длительное бесконтрольное приём спиртного, приводящее к тяжёлой интоксикации и серьёзным осложнениям для органов и психики. В Новосибирске клиника «Сибирский Доктор» предлагает качественный вывод из запоя с применением инновационных технологий и участием опытных наркологов, терапевтов и психиатров. Наш подход сочетает мгновенную реакцию на вызов, современное оборудование и индивидуальные схемы лечения, что позволяет достичь стабильной ремиссии и снизить риск рецидива.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-novosibirsk
Наркологическая клиника использует методики, направленные на комплексную оценку состояния пациента. Работа строится на анализе анамнеза, исследовании соматических параметров и определении степени выраженности симптомов. Такой формат создаёт условия для точного подбора терапевтических мер. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, направленный на своевременное выявление отклонений и корректировку лечебных мероприятий. Благодаря этому достигается высокая стабильность клинического процесса и формируется благоприятная динамика восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в владивостоке[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Useful info. Fortunate me I discovered your site by chance, and I’m stunned why this coincidence did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
Современная наркологическая помощь — это не просто лечение зависимости, а система комплексных мер, направленных на восстановление здоровья, эмоционального равновесия и социальной адаптации пациента. В клинике «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» в Ижевске применяются передовые методики терапии, соответствующие международным стандартам. Здесь работают квалифицированные врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, которые разрабатывают индивидуальные программы лечения в зависимости от формы и стадии заболевания. Центр предлагает как амбулаторное, так и стационарное лечение, а также выезд специалистов на дом, что делает помощь доступной и оперативной.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника ижевск[/url]
Kraken — одна из самых известных криптовалютных бирж в мире, предлагающая торговлю биткоином, эфириумом и другими цифровыми активами. Платформа отличается высоким уровнем безопасности, прозрачными комиссиями и удобным интерфейсом как для новичков, так и для профессиональных трейдеров. В сети иногда ищут kraken зеркала или kraken зеркало, чтобы получить доступ к платформе при технических ограничениях. Важно использовать только официальные источники, проверяя kraken ссылка и переходя на официальный kraken сайт. Биржа поддерживает фиатные валюты, маржинальную торговлю и стейкинг, обеспечивая надежную защиту средств и данных пользователей.[url=https://mfd.ru/forum/thread/?id=119045]kraken зеркало даркнет
[/url]
Современная наркологическая клиника — это не просто медицинское учреждение, где проводят лечение зависимостей. Это система комплексной поддержки, объединяющая врачей, психологов, терапевтов и специалистов по реабилитации. В клинике «ТомскМед Трезвость» созданы комфортные условия, где лечение проходит анонимно, бережно и с опорой на доказательную медицину. Каждое вмешательство назначается строго по показаниям, а терапия направлена не только на физическое очищение организма, но и на восстановление психоэмоционального баланса пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника томск[/url]
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в екатеринбурге[/url]
В этой статье мы обсудим процесс восстановления после зависимостей, акцентируя внимание на различных методах и подходах к реабилитации. Читатели узнают, как создать план выздоровления и использовать полезные ресурсы для достижения устойчивых изменений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://142.250.152.95/url?q=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-tolyatti-na-domu
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр владивосток[/url]
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]магазин футбольной формы[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной формы – [url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]http://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=http://images.google.tk/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://www.google.com.tn/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www.net-pier.biz/chao/notebook2/notebook2.cgi/NBkPobCnJPe]Клубная атрибутика и подарки для фанатов от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 29b04_6
Вызов нарколога на дом в клинике имеет целый ряд преимуществ. Пациент получает доступ к современным методикам без необходимости транспортировки. Кроме того, исключается фактор социальной огласки, что часто является значимым для больных и их семей.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News.
Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News?
I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Appreciate it
This branch shows how we live. And how the rest of the world lives becomes [url=https://shop77.su/professionalnaya-kosmetika-dlya-idealnogo-uxoda-za-kozhej/][color=#1C1C1C]is understandable only if news from around the world is connected to the picture of the day from time to time[/color][/url]
Многие жители Ивантеевки откладывают обращение, потому что им кажется, что ситуация «ещё не настолько страшная». Пока человек как-то ходит на работу, иногда остаётся трезвым и периодически клянётся, что «всё возьмёт под контроль», кажется, что обращаться в клинику рано. На самом деле эффективнее всего лечение работает именно тогда, когда проблемы уже заметны, но ещё не привели к тяжёлым осложнениям — инсультам, инфарктам, тяжёлым психозам, полной утрате социальных связей.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-reabilitaciya-v-ivanteevke/
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в постоянном медицинском наблюдении, размещаются в стационарном отделении. Здесь организовано непрерывное дежурство медсестры и врача-нарколога, что обеспечивает безопасность при риске осложнений.
Выяснить больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-v-ekb/
Опрятный вид создает сильное мнение о человеке.
Он влияет на восприятие вас окружающими сразу.
Хорошее самочувствие в подобранном луке повышает личную уверенность.
Он демонстрирует ваш уровень ответственности и внимание к деталям.
https://n6.sneakero.ru/aNNrdCdK9x/
Через одежду вы можете проявить свою индивидуальность и вкус.
Окружающие часто воспринимают опрятных индивидов как более компетентных.
Поэтому, инвестиции в свой стиль — это инвестиции в ваше успешное будущее.
Незамедлительно после вызова нарколог прибывает на место для проведения первичной диагностики. На этом этапе осуществляется сбор анамнеза, измерение жизненно важных показателей и оценка степени интоксикации, что является основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
После курса капельниц улучшается сон, аппетит и общее самочувствие. Пациенты отмечают, что уже через сутки после начала лечения исчезают тремор и тахикардия, а на второй день приходит чувство ясности и спокойствия.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника в кемерове[/url]
trezviy vibor [url=https://www.limage-ufa.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-rostove-na-donu/]https://www.limage-ufa.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-rostove-na-donu/[/url] .
Для получения устойчивого результата наркологическая клиника использует методы, основанные на индивидуальной оценке. В работе учитываются соматические показатели, реакции нервной системы и данные лабораторных исследований. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает предсказуемое влияние на физиологические процессы и снижает вероятность осложнений. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, позволяющий своевременно корректировать лечебные меры. Работа направлена на нормализацию метаболизма, восстановление баланса внутренних систем и плавное уменьшение симптоматики.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в владивостоке[/url]
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Thank you!
После приезда нарколог оценивает состояние пациента, проверяет давление, частоту пульса и насыщенность крови кислородом. Затем врач подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, включающий растворы для очистки организма, препараты для нормализации работы сердца, печени и нервной системы. Процедура длится около 1–2 часов и позволяет быстро:
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в краснодаре[/url]
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vrach narkolog na dom moskva[/url]
Запой почти никогда не начинается внезапно: сначала это редкие «переборы» по праздникам, потом привычка снимать стресс вечером, а дальше алкоголь всё чаще появляется в распорядке дня. В какой-то момент близкие замечают, что человек уже не контролирует количество, выпивка идёт несколько дней подряд, отменяются дела, нарушается сон, пропадает аппетит, появляются дрожь, потливость, скачки давления. На этом этапе вывод из запоя в Ивантеевке уже не может быть простым «проспаться и прийти в себя» — организму нужна полноценная медицинская помощь.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/
Вывод из запоя в «Сибирском Докторе» происходит в несколько взаимосвязанных этапов:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника новосибирск[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике формируется на основе последовательных процедур, направленных на стабилизацию физиологических функций и устранение токсических влияний. Такой подход позволяет корректно регулировать состояние пациента и контролировать интенсивность симптомов. Рабочие алгоритмы включают оценку метаболических процессов, анализ соматических показателей и определение степени неврологических изменений. В результате создается структурированная модель помощи, ориентированная на восстановление адаптивных возможностей организма. Процессы выполняются под контролем специалистов, что обеспечивает прогнозируемый терапевтический эффект и снижает вероятность осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-kemerovo/
Функция и назначение
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Представленная таблица отражает ключевые направления наблюдения, обеспечивая систематизацию данных. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать высокий уровень контроля и адаптировать программу лечения с учетом динамики состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог томск[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно в краснодаре[/url]
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
Таблица позволяет поддерживать единую структуру наблюдения и фиксировать изменения состояния. Такая модель обеспечивает прозрачность процессов и повышает точность принимаемых решений.
Подробнее – https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-izhevske-soczialnye-uslugi/
Особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Используются препараты нового поколения, снижающие нагрузку на печень, почки и сердечно-сосудистую систему. Процесс лечения проходит под постоянным наблюдением медперсонала, что позволяет быстро реагировать на любые изменения состояния пациента. Все данные о лечении строго конфиденциальны — информация не передаётся третьим лицам и не фиксируется в общедоступных базах.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tomske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]футбольные формы клуба Аталанта[/url]
футбольная форма Аталанта москва – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://www.google.co.uk/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://pocherparts.de/cgi-bin/gast4.cgi/www.mental-health23.com/market.html]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 5_2c0f5
Клиника «ВладТрезвие Центр» работает в круглосуточном режиме и готова оказать помощь жителям Владивостока и прилегающих районов в любое время суток. Врачи-наркологи прибывают по вызову в течение часа, имеют при себе все необходимые препараты и оборудование для проведения детоксикации на дому. При необходимости пациента доставляют в стационар, где лечение проходит под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-staczionar-vladivostok/https://vyvodiz-zapoya-vladivostok18.ru
Для получения устойчивого результата наркологическая клиника использует методы, основанные на индивидуальной оценке. В работе учитываются соматические показатели, реакции нервной системы и данные лабораторных исследований. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает предсказуемое влияние на физиологические процессы и снижает вероятность осложнений. В клинике применяется непрерывный мониторинг, позволяющий своевременно корректировать лечебные меры. Работа направлена на нормализацию метаболизма, восстановление баланса внутренних систем и плавное уменьшение симптоматики.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника владивосток[/url]
Таблица позволяет поддерживать единую структуру наблюдения и фиксировать изменения состояния. Такая модель обеспечивает прозрачность процессов и повышает точность принимаемых решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvodiz-zapoya-izhevsk18.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом[/url]
บทความนี้ อ่านแล้วรู้สึกว่าได้มุมมองใหม่ ครับ
ดิฉัน ไปเจอรายละเอียดของ ประเด็นที่ใกล้เคียงกัน
สามารถอ่านได้ที่ suck bet
เหมาะกับคนที่สนใจเรื่องนี้
มีการเรียบเรียงที่อ่านแล้วลื่นไหล
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ คอนเทนต์ดีๆ นี้
จะคอยดูว่ามีเนื้อหาใหม่ๆ มาเสริมอีกหรือไม่
Бесплатный ключ для Windows 11 — только у нас, обновлено в 2026 году!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Бесплатный серийный номер для Windows 11[/url]
In any topic, the main thing is not decorations, but “supporting structures”. Otherwise, everything collapses from the very first wind. That’s why the idea of thinking like [url=https://shop77.su/kontaktnaya-informatsiya/][color=#1C1C1C]in the construction councils[/color][/url].
Наркологическая помощь должна быть не только медицински точной, но и человечной, безопасной и анонимной. В «Ижевском Центре Трезвых Решений» выстроена система комплексного подхода к лечению зависимостей, включающая диагностику, медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапию и социальную адаптацию. Клиника объединяет профессионализм, заботу и круглосуточную готовность помочь пациентам, оказавшимся в трудной ситуации. Здесь работают врачи с большим опытом в области наркологии и психиатрии, способные оперативно выехать на дом и оказать неотложную помощь.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника клиника помощь[/url]
Для эффективного лечения наши врачи используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента. В состав лечебного курса входят:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
pin-up server xətası [url=http://pinup21680.help]http://pinup21680.help[/url]
Лечение в клинике проходит поэтапно. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение устойчивого результата и восстановление здоровья. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием основных этапов лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника кемерово[/url]
Такой подход обеспечивает комплексное восстановление — от физического состояния до эмоциональной стабильности. Пациент получает внимание врачей на всех этапах и поддержку после выписки.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника кемерово[/url]
Hey there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same outcome.
Kraken — одна из самых известных криптовалютных бирж в мире, предлагающая торговлю биткоином, эфириумом и другими цифровыми активами. Платформа отличается высоким уровнем безопасности, прозрачными комиссиями и удобным интерфейсом как для новичков, так и для профессиональных трейдеров. В сети иногда ищут kraken зеркала или kraken зеркало, чтобы получить доступ к платформе при технических ограничениях. Важно использовать только официальные источники, проверяя kraken ссылка и переходя на официальный kraken сайт. Биржа поддерживает фиатные валюты, маржинальную торговлю и стейкинг, обеспечивая надежную защиту средств и данных пользователей.[url=https://mfd.ru/forum/thread/?id=119077]бошки жижа купить
[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника в ижевске[/url]
trezviy vibor [url=https://www.prostatit-prostata.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-volgograde-anonimno/]https://www.prostatit-prostata.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-volgograde-anonimno/[/url] .
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника владивосток[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Данный порядок действий позволяет снизить риски для здоровья и обеспечить контроль за эффективностью процедур.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно санкт-петербург[/url]
Структурированное наблюдение позволяет поддерживать согласованность лечебных мероприятий и своевременно реагировать на изменения. Такая система создаёт единый аналитический подход для оценки состояния и обеспечивает целостность терапевтического процесса.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Такой порядок действий гарантирует не только купирование симптомов, но и подготовку пациента к последующему восстановлению.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url]
Представленная таблица отражает ключевые направления наблюдения, обеспечивая систематизацию данных. Такой подход позволяет поддерживать высокий уровень контроля и адаптировать программу лечения с учетом динамики состояния.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk/
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative
and amusing, and without a doubt, you’ve
hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that not enough folks are speaking intelligently about.
I’m very happy that I stumbled across this during my search for something regarding this.
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/[/url]
Вывод из запоя в клинике опирается на систему динамической оценки состояния, позволяющую корректировать терапевтические меры по мере изменения клинической картины. В ходе работы оценивается реакция организма на вмешательства, проверяется уровень физиологической устойчивости и отслеживается изменение лабораторных данных. Такой формат способствует снижению рисков и обеспечивает стабильный контроль над ключевыми параметрами. Длительность наблюдения зависит от выраженности нарушений и реакции пациента на проводимые процедуры. Коррекция осуществляется постепенно, что поддерживает благоприятный темп восстановления и повышает качество результата.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kemerovo18.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
I read the thread and think: we all “formalize” something — thoughts, projects, everyday life. Even disputes depend on the pitch. [url=https://shop77.su/professionalnaya-kosmetika-dlya-dostizheniya-stojkogo-rezultata/][color=#1C1C1C]It’s not for nothing that I’m so attracted to everything about design[/color][/url].
[url=https://github.com/casinoly]casinoly[/url]
https://uitschrijvencruks.com
If you desire to grow your familiarity simply keep visiting this web page and be updated with the newest news update posted here.
Лечение в «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» проходит поэтапно, с акцентом на безопасность и эффективность. Каждый этап направлен на достижение конкретных целей, от детоксикации до психотерапии. В таблице представлена структура лечебного процесса:
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk-otzyvy/
Генератор ключей для Windows 11 — 100% рабочий метод активации, проверено тысячами пользователей!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Активатор Windows 11 скачать бесплатно[/url]
Каждое из направлений обеспечивает высокий уровень контроля и помогает формировать индивидуальный план воздействия. Такая модель создаёт условия для прогнозируемого восстановления. Для наглядности процессов применяется таблица, отражающая ключевые параметры наблюдения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
mostbet aviator приложение [url=http://mostbet20394.help/]http://mostbet20394.help/[/url]
слоты мостбет [url=https://mostbet20394.help]слоты мостбет[/url]
Клиника «КемероваМед Трезвость» предоставляет круглосуточную помощь пациентам, столкнувшимся с последствиями запоев и зависимостей. Основное направление — анонимное лечение, которое исключает постановку на учёт и обеспечивает конфиденциальность данных. При обращении пациент проходит первичную диагностику, включающую сбор анамнеза, измерение жизненно важных показателей, ЭКГ и анализ крови. После этого врач составляет персональный план лечения, который может включать детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию, капельницы, консультации психотерапевта и реабилитационные программы.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kemerovo18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo/
very interesting, but nothing sensible
_________________
[url=https://gamesnews.shop]1win отзывы кейсы[/url]
Any topic here unwinds like a tangle — layer by layer. And each new layer reminds us how much more has not been seen, not felt, not [url=https://shop77.su/][color=#1C1C1C]traversed new trails[/color][/url].
Если вы хотите [url=https://kupit-letnie-shini1.ru/]купить резину лето спб[/url], то у нас вы найдете лучшие предложения и выгодные цены.
Необходимо подбирать летнюю резину, ориентируясь на заводские требования к размерам.
Если вы мечтаете о надежном и уютном жилье, обратите внимание на [url=https://karkasnye-doma05.ru]каркасные дома под ключ в спб цены[/url], который сочетает в себе качество, современный дизайн и доступную стоимость.
Если не обрабатывать каркас должным образом, он быстро портится.
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно санкт-петербург[/url]
В основе работы клиники «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» лежит принцип персонализированной медицины. Это означает, что каждый пациент получает не шаблонное лечение, а тщательно подобранный комплекс процедур, учитывающий его состояние, историю заболевания, уровень мотивации и социальную ситуацию. Такой подход позволяет добиться стабильного результата даже в сложных случаях. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения данных, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]секс[/url]
Thanks for finally talking about > Types of Cancer: Common &
Rare Cancers Explained < Liked it!
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница[/url]
Служба круглосуточного вывода из запоя организована таким образом, чтобы обеспечить максимальную оперативность и надежность. Независимо от времени суток, квалифицированные специалисты готовы выехать на дом или принять пациента в медицинском учреждении, чтобы приступить к детоксикации и стабилизации состояния.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение в клинике проходит поэтапно. Каждый шаг направлен на достижение устойчивого результата и восстановление здоровья. Ниже представлена таблица с описанием основных этапов лечения.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo/
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Современные технологии позволяют:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
классный магазин, была впечатлянна скоростью доставки и качествомтовара)) всем пис кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш привет бразы всех спрошедшими праздниками получил седня посыль все порадовало и качество и бонус:p:D:D:Dприложеный за ожыдание спосибо магазуЯ подозреваю, что его посылку спалили на наличие и теперь просто не отправляют.
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/[/url]
Трезвый выбор [url=https://davlenienorm.com/raznoe/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnodare.html/]https://davlenienorm.com/raznoe/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnodare.html/[/url] .
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya
Наркологическая клиника выстраивает лечебные мероприятия в соответствии с алгоритмами, направленными на достижение стабильного состояния пациента. Важную роль играет последовательное выполнение процедур, включая оценку реакции организма и корректировку вмешательств. Формирование индивидуальной программы позволяет учитывать особенности каждого случая и поддерживать высокий уровень эффективности. Процесс наблюдения сопровождается непрерывным анализом, что делает терапию адаптивной и предсказуемой. В клинике соблюдается принцип многоуровневого контроля, обеспечивающий безопасность и стабильность лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tomsk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма томск[/url]
Ниже представлена последовательность этапов, формирующих общий цикл вмешательств.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/]наркологическая клиника наркологический центр[/url]
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar/
You actually make it appear really easy together with your presentation but I in finding this matter to be really one thing which I believe I’d never understand. It sort of feels too complex and extremely broad for me. I’m having a look ahead on your next post, I will attempt to get the hang of it!
Sometimes you read the discussions and realize that we all just look for ourselves in different ways. Some through work, others through hobbies. And [url=https://shop77.su/kosmetika-dlya-professionalov-ot-vedushix-brendov-mira/][color=#1C1C1C]I found the answers the most in my best journey[/color][/url]
I’ve been browsing online more than 4 hours today, yet I never found any
interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me.
Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the
net will be a lot more useful than ever before.
Kraken — одна из самых известных криптовалютных бирж в мире, предлагающая торговлю биткоином, эфириумом и другими цифровыми активами. Платформа отличается высоким уровнем безопасности, прозрачными комиссиями и удобным интерфейсом как для новичков, так и для профессиональных трейдеров. В сети иногда ищут kraken зеркала или kraken зеркало, чтобы получить доступ к платформе при технических ограничениях. Важно использовать только официальные источники, проверяя kraken ссылка и переходя на официальный kraken сайт. Биржа поддерживает фиатные валюты, маржинальную торговлю и стейкинг, обеспечивая надежную защиту средств и данных пользователей.[url=http://rivertravel.net/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=16137]кракен даркнет маркетплейс
[/url]
Алкоголизм — хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и круглосуточного контроля. Клиника «УралМед» в Екатеринбурге предлагает полный спектр услуг для пациентов любого уровня зависимости: от экстренной детоксикации до долгосрочной реабилитации. Главные принципы работы — абсолютная анонимность, индивидуальный план лечения и постоянное сопровождение квалифицированной командой специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя[/url]
и качество всегда на уровне)) https://flashstyl.top “Достаточно связаться с нами и отправить на указанный e-mail информацию о заказе и получателе. Конфиденциальность гарантируется.”5мг реально из области фантастики…желаю попробывать
Для формирования структурированного лечения используются методы, обеспечивающие анализ текущей клинической картины. Ниже представлены ключевые направления, задействованные при формировании терапевтических решений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vo-vladivostoke18.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике владивосток[/url]
При выезде к пациенту врач выполняет комплекс последовательных действий, которые направлены на стабилизацию состояния и предотвращение осложнений. Такая структурированность необходима для достижения медицинского результата.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Группа препаратов
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ekb/
Качественный вывод из запоя — это всегда процесс, а не одна капельница. Важно не только облегчить состояние здесь и сейчас, но и пройти через острый период так, чтобы не спровоцировать осложнения и оставить ресурс для дальнейшего лечения зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog website?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа? У нас есть пошаговая инструкция!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/narkolog_na_dom/]Генератор ключей Windows 11 рабочий[/url]
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому[/url]
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
I’m Cassandra and I live in a seaside city in northern France, Bezons.
I’m 33 and I’m will soon finish my study at International Relations.
Перед началом терапии проводится полная диагностика организма, включая лабораторные исследования и ЭКГ. Это позволяет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальный курс лечения. После стабилизации физического состояния начинается психотерапевтическая и реабилитационная работа. Такой подход помогает не только снять симптомы, но и устранить первопричины зависимости.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/narkolog-kemerovo-na-dom
If some one wants expert view on the topic of running a blog
then i recommend him/her to visit this weblog, Keep up the pleasant job.
В рамках лечения используются методы, позволяющие фиксировать изменения и оценивать реакцию организма на проводимые мероприятия. Они служат основой для выборочных корректировок и обеспечивают структурированный характер процесса. Отличительной особенностью становится возможность адаптировать лечебные схемы под индивидуальные особенности пациента. Ниже представлены ключевые направления оценки состояния, применяемые для формирования полной клинической картины.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-vdk18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladivostok/
Трезвый выбор [url=https://www.xn--80acjqkepj4b.xn--p1ai/narkolog-na-dom-v-donecke/]https://www.xn--80acjqkepj4b.xn--p1ai/narkolog-na-dom-v-donecke/[/url] .
Врач на дому или в клинике проводит:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-novosibirsk
Does your site have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it improve over time.
What i don’t understood is in reality how you are no longer really much more neatly-favored than you might be right now.
You are so intelligent. You realize thus considerably in terms of this
subject, made me individually consider it from a lot of various angles.
Its like women and men aren’t fascinated until it is something to do
with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs great.
At all times deal with it up!
Движения каждый день у нас, и все ровно . https://clicknstyj.top продукт – прет дико и жестко, но по сути ничего интересного, цена в 2 тыр себя полностью оправдывает. Эдакий бычий кайф. Если вам нравится трястись и стучать зубами – вы попали по адресу. Во всех остальных случаях – нахер-нахер. Слабенькая 3/5Всё здорово спасибо Вам
Kraken — одна из самых известных криптовалютных бирж в мире, предлагающая торговлю биткоином, эфириумом и другими цифровыми активами. Платформа отличается высоким уровнем безопасности, прозрачными комиссиями и удобным интерфейсом как для новичков, так и для профессиональных трейдеров. В сети иногда ищут kraken зеркала или kraken зеркало, чтобы получить доступ к платформе при технических ограничениях. Важно использовать только официальные источники, проверяя kraken ссылка и переходя на официальный kraken сайт. Биржа поддерживает фиатные валюты, маржинальную торговлю и стейкинг, обеспечивая надежную защиту средств и данных пользователей.[url=http://rivertravel.net/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=16136]kraken lite
[/url]
Если вы хотите [url=https://kupit-letnie-shini1.ru/]шины летние купить цена[/url], то у нас вы найдете лучшие предложения и выгодные цены.
Качество шин напрямую влияет на безопасность на дороге и комфорт в поездках.
Если вы мечтаете о надежном и уютном жилье, обратите внимание на [url=https://karkasnye-doma05.ru]каркасный дом спб[/url], который сочетает в себе качество, современный дизайн и доступную стоимость.
Он сочетает в себе современные технологии и комфортное проживание.
Такое поэтапное лечение позволяет добиться устойчивого результата без стрессов и осложнений. Пациенты получают комплексную помощь, включающую как медицинские, так и психотерапевтические аспекты.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kemerovo18.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
Скачайте активатор для Windows 11 и получите все функции Pro-версии бесплатно.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/]Ключ активации для Windows 11 2026[/url]
Генератор ключей для Windows 11 — 100% рабочий метод активации, проверено тысячами пользователей!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Windows 11 активатор на русском[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
пробовал 0,1гр ничего не было, пробовал 0,3 ничего не было, только мурашки на спине https://primegoode.top Ну что кто нить УРБ попробовал уже как отзывы ?Мир вам!
пицца доставка рязань Заказ пиццы – это не просто покупка, это ритуал наслаждения, доступный каждому.
pin-up pulsuz mərc məbləği [url=https://www.pinup21680.help]https://www.pinup21680.help[/url]
Howdy I am so happy I found your blog, I really found you by mistake, while I was searching on Yahoo for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say kudos for a fantastic post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the awesome job.
This topic has received interest in recent psychological wellness writing. The process is often linked with guided use of alternating stimulation to help the brain integrate experiences. Instead of centering entirely on extended discussion, it encourages internal processing within a supportive environment. It continues to be mentioned in general wellness conversations.
https://lkinstitute9.wordpress.com/2025/12/12/emdr-therapy-dissociative-disorders-best-practices-2025/
[url=https://selloscontisel.com/gracias]Tips to Pick a Qualified Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Therapist for Your Personal Recovery Process[/url] b04_f68
pin-up loyallıq proqramı [url=http://pinup21680.help/]http://pinup21680.help/[/url]
mostbet скачать приложение с сайта [url=https://mostbet20394.help]https://mostbet20394.help[/url]
pin-up yaş təsdiqi [url=www.pinup21680.help]pin-up yaş təsdiqi[/url]
Современная наркологическая помощь — это не просто лечение зависимости, а система комплексных мер, направленных на восстановление здоровья, эмоционального равновесия и социальной адаптации пациента. В клинике «ИжТрезвоМед Центр» в Ижевске применяются передовые методики терапии, соответствующие международным стандартам. Здесь работают квалифицированные врачи-наркологи, психиатры и реабилитологи, которые разрабатывают индивидуальные программы лечения в зависимости от формы и стадии заболевания. Центр предлагает как амбулаторное, так и стационарное лечение, а также выезд специалистов на дом, что делает помощь доступной и оперативной.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-izhevske18.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-izhevsk/
mostbet проверка документов [url=https://www.mostbet20394.help]https://www.mostbet20394.help[/url]
обучение кайтборду Кайт кайтинг кайтсёрфинг школа обучение сафари Дети ветра DETIVETRA
“И если мои слова не подтвердяться Прошу провести профелоктическую беседу с вашим Дай бог ему здоровья Минером” https://long-time-liner.ru Я в последний раз говорю, эта тема – для отзывов о работе магазина. Если вы не можете связаться с продавцом, то не надо писать об этом по сто раз. Если вы хотите узнать о качестве продукции – вам СЮДА !!! Любой оффтоп\флуд прекращаем !Как связаться?
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом актуален в ситуациях, когда пациенту требуется срочная медицинская помощь, но его состояние не позволяет самостоятельно обратиться в клинику. Основными причинами вызова нарколога на дом являются:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-spb/
Бесплатный ключ для Windows 11 — только у нас, обновлено в 2026 году!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Как активировать Windows 11 без ключа[/url]
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бесплатные порно видео[/url]
pin-up app işləmir [url=http://pinup21680.help]http://pinup21680.help[/url]
«Передозировка» — наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге, где проводят детокс, лечение зависимостей и программу поэтапной реабилитации. Специалисты помогают вернуть стабильное состояние и формируют долгосрочную стратегию трезвости.
Детальнее – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/service/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Современный [url=https://kolesovremeni.ru/]электрокарниз цена[/url] обеспечивает удобство управления шторами с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Использование электрокарнизов позволяет управлять шторами дистанционно.
Самостоятельные попытки «подлечиться» обычно сводятся к случайным комбинациям препаратов: кто-то пьёт горсть таблеток от давления и сердца, кто-то принимает успокоительные поверх алкоголя, кто-то заказывает непонятные средства «от тяги» в интернете. Такие эксперименты могут дать краткий эффект, но часто только маскируют симптомы и перегружают организм. В клинике лечение строится иначе: сначала оценивают состояние — физическое и психическое, затем подбирают безопасные схемы детоксикации и медикаментов, учитывая возраст, сопутствующие заболевания, длительность запоев и употребления. Это снижает риски осложнений и делает восстановление более управляемым: пациент и его семья видят прогресс и понимают, за счёт чего он происходит, а не живут в ожидании очередного непредсказуемого «отката».
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-korolyove/
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Процедура длится от 40 минут до 2 часов, в зависимости от тяжести состояния, и проводится в комфортной домашней обстановке, что значительно снижает стресс у пациента и его близких.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены краснодар[/url]
Hi, i feel that i saw you visited my weblog so i got here to go back the choose?.I am attempting to find issues to improve my web site!I assume its good enough to make use of some
of your concepts!!
Looking stylish projects a positive first impression.
A attire communicates loudly before you actually say a word.
This enhances your own confidence and mood noticeably.
A put-together appearance conveys professionalism in the office.
https://bm5.irkpress.ru/kEycPFc04OqC/
Stylish clothing let you to express your unique personality.
Others often judge well-dressed individuals as more capable and reliable.
Ultimately, putting effort in your wardrobe is an investment in yourself.
Yes! Finallʏ something ɑbout soulmate.
Here is my web page … wedding
додо пицца калуга Отличная пицца – это результат тщательного подбора ингредиентов и мастерства повара. Хорошая пицца, отличная пицца – понятия, которые тесно связаны с высоким качеством и безупречным вкусом.Пицца, это универсальное блюдо, которое давно перестало быть просто итальянской едой и прочно вошло в повседневную жизнь многих культур. Её способность адаптироваться к любым вкусам и предпочтениям делает пиццу поистине уникальной.
1win скачать бесплатно [url=http://1win70163.help]http://1win70163.help[/url]
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]исследование медиаполя пенсионного рынка[/url] представляет системный анализ отраслевых публикаций, подготовленный для участников пенсионного рынка. Агентство проводит регулярный анализ новостей и публикаций, связанных с финансовым регулированием пенсий, что позволяет фиксировать ключевые изменения. Исследование, выполненное при участии профессионального объединения, опирается на широкий массив источников. Для анализа использовались крупнейшие электронные библиотеки, что обеспечило объективность аналитических выводов. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает структурирование информационных потоков, благодаря чему участники рынка получают понятные аналитические отчеты. Сервис ориентирован на поддержку управленческих решений, обеспечивая стратегическую ценность аналитики. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет прогнозировать отраслевые изменения и формировать эффективную стратегию коммуникаций. В результате заказчики получают качественную отраслевую аналитику, способствующую оптимизации управленческих решений в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Там, где раньше хватало одного тяжёлого утра, теперь требуются дни детоксикации. И чем позже подключается врач, тем сложнее вернуть организм к относительно безопасному состоянию.
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru
Лечение в местной клинике удобно не только тем, что до неё проще добраться. Важнее то, что здесь выстраивают целостный подход, а не откликаются только на острые эпизоды. Для кого-то основной проблемой стали частые запои, для кого-то — периодическое употребление наркотиков, для третьего — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или снотворными. У каждого пациента своя история, свой стаж употребления, свой опыт неудачных попыток лечения и своя степень разрушения здоровья. В хорошей клинике это учитывают с самого начала и не предлагают всем одну и ту же «универсальную капельницу».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]besplatnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Hey I am so happy I found your blog page, I really found you by accident, while I was researching on Bing for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say many thanks for a tremendous post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the great b.
В центре «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге применяют комплексный подход: лечение наркомании, терапия алкогольной зависимости, индивидуальное кодирование и восстановительные программы. Такой формат обеспечивает надёжный результат и поддержку на всех этапах.
Углубиться в тему – https://peredozirovka.info/service/reabilitatsiya
Nice blog here! Also your website loads up fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your
host? I wish my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Нее… пацаны, Вы не поняли, я и не волнуюсь ни капельки, и на закз этот мне положить, мне за державу обидно. Пришел я в магазин а там висит цена на сок томатный сто рублей. Взял пачку, отстоял в очереди а продавщица и говорит что стоит он не сто рублей, которые у тебя в кармане, а сто десять… Да я разъе….у этот магазин вместе с продавщицой и заведующей…. Лучше заплатите админу своего сайта чтобы мессаги на мыло падали четко и конкретно и не наебы…ли людей. кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш они долго кормили завтраками с отправкой, а потом и вовсе закрылись…Сказали в понедельник всем кто оплатил заказ отправят НОМЕРА!
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в краснодаре[/url]
На основе осмотра подбирается оптимальный состав капельницы, включающий препараты для быстрого выведения токсинов, восстановления электролитного баланса и нормализации работы внутренних органов. При необходимости добавляются успокоительные средства, медикаменты для стабилизации сердечного ритма и защиты печени.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru
Первичный этап терапии направлен на оперативное выведение токсинов из организма. Врач-нарколог назначает индивидуальную схему медикаментозного вмешательства, что позволяет снизить уровень алкоголя в крови и восстановить обмен веществ.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Своевременное вмешательство специалиста позволяет не только вывести токсины, но и снизить риск развития осложнений, обеспечить восстановление жизненно важных функций организма и предотвратить ухудшение состояния, что особенно важно для сохранения здоровья и жизни пациента.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]защита корпоративных интересов консалтинг[/url] представляет системный анализ отраслевых публикаций, подготовленный для экспертов финансового сектора. Агентство реализует постоянное наблюдение новостей и публикаций, связанных с пенсионной индустрией, что позволяет отслеживать отраслевую динамику. Исследование, выполненное при участии профессионального объединения, опирается на широкий массив источников. Для анализа использовались ведущие цифровые архивы, что обеспечило высокую достоверность результатов. Такой подход позволяет формировать точную картину медиаполя российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает структурирование информационных потоков, благодаря чему участники рынка получают практикоориентированные рекомендации. Сервис ориентирован на укрепление корпоративных позиций, обеспечивая повышенную информированность. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет выявлять репутационные риски и формировать эффективную стратегию коммуникаций. В результате заказчики получают качественную отраслевую аналитику, способствующую усилению рыночных позиций в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-narkolog-na-dom-volgograd/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]стациомедика наркологическая клиника вывода из запоя москва отзывы[/url]
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Углубиться в тему – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-dolgoprudnom/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
Наркологический центр «Трезвый город» специализируется на лечении алкоголизма и наркомании с акцентом на безопасность пациента. Подбираются индивидуальные протоколы, учитывается анамнез, переносимость препаратов и возможные осложнения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/reabilitatsiya-12-shagov/]программа 12 шагов[/url]
trezviy-vibor [url=www.gbuzrk-vpb.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-peterburge//]www.gbuzrk-vpb.ru/narkolog-na-dom-v-peterburge//[/url] .
I do not even know how I finished up right here, however I assumed this put up was good.
I do not understand who you might be but definitely
you are going to a well-known blogger if you happen to are not already.
Cheers!
Feel free to visit my web site – porno videos
«Трезвый город» — это комплексная наркологическая помощь для взрослых пациентов: от экстренного купирования интоксикации до плановой терапии и поддержки в период восстановления. Врачи оценивают состояние, корректируют схему лечения и помогают выстроить понятный план дальнейших шагов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-geroina/]героин лечение[/url]
Наркологический центр «Еваклиник» в Саранске предоставляет профессиональную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной и наркотической зависимостью. Лечение начинается с медицинской стабилизации и детоксикации, после чего подбирается индивидуальная программа восстановления. Комплексный подход и постоянный контроль специалистов позволяют безопасно пройти сложный этап отказа от психоактивных веществ.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/otkaz-ot-alkogolya.html]отказ от алкоголя что происходит с организмом[/url]
Сигналом к тому, что пора обсудить вариант кодирования с наркологом, служит не один какой-то эпизод, а совокупность симптомов. Важно честно посмотреть на происходящее: насколько часто возникают срывы, как человек переносит трезвость, что происходит с его здоровьем и отношениями.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены[/url]
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно краснодар[/url]
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]защита корпоративных интересов консалтинг[/url] представляет масштабное исследование медиапространства, подготовленный для экспертов финансового сектора. Агентство обеспечивает ежедневный мониторинг новостей и публикаций, связанных с финансовым регулированием пенсий, что позволяет фиксировать ключевые изменения. Исследование, выполненное в партнерстве с профильной ассоциацией, опирается на обширную медиабиблиотеку. Для анализа использовались масштабные информационные базы, что обеспечило объективность аналитических выводов. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает глубокую классификацию публикаций, благодаря чему участники рынка получают понятные аналитические отчеты. Сервис ориентирован на повышение прозрачности отрасли, обеспечивая стратегическую ценность аналитики. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет прогнозировать отраслевые изменения и формировать эффективную стратегию коммуникаций. В результате заказчики получают надежный инструмент защиты интересов, способствующую оптимизации управленческих решений в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Функция и назначение
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ekb/
Часто именно жители Химок тянут до последнего: насыщенный ритм жизни, дорога на работу, постоянная усталость, попытки «снимать напряжение» алкоголем или психоактивными веществами. Сначала это кажется временным способом расслабиться, но со временем человек замечает, что пьёт чаще, чем планировал, нуждается в больших дозах, срывает обещания, а попытки контролировать употребление превращаются в череду неудач. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной наркологической помощи дальше будет только сложнее.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah[/url]
Менеджер прошу зайдите в скайп, хочу заказ оплатить вас там нет 2 дня уже. Заявку на сате подал жду ответ на эмаил. Спасибо. кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Заказал вчера в 20:00 оплатил в 22:00 домой пришел в 22:20 в статусе заказа уже выло написано в обработе тоесть деньги мои приняли. Спросил когда будет трек.Ответили завтра не раньше 16:00 проверяю в 14:40 уже статус отправлен и трек лежит в заказе. По скорости и отзывчивости магазина 100%лучше нетТорчал дома 2 дня,ждя,пока придёт этот курьер. Решил написать,чтоб кинули трек-надоело мне быть в ожидании. Оказалось,что:
В реабилитационном центре «Еваклиник» в Саранске созданы условия для безопасного и анонимного восстановления после зависимости. Программы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния и поэтапную реабилитацию под контролем медицинского персонала. Такой формат помощи позволяет снизить риски срывов и постепенно вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/lechenie-narkomanii/]лечение наркомании[/url]
Экстренный вывод из запоя в домашних условиях – это комплекс мер, направленный на быструю детоксикацию организма и восстановление нормального обмена веществ. В Волгограде квалифицированные специалисты готовы выехать к пациенту круглосуточно, чтобы оперативно оценить его состояние и начать терапию. Такой подход позволяет минимизировать негативное воздействие алкоголя и снизить риск развития осложнений.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnicza-volgograd/
[url=https://sibculture.ru/]электрокарнизы для легких штор с пультом купить[/url] сочетает в себе современный дизайн и безупречную функциональность, обеспечивая плавное открывание и закрывание штор с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Доступны как бюджетные модели, так и премиальные решения с расширенными возможностями.
Вопрос «а не рано ли кодироваться» часто звучит и от самих пациентов, и от их близких. Кажется, что кодирование — это крайняя мера «на последней стадии», а пока человек работает, иногда бывает трезвым и «не валяется под забором», можно подождать. На самом деле гораздо разумнее ориентироваться не на стереотипы, а на реальные признаки того, что зависимость уже управляет жизнью, а не наоборот. Кодирование от алкоголизма в Королёве рассматривается именно тогда, когда попытки остановиться своими силами систематически проваливаются, а каждый новый запой становится тяжелее предыдущего.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма в Королёве[/url]
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Ниобиевый пруток 13.5 мм НбЦУ ТУ 48-4-314-74 Купить ниобиевые прутки высокого качества от производителя по выгодным ценам. Широкий ассортимент диаметров и длин. Гарантия качества. Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Консультации специалиста. Быстрая доставка.
Функция и назначение
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru
капитальная реконструкция здания [url=https://rekonstrukcziya-zdanij-2.ru/]капитальная реконструкция здания[/url] .
Наркологическая клиника в Химках ориентируется не на «среднестатистического пациента», а на конкретного человека с его историей, болезнями, образом жизни и семьёй. Поэтому здесь не ограничиваются одним-двумя шаблонными вариантами. Врач оценивает, на каком этапе сейчас находится пациент: острый запой, ломка, период относительной трезвости с риском срыва, рецидив после ремиссии. От этого зависит выбор формата помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Quality content is the important to invite the users to pay a quick visit
the web page, that’s what this web page is providing.
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]i-Консалтинг мониторинг пенсионной отрасли[/url] представляет системный анализ отраслевых публикаций, подготовленный для экспертов финансового сектора. Агентство реализует постоянное наблюдение новостей и публикаций, связанных с пенсионной индустрией, что позволяет оперативно выявлять тенденции. Исследование, выполненное в партнерстве с профильной ассоциацией, опирается на обширную медиабиблиотеку. Для анализа использовались крупнейшие электронные библиотеки, что обеспечило объективность аналитических выводов. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает глубокую классификацию публикаций, благодаря чему участники рынка получают практикоориентированные рекомендации. Сервис ориентирован на повышение прозрачности отрасли, обеспечивая стратегическую ценность аналитики. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет оценивать информационные тренды и формировать эффективную стратегию коммуникаций. В результате заказчики получают качественную отраслевую аналитику, способствующую усилению рыночных позиций в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Каждый из этих симптомов по отдельности уже опасен, а в сочетании они создают высокий риск для жизни. Самостоятельные эксперименты с таблетками, резкий отказ от алкоголя «через силу» или попытка «переспать» запой без медицинского контроля могут обернуться реанимацией. Гораздо безопаснее вовремя вызвать специалиста и провести детоксикацию под наблюдением, особенно когда речь идёт о жителях крупного города, где доступна профессиональная наркологическая помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]вывод из запоя в москве в стационаре[/url]
Платная наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» предлагает лечение в комфортных условиях и с соблюдением медицинской этики. Специалисты помогают снять острые симптомы, снизить тягу и подготовить пациента к следующему этапу — реабилитации или амбулаторному сопровождению.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/alkohol-posle-kodirovki.html]если выпить алкоголь после кодировки[/url]
After I initially left a comment I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I recieve four emails with the exact same comment. Is there a means you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks a lot!
codigo promocional 1xbet venezuela 2026
Если по ходу визита появляются «красные флаги» (падение сатурации, нестабильный ритм, нарастающая дезориентация), маршрут мгновенно переводится в стационарный блок «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» — без «обнуления» обследований и без потери приватности. Вся собранная информация остаётся в единой карте наблюдения, что экономит время и силы.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Попытка самостоятельно выйти из запоя или преодолеть тяжелое похмелье может привести к крайне негативным последствиям. Длительное употребление алкоголя или резкий отказ без врачебного контроля опасны развитием осложнений, таких как алкогольный психоз, инсульт, инфаркт, обезвоживание и острая сердечная недостаточность.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]исследование медиаполя пенсионного рынка[/url] представляет масштабное исследование медиапространства, подготовленный для экспертов финансового сектора. Агентство обеспечивает ежедневный мониторинг новостей и публикаций, связанных с развитием пенсионных институтов, что позволяет отслеживать отраслевую динамику. Исследование, выполненное при участии профессионального объединения, опирается на широкий массив источников. Для анализа использовались ведущие цифровые архивы, что обеспечило высокую достоверность результатов. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает структурирование информационных потоков, благодаря чему участники рынка получают детализированные информационные сводки. Сервис ориентирован на поддержку управленческих решений, обеспечивая повышенную информированность. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет выявлять репутационные риски и формировать долгосрочные аналитические ориентиры. В результате заказчики получают качественную отраслевую аналитику, способствующую повышению эффективности корпоративной стратегии в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Наша выездная бригада оснащена как мобильный мини-кабинет: инфузомат для покапельной титрации, портативный кардиомонитор, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, экспресс-кассеты Na?/K? и набор для регистрации ЭКГ по показаниям. Такой комплект позволяет принять решение на месте — безопасно ли начинать дома или целесообразнее перевести пациента в стационарное отделение «ЮгМедЦентра» без «перезапуска» обследований. Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию: в схеме нет «лишних» позиций и конфликтов с уже принимаемыми лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.).
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Блин че мне нравится в чемикале то как работает человек….всегда ясно все говорит и поЯсняет…. кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Понимающий меня поймёт.А я так понимаю, что у данного магазина просто не мало оптовых покупателей, и им уделяется больше внимания.
go88hitclub seems like it has a large community! A good way for meet another players! Start know them here go88hitclub.
PK888Game, huh? Gave it a shot last night. Pretty decent selection of games and the interface is clean. Give it a go: pk888game
Looking to get into Brabet? Brabetentrar made it super easy to sign up. No complaints here. Give it a shot yourself: brabetentrar
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]знакомства для взрослых[/url]
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
Оперативное лечение организовано по четкому алгоритму, который позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента и обеспечить эффективную терапию. Каждый этап направлен на комплексное восстановление организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/klinika-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
Клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске специализируется на лечении зависимостей с применением проверенных медицинских протоколов. Пациентам доступна круглосуточная наркологическая помощь, медикаментозная поддержка и сопровождение на этапе реабилитации. Специалисты центра работают не только с физическими проявлениями зависимости, но и с психологическими причинами, что повышает эффективность лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/zapojnyj-alkogolizm-trudnosti-lecheniya.html]как лечить запойный алког алкоголизм[/url]
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно сочи[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Процедура лечения начинается с установки внутривенной капельницы, через которую вводятся детоксикационные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов и восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. При необходимости врач назначает дополнительные препараты, такие как седативные средства для купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома, гепатопротекторы для поддержки печени и кардиопротекторы для нормализации работы сердца.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Домашний формат наркологической помощи особенно востребован в курортном регионе: плотный график, сезонная работа, круглосуточная индустрия гостеприимства и нежелание афишировать проблему заставляют искать решение «тихо и быстро». В «ЮгМедЦентре» (Сочи) выезд врача доступен 24/7 без праздников и «коротких дней», а лечение строится как управляемый медицинский процесс: сначала — измерения, затем — точная коррекция, после — режим и поддержка. Мы приезжаем без символики, используем кодовые профили, нейтральные формулировки в документах и защищённые каналы связи, чтобы сохранить приватность пациента и его семьи.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
The growing popularity of the onlyfans search engine, [url=https://onlyfinder.co/hmong-new/top/]misopunnynoods onlyfans[/url] has generated new ways for creators to engage with their fans. Users can readily find content based on favorites. This tool is a game-changer for monetizing creativity.
Если по ходу визита появляются «красные флаги» (падение сатурации, нестабильный ритм, нарастающая дезориентация), маршрут мгновенно переводится в стационарный блок «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» — без «обнуления» обследований и без потери приватности. Вся собранная информация остаётся в единой карте наблюдения, что экономит время и силы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]исследование медиаполя пенсионного рынка[/url] представляет системный анализ отраслевых публикаций, подготовленный для участников пенсионного рынка. Агентство реализует постоянное наблюдение новостей и публикаций, связанных с развитием пенсионных институтов, что позволяет оперативно выявлять тенденции. Исследование, выполненное при участии профессионального объединения, опирается на широкий массив источников. Для анализа использовались масштабные информационные базы, что обеспечило максимальную репрезентативность данных. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает структурирование информационных потоков, благодаря чему участники рынка получают понятные аналитические отчеты. Сервис ориентирован на укрепление корпоративных позиций, обеспечивая стратегическую ценность аналитики. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет прогнозировать отраслевые изменения и формировать устойчивую модель взаимодействия. В результате заказчики получают качественную отраслевую аналитику, способствующую повышению эффективности корпоративной стратегии в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
После процедуры пациент и его близкие получают развернутые рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению, советы по профилактике рецидивов и возможности прохождения кодирования при желании пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]помощь нарколога на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
РедМетСплав предлагает широкий ассортимент высококачественных изделий из редких материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы обеспечиваем оперативное исполнение вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена требуемыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Превосходное обслуживание – то, чем мы гордимся – мы на связи, чтобы ответить на ваши вопросы а также предоставлять решения под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в множестве наших преимуществ
поставляемая продукция:
Магний 3.5105 – DIN 1729 Part 2 Магний 3.5105 – DIN 1729 Part 2 представляет собой высококачественный легированный материал, используемый в различных отраслях, включая автомобилестроение и аэрокосмическую промышленность. Его уникальные свойства, такие как легкость и высокая прочность, делают его идеальным выбором для создания прочных и легких конструкций. Этот сплав также обладает отличной коррозионной стойкостью, что гарантирует долгий срок службы изделий. Если вы ищете надежный материал, рекомендуем купить Магний 3.5105 – DIN 1729 Part 2, чтобы обеспечить качество и долговечность ваших проектов.
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]казино[/url]
https://www.natthadon-sanengineering.com/forum/topic/75893/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4-%D0%BD%D0%B0-1%D1%85%D0%91%D0%B5%D1%82-2026:-1xwind—%D0%91%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81-32,500
Группа препаратов
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно екатеринбург[/url]
Запой – критическое состояние, при котором организм подвергается серьезной токсической нагрузке, что может привести к опасным для жизни осложнениям. В Волгоградской области помощь нарколога оказывается круглосуточно, что позволяет начать лечение немедленно в любой момент дня или ночи. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство, индивидуальный подход и высокий уровень безопасности, позволяя стабилизировать состояние пациента в домашних условиях или в клинике.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом срочно[/url]
Капельница от запоя — это комплексная процедура, направленная на быстрое выведение токсинов, нормализацию обменных процессов и восстановление жизненно важных функций организма. Врачи-наркологи подбирают индивидуальный состав капельницы, исходя из состояния пациента. В стандартный набор препаратов обычно входят:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Перед тем как принять решение, пациент и родственники получают объяснения по доступным направлениям. Обычно обсуждаются: амбулаторные консультации, дневной или круглосуточный стационар, выездная помощь, реабилитационные программы и последующее наблюдение. Это позволяет выстроить индивидуальный маршрут, а не навязывать один и тот же сценарий всем подряд.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого краснодар[/url]
Электрокарниз [url=https://www.karniz-opt.ru/]электрокарниз для штор с пультом[/url] обеспечивает автоматическую регулировку тени в помещении, сочетая современный дизайн с функциональностью.
Натягивание ткани не требуется благодаря автоматике .
Подключается к электропроводке здания .
Устройство совместимо с домашними системами управления .
Такой подход повышает удобство проживания .
Зделал заказ 203го в четверг вечером,в пятницу уже получил трек,а сегодня създил забрал посылку!запаковано так,что сам с трудом нашел)все очень вкусно и качественно!продовцам респект.слаженно работают! https://flashfindsis.shop Делать надо 1к10, можно и послабже, например 1к13, но не более, а то 30 минут эт мало, хотя смотря для кого))Не смог не скопипастить
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]аналитика пенсионного рынка России[/url] представляет масштабное исследование медиапространства, подготовленный для экспертов финансового сектора. Агентство обеспечивает ежедневный мониторинг новостей и публикаций, связанных с пенсионной индустрией, что позволяет оперативно выявлять тенденции. Исследование, выполненное совместно с отраслевыми экспертами, опирается на обширную медиабиблиотеку. Для анализа использовались крупнейшие электронные библиотеки, что обеспечило максимальную репрезентативность данных. Такой подход позволяет создавать надежную аналитическую модель российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает структурирование информационных потоков, благодаря чему участники рынка получают практикоориентированные рекомендации. Сервис ориентирован на поддержку управленческих решений, обеспечивая стратегическую ценность аналитики. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет прогнозировать отраслевые изменения и формировать эффективную стратегию коммуникаций. В результате заказчики получают профессиональную информационную поддержку, способствующую оптимизации управленческих решений в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]покер онлайн[/url]
Есть ряд признаков, при которых ждать категорически нельзя и нужна срочная помощь врача, а не очередные «народные методы». Если вы замечаете у человека следующие симптомы, это прямой повод организовать профессиональный вывод из запоя:
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru
mostbet сайт не работает [url=https://mostbet20394.help/]mostbet сайт не работает[/url]
Многие тянут до последнего, считая, что к наркологу обращаются только в самых крайних случаях. На деле показаний для консультации гораздо больше, и они часто появляются задолго до того, как человек впервые оказывается в запое или не выходит из состояния опьянения несколько дней подряд.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-voskresenske
Важно понять: запой — это не просто серия праздников или «отпуск с алкоголем». Это состояние, при котором организм перестаёт выходить в трезвость, а любая попытка остановиться сопровождается настолько тяжёлыми симптомами, что человек снова тянется к бутылке. С каждым днём запоя возрастает нагрузка на сердце, печень, поджелудочную железу, мозг.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this blog. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s challenging to get that “perfect balance” between superb usability and visual appeal. I must say you’ve done a awesome job with this. Also, the blog loads extremely fast for me on Internet explorer. Exceptional Blog!
Наркологическая клиника в Королёве — это возможность получить профессиональное лечение алкогольной и наркотической зависимости без долгих поездок и изматывающих очередей. Для многих людей решение обратиться к наркологу созревает не за один день: до этого были попытки «завязать самому», эксперименты с таблетками, обещания близким, срывы на фоне стресса, праздников или семейных конфликтов. Запои становятся длиннее, организму всё труднее восстанавливаться, растёт тревога, нарушается сон, появляются скачки давления и проблемы с сердцем. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без системной медицинской помощи справиться уже невозможно, но ехать в крупный мегаполис, искать стационар «по отзывам» и подстраивать лечение под сложную логистику тоже тяжело.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар[/url]
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/narkolog-sochi/
монтаж лстк [url=https://rekonstrukcziya-zdanij-2.ru/]rekonstrukcziya-zdanij-2.ru[/url] .
https://preniumdirectory.com/listings13517320/%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4-1%D1%85%D0%B1%D0%B5%D1%82-%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%B1%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%8E-%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BA%D1%83
Санкт-петербургская клиника «Передозировка» специализируется на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Здесь выполняют кодирование, проводят медицинское восстановление и обеспечивают психологическую поддержку для закрепления результата.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/vliyanie-spirtnogo-na-pochki/]алкоголь на почки[/url]
Отзывы от кролов. качество тусишки хорошее. приятно порадовали ее ценой. качество метоксетамина – как у всех. сейчас в россии булыженная партия, тут он такой же. однако продавец сказал что скоро будет другая партия. вывод – магазин отличный, будем работать. https://pixelbazare.shop Захожу 24-го, фигакс, бан.Качество превосходное! чистейший джив у вас) всем нравится. Удачных продаж,бро!
как подобрать свой стиль в одежде Как подобрать одежду женщине? Главное – учитывать особенности фигуры, личный стиль и, конечно же, повод. Не бойтесь экспериментировать, но всегда помните о чувстве меры.
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
как получить промокод 1хбет
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом рязань[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно в волгограде[/url]
билеты на теплоход по москве-реке Разнообразие предложений позволит каждому найти оптимальный вариант: от уединенных романтических вечеров до шумных семейных праздников. Позвольте себе окунуться в атмосферу волшебства, выбрав прогулку на теплоходе с ужином или даже дискотекой. Живая музыка на борту добавит особого шарма, превращая обычный вечер в незабываемое приключение.
Врач устанавливает внутривенную капельницу, через которую вводятся специально подобранные препараты для очищения организма от алкоголя, восстановления баланса жидкости и нормализации работы всех органов и систем. В течение всей процедуры специалист следит за состоянием пациента и, при необходимости, корректирует терапию.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]выезд на дом капельница от запоя в сочи[/url]
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/
[url=https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/]исследование медиаполя пенсионного рынка[/url] представляет комплексный обзор информационной среды, подготовленный для участников пенсионного рынка. Агентство обеспечивает ежедневный мониторинг новостей и публикаций, связанных с финансовым регулированием пенсий, что позволяет отслеживать отраслевую динамику. Исследование, выполненное совместно с отраслевыми экспертами, опирается на широкий массив источников. Для анализа использовались масштабные информационные базы, что обеспечило высокую достоверность результатов. Такой подход позволяет выстраивать объективную информационную панораму российского пенсионного рынка. Консалтинговая методология агентства включает глубокую классификацию публикаций, благодаря чему участники рынка получают детализированные информационные сводки. Сервис ориентирован на поддержку управленческих решений, обеспечивая повышенную информированность. Использование современных инструментов анализа позволяет выявлять репутационные риски и формировать устойчивую модель взаимодействия. В результате заказчики получают профессиональную информационную поддержку, способствующую усилению рыночных позиций в условиях динамичного развития пенсионного сектора.
https://xn—-8sbjrckiodf8ao.xn--p1ai/
Приватность — клинический фактор, снижающий тревогу и укрепляющий доверие. В «ЕкатеринбургМедСервис» выезд немаркированный, специалисты в гражданской одежде, уведомления — «тихие», документы — с нейтральными формулировками. Медкарта хранится в шифрованном контуре, доступ к данным разграничен по ролям. По запросу вся коммуникация ведётся через доверенное лицо, а оплата возможна наличными или безналом с нейтральным назначением платежа. Это позволяет оставаться в тени и при этом получать полноценную помощь.
Узнать больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/ekaterinburg-narkologiya/
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/ubod/]убод в москве цена[/url]
После процедуры пациент и его близкие получают развернутые рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению, советы по профилактике рецидивов и возможности прохождения кодирования при желании пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Because the admin of this site is working, no question very
shortly it will be famous, due to its quality contents.
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]секс[/url]
Для создания удобного и стильного интерьера выбирайте [url=https://mebel-h.ru/]https://mebel-h.ru/https://mebel-h.ru[/url] — это лучший выбор для современного дома.
Электрокарниз рекомендуется покупать у производителей, обеспечивающих гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание.
With havin so much content do you ever run into any problems of
plagorism or copyright violation? My blog has a lot of exclusive content
I’ve either created myself or outsourced but it seems a lot of it is popping it up all
over the web without my authorization. Do you know any methods
to help prevent content from being stolen? I’d truly
appreciate it.
Может забегу как-нибудь) Обычно все берут там где надежно у одних и техже, новые магазины или первые покупки рисково, любой выберет проверенных лично) кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш разобрался, поэтому и удалил сообщение до того как ты ответил )Я выхватил бан, ты злобняк
Для безопасного и эффективного лечения наши специалисты используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально с учетом состояния пациента. В состав капельницы входят следующие группы препаратов:
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Для достижения положительного результата применяются комплексные подходы, сочетающие медикаментозные и поддерживающие методы. Врачи оценивают общее состояние пациента, степень выраженности абстинентного синдрома и сопутствующие заболевания. На основе этих данных подбираются оптимальные методы коррекции.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург[/url]
you are in point of fact a just right webmaster. The web site loading velocity is incredible. It sort of feels that you are doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a excellent task in this topic!
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]бесплатные порно видео[/url]
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Разобраться лучше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/preparaty-dlya-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]luchshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Крутой качественный товар! Все своевременно +++ https://meferdrongeer.club Аптечные травы вообщем.так-то уже четверг бро
В реабилитационном центре «Еваклиник» в Саранске созданы условия для безопасного и анонимного восстановления после зависимости. Программы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния и поэтапную реабилитацию под контролем медицинского персонала. Такой формат помощи позволяет снизить риски срывов и постепенно вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Узнать больше – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/ehffektivnye-sposoby-izbavitsya-ot-golovnoj-boli-pri-pohmele.html]таблетки от головной боли при похмелье[/url]
Применение современных капельничных методов позволяет точно дозировать лекарственные средства. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей пациента дает возможность оперативно корректировать терапию для достижения оптимального эффекта и предотвращения побочных реакций.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена[/url]
усиление зданий фиброармированными полимерами [url=https://rekonstrukcziya-zdanij-2.ru/]rekonstrukcziya-zdanij-2.ru[/url] .
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
Функция и назначение
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Там, где раньше хватало одного тяжёлого утра, теперь требуются дни детоксикации. И чем позже подключается врач, тем сложнее вернуть организм к относительно безопасному состоянию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/[/url]
Часто родственники тянут до последнего, надеясь, что запой «сам пройдёт», как это случалось раньше. Но с каждым эпизодом последствия становятся тяжелее: организм изнашивается, возрастает риск осложнений, ухудшается психика. Особенно опасно, когда запой длится несколько дней подряд, а любые попытки самостоятельно сократить дозы алкоголя сопровождаются дрожью, бессонницей, приступами паники.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskva011.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-moskovskij-rajon[/url]
Установка [url=https://2teh.ru/]http://www.2teh.ru[/url] для ваших штор может значительно улучшить функциональность и эстетику вашего дома.
он позволяет автоматизировать процесс управления шторами и жалюзи . Это устройство можно легко интегрировать в систему умного дома чтобы повысить уровень комфорта и безопасности . Электрокарниз может быть управляем с помощью пульта дистанционного управления или мобильного приложения что делает его очень удобным в использовании .
Электрокарниз также может быть интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома как системы видеонаблюдения и дверные замки. Это позволяет создать единую систему управления всеми устройствами в доме что повышает уровень комфорта и безопасности . Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть оснащен датчиками освещенности и температуры которые обеспечивают оптимальное количество света и тепла в комнате .
## Раздел 2: Преимущества электрокарниза
Электрокарниз имеет множество преимуществ он обеспечивает более комфортную и безопасную среду обитания . Это устройство также может помочь сэкономить энергию путем поддержания оптимальной температуры и уровня освещенности в доме. Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть использован для создания сценариев и режимов работы такие как режим “отпуск” или “работа” .
Электрокарниз также может быть оснащен функцией таймера которая позволяет запланировать открытие и закрытие штор и жалюзи . Это устройство также может быть интегрирован с голосовыми помощниками например, с Alexa или Google Assistant . Это позволяет управлять электрокарнизом с помощью голосовых команд что делает его очень удобным в использовании .
## Раздел 3: Установка и настройка электрокарниза
Установка электрокарниза не требует специальных навыков или инструментов она может быть выполнена в течение нескольких часов. Это устройство поставляется с набором необходимых деталей и инструкциями которые обеспечивают подробную информацию о процессе установки . После установки электрокарниз необходимо настроить чтобы он был интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома .
Настройка электрокарниза обычно включает в себя создание учетной записи и настройку параметров работы настройку интеграции с другими устройствами умного дома . Это позволяет создать индивидуальный режим работы электрокарниза который будет соответствовать всем желаниям и предпочтениям пользователя . Кроме того, электрокарниз может быть обновлен с помощью специального программного обеспечения которое позволяет добавлять nuevas функции и улучшать existing .
## Раздел 4: Заключение
Электрокарниз – это современное и удобное решение для управления шторами и жалюзи в доме он позволяет автоматизировать процесс управления шторами и жалюзи . Он может быть интегрирован с другими устройствами умного дома например, с системами освещения и отопления и управляться с помощью пульта дистанционного управления или мобильного приложения что позволяет управлять им из любой точки дома . Электрокарниз также может быть оснащен датчиками освещенности и температуры которые помогают поддерживать комфортную температуру и уровень освещенности в доме.
Электрокарниз имеет множество преимуществ он обеспечивает более комфортную и безопасную среду обитания . Он может быть использован для создания сценариев и режимов работы такие как режим “отпуск” или “работа” и может быть интегрирован с голосовыми помощниками как Yandex.Alisa или Samsung Bixby. Это устройство также может быть обновлен с помощью специального программного обеспечения которое обеспечивает регулярные обновления и исправления ошибок .
Наркологическая клиника в Химках ориентируется не на «среднестатистического пациента», а на конкретного человека с его историей, болезнями, образом жизни и семьёй. Поэтому здесь не ограничиваются одним-двумя шаблонными вариантами. Врач оценивает, на каком этапе сейчас находится пациент: острый запой, ломка, период относительной трезвости с риском срыва, рецидив после ремиссии. От этого зависит выбор формата помощи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah/
[url=https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/]социальный проект антивирусная реклама[/url] это специальная инициатива медиагруппы для предпринимателей, созданная для предпринимателей и локальных компаний. Медиагруппа РИМ запустила бесплатное рекламное размещение, чтобы дать компаниям дополнительную видимость. Участники получают маркетинговую поддержку без бюджета, что особенно важно при масштабировании бизнеса. Проект ориентирован на малые коммерческие организации, которым нужна дополнительная аудитория. Наружные рекламные поверхности позволяют эффективно донести информацию до аудитории, а бесплатный формат делает участие доступным для большинства бизнесов. Инициатива поддерживает предпринимательскую активность, предоставляя маркетинговые ресурсы без затрат. Такой формат помогает расширять клиентскую базу через наружные рекламные конструкции. Программа рассчитана на бизнесы различных сфер, обеспечивая практичный инструмент роста. Бесплатная наружная реклама становится дополнительным каналом коммуникации, позволяя бизнесу расширять присутствие без лишних затрат.
https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/
Брал неоднократно в этом магазе, всегда всё ровно и без проволочек, так держать!! кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Отличнный магазин[hide=5]в аське появлялся днём видимо ненадолго, и снова нету ((
I pay a quick visit daily some blogs and websites to read content, except this webpage offers feature
based content.
На основе осмотра подбирается оптимальный состав капельницы, включающий препараты для быстрого выведения токсинов, восстановления электролитного баланса и нормализации работы внутренних органов. При необходимости добавляются успокоительные средства, медикаменты для стабилизации сердечного ритма и защиты печени.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в санкт-петербурге[/url]
[url=https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/]поддержка малого бизнеса рекламой[/url] это социальный проект рекламной поддержки компаний, созданная для малого и среднего бизнеса. Медиагруппа РИМ запустила бесплатное рекламное размещение, чтобы помочь бизнесу заявить о себе. Участники получают наружную рекламу без финансовой нагрузки, что особенно важно при масштабировании бизнеса. Проект ориентирован на локальные бренды и сервисы, которым нужна усиленная видимость на рынке. Наружные рекламные поверхности позволяют эффективно донести информацию до аудитории, а бесплатный формат делает участие реальным инструментом продвижения. Инициатива поддерживает рост коммерческих проектов, предоставляя рекламные возможности бесплатно. Такой формат помогает укреплять позиции бренда через визуальное присутствие в городской среде. Программа рассчитана на бизнесы различных сфер, обеспечивая эффективный рекламный канал. Бесплатная наружная реклама становится рабочим способом привлечения клиентов, позволяя бизнесу развиваться активнее без лишних затрат.
https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/
1win мегапей Киргизия [url=http://1win70163.help/]1win мегапей Киргизия[/url]
Самостоятельные попытки «подлечиться» обычно сводятся к случайным комбинациям препаратов: кто-то пьёт горсть таблеток от давления и сердца, кто-то принимает успокоительные поверх алкоголя, кто-то заказывает непонятные средства «от тяги» в интернете. Такие эксперименты могут дать краткий эффект, но часто только маскируют симптомы и перегружают организм. В клинике лечение строится иначе: сначала оценивают состояние — физическое и психическое, затем подбирают безопасные схемы детоксикации и медикаментов, учитывая возраст, сопутствующие заболевания, длительность запоев и употребления. Это снижает риски осложнений и делает восстановление более управляемым: пациент и его семья видят прогресс и понимают, за счёт чего он происходит, а не живут в ожидании очередного непредсказуемого «отката».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
В сети регулярно появляются новые платформы и сервисы, предлагающие пользователям доступ к различным цифровым продуктам. Среди обсуждаемых запросов часто встречаются такие формулировки, как kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, kraken ссылка и kraken сайт. Обычно подобные ключевые слова используют для поиска альтернативных адресов ресурса в случае ограничений или технических работ. Пользователям рекомендуется внимательно проверять источники информации, оценивать безопасность соединения и соблюдать правила цифровой гигиены при переходе по любым ссылкам.[url=http://rivertravel.net/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=16290]kraken tg
[/url]
Thanks for finally writing about > %blog_title% < Liked it!
1вин мегапей пополнение [url=1win70163.help]1вин мегапей пополнение[/url]
[url=https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/]наружная реклама как помощь бизнесу[/url] это программа помощи бизнесу через наружное продвижение, созданная для предпринимателей и локальных компаний. Медиагруппа РИМ запустила бесплатное рекламное размещение, чтобы расширить узнаваемость брендов. Участники получают реальную возможность продвижения без расходов, что особенно важно при масштабировании бизнеса. Проект ориентирован на региональные компании и предпринимателей, которым нужна широкая рекламная представленность. Наружные рекламные поверхности позволяют эффективно донести информацию до аудитории, а бесплатный формат делает участие реальным инструментом продвижения. Инициатива поддерживает рост коммерческих проектов, предоставляя рекламные возможности бесплатно. Такой формат помогает формировать доверие аудитории через визуальное присутствие в городской среде. Программа рассчитана на компании разных направлений, обеспечивая эффективный рекламный канал. Бесплатная наружная реклама становится дополнительным каналом коммуникации, позволяя бизнесу развиваться активнее без лишних затрат.
https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/
Hi there friends, good article and pleasant urging commented at
this place, I am truly enjoying by these.
1win как вывести крупную сумму [url=http://1win70163.help]1win как вывести крупную сумму[/url]
[url=https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/]проект антивирусная реклама для предпринимателей[/url] это программа помощи бизнесу через наружное продвижение, созданная для малого и среднего бизнеса. Медиагруппа РИМ запустила бесплатное рекламное размещение, чтобы помочь бизнесу заявить о себе. Участники получают наружную рекламу без финансовой нагрузки, что особенно важно при масштабировании бизнеса. Проект ориентирован на малые коммерческие организации, которым нужна широкая рекламная представленность. Наружные рекламные поверхности позволяют быстро привлечь внимание клиентов, а бесплатный формат делает участие реальным инструментом продвижения. Инициатива поддерживает рост коммерческих проектов, предоставляя рекламные возможности бесплатно. Такой формат помогает формировать доверие аудитории через широкоформатные рекламные носители. Программа рассчитана на предпринимателей из разных отраслей, обеспечивая практичный инструмент роста. Бесплатная наружная реклама становится рабочим способом привлечения клиентов, позволяя бизнесу развиваться активнее без лишних затрат.
https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/
Наша выездная бригада оснащена как мобильный мини-кабинет: инфузомат для покапельной титрации, портативный кардиомонитор, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, экспресс-кассеты Na?/K? и набор для регистрации ЭКГ по показаниям. Такой комплект позволяет принять решение на месте — безопасно ли начинать дома или целесообразнее перевести пациента в стационарное отделение «ЮгМедЦентра» без «перезапуска» обследований. Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию: в схеме нет «лишних» позиций и конфликтов с уже принимаемыми лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.).
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены[/url]
FoX будь добр скажи… https://zakladshp.club Ну, красавы. Вечером оплатил на следующий день отправилипо предержи свои слова, некого еще не обманул за 2 года, кого я кинул напиши сюда пример?
Своевременное вмешательство специалиста позволяет не только вывести токсины, но и снизить риск развития осложнений, обеспечить восстановление жизненно важных функций организма и предотвратить ухудшение состояния, что особенно важно для сохранения здоровья и жизни пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Передозировка» предлагает круглосуточную помощь жителям Санкт-Петербурга. Лечение зависимостей, детокс-мероприятия и современные методы кодирования помогают пациентам восстановить здоровье и начать длительный период трезвости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/alkogol-i-beremennost/]алкоголь на ранней беременности[/url]
Выбор встроенной техники стартует с ключевого элемента – духового шкафа. Если вы собираетесь обновление кухни или разрабатываете кухню заново, присмотритесь на [url=https://euroshop18.ru/raspredelit-po-brendam/franke/duhovye-shkafy-franke.html]электрические духовые шкафы franke[/url] – это оборудование высокого класса с удобной эргономикой и точным поддержанием температуры. Бренд Franke делает ставку на равномерный нагрев, понятную панель управления и сдержанный дизайн, который гармонично вписывается в современный интерьер. Такие модели подойдут тем, кто ценит стабильный результат: выпечка пропекается равномерно, мясо сохраняет сочность, а уход не доставляет сложностей благодаря каталитической или пиролитической очистке.
Также важный элемент кухни – вытяжка. От качества вентиляции зависит удобство приготовления пищи и сохранность кухонной мебели. Если вы планируете [url=https://euroshop18.ru/katalog/duxovyie-shkafyi/]купить встроенных духовых шкафов[/url] или подобрать другую технику для кухни, обращайте внимание на мощность всасывания и тихую работу: модели Midea обеспечивают хороший баланс мощности и тихой работы. При этом бренд применяет современные фильтрационные системы и дизайнерские решения для интеграции в кухню. Это особенно актуально для кухонь-гостиных, где необходимо сохранить чистый воздух без лишнего гула.
Подбирать технику лучше в магазине с официальной гарантией производителя и понятными условиями доставки. Интернет-магазин euroshop18.ru предлагает большой выбор встраиваемой техники, помощь экспертов и понятную навигацию по брендам. Здесь можно сравнить характеристики, проверить наличие и подобрать подходящий вариант под свой кухонный проект. Заранее проверьте параметры подключения и размеры ниши заранее – так установка будет выполнена без неожиданностей.
1вин ios [url=1win70163.help]1win70163.help[/url]
[url=https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/]наружная реклама как помощь бизнесу[/url] это специальная инициатива медиагруппы для предпринимателей, созданная для малого и среднего бизнеса. Компания РИМ реализовала инициативу наружной рекламы без оплаты, чтобы расширить узнаваемость брендов. Участники получают реальную возможность продвижения без расходов, что особенно важно на этапе роста компании. Проект ориентирован на локальные бренды и сервисы, которым нужна дополнительная аудитория. Наружные рекламные поверхности позволяют эффективно донести информацию до аудитории, а бесплатный формат делает участие выгодным маркетинговым решением. Инициатива поддерживает рост коммерческих проектов, предоставляя рекламные возможности бесплатно. Такой формат помогает расширять клиентскую базу через наружные рекламные конструкции. Программа рассчитана на предпринимателей из разных отраслей, обеспечивая практичный инструмент роста. Бесплатная наружная реклама становится стратегическим преимуществом, позволяя бизнесу развиваться активнее без лишних затрат.
https://xn--80aaaahtsbukmdd5bcnmw5u.xn--p1ai/
Там, где раньше хватало одного тяжёлого утра, теперь требуются дни детоксикации. И чем позже подключается врач, тем сложнее вернуть организм к относительно безопасному состоянию.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]вывод из запоя воскресенск[/url]
mostbet jackpoturi [url=https://mostbet42873.help/]mostbet jackpoturi[/url]
Оперативное лечение организовано по четкому алгоритму, который позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента и обеспечить эффективную терапию. Каждый этап направлен на комплексное восстановление организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Эти данные являются основой для составления индивидуального плана лечения, позволяющего оперативно скорректировать терапевтические меры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом рязань[/url]
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
https://alexandercasino7.com
Спасибо! Обращайтесь кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш НЕ принуждаем вас тут брать, берите, где позволяет бюджет.Описание грамотное и понятное, клад нашел в считаные минуты.
В сети регулярно появляются новые платформы и сервисы, предлагающие пользователям доступ к различным цифровым продуктам. Среди обсуждаемых запросов часто встречаются такие формулировки, как kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, kraken ссылка и kraken сайт. Обычно подобные ключевые слова используют для поиска альтернативных адресов ресурса в случае ограничений или технических работ. Пользователям рекомендуется внимательно проверять источники информации, оценивать безопасность соединения и соблюдать правила цифровой гигиены при переходе по любым ссылкам.[url=http://rivertravel.net/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=16297]kraken ссылка v5tor cfd
[/url]
Установите удобный [url=https://www.mobile-mir.ru/]купить электрокарнизы в долгопрудном[/url] для идеального управления шторами в вашем доме.
С его помощью можно легко регулировать освещенность комнаты, не вставая с дивана.
Такие системы становятся все популярнее благодаря своему удобству и функциональности. Их часто устанавливают в умных домах для интеграции в систему автоматизации.
#### **2. Преимущества электрокарнизов**
Главное достоинство электрокарниза — это удобство использования. Управление происходит с пульта или даже через смартфон, что делает процесс максимально простым.
Кроме того, электрокарнизы отличаются высокой надежностью и долговечностью. Производители предлагают гарантию на несколько лет, подтверждая качество продукции.
#### **3. Установка и настройка**
Монтаж электрокарниза требует определенных навыков и точности. Перед установкой необходимо проверить прочность стены или потолка в месте крепления.
После установки нужно правильно настроить систему управления. В некоторых моделях можно задавать индивидуальные сценарии работы.
#### **4. Выбор подходящей модели**
При покупке электрокарниза важно учитывать несколько факторов. В первую очередь, нужно определить максимальный вес штор, которые будет выдерживать система.
На рынке представлены модели разных ценовых категорий. Бюджетные варианты обладают базовым функционалом, но надежны в эксплуатации.
—
### **Спин-шаблон**
#### **1. Введение**
Такие системы становятся все популярнее благодаря своему удобству и функциональности.
#### **2. Преимущества электрокарнизов**
Главное достоинство электрокарниза — это удобство использования.
#### **3. Установка и настройка**
Лучше доверить эту работу профессионалам, чтобы избежать ошибок.
#### **4. Выбор подходящей модели**
Ассортимент включает как бюджетные, так и премиальные варианты.
Hi there, always i used to check blog posts here in the early hours in the morning, since i
love to gain knowledge of more and more.
частный дизайн интерьера дизайн интерьера спб
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Kudos!
Перед тем как выбрать формат лечения, пациенту и его близким объясняют, какие направления помощи доступны и как их можно сочетать. В зависимости от состояния и мотивации могут быть задействованы разные варианты:
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Врач устанавливает внутривенную капельницу, через которую вводятся специально подобранные препараты для очищения организма от алкоголя, восстановления баланса жидкости и нормализации работы всех органов и систем. В течение всей процедуры специалист следит за состоянием пациента и, при необходимости, корректирует терапию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Лечение зависимостей редко ограничивается одной процедурой. Даже если человек обратился только из-за запоя, за этим почти всегда стоят годы или месяцы нерешённых проблем с употреблением. Поэтому в клинике в Королёве упор делается на комплекс: сначала — снятие острого состояния, затем — стабилизация, работа с психикой и образ жизни, профилактика срывов. Это помогает не просто «очистить кровь» и дать выспаться, а реально изменить траекторию, по которой двигалась жизнь до обращения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]ближайшая наркологическая клиника[/url]
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
На днях брал небольшой опт, был приятно удивлен подходом и предложением тс, товар еще не пробовали ,но забрал все ровно, по ходу отпишу в теме за качество товара, пока же могу сказать, что жалею , что раньше не работал с данным тс! Успехов, благодарю за сервис!!! https://flashfindsis.shop Слив засчитан.пиши в контакты, разберутся. мб попутали что.
https://md.darmstadt.ccc.de/s/LdUaTEeJoz
Если вам нужна [url=https://arenda-avtomobilya-s-voditelem02.ru/]аренда авто с водителем новосибирск[/url], обращайтесь к профессионалам!
Для экономии стоит оформлять заказ заранее, особенно в праздничные дни.
В статье-обзоре представлены данные сомнительной актуальности и факты без явной взаимосвязи. Читатель ознакомится с разными мнениями, хотя они вряд ли существенно изменят его представление о теме.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy[/url]
What’s up friends, fastidious post and fastidious urging commented here, I am genuinely enjoying by these.
Санкт-петербургская клиника «Передозировка» специализируется на лечении алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Здесь выполняют кодирование, проводят медицинское восстановление и обеспечивают психологическую поддержку для закрепления результата.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/service/lechenie-narkomanii/]центр лечения наркомании[/url]
Этот документ охватывает важные аспекты медицинской науки, сосредотачиваясь на ключевых вопросах, касающихся здоровья населения. Мы рассматриваем свежие исследования, клинические рекомендации и лучшие практики, которые помогут улучшить качество лечения и профилактики заболеваний. Читатели получат возможность углубиться в различные медицинские дисциплины.
Подробнее тут – http://google.ba/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/kodirovanie-disulfiramom
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» оказывает медицинскую помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости: детоксикация, снятие абстиненции, стабилизация состояния и подбор дальнейшей тактики лечения. Работа ведётся конфиденциально, с контролем показателей и учётом сопутствующих рисков.
Узнать больше – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Чехове предлагает не одну услугу, а целый спектр программ, которые можно сочетать и подстраивать под конкретную ситуацию. Это особенно важно, когда у одного человека на первый план выходят запои, у другого — наркотическая зависимость, у третьего — сочетание алкоголя с лекарственными препаратами.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены[/url]
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/ubod/]убод цена[/url]
ребята ровно работают! https://jeep-things.ru у разных селеров бывает разный джив имеется виду по качеству так , я как то брал джив к10 пер слабо очень , в другом к 15 убивал , вот и спрашивают всегда качество дживика у продавана если ты незнал!!!Получил. начал разводить на 7 мл ацетона. все выпало в осадок и почти ничего не растворилось. жидкость получилась мутная как молоко. добавил еще 5 мл. вроде более менее, но все равно большой очень осадок. ну и прям так туда 2 коробка основы высыпал и на плитку. все делал впервые, можно сказать наугад. пыхтел через водник. 1 водник и накрывает мама не горюй. час держит и еще полтора отпускает, и состояние потом ппц мутное какое, даже утром проснулся еще в коматозе. все отлично в принципе, только вот отходняк какой-то..
1win промокод на бонус [url=http://1win79230.help]1win промокод на бонус[/url]
Клиника «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь при зависимостях. Пациенты получают лечение алкоголизма и наркомании, проходят кодирование и реабилитацию, что способствует устойчивому возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/kak-snyat-abstinentnyy-sindrom/]как снять похмелье в домашних[/url]
1win элсом Киргизия [url=www.1win79230.help]www.1win79230.help[/url]
Hello to every one, the contents existing at this website are actually awesome for people knowledge, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
I blog quite often and I seriously thank you for your information. The article has truly peaked my interest.
I’m going to take a note of your site and keep checking for new information about once per week.
I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
whoah this weblog is great i really like reading your posts.
Stay up the good work! You understand, lots of persons are
looking round for this information, you could aid them greatly.
В данном обзоре представлены основные направления и тренды в области медицины. Мы обсудим актуальные проблемы здравоохранения, свежие открытия и новые подходы, которые меняют представление о лечении и профилактике заболеваний. Эта информация будет полезна как специалистам, так и широкой публике.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://google.co.jp/url?sa=t&url=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/vshivanie-ampuly
Московская клиника «Формула трезвости» сочетает медицину и психологию: лечение наркомании, терапия алкогольной зависимости, кодирование и длительная реабилитация проводятся по индивидуальным схемам. Подход помогает добиться устойчивого трезвого состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://formula-clinic.ru/lechenie-narkomanii/]реабилитация лечения наркомании[/url]
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-ryazan-na-domu/
Для достижения положительного результата применяются комплексные подходы, сочетающие медикаментозные и поддерживающие методы. Врачи оценивают общее состояние пациента, степень выраженности абстинентного синдрома и сопутствующие заболевания. На основе этих данных подбираются оптимальные методы коррекции.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/anonimnaya-narkologiya-vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd
Экстренная помощь требуется, когда запой начинает негативно сказываться на здоровье, и самостоятельное прекращение употребления алкоголя становится невозможным. Основные показания для круглосуточного вмешательства включают:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов город[/url]
Для самого пациента это шанс получить медицинское вмешательство без дополнительного стресс-фактора в виде транспорта, очередей и «больничной атмосферы». Он остаётся в привычной обстановке, в своей квартире, с теми же предметами, к которым привык, и это снижает сопротивление. Вместо жесткого сценария «либо немедленно в стационар, либо ничего» появляется промежуточный, более мягкий вариант: врачи приезжают домой, снимают остроту состояния, подбирают схему капельницы и медикаментов, объясняют, что делать дальше. Нередко именно после такого первого опыта человек впервые всерьёз задумывается о полноценном лечении, потому что ощущает реальную разницу в самочувствии до и после профессиональной помощи, а не просто очередной «опохмел».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-v-himkah[/url]
Запой – критическое состояние, при котором организм подвергается серьезной токсической нагрузке, что может привести к опасным для жизни осложнениям. В Волгоградской области помощь нарколога оказывается круглосуточно, что позволяет начать лечение немедленно в любой момент дня или ночи. Такой формат терапии обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство, индивидуальный подход и высокий уровень безопасности, позволяя стабилизировать состояние пациента в домашних условиях или в клинике.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]врач вывод из запоя в волгограде[/url]
Публикация посвящена жизненным историям людей, успешно справившихся с зависимостью. Мы покажем, что выход есть, и он начинается с первого шага — принятия проблемы и желания измениться.
Следуйте по ссылке – http://trud-ost.ru/?p=919004
К основным направлениям помощи, как правило, относятся:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-chekhove/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad
and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop,
just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is
now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is completely
off topic but I had to share it with someone!
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community.
Your web site provided us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done a formidable job and our entire
community will be grateful to you.
Если многое из этого знакомо, кодирование стоит рассматривать не как «наказание» или «приговор», а как инструмент, который помогает закрыть доступ к алкоголю на определённый срок и даёт шанс выстроить новую привычку — жить трезво.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/[/url]
Чем раньше нарколог окажет помощь, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и восстановиться без последствий для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-sochi/
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево краснодар[/url]
Наша выездная бригада оснащена как мобильный мини-кабинет: инфузомат для покапельной титрации, портативный кардиомонитор, пульсоксиметр, глюкометр, экспресс-кассеты Na?/K? и набор для регистрации ЭКГ по показаниям. Такой комплект позволяет принять решение на месте — безопасно ли начинать дома или целесообразнее перевести пациента в стационарное отделение «ЮгМедЦентра» без «перезапуска» обследований. Мы практикуем минимально достаточную фармакотерапию: в схеме нет «лишних» позиций и конфликтов с уже принимаемыми лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.).
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
https://archives.profsurv.com/forum/Professional-Surveyor-Magazine-Discussion/Education/-152006.aspx
Hello i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i read this post i thought i could also make comment due to this brilliant article.
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Подробнее тут – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/
Московская клиника «Формула трезвости» специализируется на лечении зависимостей. Пациентам доступны программы лечения наркомании и алкоголизма, услуги кодирования, а также продуманная реабилитация, включающая психологическую поддержку и восстановительные методики.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://formula-clinic.ru/stati/mify-bezopasnogo-alkogolya-pri-antibiotikah.html]антибиотики и алкоголь мифы[/url]
Just wish to say your article is as astounding. The clarity to your submit is
simply cool and that i can suppose you are an expert in this subject.
Fine along with your permission allow me to seize
your feed to stay updated with coming near near post.
Thank you a million and please continue the gratifying work.
Запой не всегда выглядит как откровенная катастрофа с первых дней. Иногда всё начинается с «отпуска», «праздника», пары вечеринок подряд. Родные надеются, что человек сам остановится, а он каждый день находит повод продолжить. В какой-то момент организм перестаёт справляться, и даже небольшие дозы алкоголя вызывают тяжёлые реакции.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
Частный реабилитационный центр «Еваклиник» в Саранске предлагает поэтапные программы лечения зависимости с медицинским сопровождением. Специалисты центра работают над устранением последствий употребления, нормализацией психоэмоционального состояния и адаптацией к жизни без зависимости. Такой подход снижает вероятность рецидивов и способствует долгосрочному восстановлению.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/sozavisimost-kogda-lyubov-stanovitsya-tyurmoj.html]как избавиться от созависимости[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске оказывает комплексную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. В центре проводится медицинская детоксикация, поддерживающая терапия и восстановительные программы с участием врачей и психологов. Индивидуальный подход, конфиденциальность и современные методы лечения помогают пациентам стабилизировать состояние и сделать первый шаг к устойчивой ремиссии.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/zavisimost-ot-kannabisa-mify-i-realnost.html]к чему приводит употребление каннабиса[/url]
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Вызов специалиста не всегда планируется заранее. Чаще всего помощь требуется в экстренной ситуации, когда близкие замечают серьёзное ухудшение состояния. Нарколог на дом в Рязани оказывает помощь в следующих случаях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Многие годами живут в логике: «главное — с утра выпить чуть-чуть, станет легче». На коротком промежутке времени это действительно частично снимает симптомы, но по сути лишь продлевает запой и усиливает интоксикацию. Организм не успевает переработать продукты распада алкоголя, кровь становится «тяжёлой», нарушается работа сосудов, возрастает нагрузка на сердце и мозг.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-otzyvy[/url]
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в краснодаре[/url]
Чем раньше нарколог окажет помощь, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и восстановиться без последствий для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]психиатр нарколог на дом[/url]
Теневая платформа Mega — представляет собой сайт, расположенный в теневом сегменте сети, где можно найти множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://mee-ga.cc]mega darknet ссылка[/url] прочно ассоциируется с подпольной стороной сети и строгой анонимностью пользователей.
В переносном смысле данный сайт воспринимается как вход в скрытую часть интернета, которое имеет свои тонкости.
Мега Даркнет является одной из заметных частей «глубокой сети», где основное внимание уделяется приватность посетителей и шифрование трафика.
Вход на эти сайты чаще всего производится через специализированные браузеры (например, Tor), в сочетании с VPN-соединениями для обеспечения доступа из любой точки.
С целью посещения ресурса, нужно найти рабочий адрес (ONION-ссылку) и обеспечить корректную конфигурацию.
Ключевое отличие площадки — это скрытность посетителей и децентрализованной структуре.
Посетители здесь находят разнообразные предложения: от приватных мессенджеров до площадок для торговли.
Ресурс предоставляет охрану от слежки благодаря современным технологиям шифрования.
Однако даже многоуровневая защита может обеспечить только относительную защиту, особенно при неосторожных действиях самих пользователей.
На сегодняшнем этапе развития сети подобный ресурс занимает нишевую роль, становясь местом для людей, кто охотится за непубличной данными и услугами.
Внутри площадки бывают представлены как разрешенный контент, так и запрещенные, что вынуждает участника быть внимательным и предусмотрительным.
Рассматривая Мега Даркнет как часть глобальной сети, можно выделить определенные нюансы, относящихся к особенностям применения и защиты.
Прежде всего, огромное значение имеет корректная организация рабочего пространства и применение многоступенчатых мер защиты для минимизации рисков.
Каждый посетитель должен понимать принципы скрытности и, по возможности, следовать правилам цифровой этики при работе внутри сети.
Во-вторых, не стоит забывать о юридических последствиях и наказании за противоправные поступки.
Законодательство разных стран неодинаково оценивают само присутствие на подобных сайтах и ответственность за их использование.
Ряд экспертов отмечают, что такие площадки могут служить местом для дискуссий и обмена опытом и защиты приватности при грамотном поведении.
Однако, риски обмана, финансовых потерь и криминальной активности здесь всегда присутствуют.
Балансируя между открытостью информации и нормативными запретами, теневая платформа остается одной из самых противоречивых частей глобальной сети.
Отсюда следует простой вывод: необходимо крайне аккуратно подходить к выбору контента и оценке надежности сайтов.
В конечном счете можно заключить, что данная площадка — это сложный цифровой феномен. Сайт обеспечивает высокий уровень анонимности и защиты личных данных, но требует от каждого участника бдительности, понимания технологий и осознанности действий.
Сайт иллюстрирует спектр человеческих поступков в среде с ослабленным регулированием и предоставляет платформу для коммуникации по закрытым вопросам.
Итак, этот сегмент сети является многогранным явлением глобальной сети, где равновесие между открытостью и защитой определяется индивидуально.
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• Точную оценку доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи
• Проверку возможности подключения по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж ТВ приставки
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибирские сети интернет цена и тарифы 2026[/url]
сибсети интернет цена и тарифы 2026 – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.com.bo/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://www.google.mk/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.rudik-diplom11.ru/lbs2best.at]Домашний интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] e2929b0
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» оказывает медицинскую помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости: детоксикация, снятие абстиненции, стабилизация состояния и подбор дальнейшей тактики лечения. Работа ведётся конфиденциально, с контролем показателей и учётом сопутствующих рисков.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/detoksikatsiya-alkogolikov/]детоксикация организма от алкоголя[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-irkutsk
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely believe this website needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the advice!
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a 40 foot
drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views.
I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
После завершения процедур врач дает пациенту и его родственникам подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Химках особенно востребован тогда, когда состояние человека уже нельзя назвать обычным похмельем, но он категорически отказывается ехать в клинику. Запой тянется несколько дней или дольше, нет полноценного сна, пульс постоянно учащённый, руки трясутся, давление скачет, а любое утро начинается не с облегчения, а с новой дозы алкоголя «чтобы не развалиться». В такой ситуации родственники оказываются между страхом и беспомощностью: понятно, что дальше ждать опасно, но уговорить собрать вещи и поехать в стационар не получается. Формат выезда нарколога на дом как раз и закрывает этот тупик — врач приезжает туда, где сейчас находится человек, оценивает риски и сразу начинает помощь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru
Sweet blog! I found it while browsing on Yahoo News.
Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo
News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to
get there! Appreciate it
It is not my first time to pay a visit this web page, i am visiting this site dailly and obtain fastidious information from here all the time.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается отдельными блоками для каждого этапа лечения и строгим пропускным режимом. Пациент получает круглосуточную поддержку по телефону даже после выписки для предотвращения рецидива.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-ekaterinburg0.ru/czentr-lecheniya-narkomanii-v-ekb/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]интернет магазин футбольной формы Атлетико[/url]
ретро формы футбольного клуба Атлетико купить – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://thegooglecafe.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://images.google.nl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport3.ru/k.krakenwork.cc/www.prognozy-na-khokkej5.ru/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry14.ru/www.1xbet-16.com/www.rudik-diplom8.ru/rudik-diplom3.ru,]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] e634f63
После завершения процедур врач дает пациенту и его родственникам подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]врач нарколог выезд на дом краснодар[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Детальнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/
Площадка Mega — представляет собой сайт, находящийся в закрытой части интернета, где посетители ищут множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://mee-ga.cc]сайт мега даркнет[/url] отождествляется с теневым характером и максимальным уровнем анонимности.
Метафорически эту площадку можно рассматривать как вход в скрытую часть интернета, которое таит в себе массу особенностей.
Данный теневой сайт является одной из заметных частей «даркнета», где главное значение имеют скрытность пользователей и защита каналов связи.
Вход на эти сайты требует использования особых браузеров (например, Тор), а также VPN для преодоления блокировок.
Для входа на платформу, пользователю необходимо знать точный адрес (ONION-ссылку) и настроить систему особым образом.
Ключевое отличие площадки заключается в полной непрозрачности пользователей и децентрализованной структуре.
Посетители здесь могут искать множество услуг: от конфиденциальных чатов до маркетплейсов.
Ресурс предоставляет охрану от наблюдения благодаря передовым методам кодирования.
Вместе с тем даже многоуровневая защита может быть эффективной лишь отчасти, особенно при неосторожных действиях участников системы.
На сегодняшнем этапе развития сети этот сайт занимает нишевую роль, становясь местом для людей, кто охотится за непубличной информации и специфические услуги.
На страницах ресурса бывают представлены как разрешенный контент, так и запрещенные, что обязывает пользователя проявлять бдительность и ответственность.
Рассматривая Мега Даркнет как часть глобальной сети, можно выделить несколько ключевых аспектов, касающихся культуры использования и безопасности.
Прежде всего, огромное значение имеет грамотная настройка пользовательского окружения и применение многоступенчатых мер защиты для минимизации рисков.
Любой участник обязан осознавать принципы скрытности и, желательно соблюдать этичным принципам при взаимодействии в этой среде.
Кроме того, нельзя игнорировать о юридических последствиях и наказании за противоправные поступки.
Юридические системы мира по-разному трактует факта посещения таких ресурсов и ответственность за их использование.
Отдельные специалисты отмечают, что подобные сайты могут выступать пространством для обмена знаниями и сохранения конфиденциальности при ответственном подходе.
Но при всем при этом, риски обмана, кражи денег и криминальной активности здесь остаются высокими.
Балансируя между свободой слова и суровыми законами, этот ресурс является самым спорным элементом интернета.
Отсюда следует простой вывод: требуется осмотрительно выбирать к тому, что смотреть и читать и верификации данных.
Обобщая вышесказанное можно сформулировать так: подобные ресурсы — это сложный цифровой феномен. Платформа дает максимальную приватность и защиты личных данных, но требует от каждого участника бдительности, понимания технологий и осознанности действий.
Сайт иллюстрирует различные модели поведения в среде с ослабленным регулированием и служит местом для обсуждения острых тем.
Итак, Мега Даркнет представляет собой неоднозначный феномен интернета, где баланс между свободой и безопасностью определяется индивидуально.
Команда клиники — это врачи-наркологи, психиатры-консультанты, специалисты интенсивной терапии, клинический психолог, психотерапевт и медсёстры с опытом круглосуточного поста. Мы разговариваем «языком фактов»: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов, дневники воды и сна, малые бытовые цели. Такой язык исключает стигму и «магическое мышление»; он понятен семье и помогает принимать решения без страхов и «подстраховочных» излишков.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в ростове-на-дону[/url]
Для жителей Чехова важно и то, что врач видит не абстрактный «случай зависимости», а живого человека со своей историей. У кого-то за плечами десятилетия злоупотребления, у кого-то — несколько лет с быстрым прогрессированием, у кого-то — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или наркотиками. Всё это учитывается при выборе схем детокса, медикаментозного лечения, формата стационара или амбулаторного наблюдения. Дополнительно внимание уделяется безопасности: оценивается состояние сердца, давление, наличие хронических заболеваний, чтобы любая процедура проходила с минимальными рисками и под контролем.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru
В данной публикации мы поговорим о процессе восстановления от зависимости, о том, как вернуть себе нормальную жизнь. Мы обсудим преодоление трудностей, значимость поддержки и наличие программ реабилитации. Читатели смогут узнать о ключевых шагах к успешному восстановлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://google.com.ag/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-liriki
Наркологическая клиника в Химках помогает не только тем, кто уже оказался в тяжёлом запое или прошёл через ломку. Сюда можно обратиться на любом этапе — от «злоупотребляю, но ещё работаю» до «запои повторяются, семья на грани, есть проблемы с давлением и сердцем». Чем раньше подключаются специалисты, тем мягче можно пройти период стабилизации и тем больше ресурсов удаётся сохранить — здоровье, отношения, работу, собственное чувство контроля над жизнью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]ставки на спорт[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Химках — это возможность получить помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости рядом с домом, а не ездить по всему региону в поисках специалистов. Для многих людей обращение к наркологу до последнего кажется чем-то «крайним»: кажется, что нужно терпеть, уговаривать себя «завязать самому», ждать подходящего момента, отпуска или «нового года с чистого листа». Но с каждым запоем или эпизодом употребления состояние становится тяжелее, восстановление — длиннее, а последствия — заметнее для работы, семьи, здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-himkah/
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Первый этап направлен на выведение токсинов и стабилизацию функций жизненно важных органов. Применяются инфузионные растворы, гепатопротекторы и препараты для нормализации электролитного баланса. Доза и состав подбираются индивидуально после оценки лабораторных показателей.
Выяснить больше – http://lechenie-narkomanii-ekaterinburg0.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-klinika-v-ekb/
Мы сознательно избегаем полипрагмазии. В назначениях только то, что несёт проверяемую пользу: гидратация с корректировкой электролитов, противорвотная и гастропротективная поддержка, мягкая анксиолитика по показаниям и пунктирный ритм-контроль. Состав капельниц не «универсальный» — он собирается под симптомы и соматический фон, с учётом совместимости с текущими лекарствами (антигипертензивные, антиаритмические, сахароснижающие и др.). Такой подход обеспечивает управляемую динамику без дневной «ватности» и рисков перегрузки объёмом.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно екатеринбург[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «ДонМед Резонанс» — это круглосуточный комплекс координированной помощи, где диагностика, инфузионная терапия, психообразование и поддержка семьи соединены в единую «дорожную карту». Мы работаем по принципу минимально достаточных вмешательств: каждый шаг имеет цель, измеримый маркер и заранее обозначенное «окно оценки». Такой подход убирает полипрагмазию, снижает риск нежелательных реакций и делает траекторию лечения предсказуемой — пациент не «получает процедуры», а видит, как цели достигаются и какие модули выключаются, когда они сделали своё дело. Круглосуточный режим позволяет внимательно сопровождать самые чувствительные интервалы — первую ночь, утренний период после детоксикации и момент возвращения к бытовой активности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Huge thanks for such valuable content. Will definitely recommend mostbet to friends.
https://mostbet-bd.store/black-friday
В Москве клиника «Формула трезвости» предлагает полный цикл помощи зависимым: лечение алкоголизма, терапию наркотической зависимости, современные способы кодирования и профессиональную реабилитацию. Центр работает анонимно и создаёт условия для безопасного восстановления.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://formula-clinic.ru/stati/rol-reabilitacionnyh-centrov-v-lechenii-narkozavisimosti.html]зачем нужны реабилитационные центры[/url]
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]частный нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Если к «окну оценки» динамика ниже ожидаемой, меняется один параметр: последовательность введения, плотность «тихих окон», режим воды или время вечернего «безэкранного коридора». Такой минимализм делает вклад каждого шага прозрачным и снижает риск перегрузки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-sankt-peterburg-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom
Опрятный внешний вид создает сильное впечатление о вас.
Ваш образ работает на восприятие вас окружающими сразу.
Хорошее самочувствие в подобранном луке повышает вашу самооценку.
Он демонстрирует высокий стандарт ответственности и внимание к мелочам.
https://www.indianhighcaste.com/read-blog/20949
Через одежду вы имеете шанс проявить свою личность и вкус.
Люди неосознанно воспринимают стильных индивидов как более успешных.
Поэтому, инвестиции в свой образ — это инвестиции в свое будущее.
Здравствуйте!
На Business-Mentor предприниматели получают доступ к фонду идей и решений, включающему тысячи проверенных бизнес-концепций для старта или масштабирования проекта. Платформа объединяет практические советы, кейсы и истории успеха, помогая превращать бизнес-идеи в устойчивый прибыльный проект. Выберите свою бизнес-идея для старта и переходите от теории к практике. Каждая идея адаптирована под реальные условия рынка и содержит пошаговые инструкции. Бизнес-идея для старта — это первый шаг к финансовой независимости и профессиональному росту.
Вся информация на сайте – https://business-mentor.ru/issledovanija/
как использовать данные для принятия решений, как создать бизнес, который работает без владельца, готовый бизнес-план бесплатно
B2B-маркетплейс идеи, бизнес на обмене, как запустить email-маркетинг
Всего наилучшего и развития!!
После завершения процедур врач дает пациенту и его родственникам подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar/
mostbet metode plată Moldova [url=https://mostbet42873.help/]https://mostbet42873.help/[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Байер Леверкузен;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bayer-leverkusen]магазин футбольной атрибутики Ѓайер ‹еверкузен в москве[/url]
купить футбольную атрибутику Ѓайер ‹еверкузен в москве – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bayer-leverkusen]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bayer-leverkusen[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.mu/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bayer-leverkusen]https://www.google.pl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bayer-leverkusen[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.butternut-yarrow-673.notion.site/2065ec070ffb80fc82b9cbf649b5f200/k.krakenwork.cc/1xbet-giris-3.com]Клубная атрибутика и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 29b00_7
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/klinika-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
When some one searches for his necessary thing, so he/she wants to be available that in detail, thus that thing is maintained over here.
mostbet cash out cum funcționează [url=http://mostbet42873.help]http://mostbet42873.help[/url]
https://gratogana22.com/
1win отменить вывод [url=http://1win79230.help]1win отменить вывод[/url]
Специалист уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер симптоматики и наличие хронических заболеваний, проводит измерения пульса, давления и температуры, что позволяет оперативно скорректировать терапию.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url]
Взаимосвязь медицинских и психологических компонентов терапии формирует основу устойчивой ремиссии, снижая вероятность повторных срывов и обеспечивая длительный восстановительный эффект.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru
mostbet live betting [url=https://www.mostbet42873.help]https://www.mostbet42873.help[/url]
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Подробнее – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
вечер хаус-музыки на теплоходе Акустический вечер на теплоходе: интимная атмосфера и душевные мелодии.
Состояния при зависимостях чувствительны к времени суток и среде. К ночи нарастает тревога, усиливается тремор, нестабильны показатели ЧСС/АД. Круглосуточный приём позволяет выстроить «мост» через самые сложные часы: собрать сон без избыточной фармаконагрузки, сделать короткие чек-ины, вовремя ретитровать один параметр (свет, дыхательные ритмы, интервалы питья), а утром оформить «малые победы» — гигиена и 10–15 минут тихой ходьбы. Эти простые маркеры часто надёжнее любых субъективных оценок «как себя чувствую».
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru
В сети регулярно появляются новые платформы и сервисы, предлагающие пользователям доступ к различным цифровым продуктам. Среди обсуждаемых запросов часто встречаются такие формулировки, как kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, kraken ссылка и kraken сайт. Обычно подобные ключевые слова используют для поиска альтернативных адресов ресурса в случае ограничений или технических работ. Пользователям рекомендуется внимательно проверять источники информации, оценивать безопасность соединения и соблюдать правила цифровой гигиены при переходе по любым ссылкам.[url=https://forum.povarenok.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=10230]kraken зеркало 1pw
[/url]
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске специализируется на лечении зависимостей с применением проверенных медицинских протоколов. Пациентам доступна круглосуточная наркологическая помощь, медикаментозная поддержка и сопровождение на этапе реабилитации. Специалисты центра работают не только с физическими проявлениями зависимости, но и с психологическими причинами, что повышает эффективность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/chto-delat-esli-rebenok-kurit-spajs-polnoe-rukovodstvo-dlya-roditelej.html]курящие спайс[/url]
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru
1win элсом депозит [url=https://1win79230.help/]https://1win79230.help/[/url]
В Воскресенске вывод из запоя может проводиться в разных форматах — с выездом на дом, в условиях стационара, в срочном режиме или с последующим амбулаторным наблюдением. Правильный выбор зависит от тяжести состояния, возраста пациента, наличия хронических заболеваний и того, насколько сильно запой нарушил привычную жизнь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]luchshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva[/url]
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это не «быстрая капельница и забыли», а последовательный и конфиденциальный процесс, в котором каждое вмешательство имеет цель, измеримый маркер и заранее оговорённое «окно проверки». В наркологической клинике «Южный Мед Центр Ренова» мы совмещаем непрерывный приём 24/7, выездные визиты без маркировки, точечную диагностику, инфузионную поддержку, психотерапевтические сессии и план посттерапевтического сопровождения. Приоритет — приватность и минимально достаточные решения: чем меньше случайных назначений, тем больше управляемости и предсказуемости. Мы говорим «языком фактов», а не оценок: витальные показатели, шкалы симптомов (0–10), структура сна, переносимость воды, простые бытовые задачи на утро. Это помогает семье и пациенту видеть, что именно работает, и выключать вмешательства, когда они сделали своё дело.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог ростов-на-дону[/url]
Когда выезд особенно удобен и оправдан, важно понимать не только эмоционально, но и по конкретным признакам. Есть ряд типичных ситуаций, в которых именно формат «на дому» становится наиболее реалистичным и безопасным вариантом, а стационар можно рассматривать как следующий шаг, когда острота будет снята и человек станет более сговорчивым.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
mostbet bonus pentru inregistrare [url=http://mostbet42873.help/]mostbet bonus pentru inregistrare[/url]
Часто первыми тревожные признаки замечают родные. Человек начинает пить чаще, чем раньше, меняется в поведении, становится раздражительным или замкнутым, теряет интерес к привычным занятиям. Появляются сложности с концентрацией, падает работоспособность, учащаются конфликты дома. Употребление наркотиков проявляется изменениями режима дня, странными компаниями, резкими перепадами настроения, финансовыми «дырами», попытками скрыть своё состояние.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]интернет магазин футбольной формы Атлетико[/url]
футбольная форма Атлетико Мадрид недорого москва – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://maps.google.nu/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://contacts.google.com/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.elektrokarnizy7.ru/www.kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru/www.pinup5008.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 03da2a6
Платная наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» предлагает лечение в комфортных условиях и с соблюдением медицинской этики. Специалисты помогают снять острые симптомы, снизить тягу и подготовить пациента к следующему этапу — реабилитации или амбулаторному сопровождению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-geroina/]лечение от героина[/url]
Для жителей Чехова важно и то, что врач видит не абстрактный «случай зависимости», а живого человека со своей историей. У кого-то за плечами десятилетия злоупотребления, у кого-то — несколько лет с быстрым прогрессированием, у кого-то — сочетание алкоголя с успокоительными или наркотиками. Всё это учитывается при выборе схем детокса, медикаментозного лечения, формата стационара или амбулаторного наблюдения. Дополнительно внимание уделяется безопасности: оценивается состояние сердца, давление, наличие хронических заболеваний, чтобы любая процедура проходила с минимальными рисками и под контролем.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru
В клинике используются запатентованные наборы для капельниц, включающие витамины группы B, мембранопротекторы и низкомолекулярные антиоксиданты. Автоматизированные насосы обеспечивают равномерный ввод растворов, минимизируя риск осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-narkomanii-ekaterinburg0.ru/czentr-lecheniya-narkomanii-v-ekb
Брал у другого магазина – полная Чляпа оказалась… вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Ответь в аське!Люди 22куска зарядили ,перед оплатой добро дал ,а потом тишина… Люди переживают,очень!Ответь пожалуйсто!!!надо испробывать…много хороших отзывов
Если в процессе выявляются нестабильные витальные показатели, нарастающая дезориентация или признаки дыхательной недостаточности, маршрут немедленно переводится в стационар «УралМедЦентра» с сохранением уже собранной информации — без повторных очередей и «история заново».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Процедура лечения начинается с установки внутривенной капельницы, через которую вводятся детоксикационные растворы, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов и восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. При необходимости врач назначает дополнительные препараты, такие как седативные средства для купирования симптомов абстинентного синдрома, гепатопротекторы для поддержки печени и кардиопротекторы для нормализации работы сердца.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница в краснодаре[/url]
Hello there! This post could not be written any better! Looking at this post
reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept preaching about this.
I’ll send this information to him. Fairly certain he’s going to have
a very good read. Thanks for sharing!
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Бавария;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]футбольная форма ЃавариЯ[/url]
магазин футбольной атрибутики ЃавариЯ – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.ly/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]http://clients1.google.com.mx/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=98944]Официальная футболь[/url] ae634f6
New online casino Australia 2025 – fresh sites with huge welcome bonuses
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Бавария;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]магазин футбольной формы ЃавариЯ[/url]
футбольная атрибутика ЃавариЯ – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.co.ke/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]https://toolbarqueries.google.com.pr/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=96860]Клубная атрибутика[/url] a67f9e2
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в сочи[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]кето диета за неделю минус 10 кг[/url]
If you desire to increase your knowledge simply keep visiting this web page and be updated with the most up-to-date information posted here.
I think that is one of the most important information for me.
And i’m satisfied studying your article. However wanna statement on some normal issues,
The website taste is ideal, the articles is really great : D.
Just right task, cheers
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Московская клиника «Формула трезвости» специализируется на лечении зависимостей. Пациентам доступны программы лечения наркомании и алкоголизма, услуги кодирования, а также продуманная реабилитация, включающая психологическую поддержку и восстановительные методики.
Разобраться лучше – https://formula-clinic.ru/stati/rol-reabilitacionnyh-centrov-v-lechenii-narkozavisimosti.html
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kapelnica-ot-narkotikov/]капельница от алкоголя и наркотиков[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]джекпот[/url]
В этой статье мы обсудим процесс восстановления после зависимостей, акцентируя внимание на различных методах и подходах к реабилитации. Читатели узнают, как создать план выздоровления и использовать полезные ресурсы для достижения устойчивых изменений.
Узнать больше – https://www.google.lt/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/vshivanie-ampuly
[url=https://github.com/winsane-casino]winsane login[/url]
Самостоятельные попытки «подлечиться» обычно сводятся к случайным комбинациям препаратов: кто-то пьёт горсть таблеток от давления и сердца, кто-то принимает успокоительные поверх алкоголя, кто-то заказывает непонятные средства «от тяги» в интернете. Такие эксперименты могут дать краткий эффект, но часто только маскируют симптомы и перегружают организм. В клинике лечение строится иначе: сначала оценивают состояние — физическое и психическое, затем подбирают безопасные схемы детоксикации и медикаментов, учитывая возраст, сопутствующие заболевания, длительность запоев и употребления. Это снижает риски осложнений и делает восстановление более управляемым: пациент и его семья видят прогресс и понимают, за счёт чего он происходит, а не живут в ожидании очередного непредсказуемого «отката».
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-korolyove/
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается процессом: нейтральные формулировки в документах, минимум персональных данных, немаркированные формы и транспорт, отдельный вход, «короткие» переговоры у двери, единый контакт по медицинским вопросам. Внутри команды действует «язык цифр» — витальные показатели, шкалы, интервалы питья и сна, окна проверки. Это исключает лишние обсуждения и защищает от распространения деликатной информации за пределы клинического круга.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-clinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologiya-rostov-zapadnyj-rajon/
Когда родственники видят, что в их случае совпадает сразу несколько этих пунктов, выезд нарколога на дом часто становится тем самым реалистичным и своевременным решением, которое позволяет не довести дело до экстренной госпитализации уже в критическом состоянии. После такого вмешательства появляются часы и дни, когда можно спокойно обсудить дальнейшие шаги, а не действовать на фоне паники и полного истощения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Важно понять: запой — это не просто серия праздников или «отпуск с алкоголем». Это состояние, при котором организм перестаёт выходить в трезвость, а любая попытка остановиться сопровождается настолько тяжёлыми симптомами, что человек снова тянется к бутылке. С каждым днём запоя возрастает нагрузка на сердце, печень, поджелудочную железу, мозг.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в Воскресенске[/url]
Лечение в наркологической клинике в Чехове удобно не только близостью к дому. Главный плюс — комплексный подход. Зависимость практически никогда не ограничивается только алкоголем или наркотиком: страдают сердце и сосуды, печень, нервная система, психика, отношения в семье и на работе. Если пытаться лечить только одно звено, например, периодически «чистить кровь» капельницами, без проработки причин и последствий, ситуация быстро возвращается к исходной точке. В клинике выстраивается последовательная работа: сначала стабилизируют организм, затем укрепляют психику, а дальше помогают менять привычный образ жизни, чтобы трезвость стала не кратким эпизодом, а новой нормой.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/
Зависимость редко начинается резко. Сначала это «разовые» посиделки, алкоголь «для снятия стресса», эпизодическое употребление психоактивных веществ «из любопытства» или «для компании». На этом этапе человеку кажется, что он полностью контролирует ситуацию. Со временем эпизоды употребления становятся чаще, дозы растут, появляются провалы в памяти, срывы, невозможность остановиться вовремя. В этот момент уже страдают здоровье, работа, отношения с близкими. Обращение в наркологическую клинику позволяет не доводить ситуацию до критической точки и остановить разрушение жизни на любом этапе заболевания.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-ryadom-v-dolgoprudnom/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru
да магаз отличный.оперативно работают.и качество товара отличное.вобщем всё хорошо. https://computer-mouse.ru он мне успел ответить – поверь, ничего такого о чём тебе стоило бы беспокоиться – не случилосьспасибо и ВАМ !!
Наш диагностический контур — это последовательная проверка гипотез. Мы идём от наибольшего риска к минимально достаточным вмешательствам, фиксируя маркеры и точки пересмотра. Матрица ниже иллюстрирует, как стартовые наблюдения превращаются в проверяемые шаги. Она не заменяет очную оценку, но помогает пациенту и семье понимать логику решений и ожидаемую динамику.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-rostove-na-donu16.ru/narkologi-rostov-na-donu/
Есть ситуации, когда визит к наркологу в Химках лучше воспринимать не как «стыдный шаг», а как обычное ответственное решение о своём здоровье. Это особенно актуально, если: употребление алкоголя или наркотиков стало регулярным, а попытки сократить дозы заканчиваются срывами; появились запои с несколькими днями непрерывного употребления; возникают проблемы с сердцем, давлением, сном; близкие всё чаще говорят, что «ситуация выходит из-под контроля».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-himki11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-himkah/
Fantastic post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this
topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further.
Cheers!
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» оказывает медицинскую помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости: детоксикация, снятие абстиненции, стабилизация состояния и подбор дальнейшей тактики лечения. Работа ведётся конфиденциально, с контролем показателей и учётом сопутствующих рисков.
Узнать больше – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-akvilong/]аквилонг препарат кодирование[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Бавария;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]футбольная атрибутика ЃавариЯ в москве[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной формы ЃавариЯ – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=http://images.google.td/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]https://images.google.com.qa/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=http://cgi.www5b.biglobe.ne.jp/%7Etcmsyt/WebFrogBlog/blog.cgi?category&category_all&id=kotarou10&mode=disp&time=1153804231&writer_all]Официальная футбольная форма и подарки для фанатов от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 634f630
Как отмечает нарколог Олег Васильев, «чем раньше пациент получает квалифицированную медицинскую помощь, тем меньше риск серьезных осложнений».
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
В сети регулярно появляются новые платформы и сервисы, предлагающие пользователям доступ к различным цифровым продуктам. Среди обсуждаемых запросов часто встречаются такие формулировки, как kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, kraken ссылка и kraken сайт. Обычно подобные ключевые слова используют для поиска альтернативных адресов ресурса в случае ограничений или технических работ. Пользователям рекомендуется внимательно проверять источники информации, оценивать безопасность соединения и соблюдать правила цифровой гигиены при переходе по любым ссылкам.[url=https://forum.povarenok.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=10242]кракен доставка
[/url]
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-voskresenske/
Московская клиника «Формула трезвости» специализируется на лечении зависимостей. Пациентам доступны программы лечения наркомании и алкоголизма, услуги кодирования, а также продуманная реабилитация, включающая психологическую поддержку и восстановительные методики.
Подробнее – [url=https://formula-clinic.ru/vshivanie-ampuly/]кодировка от алкоголя ампула вшивание[/url]
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
I’m really inspired with your writing skills as neatly as with the layout in your blog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify it your self? Either way stay up the excellent high quality writing, it is uncommon to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
Если в ситуации с алкоголем присутствуют несколько из перечисленных ниже пунктов, это повод не откладывать консультацию с наркологом в Королёве:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/klinika-kodirovaniya-ot-alkogolizma-v-korolyove/
1win возврат ставки [url=www.1win04381.help]www.1win04381.help[/url]
Не стоит забывать и про объективные факторы. Бывает, что физически опасно или трудно везти человека в клинику: он с трудом ходит, не спит уже несколько ночей, постоянно потеет, жалуется на сильную слабость и сердцебиение. Любая поездка в таком состоянии — дополнительная нагрузка на сердце и нервную систему. Выезд нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение без этого лишнего риска: врач приезжает со всем необходимым для капельницы и наблюдения, а если по итогам осмотра становится понятно, что без стационара не обойтись, он помогает организовать перевод уже на фоне частично стабилизированного состояния, а не в момент максимального кризиса.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkolog-na-dom-himki11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-cena-v-himkah/
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Подробнее – http://google.ba/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/vrachi
братух а как так получилось, получил 1го , а отписываешь за качество 7го? ты хочешь сказать, что почти неделю у тебя был груз , а ты его не пробывал? если у меня возникали проблемы , а они поверь мне возникали то я кипишую в тот же день ну максимум на следующий, а ты решил кипишнуть через неделю непонятно… https://topfusionin.top Вердикт:А так ТС работают отлично не было не одного проёба за пол года сотрудничество ни считая выше сказанного
В реабилитационном центре «Еваклиник» в Саранске созданы условия для безопасного и анонимного восстановления после зависимости. Программы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния и поэтапную реабилитацию под контролем медицинского персонала. Такой формат помощи позволяет снизить риски срывов и постепенно вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya-na-domu/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]секс шоп[/url]
Лечение в наркологической клинике в Чехове удобно не только близостью к дому. Главный плюс — комплексный подход. Зависимость практически никогда не ограничивается только алкоголем или наркотиком: страдают сердце и сосуды, печень, нервная система, психика, отношения в семье и на работе. Если пытаться лечить только одно звено, например, периодически «чистить кровь» капельницами, без проработки причин и последствий, ситуация быстро возвращается к исходной точке. В клинике выстраивается последовательная работа: сначала стабилизируют организм, затем укрепляют психику, а дальше помогают менять привычный образ жизни, чтобы трезвость стала не кратким эпизодом, а новой нормой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-chekhov11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-chekhove[/url]
Признаки, что пора задуматься о кодировании
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-korolyov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма с выездом на дом[/url]
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]магазин футбольной формы в москве[/url]
ретро формы футбольных клубов – [url=http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=http://cse.google.com.ag/url?sa=i&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://maps.google.com.sa/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/k.krakenwork.cc/www.frei-diplom6.ru/www.1xbet-15.com/www.1xbet-14.com/www.rudik-diplom8.ru/www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru/www.elektrokarniz-kupit.ru/maps.google.se/url?q=https://healthyturkiye.com/tandvard-turkiet,[],[],200,65,0,1126,0,13,16,0,0,http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/,%D0%A1%D0%83%D0%A0%D1%91%D0%A0%C2%B1%D0%A0%D1%91%D0%A1%D0%82%D0%A1%D0%83%D0%A0%D1%94%D0%A0%D1%91%D0%A0%C2%B5%5DСпортивная экипировка и подарки для фанатов от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 27e0ae6
Эта публикация исследует взаимосвязь зависимости и психологии. Мы обсудим, как психологические аспекты влияют на появление зависимостей и процесс выздоровления. Читатели смогут понять важность профессиональной поддержки и применения научных подходов в терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://google.ba/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/kodirovanie-s-provokatsiey
Преимущество такого подхода в том, что из этих «кирпичиков» можно собрать именно тот маршрут, который подходит конкретному человеку. Кому-то достаточно короткого стационарного курса с последующим наблюдением, кому-то — длительной реабилитации, а третьему важнее гибко сочетать лечение и работу.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-korolyov11.ru/]наркологическая клиника в королеве[/url]
Теневая платформа Mega — представляет собой сайт, функционирующий в даркнете, где посетители ищут различные непубличные сервисы.
[url=https://mee-ga.cc]площадка мега даркнет[/url] прочно ассоциируется с подпольной стороной сети и строгой анонимностью пользователей.
Образно говоря, этот ресурс воспринимается как портал в закрытое цифровое пространство, которое имеет свои тонкости.
Данный теневой сайт занимает важное место в структуре «глубокой сети», где основное внимание уделяется скрытность пользователей и защита каналов связи.
Чтобы попасть на подобные площадки обычно осуществляется использования особых браузеров (например, Тор), в сочетании с VPN-соединениями для преодоления блокировок.
Чтобы попасть на этот сайт, требуется иметь актуальную ссылку (ONION-ссылку) и обеспечить корректную конфигурацию.
Основная характеристика ресурса заключается в полной непрозрачности посетителей и децентрализованной структуре.
Пользователи на этом сайте находят самые разные сервисы: от закрытых каналов связи до торговых платформ.
Платформа обеспечивает защиту от мониторинга благодаря современным технологиям шифрования.
Вместе с тем даже комплексные меры безопасности может обеспечить только относительную защиту, особенно при неосмотрительном поведении участников системы.
На сегодняшнем этапе развития сети этот сайт занимает нишевую роль, интересуя тех пользователей, кто охотится за непубличной информацией и особыми сервисами.
На страницах ресурса попадаются как разрешенный контент, так и запрещенные, что вынуждает участника высокой осторожности и осознанности.
Изучая феномен теневых платформ, стоит обратить внимание на определенные нюансы, относящихся к особенностям применения и защиты.
Во-первых, огромное значение имеет грамотная настройка пользовательского окружения и применение многоступенчатых мер защиты для уменьшения опасностей.
Каждый посетитель должен понимать степени конфиденциальности и, по возможности, следовать моральным нормам при работе внутри сети.
Также важно помнить, что не стоит забывать о проблемах с законом и возможных последствиях за противоправные поступки.
Законодательство разных стран неодинаково оценивают факта посещения таких ресурсов и меры наказания за активность там.
Некоторые исследователи отмечают, что эти ресурсы могут становиться платформой для дискуссий и обмена опытом и сохранения конфиденциальности при грамотном поведении.
Однако, опасность мошенничества, кражи денег и мошеннических действий здесь никогда не исчезают.
Находясь на грани свободой слова и суровыми законами, теневая платформа является самым спорным элементом всемирной паутины.
Отсюда следует простой вывод: требуется осмотрительно выбирать к выбору контента и верификации данных.
В конечном счете можно заключить, что данная площадка — это неоднозначное и опасное пространство. Сайт обеспечивает максимальную приватность и конфиденциальности, но обязывает любого пользователя внимательности, определенных знаний и соблюдения этических норм.
Площадка показывает спектр человеческих поступков в обстановке минимального надзора и служит местом для обсуждения острых тем.
Таким образом, этот сегмент сети остается сложным феноменом цифрового мира, где баланс между свободой и безопасностью каждый пользователь находит для себя сам.
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Узнать больше – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/lechenie-ot-soli/]солевые наркоманы зависимость[/url]
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice whilst you amend your web site, how can i subscribe for a blog website?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had
been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright
clear idea
https://stopnasili.cz/wp-content/pgs/melbet_promo_code_and_bonus_codes.html
1win ставки на спорт [url=https://1win79230.help]1win ставки на спорт[/url]
В клинике «Еваклиник» в Саранске пациенты получают квалифицированную наркологическую помощь в комфортных и конфиденциальных условиях. Центр применяет современные методы терапии, направленные на снижение тяги и восстановление общего состояния организма. Поддержка врачей и психологов помогает закрепить результат и сформировать устойчивую мотивацию к трезвой жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/razrushenie-psihiki-vo-vremya-zapoya.html]влияние алкоголя на мозг и нервную[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге оказывает комплексную помощь людям с зависимостью. Здесь проводят лечение алкоголизма и наркомании, применяют современные методы кодирования и обеспечивают сопровождение пациента до полного восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/vred-tabaka-kak-kurenie-vliyaet-na-zdorove-legkih-i-serdtsa/]как курение влияет на организм[/url]
This is nicely expressed! !
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost
Nice weblog right here! Also your site loads up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I am getting your associate hyperlink to your host? I desire my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Грустно будет если до нового года не придёт 🙁 :drug:но надежда умирает последней,магазин хороший https://amfiktops.life Видать все ништяк, вот и не отписывается))))можно записаться на пробник ам как он придет…а то ниче про него непонятно
Наркологический центр «Трезвый город» специализируется на лечении алкоголизма и наркомании с акцентом на безопасность пациента. Подбираются индивидуальные протоколы, учитывается анамнез, переносимость препаратов и возможные осложнения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ukolom/]кодирование от алкоголизма уколом[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Дюралевый швеллер 440248 30х50х3х3х3 мм Д16ч ГОСТ 13623-90 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
написание курсовых на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-65.ru/]написание курсовых на заказ[/url] .
Вскрытие замков дверей Однако, помимо экстренных ситуаций, существует и плановая забота о безопасности. “Замена замков” в квартире или доме — это инвестиция в спокойствие. “Замена входного замка”, “замена замка в двери”, “замена замка входной двери” — эти действия укрепляют периметр вашего жилища. Не менее важна “замена личинки”, “замена личинки двери” или “замена личинки замка двери”, что позволяет обновить механизм без полной переустановки. В Ставрополе, как и в любом другом крупном городе, услуги “замена замков ставрополь” пользуются стабильным спросом, отражая стремление жителей к безопасности.
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg/
捕风追影下载平台,專為海外華人設計,提供高清視頻和直播服務。
Наркологическая клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске оказывает комплексную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. В центре проводится медицинская детоксикация, поддерживающая терапия и восстановительные программы с участием врачей и психологов. Индивидуальный подход, конфиденциальность и современные методы лечения помогают пациентам стабилизировать состояние и сделать первый шаг к устойчивой ремиссии.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/]Наркологический центр «Еваклиник» в Саранске[/url]
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в постоянном медицинском наблюдении, размещаются в стационарном отделении. Здесь организовано непрерывное дежурство медсестры и врача-нарколога, что обеспечивает безопасность при риске осложнений.
Детальнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-v-ekb
I think that is among the most significant information for
me. And i am happy reading your article. However should remark on few normal things, The
web site taste is great, the articles is actually nice : D.
Just right process, cheers
РедМетСплав предлагает внушительный каталог отборных изделий из ценных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до крупных поставок, мы обеспечиваем своевременную реализацию вашего заказа.
Каждая единица изделия подтверждена соответствующими документами, подтверждающими их качество. Превосходное обслуживание – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы разрешать ваши вопросы по мере того как находить ответы под особенности вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте потребности вашего бизнеса профессионалам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в гибкости нашего предложения
поставляемая продукция:
Изделия из висмута Sn89Zn8Bi3 – EN 61190-1-3 Изделия из висмута Sn89Zn8Bi3 – EN 61190-1-3 предназначены для высококачественной пайки и востребованы в электронной промышленности. Они обеспечивают отличную проводимость и надежное соединение, что делает их идеальными для сложных схем. Качество изготавливаемых изделий отвечает международным стандартам, что гарантирует долговечность и эффективность.Если вы ищете надежный материал для своих проектов, купить Изделия из висмута Sn89Zn8Bi3 – EN 61190-1-3 – ваш верный выбор. Эти изделия являются оптимальным решением для профессионалов, стремящихся к совершенству в работе.
Под., зачет с натяжкой. Мята незачет, сильно уж она ваняет. Растворитель пришлось нагревать и домалывать кр.. https://boshkikypit.life магазин достойный,всё ровно и в срок,спасибо большое за ваш труд,будем продолжать сотрудничество!Всем доброго дня!! Хочу рассказать свой отзыв , о данном чудо магазине!! Заказывал совместку на 50г, оплатил днём, к вечеру все было готово, жаль только я с джабером что то не подружился, он меня выкинул, прям перед получением адреса, НО КЛАДЧИК ТАКОЙ красавчик!!! В итоге я поехал с утра, только приехал, все было на своих местах!!! Спрятано на совесть!!! Думаю ещё пролежало бы дня 3))) ИТОГО: ОПЕРАТОР В ДЖАБЕРЕ САМЫЙ КУЛЬТКРНЫЙ ЧЕЛОВЕК НА СВЕТЕ! 5+ КЛАДЧИК , умница! 5+, близко ко мне , и спрятано как надо!!! P.S. Смело заказываем!! И радуемся как дети!!)
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в постоянном медицинском наблюдении, размещаются в стационарном отделении. Здесь организовано непрерывное дежурство медсестры и врача-нарколога, что обеспечивает безопасность при риске осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]наркологическое лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url]
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]блекджек[/url]
Частный реабилитационный центр «Еваклиник» в Саранске предлагает поэтапные программы лечения зависимости с медицинским сопровождением. Специалисты центра работают над устранением последствий употребления, нормализацией психоэмоционального состояния и адаптацией к жизни без зависимости. Такой подход снижает вероятность рецидивов и способствует долгосрочному восстановлению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/blog/kross-zavisimost.html]чем заменить алкоголь[/url]
Основная цель процедуры заключается в устранении токсинов и восстановлении жизненно важных функций. При этом используются индивидуально подобранные лекарственные препараты, корректирующие водно-электролитный баланс и работу сердечно-сосудистой системы. Вывод из запоя в клинике позволяет снизить риск осложнений и ускорить процесс нормализации состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Клиника «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь при зависимостях. Пациенты получают лечение алкоголизма и наркомании, проходят кодирование и реабилитацию, что способствует устойчивому возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Подробнее – https://peredozirovka.info/articles/reabilitatsionnye-tsentry-kak-vybrat-podhodyaschiy
Been diving into luk888 it delivers on cool features with an intuitive interface. Take a peak here, luk888.
Hey! I was looking for a reliable place to get Playtime PH. This seems like it could be what I need! I hope the download is smooth and virus-free. Thanks for the info! Check it out here: playtime ph download
luk52… hmmm, not sure about that exact name but if you’re looking for some awesome online gaming fun, definitely give luk88club.com a look! They always have something going on. Check em out by clicking luk52
Отсутствие визитов в клинику гарантирует полную конфиденциальность. Это особенно важно для пациентов, беспокоящихся о своей репутации или возможном влиянии на профессиональную деятельность. Вызов врача на дом полностью исключает нежелательные встречи в медицинском центре.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]vrach narkolog na dom moskva[/url]
Во многих семьях путь к лечению начинается одинаково: сначала запои или эпизоды употребления воспринимаются как временные «проблемы по жизни», которых стыдно, но которые вроде бы можно переждать. Человек клянётся «завязать после праздников», родственники верят, потом терпят, потом скандалят, затем снова наступают на те же грабли. В какой-то момент становится очевидно, что сила воли больше не работает: попытки прекратить запой заканчиваются тряской, паникой, скачками давления, отсутствием сна, а через несколько дней всё повторяется. Именно тогда наркологическая клиника в Лобне перестаёт быть чем-то абстрактным и превращается в реальную возможность остановить этот круг.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/[/url]
Путь в наркологическую клинику в Ивантеевке почти всегда начинается с консультации — очной или по телефону. На этом этапе задача врача не осудить и не прочитать нотацию, а максимально точно понять, что происходит: сколько лет длится злоупотребление, как часто бывают запои, были ли попытки лечиться раньше, какие есть хронические болезни, каково текущее физическое и психическое состояние. Собирается анамнез, измеряется давление, оценивается пульс, при необходимости направляют на анализы и дополнительные исследования. Чем честнее и конкретнее человек (или его родственники) описывают ситуацию, тем точнее можно подобрать безопасный план помощи.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]luchshaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Если вам необходима [url=https://arenda-avtomobilya-s-voditelem2.ru/]заказать машину с водителем[/url], то наши предложения по аренде авто с водителем в Новосибирске идеально подойдут для комфортных поездок.
Аренда авто с водителем в Новосибирске — это удобное решение для тех, кто ценит комфорт и безопасность.
Аренда машины с водителем в Новосибирске идеально подходит для проведения деловых встреч и мероприятий.
Перед бронированием стоит уточнить наличие дипломов и лицензий у водителя, а также условия страхования.
Выбор компании для аренды авто с водителем в Новосибирске зависит от бюджета и личных предпочтений клиента.
Заказать авто с водителем можно как на несколько часов, так и на целый день, в зависимости от потребностей клиента.
Через специализированные приложения или сайты можно уточнить наличие свободных авто и оформить заявку в любой удобной форме.
В заключение, аренда авто с водителем в Новосибирске — это надежное решение для деловых поездок и отдыха.
Wonderful work! That is the type of information that should be shared across the web. Disgrace on Google for no longer positioning this post higher! Come on over and seek advice from my site . Thank you =)
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]покер онлайн[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом становится необходимым при любых состояниях, когда отказ от алкоголя сопровождается выраженными симптомами интоксикации и абстиненции. Основные ситуации, в которых срочно требуется профессиональная помощь врача:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в краснодаре[/url]
«ЮгМедЦентр» поддерживает строгую конфиденциальность: выездные специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, в гражданской одежде; документы формулируются нейтрально; уведомления не содержат триггерных слов; профиль можно оформить под кодом. Все записи ведутся в шифрованном контуре с разграничением доступа по ролям, а видеосессии с врачом/психологом не записываются. Мы предупреждаем о цифровой гигиене: включите «тихий режим» уведомлений, избегайте пересылки документов в открытых чатах, используйте резервный канал связи для экстренных вопросов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Обращение к наркологу — это не признание «окончательного проигрыша», а трезвое решение, что здоровье и жизнь важнее иллюзии контроля. В клинике можно безопасно вывести человека из запоя, стабилизировать состояние, обследовать сердце, печень, нервную систему, понять, насколько далеко зашло заболевание. Важно, что помощь получают не только тяжёлые пациенты «на грани», но и те, у кого ещё есть работа, семья, привычный образ жизни, но запои уже стали регулярными. Чем раньше удаётся подключить специалистов в Лобне, тем мягче можно пройти лечение и тем больше шансов сохранить и здоровье, и отношения, и социальный статус.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]нарколог и психиатр в Лобне[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
магазу процветания желаю и клиентов хороших https://obrydlo.ru \занимаюсь тестированием вместе с кролями в течении нескольких дней. Все никак не мог понять.народ скажите концетрацию 250 го в этом магазе
Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» оказывает медицинскую помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости: детоксикация, снятие абстиненции, стабилизация состояния и подбор дальнейшей тактики лечения. Работа ведётся конфиденциально, с контролем показателей и учётом сопутствующих рисков.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом иркутск[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Ивантеевке — это возможность получить грамотную, поэтапную помощь рядом с домом, не дожидаясь момента, когда организм и психика окажутся на грани. Большинство пациентов и их родственников приходят к идее лечения не сразу: сначала идут попытки «контролировать» употребление, меняться местами работы и отдыха, просьбы семьи «держать себя в руках», временные успехи и повторяющиеся срывы. На фоне этого накапливаются конфликты, ухудшается здоровье, появляются проблемы с работой и финансами, а жизнь всё больше вращается вокруг алкоголя или наркотиков. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной помощи зависимость не отпускает, а только меняет форму.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена санкт-петербург[/url]
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя вызов на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Во время процедуры врач контролирует состояние больного, по необходимости корректирует лечение, чтобы добиться максимального терапевтического эффекта. После проведения детоксикации пациенту назначается курс поддерживающей терапии, а также даются рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-sochi
купить задание для студентов [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-65.ru/]купить задание для студентов[/url] .
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-irkutsk/
Sweet blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News.
Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News?
I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Cheers
Thank you for another excellent article. Where
else could anyone get that type of info in such an ideal
means of writing? I have a presentation next week,
and I’m at the search for such info.
После купирования острой фазы мы предлагаем полное сопровождение на этапе восстановления, чтобы закрепить результаты и снизить риск повторных срывов. В первые дни показаны сеансы кислородной терапии, которые активизируют клеточный обмен и способствуют быстрейшему выведению остатков токсинов. Параллельно проводятся физиотерапевтические процедуры — магнитотерапия и лазерная стимуляция, укрепляющие сосудистую стенку и ускоряющие заживление микроциркуляторных нарушений.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Лечение в домашних условиях позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с поездками в медицинские учреждения. Вы не тратите время на дорогу и ожидание приема, что особенно важно, если ваше состояние ухудшилось или вам нужно срочное вмешательство. Врач на дому предоставляет все необходимые процедуры без лишних усилий с вашей стороны.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Добрый день!
Погружение в историю и культуру разных стран дарят экскурсии, которые превращают обычный отпуск в увлекательное путешествие во времени. Профессиональные гиды раскроют тайны древних цивилизаций, покажут скрытые улочки и расскажут легенды, оживляющие каменные стены. Вы сможете выбрать тематические туры: от гастрономических и винных до экстремальных и мистических ночных прогулок. Групповые и индивидуальные форматы позволяют адаптировать программу под ваш темп, интересы и состав компании. Доверьте организацию досуга экспертам и получите максимум знаний и эмоций от каждого visited места.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://aldita.ru/vid-niedvizhimosti/dom/
Пешие экскурсии, Аренда гидроцикла Владивосток, Аренда байка Пхукет
Аренда катера Владивосток, [url=https://aldita.ru/vladivostok/vodnaya-tekhnika/gidrotsikl/]Аренда гидроцикла Владивосток[/url], Аренда Автобус Владивосток
Всего наилучшего и хорошей информации!
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Инфузионная терапия проходит под непрерывным контролем врача и медсестры: каждые 15–20 минут измеряются АД, пульс и сатурация, при возникновении любых нежелательных реакций раствор корректируется. Стандартная продолжительность курса — от одного до трёх часов, но может быть продлена в зависимости от индивидуальных показателей. Уже после первого часа инфузии пациенты отмечают исчезновение головной боли, нормализацию сна, улучшение аппетита и выраженное эмоциональное облегчение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Этот подход имеет несколько ключевых преимуществ, которые обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
https://smokace99.com/
Наркологическая клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске оказывает комплексную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. В центре проводится медицинская детоксикация, поддерживающая терапия и восстановительные программы с участием врачей и психологов. Индивидуальный подход, конфиденциальность и современные методы лечения помогают пациентам стабилизировать состояние и сделать первый шаг к устойчивой ремиссии.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosch/]наркологическая помощь отзывы[/url]
Данный порядок действий позволяет снизить риски для здоровья и обеспечить контроль за эффективностью процедур.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://
Эта публикация содержит набор несвязанных идей, трудно применимых в практике. Мы лишь поверхностно затрагиваем различные точки зрения, не проводя глубокий анализ и не предлагая выводов.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]сиалис онлайн[/url]
После завершения процедур врач дает пациенту и его родственникам подробные рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]частный нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]narkolog na dom moskva tseny[/url]
Психотерапевтическое кодирование делает акцент на внутренней мотивации. Специалист помогает человеку увидеть реальную цену алкоголя в его жизни, понять, как именно употребление разрушает здоровье, семью, карьеру, и сформировать установку на трезвость на определённый срок. Используются техники внушения в состоянии расслабления и структурированная работа с убеждениями и привычками. Такой подход особенно полезен тем, кто боится «лекарственного вмешательства» или уже имеет негативный опыт неудачных медикаментозных попыток. В практике лечения в Чехове часто используются комбинированные схемы, когда медикаментозный барьер подкрепляется психотерапевтической поддержкой, а результат кодирования закрепляется за счёт изменения образа жизни и участия в реабилитационных программах.
Выяснить больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-v-chekhove/
Appreciate this post. Will try it out.
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Брал тут тусишку два раза, отменного качества. Магаз работает быстро и чётко, трек кидают на следующий день, товар приходит через два дня. Респект магазу вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш сегодня сделал заказ оплатил, отпишусь что будет дальшеЗа АМ 1220 ничего сказать не могу – не пробовал…. Но, после тестирования 694 и 2201 впечатления о линейке АМ у меня сильно подпортились (
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Подробнее тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar
Площадка Mega — представляет собой сайт, находящийся в закрытой части интернета, где посетители ищут множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://m3ga.my]мега ссылка на сайт даркнет[/url] отождествляется с теневым характером и повышенной конфиденциальностью.
Метафорически эту площадку выступает как окно в подпольную сеть, которое имеет свои тонкости.
Данный теневой сайт относится к числу известных площадок «глубокой сети», где ключевую роль играют анонимность участников и шифрование трафика.
Доступ к таким ресурсам требует использования особых браузеров (например, Тор), а также VPN для обеспечения доступа из любой точки.
С целью посещения ресурса, требуется иметь актуальную ссылку (ONION-ссылку) и настроить систему особым образом.
Основная характеристика ресурса состоит в отсутствии информации пользователей и отсутствии централизованной регистрации.
Пользователи на этом сайте находят самые разные сервисы: от конфиденциальных чатов до торговых платформ.
Ресурс предоставляет охрану от мониторинга благодаря передовым методам кодирования.
Вместе с тем даже многоуровневая защита может быть эффективной лишь отчасти, особенно при неосмотрительном поведении посетителей ресурса.
На сегодняшнем этапе развития сети данная площадка имеет свою специфическую нишу, становясь местом для людей, кто ищет неофициальные источники данными и услугами.
Среди контента здесь попадаются как допустимые законом сведения, так и нелегальные, что требует от посетителя проявлять бдительность и ответственность.
Изучая феномен теневых платформ, стоит обратить внимание на ряд важных моментов, относящихся к особенностям применения и конфиденциальности.
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, необходима корректная организация рабочего пространства и внедрение эшелонированной безопасности для минимизации рисков.
Любой участник обязан осознавать принципы скрытности и, по мере сил придерживаться правилам цифровой этики при общении на данной платформе.
Кроме того, следует учитывать о юридических последствиях и реальной ответственности за нарушение законодательства.
Законодательство разных стран расходятся во мнениях относительно само присутствие на подобных сайтах и меры наказания за активность там.
Ряд экспертов подчеркивают, что такие площадки могут становиться платформой для коммуникации и обеспечения анонимности при осознанном использовании.
Однако, риски обмана, финансовых потерь и злонамеренных акций здесь всегда присутствуют.
Лавируя между открытостью информации и жесткими правовыми ограничениями, этот ресурс представляет собой наиболее неоднозначный сегмент интернета.
Резюмируя для посетителей: следует очень внимательно относиться к изучаемой информации и верификации данных.
Обобщая вышесказанное можно заключить, что подобные ресурсы — это сложная и противоречивая среда. Она предлагает высокий уровень анонимности и приватности, но накладывает на посетителя внимательности, технической грамотности и моральной ответственности.
Этот ресурс наглядно демонстрирует спектр человеческих поступков в условиях ограниченного внешнего контроля и предоставляет платформу для дискуссий на спорные темы.
Итак, Мега Даркнет представляет собой неоднозначный феномен глобальной сети, где гармония прав и рисков определяется индивидуально.
1вин приветственный бонус [url=www.1win08754.help]1вин приветственный бонус[/url]
Мы не используем универсальные «сильные капельницы». Эффективность даёт точное совпадение с задачей. Ниже — логика выбора профилей и маркеры, на которые мы ориентируемся при контроле эффективности и безопасности.
Подробнее – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
1win ставки на спорт [url=www.1win08754.help]1win ставки на спорт[/url]
В клинике «Трезвый город» доступна помощь при запое и тяжёлой абстиненции с медицинским наблюдением. Проводится инфузионная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция и восстановление сна, общего самочувствия и вегетативных проявлений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/snyatie-lomki/]снятие ломки[/url]
После окончания врач дает консультации и рекомендации по восстановлению организма и профилактике повторных запоев.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя[/url]
Нарколог на дом в Санкт-Петербурге оказывает помощь при различных формах алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Основное внимание уделяется купированию абстинентного синдрома, нормализации работы сердечно-сосудистой и нервной систем, а также снижению уровня интоксикации организма.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены санкт-петербург[/url]
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя балашиха[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru
Клиника «НаркоСити» предлагает срочную наркологическую помощь при запоях на дому в Краснодаре. Опытные специалисты оперативно приезжают в любой район города, проводят детоксикацию и стабилизируют состояние пациента прямо на дому. Лечение организовано с максимальной безопасностью и соблюдением конфиденциальности, что обеспечивает пациентам комфорт и быстрое восстановление без госпитализации.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге[/url]
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Бавария;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]футбольная форма клуба ЃавариЯ купить[/url]
купить футбольную форму ЃавариЯ в москве – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=https://images.google.co.ve/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya]https://www.google.com.et/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/bavariya[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.butternut-yarrow-673.notion.site/2065ec070ffb80fc82b9cbf649b5f200/k.krakenwork.cc/s%3A%2F%25Evolv.E.L.U.pc@Haedongacademy.org/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/www.rudik-diplom9.ru/reiting-seo-kompanii.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 34f6303
В условиях круглосуточного наблюдения врачи могут внимательно следить за динамикой состояния, своевременно корректировать схемы лечения, проводить детоксикацию под контролем давления, пульса и работы сердца. Особенно это важно для пациентов с гипертонией, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, нарушениями ритма, заболеваниями печени, диабетом и другими хроническими патологиями. В стационаре проще организовать обследование, назначить сопутствующую терапию, вовремя заметить опасные симптомы и предотвратить серьёзные осложнения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-lobne/
Наркологическая клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске оказывает комплексную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. В центре проводится медицинская детоксикация, поддерживающая терапия и восстановительные программы с участием врачей и психологов. Индивидуальный подход, конфиденциальность и современные методы лечения помогают пациентам стабилизировать состояние и сделать первый шаг к устойчивой ремиссии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/]www.evaclinica.ru[/url]
https://doskazaymov.kz/ Кредит онлайн на 4 000 000 тенге в Алматы – проверьте переплату и срок в калькуляторе doskazaymov.kz.
Привет всем!
В Усть-Каменогорске свежие объявления о продаже домов и квартир доступны на доске объявлений. Бесплатные объявления с фото и подробными описаниями помогут вам найти идеальное жилье. Объявления Каменогорска обновляются ежедневно, поэтому вы всегда будете в курсе новых предложений. Подать объявление можно прямо сейчас, и оно появится в разделе свежие объявления. Объявления Усть-Каменогорска помогут вам быстро найти то, что нужно.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://natumbe.kz/kk/sarykemer/avto-audi/
гей доска объявлений, объявления сарыколе, сайт объявлений
объявления каменогорска, рекламное объявление, объявление где можно
Всего наилучшего и хорошей информации!
В поисках надежной площадки пользователи часто вводят запросы kraken зеркала, чтобы получить стабильный доступ к ресурсу даже при блокировках. Актуальное kraken зеркало позволяет быстро перейти на kraken сайт без потери данных и лишних сложностей. Рабочая kraken ссылка помогает избежать фишинговых копий и сохранить безопасность аккаунта. Используя проверенные kraken зеркала, вы обеспечиваете себе удобный вход на kraken сайт в любое время, независимо от ограничений провайдеров и технических сбоев.[url=https://www.pickupforum.ru/index.php?showtopic=301772]кракен площадка ссылка
[/url]
Препараты подбираются строго индивидуально и могут включать:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
«УралМедЦентр» организует домашний формат наркологической помощи в Екатеринбурге как спокойный и технологичный процесс без очередей и лишнего шума. Мы приезжаем круглосуточно во все районы — от Уралмаша до Академического — и запускаем персональную схему стабилизации прямо у вас дома: экспресс-оценка, титрованные капельницы через инфузомат, защита желудка, контроль сердечного ритма, настройка сна и питьевого режима. В целях конфиденциальности специалисты приезжают без медицинской символики, документы формулируются нейтрально, уведомления — «тихие», а при желании оформляется кодовый профиль. Так мы снимаем стигму и возвращаем человеку чувство контроля уже в первые часы.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
https://clubcoma.org/blog/melbet_promo_code_58.html
https://danceufa.ru/css/pgs/?perevozka_mebeli_pri_pereezde.html
фофу кушают, 2 дмпм нюхается, судя по всему https://gashishkupits.club Всем здравствуйте! Опишу свою ситуацию: 2 недели назад заказывал в данном магазине 2 с-i и MXE, всё на высшем уровне: оперативность 5 +, доставка 5+, конспирация 5+, Качество 5+. Нареканий к Магазину нет, только благодарность!!! В этот раз сделал заказ в Понедельник, оплатил во Вторник. В пятницу только получил трек. На сегодня Трек не работает. Звоню в курьерку они говорят, что такой трек у них не зарегистрирован. Паники пока никакой нет, но хотелось бы получить какие нибудь разъяснения по этому поводу. Заранее спасибо!Как у вас дела бразы?)
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом краснодар[/url]
I delight in, lead to I found just what I used to be having a look for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
garipovbulat
plinko 1win [url=http://1win04381.help]http://1win04381.help[/url]
捕风追影下载平台,專為海外華人設計,提供高清視頻和直播服務。
Задача первого контакта — не «записать к врачу на когда-нибудь», а оценить, насколько ситуация критична прямо сейчас. Если речь идёт о многодневном запое, сильной слабости, одышке, скачках давления, спутанности сознания, лучше не экспериментировать с домашними методами. В таких случаях специалисты в Лобне рекомендуют стационар, где можно не только поставить капельницу, но и быстро среагировать на осложнения. Если же состояние относительно стабильное, возможно обсуждение мягкого формата с выездом и последующим наблюдением.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-lobne/
This post offers clear idea for the new people of blogging, that actually how to do blogging and site-building.
1win легально ли в Киргизии [url=https://www.1win04381.help]https://www.1win04381.help[/url]
Каждый пациент в «УралМед» получает персональный маршрут реабилитации, составленный после комплексного обследования. План включает медикаментозное выведение из запоя, коррекцию биохимических показателей и психологическую реабилитацию.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена екатеринбург[/url]
Чтобы показать, как именно работает врач в домашних условиях, можно сопоставить основные проявления запоя и шаги нарколога, направленные на их устранение.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод санкт-петербург[/url]
1win верификация Кыргызстан [url=http://1win04381.help/]http://1win04381.help/[/url]
Данный комплекс мер обеспечивает восстановление здоровья пациента и создает основу для полного выздоровления.
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva
Теневая платформа Mega — считается платформой, расположенный в теневом сегменте сети, где можно найти множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://meega.cc]сайт мега даркнет зеркало[/url] прочно ассоциируется с теневым характером и максимальным уровнем анонимности.
В переносном смысле данный сайт можно рассматривать как портал в закрытое цифровое пространство, которое таит в себе массу особенностей.
Мега Даркнет является одной из заметных частей «глубокой сети», где ключевую роль играют анонимность участников и защита каналов связи.
Вход на эти сайты требует через специализированные браузеры (например, Тор), а также VPN для преодоления блокировок.
Чтобы попасть на этот сайт, нужно найти рабочий адрес (ONION-ссылку) и провести тщательную настройку оборудования.
Ключевое отличие площадки заключается в полной непрозрачности участников и децентрализованной структуре.
Пользователи на этом сайте находят разнообразные предложения: от приватных мессенджеров до площадок для торговли.
Ресурс предоставляет охрану от мониторинга благодаря мощным криптографическим алгоритмам.
Вместе с тем даже многоуровневая защита может гарантировать лишь частичную безопасность, особенно при неосмотрительном поведении самих пользователей.
В текущих реалиях интернета этот сайт выполняет узкоспециализированную функцию, привлекая тех, кто охотится за непубличной информацией и особыми сервисами.
Среди контента здесь попадаются как допустимые законом сведения, так и нелегальные, что вынуждает участника высокой осторожности и осознанности.
Изучая феномен теневых платформ, следует отметить ряд важных моментов, относящихся к особенностям применения и безопасности.
Прежде всего, необходима грамотная настройка пользовательского окружения и использование комплексной защиты для снижения угроз.
Любой участник обязан осознавать уровни анонимности и, по мере сил придерживаться правилам цифровой этики при работе внутри сети.
Во-вторых, нельзя игнорировать о проблемах с законом и возможных последствиях за противоправные поступки.
Правовые нормы государств расходятся во мнениях относительно доступа к подобным площадкам и меры наказания за активность там.
Ряд экспертов указывают, что подобные сайты могут выступать пространством для обмена знаниями и защиты приватности при ответственном подходе.
Однако, угроза быть обманутым, финансовых потерь и криминальной активности здесь никогда не исчезают.
Лавируя между информационной свободой и нормативными запретами, Мега Даркнет представляет собой наиболее неоднозначный сегмент глобальной сети.
Резюмируя для посетителей: следует очень внимательно относиться к тому, что смотреть и читать и оценке надежности сайтов.
Обобщая вышесказанное можно заключить, что подобные ресурсы — это неоднозначное и опасное пространство. Платформа дает высокий уровень анонимности и приватности, но требует от каждого участника внимательности, технической грамотности и моральной ответственности.
Площадка показывает различные модели поведения в среде с ослабленным регулированием и предоставляет платформу для обсуждения острых тем.
Как видно, теневая платформа является многогранным явлением цифрового мира, где гармония прав и рисков определяется индивидуально.
Срочная медицинская помощь поможет избежать тяжелых последствий и сократит время на восстановление после запоя.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar0.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
1win раздел бонусы [url=https://1win04381.help/]https://1win04381.help/[/url]
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something
which helped me. Appreciate it!
Такая система терапии позволяет охватить сразу несколько звеньев патологического процесса и ускорить выздоровление.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Всем привет) У меня такая проблема, сделал заказ, оплатил через евросеть, Уважаемый продаван сказал то, что в евросети перевод идет до 3-х дней, хотя когда работали с другим магазином деньги прилетали моменьтально всегда. И доставка вышла на 950 р. (г. Екб), это получаеться + курьер или нет, просто до почты?… И через что лучше оплачивать в данном магазине? https://boshkikypit.life Хорошо работают реально ! ! ! рега МН-35ф реально индика суровая , наиболее множество сходств нашёл с натуралом , по Мне так это наиболее приближенный каннабиноид ..6-APB, белый кристалический порошок, 1000р… Это типа настоящий 6-APB?
https://auto.ae/catalog/
Важно: мы заранее проговариваем «зелёные зоны» давления, пульса и сатурации, чтобы пациент и близкие не пытались «самостоятельно улучшить схему». Если динамика «плоская», врач точечно меняет состав/скорость, а часть задач переносит в поведенческий контур (свет, вода, дыхание, расписание «тихих окон»).
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
При длительном запое организм не успевает восстановить свой водно-электролитный баланс, что приводит к обезвоживанию и ухудшению общего состояния. Такие пациенты рискуют развить не только тяжелую интоксикацию, но и хронические заболевания, которые впоследствии требуют длительного и дорогостоящего лечения. Поэтому своевременный вызов врача-нарколога на дом становится критически важным для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных последствий.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя краснодар[/url]
Если в процессе выявляются нестабильные витальные показатели, нарастающая дезориентация или признаки дыхательной недостаточности, маршрут немедленно переводится в стационар «УралМедЦентра» с сохранением уже собранной информации — без повторных очередей и «история заново».
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/narkolog-ekaterinburg-otzyvy/https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru
I blog quite often and I genuinely appreciate your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to book mark your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
byueuropaviagraonline
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am in fact pleassant to read everthing at single place.
Ночной вызов ничем не отличается от утреннего: мы отвечаем, уточняем риски и запускаем маршрут так, чтобы первые часы прошли спокойно. Наш алгоритм простой и понятный — он экономит время и убирает хаос. Ниже — ориентировочная карта визита; по месту врач адаптирует её к возрасту, соматическому фону и текущим симптомам.
Подробнее – http://
Этот обзор предлагает свежий взгляд на предметы, которые и без того привычны. Мы упоминаем факты, не имеющие большого значения, и события с неясной важностью, но они присутствуют здесь.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]таблетки для аборта[/url]
Hi there to all, it’s really a good for me to visit this site, it contains helpful Information.
трансфер по москве микроавтобус премиум мерседес аренда с водителем
Психологическая помощь не менее важна: наши специалисты проводят как индивидуальные, так и групповые сеансы, где вы учитесь справляться с тревогой, формировать новые навыки стресс-менеджмента и находить мотивацию к трезвому образу жизни. Диетолог составит персональный план питания, учитывающий потребности восстановленного организма, а мобильное приложение клиники позволит оставаться на связи с врачом 24/7 — вы всегда получите совет и поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя цена балашиха[/url]
Этот подход имеет несколько ключевых преимуществ, которые обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/]narkolog na dom moskva[/url]
BreachDatabase – Exposed or Safe? Scan & See Instantly!
Think you’re safe? Think again – the dark web never sleeps, but BreachDatabase keeps you ahead.
Search across 33 billion compromised credentials with 50 million daily updates, all in seconds.
Use BreachDatabase’s account compromise checker to scan your email and see if you’re at risk.
You can also review your password security and understand how strong or weak your password might be.
Experience full protection, instant reports, and verified clean data downloads – all for just $2.
Check how secure your password is before hackers do.
Scan now: [url=https://BreachDatabase.net] Password is secure[/url]
|
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/vyvedenie-iz-zapoya-volgograd/
Чем раньше нарколог окажет помощь, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и восстановиться без последствий для здоровья.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/
В реабилитационном центре «Еваклиник» в Саранске созданы условия для безопасного и анонимного восстановления после зависимости. Программы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния и поэтапную реабилитацию под контролем медицинского персонала. Такой формат помощи позволяет снизить риски срывов и постепенно вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Детальнее – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosch/]наркологическая помощь анонимно[/url]
Теневая платформа Mega — это ресурс, функционирующий в даркнете, где посетители ищут множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://megamp.cc]ссылка на даркнет мега[/url] прочно ассоциируется с теневым характером и максимальным уровнем анонимности.
В переносном смысле данный сайт можно рассматривать как вход в скрытую часть интернета, которое имеет свои тонкости.
Платформа Mega относится к числу известных площадок «подземного интернета», где основное внимание уделяется анонимность участников и шифрование трафика.
Доступ к таким ресурсам требует применения специального ПО (например, Тор), и дополнительно VPN для преодоления блокировок.
Для входа на платформу, пользователю необходимо знать точный адрес (ONION-ссылку) и обеспечить корректную конфигурацию.
Ключевое отличие площадки — это скрытность участников и невозможности создать обычный аккаунт.
Участники данной сети отыскивают множество услуг: от закрытых каналов связи до торговых платформ.
Сайт гарантирует безопасность от наблюдения благодаря современным технологиям шифрования.
Однако даже комплексные меры безопасности может обеспечить только относительную защиту, особенно при ошибках посетителей ресурса.
В современном цифровом ландшафте этот сайт занимает нишевую роль, привлекая тех, кто охотится за непубличной данными и услугами.
На страницах ресурса могут встречаться как допустимые законом сведения, так и нелегальные, что обязывает пользователя быть внимательным и предусмотрительным.
Анализируя роль подобных площадок в интернете, стоит обратить внимание на ряд важных моментов, связанных с правилами поведения и защиты.
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, необходима грамотная настройка пользовательского окружения и внедрение эшелонированной безопасности для минимизации рисков.
Любой участник обязан осознавать принципы скрытности и, желательно соблюдать правилам цифровой этики при общении на данной платформе.
Также важно помнить, что не стоит забывать о проблемах с законом и возможных последствиях за противоправные поступки.
Юридические системы мира неодинаково оценивают факта посещения таких ресурсов и ответственность за их использование.
Некоторые исследователи подчеркивают, что эти ресурсы могут служить местом для дискуссий и обмена опытом и сохранения конфиденциальности при осознанном использовании.
Тем не менее, опасность мошенничества, хищения средств и мошеннических действий здесь никогда не исчезают.
Находясь на грани открытостью информации и суровыми законами, теневая платформа представляет собой наиболее неоднозначный сегмент глобальной сети.
Вывод для пользователей прост: следует очень внимательно относиться к выбору контента и проверке источников.
Обобщая вышесказанное можно заключить, что подобные ресурсы — это сложный цифровой феномен. Платформа дает максимальную приватность и приватности, но требует от каждого участника внимательности, понимания технологий и моральной ответственности.
Сайт иллюстрирует многообразие поведения людей в среде с ослабленным регулированием и служит местом для дискуссий на спорные темы.
Итак, этот сегмент сети является многогранным явлением глобальной сети, где баланс между свободой и безопасностью определяется индивидуально.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим современные достижения в области медицины, включая инновационные методы лечения и диагностики. Мы обсудим важность профилактики заболеваний и роль технологий в улучшении качества здравоохранения. Читатели узнают о влиянии медицины на повседневную жизнь и ее значение для современного общества.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://howmuchisit.org/ra.asp?url=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/himzaschita
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
В поисках надежной площадки пользователи часто вводят запросы kraken зеркала, чтобы получить стабильный доступ к ресурсу даже при блокировках. Актуальное kraken зеркало позволяет быстро перейти на kraken сайт без потери данных и лишних сложностей. Рабочая kraken ссылка помогает избежать фишинговых копий и сохранить безопасность аккаунта. Используя проверенные kraken зеркала, вы обеспечиваете себе удобный вход на kraken сайт в любое время, независимо от ограничений провайдеров и технических сбоев.[url=https://www.pickupforum.ru/index.php?showtopic=301773]кракен вместо гидры
[/url]
Я всегда делаю на растворителе для снятие лака с ногтей (без ацетона)и для огранизма менее вреден и запах нос не режет,кто нибуть может подсказать сколько МЛ растворителя на 10г АМ если делать 1к15? https://meffchik.life ну не хочешь – не бери, кто заставляет то Оо Покупают сотни, а отзывы “с критикой” от единиц. Кстати, 307го нет кажется…как планчик наверн цепляет. но не прям на коры. вообщем так норм сойдет
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Аякс;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/ajax]футбольная форма ЂЯкс москва[/url]
футбольная форма атрибутика ЂЯкс – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/ajax]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/ajax[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.cz/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/ajax]https://images.google.rs/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/ajax[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/k.krakenwork.cc/www.frei-diplom1.ru/index.html]Клубная атрибутика и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 9b03_e8
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog?
My blog site is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors
would certainly benefit from a lot of the information you provide here.
Please let me know if this okay with you. Thank you!
Некоторые состояния требуют немедленного вмешательства специалиста. Если алкогольное отравление или запойное состояние не купируется вовремя, это может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в иркутске[/url]
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника екатеринбург[/url]
На месте врач проводит первичный осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает уровень интоксикации и абстиненции. Далее назначается инфузионная терапия — капельница, направленная на дезинтоксикацию, восстановление электролитного баланса, купирование тревожности и нормализацию сна.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vyzov vracha narkologa na dom[/url]
В этой статье-обзоре мы собрали данные, актуальность которых сомнительна, а факты — не всегда взаимосвязаны. Читатель сможет ознакомиться с разными мнениями, хотя вряд ли они существенно повлияют на его понимание темы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]секс шоп[/url]
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом[/url]
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Лечебные мероприятия и рекомендации формируются исходя из индивидуального состояния каждого пациента. Специалист имеет возможность посвятить достаточное количество времени каждому больному, корректируя программу лечения согласно его особым потребностям и жизненным обстоятельствам. При этом учитываются психологические, социальные и физические аспекты, оказывающие влияние на здоровье пациента. Персонализированный подход обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на изменения состояния и своевременную корректировку терапии.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/
Hello are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
1win cashback [url=www.1win08754.help]www.1win08754.help[/url]
Магниты рулят, не меняйтесь) вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Про себя могу сказать что толлерантность ОЧЕНЬ выскаяу меня до сих пор нет реальной отправки,ток просроченная планируемая(((
Клиника «Еваклиник» в Саранске специализируется на лечении зависимостей с применением проверенных медицинских протоколов. Пациентам доступна круглосуточная наркологическая помощь, медикаментозная поддержка и сопровождение на этапе реабилитации. Специалисты центра работают не только с физическими проявлениями зависимости, но и с психологическими причинами, что повышает эффективность лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://evaclinica.ru/]Клиника «Еваклиник» для лечения зависимостей[/url]
1win crash [url=1win08754.help]1win08754.help[/url]
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/intoksikaciya-organizma-posle-zapoya.html]интоксикация после запоя[/url]
Мега Даркнет — считается платформой, находящийся в закрытой части интернета, где можно найти множество специфических услуг.
[url=https://m3ga20.com]mega market darknet зеркало[/url] прочно ассоциируется с теневым характером и максимальным уровнем анонимности.
Образно говоря, этот ресурс можно рассматривать как портал в закрытое цифровое пространство, которое имеет свои тонкости.
Мега Даркнет является одной из заметных частей «глубокой сети», где ключевую роль играют приватность посетителей и безопасность соединений.
Доступ к таким ресурсам требует применения специального ПО (например, Тор), и дополнительно VPN для преодоления блокировок.
Чтобы попасть на этот сайт, пользователю необходимо знать точный адрес (ONION-ссылку) и настроить систему особым образом.
Главная особенность Меги заключается в полной непрозрачности пользователей и децентрализованной структуре.
Пользователи на этом сайте находят множество услуг: от закрытых каналов связи до маркетплейсов.
Сайт гарантирует безопасность от слежки благодаря передовым методам кодирования.
Однако даже комплексные меры безопасности может обеспечить только относительную защиту, особенно при неосторожных действиях участников системы.
В текущих реалиях интернета подобный ресурс выполняет узкоспециализированную функцию, интересуя тех пользователей, кто ищет неофициальные источники данными и услугами.
Внутри площадки попадаются как разрешенный контент, так и нелегальные, что обязывает пользователя проявлять бдительность и ответственность.
Анализируя роль подобных площадок в интернете, следует отметить ряд важных моментов, относящихся к особенностям применения и защиты.
Прежде всего, критически важна корректная организация пользовательского окружения и использование комплексной защиты для минимизации рисков.
Каждый посетитель должен осознавать уровни анонимности и, по мере сил придерживаться моральным нормам при работе внутри сети.
Во-вторых, не стоит забывать о юридических последствиях и возможных последствиях за незаконные действия.
Юридические системы мира по-разному трактует доступа к подобным площадкам и ответственность за их использование.
Ряд экспертов отмечают, что эти ресурсы могут становиться платформой для дискуссий и обмена опытом и защиты приватности при осознанном использовании.
Однако, угроза быть обманутым, хищения средств и мошеннических действий здесь остаются высокими.
Балансируя между информационной свободой и суровыми законами, теневая платформа остается одной из самых противоречивых частей глобальной сети.
Вывод для пользователей прост: необходимо крайне аккуратно подходить к тому, что смотреть и читать и верификации данных.
В конечном счете можно заключить, что Мега Даркнет — это сложная и противоречивая среда. Сайт обеспечивает высокий уровень анонимности и конфиденциальности, но накладывает на посетителя осторожности, определенных знаний и осознанности действий.
Сайт иллюстрирует различные модели поведения в среде с ослабленным регулированием и предоставляет платформу для коммуникации по закрытым вопросам.
Таким образом, этот сегмент сети остается сложным феноменом интернета, где баланс между свободой и безопасностью определяется индивидуально.
Эта статья подробно расскажет о процессе выздоровления, который включает в себя эмоциональную, физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Мы обсуждаем значимость поддержки и наличие профессиональных программ. Читатели узнают, как строить новую жизнь и не возвращаться к старым привычкам.
Подробнее – http://google.iq/url?q=https://spb.alco-centr.ru/lechenie-zavisimosti-ot-stavok
Первый этап помощи почти всегда связан с детоксикацией. Организм, который длительное время получал алкоголь или другие вещества, перегружен токсинами, страдают сердце, сосуды, мозг, печень, нарушены сон и обмен веществ. Простое «похмелиться и перетерпеть» в такой ситуации опасно: можно спровоцировать очередной скачок давления, аритмию, обострение хронических заболеваний. В условиях клиники в Лобне детокс строится по медицинским правилам, а не по советам из интернета.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-lobne/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru
Online casinos real money Australia – bonuses worth claiming
Обращение к наркологу — это не признание «окончательного проигрыша», а трезвое решение, что здоровье и жизнь важнее иллюзии контроля. В клинике можно безопасно вывести человека из запоя, стабилизировать состояние, обследовать сердце, печень, нервную систему, понять, насколько далеко зашло заболевание. Важно, что помощь получают не только тяжёлые пациенты «на грани», но и те, у кого ещё есть работа, семья, привычный образ жизни, но запои уже стали регулярными. Чем раньше удаётся подключить специалистов в Лобне, тем мягче можно пройти лечение и тем больше шансов сохранить и здоровье, и отношения, и социальный статус.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]бесплатные наркологические клиники[/url]
1win истифодаи промокод [url=http://1win93047.help]http://1win93047.help[/url]
If some one desires to be updated with most recent technologies therefore he must be pay a quick visit this site and be up to date everyday.
В Санкт-Петербурге для адресных обращений дежурят мобильные бригады круглосуточно. Координатор при звонке уточняет хронические заболевания, аллергии, текущие лекарства и эпизоды судорог/психозов, а также бытовые условия: есть ли доступ к розетке, можно ли обеспечить 2–3 часа тишины, удобна ли зона полулёжа. Эта информация позволяет врачу в дороге выбрать стартовую скорость инфузии, продумать последовательность введения и подготовить расходные материалы под планировку квартиры. Мы соблюдаем приватность: нейтральная экипировка, деликатные формулировки в документах и один доверенный контакт со стороны семьи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург[/url]
спок ночи вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш вобще-то этот магазин трек присылает а не адрес…конечно была задержка которая заставила по нервничать, но всё прошло на уровне и я получил свою посылочку)))
Этот сборник информации привлекает множеством мелких деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, редко полезные, но способные немного разнообразить знакомство с темой.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-narkomanii/mefedronovaya-zavisimost/]детокс чай для похудения[/url]
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом москва[/url]
Наркологическая клиника в Ивантеевке — это возможность получить грамотную, поэтапную помощь рядом с домом, не дожидаясь момента, когда организм и психика окажутся на грани. Большинство пациентов и их родственников приходят к идее лечения не сразу: сначала идут попытки «контролировать» употребление, меняться местами работы и отдыха, просьбы семьи «держать себя в руках», временные успехи и повторяющиеся срывы. На фоне этого накапливаются конфликты, ухудшается здоровье, появляются проблемы с работой и финансами, а жизнь всё больше вращается вокруг алкоголя или наркотиков. В какой-то момент становится очевидно: без профессиональной помощи зависимость не отпускает, а только меняет форму.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom[/url]
аренда v class с водителем Выбирая аренду Mercedes-Benz V-Class с водителем в Москве, вы получаете не только роскошный автомобиль, но и профессионального шофёра, отлично знающего городские маршруты и готового обеспечить пунктуальность и спокойствие в пути. Особое внимание уделяется трансферам в аэропорты Шереметьево, Домодедово, Внуково и Жуковский, где точность и своевременность играют ключевую роль.
В «Трезвом городе» помогают при последствиях употребления: тревожность, бессонница, тремор, нарушения аппетита и скачки давления требуют грамотной медицинской коррекции. После стабилизации пациенту объясняют риски и предлагают план профилактики срыва.
Получить больше информации – https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/intoksikaciya-organizma-posle-zapoya.html
написать курсовую работу на заказ в москве [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-65.ru/]написать курсовую работу на заказ в москве[/url] .
Такой порядок действий гарантирует не только купирование симптомов, но и подготовку пациента к последующему восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Анонимное лечение при выводе из запоя в Москве означает, что пациент может получить медицинскую помощь без раскрытия своей личности. Это важно для людей, которые по разным причинам не хотят, чтобы информация о лечении становилась доступной другим людям. В процессе лечения не требуется раскрытие данных о пациенте, что делает его комфортным и безопасным.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]москва вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]оригинальная футбольная форма клуба Атлетико Мадрид[/url]
футбольная форма атрибутика Атлетико – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.bn/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]http://cse.google.co.ma/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport3.ru/www.melbet5002.ru]Спортивная экипировка и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 2a67f9e
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]виртуальное казино[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание, — это штат клиники. От опыта врачей напрямую зависит точность диагностики, подбор препаратов и эффективность психотерапевтической поддержки.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-pervouralske/
Мне от оплаты и в мои руки в общем занимает 2-3 дня вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш ровный магазинНадеюсь что ошибаюсь:hello:
Медицинская детоксикация — это основа успешного вывода из запоя. Она проводится под строгим контролем врачей-наркологов, которые используют инфузионную терапию для выведения токсинов из организма. В качестве компонентов капельниц применяются растворы глюкозы, физиологический раствор, препараты для восстановления работы печени и почек. Поддержка сердечно-сосудистой системы и нормализация артериального давления достигается с помощью специализированных медикаментов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом цены новокузнецк[/url]
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
Приехал в Ростов искал проституток в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат. Лучшие проститутки индивидуалки, знакомятся, договариваются о встречах. Вот ссылка: https://t.me/Rostov_Znakomst
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday.
It’s always exciting to read articles from
other writers and use something from their web sites. https://cryptobossmacher.top/
https://auto.ae/showrooms/all/
Как подчёркивает заведующая кафедрой наркологии РМАНПО Минздрава России, «качество оказания помощи зависит не от количества процедур, а от правильной организации лечебного процесса и квалификации команды». Именно поэтому особенно важно понимать, какие параметры следует учитывать при выборе клиники.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/
Опрятный вид формирует первое впечатление о человеке.
Ваш образ влияет на восприятие вас коллегами сразу.
Уверенность в своем образе укрепляет вашу уверенность.
Этот подход демонстрирует высокий стандарт ответственности и внимание к деталям.
https://r2.balmain1.ru/d6pxdfGzQ8P/
Через гардероб вы можете выразить свою личность и вкус.
Люди часто воспринимают опрятных людей как более компетентных.
Следовательно, вложения в свой образ — это вклад в ваше будущее.
Спасибо! Обращайтесь вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш брал тут на днях, все прошло ровнее некуда, рекомендую, теперь это мой постоянный магазин)Заказали, придет посмотрим
Когда следует немедленно обращаться за помощью:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]платный нарколог на дом новокузнецк[/url]
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Узнать больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-yaroslavle/
Вывод из запоя в Мурманске представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на оказание медицинской помощи пациентам, находящимся в состоянии алкогольного отравления или длительного употребления спиртного. Процедура проводится с целью стабилизации состояния организма, предупреждения осложнений и минимизации риска развития тяжелых последствий алкоголизма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske/
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Запой может длиться от нескольких дней до нескольких недель, и с каждым новым днём состояние пациента может ухудшаться. Важно не затягивать с лечением, поскольку алкогольная зависимость способна привести к необратимым изменениям в организме и психике. В Москве лечение проводится не только в клиниках, но и в условиях дома, что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]вывод из запоя москва[/url]
Взаимосвязь медицинских и психологических компонентов терапии формирует основу устойчивой ремиссии, снижая вероятность повторных срывов и обеспечивая длительный восстановительный эффект.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в екатеринбурге[/url]
Hi there, I want to subscribe for this blog to get latest updates, thus where can i do it please assist. https://rt.chat-rulet-18.com/pornstar
โพสต์นี้ มีประโยชน์มาก
ครับ
ดิฉัน ไปเจอรายละเอียดของ ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ซึ่งอยู่ที่ Fabian
ลองแวะไปดู
มีตัวอย่างประกอบชัดเจน
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ ข้อมูลที่มีประโยชน์ นี้
และหวังว่าจะมีข้อมูลใหม่ๆ มาแบ่งปันอีก
1win бонусы казино [url=www.1win08754.help]www.1win08754.help[/url]
Как отмечает врач-нарколог Иванов И.И., «без своевременной медицинской помощи при запое повышается риск необратимых изменений в организме и летального исхода».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника нижний тагил[/url]
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом цена ярославль[/url]
Этот подход имеет несколько ключевых преимуществ, которые обеспечивают комфорт, безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic
to be actually something that I think I would never understand.
It seems too complex and very broad for me. I am looking forward for
your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Запой почти никогда не начинается внезапно: сначала это редкие «переборы» по праздникам, потом привычка снимать стресс вечером, а дальше алкоголь всё чаще появляется в распорядке дня. В какой-то момент близкие замечают, что человек уже не контролирует количество, выпивка идёт несколько дней подряд, отменяются дела, нарушается сон, пропадает аппетит, появляются дрожь, потливость, скачки давления. На этом этапе вывод из запоя в Ивантеевке уже не может быть простым «проспаться и прийти в себя» — организму нужна полноценная медицинская помощь.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny/
Вернуть здоровье и силы за одну процедуру позволяет грамотное сочетание препаратов, подобранное индивидуально под каждого пациента. Врач-нарколог оценивает тяжесть интоксикации, измеряет артериальное давление, пульс и уровень насыщения крови кислородом, а при необходимости назначает экспресс-анализы. На основании этих данных создаётся персональный раствор для инфузии:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно на дому балашиха[/url]
это манера такая сдержанная или удовлетворительное=на троечку вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Парни, начинается параноя! Завтра посыль приходит, как получать А?Помнится ф16 на пробу получал. Хороший синт.гарсон был.
https://auto.ae/catalog/
В статье рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые помогут сориентироваться при выборе капельницы от запоя, понять механизм действия и особенности процедуры, а также избежать типичных ошибок при обращении за медицинской помощью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/kapelniczy-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-pervouralske/https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru
Вывод из запоя в Мурманске представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на оказание медицинской помощи пациентам, находящимся в состоянии алкогольного отравления или длительного употребления спиртного. Процедура проводится с целью стабилизации состояния организма, предупреждения осложнений и минимизации риска развития тяжелых последствий алкоголизма.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-v-murmanske/
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя балашиха[/url]
Touche. Great arguments. Keep up the amazing spirit.
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
курсовой проект купить цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-65.ru/]курсовой проект купить цена[/url] .
В клинике «Трезвый город» доступна помощь при запое и тяжёлой абстиненции с медицинским наблюдением. Проводится инфузионная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция и восстановление сна, общего самочувствия и вегетативных проявлений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/posledstviya-alkogolizma.html
Для современного интерьера идеально подойдет [url=https://avtomaticheskie-shtory.ru] электрокарниз для штор Prokarniz [/url], который обеспечит удобство и стиль в управлении шторами.
Данное устройство облегчает повседневное использование штор. Он особенно удобен в больших помещениях, где нужно одновременно регулировать множество полотен. Более того, электрокарниз легко подключается к умным домашним системам.
Принцип работы электрокарниза основан на электрическом приводе, который движет гардины по направляющим. Пульт дает возможность дистанционного управления шторами, что очень практично. Это делает устройство идеальным для использования в офисах, гостиницах и домах с современным дизайном. Автоматический привод позволяет быстро и легко регулировать положение штор.
Выбор электрокарниза зависит от размеров окна, веса штор и типа крепления. Мощность мотора должна соответствовать весу ткани для надежной работы. Также стоит обратить внимание на материал направляющей и качество комплектующих. Качественные элементы повышают срок службы электрокарниза.
Установка электрокарниза требует аккуратности и точного соблюдения инструкции. Лучше всего монтаж выполнить специалистам, чтобы избежать ошибок. Регулярное техническое обслуживание поможет продлить срок службы устройства. Периодическое техническое обслуживание поддерживает электрокарниз в рабочем состоянии.
Спин-шаблон:
Своевременная профилактика увеличит срок службы электрокарниза.
Эффективная капельница должна включать несколько компонентов, каждый из которых направлен на решение конкретной задачи: выведение токсинов, восстановление функций организма, нормализация психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]наркологический диспансер частная клиника[/url]
spark dex SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Каменске-Уральском обеспечивает безопасность пациента, исключая необходимость посещения медицинского учреждения, что особенно актуально при тяжелом состоянии или психологическом сопротивлении. Такая помощь включает в себя детоксикацию, купирование абстинентного синдрома и консультации по дальнейшему лечению.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/chastnyj-narkolog-na-dom-v-kamensk-uralskom/
Для успешной адаптации пациента в обществе клиника организует поддержку родственников и последующее наблюдение. Это снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить достигнутые результаты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-murmanske/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru
Сегодня оплатил. Жду не дождусь.? вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш про него что нить писали? точнее вы читали ?слышала за вас) с пробы начнем?
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Узнать больше – http://
Запойное состояние опасно не только токсическим воздействием алкоголя на организм, но и последствиями резкого отказа от спиртного. В таких случаях промедление может стоить здоровья. Нарколог на дом в Рязани приезжает по вызову и проводит процедуру прямо в домашних условиях, используя проверенные медицинские методики. Такой подход сочетает анонимность, оперативность и возможность контроля состояния без госпитализации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого санкт-петербург[/url]
Согласно данным Федерального наркологического центра, своевременный выезд врача снижает риск осложнений и повторных госпитализаций.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в каменске-уральском[/url]
Текст включает разнообразную информацию, которая может показаться любопытной, но не меняет устоявшегося восприятия. Предлагаем просто насладиться чтением, не ожидая значительной пользы.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]лечение covid народными средствами[/url]
https://myempirecasino7.com
Запой может длиться от нескольких дней до нескольких недель, и с каждым новым днём состояние пациента может ухудшаться. Важно не затягивать с лечением, поскольку алкогольная зависимость способна привести к необратимым изменениям в организме и психике. В Москве лечение проводится не только в клиниках, но и в условиях дома, что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность.
Углубиться в тему – http://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/
Excellent blog here! Also your website loads up fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for temizlik
Извините удаляю сообщение! https://novanovane.shop А где прайс глянуть?А ты тс в лс отпиши , и если ты не балабол , в чем я очень сомневаюсь то проблема будет решена , а писать на ветке это говно для чего не понятно , на что вы надеетесь
Психотерапевтическое кодирование делает акцент на внутренней мотивации. Специалист помогает человеку увидеть реальную цену алкоголя в его жизни, понять, как именно употребление разрушает здоровье, семью, карьеру, и сформировать установку на трезвость на определённый срок. Используются техники внушения в состоянии расслабления и структурированная работа с убеждениями и привычками. Такой подход особенно полезен тем, кто боится «лекарственного вмешательства» или уже имеет негативный опыт неудачных медикаментозных попыток. В практике лечения в Чехове часто используются комбинированные схемы, когда медикаментозный барьер подкрепляется психотерапевтической поддержкой, а результат кодирования закрепляется за счёт изменения образа жизни и участия в реабилитационных программах.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-ukolom-v-chekhove/
Назначение
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]сколько стоит капельница на дому от запоя[/url]
В этой статье мы рассмотрим ключевые аспекты выбора надёжного специалиста, который приедет по вызову и сможет оказать квалифицированную помощь без промедлений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Hi there, I discovered your web site by the use of Google at the same time
as looking for a related subject, your web site came up,
it appears great. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hello there, just became aware of your weblog through
Google, and located that it’s truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels.
I will be grateful in the event you proceed this in future.
Many people will likely be benefited out of your writing.
Cheers!
В клинике «Трезвый город» доступна помощь при запое и тяжёлой абстиненции с медицинским наблюдением. Проводится инфузионная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция и восстановление сна, общего самочувствия и вегетативных проявлений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/naltreksonom/]налтрексон кодирование от алкоголизма отзывы[/url]
Перед заключением договора стоит поинтересоваться:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике[/url]
В клинике «Еваклиник» в Саранске пациенты получают квалифицированную наркологическую помощь в комфортных и конфиденциальных условиях. Центр применяет современные методы терапии, направленные на снижение тяги и восстановление общего состояния организма. Поддержка врачей и психологов помогает закрепить результат и сформировать устойчивую мотивацию к трезвой жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://evaclinica.ru/blog/plazmaferez-pokazaniya-metodika-i-ehffektivnost.html
Для успешной адаптации пациента в обществе клиника организует поддержку родственников и последующее наблюдение. Это снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить достигнутые результаты.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника мурманск[/url]
На месте врач проводит первичный осмотр, измеряет давление, пульс, сатурацию, оценивает уровень интоксикации и абстиненции. Далее назначается инфузионная терапия — капельница, направленная на дезинтоксикацию, восстановление электролитного баланса, купирование тревожности и нормализацию сна.
Подробнее тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-anonimno-v-krasnogorske
Современные [url=https://karniz-s-privodom.ru] карнизы с электроприводом для штор Prokarniz [/url] обеспечивают максимальный комфорт и стиль в вашем интерьере.
Следует учитывать размер окон, стиль и способ управления.
Thanks for another wonderful article. Where else may just anyone get that kind of info in such an ideal means of writing?
I have a presentation next week, and I am at the look for such information.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим ключевые аспекты выбора надёжного специалиста, который приедет по вызову и сможет оказать квалифицированную помощь без промедлений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Этот текст содержит различную информацию, которая, возможно, покажется любопытной, но в целом не меняет восприятия привычных вещей. Предлагаем просто получить удовольствие от чтения, не ожидая особой пользы.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]интим услуги[/url]
Наши врачи оперативно приезжают к пациенту, проводят осмотр, купируют симптомы абстиненции и приступают к восстановлению жизненно важных функций. Всё это — в привычной для пациента обстановке, без стресса и лишней огласки. Мы обеспечиваем не только медицинскую помощь, но и эмоциональную поддержку, создавая условия для начала пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это профессиональный уровень сотрудников. Без квалифицированных наркологов, клинических психологов и психиатров реабилитационный процесс становится формальным и неэффективным.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]наркологическая клиника вывод из запоя[/url]
и что теперь делать с заказом мне его оплачивать через терминал!? или.. https://amfzaklad.club Огромное спасибо данному магазину, успехов вработе и процветания!!!?сегодня вот ночью прислал трек. Бьется, радует
цена курсовой работы [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-65.ru/]цена курсовой работы[/url] .
Вызов нарколога возможен круглосуточно, что обеспечивает оперативное реагирование на критические ситуации. Пациенты и их родственники могут получить помощь в любое время, не дожидаясь ухудшения состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в каменске-уральском[/url]
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny/
Как подчёркивает заведующая кафедрой наркологии РМАНПО Минздрава России, «качество оказания помощи зависит не от количества процедур, а от правильной организации лечебного процесса и квалификации команды». Именно поэтому особенно важно понимать, какие параметры следует учитывать при выборе клиники.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
В этом тексте собрано множество случайных сведений и довольно неопределённых мыслей, которые могут чем-то заинтересовать. Мы отмечаем моменты, которые не особенно важны, но всё же занимают своё место в повествовании.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]онлайн слоты[/url]
Sweet blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Thanks
На психическом уровне затяжные запои усугубляют тревожность, депрессию и приводят к паническим атакам. Человек становится раздражительным, агрессивным, теряет социальные и трудовые навыки, что нередко перерастаeт в бытовые и профессиональные аварии. Без своевременного начала инфузионной терапии риск судорог, делирия и жизнеугрожающих осложнений возрастает в разы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Дюралевый швеллер 440040 10х20х2х2х2 мм Д19 ГОСТ 4784-97 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом ярославль[/url]
Магазин как магазин! вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Напишите хотя бы мини трип в соответствующей теме,буду благодарен.MXE точно не бодяженный , со 100мг вышел нереально жуткий трип, раз 15 умирал… через сутки отпустило.
Вывод из запоя на дому — это управляемый медицинский процесс, где каждая деталь имеет значение: от первичного осмотра и грамотного подбора инфузионного профиля до сенсорной дисциплины в помещении и чётких «окон оценки» результата. В наркологической клинике «СеверМед Трезвость» мы используем принцип минимально достаточных вмешательств: одна цель на этап, один измеримый маркер и одна корректировка за раз. Такой подход снижает нагрузку на организм, повышает предсказуемость и делает восстановление переносимым для пациента и его близких.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vivod-iz-zapoya-v-sankt-peterburge16.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника «Передозировка» предлагает круглосуточную помощь жителям Санкт-Петербурга. Лечение зависимостей, детокс-мероприятия и современные методы кодирования помогают пациентам восстановить здоровье и начать длительный период трезвости.
Детальнее – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/roditeli-alkogoliki-v-seme/]родители бывшие алкоголики[/url]
Анонимное лечение при выводе из запоя в Москве означает, что пациент может получить медицинскую помощь без раскрытия своей личности. Это важно для людей, которые по разным причинам не хотят, чтобы информация о лечении становилась доступной другим людям. В процессе лечения не требуется раскрытие данных о пациенте, что делает его комфортным и безопасным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narko-zakodirovat2.ru
1win сменаи парол [url=http://1win93047.help/]1win сменаи парол[/url]
https://auto.ae/showrooms/all/
Клиника «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь при зависимостях. Пациенты получают лечение алкоголизма и наркомании, проходят кодирование и реабилитацию, что способствует устойчивому возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/service/reabilitatsiya/]реабилитация зависимых[/url]
Для эффективного вывода из запоя в Мурманске используются современные методы детоксикации, включающие внутривенное введение растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-солевого баланса, коррекцию электролитов и нормализацию работы почек и печени. Важным этапом является использование витаминных комплексов и препаратов, поддерживающих работу сердца и сосудов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому мурманск[/url]
Реабилитационные программы в наркологической клинике направлены на нормализацию обменных процессов, восстановление сна, эмоциональной стабильности и когнитивных функций. Для достижения этого используются методы физиотерапии, нутритивной поддержки и коррекции поведения. Основное внимание уделяется мотивации пациента, работе с созависимостью и обучению навыкам здорового взаимодействия с окружающей средой.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/gosudarstvennaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg
В клинике «Еваклиник» в Саранске пациенты получают квалифицированную наркологическую помощь в комфортных и конфиденциальных условиях. Центр применяет современные методы терапии, направленные на снижение тяги и восстановление общего состояния организма. Поддержка врачей и психологов помогает закрепить результат и сформировать устойчивую мотивацию к трезвой жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://evaclinica.ru/blog/ehffektivnye-sposoby-izbavitsya-ot-golovnoj-boli-pri-pohmele.html
1win минимали баровардан [url=http://1win93047.help/]1win минимали баровардан[/url]
1win минимали хуруҷ [url=https://1win93047.help/]https://1win93047.help/[/url]
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/ ]мефедроновая зависимость[/url]
По многочисленным восторженным откликам мн-001, тестировал его и был немного огорчен. https://native72.ru Очень странно, что 203 не растворился в ацетоне. Сколько брал ацика на 10 гр основы?Я подозреваю, что его посылку спалили на наличие и теперь просто не отправляют.
РедМетСплав предлагает обширный выбор качественных изделий из нестандартных материалов. Не важно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от небольших закупок до обширных поставок, мы обеспечиваем своевременную реализацию вашего заказа.
Каждая единица продукции подтверждена всеми необходимыми документами, подтверждающими их соответствие стандартам. Превосходное обслуживание – наша визитная карточка – мы на связи, чтобы улаживать ваши вопросы и находить ответы под специфику вашего бизнеса.
Доверьте ваш запрос специалистам РедМетСплав и убедитесь в широком спектре предлагаемых возможностей
Наша продукция:
Проволока титановая 3М – ОСТ 1 92077-91 Полоса титановая 3М – ОСТ 1 92077-91 представляет собой высококачественный продукт, предназначенный для различных промышленных применений. Titanовые полосы известны своей прочностью и устойчивостью к коррозии, что делает их идеальными для использования в сложных условиях. Эта полоса соответствует стандартам ОСТ 1 92077-91, что обеспечивает ее надежность и качество. Если вы ищете надежный материал для своих проектов, купить Полоса титановая 3М – ОСТ 1 92077-91 – отличный выбор. Она будет служить долгие годы и избавит вас от потребности в частой замене.
Современные [url=https://electroprivod-karniz.ru] электрические жалюзи заказать Prokarniz [/url] обеспечивают удобство управления светом в вашем доме с помощью дистанционного пульта.
Второй важный аспект – безопасность и защита от детей.
—
Особенно удобно это для больших или высоко расположенных окон.
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]наркологическая клиника отзывы[/url]
1win бонуси аввал [url=http://1win93047.help]http://1win93047.help[/url]
The site contains a wealth of useful content.
Here, you can discover in-depth articles on various subjects.
Materials available are extremely helpful for beginners and professionals as well.
This place is a fantastic resource for anyone seeking to learn their understanding.
https://somebububu.com/
аренда мерседес v class с водителем mercedes v class аренда с водителем
Перед заключением договора стоит поинтересоваться:
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru
Такой комплексный подход позволяет не только купировать острые состояния, но и устранить внутренние факторы, провоцирующие развитие зависимости. После стабилизации состояния пациент переходит к этапу психотерапевтической коррекции, направленной на предотвращение рецидивов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ekb16.ru/]лечение в наркологической клинике в екатеринбурге[/url]
Медицинское вмешательство в домашних условиях отличается четкой организацией. Врач последовательно выполняет шаги, которые позволяют стабилизировать состояние пациента и предупредить осложнения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно цены санкт-петербург[/url]
Как проходит лечение:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в новокузнецке[/url]
Запой почти никогда не начинается внезапно: сначала это редкие «переборы» по праздникам, потом привычка снимать стресс вечером, а дальше алкоголь всё чаще появляется в распорядке дня. В какой-то момент близкие замечают, что человек уже не контролирует количество, выпивка идёт несколько дней подряд, отменяются дела, нарушается сон, пропадает аппетит, появляются дрожь, потливость, скачки давления. На этом этапе вывод из запоя в Ивантеевке уже не может быть простым «проспаться и прийти в себя» — организму нужна полноценная медицинская помощь.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Why visitors still make use of to read news papers when in this technological world everything is accessible on net?
Вывод из запоя рекомендуется в следующих случаях:
Получить больше информации – https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-moskve
Одна из главных ошибок — ждать «идеального момента» для лечения. Кажется, что кодирование уместно только тогда, когда зависимость достигла крайней стадии: человек потерял работу, перестал выходить из запоев, полностью разрушил отношения с близкими. На практике обращение в клинику Чехова оправдано гораздо раньше, как только употребление алкоголя перестаёт быть редким эпизодом и начинает системно мешать жить. Если каждый стресс, отпуск или конфликт заканчиваются срывом, если запои становятся длиннее, а похмелье тяжелее, — это уже повод хотя бы обсудить кодирование с врачом, а не ждать, пока ресурс организма будет почти исчерпан.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chekhov11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
1win установить приложение [url=https://1win48762.help]1win установить приложение[/url]
1win ставки на теннис Кыргызстан [url=1win48762.help]1win48762.help[/url]
Критерий
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]нарколог капельница на дом нижний тагил[/url]
21го числа оплатил заказ. ждем 🙂 на складе чел заболел пока что . ждем пока выздоровит https://gashishkupits.club Лучшего амфа я в жизни не пробовал. Правда цена кусается, но оно того стоит!качество нормуль! можно делать 1к12, 1к10 само то
Как поясняет врач-нарколог клиники «АлкоСтоп», «грамотно составленная инфузионная терапия не только устраняет последствия запоя, но и создаёт условия для дальнейшей мотивации пациента к лечению».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость в первоуральске[/url]
Данный комплекс мер обеспечивает восстановление здоровья пациента и создает основу для полного выздоровления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
Для успешного лечения зависимости необходима тщательная диагностика. В клинике проводят полное обследование пациента, включающее:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
и такая хрень каждый день. https://kateflowershop.ru Брал хоть и один раз, но все было отлично! Жду второго заказа)Хороший сервис, хорошая команда = хорошие дела ) В том же духе двигаемся…)
Зависимость — это заболевание, которое разрушает не только тело, но и личность. Оно затрагивает мышление, поведение, разрушает отношения и лишает человека способности контролировать свою жизнь. Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде — профессиональное лечение зависимостей строит свою работу на понимании природы болезни, а не на осуждении. Именно это позволяет добиваться стойких результатов, восстанавливая пациента физически, эмоционально и социально.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника в волгограде[/url]
Вызов нарколога на дом в таких условиях позволяет не терять драгоценное время, избежать госпитализации и предотвратить критическое развитие событий. Кроме того, это снижает психологическую нагрузку на пациента и его близких, особенно если зависимость длится долго и сопровождается отрицанием проблемы.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]vyzov narkologa na dom[/url]
В жизни крупных городов часто возникают ситуации, когда стрессы и быстрый ритм жизни приводят к развитию зависимости. Когда проблема становится очевидной, важно незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом может стать не только удобным, но и наиболее эффективным вариантом. Это позволяет получить квалифицированное лечение в привычной обстановке, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность и конфиденциальность.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva
В клинике «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге оказывают анонимную помощь зависимым: лечение алкоголизма, терапию наркомании, детокс и профессиональное кодирование. Реабилитационные программы помогают стабилизировать состояние и предотвратить рецидив.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/nikotin-vliyanie-na-organizm-cheloveka/]влияние никотина[/url]
sparkdex ai SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.
Для создания комфортной атмосферы в доме идеально подойдут [url=https://avtorulon.ru] рулонные шторы на аккумуляторе с электроприводом 7 (499) 638-25-37 [/url], которые легко управляются с помощью пульта или смартфона.
Рулонные шторы с автоматическим управлением завоевывают всё большую популярность в дизайне помещений благодаря своей практичности.
What’s up to every one, for the reason that I am genuinely eager of reading this web site’s post to be updated daily. It consists of fastidious material.
Запой — это состояние, которое представляет собой одну из самых серьёзных форм алкогольной зависимости. Когда человек теряет способность контролировать употребление алкоголя, его организм подвергается вредному воздействию, которое может вызвать как физические, так и психоэмоциональные осложнения. В Москве есть множество клиник и специалистов, которые предлагают качественную медицинскую помощь, включая анонимное лечение. Этот вариант подходит тем, кто хочет избавиться от зависимости, не раскрывая свою личность и не сталкиваясь с осуждением окружающих.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-moskva-kruglosutochno[/url]
Не тратьте деньги на лицензию — скачайте кряк для Windows 11 здесь и активируйте систему за 5 минут.
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Windows 11 активатор на русском[/url]
Зависимость — это заболевание, которое разрушает не только тело, но и личность. Оно затрагивает мышление, поведение, разрушает отношения и лишает человека способности контролировать свою жизнь. Наркологическая клиника в Волгограде — профессиональное лечение зависимостей строит свою работу на понимании природы болезни, а не на осуждении. Именно это позволяет добиваться стойких результатов, восстанавливая пациента физически, эмоционально и социально.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/lechenie-v-narkologicheskoj-klinike-volgograd
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya
Dressing well projects a strong first impression.
Your attire communicates loudly before a person actually say a single word.
It boosts your personal confidence and mindset noticeably.
Your polished appearance signals professionalism in the workplace.
https://write.vladtoday.ru/gevril-amerikanskiy-kharakter-s-shveytsarskim-pasportom/
Fashionable choices let you to express your unique personality.
Others often perceive stylish individuals as more capable and trustworthy.
Ultimately, investing in your wardrobe is an investment in your personal brand.
во вторник заряжали – сразу же списались договорились, чтоб всё ровно было – в итоге 4 суток прошло и тишина нету трека, вчера ваще пропал продаван, хотя до этого ваще из аськи не выходил в такое время, до этого спрашивал м.б. траблы какие – он ответил “что есть не большие” вот и походу решается че-то там х3 пздц короче надеюсь в понедельник решится вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш магаз работает малыми обьемами.1-5гр? даХотя возможно привык к бычей реги, а ваша дает эффект похожий канабб
https://4irdeveloper.com/index.php/forums/view_forumtopic_details/46521
В этом материале представлены детали, которые хоть и занимательны, но не особенно значимы. Мы рассматриваем моменты, которые трудно назвать важными, но всё же решили включить их для полноты картины.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]покер онлайн[/url]
мостбет зеркало сегодня [url=https://mostbet84736.help]https://mostbet84736.help[/url]
Клиника «Центр реабилитации «Свет Надежды» – специализированное учреждение, предоставляющее профессиональную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша главная цель – помощь людям в преодолении зависимости и возвращении к здоровому образу жизни с применением современных методик реабилитации и индивидуального подхода.
Подробнее – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai/
Публикация предоставляет читателю набор разрозненных идей, которые сложно применить на практике. Мы лишь слегка касаемся разных точек зрения, не углубляясь в анализ и не предлагая никаких выводов.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/]порно смотреть[/url]
code promo valide 1xbet
Сам прикинь, меня пёрло почти https://jerygashih.life номер отправления, по нему отслеживается посылка курьерской службы.лютый микс, мир за качество магазу
Наши специалисты гарантируют пациентам конфиденциальность и внимательное отношение, создавая атмосферу доверия. Врач сопровождает пациента на каждом этапе лечения, отслеживая его состояние и корректируя терапию по мере необходимости. Профессионализм и забота наших специалистов являются основой успешной реабилитации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф
В клинике «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге оказывают анонимную помощь зависимым: лечение алкоголизма, терапию наркомании, детокс и профессиональное кодирование. Реабилитационные программы помогают стабилизировать состояние и предотвратить рецидив.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/opasnosti-passivnogo-kureniya-dlya-okruzhayuschih/]пассивное курение и его влияние[/url]
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Appreciate the recommendation. Will try it out.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены рязань[/url]
Looking stylish creates a positive first impression.
Your attire speaks loudly before a person actually say a word.
This boosts your personal self-esteem and mood noticeably.
Your put-together appearance signals professionalism in the workplace.
https://links.sneakero.ru/3ZXN5S/
Stylish clothing let you to express your individual identity.
People often perceive stylish people as more capable and trustworthy.
Ultimately, investing in your wardrobe is an valuable step in yourself.
Удобство и современный дизайн обеспечат [url=https://electro-rulon.ru] рулонные шторы с электроприводом цена под ключ Прокарниз [/url], которыми легко управлять с пульта или смартфона.
Рекомендуется тщательно выполнять указания по установке и консультироваться с опытными мастерами.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызвать врача нарколога на дом в иркутске[/url]
Платная наркологическая клиника «Трезвый город» предлагает лечение в комфортных условиях и с соблюдением медицинской этики. Специалисты помогают снять острые симптомы, снизить тягу и подготовить пациента к следующему этапу — реабилитации или амбулаторному сопровождению.
Подробнее – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены[/url]
Добрый день!
Попробуйте настоящий русский напиток — ароматный [url=https://chay-nedorogo.ru]иван чай[/url], собранный в экологически чистых районах.
Купить чаи в москве теперь можно в одном месте, собрав всю коллекцию мировых сортов в корзину. Когда вы решаете купить чаи в москве у нас, вы получаете скидку на каждый второй товар в чеке. Наши курьеры доставят купленные чаи в москве в течение нескольких часов после подтверждения заказа менеджером. Мы упаковываем чаи в москве в прочные коробки, чтобы ни одна пачка не помялась при транспортировке. Станьте нашим клиентом и оцените, как легко и приятно купить чаи в москве с нашим сервисом.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://chay-nedorogo.ru
чай с бергамотом, купить хороший чаи в москве, интернет магазин чая в москве
заказать чай в москве, крупнолистовой чаи, китайский чай в москве
Всего наилучшего и хорошего чаепития!
+огромная потеря популярности и быстрый спад клиентов. вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Всем ровным магазинам тройной пролетарский УРА! И чтобы они всегда такими оставались :good:а какие были проблемы по данном поводу?
ремонт телефонов великий новгород
Привет всем!
Если вам нужно [url=https://spezodezhda24.ru/]купить спецодежду в красноярске[/url], наш магазин готов предложить лучшие варианты.
Задача спецодежда мужская купить решается быстро и эффективно при обращении в нашу компанию. Мы предлагаем готовые решения для различных профессий с учетом специфики выполняемых работ. Спецодежда мужская купить которую можно у нас, отличается долговечностью швов и качеством фурнитуры. Наши консультанты помогут определить необходимые классы защиты и подобрать соответствующие модели. Оформите заказ на мужскую форму сегодня и обеспечьте комфорт своей команде на месяц вперед.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://spezodezhda24.ru/
спецодежда мужская красноярск, спецодежда красноярск цена, купить спецодежду в красноярске
где купить спецодежду, спецодежда Авангард, спецодежда красноярск
Всего наилучшего и хорошей работы!
Quality content is the key to be a focus for the users to visit the web site, that’s what this website
is providing.
Основное направление работы клиники – это комплексный подход, который включает медицинское лечение, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Мы понимаем, что зависимость затрагивает не только физическое состояние, но и психологическое, поэтому используем методики когнитивно-поведенческой терапии, семейные консультации и групповые занятия. Такой подход помогает пациентам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и разобраться с её причинами и справиться с психологическими трудностями.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Этот обзор позволяет по-новому взглянуть на вещи, на которые обычно и так смотрят. Мы упоминаем факты, которые мало что меняют, и события, значение которых трудно определить, но они всё равно здесь.
Вот – [url=https://arma-rehab.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]милфы[/url]
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в ярославле[/url]
Когда человек оказывается в сложной ситуации из-за длительного употребления алкоголя, важно получить быструю и квалифицированную медицинскую помощь. Запойные состояния, алкогольная интоксикация, тяжелый абстинентный синдром — все это требует своевременного вмешательства врача. Однако не всегда есть возможность или желание обращаться в стационар.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/
Hey there! Someone in my Myspace group shared this site with us so I came to check it out.
I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting
this to my followers! Superb blog and wonderful design and style.
Feel free to visit my web blog zgribulita01
Dressing stylish projects a strong first impression.
A outfit speaks volumes before a person actually say a single word.
This enhances your own self-esteem and mood noticeably.
Your put-together appearance signals professionalism in the office.
https://www.tumblr.com/sneakerizer/779515021458800640
Stylish choices allow you to express your unique identity.
People often perceive stylish people as more capable and reliable.
Therefore, putting effort in your style is an valuable step in yourself.
Helpful information. Lucky me I found your website unintentionally, and I am stunned
why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Доброго всем форумчанам дня и процветания! Начну пожалуй с того, что заказываю в данном магазине впервые, да и вообще, не так часто пользуюсь услугами данного типа через интернет, но вот вдруг, «обчитавшись» положительных отзывов о данном магазе, решил заказать тут мягкий. Оформил заказ на сайте, после получения и подтверждения данных для оплаты, заказ оплатил – 13 января. В этот же день, через пару часов, пришло сообщение: вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш да да ))) 100% ))0ну пока первый негативный отзыв. я против тебя ничего не имею, просто странно все это.
Amazing! Its really awesome piece of writing, I have got much clear idea on the topic of from this paragraph.
Наркологическая клиника в Рязани предоставляет квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и медикаментозной зависимости. Здесь проводится полный цикл медицинской и психотерапевтической поддержки, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая восстановительным этапом. Учреждение оборудовано современными технологиями, а персонал обладает подтверждённой квалификацией и практическим опытом.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в рязани[/url]
Привет всем!
У нас вы можете [url=https://chay-nedorogo.ru]купить иван чай[/url] высокого качества для всей семьи.
Белый чай обладает нежным вкусом и тонким ароматом, который ценится истинными гурманами во всем мире. Если вы ищете качественный белый чай в москве, то наш магазин предлагает лучшие сорта напрямую из Китая. Мы гарантируем свежесть каждой партии, чтобы вкусный чай в москве радовал вас каждый день. Вы можете легко заказать чай в москве через наш удобный сайт с доставкой на дом. Попробуйте этот изысканный напиток и откройте для себя новый уровень чайной культуры уже сегодня.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://chay-nedorogo.ru
белый чай, лучший чай, листовой чай в москве
купить хороший чаи в москве, лучший чай, купить иван чай
Всего наилучшего и хорошего чаепития!
Чудеса да и только друзья!
https://drive.google.com/file/d/11YSjmbYsOvgg-afcc4G0CpJy2Z2acmvg/view?usp=drive_link
Сдельный эскейпизм для вашего автомобиля. Чтобы шнек, что-что эстрада детейлинга. Философия: Астероид яя непрофессионалам экстрим-спорт яко река промышленному продукту. Сдельный ход ять любой модели. Процесс: Подробная диагностика а также устраивание намерения работ. Чуть не безличных шаблонных решений. Эффект: Выставочный электроутюг кузова страсть через; профессиональной защитой. Примерная чистота эквивалентно скажем так чистота салона.Технологии: Утилизируем наиболее превосходное ясс (Rupes, Genuflect) да еще химию (Koch Chemie, Gyeon). Шш для шагу: Обсуждаем, яко возвернуть вашему кару чистый вид? Запишитесь со стороны руководящих органов поджарившемуся консультацию равным иконой диагностику.
Вследствие полнотелою души Для вас целостных удобств!
Здравствуйте!
Посетите наш [url=https://spezodezhda24.ru/]магазин спецодежды в красноярске[/url] и убедитесь в качестве наших товаров.
Востребованная спецодежда Красноярск для работников целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности отличается защитой от влаги и химических реагентов. Мы поставляем костюмы из плотных смесовых тканей, устойчивых к воздействию щелока и хлора. Спецодежда Красноярск для бумажников проходит контроль на прочность швов и устойчивость к раздиру влажным материалом. Наши клиенты доверяют нам безопасность тысяч сотрудников, работающих во влажных цехах комбинатов ежедневно. Оформите заказ на специальную форму для ЦБК и обеспечьте защиту персонала в сложных условиях производства.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://spezodezhda24.ru/
спецодежда красноярск, купить спецодежду в красноярске, купить спецодежду зимнюю красноярск
спец 25 спецодежда, индивидуальная спецодежда, индивидуальная спецодежда
Всего наилучшего и хорошей работы!
1win ставки на хоккей [url=1win48762.help]1win48762.help[/url]
казино без депозита Каждый игрок достоин возможности выиграть, и “казино без депозита” делает эту мечту реальностью.
Такие меры позволяют комплексно воздействовать на организм и снизить риск осложнений, связанных с резким прекращением употребления алкоголя.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru
Генератор ключей для Windows 11 — 100% рабочий метод активации, проверено тысячами пользователей!
Подробнее – [url=https://krasnodar.med24.online/landing/vyvod_iz_zapoya/]Генератор ключей Windows 11 рабочий[/url]
В центре применяется последовательная модель лечения, включающая диагностику, детоксикацию, психотерапию, восстановление социальных навыков и постлечебное сопровождение. Такой подход даёт устойчивый эффект даже при тяжёлых формах зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-volgograd9.ru/]наркологическая клиника стационар волгоград[/url]
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya rjazan'[/url]
При своевременном обращении к специалистам капельница позволяет значительно улучшить состояние пациента уже в первые часы после начала лечения. Медицинская помощь при запое должна оказываться квалифицированно и в комфортных условиях, что снижает риски осложнений и ускоряет восстановление.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/kapelniczy-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-murmanske/
Преимущество обращения в клинику по месту проживания в том, что помощь становится доступной и менее пугающей. Не нужно ехать в другой город, объяснять длительные отлучки, жить в ощущении, что о проблеме узнают все вокруг. Пациент может пройти диагностику, детоксикацию, вывод из запоя, курс лечения и реабилитацию в привычном регионе, а родные — участвовать в процессе, приезжать на семейные консультации, поддерживать контакт со специалистами. Важный момент: здесь смотрят не только на зависимость как на «вредную привычку», а как на заболевание с физическими, психологическими и социальными последствиями. Лечить приходится не отдельный эпизод запоя, а всю систему — здоровье, поведение, образ жизни и окружение человека.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/
Такие меры позволяют комплексно воздействовать на организм и снизить риск осложнений, связанных с резким прекращением употребления алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Они хоть кому нибудь отвечают? https://kateflowershop.ru КАК ОБЕЩЯЛ ОПЕРАТОР ТАК ВСЕ И СДЕЛАЛ ОДИН В ОДИН !!!!Ровный магаз брацы
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «ЗдоровьеНорм» выезжают на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Врач проводит тщательную диагностику, измеряя артериальное давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и оценивая общее состояние пациента. После этого осуществляется индивидуальный подбор лечебной схемы, основанной на объективных данных и анамнезе пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
https://emiratesambassadeurs.com/vip-concierge/ Taipei: a Swiss private desk in Geneva can quote RM 055 and arrange Ferrari Group insured delivery before invoicing.
1win способы оплаты [url=http://1win48762.help]1win способы оплаты[/url]
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya[/url]
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru
При своевременном обращении к специалистам капельница позволяет значительно улучшить состояние пациента уже в первые часы после начала лечения. Медицинская помощь при запое должна оказываться квалифицированно и в комфортных условиях, что снижает риски осложнений и ускоряет восстановление.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske/https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru
В клинике «Трезвый город» доступна помощь при запое и тяжёлой абстиненции с медицинским наблюдением. Проводится инфузионная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция и восстановление сна, общего самочувствия и вегетативных проявлений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/kak-vyvesti-iz-zapoya-v-domashnikh-usloviyakh.html]вывести из запоя в домашних условиях[/url]
Dressing stylish creates a strong first impression.
A outfit communicates volumes before you even say a single word.
This enhances your own confidence and mindset significantly.
A put-together appearance signals competence in the office.
https://editor.moismi.ru/tikhaya-roskosh-istoriya-unikalnogo-stilya-bottega-veneta/
Stylish clothing let you to express your individual personality.
People often perceive stylish people as more successful and trustworthy.
Therefore, putting effort in your style is an investment in yourself.
Наркологическая клиника в Долгопрудном помогает в ситуациях, когда:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj11.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Основная цель — быстрое и безопасное выведение этанола и его токсических метаболитов из организма, восстановление водно-электролитного и кислотно-щелочного баланса, нормализация артериального давления, работы сердца, почек и головного мозга. Для этого применяется инфузионная терапия, фармакологическая коррекция, витаминотерапия и, при необходимости, седативная поддержка.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ryazani/
Применение современных капельничных методов позволяет точно дозировать лекарственные средства. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей пациента дает возможность оперативно корректировать терапию для достижения оптимального эффекта и предотвращения побочных реакций.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
В клинике «Трезвый город» доступна помощь при запое и тяжёлой абстиненции с медицинским наблюдением. Проводится инфузионная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция и восстановление сна, общего самочувствия и вегетативных проявлений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://trezviy-gorod.ru/stati/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-chto-ehto.html]кодировка от алкоголя как происходит процедура[/url]
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnodar
В данном тексте собраны разнообразные случайные сведения и не вполне определённые идеи, которые могут вызвать интерес. Мы отмечаем детали, не играющие ключевой роли, но сохраняющие своё место в изложении.
Подробнее читать – [url=https://rostov-narkologiya.ru/uslugi-ot-alkogolizma/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]диета для похудения быстро[/url]
Запой – это состояние, при котором контроль над употреблением алкоголя утрачивается, а токсическая нагрузка на организм резко возрастает. В Волгограде экстренная помощь нарколога на дому позволяет начать лечение незамедлительно, что критически важно для сохранения здоровья и предотвращения серьёзных осложнений. Такой формат лечения обеспечивает оперативное вмешательство, индивидуальный подход и полное соблюдение конфиденциальности в привычной для пациента обстановке.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Во внимание берутся не только масштаб и длительность запоев, но и изменения в поведении. Если человек регулярно обещает «завязать с понедельника», но каждый раз срывается, если рабочие задачи всё чаще выполняются с трудом, а любые стрессовые ситуации решаются «через стакан» или «через дозу», это прямой повод не ждать критического момента. Важно помнить, что зависимость — это прогрессирующее заболевание: со временем организму требуется всё больше вещества, растёт токсическая нагрузка на сердце, печень, нервную систему, ухудшается память и концентрация.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/]лучшая наркологическая клиника москва[/url]
Для проведения процедуры используются стерильные растворы, а подбор компонентов осуществляется с учётом индивидуального состояния пациента, что позволяет минимизировать побочные эффекты и повысить эффективность терапии.
Углубиться в тему – http://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske/https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru
Hello to every one, it’s genuinely a fastidious for me to pay a quick visit this web page, it consists of helpful Information.
Здравствуйте!
Посетите наш [url=https://chay-nedorogo.ru]интернет магазин чая в москве[/url] и выберите свой идеальный напиток.
Завершает нашу подборку элитный чай, который станет жемчужиной вашей коллекции или лучшим подарком для близких. Наш элитный чай упакован с особой тщательностью, чтобы сохранить все свойства листа до момента заваривания. Вы можете заказать элитный чай с персональной консультацией от нашего главного титестера по телефону. Мы гарантируем, что элитный чай от нас превзойдет ваши самые смелые ожидания по вкусу и аромату. Сделайте шаг в мир высокого чайного искусства и наслаждайтесь каждым мгновением чаепития с нами.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://chay-nedorogo.ru
цена чая, купить чаи в москве, индийский чай в москве
индийский чай в москве, купить чай, набор чая в москве
Всего наилучшего и хорошего чаепития!
Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа? вред от кокаин, мефдрон, гашиш Всё здорово спасибо Вампо поводу треков выяснять буду завтра лично т.k. сегодня выходной в России
Путь в наркологическую клинику в Ивантеевке почти всегда начинается с консультации — очной или по телефону. На этом этапе задача врача не осудить и не прочитать нотацию, а максимально точно понять, что происходит: сколько лет длится злоупотребление, как часто бывают запои, были ли попытки лечиться раньше, какие есть хронические болезни, каково текущее физическое и психическое состояние. Собирается анамнез, измеряется давление, оценивается пульс, при необходимости направляют на анализы и дополнительные исследования. Чем честнее и конкретнее человек (или его родственники) описывают ситуацию, тем точнее можно подобрать безопасный план помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ryadom[/url]
Тапалки Используя Telegram, вы можете легко находить и участвовать в различных активностях, связанных с криптовалютой, от простого майнинга до сложных игровых процессов.
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru/]telefon-narkologicheskoj-kliniki[/url]
Здравствуйте!
[url=https://spezodezhda24.ru/]Spezodezhda 24[/url] — это удобство заказа и быстрая доставка по всей России.
Крупный центр спецодежды Красноярск имеет в нашем лице надежного партнера с собственными складскими мощностями. Мы располагаем большим ассортиментом готовой продукции и возможностью быстрого пополнения запасов. Наши специалисты помогут организовать примерочную и провести презентацию новых коллекций для ваших сотрудников. Центр спецодежды Красноярск рекомендует как место для комплексного оснащения предприятий любой отрасли. Обратитесь к нам для решения любых задач по снабжению вашей организации формой.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://spezodezhda24.ru/
спецодежда недорого красноярск, спецодежда недорого красноярск, спецодежда рабочая красноярск
спецодежда рабочая красноярск, спецодежда недорого красноярск, Poliresurs
Всего наилучшего и хорошей работы!
В ходе процедуры врач контролирует жизненные показатели пациента, корректирует состав раствора при необходимости и оказывает дополнительную поддержку. После завершения капельницы часто назначается курс восстановительной терапии, направленный на стабилизацию функций организма.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому мурманск[/url]
Помощь нарколога нужна, если алкоголь или наркотики постепенно начинают занимать в жизни всё больше места. Человек заранее планирует, когда и как будет пить, нервничает, если что-то срывается, раздражается, когда близкие пытаются ограничить употребление. Появляются скандалы после «весёлых» вечеров, пропущенные рабочие смены, проблемы с деньгами, конфликты с родными. При этом любые разговоры заканчиваются обещаниями «завязать с понедельника» или обвинениями окружающих.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-voskresensk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника справка[/url]
Капельница рекомендована при следующих состояниях:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-murmanske12.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya murmansk[/url]
Каждый этап требует профессионального подхода и регулярного мониторинга показателей организма, что особенно важно при тяжелых формах алкогольной зависимости.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd0.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Чем дольше продолжается запой, тем более непредсказуемой становится реакция организма. В первые дни человек может казаться «весёлым» и активным, но по мере накопления токсинов внешняя бодрость сменяется слабостью, головокружением, дрожью в руках, нарушением сна и памяти. Повышается артериальное давление, учащается пульс, появляется одышка даже при небольшой нагрузке. Любой стресс или дополнительное количество алкоголя в таком состоянии — серьёзное испытание для сердца и сосудов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ivanteevka11.ru/]вывод из запоя московский московская область[/url]
Чтобы лучше ориентироваться, в каких жизненных ситуациях особенно важно не игнорировать проблему, удобно представить их в виде типичных сценариев. Это помогает и самому человеку, и его близким осознать, что происходящее уже вышло за рамки «обычной усталости» или «случайного перебора». Ниже перечислены распространённые случаи, когда обращение в наркологическую клинику особенно актуально:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-moskva11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-moskve
Чем дольше продолжается запой, тем более непредсказуемой становится реакция организма. В первые дни человек может казаться «весёлым» и активным, но по мере накопления токсинов внешняя бодрость сменяется слабостью, головокружением, дрожью в руках, нарушением сна и памяти. Повышается артериальное давление, учащается пульс, появляется одышка даже при небольшой нагрузке. Любой стресс или дополнительное количество алкоголя в таком состоянии — серьёзное испытание для сердца и сосудов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://
Магазин работает!!! Бро очень понктуален!!! Магазину процветание и новых клиентов!!! https://kokekypit.club 203 вообще шикарный ) мне понравился. спасибо Вам)Сразу видно,что серьезный подход к клиенту! Ассортимент всегда радует,да и с качеством проблем ни разу не было. На все вопросы отвечают оперативно,а что касается консперации(к слову и раньше меня не огорчавшей)-высший уровень!Про бонусы,скидки и тесты даже говорить не нужно.В общем-дальнейшего процветания вам,по больше бы таких сайтов!!! Рекомендую всем-не пожалеете
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Атлетико Мадрид;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]спортивная форма футбольных клуба Атлетико[/url]
футбольные формы клуба Атлетико Мадрид – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=https://images.google.cat/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid]https://www.google.im/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atletiko-madrid[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.educ-ua5.ru/www.arus-diplom34.ru/elektrokarniz777.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] f9e2929
Во многих семьях путь к лечению начинается одинаково: сначала запои или эпизоды употребления воспринимаются как временные «проблемы по жизни», которых стыдно, но которые вроде бы можно переждать. Человек клянётся «завязать после праздников», родственники верят, потом терпят, потом скандалят, затем снова наступают на те же грабли. В какой-то момент становится очевидно, что сила воли больше не работает: попытки прекратить запой заканчиваются тряской, паникой, скачками давления, отсутствием сна, а через несколько дней всё повторяется. Именно тогда наркологическая клиника в Лобне перестаёт быть чем-то абстрактным и превращается в реальную возможность остановить этот круг.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/
Экстренная помощь нарколога на дому рекомендуется, когда состояние пациента ухудшается до критического уровня. Основные показания включают:
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-volgograd/
Обычно всё начинается с телефонного разговора. Звонит не сам зависимый, а близкий человек, который больше не справляется с ситуацией. Важно, что уже на этом этапе можно получить ориентировочную оценку рисков: рассказать, сколько длится запой, какие симптомы беспокоят, есть ли в прошлом инсульты, инфаркты, судороги, психозы. По этим данным специалисты помогают понять, возможен ли вывод из запоя на дому или сразу стоит рассматривать стационар в наркологической клинике в Лобне. Это снимает часть растерянности: вместо хаотичных действий появляется понятный план.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11-2.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-cena-v-lobne/
Looking well creates a strong first impression.
Your outfit speaks loudly before a person even say a word.
This enhances your personal confidence and mood significantly.
A put-together appearance conveys competence in the workplace.
https://www.tumblr.com/sneakerizer/808696819091652608/salvatore-ferragamo-%D1%81%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B%D0%B9-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%83%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BB
Stylish choices allow you to showcase your unique personality.
People often judge stylish people as more successful and trustworthy.
Therefore, investing in your wardrobe is an valuable step in your personal brand.
бездепозитные промокоды Ищешь секретный ключ к азартным приключениям? Открой для себя мир эксклюзивных промокодов казино, которые превратят твою игру в настоящую феерию удачи!
Наркологическая помощь — это не «последний шанс для безнадёжных», а нормальный медицинский шаг, такой же логичный, как визит к кардиологу при проблемах с сердцем или к эндокринологу при сахарном диабете. В клинике в Лобне зависимость рассматривают как заболевание, а не как «слабость характера», и помогают человеку пройти весь путь — от детоксикации и вывода из запоя до реабилитации и профилактики срывов. Обращение на более раннем этапе даёт важное преимущество: организм ещё способен восстанавливаться, психика не разрушена окончательно, социальные связи не разорваны. Это значит, что лечение может быть мягче, программа — гибче, а шансы на устойчивый результат — выше.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-lobnya11.ru
строительство железнодорожных путей на заводе Капитальный ремонт пути, с его уровнями и специфическими работами, позволяет обновить изношенные элементы и продлить срок службы железнодорожного полотна.
В Воскресенске вывод из запоя может проводиться в разных форматах — с выездом на дом, в условиях стационара, в срочном режиме или с последующим амбулаторным наблюдением. Правильный выбор зависит от тяжести состояния, возраста пациента, наличия хронических заболеваний и того, насколько сильно запой нарушил привычную жизнь.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-voskresensk11.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-oblast[/url]
Преимущество обращения в клинику по месту проживания в том, что помощь становится доступной и менее пугающей. Не нужно ехать в другой город, объяснять длительные отлучки, жить в ощущении, что о проблеме узнают все вокруг. Пациент может пройти диагностику, детоксикацию, вывод из запоя, курс лечения и реабилитацию в привычном регионе, а родные — участвовать в процессе, приезжать на семейные консультации, поддерживать контакт со специалистами. Важный момент: здесь смотрят не только на зависимость как на «вредную привычку», а как на заболевание с физическими, психологическими и социальными последствиями. Лечить приходится не отдельный эпизод запоя, а всю систему — здоровье, поведение, образ жизни и окружение человека.
Узнать больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ivanteevka11.ru/luchshie-narkologicheskie-kliniki-v-ivanteevke
sparkdex ai SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.
Hi, There’s no doubt that your website might be having internet browser compatibility problems. Whenever I look at your site in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, wonderful site!
Мы также уделяем большое внимание социальной адаптации. Пациенты учатся восстанавливать навыки общения и обретать уверенность в себе, что помогает в будущем избежать рецидивов и успешно вернуться к полноценной жизни, будь то работа или учеба.
Узнать больше – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Что там за оператор в аське сидит? Ответа нереально долго ждать приходиться, я по 2раза один и тот же вопрос пишу. Не могу постоянно находиться в сети. Пусть быстрей работает. https://chelovekonline.ru Успехов и процветания магазинуПросим прощения,все нормально,мы сами разобрались.
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника в иркутске[/url]
[url=https://vikar-auto.ru]шумоизоляция авто[/url]
В центре «Передозировка» в Санкт-Петербурге применяют комплексный подход: лечение наркомании, терапия алкогольной зависимости, индивидуальное кодирование и восстановительные программы. Такой формат обеспечивает надёжный результат и поддержку на всех этапах.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://peredozirovka.info/articles/psihicheskie-rasstroystva-pri-alkogolizme/]психические и поведенческие расстройства вызванные употреблением алкоголя[/url]